

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the complete ib extended essay guide: examples, topics, and ideas.
International Baccalaureate (IB)

IB students around the globe fear writing the Extended Essay, but it doesn't have to be a source of stress! In this article, I'll get you excited about writing your Extended Essay and provide you with the resources you need to get an A on it.
If you're reading this article, I'm going to assume you're an IB student getting ready to write your Extended Essay. If you're looking at this as a potential future IB student, I recommend reading our introductory IB articles first, including our guide to what the IB program is and our full coverage of the IB curriculum .
IB Extended Essay: Why Should You Trust My Advice?
I myself am a recipient of an IB Diploma, and I happened to receive an A on my IB Extended Essay. Don't believe me? The proof is in the IBO pudding:
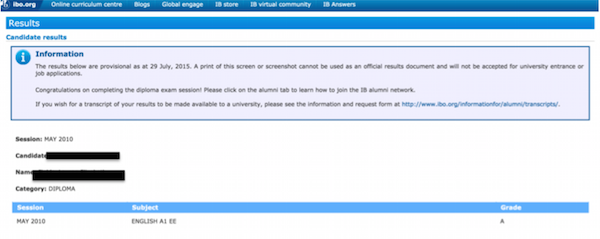
If you're confused by what this report means, EE is short for Extended Essay , and English A1 is the subject that my Extended Essay topic coordinated with. In layman's terms, my IB Diploma was graded in May 2010, I wrote my Extended Essay in the English A1 category, and I received an A grade on it.
What Is the Extended Essay in the IB Diploma Programme?
The IB Extended Essay, or EE , is a mini-thesis you write under the supervision of an IB advisor (an IB teacher at your school), which counts toward your IB Diploma (learn more about the major IB Diploma requirements in our guide) . I will explain exactly how the EE affects your Diploma later in this article.
For the Extended Essay, you will choose a research question as a topic, conduct the research independently, then write an essay on your findings . The essay itself is a long one—although there's a cap of 4,000 words, most successful essays get very close to this limit.
Keep in mind that the IB requires this essay to be a "formal piece of academic writing," meaning you'll have to do outside research and cite additional sources.
The IB Extended Essay must include the following:
- A title page
- Contents page
- Introduction
- Body of the essay
- References and bibliography
Additionally, your research topic must fall into one of the six approved DP categories , or IB subject groups, which are as follows:
- Group 1: Studies in Language and Literature
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Group 4: Sciences
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Group 6: The Arts
Once you figure out your category and have identified a potential research topic, it's time to pick your advisor, who is normally an IB teacher at your school (though you can also find one online ). This person will help direct your research, and they'll conduct the reflection sessions you'll have to do as part of your Extended Essay.
As of 2018, the IB requires a "reflection process" as part of your EE supervision process. To fulfill this requirement, you have to meet at least three times with your supervisor in what the IB calls "reflection sessions." These meetings are not only mandatory but are also part of the formal assessment of the EE and your research methods.
According to the IB, the purpose of these meetings is to "provide an opportunity for students to reflect on their engagement with the research process." Basically, these meetings give your supervisor the opportunity to offer feedback, push you to think differently, and encourage you to evaluate your research process.
The final reflection session is called the viva voce, and it's a short 10- to 15-minute interview between you and your advisor. This happens at the very end of the EE process, and it's designed to help your advisor write their report, which factors into your EE grade.
Here are the topics covered in your viva voce :
- A check on plagiarism and malpractice
- Your reflection on your project's successes and difficulties
- Your reflection on what you've learned during the EE process
Your completed Extended Essay, along with your supervisor's report, will then be sent to the IB to be graded. We'll cover the assessment criteria in just a moment.

We'll help you learn how to have those "lightbulb" moments...even on test day!
What Should You Write About in Your IB Extended Essay?
You can technically write about anything, so long as it falls within one of the approved categories listed above.
It's best to choose a topic that matches one of the IB courses , (such as Theatre, Film, Spanish, French, Math, Biology, etc.), which shouldn't be difficult because there are so many class subjects.
Here is a range of sample topics with the attached extended essay:
- Biology: The Effect of Age and Gender on the Photoreceptor Cells in the Human Retina
- Chemistry: How Does Reflux Time Affect the Yield and Purity of Ethyl Aminobenzoate (Benzocaine), and How Effective is Recrystallisation as a Purification Technique for This Compound?
- English: An Exploration of Jane Austen's Use of the Outdoors in Emma
- Geography: The Effect of Location on the Educational Attainment of Indigenous Secondary Students in Queensland, Australia
- Math: Alhazen's Billiard Problem
- Visual Arts: Can Luc Tuymans Be Classified as a Political Painter?
You can see from how varied the topics are that you have a lot of freedom when it comes to picking a topic . So how do you pick when the options are limitless?

How to Write a Stellar IB Extended Essay: 6 Essential Tips
Below are six key tips to keep in mind as you work on your Extended Essay for the IB DP. Follow these and you're sure to get an A!
#1: Write About Something You Enjoy
You can't expect to write a compelling essay if you're not a fan of the topic on which you're writing. For example, I just love British theatre and ended up writing my Extended Essay on a revolution in post-WWII British theatre. (Yes, I'm definitely a #TheatreNerd.)
I really encourage anyone who pursues an IB Diploma to take the Extended Essay seriously. I was fortunate enough to receive a full-tuition merit scholarship to USC's School of Dramatic Arts program. In my interview for the scholarship, I spoke passionately about my Extended Essay; thus, I genuinely think my Extended Essay helped me get my scholarship.
But how do you find a topic you're passionate about? Start by thinking about which classes you enjoy the most and why . Do you like math classes because you like to solve problems? Or do you enjoy English because you like to analyze literary texts?
Keep in mind that there's no right or wrong answer when it comes to choosing your Extended Essay topic. You're not more likely to get high marks because you're writing about science, just like you're not doomed to failure because you've chosen to tackle the social sciences. The quality of what you produce—not the field you choose to research within—will determine your grade.
Once you've figured out your category, you should brainstorm more specific topics by putting pen to paper . What was your favorite chapter you learned in that class? Was it astrophysics or mechanics? What did you like about that specific chapter? Is there something you want to learn more about? I recommend spending a few hours on this type of brainstorming.
One last note: if you're truly stumped on what to research, pick a topic that will help you in your future major or career . That way you can use your Extended Essay as a talking point in your college essays (and it will prepare you for your studies to come too!).
#2: Select a Topic That Is Neither Too Broad nor Too Narrow
There's a fine line between broad and narrow. You need to write about something specific, but not so specific that you can't write 4,000 words on it.
You can't write about WWII because that would be a book's worth of material. You also don't want to write about what type of soup prisoners of war received behind enemy lines, because you probably won’t be able to come up with 4,000 words of material about it. However, you could possibly write about how the conditions in German POW camps—and the rations provided—were directly affected by the Nazis' successes and failures on the front, including the use of captured factories and prison labor in Eastern Europe to increase production. WWII military history might be a little overdone, but you get my point.
If you're really stuck trying to pinpoint a not-too-broad-or-too-narrow topic, I suggest trying to brainstorm a topic that uses a comparison. Once you begin looking through the list of sample essays below, you'll notice that many use comparisons to formulate their main arguments.
I also used a comparison in my EE, contrasting Harold Pinter's Party Time with John Osborne's Look Back in Anger in order to show a transition in British theatre. Topics with comparisons of two to three plays, books, and so on tend to be the sweet spot. You can analyze each item and then compare them with one another after doing some in-depth analysis of each individually. The ways these items compare and contrast will end up forming the thesis of your essay!
When choosing a comparative topic, the key is that the comparison should be significant. I compared two plays to illustrate the transition in British theatre, but you could compare the ways different regional dialects affect people's job prospects or how different temperatures may or may not affect the mating patterns of lightning bugs. The point here is that comparisons not only help you limit your topic, but they also help you build your argument.
Comparisons are not the only way to get a grade-A EE, though. If after brainstorming, you pick a non-comparison-based topic and are still unsure whether your topic is too broad or narrow, spend about 30 minutes doing some basic research and see how much material is out there.
If there are more than 1,000 books, articles, or documentaries out there on that exact topic, it may be too broad. But if there are only two books that have any connection to your topic, it may be too narrow. If you're still unsure, ask your advisor—it's what they're there for! Speaking of advisors...

Don't get stuck with a narrow topic!
#3: Choose an Advisor Who Is Familiar With Your Topic
If you're not certain of who you would like to be your advisor, create a list of your top three choices. Next, write down the pros and cons of each possibility (I know this sounds tedious, but it really helps!).
For example, Mr. Green is my favorite teacher and we get along really well, but he teaches English. For my EE, I want to conduct an experiment that compares the efficiency of American electric cars with foreign electric cars.
I had Ms. White a year ago. She teaches physics and enjoyed having me in her class. Unlike Mr. Green, Ms. White could help me design my experiment.
Based on my topic and what I need from my advisor, Ms. White would be a better fit for me than would Mr. Green (even though I like him a lot).
The moral of my story is this: do not just ask your favorite teacher to be your advisor . They might be a hindrance to you if they teach another subject. For example, I would not recommend asking your biology teacher to guide you in writing an English literature-based EE.
There can, of course, be exceptions to this rule. If you have a teacher who's passionate and knowledgeable about your topic (as my English teacher was about my theatre topic), you could ask that instructor. Consider all your options before you do this. There was no theatre teacher at my high school, so I couldn't find a theatre-specific advisor, but I chose the next best thing.
Before you approach a teacher to serve as your advisor, check with your high school to see what requirements they have for this process. Some IB high schools require your IB Extended Essay advisor to sign an Agreement Form , for instance.
Make sure that you ask your IB coordinator whether there is any required paperwork to fill out. If your school needs a specific form signed, bring it with you when you ask your teacher to be your EE advisor.
#4: Pick an Advisor Who Will Push You to Be Your Best
Some teachers might just take on students because they have to and aren't very passionate about reading drafts, only giving you minimal feedback. Choose a teacher who will take the time to read several drafts of your essay and give you extensive notes. I would not have gotten my A without being pushed to make my Extended Essay draft better.
Ask a teacher that you have experience with through class or an extracurricular activity. Do not ask a teacher that you have absolutely no connection to. If a teacher already knows you, that means they already know your strengths and weaknesses, so they know what to look for, where you need to improve, and how to encourage your best work.
Also, don't forget that your supervisor's assessment is part of your overall EE score . If you're meeting with someone who pushes you to do better—and you actually take their advice—they'll have more impressive things to say about you than a supervisor who doesn't know you well and isn't heavily involved in your research process.
Be aware that the IB only allows advisors to make suggestions and give constructive criticism. Your teacher cannot actually help you write your EE. The IB recommends that the supervisor spends approximately two to three hours in total with the candidate discussing the EE.
#5: Make Sure Your Essay Has a Clear Structure and Flow
The IB likes structure. Your EE needs a clear introduction (which should be one to two double-spaced pages), research question/focus (i.e., what you're investigating), a body, and a conclusion (about one double-spaced page). An essay with unclear organization will be graded poorly.
The body of your EE should make up the bulk of the essay. It should be about eight to 18 pages long (again, depending on your topic). Your body can be split into multiple parts. For example, if you were doing a comparison, you might have one third of your body as Novel A Analysis, another third as Novel B Analysis, and the final third as your comparison of Novels A and B.
If you're conducting an experiment or analyzing data, such as in this EE , your EE body should have a clear structure that aligns with the scientific method ; you should state the research question, discuss your method, present the data, analyze the data, explain any uncertainties, and draw a conclusion and/or evaluate the success of the experiment.
#6: Start Writing Sooner Rather Than Later!
You will not be able to crank out a 4,000-word essay in just a week and get an A on it. You'll be reading many, many articles (and, depending on your topic, possibly books and plays as well!). As such, it's imperative that you start your research as soon as possible.
Each school has a slightly different deadline for the Extended Essay. Some schools want them as soon as November of your senior year; others will take them as late as February. Your school will tell you what your deadline is. If they haven't mentioned it by February of your junior year, ask your IB coordinator about it.
Some high schools will provide you with a timeline of when you need to come up with a topic, when you need to meet with your advisor, and when certain drafts are due. Not all schools do this. Ask your IB coordinator if you are unsure whether you are on a specific timeline.
Below is my recommended EE timeline. While it's earlier than most schools, it'll save you a ton of heartache (trust me, I remember how hard this process was!):
- January/February of Junior Year: Come up with your final research topic (or at least your top three options).
- February of Junior Year: Approach a teacher about being your EE advisor. If they decline, keep asking others until you find one. See my notes above on how to pick an EE advisor.
- April/May of Junior Year: Submit an outline of your EE and a bibliography of potential research sources (I recommend at least seven to 10) to your EE advisor. Meet with your EE advisor to discuss your outline.
- Summer Between Junior and Senior Year: Complete your first full draft over the summer between your junior and senior year. I know, I know—no one wants to work during the summer, but trust me—this will save you so much stress come fall when you are busy with college applications and other internal assessments for your IB classes. You will want to have this first full draft done because you will want to complete a couple of draft cycles as you likely won't be able to get everything you want to say into 4,000 articulate words on the first attempt. Try to get this first draft into the best possible shape so you don't have to work on too many revisions during the school year on top of your homework, college applications, and extracurriculars.
- August/September of Senior Year: Turn in your first draft of your EE to your advisor and receive feedback. Work on incorporating their feedback into your essay. If they have a lot of suggestions for improvement, ask if they will read one more draft before the final draft.
- September/October of Senior Year: Submit the second draft of your EE to your advisor (if necessary) and look at their feedback. Work on creating the best possible final draft.
- November-February of Senior Year: Schedule your viva voce. Submit two copies of your final draft to your school to be sent off to the IB. You likely will not get your grade until after you graduate.
Remember that in the middle of these milestones, you'll need to schedule two other reflection sessions with your advisor . (Your teachers will actually take notes on these sessions on a form like this one , which then gets submitted to the IB.)
I recommend doing them when you get feedback on your drafts, but these meetings will ultimately be up to your supervisor. Just don't forget to do them!

The early bird DOES get the worm!
How Is the IB Extended Essay Graded?
Extended Essays are graded by examiners appointed by the IB on a scale of 0 to 34 . You'll be graded on five criteria, each with its own set of points. You can learn more about how EE scoring works by reading the IB guide to extended essays .
- Criterion A: Focus and Method (6 points maximum)
- Criterion B: Knowledge and Understanding (6 points maximum)
- Criterion C: Critical Thinking (12 points maximum)
- Criterion D: Presentation (4 points maximum)
- Criterion E: Engagement (6 points maximum)
How well you do on each of these criteria will determine the final letter grade you get for your EE. You must earn at least a D to be eligible to receive your IB Diploma.
Although each criterion has a point value, the IB explicitly states that graders are not converting point totals into grades; instead, they're using qualitative grade descriptors to determine the final grade of your Extended Essay . Grade descriptors are on pages 102-103 of this document .
Here's a rough estimate of how these different point values translate to letter grades based on previous scoring methods for the EE. This is just an estimate —you should read and understand the grade descriptors so you know exactly what the scorers are looking for.
Here is the breakdown of EE scores (from the May 2021 bulletin):
How Does the Extended Essay Grade Affect Your IB Diploma?
The Extended Essay grade is combined with your TOK (Theory of Knowledge) grade to determine how many points you get toward your IB Diploma.
To learn about Theory of Knowledge or how many points you need to receive an IB Diploma, read our complete guide to the IB program and our guide to the IB Diploma requirements .
This diagram shows how the two scores are combined to determine how many points you receive for your IB diploma (3 being the most, 0 being the least). In order to get your IB Diploma, you have to earn 24 points across both categories (the TOK and EE). The highest score anyone can earn is 45 points.
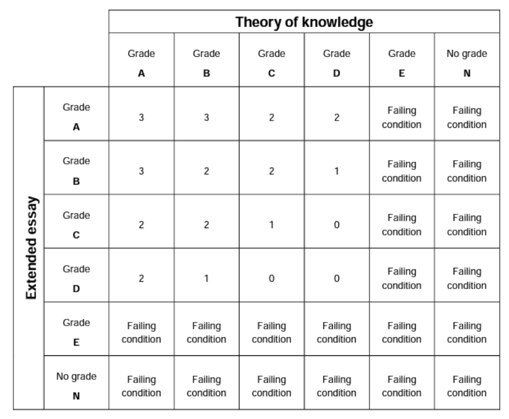
Let's say you get an A on your EE and a B on TOK. You will get 3 points toward your Diploma. As of 2014, a student who scores an E on either the extended essay or TOK essay will not be eligible to receive an IB Diploma .
Prior to the class of 2010, a Diploma candidate could receive a failing grade in either the Extended Essay or Theory of Knowledge and still be awarded a Diploma, but this is no longer true.
Figuring out how you're assessed can be a little tricky. Luckily, the IB breaks everything down here in this document . (The assessment information begins on page 219.)
40+ Sample Extended Essays for the IB Diploma Programme
In case you want a little more guidance on how to get an A on your EE, here are over 40 excellent (grade A) sample extended essays for your reading pleasure. Essays are grouped by IB subject.
- Business Management 1
- Chemistry 1
- Chemistry 2
- Chemistry 3
- Chemistry 4
- Chemistry 5
- Chemistry 6
- Chemistry 7
- Computer Science 1
- Economics 1
- Design Technology 1
- Design Technology 2
- Environmental Systems and Societies 1
- Geography 1
- Geography 2
- Geography 3
- Geography 4
- Geography 5
- Geography 6
- Literature and Performance 1
- Mathematics 1
- Mathematics 2
- Mathematics 3
- Mathematics 4
- Mathematics 5
- Philosophy 1
- Philosophy 2
- Philosophy 3
- Philosophy 4
- Philosophy 5
- Psychology 1
- Psychology 2
- Psychology 3
- Psychology 4
- Psychology 5
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 1
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 2
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 3
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 1
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 2
- Visual Arts 1
- Visual Arts 2
- Visual Arts 3
- Visual Arts 4
- Visual Arts 5
- World Religion 1
- World Religion 2
- World Religion 3

What's Next?
Trying to figure out what extracurriculars you should do? Learn more about participating in the Science Olympiad , starting a club , doing volunteer work , and joining Student Government .
Studying for the SAT? Check out our expert study guide to the SAT . Taking the SAT in a month or so? Learn how to cram effectively for this important test .
Not sure where you want to go to college? Read our guide to finding your target school . Also, determine your target SAT score or target ACT score .

As an SAT/ACT tutor, Dora has guided many students to test prep success. She loves watching students succeed and is committed to helping you get there. Dora received a full-tuition merit based scholarship to University of Southern California. She graduated magna cum laude and scored in the 99th percentile on the ACT. She is also passionate about acting, writing, and photography.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
What Is an IB Extended Essay and How to Write It?
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
The IB extended essay is a paper of up to 4,000 words that is required for students enrolled in the International Baccalaureate (IB) diploma program. The extended essay allows students to engage in independent research on a topic within one of the available subject areas.
The extended essay should be an original piece of academic writing that demonstrates the following student's abilities:
- Formulating a research question
- Conductig independent investigation
- Presenting key findings in a scholarly format.
Check out this article by StudyCrumb to discover how to write an IB extendend essay properly. We will give you a complete writing guide and critical tips you need for this essay type.
IB Extended Essay: What Is It?
An extended essay is independent research. Usually students choose a topic in consultation with a mentor. It is an integral part of the International Baccalaureate (IB) degree program. This means that you won't receive a degree without a successfully written paper. It requires 4,000-word study on a chosen narrow topic. To get a high score, you should meet all required structure and formatting standards. This is the result of approximately 40 working hours. Its purpose is giving you the opportunity to try independent research writing. It's approved that these skills are critical for student success at university. The following sections explain how to write an extended article with examples. So keep reading!
Choosing a Mentor for Extended Essay
IB extended essay guidelines require supervisor meetings, totaling 3-5 hours. They include three critical reflections. A mentor won't write a paper instead of you but can help adjust it. So it is important to consult with them, but no one will proofread or correct actual research for you. In general, initially treat an essay as an exclusively individual work. So your role and contribution are maximal.
Extended Essay Outline
Let's take a look at how to write an extended essay outline. In this part, you organize yourself so that your work develops your idea. So we especially recommend you work out this step with your teacher. You can also find any outline example for essay . In your short sketch, plan a roadmap for your thoughts. Think through and prepare a summary of each paragraph. Then, expand annotation of each section with a couple more supporting evidence. Explain how specific examples illustrate key points. Make it more significant by using different opinions on general issues.
Extended Essay: Getting Started
After you chose an extended essay topic and made an outline, it's time to start your research. Start with a complete Table of Contents and make a choice of a research question. Select the subject in which you feel most confident and which is most interesting for you. For example, if at school you are interested in natural science, focus on that. If you have difficulties choosing a research question, rely on our essay topic generator .
Extended Essay Introduction
In the introduction of an extended essay, present a thesis statement. But do it in such a way that your readers understand the importance of your research. State research question clearly. That is the central question that you are trying to answer while writing. Even your score depends on how you develop your particular research question. Therefore, it is essential to draw it up correctly. Gather all relevant information from relevant sources. Explain why this is worth exploring. Then provide a research plan, which you will disclose further.
Extended Essay Methodology
In accordance with extended essay guidelines, it's mandatory to choose and clearly state a methodological approach. So, it will be apparent to your examiner how you answered your research question. Include your collection methods and tools you use for collection and analysis. Your strategies can be experimental or descriptive, quantitative or qualitative. Research collection tools include observations, questionnaires, interviews, or background knowledge.
Extended Essay Main Body
Well, here we come to the most voluminous part of the extended essay for IB! In every essay body paragraph , you reveal your research question and discuss your topic. Provide all details of your academic study. But stay focused and do it without dubious ideas. Use different sources of information to provide supporting arguments and substantial evidence. This will impress professors. For this section, 3 main paragraphs are enough. Discuss each idea or argument in a separate paragraph. You can even use supporting quotes where appropriate. But don't overcomplicate. Make your extended essay easy to read and logical. It's critical to stay concise, so if you aren't sure how to make your text readable, use our tool to get a readbility test . Following the plan you outlined earlier is very important. Analyze each fact before including it in your writing. And don't write unnecessary information.
Extended Essay Conclusion
Now let's move on to the final part of IB extended essay guidelines. In conclusion, focus on summarizing the main points you have made. No new ideas or information can be introduced in this part. Use conclusion as your last chance to impress your readers. Reframe your own strong thesis. Here you must show all key points. Do not repeat absolutely every argument. Better try to make this part unique. This will show that you have a clear understanding of the topic you have chosen. And even more professional will be recommendations of new areas for future research. One good paragraph may be enough here. Although in some cases, two or three paragraphs may be required.
Extended Essay Bibliography & Appendices
To write an impressive extended essay, you should focus on appropriate information. You must create a separate page for bibliography with all sources you used. Tip from us: start writing this page with the first quote you use. Don't write this part last or postpone. In turn, appendices are not an essential section. Examiners will not pay much attention to this part. Therefore, include all information directly related to analysis and argumentation in the main body. Include raw data in the appendix only if it is really urgently needed. Moreover, it is better not to refer to appendices in text itself. This can disrupt the narrative of the essay.
Extended Essay Examples
We have prepared a good example of an extended essay. You can check it by downloading it for free. You can use it as a template. However, pay attention that your paper is required to be unique. Don't be afraid to present all the skills you gained during your IB.
Final Thoughts on IB Extended Essay
In this article, we presented detailed IB extended essay guidelines. An extended essay is a daunting academic challenge to write. It is a research paper with a deep thematic analysis of information. But we have described several practical and straightforward tips. Therefore, we are sure that you will succeed!
If topics seem too complex, turn to our top essay writers. They will accomplish any IB assignment in the best way your professor can evaluate it!

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like


- Westbourne Voices
- Awards and Affiliations
- Virtual Tour
- Admissions Overview
- School Admissions Process
- Nursery Admissions Process
- International Student Admissions
- Visits & Open Days
- Welcome to Nursery
- Nursery Life
- Nursery Curriculum
- Nursery Sessions
- Nursery Fees and Applications
- Stepping up to Prep School
- Welcome to Prep School
- Prep Academic Curriculum
- Prep Co-Curricular
- Prep School Case Studies
- Stepping up to Senior School
- Welcome to Senior School
- GCSE Subjects
- Senior Co-curricular
- Stepping Up to Sixth Form
- Welcome to Sixth Form
- IB Subjects
- IB Inner Core
- Oxbridge and Russell Group
- Careers Guidance
- Super Curriculum
- Sixth Form Case Studies
- Westbourne Life
- Welcome to Boarding
- Boarding Options
- Boarding Life
- Boarding FAQs
- Boarding Case Studies
- Future Leaders Lab
- School Uniform
- School Transport
- Visiting Information

How To Write The Extended Essay (With Topics and Examples)
This comprehensive guide navigates through every aspect of the EE, from selecting a topic and developing a research question to conducting in-depth research and writing a compelling essay. It offers practical strategies, insights, and tips to help students craft a piece of work that not only meets the rigorous standards of the IB but also reflects their academic passion and curiosity. Join us as we explore the keys to success in the Extended Essay, preparing you for an intellectually rewarding experience.
Posted: 13th February 2024
Section jump links:
Section 1: Understanding the IB Extended Essay
Section 2: the importance of the extended essay, section 3: selecting a topic, section 4: developing your research question, section 5: research methodology and theoretical frameworks, section 6: evaluating sources and data, section 7: integrating evidence and analysis, section 8: writing and structuring the extended essay, section 9: reflection and the rppf, section 10: the significance of academic discipline in the ee, section 11: good practice in extended essay writing, section 12: managing the extended essay process, section 13: collaboration and feedback, section 14: avoiding plagiarism, section 15: emphasising original thought, section 16: final presentation and viva voce, section 17: beyond the extended essay, what is the ib extended essay.
The International Baccalaureate (IB) Extended Essay (EE) is a cornerstone of the IB Diploma Programme . It’s an independent, self-directed piece of research, culminating in a 4,000-word paper. This project offers students an opportunity to investigate a topic of their own choice, bridging the gap between classwork and the kind of research required at the university level.
Key Objectives and the Role of the EE in the IB Curriculum
The Extended Essay has several key objectives:
- To provide students with the chance to engage in an in-depth study of a question of interest within a chosen subject.
- To develop research, thinking, self-management, and communication skills.
- To introduce students to the excitement and challenges of academic research.
The EE plays a critical role in the IB curriculum by:
- Encouraging intellectual discovery and creativity.
- Facilitating academic growth and personal development through research and writing.
- Preparing students for the rigours of higher education.
Extended Essay Word Count and Requirements
The EE has a maximum word count of 4,000 words. This does not include the abstract, contents page, bibliography, or footnotes (which must be used sparingly). Here are some essential requirements:
- Research Question: Your essay must be focused on a clear, concise research question. You should aim to provide a comprehensive answer to this question through your research and writing.
- Subject : The EE can be written in one of the student’s six chosen subjects for the IB diploma or in a subject recognized by the IB.
- Supervision : Each student is assigned a supervisor (usually a teacher in their school) who provides guidance and support throughout the research and writing process.
- Assessment: The essay is externally assessed by the IB, contributing up to three points towards the total score for the IB diploma, depending on the grade achieved and the performance in the Theory of Knowledge course.
The Extended Essay is not just an academic requirement but a unique opportunity to explore a topic of personal interest in depth. This can be an incredibly rewarding experience, providing valuable skills and insights that will serve you well in your future academic and professional endeavours.

The EE is more than just a requirement for the IB Diploma. It’s an essential part of the IB experience , offering profound benefits for students. Let’s explore why the EE holds such significance.
Academic and Personal Development Benefits
Skill enhancement:.
The EE fosters a range of academic skills crucial for success in higher education and beyond. It teaches students how to:
- Conduct comprehensive research
- Develop a coherent argument
- Write extensively on a subject
- Manage time effectively
Personal Growth:
Beyond academic prowess, the EE encourages personal development. Students learn to:
- Pursue their interests deeply
- Overcome challenges independently
- Reflect on their learning process
- Enhance their curiosity and creativity
Contribution to University Admissions
Standout applications:.
The EE can be a significant advantage in university applications . It demonstrates a student’s ability to undertake serious research projects and commit to an intensive academic task. Universities value this dedication, seeing it as indicative of a student’s readiness for undergraduate studies.
Showcase of Skills:
The EE allows students to showcase their research, writing, and analytical skills. It provides concrete evidence of their academic abilities and their capacity to engage deeply with a topic of interest.
Skill Development: Research, Writing, and Critical Thinking
Research Skills:
Students learn to navigate academic literature, evaluate sources, and gather relevant data. This process sharpens their research skills, laying a solid foundation for future academic endeavours.
Writing Skills:
Crafting a 4,000-word essay challenges students to express their ideas clearly and persuasively. It hones their writing skills, teaching them the art of structured and focused academic writing.
Critical Thinking:
The EE encourages students to analyse information critically, assess arguments, and develop their viewpoints. This critical engagement fosters a sophisticated level of thought, beneficial in both academic and real-world contexts.
In conclusion, the Extended Essay is a pivotal element of the IB Diploma Programme. It’s an invaluable opportunity for intellectual and personal growth, preparing students for the challenges of higher education and beyond. With its emphasis on independent research and writing, the EE equips students with the skills and confidence to navigate their future academic journeys successfully.

Choosing a topic for your Extended Essay is the first step in a journey towards developing a deep understanding of a specific area of interest. It’s crucial to select a topic that is not only academically viable but also personally engaging. Here’s how to navigate this critical phase.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Your EE Topic
Interest and passion:.
Select a topic that fascinates you. Your interest will sustain motivation over the months of research and writing.
Availability of Resources:
Ensure there are enough resources available on your chosen topic. Access to libraries, databases, and experts in the field is essential for comprehensive research.
Scope and Focus:
The topic should be narrow enough to allow for in-depth study yet broad enough to find sufficient research material. Balancing specificity with resource availability is key.
IB Subject Areas:
Your topic must align with one of the subjects you are studying in the IB Diploma Programme or an approved subject area. Familiarity with the subject’s methodology and criteria is crucial for success.
How to Align Your Interests with the IB Subjects
Explore the syllabus:.
Review the syllabus of your IB subjects to identify topics that interest you. This can provide a framework for your EE.
Consult with Teachers:
Teachers can offer insights into feasible topics that align with the IB criteria and offer guidance on how to approach them.
Consider Interdisciplinary Topics:
Some of the most engaging EEs explore the intersection between different subjects. If this interests you, ensure your approach meets the criteria for an interdisciplinary essay under the IB’s World Studies EE option.
Extended Essay Topics: Examples Across Various Disciplines
- Sciences: How does the introduction of non-native plant species affect biodiversity in your local ecosystem?
- History : What was the impact of Winston Churchill’s leadership on Britain’s role in World War II?
- English: How does the use of unreliable narrators influence the reader’s perception in Ian McEwan’s novels?
- Mathematics: Investigating the application of the Fibonacci sequence in predicting stock market movements.
- Visual Arts: Exploring the influence of Japanese art on Claude Monet’s painting style.
Selecting the right topic is foundational to your EE journey. It shapes your research direction, influences your engagement with the essay, and ultimately contributes to the satisfaction and success of your EE experience. Take your time, consult widely, and choose a topic that you are eager to explore in depth.

Crafting a focused and clear research question is a pivotal element of your Extended Essay. This question not only guides your research but also frames your essay’s entire structure. It’s the question to which your essay will provide an answer, and as such, it requires thoughtful consideration and precision.
A well-developed research question should be specific, relevant, and challenging. It should invite analysis, discussion, and the exploration of significant academic literature. Here’s a deeper look into formulating a robust research question for your EE.
Characteristics of a Strong Research Question
The hallmark of a strong research question is its specificity. It shouldn’t be too broad, as this could lead to a superficial treatment of the topic.
Conversely, a question that’s too narrow might not allow for comprehensive exploration or significant discussion. Finding a balance is key. The question should also be focused on a particular aspect of a subject area, enabling in-depth analysis within the word count limit.
Another important characteristic is the question’s alignment with available resources. Before finalising your question, ensure that you have access to sufficient data and scholarly research to support your investigation. This might involve preliminary searches in academic databases, libraries, or consultation with your supervisor.
Tips for Refining Your Research Question
Start by brainstorming broad topic areas that interest you. Once you’ve identified a general area of interest, begin narrowing down by asking yourself specific questions about the topic. What aspects of this topic are unexplored or underexplored? What specific angle can I take that will make my research unique?
It’s also beneficial to review past EEs or academic journals for inspiration. Seeing how others have structured their research questions can provide valuable insight into crafting your own. However, ensure your question remains original and tailored to your interests.
Examples of Effective Research Questions
To give you an idea of what a well-formulated research question looks like, here are a few examples:
- Biology: How does the concentration of a specific nutrient affect the growth rate of plant species X in a hydroponic setup compared to soil-based growth?
- History: To what extent did the public speeches of Martin Luther King Jr. influence the public’s perception of the Civil Rights Movement in the United States between 1963 and 1968?
- Economics: How significant is the impact of recent economic policies on small businesses in [specific location] during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- English Literature: How does the use of magical realism in Gabriel García Márquez’s ‘One Hundred Years of Solitude’ reflect the political and social issues of post-colonial Latin America?
Developing your research question is an iterative process. It may evolve as you delve deeper into your research. Be open to refining your question based on the information you discover and discussions with your supervisor. A well-crafted research question will not only guide your research effectively but also engage your interest throughout the writing process, leading to a more meaningful and insightful Extended Essay.

A critical component of your Extended Essay is selecting an appropriate research methodology and theoretical framework. These elements are foundational to conducting your research and crafting your argument, influencing how you collect, analyse, and interpret data.
Understanding Research Methodologies
Research methodology refers to the systematic approach you take to investigate your research question. It encompasses the methods and procedures you use to collect and analyse data. Your chosen methodology should align with the nature of your research question and the objectives of your essay.
In the sciences, for example, your methodology might involve experiments, observations, or simulations to gather empirical data. In the humanities, you may lean towards content analysis, comparative analysis, or historical investigation, relying on textual or archival sources.
Selecting the right methodology is crucial. It should provide a clear path to answering your research question, considering the resources available and the scope of your essay. It’s also important to justify your choice of methodology in your essay, explaining why it’s appropriate for your research question and how it will help you achieve your objectives.
Applying Theoretical Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks provide a lens through which your research is conducted and interpreted. They offer a structured way to understand and analyse your findings, grounding your study in existing knowledge and theories.
Choosing a theoretical framework involves identifying relevant theories, models, or concepts that apply to your topic. For instance, if you’re exploring media representation of gender, you might utilise feminist theory as a framework to analyse your findings. In economics, you might apply game theory to understand competitive behaviours in a market.
The framework should guide your analysis, providing a coherent basis for interpreting your data. It helps to structure your argument, offering a deeper insight into the significance of your findings within the broader academic discourse.
Integrating Methodology and Frameworks into Your Research
Successfully integrating your chosen methodology and theoretical framework involves a few key steps:
- Clarify the Scope: Ensure your research question, methodology, and theoretical framework align in scope and focus. They should work together seamlessly to guide your research.
- Justify Your Choices: Explain the rationale behind your chosen methodology and framework. Discuss why they are suitable for your research question and how they will support your investigation.
- Apply Consistently: Use your methodology and framework consistently throughout your research and analysis. This consistency strengthens the coherence and academic rigour of your essay.
Reflecting on these components during the planning stage can enhance the quality of your research and the clarity of your argument. Your methodology and theoretical framework are not just academic requirements; they’re tools that shape the direction and depth of your inquiry, enabling a more structured and insightful exploration of your topic.

In the journey of crafting an Extended Essay (EE), the ability to critically evaluate sources and data stands as a fundamental skill. This evaluation is crucial in establishing the credibility and reliability of the information that forms the backbone of your research. Understanding how to discern the quality and relevance of your sources ensures that your EE is built on a solid foundation of trustworthy information.
Criteria for Selecting Credible and Relevant Sources
Authority: Consider the source’s authorship. Look for works by experts in the field, academic institutions, or reputable organisations. The author’s qualifications and affiliations can significantly impact the reliability of the information.
Accuracy: The information should be supported by evidence, referenced appropriately, and free from factual errors. Reliable sources often undergo a peer-review process, ensuring that the content is scrutinised and validated by other experts in the field.
Currency: The relevance of information can diminish over time, especially in fields that evolve rapidly, such as science and technology. Ensure that the sources you use are up-to-date, reflecting the latest research and developments.
Purpose: Understand the purpose behind the information. Is it to inform, persuade, entertain, or sell? Recognising the intent can help you assess potential biases, which is particularly important when dealing with controversial topics.
Techniques for Evaluating the Reliability and Validity of Data
Cross-Verification: Cross-check information across multiple sources to verify its accuracy and reliability. Consistency among various sources can be a good indicator of the information’s validity.
Statistical Analysis: When dealing with numerical data, consider its statistical significance and the methodology used in its collection. Reliable data should be gathered using sound scientific methods and accurately represent the population or phenomena studied.
Source Evaluation Tools: Utilise tools and checklists designed to evaluate the credibility of sources. These can provide a structured approach to assessing the quality of your research materials.
Incorporating Primary vs. Secondary Sources Effectively
Primary Sources: These are firsthand accounts or direct evidence concerning the topic you’re researching. They include interviews, surveys, experiments, and historical documents. Primary sources offer original insights and data, allowing for a deeper and more personal engagement with your subject.
Secondary Sources: These sources analyse, interpret, or summarise information from primary sources. They include textbooks, articles, and reviews. Secondary sources can provide context, background, and a broader perspective on your topic.
Balancing primary and secondary sources enriches your research, providing both the raw data and the interpretations that help frame your analysis. By rigorously evaluating sources and data, you ensure that your Extended Essay rests on a foundation of credible and relevant information, enhancing the depth and rigour of your investigation.

The heart of a compelling Extended Essay (EE) lies in the seamless integration of evidence and analysis. This integration not only supports and substantiates your arguments but also demonstrates your ability to critically engage with your research topic. Here’s how to weave evidence and analysis together in a way that enhances the strength and persuasiveness of your EE.
Strategies for Integrating Evidence Seamlessly into Your Argument
Directly Link Evidence to Your Thesis: Every piece of evidence you include should directly support or relate to your thesis statement. This ensures that all the information contributes to building your argument coherently.
Use Evidence to Illustrate Points: Utilise examples, data, quotes, and case studies as concrete evidence to illustrate your points. This makes abstract concepts more tangible and convincing to the reader.
Analyse, Don’t Just Present: For every piece of evidence, provide analysis and interpretation. Explain how it supports your argument, what it demonstrates, and its implications for your research question.
Balancing Descriptive and Analytical Writing
Avoid Over-Description: While some description is necessary to set the context, avoid dedicating too much space to merely describing your evidence. The focus should be on analysis.
Develop a Critical Voice: Cultivate a critical approach to your evidence. This means evaluating its reliability, considering its limitations, and discussing its relevance to your argument.
Synthesise Information: Aim to synthesise evidence from multiple sources to support your points. This demonstrates comprehensive understanding and the ability to draw connections across your research.
How to Critically Analyse Sources and Data Within Your Essay
Question the Source: Consider the source’s origin, purpose, and potential bias. How might these factors influence the information presented?
Evaluate Methodology: If the evidence comes from a study or experiment, evaluate the methodology used. Is it sound and appropriate for the research question?
Consider the Broader Context: Place your evidence within the broader scholarly conversation on your topic. How does it fit with, challenge, or expand existing knowledge?
By thoughtfully integrating evidence and providing in-depth analysis, you can create a nuanced and compelling EE that goes beyond mere description to offer original insights into your topic. This approach not only strengthens your argument but also showcases your critical thinking and analytical skills, essential qualities for success in the IB Diploma Programme and beyond.
The Extended Essay presents an opportunity for IB students to engage deeply with a topic of their choice. However, to effectively communicate your research and insights, your essay must be well-structured and clearly written.
This section provides guidance on how to write and structure your EE, ensuring your work is coherent, persuasive, and academically rigorous.
Outline of the Extended Essay Structure
A well-organised structure is crucial for the readability and coherence of your EE. Typically, an Extended Essay includes the following components:
- Title Page: Displays the essay title, research question, subject the essay is registered in, and word count.
- Abstract: A concise summary of the essay, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusion (Note: For essays submitted in 2018 and forward, the IB no longer requires an abstract, so check the most current guidelines).
- Contents Page: Lists the sections and subsections of your essay with page numbers.
- Introduction: Introduces the research question and your essay’s purpose, outlining the scope of the investigation.
- Body : The main section of your essay, divided into clearly titled subsections, each addressing specific aspects of the research question. It’s where you present your argument, supported by evidence.
- Conclusion: Summarises the findings, discusses the implications, and reflects on the research’s limitations and potential areas for further study.
- References/Bibliography: Lists all sources used in the essay in a consistent format, following the chosen citation style.
- Appendices: (If necessary) Contains supplementary material that is relevant to the research but not essential to its explanation.
Detailed Breakdown of Each Section
Introduction:
The introduction sets the stage for your research. It should clearly state your research question and explain the significance of the topic. Briefly outline the theoretical framework and methodology, and provide an overview of the essay’s structure.
The body is the heart of your essay. It should be logically organised to build your argument step by step. Each paragraph should start with a clear topic sentence, followed by evidence and analysis. Use subheadings to divide the sections thematically or methodologically, ensuring each part contributes to answering the research question.
- Developing Arguments: Present and critique different perspectives, systematically leading the reader through your analytical process.
- Using Evidence: Incorporate relevant data, quotes, and examples to support your arguments. Ensure all sources are appropriately cited.
- Analysis and Discussion: Go beyond describing your findings; analyse and interpret them in the context of your research question and theoretical framework.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should not introduce new information. Instead, it should synthesise your findings, highlighting how they contribute to understanding the research question. Reflect on the research process, acknowledging any limitations and suggesting areas for further investigation.
Importance of Coherence and Logical Flow
Maintaining coherence and a logical flow throughout your EE is essential. Transition sentences between paragraphs and sections can help link ideas smoothly, guiding the reader through your argument. A coherent structure ensures that your essay is accessible and persuasive, making a strong impression on the reader.
A well-written and structured EE is a testament to your understanding of the research process and your ability to communicate complex ideas effectively. By adhering to a clear structure and focusing on coherence and logical progression, you can craft an essay that is engaging, insightful, and academically rigorous.

A unique and integral component of the IB Extended Essay (EE) process is the Reflections on Planning and Progress Form (RPPF). The RPPF serves as a personal and academic exploration tool, guiding students through the planning, research, and writing phases of their EE. It encourages students to reflect on their learning journey, documenting insights gained, challenges encountered, and the evolution of their thinking.
The Role of Reflection in the EE Process
Reflection is at the heart of the EE, enabling students to engage critically with their own learning processes. It helps in:
- Self-Assessment: Encouraging students to consider their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Skill Development: Facilitating a deeper understanding of the research and writing skills developed during the EE process.
- Critical Thinking: Promoting an evaluative approach to the research process, allowing students to make informed decisions about their methodologies, sources, and arguments.
How to Effectively Complete the RPPF
Completing the RPPF involves three formal reflection sessions, which are crucial milestones in the EE journey:
- Initial Reflection: Focuses on the selection of the topic and formulation of the research question. Students should discuss their motivations, initial ideas, and anticipated challenges.
- Interim Reflection: Occurs midway through the process. Students reflect on the progress made, adjustments to their research plan, and any challenges they’ve faced. It’s an opportunity to reassess the direction of the EE and make necessary modifications.
- Final Reflection: After completing the EE, students reflect on their overall experience, the skills they’ve developed, and the knowledge they’ve gained. This reflection should also consider the impact of the research process on their personal and academic growth.
In each reflection, students should be honest and critical, providing insights into their learning journey. The reflections are not just about documenting successes but also about understanding the learning process, including setbacks and how they were overcome.
Examples of Reflective Questions and Insightful Responses
Initial reflection:.
Question: “What excites me about my chosen topic?”
Insightful Response: Discuss the personal or academic interest in the topic, any prior knowledge, and what you hope to discover through your research.
Interim Reflection:
Question: “What challenges have I encountered in my research, and how have I addressed them?”
Insightful Response: Describe specific obstacles, such as difficulty accessing resources or refining the research question, and the strategies employed to overcome them.
Final Reflection:
Question: “How has my understanding of the topic evolved through the research process?”
Insightful Response: Reflect on how the research challenged or confirmed initial assumptions and what was learned about the topic and the research process itself.
The RPPF is not just a formal requirement but a valuable component of the EE that enriches the student’s learning experience. By fostering reflection, the RPPF helps students to articulate their journey, offering insights into the complexities of research and the personal growth that accompanies the creation of an extended academic work.

The Extended Essay allows students to explore a topic of interest within the framework of an IB subject. The choice of academic discipline not only shapes the content and focus of the essay but also influences the methodologies and theoretical frameworks that students may employ. Understanding and adhering to the conventions and requirements of the chosen discipline is crucial for the success of the EE.
Adhering to Disciplinary Conventions and Guidelines
Each academic discipline has its own set of conventions regarding research methodologies, writing styles, and citation formats. For example, a science EE might require empirical research and quantitative analysis, whereas an essay in the humanities might focus on qualitative analysis and critical interpretation of texts.
Key considerations include:
- Methodology: The choice of methodology should align with disciplinary norms. Science EEs might involve experiments, whereas essays in history might rely on primary source analysis.
- Structure: While the basic structure of the EE remains consistent across subjects, the presentation of arguments and evidence might vary. Essays in the arts and humanities might follow a thematic structure, while those in the sciences might be organised around experimental findings.
- Citation Style: Different disciplines prefer specific citation styles. For instance, APA might be favoured in psychology, while MLA is commonly used in literature essays. Adhering to the appropriate style is crucial for academic integrity.
How Different Disciplines Influence the Approach to Research and Writing
The academic discipline not only dictates the formal aspects of the EE but also influences the approach to research and writing. For instance, an EE in Visual Arts would require a different analytical lens compared to an EE in Economics. The former might analyse the impact of cultural contexts on artistic expressions, while the latter could evaluate economic theories through case studies.
Disciplinary perspectives also affect:
- Argumentation : The way arguments are constructed and evidenced can differ. In the sciences, arguments are often built around data and logical reasoning, while in the humanities, they might be more interpretative, drawing on various theoretical perspectives.
- Critical Engagement: The extent and nature of critical engagement with sources can vary. In subjects like History or English, a critical analysis of diverse interpretations is fundamental, whereas in the Sciences, the focus might be on empirical evidence and hypothesis testing.
Examples of Disciplinary Perspectives in Extended Essay Examples
- Biology EE: An investigation into the effects of environmental changes on local biodiversity, employing scientific methods for data collection and analysis.
- Economics EE: An analysis of the impact of a specific economic policy on a local economy, using economic theories and models to interpret data.
- English Literature EE: A comparative study of the theme of alienation in two novels, using literary theories to explore the authors’ narrative techniques.
Understanding the significance of academic discipline in the EE ensures that students approach their research with the appropriate methodologies and analytical frameworks. It encourages respect for the depth and breadth of the subject area, contributing to a more nuanced and informed exploration of the chosen topic.

Writing an Extended Essay involves more than just conducting research and presenting findings; it requires careful planning, effective engagement with your supervisor, and a critical approach to your sources. Here are some best practices to help you navigate the EE writing process successfully.
Time Management and Planning
Time management is crucial in the EE process. The project spans several months, so it’s essential to break down the work into manageable stages. Create a timeline early in the process, including key milestones such as completing the research, drafting sections, and finalising the essay. Allocate time for unexpected challenges and ensure you have buffer periods for revision and feedback.
Planning Tips:
- Set Goals: Establish clear, achievable goals for each phase of your EE journey.
- Use Tools: Leverage planning tools or software to organise your tasks and deadlines.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review your progress against your plan and adjust as necessary.
Engaging with Supervisors Effectively:Your supervisor is a valuable resource throughout the EE process. They can provide guidance on your research question, methodology, and essay structure, as well as feedback on your drafts.
Maximising Supervisor Engagement:
- Prepare for Meetings: Come to each meeting with specific questions or sections of your essay you want feedback on.
- Be Open to Feedback: Constructive criticism is essential for improvement. Listen to your supervisor’s suggestions and consider how to incorporate them into your work.
- Communicate Regularly: Keep your supervisor informed of your progress and any challenges you encounter.
Critical Engagement with Sources
A critical approach to the sources you use is fundamental to a high-quality EE. Evaluate the reliability, relevance, and bias of your sources to ensure your essay is grounded in credible evidence.
Strategies for Source Evaluation:
- Source Variety: Use a range of sources, including academic journals, books, and reputable online resources, to provide a balanced perspective on your topic.
- Critical Analysis : Don’t just summarise sources. Analyse their arguments, identify limitations, and consider how they contribute to your research question.
- Citation and Paraphrasing: Accurately cite all sources to avoid plagiarism. When paraphrasing, ensure you’re genuinely rephrasing ideas in your own words while still crediting the original author.
Good practice in EE writing is not just about adhering to academic standards; it’s about engaging deeply with your topic, embracing the research process, and developing skills that will serve you well in your academic and professional future. By managing your time effectively, leveraging the support of your supervisor, and critically engaging with sources, you can craft an EE that is not only academically rigorous but also personally rewarding.

Successfully navigating the Extended Essay process requires more than just academic skill; it demands effective project management. This encompasses planning, organising, and executing your EE from initial conception to final submission. Here are strategies to help you manage the EE process, ensuring a smooth journey and a rewarding outcome.
Planning and Time Management Strategies Specific to the EE
Develop a Detailed Plan: Start by breaking down the EE process into stages: topic selection, research, drafting, and revising. Assign deadlines to each stage based on the final submission date, allowing extra time for unforeseen delays.
Use a Calendar or Planner: Keep track of deadlines, meetings with your supervisor, and other important dates. Digital tools can be particularly useful, offering reminders and helping you stay organised.
Set Regular Milestones: Milestones offer checkpoints to assess your progress. These could be completing the research phase, finishing a first draft, or finalising your citations. Celebrate these achievements to stay motivated.
Milestones and Checklists to Keep You on Track
Create Checklists: For each phase of the EE process, develop a checklist of tasks. This could include conducting initial research, writing specific sections of the essay, or completing rounds of revision.
Regular Progress Reviews: Schedule weekly or bi-weekly reviews of your progress against your plan. Adjust your plan as needed based on these reviews.
Stay Flexible: Be prepared to adapt your plan. Research might take longer than expected, or you might decide to change your focus slightly after discussing with your supervisor.
Dealing with Challenges and Setbacks During the EE Journey
Anticipate Potential Issues: Think ahead about what might go wrong and how you would address it. Having contingency plans can reduce stress and keep you on track.
Seek Support When Needed: Don’t hesitate to reach out to your supervisor, peers, or other mentors if you encounter obstacles. They can offer advice, support, and perspective.
Maintain a Positive Attitude: Challenges are part of the learning process. View setbacks as opportunities to improve your problem-solving and resilience skills.
Managing the EE process effectively is about more than just completing a requirement for the IB Diploma; it’s an exercise in self-management and personal growth. By carefully planning your work, setting and celebrating milestones, and being prepared to tackle challenges, you can navigate the EE process with confidence and achieve a result that reflects your hard work and dedication.

Mastering the art of collaboration and effectively incorporating feedback are pivotal aspects of crafting a high-calibre Extended Essay (EE). These processes enrich your work, offering new perspectives and insights that can significantly enhance the depth and quality of your research and writing. Let’s delve into how to navigate these collaborative interactions and integrate feedback productively.
Effective Collaboration with Your Supervisor
Your supervisor is a key ally in your EE journey, providing guidance, support, and expert insight into your chosen topic. Building a productive relationship with your supervisor involves clear communication, active engagement, and receptiveness to their advice.
- Prepare for Meetings: Maximise the value of your meetings by preparing questions and topics for discussion. This shows initiative and helps you focus on areas where you need the most guidance.
- Be Open to Suggestions: Your supervisor brings a wealth of experience and knowledge. Being open to their suggestions can unlock new avenues of inquiry and refine your research focus.
- Follow Up: After meetings, review the guidance provided and take action. Following up on suggestions and demonstrating progress is key to a fruitful collaboration.
Incorporating Feedback Constructively
Feedback is a gift, offering you fresh eyes on your work and highlighting areas for improvement. Whether it comes from your supervisor, peers, or other mentors, constructive feedback is instrumental in elevating the quality of your EE.
- Critically Evaluate Feedback: Not all feedback will be equally applicable or helpful. Assess suggestions critically and decide which ones align with your research goals and vision for your EE.
- Implement Changes Thoughtfully: When integrating feedback, do so thoughtfully and systematically. Consider how each piece of advice enhances your argument or strengthens your analysis.
- Maintain Your Own Voice: While it’s important to consider feedback, your EE should ultimately reflect your ideas, analysis, and voice. Balance the input from others with your own scholarly insights.
Balancing Independent Research with Guidance
Navigating the balance between independent research and the guidance received is a delicate aspect of the EE process. While the EE is your project, drawing on the expertise and feedback of others can significantly enhance its depth and scope.
- Value Independence: Embrace the opportunity to conduct independent research, making your EE a true reflection of your interests and intellectual curiosity.
- Seek Guidance Wisely: Utilise your supervisor and other resources judiciously. They can provide clarity, offer new perspectives, and help you navigate complex aspects of your research.
- Synthesise Input: Integrate the guidance and feedback you receive in a way that complements your research, ensuring that your EE remains a coherent and cohesive piece of scholarly work.
The interplay between collaboration, feedback, and independent research is central to the EE process. By engaging effectively with your supervisor, thoughtfully incorporating feedback, and maintaining a balance between guidance and your own scholarly pursuits, you can craft an EE that is not only academically rigorous but also a true testament to your growth as a learner.
Plagiarism is a critical concern in academic writing, including the Extended Essay. It involves using someone else’s work without proper acknowledgment, which can compromise the integrity of your essay and result in severe penalties. Understanding what constitutes plagiarism and how to avoid it is essential for maintaining academic honesty and ensuring the credibility of your research.
Understanding What Constitutes Plagiarism
Plagiarism can take many forms, from directly copying text without quotation marks to paraphrasing someone else’s ideas without proper citation. It also includes using images, charts, or data without acknowledging the source. Even unintentional plagiarism, where sources are not deliberately misrepresented but are inadequately cited, can have serious consequences.
How to Properly Cite Sources and Paraphrase
Citing Sources : Every time you use someone else’s words, ideas, or data, you must cite the source. This not only includes quotes and paraphrases but also data, images, and charts. Familiarise yourself with the citation style recommended for your subject area, whether it be APA, MLA, Chicago, or another, and apply it consistently throughout your essay.
Paraphrasing: Paraphrasing involves rewording someone else’s ideas in your own words. It’s essential to do more than just change a few words around; you need to completely rewrite the concept, ensuring you still cite the original source. Good paraphrasing demonstrates your understanding of the material and integrates it seamlessly into your argument.
Using Plagiarism Detection Tools
Many schools and students use plagiarism detection tools to check the originality of their work before submission. These tools compare your essay against a vast database of published material and other student submissions to identify any matches. Utilising these tools can help you identify areas of your essay that need better paraphrasing or citation.
Avoiding plagiarism in the EE involves diligent research, careful writing, and thorough citation. It’s about respecting the intellectual property of others while demonstrating your own understanding and analysis of the topic. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your EE is both original and academically honest, reflecting the hard work and integrity that define the IB learner profile.

In the Extended Essay, showcasing original thought is not just encouraged; it’s a cornerstone of what makes an EE stand out. Originality in this context means more than just avoiding plagiarism; it involves presenting unique perspectives, developing novel arguments, or exploring new areas within a subject. Here’s how you can emphasise original thought in your EE.
The Value of Originality and Creativity
Originality and creativity in the EE demonstrate your ability to think independently and engage critically with your subject. It shows that you’re not just capable of summarising existing knowledge but also contributing to the conversation in your discipline. This level of engagement is what the IB looks for in assessing the EE, as it reflects a deeper understanding and application of the subject matter.
Balancing Academic Rigour with Personal Voice and Analysis
While it’s important to ground your EE in academic research and follow disciplinary conventions, finding a balance with your personal voice and analysis is key to originality. Here are ways to achieve this balance:
- Personal Insight : Inject your essay with your insights, interpretations, and conclusions based on the research. This personal engagement with the topic distinguishes your EE from a mere literature review.
- Critical Analysis: Go beyond describing what others have said. Critique the arguments, identify gaps in the research, and propose new ways of understanding the subject.
- Innovative Approach: Consider addressing less explored aspects of your topic or applying theories and methodologies from other disciplines to bring fresh perspectives.
Strategies for Developing and Showcasing Original Thought
Question Assumptions: Start by questioning the prevailing assumptions or widely held beliefs in your subject area. This critical stance can open up avenues for original analysis.
Interdisciplinary Connections: Drawing connections between different disciplines can reveal new insights and approaches that enrich your essay.
Reflect on Your Learning: Use the insights gained from your coursework and personal interests to inform your approach. Often, your unique educational and life experiences can inspire original perspectives.
Emphasising original thought in your EE is about striking a balance between demonstrating your mastery of the subject and pushing beyond the boundaries of existing knowledge. It involves a blend of thorough research, critical thinking, and creative engagement with the topic. By fostering a unique perspective and injecting your personal voice into your analysis, you can create an EE that is not only academically rigorous but also distinctly yours, leaving a lasting impression on your readers.

The culmination of the Extended Essay process includes the final presentation and the Viva Voce, a concluding interview between the student and their supervisor. These components serve not only as a summation of your EE journey but also as an opportunity to reflect on your learning and the skills you’ve developed. Understanding the significance and how to prepare for these elements is crucial for a successful EE completion.
Preparing for the Final Presentation
The final presentation is an opportunity to share the highlights of your EE journey, including your research question, methodology, key findings, and any challenges you overcame. It’s a moment to showcase the depth of your research and the personal growth you experienced throughout the process.
Key Elements to Include:
- Overview of Your Research: Briefly summarise your research question and why you chose it, highlighting your methodology and the scope of your investigation.
- Significant Findings: Share the key insights and discoveries you made during your research. This is a chance to underscore the original contributions of your EE.
- Challenges and Solutions : Discuss any significant obstacles you faced and how you addressed them. Reflecting on these challenges shows your problem-solving skills and resilience.
- Reflections on the Process: Share what you’ve learned about yourself as a learner, the skills you’ve developed, and how the EE has impacted your academic and personal growth.
Tips for a Successful Viva Voce
The Viva Voce is a short interview with your supervisor after you’ve submitted your EE. It’s an integral part of the reflection process, allowing you to discuss the successes and challenges of your research journey.
To Prepare for the Viva Voce:
- Review Your EE: Be familiar with your essay’s content, as you’ll discuss your work in detail. Be ready to explain your research decisions and reflect on your learning process.
- Anticipate Questions: Your supervisor might ask about how you selected your topic, the development of your research question, your approach to research and writing, and the skills you’ve developed.
- Reflect on Your Learning: Think about the entire EE process, including what you learned, how you’ve grown, and how the experience might influence your future academic or career goals.

How the Viva Voce Contributes to Your Overall EE Assessment
While the Viva Voce doesn’t directly affect your EE grade, it plays a crucial role in the holistic assessment of your IB Diploma. It demonstrates the authenticity of your work and your engagement with the EE process, providing insights into your approach, dedication, and intellectual growth.
The final presentation and Viva Voce are essential milestones that mark the completion of your EE journey. They offer a platform to reflect on the challenges you’ve navigated, the knowledge you’ve gained, and the skills you’ve honed. Preparing thoroughly for these elements ensures you can confidently articulate your research journey, showcasing the depth of your inquiry and your development as an IB learner.

The journey through the Extended Essay is more than an academic exercise; it’s a transformative experience that equips IB Diploma students with skills and insights that extend far beyond the programme.
Reflecting on how the EE prepares you for future academic and professional endeavours can highlight the lasting value of this rigorous project.
How the Skills Developed During the EE Can Benefit You in Future Academic and Professional Endeavours
Research and Analytical Skills: The EE demands a high level of research and analysis, teaching students how to gather, assess, and interpret data. These skills are invaluable in higher education and many professional fields, where evidence-based decision-making is crucial.
Critical Thinking: Crafting an EE requires students to evaluate sources critically, consider multiple perspectives, and develop well-reasoned arguments. This ability to think critically is highly sought after in both academia and the workplace.
Project Management: Completing an EE involves planning, organisation, time management, and problem-solving. Managing such a long-term project successfully can boost your confidence in handling complex tasks and projects in the future.
Communication: Writing the EE enhances your ability to communicate complex ideas clearly and effectively, a skill that is essential in any professional setting. Additionally, the final presentation and Viva Voce develop your verbal communication and presentation skills.
Examples of How the EE Has Helped Alumni in Their Post-IB Journeys
Many IB alumni attribute their success in university and their careers to the foundation laid by their EE experience. For instance, alumni often report that the EE made the transition to university-level research and writing much smoother. Others have found that the skills developed through the EE, such as critical thinking and project management, have set them apart in job interviews and workplace projects.
Encouragement to View the EE as a Stepping Stone to Lifelong Learning
The EE is not just a requirement for the IB Diploma; it’s an introduction to a lifelong journey of inquiry and discovery. It encourages a mindset of curiosity and a habit of continuous learning that can enrich both your personal and professional life. Viewing the EE through this lens can transform it from a daunting task into an exciting opportunity to explore your passions and develop essential skills for the future.
The Extended Essay is a hallmark of the IB Diploma Programme, embodying the essence of inquiry, critical thinking, and scholarly engagement. From selecting a topic and formulating a research question to conducting in-depth research and presenting findings, the EE challenges students to transcend the boundaries of traditional learning, fostering skills and insights that extend far beyond the confines of the classroom.
This comprehensive guide has navigated the critical aspects of the EE process, offering strategies for managing time, engaging with supervisors, and ensuring academic integrity. It has underscored the importance of original thought, the role of academic discipline, and the value of reflection, aiming to equip students with the tools they need to succeed in this rigorous academic endeavour.
The Extended Essay is a testament to your dedication, intellectual curiosity, and academic prowess. Embrace this opportunity to shine, to explore, and to make your mark on the world of knowledge.
How can we help?

IB Extended Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide

The International Baccalaureate (IB) Extended Essay is a substantial research project that challenges high school students to explore a topic of personal interest within one of the IB's six subject areas. This extended essay, typically around 4,000 words in length, allows students to engage in independent research and develop critical thinking and writing skills. In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through the process of completing your IB Extended Essay successfully.
1. Choose Your Subject Area and Topic
- Subject Area: First, select one of the six IB subject areas that you're passionate about and in which you have a strong academic background. These areas include Language and Literature, Language Acquisition, Individuals and Societies, Sciences, Mathematics, and the Arts.
- Topic: Narrow down your subject area to a specific topic or research question that genuinely interests you. Your topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow, allowing for in-depth exploration within the word limit.
2. Develop a Research Question
- Research Question: Create a clear and focused research question that guides your investigation. Your research question should be specific, open-ended, and relevant to your chosen subject area.
3. Conduct Preliminary Research
- Literature Review: Start with preliminary research to gain an understanding of the existing scholarship and literature related to your topic. This will help you refine your research question and identify gaps in the current knowledge.
4. Create a Research Plan
- Timeline: Develop a timeline that outlines key milestones and deadlines for your extended essay. This plan should include research, data collection (if applicable), writing, and revision phases.
5. Collect and Analyze Data (if applicable)
- If your extended essay requires data collection (e.g., experiments, surveys, interviews), conduct this research following ethical guidelines. Ensure that your data collection is well-documented and relevant to your research question.
6. Outline Your Essay
- Structure: Create a clear and organized outline for your extended essay. Typically, your essay will include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The body should be divided into sections or chapters that address different aspects of your research.
- Thesis Statement: Develop a strong thesis statement that presents your main argument or hypothesis.
7. Write Your Extended Essay
- Introduction: Start with a compelling introduction that introduces your research question and provides context for your study.
- Body: Present your research findings and analysis in a logical and structured manner. Ensure that each paragraph contributes to your argument and supports your thesis.
- Citations: Properly cite all sources using a consistent citation style (e.g., MLA, APA). Be diligent in avoiding plagiarism.
- Conclusion: Summarize your main findings, restate your thesis, and discuss the significance of your research.
8. Revise and Edit
- Review: Take time to review and revise your extended essay. Check for clarity, coherence, grammar, spelling, and formatting errors.
- Peer Review: Consider having a peer or teacher review your essay for feedback and suggestions.
9. Create Citations and Bibliography
- Generate a comprehensive bibliography that includes all the sources you used in your research. Ensure that your citations are accurate and properly formatted.
10. Submit Your Extended Essay
- Follow your school's guidelines for submission, including deadlines and formatting requirements.
11. Reflect on the Process
- After completing your extended essay, take some time to reflect on your research journey. Consider what you learned, the challenges you faced, and the skills you developed.
12. Celebrate Your Achievement
- Completing an IB Extended Essay is a significant accomplishment. Celebrate your hard work and the knowledge you've gained throughout the process.
The IB Extended Essay is an opportunity for high school students to engage in independent research and develop essential academic skills. By following this step-by-step guide and staying committed to your research and writing, you can successfully complete your extended essay and present a well-researched and well-structured project that demonstrates your academic abilities and passion for your chosen subject area.
You Might Also Like

A Brief Introduction to College Scholarships
Do you know how to win college scholarship? Know detail information about college scholarship & how to get scholarship successfully? - Read our blog carefully

The Secret to Getting off the Waitlist
So how would you go about making a letter of continued interest while you’re on the waiting status? Here’s a guide we’ve got for you.

Planning for Successful College Applications
Know the right way for successful college application and how to get prepared for college admission to gain admission in your dream college - Read our blog

Free Resources

Extended Essay: Step 10. Plan a structure for your essay
- Extended Essay- The Basics
- Step 1. Choose a Subject
- Step 2. Educate yourself!
- Using Brainstorming and Mind Maps
- Identify Keywords
- Do Background Reading
- Define Your Topic
- Conduct Research in a Specific Discipline
- Step 5. Draft a Research Question
- Step 6. Create a Timeline
- Find Articles
- Find Primary Sources
- Get Help from Experts
- Search Engines, Repositories, & Directories
- Databases and Websites by Subject Area
- Create an Annotated Bibliography
- Advice (and Warnings) from the IB
- Chicago Citation Syle
- MLA Works Cited & In-Text Citations
- Step 9. Set Deadlines for Yourself
- Step 10. Plan a structure for your essay
- Evaluate & Select: the CRAAP Test
- Conducting Secondary Research
- Conducting Primary Research
- Formal vs. Informal Writing
- Presentation Requirements
- Evaluating Your Work
How to Write an Outline
One way to plan a structure for your essay is by writing an outline. An outline breaks down the parts of your thesis in a clear, hierarchical manner. Most students find that writing an outline before beginning the paper is most helpful in organizing one's thoughts. If your outline is good, your paper should be easy to write. Use this worksheet from the Learning & Advising Center at Philadelphia University to help with writing your own outline.

The basic format for an outline uses an alternating series of numbers and letters, indented accordingly, to indicate levels of importance. Here is an example of an outline on a paper about the development of Japanese theater from the Universtiy at Albany, State University of New York:
"How to Write an Outline." U at Albany, State U of New York. U at Albany, State U of New York, 2011. Web. 5 Dec. 2012 <http://www.albany.edu/eas/170/outline.htm>.

Twelve-step Plan for Researching the Extended Essay - Step 10
10. Plan a structure for the essay. This may change as the research develops but it is useful to have a sense of direction from the start.

- << Previous: Step 9. Set Deadlines for Yourself
- Next: Step 11. Read, Read, Read! >>
- Last Updated: May 8, 2024 3:48 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westsoundacademy.org/ee
What Is An Extended Essay & How to Write It?
Read this article for 5 tips to ace your IB Extended Essay. this article shows IB students how to write an Extended Essay for IB Diploma.

Table of content
Introduction , what is ib extended essay, choosing your mentor, how to select your topic, the structure of ib extended essay, research question, table of contents, methodology, the main body, the conclusion, bibliography, ib extended essay checklist.
Introduce and elaborate topic that you are researching in your EE.
- A crisp description of what you will explore and how you will do so. If you are aiming at a particular firm/industry, discuss the problems and your investigation method.
- To provide context to your question, you must address the situation from where the question is coming.
- State your research question and emphasize the importance of answering that question.
- Please describe how your research is helpful and exciting and how it is valuable to your audience.
This article will reveal helpful information on what your IB Extended Essay (EE) requires. Consider this your IB Extended Essay Checklist, which covers everything you must know about your EE.
Hey! Make sure you listen to Ivy, who will explain what NOT to do on your EE.
These mountains you are carrying, you were only supposed to climb!
Understand that no warrior ever conquered the battlefield with an unhinged mind. We say this because, being past IB students, we have seen and faced what we are about to and have a good knowledge and acquired the ability to differentiate between more enormous beasts and smaller beasts.
IB Extended Essay is a smaller beast considering that you give it enough time before it becomes more prominent. All you need to do is relax your mind, de-stress and follow a simple procedure explained further in the article. There is no need to panic. Trust us, listen to us, and be like us!
Moving ahead from punny insertions, let us tell you why the IB extended essay can be an easy and exciting mountain to climb:
- Subject of your choice (Good practice to choose from your HLs)
- Independence of choosing a topic
- Choice of choosing your mentor
- Continuous feedback and support from your chosen mentor.
IB extended essay (IB EE) is another one of the mandatory requirements of the IB Diploma Programme. It is a mini-thesis that you write under the supervision of a mentor/advisor. Your mentor will be an IB teacher from your school. The students must conduct independent research on a topic of their choice, which must be at most the limit of 4000 words. You begin by choosing a research question as a topic that will be further approved by IBO. It is up to you to either do a typical research paper, conduct an experiment/solve a problem-type EE.
I can write too many paragraphs giving you unnecessary information but let’s cut to the chase and admit the heart wants what it wants. You will go with an advisor/mentor with whom you will connect the most. However, suppose your judgment is clouded between the advisor you want to choose solely because you click with them better and the mentor who is knowledgeable about your chosen topic and can help you improve your research work. In that case, the choice is pretty straightforward: listen to your brain. Get rid of your toxic love and make a wise decision to choose a knowledgeable mentor. If you are lucky, the mentor you connect with and the one with ample knowledge about your chosen topic will be the same person. On that note, consider only two things while choosing your advisor:
- An advisor who is familiar with your topic
- An advisor who will push you to be your best
Before diving into the topic selection and the structure of your IB extended essay, refer to this table to get an insight into the grade breakdown table. This will be helpful in your planning phase.
Moving ahead towards essential aspects of this article. After choosing your mentor, the next step for ‘how to write an EE’ is choosing a topic with the help of your mentor’s input. It is as essential as our TOK Essay and TOK presentation .
Keep the following in mind while selecting your topic:
- Choose a topic that interests you.
- A topic that has enough resources and material.
- Choose a topic that is neither too narrow (so you have enough material) nor too broad (to avoid exceeding the word limit of 4000 words)
Before we dive into the structure, let us make one thing clear, there is a difference between the title and the research question. A title is different from your research question. Your research question is a clear and focused summative statement of your research. For instance, “The Effect of Gender and Age on the photoreceptor cells in the human retina” is a title whereas the following as the examples of research questions:
“Does the efficiency of Rods and cones decrease with age?
“What is the efficiency of L-cone vs M-cone vs S-cone?“
“To what extent are rod cells more efficient than the three cone cells?”
“Does the efficieny of rods and cones differ between genders?”
This will include the following:
- Introduction
Quick Note: The content on this page will not be included in your essay word count.
NO ABSTRACT REQUIRED. The latest IB guide states that an abstract should not be included in EE anymore.
You should split this section into two major areas to cover all the essential aspects.
- Section - 1 Explaining your sources
- Section - 2 Related topics, theories, and arguments that you will use to explore
Quick Note: Ensure that besides giving the readers an insight into the theories, arguments, and resources you plan to use for your research, you also point out the weaknesses and limitations.
Section- 1: Sources
- Describe each of your major sources of primary and secondary research.
- Inform the readers how these sources are helpful.
- To provide the readers with insight into each source's weaknesses or limitations. For example, there may have been room for bias or a limited scope of your research. Or there are other reasons why other data you used could be unreliable or invalid.
- Some useful sources of secondary research are company annual reports, news articles, magazine articles, business textbooks, and encyclopedias.
- Mention any adjustments (at least one) you made to your research as you progressed with your EE.
Section- 2: Related topics, theories, and arguments
- Briefly explain the ideas you will use and why (what are you aiming to support by using these).
- Address weaknesses or limitations of each addressed topic, theory, or related argument.
- Mention any changes made to these as you progressed with your EE.
This part of your essay will be the most elaborate. It will concentrate on research, analysis, discussion, and evaluation.
To maintain the flow of your previous section, we suggest splitting this section into two parts, identical to the previous bifurcation, to showcase your understanding of the IB concepts learned in your business management class and the other addressing the insightful material outside of your course.
Section-1: Related arguments, theories, and topics form your course learning
- Include 4 or 5 of these to help you answer your research question.
- It is suggested that you include at least one financial element. Address your qualitative tools before the quantitative ones.
Section- 2: Beyond your Course
Take up this section as an opportunity for you to educate your reader/evaluator.
- Review several related theories and concepts more extensively than the course does.
- Impress your reader by giving the sense that you know how the particular industry works. Showcase your expertise or knowledge gained through expert opinions in several aspects of your question.
- Please add some analytical insight in this section rather than just descriptive. Be careful to ensure that all of your theories in this section are really helping you answer your research question.
- You can use a graph here, but it must link to the research question.
- Use theories and supportive arguments that apply to your research and are beyond your course (if relevant).
Quick Note: Relate every paragraph to your research question.
This section is self-explanatory. It is time to bind all your areas together.
- It would help if you concentrated on making your EE sections cohesive.
- Please address what you have researched and how it helps answer your research question.
- Keep everything new in your conclusion.
- Shine through by including mini-conclusions to synthesize your essay.
- You can include several evaluative insights as well, if applicable.
- Mention some weaknesses and limitations of your research and their effect on your research. You can even address the inaccuracies these limitations may have caused and state the reason behind them.
- Explain at least one thing that you would have done differently if you were to do it again.
Quick Note: Don’t include a recommendations section in your EE
This section gives the reader an insight into your research resources. It may include:
- Books –textbooks, internet resources, journals, academic papers, competitor interviews, etc.
- Primary Resource (if applicable) –Interview, data (focus group, survey, etc.).
Quick note: The content on this page will not be included in your essay word count.
Take this section as more of an essential formality of showcasing the process of hard work that you have put in.
- Transcripts from your interviews,
- The additional analysis you didn't fit in the body of your EE.
- Any other exciting data which you would like to refer to in the body of your work.
With this, we come to the end of our article on what is an IB extended essay and how to write an extended essay. As we mentioned earlier, it is relatively easy. All you need is dedication, set timelines, and proper research. So, don't worry; no rabbits can pull out your hat today. If you want to score a 36 on 36 your Extended Essay, check out our Extended Essay Guide , which offers '5 never heard before' tips to help you write a quality essay.
Make an IB Extended Essay Checklist! I cannot emphasize enough on this point. The submission for your EE happens simultaneously when you are expected to take your exams. There will be a million things that you would have to keep track of. There is a high chance of forgetting to make that final edit or perfecting your EE's introduction in the midst of it all. Therefore, an IB Extended Essay Checklist will ensure you do everything. IB Extended Essay Checklist will be your savior during the final submission days.
We want Nail IB to be your virtual companion to hustle through IB. We have many helpful blogs that will help you navigate your way through IB. Apart from our blogs, we offer a "Take A Test' module, which allows IB students to evaluate their level in the IB Program. Make sure to try a test and see your strengths and weaknesses. And finally, to ensure you have all the resources you might need to nail IB, we have curated special student bundles for your convenience.
IB Resources you will love!
55234 + free ib flashcards, 136 + free ia samples, 3962 + ib videos by experts, 20099 + ib sample practice questions, ib resources for 30 + subjects.
- Regulated Courses
- QLS Endorsed Courses (TRENDING)
- Accounting & Finance
- Employability
- IT & Software
- Office Productivity
- Personal Development
- Teaching & Academics
- All Courses
- Prime Membership
- For Business

No products in the basket.
- Login/Signup

Registering for this site is easy. Just fill in the fields below, and we'll get a new account set up for you in no time.
Sign in to your One Education account
Not a member yet? Sign up
OR CONTINUE WITH

How to Write an Extended Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide
Alisha Rayes
Writing an extended essay can be daunting, but it can be a fun and rewarding experience with the right approach. To write a successful extended essay, you will need to choose a topic you are passionate about, research it, and plan your essay carefully. With a little hard work and dedication, you can write an excellent extended essay that will impress your teachers and earn you an excellent grade. So, where do you begin? Let’s discover!
Table of Contents
What is the ib extended essay (ee).
The IB Extended Essay (EE) is a 4,000-word research paper required for all IB Diploma candidates. The EE is an opportunity for students to engage in independent research on a topic of their choice. The research process involves formulating a research question, conducting a literature review, designing and conducting experiments (if applicable), and writing a research paper.
The Extended Essay is a flexible component of the IB Diploma that can be written either as an individual or group project.
Students have up to six months (or longer for Science students) to complete their EE. They are expected to spend at least 20 hours per week on their essay during this period. Although some students may choose to spend more time on it, others only have a little time left to search for an extended essay writer online to write their papers.
The IB EE is similar in format and style to an undergraduate research paper but with some differences that reflect the nature of the IB program. For example, the IB EE must contain an introduction, a body comprising several paragraphs or sections, and a conclusion.

What Are the Requirements?
The IB Extended Essay assignment has some requirements that must be met to complete the assignment successfully. The requirements are:
- A minimum of 4000 words is required for this assignment.
- Your IB supervisor must approve a research question to ensure it is feasible and aligns with the IB curriculum.
- An in-depth exploration of your chosen topic could involve looking at the history of the topic, examining different interpretations, and considering how it has been addressed in different contexts.
- The incorporation of at least 12 sources is required for this assignment, including at least 6 academic sources. All sources must be properly cited in APA format.
- An extended essay should include a detailed bibliography with at least 3 peer-reviewed sources. The bibliography should be formatted according to the style guide of the essay’s discipline.
- The essay must include a research question that the student will answer throughout their essay. The question must be specific and clearly defined, and the student must provide evidence to support their answer.
Submitting your first draft to the supervisor you have chosen is recommended. This will help ensure that you are on the right track and that your supervisor can provide useful feedback.
How to Choose Your Advisor?
When choosing an advisor for your extended essay, it is essential to choose someone knowledgeable about the topic you are interested in and who can provide helpful feedback. Here are a few tips to help you choose the right advisor for your project:
Your advisor should be an expert in the topic you are writing about and who can help you achieve your academic goals. Make sure you talk to them about your plans and ask for their advice.
Look for someone approachable and helpful. They should be willing to provide feedback and suggestions and be willing to answer any questions you have.
Look for someone who has experience with extended essays. An advisor with experience with extended essays will help you navigate the process and understand the expectations of the essay format. In addition, they will provide feedback and guidance on the best way to approach your project.
Consider their availability and availability schedule. Make sure your advisor is available during the times that are best for you, and check their availability schedule to see if they are available for Skype or in-person meetings.
What Are Extended Essay Categories?
The Extended Essay (EE) is a research paper of up to 4,000 words on a topic of the student’s choice within one of the six prescribed EE thematic categories. The EE is an opportunity for students to demonstrate their research and writing skills and their ability to think critically about a topic.
The main categories are studies in mathematics, language and literature, sciences, language acquisition, individuals and societies, and the arts.
Suggested reading – 4 Advice on How to Study Sociology .
How to Write an Extended Essay?
Extended essays can be tricky to write, but with the right approach, they can be both informative and engaging. To write a successful extended essay, you must choose a topic you are passionate about, thoroughly conduct research, and develop a strong argument.
Additionally, your extended essay should be well-written and well-organized to engage your reader and communicate your ideas effectively . Let’s look closer at the main steps of writing an extended essay.
Choose a Topic
The first step to writing any successful extended essay is finding the right topic. You’ll want to pick a subject that intrigues you because you will spend a lot of time researching and writing this paper. Once you’ve found your topic, make sure it can be covered in 4,000 words.
If you try to cover too much information in your extended essay, it will end up feeling very thin – like an introduction with no substance. This can make the reader feel like they’ve wasted their time reading your paper, which is something you want to avoid at all costs.
Research Information
Once you’ve chosen your topic, get researching! You’ll want to gather as much information as possible about the subject at hand. Make sure that the sources of information you’re using are reliable and unbiased; if not, this could skew the tone of your extended essay in a way that makes it appear biased or unfair towards certain groups or people.
Develop a Research Question
This step aims to help you narrow down the amount of information that will be included in your extended essay. If you’re writing an argumentative paper, for example, then your research question should be something like “Should students be required to wear school uniforms?” After you’ve come up with a research question, ensure that everything else you include in your extended essay supports this idea.
Develop Structure and an Outline of EE
The structure of your paper should include a brief introduction and conclusion as well as three main sections: body paragraphs (usually about 1-3 per topic), subheadings, and tables or figures. Your introduction should set up the reader for what they will be reading in the rest of your extended essay; don’t just repeat information from your introduction in the body paragraphs.
Write the First Draft
After you’ve created your outline, write the first draft of your extended essay. This should be a rough draft that doesn’t adhere to any particular structure or format; just get down all your ideas on paper at this point. After you have finished writing your first draft, go over it carefully and make edits as necessary. Then, submit your revised draft to your mentor for review and suggestions.
Write the Final Draft of Your EE
When you’ve received feedback from your mentor and made any necessary changes, it’s time to write the final draft of your extended essay. You want to ensure that this is a finished product that’s free from any spelling or grammatical errors. If it doesn’t look professional, it won’t get graded!
Proofread the Work
After you’ve finished writing your extended essay , proofread and check for any errors before submitting it to the professor. It’s also a good idea to have someone else read over your work in case they find mistakes you missed; this can help prevent any problems with grading down the line.
Now You Know How to Write a Good IB EE
In summary, if you’re like most students, you’ve probably been assigned an extended essay as part of your coursework. Whether you’re writing about a topic of your choice or responding to a question, writing an extended essay can be challenging.
The first step is to gather your research. Writing an extended essay is about providing your readers with insights they didn’t already have, so it’s essential to do your research thoroughly. Go beyond reading the assigned article or watching the video; take the time to read other related sources, gather data, and interview experts. This will not only give you a more comprehensive understanding of the topic, but it will also make you more credible as an essay writer.
Once you understand the topic well, it’s time to develop a thesis statement. This statement will be the backbone of your argument and help guide your writing. Make sure that your thesis is well-supported by your research and that it is logically consistent with the rest of your essay.
Next, it’s important to develop your argument. This section of your essay should provide readers with insights they didn’t already have and should be based on your research and thesis statement. Be sure to articulate your points clearly and use concrete examples to illustrate your points.
Finally, it’s important to structure your essay logically. By following these tips, you can develop an effective extended essay that will amaze your professors and earn high marks.
Use the guide wisely and get the best possible grade for your IB extended essay. Good luck, my friend 😉

1. How to write ee?
Writing an extended essay involves selecting a topic, conducting research, creating a thesis statement, outlining the essay, writing the body paragraphs, and concluding with a reflection. It’s crucial to gather credible sources, organize your ideas logically, and adhere to the required formatting style. Additionally, revising and proofreading are essential to ensure clarity and coherence in your writing.
2. How to start an extended essay?
Starting an extended essay involves selecting a topic that interests you deeply, conducting thorough research to gather relevant information, and formulating a clear and focused research question. Once you have your topic and question, create an outline to organize your ideas and structure your essay effectively. Finally, make sure to consult with your supervisor or teacher throughout the process to receive guidance and feedback.
3. How to write a good extended essay?
Writing a strong extended essay involves selecting a topic of personal interest, conducting thorough research, and organizing ideas effectively. It’s crucial to develop a clear thesis statement and structure your essay with a logical flow. Make sure to support your arguments with evidence and critically analyze your sources. Lastly, revise and edit your essay carefully to ensure clarity, coherence, and proper formatting.
4. How to start an ee?
Beginning an extended essay involves selecting a topic that interests you deeply and aligns with your academic pursuits and passions. This topic should be sufficiently narrow to allow for in-depth exploration while also being broad enough to provide scope for research and analysis.
5. What is the first procedure used when writing an extended essay?
When starting an extended essay, the initial step involves selecting a topic that genuinely interests you and aligns with your academic pursuits and personal passions.
6. What is an extended essay in ib?
An extended essay in IB is a research project that students undertake to explore a specific topic within one of the subjects they’re studying. It’s an opportunity for them to delve deeply into a subject they’re passionate about, demonstrating their analytical and critical thinking skills while producing a substantial piece of academic writing.
7. What is the product of the seventh procedure of writing an extended essay?
The product of the seventh procedure of writing an extended essay involves drafting the body paragraphs with relevant evidence and analysis to support your thesis statement.
8. What are the skills needed in the fourth procedure of writing an extended essay?
In the fourth step of writing an extended essay, you’ll need to employ critical thinking skills, analyze your research findings, and demonstrate a clear understanding of your chosen topic. Additionally, effective communication skills are crucial for conveying your arguments and ideas concisely and persuasively.
9. How to structure an ee?
Structuring an extended essay involves organizing your ideas into clear sections, such as introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion, ensuring coherence and logical progression throughout the essay. Each section serves a specific purpose, from introducing the topic to presenting arguments and evidence, culminating in a concise summary of your findings. This structured approach helps readers follow your reasoning and enhances the overall effectiveness of your essay.
10. How to write an extended essay conclusion?
Crafting an extended essay conclusion involves summarizing key points. Restate your thesis and main arguments. Reflect on the significance of your findings. Avoid introducing new ideas. Aim for clarity and closure.

- How to Study Effectively for Exams at Home?
Josh Ashton
May 17, 2024

- How to Choose the Right Medical School: A Step-by-Step Guide
May 14, 2024
- What is an Early Help Assessment?
May 07, 2024

- Upskill for Impact: Online Guide to Boosting Your Teaching with Professional Development
April 30, 2024
Recent Posts
- Free Online Courses: How to Study Online Courses for Free in 2024
- Bright career
- Personal development
- Uncategorized
Never Miss An Update
Get weekly industry tips sent straight to your inbox
COPYRIGHT © 2022 One Education
Privacy Overview
Upgrade to get unlimited access to all courses for only £49/year.
Membership renews after 12 months. You can cancel anytime from your account.


Extended Essay Guide: The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Writing Your Research Question
- Finding Resources
- Research Plan Ouline
- Drafting Your Paper
- The Introduction
- The Conclusion
- Citations/Bibliography
- Proofreading Your Paper
- IB Assessment Criteria/Subject Specific Guides/Exemplars/Etc
Extended Essay Introduction
The goal of the introduction is to introduce the topic and provide enough information about it in order to enable the reader to comprehend the significance of your research question. The research question must be clearly and precisely stated in the introduction. The research question is the central question you are trying to answer through your research and writing of the extended essay. This question, if properly composed, will both enable you to maintain your focus on a topic of narrow and limited scope while also help you to maintain the purpose and orientation of your entire investigation. Your extended essay will be assessed in part according to the extent to which the essay appropriately addresses and develops your specific research question. The readers will also evaluate your success in collecting information relevant to the research question. Establish the significance of the research question and explain why it is worthy of study. Briefly and concisely preview your body by providing a plan of investigation (game plan) for the rest of the paper. The game plan briefly explains how you intend to answer the research question.
Introduction Checklist
____ Does your introduction include some background information and place the topic in an appropriate context
_____ Is your research question clearly and exactly focused, and stated (in bold)?
_____ Does your introduction explain the significance and context of your topic? (This topic is an important because…)
_____ Does your introduction explain why your topic is worthy of investigation and still have contemporary relevance? (This topic is worthy of investigation because…)
_____ Does your introduction explain how the research question relates to existing knowledge?
_____ Do you avoid writing lengthy, irrelevant background material?
_____ Do you give the game plan for the rest of the essay?
- _____ Is it clear where your intro ends?
EE Introduction
Background information.
Background information identifies and describes the history and nature of your research question with reference to the existing literature. Background information expands upon the key points stated in the beginning of your introduction but is not intended to be the main focus of the paper. Sufficient background information helps your reader determine if you have a basic understanding of the research question being investigated and promotes confidence in the overall quality of your analysis and conclusion. This information provides the reader with the essential context needed to understand the research question and its significance.
Websites to help:
Background of the Problem Section: What do you Need to Consider?
How to Write a Research Paper .
- << Previous: Drafting Your Paper
- Next: The Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Nov 15, 2016 1:55 PM
- URL: https://baltimorecitycollege.libguides.com/eeguide

Extended Essay: Introduction to the EE
- Introduction to the EE
- Step 1 - Choose a subject
- World Studies
- Step 3 - The Researchers Reflection Space
- Identify Sources
- Tools for Note Taking
- Video Guides
- Step 5 - Creating Research Questions
- Step 6 - Outlines and Plans
- Step 7 - Citing
- Criteria E - 3 Reflections
- Know Your Criteria
- Criteria D - Check your Formatting
- 4000 words final hand in
Introduction to EE

The 12 Step Guide - Follow this (Use the tabs at the top)
How to start...
Jan 15th - the ee begins -, summary of tasks to complete, welcome to the beginning of the extended essay - a 4000 word research based essay. you will need to stick to all deadlines that are given you. , initial tasks, bookmarking: add the cislibguide extended essay and the ibo extended essay pages to your bookmarks., educate yourself: look at the information in the subject pages of mycis - note - if you want further information on world studies ee go to ew414 on wednesday 17th at smart., create a folder for all your ee work: entitle this firstname_lastname_extended_essay2024. share your folder: with p [email protected] and [email protected] . you will also share your folder with your supervisor once they have been assigned.** ., link your folder to the researchers reflection space on managebac: in this area: -.
- a) Add the link to your EE folder.
- b) Write down your initial ideas as to what you might want to do your EE in and what potential topics you want to do.
- c) Add your mindmap of ideas (see below)
5. Sign the Extended Essay Essential Agreement: This is a mandatory form you must fill in to show that you understand the expectations that we have regarding academic honesty, the use of the RRS and your Google Folder.
7. Read Example Essays: I n subjects that you may be interested in download and read through some example assessed essays . Note - there are some from the IB and there are also A grade essays from past CIS students in the subject specific areas of this site . Be ready to explain to your supervisor on day 1 all that is expected of a good essay.
8. complete your proposal: you will need to download the proposal form . this must be completed as well as possible showing that you have looked for sources of information that are not just from the internet but also using the school academic databases - https://cis.libguides.com/extendedessay/databases . here is a document with examples of acceptable and unacceptable proposals., how and where to submit the proposal, deadline: friday january 27th to managebac - also print out a hard copy and give to your ag teacher., note - you must give options in two different subject areas as places are limited in some popular subjects e.g. business, psychology., please note, some subjects are more popular than others, and not everyone can have their first choice. you are more likely to get your first choice if your proposal is excellent., day 0 - research workshops.
- Next: Step 1 - Choose a subject >>
- Last Updated: Mar 10, 2024 10:40 PM
- URL: https://cis.libguides.com/extendedessay

Extended Essay: Writing an EE Introduction
- General Timeline
- Group 1: English Language and Literature
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Group 4: Sciences
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Group 6: The Arts
- Interdisciplinary essays
- Six sub-categories for WSEE
- IB Interdisciplinary EE Assessment Guide
- Brainstorming
- Pre-Writing
- Research Techniques
- The Research Question
- Paraphrasing, Summarising and Quotations
Writing an EE Introduction
- Writing the main body of your EE
- Writing your EE Conclusion
- Sources: Finding, Organising and Evaluating Them
- Conducting Interviews and Surveys
- Citing and Referencing
- Check-in Sessions
- First Formal Reflection
- Second Formal Reflection
- Final Reflection (Viva Voce)
- Researcher's Reflection Space (RRS) Examples
- Information for Supervisors
- How is the EE Graded?
- EE Online Resources
- Stavanger Public Library
- Exemplar Essays
- Extended Essay Presentations
- ISS High School Academic Honesty Policy
The most important thing you need to know about writing your introduction is that it should be written LAST. Although that sounds counterintuitive, that it is the best way to do it. Simply put, there is just no way to know everything that should go into your introduction until you have completed your research.
Once you have written the bulk of your paper including your reasoned argument and conclusion, you will then have all the info you need to complete your introduction.
Here are the basic components of what needs to be included in your EE introduction:
- Academic Context: You need to show how your question fits into existing knowledge about your topic.
- Outline of your argument: Go through your reasoned argument chronologically – in the order it appears in your paper.
- Scope: How have you approached your RQ? What types of sources were used – did you use any unconventional methods?
- Worthiness: why is your RQ worthy of investigation?
From the EE Guide:
The introduction should tell the reader what to expect in the essay. The introduction should make clear to the reader the focus of the essay, the scope of the research, in particular an indication of the sources to be used, and an insight into the line of argument to be taken.
While students should have a sense of the direction and key focus of their essay, it is sometimes advisable to finalize the introduction once the body of the essay is complete.
I strongly urge you to read Chapter 5 of the Oxford EE Guide as it gives much more detail about writing your introduction along with examples.
***Remember to state your Research Question clearly in the introduction and remember to do your introduction LAST !
Academic Writing Tips
Formal vs. Informal Writing A chart giving the differences between informal and formal essays in seven areas (author's viewpoint; subject/content (sources of evidence); tone; structure; location of the research question; vocabulary; and purpose. Also included are examples comparing informal and formal writing for essays in English, biology, and psychology.
How to Avoid Colloquial (Informal) Writing While it may be acceptable in friendly e-mails and chat rooms, excessive colloquialism is a major pitfall that lowers the quality of formal written text. Here are some steps/tips that you can follow to help improve your overall writing.
Elements of Academic Context
- Evidence that you’ve carefully considered the subject.
- A clear, appropriately qualified thesis
- A response to what others have said
- Good reasons supported by evidence
- Acknowledgement of multiple perspectives
- Carefully documented sources
- A confidant, authoritative stance
- An indication of why your topic matters
- Careful attention to correctness
From Scotch College
Writing the introduction.
An introduction for an Extended Essay requires students to include the following aspects:

Aside from giving the essay a structural outline that any reader can follow, these aspects also help ensure that expectations for Criterion A (Focus and Method) are met.
Context : Explicitly stating your research question and providing some context that situated your question within existing knowledge is the key to a strong introduction. This does not mean providing detailed background information but rather indicating to an examiner what existing theories, critical approaches , methods or factors have already been suggested or exist to answer your research question.
Outline of the argument : Including the research question in your introduction is a quick way of ensuring you've made clear what you will be focusing on. In addition to this, it allows you to specify which aspects, factors or key features you will be investigating that will help you answer your overall question. Doing this in the order they appear in the main body is advised.
Scope : It is vital that you indicate in your introduction how you've gone about answering your research question. This means indicating to the examiner what source material has been used, or scientific methodologies followed or critical interpretations challenged and so on.
Stating that your essay utilised websites, books and journals is not as good as indicating exactly which authors, theories or methods have been used.
Worthiness : Finally, it is important, to indicate why your research question is worthy of investigation. Using the phrase "this research question is worthy of investigation because..." forces you to consider worthiness by default.
Exemplar of Introduction
Muawiya's accession to the caliphate is a hotly debated topic among historians with some, such as Kennedy, arguing that he owes his elevation to the weakness of opposition as reflected in the figure of Caliph Ali, while others, such as Shaban, arguing that his success owes itself in large measure to the tangible economic benefits that support Muawiya provided the Arab tribes...
... this essay seeks to challenge the orthodox interpretation offered by Kennedy and instead argue that Muawiya's success owes much to the changing socio-economic dynamic among Arab tribesmen within the newly formed Islamic Empire...
... the essay will also simultaneously explore what other factors, including the governorship of Syria, the conflict of Byzantium, the dwindling role of the Ansar, and the role the Kharijites played in helping Muawiya take over the Caliphate while relying on the works of principal historians such as Kennedy, Shaban, Armstrong and Hawting.
... this research question is worthy of investigation because Muawiya's rise to the caliphate marks a significant turning point in the development of the Islamic Empire during the seventh century and beyond. It established the tradition of dynastic and monarchic succession that would become commonplace in the ensuring centuries... the role played by Caliph Ali in supplanting the Rashidun model with a dynastic model is of critical significance to this early medieval period as it created the conditions for the schism between Sunni and Shi'a practices...
Introduction – Roughly 800 words
- Must include the RQ in bold – preferably in the first paragraph
- Context: What key aspects can you discuss to ensure you’ve provided some academic context underpinning your research question?
- For locally based investigations ensure you clearly identify and locate the local context
- Outline of argument: What features, aspects, factors, theories and so forth will your essay utilize in order to arrive at a conclusion?
- Give an overview of methodology and scope – how do you plan to answer the question? What authors, scientists, case studies, theories and so on have been consulted to answer your research question?
- What is the significance of your research? Why is this topic worthy of consideration?
EE Introduction Checklist
→does your introduction include some background information and place the topic in an appropriate context , →is your research question clearly focused, and highlighted in some way (bold, italics, etc), →does your introduction explain the significance and context of your topic (this topic is an important because…), →does your introduction explain why your topic is worthy of investigation , →does your introduction explain how the research question relates to existing knowledge (academic context) , →do you avoid writing lengthy, irrelevant background material, →do you outline a cohesive reasoned argument, →is it clear where your intro ends.
- << Previous: Paraphrasing, Summarising and Quotations
- Next: Writing the main body of your EE >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:11 AM
- URL: https://isstavanger.libguides.com/c.php?g=695888
The Extended Essay Step-By-Step Guide 3: The Research

The Easter Break is nearly upon us. Ten years ago this might have been a cue to eat more chocolate than you can handle. But if you’re in DP1 of the IB that small thing called the Extended Essay will be hovering on the horizon. You know that you should think about it over the break, but whether you do or not might depend on how much Netflix you have to catch up on. To start the research or not to start?

If you read our first post in this step-by-step guide, on choosing an Extended Essay topic, you’ll know that we think you should definitely start as soon as you can.
So what do I mean by research? I’m talking about the intense stuff. The in-depth exploration that will inform your essay, and which you will be able to use later on in your Bibliography. Good research is the key to making everything easy for you during the writing stage. If you’ve done the research properly, then the essay structure, the case study, or the experiment will practically plan itself.
But how do you do the research so that it is as effective as possible without taking over your entire Easter break?
1. Know WHAT you’ll need
Read the Extended Essay Guide for your subject (yes I am going to recommend that in every part of this guide, so you may as well do it now!). For all subjects it will tell you whether you need primary research, secondary data, or a combination. Work out whether ‘research’ for you means gathering data compiled by someone else, creating your own data, reading other people’s opinions, or digging out hard facts. Depending on what your subject and topic is, your research might be the crux of your entire essay, or it might simply give you ideas to enhance your own thoughts.
Use the Guide to define the limits of your research. Your Extended Essay has to focus on your chosen subject as defined by the IBO (and World Studies has its own definition and requirements). That means you must define your subject in the same way, e.g. “Biology is the science that deals with living organisms and life processes”. Use this to work out where your research should take you. And don’t waste time doing research that takes you into another subject area, E.g. Medicine.
Work out how recent your research needs to be. Again, this is a way to save time! Economics, for example, shouldn’t be historical. That means your information needs to be recent! Equally research in the Sciences goes out of date very quickly so stick within the last couple decades, and newer is better! (as long as it’s reliable… I’ll get onto that). For Literature and History, it’s less important that your sources are new, although it’s easier than you might think to quote what sounds like a very insightful idea only to realise it was first written in the 1920s!

Exercise 1: Read the guidelines for your subject and write down what kind of research you’ll be doing. Is it Primary or Secondary? Will you conduct your own experiment or use data from someone else’s? Are you looking for factual information or theories? What window of time do you want your research to have come from? 2013-2016, or 1980-2016? Write it down now because later you can check your progress against this to make sure you’re staying on track.
2. Know WHERE you’ll find it
For the Extended Essay you’ll need to go beyond Google and beyond the shelves of your library. A good Extended Essay Bibliography should be a varied pick and mix selection* of online and off-line sources, modern dates, and obscure and established publications. Remember those 40 hours the IB recommends you spend on your Extended Essay? Your Bibliography is proof that you have been working hard!
But how do you get all those sources? Ask your teachers. If you don’t have a supervisor yet, I can guarantee you that your librarian knows more about what you have access to than you realise. Find out what subscriptions your school has, both online and off. If your library doesn’t have a book in stock it might be able to order a book in for you. Find this out.
For Science, it’s vital that your research is up to date. That means your material will probably come from journals, (reliable) websites, and studies by other scientists. Consider approaching universities and other academics who may be able to point you in the right direction.
On the other hand for something such as Literature your primary research should mean reading your chosen texts, whether they are novels, plays or poems. Consider supplementing this with other first-hand materials such as journal entries, letters or essays by the author or their contemporaries. Finally secondary research encompasses the ideas of other academics, although the Guide states that these should not replace your own analysis and ideas.
It’s not too hard to work out whether a source is reliable or not. Most of the time it’s common sense; can you name the author? Do they have experience in what they’re talking about or might they know less than you? It’s okay to use sources that may have a bias or might be ignorant of one thing or another, but the key is to be aware of this and make it clear in your essay that you are aware of it.

Here are some good online places to go for information:
Google Scholar : Basically Google except that it will show you only the academic resources related to your search: articles, essays and legal documents. In other words, all of the stuff here should be fair game to put in a Bibliography.
Google Books : Free books! Lots of them! And the best part is you don’t have to admit you used Google; for all the examiner knows you dug through the dusty shelves of a library yourself. Even for books which only have a preview this is useful to work out if a hard copy of the book would be useful to you.
JSTOR : If your school has a subscription to this, use it! A database of hundreds of academic journals which make for great background research. However be aware it doesn’t include the latest research, so make sure what you find here will stick within the dates you defined earlier on.
Public Library of Science (PLOS) : An open access online library of scientific literature. Includes science-related journals.
www.online-literature.com A website full of poetry, short stories and novels of almost every ‘classic’ author whose work is out of copyright. When it comes to referencing later, it will probably look better to go and dig out a hard copy of the work purely for reference purposes, but this is handy for initial browsing.
Wikipedia : Didn’t think I’d put this on here, did you? This is obviously not good as a source in itself, however if you scroll to the bottom of most Wikipedia pages you’ll often find a pretty comprehensive list of sources that are directly relevant to the topic and which you could use as a starting point for your own research.
Exercise 2: Make a list of the resources you think will be useful for your essay, and which you know you have access to. And remember that different search engines are useful for different subjects.
3. Know HOW you’ll get it
Believe it or not, research requires research. It won’t happen by accident and takes careful planning in order to get the most out of the sources that you use.
After you know where you might find useful sources, do some initial digging to find out what’s out there that will be specifically useful for your chosen topic. As I mentioned, Wikipedia could be a starting place for this. Or you might need to do a quick search through the database of your school and local libraries and place orders for books. Whatever you do, keep a list of everything you find that might be useful to you, and use it as a checklist. You won’t have time to read it all at once.
Plan out your research time in blocks to make sure that it happens. And think about what you can do in different places. It goes without saying that you’ll be able to do your online research at home, but think about what articles you could download to read when you don’t have internet. If you take a book out of a library you will be able to read that when you don’t have a laptop in front of you.
Finally, think about when the research will be most useful to you. Is there information you need to know before you undertake a lab investigation? What about data that will make more sense after you’ve done some initial reading? Thinking about all of these things will make sure that your research is as effective as it can be.
Exercise 3: Make a plan of attack (also known as a schedule) for what you’re going to do in what order, and how long it will take. Fo r example (this one is for English A):

4. Keep track of everything!
You’ll need a reference for anything you use that you didn’t pluck out of your own head. This applies to:
- Ideas and Summaries
By ideas and summaries I mean any theory or idea that is not common knowledge. So you don’t need to reference the fact the spinach is green but you might need to reference what green food colouring is made of.
There is no set referencing system that you need to use in your Extended Essay, but you do get marked on how you use it. So make sure that whatever you choose, you use it consistently. Ask your supervisor which one they would recommend, and it’s useful at this stage to have a skim of what information you need to keep track of as you go along. Guides for the different systems are easily accessible online on websites like this one:
Anytime you read something that might be useful, make a note of all the information you’ll need to include in a Bibliography later. That will usually include the author name, title, the publisher, the year and place it was published, and the page numbers.
Keep track of your research by extracting the key material onto your own document. Whether that means copy and pasting the vital quotes, summarising the idea or saving an image you might want to use, make it as accessible for yourself as possible! Don’t just keep a document of links to articles you found interesting! When you want to plan your essay I promise you that you won’t remember what it says. This:
https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=q4uEZnTJJIsC&pg=PA143&dq=virginia+woolf+mrs+dalloway+freedom&hl=en&sa=X&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=virginia%20woolf%20mrs%20dalloway%20freedom&f=false
Is much less useful than this:
“When beginning Mrs Dalloway, Woolf intended to write “six or seven” grouped short texts” p. 143, Wild Outbursts of Freedom: Reading Virginia Woolf’s Short Fiction , Nena Skrbic (2004), Praeger Publishers, Westport, CT
Exercise 4 : decide how you will organise your research:
- Create a EE research folder on your laptop and create blank documents inside it, labelled depending on what you might need, e.g. journal articles, primary research, hard copy books.
- Assign a physical EE folder for any handwritten notes that you make, whether in a library or just out and about.
- Choose your referencing system.
Got that? Okay… I think you’re ready!
Read Part 4: The Question
Share article links
Related Articles
- IB Extended Essay
5 Simple Steps for Redrafting your Extended Essay
You poured your heart and soul into it. You gave it your sweat, blood and tears (hopefully not blood). It took you a full year just to come up with a question in the first place. I’m talking, of course, about your Extended Essay. DP2 students, the time has come when schools are asking for […]

The Extended Essay Step-by-Step Guide 2: Your Topic
There is a secret that could help all you first year IB students out there. It is the key to making next year a whole lot easier. It will reduce stress, make the workload easier to handle, and give you time. What is the secret? It’s that you’re better off starting the Extended Essay as soon […]

The Extended Essay Step-By-Step Guide 4: The Question
Welcome back to our step-by-step guide to the Extended Essay! So far in this series, we’ve covered how to choose your topic and get on with your research. Here in Part 3, I want to talk all about how to make sure you have the perfect question. I know. I’ve mentioned the question before. Some […]
How to Write a 3000 word Essay in Less Than 60 Minutes

Writing a 3000 word essay in under an hour might seem impossible, especially when facing a tight deadline. However, with the right approach, it's not as daunting as it sounds. A good example of this is our guide on how to write a 1000 word essay .
This article shares 5 practical tips and strategies to help you write efficiently and effectively within a limited timeframe.
%20(1).webp)
EssayPro Guide on How to Write Your Essay Faster
Our team of experts has created a how-to guide for you on how to write your essay fast. Here you go:
Voice-to-Text Software
Voice-to-text software can significantly expedite essay writing by allowing users to dictate their thoughts and ideas, bypassing manual typing verbally. This technology enables a continuous writing flow, as individuals can speak their ideas naturally and conversationally without interruptions.
For example, instead of pausing to search for the right words or phrases, users can express their thoughts fluidly, resulting in a faster and more efficient writing process. Additionally, voice-to-text software eliminates the physical strain associated with typing for extended periods, allowing users to maintain productivity and focus for longer durations.
Furthermore, voice-to-text software offers flexibility in writing environments, as users can dictate their essays from virtually anywhere using a smartphone, tablet, or computer. For instance, individuals can dictate their essays while commuting, exercising, or completing other tasks, maximizing their time and productivity.
You can use the following voice-to-text tools:
- Dragon NaturallySpeaking
- Google Docs Voice Typing
- Microsoft Dictate
- Apple Dictation
Need Urgent Help with Your Essay?
Don’t strain yourself – use professional writing services .
The Stream-of-Consciousness Writing
Stream-of-consciousness writing is a technique that involves recording thoughts as they come to mind, without filtering or censoring them. This approach can be particularly useful for writing essays in less than 60 minutes as it allows for a rapid flow of ideas and content generation.
By bypassing the need for careful planning and organization, stream-of-consciousness writing enables writers to quickly capture their thoughts on paper and generate raw material for their essays. For example, writers can focus solely on expressing their ideas and arguments instead of worrying about sentence structure or grammar, resulting in a faster and more spontaneous writing process.
Moreover, stream-of-consciousness writing can help writers overcome writer's block and tap into their creativity more effectively. This can lead to more original and compelling essay content. For instance, writers may discover new angles or perspectives on their topic that they hadn't considered before, enriching their essays with fresh insights and perspectives.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use the stream-of-consciousness technique to write an essay:
- Set a timer.
- Clear distractions.
- Choose a topic.
- Begin writing.
- Write continuously.
- Don't edit or censor.
- Keep the pen moving.
- Embrace tangents.
- Stay in the moment.
- Review and edit later.
AI Writing Tools
AI writing tools can significantly expedite the essay writing process by automating various aspects of content creation, such as generating ideas, structuring arguments, and even drafting entire paragraphs. These tools leverage advanced natural language processing (NLP) algorithms to analyze input data and produce coherent, contextually relevant text output.
For example, platforms like OpenAI's GPT-3 and Grammarly's AI-powered writing assistant offer features such as auto-completion, grammar and style suggestions, and even content generation based on user prompts.
Furthermore, AI writing tools can assist writers in overcoming writer's block and generating ideas more efficiently. For instance, tools like Articoolo and QuillBot can generate article outlines or paraphrase existing text to provide inspiration and generate new content.
Here are reliable AI essay writing tools:
- EssayPro Writing App
WARNING: While these tools can aid in content creation and idea generation, relying too heavily on them may lead to plagiarism or submitting low-quality, unoriginal work. Writers should use AI writing tools to supplement their research and writing process rather than replace critical thinking and academic rigor.
Collage Essay Method
The collage essay method is a creative approach to essay writing that involves assembling visual and textual materials into a collage to represent different aspects of the essay topic. This technique can be particularly effective in generating ideas quickly and organizing thoughts in a visually engaging manner.
For example, imagine you're tasked with writing an essay on climate change. You could gather images, quotes, statistics, and diagrams related to climate change and arrange them on a poster board or digital canvas. The collage is a brainstorming tool to spark ideas and inspire the writing process by visually representing key concepts and arguments.
Moreover, the collage essay method encourages a nonlinear approach to essay writing, allowing writers to explore ideas from multiple perspectives and make connections between different topic elements.
For instance, while arranging materials for the climate change collage, you might notice patterns or themes emerging that you hadn't considered before. This can lead to new insights and angles for your essay, enriching the content with diverse perspectives and supporting evidence.
Here are some useful tips for using the collage essay method for writing an essay fast:
- Gather diverse materials.
- Start with a central theme.
- Arrange materials strategically.
- Focus on visual impact.
- Incorporate text and images.
- Make connections between elements.
- Be open to unexpected insights.
- Iterate and refine as needed.
Role-Playing Scenario
The role-playing scenario method offers a fresh and engaging approach to essay writing, injecting creativity and empathy into the process. By immersing oneself in a specific role, writers can tap into their imagination and explore complex topics from various angles.
For instance, if you're tasked with writing about the ethical implications of artificial intelligence, you could adopt the perspective of a futuristic AI developer or a concerned citizen living in a world dominated by AI technology. This imaginative exercise sparks inspiration and encourages deeper reflection on the subject matter, leading to more insightful and thought-provoking essays.
Furthermore, the role-playing scenario cultivates empathy and understanding by encouraging writers to embody diverse viewpoints and experiences. Whether you're writing about climate change, social justice, or economic policy, stepping into the shoes of different characters allows you to see the world through their eyes and develop a more nuanced understanding of complex issues.
For example, by pretending to be a climate scientist researching the effects of deforestation, you might gain a deeper appreciation for the urgency of environmental conservation efforts. This empathetic approach to essay writing fosters a greater connection with both the subject matter and the audience, resulting in essays that are not only informative but also engaging and impactful.
How to adopt the role-playing scenario technique for writing an essay:
- Choose a relevant persona.
- Research and understand their background.
- Embody the persona's mindset.
- Write from their perspective.
- Maintain consistency with the persona.
- Review and adjust as needed.
- Use insights to enrich your essay.
There’s nothing impossible if you put an effort into it. Although 60 minutes sounds like a very limited period, a smart student can use it to produce a pretty decent essay and even have a few minutes left! So, how to write essays faster ?
The tips we gave you above do work, which thousands of students with hectic schedules have already proved. A word of warning, though – don’t rush to use tools like ChatGPT to generate an essay in 5 minutes because it’s hazardous for academic integrity. Remember – AI tools are assistants, and generated texts are to be rewritten from A to Z, which can also be done in an hour or less. If you’re awfully tired and physically can’t think or type, you better ask a professional human writer to help you.
Too Exhausted to Finish the Essay?
Expert writers will do an essay for you from scratch.
Can You Write an Essay in 30 Minutes?
Can i write a 3000 word essay in 1 hour, how long does it take to write a 3000 words essay.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Howard, D. (2022, December 15). How to Write an Essay Fast . Nexus Education. https://nexus-education.com/blog-posts/how-to-write-an-essay-fast/
- 20 Top Tips for Writing an Essay in a Hurry . (2024, February 20). Oxford Royale. https://www.oxford-royale.com/articles/writing-essay-hurry/
- 4 Ways to Write Essays Faster – The Bookshelf . (n.d.). https://blogs.cornell.edu/learning/4-ways-to-write-essays-faster/
Related Articles
%20(3).webp)
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Letter of Recommendation
What I’ve Learned From My Students’ College Essays
The genre is often maligned for being formulaic and melodramatic, but it’s more important than you think.

By Nell Freudenberger
Most high school seniors approach the college essay with dread. Either their upbringing hasn’t supplied them with several hundred words of adversity, or worse, they’re afraid that packaging the genuine trauma they’ve experienced is the only way to secure their future. The college counselor at the Brooklyn high school where I’m a writing tutor advises against trauma porn. “Keep it brief , ” she says, “and show how you rose above it.”
I started volunteering in New York City schools in my 20s, before I had kids of my own. At the time, I liked hanging out with teenagers, whom I sometimes had more interesting conversations with than I did my peers. Often I worked with students who spoke English as a second language or who used slang in their writing, and at first I was hung up on grammar. Should I correct any deviation from “standard English” to appeal to some Wizard of Oz behind the curtains of a college admissions office? Or should I encourage students to write the way they speak, in pursuit of an authentic voice, that most elusive of literary qualities?
In fact, I was missing the point. One of many lessons the students have taught me is to let the story dictate the voice of the essay. A few years ago, I worked with a boy who claimed to have nothing to write about. His life had been ordinary, he said; nothing had happened to him. I asked if he wanted to try writing about a family member, his favorite school subject, a summer job? He glanced at his phone, his posture and expression suggesting that he’d rather be anywhere but in front of a computer with me. “Hobbies?” I suggested, without much hope. He gave me a shy glance. “I like to box,” he said.
I’ve had this experience with reluctant writers again and again — when a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously. Of course the primary goal of a college essay is to help its author get an education that leads to a career. Changes in testing policies and financial aid have made applying to college more confusing than ever, but essays have remained basically the same. I would argue that they’re much more than an onerous task or rote exercise, and that unlike standardized tests they are infinitely variable and sometimes beautiful. College essays also provide an opportunity to learn precision, clarity and the process of working toward the truth through multiple revisions.
When a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously.
Even if writing doesn’t end up being fundamental to their future professions, students learn to choose language carefully and to be suspicious of the first words that come to mind. Especially now, as college students shoulder so much of the country’s ethical responsibility for war with their protest movement, essay writing teaches prospective students an increasingly urgent lesson: that choosing their own words over ready-made phrases is the only reliable way to ensure they’re thinking for themselves.
Teenagers are ideal writers for several reasons. They’re usually free of preconceptions about writing, and they tend not to use self-consciously ‘‘literary’’ language. They’re allergic to hypocrisy and are generally unfiltered: They overshare, ask personal questions and call you out for microaggressions as well as less egregious (but still mortifying) verbal errors, such as referring to weed as ‘‘pot.’’ Most important, they have yet to put down their best stories in a finished form.
I can imagine an essay taking a risk and distinguishing itself formally — a poem or a one-act play — but most kids use a more straightforward model: a hook followed by a narrative built around “small moments” that lead to a concluding lesson or aspiration for the future. I never get tired of working with students on these essays because each one is different, and the short, rigid form sometimes makes an emotional story even more powerful. Before I read Javier Zamora’s wrenching “Solito,” I worked with a student who had been transported by a coyote into the U.S. and was reunited with his mother in the parking lot of a big-box store. I don’t remember whether this essay focused on specific skills or coping mechanisms that he gained from his ordeal. I remember only the bliss of the parent-and-child reunion in that uninspiring setting. If I were making a case to an admissions officer, I would suggest that simply being able to convey that experience demonstrates the kind of resilience that any college should admire.
The essays that have stayed with me over the years don’t follow a pattern. There are some narratives on very predictable topics — living up to the expectations of immigrant parents, or suffering from depression in 2020 — that are moving because of the attention with which the student describes the experience. One girl determined to become an engineer while watching her father build furniture from scraps after work; a boy, grieving for his mother during lockdown, began taking pictures of the sky.
If, as Lorrie Moore said, “a short story is a love affair; a novel is a marriage,” what is a college essay? Every once in a while I sit down next to a student and start reading, and I have to suppress my excitement, because there on the Google Doc in front of me is a real writer’s voice. One of the first students I ever worked with wrote about falling in love with another girl in dance class, the absolute magic of watching her move and the terror in the conflict between her feelings and the instruction of her religious middle school. She made me think that college essays are less like love than limerence: one-sided, obsessive, idiosyncratic but profound, the first draft of the most personal story their writers will ever tell.
Nell Freudenberger’s novel “The Limits” was published by Knopf last month. She volunteers through the PEN America Writers in the Schools program.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For the Extended Essay, you will choose a research question as a topic, conduct the research independently, then write an essay on your findings. The essay itself is a long one—although there's a cap of 4,000 words, most successful essays get very close to this limit.
Starting your Extended Essay is a big challenge. The best advice I can give you is start early and choose your research question carefully. Starting early is a time-management aspect you'll have to figure out on your own. But I can help you a lot on the second part. Coming up with an appropriate question is about 25% of the whole battle.
To write an impressive extended essay, you should focus on appropriate information. You must create a separate page for bibliography with all sources you used. Tip from us: start writing this page with the first quote you use. Don't write this part last or postpone. In turn, appendices are not an essential section.
The extended essay is an independent, self-directed piece of research, finishing with a 4,000-word paper. One component of the International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) core, the extended essay is mandatory for all students. Read about the extended essay in greater detail. You can also read about how the IB sets deadlines for ...
Just write. No one will see it but you. Exercise 2: Pick one of the three options above and try it: write your favourite 'piece' of the essay first, write as much as you can by hand in one writing sprint, or lose the grammar and just get the ideas down in the right order. 3. Perfect Your Extended Essay Language.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write an extended essay, from research question to complete essay. 1. Define the Topic and Draft the Research Question. 2. Create a Timeline. 3. Research sources and expand knowledge about the topic. 4. Set Deadlines.
Section 3: Selecting a Topic. Choosing a topic for your Extended Essay is the first step in a journey towards developing a deep understanding of a specific area of interest. It's crucial to select a topic that is not only academically viable but also personally engaging. Here's how to navigate this critical phase.
Extended Essay Guide, 2007 for exams starting 2010. Other Resources Consulted or Used in the Creation of this Guidebook Include: ... your extended essay. The research question is the central theme of your paper: it is the thing you are arguing. Therefore, for most subject areas, it is vitally important to craft a research question that is ...
Your dedication and enjoyment will shine through your writing! Start your extended essay early: Give yourself time to think about your topic, plan, research and begin the writing process with less stress— give yourself time to enjoy it without being overwhelmed. Pace your research: Establish a timeline with mini-goals to achieve.
This extended essay, typically around 4,000 words in length, allows students to engage in independent research and develop critical thinking and writing skills. In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through the process of completing your IB Extended Essay successfully. 1. Choose Your Subject Area and Topic.
To write a comprehensive Extended Essay on any subject within the 40 hours: 1. Choose a Topic. The first step to write an EE is to choose an Extended Essay topic to explore. Unfortunately, you can't scrape a good topic off a book or ask a friend in your IB class to share their thoughts.
The extended essay (often called the EE) is a 4000-word structured essay on a topic of your choice, which can take many different forms. Ultimately, what your EE ends up looking like depends on the topic that you choose. Some students choose to write their extended essay on an aspect of literature or
Award of Diploma Points - the role of The Extended Essay, and TOK The extended essay contributes to the overall diploma score through the award of points in conjunction with theory of knowledge. A maximum of three points are awarded according to a student's combined performance in both the extended essay and theory of knowledge.
Outlining is best done as a middle stage in the writing process, not at the very beginning. Follow these steps in the order given before attempting an outline: 1. Read, gather information, and think about your essay topic. 2. Take notes, jot down ideas, use your Researcher's Reflection Space. 3.
In this video, I share my step-by-step guide to writing a perfect IB Extended Essay. I cover everything from topic selection to research to writing to revisi...
If you want to score a 36 on 36 your Extended Essay, check out our Extended Essay Guide, which offers '5 never heard before' tips to help you write a quality essay. IB Extended Essay Checklist. Make an IB Extended Essay Checklist! I cannot emphasize enough on this point. The submission for your EE happens simultaneously when you are expected to ...
Choose a Topic. The first step to writing any successful extended essay is finding the right topic. You'll want to pick a subject that intrigues you because you will spend a lot of time researching and writing this paper. Once you've found your topic, make sure it can be covered in 4,000 words.
The viva voce is a short interview between the student and the supervisor, and is a recommended conclusion to the extended essay process. Students who do not attend the viva voce may be disadvantaged. The viva voce serves the following purposes. A check on plagiarism and malpractice in general.
Extended Essay Introduction. The goal of the introduction is to introduce the topic and provide enough information about it in order to enable the reader to comprehend the significance of your research question. The research question must be clearly and precisely stated in the introduction. The research question is the central question you are ...
Start them young. The concept of writing an essay would draw a blank look from most four-year-olds. ... Let us know how you prepare your students for the extended essay - email [email protected] educator, Extended Essay, Students, Teachers. Why every school should care about inclusive education. Everything you need to know about the 2015 IB ...
a) Add the link to your EE folder. b) Write down your initial ideas as to what you might want to do your EE in and what potential topics you want to do. c) Add your mindmap of ideas (see below) 5. Sign the Extended Essay Essential Agreement: This is a mandatory form you must fill in to show that you understand the expectations that we have ...
An introduction for an Extended Essay requires students to include the following aspects: Aside from giving the essay a structural outline that any reader can follow, these aspects also help ensure that expectations for Criterion A (Focus and Method) are met. Context: Explicitly stating your research question and providing some context that ...
Step 1: Always start with your extended essay requirements. It will help you to narrow things down and take notes to use further in your writing. Step 2: Define your subject and draft your research outline. Submit up to three ideas to determine the best one.
The Extended Essay Step-By-Step Guide 3: The Research. The Easter Break is nearly upon us. Ten years ago this might have been a cue to eat more chocolate than you can handle. But if you're in DP1 of the IB that small thing called the Extended Essay will be hovering on the horizon. You know that you should think about it over the break, but ...
This can lead to new insights and angles for your essay, enriching the content with diverse perspectives and supporting evidence. Here are some useful tips for using the collage essay method for writing an essay fast: Gather diverse materials. Start with a central theme. Arrange materials strategically. Focus on visual impact.
Chevrolet Cars, Trucks, SUVs, Crossovers and Vans
I can imagine an essay taking a risk and distinguishing itself formally — a poem or a one-act play — but most kids use a more straightforward model: a hook followed by a narrative built around ...
Since Russia's invasion in February 2022, Ukraine has become far and away the top recipient of U.S. foreign aid. This marks the first time that a European country has held the top spot since the ...
This interactive map complements the static control-of-terrain maps that ISW daily produces with high-fidelity.
A new tool called Writable, which uses ChatGPT to help grade student writing assignments, is being offered widely to teachers in grades 3-12.. Why it matters: Teachers have quietly used ChatGPT to grade papers since it first came out — but now schools are sanctioning and encouraging its use. Driving the news: Writable, which is billed as a time-saving tool for teachers, was purchased last ...