Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Writing Transitions

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Good transitions can connect paragraphs and turn disconnected writing into a unified whole. Instead of treating paragraphs as separate ideas, transitions can help readers understand how paragraphs work together, reference one another, and build to a larger point. The key to producing good transitions is highlighting connections between corresponding paragraphs. By referencing in one paragraph the relevant material from previous paragraphs, writers can develop important points for their readers.
It is a good idea to continue one paragraph where another leaves off. (Instances where this is especially challenging may suggest that the paragraphs don't belong together at all.) Picking up key phrases from the previous paragraph and highlighting them in the next can create an obvious progression for readers. Many times, it only takes a few words to draw these connections. Instead of writing transitions that could connect any paragraph to any other paragraph, write a transition that could only connect one specific paragraph to another specific paragraph.
Writing Studio
Common transition words and phrases.
In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. Download this page as a PDF: Transitions Return to Writing Studio Handouts
Transitions clarify the logic of your argument by orienting your reader as you develop ideas between sentences and paragraphs. These tools should alert readers to shifts in your argument while and also maintain the smoothness and clarity of your prose. Below, you’ll find some of the most commonly used transition categories and examples of each. Depending on the example, these suggestions may be within sentences or at the beginning of sentences.
Transitions by Category
1. addition.
Use when presenting multiple ideas that flow in the same direction, under the same heading/ idea also, another, finally, first, first of all, for one thing, furthermore, in addition, last of all, likewise, moreover, next, and, second, the third reason
2. Sequence/ Order
Use to suggest a temporal relationship between ideas; places evidence in sequence first, second (etc.), next, last, finally, first of all, concurrently, immediately, prior to, then, at that time, at this point, previously, subsequently, and then, at this time, thereafter, previously, soon, before, after, followed by, after that, next, before, after, meanwhile, formerly, finally, during
3. Contrast
Use to demonstrate differences between ideas or change in argument direction but, however, in contrast, on the other hand, on the contrary, yet, differ, difference, balanced against, differing from, variation, still, on the contrary, unlike, conversely, otherwise, on the other hand, however
4. Exception
Use to introduce an opposing idea however, whereas, on the other hand, while, instead, in spite of, yet, despite, still, nevertheless, even though, in contrast, but, but one could also say…
5. Comparison
Use to demonstrate similarities between ideas that may not be under the same subject heading or within the same paragraph like, likewise, just, in a different way / sense, whereas, like, equally, in like manner, by comparison, similar to, in the same way, alike, similarity, similarly, just as, as in a similar fashion, conversely
6. Illustration
Use to develop or clarify an idea, to introduce examples, or to show that the second idea is subordinate to the first for example, to illustrate, on this occasion, this can be seen, in this case, specifically, once, to illustrate, when/where, for instance, such as, to demonstrate, take the case of, in this case
7. Location
Use to show spatial relations next to, above, below, beneath, left, right, behind, in front, on top, within
8. Cause and Effect
Use to show that one idea causes, or results from, the idea that follows or precedes it because, therefore, so that, cause, reason, effect, thus, consequently, since, as a result, if…then, result in
9. Emphasis
Use to suggest that an idea is particularly important to your argument important to note, most of all, a significant factor, a primary concern, a key feature, remember that, pay particular attention to, a central issue, the most substantial issue, the main value, a major event, the chief factor, a distinctive quality, especially valuable, the chief outcome, a vital force, especially relevant, most noteworthy, the principal item, above all, should be noted
10. Summary or Conclusion
Use to signal that what follows is summarizing or concluding the previous ideas; in humanities papers, use these phrases sparingly. to summarize, in short, in brief, in sum, in summary, to sum up, in conclusion, to conclude, finally
Some material adapted from Cal Poly Pomona College Reading Skills Program and “ Power Tools for Technical Communication .”
Writing Effective Sentence Transitions (Advanced)
Transitions are the rhetorical tools that clarify the logic of your argument by orienting your reader as you develop ideas between sentences and paragraphs. The ability to integrate sentence transitions into your prose, rather than simply throwing in overt transition signals like “in addition,” indicates your mastery of the material. (Note: The visibility of transitions may vary by discipline; consult with your professor to get a better sense of discipline or assignment specific expectations.)
Transition Signals
Transition signals are words or phrases that indicate the logic connecting sets of information or ideas. Signals like therefore, on the other hand, for example, because, then, and afterwards can be good transition tools at the sentence and paragraph level. When using these signals, be conscious of the real meaning of these terms; they should reflect the actual relationship between ideas.
Review Words
Review words are transition tools that link groups of sentences or whole paragraphs. They condense preceding discussion into a brief word or phrase. For example: You’ve just completed a detailed discussion about the greenhouse effect. To transition to the next topic, you could use review words like “this heat-trapping process” to refer back to the green house effect discussion. The relative ability to determine a cogent set of review words might signal your own understanding of your work; think of review words as super-short summaries of key ideas.
Preview words
Preview words condense an upcoming discussion into a brief word or phrase. For example: You’ve just explained how heat is trapped in the earth’s atmosphere. Transitioning to the theory that humans are adding to that effect, you could use preview words like “sources of additional CO2 in the atmosphere include” to point forward to that discussion.
Transition Sentences
The strongest and most sophisticated tools, transition sentences indicate the connection between the preceding and upcoming pieces of your argument. They often contain one or more of the above transition tools. For example: You’ve just discussed how much CO2 humans have added to the atmosphere. You need to transition to a discussion of the effects. A strong set of transition sentences between the two sections might sound like this:
“These large amounts of CO2 added to the atmosphere may lead to a number of disastrous consequences for residents of planet earth. The rise in global temperature that accompanies the extra CO2 can yield effects as varied as glacial melting and species extinction.”
In the first sentence, the review words are “These large amounts of CO2 added to the atmosphere”; the preview words are “number of disastrous consequences”; the transition signals are “may lead to.” The topic sentence of the next paragraph indicates the specific “disastrous consequences” you will discuss.
If you don’t see a way to write a logical, effective transition between sentences, ideas or paragraphs, this might indicate organizational problems in your essay; you might consider revising your work.
Some material adapted from Cal Poly Pomona College Reading Skills Program and “ Power Tools for Technical Communication .”
Last revised: 07/2008 | Adapted for web delivery: 05/2021
In order to access certain content on this page, you may need to download Adobe Acrobat Reader or an equivalent PDF viewer software.
Module 3: Writing Essentials
Paragraphs and paragraph transitions, learning objective.
- Describe techniques for effective use of transitions in paragraphs
When to Paragraph
How do you know when “enough is enough” with a paragraph? How do you know when you have enough information in one paragraph and have to start a new one? And how much is too much? There is no simple answer. Paragraphing conventions differ depending on the task and the genre. For example, digital writing typically requires shorter paragraphs with multiple short paragraphs on the screen.
As you write, deal with your paragraph length as part of your revision process. Find places where the information shifts in focus, and put a paragraph break in those places. You can do your best to paragraph as you draft, but know that you’ll address paragraphing more during the revision process.
Overall Paragraph Structure of an Essay
Often, essays are constructed in a format that looks something like this outline shown below. Depending on the purpose of your writing assignment, this format may vary depending on the rhetorical style. You are probably familiar with this general format for the five-paragraph essay. You can build off of this basic structure to write essays that are not too rigid or overly structured even if people dismiss the five-paragraph essay. As you write longer essays in college and possibly for your job, five paragraphs may not be enough for all of your ideas, but this structure works for organizing your ideas. N otice the way that paragraphs separate each topic and provide supporting evidence to the topic sentence.
- Background information on topic
- Overall point of view of the topic (thesis)
- Overview of components to be discussed (structure)
- Topic sentence outlining first component
- Sentences giving explanations and providing evidence to support topic sentence
- Concluding sentence – link to next paragraph
- Topic sentence outlining second component
- Sentences giving explanations and providing evidence to back topic sentence
- Topic sentence outlining third component
- Summary of the main points of the body
- Restatement of the main point of view
- Justification/evaluation (if required by task)
Can you determine the best order for these paragraphs? What clues can you use to figure out the best arrangement? Pay close attention to the first sentences of each section.

Figure 1 . Just as architects carefully construct buildings, a well-structured essay will help readers to clearly follow and understand your ideas.
Linking Paragraphs: Transitions
In writing traditional five-paragraph essays, you may have been taught very basic transition sentences: “My first point is,” “In conclusion,” etc.
In college, your professors will expect less formulaic writing. Strong transition words or phrases that indicate linkages in ideas are the key to taking your writing to the next level and moving from the formulaic to the organic.
When writing your argument, you need to lead your readers from one idea to the next, showing how those ideas are logically linked. Transition words and phrases help you keep your paragraphs and groups of paragraphs logically connected for a reader.
Below are some examples of transition words to help as you transition both within paragraphs and from one paragraph to the next.
Transition Words and Phrases
We divide these transition words and phrases into four categories. Click on the arrows below to learn more about additive, adversative, causal, and sequential transition.
Making Connections
In general, if you feel your readers may have a hard time making connections, providing transition words (e.g., “due to” or “on the other hand”) can help lead them. Transitions between paragraphs may appear at the end of the first paragraph, at the beginning of the second paragraph, or in both places. If the transition introduces new ideas, it usually appears at the beginning of the second paragraph.
Below is a chart of transition words that are useful for linking ideas within a paragraph. Click on the arrows to read more about transitions that can help guide your reader.
Select the most appropriate transitions in the following passage:
Proofreading Your Writing
From sentence to sentence, paragraph to paragraph, your ideas should flow into each other smoothly and without interruptions or delays. If someone tells you that your paper sounds choppy or jumps around, you probably have a problem with transitions. Compare these two sentences:
- Proofreading is an important step in the writing process. Read your paper. You can say it aloud to catch errors. Use spell check on your computer.
- Proofreading is an important step in the writing process. One technique is to read your paper aloud, which will help you catch errors you might overlook when reading silently. Another strategy is to use spell check on your computer.
Both sentences contain the same information. The second example, however, has better transitions between ideas. Transition words and phrases can make a huge difference in the readability of your writing. If you have to pick one aspect of your writing to focus on during the revision process, consider focusing on adding effective transitions to help your reader follow your thinking.
- Revision and adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Paragraphing and Transitioning. Provided by : Excelsior College. Located at : http://owl.excelsior.edu/writing-process/paragraphing/paragraphing-and-transitioning/ . Project : Excelsior OWL. License : CC BY: Attribution
- TRANSITION WORDS. Authored by : Gregory M. Campbell. Located at : https://msu.edu/~jdowell/135/transw.html . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Paragraph Structure. Authored by : Meredith Harper. Provided by : University of Mississippi. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Climate change is turning dehydration into a deadly epidemic. Authored by : Jane Palmer. Located at : https://mosaicscience.com/story/climate-change-deadly-epidemic-chronic-kidney-disease/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Transitions. Provided by : Bay College. Located at : https://human.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Composition/Book%3A_Rhetoric_and_Composition_(Bay_College)/02%3A_The_Writing_Process/2.5%3A_Revising_and_Editing . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Essay Structure. Provided by : QUT Cite Write. Located at : http://www.citewrite.qut.edu.au/write/essay.jsp . Project : Writing an Essay. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Arranging your Ideas Example. Authored by : Meredith Harper. Provided by : University of Mississippi. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of architects. Authored by : Borko Manigoda. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/architect-people-plan-construction-3979490/ . License : Other . License Terms : https://pixabay.com/service/terms/#license
- Section on Smoothing Your Writing. Authored by : Marianne Botos, Lynn McClelland, Stephanie Polliard, Pamela Osback. Located at : https://pvccenglish.files.wordpress.com/2010/09/eng-101-inside-pages-proof2-no-pro.pdf . Project : Horse of a Different Color: English Composition and Rhetoric. License : CC BY: Attribution

Essay Writing: Paragraphs and Transitions
- Essay Writing Basics
- Purdue OWL Page on Writing Your Thesis This link opens in a new window
- Paragraphs and Transitions
- How to Tell if a Website is Legitimate This link opens in a new window
- Formatting Your References Page
- Cite a Website
- Common Grammatical and Mechanical Errors
- Additional Resources
- Proofread Before You Submit Your Paper
- Structuring the 5-Paragraph Essay
Paragraph Structure
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Begins with a sentence that captures the reader’s attention
1) You may want to use an interesting example, a surprising statistic, or a challenging question.
B. Gives background information on the topic.
C. Includes the THESIS STATEMENT which:
1) States the main ideas of the essay and includes:
b. Viewpoint (what you plan to say about the topic)
2) Is more general than supporting data
3) May mention the main point of each of the body paragraphs
II. BODY PARAGRAPH #1
A. Begins with a topic sentence that:
1) States the main point of the paragraph
2) Relates to the THESIS STATEMENT
B. After the topic sentence, you must fill the paragraph with organized details, facts, and examples.
C. Paragraph may end with a transition.
III. BODY PARAGRAPH #2
B. After the topic sentence, you must fill the paragraph with organized details, facts, and examples.
IV. BODY PARAGRAPH #3
3) States the main point of the paragraph
4) Relates to the THESIS STATEMENT
V. CONCLUSION
A. Echoes the THESIS STATEMENT but does not repeat it.
B. Poses a question for the future, suggests some action to be taken, or warns of a consequence.
C. Includes a detail or example from the INTRODUCTION to “tie up” the essay.
D. Ends with a strong image – or a humorous or surprising statement.
Transition Words and Phrases
More transitions and linking expressions, a monroe college research guide.
THIS RESEARCH OR "LIBGUIDE" WAS PRODUCED BY THE LIBRARIANS OF MONROE COLLEGE
- << Previous: Purdue OWL Page on Writing Your Thesis
- Next: Sources >>
- Last Updated: May 1, 2024 9:34 AM
- URL: https://monroecollege.libguides.com/essaywriting
- Research Guides |
- Databases |
Transitions
Transitions between paragraphs.
While within-paragraph transitions serve the purpose of alerting readers of upcoming shifts in perspective or voice , between-paragraph transitions serve the unique purpose of alerting readers of upcoming shifts in argument or idea . Because one of the core rules of effective paragraph-writing is limiting each paragraph to only one controlling idea (see the Basic Paragraph Resource Center lesson), shifts in argument or idea only tend to happen between paragraphs within the academic essay.
There are literally dozens of transition words to choose from when shifting focus from one idea to another. There are transition words that show cause and effect, contrast, similarity, emphasis, and even sequence. To give you a general idea of the options available to you, below are examples of just a few of those categories and word combinations:

With so many available options, you may be wondering how you will ever be able to figure out which word or set of words would work best where.
Guiding Questions
While there are many approaches you could take, let’s take a look at a few basic guiding questions you should be asking yourself as you look over your own essay and create your own between-paragraph transitions:
- What is the purpose of this paragraph? Is it to introduce, inform, persuade, address an opposing viewpoint, revisit or add emphasis to already discussed ideas?
- Does the idea I’m sharing in this paragraph relate to or support any other idea or argument shared within the essay up to this point?
- Does the idea I’m sharing in this paragraph present a different viewpoint or idea?
- Is the idea I’m sharing separate from or dependent upon other ideas being shared within the essay?
Your answer to these four basic questions should help you more easily identify which categories of transition words might work best at the beginning of each of your paragraphs.
A Couple Tips to Get Started
Selecting proper transitions takes time and practice. To get you started on the right foot though, here are a couple tips to point you in the right direction:
- Your body paragraphs would likely benefit most from the Addition and Order transition word categories as they tend to string together related or culminating ideas or arguments
- Your concluding paragraph would likely benefit most from the Emphasis word category as one of its primary objectives is to revisit and re-emphasize major ideas presented in the essay
To see the power of an appropriately-used transition in action, let’s consider the following prompt question example. Imagine you were asked to write an essay based on the following prompt:
- Do you believe that people have a specific “calling” in life? Why or why not?
A possible thesis statement (or answer to that prompt question) might be::
- My spiritual study, secular study, and my own life experience has taught me that life callings tend to emerge not just once, but perhaps even multiple times, at crossway of spiritual gifts and need in the world.
Ponder and Record
- Based on the thesis statement above, how many body paragraphs do you think this essay will need to have?
- What controlling ideas (or arguments) might each body paragraph be engaging?
- Are these arguments in any way related to each other or building on each other?
- How might these body paragraphs benefit from transition words in the Addition or Order categories?
Body Paragraph Transitions
In answering the questions above, you likely realized that three body paragraphs will be required in this essay based on its current thesis statement. One body paragraph will focus on “spiritual” findings, another on “secular,” and then finally one supported by “personal experience.”
You also likely realized that the Addition transition word category cannot be applied to the first body paragraph as no arguments have been made yet that can be added to. This means that the first body paragraph would likely benefit most from a transition word selected from the Order category. An example of this in application might look like the following:
Body Paragraph #1 Topic Sentence
Above all, my spiritual study of the scriptures as well as the words of latter-day prophets have supported my belief that life callings emerge at the intersection of spiritual gifts and need in the world.
- What does the selection of the transitional phrase “above all” suggest about the controlling idea that will be discussed in this paragraph?
- What does it suggest about the ideas that will follow in subsequent paragraphs?
To see more “between-paragraph” transition words in action, let’s look at what the next body paragraph topic sentence might look like with the added benefit of transition words:
Body Paragraph #2 Topic Sentence
In addition to my spiritual study, my secular study of the “life calling” also supports this idea that life callings emerge again and again at the intersection of spiritual gifts and need in the world.
- What is the transitional phrase used in the topic sentence above?
- Which list is the transitional phrase “in addition” drawn from?
- What purpose does it serve in this paragraph? How does it add value?
To really emphasize the value-add of between-paragraph transitions, let’s look at one final body paragraph example:
Body Paragraph #3 Topic Sentence
Finally, my own life experience has taught me that the concept of the “life calling” truly does lie at the intersection of gifts and need in the world.
- Which list is the transitional phrase “finally” drawn from?
Concluding Paragraph
As mentioned above, the category of transition words that would most benefit your concluding paragraph is Emphasis . Since one of the main purposes of the concluding paragraph is to revisit ideas shared within the essay, transition words that express emphasis would be a natural fit and value-add. To see the power of this addition, feel free to examine the example below:
Concluding Paragraph Example
Without a doubt, I have come to realize over the years that a life calling is so much more than simply acting on a single moment in time— it is developing gifts and talents and constantly reassessing what value-add those gifts and talents can bring to the world at that particular moment.
- What transitional phrase is used in the above concluding paragraph topic sentence?
- How does the addition of “without a doubt” add emphasis to the conclusion? How does its addition help fulfill one of the concluding paragraph’s primary purposes?
Within-paragraph and between-paragraph transitions are truly the best ways to alert readers to upcoming changes in perspective and voice as well as argument or idea. As you write and then review your own writing, really try to consider which transition words would best help you create the most powerful and organized experience for your readers.
- Transcripts
- Cost & Tuition

Make Transitions Between Paragraphs
Transitions are words and phrases that connect words, sentences and paragraphs. Transitions help to make an essay flow better and logically.
Some examples of transition words are:
above all, actually, arguably, at the same time, by, consequently, currently, even so, finally, first, second, third, for this reason, for instance, for example, furthermore, however, incidently, in addition, in conclusion, in fact, in my opinion, ironically, meanwhile, moreover, next, of course, on the other hand, otherwise, presently, presumably, regrettably, similarly, still, then, therefore, too, also, ultimately
In the following passage, one or more words at the beginning of the second paragraph have been deleted. Use a transitional word or phrase to clarify the shift between the two paragraphs.
As the children growing up in a small town, my brother and I were the only ones whose father was “different.” He couldn’t sing the national anthem or remember the words of the Pledge of Allegiance. He found it difficult to comprehend the intricacies of football and baseball.
….he was a very special parent. On rainy days he was always waiting for us at the school door, boots in hand; if we were ill he was there to take us home. He worked in town and was available to take us to music and dancing lessons or on little drives. When I was a small child, he planted beside my window a beautiful oak tree that grew to be taller than our house.
Janet Heller, “About Morris Heller”
2. In the following passage, the first sentence of the second paragraph and the first two sentences of the third paragraph have been deleted. For each of those paragraphs, write one or two opening sentences to clarify the transition from one paragraph to the next.
Outside, in our childhood summers—the war. It was the summers of 1939 to 1945. I was six and finally twelve; and the war was three thousand miles to the right where London, Warsaw, Cologne crouched huge, immortal under nights of bombs or, farther, to the left where our men (among them three cousins of mine) crawled over dead friends from foxhole to foxhole toward Tokyo or, terribly, where there were children (our age, our size) starving, fleeing, trapped, abandoned.
………………..A shot would ring in the midst of our play, freezing us in the knowledge that here at last were the first Storm Troopers till we thought and looked—Mrs. Hightower’s Ford. And, any plane passing overhead after dark seemed pregnant with black chutes ready to blossom. There were hints that war was nearer than it seemed—swastikaed subs off Hatteras or the German sailor’s body washed up at Virginia Beach with a Norfolk movie ticket in his pocket.
…………………Our deadly threats were polio, being hit by a car, drowning in pure chlorine if we swam after eating. No shot was fired for a hundred miles. (Fort Bragg—a hundred miles.) We had excess food to shame us at every meal, excess clothes to fling about us in the heat of play.
Reynolds Price, Permanent Errors

How to write a transition sentence
- December 4, 2023
Transitions show the reader how different parts of your essay, paper, or thesis are connected.
Transition sentences will help you create a well-structured research paper or essay with sentences that flow naturally from one point to the next. So it is essential to learn how to effectively create transition sentences.
What is a transition?
A transition in writing is a word or phrase and a sentence that connects one concept to the next. This link can be made within a paragraph or between paragraphs.
Transitions are an important aspect of academic writing, as they help to create a cohesive and well-structured document that is easy for the reader to follow.
Transition word example
....Many people enjoy playing video games, but there are also those who view them as a waste of time. On the other hand Transition example within a paragraph , some experts argue that video games can actually be beneficial for cognitive development.
In this example, the transition part is “On the other hand”, which signals to the reader that a contrasting viewpoint is about to be presented.
Transition sentence example
Paragraphs from an essay about exercise
There are several benefits to regular exercise, such as improved cardiovascular health and increased strength and endurance ....(paragraph continues)... However, it is important to keep in mind that exercise can also pose certain risks, especially if proper precautions are not taken. Transition sentence: Signals the change of focus for the first sentence of next paragraph One of the most common risks associated with exercise is injury, which can range from minor sprains and strains to more serious issues like fractures and dislocations The first sentence of the following paragraph ....(paragraph continues) ....(paragraph continues)
In this example, this transition sentence signals to the reader that a shift in focus is occurring and prepares them for the discussion of exercise risks in the next paragraph.
Now that you’ve had a basic introduction to what a transition is, let’s dig deeper into the topic by seeing even more examples.
Transition between paragraphs
With this type of transition, you simply state a hint from the following paragraph to prepare the reader what’s coming. In other words, you create a link between two consecutive paragraphs.
Let’s have a look at the example below.
The paragraph tells the difficulties the company faced, but the last sentence hints the steps taken, and the following starts explaining these steps.
Transitions between paragraphs example
In recent months, the corporation has faced several difficulties. Sales have been declining, and competition has intensified, putting pressure on the company's bottom line. Despite these challenges, the company is taking steps to turn things around. Transition sentence Management has adopted cost-cutting initiatives to diversify its revenue streams and is seeking new markets. These efforts are projected to provide better financial results in the following quarters.... ...paragraph continues.
The transition above shows the reader how the two paragraphs are connected.
In below example, the transition sentence with “However” indicates how it relates to the previous paragraph.
Transitions between paragraphs example 2
...(Paragraph starts) ...(Paragraph continues) The usage of technology has transformed how we live and work. As a result, we have access to many products that make our lives more accessible and efficient, from cell phones to computers. However, this increased dependence on technology has also raised concerns about its impact on our well-being. Transition sentence According to research, excessive screen usage has been linked to eye strain, migraines, and poor sleep patterns. It is critical to exercise moderation and create good technology habits to reduce these detrimental consequences.
Now, this transition below connects the two paragraphs by demonstrating that the incident stated in the first paragraph was a result of the event described in the second paragraph.
Transition sentence example 3
A strong storm slammed the city Wednesday night, causing widespread damage and power disruptions. Other trees were uprooted, and several structures were damaged. The storm was the result of the convergence of several weather systems over the region. Transition sentence Meteorologists had been watching the passage of these weather systems for several days and had issued a severe weather warning. However, despite the notice, the severity of the storm took many inhabitants by surprise.
Choosing transition words
When moving the emphasis from one detail to another, there are literally dozens of transition phrases to select from. Here are some samples of some of the categories and word combinations accessible to you to give you a broad sense of options.
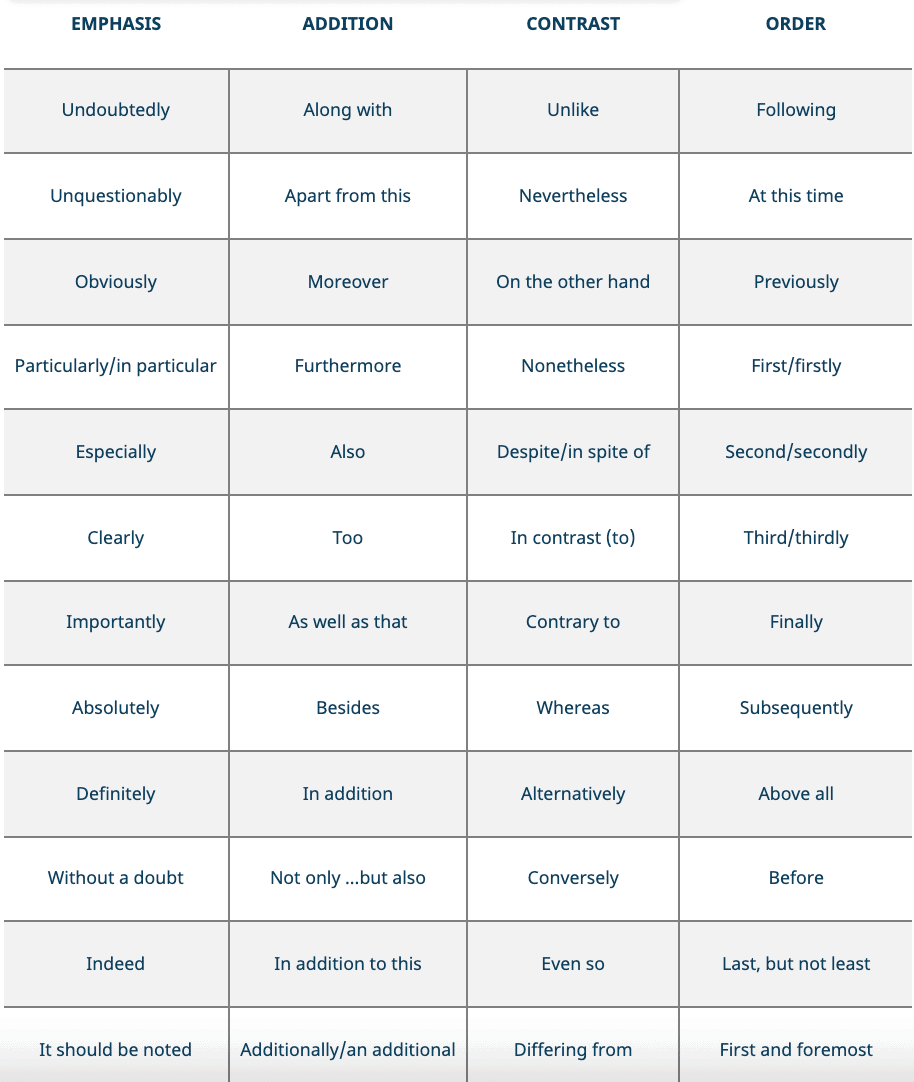
Things to consider when choosing transition words
Your answers to these four fundamental questions should make it easier for you to figure out which types of transition words might work best at the start of each paragraph .
- What exactly is the point of this paragraph? Is it to present, inform, convince, address a different point of view, review or emphasize previously mentioned concepts?
- Is the concept I’m presenting in this paragraph related to or supportive of any other concept or argument presented in the essay so far?
- Is the argument I’m making in this paragraph presenting a new perspective or idea?
- Is the concept I’m presenting different from or dependent on other concepts discussed in the essay?
Transitions within a paragraph
The known-new contract.
A valuable writing idea is the known-new contract, which infers that a new sentence should start with reference to information from the prior sentence and then relate it to new information.
The known-new contract transition example
Original paragraph The internet has revolutionized the way we communicate with one another. It allows us to connect with people all over the world, access a wealth of information, and even shop online. However, with all these benefits come certain risks, such as identity theft, online scams, and cyberbullying. Paragraph with known-new contract While Transition word the internet has brought about many benefits, including Transition word the ability to connect with people from all over the world, access to vast amounts of information, and online shopping, it also poses certain risks. These risks Highlighting the known information include identity theft, online scams, and cyberbullying, among others.
Start by composing a sentence
As seen from the above example, in the first half of the sentence, start with something that the reader already knows. Towards the end of the sentence, tell the reader something new.

Compose a new sentence
As this information is now known, start with the new information from the previous sentence. Near the end of the sentence, tell the reader something new.
The known-new contract is only a suggestion. It’s not necessary to build every sentence this way, but it’s a good strategy to follow if you’re having trouble keeping your sentences together.
In-depth transition examples
- The British were no match for Napoleon and his navy. In fact, Napoleon lost nearly every sea engagement he fought. The French army was a formidable force. It conquered most of continental Europe under Napoleon’s instructions.
- The British were no match for Napoleon and his navy. In fact, Napoleon lost nearly every sea engagement he fought. The French army, on the other hand, was extremely strong and powerful. It conquered most of continental Europe under Napoleon’s instructions.
- The historical society held a bake sale, car wash, and book fair in October. The department chair was ecstatic with the student's achievements. The historical society does not have sufficient funds to travel to Ottawa. The students are all highly dissatisfied.
- The historical society held a bake sale, car wash, and book fair in October. The department chair was ecstatic with the students’ achievements. Despite their best efforts, the historical organization was unable to raise enough funds to travel to Ottawa. The students are all highly dissatisfied.
- In Book A, the characters are faced with the moral dilemma of a disputed inheritance, which is a large sum of money. The inheritance in Book B is an ancient house. The characters in Book B are confronted with a similar issue.
- In Book A, the characters are faced with a moral dilemma: a disputed inheritance. Despite the fact that the inheritance in Book B is an ancient house rather than a large sum of money, the essence of the situation is very similar.
Transition best practices
Only use a transition sentence when discussing two different concepts.
You don’t need a transition in a paragraph that discusses the same two topics or examples.
Avoid excessive use of transition words
While transition words like “in addition,” “however,” and “also” can be highly useful, they should be used in moderation. Otherwise, the paper will come out as pretentious.
Don’t try connecting two ideas forcefully
If two concepts are placed next to each other in your paper but do not appear to be linked, one of them may not belong or should be relocated to a separate part.
Transition sentences are necessary for a well-structured paper as they offer new ideas and assist the reader’s comprehension. If you follow these steps and tips, writing excellent transition sentences won’t be too hard. Before writing, feel free to analyze our sample essays .
Recently on Tamara Blog
How to write a discussion essay (with steps & examples), writing a great poetry essay (steps & examples), how to write a process essay (steps & examples), writing a common app essay (steps & examples), how to write a synthesis essay (steps & examples), how to write a horror story.
- Facts and Figures
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- Non-traditional Admissions
- Pay Deposit
- Undergraduate Majors
- Graduate Programs
- Honors College
- Study Abroad
- Professional & Continuing
- Online Programs
- Career Planning
- Living on Campus
- Clubs & Organizations
- Spirit & Traditions
- About Harrisonburg
- Pay Your Deposit
- Office of Financial Aid
- Freshman Scholarships
- James Madison University -->
- Volume 1 (2000-01)
- Volume 2 (2001-02)
- Volume 3 (2002-03)
- Volume 4 (2003-04)
- Volume 5 (2004-05)
- Volume 6 (2005-06)
- Volume 7 (2006-07)
- Volume 8 (2007-08)
- Volume 9 (2008-09)
- Volume 10 (2009-10)
- Volume 11 (2010-11)
- Volume 12 (2011-12)
- Tactic / Style Index
- Subject Index
- Title Index
- Author Index
Twelve Years of e-Vision
From 2000-2012, the e-Vision Journal of First-Year Writing published the excellent work created by students in James Madison University's first-year writing courses.
Through twelve volumes, e-Vision and the undergraduate students who served on the e-Vision Editorial Board gave these engaging, provocative, fundamentally useful texts the wider audience they deserve.
All 104 e-Vision essays have been published again on JMU's Scholarly Commons platform.
If you've ever wondered just how wide that wider e-Vision audience might be, check out the map below.

e-Visionon on Scholarly Commons
The e-Vision Index
Looking for essays that model a specific tactic or style, or that engage a specific subject? Trying to track down a specific e-Vision writer or essay?
TACTIC and STYLE INDEX : Useful lists of effective essays that offer rhetorical analysis, engage primary and secondary sources, incorporate multimedia, organize and transition between paragraphs, begin well and end better, target and connect with a specific audience, create a memorable style or voice….
SUBJECT INDEX : Art, popular culture, the environment, gender roles, 9/11, racial and ethnic identity, religion and spirituality, writing about reading and writing, family and wellness, technology, dystopia.... It's all here.
TITLE INDEX : Browse through 104 really good titles.
AUTHOR INDEX : You love the writer, but cannot remember the name. All 102 e-Vision authors are available here.
e-Vision: Publishing History
The student editors and faculty advisors who created e-Vision in 2000 hoped that the journal could be a celebration, a showcase, and a resource. Through 12 volumes and almost 100 editors, the "About Volume 1 of e-Vision " page stood as the journal's mission statement. Both before and after the e-Vision extracurricular commitment (with snacks) became a for-credit course, editors often served through multiple volumes, with at least five editors contributing over three different volumes.
- About Volume 1 of e-Vision
e-Vision honors its history. The e-Vision Scholarly Commons site preserves most of the journal's published material, and we’re still working to fill or fix a few of the blanks. e-Vision built versions 1 and 3 of its website from scratch, and the template we adopted for version 2 served us well:
- e-Vision website version 1 (2000-2003)
- e-Vision website version 2 (2004-2008)
- e-Vision website version 3 (2009-2012)
The e-Vision Editorial Board always believed that the excellent work published from JMU's first-year writing courses could be more than increasingly dated relics buried at the back of an increasingly dusty trophy case. Before Adobe Dreamweaver deprecated and then did away with popout menus as a design option, e-Vision editors began cross-referencing our growing list of published essays. In the process, we discovered that e-Vision essays do more than offer models of thought, style, organization, and genre. Across courses, volumes, and years, e-Vision essays talk to one another in provocative, engaging, and fundamentally useful ways.
- e-Vision Tactic and Style Index from version 3 of the e-Vision site
- e-Vision Subject Index from version 3 of the e-Vision site
e-Vision is sponsored by James Madison University's School of Writing, Rhetoric and Technical Communication. For more information, contact Kevin Jefferson ( [email protected] ).
_____________
In 2012, WRTC launched Lexia , a journal dedicated to publishing the excellent work produced in all WRTC undergraduate courses. Through five volumes—2013-2017— Lexia undergraduate editors shared the diverse texts created in the disciplines of writing, rhetoric, and technical communications.
The Wider e-Vision Audience
Can't see the map? Click here: https://www.jmu.edu/evision/
Back to Top
- Expenditures
- Accessibility
- Social Media

7 Best Ways to Shorten an Essay
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Published: May 14, 2024
Are you removing a lot of words and paragraphs from your essay but still not seeing the word count budge? Whether you’re meeting a strict word count or refining your message, reducing your essay’s length without sacrificing content quality can be challenging.
Luckily, besides just aiming for the minimum word count, there are some pretty simple solutions, like using artificial intelligence, conducting thorough research, and trimming unnecessary words. But there’s more.
In this guide, we’ll unpack some practical tips to help you make your essay concise and impactful. Time to make every word count!
7 Best Ways To Shorten an Essay
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the best ways you can shorten your essay:
1. Use Artificial intelligence
When we talk about academic writing, artificial intelligence (AI) can be a game changer, especially when it comes to reducing the length of your essays.
Tools like Smodin can help make your content more concise while enhancing overall quality. AI can help you shorten your essay through the following methods:
- Automated rewriting : AI rewriting tools can reformulate existing content to make it more straightforward while maintaining the original meaning.
- Sentence simplification : Algorithms can analyze your sentences and suggest simpler alternatives, helping eliminate redundant information and reduce word count.
- Research assistance : Certain platforms have AI-powered research tools that allow you to quickly gather the most relevant information. This ensures that every word in your essay contributes to your argument without unnecessary fillers.
- Plagiarism check : Ensuring your essay is plagiarism-free is crucial. For example, Smodin’s plagiarism detection tools help you identify and replace copied content with original, concise expressions.
- Instant feedback : Receive real-time suggestions on how to streamline your text, focusing on the essentials to effectively communicate your message.
- Reference generation : Automatically generate and insert citations in the correct format, which helps save you time while maintaining the academic integrity of your essay and keeping it short.
2. Identify Unnecessary Words and Remove Them
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to shorten your essay is by identifying and eliminating unnecessary words.
This approach helps decrease word count and sharpens your arguments, making your writing more compelling. You can identify and remove extra words by doing the following:
- Spot wordy phrases : Often, phrases can be condensed without losing meaning. For example, the phrase “due to the fact that” can be replaced with “because.” Be on the lookout for wordy phrases that increase word count needlessly.
- Remove unnecessary prepositional phrases : Prepositional phrases can be redundant or add unnecessary detail. Evaluate whether these phrases add value or just extra words. Cutting them can make sentences more direct.
- Avoid redundancies : Redundant pairs like “absolutely essential” or “future plans” can be reduced to one word without losing informational value.
- Trim excess adjectives and adverbs : Adjectives and adverbs can make writing better but can also lead to over-description. Use them sparingly, especially when they don’t contribute additional meaning to the nouns and verbs they modify.
- Fewer words; more impact : Aim for brevity by using fewer words to express the same idea. This will help to reduce the word count while making your writing more impactful and clear.
3. Tighten Sentence Structure
Tightening your sentence structure is crucial for making your essay more concise and readable. Use active voice to make your writing clearer and more dynamic. This is especially important in academic writing, where you have to get to the point quickly.
In academic essays, shifting from passive voice to active voice can shorten and strengthen your sentences. For example, instead of writing, “The experiment was conducted by the students,” you can say, “The students conducted the experiment.” This reduces the number of words and places the action directly with the subject, making your sentences more direct.
Combining two separate sentences into one can streamline your ideas and reduce redundancies. Look for opportunities where sentences can be merged without losing their significance. For example, “He wrote the book. It became a bestseller.” can be rephrased as “He wrote the book, which became a bestseller.”
Also, avoid unnecessary qualifiers and modifiers that don’t add substantial information. Sentences often become bogged down with these extras, making them cluttered and long.
4. Conduct Thorough Research
When writing essays, extensive research can make the final output a lot shorter. Effective research helps you gather precise information that’s relevant to your topic. This means you’ll write more directly and avoid needless elaboration. Here’s how you can conduct research effectively:
- Define the scope of your research : Determine what information is essential to the argument. This initial step will help you focus your research efforts and prevent irrelevant data.
- Identify key sources : Begin with scholarly databases and academic journals that offer peer-reviewed articles. These sources provide credible, authoritative information that can be crucial for academic writing.
- Use precise keywords : When searching for information, use specific keywords related to your essay topic. Precision here will help find the most relevant articles and studies, reducing time spent on unnecessary reading.
- Evaluate sources : Assess the relevance and reliability of each source. Check the publication date to ensure the information is current and relevant to your topic.
- Take notes efficiently : As you research, jot down important points, quotes, and references. Organize these notes according to the sections in your essay to make writing faster.
- Synthesize information : Combine information from multiple sources to build a strong argument. This will allow you to write comprehensively and with fewer words, as each sentence carries more weight.
5. Improve Your Paragraph Structure
Streamlining paragraphs can make your essay shorter and more digestible for the reader. With a well-structured paragraph, you can focus on a single idea supported by concise statements.
Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that clearly states the main idea. This sentence sets the direction and tone, letting the reader know what to expect. It also helps ensure that every following sentence relates directly to the main idea.
Condense supporting information by merging ideas that logically coexist within a single sentence or phrase. After that, evaluate each sentence for its contribution to the paragraph’s main idea. Remove any information that is repeated or goes into too much detail.
Focus on providing evidence and explanations that directly support the main point. You should also end each paragraph with a sentence that reinforces the main idea and potentially links to the next paragraph. This creates smooth transitions and keeps the essay focused and cohesive.
6. Refine the Introduction and Conclusion
These sections frame your essay and influence how your arguments are perceived. Here are some ways to keep them concise yet effective.
Introduction
The introduction should be engaging and concise, clearly stating the purpose and scope of your essay. Begin with a hook that grabs the reader’s attention, followed by background information that sets the context. Incorporate your thesis statement early on, ideally at the end of the intro.
The conclusion needs to reinforce the thesis. Summarize key points in the essay and show how they support the thesis. Provide a final thought that leaves the reader with something to ponder.
Also, remember to keep it tight – the conclusion isn’t a place for introducing new ideas. It should wrap up the ones you presented and prompt the reader to pose their own questions.
7. Edit and Proofread
Keep your essay concise and error-free by allocating ample time for editing and proofreading. These processes scrutinize your work at different levels, from the overall structure to word choices and punctuation. Here’s how you can go about it:
Start by reading through your entire paper to get a feel for its flow and coherence. Check if all paragraphs support your thesis statement and if section transitions are smooth. This will help you spot areas where the argument might be weak, or wording could be clearer.
Focus next on paragraph structure. Ensure each paragraph sticks to one main idea and that all sentences directly support the idea. Remove any repetitive or irrelevant sentences that don’t add value.
Then, look for clarity and style. Replace complex words with simpler alternatives to maintain readability. Keep your tone consistent throughout the paper. Adjust the sentence length and structure to enhance the flow and make it more engaging.
Proofreading
Proofreading comes after editing. The focus here is catching typing errors, grammatical mistakes, and inconsistent formatting. It’s always best to proofread with fresh eyes, so consider taking a break before this step.
Use tools like spell checkers, but don’t rely solely on them. Read your essay aloud or have someone else review it. Hearing the words can help you catch errors you may have missed.
Lastly, check for punctuation errors and ensure all citations and references are formatted according to the required academic style. This and all of the above are areas in which AI can help get the job done with speed and precision.
Why You Might Need to Shorten Your Essay
Ever heard the expression “less is more”? When it comes to academic writing, it normally is. Keeping your essays concise offers several benefits:
- Enhances clarity : A shorter essay forces you to focus on the main points and critical arguments, reducing the risk of going off-topic. This clarity makes your writing more impactful and easier for the reader to follow.
- Meets word limits : Many academic assignments have a maximum word count. Learning to express your thoughts concisely helps you stay within these limits without sacrificing essential content.
- Saves time : For both the writer and the reader, shorter essays take less time to write, revise, and read. This efficiency is especially valuable in academic settings where time is usually limited.
- Increases engagement : Readers are more likely to stay engaged with a document that gets to the point quickly. Lengthy texts can deter readers, especially if the content has unnecessary words or redundant points.
- Improves writing skills : Shortening essays helps refine your writing skills. You become better at identifying and eliminating fluff, focusing instead on what really adds value to your paper.
Overall, adopting a more succinct writing style helps you meet academic requirements and polish your communication skills.
Why Use Smodin To Shorten an Essay
Using AI-powered platforms like Smodin to shorten your essay is both the simplest and the least time-consuming method available. Here’s why you should probably make Smodin your go-to essay shortener:
- Efficiency : Smodin eases the editing process, using advanced algorithms to quickly identify areas where content can be condensed without losing meaning.
- Accuracy : With its powerful AI, Smodin ensures that the essence of your essays stays intact while getting rid of unnecessary words, making your writing more precise.
- Ease of use : Smodin is user-friendly, making it accessible even to those who aren’t the most tech-savvy. Its easy-to-grasp interface allows for seamless navigation and operation.
Smodin’s offerings
- Rewriter : Available in over 50 languages, this tool helps rewrite text to be more concise.
- Article Writer : Assists in drafting articles that are crisp and to the point.
- Plagiarism and Auto Citation : Ensures your essay is original and correctly cited, which is crucial in academic writing.
- Language Detection : Identifies the language of the text, ensuring the right adjustments are made for clarity.
All these tools and more are what make Smodin an excellent choice for academics looking to reduce the length of their essays.
Final Thoughts
Word counts can be a real headache, especially when you need to say a lot with a little. Thankfully, by identifying unnecessary words, tightening your sentences, and using tools like Smodin, you can make your essay concise without losing its meaning. Remember, a shorter essay doesn’t just meet word limits; and it’s clear, more compelling, and more likely to keep your reader engaged.
Keep it short, keep it sweet, and make every word count! Get started for free right now with Smodin.
- Shoemaker Lumber
- Harbor Outfitters
- Somers Point Lumber
- Super Clean 4 U
- Mike’s Seafood
- Fishing Report

How to Build Your Compare and Contrast Essay? Structure and Examples

A compare and contrast essay examines the topics for discussion from multiple points of view. Usually, high schoolers and college students have to submit these essays to their tutors for the evaluation of their analytical thinking skills. Also, these essays are the best way to prepare students for the advanced forms of academic writing.
Such papers become relatively easy to write when you follow a step-by-step approach and research your topic well enough. Wherever confused, you can get help from online essay writers , your tutor or peers. They can help you with crafting your homework and, hence, improve your grades.
This article explores in detail the tips for a compare and contrast essay structure and provides you with examples of successful papers. Let’s define this essay type first, and after that, we shall move towards the writing guidelines.
What Is a Compare and Contrast Essay?
As per the definition by Walden University, a compare and contrast essay highlight the differences and similarities between two or more perspectives. The essay consists of an introduction, a thesis statement, a main body where the contrast is made and then a conclusion. In such papers, students are expected to discuss both the similarities and differences of the topic under consideration.
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay?
As this is a compare and contrast paper, it goes without saying that you will discuss both the similarities and dissimilarities of the topic. It requires you to analyse your title in detail and demonstrate your critical thinking skills. Here are the tips and structure guidelines for you to follow when writing a compare and contrast essay:

1. Start by Brainstorming the Topic
The best comparison essays demonstrate a high level of analysis to the readers and that means you will have to brainstorm your topic well before you start the writing process. Usually, students use a Venn diagram to brainstorm their ideas. They draw overlapping circles in a Venn diagram and mention the characteristics of each subject in each circle. The overlapping part of the circle shows the similarities of the subjects and the side parts show the differences of both.
Drawing a Venn diagram makes it easy for students to keep track of different points in their minds. Here is an image from Lib Guides which can help you understand the concept in further detail:
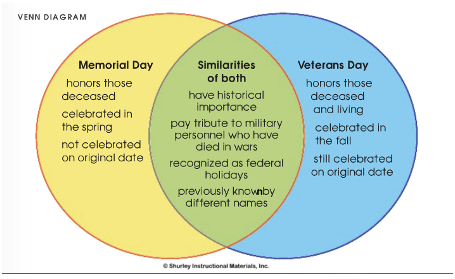
2. Craft a Thesis Statement
Once you have mapped out the differences and similarities between your topics, you will start to understand the relationship between the subjects you are comparing. This, in turn, helps you craft a strong thesis statement that functions as a road map for your essay. A compare and contrast essay thesis statement should be clear, i.e., it should not only tell the readers about what you will do but also address the importance and purpose of comparing and contrasting the material.
Your statement should clearly identify the topic that is being discussed and include the central points of your essay. When crafting this section, ensure that you keep your audience in mind.
3. Make an Outline
After you are done curating the data for your work, you will move from the prewriting stage to crafting the compare and contrast essay outline. A good outline follows the format of a standard essay and has the following three parts:
- Introductory paragraphs
- Body paragraphs
Keep in mind that you will have to follow the same format for the rest of your paper, so make a flexible outline. An outline is exactly what distinguishes a focused essay from a mediocre one. After that, you move towards writing the compare and contrast essay introduction. For success, you should work on making the topic sentence of your introduction interesting for the readers. It would be better to add a hook to it to engage the attention of readers.
4. Structure Your Paper
The structure of a compare and contrast essay measures its success. Consider how you will present the information in your papers. It will be best if you choose to present all the similarities first and then move towards discussing the differences between both subjects. Choose if you will go with the block method or the point-by-point method (we have discussed both of them in detail later in this article).
Here is a structure template for your work from the Helpful Professor, and you can use it to organise your essay:
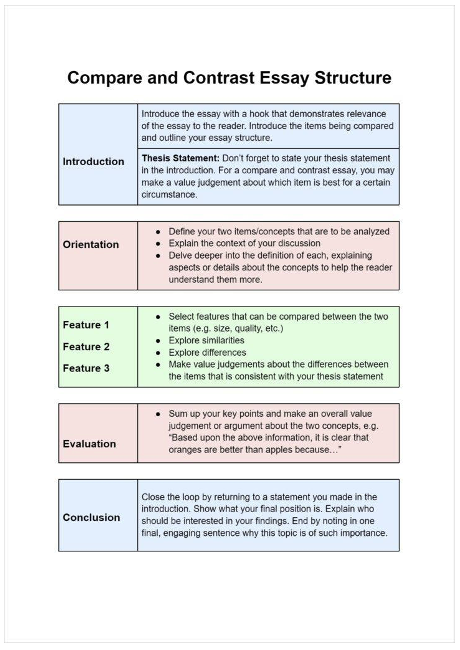
In the introduction section, you should introduce your topic in detail to the readers and include the research background. In the main body, you state the central similarities and main differences of both subjects. In the conclusion section, you provide the readers with a summary of your comparison and contrast. You should ensure that you have not added any new or vague information in the conclusion of your work. Just keep it simple for you to write and for the readers to understand.
5. Use Clear Transitions
When you write an essay on the comparison of two different topics, amply use the transition phrases and sentences to shift between the alternating methods of discussion. Transitions are really important for compare and contrast essays as they help you move between different perspectives and topics smoothly.
Some of the transitions that you can use in your papers for the comparison of two subjects are the following:
- Consistent with, and more
Here is another bunch of transitions that you can use to show the contrast between different kinds of ideas in your essays:
- On the other hand
- Rather than, and more
However, you should ensure that you are not stuffing your papers with unnecessary or too many transitions because they make it exhausting for the readers to logically understand your papers. Just make sure that your ideas and arguments are expressed in a clear way and that they make complete sense to the readers.
6. Make the Comparisons
When making the contrasts between the two subjects, be sure that you are dealing with the similar qualities of each item. Check if the approaches you are comparing have something in common in them or not. Also, you should if they can be appropriately compared to each other. For instance, you can only compare the qualitative features of one subject with the qualitative traits of the other. And the same goes for the quantitative elements of both subjects.
If you are facing trouble with finding the right arguments for your work, feel free to acquire reliable essay writing services online to craft your paper. Their writers have a penchant for crafting excellent comparison essays to meet the needs of students.
7. Include the Analysis
When writing your compare and contrast essay, it may be very tempting for you to just provide the readers with the summary of your essay but not act on it. The analysis of your work focuses on the importance of contrasts and comparisons. For example, if you are writing an essay on the increasing shortage of nurses in the field of medicine and healthcare, you should help your readers understand the importance of your comparison and research work.
Also, highlight the results of your work i.e., tell the audience if there are some noticeable findings and discrepancies which need further investigation by the relevant authorities. It increases the worth and value of your research work.
8. Proofread Your Essay
When you are done writing the compare and contrast essay conclusion and the paper is finished, it is time for you to revise, edit and proofread it. Take your time to relax and you feel fresh mentally; you should come back to the papers for a final review. Your essay will not be complete until you have done a careful proofreading check. Ensure that each subject gets equal space in your document.
Of course, you will have to check for punctuation and spelling mistakes and look for overall clarity in your papers. You can also acquire the help of expert editors and proof-readers online to refine your work and improve its quality.
What Is the Structure of a Compare and Contrast Paragraph?
You can use two methods to structure the paragraphs of a compare and contrast essay. As per the EAP Foundation, you can either use a block structure or discuss the arguments point-by-point.
- For the block method, you give all the information about one part of the essay first and then move towards providing the information about the second part.
- In a point-by-point structure, you will discuss the main arguments in the form of tips and points.
What Are the Two Main Structures for Writing a Compare and Contrast Essay?
San Jose State University specifies a format for students to follow when working on the structure of their compare and contrast essay outline. The structures we have mentioned in the above section are to be followed when outlining your work, i.e., it will either be the block approach or the point-by-point approach.
Here is an example of how you can plan your argument in the block approach:
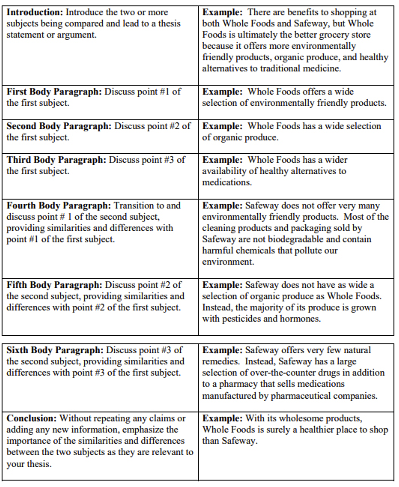
Now, here is an example of how you can follow the compare and contrast essay format when doing the point-by-point discussion:
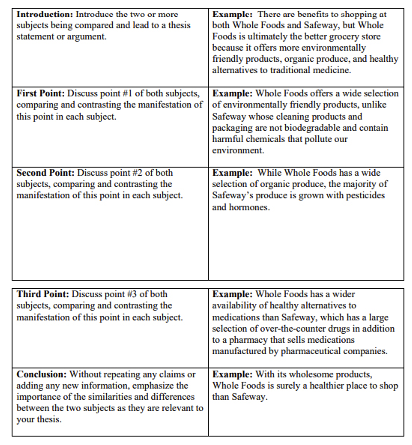
What Are the Main Features of a Compare Contrast Essay?
By now, you must have an idea of how to craft a successful comparison and contrast homework in the best way. According to the instructions of Kellogg Community College, the main features of compare and contrast essays are listed below:
- In such an essay, you focus on the characteristics of the objects being compared.
- You will have to enlist the defining features of the objects you are comparing.
- Such essays need the students to organise their ideas per the format specified by their teachers.
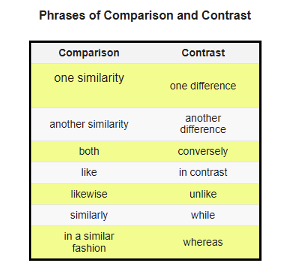
- You will have to use multiple comparisons and phrases of contrast to let the readers know how the two objects are being analysed.
Here are some of the phrases of comparison and contrast that you can use to make your points more impactful for the readers of your work:
Good Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
At this point, it might be a good idea to research the top topics for such essays in 2024. Be sure to choose a topic that you can justify to both sides. Simply focusing on one side of comparison or contrast will not solve any of your problems. Some of the good compare and contrast essay ideas are listed here:
- Whether the chemical drugs should be used or not?
- What is the difference between allopathic and homoeopathic medications?
- Should plastic surgery be done or not?
- Which ones are better: iOS or Android phones?
- Should economics be taken as a compulsory subject or not?
- Is studying at home better than studying in school?
- What is preferable: late night workout or early morning workout?
- Provide a comparison of the life in college versus the life in high school.
Compare and Contrast Essay Examples
It is really beneficial for college students to review a couple of comparisons and contrasts essays before choosing the perfect one for them. We have chosen this example from Helpful Professor, which you can use as a perfect compare and contrast essay template:

Bottom Line
In a nutshell, during the compare and contrast essay writing process, you must identify and explore at least 3 or more key points to discuss. Ensure that you show the differences and similarities between these points to your readers and develop a strong thesis. We have already discussed the best ways to organise your thoughts and write such essays in the above sections.
Before the submission, review your essays in great detail and make sure that you have communicated your ideas in a clear manner to your audience. Also, there must be no grammatical, structural, thematic or contextual mistakes in your papers. If you feel that you need personalised help with your papers, you can always buy essay online from professional service providers. With their years of experience, they are the best people to assist you in crafting remarkable essays.
By Chris Bates
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

Why Should You Take Private Surf Lessons?

Begin Your Day with Adventure: Experience a Morning Catamaran Snorkel

Crafting Effective Discussion Post Responses in Online Classes

EVEN MORE NEWS

POPULAR CATEGORY
- Latest Stories 4700
- Trending 4144
- What to do 133
- do not include in newsletter 84
- Privacy Policy
- Questions & Concerns

COMMENTS
Clear transitions are crucial to clear writing: They show the reader how different parts of your essay, paper, or thesis are connected. Transition sentences can be used to structure your text and link together paragraphs or sections. Example of a transition sentence for a new paragraph. In this case, the researchers concluded that the method ...
Transitions. Transitions help your readers move between ideas within a paragraph, between paragraphs, or between sections of your argument. When you are deciding how to transition from one idea to the next, your goal should be to help readers see how your ideas are connected—and how those ideas connect to the big picture.
A transition between paragraphs can be a word or two (however, for example, similarly), a phrase, or a sentence. Transitions can be at the end of the first paragraph, at the beginning of the second paragraph, or in both places. Transitions within paragraphs: As with transitions between sections and paragraphs, transitions within paragraphs act ...
An important part of essay writing is learning how to effectively employ paragraph transitions—shifting from one paragraph or idea to the next. Learning to effectively use the different types of transitions will help you write more cohesive pieces and improve the clarity of your writing.
Writing Transitions. Good transitions can connect paragraphs and turn disconnected writing into a unified whole. Instead of treating paragraphs as separate ideas, transitions can help readers understand how paragraphs work together, reference one another, and build to a larger point. The key to producing good transitions is highlighting ...
Transitions Quick Guide. There are two kinds of transitions: (a) transitional words and phrases that are used at the start of a sentence to show how the sentence connects with the previous sentence and (b) transitional sentences that are used at the start of a paragraph to show how the paragraph logically connects with the previous paragraph.
The topic sentence of the next paragraph indicates the specific "disastrous consequences" you will discuss. REMEMBER. If you don't see a way to write a logical, effective transition between sentences, ideas or paragraphs, this might indicate organizational problems in your essay; you might consider revising your work.
Transitions between paragraphs may appear at the end of the first paragraph, at the beginning of the second paragraph, or in both places. If the transition introduces new ideas, it usually appears at the beginning of the second paragraph. Below is a chart of transition words that are useful for linking ideas within a paragraph.
Transitions can be useful between paragraphs to connect two ideas. Effective transitions high-light the key information from one paragraph to the next and help to create a logic flow be-tween ideas. These transitions do not always have to use transitional words or phrases; how-ever, they can be useful. P1 represents the last sentence in ...
BODY PARAGRAPH #2. A. Begins with a topic sentence that: 1) States the main point of the paragraph. 2) Relates to the THESIS STATEMENT. B. After the topic sentence, you must fill the paragraph with organized details, facts, and examples. C. Paragraph may end with a transition. IV. BODY PARAGRAPH #3.
Transitions Transitions Between Paragraphs. While within-paragraph transitions serve the purpose of alerting readers of upcoming shifts in perspective or voice, between-paragraph transitions serve the unique purpose of alerting readers of upcoming shifts in argument or idea.Because one of the core rules of effective paragraph-writing is limiting each paragraph to only one controlling idea (see ...
Transitions are words and phrases that connect words, sentences and paragraphs. Transitions help to make an essay flow better and logically. above all, actually, arguably, at the same time, by, consequently, currently, even so, finally, first, second, third, for this reason, for instance, for ...
A transition between paragraphs can be a word or two (however, for example, similarly), a phrase, or a sentence. Transitions can be at the end of the first paragraph, at the beginning of the second paragraph, or in both places. 3. Transitions within paragraphs—As with transitions between sections and paragraphs,
How to transition between paragraphs and sentencesWhen writing an essay, the connections between your ideas are clear in your head, but those connections may...
These signposts ought to be everywhere within your paper, moving your reader between phrases and sentences in addition to paragraphs or larger chunks. Sometimes multiple signposts are needed to guide a reader across the bridge, because of the complex relationship of those two ideas. The primary goal to keep in mind, though, is to make sure your ...
If the new paragraph carries the weight of the transition, then the first sentence pointing out the problem may serve as bridge and a separate topic sentence may show the solution, or you may spend the entire paragraph talking about the hole in logic and the paragraph after addressing that hole. Transitions require co-ordination from both sides.
A transition in writing is a word or phrase and a sentence that connects one concept to the next. This link can be made within a paragraph or between paragraphs.. Transitions are an important aspect of academic writing, as they help to create a cohesive and well-structured document that is easy for the reader to follow.
Knowing how to use transitions words in an essay effectively is key to a well-structured, A-worthy paper. Discover what you need to know to achieve this. ... If you aren't sure what transition word to use in your writing or what the relationship is between two paragraphs, you can create a transition by repeating a word or phrase. ...
Body Paragraphs. Each body paragraph in a critical thinking essay should focus on a single idea that supports the thesis. Start with a topic sentence that clearly states the main point of the paragraph. Follow this with evidence, which could include quotes, data, or examples from credible sources. Analyze this evidence critically, explaining ...
Looking for essays that model a specific tactic or style, or that engage a specific subject? Trying to track down a specific e-Vision writer or essay? TACTIC and STYLE INDEX: Useful lists of effective essays that offer rhetorical analysis, engage primary and secondary sources, incorporate multimedia, organize and transition between paragraphs, begin well and end better, target and connect with ...
Transitions Transitions help your readers move between ideas within a paragraph, between paragraphs, or between sections of your argument. When you are deciding how to transition from one idea to the next, your goal should be to help readers see how your ideas are connected—and how those ideas connect to the big picture.
2. Identify Unnecessary Words and Remove Them. One of the simplest yet most effective ways to shorten your essay is by identifying and eliminating unnecessary words. This approach helps decrease word count and sharpens your arguments, making your writing more compelling. You can identify and remove extra words by doing the following: Spot wordy ...
5. Use Clear Transitions. When you write an essay on the comparison of two different topics, amply use the transition phrases and sentences to shift between the alternating methods of discussion. Transitions are really important for compare and contrast essays as they help you move between different perspectives and topics smoothly.