
Research Topics & Ideas: Environment
100+ Environmental Science Research Topics & Ideas

Finding and choosing a strong research topic is the critical first step when it comes to crafting a high-quality dissertation, thesis or research project. Here, we’ll explore a variety research ideas and topic thought-starters related to various environmental science disciplines, including ecology, oceanography, hydrology, geology, soil science, environmental chemistry, environmental economics, and environmental ethics.
NB – This is just the start…
The topic ideation and evaluation process has multiple steps . In this post, we’ll kickstart the process by sharing some research topic ideas within the environmental sciences. This is the starting point though. To develop a well-defined research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , along with a well-justified plan of action to fill that gap.
If you’re new to the oftentimes perplexing world of research, or if this is your first time undertaking a formal academic research project, be sure to check out our free dissertation mini-course. Also be sure to also sign up for our free webinar that explores how to develop a high-quality research topic from scratch.
Overview: Environmental Topics
- Ecology /ecological science
- Atmospheric science
- Oceanography
- Soil science
- Environmental chemistry
- Environmental economics
- Environmental ethics
- Examples of dissertations and theses
Topics & Ideas: Ecological Science
- The impact of land-use change on species diversity and ecosystem functioning in agricultural landscapes
- The role of disturbances such as fire and drought in shaping arid ecosystems
- The impact of climate change on the distribution of migratory marine species
- Investigating the role of mutualistic plant-insect relationships in maintaining ecosystem stability
- The effects of invasive plant species on ecosystem structure and function
- The impact of habitat fragmentation caused by road construction on species diversity and population dynamics in the tropics
- The role of ecosystem services in urban areas and their economic value to a developing nation
- The effectiveness of different grassland restoration techniques in degraded ecosystems
- The impact of land-use change through agriculture and urbanisation on soil microbial communities in a temperate environment
- The role of microbial diversity in ecosystem health and nutrient cycling in an African savannah
Topics & Ideas: Atmospheric Science
- The impact of climate change on atmospheric circulation patterns above tropical rainforests
- The role of atmospheric aerosols in cloud formation and precipitation above cities with high pollution levels
- The impact of agricultural land-use change on global atmospheric composition
- Investigating the role of atmospheric convection in severe weather events in the tropics
- The impact of urbanisation on regional and global atmospheric ozone levels
- The impact of sea surface temperature on atmospheric circulation and tropical cyclones
- The impact of solar flares on the Earth’s atmospheric composition
- The impact of climate change on atmospheric turbulence and air transportation safety
- The impact of stratospheric ozone depletion on atmospheric circulation and climate change
- The role of atmospheric rivers in global water supply and sea-ice formation

Topics & Ideas: Oceanography
- The impact of ocean acidification on kelp forests and biogeochemical cycles
- The role of ocean currents in distributing heat and regulating desert rain
- The impact of carbon monoxide pollution on ocean chemistry and biogeochemical cycles
- Investigating the role of ocean mixing in regulating coastal climates
- The impact of sea level rise on the resource availability of low-income coastal communities
- The impact of ocean warming on the distribution and migration patterns of marine mammals
- The impact of ocean deoxygenation on biogeochemical cycles in the arctic
- The role of ocean-atmosphere interactions in regulating rainfall in arid regions
- The impact of ocean eddies on global ocean circulation and plankton distribution
- The role of ocean-ice interactions in regulating the Earth’s climate and sea level

Tops & Ideas: Hydrology
- The impact of agricultural land-use change on water resources and hydrologic cycles in temperate regions
- The impact of agricultural groundwater availability on irrigation practices in the global south
- The impact of rising sea-surface temperatures on global precipitation patterns and water availability
- Investigating the role of wetlands in regulating water resources for riparian forests
- The impact of tropical ranches on river and stream ecosystems and water quality
- The impact of urbanisation on regional and local hydrologic cycles and water resources for agriculture
- The role of snow cover and mountain hydrology in regulating regional agricultural water resources
- The impact of drought on food security in arid and semi-arid regions
- The role of groundwater recharge in sustaining water resources in arid and semi-arid environments
- The impact of sea level rise on coastal hydrology and the quality of water resources

Topics & Ideas: Geology
- The impact of tectonic activity on the East African rift valley
- The role of mineral deposits in shaping ancient human societies
- The impact of sea-level rise on coastal geomorphology and shoreline evolution
- Investigating the role of erosion in shaping the landscape and impacting desertification
- The impact of mining on soil stability and landslide potential
- The impact of volcanic activity on incoming solar radiation and climate
- The role of geothermal energy in decarbonising the energy mix of megacities
- The impact of Earth’s magnetic field on geological processes and solar wind
- The impact of plate tectonics on the evolution of mammals
- The role of the distribution of mineral resources in shaping human societies and economies, with emphasis on sustainability
Topics & Ideas: Soil Science
- The impact of dam building on soil quality and fertility
- The role of soil organic matter in regulating nutrient cycles in agricultural land
- The impact of climate change on soil erosion and soil organic carbon storage in peatlands
- Investigating the role of above-below-ground interactions in nutrient cycling and soil health
- The impact of deforestation on soil degradation and soil fertility
- The role of soil texture and structure in regulating water and nutrient availability in boreal forests
- The impact of sustainable land management practices on soil health and soil organic matter
- The impact of wetland modification on soil structure and function
- The role of soil-atmosphere exchange and carbon sequestration in regulating regional and global climate
- The impact of salinization on soil health and crop productivity in coastal communities
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Chemistry
- The impact of cobalt mining on water quality and the fate of contaminants in the environment
- The role of atmospheric chemistry in shaping air quality and climate change
- The impact of soil chemistry on nutrient availability and plant growth in wheat monoculture
- Investigating the fate and transport of heavy metal contaminants in the environment
- The impact of climate change on biochemical cycling in tropical rainforests
- The impact of various types of land-use change on biochemical cycling
- The role of soil microbes in mediating contaminant degradation in the environment
- The impact of chemical and oil spills on freshwater and soil chemistry
- The role of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in shaping water and soil chemistry
- The impact of over-irrigation on the cycling and fate of persistent organic pollutants in the environment
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Economics
- The impact of climate change on the economies of developing nations
- The role of market-based mechanisms in promoting sustainable use of forest resources
- The impact of environmental regulations on economic growth and competitiveness
- Investigating the economic benefits and costs of ecosystem services for African countries
- The impact of renewable energy policies on regional and global energy markets
- The role of water markets in promoting sustainable water use in southern Africa
- The impact of land-use change in rural areas on regional and global economies
- The impact of environmental disasters on local and national economies
- The role of green technologies and innovation in shaping the zero-carbon transition and the knock-on effects for local economies
- The impact of environmental and natural resource policies on income distribution and poverty of rural communities
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Ethics
- The ethical foundations of environmentalism and the environmental movement regarding renewable energy
- The role of values and ethics in shaping environmental policy and decision-making in the mining industry
- The impact of cultural and religious beliefs on environmental attitudes and behaviours in first world countries
- Investigating the ethics of biodiversity conservation and the protection of endangered species in palm oil plantations
- The ethical implications of sea-level rise for future generations and vulnerable coastal populations
- The role of ethical considerations in shaping sustainable use of natural forest resources
- The impact of environmental justice on marginalized communities and environmental policies in Asia
- The ethical implications of environmental risks and decision-making under uncertainty
- The role of ethics in shaping the transition to a low-carbon, sustainable future for the construction industry
- The impact of environmental values on consumer behaviour and the marketplace: a case study of the ‘bring your own shopping bag’ policy
Examples: Real Dissertation & Thesis Topics
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses to see how this all comes together.
Below, we’ve included a selection of research projects from various environmental science-related degree programs to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- The physiology of microorganisms in enhanced biological phosphorous removal (Saunders, 2014)
- The influence of the coastal front on heavy rainfall events along the east coast (Henson, 2019)
- Forage production and diversification for climate-smart tropical and temperate silvopastures (Dibala, 2019)
- Advancing spectral induced polarization for near surface geophysical characterization (Wang, 2021)
- Assessment of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter and Thamnocephalus platyurus as Tools to Monitor Cyanobacterial Bloom Development and Toxicity (Hipsher, 2019)
- Evaluating the Removal of Microcystin Variants with Powdered Activated Carbon (Juang, 2020)
- The effect of hydrological restoration on nutrient concentrations, macroinvertebrate communities, and amphibian populations in Lake Erie coastal wetlands (Berg, 2019)
- Utilizing hydrologic soil grouping to estimate corn nitrogen rate recommendations (Bean, 2019)
- Fungal Function in House Dust and Dust from the International Space Station (Bope, 2021)
- Assessing Vulnerability and the Potential for Ecosystem-based Adaptation (EbA) in Sudan’s Blue Nile Basin (Mohamed, 2022)
- A Microbial Water Quality Analysis of the Recreational Zones in the Los Angeles River of Elysian Valley, CA (Nguyen, 2019)
- Dry Season Water Quality Study on Three Recreational Sites in the San Gabriel Mountains (Vallejo, 2019)
- Wastewater Treatment Plan for Unix Packaging Adjustment of the Potential Hydrogen (PH) Evaluation of Enzymatic Activity After the Addition of Cycle Disgestase Enzyme (Miessi, 2020)
- Laying the Genetic Foundation for the Conservation of Longhorn Fairy Shrimp (Kyle, 2021).
Looking at these titles, you can probably pick up that the research topics here are quite specific and narrowly-focused , compared to the generic ones presented earlier. To create a top-notch research topic, you will need to be precise and target a specific context with specific variables of interest . In other words, you’ll need to identify a clear, well-justified research gap.
Need more help?
If you’re still feeling a bit unsure about how to find a research topic for your environmental science dissertation or research project, be sure to check out our private coaching services below, as well as our Research Topic Kickstarter .
Need a helping hand?
You Might Also Like:

10 Comments
research topics on climate change and environment
I wish to learn things in a more advanced but simple way and with the hopes that I am in the right place.
Thank so much for the research topics. It really helped
the guides were really helpful
Research topics on environmental geology
Thanks for the research topics….I need a research topic on Geography
hi I need research questions ideas
I want the research on environmental planning and management
I want a topic on environmental sustainability
It good coaching
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy

Home » 500+ Environmental Research Topics
500+ Environmental Research Topics

Environmental research is a crucial area of study in today’s world, as we face an increasing number of complex and pressing environmental challenges. From climate change to pollution, biodiversity loss to natural resource depletion, there is an urgent need for scientific inquiry and investigation to inform policy, decision-making, and action. Environmental research encompasses a broad range of disciplines, including ecology, biology , geology, chemistry , and physics , among others, and explores a diverse array of topics , from ocean acidification to sustainable agriculture. Through rigorous scientific inquiry and a commitment to generating evidence-based solutions, environmental research plays a vital role in promoting the health and well-being of our planet and its inhabitants. In this article, we will cover some trending Environmental Research Topics.
Environmental Research Topics
Environmental Research Topics are as follows:
- Climate change and its impacts on ecosystems and society
- The effectiveness of carbon capture and storage technology
- The role of biodiversity in maintaining healthy ecosystems
- The impact of human activity on soil quality
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine life
- The effectiveness of renewable energy sources
- The impact of deforestation on local communities and wildlife
- The relationship between air pollution and human health
- The impact of agricultural practices on soil erosion
- The effectiveness of conservation measures for endangered species
- The impact of overfishing on marine ecosystems
- The role of wetlands in mitigating climate change
- The impact of oil spills on marine ecosystems
- The impact of urbanization on local ecosystems
- The impact of climate change on global food security
- The effectiveness of water conservation measures
- The impact of pesticide use on pollinators
- The impact of acid rain on aquatic ecosystems
- The impact of sea level rise on coastal communities
- The effectiveness of carbon taxes in reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of habitat destruction on migratory species
- The impact of invasive species on native ecosystems
- The role of national parks in biodiversity conservation
- The impact of climate change on coral reefs
- The effectiveness of green roofs in reducing urban heat island effect
- The impact of noise pollution on wildlife behavior
- The impact of air pollution on crop yields
- The effectiveness of composting in reducing organic waste
- The impact of climate change on the Arctic ecosystem
- The impact of land use change on soil carbon sequestration
- The role of mangroves in coastal protection and carbon sequestration
- The impact of microplastics on marine ecosystems
- The impact of ocean acidification on marine organisms
- The effectiveness of carbon offsets in reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of deforestation on climate regulation
- The impact of groundwater depletion on agriculture
- The impact of climate change on migratory bird populations
- The effectiveness of wind turbines in reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of urbanization on bird diversity
- The impact of climate change on ocean currents
- The impact of drought on plant and animal populations
- The effectiveness of agroforestry in improving soil quality
- The impact of climate change on water availability
- The impact of wildfires on carbon storage in forests
- The impact of climate change on freshwater ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green energy subsidies
- The impact of nitrogen pollution on aquatic ecosystems
- The impact of climate change on forest ecosystems
- The effectiveness of community-based conservation initiatives
- The impact of climate change on the water cycle
- The impact of mining activities on local ecosystems
- The impact of wind energy on bird and bat populations
- The effectiveness of bioremediation in cleaning up contaminated soil and water
- The impact of deforestation on local climate patterns
- The impact of climate change on insect populations
- The impact of agricultural runoff on freshwater ecosystems
- The effectiveness of smart irrigation systems in reducing water use
- The impact of ocean currents on marine biodiversity
- The impact of climate change on wetland ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green buildings in reducing energy use
- The impact of climate change on glacier retreat and sea level rise
- The impact of light pollution on nocturnal wildlife behavior
- The impact of climate change on desert ecosystems
- The effectiveness of electric vehicles in reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of ocean pollution on human health
- The impact of land use change on water quality
- The impact of urbanization on bird populations
- The impact of oil spills on marine ecosystems and wildlife
- The effectiveness of green energy storage technologies in promoting renewable energy use
- The impact of climate change on freshwater availability and water management
- The impact of industrial pollution on air quality and human health
- The effectiveness of urban green spaces in promoting human health and well-being
- The impact of climate change on snow cover and winter tourism
- The impact of agricultural land use on biodiversity and ecosystem services
- The effectiveness of green incentives in promoting sustainable consumer behavior
- The impact of ocean acidification on shellfish and mollusk populations
- The impact of climate change on river flow and flooding
- The effectiveness of green supply chain management in promoting sustainable production
- The impact of noise pollution on avian communication and behavior
- The impact of climate change on arctic ecosystems and wildlife
- The effectiveness of green marketing in promoting sustainable tourism
- The impact of microplastics on marine food webs and human health
- The impact of climate change on invasive species distributions
- The effectiveness of green infrastructure in promoting sustainable urban development
- The impact of plastic pollution on human health and food safety
- The impact of climate change on soil microbial communities and nutrient cycling
- The effectiveness of green technologies in promoting sustainable industrial production
- The impact of climate change on permafrost thaw and methane emissions
- The impact of deforestation on water quality and quantity
- The effectiveness of green certification schemes in promoting sustainable production and consumption
- The impact of noise pollution on terrestrial ecosystems and wildlife
- The impact of climate change on bird migration patterns
- The effectiveness of green waste management in promoting sustainable resource use
- The impact of climate change on insect populations and ecosystem services
- The impact of plastic pollution on human society and culture
- The effectiveness of green finance in promoting sustainable development goals
- The impact of climate change on marine biodiversity hotspots
- The impact of climate change on natural disasters and disaster risk reduction
- The effectiveness of green urban planning in promoting sustainable cities and communities
- The impact of deforestation on soil carbon storage and climate change
- The impact of noise pollution on human communication and behavior
- The effectiveness of green energy policy in promoting renewable energy use
- The impact of climate change on Arctic sea ice and wildlife
- The impact of agricultural practices on soil quality and ecosystem health
- The effectiveness of green taxation in promoting sustainable behavior
- The impact of plastic pollution on freshwater ecosystems and wildlife
- The impact of climate change on plant-pollinator interactions and crop production
- The effectiveness of green innovation in promoting sustainable technological advancements
- The impact of climate change on ocean currents and marine heatwaves
- The impact of deforestation on indigenous communities and cultural practices
- The effectiveness of green governance in promoting sustainable development and environmental justice
- The effectiveness of wetland restoration in reducing flood risk
- The impact of climate change on the spread of vector-borne diseases
- The effectiveness of green marketing in promoting sustainable consumption
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine ecosystems
- The impact of renewable energy development on wildlife habitats
- The effectiveness of environmental education programs in promoting pro-environmental behavior
- The impact of deforestation on global climate change
- The impact of microplastics on freshwater ecosystems
- The effectiveness of eco-labeling in promoting sustainable seafood consumption
- The impact of climate change on coral reef ecosystems
- The impact of air pollution on human health and mortality rates
- The effectiveness of eco-tourism in promoting conservation and community development
- The impact of climate change on agricultural production and food security
- The impact of wind turbine noise on wildlife behavior and populations
- The impact of light pollution on nocturnal ecosystems and species
- The effectiveness of green energy subsidies in promoting renewable energy use
- The impact of invasive species on native ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of climate change on ocean acidification and marine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green public procurement in promoting sustainable production
- The impact of deforestation on soil erosion and nutrient depletion
- The impact of noise pollution on human health and well-being
- The effectiveness of green building standards in promoting sustainable construction
- The impact of climate change on forest fires and wildfire risk
- The impact of e-waste on human health and environmental pollution
- The impact of climate change on polar ice caps and sea levels
- The impact of pharmaceutical pollution on freshwater ecosystems and wildlife
- The effectiveness of green transportation policies in reducing carbon emissions
- The impact of climate change on glacier retreat and water availability
- The impact of pesticide use on pollinator populations and ecosystems
- The effectiveness of circular economy models in reducing waste and promoting sustainability
- The impact of climate change on coastal ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of plastic waste on terrestrial ecosystems and wildlife
- The effectiveness of green chemistry in promoting sustainable manufacturing
- The impact of climate change on ocean currents and weather patterns
- The impact of agricultural runoff on freshwater ecosystems and water quality
- The effectiveness of green bonds in financing sustainable infrastructure projects
- The impact of climate change on soil moisture and desertification
- The impact of noise pollution on marine ecosystems and species
- The effectiveness of community-based conservation in promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health
- The impact of climate change on permafrost ecosystems and carbon storage
- The impact of urbanization on water pollution and quality
- The effectiveness of green jobs in promoting sustainable employment
- The impact of climate change on wetland ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of plastic pollution on terrestrial ecosystems and wildlife
- The effectiveness of sustainable fashion in promoting sustainable consumption
- The impact of climate change on phenology and seasonal cycles of plants and animals
- The impact of ocean pollution on human health and seafood safety
- The effectiveness of green procurement policies in promoting sustainable supply chains
- The impact of climate change on marine food webs and ecosystems
- The impact of agricultural practices on greenhouse gas emissions and climate change
- The effectiveness of green financing in promoting sustainable investment
- The effectiveness of rainwater harvesting systems in reducing water use
- The impact of climate change on permafrost ecosystems
- The impact of coastal erosion on shoreline ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green infrastructure in reducing urban heat island effect
- The impact of microorganisms on soil fertility and carbon sequestration
- The impact of climate change on snowpack and water availability
- The impact of oil and gas drilling on local ecosystems
- The effectiveness of carbon labeling in promoting sustainable consumer choices
- The impact of marine noise pollution on marine mammals
- The impact of climate change on alpine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green supply chain management in reducing environmental impact
- The impact of climate change on river ecosystems
- The impact of urban sprawl on wildlife habitat fragmentation
- The effectiveness of carbon trading in reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of ocean warming on marine ecosystems
- The impact of agricultural practices on water quality and quantity
- The effectiveness of green roofs in improving urban air quality
- The impact of climate change on tropical rainforests
- The impact of water pollution on human health and livelihoods
- The effectiveness of green bonds in financing sustainable projects
- The impact of climate change on polar bear populations
- The impact of human activity on soil biodiversity
- The effectiveness of waste-to-energy systems in reducing waste and emissions
- The impact of climate change on Arctic sea ice and marine ecosystems
- The impact of sea level rise on low-lying coastal cities and communities
- The effectiveness of sustainable tourism in promoting conservation and community development
- The impact of deforestation on indigenous peoples and their livelihoods
- The impact of climate change on sea turtle populations
- The effectiveness of carbon-neutral and carbon-negative technologies
- The impact of urbanization on water resources and quality
- The impact of climate change on cold-water fish populations
- The effectiveness of green entrepreneurship in promoting sustainable innovation
- The impact of wildfires on air quality and public health
- The impact of climate change on human migration patterns and social systems
- The impact of noise pollution on bird communication and behavior in urban environments
- The impact of climate change on estuarine ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of deforestation on water availability and river basin management
- The impact of climate change on plant phenology and distribution
- The effectiveness of green marketing in promoting sustainable consumer behavior
- The impact of plastic pollution on freshwater ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of climate change on marine plastic debris accumulation and distribution
- The effectiveness of green innovation in promoting sustainable technology development
- The impact of climate change on crop yields and food security
- The impact of noise pollution on human health and well-being in urban environments
- The impact of climate change on Arctic marine ecosystems and biodiversity
- The effectiveness of green transportation infrastructure in promoting sustainable mobility
- The impact of deforestation on non-timber forest products and forest-dependent livelihoods
- The impact of climate change on wetland carbon sequestration and storage
- The impact of plastic pollution on sea turtle populations and nesting behavior
- The impact of climate change on marine biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in the Southern Ocean
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable agriculture
- The impact of climate change on oceanographic processes and upwelling systems
- The impact of noise pollution on terrestrial wildlife communication and behavior
- The impact of climate change on coastal erosion and shoreline management
- The effectiveness of green finance in promoting sustainable investment
- The impact of deforestation on indigenous communities and traditional knowledge systems
- The impact of climate change on tropical cyclones and extreme weather events
- The effectiveness of green buildings in promoting energy efficiency and carbon reduction
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine food webs and trophic interactions
- The impact of climate change on algal blooms and harmful algal blooms in marine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green business partnerships in promoting sustainable development goals
- The impact of climate change on ocean deoxygenation and its effects on marine life
- The impact of noise pollution on human sleep and rest patterns in urban environments
- The impact of climate change on freshwater availability and management
- The effectiveness of green entrepreneurship in promoting social and environmental justice
- The impact of deforestation on wildlife habitat and biodiversity conservation
- The impact of climate change on the migration patterns and behaviors of birds and mammals
- The effectiveness of green urban planning in promoting sustainable and livable cities
- The impact of plastic pollution on microplastics and nanoplastics in marine ecosystems
- The impact of climate change on marine ecosystem services and their value to society
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable forestry
- The impact of climate change on ocean currents and their effects on marine biodiversity
- The impact of noise pollution on urban ecosystems and their ecological functions
- The impact of climate change on freshwater biodiversity and ecosystem functioning
- The effectiveness of green policy implementation in promoting sustainable development
- The impact of deforestation on soil carbon storage and greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of climate change on marine mammals and their ecosystem roles
- The effectiveness of green product labeling in promoting sustainable consumer behavior
- The impact of plastic pollution on coral reefs and their resilience to climate change
- The impact of climate change on waterborne diseases and public health
- The effectiveness of green energy policies in promoting renewable energy adoption
- The impact of deforestation on carbon storage and sequestration in peatlands
- The impact of climate change on ocean acidification and its effects on marine life
- The effectiveness of green supply chain management in promoting circular economy principles
- The impact of noise pollution on urban birds and their vocal communication
- The impact of climate change on ecosystem services provided by mangrove forests
- The effectiveness of green marketing in promoting sustainable fashion and textiles
- The impact of plastic pollution on deep-sea ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of climate change on marine biodiversity hotspots and conservation priorities
- The effectiveness of green investment in promoting sustainable infrastructure development
- The impact of deforestation on ecosystem services provided by agroforestry systems
- The impact of climate change on snow and ice cover and their effects on freshwater ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green tourism in promoting sustainable tourism practices
- The impact of noise pollution on human cognitive performance and productivity
- The impact of climate change on forest fires and their effects on ecosystem services
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable seafood consumption
- The impact of climate change on insect populations and their ecosystem roles
- The impact of plastic pollution on seabird populations and their reproductive success
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable public sector spending
- The impact of deforestation on soil erosion and land degradation
- The impact of climate change on riverine ecosystems and their ecosystem services
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable fisheries
- The impact of noise pollution on marine mammals and their acoustic communication
- The impact of climate change on terrestrial carbon sinks and sources
- The effectiveness of green technology transfer in promoting sustainable development
- The impact of deforestation on non-timber forest products and their sustainable use
- The impact of climate change on marine invasive species and their ecological impacts
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable private sector spending
- The impact of plastic pollution on zooplankton populations and their ecosystem roles
- The impact of climate change on wetland ecosystems and their services
- The effectiveness of green education in promoting sustainable behavior change
- The impact of deforestation on watershed management and water quality
- The impact of climate change on soil nutrient cycling and ecosystem functioning
- The effectiveness of green technology innovation in promoting sustainable development
- The impact of noise pollution on human health in outdoor recreational settings
- The impact of climate change on oceanic nutrient cycling and primary productivity
- The effectiveness of green urban design in promoting sustainable and resilient cities
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine microbial communities and their functions
- The impact of climate change on coral reef bleaching and recovery
- The impact of deforestation on ecosystem services provided by community-managed forests
- The impact of climate change on freshwater fish populations and their ecosystem roles
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable tourism
- The impact of noise pollution on human stress and cardiovascular health
- The impact of climate change on glacier retreat and their effects on freshwater ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green technology diffusion in promoting sustainable development
- The impact of plastic pollution on sea grass beds and their ecosystem services
- The impact of climate change on forest phenology and productivity.
- The effectiveness of green transportation policies in promoting sustainable mobility
- The impact of deforestation on indigenous peoples’ livelihoods and traditional knowledge
- The impact of climate change on Arctic ecosystems and their biodiversity
- The effectiveness of green building standards in promoting sustainable architecture
- The impact of noise pollution on nocturnal animals and their behavior
- The impact of climate change on migratory bird populations and their breeding success
- The effectiveness of green taxation in promoting sustainable consumption and production
- The impact of deforestation on wildlife corridors and ecosystem connectivity
- The impact of climate change on urban heat islands and their effects on public health
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable forestry practices
- The impact of plastic pollution on sea turtle populations and their nesting success
- The impact of climate change on invasive plant species and their ecological impacts
- The effectiveness of green business practices in promoting sustainable entrepreneurship
- The impact of noise pollution on urban wildlife and their acoustic communication
- The impact of climate change on alpine ecosystems and their services
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable agriculture and food systems
- The impact of deforestation on soil carbon stocks and their effects on climate change
- The impact of climate change on wetland methane emissions and their contribution to greenhouse gas concentrations
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable forestry and timber production
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine mammal populations and their health
- The impact of climate change on marine fisheries and their sustainable management
- The effectiveness of green investment in promoting sustainable entrepreneurship and innovation
- The impact of noise pollution on bat populations and their behavior
- The impact of climate change on permafrost thaw and its effects on Arctic ecosystems
- The impact of deforestation on ecosystem services provided by sacred groves
- The impact of climate change on tropical cyclones and their impacts on coastal ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green technology transfer in promoting sustainable agriculture and food systems
- The impact of plastic pollution on benthic macroinvertebrate populations and their ecosystem roles
- The impact of climate change on freshwater invertebrate populations and their ecosystem roles
- The effectiveness of green tourism in promoting sustainable wildlife tourism practices
- The impact of noise pollution on amphibian populations and their communication
- The impact of climate change on mountain ecosystems and their biodiversity
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable agriculture and food systems
- The impact of deforestation on indigenous peoples’ food security and nutrition
- The impact of climate change on plant-pollinator interactions and their ecosystem roles
- The impact of plastic pollution on freshwater ecosystems and their services
- The impact of climate change on oceanic currents and their effects on marine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green investment in promoting sustainable transportation infrastructure
- The impact of noise pollution on human sleep quality and mental health
- The impact of climate change on marine viruses and their effects on marine life
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable packaging and waste reduction
- The impact of deforestation on ecosystem services provided by riparian forests
- The impact of climate change on insect-pollinated crops and their yields
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable waste management
- The impact of plastic pollution on estuarine ecosystems and their services
- The impact of climate change on groundwater recharge and aquifer depletion
- The effectiveness of green education in promoting sustainable tourism practices
- The impact of climate change on coral reefs and their biodiversity
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable clothing and textile production
- The impact of deforestation on riverine fish populations and their fishery-dependent communities
- The impact of climate change on mountain water resources and their availability
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable tourism accommodations
- The impact of plastic pollution on deep-sea ecosystems and their biodiversity
- The impact of climate change on sea-level rise and its effects on coastal ecosystems and communities
- The effectiveness of green energy policies in promoting renewable energy production
- The impact of noise pollution on human cardiovascular health
- The impact of climate change on biogeochemical cycles in marine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable personal care and cosmetic products
- The impact of deforestation on carbon sequestration and its effects on climate change
- The impact of climate change on wildfire frequency and severity
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable energy-efficient technologies
- The impact of plastic pollution on beach ecosystems and their tourism potential
- The impact of climate change on marine mammals and their habitat range shifts
- The effectiveness of green urban design in promoting sustainable and livable neighborhoods
- The impact of noise pollution on urban human and wildlife communities
- The impact of climate change on soil microorganisms and their roles in nutrient cycling
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable electronics and e-waste management
- The impact of deforestation on watershed services and their effects on downstream ecosystems and communities
- The impact of climate change on human migration patterns and their impacts on urbanization
- The effectiveness of green investment in promoting sustainable water management and infrastructure
- The impact of plastic pollution on seabird populations and their nesting success
- The impact of climate change on ocean acidification and its effects on marine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable fisheries and aquaculture
- The impact of noise pollution on terrestrial carnivore populations and their communication
- The impact of climate change on snow and ice dynamics in polar regions
- The effectiveness of green tourism in promoting sustainable cultural heritage preservation
- The impact of deforestation on riverine water quality and their effects on aquatic life
- The impact of climate change on forest fires and their ecological effects
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable home appliances and energy use
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine invertebrate populations and their ecosystem roles
- The impact of climate change on soil erosion and its effects on agricultural productivity
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable construction materials and waste reduction
- The impact of noise pollution on marine mammal populations and their behavior
- The impact of climate change on ocean circulation and its effects on marine life
- The effectiveness of green investment in promoting sustainable forest management
- The impact of deforestation on medicinal plant populations and their traditional uses
- The impact of climate change on wetland ecosystems and their carbon storage capacity
- The effectiveness of green urban planning in promoting sustainable and resilient cities
- The impact of plastic pollution on seabed ecosystems and their biodiversity
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable palm oil production
- The impact of noise pollution on bird populations and their communication
- The impact of climate change on freshwater quality and its effects on aquatic life
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable food packaging and waste reduction
- The impact of deforestation on streamflow and its effects on downstream
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

200+ Funny Research Topics

500+ Sports Research Topics

300+ American History Research Paper Topics

500+ Cyber Security Research Topics

500+ Economics Research Topics

500+ Physics Research Topics
233 Pollution Essay Topics + Examples
Environmental pollution comes in many forms: noise, light, plastic, greenhouse gas emissions, etc. If you’re looking for interesting topics about pollution for essay or research paper, you’re at the right place! StudyCorgi has prepared a list of catchy pollution titles for your writing assignments. On this page, you’ll find research questions about pollution of different types. Read on to find a good research title about pollution for your paper!
🏆 Best Essay Topics on Pollution
✍️ pollution essay topics for college, 👍 good pollution research topics & essay examples, 🌶️ hot pollution essay examples, 🎓 most interesting pollution research titles, 💡 simple pollution topics for research paper, 📌 easy pollution essay topics, ❓ pollution research questions.
- Causes and Effects of Pollution
- Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health
- Effects of Air Pollution on Health
- Air Pollution Solutions: How to Improve Air Quality
- Water Pollution Causes, Effects and Solutions
- Reduce Plastic Pollution: What Can We Do Today?
- Air Pollution: Effects
- The Acid Rain Pollution: Causes and Solutions Acid rain is an environmental problem induced by accumulating acidic compounds in the atmosphere. Acid rain is harmful to the environment in both positive and negative ways.
- Environmental Pollution: Causes and Consequences Environmental pollution is currently one of the most important and prevalent issues in modern life. Every day, a human appears to contribute to the pollution of our green world.
- Pollution as a Global Challenge Pollution is a global environmental problem that diminishes the quality of life of communities across the world.
- Noise Pollution and Its Effect on Health This type of pollution is typical for industrial and modern post-industrial society and is most often associated with life in a large city with an active infrastructure.
- Plastic Pollution – Problem of Modern World Today, almost every person knows that plastic kills millions of animals every year by entanglement or starvation.
- Marine Pollution: Causes and Consequences Changes in marine and ocean conditions can directly affect the global climate because of their close connection to the planet’s energy fluxes and biogeochemical cycles.
- Marine Pollution in Australia This paper will set out to engage in a detailed discussion about marine pollution in Australia. It will begin by highlighting the major sources of marine pollution.
- Garbage Pollution’s Impact on Air, Water and Land Garbage pollutes the planet, and to stop this adverse effect, the authorities’ involvement is needed. One solution lies in the plane of economics and politics.
- Air Pollution in New York City The emissions from cars, buses, trucks and burning of fuels play a significant role in polluting the air in New York City, which becomes harmful to people.
- Community’s Role in Fighting Air Pollution People living in industrial areas form communities and do their best to close industrial plants or force them to reduce the emission of harmful substances.
- Preventing Land Pollution With Effective Measures This paper explores the issue of land pollution, its causes, and the importance of preventative measures and discusses the role of activities aimed at extracting economic benefits.
- The Problem of Ocean Pollution Today One of the main causes of the oceans being polluted is trash that includes various manufactured products like plastic bottles, shopping bags, food wrappers, and cigarettes.
- Noise Pollution: Potential Solutions Citizens may apply multiple useful cost-effective techniques to reduce noise pollution in their apartments by themselves.
- Soil Pollution: Causes and Effects There are two types of soil contamination: specific (occurring in small areas) and widespread (affecting large regions).
- Pollution Forms, Effects and Mitigation This article discusses the major forms of pollution, including air, water, noise, and soil pollution. It puts on sources of pollutants, effects of pollution, and methods of mitigating pollution.
- Plastic Pollution: Study the Problem The problem of plastic pollution has damaged physical health of people around the globe. Social practices can address the problem in a variety of ways.
- Environmental Pollution: Causes and Solutions Pollution of the oceans, depletion of the ozone layer, and air quality in large cities adversely affect the health of people and animals.
- Air Pollution: Conducting a Quantitative Study In conducting a quantitative study, the major research question would be: “what are the potential contributors to air pollution and how can they be prevented?”
- Air Pollution Threats: Parent Education The purpose of this pamphlet is to educate parents on the dangers of air pollution and suggest preventive strategies to keep their children safe.
- Noise Pollution Issue Investigation The essay defines the problem of noise pollution as quite serious, as harmful sounds can have a negative impact on human health.
- The Issue of Environment Pollution in Peru For their scavenger habits, the Peruvians use black vultures, or coragyps atrarus. This species is extensive in population and does not fall under special protection.
- Electric Vehicles: Addressing Air Pollution The environmental damages and air pollution levels are partially the result of the extensive use of vehicles that run on gas. However, electric vehicles can solve this problem.
- Environmental Pollution in China During the last years, environmental degradation in China has been becoming severe, but if people and government are aware and involved, it will be possible to improve the situation.
- Pollution and Children’s Health Environmental pollution poses a significant threat to children’s health worldwide, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
- Environmental Wellness and Problem of Air Pollution Air pollution is one of the main factors affecting the environment. It can be considered as any change in its properties that has a deleterious effect.
- The Problem of Environmental Pollution: Fresh Water One of the more important concerns that are fast becoming a major threat is pollution and no form of pollution seemed to be bigger than that of freshwater pollution.
- Will Banning Plastic Bags Not Solve Pollution Problem? While banning plastic bags is necessary, it remains a controversial issue. This essay aims to prove that this measure is not sufficient.
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Air Pollution Mobility changes in all types of indoor and outdoor settings have a substantial long-term influence on CO emissions at the national and regional levels.
- Environmental and Public Health Risks Caused by Plastic Pollution Plastic toxicity is an issue globally. Vulnerability to harmful chemicals used in the manufacture of plastics has detrimental repercussions for human health.
- Impact of Water Pollution: Water Challenges of an Urbanizing World Water is a source of life on Earth, and it is one of the very first needs of living beings. It is a vital resource for the development of the economic and social sectors.
- Land Pollution and Ways to Minimize Pollution in the US The biggest environmental challenge that has been witnessed in the US is land pollution – the disposal of material wastes into the soil or substances that can contaminate it.
- Multidisciplinary Approach to Water Pollution This paper shows how the multidisciplinary approach addresses water pollution as a public health issue. It is important to understand what the model entails.
- The Problem of Environmental Water Pollution This paper discusses a public health concern by explaining the causes of water pollution, how it affects human communities, and the possible strategies.
- Air Pollution Resulting From Small Gas Powered Engines The paper seeks to discuss the effects of small gas-powered engines on air pollution and suggest possible solutions to reduce the levels of air pollution.
- Clean Air Act: Overall Air Pollution Reducing The problem of environmental pollution and, in particular, the air became especially urgent after the emergence of large industrial enterprises operating on harmful fuel.
- Iron Ore Industry and Environmental Pollution This paper is an economic analysis of environmental pollution as a current issue or problem facing the iron ore industry.
- Noise Pollution as a Problem in Los Angeles Los Angeles is a bustling city: cars are humming, construction works are underway, dogs are barking, and music concerts are held outdoors; it does not fall silent at night.
- Beijing Looks for Answers to Air Pollution Beijing has undertaken various projects aimed at improving the city’s infrastructure, reducing pollution from coal-fired power plants, and reducing vehicle emissions.
- Air Pollution in the UAE and Its Management The following project focuses on investigating the problem of air pollution in the UAE and how it can be managed.
- Plastic Pollution in Arizona and Recycling Measures It is advisable to use existing approaches in combination and stay informed of the latest advances in technology to achieve the best effects and prevent the issue from compounding.
- How Pollution Is Poisoning the Leisure and Recreation Industry This paper will critically examine the sources of pollution and how pollution impacts the leisure and recreation industry.
- How Air Pollution Impacts Health Air pollution causes a wide range of serious health abnormalities in one’s body. It severely affects the respiratory system, leading to a number of complications.
- The Amazon Pollution and Its Effect on Birds The impact of the pollution of the Amazon on birds, their populations, and habits is significant and is the object of concern to many stakeholders.
- Global Food Supplies, Overpopulation and Pollution The essay explores the problem of the threats to global food supplies and presents solutions and a critique of their effectiveness in alleviating this challenge.
- Air Pollution and Exposure Reduction in India This paper explains what I would teach Indian citizens regarding the delicate particulate matter (PM2.5) effects and the strategies to implement to reduce PM2.5 exposures.
- Aspects of Global Pollution of Water Global pollution of water resources has devasting effects on the environment that include the destruction of the ocean ecosystem and biodiversity.
- Water Pollution in the Florida State The researchers claimed that plastic pollution was caused by the tourists and citizens who live along the coastline and dumping from the industries.
- A Threat to the Natural Habitat of Opossums Due to Pollution Because the natural habitat of opossums is gradually decreased due to the human actions, these animals can become a major problem in the cities, where trash is poorly managed.
- The Importance of Solving a Social Issue of Environmental Plastic Pollution Plastic single-use cheap objects constitute a large volume of all waste globally, forming big plastic patches in the oceans, seas, and land, thus harming the marine and land wildlife.
- Recent News About Plastic Pollution For discussion of plastic pollution and associated health problem, was presented an article written by Laura Parker (2020) in National Geographic.
- Plastic Pollution Through the Lens of Social Sciences When analyzing the problem through the lens of social sciences, it becomes clear that the problem of plastic pollution is complicated.
- Marina Barrage: Land Contamination and Noise Pollution Assessment Methods and techniques of noise pollution control involve measuring the noise level several times during the non-rainy season.
- Industrial Pollution in China and the USA Industries in China and the USA produce sulfur dioxide gas into the atmosphere, when it rains the gas reacts with water to produce sulphuric acid.
- Pollution And Health: An Analysis Global warming is a real threat to the global community, and we can save the future generations by employing simple solutions to considerably minimize pollution and the global warming.
- Traffic and Pollution in Los Angeles In Los Angeles, high car fuel consumption causes both environmental and health issues. The most cost-effective solution is to replace all cars in the city with donkeys.
- International Marine Pollution Law International Marine law is essential in governing the natural resources from illegal acts of pollution that poses dangers to marine life and the life depending on the waters of oceans or seas.
- Air Pollution and Coping Strategies Many human activities cause air pollution, including emissions from vehicles and power plants, negatively impacting human health and economic efficiency.
- Environmental Issues: Air Pollution One of the central environmental problems in today’s world is air pollution. With the development of cities, people expand the reach of their technology.
- Air Pollution in South Carolina In South Carolina, one of the most urgent environmental problems is air pollution with ozone and particles, which is hazardous to human health due to deadly diseases likelihood.
- Plastic Pollution: Recycle More or Produce Less? It is essential to resist the capitalistic urge to consume and produce more and, among other innovative solutions, scale down the volume of the virgin plastic generated.
- The Aerodyne Research Firm: Air Pollution Studies Aerodyne Research is a limited liability company that researches air and air pollution levels, one of the world’s most pressing environmental issues today.
- Water Pollution and How to Address It A person must protect nature – in particular water resources. After all, the possibilities of water resources are not unlimited and sooner or later, they may end.
- Electric Vehicles: The Roles in Air Pollution The main purpose of electric vehicles is to eliminate the direct contribution to air pollution through emissions.
- Water Pollution: Effects and Treatment Pollution of water bodies is a serious hazard to humans and the aquatic ecology, and population growth is hastening climate change.
- Research Project on Environmental Pollution in Brooklyn The issue of environmental pollution is widespread around the world. People attempt to change the situation with their forces.
- Air Pollution Crisis and Climate Change in China Air pollution is a serious problem in many countries, including China. The main source of air pollutants is fumes from burning fuels in industries or vehicles.
- Methodological Flaws in Studies of Air Pollution and COVID-19 Death Rates The research reviews the considerations related to studying the correlation between ambient air pollution and its effects on the symptoms of COVID-19.
- Waste Pollution as a Global Environmental Problem Waste pollution is a global environmental problem that threatens life on Earth, as it is associated with the devastation of ecological resources and economic issues.
- Advocacy Regarding Environmental Pollution in Brooklyn This letter is intended to address several points to seek a contribution to the severe problem of environmental pollution because of multiplying businesses in Brooklyn.
- Air Pollution in the United States Environmental problems affect climatic conditions negatively. In this case, we will discuss air pollution. Air pollution introduces harmful substances into the air.
- Air Quality and Pollution: Solution Measures This essay will discuss various policies and measures that can be implemented to facilitate a better quality of air for generations to come.
- Air Pollution Crisis in China and Its Impact on Economy In large industrialized countries such as China, the emission of carbon dioxide has a negative impact on climate conditions, which is hitting the national economy.
- The Effects of Air Pollution The paper addresses air pollution, its causes, significant pollutants, adverse effects of indoor pollutants and air pollution, and air pollution control.
- Papahanaumokuakea Plastic Sea Pollution This paper discusses the article devoted to the plastic sea pollution affecting Papahanaumokuakea Marine National Monuments.
- Pollution Rights Trading Will Effectively Control Environmental Problems The further use of the cap-and-trade system and its constant perfection can contribute to controlling the environmental issues related to harmful emissions.
- Von Wong on Environmental Pollution Awareness The subject of the study discussed in the following review considers the works of Mr. Wong and their significance in raising environmental awareness.
- Causes and Risks of Water Pollution The paper describes the effects of water pollution on human health from the perspective of existing findings on this topic and the assessment of information.
- Outdoor Air Pollution and Uncontrolled Asthma in the San Joaquin Valley, California The study’s purpose was to examine the relationship between air pollution and cases of uncontrolled asthma in the San Joaquin Valley.
- The Drastic Effects of Human Pollution on the Environment To deal with pollution, an individual can help a fair share by cleaning up trash after themselves and taking note of the issue around them.
- Air Pollution and Its Consequences The paper states that air pollution has been an increasingly major problem affecting the economy, people’s health, and the environment.
- Water Pollution of New York City Rivers The aim of the analysis was to assess the effects of CSOs on water quality and the environment at different sites along the Harlem River.
- Hydraulic Fracking and Methane Pollution in the US Hydraulic fracking and methane emissions in the US is a highly contentious matter, and various groups have different positions on the issue.
- Ozone Pollution Policy in Seoul by Yoo & Chae According to Yoo and Chae, ozone pollution is a serious issue in Seoul, Korea: “The number of ozone warnings has increased from 2 in 1995 to 10 in 1996, to 19 in 1997”.
- Corporations and Environment: Pollution Management in the European Union In this essay, the research is about the pollution management regulations in the European Union with comparison to the other countries in the world.
- Fish Consumption Limits Due to Mercury Pollution Fish is vital in any healthy diet. They are a lean, low-calorie source of protein and are normally recommended by health experts around the world.
- Role of Small Gas-Powered Engines in Air Pollution The purpose of this paper is to discuss the role of small gas-powered engines in air pollution and the associated controversy.
- The Correlation Between Air Pollution and Health The sampled study analyzes and explains how air pollution affect life expectancy and other measures of health.
- The Causes of Water Pollution Water pollution is a significant decrease in water resources’ quality due to the ingress of various chemicals and solid waste. The causes of pollution are related to human activities.
- The Impact of Air Pollution on Human Health and Well-Being Air pollution causes a wide range of health abnormalities in one’s body. A number of pollutants can cause lung cancer and even some non-lung cancer forms.
- The World’s Focus On Plastic Pollution People should not pick battles in the global war on ecology. There are numerous issues to tackle, and, according to researchers, humanity does not have a lot of time.
⭐ Catchy Pollution Essay Topics
- Milestone 3: Plastic Pollution Plastic pollution is a global issue that affects every person on our planet directly or indirectly. The problem of plastic pollution became evident in the late 1960s.
- How Pollution Affects Humans and Environment The purpose of this research paper is to establish the outcome pollution of ways pollution affects humans and the environment as well as ponder upon the ways to combat the issue.
- Marine Pollution and Its Anthropogenic Factors This paper examines the causes of the environmental problem of marine pollution, primarily related to anthropogenic factors, and considers its consequences.
- The Problem of Plastic Pollution: Negative Impacts The problem of plastic pollution affects biodiversity and human wellness. In particular, birds, animals, and fish die from entanglement and starvation.
- Air Pollution as a Health Risk Factor: Policy Proposal Air pollution is one of the most critical health risk factors. Prolonged exposure to polluted air can result in cancer and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Providing Solutions for Air Pollution The reasons for air pollution regulations, explaining the concept of averaging time in the U.S. National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS), explaining emission offsets.
- Noise Pollution: A Closer Look at the Problem Environmental noises are widespread all over the world and are particularly typical for densely populated cities.
- Burning Issue of Water Pollution in Washington The problem of polluted drinking water in Washington should be solved immediately despite various obstacles, such as pressure for money, etc.
- Environmental Pollution Impact and Ways to Reduce It Pollution can be defined as the introduction of contaminants into the environment which can cause environmental imbalances, instability and harm to living organisms.
- The Alleviation Plans to Air Pollution Throughout the World Air Quality Mitigation Plan is a proposed project which aims at reducing the emissions that affect the air quality by at least fifteen percent.
- Evaluation of Three Solutions to the Problem of Pollution Externalities In economics terms an externality or a spill-over can be defined as an effect caused by a party that is not directly concerned with making the economic decision.
- Three Solutions to Problem of Pollution Externalities Pollution, which is a negative externality are caused by production or consumption processes. Pollution is divided in several types which include water, air, land, radioactive, noise, and thermal pollution.
- Water and Soil Pollution: Effects on the Environment Water and soil pollution is the process of contaminating water and soil. In this project, we will investigate the apparent main pollutants of the Spring Mill Lake.
- Bioremediation Technology Against Environmental Pollution The rapid environmental pollution which occurs due to poor solid waste disposal can be collected by the use of bioremediation technology.
- Gasoline Consumption Statistics and Reduction of Environmental Pollution Gasoline is made out of processed crude oil and has a very strong smell. It contains over 150 chemicals that include the BTEX compounds, that is, benzene, toluene, ethyl benzene and xylene.
- Methods of Planet Pollution Prevention The world is currently experiencing several environmental problems. The majority of these problems are due to drastic globalization and the vast natural processes.
- Air Pollution: Effects and Regulations This essay analyzes the air pollution effects and regulations based on a simple observation of a smoke coming from a large smokestack.
- Can Pollution Free Corporations Exist? A multinational corporation refers to an enterprise that delivers services in at least two countries. In addition to this, a multi-national corporation manages production establishments.
- The WWF’s Environmental Advertisement on Marine and Ocean Pollution Visual image can also make a convincing point, and this is particularly applicable to social and environmental advertising.
- Water Pollution Index of Batujai Reservoir, Central Lombok Regency-Indonesia Despite having 6% of the world’s water resources, Indonesia’s environmental policies have not only been raising concerns but also pushed the country to the brink of water crisis.
- Evaluating the Efficacy of Government Spending on Air Pollution Control: A Case Study From Beijing While living in a city often means better conditions and access to goods and services, rapid urban development has been associated with adverse health outcomes due to air pollution.
- Pollution Impact on the Environment Pollution destroys the environment and kills all kinds of living organisms that inhabit the planet. The mortality rate of people with cancer grows every year.
- Industrial Pollution and Environmental Regulation Environmental regulations should be not be overlooked by manufacturing companies because they can be forced to pay heavy fines if their activities detrimentally affect the environment.
- Reducing the Rate of Pollution This work presents a proposal of the project aimed at developing a strategy initiated by the E227 Global Solutions Company to reduce the rate of pollution it generates annually.
- Chemical Pollution and Loans in Business Ethics This paper examines two scenarios and evaluates the application of different ethical approaches to offer solutions to the dilemmas facing victims.
- Beijing’s Air Pollution Crisis Resolution Beijing’s struggle with poor air quality is far from over. Nevertheless, the government demonstrated its commitment to reducing particulate matter in the atmosphere.
- Pollution and Noise as Environmental Health Issues This paper explores the concept of environmental health and the issues related to its use. On the whole, a detailed explanation of the term “environmental health” is provided.
- Air Pollution Health Risks Information Campaign This paper is dedicated to developing and planning an information campaign about Air Pollution Health Risks in a suburban community with a population of 20,000.
- Environmental Pollution Effects on Health Environmental contaminations such as lead taxation, noise and air pollution harmfully affect physical, psychological health and behavioral patterns of adults and children.
- Water Pollution This essay seeks to examine the concept of water pollution, its causes, effects and solutions to water pollution.
- Relationships Between Asthma and Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Effects on the Environment
- Causes and Negative Effects of Acid Rain Pollution
- Environmental Problems and Policies in Kazakhstan: Air Pollution, Waste, and Water
- Particulate Matter Air Pollution: Effects on the Cardiovascular System
- Tackling Environmental Pollution With Green Taxes
- Understanding China’s Urban Pollution Dynamics
- Types, Effects, and Controls of Air Pollution
- Environment Pollution Significantly Harms the Species of Dolphin
- Trees: Water Pollution and Natural Air Filter
- The Hazardous Acid Rain, a Form of Air Pollution
- Water Shortage and Pollution of Water Source Crisis
- Marine Life, Ocean Pollution, and Other Human Environmental Impacts
- What Can the Public Do to Curb Pollution
- Analysis Harm and Causes of Noise Pollution
- Natural Gas, Pollution, and Our Environment
- Transportation: Pollution and Public Transport Issues
- Noise Pollution and Control in Heckler & Koch
- Heat Transfer, Energy Saving and Pollution Control in UHP Electric-Arc Furnaces
- Water Pollution Filthy Treatment Control Sewage
- Pollution and General Degradation of the Ecology Biology
- What Will the Effects Be if We Don’t Stop Plastic Pollution in Our Oceans
- How Power Plants Around Lake Erie Have Caused Environmental Pollution
- Controlling Automotive Air Pollution: The Case of Colombo City
- Forest Fires, Air Pollution, and Mortality in Southeast Asia
- Air and Water Pollution in New Orleans
- Valuing Health Impacts From Air Pollution in Europe
- What Are the Leading Factors of Water Pollution Around the World
- Coal Pollution Invades Water, Air, and Land
- Environmental Pollution and Population Health in Russian Regions
- Valuing the Health Impacts of Air Pollution in Hong Kong
- Military Training Exercises, Pollution, and Their Consequences for Health
- Why Air Pollution Can Harm the Environment Dramatically
- Noise Pollution: Practical Solutions to a Serious Problem
- The Causes and Effects of Acid Rain, a Form of Air Pollution
- How Trees Prevent Air Pollution?
- Haze: Air Pollution and Current Visibility Problems
- Light Pollution, and the Effects of Light Pollution
- Global Warming and Its Correlation With the Amount of Pollution Worldwide
- Industrial Pollution and Export-Oriented Policies in Brazil
- Policy Implications Toward Green Economics in Pollution Prevention: Theory and Problems in Japan
- Coral Reef Pollution Can Hurt Bermuda’s Tourism Industry
- Household Electrification and Indoor Air Pollution
- Unwatched Pollution: The Effect of Incomplete Monitoring on Air Quality
- Will Pollution Free Cars Become a Reality of the Near Future
- Ethanol-Blended Gasoline Policy and Ozone Pollution in Sao Paulo
- Will COVID-19 Containment and Treatment Measures Drive Shifts in Marine Litter Pollution?
- Negative Pollution Taxes for Controlling Wind Erosion
- Water Pollution Affects Plants and Organisms Living
- Transportation and Air Pollution in the United States
- How Do Golf Courses Affect Water Pollution and Depletion?
- Air Quality, Air Pollution and the Impacts on the Climate
- State Responsibility for Transboundary Air Pollution in International Law
- Light Pollution, Sleep Deprivation, and Infant Health at Birth
- Reducing Air Pollution Through the Use of Oxygenated Gasoline
- Light Pollution: The Dark Side of Outdoor Lighting
- Environmental Pollution and Natural Resource Management
- Air and Water Pollution in Saigon
- Greenhouse Gas Pollution and the United States
- Indoor Air Pollution and Its Effect on Your Health
- Water Pollution Through Urban and Rural Land
- Water Scarcity and Pollution: Don’t Let Our Tear Become Last Drop of Water
- The Factors That Contributes to Pollution and Their Effects on Our World
- Environmental Regulations, Air and Water Pollution, and Infant Mortality in India
- Climate Change and Air Pollution in Australia
- Smog Pollution and Its Effects on Human Health
- Impact of the Oil Industry on Air Pollution
- Strategies for Mitigating Air Pollution in Mexico City
- Factors That Causes Water Pollution and Its Effects on the World Today
- Technology, International Trade, and Pollution From Us Manufacturing
- Noise Pollution and Mitigation in Urban Developments
- Plastic Pollution and Its Effects on the Environment
- The Los Angeles Basin Pollution Problems
- The Sources, Environmental Impact, and Control of Water Pollution
- Are Chinese Green Transport Policies Effective for Anti-Pollution?
- Are Emission Performance Standards Effective in Pollution Control?
- What Are the Seven Types of Pollution?
- How Is Pollution Caused?
- Are Land Values Related to Ambient Air Pollution Levels?
- What Are the Harmful Effects of Pollution?
- Why Is It Important to Stop Pollution?
- What Will Happen if We Don’t Stop Air Pollution?
- What Are the Future Effects of Pollution?
- Are There Increasing Returns to Pollution Abatement?
- When Did Pollution Start Happening?
- What Is the Biggest Pollution Problem?
- Can Scooters Cut Down Commutes and Air Pollution?
- What Is Man-Made Pollution?
- How Is Pollution Harmful to Animals?
- How Has Pollution Changed Over the Years?
- Can Urban Pollution Shrink Rural Districts?
- Which Country Has No Pollution?
- How Does Pollution Affect Climate?
- Can Voluntary Pollution Prevention Programs Fulfill Their Promises?
- Does Air Pollution Crowd Out Foreign Direct Investment Inflows?
- How Does Pollution Affect the Ocean?
- Does Air Pollution Help Reduce Global Warming?
- How Does Pollution Affect Natural Resources?
- Does Disclosure Reduce Pollution?
- Why Is Environment Pollution Increase?
- Does Pollution Cause Acid Rain?
- How Can Leaders Tackle With Water Pollution in China?
- How Does Plastic Pollution Affect Humans?
- Why Does Air Pollution Can Harm the Environment Dramatically?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, November 12). 233 Pollution Essay Topics + Examples. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/pollution-essay-topics/
"233 Pollution Essay Topics + Examples." StudyCorgi , 12 Nov. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/pollution-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '233 Pollution Essay Topics + Examples'. 12 November.
1. StudyCorgi . "233 Pollution Essay Topics + Examples." November 12, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/pollution-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "233 Pollution Essay Topics + Examples." November 12, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/pollution-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "233 Pollution Essay Topics + Examples." November 12, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/pollution-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Pollution were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 8, 2024 .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Public Health
Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review
Ioannis manisalidis.
1 Delphis S.A., Kifisia, Greece
2 Laboratory of Hygiene and Environmental Protection, Faculty of Medicine, Democritus University of Thrace, Alexandroupolis, Greece
Elisavet Stavropoulou
3 Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois (CHUV), Service de Médicine Interne, Lausanne, Switzerland
Agathangelos Stavropoulos
4 School of Social and Political Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom
Eugenia Bezirtzoglou
One of our era's greatest scourges is air pollution, on account not only of its impact on climate change but also its impact on public and individual health due to increasing morbidity and mortality. There are many pollutants that are major factors in disease in humans. Among them, Particulate Matter (PM), particles of variable but very small diameter, penetrate the respiratory system via inhalation, causing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, reproductive and central nervous system dysfunctions, and cancer. Despite the fact that ozone in the stratosphere plays a protective role against ultraviolet irradiation, it is harmful when in high concentration at ground level, also affecting the respiratory and cardiovascular system. Furthermore, nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), dioxins, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are all considered air pollutants that are harmful to humans. Carbon monoxide can even provoke direct poisoning when breathed in at high levels. Heavy metals such as lead, when absorbed into the human body, can lead to direct poisoning or chronic intoxication, depending on exposure. Diseases occurring from the aforementioned substances include principally respiratory problems such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), asthma, bronchiolitis, and also lung cancer, cardiovascular events, central nervous system dysfunctions, and cutaneous diseases. Last but not least, climate change resulting from environmental pollution affects the geographical distribution of many infectious diseases, as do natural disasters. The only way to tackle this problem is through public awareness coupled with a multidisciplinary approach by scientific experts; national and international organizations must address the emergence of this threat and propose sustainable solutions.
Approach to the Problem
The interactions between humans and their physical surroundings have been extensively studied, as multiple human activities influence the environment. The environment is a coupling of the biotic (living organisms and microorganisms) and the abiotic (hydrosphere, lithosphere, and atmosphere).
Pollution is defined as the introduction into the environment of substances harmful to humans and other living organisms. Pollutants are harmful solids, liquids, or gases produced in higher than usual concentrations that reduce the quality of our environment.
Human activities have an adverse effect on the environment by polluting the water we drink, the air we breathe, and the soil in which plants grow. Although the industrial revolution was a great success in terms of technology, society, and the provision of multiple services, it also introduced the production of huge quantities of pollutants emitted into the air that are harmful to human health. Without any doubt, the global environmental pollution is considered an international public health issue with multiple facets. Social, economic, and legislative concerns and lifestyle habits are related to this major problem. Clearly, urbanization and industrialization are reaching unprecedented and upsetting proportions worldwide in our era. Anthropogenic air pollution is one of the biggest public health hazards worldwide, given that it accounts for about 9 million deaths per year ( 1 ).
Without a doubt, all of the aforementioned are closely associated with climate change, and in the event of danger, the consequences can be severe for mankind ( 2 ). Climate changes and the effects of global planetary warming seriously affect multiple ecosystems, causing problems such as food safety issues, ice and iceberg melting, animal extinction, and damage to plants ( 3 , 4 ).
Air pollution has various health effects. The health of susceptible and sensitive individuals can be impacted even on low air pollution days. Short-term exposure to air pollutants is closely related to COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, asthma, respiratory disease, and high rates of hospitalization (a measurement of morbidity).
The long-term effects associated with air pollution are chronic asthma, pulmonary insufficiency, cardiovascular diseases, and cardiovascular mortality. According to a Swedish cohort study, diabetes seems to be induced after long-term air pollution exposure ( 5 ). Moreover, air pollution seems to have various malign health effects in early human life, such as respiratory, cardiovascular, mental, and perinatal disorders ( 3 ), leading to infant mortality or chronic disease in adult age ( 6 ).
National reports have mentioned the increased risk of morbidity and mortality ( 1 ). These studies were conducted in many places around the world and show a correlation between daily ranges of particulate matter (PM) concentration and daily mortality. Climate shifts and global planetary warming ( 3 ) could aggravate the situation. Besides, increased hospitalization (an index of morbidity) has been registered among the elderly and susceptible individuals for specific reasons. Fine and ultrafine particulate matter seems to be associated with more serious illnesses ( 6 ), as it can invade the deepest parts of the airways and more easily reach the bloodstream.
Air pollution mainly affects those living in large urban areas, where road emissions contribute the most to the degradation of air quality. There is also a danger of industrial accidents, where the spread of a toxic fog can be fatal to the populations of the surrounding areas. The dispersion of pollutants is determined by many parameters, most notably atmospheric stability and wind ( 6 ).
In developing countries ( 7 ), the problem is more serious due to overpopulation and uncontrolled urbanization along with the development of industrialization. This leads to poor air quality, especially in countries with social disparities and a lack of information on sustainable management of the environment. The use of fuels such as wood fuel or solid fuel for domestic needs due to low incomes exposes people to bad-quality, polluted air at home. It is of note that three billion people around the world are using the above sources of energy for their daily heating and cooking needs ( 8 ). In developing countries, the women of the household seem to carry the highest risk for disease development due to their longer duration exposure to the indoor air pollution ( 8 , 9 ). Due to its fast industrial development and overpopulation, China is one of the Asian countries confronting serious air pollution problems ( 10 , 11 ). The lung cancer mortality observed in China is associated with fine particles ( 12 ). As stated already, long-term exposure is associated with deleterious effects on the cardiovascular system ( 3 , 5 ). However, it is interesting to note that cardiovascular diseases have mostly been observed in developed and high-income countries rather than in the developing low-income countries exposed highly to air pollution ( 13 ). Extreme air pollution is recorded in India, where the air quality reaches hazardous levels. New Delhi is one of the more polluted cities in India. Flights in and out of New Delhi International Airport are often canceled due to the reduced visibility associated with air pollution. Pollution is occurring both in urban and rural areas in India due to the fast industrialization, urbanization, and rise in use of motorcycle transportation. Nevertheless, biomass combustion associated with heating and cooking needs and practices is a major source of household air pollution in India and in Nepal ( 14 , 15 ). There is spatial heterogeneity in India, as areas with diverse climatological conditions and population and education levels generate different indoor air qualities, with higher PM 2.5 observed in North Indian states (557–601 μg/m 3 ) compared to the Southern States (183–214 μg/m 3 ) ( 16 , 17 ). The cold climate of the North Indian areas may be the main reason for this, as longer periods at home and more heating are necessary compared to in the tropical climate of Southern India. Household air pollution in India is associated with major health effects, especially in women and young children, who stay indoors for longer periods. Chronic obstructive respiratory disease (CORD) and lung cancer are mostly observed in women, while acute lower respiratory disease is seen in young children under 5 years of age ( 18 ).
Accumulation of air pollution, especially sulfur dioxide and smoke, reaching 1,500 mg/m3, resulted in an increase in the number of deaths (4,000 deaths) in December 1952 in London and in 1963 in New York City (400 deaths) ( 19 ). An association of pollution with mortality was reported on the basis of monitoring of outdoor pollution in six US metropolitan cities ( 20 ). In every case, it seems that mortality was closely related to the levels of fine, inhalable, and sulfate particles more than with the levels of total particulate pollution, aerosol acidity, sulfur dioxide, or nitrogen dioxide ( 20 ).
Furthermore, extremely high levels of pollution are reported in Mexico City and Rio de Janeiro, followed by Milan, Ankara, Melbourne, Tokyo, and Moscow ( 19 ).
Based on the magnitude of the public health impact, it is certain that different kinds of interventions should be taken into account. Success and effectiveness in controlling air pollution, specifically at the local level, have been reported. Adequate technological means are applied considering the source and the nature of the emission as well as its impact on health and the environment. The importance of point sources and non-point sources of air pollution control is reported by Schwela and Köth-Jahr ( 21 ). Without a doubt, a detailed emission inventory must record all sources in a given area. Beyond considering the above sources and their nature, topography and meteorology should also be considered, as stated previously. Assessment of the control policies and methods is often extrapolated from the local to the regional and then to the global scale. Air pollution may be dispersed and transported from one region to another area located far away. Air pollution management means the reduction to acceptable levels or possible elimination of air pollutants whose presence in the air affects our health or the environmental ecosystem. Private and governmental entities and authorities implement actions to ensure the air quality ( 22 ). Air quality standards and guidelines were adopted for the different pollutants by the WHO and EPA as a tool for the management of air quality ( 1 , 23 ). These standards have to be compared to the emissions inventory standards by causal analysis and dispersion modeling in order to reveal the problematic areas ( 24 ). Inventories are generally based on a combination of direct measurements and emissions modeling ( 24 ).
As an example, we state here the control measures at the source through the use of catalytic converters in cars. These are devices that turn the pollutants and toxic gases produced from combustion engines into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis through redox reactions ( 25 ). In Greece, the use of private cars was restricted by tracking their license plates in order to reduce traffic congestion during rush hour ( 25 ).
Concerning industrial emissions, collectors and closed systems can keep the air pollution to the minimal standards imposed by legislation ( 26 ).
Current strategies to improve air quality require an estimation of the economic value of the benefits gained from proposed programs. These proposed programs by public authorities, and directives are issued with guidelines to be respected.
In Europe, air quality limit values AQLVs (Air Quality Limit Values) are issued for setting off planning claims ( 27 ). In the USA, the NAAQS (National Ambient Air Quality Standards) establish the national air quality limit values ( 27 ). While both standards and directives are based on different mechanisms, significant success has been achieved in the reduction of overall emissions and associated health and environmental effects ( 27 ). The European Directive identifies geographical areas of risk exposure as monitoring/assessment zones to record the emission sources and levels of air pollution ( 27 ), whereas the USA establishes global geographical air quality criteria according to the severity of their air quality problem and records all sources of the pollutants and their precursors ( 27 ).
In this vein, funds have been financing, directly or indirectly, projects related to air quality along with the technical infrastructure to maintain good air quality. These plans focus on an inventory of databases from air quality environmental planning awareness campaigns. Moreover, pollution measures of air emissions may be taken for vehicles, machines, and industries in urban areas.
Technological innovation can only be successful if it is able to meet the needs of society. In this sense, technology must reflect the decision-making practices and procedures of those involved in risk assessment and evaluation and act as a facilitator in providing information and assessments to enable decision makers to make the best decisions possible. Summarizing the aforementioned in order to design an effective air quality control strategy, several aspects must be considered: environmental factors and ambient air quality conditions, engineering factors and air pollutant characteristics, and finally, economic operating costs for technological improvement and administrative and legal costs. Considering the economic factor, competitiveness through neoliberal concepts is offering a solution to environmental problems ( 22 ).
The development of environmental governance, along with technological progress, has initiated the deployment of a dialogue. Environmental politics has created objections and points of opposition between different political parties, scientists, media, and governmental and non-governmental organizations ( 22 ). Radical environmental activism actions and movements have been created ( 22 ). The rise of the new information and communication technologies (ICTs) are many times examined as to whether and in which way they have influenced means of communication and social movements such as activism ( 28 ). Since the 1990s, the term “digital activism” has been used increasingly and in many different disciplines ( 29 ). Nowadays, multiple digital technologies can be used to produce a digital activism outcome on environmental issues. More specifically, devices with online capabilities such as computers or mobile phones are being used as a way to pursue change in political and social affairs ( 30 ).
In the present paper, we focus on the sources of environmental pollution in relation to public health and propose some solutions and interventions that may be of interest to environmental legislators and decision makers.
Sources of Exposure
It is known that the majority of environmental pollutants are emitted through large-scale human activities such as the use of industrial machinery, power-producing stations, combustion engines, and cars. Because these activities are performed at such a large scale, they are by far the major contributors to air pollution, with cars estimated to be responsible for approximately 80% of today's pollution ( 31 ). Some other human activities are also influencing our environment to a lesser extent, such as field cultivation techniques, gas stations, fuel tanks heaters, and cleaning procedures ( 32 ), as well as several natural sources, such as volcanic and soil eruptions and forest fires.
The classification of air pollutants is based mainly on the sources producing pollution. Therefore, it is worth mentioning the four main sources, following the classification system: Major sources, Area sources, Mobile sources, and Natural sources.
Major sources include the emission of pollutants from power stations, refineries, and petrochemicals, the chemical and fertilizer industries, metallurgical and other industrial plants, and, finally, municipal incineration.
Indoor area sources include domestic cleaning activities, dry cleaners, printing shops, and petrol stations.
Mobile sources include automobiles, cars, railways, airways, and other types of vehicles.
Finally, natural sources include, as stated previously, physical disasters ( 33 ) such as forest fire, volcanic erosion, dust storms, and agricultural burning.
However, many classification systems have been proposed. Another type of classification is a grouping according to the recipient of the pollution, as follows:
Air pollution is determined as the presence of pollutants in the air in large quantities for long periods. Air pollutants are dispersed particles, hydrocarbons, CO, CO 2 , NO, NO 2 , SO 3 , etc.
Water pollution is organic and inorganic charge and biological charge ( 10 ) at high levels that affect the water quality ( 34 , 35 ).
Soil pollution occurs through the release of chemicals or the disposal of wastes, such as heavy metals, hydrocarbons, and pesticides.
Air pollution can influence the quality of soil and water bodies by polluting precipitation, falling into water and soil environments ( 34 , 36 ). Notably, the chemistry of the soil can be amended due to acid precipitation by affecting plants, cultures, and water quality ( 37 ). Moreover, movement of heavy metals is favored by soil acidity, and metals are so then moving into the watery environment. It is known that heavy metals such as aluminum are noxious to wildlife and fishes. Soil quality seems to be of importance, as soils with low calcium carbonate levels are at increased jeopardy from acid rain. Over and above rain, snow and particulate matter drip into watery ' bodies ( 36 , 38 ).
Lastly, pollution is classified following type of origin:
Radioactive and nuclear pollution , releasing radioactive and nuclear pollutants into water, air, and soil during nuclear explosions and accidents, from nuclear weapons, and through handling or disposal of radioactive sewage.
Radioactive materials can contaminate surface water bodies and, being noxious to the environment, plants, animals, and humans. It is known that several radioactive substances such as radium and uranium concentrate in the bones and can cause cancers ( 38 , 39 ).
Noise pollution is produced by machines, vehicles, traffic noises, and musical installations that are harmful to our hearing.
The World Health Organization introduced the term DALYs. The DALYs for a disease or health condition is defined as the sum of the Years of Life Lost (YLL) due to premature mortality in the population and the Years Lost due to Disability (YLD) for people living with the health condition or its consequences ( 39 ). In Europe, air pollution is the main cause of disability-adjusted life years lost (DALYs), followed by noise pollution. The potential relationships of noise and air pollution with health have been studied ( 40 ). The study found that DALYs related to noise were more important than those related to air pollution, as the effects of environmental noise on cardiovascular disease were independent of air pollution ( 40 ). Environmental noise should be counted as an independent public health risk ( 40 ).
Environmental pollution occurs when changes in the physical, chemical, or biological constituents of the environment (air masses, temperature, climate, etc.) are produced.
Pollutants harm our environment either by increasing levels above normal or by introducing harmful toxic substances. Primary pollutants are directly produced from the above sources, and secondary pollutants are emitted as by-products of the primary ones. Pollutants can be biodegradable or non-biodegradable and of natural origin or anthropogenic, as stated previously. Moreover, their origin can be a unique source (point-source) or dispersed sources.
Pollutants have differences in physical and chemical properties, explaining the discrepancy in their capacity for producing toxic effects. As an example, we state here that aerosol compounds ( 41 – 43 ) have a greater toxicity than gaseous compounds due to their tiny size (solid or liquid) in the atmosphere; they have a greater penetration capacity. Gaseous compounds are eliminated more easily by our respiratory system ( 41 ). These particles are able to damage lungs and can even enter the bloodstream ( 41 ), leading to the premature deaths of millions of people yearly. Moreover, the aerosol acidity ([H+]) seems to considerably enhance the production of secondary organic aerosols (SOA), but this last aspect is not supported by other scientific teams ( 38 ).
Climate and Pollution
Air pollution and climate change are closely related. Climate is the other side of the same coin that reduces the quality of our Earth ( 44 ). Pollutants such as black carbon, methane, tropospheric ozone, and aerosols affect the amount of incoming sunlight. As a result, the temperature of the Earth is increasing, resulting in the melting of ice, icebergs, and glaciers.
In this vein, climatic changes will affect the incidence and prevalence of both residual and imported infections in Europe. Climate and weather affect the duration, timing, and intensity of outbreaks strongly and change the map of infectious diseases in the globe ( 45 ). Mosquito-transmitted parasitic or viral diseases are extremely climate-sensitive, as warming firstly shortens the pathogen incubation period and secondly shifts the geographic map of the vector. Similarly, water-warming following climate changes leads to a high incidence of waterborne infections. Recently, in Europe, eradicated diseases seem to be emerging due to the migration of population, for example, cholera, poliomyelitis, tick-borne encephalitis, and malaria ( 46 ).
The spread of epidemics is associated with natural climate disasters and storms, which seem to occur more frequently nowadays ( 47 ). Malnutrition and disequilibration of the immune system are also associated with the emerging infections affecting public health ( 48 ).
The Chikungunya virus “took the airplane” from the Indian Ocean to Europe, as outbreaks of the disease were registered in Italy ( 49 ) as well as autochthonous cases in France ( 50 ).
An increase in cryptosporidiosis in the United Kingdom and in the Czech Republic seems to have occurred following flooding ( 36 , 51 ).
As stated previously, aerosols compounds are tiny in size and considerably affect the climate. They are able to dissipate sunlight (the albedo phenomenon) by dispersing a quarter of the sun's rays back to space and have cooled the global temperature over the last 30 years ( 52 ).
Air Pollutants
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports on six major air pollutants, namely particle pollution, ground-level ozone, carbon monoxide, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and lead. Air pollution can have a disastrous effect on all components of the environment, including groundwater, soil, and air. Additionally, it poses a serious threat to living organisms. In this vein, our interest is mainly to focus on these pollutants, as they are related to more extensive and severe problems in human health and environmental impact. Acid rain, global warming, the greenhouse effect, and climate changes have an important ecological impact on air pollution ( 53 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) and Health
Studies have shown a relationship between particulate matter (PM) and adverse health effects, focusing on either short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic) PM exposure.
Particulate matter (PM) is usually formed in the atmosphere as a result of chemical reactions between the different pollutants. The penetration of particles is closely dependent on their size ( 53 ). Particulate Matter (PM) was defined as a term for particles by the United States Environmental Protection Agency ( 54 ). Particulate matter (PM) pollution includes particles with diameters of 10 micrometers (μm) or smaller, called PM 10 , and extremely fine particles with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers (μm) and smaller.
Particulate matter contains tiny liquid or solid droplets that can be inhaled and cause serious health effects ( 55 ). Particles <10 μm in diameter (PM 10 ) after inhalation can invade the lungs and even reach the bloodstream. Fine particles, PM 2.5 , pose a greater risk to health ( 6 , 56 ) ( Table 1 ).
Penetrability according to particle size.
Multiple epidemiological studies have been performed on the health effects of PM. A positive relation was shown between both short-term and long-term exposures of PM 2.5 and acute nasopharyngitis ( 56 ). In addition, long-term exposure to PM for years was found to be related to cardiovascular diseases and infant mortality.
Those studies depend on PM 2.5 monitors and are restricted in terms of study area or city area due to a lack of spatially resolved daily PM 2.5 concentration data and, in this way, are not representative of the entire population. Following a recent epidemiological study by the Department of Environmental Health at Harvard School of Public Health (Boston, MA) ( 57 ), it was reported that, as PM 2.5 concentrations vary spatially, an exposure error (Berkson error) seems to be produced, and the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects are not yet completely elucidated. The team developed a PM 2.5 exposure model based on remote sensing data for assessing short- and long-term human exposures ( 57 ). This model permits spatial resolution in short-term effects plus the assessment of long-term effects in the whole population.
Moreover, respiratory diseases and affection of the immune system are registered as long-term chronic effects ( 58 ). It is worth noting that people with asthma, pneumonia, diabetes, and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases are especially susceptible and vulnerable to the effects of PM. PM 2.5 , followed by PM 10 , are strongly associated with diverse respiratory system diseases ( 59 ), as their size permits them to pierce interior spaces ( 60 ). The particles produce toxic effects according to their chemical and physical properties. The components of PM 10 and PM 2.5 can be organic (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, dioxins, benzene, 1-3 butadiene) or inorganic (carbon, chlorides, nitrates, sulfates, metals) in nature ( 55 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) is divided into four main categories according to type and size ( 61 ) ( Table 2 ).
Types and sizes of particulate Matter (PM).
Gas contaminants include PM in aerial masses.
Particulate contaminants include contaminants such as smog, soot, tobacco smoke, oil smoke, fly ash, and cement dust.
Biological Contaminants are microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, mold, and bacterial spores), cat allergens, house dust and allergens, and pollen.
Types of Dust include suspended atmospheric dust, settling dust, and heavy dust.
Finally, another fact is that the half-lives of PM 10 and PM 2.5 particles in the atmosphere is extended due to their tiny dimensions; this permits their long-lasting suspension in the atmosphere and even their transfer and spread to distant destinations where people and the environment may be exposed to the same magnitude of pollution ( 53 ). They are able to change the nutrient balance in watery ecosystems, damage forests and crops, and acidify water bodies.
As stated, PM 2.5 , due to their tiny size, are causing more serious health effects. These aforementioned fine particles are the main cause of the “haze” formation in different metropolitan areas ( 12 , 13 , 61 ).
Ozone Impact in the Atmosphere
Ozone (O 3 ) is a gas formed from oxygen under high voltage electric discharge ( 62 ). It is a strong oxidant, 52% stronger than chlorine. It arises in the stratosphere, but it could also arise following chain reactions of photochemical smog in the troposphere ( 63 ).
Ozone can travel to distant areas from its initial source, moving with air masses ( 64 ). It is surprising that ozone levels over cities are low in contrast to the increased amounts occuring in urban areas, which could become harmful for cultures, forests, and vegetation ( 65 ) as it is reducing carbon assimilation ( 66 ). Ozone reduces growth and yield ( 47 , 48 ) and affects the plant microflora due to its antimicrobial capacity ( 67 , 68 ). In this regard, ozone acts upon other natural ecosystems, with microflora ( 69 , 70 ) and animal species changing their species composition ( 71 ). Ozone increases DNA damage in epidermal keratinocytes and leads to impaired cellular function ( 72 ).
Ground-level ozone (GLO) is generated through a chemical reaction between oxides of nitrogen and VOCs emitted from natural sources and/or following anthropogenic activities.
Ozone uptake usually occurs by inhalation. Ozone affects the upper layers of the skin and the tear ducts ( 73 ). A study of short-term exposure of mice to high levels of ozone showed malondialdehyde formation in the upper skin (epidermis) but also depletion in vitamins C and E. It is likely that ozone levels are not interfering with the skin barrier function and integrity to predispose to skin disease ( 74 ).
Due to the low water-solubility of ozone, inhaled ozone has the capacity to penetrate deeply into the lungs ( 75 ).
Toxic effects induced by ozone are registered in urban areas all over the world, causing biochemical, morphologic, functional, and immunological disorders ( 76 ).
The European project (APHEA2) focuses on the acute effects of ambient ozone concentrations on mortality ( 77 ). Daily ozone concentrations compared to the daily number of deaths were reported from different European cities for a 3-year period. During the warm period of the year, an observed increase in ozone concentration was associated with an increase in the daily number of deaths (0.33%), in the number of respiratory deaths (1.13%), and in the number of cardiovascular deaths (0.45%). No effect was observed during wintertime.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is produced by fossil fuel when combustion is incomplete. The symptoms of poisoning due to inhaling carbon monoxide include headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, and, finally, loss of consciousness.
The affinity of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin is much greater than that of oxygen. In this vein, serious poisoning may occur in people exposed to high levels of carbon monoxide for a long period of time. Due to the loss of oxygen as a result of the competitive binding of carbon monoxide, hypoxia, ischemia, and cardiovascular disease are observed.
Carbon monoxide affects the greenhouses gases that are tightly connected to global warming and climate. This should lead to an increase in soil and water temperatures, and extreme weather conditions or storms may occur ( 68 ).
However, in laboratory and field experiments, it has been seen to produce increased plant growth ( 78 ).
Nitrogen Oxide (NO 2 )
Nitrogen oxide is a traffic-related pollutant, as it is emitted from automobile motor engines ( 79 , 80 ). It is an irritant of the respiratory system as it penetrates deep in the lung, inducing respiratory diseases, coughing, wheezing, dyspnea, bronchospasm, and even pulmonary edema when inhaled at high levels. It seems that concentrations over 0.2 ppm produce these adverse effects in humans, while concentrations higher than 2.0 ppm affect T-lymphocytes, particularly the CD8+ cells and NK cells that produce our immune response ( 81 ).It is reported that long-term exposure to high levels of nitrogen dioxide can be responsible for chronic lung disease. Long-term exposure to NO 2 can impair the sense of smell ( 81 ).
However, systems other than respiratory ones can be involved, as symptoms such as eye, throat, and nose irritation have been registered ( 81 ).
High levels of nitrogen dioxide are deleterious to crops and vegetation, as they have been observed to reduce crop yield and plant growth efficiency. Moreover, NO 2 can reduce visibility and discolor fabrics ( 81 ).
Sulfur Dioxide (SO 2 )
Sulfur dioxide is a harmful gas that is emitted mainly from fossil fuel consumption or industrial activities. The annual standard for SO 2 is 0.03 ppm ( 82 ). It affects human, animal, and plant life. Susceptible people as those with lung disease, old people, and children, who present a higher risk of damage. The major health problems associated with sulfur dioxide emissions in industrialized areas are respiratory irritation, bronchitis, mucus production, and bronchospasm, as it is a sensory irritant and penetrates deep into the lung converted into bisulfite and interacting with sensory receptors, causing bronchoconstriction. Moreover, skin redness, damage to the eyes (lacrimation and corneal opacity) and mucous membranes, and worsening of pre-existing cardiovascular disease have been observed ( 81 ).
Environmental adverse effects, such as acidification of soil and acid rain, seem to be associated with sulfur dioxide emissions ( 83 ).
Lead is a heavy metal used in different industrial plants and emitted from some petrol motor engines, batteries, radiators, waste incinerators, and waste waters ( 84 ).
Moreover, major sources of lead pollution in the air are metals, ore, and piston-engine aircraft. Lead poisoning is a threat to public health due to its deleterious effects upon humans, animals, and the environment, especially in the developing countries.
Exposure to lead can occur through inhalation, ingestion, and dermal absorption. Trans- placental transport of lead was also reported, as lead passes through the placenta unencumbered ( 85 ). The younger the fetus is, the more harmful the toxic effects. Lead toxicity affects the fetal nervous system; edema or swelling of the brain is observed ( 86 ). Lead, when inhaled, accumulates in the blood, soft tissue, liver, lung, bones, and cardiovascular, nervous, and reproductive systems. Moreover, loss of concentration and memory, as well as muscle and joint pain, were observed in adults ( 85 , 86 ).
Children and newborns ( 87 ) are extremely susceptible even to minimal doses of lead, as it is a neurotoxicant and causes learning disabilities, impairment of memory, hyperactivity, and even mental retardation.
Elevated amounts of lead in the environment are harmful to plants and crop growth. Neurological effects are observed in vertebrates and animals in association with high lead levels ( 88 ).
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(PAHs)
The distribution of PAHs is ubiquitous in the environment, as the atmosphere is the most important means of their dispersal. They are found in coal and in tar sediments. Moreover, they are generated through incomplete combustion of organic matter as in the cases of forest fires, incineration, and engines ( 89 ). PAH compounds, such as benzopyrene, acenaphthylene, anthracene, and fluoranthene are recognized as toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic substances. They are an important risk factor for lung cancer ( 89 ).
Volatile Organic Compounds(VOCs)
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as toluene, benzene, ethylbenzene, and xylene ( 90 ), have been found to be associated with cancer in humans ( 91 ). The use of new products and materials has actually resulted in increased concentrations of VOCs. VOCs pollute indoor air ( 90 ) and may have adverse effects on human health ( 91 ). Short-term and long-term adverse effects on human health are observed. VOCs are responsible for indoor air smells. Short-term exposure is found to cause irritation of eyes, nose, throat, and mucosal membranes, while those of long duration exposure include toxic reactions ( 92 ). Predictable assessment of the toxic effects of complex VOC mixtures is difficult to estimate, as these pollutants can have synergic, antagonistic, or indifferent effects ( 91 , 93 ).
Dioxins originate from industrial processes but also come from natural processes, such as forest fires and volcanic eruptions. They accumulate in foods such as meat and dairy products, fish and shellfish, and especially in the fatty tissue of animals ( 94 ).
Short-period exhibition to high dioxin concentrations may result in dark spots and lesions on the skin ( 94 ). Long-term exposure to dioxins can cause developmental problems, impairment of the immune, endocrine and nervous systems, reproductive infertility, and cancer ( 94 ).
Without any doubt, fossil fuel consumption is responsible for a sizeable part of air contamination. This contamination may be anthropogenic, as in agricultural and industrial processes or transportation, while contamination from natural sources is also possible. Interestingly, it is of note that the air quality standards established through the European Air Quality Directive are somewhat looser than the WHO guidelines, which are stricter ( 95 ).
Effect of Air Pollution on Health
The most common air pollutants are ground-level ozone and Particulates Matter (PM). Air pollution is distinguished into two main types:
Outdoor pollution is the ambient air pollution.
Indoor pollution is the pollution generated by household combustion of fuels.
People exposed to high concentrations of air pollutants experience disease symptoms and states of greater and lesser seriousness. These effects are grouped into short- and long-term effects affecting health.
Susceptible populations that need to be aware of health protection measures include old people, children, and people with diabetes and predisposing heart or lung disease, especially asthma.
As extensively stated previously, according to a recent epidemiological study from Harvard School of Public Health, the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects have not been completely clarified ( 57 ) due to the different epidemiological methodologies and to the exposure errors. New models are proposed for assessing short- and long-term human exposure data more successfully ( 57 ). Thus, in the present section, we report the more common short- and long-term health effects but also general concerns for both types of effects, as these effects are often dependent on environmental conditions, dose, and individual susceptibility.
Short-term effects are temporary and range from simple discomfort, such as irritation of the eyes, nose, skin, throat, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness, and breathing difficulties, to more serious states, such as asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis, and lung and heart problems. Short-term exposure to air pollution can also cause headaches, nausea, and dizziness.
These problems can be aggravated by extended long-term exposure to the pollutants, which is harmful to the neurological, reproductive, and respiratory systems and causes cancer and even, rarely, deaths.
The long-term effects are chronic, lasting for years or the whole life and can even lead to death. Furthermore, the toxicity of several air pollutants may also induce a variety of cancers in the long term ( 96 ).
As stated already, respiratory disorders are closely associated with the inhalation of air pollutants. These pollutants will invade through the airways and will accumulate at the cells. Damage to target cells should be related to the pollutant component involved and its source and dose. Health effects are also closely dependent on country, area, season, and time. An extended exposure duration to the pollutant should incline to long-term health effects in relation also to the above factors.
Particulate Matter (PMs), dust, benzene, and O 3 cause serious damage to the respiratory system ( 97 ). Moreover, there is a supplementary risk in case of existing respiratory disease such as asthma ( 98 ). Long-term effects are more frequent in people with a predisposing disease state. When the trachea is contaminated by pollutants, voice alterations may be remarked after acute exposure. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may be induced following air pollution, increasing morbidity and mortality ( 99 ). Long-term effects from traffic, industrial air pollution, and combustion of fuels are the major factors for COPD risk ( 99 ).
Multiple cardiovascular effects have been observed after exposure to air pollutants ( 100 ). Changes occurred in blood cells after long-term exposure may affect cardiac functionality. Coronary arteriosclerosis was reported following long-term exposure to traffic emissions ( 101 ), while short-term exposure is related to hypertension, stroke, myocardial infracts, and heart insufficiency. Ventricle hypertrophy is reported to occur in humans after long-time exposure to nitrogen oxide (NO 2 ) ( 102 , 103 ).
Neurological effects have been observed in adults and children after extended-term exposure to air pollutants.
Psychological complications, autism, retinopathy, fetal growth, and low birth weight seem to be related to long-term air pollution ( 83 ). The etiologic agent of the neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's and Parkinson's) is not yet known, although it is believed that extended exposure to air pollution seems to be a factor. Specifically, pesticides and metals are cited as etiological factors, together with diet. The mechanisms in the development of neurodegenerative disease include oxidative stress, protein aggregation, inflammation, and mitochondrial impairment in neurons ( 104 ) ( Figure 1 ).

Impact of air pollutants on the brain.
Brain inflammation was observed in dogs living in a highly polluted area in Mexico for a long period ( 105 ). In human adults, markers of systemic inflammation (IL-6 and fibrinogen) were found to be increased as an immediate response to PNC on the IL-6 level, possibly leading to the production of acute-phase proteins ( 106 ). The progression of atherosclerosis and oxidative stress seem to be the mechanisms involved in the neurological disturbances caused by long-term air pollution. Inflammation comes secondary to the oxidative stress and seems to be involved in the impairment of developmental maturation, affecting multiple organs ( 105 , 107 ). Similarly, other factors seem to be involved in the developmental maturation, which define the vulnerability to long-term air pollution. These include birthweight, maternal smoking, genetic background and socioeconomic environment, as well as education level.
However, diet, starting from breast-feeding, is another determinant factor. Diet is the main source of antioxidants, which play a key role in our protection against air pollutants ( 108 ). Antioxidants are free radical scavengers and limit the interaction of free radicals in the brain ( 108 ). Similarly, genetic background may result in a differential susceptibility toward the oxidative stress pathway ( 60 ). For example, antioxidant supplementation with vitamins C and E appears to modulate the effect of ozone in asthmatic children homozygous for the GSTM1 null allele ( 61 ). Inflammatory cytokines released in the periphery (e.g., respiratory epithelia) upregulate the innate immune Toll-like receptor 2. Such activation and the subsequent events leading to neurodegeneration have recently been observed in lung lavage in mice exposed to ambient Los Angeles (CA, USA) particulate matter ( 61 ). In children, neurodevelopmental morbidities were observed after lead exposure. These children developed aggressive and delinquent behavior, reduced intelligence, learning difficulties, and hyperactivity ( 109 ). No level of lead exposure seems to be “safe,” and the scientific community has asked the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to reduce the current screening guideline of 10 μg/dl ( 109 ).
It is important to state that impact on the immune system, causing dysfunction and neuroinflammation ( 104 ), is related to poor air quality. Yet, increases in serum levels of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM) and the complement component C3 are observed ( 106 ). Another issue is that antigen presentation is affected by air pollutants, as there is an upregulation of costimulatory molecules such as CD80 and CD86 on macrophages ( 110 ).
As is known, skin is our shield against ultraviolet radiation (UVR) and other pollutants, as it is the most exterior layer of our body. Traffic-related pollutants, such as PAHs, VOCs, oxides, and PM, may cause pigmented spots on our skin ( 111 ). On the one hand, as already stated, when pollutants penetrate through the skin or are inhaled, damage to the organs is observed, as some of these pollutants are mutagenic and carcinogenic, and, specifically, they affect the liver and lung. On the other hand, air pollutants (and those in the troposphere) reduce the adverse effects of ultraviolet radiation UVR in polluted urban areas ( 111 ). Air pollutants absorbed by the human skin may contribute to skin aging, psoriasis, acne, urticaria, eczema, and atopic dermatitis ( 111 ), usually caused by exposure to oxides and photochemical smoke ( 111 ). Exposure to PM and cigarette smoking act as skin-aging agents, causing spots, dyschromia, and wrinkles. Lastly, pollutants have been associated with skin cancer ( 111 ).
Higher morbidity is reported to fetuses and children when exposed to the above dangers. Impairment in fetal growth, low birth weight, and autism have been reported ( 112 ).
Another exterior organ that may be affected is the eye. Contamination usually comes from suspended pollutants and may result in asymptomatic eye outcomes, irritation ( 112 ), retinopathy, or dry eye syndrome ( 113 , 114 ).
Environmental Impact of Air Pollution
Air pollution is harming not only human health but also the environment ( 115 ) in which we live. The most important environmental effects are as follows.
Acid rain is wet (rain, fog, snow) or dry (particulates and gas) precipitation containing toxic amounts of nitric and sulfuric acids. They are able to acidify the water and soil environments, damage trees and plantations, and even damage buildings and outdoor sculptures, constructions, and statues.
Haze is produced when fine particles are dispersed in the air and reduce the transparency of the atmosphere. It is caused by gas emissions in the air coming from industrial facilities, power plants, automobiles, and trucks.
Ozone , as discussed previously, occurs both at ground level and in the upper level (stratosphere) of the Earth's atmosphere. Stratospheric ozone is protecting us from the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. In contrast, ground-level ozone is harmful to human health and is a pollutant. Unfortunately, stratospheric ozone is gradually damaged by ozone-depleting substances (i.e., chemicals, pesticides, and aerosols). If this protecting stratospheric ozone layer is thinned, then UV radiation can reach our Earth, with harmful effects for human life (skin cancer) ( 116 ) and crops ( 117 ). In plants, ozone penetrates through the stomata, inducing them to close, which blocks CO 2 transfer and induces a reduction in photosynthesis ( 118 ).
Global climate change is an important issue that concerns mankind. As is known, the “greenhouse effect” keeps the Earth's temperature stable. Unhappily, anthropogenic activities have destroyed this protecting temperature effect by producing large amounts of greenhouse gases, and global warming is mounting, with harmful effects on human health, animals, forests, wildlife, agriculture, and the water environment. A report states that global warming is adding to the health risks of poor people ( 119 ).
People living in poorly constructed buildings in warm-climate countries are at high risk for heat-related health problems as temperatures mount ( 119 ).
Wildlife is burdened by toxic pollutants coming from the air, soil, or the water ecosystem and, in this way, animals can develop health problems when exposed to high levels of pollutants. Reproductive failure and birth effects have been reported.
Eutrophication is occurring when elevated concentrations of nutrients (especially nitrogen) stimulate the blooming of aquatic algae, which can cause a disequilibration in the diversity of fish and their deaths.
Without a doubt, there is a critical concentration of pollution that an ecosystem can tolerate without being destroyed, which is associated with the ecosystem's capacity to neutralize acidity. The Canada Acid Rain Program established this load at 20 kg/ha/yr ( 120 ).
Hence, air pollution has deleterious effects on both soil and water ( 121 ). Concerning PM as an air pollutant, its impact on crop yield and food productivity has been reported. Its impact on watery bodies is associated with the survival of living organisms and fishes and their productivity potential ( 121 ).
An impairment in photosynthetic rhythm and metabolism is observed in plants exposed to the effects of ozone ( 121 ).
Sulfur and nitrogen oxides are involved in the formation of acid rain and are harmful to plants and marine organisms.
Last but not least, as mentioned above, the toxicity associated with lead and other metals is the main threat to our ecosystems (air, water, and soil) and living creatures ( 121 ).
In 2018, during the first WHO Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health, the WHO's General Director, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, called air pollution a “silent public health emergency” and “the new tobacco” ( 122 ).
Undoubtedly, children are particularly vulnerable to air pollution, especially during their development. Air pollution has adverse effects on our lives in many different respects.
Diseases associated with air pollution have not only an important economic impact but also a societal impact due to absences from productive work and school.
Despite the difficulty of eradicating the problem of anthropogenic environmental pollution, a successful solution could be envisaged as a tight collaboration of authorities, bodies, and doctors to regularize the situation. Governments should spread sufficient information and educate people and should involve professionals in these issues so as to control the emergence of the problem successfully.
Technologies to reduce air pollution at the source must be established and should be used in all industries and power plants. The Kyoto Protocol of 1997 set as a major target the reduction of GHG emissions to below 5% by 2012 ( 123 ). This was followed by the Copenhagen summit, 2009 ( 124 ), and then the Durban summit of 2011 ( 125 ), where it was decided to keep to the same line of action. The Kyoto protocol and the subsequent ones were ratified by many countries. Among the pioneers who adopted this important protocol for the world's environmental and climate “health” was China ( 3 ). As is known, China is a fast-developing economy and its GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is expected to be very high by 2050, which is defined as the year of dissolution of the protocol for the decrease in gas emissions.
A more recent international agreement of crucial importance for climate change is the Paris Agreement of 2015, issued by the UNFCCC (United Nations Climate Change Committee). This latest agreement was ratified by a plethora of UN (United Nations) countries as well as the countries of the European Union ( 126 ). In this vein, parties should promote actions and measures to enhance numerous aspects around the subject. Boosting education, training, public awareness, and public participation are some of the relevant actions for maximizing the opportunities to achieve the targets and goals on the crucial matter of climate change and environmental pollution ( 126 ). Without any doubt, technological improvements makes our world easier and it seems difficult to reduce the harmful impact caused by gas emissions, we could limit its use by seeking reliable approaches.
Synopsizing, a global prevention policy should be designed in order to combat anthropogenic air pollution as a complement to the correct handling of the adverse health effects associated with air pollution. Sustainable development practices should be applied, together with information coming from research in order to handle the problem effectively.
At this point, international cooperation in terms of research, development, administration policy, monitoring, and politics is vital for effective pollution control. Legislation concerning air pollution must be aligned and updated, and policy makers should propose the design of a powerful tool of environmental and health protection. As a result, the main proposal of this essay is that we should focus on fostering local structures to promote experience and practice and extrapolate these to the international level through developing effective policies for sustainable management of ecosystems.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
IM is employed by the company Delphis S.A. The remaining authors declare that the present review paper was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
JavaScript appears to be disabled on this computer. Please click here to see any active alerts .
Research on Health Effects from Air Pollution
Decades of research have shown that air pollutants such as ozone and particulate matter (PM) increase the amount and seriousness of lung and heart disease and other health problems. More investigation is needed to further understand the role poor air quality plays in causing detrimental effects to health and increased disease, especially in vulnerable populations. Children, the elderly, and people living in areas with high levels of air pollution are especially susceptible.
Results from these investigations are used to support the nation's air quality standards under the Clean Air Act and contribute to improvements in public health.
On this page:
Health Effects of Air Pollutants on Vulnerable Populations
Long-term and short-term effects from exposure to air pollutants.
- Multipollutant Exposures and Changes in Environmental Conditions
- Leveraging Big Data for Innovations in Health Science
Health Effects of Wildfire Smoke
Public health intervention and communications strategies, integrated science assessments for air pollutants.
Research has shown that some people are more susceptible than others to air pollutants. These groups include children, pregnant women, older adults, and individuals with pre-existing heart and lung disease. People in low socioeconomic neighborhoods and communities may be more vulnerable to air pollution because of many factors. Proximity to industrial sources of air pollution, underlying health problems, poor nutrition, stress, and other factors can contribute to increased health impacts in these communities.
There is a need for greater understanding of the factors that may influence whether a population or age group is at increased risk of health effects from air pollution. In addition, advances to analytical approaches used to study the health effects from air pollution will improve exposure estimates for healthy and at-risk groups.
The research by EPA scientists and others inform the required reviews of the primary National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS), which is done with the development of Integrated Science Assessments (ISAs). These ISAs are mandated by Congress every five years to assess the current state of the science on criteria air pollutants and determine if the standards provide adequate protection to public health.
Research is focused on addressing four areas:
- Identifying and characterizing whether there are key reproductive factors and critical stages of development that are impacted by air pollution exposures;
- Determining the role of acute and chronic sociodemographic factors in air pollution health disparities;
- Understanding how diet modifies responses to air pollution;
- Evaluating long-term lifestyle and chronic disease effects on air pollution-induced respiratory and cardiovascular responses
A multi-disciplinary team of investigators is coordinating epidemiological, human observational, and basic toxicological research to assess the effects of air pollution in at-risk populations and develop strategies to protect these populations, particularly those with pre-existing disease. The results from these products will improve risk assessments by clarifying the role of modifying factors such as psychosocial stress (e.g. noise) and diet, and determining the impact of individual susceptibility on the relationship between air pollutant exposures and health.
Related Links
- Healthy Heart Research
- Integrated Science Assessments
- Criteria Air Pollutants

People can experience exposure to varying concentrations of air pollution. Poor air quality can impact individuals for a short period of time during the day, or more frequently during a given day. Exposure to pollutants can also occur over multiple days, weeks or months due to seasonal air pollution, such as increased ozone during the summer or particulate matter from woodstoves during the winter.
The health impact of air pollution exposure depends on the duration and concentrations, and the health status of the affected populations. Studies are needed to increase knowledge of the exposure duration and the possible cumulative increase in risk.
The research is focused on three main areas:
- Short-term peak exposures, such as wildfires, traffic-related sources, or other episodic events;
- Intermittent and cumulative exposures;
- Mechanisms underlying the exposure risks
Researchers are evaluating the health responses of intermittent multiple days versus one-day air pollution exposure in controlled human exposure, animal, and in vitro models and associated cellular and molecular mechanisms. They are employing population-based models and electronic health records to assess the health effects of short-term and long-term exposures and identifying populations at greatest risk of health effects. The work is improving our understanding of the possible cumulative effects of multiple short-term peak exposures and the relationship of these exposures to longer-term exposures and risks.
Multipollutant Exposures and Changes in Environmental Conditions

EPA research is providing information to understand how individuals may respond to two or more pollutants or mixtures and how environmental conditions may impact air quality. While risk estimates for exposure to individual criteria air pollutants such as PM and ozone are well established, the acute and cumulative effects of combinations of pollutants is not well understood. In addition, research is needed to determine how changes in the environment affect both pollutant formation and subsequent responsiveness to exposures in healthy and susceptible individuals.
The research is focused on three specific questions:
- What is the role of temperature and photochemical aging on the health impact of wildfire smoke and air pollution mixtures?
- What is the effect of changing environmental conditions (i.e., temperature and humidity) on responsiveness to air pollution?
- Does prior pollutant exposure modify responsiveness to subsequent exposures?
The integrated, multi-disciplinary research includes:
- Epidemiologic analyses of environmental influences on morbidity and mortality in populations,
- Simulations of changing environmental conditions in multi-pollutant formation in atmospheric chamber studies coupled with clinical and toxicological assessments in healthy and at-risk populations,
- Evaluation of pre-exposure as a modifying effect on subsequent exposures
The results are revealing how changes in environmental conditions affect pollutant formation and subsequent health impact in at-risk populations. The research findings are informing EPA’s Integrated Science Assessments for criteria air pollutants and assisting with future regulatory decisions on the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS).
Leveraging Big Data for Innovations in Health Science

EPA is at the cutting edge of health science, using electronic health records, novel data systems, tissue-like advanced cellular models, molecular approaches, and animal models to evaluate the health impacts of air pollution. Researchers are using these powerful new techniques to identify factors that may increase sensitivity and vulnerability to air pollution effects.
The research is building capacity for future risk assessment and regulatory analyses that go beyond traditional lines of evidence to more clearly define populations and lifestages at increased risk of health effects from air pollution.
To continue to protect public health from poor air quality, researchers must consider new epidemiological, toxicological and clinical approaches to understand the health risks of poor air quality and the biological mechanisms responsible for these risks. At the center of these new research approaches is an explosion of data availability and methodological approaches for handling large clinical and molecular datasets, also known as "big data."
While data of increasing size, depth, and complexity have accelerated research for many industries and scientific fields, big data is sometimes less recognized for the impacts it is having on environmental health studies. Increasingly, researchers are able to examine vulnerable populations with unprecedented precision and detail while also evaluating hundreds of thousands of molecular biomarkers in order to understand biological mechanisms associated with exposure.
- Development of the InTelligence And Machine LEarning (TAME) Toolkit for Introductory Data Science, Chemical-Biological Analyses, Predictive Modeling, and Database Mining for Environmental Health Research (Journal Article)

Larger and more intense wildfires are creating the potential for greater smoke production and chronic exposures in the United States, particularly in the West. Wildfires increase air pollution in surrounding areas and can affect regional air quality.
The health effects of wildfire smoke can range from eye and respiratory tract irritation to more serious disorders, including reduced lung function, exacerbation of asthma and heart failure, and premature death. Children, pregnant women, and the elderly are especially vulnerable to smoke exposure. Emissions from wildfires are known to cause increased visits to hospitals and clinics by those exposed to smoke.
It is important to more fully understand the human health effects associated with short- and long-term exposures to smoke from wildfires as well as prescribed fires, together referred to as wildland fires. EPA is conducting research to advance understanding of the health effects from different types of fires as well as combustion phases. Researchers want to know:
- What is the full extent of health effects from smoke exposure?
- Who is most at risk?
- Are there differences in health effects from different wildfire fuel types or combustion phases (burning versus flaming)?
- What strategies and approaches are most effective in protecting public health?
- What are the environmental, social and economic impacts of wildfire emissions?
- Wildland Fire Research
- Smoke-Ready Toolbox for Wildfires
- Smoke Sense Project and App

Many communities throughout the United States face challenges in providing advice to residents about how best to protect their health when they are exposed to elevated concentrations of air pollutants from motor vehicle and industrial emissions and other sources of combustion, including wildland fire smoke.
Researchers are studying intervention strategies to reduce the health impacts from exposure to air pollution as well as ways to effectively communicate these health risks. To translate the science for use in public health communication and community empowerment, EPA is collaborating with other federal agencies, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), and state and local agencies and tribes. The objectives are to identify ways to lower air pollution exposure or mitigate the biological responses at individual, community or ecosystem levels, and ultimately evaluate whether such interventions have benefits as measured by indicators of health, well-being or economics.
Studies are evaluating the interactions between behavior and social and economic factors to more thoroughly understand how these factors may influence health and well-being outcomes, which can inform effective and consistent health risk messaging.
- Healthy Heart Toolkit and Research
- Video: Air Quality Impacts on Public Health

EPA sets National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for six principal criteria air pollutants —nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone and lead—all of which have been shown to be harmful to public health and the environment.
The Agency’s Integrated Science Assessments (ISAs) form the scientific foundation for the review of the NAAQS standards by providing the primary (human health-based) assessments and secondary (welfare-based, e.g. ecology, visibility, materials) assessments. The ISAs are assessments of the state of the science on the criteria pollutants. They are conducted as mandated under the Clean Air Act.
- Air Research Home
- Air Monitoring & Emissions
- Air Quality Modeling
- Wildland Fires
- Health Effects from Air Pollution
- Air & Energy
- Outreach, Tools & Resources
Advertisement
Understanding of environmental pollution and its anthropogenic impacts on biological resources during the COVID-19 period
- Resilient and Sustainable Water Management in Agriculture
- Published: 29 December 2022
Cite this article

- Jiban Kumar Behera 1 ,
- Pabitra Mishra 1 ,
- Anway Kumar Jena 1 ,
- Manojit Bhattacharya 1 &
- Bhaskar Behera 2
2642 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The global outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic has given rise to a significant health emergency to adverse impact on environment, and human society. The COVID-19 post-pandemic not only affects human beings but also creates pollution crisis in environment. The post-pandemic situation has shown a drastic change in nature due to biomedical waste load and other components. The inadequate segregation of untreated healthcare wastes, chemical disinfectants, and single-use plastics leads to contamination of the water, air, and agricultural fields. These materials allow the growth of disease-causing agents and transmission. Particularly, the COVID-19 outbreak has posed a severe environmental and health concern in many developing countries for infectious waste. In 2030, plastic enhances a transboundary menace to natural ecological communities and public health. This review provides a complete overview of the COVID-19 pandemic on environmental pollution and its anthropogenic impacts to public health and natural ecosystem considering short- and long-term scenarios. The review thoroughly assesses the impacts on ecosystem in the terrestrial, marine, and atmospheric realms. The information from this evaluation can be utilized to assess the short-term and long-term solutions for minimizing any unfavorable effects. Especially, this topic focuses on the excessive use of plastics and their products, subsequently with the involvement of the scientific community, and policymakers will develop the proper management plan for the upcoming generation. This article also provides crucial research gap knowledge to boost national disaster preparedness in future perspectives.
Similar content being viewed by others
Plastic Impacts in Argentina: a Critical Research Review Contributing to the Global Knowledge

Megaplastics to Nanoplastics: Emerging Environmental Pollutants and Their Environmental Impacts

Role of Environmental Science in Solving the Plastic Pollution Issue
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Plastic is mostly used for packaging, equipment, and disposable and medical appliance due to its high strength and durability. Plastic has a significant role in the healthcare industry and public health security, as the COVID-19 outbreak has shown (Parashar and Hait 2021 ). The novel coronavirus creates an unprecedented and dramatic universal calamity; it is the 3rd zoonotic eruption of the twenty-first century. That disease was first reported in India in January 2020 in the state of Kerala. More than 4 crore people affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection in India up to the month of September 2022 and 5 lakhs of death cases were reported till now. The COVID-19 outbreak has given rise to a global health crisis with an adverse impact on biodiversity, as well as on the economy and human society (Tripathi et al. 2020 ). The lockdown period was declared on the 24th of March 2022 in India with 4 phases, i.e., 21 days, 19 days, 14 days, and another 14 days (Fig. 1a ). Post-COVID-19 pandemic not only affects human beings but also creates various challenges on regulations and management practices of single-used plastic pollution crisis worldwide. Even though, air pollution and environmental noise reduction have been reported during the COVID-19 pandemic because people were confined at home and followed waste management strategies (Jena and Patnaik 2021 ). Assessment of the many crucial environmental effects of the COVID-19 pandemic has grown to be a high priority for academics and research personnel all around the world. It also noted during the lockdown period that our system can readjust to its pure or virtually pristine form. The lockdown has been shown to have numerous positive benefits, providing a doable corrective action for improving the standard of various natural resources. Consequently, typical production of single-use waste products (gowns, masks, PPE kits, hand sanitizers, and gloves) from both health amenities and households lately emerged to be a waste emergency to a drastic change in nature. Inappropriate management of households and medical waste may lead to serious damage to present flora and fauna and when it is directly discharged into the ambient environment. Untreated solid or liquid waste from both medical and household can create serious concern about environmental pollution (water and soil) and can induce severe health threat that ultimately causes infectious disease like TB, cholera, other respiratory and abdominal infection, AIDS, and hepatitis (Aggarwal and Kumar 2015 ). In India, about 0.34 kg of solid waste is created per capita on daily basis. Whereas, approximately 75% of biomedical waste does not recover, 40% of waste goes to landfills, and 32% leaks out of the collection system. The COVID-19 pandemic directs as consequence of a 40% increase in the global production of biomedical waste. Remarkably, 8% of biomedical waste was generated and that changed soil quality on dumping sites. According to WHO, nearly about 85% are non-hazardous wastes which exist in the open environment. The remaining 10% may be infectious or hazardous in nature, and 5% of toxic or chemical and radioactive waste may enter into the water, air, and soil bodies. It also noted that the COVID-19 pandemic wave generates 20% of biomedical waste on any given day in India (Fig. 1a ). The global outbreak of COVID-19 increased healthcare waste production undesirably in our environment. In this critical situation of the pandemic, the number of quarantine policies has been encouraged like online shopping and home delivery for every public daily need which also eventually increases household wastes (Somani et al. 2020 ). Whereas, the disposal of general municipal wastes is not much dangerous as the biochemical wastes increase the level of pollutants in nature. The disposal of biochemical wastes needs proper treatment before being discarded as they can be potent elements to spread infections. Contact with hazardous chemicals and radioactive wastes can be responsible for carcinogenic health issues in human beings. A rapid increase of hospitalized patients in this pandemic situation has produced a huge amount of healthcare wastes (Kulkarni and Anantharama 2020 ). On the other hand, due to a lack of proper knowledge about infectious waste management practices, most of these wastes from hospitals and isolation centers are dumped in open places (Singh et al. 2020 ). Some of these wastes are directly discarded in the nearest water sources, although a sudden rise in waste due to pandemic situations is a big challenge for the local waste management authorities in every place. Dumping and burning of untreated biochemical and domestic wastes are the main reasons for pollution and infections in the locality. Heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, and mercury are one of the most dangerous elements of biochemical wastes. When they get absorbed by plants and enter the food chain, it results in deadly effects on lives. Thus, it becomes very necessary to study the harmful effect of environmental pollution and its anthropogenic impact on human beings after the pandemic situation. Therefore, awareness should be created among people and prepare us for every worse situation in the future days. The anthropogenic activities of untreated biomedical waste (BMW) have various sources like toxicity, infectious, and radioactivity. Various medical wastes are made up of single-use plastic materials and these untreated materials cause contamination and COVID-19 infection. The SARS-CoV-2 virus remains in single-used plastic and other materials for several time periods and up to several days (Nghiem et al. 2020 ). A huge number of viral tests and the admission of infected persons into hospitals or home isolation for their own safety led to a rise in the quantity of single-use plastic. Lockdowns, social exclusion, and prohibitions on public gatherings also rapidly increase the reliance on Internet purchasing, and packaging of frequently used plastics (Thakur 2021 ; Picheta 2020 ). Consequently, the amount of plastic garbage being treated is not keeping up with the daily rise in plastic product demand. Particularly in health centers, waste processing is very difficult, and not all single-used biomedical materials and packed products are managed or recycled. Subsequently, this inadequately handled biomedical plastic waste is released into the open ecosystem (Woodall et al. 2014 ). Several studies and research outputs find that the excess use of beauty products and pharmaceuticals contains antibacterial and fungicide molecules, and are progressively increased in the environment (Du et al. 2019 ). These agents are extremely toxic and create serious endocrine disruption and other neurological disorders. These substances adversely affect the aquatic flora and fauna (Capoor and Parida 2021a , b ). Numerous works of research discovered that COVID-19 waste can cause a number of ailments and may have long-term effects on daily living. It might have a serious effect on species invasion, emergence of new illnesses, eventual demise of living things, and even the ability to endanger the whole environmental system.
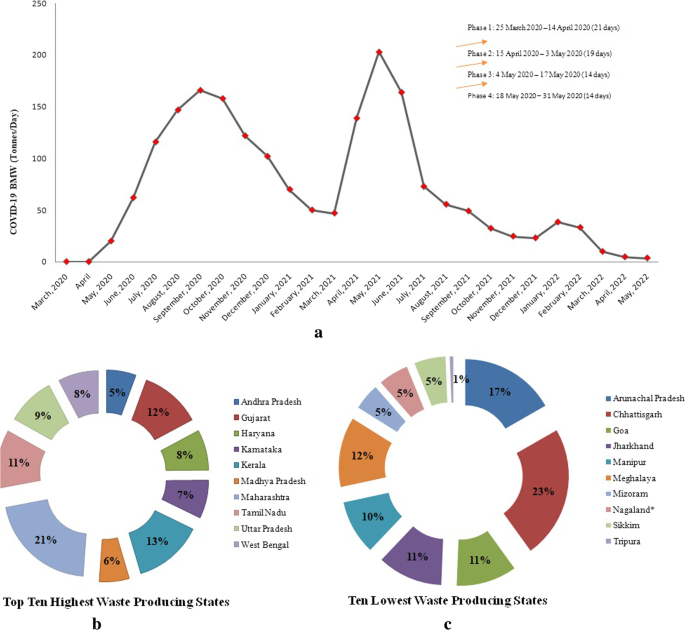
The graphical representation of COVID-19 biomedical waste generation scenario of India and its different state provinces. a Monthwise average COVID-19 biomedical waste generation in India during the period from May 2020 to March 2021 with four phases of lockdown period. b Top ten highest waste-producing states during the period from May 2020 to March 2021. c Ten lowest waste-producing states during the period from May 2020 to March 2021
While few existing studies are looking at the long-term detrimental effects of COVID-19 on the environment and other waste management practices, there are multiple investigations and articles detailing the beneficial consequences of COVID-19 on the environment. The COVID-19 immediate and long-term ramifications on the ecology, waste disposal, and health practices of human beings are covered in the current article. For upcoming initiatives and goal-specific policies, it is also crucial to assess the long-term harmful effects of COVID-19 on the ecosystem. All data analysis can also be utilized to evaluate immediate and long-term mitigation strategies against the potential negative effects of COVID-19.
Main sources’ effects on environmental pollution and anthropogenic contributions
Covid-19 waste: what is it.
Generally, biomedical waste known as infectious waste or medical waste is described as trash produced during the diagnosis, immunization, and treatment of animals or humans in research and clinical testing in hospitals as well as biological research facilities. The generated total amount of waste is 85% and the rest is hazardous waste. Some of the 10% of the waste is considered potentially dangerous waste, which includes radioactive, lethal, chemical, and sharps trash, like infectious waste (Prüss et al. 2014 ; Chand et al. 2020 ). Any trash product produced by the isolation, treatment, quarantine, and diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals is referred to as BMW during the COVID-19 epidemic. The COVID-19 patients who contaminated those wastes render contagious; otherwise, these are handled by the solid waste management rules from 2016. Between March 2020 and November 2021, the WHO analyzed about 87,000 tonnes of PPE, 140 million test kits (approximately 2600 tonnes of plastic), 731,000 l of chemical waste, and an additional 14,000 tonnes of vaccine-related waste that have been produced worldwide.
Immensity of the BMW problems worldwide
The World Health Organization (WHO) reported that a total of 24 countries have 58% facilities of proper management practices of BMW before COVID-19 (Capoor and Parida 2021a , b ). About 10,000 tonnes of extra medical waste are produced around the world, as per the WHO report. In developing countries, COVID-19 has created several major problems in BWM management due to increases in hazardous waste. During the COVID-19 infection period, China produced 247 tonnes of BMW per day; at the same time, India, Bangladesh, and the USA generated BMW was ~ 101 metric tonnes, 2.5 million tonnes, and 206 tonnes per day respectively (Singh et al. 2020 ; Rahman et al. 2020 ; Dehal et al. 2022 ). According to National Green Tribunal, the capital of India increases daily by 11% of COVID-19 BMW than pre-COVID-19 period. However, during the pandemic period, BMW production increases 5 times within the healthcare system worldwide (WHO 2020a , b ).
At the time of the COVID-19 outbreak worldwide, the frontline worker utilizes around 89 million masks, 1.59 million face shields, 30 million gowns, and 76 million gloves each month. According to the WHO, 40% of protective care was produced during the initial stages of the epidemic. From June to July 2020, this equipment steadily rose from 5.5 to 50.4 million (Haque et al. 2021 ). Due to the enormous demand for protective gear, China has offered 150 nations and 7 international organizations 1.73 billion protective garments and 17.9 billion masks through the month of October 2020 (Table 1 ) ( https://www.ebmg.online/plastics ). Regrettably, the epidemic causes a significant amount of microplastic garbage to be produced daily. The presence of plastic in freshwater, marine water, and soil habitats poses a significant threat to our ecosystem and public health aspects. In the pandemic period in India, about 7.3 lakh tonnes are hospital waste, 26,787 tonnes are test kits, 5 lakh tonnes are face masks, of which 4 lakh tonnes are medical masks, and the remaining 1 lakh tonnes are N95 and express delivery packaging plastics, which is equivalent to about 3 lakh tonnes of BMW. The details of such produced BMW are listed in Table 1 .
The situation with plastic trash linked to COVID-19 epidemic
Population and the total number of confirmed COVID-19 cases data were collected from 30 districts of the state of Odisha, India (data source: https://statedashboard.odisha.gov.in/ ). Additionally, the baseline information about the total population in each district and the percentage of the urban population was collected (data source: https://www.populationu.com/in/odisha-population ). This model has used a spatial variation of the pandemic in different countries. These crucial data are important to evaluate the post-COVID-19-related various waste generation in Odisha state, India (Table 2 ).
Medical waste estimation
In low- and high-income areas, 0.2 and 0.5 kg/day of hazardous biomedical waste are produced each day, respectively, according to World Health Organization (WHO). Odisha reflects a yearly biomedical waste growth rate of more than 7%, and by 2021, it is predicted that the state’s daily biomedical waste production might reach 6.65 metric tonnes (Das et al. 2020 ). The most BMWs were produced in different states like Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal between May 2020 and March 2021 (Fig. 1b ). Moreover, the Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Jharkhand, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura are the states having with the lowest BMW generation (Fig. 1c ). However, Delhi generates more than 2978 tons of BMW rather the other union territory regions’ combined condition (Fig. 2 ). The average waste created per individual bed and the numbers of infected individuals are directly related to the amount of medical waste produced in diverse locations. For example, in Odisha state, there are 9274 beds in 56 hospitals, 7251 beds in quarantine camps or COVID-19 centers, a total of 31 RT-PCR testing laboratories, all Community Health Center (CHC) and Primary Health Care (PHC) collection sites, and 36 TrueNAT testing labs responsible for the generation of COVID-19 waste materials (Fig. 3 ). Our current study assesses the BWM production, collection, and scientific management on a daily basis during the COVID-19 pandemic in 30 districts of Odisha state. Because of this, the predicted values for BMW in numerous cities in Odisha showed the yearly average value per day has climbed from 0.3 kg/bed/day in 2019 to 1.6 kg/bed/day in 2021 (Goswami et al. 2021 ). A significant partial correlation exists between the SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals and the average output of BMW in Odisha during the COVID-19 pandemic period. Khordha district of Odisha state is the place where the maximum BMWs are produced, and Deogharh is where 14.03 tons of single-use products is produced in daily basis (Fig. 4 ) (Table 3 ). As a result, when evaluating the medical waste, the earlier studies estimated BMW of 1.6 kg/bed/day during the COVID-19 period and was given more focus (Sangkham 2020 ; Saxena et al. 2021 ).
where M w = medical waste (tons/day), N cc = number of COVID-19 cases (infected persons), and M wgr = medical waste generation rate, that is, 1.6 kg/bed/day.
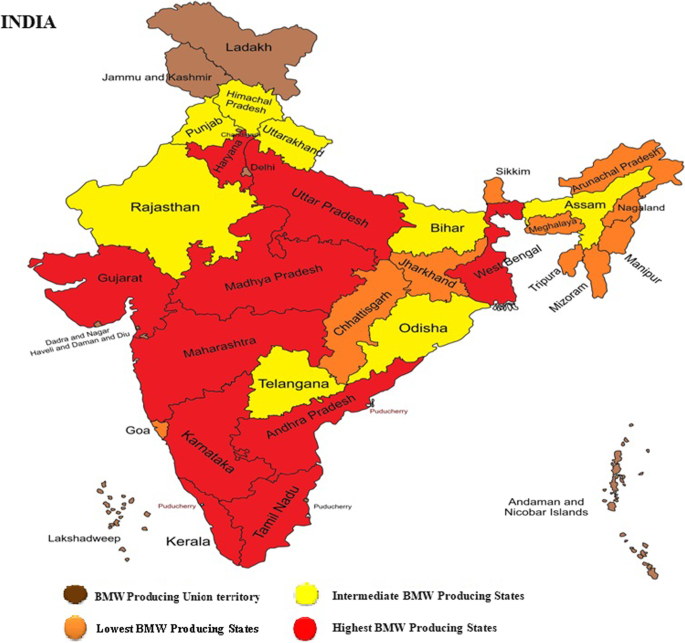
State and union territory categories by generation of COVID-19 biomedical waste during the period from May 2020 to March 2021
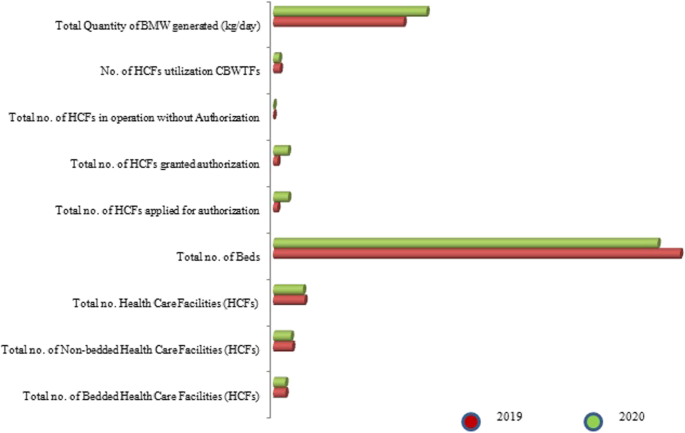
Annual report information on the management of biomedical waste in Odisha in 2019 and 2020
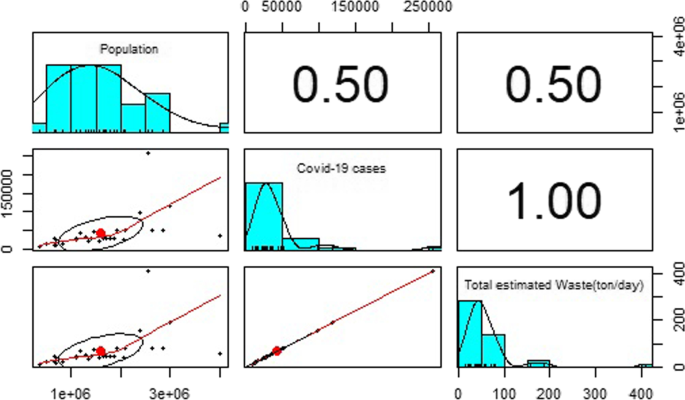
Correlation plot showing the total estimated waste product in tons per day directly depended on confirmed case with total population of Odisha, India, during the COVID-19 outbreak
Using the weblink ( https://statedashboard.odisha.gov.in ), you may view the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases throughout numerous districts in the Odisha area, as well as the infected individuals receiving medical treatment or home quarantine, along with the individuals who have passed away after contracting the COVID-19.
Short- and long-term impacts of the pandemic period on environment
Both positive and negative effects impacted the global environment and climate disruption caused by COVID-19. Several researchers confirmed that levels of air quality gases of NO 2 , CO, SO 2 , NOx, PM2.5, VOCs, and water quality index improved worldwide during the pandemic period (Yunus et al. 2020 ). Furthermore, due to movement restrictions of the people and slow social and economic activities, the quality of water has improved in several urban and rural areas, with improved air quality in different parts of India (Selvam et al. 2020 ). However, a huge amount of BMW generation shows negative impacts on biodiversity.
COVID-19 pandemic environmental benefits: a near-term reality
Reduction of air pollution and ghg emission.
Unlike before COVID-19, air quality analysis decreased throughout the lockdown period. Industries, businesses, and transportation mechanisms also contributed to a sharp decline in air pollutants and other greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions during nationwide lockdowns. There has been a roughly 50% decrease in CO and N 2 O enhanced the O 2 level by 16–48% in India because power plant operations have been partially shut down (Biswal et al. 2020 ; Selvam et al. 2020 ). Throughout the lockdown period, air pollutions fall down and were reported by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in various parts of the industrialized state of Gujarat, India. The concentration level of PM2.5 plummeted by 38–78%; subsequently, the PM10 level decreased in the range of 32–80% than before the lockdown, respectively (Lokhandwala and Gautam 2020 ). One of the key gases of NO 2 emission has been reduced by 70% in the capital of India, which is emitted from the burning of fossil fuels (Ghosh 2020 ). The level of NO 2 , PM10, and PM2.5 was reduced by 46–50% during the nationwide lockdown in the entire Odisha (IEP 2020 ; Thiessen 2020 ; Mekonnen and Aragaw 2021 ). Correspondingly, 72% and 11% of key contributors in transport sectors are vehicles and aviation which emit GHG gases. According to IEA, 7% of CO 2 emission has been reduced during the COVID-19 pandemic (Henriques 2020 ; IEA 2020 ).
Reduction of water pollution
In Odisha, water pollution is a common case, where industrial and domestic wastes are dumped into the sea and rivers. During the lockdown period, the export and import businesses have stopped and a sudden drop in sewage and industrial effluents caused reduction of the pollution load in rivers and marine water (Yunus et al. 2020 ).
Reduction of noise pollution
Noise pollution adversely affects living organisms due to undesired human activities like machines, vehicles, and construction sites. Due to noise pollution, nearly about 360 million people are affected by hearing loss worldwide. During this pandemic, travel and vehicular restrictions have considerably changed the level of noise pollution in Delhi City of India around 50–60 dB, out of 100 dB (Gandhiok and Ibrar 2020 ; Somani et al. 2020 ).
The closure of numerous industrial and commercial operations that rely on fossil fuels resulted in a notable decrease in GHG emissions, VOCs, and other particulate matter. The bulk of global investigations has shown that the air, water, and noise quality significantly improved during the shutdown conditions. The worldwide lockdown had a huge influence on the energy supply, which resulted in lowering of GHG emissions and noticeable reductions in energy usages. The findings unequivocally demonstrated the long-term positive effects on the potential for global warming. Decreased demand for all fossil fuel–related energy sources and heavily relying on other renewable resources are also essential needs.
Environmental consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic: a terrifying trip
Issues with the handling of uprising biomedical waste.
The current BMW collection and recycling infrastructure is under a lot of stress, which has resulted in inefficient waste reduction techniques like portable incinerations and open-air disposal of single-use plastics; these are also crucial factors for the safety of frontline workers (Basu and Basu 2021 ). In the face of mounting concern, the manufacturing line for single-use plastics is working to seize the moment and revitalize a once-thriving but now failing sector (Mousazadeh et al. 2021 ). Currently, many supermarkets prohibited customers from bringing their own cloth bags because they worry people might decide to buy their things in single-use plastic packaging substitutes. Additionally, a rise in online food orders has contributed to an increase in plastic consumption per person, illustrating how the COVID-19 pandemic has intensified environmental harm on a worldwide basis. As a result, there has been undoubtedly a large increase in the use of plastics, which will aggravate the leakage of microplastics into the environment. The use of plastic has increased dramatically (40%), as have other applications (17%), such as medical equipment and other associated ones. During COVID-19, the generation of BMW suddenly increased all over the world, which is considered an important threat to public health and biodiversity. In COVID-19, the BMW is generated from infected people, sample collection site, and diagnosis centers (Zambrano-Monserrate et al. 2020 ). In India, during the 1st lockdown period, medical waste has increased from 550 to 600 kg/day to around 1000 kg/day. Science COVID-19, the production of single-use plastic is increased globally. It is reported that about 14,607,834 face masks are used and a large number of BMW are produced during the COVID-19 period in Odisha; for a long period, these masks release dioxin and various toxic elements that pollute land and water ecosystem (Selvam et al. 2020 ).
The concerning issues of microplastic contamination in our environment have grown significantly. These are typically located in natural settings. In addition, individuals are utterly dependent on plastic and its other form (microplastic) produced by numerous events of pandemics (Oyedotun et al. 2020 ). Microplastic has a higher COVID-19 viral persistence rate than other materials. Therefore, it has been suggested that a potential source of microplastic in the surroundings is single-use plastic-based protective gear (Knowlton 2020 ; Sridharan et al. 2021 ). The N-95 masks are erected by polypropylene, whereas Tyvek is used to make the safety gloves and face shields. Dioxin was released into the surroundings by such two microplastics (Wang et al. 2021a , b ). Polypropylene fibers make up the bulk of the microplastic released from different types of face masks (Chen et al. 2021 ). Organic waste and household protective equipment are also responsible for spreading several viral infections to regular people. Due to the absorption of heavy metals and organic contaminants by the natural environment, microplastics have a significant role to hinder this phenomenon. These microplastics affect the endocrine system and are considered harmful. By 2025, it is predicted that there will be 250 million metric tons of microplastic in marine waste worldwide (Jambeck et al. 2015 ; Ye et al. 2020 ).
Impact of biomedical waste on water
As COVID-19 spreads very rapidly because of close contact from one individual to another, more production of personal healthcare equipment is necessary to stop the harmful impact of biomedical waste on water. Dumping of healthcare wastes without proper treatment measures not only affects soil but also affects the groundwater level of that particular site as liquid toxic pollutants leach out and get mixed with groundwater. From hospitals to COVID care centers, direct disposal of medical wastes into the nearest pond or river has been noticed worldwide during the COVID-19 pandemic situation (Aggarwal and Kumar 2015 ). The toxic metals of these wastes alter the biology of water, which has a number of negative impacts on the water ecosystem. Plastic wastes in water bodies harm aquatic lives which eventually affects human beings. Additionally, this polluted water can spread infections very rapidly in the nearby locality. Research laboratories release various non-biodegradable chemical and radioactive elements in liquid form having carcinogenic effects on human health (Patil and Pokhrel 2005 ). In contact with air or water, the antibacterial substances (triclocarban and triclosan) found in laundry and cleaning products also create a protective surface layer. These contaminants have an adverse effect on both the habitats of humans and marine life (Ion et al. 2019 ). Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine are released into the water system in huge amounts, which has significant ecotoxicological effects on living things (Kuroda et al. 2021 ). The components of the environment interact with one another. Handwashing soap contains bisphenol A (BPA), which has several negative impacts on soil and water quality. BPA has been shown to affect the endocrine system in a number of different organ systems in laboratory experiments (Dodson et al. 2012 ; Kim et al. 2021 ).
All major rivers of Odisha link up with the Bay of Bengal, in the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Inadequately treated water released microplastics into these waterways, finally transferring microplastic into the Indian Ocean. The basic water qualities were analyzed throughout pre-COVID, COVID, and post-COVID periods like temperature of water, pH, DO, BOD, COD, TC, and FC, which have been shrivelled. During the COVID period, the TC and FC variables of the Bay of Bengal are relatively high than the pre- and post-COVID pandemic at the Paradeep region of Odisha (Fig. 5a ). Principal component analysis (PCA) of the fundamental water quality indicators such as water temperature, pH, DO, BOD, COD, TC, and FC of three important lakes, i.e., Anshupa, Chilka, and Tampara, has been inspected. Tampara Lake has higher peak metrics in the pre-COVID period (Fig. 5b ). The DO, TC, FC, and COD are peak in Chilka Lake but only BOD more in Tampara during the pandemic period (Fig. 5c ). Throughout post-COVID, TC and FC are high in Anshupa Lake, BOD, and COD is high in Tampara Lake (Fig. 5d ). Unlikely, the pH and water temperature are always showed elevated in Chilka. The major rivers in Odisha are the Mahanadi, Subarnarekha, Brahmani, Baitarani, Budhabalanga, and Rushikuly. The basic water quality parameters of these rivers were analyzed in-between pre-COVID, COVID, and post-COVID, and these parameters are water temperature, pH, DO, BOD, COD, TC, and FC, which have been consistently investigated. In pre-COVID time, the TC, FC, and BOD parameters are unsatisfactory in Mahanadi, Brahmani, Budhabalanga, and Rushikuly than other two rivers (Fig. 6 ). On the other hand, the TC and FC levels are high in Mahanadi, and only BOD and TC are unsatisfactory in Brahmani during the pandemic period (Fig. 6 ). Throughout the post-COVID, BOD, TC, and FC water quality parameters are higher in Mahanadi and Brahmani than in other rivers (Fig. 6 ). Unlikely, all these water parameter concentrations will increase in the future days due to the rise of single-use plastics.
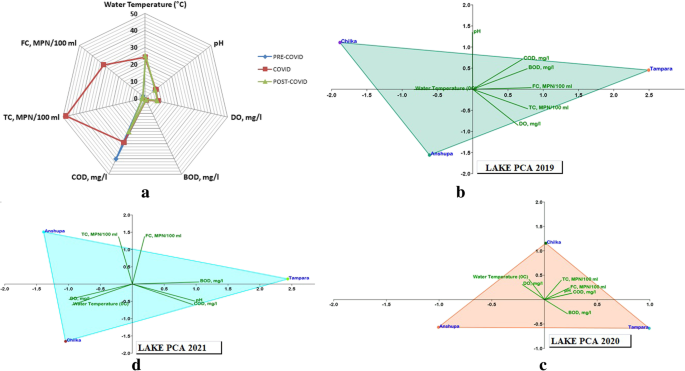
Water quality assessment plots during pre-COVID, COVID, and post-COVID phases at three significant lakes of Odisha state, India. a The Bay of Bengal’s paradeep coast’s water temperature, pH, DO, BOD, COD, and TC are the primary water quality variables examined during pre-COVID, COVID, and post-COVID. b Anshupa, Chilka, and Tampara, three significant lakes were studied using principal component analysis (PCA) of basic water quality indicators such as water temperature, pH, DO, BOD, COD, TC, and FC at pre-COVID phase, c COVID phase, and d post-COVID phase (data source: http://ospcboard.org/environmental-monitoring-data/ )
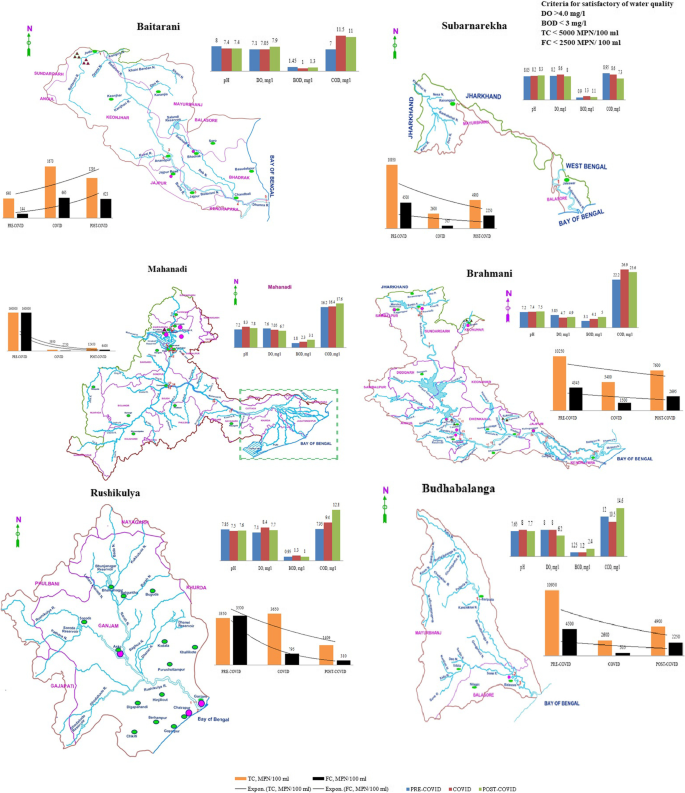
Pre- and post-pandemic COVID-19 outbreak variations in physicochemical parameters, such as pH, DO, BOD, COD, TC, and FC concentration, were seen along the major rivers in Odisha, including the Mahanadi, Subarnarekha, Brahmani, Baitarani, and Rushikuly (data source: http://ospcboard.org/environmental-monitoring-data/ )
Biomedical waste’s effects on soil
According to the WHO, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, acetylsalicylate, and diclofenac, were utilized in pandemic outbreaks, while furosemide has been recommended for SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals (Brennecke et al. 2020 ; WHO 2020a , b ). Solid waste management during pandemic situations especially during the COVID-19 outbreak has been a great challenge for many developing countries. The global pandemic has reported the dumping of an unusual amount of contaminated PPE kits, masks, and gloves by healthcare workers. Numerous other wastes from the isolation wards near the municipal dumping sites have also been reported (Jena and Patnaik 2021 ). It not only changes the soil quality of that site but also becomes an unhygienic place for citizens. Improper disposal of medicines and patients’ urine and feces during the treatment process not only infects the soil but also creates a nasty environment to the atmosphere (Shah et al. 2001 ). Alcohol-based products like hand sanitizers harm aquatic life when discharged into the environment. In addition, it affects groundwater indirectly through the soil. The soil and water ecology is impacted by triclosan, hydroxychloroquine, triclosan, and triclocarban. The anti-inflammatory medications also have an impact, exacerbating the negative effects of COVID-19 (Selvaranjan et al. 2021 ).
One-third of the ecosystem’s components are made up of plastic garbages, and soil by which it enters the initial habitat (de Souza Machado et al. 2018 ). Numerous types of microplastics exist in the terrestrial ecosystems’ soil, including agricultural systems, food plains, forests, and sands. These microplastics can come from various sources, including landfills, sewage sludge, composts, and wastewater-irrigation systems (Kumar et al. 2020 ; Scheurer and Bigalke 2018 ; Ng et al. 2021 ; Wang et al. 2020 ). Plastic garbage may modify the permeability and water-holding capacity of the soil and impair its bulk density and structural integrity (de Souza Machado et al. 2018 ; Wan et al. 2019 ). Additionally, it also affects various chemical and physical characteristics, such as enzyme activity and hydrogen ion concentration (Fei et al. 2020 ; Boots et al. 2019 ). The carbon, phosphorus, and nitrogen cycles in soil are crucial to the soil’s fertility and nutrients; it may also be impacted by COVID-19 waste (Zhang et al. 2019 ). The microplastic-containing harmful chemical sinks may modify the soil’s physicochemical qualities, bioavailability, and biodiversity as well as its mobility and adsorption capacity (Hüffer et al. 2019 ). The adsorption of microplastic by soil microorganisms and microbial communities may influence the possible dangers to both humans and animals (Zhang et al. 2019 ; Imran et al. 2019 ). There is still more research needed to access the possible effects and ecological concerns on terrestrial ecosystems of the interaction between protective equipment-associated microplastics and the COVID-19 virus in soils and waters.
Exposure and hazardous gas emissions during incineration
As biochemical wastes contain many infectious agents as well as hazardous chemical elements, improper disposal of this waste can lead to fatal effects on society. Open flaming of biochemical wastes produces injurious gases such as fly ash, carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), and other toxic flue gases. These not only pollute our environment but also cause many respiratory and skin diseases. Exposure to dioxins and mercury emitted by the burning of plastic and other medical wastes leads to hormonal misbalance and reproductive and developmental problems in living animals. Moreover, the increased atmospheric carbon dioxide ultimately affects global climate change and the food chain process (Manzoor and Sharma 2019 ).
Impacts of microplastics on the atmosphere
COVID-19, at first glance, reduces greenhouse gas emissions and enhances air quality. On the other hand, as plastic waste pollution rises over time, a hidden catastrophe will be the real cause of increasing worldwide GHG emissions. Plastic garbage is responsible for 850 million metric tons of annual GHG emissions, which will rise to 56 billion tons by 2050. The single-use protective plastic emits 0.05 kg of CO 2 when shipping is not included, whereas the shipping emits 0.059 kg of CO 2 gas. The washing of single-use plastic contributed to the 0.36 kg of CO 2 that was released (Klemeš et al. 2020 ; Silva et al. 2021 ). Additionally, dangerous substances like dioxins and furans can be released during landfalls and the combustion of garbage from protective equipment, which can pollute the atmosphere (Vanapalli et al. 2021 ). Recent research has discovered that the protective gear can also fracture and linger in the air as microplastics (Zhang et al. 2021 ). As a result, the atmosphere plays a crucial role in the cycle of microplastics related to safety gear and contributes to the spreading of microplastics in various contexts. Additionally, the atmosphere contributes to producing protective gear made up of plastic through the microplastic cycle, and microplastic wastes degrade air quality, impact the climate, and absorb associated dangerous substances.
Effects of COVID-19 on energy sources
In the energy sector, the COVID-19 epidemic has caused serious problems. Coal accounts for around 40% of the electric energy produced by the major fuels globally. China, India, and Australia together generate 70% of the world’s coal. About 8.1 billion tons of coal were produced year by 2019; however, during the pandemic, that quantity fell sharply to only 40,000 metric tons in 2020 (Rizou et al. 2020 ; Mousazadeh et al. 2021 ). Similarly to this, during the initial lockdown period, world oil consumption declines by around 5% (Atolani et al. 2020 ). Consequently, there has been a significant lowering in the global use of power. Reducing air pollution due to lower NO 2 production during COVID-19 leads to less electricity usage, which enhances the environment’s well-being (Lian et al. 2020 ).
Animal and aquatic life’s response to microplastics
Different detergents are released into water sources, creating foam. Some aquatic plants, including Potamogeton and Ranunculus aquatilis , cannot survive in a detergent level of 2.5 ppm (Kumar et al. 2021 ). In soils, harmful compounds build up and deteriorate the quality of the soil texture. Numerous aquatic ecosystems and biota are harmed by domestic water. The plasma of marine fish and some marine organisms has been found to include certain newly developed medicinal compounds (Vasquez et al. 2014 ). Ibuprofen, an anti-inflammatory drug, has been linked to substantial, long-lasting harmful effects on aquatic creature reproduction (De Girolamo et al. 2020 ; Carlsson et al. 2006 ).
Without any doubt, the COVID-19 epidemic causes water pollution around the planet. Low-density polymers in polystyrene and polypropylene cause them to float in seawater whereas high-density polymers such as polyethylene terephthalate, polyvinyl chloride, and polyvinyl alcohol readily sink on the bottom (De-la-Torre and Aragaw 2021 ). Therefore, key threats to its biodiversity are acidification of saltwater and microplastic degradation of the environment. Every year, seas are getting between 57,000 and 265,000 million metric tons of microplastic trash. In recent years, microplastics have been discovered in the groundwater, rivers, and lakes of India (Selvam et al. 2021 ).
Numerous studies have shown that face mask pollution impacted animals. However, the animal population and its habitat dramatically grew throughout the lockdown period. Conversely, inappropriate disposal of single-use plastics puts animals at the risk of suffocation and death by ingestion, trapping, and entanglement (Fig. 7a ). Researchers also discovered that single-use plastic has an immediate and long-term impact on animal health, resulting in body deterioration, mobility issues that limit the feeding activity, changes in physiological blood parameters, strangulations, and considerable amount of reduction in biodiversity (Seif et al. 2018 ; Lavers et al. 2019 ). Consumption of microplastics can occasionally have an adverse impact on the animal’s ability to reproduce and their nutritional needs (Tavares et al. 2016 ; Thompson et al. 2020 ). Microplastics interact with intestinal-active microorganisms, reducing mucus outputs and causing dysbiosis (Wang et al. 2021a , b ). Microplastics may accumulate by organisms and move up the food chain from lower biota to higher consumers, making food sources the most important way to enter the body of animals. According to experts, at least one microplastic is accumulated by 67% of sharks (Parton et al. 2020 ). COVID-19 face mask–released elements (exposure polymers) inhibit the development and reproduction of young earthworms. The adult earthworms’ spermatogenesis and intracellular esterase activities were similarly inhibited. The animal body’s tissue and cellular levels can be negatively impacted by microplastic (Kwak and An 2021 ). As a result of their additive and synergistic effects, the chemical pollutants connected to microplastics can have more severe impacts that ultimately damage different animal systems (Roda et al. 2020 ). In general, the COVID-19 protective gears cause harm to exposure adjacent animals by trapping, entanglement, and ingestion.
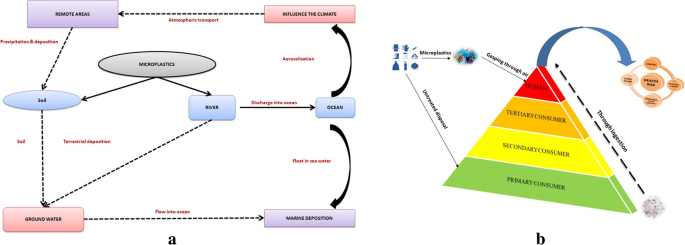
The conceptual model of microplastic impacts in natural environment condition. a The cycle of plastic and microplastic is produced from protective equipment. Discarded protective gear causes a microplastic cycle and large accumulation of plastics and microplastics in many ecosystems, contaminating the aquatic, terrestrial, and atmosphere. b Possible health issues brought on by personal protective pollution. Humans can be exposed to the protective suits linked to nanoplastics by consumption and breathing, which can cause illnesses in various ways
Impact of microplastics on human
Understanding the harm to human health posed by COVID-19 protective equipment linked with plastics and microplastics presents significant hurdles due to the paucity of research on adsorption properties and toxicological assessment of contaminated components. There is proof that airborne viruses or respiratory droplets from patients can be directly deposited onto personal protective equipment and stay active for more than 72 h. In 2018, many researchers discovered microplastics for the first time in the human lungs, spleen, kidneys, and liver. Microplastic is ingested into the colon and placenta of humans (Ragusa et al. 2021 ). With commercial marine and freshwater species, edible fruits and vegetables, consumption of soft drinks, drinking of water, and commercial marine as well as freshwater species, the concentration of microplastics consumed in the human body rises possessively. On average, 0.1 to 5 g of microplastics may enter bodies every week globally (Senathirajah et al. 2021 ). Some researchers noted that presently human blood samples contain 1.6 g/ml of plastic particles (Leslie et al. 2022 ). Top consumers have a higher concentration of microplastics than lower tropic levels, making them more riskier (Fig. 7b ) (Carbery et al. 2018 ). The intestinal function is destroyed by the oxidative stress and inflammation brought on by the interaction of microplastics with the gut floor (Huang et al. 2021 ). Inflammation promotes cell death, epithelial barrier degradation causes cardiovascular illnesses, diabetes, and cancers, and airborne microplastics can harm and cause oxidative stress (Dong et al. 2020 ; Prata 2018 ; Yang et al. 2021 ) (Fig. 7b ). Therefore, more scientific research should be required to establish that protective gear made of microplastic may certainly absorb viruses but shows as the potential contaminant source.
Concluding thoughts, future vision, and perspectives
This article emphasized the relationship between hazards to those, directly and indirectly, connected to this profession, poor and non-scientific handling of biological waste materials. The COVID-19 epidemic has unprecedentedly impacted the environment, human life, and the global economy. The COVID-19 pandemic could provide short-term advantages for the natural environment. However, the long-term environmental problems brought on by this viral pandemic might have enduring impacts and provide difficulties for all nations. Due to the widespread use of anti-microbial hand sanitizers, disinfectants, and pharmaceuticals, including triclocarban, triclosan, and hydroxychloroquine, dangerous emergent pollutants such as COVID-19 have also had a severe impact on the water qualities and soil ecology. In addition, after the COVID-19 incident, the amount of plastic garbage has increased dramatically. Protective gear can lower the chance of contracting the COVID-19 virus during the pandemic, but repeated usage and inappropriate discarding make the polymer issue in severe condition. It poses significant risks to aquatic life and people by being a significant source of microplastic discharge and build-up in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Presently, not only is too much plastic garbage damaging the marine and terrestrial environments, but it will also eventually break down into tiny plastics called microplastic and nanoscale plastic. Even more severe, irrevocable harm to both people and the environment can be brought on by these micro- and nanoscale plastics. People should be mindful of the long-term effects of plastic consumption and disposal since the COVID-19 epidemic has worsened the plastic pollution situation. According to our condensed statistics and speculative estimation, the COVID-19 epidemic has caused to gear up a tremendous amount of plastic to be produced globally. The present technologies cannot handle the plastic overload situation; hence, innovative methods for managing plastic waste are urgently required. As a result, it is crucial to enact laws and regulations restricting plastic use and inform people on how to manage, reuse, and recycle their plastic trash. Work should be done in the future to develop backup strategies for managing plastic trash in emergency scenarios and preventing plastic pollution. Future studies should also concentrate on the destiny and transportation of micro- and nanoscale plastics since the discarded plastic eventually degrades into these sizes. Further study is necessary to understand how plastic sizes and surface characteristics affect their destiny and transport behavior. Considering the mitigation strategies, recovery of the previous environment during the COVID-19 lockdown period showed environmental degradation. Such undesired incidents are also caused by humans that might be reversible, and applied strategies should be implicated to rebuild the “accidentally positive” phenomenon. One of the best examples is the “smart green city” concept. Subsequently, steps should be taken to remove the conventional plastics with greener alternative components; adding a reliable disposal platform for PPE beyond incineration and the option of landfilling. However, it may be assumed that clustering in the surroundings will be a key factor controlling their activity and offer information on how they can be moved through the environment or eliminated in treatment facilities. That would enable more methodical management of the long-term effects of global plastic pollution. It serves as a reminder of our disregard for the environment and the consequences of human-caused climate change.
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Abbreviations
Coronavirus disease 2019
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
World Health Organization
Greenhouse gas
Dissolved oxygen
Biological oxygen demand
Chemical oxygen demand
Total concentration
International Energy Agency
Personal protective equipment
Central Pollution Control Board
Tuberculosis
Community Health Center
Primary Health Care
- Biomedical waste
Volatile organic compounds
Aggarwal H, Kumar P (2015) Need for biomedical waste management. J Med Soc 29(1):58–58
Article Google Scholar
Atolani O, Baker MT et al (2020) COVID-19: critical discussion on the applications and implications of chemicals in sanitizers and disinfectants. EXCLI J 19:785
Google Scholar
Basu A, Basu LB (2021) Questioning the green recovery: a take on Post-COVID scenario. In: Mishra M, Singh RB (eds) COVID-19 pandemic trajectory in the developing world, no 6. Springer, Singapore, pp 117–144
Biswal A, Singh T et al (2020) COVID-19 lockdown and its impact on tropospheric NO2 concentrations over India using satellite-based data. Heliyon 6(9):e04764
Boots B, Russell CW et al (2019) Effects of microplastics in soil ecosystems: above and below ground. Environ Sci Technol 53(19):11496–11506
Brennecke A, Villar L et al (2020) Is inhaled furosemide a potential therapeutic for COVID-19? Am J Med Sci 360(3):216–221
Capoor MR, Parida A (2021a) Biomedical waste and solid waste management in the time of covid-19: a comprehensive review of the national and international scenario and guidelines. J Lab Phys 13(02):175–182
Capoor MR, Parida A (2021b) Current perspectives of biomedical waste management in context of COVID-19. Indian J Med Microbiol 39(2):171–178
Carbery M, O’Connor W et al (2018) Trophic transfer of microplastics and mixed contaminants in the marine food web and implications for human health. Environ Int 115:400–409
Carlsson C, Johansson A-K et al (2006) Are pharmaceuticals potent environmental pollutants?: part I: environmental risk assessments of selected active pharmaceutical ingredients. Sci Total Environ 364(1–3):67–87
Chand S, Shastry C et al (2020) Water, sanitation, hygiene and biomedical waste disposal in the healthcare system: a review. Biomedicine 40(1):14–19
Chen X, Chen X et al (2021) Used disposable face masks are significant sources of microplastics to environment. Environ Pollut 285:117485
Das A, Garg R et al (2020) Biomedical waste management: the challenge amidst COVID-19 pandemic. J Lab Phys 12(02):161–162
De-la-Torre GE, Aragaw TA (2021) What we need to know about PPE associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 163:111879
De Girolamo L, Peretti GM et al (2020) COVID-19—the real role of NSAIDs in Italy. BioMed Central 15:1–3
de Souza Machado AA, Lau CW et al (2018) Impacts of microplastics on the soil biophysical environment. Environ Sci Technol 52(17):9656–9665
Dehal A, Vaidya AN et al (2022) Biomedical waste generation and management during COVID-19 pandemic in India: challenges and possible management strategies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(10):14830–14845
Dodson RE, Nishioka M et al (2012) Endocrine disruptors and asthma-associated chemicals in consumer products. Environ Health Perspect 120(7):935–943
Dong C-D, Chen C-W et al (2020) Polystyrene microplastic particles: in vitro pulmonary toxicity assessment. J Hazard Mater 385:121575
Du H, Shi S et al (2019) Hydrophobic-force-driven adsorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solution by polyethylene glycol diacrylate hydrogel microsphere. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(22):22362–22371
Fei Y, Huang S et al (2020) Response of soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities to the accumulation of microplastics in an acid cropped soil. Sci Total Environ 707:135634
Gandhiok J, Ibrar M (2020) “COVID-19: noise pollution falls as lockdown rings in sound of silence.” Times of India. 1–6. from https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/covid-19-noise-pollution-falls-as-lockdown-rings-in-sound-of-silence/articleshow/75309318.cms . Accessed May 23 2022
Ghosh I (2020) “The emissions impact of coronavirus lockdowns, as shown by satellites.” Visual Capitalist 21. https://www.visualcapitalist.com/coronavirus-lockdowns-emissions/ . Accessed June 12 2022
Goswami M, Goswami PJ et al (2021) Challenges and actions to the environmental management of bio-medical waste during COVID-19 pandemic in India. Heliyon 7(3):e06313
Haque MS, Sharif S et al (2021) SARS-CoV-2 pandemic-induced PPE and single-use plastic waste generation scenario. Waste Manag Res 39(1_suppl):3–17
Henriques M (2020) “Will COVID-19 have a lasting impact on the environment.” BBC news. https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20200326-covid-19-the-impact-of-coronavirus-on-the-environment . Accessed on June 24 2022
Huang Z, Weng Y et al (2021) Microplastic: a potential threat to human and animal health by interfering with the intestinal barrier function and changing the intestinal microenvironment. Sci Total Environ 785:147365
Hüffer T, Metzelder F et al (2019) Polyethylene microplastics influence the transport of organic contaminants in soil. Sci Total Environ 657:242–247
IEA (2020) “Oil market report: March 2020. The International Energy Agency, Paris, France. https://www.iea.org/reports/oil-market-report-march-2020 . Accessed on Jul 25 2022
IEP (2020) “Impact of lockdown (25th March to 15th April) on air quality.” https://www.iea.org/reports/oil-market-report-march-2020 . Accessed 13 Apr 2020
Imran M, Das KR et al (2019) Co-selection of multi-antibiotic resistance in bacterial pathogens in metal and microplastic contaminated environments: an emerging health threat. Chemosphere 215:846–857
Ion I, Ivan GR et al (2019) Adsorption of triclocarban (TCC) onto fullerene C60 in simulated environmental aqueous conditions. Sep Sci Technol 54(17):2759–2772
Jambeck JR, Geyer R et al (2015) Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 347(6223):768–771
Jena B, Patnaik S, Patnaik N, Patnaik N (2021) Impact of improper biomedical waste disposal on human health and environment during covid-19 pandemic. Eur J Mol Clin Med 8(3):4137–4143
Kim S, Gholamirad F et al (2021) Enhanced adsorption performance for selected pharmaceutical compounds by sonicated Ti3C2TX MXene. Chem Eng J 406:126789
Klemeš JJ, Van Fan Y et al (2020) The energy and environmental footprints of COVID-19 fighting measures–PPE, disinfection, supply chains. Energy 211:118701
Knowlton KU (2020) Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 induced cardiac injury from the perspective of the virus. J Mol Cell Cardiol 147:12
Kulkarni BN, Anantharama V (2020) Repercussions of COVID-19 pandemic on municipal solid waste management: challenges and opportunities. Sci Total Environ 743:140693
Kumar A, Jain V et al (2021) Environmental impact of COVID-19 pandemic: more negatives than positives. Environ Sustain 4(3):447–454
Kumar M, Xiong X et al (2020) Microplastics as pollutants in agricultural soils. Environ Pollut 265:114980
Kuroda K, Li C et al (2021) Predicted occurrence, ecotoxicological risk and environmentally acquired resistance of antiviral drugs associated with COVID-19 in environmental waters. Sci Total Environ 776:145740
Kwak JI, An Y-J (2021) Post COVID-19 pandemic: biofragmentation and soil ecotoxicological effects of microplastics derived from face masks. J Hazard Mater 416:126169
Lavers JL, Hutton I et al (2019) Clinical pathology of plastic ingestion in marine birds and relationships with blood chemistry. Environ Sci Technol 53(15):9224–9231
Leslie HA, Van Velzen MJ et al (2022) Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ Int 163:107199
Lian X, Huang J et al (2020) Impact of city lockdown on the air quality of COVID-19-hit of Wuhan city. Sci Total Environ 742:140556
Lokhandwala S, Gautam P (2020) Indirect impact of COVID-19 on environment: a brief study in Indian context. Environ Res 188:109807
Manzoor J, Sharma M (2019) Impact of biomedical waste on environment and human health. Environ Claims J 31(4):311–334
Mekonnen BA, Aragaw TA (2021) Environmental sustainability and COVID-19 pandemic: an overview review on new opportunities and challenges. In: Muthu SS (ed) COVID-19. Environmental footprints and eco-design of products and processes. Springer, Singapore, pp 117–140
Mousazadeh M, Paital B et al (2021) Positive environmental effects of the coronavirus 2020 episode: a review. Environ Dev Sustain 23(9):12738–12760
Ng EL, Lin SY et al (2021) Microplastic pollution alters forest soil microbiome. J Hazard Mater 409:124606
Nghiem LD, Morgan B et al (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic: considerations for the waste and wastewater services sector. Case Stud Chem Environ Eng 1:100006
Oyedotun TDT, Kasim OF et al (2020) Municipal waste management in the era of COVID-19: perceptions, practices, and potentials for research in developing countries. Res Globalization 2:100033
Parashar N, Hait S (2021) Plastics in the time of COVID-19 pandemic: protector or polluter? Sci Total Environ 759:144274
Parton KJ, Godley BJ et al (2020) Investigating the presence of microplastics in demersal sharks of the North-East Atlantic. Sci Rep 10(1):1–11
Patil GV, Pokhrel K (2005) Biomedical solid waste management in an Indian hospital: a case study. Waste Manage 25(6):592–599
Picheta R (2020) Coronavirus is causing a flurry of plastic waste. Campaigners fear it may be permanent. CNN
Prata JC (2018) Airborne microplastics: consequences to human health? Environ Pollut 234:115–126
Prüss A, Emmanuel J, et al (2014) “Safe management of wastes from health-care activities.” 2 nd Edition, ISBN 978 92 4 154856 4, 1–329
Ragusa A, Svelato A et al (2021) Plasticenta: first evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ Int 146:106274
Rahman MM, Bodrud-Doza M et al (2020) Biomedical waste amid COVID-19: perspectives from Bangladesh. Lancet Glob Health 8(10):e1262
Rizou M, Galanakis IM et al (2020) Safety of foods, food supply chain and environment within the COVID-19 pandemic. Trends Food Sci Technol 102:293–299
Roda JFB, Lauer MM et al (2020) Microplastics and copper effects on the neotropical teleost Prochilodus lineatus: is there any interaction? Comp Biochem Physiol A: Mol Integr Physiol 242:110659
Sangkham S (2020) Face mask and medical waste disposal during the novel COVID-19 pandemic in Asia. Case Stud Chem Environ Eng 2:100052
Saxena P, Pradhan IP et al (2021) Redefining bio medical waste management during COVID-19 in india: a way forward. Mater Today: Proc 60:849–858
Scheurer M, Bigalke M (2018) Microplastics in Swiss floodplain soils. Environ Sci Technol 52(6):3591–3598
Seif S, Provencher J et al (2018) Plastic and non-plastic debris ingestion in three gull species feeding in an urban landfill environment. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 74(3):349–360
Selvam S, Jesuraja K et al (2021) Hazardous microplastic characteristics and its role as a vector of heavy metal in groundwater and surface water of coastal south India. J Hazard Mater 402:123786
Selvam S, Muthukumar P et al (2020) SARS-CoV-2 pandemic lockdown: effects on air quality in the industrialized Gujarat state of India. Sci Total Environ 737:140391
Selvaranjan K, Navaratnam S et al (2021) Environmental challenges induced by extensive use of face masks during COVID-19: a review and potential solutions. Environ Chall 3:100039
Senathirajah K, Attwood S et al (2021) Estimation of the mass of microplastics ingested–a pivotal first step towards human health risk assessment. J Hazard Mater 404:124004
Shah S, Mehta M, et al (2001) “Occupational health hazards encountered at health care facility and medical college in India.” American Industrial Hygiene Association. https://www.who.int/tools/occupational-hazards-in-health-sector#:~:text=The%20most%20common%20occupational%20infections,infections%20(coronaviruses%2C%20influenza ). Accessed on 14 Jul 2022
Silva ALP, Prata JC et al (2021) Increased plastic pollution due to COVID-19 pandemic: challenges and recommendations. Chem Eng J 405:126683
Singh N, Tang Y et al (2020) Environmentally sustainable management of used personal protective equipment. Environ Sci Technol 54(14):8500–8502
Somani M, Srivastava AN et al (2020) Indirect implications of COVID-19 towards sustainable environment: an investigation in Indian context. Bioresour Technol Rep 11:100491
Sridharan S, Kumar M et al (2021) Microplastics as an emerging source of particulate air pollution: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 418:126245
Tavares DC, da Costa LL et al (2016) Nests of the brown booby (Sula leucogaster) as a potential indicator of tropical ocean pollution by marine debris. Ecol Ind 70:10–14
Thakur V (2021) Framework for PESTEL dimensions of sustainable healthcare waste management: learnings from COVID-19 outbreak. J Clean Prod 287:125562
Thiessen T (2020) How clean air cities could outlast COVID-19 lockdowns. https://www.forbes.com/sites/tamarathiessen/2020/04/10/how-clean-air-cities-could-outlast-covid-19-lockdowns/?sh=44bbeca06bb5 . Accessed on 12 June 2022
Thompson DL, Ovenden TS et al (2020) The prevalence and source of plastic incorporated into nests of five seabird species on a small offshore island. Mar Pollut Bull 154:111076
Tripathi A, Tyagi VK et al (2020) Challenges, opportunities and progress in solid waste management during COVID-19 pandemic. Case Stud Chem Environ Eng 2:100060
Vanapalli KR, Sharma HB et al (2021) Challenges and strategies for effective plastic waste management during and post COVID-19 pandemic. Sci Total Environ 750:141514
Vasquez MI, Lambrianides A et al (2014) Environmental side effects of pharmaceutical cocktails: what we know and what we should know. J Hazard Mater 279:169–189
Wan Y, Wu C et al (2019) Effects of plastic contamination on water evaporation and desiccation cracking in soil. Sci Total Environ 654:576–582
Wang J, Peng C et al (2021a) The impact of microplastic-microbe interactions on animal health and biogeochemical cycles: a mini-review. Sci Total Environ 773:145697
Wang J, Xu X et al (2021b) Heterogeneous effects of COVID-19 lockdown measures on air quality in Northern China. Appl Energy 282:116179
Wang W, Ge J et al (2020) Environmental fate and impacts of microplastics in soil ecosystems: progress and perspective. Sci Total Environ 708:134841
WHO (2020a) Water, sanitation, hygiene and waste management for COVID-19: technical brief, 03 March 2020a, World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331305 . Accessed on 12 Jul 2022
WHO (2020b) Water, sanitation, hygiene, and waste management for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19: interim guidance, 29 July 2020b, World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-IPC-WASH-2020.4 . Accessed on 12 Jul 2022
Woodall LC, Sanchez-Vidal A et al (2014) The deep sea is a major sink for microplastic debris. Royal Soc Open Sci 1(4):140317
Yang S, Cheng Y et al (2021) In vitro evaluation of nanoplastics using human lung epithelial cells, microarray analysis and co-culture model. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 226:112837
Ye S, Cheng M et al (2020) Insights into catalytic removal and separation of attached metals from natural-aged microplastics by magnetic biochar activating oxidation process. Water Res 179:115876
Yunus AP, Masago Y et al (2020) COVID-19 and surface water quality: improved lake water quality during the lockdown. Sci Total Environ 731:139012
Zambrano-Monserrate MA, Ruano MA et al (2020) Indirect effects of COVID-19 on the environment. Sci Total Environ 728:138813
Zhang EJ, Aitchison LP, Phillips N, Shaban RZ, Kam AW (2021) Protecting the environment from plastic PPE. BMJ 372:n109
Zhang M, Zhao Y et al (2019) Microplastics from mulching film is a distinct habitat for bacteria in farmland soil. Sci Total Environ 688:470–478
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Zoology, Fakir Mohan University, Vyasa Vihar, Balasore, 756020, Odisha, India
Jiban Kumar Behera, Pabitra Mishra, Anway Kumar Jena & Manojit Bhattacharya
Department of Biosciences and Biotechnology, Fakir Mohan University, Vyasa Vihar, Balasore, 756020, Odisha, India
Bhaskar Behera
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Jiban Kumar Behera: data curation; analysis; investigation; original draft—writing and figure development. Pabitra Mishra: analysis, validation, and figure development. Anway Kumar Jena: validation, analysis. Manojit Bhattacharya: supervision, reviewing and editing, validation. Bhaskar Behera: validation and reviewing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Manojit Bhattacharya .

Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
Not required.
Consent to participate
Consent for pulication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Behera, J.K., Mishra, P., Jena, A.K. et al. Understanding of environmental pollution and its anthropogenic impacts on biological resources during the COVID-19 period. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24789-6
Download citation
Received : 03 October 2022
Accepted : 12 December 2022
Published : 29 December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24789-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Water pollution
- Soil pollution
- Environment
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Research Paper Guides
- Research Paper Topics
Environmental Research Topics: 235 Ideas for Students
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
Are you looking for environmental research paper topics? With ongoing debates about global warming, air pollution, and other issues, there is no shortage of exciting topics to craft a research paper around. Whether you’re studying ecology, geology, or marine biology, developing the perfect environmental research topic to get your science research assignment off the ground can be challenging. Stop worrying – we got you covered. Continue reading to learn about 235 different ideas on environmental research topics. In this article, we will discuss environmental topics and show you how to choose an interesting research topic for your subject. We will also provide a list of various environmental topics from our research paper services . In addition, we will present you with environmental science research topics, discuss other ideas about the environment for research papers, and offer our final thoughts on these topics for research papers.
What Are Environmental Topics?
Environmental topics provide an analysis of environmental issues and their effect on people, culture, nature, or a particular place, often interdisciplinary, drawing from sciences, politics, economics, sociology, and public policy. Topics about environmental science may include environmental justice, engineering and communication, regulation, economics, and health. Environment research topics may focus on environmental sustainability, impact assessment, management systems, and resources. In addition, these areas for research papers offer a few opportunities to explore our relationship with the environment and consider how human activities influence it through climate change, pollution, or other factors such as natural resource usage as well as biodiversity loss.
What Makes a Good Environmental Research Topic?
When choosing an environmental research topic, it is essential to consider what makes good environmental topics. Below is an expert list outlining what your topic should be like:
- It should be interesting and relevant to your study field.
- It's essential to consider the topic's potential implications on environment-related policies. Think about the possible positive or negative effects this topic could have when implemented in terms of protecting our environment.
- A good topic should be specific enough to provide a focus for your research paper and allow you to explore a particular issue in depth.
- The research topic should be feasible and manageable to ensure that you can find the necessary information and resources.
- Environmental sciences research topics should be current and relevant to ecological developments.
How to Choose Environmental Science Topics?
When choosing research topics for environmental science, it is essential to research the available information and determine its relevance. It all depends on whether the research topic is feasible and has the potential for exploration. Environmental issue topics should be well-defined and interesting to the researcher. The reason is that the researcher should be able to provide solutions or make suggestions on improvement strategies. You can follow the below steps when choosing environmental science topics for research:
Step 1: Identify topics that are relevant to your research context. Step 2: Develop a list of research areas by extracting critical concepts from the available literature.
Step 3: Select interesting and feasible topics by considering the methods available for analysis.
Step 4: Analyze these topics to identify the gaps in current research and formulate questions for further investigation. Step 5: Review the available literature to gain insights about the chosen topic and develop a research proposal.
Step 6: Consult experts in this field to get feedback and refine the proposed research.
Don’t have time for writing your environmental research paper? Count on StudyCrumb. Send us a ‘ write a research paper for me ’ message and get professional assistance in a timely manner.
List of Environment Research Paper Topics
Environmental topics for a research paper can be overwhelming to navigate due to the vast number of issues you can discuss in your article. To help narrow down your research paper search, below is a list of environmental research topics that include climate change, renewable energy, ecology, pollution, sustainability, endangered species, ecosystems, nature, and water management. You can choose one of them as a guide to writing an excellent essay
Environmental Research Topics on Climate Change
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues that humanity is currently facing due to increased temperature levels. Climate change is amongst the most debated environmental research topics among researchers, policymakers, and governments. Here are critical areas related to climate change that you can use for your environmental science research paper topics:
- Causes and effects of climate change.
- Climate change adaptation strategies.
- Climate change impact on rural communities.
- Role of renewable energy sources in mitigating climate change.
- Carbon dioxide emission policies.
- Global warming and its impact on ocean acidification.
- Social effects of climate change.
- Permafrost melting and its implications.
- Role of international organizations in climate change.
- Climate change and forest fire: examining the role of climate change on wildfire season, frequency, and burned area.
Environmental Science Research Topics on Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is essential due to its potential to reduce ecological damage from burning fossil fuels and provides valuable topics in environmental science. You can use renewable energy technologies as a cleaner alternative for generating electricity and heating. In addition, renewable energy is crucial for cooling homes and factories in the world. The following are environmental science topics for research paper on renewable energy:
- Renewable energy types, sources, and their impact on the environment.
- Economic benefits of renewable energy.
- Research on new technologies in renewable energy.
- Role of renewable energy in protecting businesses from legal actions.
- Hydropower and its role in renewable energy.
- Chemical batteries for renewable energy storage.
- Green microgrids in optimizing renewable energy usage.
- Ocean energy and its effects on the environment.
- Geothermal drilling and its consequences.
- Biomass resources and their use in renewable energy.
Environment Research Topics on Ecology
Ecology studies how living organisms interact with each other and their environment. Also, it is an important area of research for understanding how the environment affects the function of various species and ecosystems. It also gives a background for one of the best environment research paper topics. Below are topics for environmental research paper on ecology:
- Biodiversity conservation strategies.
- Impact of pollution on ecosystems.
- Ecological research on saving endangered species from extinction.
- Role of environment in migrations patterns of animals.
- Habitat fragmentation effects on the environment.
- Ecological implications of climate change.
- Ecology and pest control strategies.
- Ecological effects of deforestation.
- Ecology and conservation of marine life.
- Ecological consequences of urbanization.
Research Topics in Environmental Science About Pollution
Pollution is an issue at the forefront of scientific research. As one of the environmental science paper topics, it offers insights into how pollution destroys the environment and its negative impact on human and animal health. Stated below are hot environmental science research topics on pollution which you can use for your article:
- Air pollution: causes & effects.
- Water pollution and its consequences for people and other living organisms.
- Issue of urban & industrial pollution.
- Noise pollution and environment-related health risks.
- Marine plastic pollution in oceans.
- Radiological waste disposal policies.
- Nuclear energy, radiation & health impacts.
- Sustainable waste management solutions.
- Impact of pollution on biodiversity.
- Soil pollution and its effects on agriculture.
Environmental Topics for Research Papers on Sustainability
One of the many topics for environmental research papers is sustainability. Sustainability is an important topic to explore, as it involves finding a way for humans to reduce their ecological footprint and ensure that the environment can recover from our activities. Stated below are environmental topics for research paper on sustainability which you can explore:
- Strategies for sustainable development.
- Renewable energy sources and their effects.
- Environmental sustainability and its economic benefits.
- Sustainable energy sources and their effects.
- Implications of sustainable agriculture on the environment.
- Ecological impacts of sustainable forestry.
- Social implications of renewable energy use.
- Strategies for mitigating ecological impact from unsustainable development.
- Psychological effects of ecological awareness on sustainable practices.
- Influence of ecological sustainability on economic growth.
Environmental Topics to Write About Endangered Species
Endangered species are one of the environmental topics of great importance to research and find solutions for their conservation. Poaching, habitat destruction, and climate change negatively impact endangered species. Also, human activities have put other species at risk of extinction by competing for resources as well as introducing invasive species. Below is a list of cool environment topics to write about endangered species:
- Endangered species conservation.
- Causes & effects of habitat fragmentation.
- Wildlife conservation strategies.
- Climate change impacts on endangered species.
- Illegal wildlife trade and trafficking.
- Marine protected areas for conserving marine life.
- Ecological restoration and reintroduction programs.
- Endangered species in developing nations.
- Human rights & animal welfare laws .
- Captive breeding for conservation purposes.
Environmental Research Paper Topics on Ecosystems
Ecosystems are fascinating to explore in environmental paper topics because they contain a variety of living organisms and are a complex web of interactions between species, the environment, and humans. The subject provides environmental issues topics for research paper essential in exploring the dynamics of ecosystems and their importance. Below is a list of topics for environmental science research paper:
- Ecosystem services & their value.
- Climate change impacts on ecosystems.
- Hydrological cycle & effects on ecosystems.
- Ecological restoration & biodiversity conservation.
- Invasive species & their impact on native species.
- Biodiversity hotspots: areas of high endemism.
- Soil degradation & its impact on ecosystems.
- Sustainable forestry practices.
- Ecological restoration of wetlands.
Environmental Topics About Nature
Nature is a broad topic that includes ecological conservation, protection, and sustainability issues. Environmental research topics about nature allow us to explore areas that focus on preserving and conserving the environment. Research papers about nature can provide insight into utilizing nature as a resource, both from a practical and ecological aspect. Below is a list of environment topics that you can explore in your essays:
- Nature conservation & preservation strategies.
- Climate change effects on natural environments.
- Natural resource management strategies.
- Policies for natural resources management.
- Impact of human development on wildlands.
- Sustainable use of natural resources.
- Role of ethics in nature conservation.
- De-extinction: pros & cons of bringing back extinct species.
- Protected areas & conservation of rare species.
Environmental Issues Topics on Water Management
Water management is an issue that has a significant impact on the environment. Exploring a topic related to water management can provide experts, among others, with insights into environmental science issues and their implications. When it's time to write your project related to water management, you can explore the following topics for environmental issues:
- Water pollution & its control.
- Groundwater management strategies.
- Climate change impact on water resources.
- Integrated water resources management.
- Wetland conservation & restoration projects.
- Industrial effluents role in water pollution.
- Desalination technologies for freshwater production.
- Urbanization impact on groundwater resources.
- Inland & coastal water management strategies.
- Wastewater treatment & reuse technologies.
Environmental Science Topics in Different Areas
Environmental science studies ecological processes and their interactions with living organisms. Exploring environmental science related topics can provide valuable insights into environmental science issues, their ecological implications, and conservation efforts. In addition, these topics can also be explored in different areas, providing a comprehensive understanding of how different factors impact the environment. This section delves into various environmental science topics for projects related to law, justice, policy, economics, biology, chemistry, and health science.
Environmental Law Research Topics
Environmental law governs environmental processes and their interactions with living organisms. Delving into environmental law can uncover invaluable information on environment paper topics, ranging from legal matters and their consequences to preservation initiatives. Students can use the following environmental issue topics for research papers for their essays:
- Climate change liability & lawsuits.
- Strategies for conservation and protection under environmental law.
- Consequences of non-compliance with regulations on the environment.
- Impact of trade agreements on environment protection.
- Regulatory strategies for hazardous waste disposal.
- Strategies for enforcement and compliance with environment-related laws.
- International environment treaties and their implications.
- Effects of climate change legislation on the environment.
- Corporate environmental policies and regulations and their effects.
- Role of law in mitigating environment-related issues.
Environmental Justice Research Topics
Environmental justice seeks to ensure equitable treatment and meaningful involvement of all people in ecological protection, regardless of their race, sex, or economic status. Environment topics related to justice can provide valuable insights into ecological issues and their impacts. Listed below are justice-related Environmental topics to research:
- Implications of unequal access to resources.
- Disproportionate impacts of climate change on vulnerable populations.
- Consequences of marginalization of marginalized communities from environmental processes.
- Links between poverty and environment degradation.
- Effects of non-participation in environment-related decision-making.
- Policies to ensure access to clean air and water.
- Impact of social inequality on environment protection.
- Intersection between gender, race, and environment justice.
- Ecological consequences of corporate negligence of marginalized communities.
- Disproportionate implications of climate change on vulnerable populations.
Environmental Policy Research Paper Topics
Environmental policy is a set of laws, rules, and regulations created to protect the environment as well as its resources. Studying environment-related policies provides an area for students to explore a range of subjects related to the environment, ranging from local to global. Below are potential environmental sciences research topics for your reference.
- Environmental policy initiatives' implications on global climate change.
- Effectiveness of carbon taxes for air pollution control.
- Land use and development impact on the environment.
- Water quality in the united states, focusing on natural resource governance.
- Educational initiative's impact on public opinion and policy outcomes.
- Social aspects of policy making and implementation on the environment.
- Promoting sustainability from a global perspective.
- Potential for justice initiatives in promoting equitable and effective management.
- Rise of green economy its impact.
- Environment policies and their potential for success.
Environmental Economics Research Topics
Environmental economics seeks to understand environmental issues from an economic perspective. Examining environmental studies topics can offer insights into ecological conservation and sustainability while connecting protection efforts with economic interests and helping inform policies. The following are creative topics about environmental science related to economics:
- Economic impacts of regulating the environment.
- Strategies for environmentally sustainable economic growth.
- Consequences of non-compliance with environment-related regulations.
- Environment conservation and protection using economic incentives.
- Taxes and subsidies and their implications on the environment.
- Economic implications of climate change legislation.
- The private sector role in environment conservation and protection.
- Green finance role in mitigating ecological issues.
- Economics of pollution control and management.
- Conservation and protection of the environment in the face of economic interests.
>> Learn more: Economics Research Topics
Environmental Biology Research Topics
Environmental biology is a field of science that focuses on understanding the interactions between living organisms and their environment. It covers environmental biology topics such as biodiversity, conservation, pollution, management, health, and sustainability. The following are environment research paper topics related to biology:
- Biodiversity conservation in managing the environment.
- Role of biotechnology in reducing air pollution.
- Environment degradation and its consequences on wildlife.
- Role of microorganisms in maintaining soil fertility.
- Ecological consequences of over-exploitation of natural resources.
- Habitat fragmentation and its role in species conservation.
- Education's role in environment conservation.
- Environment degradation and its effects on food security.
- Invasive species and their impacts on ecosystem.
Keep in mind that we have a whole blog on biological topics if you need more ideas in this field.
Environmental Chemistry Research Topics
Environmental chemistry research is a complex interdisciplinary field aiming to understand the behavior of a chemical process within an environment. It involves researching the impact of pollutants in the air, soil, water, and other ecological media. Possible research topics about the environment related to this field include:
- Effect of agricultural chemicals on water systems.
- Air pollution control strategies and their effectiveness.
- Climate change impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
- Sources and implications of persistent organic pollutants.
- Air quality monitoring for urban areas.
- Water quality monitoring in coastal areas.
- Characterization and fate of toxic compounds in soil and groundwater.
- Impact of hazardous chemical waste on the environment.
- Monitoring and remediation of contaminated sites.
- The roles of environmental chemistry in climate change research.
Need more ideas? There is one more blog with chemistry research topics on our platform.
Environmental Health Science Research Topics
Environmental health is a diverse field focusing on the natural environment as well as its effects on human health. It is an interdisciplinary field that offers environment topics for research, such as environmental epidemiology, toxicology, and ecology, in addition to risk assessment. Provided below is a list of topics for an environmental science project that is suitable for your research paper:
- Air pollution effects on human health.
- Climate change effects on health.
- Water pollution and public health.
- Noise pollution effects on well-being.
- Mental health effects of environment-related toxins.
- Human health effects of natural disasters.
- Urbanization's effect on human health.
- Sustainable development and public health.
- Role of social media in promoting environmental health and awareness.
- Biodiversity preservation and its impact on human health.
Other Ideas & Topics About Environment for Research Papers
Ecological crisis is a key issue that has continuously affected planet earth. People are becoming more aware of environmental problems as well as their impact on health, well-being, and quality of life. As such, ecological fields for research are becoming ever more critical. This section will explore interesting environmental topics related to current ecological issues, controversial, interesting topics, easy research questions for projects, as well as unique research areas which students might study. These environmental issue project ideas below will help you develop interesting fields for research papers.
Current Issues in Environmental Science
Current ecological issues are a hot topic that has become increasingly important. They provide outstanding environmental issues to write about due to their impact on the environment and human health. The following are environmental issue topics for paper writing that are currently in discussion:
- Global warming and how to prevent its impact.
- Sustainable energy and its role in protecting the environment.
- Water conservation practices.
- Renewable energy role in global ecological protection.
- Carbon footprint and climate change.
- Ozone layer depletion and its effects on human health.
- Plastic pollution and its impact.
- Land degradation and soil erosion.
- Energy industry activities effects on ecological health.
- Air pollution and its impact on human health.
- Deforestation and its consequences.
- Effect of agricultural practices on ecological health.
- Overuse and exploitation of natural resources.
- Industrial waste impact on health.
- Green technology role in ecological protection.
Controversial Environmental Topics for Research Paper
Environmental controversies constitute a significant challenge facing society today. From climate change to air and water pollution, the effects of human activity on our natural environment are increasingly becoming a focus of public debate and research. Research papers on environmental controversial topics can help inform the public as well as policymakers about the potential impacts of human activities on the environment. The following are examples of environmental controversy topics for research paper:
- Climate change: is human activity a primary cause of global warming.
- Deforestation: are current logging practices sustainable in the long term.
- Air pollution: what are the health impacts of air pollution.
- Water pollution: how is water pollution impacting biodiversity and ecosystems.
- Geothermal energy: what potential impacts does geothermal energy extraction have on the environment.
- Renewable energy: are wind and solar energy carbon-neutral.
- Arctic drilling: is drilling for oil in the arctic ocean a viable option given current climate conditions.
- Nuclear power: what health risks are associated with nuclear power plants.
- Biodiversity loss: what steps can you take to protect biodiversity from human activities.
- Endangered species: how protecting endangered species can impact conservation efforts and how they live.
- GMO foods: are genetically modified organisms safe for human consumption? how does GMO food affect humans.
- Pesticides: how does pesticide use affect our health and the environment.
- Ocean acidification: how is ocean acidification impacting marine ecosystems.
- Waste management: what are the most effective ways to manage waste and reduce pollution.
- Resource exploitation: how does the exploitation of natural resources impact local communities.
Interesting Environmental Research Topics
In the context of environmental subjects, research topics explore the effects of human activities on the environment as well as the potential solutions to the identified problems. In addition to providing insight into ecological protection and conservation, research areas in this category cover social issues related to environmentalism and ecological justice. Below are interesting environmental science topics to consider when looking for a research topic in the future:
- Effects of environment-related toxins on human health.
- Climate change effects on coastal habitats.
- Agricultural activities impacts on the environment.
- Groundwater contamination and its effects on water quality.
- Pollution from factories and its impact on the environment.
- Waste management strategies and their impacts.
- Consequences of water contamination on local wildlife.
- Impacts of mining.
- Deforestation effects on ecosystems and species diversity.
- Industrial fishing practices effects.
- Sustainable forestry practices and their impact on ecosystems.
- Nuclear energy production and its consequences.
- Reducing emissions from vehicles and their effects on air quality.
- Landfills implications on the environment.
- Implications of plastic pollution.
Easy Environmental Research Questions for Projects
When it comes to environmental science topics for project work, there are plenty of easy options. Research projects in this category can explore ecological issues as well as their consequences or potential solutions to these problems. The following is a list of the top fifteen most accessible environment project topics for your research project.
- Air pollution levels impact on urban areas.
- Agricultural practices effects on the environment.
- Developing strategies for sustainable development.
- Causes of water contamination.
- Factors contributing to global warming.
- Natural disasters effects on the environment.
- Land use changes effects on the environment.
- Energy consumption impacts on the environment.
- Climate change effects on the environment.
- Industrialization and its consequences.
- Impact of plastic pollution.
- Health risks associated with air pollution.
- Deforestation impacts on the environment.
- Soil erosion and its effects on the environment.
- Causes and consequences of species extinction.
Unique Environmental Research Topics for Students
As environmental issues become increasingly complex, research fields for students become more varied. Unique environmental research topics for college students can range from local ecological concerns to global ones. The following are fifteen unique environmental science research topics for high school students and college students:
- Climate change impact on water quality.
- Acid rain and its effects.
- Urbanization's effect on biodiversity.
- Effects of offshore drilling.
- Ocean acidification and its impact.
- Impact of privatization on natural resources.
- Effectiveness of renewable energy sources.
- Relationship between energy consumption and the environment.
- Potential impacts regarding genetic engineering on biodiversity.
- Toxic waste disposal and its impacts.
- Environment-related policies impact on water quality.
- Deforestation and its effects on soil quality.
- Causes and consequences of ozone layer depletion.
- Relationship between pollution and public health issues.
Final Thoughts on Environmental Topics for Research Papers
This article has provided 235 environmental science research topics for research papers as well as project work that high school and college students can use. Topics range from local issues, such as assessing air pollution levels in an urban area, to global concerns, like examining the ecological effects of plastic pollution. Whether its health risks are associated with air pollution in an environment or the impacts of industrialization, research can help shape your understanding of how to protect as well as preserve our planet. It is up to the students to identify good environmental research topics that are interesting and relevant to them and to delve deeper to understand the earth better.
Get in touch with our academic writing service and receive expert help. Let us know your topic, pay for research paper and get an excellent result in no time.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 23 May 2024
Monitoring, trends and impacts of light pollution
- Hector Linares Arroyo ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0034-3700 1 ,
- Angela Abascal 2 ,
- Tobias Degen 3 , 4 ,
- Martin Aubé 5 , 6 ,
- Brian R. Espey 7 ,
- Geza Gyuk 8 ,
- Franz Hölker ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5932-266X 3 , 9 ,
- Andreas Jechow ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7596-6366 3 , 10 ,
- Monika Kuffer 2 ,
- Alejandro Sánchez de Miguel 11 , 12 ,
- Alexandre Simoneau 5 , 6 ,
- Ken Walczak 8 &
- Christopher C. M. Kyba 13 , 14
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment ( 2024 ) Cite this article
319 Accesses
57 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Astronomical instrumentation
- Atmospheric chemistry
- Energy access
- Environmental impact
Light pollution has increased globally, with 80% of the total population now living under light-polluted skies. In this Review, we elucidate the scope and importance of light pollution and discuss techniques to monitor it. In urban areas, light emissions from sources such as street lights lead to a zenith radiance 40 times larger than that of an unpolluted night sky. Non-urban areas account for over 50% of the total night-time light observed by satellites, with contributions from sources such as transportation networks and resource extraction. Artificial light can disturb the migratory and reproductive behaviours of animals even at the low illuminances from diffuse skyglow. Additionally, lighting (indoor and outdoor) accounts for 20% of global electricity consumption and 6% of CO 2 emissions, leading to indirect environmental impacts and a financial cost. However, existing monitoring techniques can only perform a limited number of measurements throughout the night and lack spectral and spatial resolution. Therefore, satellites with improved spectral and spatial resolution are needed to enable time series analysis of light pollution trends throughout the night.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
92,52 € per year
only 7,71 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others

Towards an absolute light pollution indicator
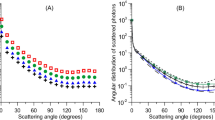
Air pollution mitigation can reduce the brightness of the night sky in and near cities
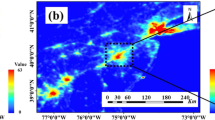
A consistent and corrected nighttime light dataset (CCNL 1992–2013) from DMSP-OLS data
Data availability.
The Radiance Light Trends webtool used to obtain the data plotted in Fig. 5 is available at https://doi.org/10.5880/GFZ.1.4.2019.001 .
Hänel, A. et al. Measuring night sky brightness: methods and challenges. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 205 , 278–290 (2018).
Article Google Scholar
Pun, C. S. J., So, C. W., Leung, W. Y. & Wong, C. F. Contributions of artificial lighting sources on light pollution in Hong Kong measured through a night sky brightness monitoring network. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 139 , 90–108 (2014).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Gaston, K. J. & Sánchez de Miguel, A. Environmental impacts of artificial light at night. Ann. Rev. Environ. Resour. 47 , 373–398 (2022).
Owens, A. C. et al. Light pollution is a driver of insect declines. Biol. Conserv. 241 , 108259 (2020).
Johnston, D. W. & Haines, T. P. Analysis of mass bird mortality in October, 1954. Auk 74 , 447–458 (1957).
Doren, B. M. V. et al. High-intensity urban light installation dramatically alters nocturnal bird migration. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114 , 11175–11180 (2017).
Korner, P., von Maravic, I. & Haupt, H. Birds and the ‘Post Tower’ in Bonn: a case study of light pollution. J. Ornithol. 163 , 827–841 (2022).
Ffrench-Constant, R. H. et al. Light pollution is associated with earlier tree budburst across the United Kingdom. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 283 , 20160813 (2016).
Lian, X. et al. Artificial light pollution inhibits plant phenology advance induced by climate warming. Environ. Pollut. 291 , 118110 (2021).
Meng, L. Green with phenology. Science 374 , 1065–1066 (2021).
Knop, E. et al. Artificial light at night as a new threat to pollination. Nature 548 , 206–209 (2017).
Rydell, J., Eklöf, J. & Sánchez-Navarro, S. Reply to ‘Comment on age of enlightenment: long-term effects of outdoor aesthetic lights on bats in churches’ by T. Onkelinx. R. Soc. Open Sci. 4 , 171630 (2017).
Camacho, L. F., Barragàn, G. & Espinosa, S. Local ecological knowledge reveals combined landscape effects of light pollution, habitat loss, and fragmentation on insect populations. Biol. Conserv. 262 , 109311 (2021).
Degen, T. et al. Street lighting: sex-independent impacts on moth movement. J. Anim. Ecol. 85 , 1352–1360 (2016).
Moore, M. V., Pierce, S. M., Walsh, H. M., Kvalvik, S. K. & Lim, J. D. Urban light pollution alters the diel vertical migration of Daphnia . Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. Verh. 27 , 779–782 (2000).
Google Scholar
Shith, S. et al. Does light pollution affect nighttime ground-level ozone concentrations? Atmosphere 13 , 1844 (2022).
Tsao, J. Y. & Waide, P. The world’s appetite for light: empirical data and trends spanning three centuries and six continents. LEUKOS 6 , 259–281 (2010).
Almeida, A. D., Santos, B., Paolo, B. & Quicheron, M. Solid state lighting review — potential and challenges in Europe. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 34 , 30–48 (2014).
Cinzano, P. & Falchi, F. Quantifying light pollution. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 139 , 13–20 (2014).
Barà, S., Bao-Varela, C. & Falchi, F. Light pollution and the concentration of anthropogenic photons in the terrestrial atmosphere. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 13 , 101541 (2022).
Gaston, K. J. et al. Pervasiveness of biological impacts of artificial light at night. Integr. Comp. Biol. 61 , 1098–1110 (2021).
Sánchez de Miguel, A., Bennie, J., Rosenfeld, E., Dzurjak, S. & Gaston, K. J. First estimation of global trends in nocturnal power emissions reveals acceleration of light pollution. Remote Sens. 13 , 3311 (2021).
Falchi, F. et al. The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Sci. Adv. 2 , e1600377 (2016).
IEA. Tracking SDG7: the energy progress report, 2022 (IEA, 2022).
IEA. DG7: data and projections (IEA, 2023).
Fotios, S. & Gibbons, R. Road lighting research for drivers and pedestrians: the basis of luminance and illuminance recommendations. Light. Res. Technol. 50 , 154–186 (2018).
Edensor, T. The gloomy city: rethinking the relationship between light and dark. Urban Stud. 52 , 422–438 (2013).
Morgan-Taylor, M. Regulating light pollution: more than just the night sky. Science 380 , 1118–1120 (2023).
Welsh, B. C., Farrington, D. P. & Douglas, S. The impact and policy relevance of street lighting for crime prevention: a systematic review based on a half-century of evaluation research. Criminol. Public Policy 21 , 739–765 (2022).
Perkins, C. et al. What is the effect of reduced street lighting on crime and road traffic injuries at night? A mixed-methods study. Public Health Res. 3 , 1–108 (2015).
Marchant, P. R. & Norman, P. D. To determine if changing to white light street lamps improves road safety: a multilevel longitudinal analysis of road traffic collisions during the relighting of Leeds, a UK city. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 15 , 1583–1608 (2022).
Levin, N. et al. Remote sensing of night lights: a review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 237 , 111443 (2020).
Combs, C. L. & Miller, S. D. A review of the far-reaching usage of low-light nighttime data. Remote Sens. 15 , 623 (2023).
Hao, Q. et al. Exploring the construction of urban artificial light ecology: a systematic review and the future prospects of light pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 , 1–26 (2023).
Ministry of the Environment of the Czech Republic. Light pollution reduction measures in Europe (2022).
Widmer, K., Beloconi, A., Marnane, I. & Vounatsou, P. Review and assessment of available information on light pollution in Europe (Eionet Report – ETC HE 2022/8) (European Environment Agency, 2022).
Barentine, J. C., Walczak, K., Gyuk, G., Tarr, C. & Longcore, T. A case for a new satellite mission for remote sensing of night lights. Remote Sens. 13 , 2294 (2021).
Hölker, F. et al. The dark side of light: a transdisciplinary research agenda for light pollution policy. Ecol. Soc. 15 , 13 (2010).
Zielinska-Dabkowska, K. M., Schernhammer, E. S., Hanifin, J. P. & Brainard, G. C. Reducing nighttime light exposure in the urban environment to benefit human health and society. Science 380 , 1130–1135 (2023).
Kyba, C. C. M., Öner Altıntaş, Y., Walker, C. E. & Newhouse, M. Citizen scientists report global rapid reductions in the visibility of stars from 2011 to 2022. Science 379 , 265–268 (2023).
Linares, H. et al. Assessing light pollution in vast areas: zenith sky brightness maps of Catalonia. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 309 , 108678 (2023).
Aubé, M., Simoneau, A. & Kollàth, Z. HABLAN: multispectral and multiangular remote sensing of artificial light at night from high altitude balloons. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 306 , 108606 (2023).
Linares, H. et al. Night sky brightness simulation over Montsec protected area. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 249 , 106990 (2020).
Abelson, E. et al. Ecological aspects and measurement of anthropogenic light at night. SSRN Electron. J . https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4353905 (2023).
Treanor, P. J. A simple propagation law for artificial night-sky illumination. Observatory 93 , 117–120 (1973).
Berry, R. L. Light pollution in southern Ontario. J. R. Astron. Soc. Can. 70 , 97 (1976).
Walker, M. F. The effects of urban lighting on the brightness of the night sky. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 89 , 405 (1977).
Garstang, R. H. Model for artificial night-sky illumination. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 98 , 364 (1986).
Aubé, M. & Simoneau, A. New features to the night sky radiance model Illumina: hyperspectral support, improved obstacles and cloud reflection. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 211 , 25–34 (2018).
Kocifaj, M. Multiple scattering contribution to the diffuse light of a night sky: a model which embraces all orders of scattering. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 206 , 260–272 (2018).
Jechow, A. et al. Design and implementation of an illumination system to mimic skyglow at ecosystem level in a large-scale lake enclosure facility. Sci. Rep. 11 , 23478 (2021).
Linares, H. et al. Modelling the night sky brightness and light pollution sources of Montsec protected area. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 217 , 178–188 (2018).
Aubé, M. & Kocifaj, M. Using two light-pollution models to investigate artificial sky radiances at Canary Islands observatories. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 422 , 819–830 (2012).
Walczak, K. et al. The GONet (ground observing network) camera: an inexpensive light pollution monitoring system. Int. J. Sustain. Light. 23 , 7–19 (2021).
Jechow, A., Kyba, C. & Hölker, F. Beyond all-sky: assessing ecological light pollution using multi-spectral full-sphere fisheye lens imaging. J. Imaging 5 , 46 (2019).
Nievas, M. & Zamorano, J. Absolute photometry and night sky brightness with all-sky cameras. MSc thesis, Univ. Complutense de Madrid (2013).
Kolláth, Z. Measuring and modelling light pollution at the Zselic Starry Sky Park. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 218 , 012001 (2010).
Bertolo, A., Binotto, R., Ortolani, S. & Sapienza, S. Measurements of night sky brightness in the Veneto region of Italy: sky quality meter network results and differential photometry by digital single lens reflex. J. Imaging 5 , 56 (2019).
Celino, I., Calegari, G. R., Scrocca, M., Zamorano, J. & Guardia, E. G. Participant motivation to engage in a citizen science campaign: the case of the TESS network. J. Sci. Commun. 20 , A03 (2021).
Tilve, V. et al. Estimating all-sky night brightness maps from finite sets of SQM measurements. Highlights Span. Astrophys. VIII 1 , 874–874 (2015).
Zamorano, J., Sánchez de Miguel, A., Nievas, M. & Tapia, C. NixNox Procedure to Build Night Sky Brightness Maps from SQM Photometers Observations (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, 2014); https://docta.ucm.es/entities/publication/ab6eb18d-0597-49ee-af6b-2d445c712257 .
Marseille, C., Aubé, M., Barreto, Á. & Simoneau, A. Remote sensing of aerosols at night with the CoSQM sky brightness data. Remote Sens. 13 , 4623 (2021).
Ribas, S. J. Caracterització de la Contaminació Lumínica en Zones Protegides i Urbanes . PhD thesis, Univ. de Barcelona (2016).
Linares Arroyo, H. Light Pollution Study and Characterization in Catalonia . PhD thesis, Univ. de Barcelona (2021).
Gokus, A. et al. Nachtlichter app: a citizen science tool for documenting outdoor light sources in public spaces. Int. J. Sustain. Light. 25 , 24–66 (2023).
Sanchez de Miguel, A., Kyba, C. C. M., Zamorano, J., Gallego, J. & Gaston, K. J. The nature of the diffuse light near cities detected in nighttime satellite imagery. Sci. Rep. 10 , 7829 (2020).
Rodríguez, A., Rodríguez, B., Acosta, Y. & Negro, J. J. Tracking flights to investigate seabird mortality induced by artificial lights. Front. Ecol. Evol . https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2021.786557 (2022).
Kyba, C. C. M. et al. Artificially lit surface of Earth at night increasing in radiance and extent. Sci. Adv. 3 , e1701528 (2017).
Sánchez de Miguel, A. et al. Colour remote sensing of the impact of artificial light at night (I): the potential of the International Space Station and other DSLR-based platforms. Remote Sens. Environ. 224 , 92–103 (2019).
Elvidge, C. D. et al. The VIIRS Day/Night Band: a flicker meter in space? Remote Sens. 14 , 1316 (2022).
Coesfeld, J. et al. Variation of individual location radiance in VIIRS DNB monthly composite images. Remote Sens. 10 , 1964 (2018).
Li, T. et al. Continuous monitoring of nighttime light changes based on daily NASA’s Black Marble product suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 282 , 113269 (2022).
Tong, K. P. et al. Angular distribution of upwelling artificial light in Europe as observed by Suomi-NPP satellite. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 249 , 107009 (2020).
Kyba, C. et al. Direct measurement of the contribution of street lighting to satellite observations of nighttime light emissions from urban areas. Light. Res. Technol. 53 , 189–211 (2020).
Sanchez de Miguel, A. et al. Atlas of astronaut photos of Earth at night. Astron. Geophys. 55 , 4.36 (2014).
Guo, H. et al. SDGSAT-1: the world’s first scientific satellite for Sustainable Development Goals. Sci. Bull. 68 , 34–38 (2022).
Cheng, B. et al. Automated extraction of street lights from JL1-3B nighttime light data and assessment of their solar energy potential. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 13 , 675–684 (2020).
Simons, A. L., Yin, X. & Longcore, T. High correlation but high scale-dependent variance between satellite measured night lights and terrestrial exposure. Environ. Res. Commun. 2 , 021006 (2020).
Smith, R. A., Gagné, M. & Fraser, K. C. Pre-migration artificial light at night advances the spring migration timing of a trans-hemispheric migratory songbird. Environ. Pollut. 269 , 116136 (2021).
Robert, K. A., Lesku, J. A., Partecke, J. & Chambers, B. Artificial light at night desynchronizes strictly seasonal reproduction in a wild mammal. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 282 , 20151745 (2015).
Storms, M. et al. The rising moon promotes mate finding in moths. Commun. Biol. 5 , 1234567890 (2022).
Luginbuhl, C. B., Boley, P. A. & Davis, D. R. The impact of light source spectral power distribution on sky glow. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 139 , 21–26 (2014).
Cox, D., Sánchez de Miguel, A., Bennie, J., Dzurjak, S. & Gaston, K. Majority of artificially lit Earth surface associated with the non-urban population. Sci. Total Environ. 841 , 156782 (2022).
Cox, D. T., Sánchez de Miguel, A., Dzurjak, S. A., Bennie, J. & Gaston, K. J. National scale spatial variation in artificial light at night. Remote Sens. 12 , 1591 (2020).
Falchi, F. et al. Light pollution in USA and Europe: the good, the bad and the ugly. J. Environ. Manag. 248 , 109227 (2019).
Aubé, M., Kocifaj, M., Zamorano, J., Lamphar, H. S. & Sanchez de Miguel, A. The spectral amplification effect of clouds to the night sky radiance in Madrid. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 181 , 11–23 (2016).
Jechow, A. et al. Imaging and mapping the impact of clouds on skyglow with all-sky photometry. Sci. Rep. 7 , 6741 (2017).
Ribas, S. J., Torra, J., Paricio, S. & Canal-Domingo, R. How clouds are amplifying (or not) the effects of ALAN. Int. J. Sustain. Light. 18 , 32–39 (2016).
Jechow, A. & Hölker, F. Snowglow — the amplification of skyglow by snow and clouds can exceed full moon illuminance in suburban areas. J. Imaging 5 , 69 (2019).
Kyba, C. C. M., Ruhtz, T., Fischer, J. & Hölker, F. Red is the new black: how the colour of urban skyglow varies with cloud cover. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 425 , 701–708 (2012).
European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Zissis G., Bertoldi, P., Serrenho, T. Update on the status of LED-lighting world market since 2018. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/759859 (Publications Office of the European Union, 2021).
Kuechly, H. U. et al. Aerial survey and spatial analysis of sources of light pollution in Berlin, Germany. Remote Sens. Environ. 126 , 39–50 (2012).
Barà, S. et al. Estimating the relative contribution of streetlights, vehicles, and residential lighting to the urban night sky brightness. Light. Res. Technol. 51 , 1092–1107 (2018).
Luginbuhl, C. B. et al. From the ground up II: sky glow and near-ground artificial light propagation in Flagstaff, Arizona. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 121 , 204–212 (2009).
Elvidge, C. D. et al. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2 , 595–622 (2009).
Boslett, A., Hill, E., Ma, L. & Zhang, L. Rural light pollution from shale gas development and associated sleep and subjective well-being. Resour. Energy Econ. 64 , 101220 (2021).
Barentine, J. C. What does lettuce have to do with my night sky? DarkSky International https://www.darksky.org/greenhouse-light-pollution/ (2020).
Walczak, K. A land of perpetual false dawn. DarkSky International https://www.darksky.org/light-pollution-industrial-greenhouses/ (2021).
Guetté, A., Godet, L., Juigner, M. & Robin, M. Worldwide increase in artificial light at night around protected areas and within biodiversity hotspots. Biol. Conserv. 223 , 97–103 (2018).
Koen, E. L., Minnaar, C., Roever, C. L. & Boyles, J. G. Emerging threat of the 21st century lightscape to global biodiversity. Glob. Change Biol. 24 , 2315–2324 (2018).
Garrett, J. K., Donald, P. F. & Gaston, K. J. Skyglow extends into the world’s key biodiversity areas. Anim. Conserv. 23 , 153–159 (2019).
Hölker, F., Jechow, A., Schroer, S., Tockner, K. & Gessner, M. O. Light pollution of freshwater ecosystems: principles, ecological impacts and remedies. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 378 , 20220360 (2023).
Davies, T. W., Duffy, J. P., Bennie, J. & Gaston, K. J. The nature, extent, and ecological implications of marine light pollution. Front. Ecol. Environ. 12 , 347–355 (2014).
Rousseau, Y., Watson, R. A., Blanchard, J. L. & Fulton, E. A. Evolution of global marine fishing fleets and the response of fished resources. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116 , 12238–12243 (2019).
UNCTAD. Handbook of Statistics 2020, United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UN, 2020).
Mgana, H. et al. Adoption and consequences of new light-fishing technology (LEDs) on Lake Tanganyika, East Africa. PLoS ONE 14 , e0216580 (2019).
Nguyen, K. Q. & Winger, P. D. Artificial light in commercial industrialized fishing applications: a review. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 27 , 106–126 (2018).
Elvidge, C. D. et al. Rating the effectiveness of fishery closures with visible infrared imaging radiometer suite boat detection data. Front. Mar. Sci. 5 , 132 (2018).
Dobler, G. et al. Dynamics of the urban lightscape. Inf. Syst. 54 , 115–126 (2015).
Robles, J. et al. Evolution of brightness and color of the night sky in Madrid. Remote Sens. 13 , 1511 (2021).
Romàn, M. O. & Stokes, E. C. Holidays in lights: tracking cultural patterns in demand for energy services. Earth’s Future 3 , 182–205 (2015).
Stathakis, D. & Baltas, P. Seasonal population estimates based on night-time lights. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 68 , 133–141 (2018).
Zhang, C., Pei, Y., Li, J., Qin, Q. & Yue, J. Application of Luojia 1-01 nighttime images for detecting the light changes for the 2019 spring festival in western cities, China. Remote Sens. 12 , 1416 (2020).
Molthan, A. & Jedlovec, G. Satellite observations monitor outages from superstorm Sandy. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 94 , 53–54 (2013).
Romàn, M. O. et al. Satellite-based assessment of electricity restoration efforts in Puerto Rico after hurricane Maria. PLoS ONE 14 , e0218883 (2019).
Kocifaj, M. Towards a comprehensive city emission function (CCEF). J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 205 , 253–266 (2018).
Levin, N. & Zhang, Q. A global analysis of factors controlling VIIRS nighttime light levels from densely populated areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 190 , 366–382 (2017).
Kocifaj, M. & Barà, S. Night-time monitoring of the aerosol content of the lower atmosphere by differential photometry of the anthropogenic skyglow. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 500 , L47–L51 (2020).
Posch, T., Binder, F. & Puschnig, J. Systematic measurements of the night sky brightness at 26 locations in Eastern Austria. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 211 , 144–165 (2018).
Pritchard, S. B. The trouble with darkness: NASA’s Suomi satellite images of Earth at night. Environ. Hist. 22 , 312–330 (2017).
Barà, S., Bao-Varela, C. & Kocifaj, M. Modeling the artificial night sky brightness at short distances from streetlights. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 296 , 108456 (2023).
Barà, S. & Bao-Varela, C. Skyglow inside your eyes: intraocular scattering and artificial brightness of the night sky. Int. J. Sustain. Light. 25 , 1–9 (2023).
Sánchez de Miguel, A., Bennie, J., Rosenfeld, E., Dzurjak, S. & Gaston, K. J. Environmental risks from artificial nighttime lighting widespread and increasing across Europe. Sci. Adv. 8 , eabl6891 (2022).
Sánchez de Miguel, A. et al. Sky quality meter measurements in a colour-changing world. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 467 , 2966–2979 (2017).
Kinney, J. A. S. Comparison of scotopic, mesopic, and photopic spectral sensitivity curves. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 48 , 185–190 (1958).
Rea, M., Bullough, J., Freyssinier-Nova, J. & Bierman, A. A proposed unified system of photometry. Light. Res. Technol. 36 , 85–109 (2004).
Crumey, A. Human contrast threshold and astronomical visibility. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 442 , 2600–2619 (2014).
Kollàth, Z., Dömény, A., Kollàth, K. & Nagy, B. Qualifying lighting remodelling in a Hungarian city based on light pollution effects. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 181 , 46–51 (2016).
Hung, L.-W., Anderson, S. J., Pipkin, A. & Fristrup, K. Changes in night sky brightness after a countywide LED retrofit. J. Environ. Manag. 292 , 112776 (2021).
Longcore, T. et al. Rapid assessment of lamp spectrum to quantify ecological effects of light at night. J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 329 , 511–521 (2018).
McCallum, I. et al. Estimating global economic well-being with unlit settlements. Nat. Commun . 13 , 2459 (2022).
Barentine, J. C. et al. Skyglow changes over Tucson, Arizona, resulting from a municipal LED street lighting conversion. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 212 , 10–23 (2018).
Aubé, M. & Roby, J. Sky brightness levels before and after the creation of the first International Dark Sky Reserve, Mont-Mégantic Observatory, Québec, Canada. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 139 , 52–63 (2014).
Kyba, C. C. M., Hänel, A. & Hölker, F. Redefining efficiency for outdoor lighting. Energy Environ. Sci. 7 , 1806–1809 (2014).
Fouquet, R. & Pearson, P. Seven centuries of energy services: the price and use of light in the United Kingdom (1300-2000). Energy J. 27 , 138–178 (2006).
Tsao, J. Y., Saunders, H. D., Creighton, J. R., Coltrin, M. E. & Simmons, J. A. Solid-state lighting: an energy-economics perspective. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 43 , 354001 (2010).
Bachanek, K. H., Tundys, B., Wiśniewski, T., Puzio, E. & Maroušková, A. Intelligent street lighting in a smart city concepts — a direction to energy saving in cities: an overview and case study. Energies 14 , 3018 (2021).
Kyba, C. C. M., Mohar, A., Pintar, G. & Stare, J. Reducing the environmental footprint of church lighting: matching facade shape and lowering luminance with the EcoSky LED. Int. J. Sustain. Light. 20 , 1 (2018).
Schroer, S. & Hölker, F. in Handbook of Advanced Lighting Technology 1–17 (Springer, 2014).
Schulte-Römer, N., Meier, J., Söding, M. & Dannemann, E. The LED paradox: how light pollution challenges experts to reconsider sustainable lighting. Sustainability 11 , 6160 (2019).
Zielińska-Dabkowska, K. M., Xavia, K. & Bobkowska, K. Assessment of citizens’ actions against light pollution with guidelines for future initiatives. Sustainability 12 , 4997 (2020).
Ngarambe, J., Lim, H. S. & Kim, G. Light pollution: is there an environmental Kuznets curve? Sustain. Cities Soc. 42 , 337–343 (2018).
Barà, S., Falchi, F., Lima, R. C. & Pawley, M. Can we illuminate our cities and (still) see the stars? Int. J. Sustain. Light. 23 , 58–69 (2021).
Dobler, G., Ghandehari, M., Koonin, S. & Sharma, M. A hyperspectral survey of New York City lighting technology. Sensors 16 , 2047 (2016).
Zschorn, M. & Mattern, J. Counting lights for sustainability — insights from the citizen science project Nachtlicht-BüHNE. In Proc. Austrian Citizen Science Conference 2022 – PoS ( ACSC2022 ) (Sissa Medialab, 2023).
Muñoz-Gil, G., Dauphin, A., Beduini, F. A. & Sánchez de Miguel, A. Citizen science to assess light pollution with mobile phones. Remote Sens. 14 , 4976 (2022).
Riegel, K. W. Light pollution. Science 179 , 1285–1291 (1973).
Walker, M. F. The California site survey. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 82 , 672 (1970).
Walker, M. F. Light pollution in California and Arizona. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 85 , 508 (1973).
Kyba, C. C. M., Ruhtz, T., Fischer, J. & Hölker, F. Cloud coverage acts as an amplifier for ecological light pollution in urban ecosystems. PLoS ONE 6 , e17307 (2011).
Stark, H. et al. City lights and urban air. Nat. Geosci. 4 , 730–731 (2011).
Kylling, A. et al. Actinic flux determination from measurements of irradiance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 108 , 4506 (2003).
Madronich, S. Photodissociation in the atmosphere: 1. Actinic flux and the effects of ground reflections and clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 92 , 9740–9752 (1987).
Degen, T., Kollàth, Z. & Degen, J. X, Y, and Z: a bird’s eye view on light pollution. Ecol. Evol. 12 , e9608 (2022).
Hölker, F. et al. 11 pressing research questions on how light pollution affects biodiversity. Front. Ecol. Evol. 9 , 767177 (2021).
Grubisic, M. et al. Light pollution, circadian photoreception, and melatonin in vertebrate. Sustainability 11 , 6400 (2019).
Liu, J. A., Meléndez-Fernàndez, O. H., Bumgarner, J. R. & Nelson, R. J. Effects of light pollution on photoperiod-driven seasonality. Horm. Behav. 141 , 105150 (2022).
Lin, C.-H., Takahashi, S., Mulla, A. J. & Nozawa, Y. Moonrise timing is key for synchronized spawning in coral Dipsastraea speciosa . Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118 , e2101985118 (2021).
Gaston, K., Visser, M. & Hölker, F. The biological impacts of artificial light at night: the research challenge. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 370 , 20140133 (2015).
Walbeek, T. J., Harrison, E. M., Gorman, M. R. & Glickman, G. L. Naturalistic intensities of light at night: a review of the potent effects of very dim light on circadian responses and considerations for translational research. Front. Neurol. 12 , 625334 (2021).
Gaston, K. J., Davies, T. W., Nedelec, S. L. & Holt, L. A. Impacts of artificial light at night on biological timings. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 48 , 49–68 (2017).
Silva, A. D., Valcu, M. & Kempenaers, B. Light pollution alters the phenology of dawn and dusk singing in common European songbirds. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 370 , 20140126 (2015).
Dominoni, D. M., Jensen, J. K., Jong, M., Visser, M. E. & Spoelstra, K. Artificial light at night, in interaction with spring temperature, modulates timing of reproduction in a passerine bird. Ecol. Appl. 30 , e02062 (2020).
Meng, L. et al. Artificial light at night: an underappreciated effect on phenology of deciduous woody plants. PNAS Nexus 1 , pgac046 (2022).
Zheng, Q., Teo, H. C. & Koh, L. P. Artificial light at night advances spring phenology in the United States. Remote Sens. 13 , 399 (2021).
Bennie, J., Davies, T. W., Cruse, D. & Gaston, K. J. Ecological effects of artificial light at night on wild plants. J. Ecol. 104 , 611–620 (2016).
Evens, R. et al. Skyglow relieves a crepuscular bird from visual constraints on being active. Sci. Total Environ. 900 , 165760 (2023).
Kupprat, F., Hölker, F. & Kloas, W. Can skyglow reduce nocturnal melatonin concentrations in Eurasian perch? Environ. Pollut. 262 , 114324 (2020).
Foster, J. J. et al. Light pollution forces a change in dung beetle orientation behavior. Curr. Biol. 31 , 3935–3942.e3 (2021).
Berge, J. et al. Artificial light during the polar night disrupts arctic fish and zooplankton behaviour down to 200m depth. Commun. Biol . 3 , 102 (2020).
Dimitriadis, C., Fournari – Konstantinidou, I., Sourbès, L., Koutsoubas, D. & Mazaris, A. D. Reduction of sea turtle population recruitment caused by nightlight: evidence from the Mediterranean region. Ocean Coast. Manage. 153 , 108–115 (2018).
Weisshaupt, N., Leskinen, M., Moisseev, D. N. & Koistinen, J. Anthropogenic illumination as guiding light for nocturnal bird migrants identified by remote sensing. Remote Sens. 14 , 1616 (2022).
Hale, J. D., Fairbrass, A. J., Matthews, T. J., Davies, G. & Sadler, J. P. The ecological impact of city lighting scenarios: exploring gap crossing thresholds for urban bats. Glob. Change Biol. 21 , 2467–2478 (2015).
Korpach, A. M. et al. Urbanization and artificial light at night reduce the functional connectivity of migratory aerial habitat. Ecography 8 , e05581 (2022).
Ditmer, M. A., Stoner, D. C. & Carter, N. H. Estimating the loss and fragmentation of dark environments in mammal ranges from light pollution. Biol. Conserv. 257 , 109135 (2021).
Pérez Vega, C., Jechow, A., Campbell, J. A., Zielinska-Dabkowska, K. M. & Hölker, F. Light pollution from illuminated bridges as a potential barrier for migrating fish — linking measurements with a proposal for a conceptual model. Basic Appl. Ecol. 74 , 1–12 (2024).
Szaz, D. et al. Lamp-lit bridges as dual light-traps for the night-swarming mayfly, Ephoron virgo : interaction of polarized and unpolarized light pollution. PLoS ONE 10 , e0121194 (2015).
Stepanian, P. M. et al. Declines in an abundant aquatic insect, the burrowing mayfly, across major North American waterways. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 2987–2992 (2020).
Manfrin, A. et al. Artificial light at night affects organism flux across ecosystem boundaries and drives community structure in the recipient ecosystem. Front. Environ. Sci . https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2017.00061 (2017).
McLaren, J. D. et al. Artificial light at night confounds broad-scale habitat use by migrating birds. Ecol. Lett. 21 , 356–364 (2018).
Hölker, F. et al. Microbial diversity and community respiration in freshwater sediments influenced by artificial light at night. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 370 , 20140130 (2015).
Sanders, D. & Gaston, K. J. How ecological communities respond to artificial light at night. J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 329 , 394–400 (2018).
Poulin, R. Light pollution may alter host–parasite interactions in aquatic ecosystems. Trends Parasitol. 39 , 1050–1059 (2023).
Nelson, T. R. et al. Riverine fish density, predator-prey interactions, and their relationships with artificial light at night. Ecosphere 13 , e4261 (2022).
Giavi, S., Fontaine, C. & Knop, E. Impact of artificial light at night on diurnal plant-pollinator interactions. Nat. Commun. 12 , 1690 (2021).
Hölker, F., Wolter, C., Perkin, E. & Tockner, K. Light pollution as a biodiversity threat. Trends Ecol. Evol. 25 , 681-2 (2010).
Lewanzik, D. & Voigt, C. C. Artificial light puts ecosystem services of frugivorous bats at risk. J. Appl. Ecol. 51 , 388–394 (2014).
Agboola, O. et al. A review on the impact of mining operation: monitoring, assessment and management. Results Eng. 8 , 100181 (2020).
Dale, A. T. et al. Preliminary comparative life-cycle impacts of streetlight technology. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 17 , 193–199 (2011).
Tähkämö, L., Räsänen, R.-S. & Halonen, L. Life cycle cost comparison of high-pressure sodium and light-emitting diode luminaires in street lighting. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 21 , 137–145 (2015).
Rahman, S. M., Pompidou, S., Alix, T. & Laratte, B. A review of LED lamp recycling process from the 10 R strategy perspective. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 28 , 1178–1191 (2021).
United Nations. UN Environment Programme: the rapid transition to energy efficient lighting: an integrated policy approach (UN, 2013).
Noon, K. A., De Napoli, K., Swanton, P., Guedes, C. & Hamacher, D. The Routledge Handbook of Social Studies of Outer Space (Routledge, 2023).
Streetlight-EPC. Streetlight-EPC - Guide. Joint Research Centre — European Energy Efficiency Platform https://e3p.jrc.ec.europa.eu/publications/streetlight-epc-guide (2015).
Cupertino, M. D. C. et al. Light pollution: a systematic review about the impacts of artificial light on human health. Biol. Rhythm Res. 54 , 263–275 (2022).
Rybnikova, N. & Portnov, B. A. Population-level study links short-wavelength nighttime illumination with breast cancer incidence in a major metropolitan area. Chronobiol. Int. 35 , 1198–1208 (2018).
Stevens, R. G. Testing the light-at-night (LAN) theory for breast cancer causation. Chronobiol. Int. 28 , 653–656 (2011).
Garcia-Saenz, A. et al. Association between outdoor light-at-night exposure and colorectal cancer in Spain. Epidemiology 31 , 718–727 (2020).
Fonken, L. K. et al. Light at night increases body mass by shifting the time of food intake. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107 , 18664–18669 (2010).
Spiegel, K., Knutson, K., Leproult, R., Tasali, E. & Cauter, E. V. Sleep loss: a novel risk factor for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. J. Appl. Physiol. 99 , 2008–2019 (2005).
Bedrosian, T. A., Fonken, L. K., Walton, J. C., Haim, A. & Nelson, R. J. Dim light at night provokes depression-like behaviors and reduces CA1 dendritic spine density in female hamsters. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36 , 1062–1069 (2011).
McIsaac, M. A., Sanders, E., Kuester, T., Aronson, K. J. & Kyba, C. C. M. The impact of image resolution on power, bias, and confounding. Environ. Epidemiol. 5 , e145 (2021).
Nadybal, S. M., Collins, T. W. & Grineski, S. E. Light pollution inequities in the continental United States: a distributive environmental justice analysis. Environ. Res. 189 , 109959 (2020).
Xiao, Q. et al. Cross-sectional association between outdoor artificial light at night and sleep duration in middle-to-older aged adults: the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Environ. Res. 180 , 108823 (2020).
Park, Y.-M. M., White, A. J., Jackson, C. L., Weinberg, C. R. & Sandler, D. P. Association of exposure to artificial light at night while sleeping with risk of obesity in women. JAMA Intern. Med. 179 , 1061 (2019).
Mendoza, R. U. Why do the poor pay more? Exploring the poverty penalty concept. J. Int. Dev. 23 , 1–28 (2011).
Braubach, M. & Fairburn, J. Social inequities in environmental risks associated with housing and residential location — a review of evidence. Eur. J. Public Health 20 , 36–42 (2010).
Mullin, K., Mitchell, G., Nawaz, N. R. & Waters, R. D. Natural capital and the poor in England: towards an environmental justice analysis of ecosystem services in a high income country. Landsc. Urban Plan. 176 , 10–21 (2018).
Elvidge, C. D., Baugh, K. E., Kihn, E. A., Kroehl, H. W. & Davis, E. R. Mapping city lights with nighttime data from the DMSP Operational Linescan System. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 63 , 727–734 (1997).
Forbes, D. J. Multi-scale analysis of the relationship between economic statistics and DMSP-OLS night light images. GISci. Remote Sens. 50 , 483–499 (2013).
Kyba, C. et al. High-resolution imagery of Earth at night: new sources, opportunities and challenges. Remote Sens. 7 , 1–23 (2014).
Bouman, M. J. Luxury and control. J. Urban Hist. 14 , 7–37 (1987).
Xiao, Q. et al. Artificial light at night and social vulnerability: an environmental justice analysis in the U.S. 2012-2019. Environ. Int. 178 , 108096 (2023).
Martinez, L. & Bordonaro, E. Lighting inequality in an urban context: design approach and case studies. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1099 , 012006 (2022).
Mann, M., Melaas, E. & Malik, A. Using VIIRS Day/Night Band to measure electricity supply reliability: preliminary results from Maharashtra, India. Remote Sens. 8 , 711 (2016).
Zhou, Y., Li, X., Asrar, G. R., Smith, S. J. & Imhoff, M. A global record of annual urban dynamics (1992–2013) from nighttime lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 219 , 206–220 (2018).
Zhu, Z. et al. Understanding an urbanizing planet: strategic directions for remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 228 , 164–182 (2019).
Vilaysouk, X. et al. Estimating the total in-use stock of Laos using dynamic material flow analysis and nighttime light. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 170 , 105608 (2021).
Henderson, J. V., Storeygard, A. & Weil, D. N. Measuring economic growth from outer space. Am. Econ. Rev. 102 , 994–1028 (2012).
Statista. Gross domestic product (GDP) at current prices of Wuhan City in China from 2012 to 2022. Statista https://www.statista.com/statistics/1374056/china-gross-domestic-product-gdp-of-wuhan/ (2023).
Duan, H., Cao, Z., Shen, M., Liu, D. & Xiao, Q. Detection of illicit sand mining and the associated environmental effects in China’s fourth largest freshwater lake using daytime and nighttime satellite images. Sci. Total Environ. 647 , 606–618 (2019).
Elvidge, C., Zhizhin, M., Baugh, K. & Hsu, F.-C. Automatic boat identification system for VIIRS low light imaging data. Remote Sens. 7 , 3020–3036 (2015).
Geliot, S., Coesfeld, J. & Kyba, C. C. M. Scale and impact of sports stadium grow lighting systems in England. Int. J. Sustain. Light. 24 , 39–51 (2022).
Daniel, J., Secor, W. & Campbell, B. Impact of information on attitudes regarding greenhouse lighting externality regulation. J. Agric. Appl. Econ. 55 , 358–375 (2023).
Li, X., Liu, S., Jendryke, M., Li, D. & Wu, C. Night-time light dynamics during the Iraqi civil war. Remote Sens. 10 , 858 (2018).
Miller, S. et al. Illuminating the capabilities of the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Day/Night Band. Remote Sens. 5 , 6717–6766 (2013).
Miller, S. D. et al. Honing in on bioluminescent milky seas from space. Sci. Rep. 11 , 15443 (2021).
Zhou, L. et al. Observed atmospheric features for the 2022 Hunga Tonga volcanic eruption from Joint Polar Satellite System science data products. Atmosphere 14 , 263 (2023).
Ranzoni, J., Giuliani, G., Huber, L. & Ray, N. Modelling the nocturnal ecological continuum of the State of Geneva, Switzerland, based on high-resolution nighttime imagery. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 16 , 100268 (2019).
Elvidge, C. D. et al. The Nightsat mission concept. Int. J. Remote Sens. 28 , 2645–2670 (2007).
Falchi, F., Barà, S., Cinzano, P., Lima, R. C. & Pawley, M. A call for scientists to halt the spoiling of the night sky with artificial light and satellites. Nat. Astron. 7 , 237–239 (2023).
Vruno, F. D. et al. Unintended electromagnetic radiation from Starlink satellites detected with LOFAR between 110 and 188 MHz. Astron. Astrophys . 676 , A75 (2023).
Cui, Z. & Xu, Y. Impact simulation of Starlink satellites on astronomical observation using Worldwide Telescope. Astron. Comput. 41 , 100652 (2022).
Kocifaj, M., Kundracik, F., Barentine, J. C. & Barà, S. The proliferation of space objects is a rapidly increasing source of artificial night sky brightness. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 504 , L40–L44 (2021).
Lewis, H. G. Understanding long-term orbital debris population dynamics. J. Space Saf. Eng. 7 , 164–170 (2020).
Lackner, H. Yemen in Crisis : Road to War (Verso Books, 2019).
Rao, C. & Yan, B. Study on the interactive influence between economic growth and environmental pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 , 39442–39465 (2020).
Download references
Acknowledgements
A.A., A.S, C.C.M.K., F.H., H.L.A., M.A., M.K. and T.D. received funding for this work through ESA’s New Earth Observation Mission Ideas (NEOMI) program under contract 4000139244/22/NL. A.S.d.M. has been funded by European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement number 847635 (UNA4CAREER). A.J. was supported by the project BELLVUE “Beleuchtungsplanung: Verfahren und Methoden für eine naturschutzfreundliche Beleuchtungsgestaltung” by the BfN with funds from the BMU (FKZ: 3521 84 1000).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Stars4All Foundation, Madrid, Spain
Hector Linares Arroyo
Faculty of Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation (ITC), University of Twente, Twente, Netherlands
Angela Abascal & Monika Kuffer
Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries (IGB), Berlin, Germany
Tobias Degen, Franz Hölker & Andreas Jechow
Department of Zoology II, University of Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany
Tobias Degen
Département de Physique, Cégep de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada
Martin Aubé & Alexandre Simoneau
Département de Géomatique Appliquée, Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada
School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, University of Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Brian R. Espey
Adler Planetarium, Chicago, IL, USA
Geza Gyuk & Ken Walczak
Institute of Biology, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Franz Hölker
Department of Engineering, Brandenburg University of Applied Sciences, Brandenburg an der Havel, Germany
Andreas Jechow
Física de la Tierra y Astrofísica. Instituto de Física de Partículas y del Cosmos (IPARCOS), Universidad Complutense, Madrid, Spain
Alejandro Sánchez de Miguel
Environment and Sustainability Institute, University of Exeter, Penryn, UK
GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, Potsdam, Germany
Christopher C. M. Kyba
Geographisches Institut, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bochum, Germany
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
H.L.A, A.A., T.D., F.H., A.J., M.K., A.S.d.M., K.W. and C.C.M.K. researched data for the article. H.L.A., A.A., M.A., T.D., B.R.E., G.G., F.H., M.K., A.S., K.W. and C.C.M.K contributed substantially to the discussion of the content. H.L.A., A.A., T.D., F.H., A.J., M.K., A.S.d.M., K.W. and C.C.M.K. wrote the article. H.L.A., A.A., A.S. and C.C.M.K. reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hector Linares Arroyo .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment thanks Qingling Zhang, Avalon Owens and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Related links
Dark Sky International: https://www.darksky.org
ImageJ: http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/
IRIS: http://www.astrosurf.com/buil/us/iris/iris.htm
The World Factbook: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/airports/country-comparison/
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Linares Arroyo, H., Abascal, A., Degen, T. et al. Monitoring, trends and impacts of light pollution. Nat Rev Earth Environ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-024-00555-9
Download citation
Accepted : 05 April 2024
Published : 23 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-024-00555-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Anthropocene newsletter — what matters in anthropocene research, free to your inbox weekly.
Top 100 Environmental Science Project Topics
Table of contents
- 1 Climate Change
- 2 Renewable Energy
- 3 Urban Ecology
- 4 Land and Water Use
- 5 Pollution
- 6 Environmental Science Topics for College Students
- 7 Energy Resources and Consumption
- 8 Population
- 9 Noise and Light Pollution
- 10.1 Conclusion
With the environment and global warming in its current predicament, it’s no surprise that environmental science job opportunities will be on the rise in the very near future.
With the environment and global warming in its current predicament, it’s no surprise that environmental science job opportunities will be on the rise in the very near future. Therefore, so are the numbers of students pursuing studies in this field. The last four decades have seen huge changes in the rate of global warming and so more than ever before, we need people to study topics in environmental science.
For anyone majoring in environmental science, anyone needing to write environmental studies project topics for a science course, or essay writer who is working on topical essays this comprehensive article will talk you through the top ten project topics to pursue. For each project topic, we’ll give you ten ideas.
Climate Change
There’ll always be an environment, but it’s looking more and more likely that it won’t be like our current one in the future. With this in mind, here are the top ten environmental project topics for college students on climate change:
- Is global warming a natural phenomenon?
- The politicization of global warming.
- How do eddy covariance towers work?
- Planetary tilt – does it affect global warming?
- The differences between climate change and the greenhouse effect.
- Why is carbon dioxide a greenhouse gas?
- How do changes to weather patterns affect the Earth’s climate?
- The concept of polar amplification.
- The barriers to climate change responses.
- The “heat island” effect.

Renewable Energy
Our advances through the industrial revolution and the use of fossil fuels are now coming back to bite us. Here are ten environmental topics for project on renewable energy:
- The pros and cons of hydropower.
- Solar energy and pollution.
- Solar energy to help the economy.
- Geothermal energy: an unlikely major energy source?
- The problems caused by renewable energies.
- Understanding geothermal energy.
- Are hydrogen fuel cells a viable alternative?
- The advantages and disadvantages of solar power.
- Transporting geothermal energy: a study.
- The challenges of large-scale biomass energy use.
Urban Ecology
Urban ecology is an important consideration for environmental science projects for college students who are eager to pay for essay to receive high grades for assignments. When we study the environment, we tend to think of green spaces and rural lands, but urban ecology is important too. As such, here are ten environmental science project ideas on this topic:
- How do unequal urban planning and greenspace distribution affect temperatures in a city?
- How does urbanization affect surrounding rural areas?
- How is the local climate affected by buildings and pavements?
- What is the urban heat island effect?
- How are water sources affected by urbanization?
- How has human development affected our green spaces?
- How is social identity linked to urbanization?
- What impact does transport have on rural locations?
- How can the natural environment be integrated into urban planning and design projects?
- What is water harvesting?

Land and Water Use
When humans use natural resources, they also disrupt natural ecosystems. This is an important area of study as we try to claw back and save some of the world’s resources from being entirely depleted. Here are ten interesting environment related topics for project on this subject:
- How have overfishing and non-sustainable fishing methods affected our oceans?
- How does using water for irrigation affect natural ecosystems?
- The impacts of different societies’ ecological footprints in terms of waste production and resource demands.
- How can we mitigate deforestation?
- An analysis of The Green Revolution.
- The impact of salt application to streams.
- How does using an ANN (artificial neural network) for rainfall-runoff affect ecosystems?
- How do land-use changes impact urban runoff?
- Relationships between water quality, land use and land use change.
- Land use effects on lake water quality.
Pollution is one of the planet and humanity’s worst enemies. Agriculture, transportation, and industry can cause horrific environmental catastrophes. Check out the possible environment science project topics on pollution:
- The impact of pollution on health care.
- The effects of environmental pollution and water pollution on marine life.
- The effects of air pollution on the food chain.
- How environmental pollution affects Arctic.
- The health hazards associated with waste accumulation and water pollution.
- How do human activities change the world’s oceans?
- Conservation and how it helps to reduce air pollution.
- The difficulty of establishing direct links between health problems, air pollution, and air quality.
- Environmental policy regarding air pollution and acid rain.
- The effect of acid rain in urban and natural areas.
Environmental Science Topics for College Students
Environmental studies at college is all about studying in-depth biological, chemical, and physical processes on Earth. Environmental sciences also incorporates social, cultural, and political processes that have an impact. When studying Environmental Science at college level, a project need to seek out ways to present complex relationships in a simple way. Here are some ideal environmental science projects for college students:
- Genetically Modified (GM) foods and their impact on the environment.
- The global impact of radiation and nuclear accidents.
- The role of the UNEP in environmental conservation.
- The impact of freak weather incidents.
- Micro-plastics in drinking water – why and how have they got there?
- The Nagasaki and Hiroshima bombings – what have we learned about nuclear bombs and the effects on the ecosystem?
- The impact of Coronavirus and maintaining the ecosystem.
- The role of the media in conservation campaigns.
- Tourism and the impact of human activities on a local and global level.
- How has the US departure from the Paris Climate Agreement changed things?
Energy Resources and Consumption
Lots of environmental studies project topics goes into looking at energy resources and consumption, which makes this a great project topic. There is already a lot of information out there, which makes this easy to research.
- What is the relationship between energy efficiency and energy conservation?
- What are the economic, social, and environmental costs of solar energy?
- Was coal pivotal in industrialization?
- The impact of fracking on the environment.
- Compare and contrast the processes of extracting oil and mining coal.
- How is ethanol produced as a biofuel?
- Nuclear energy is a viable clean energy. Discuss.
- The environmental effects of a nuclear conflict explored.
- What is plant biomass?
- The challenges of converting to large-scale biomass energy.
You can't write a list environment project topics about environmental science, without mentioning population, environmental health, and the changes we've seen over the years. A lot of environment research focuses on population and its effects. Here are some ideas:
- Population growth and its effects on GDP.
- Factors that control population growth and the effect of density.
- An exploration of population momentum.
- The importance of studying population ecology.
- The effect of human migration on populations.
- The effects of overpopulation.
- The effects of global warming on the global population.
- Is sustainable development possible in a growing population?
- What would happen if the demand for natural resources became greater than the supply?
- How serious is the world population explosion?
Noise and Light Pollution
Though lots of people don’t consider light and noise as pollutants, the reality is that they are. Noise levels and light levels can affect organisms. Here are some interesting topics for science projects on noise and light pollution:
- How is local wildlife affected by airport noise?
- What happens if orcas aren’t able to use echolocation due to freight noise?
- Migrating birds and the confusion from bright lights.
- The effect of bright lights in resorts and sea turtles emerging from nests.
- How bright city lights affect nocturnal animals.
- The disruption of nocturnal activity in frogs and toads due to artificial light glare.
- Artificial lights and the effects on migratory birds.
- Light pollution and the effects on plants.
- Changes in animal behavior due to noise pollution.
- Noise pollution and the effects on mating frogs.
Conservation Biology
With as many as 2,000 species becoming extinct each year, we’re experiencing a serious problem. Conservation biology is a huge topic of interest when you need to " write my essay " and want to succeed with this task. Here are some ideas for exploration:
- How has human behavior ramped up endangered species extinction rates?
- How do humans threaten endangered species?
- What will the effects of a loss in biodiversity be for humans?
- If honeybees become extinct, what other changes would we see?
- Why is the decline in pollinating insects so dangerous?
- What happens if we lose endangered species?
- What is the Holocene extinction event?
- The collapse of the world’s coral reef ecosystems.
- The threat of acidification in our oceans.
- How can environmental policy help threats to biodiversity?
It's clear to say that there is a huge variety in topics in environmental science. For anyone looking for an environmental science project topic, we hope this extensive list has helped narrow down your ideas. Whether you're looking for environmental research topics for college students or high school, there is something for everyone here.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Water Pollution Research Paper Topics

This comprehensive guide to water pollution research paper topics is designed to provide students studying environmental science with a wealth of options for their research papers. The guide offers a broad array of topics, divided into ten categories, each containing ten unique research topics. Additionally, the guide provides expert advice on how to choose a topic from the multitude of water pollution research paper topics and how to write a compelling research paper on water pollution. The guide also introduces iResearchNet’s writing services, which offer students the opportunity to order a custom water pollution research paper on any topic. The services boast a range of features designed to ensure the delivery of high-quality, custom-written papers.
100 Water Pollution Research Paper Topics
Water pollution is a vast and complex issue, making it a rich subject for research. The following list of water pollution research paper topics is divided into ten categories, each containing ten unique topics. This comprehensive list is designed to inspire and guide you in your quest for knowledge and understanding of water pollution.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Causes of Water Pollution
- Industrial waste and water pollution.
- Agricultural runoff and water pollution.
- Household waste and water pollution.
- Oil spills and water pollution.
- Mining and water pollution.
- Deforestation and water pollution.
- Urban development and water pollution.
- Climate change and water pollution.
- Plastic waste and water pollution.
- Radioactive waste and water pollution.
Effects of Water Pollution
- Water pollution and human health.
- Water pollution and aquatic ecosystems.
- Water pollution and biodiversity.
- Water pollution and food security.
- Water pollution and climate change.
- Water pollution and economic development.
- Water pollution and social inequality.
- Water pollution and tourism.
- Water pollution and natural disasters.
- Water pollution and future generations.
Water Pollution Solutions
- Water treatment technologies.
- Waste management strategies.
- Policy interventions for water pollution.
- Public awareness and education.
- Corporate social responsibility and water pollution.
- Sustainable agriculture practices.
- Green technology and water pollution.
- International cooperation on water pollution.
- Community-led initiatives for clean water.
- Innovation and research in water pollution control.
Water Pollution Policies
- The Clean Water Act.
- The Safe Drinking Water Act.
- The role of the EPA in water pollution control.
- Water pollution laws in developing countries.
- International laws and treaties on water pollution.
- The effectiveness of water pollution policies.
- Challenges in enforcing water pollution laws.
- Policy gaps in water pollution control.
- The role of local governments in water pollution control.
- Future directions for water pollution policies.
Water Pollution Case Studies
- The Flint water crisis.
- The Ganges River pollution.
- The Great Pacific Garbage Patch.
- Oil spills: The Deepwater Horizon case.
- Eutrophication in the Gulf of Mexico.
- Microplastics in the Great Lakes.
- Industrial pollution in the Yangtze River.
- Agricultural runoff in the Mississippi River.
- Radioactive pollution in Fukushima.
- Sewage pollution in the Thames River.
Water Pollution and Public Health
- Waterborne diseases and water pollution.
- The impact of water pollution on child health.
- Water pollution and mental health.
- The link between water pollution and cancer.
- Water pollution and antimicrobial resistance.
- The role of clean water in disease prevention.
- Health inequalities and water pollution.
- The psychological impact of water pollution.
- Water pollution and food safety.
- The future of public health in a polluted world.
Water Pollution and Climate Change
- The impact of rising temperatures on water pollution.
- Sea-level rise and water pollution.
- Climate change, extreme weather events, and water pollution.
- The role of water pollution in exacerbating climate change.
- Climate change mitigation strategies and water pollution.
- The future of water pollution in a warming world.
- Climate justice and water pollution.
- Climate change adaptation and water pollution.
- The role of climate change education in water pollution control.
- Climate change policies and water pollution.
Water Pollution and Social Issues
- Water pollution and poverty.
- Water pollution and gender inequality.
- Water pollution and racial disparities.
- Water pollution and indigenous rights.
- Water pollution and migration.
- Water pollution and conflict.
- Water pollution and education.
- Water pollution and community resilience.
- Water pollution and social activism.
- Water pollution and the media.
Water Pollution and Technology
- The role of technology in water pollution detection.
- Technological solutions for water treatment.
- The impact of digital technology on water pollution control.
- The role of AI in water pollution management.
- Technology and water pollution education.
- The future of technology in water pollution control.
- The role of technology in water conservation.
- Technology and sustainable water management.
- The impact of technology on water quality.
- Technological innovation and water pollution policies.
Water Pollution and Sustainability
- The role of sustainable development in water pollution control.
- Water pollution and the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Sustainable water management practices.
- The role of sustainability education in water pollution control.
- Sustainability and water conservation.
- The future of sustainability in a polluted world.
- The role of sustainable agriculture in water pollution control.
- Sustainable cities and water pollution.
- Sustainability and water security.
- The role of sustainability in water policy.
In conclusion, this comprehensive list of water pollution research paper topics offers a wide range of options for students interested in studying this critical environmental issue. Whether you’re interested in the causes, effects, solutions, or social implications of water pollution, there’s a topic here for you. Remember, the best research papers start with a topic you’re passionate about, so choose a topic that resonates with you and start exploring.
Water Pollution Research Guide
Water pollution is a critical environmental issue that poses significant challenges to ecosystems, human health, and sustainable development. As students of environmental science, it is vital to understand the complexities of water pollution and its implications for our planet. One of the essential tasks assigned to students in this field is to write research papers on water pollution, which not only enhance their knowledge but also contribute to the collective efforts in finding solutions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore a wide range of water pollution research paper topics, provide expert advice on choosing suitable topics, and offer valuable insights on how to write an impactful research paper.
Water pollution encompasses various sources and factors, including industrial waste, agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, and chemical contaminants. By delving into research papers on water pollution, students can gain a deeper understanding of the causes, effects, and potential mitigation strategies for this environmental concern. Moreover, these research papers serve as platforms for students to contribute to the existing body of knowledge and propose innovative solutions to combat water pollution effectively.
Throughout this guide, we will present a diverse range of water pollution research paper topics that cover different aspects of the issue. These topics will be organized into comprehensive categories to facilitate your exploration and ensure you find a subject that aligns with your interests and academic goals. By addressing topics such as the impact of industrial pollutants on aquatic ecosystems, the role of agriculture in water contamination, and the effectiveness of wastewater treatment methods, you can explore the multifaceted dimensions of water pollution and contribute to the ongoing efforts to address this global challenge.
In addition to the extensive list of water pollution research paper topics, we will provide expert advice on how to choose the most suitable topic for your study. Selecting the right research topic is crucial as it determines the scope, relevance, and impact of your research. Our expert tips will guide you through the process, helping you identify areas of interest, narrow down your focus, and ensure that your chosen topic aligns with your academic goals and research objectives.
Furthermore, we understand that writing a research paper can be a daunting task, especially for those new to the field. Therefore, we have included a dedicated section on how to write a water pollution research paper. We will provide you with a step-by-step guide, from formulating a research question to conducting literature reviews, collecting and analyzing data, and presenting your findings. Additionally, we will share tips and techniques to enhance your writing skills, improve the structure and flow of your paper, and effectively communicate your research findings.
We also recognize that time constraints and other academic commitments may sometimes hinder students from devoting ample time to their research papers. That’s why we offer our professional writing services to assist you in crafting a custom water pollution research paper tailored to your specific requirements. Our team of expert degree-holding writers possesses extensive knowledge in environmental science and will conduct in-depth research to deliver a top-quality paper that meets your academic needs.
Choosing a Water Pollution Research Topic
Choosing a compelling and impactful research topic is crucial when writing a water pollution research paper. It sets the foundation for your study and determines the scope and relevance of your research. With numerous dimensions to explore within the realm of water pollution, selecting the right topic can be a challenging task. To help you navigate this process effectively, we have compiled expert advice and practical tips to guide you in choosing the most suitable water pollution research paper topic. Consider the following ten tips:
- Identify your interests and passion : Begin by reflecting on your personal interests and areas of passion within the field of water pollution. Do you have a particular interest in industrial pollutants, agricultural runoff, or plastic waste in water bodies? Identifying your interests will help you stay motivated throughout the research process.
- Conduct preliminary research : Before finalizing a topic, conduct preliminary research to familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge in the field. Read scholarly articles, research papers, and reports related to water pollution to gain insights into existing gaps, emerging trends, and potential research areas.
- Narrow down your focus : Once you have an understanding of the broad field of water pollution, narrow down your focus to a specific aspect or subtopic that aligns with your interests and research goals. For example, you could explore the impact of microplastics on marine ecosystems or the effectiveness of water pollution regulations in urban areas.
- Consider the research context : Take into account the geographical context and research opportunities available to you. Is there a specific region or local water body where you can conduct fieldwork or gather data? Considering the research context can add depth and relevance to your study.
- Evaluate the research significance : Assess the significance and potential impact of your chosen topic. Does it address an important research gap, contribute to existing knowledge, or offer practical implications for water pollution management and conservation efforts? Aim for a topic that has both academic and real-world relevance.
- Consult with your professor or advisor : Seek guidance from your professor or research advisor, as they can provide valuable insights and suggestions based on their expertise. They can help you refine your research questions, identify suitable methodologies, and offer suggestions for relevant literature.
- Consider interdisciplinary perspectives : Water pollution is a complex issue that requires interdisciplinary approaches. Consider incorporating perspectives from other disciplines such as ecology, chemistry, public health, or policy analysis. This interdisciplinary approach can add depth and richness to your research.
- Explore emerging trends and technologies : Stay updated with the latest research advancements, emerging trends, and innovative technologies in the field of water pollution. Investigate how new methodologies, monitoring techniques, or data analysis tools can be applied to your research topic to enhance its impact and contribute to the field.
- Balance feasibility and interest : While it is essential to choose a topic that interests you, also consider its feasibility within the scope of your research project. Assess the availability of data, resources, and the time required to conduct research on your chosen topic.
- Seek ethical considerations : Consider the ethical implications of your research topic, especially if it involves human subjects, sensitive ecosystems, or policy-related issues. Ensure that your research design adheres to ethical guidelines and safeguards the welfare of those involved.
By following these expert tips, you can select a compelling and meaningful water pollution research paper topic that aligns with your interests, contributes to the field, and inspires you throughout your research journey. Remember that the chosen topic will shape your research direction and influence the significance of your findings.
How to Write a Water Pollution Research Paper
Writing a water pollution research paper requires careful planning, systematic organization of ideas, and adherence to academic standards. In this section, we will provide you with ten practical tips to guide you through the process of writing an effective and compelling research paper on water pollution.
- Understand the research question : Start by clearly understanding the research question or objective of your study. Identify the specific aspect of water pollution you aim to investigate and formulate a concise and focused research question that will guide your entire paper.
- Conduct a comprehensive literature review : Before diving into writing, conduct a thorough literature review to familiarize yourself with existing research on the topic. Identify key theories, concepts, and findings that will serve as the foundation for your own study. Analyze the gaps and controversies in the literature that your research can address.
- Develop a solid research methodology : Outline the research methodology that will best address your research question. Determine whether your study will involve quantitative analysis, qualitative research, or a combination of both. Clearly define your variables, sampling methods, data collection techniques, and analytical tools.
- Gather relevant and reliable data : Collect data from credible sources to support your research findings. This may involve fieldwork, laboratory analysis, surveys, interviews, or secondary data collection. Ensure that your data is accurate, relevant, and representative of the research problem.
- Analyze and interpret the data : Once you have collected the necessary data, conduct a rigorous analysis using appropriate statistical or qualitative techniques. Interpret the results in light of your research question and objectives. Use clear and concise language to present your findings, tables, charts, or graphs to enhance understanding.
- Structure your paper effectively : Organize your research paper in a logical and coherent manner. Begin with an introduction that provides background information, states the research question, and outlines the structure of the paper. Follow with a literature review, methodology section, results and discussion, and a conclusion that summarizes your findings and implications.
- Provide a critical analysis : While presenting your research findings, critically analyze the data and discuss its strengths, limitations, and implications. Highlight the significance of your findings in relation to existing knowledge and theories. Identify any areas for further research or potential policy implications.
- Use clear and concise language : Communicate your ideas effectively by using clear and concise language throughout the paper. Avoid jargon or complex terminology unless necessary, and ensure that your arguments and explanations are easily understood by your target audience.
- Cite and reference sources accurately : Give credit to the authors of the works you have referenced by using proper citation and referencing formats, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago style. This ensures that your paper is academically sound and avoids any plagiarism concerns.
- Revise and edit your paper : Before finalizing your research paper, thoroughly revise and edit it for clarity, coherence, grammar, and punctuation. Ensure that your arguments flow logically, the structure is coherent, and the writing is polished. Seek feedback from peers or professors to improve the quality of your paper.
By following these ten tips, you can write a comprehensive and well-structured water pollution research paper that contributes to the field and effectively communicates your findings. Remember to maintain a critical mindset, engage with relevant literature, and present your research in a clear and concise manner.
Custom Research Paper Writing Services
When it comes to writing a high-quality and impactful research paper on water pollution, iResearchNet offers a range of writing services that cater to the specific needs of students studying environmental science. Our team of expert writers, who hold advanced degrees in the field, are committed to delivering custom research papers that meet the highest academic standards. Here are thirteen features that make our writing services the ideal choice for your water pollution research paper:
- Expert degree-holding writers : Our team consists of writers with advanced degrees in environmental science and related fields. They possess in-depth knowledge and expertise in water pollution, ensuring that your research paper is written by a subject matter expert.
- Custom written works : We understand the importance of originality and customization. Your research paper will be crafted from scratch, tailored to your specific requirements and research objectives. We never resell or reuse papers, ensuring that your work is unique and plagiarism-free.
- In-depth research : Our writers are skilled researchers who are adept at conducting comprehensive literature reviews and gathering relevant data on water pollution. They will incorporate the latest research and data into your paper, providing a solid foundation for your study.
- Custom formatting : Whether you require APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, Harvard, or any other formatting style, our writers are well-versed in various citation and formatting guidelines. They will ensure that your paper adheres to the specific formatting requirements of your institution.
- Top quality : We are committed to delivering research papers of the highest quality. Our writers pay attention to detail, use credible sources, and employ rigorous analysis to provide you with a well-researched and well-written paper.
- Customized solutions : We understand that every research paper is unique, with its own set of requirements and objectives. Our writers will work closely with you to understand your specific needs and tailor their approach to meet them effectively.
- Flexible pricing : We offer competitive and transparent pricing options to accommodate various budgets. Our pricing is based on factors such as the complexity of the research paper, the deadline, and the academic level. You can choose the package that best suits your needs.
- Short deadlines : We understand that time constraints can be a challenge. With our short deadline options, you can receive a high-quality research paper even if you have limited time available. Our writers are skilled at working efficiently and meeting tight deadlines.
- Timely delivery : We prioritize timely delivery of your research paper. Our writers are committed to meeting the agreed-upon deadlines, ensuring that you have sufficient time to review the paper and make any necessary revisions.
- 24/7 support : Our customer support team is available round the clock to assist you with any queries or concerns you may have. Whether you need updates on your paper or have questions about our services, we are here to provide prompt and reliable support.
- Absolute Privacy : We prioritize the privacy and confidentiality of our clients. Your personal information and order details will be handled with the utmost care and will never be shared with third parties.
- Easy order tracking : You can easily track the progress of your order through our user-friendly platform. Stay updated on the status of your research paper and communicate with your assigned writer directly.
- Money-back guarantee : We are confident in the quality of our work. If, for any reason, you are not satisfied with the final research paper, we offer a money-back guarantee to ensure your peace of mind.
By choosing iResearchNet for your custom water pollution research paper, you can benefit from the expertise of our writers, the quality of our work, and the convenience of our services. Our goal is to provide you with a research paper that meets your requirements, contributes to the field, and helps you achieve academic success.
Order Your Custom Research Paper Today!
Are you struggling to write a research paper on water pollution? Don’t let the stress and time constraints hold you back from achieving academic success. At iResearchNet, we are here to offer you a solution. Order a custom water pollution research paper from our expert writers and experience the convenience and quality of our writing services. With our dedicated team and comprehensive features, you can have a well-researched and tailored paper that meets your academic requirements.
Don’t let the challenges of writing a water pollution research paper hinder your academic progress. Take the plunge and order your custom research paper from iResearchNet. Our writing services are designed to alleviate your burden and provide you with a high-quality, well-researched paper that showcases your understanding of the topic.
Place your order today and let our expert writers help you make a significant contribution to the field of environmental science with your water pollution research paper. Achieve academic success with confidence and trust in our reliable and professional writing services.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- Essay Topic Generator
- Summary Generator
- Thesis Maker Academic
- Sentence Rephraser
- Read My Paper
- Hypothesis Generator
- Cover Page Generator
- Text Compactor
- Essay Scrambler
- Essay Plagiarism Checker
- Hook Generator
- AI Writing Checker
- Notes Maker
- Overnight Essay Writing
- Topic Ideas
- Writing Tips
- Essay Writing (by Genre)
- Essay Writing (by Topic)
409 Environmental Research Topics

With each passing year, environmental issues become a lot more prominent matter. The effects of deforestation, pollution, and global warming have taken their toll on our planet. As a result, humanity has to face climate change, depletion of natural resources, and more related problems. Humans have begun to take steps to repair the damage done to nature. Therefore, nowadays, environmental research is a crucial study area.
On this page, our team has collected current environmental research topics and ideas on related issues. Read through them to find the perfect title for your paper. Also, check a few tips on choosing a research topic that we’ve provided below.
- 🔝 Top 20 Environmental Topics
- 🎒 Topics for High School Students
- 🎓 Topics for College Students
- 🌳 Current Topics on the Environment
- 🔬 Environmental Science Research
- 🍃 Easy Essay Topics
- 🤔 How to Pick a Topic
🔗 References
🔝 top 20 environmental topics to write about.
- Environmental economics and sustainability .
- Oil Exploration Effects on Soil and Underground Water.
- Global warming and the Arctic ecosystem.
- Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture and Food.
- Violations of the environmental law.
- Sustainable Green Building Construction.
- Protection of endangered plant species.
- Environmental Consciousness and Business Sustainability.
- Climate change and its effect on human health .
- Acid Rain Effect on Plant Growth.
- Methods of cleaning the oceans.
- The Global Climate Change as a Manmade Disaster .
- Can we save the environment through education?
- Ecology and Biological Adaptation.
- Earth Day: Global environmental impact.
- Air Pollution and Mortality Rates.
- The ecology of metropolitan cities.
- Environmental Risks: Opposing Views.
- Is overpopulation a myth or reality?
- Water Pollution and Associated Health Risks.
🎒 Environmental Essay Topics for High School Students
- Greenhouse gas emissions connection to climate change.
- Climate change influences on poverty rates.
- Health effects of climate change in third world countries.
- Environmental Damage Because of Oil Spills.
- The economic effects of climate change.
- Possible solutions for climate change.
- Animal Exploitation. Animal Agriculture and Climate Change.
- Connections between capitalistic agriculture and climate change.
- Climate change effects on sea life.
- The rise of natural disasters and climate change .
- Climate change impact on migration processes.
- The intersection of climate change and air pollution.
- Deforestation: Effects of air pollution and climate change.
- Environmental Security: Global Warming and Pollution .
- Climate change agenda and its influence on mental health.
- The microevolutionary consequences of climate change.
- Population growth and urbanization influence on climate change.
- Effects of Environmental Pollution.
- Modeling possible responses to climate change in different populations.
- Climate change risks for Africa: Drought, economic issues and population decline.
- Modern agriculture influence on water pollution.
- Water pollution effects on human health.
- The Role of Waste Management in Environment.
- Microplastic pollution and possible effects on human health.
- Possible control measures for water pollution.
- Water pollution influence on sea life.
- Concepts of Green Supply Chain Management.
- Nuclear pollution and long-term effects on human health.
- Transgenic plants: What we know about flora after the Chornobyl accident.
- How to protect the seas from nuclear pollution?
- Unsolved issues with nuclear waste disposal.
- Energy, Technology and Climate Change.
- Radioactive waste management techniques in different countries.
- The disposal of high-activity nuclear waste in the oceans.
- Federal nuclear waste disposal policy in the US.
- Global Warming: Human vs. Natural Causes .
- Can renewable energy sources solve the problems of climate change?
- Renewable energy sources : The impact on pollution.
- Renewable energy sources: Utilization methods and environmental impact.
- Recycling: Challenges and benefits.
- Canada and the Future of Water.
- Problems in composite materials recycling.
- Household recycling behavior: How to teach people to recycle.
- Plastic recycling issues and possible solutions.
- An Emergency Operations Center During Hurricane Harvey.
- Factors influencing recycling among people.
- Motivation, norms, and behaviors that support recycling .
- The Real Effects of Greenhouse Gases.
- Recycling culture: How to teach children and adults to recycle.
- What we know about pollution: Fundamentals of ecological modeling.
- Climate change: Historical perspective of the issue.
- Sustainable Building Materials and Technologies in the Construction and Building Industry.
- Ecological behaviors that can influence climate change.
- Individualistic approach to ecological problems: Ecological system theory.
- Ecological system theory in child development.
- The Environment Pollution in US.
- Future directions of the ecological system theory.
- Human influence on soil erosion.
- Soil erosion: Why we must control it.
- Soil erosion and agricultural sustainability.
- Acid Rain: Effects and Reduction.
- Soil erosion influence on ecosystems.
- Economic consequences of soil erosion in developing countries.
- Beach erosion and regulatory methods.
- Heavy metals soil pollution: Monitoring and solving the issue.
- Soil pollution influence on human health.
- History of Sustainable Global Food Economy.
- Soil pollution is an emerging threat to agriculture.
- The most important reasons for soil pollution.
- Urbanization influence on soil pollution.
- Small Green Business and Greenwashing.
- Methods of detecting and monitoring soil pollution.
- The difficulties in monitoring air pollution.
- Comparison between air pollution levels in developed and developing countries.
- Urban air pollution: Origin and control.
- Modeling techniques in predicting air pollution.
- Air pollution and its effects on the children’s immune systems.
- The effects of air pollution on children’s growth and development.
- History of Environmental Law in the USA.
🎓 Topics About Environment for College Students
- Impact of acid rain on aquatic life.
- What can ordinary people do to prevent the destruction of wildlife?
- Impact of prehistoric wildlife on modern ecosystems.
- The negative impact of melting glaciers on the environment.
- Health Physics: Particulate Pollution in Cities.
- How are climate and natural disasters connected?
- Climate refugees: Analysis of the phenomenon.
- How pesticides, herbicides, and GMOs impact human health.
- The harmful influence of the depletion of the ozone layer on wildlife.
- Global Warming: Evidence ‘Pros’ and ‘Cons.’
- Significance of national parks for ecosystems.
- Impact of climate change on the planet’s biodiversity.
- Flooding Due to Urban Development.
- The most significant agricultural problem that causes climate change.
- Importance of endemic wildlife for our environment.
- How does air pollution contribute to the growing rates of lung cancer?
- Environmental Sustainability in the Dubai Police Force.
- Dangers of oil pollution for the environment.
- Is a complete transition to green energy possible?
- Purpose and consequences of the Paris Agreement.
- Elements of a Green City: Case Study of Masdar City.
- Why do people refuse the existence of climate change and its effects?
- What can people do to prevent the extinction of endangered species?
- American Indian Environmental Movement in Arizona.
- Comparison of recycling practices in different countries.
- Government’s role in a country’s recycling efforts.
- Water Shortage and Contamination in South Florida.
- Benefits and threats of nuclear power for the environment.
- Impact of industrial plants’ performance on human health.
- Benefits of hydrogen in comparison with fossil fuels for the environment.
- Importance of coral reefs for aquatic ecosystems.
- Environmental Ethics: the Case for Animal Rights.
- Impact of climate change on respiratory diseases and allergies.
- Environmental sustainability in the hospitality industry.
- Impact of tourism on the environment.
- Hoteliers’ regulations for environmental sustainability of the business.
- Causes and effects of deforestation.
- Environmental Conservation. Resource Management.
- Impact of the destruction of the Amazon forest on the planet’s ecosystem.
- Contribution of deforestation to global warming.
- The perspective of afforestation in the modern world.
- Water Depletion Causes Overview.
- Impact of agriculture and farming on the environment.
- Causes and risks of groundwater contamination.
- The hazardous effect of bush burning.
- Carbon Tax vs. Cap-and-Trade System.
- Impact of noise pollution on human health.
- What can ordinary people do to minimize noise pollution?
- Benefits of solar energy’s use for the environment.
- Global Warming: Solutions to the Problem.
- How can technological advancements address environmental issues?
- Ecological prospects for the next decade.
- Causes and effects of desertification .
- The Australian Government and Carbon Dioxide Emission.
- Impact of sustainable consumption on the environment.
- Impact of cattle grazing on greenhouse gas production.
- Effect of invasive species on the environment.
- Air Pollution: Preventing That Environmental Domino Effect.
- How does climate change contribute to the spread of bacteria and viruses?
- Advantages and disadvantages of composting.
- Impact of environmental temperature increase on aquatic wildlife.
- The contribution of air pollution to child mortality.
- Industrial Wastes: Monetization of Wastes.
- The connection between environmental health and economic development.
- Impact of pollution on mental health disorders and human brain development.
- The connection between pesticide exposure and cognitive decline.
- How is one’s environment connected with one’s vulnerability to diseases?
- Nuclear Energy as the Most Cost-Effective Source.
- Toxic chemical risks for people in cities.
- Impact of traffic-related air pollution on human health.
- Should governments ban genetically modified organisms?
- How can individuals reduce their carbon footprints?
- Man Vs Nature: Dujiangyan Irrigation System Case Study.
- Should companies pay taxes for recycling and carbon emissions?
- Should fur sales be banned?
- Benefits and limitations related to eco-friendly packaging.
- Contribution of Wind Energy to the Energy Needs of the Globe.
- What can ordinary people do to live more sustainably?
- Impact of the construction of dams and channels on ecosystems.
- The link between ecological issues and globalization.
- Environmental Injustice During COVID-19.
- Regulations for air and water quality in my country.
- Purpose and consequences of the Kyoto Protocol.
- Global Warming: A Real Danger or a Hoax?
🌳 Current Topics Related to Environment
- What is effective crisis management for sustainable agriculture in Southeast Asia?
- Why is John Deere important to agriculture?
- Consumers Views on Green Consumerism.
- What does climate change mean for agriculture in developing countries?
- How did colonialism impact agriculture in Africa?
- Who influences government spending on agriculture?
- Solutions to the Environmental Crisis in Vietnam.
- Can climate interventions open up space for transformation?
- How cellular agriculture systems can promote food security?
- Why are cooperatives important in agriculture?
- Organic Buildings and Environmental Design Technology.
- Does urban proximity enhance technical efficiency in agriculture?
- How might we make “clean air choices” and contribute to clean air?
- Can fault modeling help the quality assurance of a system? How?
- The Health Effects of Air Pollution in America.
- What are some of the control methods used for indoor air quality problems ?
- What are some of the causes of indoor air quality problems?
- What air quality index is considered unhealthy?
- Eco-Friendly Design in London Urban Areas.
- Where do indoor air quality problems arise?
- How does air quality affect health industry stock returns?
- How does Saudi Aramco affect air and water quality in Saudi Arabia?
- Is climate change a myth, or is it science-based?
- Scope of Improvement on the Environmental Impact of Air Travel.
- How is climate change affecting human civilization?
- Should politicians change policies in light of climate change?
- s Solar Energy Important for the Future of Humanity?
- What are the differences between change and mega change?
- How human behavior promotes climate change?
- Everyday Communication on Climate Change.
- Do human activities threaten to change the climate?
- Are the agroecosystems sustainable?
- Wind Energy: Is It Viable or Not?
- Does the fear of trematodes regulate the functioning of filter feeders in coastal ecosystems?
- Is the focus on ecosystems a liability in the research on nature’s services?
- How to Protect the Egypt Nile River from Pollution?
- How does slow rock weathering balance nutrient loss during fast forest floor turnover?
- How does global warming benefit small aquatic ecosystems ?
- How does coral bleaching affect coral reefs?
- Design and Development of Greener Vehicle Ventilation System.
- What is the current status of coral reefs in Malaysia?
- How does human overpopulation affect coral reefs?
- Coral reefs: Are they the rainforests of the sea?
- Is Global Warming a Myth?
- Can herbivore management increase the persistence of Indo-Pacific coral reefs?
- What is the impact of humans on the resilience of coral reefs?
- Current Chemical Use and Addiction Trends in the US.
- Is it correct to believe that coral reefs are the source of life in our world?
- What threatens the decomposition of coral reefs?
- Climate Change and Its Impact on Freshwater.
- How are coral reefs related to shark extinction?
- What is the variety of coral reefs?
- How can people prevent coral reefs from disappearing?
- Fossil Fuel Consumption and Ways of Reduction.
- Do coral reefs enhance seagrass meadows’ blue carbon potential?
- Does fossil fuel combustion lead to global warming?
- Will electric vehicles ever outnumber those that run on fossil fuel?
- Jeddah Floods and Adaptation Strategies in the City of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- Do fossil-fuel price distortions impact the low-carbon transition in China’s energy-intensive industries?
- How does fossil evidence support the theory of plate tectonics?
- Why do we still have nuclear energy and fossil energy?
- What do weather disasters cost?
- Why do natural disasters happen?
- Alternative Energy Sources vs Fossil Fuels .
- Do natural disasters affect international trade?
- Where do natural disasters happen?
- Does collectivism affect environmental ethics?
- Why are environmental ethics important in the preservation of the natural environment?
- Sustainable Competitive Advantage in Business.
- How pollution affects humans and the environment?
- Can pollution-free corporations exist?
- Recycling of Gray Water as a Water Conservation Effort.
- What’s the connection between food systems, pollution, climate change , and energy?
- How many deaths each year are from air pollution?
- Will banning plastic bags not solve the pollution problem?
- Sustainable Building and Environmental Design.
🔬 Environmental Science Research Topics
- The impact of climate change on biodiversity.
- Water pollution and its effects on ecosystems.
- Comparative Study of Green Roof and Green Façade as Urban Ecosystem in Hot And Humid Regions.
- The role of renewable energy in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Deforestation and its impacts on the environment.
- The impact of climate change on crop yield and soil quality.
- The Evolution of Insect Wings in Relation to Environmental Changes.
- The use of enzymes in the production of biofuels from plant biomass.
- Fitting preventive practices for endangered species extinction.
- Minimisation of New Building Carbon Footprint.
- Climatic causes of increased vegetation in East Asia.
- Scientific Taxonomy and Earth’s Biodiversity.
- Environmental justice and marginalized communities.
- The role of soil health in promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
- Current developments in sustainable plastic production.
- Water Pollution Is a Problem We Need to Face.
- Future advancements in ocean plastic pollution reduction.
- The importance of biodiversity in maintaining ecosystem function.
- Ecology: The Role of Zebra Mussel and Daphnia.
- To what magnitude does tap water fluorine facilitate dental health?
- The role of government in environmental policy and regulation.
- Comparative Study of Ecological Developments From a Domestic to an Urban Level Projects.
- Socioeconomic inequalities impact excessive airborne exposure to toxic compounds .
- The role of deforestation in environmental degradation.
- The Sand Storms: Remote Sensing and Meteorological Variables.
- The effectiveness of conservation programs in protecting endangered species.
- Positive impacts of increased vegetation on global water availability.
- Solar Energy in the Modern World.
- The importance of biodiversity in maintaining ecological balance.
- The use of biotechnology in plant breeding for disease resistance.
- Climate Change Implications for Shell Australia’s Major Gas Projects.
- The consequences of overfishing in marine ecosystems.
- Do forest fires facilitate climate change?
- The Effects of Mining on Environment.
- Anthropogenic climate change and threats to coastal communities.
- The effects of acid rain on forests and aquatic life.
- Current developments in water contamination treatments.
- Nuclear Energy: Good or Bad for People.
- How does increased global food production affect climate change?
- Renewable energy and the impacts of fossil fuel extraction.
- Methodologies in Wastewater Minimization.
- The role of wetlands in water filtration and flood prevention.
- Human-induced climate change and increased hurricane rates.
- The Problem of Petroleum Oil Depletion Crisis.
- The importance of sustainable agriculture in preserving natural resources.
- The effects of genetically modified organisms on human health.
- The Role of Carbon Dioxide in Climate Change.
- Does renewable energy development threaten global biodiversity?
- Marine and Coastal Climate Change in Australia.
- The effects of pesticides on non-target species.
- Utility of nanotechnology for pest control and crop enhancement.
- Community Development Through the Wind Energy.
🍃 Easy Essay Topics on Environment
- Differences and similarities between alligators and crocodiles.
- The Major Contributors to Water Pollution.
- Why are dogs the animals that are most useful to humans?
- Human actions that cause animal extinction.
- The welfare and behavior of captive tigers.
- Introduction to Fire Prevention.
- Birds are getting in a flock as a defense strategy.
- Herbivores of the African continent.
- Carbon Pricing. Climate Change.
- Animal species who live in packs.
- The role of the flies in biodiversity.
- Cost of Plastic Recycling in US .
- Behavior and welfare of tigers in captivity.
- The severe limitations of the desert climate.
- Overview of convergent evolution, desert habitats, and coral reefs.
- Environmental Issues and Plastic Industries.
- Desert biome and the species that live there.
- Climate variations in marine desert regions.
- Global Warming and the Greenhouse Effect.
- How do plants and animals adapt to living in deserts?
- Food chains and the desert biome are linked.
- Energy flow in a food chain among organisms in a desert environment.
- The most unusual plants in the rainforest.
- Maritime Risk Assessment. Environmental Management.
- How has the fennec fox changed to survive in the desert?
- Human activities and their effect on arctic species extinction.
- Rising extinction rates : Effects on the Earth’s biodiversity.
- The biodiversity of wildlife and its constant depletion.
- Biodiversity extinction at a massive scale.
- Pollution of the Marine Environment.
- Greenhouse effect’s impact on animal species extinction.
- Effects of an organism disappearing from the food chain.
- Extinction of North Atlantic right whale.
- International Human Rights and Environmental Law.
- The extinction, threat, and confinement of threatened species.
- Protecting bees is a top human concern.
- The planet’s most intelligent animals.
- The Concept of Ecological Systems Theory.
- How can trash in the ocean influence the water?
- Why do humans need to preserve nature?
- Organic Food.
- The mineral content of drinking water and its importance.
- The friendliest animals are dolphins.
- Acid Rain:Definition and Causes.
- Are monkeys the most advanced animals?
- Should people treat poisonous animals with kindness?
- The most poisonous animals in the world.
- The Shortage of Water & Human Population Growth.
- The necessity of protecting endangered animals.
- The importance of giant panda conservation.
- Water pollution’s effects on aquatic life.
- Global Warming at Australia: Environmental Health.
- Wild animals of the North Pole.
- How polar bears survive in the extreme cold.
- Atomic Power as a Renewable Energy Source.
- Adaptation to the high temperature among desert animals.
- Remarkable characteristics of white tigers.
- Water Pollution in China.
🤔 How to Pick an Environmental Research Topic
Sometimes, selecting an appropriate research title can become a real challenge for college students. They may get lost in the details of some controversial issue. Or they can try to tackle a problem that’s too broad. In this section, we’ve explored the best way to choose a topic related to the environment that will be right for you.
- Pick an idea that you’re interested in. Unfortunately, this advice is neglected quite often. Many students tend to go for titles that sound catchy. However, your research process will become much more enjoyable if you select a topic you’re excited about.
- Research it to find sources. This step is helpful to ensure there are enough available materials for your project. So as soon as you think of a general idea, spend some time on preliminary research.
- Narrow your topic down according to the sources. Look through a couple of them to determine a common thread. If you are finding too much general information, be sure to narrow down your scope of research. Think about focusing on a particular area of environmental issues . For example, explore the human carbon footprint or pollution in the Gulf of Mexico.
- Broaden the idea if needed. Having a clear and precise topic is excellent. Yet, you need to back up your claims with evidence. Therefore, expand your search criteria if you can barely find relevant sources. For a little extra help with phrasing your title, consider using our online rephraser .
- Consider the readers. Who are you writing for? Why? Thinking about these questions will give you a clearer idea of your topic. Thus, consider your audience when choosing an environmental issue to examine.
- Transform the topic into a research question. This way, you will turn your future paper into a detailed answer. It will help you stay on point while writing. Ask open-ended questions, such as “why” and “how.”
Thanks for reading! We hope this article suggested the best environmental essay topic for you. And good luck with your research! Try reading through articles with our summary generator to speed up this process.
- Environmental Issues News – ScienceDaily
- Rate of Environmental Damage Increasing Across the Planet but There Is Still Time to Reverse Worst Impacts – Sustainable Development Goals
- Selecting a Research Topic – LibGuides at MIT Libraries
- Narrowing a Topic and Developing a Research Question – Writing Center, George Mason University
- Climate Change Impacts — National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
- Environmental Pollution and the Global Burden of Disease — British Medical Bulletin
- 11 Facts about Pollution — DoSomething.org
- UN Report: Nature’s Dangerous Decline’ Unprecedented’; Species Extinction Rates ‘Accelerating’ — UN
/
Smog over Shanghai in 2018. Over the last decade, China has sharply cut air pollution. Johannes Eisele / AFP via Getty Images
Pollution Paradox: How Cleaning Up Smog Drives Ocean Warming
New research indicates that the decline in smog particles from China’s air cleanups caused the recent extreme heat waves in the Pacific. Scientists are grappling with the fact that reducing such pollution, while essential for public health, is also heating the atmosphere.
By Fred Pearce • May 28, 2024
They call it “The Blob.” A vast expanse of ocean stretching from Alaska to California periodically warms by up to 4 degrees Celsius (7 degrees F), decimating fish stocks, starving seabirds, creating blooms of toxic algae, preventing salmon returns to rivers, displacing sea lions, and forcing whales into shipping lanes to find food.
The Blob first formed in 2013 and spread across an area of the northeast Pacific the size of Canada. It lasted for three years and keeps coming back — most recently last summer . Until now, scientists have been unable to explain this abrupt ocean heating. Climate change, even combined with natural cycles such as El Niño, is not enough.
But new analysis suggests an unexpected cause. Xiaotong Zheng, a meteorologist at the Ocean University of China, and international colleagues argue that this extraordinary heating is the result of a dramatic cleanup of Chinese air pollution. The decline in smog particles, which shield the planet from the sun’s rays, has accelerated warming and set off a chain of atmospheric events across the Pacific that have, in effect, cooked the ocean.
Other researchers spoken to by Yale Environment 360 see the finding, made with the help of in-depth climate modeling, as having potentially critical implications for future climate in the Pacific and elsewhere. Emissions of the tiny particles that cause smogs, collectively known as aerosols, are in decline across most of the world — apart from South Asia and Africa. Scientists are concerned that the cleanups will both heat the global atmosphere and lead to more intense regional ocean heat waves.
The idea that cleaning up air pollution can worsen atmospheric warming sounds counterintuitive.
Yangyang Xu, an atmospheric scientist at Texas A&M University not involved in the study, said it shows that “aerosol reductions will perturb the climate system in ways we have not experienced before. It will give us surprises.”
Indeed, that may already be happening in the Atlantic. Some researchers we spoke to argue that the exceptional heat wave that spread across the North Atlantic from spring last year until April this year, sending fish fleeing for cooler Arctic waters, may have owed its intensity to international efforts to reduce aerosol emissions from ships crossing the ocean.
The idea that cleaning up air pollution can worsen atmospheric warming sounds counterintuitive. But small particles suspended in the atmosphere, collectively known as aerosols, are very different from greenhouse gases. Instead of warming the planet by trapping solar radiation, they shade it by scattering incoming sunlight and sometimes creating clouds.
They don’t stick around in the air for more than a few days. But climate modelers calculate that while they are there, they fend off as much as a third of greenhouse warming.
The Blob, a long-lasting marine heat wave, off the Pacific coast of North America, shown here in August 2019. NASA
In recent years, however, this cooling influence has begun to decline in much of the world. Thanks to clean-air legislation intended to protect public health, aerosol emissions have been reduced in Europe and North America since the 1980s. And over the past decade, the same has happened in China, where tough government controls on dirty industries, introduced by President Xi Jinping in 2013, have cut overall aerosol emissions by 70 percent, according to Zheng.
Globally, there are now fewer anthropogenic aerosols in the air at any one time than for decades. Susanne Bauer, a climate modeler at the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies, says this “turning point of the aerosol era” occurred in the first decade of this century, and seems set to continue, as more countries seek to banish smogs.
As a result, scientists say, the aerosol mask is slipping, causing a boost to global warming in many regions. “We are currently experiencing greenhouse-gas driven global warming enhanced by aerosol removal,” says Ben Booth, a climate modeler at the U.K. Met Office.
The climatic repercussions of this are not unexpected. Predicted declines in aerosol cooling are already factored into projections of future global warming by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). But Zheng’s new findings on the cause of the warm Pacific blob suggest that we can also expect more and bigger regional climatic surprises.
Without aerosols’ cooling effect, the world would already have reached the temperature threshold of dangerous climate change.
Why so? The answer lies in the fact that aerosols do not remain aloft for long enough in the air to mix thoroughly in the atmosphere. So national pollution cleanups will create radically new maps of aerosol distribution.
Some areas will heat much more than others, and this differential warming has the potential to destabilise atmospheric circulation patterns, which are largely heat-driven. This is what appears to have been happening in the northeast Pacific, says Zheng.
When he and Hai Wang, also of the Ocean University of China, along with colleagues in the United States and Germany, modeled the likely impacts on circulation systems of the recent cleaning of the air over eastern China, they found that clearing the country’s smogs caused exceptional atmospheric heating downwind over the Pacific.
This altered air pressures and intensified the Aleutian Low, a semi-permanent area of low pressure in the Bering Sea. This in turn reduced wind speeds further east, limiting the ability of the winds to cool the ocean below, providing “a favorable condition for extreme ocean warming.”
Zheng and colleagues warn that the findings are a harbinger of future “disproportionately large” warm-blob events.
Smog shrouds the Taj Mahal in Agra, India, last November. Pawan Sharma / AFP via Getty Images
Aerosols come in many shapes and sizes, from dust and soot to tiny particles invisible to the eye. They have many natural sources, such as forest fires and dust storms. But since the Industrial Revolution the aerosol load in the atmosphere has been dramatically increased by anthropogenic sources, primarily the burning of fossil fuels such as coal and oil.
These emissions include large volumes of sulfur dioxide (SO2), a gas that reacts readily with other compounds in the air to create tiny particles that both shade the planet and can act as condensation nuclei that cause atmospheric moisture to coalesce into water droplets that form clouds.
Burning fossil fuels produces both planet-warming carbon dioxide and aerosols that mask much of the warming. Atmospheric temperatures depend on the balance between the two. The last IPCC assessment of climate science, published in 2021, calculated that greenhouse gases were producing a warming effect of around 1.5 degrees C, with 0.4 degrees of this masked by aerosols.
“Without the cooling effect of the aerosols, the world would already have reached the 1.5- degree temperature threshold of ‘dangerous’ climate change as set out by the Paris agreement,” says Johannes Quaas, a meteorologist at the University of Leipzig and former IPCC lead author.
But the balance is shifting as ever more countries act to reduce aerosol emissions.
Until recently, ships’ aerosol emissions probably cooled the planet more than their greenhouse-gas emissions warmed it.
They do so because of a growing awareness of the public health impacts of aerosols, which the World Health Organization calculates cause more than 4 million premature deaths from cancers and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases each year. Air pollution reduced life expectancy in parts of China by up to five years, according to a 2013 study .
Countries are requiring power companies, industries, and vehicle manufacturers to filter particulates and either burn low-sulfur fuel or fit equipment to strip SO2 from stack emissions — thus cleaning up aerosol and SO2 emissions without reducing the energy produced by burning the fuel.
Europe and North America have had clean air laws in place for almost half a century. Since 2013 — following a run of debilitating smogs in many cities — China has followed, at break-neck speed. Its anthropogenic aerosol emissions have fallen by 70 percent in a decade, and SO2 emissions have been reduced even more, from 20.4 million tons in 2013 to 2.4 million tons in 2022.
Chinese researchers have tracked the impact of this on local climate in some detail. Yang Yang, an atmospheric physicist at Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, calculates that by 2017, it had boosted the existing greenhouse warming trend in eastern China by 0.1 degrees C. As the cleanup extends, including to transportation, he expects this extra heating to increase to between 0.2 and 0.5 degrees C by 2030, and to more than 0.5 degrees C by 2060.
Yang predicts it will also trigger changes in local atmospheric circulation that will result in more rainfall over southern China and beyond, in nearby countries such as the Philippines. Zheng’s new research suggests that the effects are already far more long-ranging, stretching across the Pacific to create The Blob on the shores of the U.S.
Where else can we expect disrupting local climate change? Outside of China, researchers are exploring the potential for oceanic climate surprises arising from recent efforts to cut SO2 emissions from shipping.
Dirty, sulfurous diesel has long been the fuel of choice in ships’ boilers. As a result, the world’s shipping fleets until recently emitted more than 10 million tons of SO2 annually, contributing between 10 and 20 percent of the total anthropogenic climate “forcing” from aerosols, says Michael Diamond, who studies aerosols and climate at Florida State University.
Ships are a major cause of aerosol buildup over oceans, where there are usually few other anthropogenic sources. Satellite images show clear tracks of clouds stretching along major shipping routes.
Burning ships’ fuel also emits carbon dioxide, of course. But until recently, ships’ aerosol emissions have probably cooled the planet more than their greenhouse-gas emissions have warmed it. That is changing, however. Ships seem set to turn from planetary coolers to planetary warmers.
Eliminating methane, a short-lived greenhouse gas, can provide a quick fix for some of the impacts of lost aerosols.
In 2020, the U.N.’s International Maritime Organization (IMO) responded to rising pressure to clear the air around ports by reducing the sulfur content allowed in shipping fuel from 3.5 percent to 0.5 percent. Reduced ships’ SO2 emissions have already resulted in fewer clouds over shipping lanes and and higher ocean temperatures.
Diamond says he has a paper currently under peer review whose “takeaway is that something like a third of the North Atlantic marine heat wave [of the past year] might be attributable to the IMO regulations.” Booth, meanwhile, is coauthor of a paper preprinted online this month which argues that shipping emissions reductions “may help explain part of the rapid jump in global temperatures over the last 12 months.”
Where are we headed?
If the world works successfully toward lowering greenhouse gas emissions in the coming decades, while also continuing to curb aerosols, then we can still expect continued warming for which aerosol reductions are a growing cause.
A satellite view of aerosol trails left by ships crossing the North Pacific. NASA
Yang recently coauthored a paper that forecasts a mid-century world in which the warming impact of the clearer air will “far outweigh those of greenhouse gases.” There will be “increased humid heat waves with longer duration and stronger amplitudes,” he says.
So what can be done? Can the world have clean air while also keeping warming to bearable levels and avoiding worsening ocean heat waves?
Most scientists spoken to for this article agreed that the best route remains doubling down on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. But Diamond suggests the aerosol dilemma shines a spotlight on the need to give priority to cutting methane emissions .
This virulent greenhouse gas is second to carbon dioxide in importance as a planetary warmer. Right now, notes Diamond, its warming effect is almost identical to the average cooling effect of continued aerosol emissions. And because methane is a relatively short-lived greenhouse gas, persisting in the atmosphere for only around a decade, its elimination can provide a quick fix for some of the impacts of the lost aerosols. Luckily, there is low-hanging fruit to achieve this: The easiest and cheapest actions include preventing the venting of methane from gas and oil wells and pipelines.
To be clear, nobody — but nobody — suggests that we should stop the cleanup of aerosols. The death toll would just be too great.
More From E360
Can a california oilfield be retrofitted to store solar energy, how an el niño-driven drought brought hunger to southern africa, in seawater, researchers see an untapped bounty of critical metals, tracking illicit brazilian beef from the amazon to your burger, in a dammed and diked mekong, a push to restore the flow, how one south african community stopped shell oil in its tracks, will new leader end progress in saving indonesia’s forests, dire straits: can a fishing ban save the elusive european eel, scientists are trying to coax the ocean to absorb more co2, marina silva on brazil’s fight to turn the tide on deforestation, solomon islands tribes sell carbon credits, not their trees.
92 Air Pollution Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best air pollution topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics on air pollution, 💡 interesting topics to write about air pollution, ❓air pollution research questions.
- Air Pollution and Its Impact on Human Health Community needs assessment is a systematic process in which the health educator, the nurse and other health care professionals together with the members of the community determine the health problems & needs of the community […]
- Air Pollution Impacts on Weather and Climate Air pollution is rated to be the major cause of discomfort in the living creatures of the world for air is essential for the survival of every living creature.
- Air Pollution Sources, Effects and Ways of Minimizing This paper discusses the various sources of air pollution, the effects of air pollution, and ways of minimizing air pollution. Definitely, the destruction of the atmosphere is a serious issue of concern to many people, […]
- Environmental Factors and Health Promotion: Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollution This presentation offers some information about the damage of air pollution and presents a health promotion plan with helpful resources and evidence from research.
- Car Air Pollution Further, NO2 can prevent the flow of oxygen in the blood to other parts of the body like the brain. These toxic substances settle in the lungs and disrupt the normal flow of air in […]
- Air Pollution in Beijing and Its Effects on Society It is worth noting that different regions/countries/cities in the world have different levels of air pollution depending on the intensity/presence of causing agents and the techniques applied in dealing with air pollution.
- New York City Air Pollution Problem One positive impact of technological advancements on the environment in New York is the ability to provide communication options that are friendly to the environment.
- Smog and Air Pollution in Los Angeles The city is often covered with a yellow veil in the sky, so the problem of smog is an actual problem of the state.
- The Ecogeographical Impact of Air Pollution The weakness of the text is that the safety of NPs and their probable toxic effects on human health and the environment are not evaluated.
- Air Pollution and Impact of Transportation Emissions of greenhouse gases, air pollution, the release of ballast water, aquatic invasive species, and oil and chemical leaks are only some of the environmental problems that marine transportation continues to cause.
- Air Pollution and Lung Disease To design a study in order to explore the link between lung disease and air pollution, it would be possible to follow a four-step process started by identifying the level or unit of analysis.
- Air Pollution in China: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics One of the most acute environmental problems in China is air pollution, which the authorities are trying to solve, but still, many people, factories, and active processes of globalization do not allow environmental programs to […]
- Air Pollution and Vulnerability to Covid-19 In other words, the findings will be used as one of the key arguments for showing that air pollution is detrimental to both individual and societal health.
- Fundamentals of Air Pollution The components of secondary air pollution include ozone and nitrogen oxides. Smog occurs when “car exhausts are exposed to direct sunlight”.
- Air Pollution: The Problem’ Review Indoor pollution and related conditions are a big burden to the already suffering world according to the reports of the world health organization that it’s the 8th most important risk factor and is perceived to […]
- Law, Property Rights, and Air Pollution In the law of torts, ‘harm’ is considered when there is physical invasion to a person there fore in the case there was no violation of this law as the secretary was not harmed by […]
- Air Pollution in Middle East: Saudi Arabia The rate of air pollution in the world has increased gradually since the advent of the industrial revolution in the early 1800s.
- Point vs. Non-Point Air Pollution To determine the air pollution source of a large smoke stack, one has to assess the physical characteristics of the smoke; description of the color concentration intensity is it grey or extremely dark?
- Air Pollution and Health Issues in the US The industry of health care is closely connected to the industrial activities sector, which has the largest impact on the atmosphere through polluting the air, soil, and waters.
- Air Pollution Externalities and Possible Solutions In order to fully integrate public utility, power generation, policy and use of nuclear power in light of the growing concerns on the depletion of natural forms of energy as well as degradation of the […]
- Air Pollution and Ecological Perspectives of the Atmosphere The major contributors to CO2, one of the main pollutants in the atmosphere, are the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation.
- Air Pollution and Its World History From the times of industrial revolution, smoke pollution was a concern and continues to be one with vehicles and industries replacing coal and wood.
- Construction Technology and Air Pollution Hot-list section has new and transferable technology and highlights the features that appeal to construction companies, specifies and designers, owners of the building and end users.
- The Public Perceptions of Air Pollution and Related Policies in London The primary questions for consideration are the public perceptions of air pollution and related policies in London and other cities of the United Kingdom, previous surveys regarding existing policies related to the environment or air […]
- How China Cuts Its Air Pollution 5, which is the smallest and one of the most harmful polluting particles, were 54 percent lower in the last quarter of 2017 as compared to the same period in 2016, specifically in Beijing.
- Climate Change: Reducing Industrial Air Pollution One of the most effective measures of air quality in the USA is the Air Quality Index, which estimates air conditions by concentrations of such pollutants as particle solution, nitrogen and sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, […]
- Air Pollution, Its Constituents and Health Effects The National Ambient Air Quality Standards are the regulations or policies that are adopted by states to ensure the safety of the environment.
- Air Pollution in the United Arab Emirates’ Cities In the article called Evaluating the Potential Impact of Global Warming on the UAE Residential Buildings, the author focuses on the negative consequences of global warming on the situation in the United Arab Emirates.
- Climate Change, Air Pollution, Soil Degradation Then followed by outdoor air pollution, soil degradation which can also be called as soil contamination, global overpopulation, drinking water pollution, nuclear waste build-up, disappearing of the water supplies, indoor air pollution, depletion of the […]
- Air Pollution in Washington State and Healthy Living of People The problem of air pollution is closely related to the issue of the energy supply of the US. Due to the high level of air pollution in Washington state, there is a growing threat to […]
- Air Pollution as a Factor for Renal Cancer Therefore, to prevent renal cancer, it is crucial to examine the primary causes and look for better strategies to curb the issue.
- Indoor Air Pollution: The Silent Killer in Rural India The video “Indoor air pollution: The silent killer” discusses the detrimental impact of indoor air pollution in rural Indian households on people’s health. The problem of indoor air pollution is rather significant, and people should […]
- Air Pollution and China’s Governmental Measures The consequences of air pollution in China are already becoming evident, and not only they are the reason for environmental problems, but also they have a significant influence on the health of Chinese people living […]
- Air Pollution in Beijing and the Decision-Making Bias Severe air pollution in Beijing did not become a subject of worldwide concern and discussion until the 2008 Beijing Olympics, which brought the issue to the attention of the global public due to the immense […]
- “Fort McMurray Fires Cause Air Pollution” by McDiarmid As a rule, the air in Canada is clean and rich in oxygen; however, when the wildfire burst, it affected the ozone layer to a significant degree.
- Air Pollution as the Trigger of the Ecological Catastrophe The key data collection tool is a survey that is targeted at determining the main factors of air pollution, finding out the social opinion regarding the quality of air in different cities, and estimating the […]
- Water & Air Pollution and Health Issues in Brazil The main environmental effects of pollution include the destruction of marine habitats, water scarcity, and anoxia. The conclusion is informative because the writer includes strategies to alleviate the problem of air and water pollution in […]
- Air Pollution and Respiratory Illnesses in Nigeria The purpose of the article presented was to test the relationship of the respiratory system illness and air pollution in developing countries, especially in Africa.
- Air Pollution Impact on Children’s Health in the US In these parts of the country, the level of air pollution is much higher. Nevertheless, the growing number of vehicles in the United States contributes to air pollution.
- Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Health Effects It emphasizes the fact that air contamination has a negative influence on the health of the representatives of the general public.
- Air Pollution in Los Angeles The escalation of congestion in the city has worsened the problem of air pollution because of the volume of unhealthy air emitted in the atmosphere.
- Environmental Revolution: Air Pollution in China For instance, a case study of the current pollution levels in China reveals that the country is struggling with the management of hazy weather.
- Environmental Behavior and Air Pollution in Ohio Once people become aware of the harmful effects of air pollution on the environment and health, it is likely that they will adopt positive behaviors, reduce behaviors and activities that contribute to air pollution and […]
- The New York City Air Pollution As the reports say, the state of health of some of the New York residents has grown increasingly worse, mostly due to the air pollution and the diseases that it has triggered.
- Air Pollution Effects on the Health and Environment According to the National Ambient Air Quality Standards, there are six principal air pollutants, the excess of which critically affects the health, lifestyle, and welfare of the population. Still, to my mind, the priority should […]
- Dealing With Air Pollution Polluted air contains nitrogen oxides and other toxic substances that dissolve in the atmosphere to return to the Earth in the form of acid rain, which is detrimental to the ecosystem.
- Environmental Justice and Air Pollution in Canada One of the best ways is to explain that air pollution is a major contributor to the burgeoning problem of global warming.
- Principles of Air Pollution Control and Analysis The increased attention to air quality is a recent development as people were previously not concerned about the quality of air in the atmosphere.
- China’s Air Pollution Problem The fact that we do not know the rate at which the economy is slowing down denotes that we cannot tell the rate at which air pollution in the country is reducing and those who […]
- China’s Air Pollution Is Not Unique China and the United States of America have adversely been mentioned to be the leading polluters of the atmosphere. The recent statistics indicate that the gap between the level of pollution by China and that […]
- An Investigation of Green Roofs to Mitigate Air Pollution With Special Reference to Tehran, Iran Thus, the aim of the research is to inquire into the basic information on the concept of green roofs, to answer the research questions on different attributes of green roofs, methods used to construct green […]
- Air Pollution: Human Influence on Environment For these reasons, the emission of aerosols in the air has become a major issue of concern allover the world and it is one of the many issues that need to be addressed and controlled […]
- Air Pollution Sources in Houston Though pollution is virtually everywhere, the paper focuses on Houston, one of the major cities is the US that have unacceptable levels of pollutants that pose health risks to the lives of people, plants, and […]
- Air Pollution: Public Health Impact In this regard, the paper explores various articles on opencast coals mining, aviation emissions, and geological storage of carbon dioxide and public health concerns in air pollution.
- Environmental Impacts of Air Pollution The current high growth rates have contributed to high concentration of particulates and pollutants in the atmosphere owing to the population’s over reliance on various sources of energy.
- Does Air Pollution in Schools Influence Student Performance? When the quality of the air is poor, allergens are likely to be present in the air. To this end, the paper has revealed that poor IAQ may cause a number of short and long-term […]
- Air Pollution Characteristics and Effect Accumulation and deposition of this substance can damage the ozone layer and affect the visibility of the environment. The accumulation of this pollutant in the atmosphere can cause severe damage to the reproductive organs, lungs […]
- Impact of Blowing Drums on Air Pollution According to the CSB report, BP failed to “implement or heed all the safety recommendations regarding the blowdown drums before the blast”.
- Air Pollution Effects on the Health in China The justification of the study is premised on the fact that China is one of the world’s largest coal producers and consumers, hence the need to evaluate the health implications of coal pollution on the […]
- Air Pollution and Health Policy in China The proposed study aims to critically assess the health impact of various forms of air pollution arising from overreliance on coal so as to inform current and future health policy directions in China.
- Air Pollution and Its Consequences Air pollution refers to the infusion of chemicals, particles and biological matter that are hazardous and are the cause of discomfort to humanity and other living organisms into the atmosphere.
- Air Pollution by Automobiles This paper shall address specific automobile pollutants in relation to causes and public health, to draft possible recommendations to the obstacles, in order to manage the problem.
- Preposition 23: Suspension of Air Pollution Control Act On the one hand, it was approved by the California Air Resources Board that considered it more realistic to suspend the implementation of this law due to the existing $ billion deficit leading to the […]
- Climate and Air Pollution The earth has a number of climatic systems that ensure the distribution of heat across the face of the earth. Global warming is the result of retention of heat by the earth’s atmosphere originally from […]
- A Discussion of Air Pollution & Related Health Implications on the Community The first task in the multidisciplinary team should be to identify the leading sources of air pollution within the community and the nature of the specific toxics or hazardous chemicals associated with the pollutants.
- Are Land Values Related to Ambient Air Pollution Levels?
- What Are the Main Causes of Air Pollution?
- How Pollution Affects the Environment?
- Could Air Pollution Have a Negative Impact on Water Quality?
- Does Air Pollution Affect Consumption Behavior?
- How Can Air Pollution Affect an Individual’s Health?
- What Are the Natural Causes of Air Pollution?
- Does Air Pollution Affect Global Warming?
- Is Air Pollution Getting Worse?
- How Are Air Pollution Harmful to Plants?
- When Did Air Pollution Start?
- How Do American Cities Handle Air Pollution?
- Does Expanding Regional Train Service Reduce Air Pollution?
- What Affects Air Pollution the Most?
- How Does Outdoor Air Pollution Affect the Quality of Indoor Air?
- Why Can Air Pollution Harm the Environment Dramatically?
- How Do Trees Prevent Air Pollution?
- What Are the Biggest Air Pollution Sources?
- Does Air Pollution Affect Animals?
- How Can We Prevent Air Pollution at Home?
- Where Is Air Pollution the Worst?
- How Does Air Pollution Affect Humans?
- What Are the Best Ways to Reduce Air Pollution?
- Is Air Pollution the Biggest Killer?
- How Does Acid Rain Affect Air Pollution?
- Extinction Research Topics
- Ocean Pollution Titles
- Hazardous Waste Essay Topics
- Noise Pollution Essay Titles
- Overpopulation Topics
- Climate Change Titles
- Recycling Research Ideas
- Deforestation Research Ideas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 92 Air Pollution Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/air-pollution-essay-topics/
"92 Air Pollution Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/air-pollution-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '92 Air Pollution Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "92 Air Pollution Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/air-pollution-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "92 Air Pollution Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/air-pollution-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "92 Air Pollution Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/air-pollution-essay-topics/.

COMMENTS
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Chemistry. The impact of cobalt mining on water quality and the fate of contaminants in the environment. The role of atmospheric chemistry in shaping air quality and climate change. The impact of soil chemistry on nutrient availability and plant growth in wheat monoculture.
Numerous environmental contaminants have mutagenic and carcinogenic properties. Environmental contaminants have been linked to between 70 and 80% of all cancer forms. Less research has been done on the biological mechanisms of pollution-related carcinogenesis. However, several inverse models demonstrate, how pollution affects cancer and cell ...
3) Conservation. Conservation is a broad topic within environmental science, focusing on issues such as preserving environments and protecting endangered species. However, conservation efforts are more challenging than ever in the face of a growing world population and climate change.
The deleterious effects of pollution manifest in elevated rates of cancer, cardiovascular disease, respiratory ailments, mental disorders, and diarrhea. Each year, approximately 7 million ...
Environmental Research Topics are as follows: Climate change and its impacts on ecosystems and society. The effectiveness of carbon capture and storage technology. The role of biodiversity in maintaining healthy ecosystems. The impact of human activity on soil quality. The impact of plastic pollution on marine life.
233 Pollution Essay Topics + Examples. Environmental pollution comes in many forms: noise, light, plastic, greenhouse gas emissions, etc. If you're looking for interesting topics about pollution for essay or research paper, you're at the right place! StudyCorgi has prepared a list of catchy pollution titles for your writing assignments.
Environmental pollution occurs when changes in the physical, chemical, or biological constituents of the environment (air masses, temperature, climate, etc.) ... At this point, international cooperation in terms of research, development, administration policy, monitoring, and politics is vital for effective pollution control. ...
The Lancet Commission on pollution and health reported that pollution was responsible for 9 million premature deaths in 2015, making it the world's largest environmental risk factor for disease and premature death. We have now updated this estimate using data from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuriaes, and Risk Factors Study 2019. We find that pollution remains responsible for approximately ...
For example, if you are writing about air pollution, then the terms you use may range from "particulate matter" to "hygroscopicity," depending on the complexity of your essay's subject. Tip #4. The pollution essay thesis statement is a guiding line throughout your writing process.
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (ESPR) serves the international community in all broad areas of environmental science and related subjects with emphasis on chemical compounds. Covers all areas of Environmental Science and related subjects. Publishes on the natural sciences, but also includes the impacts of legislation, regulation ...
Research on Health Effects from Air Pollution. Decades of research have shown that air pollutants such as ozone and particulate matter (PM) increase the amount and seriousness of lung and heart disease and other health problems. More investigation is needed to further understand the role poor air quality plays in causing detrimental effects to ...
SERC researchers trace pollution from its origins in the air, the land, and the water. Nutrient pollution has a myriad of sources: exhaust from cars, fertilizers on farms and lawns, and sewage from cities and suburbs. When it reaches large bodies of water like the Chesapeake Bay, it can feed algal blooms that contribute to low-oxygen dead zones.
The global outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic has given rise to a significant health emergency to adverse impact on environment, and human society. The COVID-19 post-pandemic not only affects human beings but also creates pollution crisis in environment. The post-pandemic situation has shown a drastic change in nature due to biomedical waste load and other components. The inadequate segregation ...
Provided below is a list of topics for an environmental science project that is suitable for your research paper: Air pollution effects on human health. Climate change effects on health. Water pollution and public health. Noise pollution effects on well-being. Mental health effects of environment-related toxins.
Environmental pollution may broadly be classified into: (1) Natural pollution; (2) Man-made pollution. 1. Natural Pollution: Environment is polluted often by natural phenomenon, such as ...
The masking of the light of stars and galaxies by skyglow is a major problem for astronomers and led to some of the first research into light pollution being undertaken by astronomers in the ...
6 Environmental Science Topics for College Students. 7 Energy Resources and Consumption. 8 Population. 9 Noise and Light Pollution. 10 Conservation Biology. 10.1 Conclusion. With the environment and global warming in its current predicament, it's no surprise that environmental science job opportunities will be on the rise in the very near ...
Environmental research topics refer to conditions of the physical, chemical and biological aspects of the environment. This can include human activity, living organisms, weather and naturally occurring landmarks. Environmental research focuses largely on conservation or prevention. Many professionals may perform environmental research, such as ...
This comprehensive guide to water pollution research paper topics is designed to provide students studying environmental science with a wealth of options for their research papers. The guide offers a broad array of topics, divided into ten categories, each containing ten unique research topics. Additionally, the guide provides expert advice on ...
Environmental pollution is the unwarranted discharge of mass or energy into the planet's natural resource pools, such as land, air, or water, which detriments the environment's ecological stability and the health of the living things that inhabit it. There is an intensified health risk and pollution in middle and low-income countries due to ...
409 Environmental Research Topics. by OvernightEssay. May 14, 2024. 12 min. With each passing year, environmental issues become a lot more prominent matter. The effects of deforestation, pollution, and global warming have taken their toll on our planet. As a result, humanity has to face climate change, depletion of natural resources, and more ...
The idea that cleaning up air pollution can worsen atmospheric warming sounds counterintuitive. Yangyang Xu, an atmospheric scientist at Texas A&M University not involved in the study, said it shows that "aerosol reductions will perturb the climate system in ways we have not experienced before. It will give us surprises.".
Ocean pollution is the unfavorable upshot due to the entrance of chemicals and particulate substances into the ocean. The land is the key source of ocean pollution in the form of non-point water pollution. We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 809 writers online.
Titles for H.R.8579 - 118th Congress (2023-2024): To amend the Federal Water Pollution Control Act to direct the Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency to carry out further improvement of Onondaga Lake, New York, and for the purposes of integrating research, education, planning and restoration of the watershed.
The major contributors to CO2, one of the main pollutants in the atmosphere, are the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. Air Pollution and Its World History. From the times of industrial revolution, smoke pollution was a concern and continues to be one with vehicles and industries replacing coal and wood.