

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the complete ib extended essay guide: examples, topics, and ideas.
International Baccalaureate (IB)

IB students around the globe fear writing the Extended Essay, but it doesn't have to be a source of stress! In this article, I'll get you excited about writing your Extended Essay and provide you with the resources you need to get an A on it.
If you're reading this article, I'm going to assume you're an IB student getting ready to write your Extended Essay. If you're looking at this as a potential future IB student, I recommend reading our introductory IB articles first, including our guide to what the IB program is and our full coverage of the IB curriculum .
IB Extended Essay: Why Should You Trust My Advice?
I myself am a recipient of an IB Diploma, and I happened to receive an A on my IB Extended Essay. Don't believe me? The proof is in the IBO pudding:
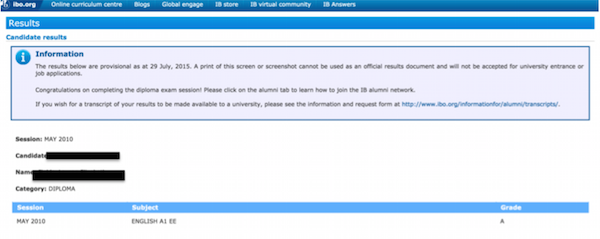
If you're confused by what this report means, EE is short for Extended Essay , and English A1 is the subject that my Extended Essay topic coordinated with. In layman's terms, my IB Diploma was graded in May 2010, I wrote my Extended Essay in the English A1 category, and I received an A grade on it.
What Is the Extended Essay in the IB Diploma Programme?
The IB Extended Essay, or EE , is a mini-thesis you write under the supervision of an IB advisor (an IB teacher at your school), which counts toward your IB Diploma (learn more about the major IB Diploma requirements in our guide) . I will explain exactly how the EE affects your Diploma later in this article.
For the Extended Essay, you will choose a research question as a topic, conduct the research independently, then write an essay on your findings . The essay itself is a long one—although there's a cap of 4,000 words, most successful essays get very close to this limit.
Keep in mind that the IB requires this essay to be a "formal piece of academic writing," meaning you'll have to do outside research and cite additional sources.
The IB Extended Essay must include the following:
- A title page
- Contents page
- Introduction
- Body of the essay
- References and bibliography
Additionally, your research topic must fall into one of the six approved DP categories , or IB subject groups, which are as follows:
- Group 1: Studies in Language and Literature
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Group 4: Sciences
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Group 6: The Arts
Once you figure out your category and have identified a potential research topic, it's time to pick your advisor, who is normally an IB teacher at your school (though you can also find one online ). This person will help direct your research, and they'll conduct the reflection sessions you'll have to do as part of your Extended Essay.
As of 2018, the IB requires a "reflection process" as part of your EE supervision process. To fulfill this requirement, you have to meet at least three times with your supervisor in what the IB calls "reflection sessions." These meetings are not only mandatory but are also part of the formal assessment of the EE and your research methods.
According to the IB, the purpose of these meetings is to "provide an opportunity for students to reflect on their engagement with the research process." Basically, these meetings give your supervisor the opportunity to offer feedback, push you to think differently, and encourage you to evaluate your research process.
The final reflection session is called the viva voce, and it's a short 10- to 15-minute interview between you and your advisor. This happens at the very end of the EE process, and it's designed to help your advisor write their report, which factors into your EE grade.
Here are the topics covered in your viva voce :
- A check on plagiarism and malpractice
- Your reflection on your project's successes and difficulties
- Your reflection on what you've learned during the EE process
Your completed Extended Essay, along with your supervisor's report, will then be sent to the IB to be graded. We'll cover the assessment criteria in just a moment.

We'll help you learn how to have those "lightbulb" moments...even on test day!
What Should You Write About in Your IB Extended Essay?
You can technically write about anything, so long as it falls within one of the approved categories listed above.
It's best to choose a topic that matches one of the IB courses , (such as Theatre, Film, Spanish, French, Math, Biology, etc.), which shouldn't be difficult because there are so many class subjects.
Here is a range of sample topics with the attached extended essay:
- Biology: The Effect of Age and Gender on the Photoreceptor Cells in the Human Retina
- Chemistry: How Does Reflux Time Affect the Yield and Purity of Ethyl Aminobenzoate (Benzocaine), and How Effective is Recrystallisation as a Purification Technique for This Compound?
- English: An Exploration of Jane Austen's Use of the Outdoors in Emma
- Geography: The Effect of Location on the Educational Attainment of Indigenous Secondary Students in Queensland, Australia
- Math: Alhazen's Billiard Problem
- Visual Arts: Can Luc Tuymans Be Classified as a Political Painter?
You can see from how varied the topics are that you have a lot of freedom when it comes to picking a topic . So how do you pick when the options are limitless?

How to Write a Stellar IB Extended Essay: 6 Essential Tips
Below are six key tips to keep in mind as you work on your Extended Essay for the IB DP. Follow these and you're sure to get an A!
#1: Write About Something You Enjoy
You can't expect to write a compelling essay if you're not a fan of the topic on which you're writing. For example, I just love British theatre and ended up writing my Extended Essay on a revolution in post-WWII British theatre. (Yes, I'm definitely a #TheatreNerd.)
I really encourage anyone who pursues an IB Diploma to take the Extended Essay seriously. I was fortunate enough to receive a full-tuition merit scholarship to USC's School of Dramatic Arts program. In my interview for the scholarship, I spoke passionately about my Extended Essay; thus, I genuinely think my Extended Essay helped me get my scholarship.
But how do you find a topic you're passionate about? Start by thinking about which classes you enjoy the most and why . Do you like math classes because you like to solve problems? Or do you enjoy English because you like to analyze literary texts?
Keep in mind that there's no right or wrong answer when it comes to choosing your Extended Essay topic. You're not more likely to get high marks because you're writing about science, just like you're not doomed to failure because you've chosen to tackle the social sciences. The quality of what you produce—not the field you choose to research within—will determine your grade.
Once you've figured out your category, you should brainstorm more specific topics by putting pen to paper . What was your favorite chapter you learned in that class? Was it astrophysics or mechanics? What did you like about that specific chapter? Is there something you want to learn more about? I recommend spending a few hours on this type of brainstorming.
One last note: if you're truly stumped on what to research, pick a topic that will help you in your future major or career . That way you can use your Extended Essay as a talking point in your college essays (and it will prepare you for your studies to come too!).
#2: Select a Topic That Is Neither Too Broad nor Too Narrow
There's a fine line between broad and narrow. You need to write about something specific, but not so specific that you can't write 4,000 words on it.
You can't write about WWII because that would be a book's worth of material. You also don't want to write about what type of soup prisoners of war received behind enemy lines, because you probably won’t be able to come up with 4,000 words of material about it. However, you could possibly write about how the conditions in German POW camps—and the rations provided—were directly affected by the Nazis' successes and failures on the front, including the use of captured factories and prison labor in Eastern Europe to increase production. WWII military history might be a little overdone, but you get my point.
If you're really stuck trying to pinpoint a not-too-broad-or-too-narrow topic, I suggest trying to brainstorm a topic that uses a comparison. Once you begin looking through the list of sample essays below, you'll notice that many use comparisons to formulate their main arguments.
I also used a comparison in my EE, contrasting Harold Pinter's Party Time with John Osborne's Look Back in Anger in order to show a transition in British theatre. Topics with comparisons of two to three plays, books, and so on tend to be the sweet spot. You can analyze each item and then compare them with one another after doing some in-depth analysis of each individually. The ways these items compare and contrast will end up forming the thesis of your essay!
When choosing a comparative topic, the key is that the comparison should be significant. I compared two plays to illustrate the transition in British theatre, but you could compare the ways different regional dialects affect people's job prospects or how different temperatures may or may not affect the mating patterns of lightning bugs. The point here is that comparisons not only help you limit your topic, but they also help you build your argument.
Comparisons are not the only way to get a grade-A EE, though. If after brainstorming, you pick a non-comparison-based topic and are still unsure whether your topic is too broad or narrow, spend about 30 minutes doing some basic research and see how much material is out there.
If there are more than 1,000 books, articles, or documentaries out there on that exact topic, it may be too broad. But if there are only two books that have any connection to your topic, it may be too narrow. If you're still unsure, ask your advisor—it's what they're there for! Speaking of advisors...

Don't get stuck with a narrow topic!
#3: Choose an Advisor Who Is Familiar With Your Topic
If you're not certain of who you would like to be your advisor, create a list of your top three choices. Next, write down the pros and cons of each possibility (I know this sounds tedious, but it really helps!).
For example, Mr. Green is my favorite teacher and we get along really well, but he teaches English. For my EE, I want to conduct an experiment that compares the efficiency of American electric cars with foreign electric cars.
I had Ms. White a year ago. She teaches physics and enjoyed having me in her class. Unlike Mr. Green, Ms. White could help me design my experiment.
Based on my topic and what I need from my advisor, Ms. White would be a better fit for me than would Mr. Green (even though I like him a lot).
The moral of my story is this: do not just ask your favorite teacher to be your advisor . They might be a hindrance to you if they teach another subject. For example, I would not recommend asking your biology teacher to guide you in writing an English literature-based EE.
There can, of course, be exceptions to this rule. If you have a teacher who's passionate and knowledgeable about your topic (as my English teacher was about my theatre topic), you could ask that instructor. Consider all your options before you do this. There was no theatre teacher at my high school, so I couldn't find a theatre-specific advisor, but I chose the next best thing.
Before you approach a teacher to serve as your advisor, check with your high school to see what requirements they have for this process. Some IB high schools require your IB Extended Essay advisor to sign an Agreement Form , for instance.
Make sure that you ask your IB coordinator whether there is any required paperwork to fill out. If your school needs a specific form signed, bring it with you when you ask your teacher to be your EE advisor.
#4: Pick an Advisor Who Will Push You to Be Your Best
Some teachers might just take on students because they have to and aren't very passionate about reading drafts, only giving you minimal feedback. Choose a teacher who will take the time to read several drafts of your essay and give you extensive notes. I would not have gotten my A without being pushed to make my Extended Essay draft better.
Ask a teacher that you have experience with through class or an extracurricular activity. Do not ask a teacher that you have absolutely no connection to. If a teacher already knows you, that means they already know your strengths and weaknesses, so they know what to look for, where you need to improve, and how to encourage your best work.
Also, don't forget that your supervisor's assessment is part of your overall EE score . If you're meeting with someone who pushes you to do better—and you actually take their advice—they'll have more impressive things to say about you than a supervisor who doesn't know you well and isn't heavily involved in your research process.
Be aware that the IB only allows advisors to make suggestions and give constructive criticism. Your teacher cannot actually help you write your EE. The IB recommends that the supervisor spends approximately two to three hours in total with the candidate discussing the EE.
#5: Make Sure Your Essay Has a Clear Structure and Flow
The IB likes structure. Your EE needs a clear introduction (which should be one to two double-spaced pages), research question/focus (i.e., what you're investigating), a body, and a conclusion (about one double-spaced page). An essay with unclear organization will be graded poorly.
The body of your EE should make up the bulk of the essay. It should be about eight to 18 pages long (again, depending on your topic). Your body can be split into multiple parts. For example, if you were doing a comparison, you might have one third of your body as Novel A Analysis, another third as Novel B Analysis, and the final third as your comparison of Novels A and B.
If you're conducting an experiment or analyzing data, such as in this EE , your EE body should have a clear structure that aligns with the scientific method ; you should state the research question, discuss your method, present the data, analyze the data, explain any uncertainties, and draw a conclusion and/or evaluate the success of the experiment.
#6: Start Writing Sooner Rather Than Later!
You will not be able to crank out a 4,000-word essay in just a week and get an A on it. You'll be reading many, many articles (and, depending on your topic, possibly books and plays as well!). As such, it's imperative that you start your research as soon as possible.
Each school has a slightly different deadline for the Extended Essay. Some schools want them as soon as November of your senior year; others will take them as late as February. Your school will tell you what your deadline is. If they haven't mentioned it by February of your junior year, ask your IB coordinator about it.
Some high schools will provide you with a timeline of when you need to come up with a topic, when you need to meet with your advisor, and when certain drafts are due. Not all schools do this. Ask your IB coordinator if you are unsure whether you are on a specific timeline.
Below is my recommended EE timeline. While it's earlier than most schools, it'll save you a ton of heartache (trust me, I remember how hard this process was!):
- January/February of Junior Year: Come up with your final research topic (or at least your top three options).
- February of Junior Year: Approach a teacher about being your EE advisor. If they decline, keep asking others until you find one. See my notes above on how to pick an EE advisor.
- April/May of Junior Year: Submit an outline of your EE and a bibliography of potential research sources (I recommend at least seven to 10) to your EE advisor. Meet with your EE advisor to discuss your outline.
- Summer Between Junior and Senior Year: Complete your first full draft over the summer between your junior and senior year. I know, I know—no one wants to work during the summer, but trust me—this will save you so much stress come fall when you are busy with college applications and other internal assessments for your IB classes. You will want to have this first full draft done because you will want to complete a couple of draft cycles as you likely won't be able to get everything you want to say into 4,000 articulate words on the first attempt. Try to get this first draft into the best possible shape so you don't have to work on too many revisions during the school year on top of your homework, college applications, and extracurriculars.
- August/September of Senior Year: Turn in your first draft of your EE to your advisor and receive feedback. Work on incorporating their feedback into your essay. If they have a lot of suggestions for improvement, ask if they will read one more draft before the final draft.
- September/October of Senior Year: Submit the second draft of your EE to your advisor (if necessary) and look at their feedback. Work on creating the best possible final draft.
- November-February of Senior Year: Schedule your viva voce. Submit two copies of your final draft to your school to be sent off to the IB. You likely will not get your grade until after you graduate.
Remember that in the middle of these milestones, you'll need to schedule two other reflection sessions with your advisor . (Your teachers will actually take notes on these sessions on a form like this one , which then gets submitted to the IB.)
I recommend doing them when you get feedback on your drafts, but these meetings will ultimately be up to your supervisor. Just don't forget to do them!

The early bird DOES get the worm!
How Is the IB Extended Essay Graded?
Extended Essays are graded by examiners appointed by the IB on a scale of 0 to 34 . You'll be graded on five criteria, each with its own set of points. You can learn more about how EE scoring works by reading the IB guide to extended essays .
- Criterion A: Focus and Method (6 points maximum)
- Criterion B: Knowledge and Understanding (6 points maximum)
- Criterion C: Critical Thinking (12 points maximum)
- Criterion D: Presentation (4 points maximum)
- Criterion E: Engagement (6 points maximum)
How well you do on each of these criteria will determine the final letter grade you get for your EE. You must earn at least a D to be eligible to receive your IB Diploma.
Although each criterion has a point value, the IB explicitly states that graders are not converting point totals into grades; instead, they're using qualitative grade descriptors to determine the final grade of your Extended Essay . Grade descriptors are on pages 102-103 of this document .
Here's a rough estimate of how these different point values translate to letter grades based on previous scoring methods for the EE. This is just an estimate —you should read and understand the grade descriptors so you know exactly what the scorers are looking for.
Here is the breakdown of EE scores (from the May 2021 bulletin):
How Does the Extended Essay Grade Affect Your IB Diploma?
The Extended Essay grade is combined with your TOK (Theory of Knowledge) grade to determine how many points you get toward your IB Diploma.
To learn about Theory of Knowledge or how many points you need to receive an IB Diploma, read our complete guide to the IB program and our guide to the IB Diploma requirements .
This diagram shows how the two scores are combined to determine how many points you receive for your IB diploma (3 being the most, 0 being the least). In order to get your IB Diploma, you have to earn 24 points across both categories (the TOK and EE). The highest score anyone can earn is 45 points.
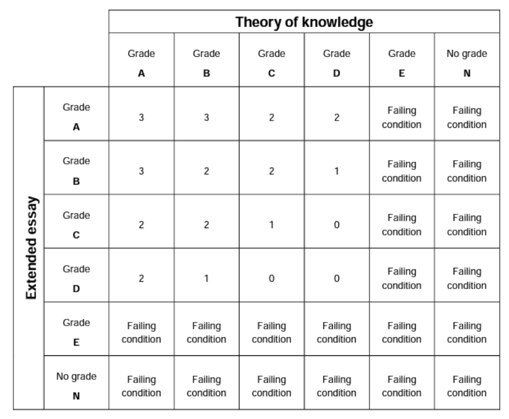
Let's say you get an A on your EE and a B on TOK. You will get 3 points toward your Diploma. As of 2014, a student who scores an E on either the extended essay or TOK essay will not be eligible to receive an IB Diploma .
Prior to the class of 2010, a Diploma candidate could receive a failing grade in either the Extended Essay or Theory of Knowledge and still be awarded a Diploma, but this is no longer true.
Figuring out how you're assessed can be a little tricky. Luckily, the IB breaks everything down here in this document . (The assessment information begins on page 219.)
40+ Sample Extended Essays for the IB Diploma Programme
In case you want a little more guidance on how to get an A on your EE, here are over 40 excellent (grade A) sample extended essays for your reading pleasure. Essays are grouped by IB subject.
- Business Management 1
- Chemistry 1
- Chemistry 2
- Chemistry 3
- Chemistry 4
- Chemistry 5
- Chemistry 6
- Chemistry 7
- Computer Science 1
- Economics 1
- Design Technology 1
- Design Technology 2
- Environmental Systems and Societies 1
- Geography 1
- Geography 2
- Geography 3
- Geography 4
- Geography 5
- Geography 6
- Literature and Performance 1
- Mathematics 1
- Mathematics 2
- Mathematics 3
- Mathematics 4
- Mathematics 5
- Philosophy 1
- Philosophy 2
- Philosophy 3
- Philosophy 4
- Philosophy 5
- Psychology 1
- Psychology 2
- Psychology 3
- Psychology 4
- Psychology 5
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 1
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 2
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 3
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 1
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 2
- Visual Arts 1
- Visual Arts 2
- Visual Arts 3
- Visual Arts 4
- Visual Arts 5
- World Religion 1
- World Religion 2
- World Religion 3

What's Next?
Trying to figure out what extracurriculars you should do? Learn more about participating in the Science Olympiad , starting a club , doing volunteer work , and joining Student Government .
Studying for the SAT? Check out our expert study guide to the SAT . Taking the SAT in a month or so? Learn how to cram effectively for this important test .
Not sure where you want to go to college? Read our guide to finding your target school . Also, determine your target SAT score or target ACT score .

As an SAT/ACT tutor, Dora has guided many students to test prep success. She loves watching students succeed and is committed to helping you get there. Dora received a full-tuition merit based scholarship to University of Southern California. She graduated magna cum laude and scored in the 99th percentile on the ACT. She is also passionate about acting, writing, and photography.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
What Is an IB Extended Essay and How to Write It?
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
The IB extended essay is a paper of up to 4,000 words that is required for students enrolled in the International Baccalaureate (IB) diploma program. The extended essay allows students to engage in independent research on a topic within one of the available subject areas.
The extended essay should be an original piece of academic writing that demonstrates the following student's abilities:
- Formulating a research question
- Conductig independent investigation
- Presenting key findings in a scholarly format.
Check out this article by StudyCrumb to discover how to write an IB extendend essay properly. We will give you a complete writing guide and critical tips you need for this essay type.
IB Extended Essay: What Is It?
An extended essay is independent research. Usually students choose a topic in consultation with a mentor. It is an integral part of the International Baccalaureate (IB) degree program. This means that you won't receive a degree without a successfully written paper. It requires 4,000-word study on a chosen narrow topic. To get a high score, you should meet all required structure and formatting standards. This is the result of approximately 40 working hours. Its purpose is giving you the opportunity to try independent research writing. It's approved that these skills are critical for student success at university. The following sections explain how to write an extended article with examples. So keep reading!
Choosing a Mentor for Extended Essay
IB extended essay guidelines require supervisor meetings, totaling 3-5 hours. They include three critical reflections. A mentor won't write a paper instead of you but can help adjust it. So it is important to consult with them, but no one will proofread or correct actual research for you. In general, initially treat an essay as an exclusively individual work. So your role and contribution are maximal.
Extended Essay Outline
Let's take a look at how to write an extended essay outline. In this part, you organize yourself so that your work develops your idea. So we especially recommend you work out this step with your teacher. You can also find any outline example for essay . In your short sketch, plan a roadmap for your thoughts. Think through and prepare a summary of each paragraph. Then, expand annotation of each section with a couple more supporting evidence. Explain how specific examples illustrate key points. Make it more significant by using different opinions on general issues.
Extended Essay: Getting Started
After you chose an extended essay topic and made an outline, it's time to start your research. Start with a complete Table of Contents and make a choice of a research question. Select the subject in which you feel most confident and which is most interesting for you. For example, if at school you are interested in natural science, focus on that. If you have difficulties choosing a research question, rely on our essay topic generator .
Extended Essay Introduction
In the introduction of an extended essay, present a thesis statement. But do it in such a way that your readers understand the importance of your research. State research question clearly. That is the central question that you are trying to answer while writing. Even your score depends on how you develop your particular research question. Therefore, it is essential to draw it up correctly. Gather all relevant information from relevant sources. Explain why this is worth exploring. Then provide a research plan, which you will disclose further.
Extended Essay Methodology
In accordance with extended essay guidelines, it's mandatory to choose and clearly state a methodological approach. So, it will be apparent to your examiner how you answered your research question. Include your collection methods and tools you use for collection and analysis. Your strategies can be experimental or descriptive, quantitative or qualitative. Research collection tools include observations, questionnaires, interviews, or background knowledge.
Extended Essay Main Body
Well, here we come to the most voluminous part of the extended essay for IB! In every essay body paragraph , you reveal your research question and discuss your topic. Provide all details of your academic study. But stay focused and do it without dubious ideas. Use different sources of information to provide supporting arguments and substantial evidence. This will impress professors. For this section, 3 main paragraphs are enough. Discuss each idea or argument in a separate paragraph. You can even use supporting quotes where appropriate. But don't overcomplicate. Make your extended essay easy to read and logical. It's critical to stay concise, so if you aren't sure how to make your text readable, use our tool to get a readbility test . Following the plan you outlined earlier is very important. Analyze each fact before including it in your writing. And don't write unnecessary information.
Extended Essay Conclusion
Now let's move on to the final part of IB extended essay guidelines. In conclusion, focus on summarizing the main points you have made. No new ideas or information can be introduced in this part. Use conclusion as your last chance to impress your readers. Reframe your own strong thesis. Here you must show all key points. Do not repeat absolutely every argument. Better try to make this part unique. This will show that you have a clear understanding of the topic you have chosen. And even more professional will be recommendations of new areas for future research. One good paragraph may be enough here. Although in some cases, two or three paragraphs may be required.
Extended Essay Bibliography & Appendices
To write an impressive extended essay, you should focus on appropriate information. You must create a separate page for bibliography with all sources you used. Tip from us: start writing this page with the first quote you use. Don't write this part last or postpone. In turn, appendices are not an essential section. Examiners will not pay much attention to this part. Therefore, include all information directly related to analysis and argumentation in the main body. Include raw data in the appendix only if it is really urgently needed. Moreover, it is better not to refer to appendices in text itself. This can disrupt the narrative of the essay.
Extended Essay Examples
We have prepared a good example of an extended essay. You can check it by downloading it for free. You can use it as a template. However, pay attention that your paper is required to be unique. Don't be afraid to present all the skills you gained during your IB.
Final Thoughts on IB Extended Essay
In this article, we presented detailed IB extended essay guidelines. An extended essay is a daunting academic challenge to write. It is a research paper with a deep thematic analysis of information. But we have described several practical and straightforward tips. Therefore, we are sure that you will succeed!
If topics seem too complex, turn to our top essay writers. They will accomplish any IB assignment in the best way your professor can evaluate it!

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

The Extended Essay Step-by-Step Guide
From setting the research question to submitting the Extended Essay, here is an easy-to-follow guide for IB EE students to follow, along with personal anecdotes with tips to apply critical thinking techniques and find success.
Before I started the IB, the thing I was most worried about was the extended essay. I’m pretty sure the reason why I was so worried is because I had no clue what writing it would actually entail. In this week’s blog, I’ll be going over the basics of the extended essay so you don’t have to worried like I was!
What is an Extended Essay?
The extended essay (often called the EE) is a 4000-word structured essay on a topic of your choice which can take many different forms. Ultimately what your EE ends up looking like depends on the topic you choose.
Some students choose to write their extended essay about literature or history, which means they write a more traditional academic essay.
However, you can choose to conduct an experiment and write up the results if you want to focus on the sciences. Or you can try and solve an arithmetic problem if you are into maths. As long as it takes an academic format, it should be okay!
What is Included in an Extended Essay?
There are several things that you have to include in your extended essay. As a side note, the requirements for the EE were changed quite drastically in 2016, so it’s important that when you look things up about the EE you are looking at the updated guidelines! You can find out more about this here .
Based on these new guidelines your EE needs to contain:
- A research question
- A cover-page
- A table of content
- An introduction
- A main body
- A conclusion
- A bibliography
- 3 reflections from the beginning, middle and the end of the research process.
The Importance of The IB ee
The extended essay provides each student with the opportunity to investigate a topic of personal interest to them, which relates to either:
-One of the student’s six DP subjects, or
-the interdisciplinary approach of a World Studies extended essay.
Students gain the following skills by writing an extended essay:
-formulating an appropriate research question
-engaging in a personal exploration and critical analysis of the topic
-communicating ideas
-developing an argument
Essentially, the assessment criteria will evaluate the student based on their ability to research a subject, or in the case of the world study extended essay, the two disciplinary perspectives applied. In both examples, you are required to demonstrate knowledge, understanding, and application.
10 Steps to Writing an IB Extended Essay
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write an extended essay, from research question to complete essay.
1. Define the Topic and Draft the Research Question
2. create a timeline, 3. research sources and expand knowledge about the topic, 4. set deadlines, 5. plan the structure according to the total word count, 6. evaluate your understanding, 7. primary and secondary research and theory, 8. write the extended essay draft to explain what you learnt, 9. analyze and edit, 10. present.
By following the steps above, you should be able to produce a logical and coherent rationale to follow when writing the extended essay for your IB diploma programme.
Can You Get Help for the IB Extended Essay?
Of course you do! In fact, you actually get a lot of help. Your school will assign you a ‘supervisor’. Your supervisor will be an IB teacher at your school and it is their responsibility to meet with you and discuss your research question, your planning and also your first draft.
What are the Next Steps?
In conclusion: your extended essay is typically something you write towards the end of your first year of IB so I wouldn’t worry too much about it right now. However, it’s likely you will have to choose your topic and research question sooner rather than later.
What I would recommend is to start thinking about what subject would interest you enough to write a mini thesis of 4,000 words on it.
Pro Tip: Find an example of an extended essay that is effective so you can see how they applied the tips above and explored their research question.
If you find lots of essays, this suggests to you that this is probably a good topic! If there isn’t very much, that doesn’t mean it’s a bad idea, but you might want to change the focus a little to make it easier to conduct research and find enough data to work with.
Don’t let the task overwhelm you: the research and writing should be fun! Students who are truly interested in their topics will likely find the most success.
Get Support from a Tutor at Lanterna for the IB Diploma Programme
Lanterna has over 300 tutors who aced the Extended Essay for their courses. They are equipped with the knowledge and experience to help you get an A in your EE. What are you waiting for? Get your own tutor today and learn valuable insights sure to help you succeed.
For more details about your IB extended essay, be sure to check out our blog post with 100 topic ideas to get you started!
It explains how you can find your research topic, formulate a research question and explain it fully in accordance with the assessment criteria, and finally tips on how to write extended essays.
Read part 2: Choose Your Topic
Share article links
Related Articles

- IB Extended Essay
Solutions for Extended Essay Summer Procrastination
Did you promise yourself you’d do your Extended Essay Draft over summer? Are you, like I was, completely lost, demoralised and on the edge of a breakdown before term has really started? Below you’ll find 3 quick easy ways to get you started and put you on the right track: Let go of that […]

25 Unique EE Ideas
The extended essay is possibly the most exciting part of the IB. You get to fully nerd out on a subject that fascinates you. The endless possibilities could leave you in a state of choice paralysis! Because of that, we have thrown out a list of 25 unique EE ideas as a lifeline, so you do […]

EE Research Question: 5 Tips to get an A
Do you struggle with figuring out your EE research question? It is the backbone of your essay, after all. This one question will dictate everything else you will write. So, there is a lot of pressure to get it right! Like most other IB students, I struggled to articulate my research question. Finding the right […]

Extended Essay Guide: The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Writing Your Research Question
- Finding Resources
- Research Plan Ouline
- Drafting Your Paper
- The Introduction
- The Conclusion
- Citations/Bibliography
- Proofreading Your Paper
- IB Assessment Criteria/Subject Specific Guides/Exemplars/Etc
Extended Essay Introduction
The goal of the introduction is to introduce the topic and provide enough information about it in order to enable the reader to comprehend the significance of your research question. The research question must be clearly and precisely stated in the introduction. The research question is the central question you are trying to answer through your research and writing of the extended essay. This question, if properly composed, will both enable you to maintain your focus on a topic of narrow and limited scope while also help you to maintain the purpose and orientation of your entire investigation. Your extended essay will be assessed in part according to the extent to which the essay appropriately addresses and develops your specific research question. The readers will also evaluate your success in collecting information relevant to the research question. Establish the significance of the research question and explain why it is worthy of study. Briefly and concisely preview your body by providing a plan of investigation (game plan) for the rest of the paper. The game plan briefly explains how you intend to answer the research question.
Introduction Checklist
____ Does your introduction include some background information and place the topic in an appropriate context
_____ Is your research question clearly and exactly focused, and stated (in bold)?
_____ Does your introduction explain the significance and context of your topic? (This topic is an important because…)
_____ Does your introduction explain why your topic is worthy of investigation and still have contemporary relevance? (This topic is worthy of investigation because…)
_____ Does your introduction explain how the research question relates to existing knowledge?
_____ Do you avoid writing lengthy, irrelevant background material?
_____ Do you give the game plan for the rest of the essay?
- _____ Is it clear where your intro ends?

EE Introduction
Background information.
Background information identifies and describes the history and nature of your research question with reference to the existing literature. Background information expands upon the key points stated in the beginning of your introduction but is not intended to be the main focus of the paper. Sufficient background information helps your reader determine if you have a basic understanding of the research question being investigated and promotes confidence in the overall quality of your analysis and conclusion. This information provides the reader with the essential context needed to understand the research question and its significance.
Websites to help:
Background of the Problem Section: What do you Need to Consider?
How to Write a Research Paper .
- << Previous: Drafting Your Paper
- Next: The Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Nov 15, 2016 1:55 PM
- URL: https://baltimorecitycollege.libguides.com/eeguide
So much is at stake in writing a conclusion. This is, after all, your last chance to persuade your readers to your point of view, to impress yourself upon them as a writer and thinker. And the impression you create in your conclusion will shape the impression that stays with your readers after they've finished the essay.
The end of an essay should therefore convey a sense of completeness and closure as well as a sense of the lingering possibilities of the topic, its larger meaning, its implications: the final paragraph should close the discussion without closing it off.
To establish a sense of closure, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude by linking the last paragraph to the first, perhaps by reiterating a word or phrase you used at the beginning.
- Conclude with a sentence composed mainly of one-syllable words. Simple language can help create an effect of understated drama.
- Conclude with a sentence that's compound or parallel in structure; such sentences can establish a sense of balance or order that may feel just right at the end of a complex discussion.
To close the discussion without closing it off, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude with a quotation from or reference to a primary or secondary source, one that amplifies your main point or puts it in a different perspective. A quotation from, say, the novel or poem you're writing about can add texture and specificity to your discussion; a critic or scholar can help confirm or complicate your final point. For example, you might conclude an essay on the idea of home in James Joyce's short story collection, Dubliners , with information about Joyce's own complex feelings towards Dublin, his home. Or you might end with a biographer's statement about Joyce's attitude toward Dublin, which could illuminate his characters' responses to the city. Just be cautious, especially about using secondary material: make sure that you get the last word.
- Conclude by setting your discussion into a different, perhaps larger, context. For example, you might end an essay on nineteenth-century muckraking journalism by linking it to a current news magazine program like 60 Minutes .
- Conclude by redefining one of the key terms of your argument. For example, an essay on Marx's treatment of the conflict between wage labor and capital might begin with Marx's claim that the "capitalist economy is . . . a gigantic enterprise of dehumanization "; the essay might end by suggesting that Marxist analysis is itself dehumanizing because it construes everything in economic -- rather than moral or ethical-- terms.
- Conclude by considering the implications of your argument (or analysis or discussion). What does your argument imply, or involve, or suggest? For example, an essay on the novel Ambiguous Adventure , by the Senegalese writer Cheikh Hamidou Kane, might open with the idea that the protagonist's development suggests Kane's belief in the need to integrate Western materialism and Sufi spirituality in modern Senegal. The conclusion might make the new but related point that the novel on the whole suggests that such an integration is (or isn't) possible.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay:
- Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas.
- Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up." These phrases can be useful--even welcome--in oral presentations. But readers can see, by the tell-tale compression of the pages, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your audience if you belabor the obvious.
- Resist the urge to apologize. If you've immersed yourself in your subject, you now know a good deal more about it than you can possibly include in a five- or ten- or 20-page essay. As a result, by the time you've finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you've produced. (And if you haven't immersed yourself in your subject, you may be feeling even more doubtful about your essay as you approach the conclusion.) Repress those doubts. Don't undercut your authority by saying things like, "this is just one approach to the subject; there may be other, better approaches. . ."
Copyright 1998, Pat Bellanca, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

How to Write an Extended Essay: from Outline to Conclusion

write an extended essay
As a student, especially those pursuing International Baccalaureate (IB), you will be faced with the challenge of coming up with an extended essay. But few students do not know how to write long essays like an extended essay. That is where we come in.
In this comprehensive guide, I will guide you on the 8 steps to follow when writing a good extended essay and provide you with examples of topics you can use.
As noted by one of our top essay writers for hire , extended essays are not like your ordinary essays. As the name suggests, they are extended versions of essays and it may take longer and a unique approach to writing them.

However, before delving into such details, it is important to first understand what extended essays are.
Need Help with your Homework or Essays?
What is an extended essay.
An extended essay (EE) is a form of writing that provides learners with a chance to carry out independent research concerning a topic of their interest.
It is part of the requirements for the International Baccalaureate (IB) program and its content is based on a freely-selected topic provided that there is an instructor for the subject in school since candidates should have a supervisor for the subjects.
To be more precise, an extended essay can be regarded as a 4000-word structured piece of writing centered on an International Baccalaureate student’s topic and it may take various forms.
What is meant by “it may take various forms” is that the way it looks depends on the topic selected. The next section will provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to write an extended essay.
People Also Read : I Can’t Write My College Essay: Here’s what to do to score A
How to Write an Extended Essay
When writing an extended essay, there 8 steps that should be taken to effectively complete it on time. Carefully read through the 8 steps to fully understand how to write an extended essay.
Step 1: Selecting a Topic and Researching on it

This is the first step that you should take before writing your extended essay.
As noted, extended essays will allow you to write on the topic of your interest.
However, various topics are provided by your instructor and it is upon you to select the topic that interests you.
You should keep in mind that the topic selected should have enough material and resources to support your topic and the position of your arguments concerning the topic.
Some topics may have limited resources.
At the same time, select a topic that is neither too broad nor too narrow. A narrow topic may lack enough material to have a 4000-word extended essay while a broad topic may require a lot of supporting material that may exceed the 4000-word limit.
If you find the first step confusing or you find it difficult to tackle it on your own, it is advisable to seek a mentor/advisor. You should select an advisor or mentor with whom you will connect well and the one who understands the topic and what is required when writing extended essays.
Such a mentor will help you select the topic that fits your interest. While helping you select a topic that is not too narrow or broad, they should push you to deliver your best. Mentors/advisors can be your instructors or friends who have completed extended essays.
Once this is done, research extensively concerning your topic and ensure that the sources of your information are peer-reviewed and credible. They should provide the most recent research or information concerning your topic.
Note the sources of your information so that you can cite and reference them in your extended essay.
Step 2: Coming up With a Research Question
This is an important step because selecting a research question will provide you with a focused and clear summative statement to be used during your research.
It will act as a roadmap or a guideline that will help you during the writing process. It will also help you formulate a clear and concise thesis statement that will summarize your arguments and the position you will take in your extended essay.
Step 3: Structuring Your Extended Essay
As aforementioned, extended essays should always take an academic format. This means that it should have an acceptable academic structure.
At the same time, since International Baccalaureate (IB) guidelines are constantly updated, you should follow the latest guidelines so that you can utilize the latest format.
The acceptable format for your extended essay will include an introduction, methodology, main body, conclusion, bibliography, and appendices.

This will be the general structure for your extended essay.
It should be noted that this structure is not an outline.
What this means is that the structure should be considered when coming up with an outline.
Once you have decided the structure of your extended essay, come up with an outline based on your topic, thesis, and arguments.
An outline will act as a guide during the drafting process and it will save a lot of time.
This is because you will have already outlined your extended essay and what you will be doing is to add content to the points you have highlighted. Ensure that individual points translate to a single paragraph.
You should also note that the extended essay will have a table of contents. Therefore, the outline will be very important when coming up with your table of contents that is located after the cover page of your extended essay.
People Also Read : 10-Page Essay Due Tomorrow? Don’t Panic, We are Here to Help
Step 4: Writing the Introduction
Once you have completed the above steps and you have come up with an outline based on the extended essay’s structure, the next step is to introduce your topic and elaborate it to your target readers.

There are various things you should consider when coming up with an introduction.
First of all, the introduction should be catchy and interesting.
This is because your readers will read it before deciding on whether to continue with the rest of the paper.
The best way to do this is to begin your introduction with something catchy or attention-grabbing sentence.
This will arouse the reader’s curiosity to know more about the topic.
The second thing you should know about the introduction is that it should offer a crisp and clear description of what you are going to talk about and the various strategies you will use to explore the topic. It all depends on the topic.
You can decide to highlight the issues that will be explored and the ways of addressing such issues. It is all about proving some brief background of what you will be exploring in the rest of the paper.
Do you remember that you formulated a research question after researching your topic? While introducing the topic of your extended essay, you should provide the context of your research question where you address the situation or the background from which the question comes.
While doing so, you should state the research question and elaborate on why answering the question is important for the paper’s findings.
The introduction should also tell the readers why the research you present in your extended essay is important, interesting, and/or valuable to the discipline and the audience.
Finally, you should conclude your introduction by writing your thesis statement. This should be the last sentence of your introduction paragraph(s).
Step 5: Methodology
This is also a very important step when writing an extended essay. To make sure that all the important aspects of the methodology are covered, you should divide this section into two.

The first section of the methodology explains your sources of information and the second section explores the related theories, topics, and arguments that will be used to explore your topic.
In the first section, you should describe every primary and/or secondary source used, why the sources are important, and their limitations.
Sources of secondary research can include news articles, annual reports for companies, business textbooks, magazine articles, and encyclopedias. The final thing you should do while in section 1 is to state the adjustments made in your research.
For the second section, you should provide a brief explanation of the theories that are going to be applied and the reason why they are the most appropriate in explaining your arguments.
Also, give the limitations of each theory, topic, or argument applied. Finally, state the changes made during the research and writing process.
Step 6: Drafting the Main Body
This should be the most elaborate part of your extended essay because you will concentrate on the research, analysis of the research, discussion, and evaluation.
You should try to retain the flow of step 5 that has steps 1 and 2. This will demonstrate that you understand the concepts of the International Baccalaureate while still addressing your topic using the relevant sources.
In the first section, for each of the theories, arguments, and topics used to address your topic, include about 4 examples of each to help you answer the research question effectively. Also, address the qualitative tools applied before the quantitative tools.
The second section goes beyond the course to educate your evaluator and/or readers concerning your topic. Explore the related concepts and theories deeply while providing different perspectives on the topic.
Remember that you should be evaluating the findings here. Use analytical insight to further explain your arguments and points of view. Graphs and other forms of data presentation can be used. However, they should apply to the research.
Step 7: Writing the Conclusion
In this step, you should sum up your arguments from all your sections. It is important to stipulate what has been researched and how it has helped answer the research question.
It should be noted that no new information should be added in the conclusion. Mention some limitations of the research and their impact, and the reasons behind such limitations.
Finally, state the thing(s) you can do differently if you were to write another extended essay.
Step 8: Bibliography and Appendices
On a different page or the next page after the conclusion, reference your sources of information using the correct format (APA, MLA, Chicago, or Harvard styles). Always remember to arrange the references from A to Z. Bibliography or references are not part of the word count.
The appendices section showcases the extra work you have done such as transcripts of the interviews conducted, additional analysis, and any other data that you found interesting but did not include in the body of your paper.
Once you are done with writing, thoroughly proofread your work and correct any grammatical or spelling errors made. Make sure that the work is well formatted with all the sections included.
At the same time, make sure that nothing in your paper is copy-pasted because it will be regarded as plagiarism. Always do this before submitting your extended essay.
People Also Read : Sources of Free Essays Online: Where to Get Free Good Essays
Best Length of an Extended Essay
While there is no universally agreed minimum word count for an extended essay, you should not write less than 3,000 words. This is because lesser than that will demonstrate that you did not adequately research your topic.
Since the acceptable word limit on the upper side is 4,000 words, always strive to write more than 3,500 words. Unlike other types of essays like a GRE Essay that is short, an extended essay is long in terms of word count.
In other cases, the minimum word count is 1,500 words, and the maximum word count is 4,000 words. It is up to the student to decide what their word count should be. It is important not to go over or under the prescribed word count by more than 10%. The upper limit of 4000 words should be a guideline rather than a firm rule.
Can the extended essay be over 4000 words?
Yes, the extended essay may be up to 4000 words in length. The upper limit is 4,000 words for all extended essays. This upper limit includes the introduction, the body, the conclusion, and any quotations, but does not include:
- the abstract
- the contents page
- acknowledgments
- any diagrams, charts, tables, and graphs
- the bibliography
How Many Pages is an Extended Essay?
4000 words is 8 pages single spaced, and 16 pages double spaced. The number of pages changes depends on the number of words, the font, and the font size. Usually, the extended essay is 4000 words in length, so it is quite a bit longer than your average essay. Double-space, Times New Roman 12 is pretty much universal, in college anyway.
What are the extended essay minimum and maximum word count?
Get a Brilliant Essay today!
Let our essay writing experts help you get that A in your next essay. Place your order today, and you will enjoy the benefits.
12 Examples of Extended Essay Topics
- What is the effect of age and gender on the photoreceptor cells in the human retina?
- How is climate change impacting the appearance of coral reefs?
- An evaluation of how antioxidants work in our bodies?
- Is there an association between viewing violence on television and the display of violent acts?
- What motivational climate should a coach employ to achieve optimal performance in athletes?
- How does the X hormone affect human behavior?
- How were women treated differently in the 1920s and 1950s Great Britain?
- What role did economics play in the unification of Germany from 1834 to 1871?
- How does the sugar concentration affect the refractive index of water?
- What factors influence the location of industries in country/city X?
- An investigation into the significance of preserving the quality of water in a continent/country/city?
- What effect does the coating of aspirin tablets have on the hydrolysis of aspirin?
People Also Read : Get Non-plagiarized and Untraceable Essays by top writers
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you redo an extended essay.
Yes. You can redo an extended essay if you appeal to the relevant institution about the reason(s) why you failed on the first try. You should provide credible and sensible reasons for you to be considered. It is only then that you are granted a retake.
Can You Fail an Extended Essay?
Yes. You can fail an extended essay if you do not follow the essay’s requirements, instructions, or rubric.
What Happens if You Fail an Extended Essay?
If you fail an extended essay, you will not graduate with a diploma. Therefore, if you fail, you should request a retake and do your best to write a good extended essay.
How many points is the extended essay worth?
The Extended Essay is a 4,000-word essay that you write on a topic of your choice. This counts towards your IB Diploma and it’s worth 3 points of your overall score.
The Extended Essay is often the most rewarding part of the IB Diploma. It gives you the chance to study something that you want to learn about in-depth, and it can be on any topic you choose – as long as there’s an expert to supervise it!
Can I publish my extended essay?
You may publish your extended essay. There are some things to consider before you do though: • Check that the subject of your essay is appropriate for publishing. Some subjects, such as science and math, may not be appropriate for publication because of how quickly the field develops. Also, check that your advisor approves of publishing the essay. • Check that you have gotten all the necessary permissions you need before you publish. • Check with your advisor if you have any doubts about these things.

Josh Jasen or JJ as we fondly call him, is a senior academic editor at Grade Bees in charge of the writing department. When not managing complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In his spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

Overcoming the feeling and fear of writing essays
Overcoming the Feeling and Fear of Writing Essays
Spaces between Paragraphs in an Essay
How Many Spaces between Paragraphs in an Essay
Double Space an Essay
Should You Double Space an Essay: When and When Not To

Extended Essay: Writing an EE Introduction
- General Timeline
- Group 1: English Language and Literature
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Group 4: Sciences
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Group 6: The Arts
- Interdisciplinary essays
- Six sub-categories for WSEE
- IB Interdisciplinary EE Assessment Guide
- Brainstorming
- Pre-Writing
- Research Techniques
- The Research Question
- Paraphrasing, Summarising and Quotations
Writing an EE Introduction
- Writing the main body of your EE
- Writing your EE Conclusion
- Sources: Finding, Organising and Evaluating Them
- Conducting Interviews and Surveys
- Citing and Referencing
- Check-in Sessions
- First Formal Reflection
- Second Formal Reflection
- Final Reflection (Viva Voce)
- Researcher's Reflection Space (RRS) Examples
- Information for Supervisors
- How is the EE Graded?
- EE Online Resources
- Stavanger Public Library
- Exemplar Essays
- Extended Essay Presentations
- ISS High School Academic Honesty Policy
The most important thing you need to know about writing your introduction is that it should be written LAST. Although that sounds counterintuitive, that it is the best way to do it. Simply put, there is just no way to know everything that should go into your introduction until you have completed your research.
Once you have written the bulk of your paper including your reasoned argument and conclusion, you will then have all the info you need to complete your introduction.
Here are the basic components of what needs to be included in your EE introduction:
- Academic Context: You need to show how your question fits into existing knowledge about your topic.
- Outline of your argument: Go through your reasoned argument chronologically – in the order it appears in your paper.
- Scope: How have you approached your RQ? What types of sources were used – did you use any unconventional methods?
- Worthiness: why is your RQ worthy of investigation?
From the EE Guide:
The introduction should tell the reader what to expect in the essay. The introduction should make clear to the reader the focus of the essay, the scope of the research, in particular an indication of the sources to be used, and an insight into the line of argument to be taken.
While students should have a sense of the direction and key focus of their essay, it is sometimes advisable to finalize the introduction once the body of the essay is complete.
I strongly urge you to read Chapter 5 of the Oxford EE Guide as it gives much more detail about writing your introduction along with examples.
***Remember to state your Research Question clearly in the introduction and remember to do your introduction LAST !
Academic Writing Tips
Formal vs. Informal Writing A chart giving the differences between informal and formal essays in seven areas (author's viewpoint; subject/content (sources of evidence); tone; structure; location of the research question; vocabulary; and purpose. Also included are examples comparing informal and formal writing for essays in English, biology, and psychology.
How to Avoid Colloquial (Informal) Writing While it may be acceptable in friendly e-mails and chat rooms, excessive colloquialism is a major pitfall that lowers the quality of formal written text. Here are some steps/tips that you can follow to help improve your overall writing.
Elements of Academic Context
- Evidence that you’ve carefully considered the subject.
- A clear, appropriately qualified thesis
- A response to what others have said
- Good reasons supported by evidence
- Acknowledgement of multiple perspectives
- Carefully documented sources
- A confidant, authoritative stance
- An indication of why your topic matters
- Careful attention to correctness
From Scotch College
Writing the introduction.
An introduction for an Extended Essay requires students to include the following aspects:

Aside from giving the essay a structural outline that any reader can follow, these aspects also help ensure that expectations for Criterion A (Focus and Method) are met.
Context : Explicitly stating your research question and providing some context that situated your question within existing knowledge is the key to a strong introduction. This does not mean providing detailed background information but rather indicating to an examiner what existing theories, critical approaches , methods or factors have already been suggested or exist to answer your research question.
Outline of the argument : Including the research question in your introduction is a quick way of ensuring you've made clear what you will be focusing on. In addition to this, it allows you to specify which aspects, factors or key features you will be investigating that will help you answer your overall question. Doing this in the order they appear in the main body is advised.
Scope : It is vital that you indicate in your introduction how you've gone about answering your research question. This means indicating to the examiner what source material has been used, or scientific methodologies followed or critical interpretations challenged and so on.
Stating that your essay utilised websites, books and journals is not as good as indicating exactly which authors, theories or methods have been used.
Worthiness : Finally, it is important, to indicate why your research question is worthy of investigation. Using the phrase "this research question is worthy of investigation because..." forces you to consider worthiness by default.
Exemplar of Introduction
Muawiya's accession to the caliphate is a hotly debated topic among historians with some, such as Kennedy, arguing that he owes his elevation to the weakness of opposition as reflected in the figure of Caliph Ali, while others, such as Shaban, arguing that his success owes itself in large measure to the tangible economic benefits that support Muawiya provided the Arab tribes...
... this essay seeks to challenge the orthodox interpretation offered by Kennedy and instead argue that Muawiya's success owes much to the changing socio-economic dynamic among Arab tribesmen within the newly formed Islamic Empire...
... the essay will also simultaneously explore what other factors, including the governorship of Syria, the conflict of Byzantium, the dwindling role of the Ansar, and the role the Kharijites played in helping Muawiya take over the Caliphate while relying on the works of principal historians such as Kennedy, Shaban, Armstrong and Hawting.
... this research question is worthy of investigation because Muawiya's rise to the caliphate marks a significant turning point in the development of the Islamic Empire during the seventh century and beyond. It established the tradition of dynastic and monarchic succession that would become commonplace in the ensuring centuries... the role played by Caliph Ali in supplanting the Rashidun model with a dynastic model is of critical significance to this early medieval period as it created the conditions for the schism between Sunni and Shi'a practices...
Introduction – Roughly 800 words
- Must include the RQ in bold – preferably in the first paragraph
- Context: What key aspects can you discuss to ensure you’ve provided some academic context underpinning your research question?
- For locally based investigations ensure you clearly identify and locate the local context
- Outline of argument: What features, aspects, factors, theories and so forth will your essay utilize in order to arrive at a conclusion?
- Give an overview of methodology and scope – how do you plan to answer the question? What authors, scientists, case studies, theories and so on have been consulted to answer your research question?
- What is the significance of your research? Why is this topic worthy of consideration?
EE Introduction Checklist
→does your introduction include some background information and place the topic in an appropriate context , →is your research question clearly focused, and highlighted in some way (bold, italics, etc), →does your introduction explain the significance and context of your topic (this topic is an important because…), →does your introduction explain why your topic is worthy of investigation , →does your introduction explain how the research question relates to existing knowledge (academic context) , →do you avoid writing lengthy, irrelevant background material, →do you outline a cohesive reasoned argument, →is it clear where your intro ends.
- << Previous: Paraphrasing, Summarising and Quotations
- Next: Writing the main body of your EE >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:11 AM
- URL: https://isstavanger.libguides.com/c.php?g=695888

Extended Essay: Formal vs. Informal Writing
- Extended Essay- The Basics
- Step 1. Choose a Subject
- Step 2. Educate yourself!
- Using Brainstorming and Mind Maps
- Identify Keywords
- Do Background Reading
- Define Your Topic
- Conduct Research in a Specific Discipline
- Step 5. Draft a Research Question
- Step 6. Create a Timeline
- Find Articles
- Find Primary Sources
- Get Help from Experts
- Search Engines, Repositories, & Directories
- Databases and Websites by Subject Area
- Create an Annotated Bibliography
- Advice (and Warnings) from the IB
- Chicago Citation Syle
- MLA Works Cited & In-Text Citations
- Step 9. Set Deadlines for Yourself
- Step 10. Plan a structure for your essay
- Evaluate & Select: the CRAAP Test
- Conducting Secondary Research
- Conducting Primary Research
- Formal vs. Informal Writing
- Presentation Requirements
- Evaluating Your Work
Differences Between Informal and Formal Essays
When writing your extended essay you should use language that is formal and academic in tone. The chart below gives you some idea of the differences between informal and formal essays. See the box below for examples of the differences in tone in informal and formal essays written on identical topics. A PDF of this chart, and the examples below, is in the box to the right , along with a list of tips for avoiding colloquial writing.
Examples of Informal and Formal Tone in Essay Writing
The following examples highlight the differences between formal and informal tone.
Language B - English
- Formal vs. Informal Writing A chart giving the differences between informal and formal essays in seven areas (author's viewpoint; subject/content (sources of evidence); tone; structure; location of the research question; vocabulary; and purpose. Also included are examples comparing informal and formal writing for essays in English, biology, and psychology.
- How to Avoid Colloquial (Informal) Writing While it may be acceptable in friendly e-mails and chat rooms, excessive colloquialism is a major pitfall that lowers the quality of formal written text. Here are some steps/tips that you can follow to help improve your overall writing.
- << Previous: Plagiarism
- Next: Presentation Requirements >>
- Last Updated: May 8, 2024 3:48 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westsoundacademy.org/ee
Extended Essay
Extended Essay Examples

26 Best Extended Essay Examples for Inspiration
Published on: May 3, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 30, 2024

People also read
A Step-by-Step Guide For Writing an Extended Essay
Extended Essay Outline Made Easy: Components, Writing Steps, & Tips
Get Inspired: 110 Unique Extended Essay Topics and Ideas
Share this article
Are you struggling to choose a topic or develop a research question for your Extended Essay? Or are you looking for examples to help guide your writing process?
Look no further!
In this blog, we will provide you with a variety of extended essay examples across different subject areas. By examining these examples, you can gain a better understanding of what a well-written extended essay looks like.
So, without further ado, let's start the blog!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is an Extended Essay?
An extended essay is a research paper that students write as part of the International Baccalaureate (IB) program . This type of essay aims to allow students to dig deeply into a topic, and develop their writing skills.
The Extended Essay must be between 3,500 and 4,000 words. It is typically written in one of the six subject areas:
- Language and Literature
- Language Acquisition
- Individuals and Societies
- Mathematics
Want to learn more about Extended essay writing? Check out his video!
Let's explore extended essay examples categorized by subject to better understand various topics and research questions within each discipline.
IB Extended Essay Examples
Here are some IB Extended Essay Examples:
IB Extended Essay Example Biology
IB Extended Essay Example World Religions
English Extended Essay Examples
English Extended Essay Example 1
English Extended Essay Example 2
History Extended Essay Examples
History Extended Essay Example 1
History Extended Essay Example 2
Psychology Extended Essay Examples
Psychology Extended Essay Example 1
Psychology Extended Essay Example 2
Economics Extended Essay Examples
Economics Extended Essay Example 1
Economics Extended Essay Example 2
Physics Extended Essay Examples -H3
Physics Extended Essay Example 1
Physics Extended Essay Example 2
Math Extended Essay Examples -H3
Math Extended Essay Example 1
Math Extended Essay Example 2
Business Extended Essay Examples -H3
Business Extended Essay Example 1
Business Extended Essay Example 2
Chemistry Extended Essay Examples
Chemistry Extended Essay Example 1
Chemistry Extended Essay Example 2
Global Politics Extended Essay Examples
Global Politics Extended Essay Example 1
Global Politics Extended Essay Example 2
Music Extended Essay Examples
Music Extended Essay Example 1
Music Extended Essay Example 2
Visual Arts Extended Essay Examples
Visual Arts Extended Essay Example 1
Visual Arts Extended Essay Example 2
World Studies Extended Essay Examples -H3
World Studies Extended Essay Example 1
World Studies Extended Essay Example 2

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Tips for Writing Extended Essays
Here are some tips for writing extended essays:
- Choose a topic that interests you and aligns with your strengths.
- Create a research question that is specific, manageable, and has enough depth to explore in detail.
- Develop a clear outline and structure for your essay, including an introduction, main body, and conclusion.
- Use a variety of sources, including academic journals, books, and primary sources, to support your arguments.
- Maintain a critical and analytical approach throughout your essay, examining various perspectives and evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of different arguments.
- Avoid plagiarism by citing your sources correctly and using your own words to explain your ideas.
- Revise and edit your essay thoroughly, ensuring that it is coherent, logical, and well-written.
- Seek feedback from your supervisor or teacher, as well as peers or family members, to improve your essay further.
In conclusion, extended essay writing is an essential part of academic life, and it requires a lot of dedication and practice. However, with the right guidance and inspiration, anyone can excel in writing a compelling extended essay.
The examples we have explored in this blog have provided valuable insights into the process. We hope they have inspired you to start your own journey toward excellence.
But if you need any additional assistance, don't hesitate to reach out to CollegeEssay.org. Our extended essay writing service consists of professional writers who are always ready to help you with your writing assignments.
We provide the best essay writing service to meet your specific needs and requirements.
So, get in touch with us today, and let our essay writer help you achieve your academic goals!
Cathy A. (Literature, Life Sciences)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
IB students around the globe fear writing the Extended Essay, but it doesn't have to be a source of stress! ... a body, and a conclusion (about one double-spaced page). An essay with unclear organization will be graded poorly. The body of your EE should make up the bulk of the essay. It should be about eight to 18 pages long (again, depending ...
Extended Essay Conclusion. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research question, but a synthesis of key points and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research. For most essays, one well-developed paragraph is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, a two ...
A Brief Guide to Writing an Effective EE Conclusion The conclusion of any research paper can be the most difficult section to write for a variety of reasons: ... evidence at the end of an otherwise-well-organized essay can just create confusion. Example: In addition to being an educational pioneer, Frederick Douglass provides an interesting ...
Student Guide to Writing the Extended Essay for details By April 30, 2020 Extended Essay First Draft Uploaded to ManageBac By June 2, 2020 Update with Supervisor; First Extended Essay Reflection due on ... conclusions might be not what you were expecting; it can be very hard to synthesize the information
The conclusion says what has been achieved, including notes of any limitations and any questions that have not been resolved. While students might draw conclusions throughout the essay based on their findings, it is important that there is a final, summative conclusion at the end. This conclusion (s) must relate to the research question posed.
To write an impressive extended essay, you should focus on appropriate information. You must create a separate page for bibliography with all sources you used. Tip from us: start writing this page with the first quote you use. Don't write this part last or postpone. In turn, appendices are not an essential section.
The extended essay is an independent, self-directed piece of research, finishing with a 4,000-word paper. One component of the International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) core, the extended essay is mandatory for all students. Read about the extended essay in greater detail. You can also read about how the IB sets deadlines for ...
The extended essay contributes to the overall diploma score through the award of points in conjunction with theory of knowledge. A maximum of three points are awarded according to a student's combined performance in both the extended essay and theory of knowledge. Both the extended essay and theory
Students writing their extended essay in Japanese or Chinese should use the following conversions. Japanese: 1 word = approximately 2 Japanese characters ... • the conclusion(s) of the extended essay. The abstract should be typed or word processed on one side of a sheet of paper, and placed immediately after the
These highlight the diverse range of topics covered by International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) students during their extended essays. Some examples are: "An analysis of costume as a source for understanding the inner life of the character". "A study of malnourished children in Indonesia and the extent of their recovery ...
10 Steps to Writing an IB Extended Essay. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write an extended essay, from research question to complete essay. 1. Define the Topic and Draft the Research Question. 2. Create a Timeline. 3. Research sources and expand knowledge about the topic. 4.
Outlining is best done as a middle stage in the writing process, not at the very beginning. Follow these steps in the order given before attempting an outline: 1. Read, gather information, and think about your essay topic. 2. Take notes, jot down ideas, use your Researcher's Reflection Space. 3.
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
When planning an extended essay, remember that you will need to choose a topic broad enough to allow your essay writing to continue to a greater length than usual. Essay writers are also usually expected to present deeper analysis and research in an extended essay, so choose a topic that allows in-depth exploration and related sub-topics.
Step 1: Always start with your extended essay requirements. It will help you to narrow things down and take notes to use further in your writing. Step 2: Define your subject and draft your research outline. Submit up to three ideas to determine the best one. Step 3: Create your writing timeline.
The Conclusion; Citations/Bibliography; ... The research question is the central question you are trying to answer through your research and writing of the extended essay. This question, if properly composed, will both enable you to maintain your focus on a topic of narrow and limited scope while also help you to maintain the purpose and ...
Harvard College Writing Center 5 Asking Analytical Questions When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay: Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas. Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up ...
Step 4: Writing the Introduction. Once you have completed the above steps and you have come up with an outline based on the extended essay's structure, the next step is to introduce your topic and elaborate it to your target readers. There are various things you should consider when coming up with an introduction.
Writing the Introduction. An introduction for an Extended Essay requires students to include the following aspects: Aside from giving the essay a structural outline that any reader can follow, these aspects also help ensure that expectations for Criterion A (Focus and Method) are met. Context: Explicitly stating your research question and ...
Differences Between Informal and Formal Essays. When writing your extended essay you should use language that is formal and academic in tone. The chart below gives you some idea of the differences between informal and formal essays. See the box below for examples of the differences in tone in informal and formal essays written on identical topics.
An extended essay is a research paper that students write as part of the International Baccalaureate (IB) program. This type of essay aims to allow students to dig deeply into a topic, and develop their writing skills. The Extended Essay must be between 3,500 and 4,000 words. It is typically written in one of the six subject areas:
Constructing an Extended Response Essay Tab # 1 ~ The Writing Process: Notes What is it? Measures ELA skills: reading, writing, & listening for information. To interpret, draw conclusions, make connections, and synthesize the text while thoughtfully responding to a task. To apply and explain specific text-based details to a task. Writing is ...