How to write a literature review introduction (+ examples)
The introduction to a literature review serves as your reader’s guide through your academic work and thought process. Explore the significance of literature review introductions in review papers, academic papers, essays, theses, and dissertations. We delve into the purpose and necessity of these introductions, explore the essential components of literature review introductions, and provide step-by-step guidance on how to craft your own, along with examples.

Why you need an introduction for a literature review
When you need an introduction for a literature review, what to include in a literature review introduction, examples of literature review introductions, steps to write your own literature review introduction.
A literature review is a comprehensive examination of the international academic literature concerning a particular topic. It involves summarizing published works, theories, and concepts while also highlighting gaps and offering critical reflections.
In academic writing , the introduction for a literature review is an indispensable component. Effective academic writing requires proper paragraph structuring to guide your reader through your argumentation. This includes providing an introduction to your literature review.
It is imperative to remember that you should never start sharing your findings abruptly. Even if there isn’t a dedicated introduction section .
Instead, you should always offer some form of introduction to orient the reader and clarify what they can expect.
There are three main scenarios in which you need an introduction for a literature review:
- Academic literature review papers: When your literature review constitutes the entirety of an academic review paper, a more substantial introduction is necessary. This introduction should resemble the standard introduction found in regular academic papers.
- Literature review section in an academic paper or essay: While this section tends to be brief, it’s important to precede the detailed literature review with a few introductory sentences. This helps orient the reader before delving into the literature itself.
- Literature review chapter or section in your thesis/dissertation: Every thesis and dissertation includes a literature review component, which also requires a concise introduction to set the stage for the subsequent review.
You may also like: How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)
It is crucial to customize the content and depth of your literature review introduction according to the specific format of your academic work.
In practical terms, this implies, for instance, that the introduction in an academic literature review paper, especially one derived from a systematic literature review , is quite comprehensive. Particularly compared to the rather brief one or two introductory sentences that are often found at the beginning of a literature review section in a standard academic paper. The introduction to the literature review chapter in a thesis or dissertation again adheres to different standards.
Here’s a structured breakdown based on length and the necessary information:
Academic literature review paper
The introduction of an academic literature review paper, which does not rely on empirical data, often necessitates a more extensive introduction than the brief literature review introductions typically found in empirical papers. It should encompass:
- The research problem: Clearly articulate the problem or question that your literature review aims to address.
- The research gap: Highlight the existing gaps, limitations, or unresolved aspects within the current body of literature related to the research problem.
- The research relevance: Explain why the chosen research problem and its subsequent investigation through a literature review are significant and relevant in your academic field.
- The literature review method: If applicable, describe the methodology employed in your literature review, especially if it is a systematic review or follows a specific research framework.
- The main findings or insights of the literature review: Summarize the key discoveries, insights, or trends that have emerged from your comprehensive review of the literature.
- The main argument of the literature review: Conclude the introduction by outlining the primary argument or statement that your literature review will substantiate, linking it to the research problem and relevance you’ve established.
- Preview of the literature review’s structure: Offer a glimpse into the organization of the literature review paper, acting as a guide for the reader. This overview outlines the subsequent sections of the paper and provides an understanding of what to anticipate.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will provide a clear and structured overview of what readers can expect in your literature review paper.
Regular literature review section in an academic article or essay
Most academic articles or essays incorporate regular literature review sections, often placed after the introduction. These sections serve to establish a scholarly basis for the research or discussion within the paper.
In a standard 8000-word journal article, the literature review section typically spans between 750 and 1250 words. The first few sentences or the first paragraph within this section often serve as an introduction. It should encompass:
- An introduction to the topic: When delving into the academic literature on a specific topic, it’s important to provide a smooth transition that aids the reader in comprehending why certain aspects will be discussed within your literature review.
- The core argument: While literature review sections primarily synthesize the work of other scholars, they should consistently connect to your central argument. This central argument serves as the crux of your message or the key takeaway you want your readers to retain. By positioning it at the outset of the literature review section and systematically substantiating it with evidence, you not only enhance reader comprehension but also elevate overall readability. This primary argument can typically be distilled into 1-2 succinct sentences.
In some cases, you might include:
- Methodology: Details about the methodology used, but only if your literature review employed a specialized method. If your approach involved a broader overview without a systematic methodology, you can omit this section, thereby conserving word count.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will effectively integrate your literature review into the broader context of your academic paper or essay. This will, in turn, assist your reader in seamlessly following your overarching line of argumentation.
Introduction to a literature review chapter in thesis or dissertation
The literature review typically constitutes a distinct chapter within a thesis or dissertation. Often, it is Chapter 2 of a thesis or dissertation.
Some students choose to incorporate a brief introductory section at the beginning of each chapter, including the literature review chapter. Alternatively, others opt to seamlessly integrate the introduction into the initial sentences of the literature review itself. Both approaches are acceptable, provided that you incorporate the following elements:
- Purpose of the literature review and its relevance to the thesis/dissertation research: Explain the broader objectives of the literature review within the context of your research and how it contributes to your thesis or dissertation. Essentially, you’re telling the reader why this literature review is important and how it fits into the larger scope of your academic work.
- Primary argument: Succinctly communicate what you aim to prove, explain, or explore through the review of existing literature. This statement helps guide the reader’s understanding of the review’s purpose and what to expect from it.
- Preview of the literature review’s content: Provide a brief overview of the topics or themes that your literature review will cover. It’s like a roadmap for the reader, outlining the main areas of focus within the review. This preview can help the reader anticipate the structure and organization of your literature review.
- Methodology: If your literature review involved a specific research method, such as a systematic review or meta-analysis, you should briefly describe that methodology. However, this is not always necessary, especially if your literature review is more of a narrative synthesis without a distinct research method.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will empower your literature review to play a pivotal role in your thesis or dissertation research. It will accomplish this by integrating your research into the broader academic literature and providing a solid theoretical foundation for your work.
Comprehending the art of crafting your own literature review introduction becomes significantly more accessible when you have concrete examples to examine. Here, you will find several examples that meet, or in most cases, adhere to the criteria described earlier.
Example 1: An effective introduction for an academic literature review paper
To begin, let’s delve into the introduction of an academic literature review paper. We will examine the paper “How does culture influence innovation? A systematic literature review”, which was published in 2018 in the journal Management Decision.

The entire introduction spans 611 words and is divided into five paragraphs. In this introduction, the authors accomplish the following:
- In the first paragraph, the authors introduce the broader topic of the literature review, which focuses on innovation and its significance in the context of economic competition. They underscore the importance of this topic, highlighting its relevance for both researchers and policymakers.
- In the second paragraph, the authors narrow down their focus to emphasize the specific role of culture in relation to innovation.
- In the third paragraph, the authors identify research gaps, noting that existing studies are often fragmented and disconnected. They then emphasize the value of conducting a systematic literature review to enhance our understanding of the topic.
- In the fourth paragraph, the authors introduce their specific objectives and explain how their insights can benefit other researchers and business practitioners.
- In the fifth and final paragraph, the authors provide an overview of the paper’s organization and structure.
In summary, this introduction stands as a solid example. While the authors deviate from previewing their key findings (which is a common practice at least in the social sciences), they do effectively cover all the other previously mentioned points.
Example 2: An effective introduction to a literature review section in an academic paper
The second example represents a typical academic paper, encompassing not only a literature review section but also empirical data, a case study, and other elements. We will closely examine the introduction to the literature review section in the paper “The environmentalism of the subalterns: a case study of environmental activism in Eastern Kurdistan/Rojhelat”, which was published in 2021 in the journal Local Environment.
The paper begins with a general introduction and then proceeds to the literature review, designated by the authors as their conceptual framework. Of particular interest is the first paragraph of this conceptual framework, comprising 142 words across five sentences:
“ A peripheral and marginalised nationality within a multinational though-Persian dominated Iranian society, the Kurdish people of Iranian Kurdistan (a region referred by the Kurds as Rojhelat/Eastern Kurdi-stan) have since the early twentieth century been subject to multifaceted and systematic discriminatory and exclusionary state policy in Iran. This condition has left a population of 12–15 million Kurds in Iran suffering from structural inequalities, disenfranchisement and deprivation. Mismanagement of Kurdistan’s natural resources and the degradation of its natural environmental are among examples of this disenfranchisement. As asserted by Julian Agyeman (2005), structural inequalities that sustain the domination of political and economic elites often simultaneously result in environmental degradation, injustice and discrimination against subaltern communities. This study argues that the environmental struggle in Eastern Kurdistan can be asserted as a (sub)element of the Kurdish liberation movement in Iran. Conceptually this research is inspired by and has been conducted through the lens of ‘subalternity’ ” ( Hassaniyan, 2021, p. 931 ).
In this first paragraph, the author is doing the following:
- The author contextualises the research
- The author links the research focus to the international literature on structural inequalities
- The author clearly presents the argument of the research
- The author clarifies how the research is inspired by and uses the concept of ‘subalternity’.
Thus, the author successfully introduces the literature review, from which point onward it dives into the main concept (‘subalternity’) of the research, and reviews the literature on socio-economic justice and environmental degradation.
While introductions to a literature review section aren’t always required to offer the same level of study context detail as demonstrated here, this introduction serves as a commendable model for orienting the reader within the literature review. It effectively underscores the literature review’s significance within the context of the study being conducted.
Examples 3-5: Effective introductions to literature review chapters
The introduction to a literature review chapter can vary in length, depending largely on the overall length of the literature review chapter itself. For example, a master’s thesis typically features a more concise literature review, thus necessitating a shorter introduction. In contrast, a Ph.D. thesis, with its more extensive literature review, often includes a more detailed introduction.
Numerous universities offer online repositories where you can access theses and dissertations from previous years, serving as valuable sources of reference. Many of these repositories, however, may require you to log in through your university account. Nevertheless, a few open-access repositories are accessible to anyone, such as the one by the University of Manchester . It’s important to note though that copyright restrictions apply to these resources, just as they would with published papers.
Master’s thesis literature review introduction
The first example is “Benchmarking Asymmetrical Heating Models of Spider Pulsar Companions” by P. Sun, a master’s thesis completed at the University of Manchester on January 9, 2024. The author, P. Sun, introduces the literature review chapter very briefly but effectively:

PhD thesis literature review chapter introduction
The second example is Deep Learning on Semi-Structured Data and its Applications to Video-Game AI, Woof, W. (Author). 31 Dec 2020, a PhD thesis completed at the University of Manchester . In Chapter 2, the author offers a comprehensive introduction to the topic in four paragraphs, with the final paragraph serving as an overview of the chapter’s structure:
PhD thesis literature review introduction
The last example is the doctoral thesis Metacognitive strategies and beliefs: Child correlates and early experiences Chan, K. Y. M. (Author). 31 Dec 2020 . The author clearly conducted a systematic literature review, commencing the review section with a discussion of the methodology and approach employed in locating and analyzing the selected records.

Having absorbed all of this information, let’s recap the essential steps and offer a succinct guide on how to proceed with creating your literature review introduction:
- Contextualize your review : Begin by clearly identifying the academic context in which your literature review resides and determining the necessary information to include.
- Outline your structure : Develop a structured outline for your literature review, highlighting the essential information you plan to incorporate in your introduction.
- Literature review process : Conduct a rigorous literature review, reviewing and analyzing relevant sources.
- Summarize and abstract : After completing the review, synthesize the findings and abstract key insights, trends, and knowledge gaps from the literature.
- Craft the introduction : Write your literature review introduction with meticulous attention to the seamless integration of your review into the larger context of your work. Ensure that your introduction effectively elucidates your rationale for the chosen review topics and the underlying reasons guiding your selection.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
The best answers to "What are your plans for the future?"
10 tips for engaging your audience in academic writing, related articles.

Introduce yourself in a PhD interview (4 simple steps + examples)

37 creative ways to get motivation to study

Types of editorial decisions after peer review (+ how to react)

Minor revisions: Sample peer review comments and examples
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing , how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 27 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Find This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window
What Will You Do Differently?
Please help your librarians by filling out this two-minute survey of today's class session..
Professor, this one's for you .
Introduction
Literature reviews take time. here is some general information to know before you start. .
- VIDEO -- This video is a great overview of the entire process. (2020; North Carolina State University Libraries) --The transcript is included --This is for everyone; ignore the mention of "graduate students" --9.5 minutes, and every second is important
- OVERVIEW -- Read this page from Purdue's OWL. It's not long, and gives some tips to fill in what you just learned from the video.
- NOT A RESEARCH ARTICLE -- A literature review follows a different style, format, and structure from a research article.
Steps to Completing a Literature Review

- Next: Find >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

I had my white colleagues walk in a Black student’s shoes for a day
Career Q&A 28 MAY 24

Changemakers — Nature’s new series celebrates champions of inclusion in science
Editorial 28 MAY 24

Researcher parents are paying a high price for conference travel — here’s how to fix it
Career Column 27 MAY 24

How researchers in remote regions handle the isolation
Career Feature 24 MAY 24

Guidelines for academics aim to lessen ethical pitfalls in generative-AI use
Nature Index 22 MAY 24
Who will make AlphaFold3 open source? Scientists race to crack AI model
News 23 MAY 24

Egypt is building a $1-billion mega-museum. Will it bring Egyptology home?
News Feature 22 MAY 24

Pay researchers to spot errors in published papers
World View 21 MAY 24
Postdoctoral Associate- Neuroscience
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Call for applications- junior and senior scientists
The BORDEAUX INSTITUTE OF ONCOLOGY (BRIC U1312, https://www.bricbordeaux.com/) is seeking to recruit new junior and senior researchers
Bordeaux (Ville), Gironde (FR)
INSERM - U1312 BRIC
Postdoctoral Scholar - Organic Synthesis
Memphis, Tennessee
The University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC)
Postdoctoral Scholar - Chemical Biology
Postdoctoral scholar - clinical pharmacy & translational science.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.


Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Literature reviews
What this guide covers, what is a literature review, literature review resources, types of literature reviews, what is the difference between a literature review and a systematic review, related information and guides, further help.
- Conduct your search
- Store and organise the literature
- Evaluate and critique the literature
- Different subject areas
- Find literature reviews
Reusing content from this guide

Attribute our work under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

The literature review process involves a number of steps.
This guide focuses on:
- evaluating.
A literature review is a survey and critical analysis of what has been written on a particular topic, theory, question or method.
"In writing the literature review, the purpose is to explore what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, what approaches and viewpoints have been adopted, and what are their strengths and weaknesses."
Source: "Focus and frame". (2008). In Eriksson, P. & Kovalainen, A. Introducing Qualitative Methods: Qualitative methods in business research (pp. 44) . London: SAGE Publications Ltd. doi: 10.4135/9780857028044.
Get an overview on doing a literature review:
- Sage research methods online - Literature review methods map Information on the literature review methodology with links to further resources - the Project Planner, books, articles, videos and more.
- Ten simple rules for writing a literature review Gives 10 tips on how to approach and carry out a literature review. By Pautasso M (2013) Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review. PLoS Comput Biol9(7): e1003149.
- The literature review. In: Doing your undergraduate program This chapter looks at the purpose of literature reviews, how it is done, setting the boundaries of your search and more.
- More books on literature reviews A selection of literature review books available via UQ Library Search.
The type of literature review you do will depend on a variety of factors:
- Your discipline
- The purpose - undergraduate assessment, PHD thesis, journal article?
- Your lecturer or supervisor's requirements
Always follow the guidelines outlined by your lecturer or supervisor or consult the instructions for authors (for journal articles), when conducting your literature review.
- is an overview of the significant literature on a topic
- typically includes a critical analysis of each work included
- demonstrates the reviewers knowledge of the topic
- is a list of citations of research sources (books, journal articles, websites etc) on a topic
- includes a brief summary and analysis or evaluation of each citation = the annotation
- a critical assessment of all research studies on a particular research question
- has specific criteria for collecting and evaluating the literature
- includes a synthesis of the findings of the included studies
- This method developed by Griffith University's School of Environment bridges the gap between traditional narrative review methods and meta-analyses to enable students to produce results that are reliable, quantifiable and reproducible.
The requirements of narrative literature reviews are usually quite different than systematic reviews . However, you may be required to adopt some of the characteristics of a systematic approach when doing your literature review. Check the guidelines or criteria that have been set by your supervisor so you know what is expected of you.
Characteristics of reviews
- Meeting the review family: Exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements This article defines different review types and discusses appropriate search methods for each type.
- Writing literature reviews - Student Support Student Support provides information on how to write effective literature reviews.
- Writing skills Learn strategies for good writing from the Graduate School.
- Systematic reviews An overview of systematic reviews and resources to support producing one.
- Subject guides See recommended resources in different subject areas.
- Grey literature Find literature that is not available in traditional channels of publishing and distribution.
- How to find guides Techniques and resources to find specific information formats.
Contact the Librarian team .
Phone: + 617 334 64312 during opening hours
Email: [email protected]
- Next: Conduct your search >>
- Last Updated: May 28, 2024 2:31 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.uq.edu.au/research-techniques/literature-reviews
How to Write a Literature Review
What is a literature review.
- What Is the Literature
- Writing the Review
A literature review is much more than an annotated bibliography or a list of separate reviews of articles and books. It is a critical, analytical summary and synthesis of the current knowledge of a topic. Thus it should compare and relate different theories, findings, etc, rather than just summarize them individually. In addition, it should have a particular focus or theme to organize the review. It does not have to be an exhaustive account of everything published on the topic, but it should discuss all the significant academic literature and other relevant sources important for that focus.
This is meant to be a general guide to writing a literature review: ways to structure one, what to include, how it supplements other research. For more specific help on writing a review, and especially for help on finding the literature to review, sign up for a Personal Research Session .
The specific organization of a literature review depends on the type and purpose of the review, as well as on the specific field or topic being reviewed. But in general, it is a relatively brief but thorough exploration of past and current work on a topic. Rather than a chronological listing of previous work, though, literature reviews are usually organized thematically, such as different theoretical approaches, methodologies, or specific issues or concepts involved in the topic. A thematic organization makes it much easier to examine contrasting perspectives, theoretical approaches, methodologies, findings, etc, and to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of, and point out any gaps in, previous research. And this is the heart of what a literature review is about. A literature review may offer new interpretations, theoretical approaches, or other ideas; if it is part of a research proposal or report it should demonstrate the relationship of the proposed or reported research to others' work; but whatever else it does, it must provide a critical overview of the current state of research efforts.
Literature reviews are common and very important in the sciences and social sciences. They are less common and have a less important role in the humanities, but they do have a place, especially stand-alone reviews.
Types of Literature Reviews
There are different types of literature reviews, and different purposes for writing a review, but the most common are:
- Stand-alone literature review articles . These provide an overview and analysis of the current state of research on a topic or question. The goal is to evaluate and compare previous research on a topic to provide an analysis of what is currently known, and also to reveal controversies, weaknesses, and gaps in current work, thus pointing to directions for future research. You can find examples published in any number of academic journals, but there is a series of Annual Reviews of *Subject* which are specifically devoted to literature review articles. Writing a stand-alone review is often an effective way to get a good handle on a topic and to develop ideas for your own research program. For example, contrasting theoretical approaches or conflicting interpretations of findings can be the basis of your research project: can you find evidence supporting one interpretation against another, or can you propose an alternative interpretation that overcomes their limitations?
- Part of a research proposal . This could be a proposal for a PhD dissertation, a senior thesis, or a class project. It could also be a submission for a grant. The literature review, by pointing out the current issues and questions concerning a topic, is a crucial part of demonstrating how your proposed research will contribute to the field, and thus of convincing your thesis committee to allow you to pursue the topic of your interest or a funding agency to pay for your research efforts.
- Part of a research report . When you finish your research and write your thesis or paper to present your findings, it should include a literature review to provide the context to which your work is a contribution. Your report, in addition to detailing the methods, results, etc. of your research, should show how your work relates to others' work.
A literature review for a research report is often a revision of the review for a research proposal, which can be a revision of a stand-alone review. Each revision should be a fairly extensive revision. With the increased knowledge of and experience in the topic as you proceed, your understanding of the topic will increase. Thus, you will be in a better position to analyze and critique the literature. In addition, your focus will change as you proceed in your research. Some areas of the literature you initially reviewed will be marginal or irrelevant for your eventual research, and you will need to explore other areas more thoroughly.
Examples of Literature Reviews
See the series of Annual Reviews of *Subject* which are specifically devoted to literature review articles to find many examples of stand-alone literature reviews in the biomedical, physical, and social sciences.
Research report articles vary in how they are organized, but a common general structure is to have sections such as:
- Abstract - Brief summary of the contents of the article
- Introduction - A explanation of the purpose of the study, a statement of the research question(s) the study intends to address
- Literature review - A critical assessment of the work done so far on this topic, to show how the current study relates to what has already been done
- Methods - How the study was carried out (e.g. instruments or equipment, procedures, methods to gather and analyze data)
- Results - What was found in the course of the study
- Discussion - What do the results mean
- Conclusion - State the conclusions and implications of the results, and discuss how it relates to the work reviewed in the literature review; also, point to directions for further work in the area
Here are some articles that illustrate variations on this theme. There is no need to read the entire articles (unless the contents interest you); just quickly browse through to see the sections, and see how each section is introduced and what is contained in them.
The Determinants of Undergraduate Grade Point Average: The Relative Importance of Family Background, High School Resources, and Peer Group Effects , in The Journal of Human Resources , v. 34 no. 2 (Spring 1999), p. 268-293.
This article has a standard breakdown of sections:
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Some discussion sections
First Encounters of the Bureaucratic Kind: Early Freshman Experiences with a Campus Bureaucracy , in The Journal of Higher Education , v. 67 no. 6 (Nov-Dec 1996), p. 660-691.
This one does not have a section specifically labeled as a "literature review" or "review of the literature," but the first few sections cite a long list of other sources discussing previous research in the area before the authors present their own study they are reporting.
- Next: What Is the Literature >>
- Last Updated: Jan 11, 2024 9:48 AM
- URL: https://libguides.wesleyan.edu/litreview

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Literature Reviews
- Tools & Visualizations
- Literature Review Examples
- Videos, Books & Links
Business & Econ Librarian

Click to Chat with a Librarian
Text: (571) 248-7542
What is a literature review?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area. Often part of the introduction to an essay, research report or thesis, the literature review is literally a "re" view or "look again" at what has already been written about the topic, wherein the author analyzes a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles. Literature reviews provide the reader with a bibliographic history of the scholarly research in any given field of study. As such, as new information becomes available, literature reviews grow in length or become focused on one specific aspect of the topic.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but usually contains an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, whereas a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. The literature review might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. Depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
A literature review is NOT:
- An annotated bibliography – a list of citations to books, articles and documents that includes a brief description and evaluation for each citation. The annotations inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy and quality of the sources cited.
- A literary review – a critical discussion of the merits and weaknesses of a literary work.
- A book review – a critical discussion of the merits and weaknesses of a particular book.
- Teaching Information Literacy Reframed: 50+ Framework-Based Exercises for Creating Information-Literate Learners
- The UNC Writing Center – Literature Reviews
- The UW-Madison Writing Center: The Writer’s Handbook – Academic and Professional Writing – Learn How to Write a Literature Review
What is the difference between a literature review and a research paper?
The focus of a literature review is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions, whereas academic research papers present and develop new arguments that build upon the previously available body of literature.
How do I write a literature review?
There are many resources that offer step-by-step guidance for writing a literature review, and you can find some of them under Other Resources in the menu to the left. Writing the Literature Review: A Practical Guide suggests these steps:
- Chose a review topic and develop a research question
- Locate and organize research sources
- Select, analyze and annotate sources
- Evaluate research articles and other documents
- Structure and organize the literature review
- Develop arguments and supporting claims
- Synthesize and interpret the literature
- Put it all together
What is the purpose of writing a literature review?
Literature reviews serve as a guide to a particular topic: professionals can use literature reviews to keep current on their field; scholars can determine credibility of the writer in his or her field by analyzing the literature review.
As a writer, you will use the literature review to:
- See what has, and what has not, been investigated about your topic
- Identify data sources that other researches have used
- Learn how others in the field have defined and measured key concepts
- Establish context, or background, for the argument explored in the rest of a paper
- Explain what the strengths and weaknesses of that knowledge and ideas might be
- Contribute to the field by moving research forward
- To keep the writer/reader up to date with current developments in a particular field of study
- Develop alternative research projects
- Put your work in perspective
- Demonstrate your understanding and your ability to critically evaluate research in the field
- Provide evidence that may support your own findings
- Next: Tools & Visualizations >>
- Last Updated: May 6, 2024 3:20 PM
- URL: https://subjectguides.library.american.edu/literaturereview
- Maps & Floorplans
- Libraries A-Z

- Ellis Library (main)
- Engineering Library
- Geological Sciences
- Journalism Library
- Law Library
- Mathematical Sciences
- MU Digital Collections
- Veterinary Medical
- More Libraries...
- Instructional Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Guides
- Schedule a Library Class
- Class Assessment Forms
- Recordings & Tutorials
- Research & Writing Help
- More class resources
- Places to Study
- Borrow, Request & Renew
- Call Numbers
- Computers, Printers, Scanners & Software
- Digital Media Lab
- Equipment Lending: Laptops, cameras, etc.
- Subject Librarians
- Writing Tutors
- More In the Library...
- Undergraduate Students
- Graduate Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Researcher Support
- Distance Learners
- International Students
- More Services for...
- View my MU Libraries Account (login & click on My Library Account)
- View my MOBIUS Checkouts
- Renew my Books (login & click on My Loans)
- Place a Hold on a Book
- Request Books from Depository
- View my ILL@MU Account
- Set Up Alerts in Databases
- More Account Information...
Introduction to Literature Reviews
Introduction.
- Step One: Define
- Step Two: Research
- Step Three: Write
- Suggested Readings
A literature review is a written work that :
- Compiles significant research published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers;
- Surveys scholarly articles, books, dissertations, conference proceedings, and other sources;
- Examines contrasting perspectives, theoretical approaches, methodologies, findings, results, conclusions.
- Reviews critically, analyzes, and synthesizes existing research on a topic; and,
- Performs a thorough “re” view, “overview”, or “look again” of past and current works on a subject, issue, or theory.
From these analyses, the writer then offers an overview of the current status of a particular area of knowledge from both a practical and theoretical perspective.
Literature reviews are important because they are usually a required step in a thesis proposal (Master's or PhD). The proposal will not be well-supported without a literature review. Also, literature reviews are important because they help you learn important authors and ideas in your field. This is useful for your coursework and your writing. Knowing key authors also helps you become acquainted with other researchers in your field.
Look at this diagram and imagine that your research is the "something new." This shows how your research should relate to major works and other sources.
Olivia Whitfield | Graduate Reference Assistant | 2012-2015
- Next: Step One: Define >>
- Last Updated: Jun 28, 2023 5:49 PM
- URL: https://libraryguides.missouri.edu/literaturereview

Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE: Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 25, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Mark Access Health Policy
- v.11(1); 2023
- PMC10392303

Rapid literature review: definition and methodology
Beata smela.
a Assignity, Cracow, Poland
Mondher Toumi
b Public Health Department, Aix-Marseille University, Marseille, France
Karolina Świerk
Clement francois, małgorzata biernikiewicz.
c Studio Slowa, Wroclaw, Poland
Emilie Clay
d Clever-Access, Paris, France
Laurent Boyer
Introduction: A rapid literature review (RLR) is an alternative to systematic literature review (SLR) that can speed up the analysis of newly published data. The objective was to identify and summarize available information regarding different approaches to defining RLR and the methodology applied to the conduct of such reviews.
Methods: The Medline and EMBASE databases, as well as the grey literature, were searched using the set of keywords and their combination related to the targeted and rapid review, as well as design, approach, and methodology. Of the 3,898 records retrieved, 12 articles were included.
Results: Specific definition of RLRs has only been developed in 2021. In terms of methodology, the RLR should be completed within shorter timeframes using simplified procedures in comparison to SLRs, while maintaining a similar level of transparency and minimizing bias. Inherent components of the RLR process should be a clear research question, search protocol, simplified process of study selection, data extraction, and quality assurance.
Conclusions: There is a lack of consensus on the formal definition of the RLR and the best approaches to perform it. The evidence-based supporting methods are evolving, and more work is needed to define the most robust approaches.
Introduction
A systematic literature review (SLR) summarizes the results of all available studies on a specific topic and provides a high level of evidence. Authors of the SLR have to follow an advanced plan that covers defining a priori information regarding the research question, sources they are going to search, inclusion criteria applied to choose studies answering the research question, and information regarding how they are going to summarize findings [ 1 ].
The rigor and transparency of SLRs make them the most reliable form of literature review [ 2 ], providing a comprehensive, objective summary of the evidence for a given topic [ 3 , 4 ]. On the other hand, the SLR process is usually very time-consuming and requires a lot of human resources. Taking into account a high increase of newly published data and a growing need to analyze information in the fastest possible way, rapid literature reviews (RLRs) often replace standard SLRs.
There are several guidelines on the methodology of RLRs [ 5–11 ]; however, only recently, one publication from 2021 attempted to construct a unified definition [ 11 ]. Generally, by RLRs, researchers understand evidence synthesis during which some of the components of the systematic approach are being used to facilitate answering a focused research question; however, scope restrictions and a narrower search strategy help to make the project manageable in a shorter time and to get the key conclusions faster [ 4 ].
The objective of this research was to collect and summarize available information on different approaches to the definition and methodology of RLRs. An RLR has been run to capture publications providing data that fit the project objective.
To find publications reporting information on the methodology of RLRs, searches were run in the Medline and EMBASE databases in November 2022. The following keywords were searched for in titles and abstracts: ‘targeted adj2 review’ OR ‘focused adj2 review’ OR ‘rapid adj2 review’, and ‘methodology’ OR ‘design’ OR ‘scheme’ OR ‘approach’. The grey literature was identified using Google Scholar with keywords including ‘targeted review methodology’ OR ‘focused review methodology’ OR ‘rapid review methodology’. Only publications in English were included, and the date of publication was restricted to year 2016 onward in order to identify the most up-to-date literature. The reference lists of each included article were searched manually to obtain the potentially eligible articles. Titles and abstracts of the retrieved records were first screened to exclude articles that were evidently irrelevant. The full texts of potentially relevant papers were further reviewed to examine their eligibility.
A pre-defined Excel grid was developed to extract the following information related to the methodology of RLR from guidelines:
- Definition,
- Research question and searches,
- Studies selection,
- Data extraction and quality assessment,
- Additional information.
There was no restriction on the study types to be analyzed; any study reporting on the methodology of RLRs could be included: reviews, practice guidelines, commentaries, and expert opinions on RLR relevant to healthcare policymakers or practitioners. The data extraction and evidence summary were conducted by one analyst and further examined by a senior analyst to ensure that relevant information was not omitted. Disagreements were resolved by discussion and consensus.
Studies selection
A total of 3,898 records (3,864 articles from a database search and 34 grey literature from Google Scholar) were retrieved. After removing duplicates, titles and abstracts of 3,813 articles were uploaded and screened. The full texts of 43 articles were analyzed resulting in 12 articles selected for this review, including 7 guidelines [ 5–11 ] on the methodology of RLRs, together with 2 papers summarizing the results of the Delphi consensus on the topic [ 12 , 13 ], and 3 publications analyzing and assessing different approaches to RLRs [ 4 , 14 , 15 ].
Overall, seven guidelines were identified: from the World Health Organization (WHO) [ 5 ], National Collaborating Centre for Methods and Tools (NCCMT) [ 7 ], the UK government [ 8 ], the Oxford Centre for Evidence Based Medicine [ 9 ], the Cochrane group [ 6 , 11 ], and one multi-national review [ 10 ]. Among the papers that did not describe the guidelines, Gordon et al. [ 4 ] proposed 12 tips for conducting a rapid review in the right settings and discussed why these reviews may be more beneficial in some circumstances. The objective of work conducted by Tricco et al. [ 13 ] and Pandor et al. [ 12 ] was to collect and compare perceptions of rapid reviews from stakeholders, including researchers, policymakers, industry, journal editors, and healthcare providers, and to reach a consensus outlining the domains to consider when deciding on approaches for RLRs. Haby et al. [ 14 ] run a rapid review of systematic reviews and primary studies to find out the best way to conduct an RLR in health policy and practice. In Tricco et al. (2022) [ 15 ], JBI position statement for RLRs is presented.
From all the seven identified guidelines information regarding definitions the authors used for RLRs, approach to the PICOS criteria and search strategy development, studies selection, data extractions, quality assessment, and reporting were extracted.
Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group developed methods guidance based on scoping review of the underlying evidence, primary methods studies conducted, as well as surveys sent to Cochrane representative and discussion among those with expertise [ 11 ]. They analyzed over 300 RLRs or RLR method papers and based on the methodology of those studies, constructed a broad definition RLR, one that meets a minimum set of requirements identified in the thematic analysis: ‘ A rapid review is a form of knowledge synthesis that accelerates the process of conducting a traditional systematic review through streamlining or omitting a variety of methods to produce evidence in a resource-efficient manner .’ This interpretation aligns with more than 50% of RLRs identified in this study. The authors additionally provided several other definitions, depending on specific situations or requirements (e.g., when RLR is produced on stakeholder’s request). It was additionally underlined that RLRs should be driven by the need of timely evidence for decision-making purposes [ 11 ].
Rapid reviews vary in their objective, format, and methods used for evidence synthesis. This is a quite new area, and still no agreement on optimal methods can be found [ 5 ]. All of the definitions are highlighting that RLRs are completed within shorter timeframes than SLRs, and also lack of time is one of the main reasons they are conducted. It has been suggested that most rapid reviews are conducted within 12 weeks; however, some of the resources suggest time between a few weeks to no more than 6 months [ 5 , 6 ]. Some of the definitions are highlighting that RLRs follow the SLR process, but certain phases of the process are simplified or omitted to retrieve information in a time-saving way [ 6 , 7 ]. Different mechanisms are used to enhance the timeliness of reviews. They can be used independently or concurrently: increasing the intensity of work by intensifying the efforts of multiple analysts by parallelization of tasks, using review shortcuts whereby one or more systematic review steps may be reduced, automatizing review steps by using new technologies [ 5 ]. The UK government report [ 8 ] referred to two different RLRs: in the form of quick scoping reviews (QSR) or rapid evidence assessments (REA). While being less resource and time-consuming compared to standard SLRs, QSRs and REAs are designed to be similarly transparent and to minimize bias. QSRs can be applied to rather open-ended questions, e.g., ‘what do we know about something’ but both, QSRs and REAs, provide an understanding of the volume and characteristics of evidence on a specific topic, allowing answering questions by maximizing the use of existing data, and providing a clear picture of the adequacy of existing evidence [ 8 ].
Research questions and searches
The guidelines suggest creating a clear research question and search protocol at the beginning of the project. Additionally, to not duplicate RLRs, the Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group encourages all people working on RLRs to consider registering their search protocol with PROSPERO, the international prospective register of reviews; however, so far they are not formally registered in most cases [ 5 , 6 ]. They also recommend involving key stakeholders (review users) to set and refine the review question, criteria, and outcomes, as well as consulting them through the entire process [ 11 ].
Regarding research questions, it is better to structure them in a neutral way rather than focus on a specific direction for the outcome. By doing so, the researcher is in a better position to identify all the relevant evidence [ 7 ]. Authors can add a second, supportive research question when needed [ 8 ]. It is encouraged to limit the number of interventions, comparators and outcomes, to focus on the ones that are most important for decision-making [ 11 ]. Useful could be also reviewing additional materials, e.g., SLRs on the topic, as well as conducting a quick literature search to better understand the topic before starting with RLRs [ 7 ]. In SLRs researchers usually do not need to care a lot about time spent on creating PICOS, they need to make sure that the scope is broad enough, and they cannot use many restrictions. When working on RLRs, a reviewer may spend more or less time defining each of the components of the study question, and the main step is making sure that PICOS addresses the needs of those who requested the rapid review, and at the same time, it is feasible within the required time frame [ 7 ]. Search protocol should contain an outline of how the following review steps are to be carried out, including selected search keywords and a full strategy, a list of data sources, precise inclusion and exclusion criteria, a strategy for data extraction and critical appraisal, and a plan of how the information will be synthesized [ 8 ].
In terms of searches running, in most cases, an exhaustive process will not be feasible. Researchers should make sure that the search is effective and efficient to produce results in a timely manner. Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group recommends involving an information specialist and conducting peer review of at least one search strategy [ 11 ]. According to the rapid review guidebook by McMaster University [ 7 ], it is important that RLRs, especially those that support policy and program decisions, are being fed by the results of a body of literature, rather than single studies, when possible. It would result in more generalizable findings applied at the level of a population and serve more realistic findings for program decisions [ 7 ]. It is important to document the search strategy, together with a record of the date and any date limits of the search, so that it can easily be run again, modified, or updated. Furthermore, the information on the individual databases included in platform services should always be reported, as this depends on organizations’ subscriptions and must be included for transparency and repeatability [ 7 , 8 ]. Good solution for RLRs is narrowing the scope or searching a limited number of databases and other sources [ 7 ]. Often, the authors use the PubMed/MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, and Embase databases. In most reviews, two or more databases are searched, and common limits are language (usually restricted to English), date, study design, and geographical area. Some RLRs include searching of grey literature; however, contact with authors is rather uncommon [ 5 , 8 ]. According to the flexible framework for restricted systematic review published by the University of Oxford, the search should be run in at least one major scientific database such as PubMed, and one other source, e.g., Google Scholar [ 9 ]. Grey literature and unpublished evidence may be particularly needed and important for intervention questions. It is related to the fact that studies that do not report the effects of interventions are less likely to be published [ 8 ]. If there is any type of evidence that will not be considered by the RLRs, e.g., reviews or theoretical and conceptual studies, it should also be stated in the protocol together with justification [ 8 ]. Additionally, authors of a practical guide published by WHO suggest using a staged search to identify existing SLRs at the beginning, and then focusing on studies with other designs [ 5 ]. If a low number of citations have been retrieved, it is acceptable to expand searches, remove some of the limits, and add additional databases and sources [ 7 ].
Searching for RLRs is an iterative process, and revising the approach is usually needed [ 7 ]. Changes should be confirmed with stakeholders and should be tracked and reflected in the final report [ 5 ].
The next step in the rapid review is the selection of studies consisting of two phases: screening of titles and abstracts, and analysis of full texts. Prior to screening initiation, it is recommended to conduct a pilot exercise using the same 30–50 abstracts and 5–10 full-texts for the entire screening team in order to calibrate and test the review form [ 11 ]. In contrast to SLRs, it can be done by one reviewer with or without verification by a second one. If verification is performed, usually the second reviewer checks only a subset of records and compares them. Cochrane Group, in contrast, recommends a stricter approach: at least 20% of references should be double-screened at titles and abstracts stage, and while the rest of the references may be screened by one reviewer, the excluded items need to be re-examined by second reviewer; similar approach is used in full-text screening [ 11 ]. This helps to ensure that bias was reduced and that the PICOS criteria are applied in a relevant way [ 5 , 8 , 9 , 11 ]. During the analysis of titles and abstracts, there is no need to report reasons for exclusion; however, they should be tracked for all excluded full texts [ 7 ].
Data extraction and quality assessment
According to the WHO guide, the most common method for data extraction in RLRs is extraction done by a single reviewer with or without partial verification. The authors point out that a reasonable approach is to use a second reviewer to check a random sample of at least 10% of the extractions for accuracy. Dual performance is more necessary for the extraction of quantitative results than for descriptive study information. In contrast, Cochrane group recommends that second reviewer should check the correctness and completeness of all data [ 11 ]. When possible, extractions should be limited to key characteristics and outcomes of the study. The same approach to data extraction is also suggested for a quality assessment process within rapid reviews [ 5 , 9 , 11 ]. Authors of the guidebook from McMaster University highlight that data extraction should be done ideally by two reviewers independently and consensus on the discrepancies should always be reached [ 7 ]. The final decision on the approach to this important step of review should depend on the available time and should also reflect the complexity of the research question [ 9 ].
For screening, analysis of full texts, extractions, and quality assessments, researchers can use information technologies to support them by making these review steps more efficient [ 5 ].
Before data reporting, a reviewer should prepare a document with key message headings, executive summary, background related to the topic and status of the current knowledge, project question, synthesis of findings, conclusions, and recommendations. According to the McMaster University guidebook, a report should be structured in a 1:2:20 format, that is, one page for key messages, two pages for an executive summary, and a full report of up to 20 pages [ 7 ]. All the limitations of the RLRs should be analyzed, and conclusions should be drawn with caution [ 5 ]. The quality of the accumulated evidence and the strength of recommendations can be assessed using, e.g., the GRADE system [ 5 ]. When working on references quoting, researchers should remember to use a primary source, not secondary references [ 7 ]. It would be worth considering the support of some software tools to automate reporting steps. Additionally, any standardization of the process and the usage of templates can support report development and enhance the transparency of the review [ 5 ].
Ideally, all the review steps should be completed during RLRs; however, often some steps may need skipping or will not be completed as thoroughly as should because of time constraints. It is always crucial to decide which steps may be skipped, and which are the key ones, depending on the project [ 7 ]. Guidelines suggest that it may be helpful to invite researchers with experience in the operations of SLRs to participate in the rapid review development [ 5 , 9 ]. As some of the steps will be completed by one reviewer only, it is important to provide them with relevant training at the beginning of the process, as well as during the review, to minimize the risk of mistakes [ 5 ].
Additional information
Depending on the policy goal and available resources and deadlines, methodology of the RLRs may be modified. Wilson et al. [ 10 ] provided extensive guidelines for performing RLR within days (e.g., to inform urgent internal policy discussions and/or management decisions), weeks (e.g., to inform public debates), or months (e.g., to inform policy development cycles that have a longer timeline, but that cannot wait for a traditional full systematic review). These approaches vary in terms of data synthesis, types of considered evidence and project management considerations.
In shortest timeframes, focused questions and subquestions should be formulated, typically to conduct a policy analysis; the report should consist of tables along with a brief narrative summary. Evidence from SLRs is often considered, as well as key informant interviews may be conducted to identify additional literature and insights about the topic, while primary studies and other types of evidence are not typically feasible due to time restrictions. The review would be best conducted with 1–2 reviewers sharing the work, enabling rapid iterations of the review. As for RLRs with longer timeline (weeks), these may use a mix of policy, systems and political analysis. Structure of the review would be similar to shorter RLRs – tabular with short narrative summary, as the timeline does not allow for comprehensive synthesis of data. Besides SLRs, primary studies and other evidence may be feasible in this timeframe, if obtained using the targeted searches in the most relevant databases. The review team should be larger, and standardized procedures for reviewing of the results and data extraction should be applied. In contrast to previous timeframe, merit review process may be feasible. For both timeframes, brief consultations with small transdisciplinary team should be conducted at the beginning and in the final stage of the review to discuss important matters.
For RLRs spanning several months, more comprehensive methodology may be adapted in terms of data synthesis and types of evidence. However, authors advise that review may be best conducted with a small review team in order to allow for more in-depth interpretation and iteration.
Studies analyzing methodology
There have been two interesting publications summarizing the results of Delphi consensus on the RLR methodology identified and included in this review [ 12 , 13 ].
Tricco et al. [ 13 ] first conducted an international survey and scoping review to collect information on the possible approaches to the running of rapid reviews, based on which, they employed a modified Delphi method that included inputs from 113 stakeholders to explore the most optimized approach. Among the six most frequent rapid review approaches (not all detailed here) being evaluated, the approach that combines inclusion of published literature only, a search of more than one database and limitations by date and language, study selection by one analyst, data extraction, and quality assessment by one analyst and one verifier, was perceived as the most feasible approach (72%, 81/113 responses) with the potentially lowest risk of bias (12%, 12/103). The approach ranked as the first one when considering timelines assumes updating of the search from a previously published review, no additional limits on search, studies selection and data extraction done by one reviewer, and no quality assessment. Finally, based on the publication, the most comprehensive RLRs can be made by moving on with the following rules: searching more than one database and grey literature and using date restriction, and assigning one reviewer working on screening, data extraction, and risk of bias assessment ( Table 1 ). Pandor et al. [ 12 ] introduced a decision tool for SelecTing Approaches for Rapid Reviews (STARR) that were produced through the Delphi consensus of international experts through an iterative and rigorous process. Participants were asked to assess the importance of predefined items in four domains related to the rapid review process: interaction with commissioners, understanding the evidence base, data extraction and synthesis methods, and reporting of rapid review methods. All items assigned to four domains achieved > 70% of consensus, and in that way, the first consensus-driven tool has been created that supports authors of RLRs in planning and deciding on approaches.
Six most frequent approaches to RLRs (adapted from Tricco et al. [ 13 ]).
Haby et al. [ 14 ] run searches of 11 databases and two websites and developed a comprehensive overview of the methodology of RLRs. With five SLRs and one RCT being finally included, they identified the following approaches used in RLRs to make them faster than full SLRs: limiting the number and scope of questions, searching fewer databases, limited searching of grey literature, restrictions on language and date (e.g., English only, most recent publications), updating the existing SLRs, eliminating or limiting hand searches of reference lists, noniterative search strategies, eliminating consultation with experts, limiting dual study selection, data extraction and quality assessment, minimal data synthesis with short concise conclusions or recommendations. All the SLRs included in this review were consistent in stating that no agreed definition of rapid reviews is available, and there is still no final agreement on the best methodological rules to be followed.
Gordon et al. [ 4 ] explained the advantages of performing a focused review and provided 12 tips for its conduction. They define focused reviews as ‘a form of knowledge synthesis in which the components of the systematic process are applied to facilitate the analysis of a focused research question’. The first tip presented by the authors is related to deciding if a focused review is a right solution for the considered project. RLRs will suit emerging topics, approaches, or assessments where early synthesis can support doctors, policymakers, etc., but also can direct future research. The second, third, and fourth tips highlight the importance of running preliminary searches and considering narrowing the results by using reasonable constraints taking into account the local context, problems, efficiency perspectives, and available time. Further tips include creating a team of experienced reviewers working on the RLRs, thinking about the target journal from the beginning of work on the rapid review, registering the search protocol on the PROSPERO registry, and the need for contacting authors of papers when data available in publications are missing or incongruent. The last three tips are related to the choice of evidence synthesis method, using the visual presentation of data, and considering and describing all the limitations of the focused review.
Finally, a new publication by Tricco et al. from 2022, describing JBI position statement [ 15 ] underlined that for the time being, there is no specific tool for critical appraisal of the RLR’s methodological quality. Instead, reviewers may use available tools to assess the risk of bias or quality of SLRs, like ROBIS, the JBI critical appraisal tools, or the assessment of multiple systematic reviews (AMSTAR).
Inconsistency in the definitions and methodologies of RLR
Although RLR was broadly perceived as an approach to quicken the conduct of conventional SLR, there is a lack of consensus on the formal definition of the RLR, so as to the best approaches to perform it. Only in 2021, a study proposing unified definition was published; however, it is important to note that the most accurate definition was only matching slightly over 50% of papers analysed by the authors, which underlines the lack of homogeneity in the field [ 11 ]. The evidence-based supporting methods are evolving, and more evidence is needed to define the most robust approaches [ 5 ].
Diverse terms are used to describe the RLR, including ‘rapid review’, focused systematic review’, ‘quick scoping reviews’, and ‘rapid evidence assessments’. Although the general principles of conducting RLR are to accelerate the whole process, complexity was seen in the methodologies used for RLRs, as reflected in this study. Also, inconsistencies related to the scope of the questions, search strategies, inclusion criteria, study screening, full-text review, quality assessment, and evidence presentation were implied. All these factors may hamper decision-making about optimal methodologies for conducting rapid reviews, and as a result, the efficiency of RLR might be decreased. Additionally, researchers may tend to report the methodology of their reviews without a sufficient level of detail, making it difficult to appraise the quality and robustness of their work.
Advantages and weaknesses of RLR
Although RLR used simplified approaches for evidence synthesis compared with SLR, the methodologies for RLR should be replicable, rigorous, and transparent to the greatest extent [ 16 ]. When time and resources are limited, RLR could be a practical and efficient tool to provide the summary of evidence that is critical for making rapid clinical or policy-related decisions [ 5 ]. Focusing on specific questions that are of controversy or special interest could be powerful in reaffirming whether the existing recommendation statements are still appropriate [ 17 ].
The weakness of RLR should also be borne in mind, and the trade-off of using RLR should be carefully considered regarding the thoroughness of the search, breadth of a research question, and depth of analysis [ 18 ]. If allowed, SLR is preferred over RLR considering that some relevant studies might be omitted with narrowed search strategies and simplified screening process [ 14 ]. Additionally, omitting the quality assessment of included studies could result in an increased risk of bias, making the comprehensiveness of RLR compromised [ 13 ]. Furthermore, in situations that require high accuracy, for example, where a small relative difference in an intervention has great impacts, for the purpose of drafting clinical guidelines, or making licensing decisions, a comprehensive SLR may remain the priority [ 19 ]. Therefore, clear communications with policymakers are recommended to reach an agreement on whether an RLR is justified and whether the methodologies of RLR are acceptable to address the unanswered questions [ 18 ].
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
The IMP research on business networks: a systematic literature review and research agenda
- Original Article
- Open access
- Published: 24 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Simone Guercini 1 ,
- Antonella La Rocca 2 &
- Andrea Perna 3 , 4
More than 40 years of Industrial Marketing and Purchasing (IMP) research have revealed that in b2b markets, business exchange is carried out in continuous buyer–seller relationships. This involves direct and indirect interaction and dynamics resulting in significant related social and material investments and in extensive interdependencies that confer on the business landscape a market-as-network structure. Since the introduction of this ideas, research on business networks has been richly alimented by researchers of the IMP community. Yet, we do not have a clear overview of what this literature has covered in the last twenty years (in the period 2002–2022), in parallel with the many changes that have affected business landscape. With this study, we aim to examine what is the status of the last 20 years of IMP literature specifically dealing with the business networks level of analysis (45 articles) and to offer key directions for imminent research in this domain while analyzing and synthesizing extant literature.
Similar content being viewed by others

The Emergence of the Business Network Approach
Approaching and extending business networks—an agenda for new research challenges.

Network Effects
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The concept of network has been continuously at the centre of attention of scholars in the business-to-business marketing field which is dominated by the North American mainstream approach and the IMP (Industrial Marketing and Purchasing) driven research (Möller & Halinen, 2022 ). Although the IMP-driven research still struggles to be cited beyond its community (Aramo-Immonen et al., 2020 ), the IMP Group (see Håkansson & Gadde, 2018 , for a review on how the research network has developed) has substantially contributed to the industrial marketing field (Möller & Halinen, 2018 ). One of the first and most important contributions of the initial founders of the IMP Group lies in the ‘discovery’ of the existence of buyer-seller relationships (Ford, 1980 ; Håkansson, 1982 ) and, soon after, that of “networks” in business markets, as evidenced by the introduction of a specific concept to describe that characteristic namely: ‘markets-as-network’ (Mattsson, 1987 ). This idea aimed to capture an empirical phenomenon that remained mostly unrecognized until that period, namely that producers and users, instead of jumping around between different counterparts, playing with the price mechanisms, appeared to interact closely and deeply with their main counterparts making significant adaptations in relation to each other (Håkansson et al., 2009 ). The picture of the business world that emerges from the IMP research tradition is characterized by relatedness and limited autonomy among single individual companies and by products being a variable defined by the parties (Håkansson & Snehota eds., 2017 ). In this tradition a network has been defined as a structure where a number of nodes (business units such as producers, customers, service companies and suppliers of finance, knowledge or influence) are related to each other by specific threads which are relationships between companies (Ford et al., 2003 ). Research in the IMP perspective takes the stance that both markets and firms are considered networks of relationships (Håkansson & Johanson, 1992 ). Consequently, much of what was traditionally thought to be within the boundaries of the firm is, in this perspective, in the “between”. Networks are seen as structures that “emerge” from the evolution of business relationships (Håkansson & Snehota, 1995 ). On one side, prevailing interdependencies between actors become institutionalized, and therefore difficult to change. On the other side, networks reveal no once-and-for all stable structures but are in a continuous process of change as relationships are established or change in their nature or cease to exist (Anderson et al., 1998 ). Stability and change are thus an inherent duality of business networks (Håkansson & Snehota, 1995 ). Seeing markets as network-like structures poses some challenges both from a methodological point of view for researchers involved in the study of networks (Abrahamsen et al., 2017 ) but also for managers who have to make sense of an evolving and complex context populated by interacting companies (Håkansson et al., 2009 ). Each manager has her own subjective interpretation of the world around them that provide each manager’s particular network picture of the process of the network and that form the basis for their networking.
Research on business network dynamics has proliferated since the observation that most research was focused on the stable character of industrial networks (Anderson et al., 1998 ), and one may ask what remains to be discovered. We believe that the undergoing transformation processes to the business landscape are a unique opportunity for studying and better understanding business networks dynamics. Indeed, the business world keeps evolving and the important topic of changes in, and implications of the interactive business world, is a wide avenue open for further research (Waluszewski et al., 2019 ). However, in order to advance our knowledge in this domain, and to contribute more broadly to the development of b2b marketing theory (Hadjikhani & LaPlaca, 2013 ; Hunt, 2013 ), we need an overview of what lines of research have been followed and what remains instead overlooked. Therefore, the research questions that guided our study are: (1) what are the main research directions that have emerged in the last 20 years of IMP research focusing on business networks level of analysis? (2) in light of identified previous studies on business networks from an IMP perspective, what are key directions and valuable areas for further research in this field?
Our findings show that further research avenues should entail the topic of sensemaking in business networks, managing ‘in’ and across networks, network structures and dynamics. We suggest that within these three interlinked areas, researchers should continue developing theoretical frameworks as well as nurturing the managerial perspective and therefore elaborating new managerial tools.
The remainder of our paper is organized as it follows. In section 2 (Methodology) we explain how we have conducted the systematic literature review (Tranfield et al., 2003 ) on IMP-related research published between 2002 and 2022, having business networks as main focus of attention. Section 3 offers an analysis of the 45 identified articles having a focus on business networks. These articles have been examined through an in-depth thematic analysis from which four sub-themes of research have emerged as prominent: (1) sensemaking in networks; (2) managing in business networks; (3) connection of multiple/different networks; (4) supply networks; and (5) networks structures and dynamics. Based on the analysis of this literature, we outline in the last section of the paper some directions for further research on business networks.
2 Methodology
To answer to the study’s research questions, the Authors decided to rely on a systematic literature review (SLR) method (Tranfield et al., 2003 ; Snyder, 2019 ) that helps to reach a reliable evaluation of the existent scientific knowledge of a certain topic. As we are interested – on one hand – to provide an IMP-driven overview of business network research and – on the other hand – to offer a possible research agenda on business network within current contexts, the choice of utilizing SLR appears suitable. In other words, SLR appears a coherent method when researchers aim at carrying out an integrated and synthetized overview of a certain topic and describe future research directions (Palöatier et al., 2018 ).
Conducting the review (Tranfield et al., 2003 ) has implied for the Authors to pre-plan the search strategy and perform the first step of the review with the identification of the literature database and the research string. The authors have selected one of the major and comprehensive research Internet data base–Scopus – and performed (on December 28th, 2022) a research of all the articles published in the period 2002–2022. The Authors have then identified a research string in reference to the subject of the review. We included in the Title field the word “network” and in the Abstract field the word “industrial marketing and purchasing” (31 results) or “IMP” (55 results) or “INA” (2 results) or “ARA” (7 results). This combination of words allowed us to identify studies dealing with networks having an explicit link with the IMP approach. Besides the word “IMP”, in an extended version and as acronym, we included the acronym of Industrial Network Approach (INA) which is sometimes used as alternative to business network approach or IMP approach and the word “ARA” (standing for Actor-Resource-Activity and referring to actor bonds, activity links and resource ties) which refers to one of the key framework for analyzing business relationships used by IMP researchers (Håkansson & Snehota, 1995 ) and as such is often used to refer to the IMP approach.
In the following step – the process of selecting and assessing studies (Tranfield et al., 2003 ) – the Authors have collectively taken several decisions. The Authors have excluded manuscripts such as book chapters, conference proceedings and conference papers in order to increase the level of validity (Podsakoff et al., 2005 ) and therefore relied on peer-reviewed article journals. Excluding results that appeared multiple times, the search resulted in 62 articles and 6 introductions to special issues. The analysis of abstracts led to exclusion of further 6 papers which, despite containing the searched key-words, fall into the following cases: key words were used but referred to other concepts; a study with a very operational objective; 2 studies focusing on analysing the IMP research community/business network studies and 2 studies for which the full text was not available. This step of the process yielded a total of 56 papers and 6 editorials. In the next stage of the systematic literature review process, all the authors have read the 56 papers and the 6 editorials. From the reading of the full articles the authors found 17 articles (which are listed in Appendix A), including 2 editorials, that are focused on concepts and/or phenomena other than business networks, although adopting a business network viewpoint. In these papers the reference to business network was used as synonymous to IMP approach, therefore appearing in our results, but without business networks being at the center of the phenomenon analyzed. In particular, of 17 excluded articles: 6 have as a main focus entrepreneurial phenomena (including one editorial), 3 are focused on conflicts, 2 on identity construction, 1 on social capital, 1 on innovation processes, 1 on competition, 1 on the flow of money and 1 on purchasing behavior. Furthermore, we excluded 1 editorial that include several topics, in line with the collected articles in the special issue, without converging on a theme specifically. According to our research goal – identified over the planning step of the review (Tranfield et al., 2003 ) – we excluded such articles and proceeded with a thematic analysis of the remaining articles. The thematic analysis has represented a central and key activity carried out in order to report the results of the SLR (Tranfield et al., 2003 ): thematic analysis is useful mostly when researchers have to scrutinize fragmented concepts once a set of scientific articles is selected for carrying out the research. So, it represented a well-suited way to accomplish our research goal: we implemented the thematic analysis in order to shed light on the key areas within the IMP business networks literature. While undertaking thematic analysis, we followed five phases of thematic analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006 ): data familiarisation, generating initial codes, searching for themes, reviewing themes, defining and naming themes and producing the final output. We summarized the studies in an Excel sheet with various columns such as journal name and rank, year published, authors, key research question, methods, key findings, themes and comments, which were our interpretations for the findings. We discussed the generated Excel sheet to create themes which are described in the literature as representing key concepts that define the subject of an article (Ryan & Bernard, 2003 ). Following this approach, we derived five themes labelled as follow: sensemaking in networks, managing in networks, connection of multiple/different networks, supply networks and networks structures and dynamics. The 45 articles, which are also reported in Appendix B, are discussed in the following section.
3 Discussion
From the full text analysis of the 45 papers resulting from our search and subsequent exclusion/inclusion process, we have identified 5 key themes (as explained in the methodology section). In this section we aim to discuss the most salient findings of the articles within each theme in order to outline, in the final section of the paper, some opportunities for further research in these or adjacent areas. The discussion is thus organized in five sub-sections: (3.1) Sensemaking in networks; (3.2) Managing in business networks; (3.3) Connection of multiple/different networks; (3.4) Supply networks; 3.5 Network structures and dynamics.
3.1 Sensemaking in networks
The 7 papers dealing with what we have labeled “sensemaking in networks” (see Table 1 ) have as common threat an interest for better understanding the link between seeing, perceiving and acting in business network context. Among these papers we can include that of Ellis and Hopkinson ( 2010 ) who is the only one that focuses on the role of communication for managerial action. In their study they investigate how the activity of communicating is made sense of by network actors and conclude that the “discursive production of communication plays a role in structuring the world(s) of IFRs [inter-firms relationships] and establishes some of the network ‘facts’ into which managers act” (p. 421). Most of the other papers, focus their attention on mental models. In the paper by Welch and Wilkinson ( 2002 ), the attention is indeed directed to the concept of “ideas” as force behind actors’ action in networks that at the same time evolve through interactions. By combining the “ideological dimension” with the “relational dimension”, the authors’ attempt is to go beyond considering the mental model or “schema” at the company level, to take into account also how the schemas of two organizations become interrelated and adapted to each other over time in line with the ongoing relationship (“schema coupling”). In addition, they also refer to the “schema configuration” at the network level as “the pattern of co-adapted ideas characterising a network and which underlie its functioning” (Welch & Wilkinson, 2002 , p.33). This work, with its final suggestions on the need to take into account business network actors’ mental models, is in line with studies focusing on the idea of mental “pictures” as a basis for managerial action. The focus in these studies is to examine what mangers see of their network context and how this is related to what they do . Laari-Salmela et al. ( 2015 ) for instance modeled a situational mechanism of strategy formation according to which managers, by interpreting the change and forming and adjusting the network picture held, make sense of strategic issues arising at the network level and act or react accordingly. The authors make a further step in the reasoning, by suggesting that by making sense of their sensemaking process, managers could become more conscious about their engagement in the act of network visioning which is about seeing beyond the existing network pictures (Laari-Salmela et al., 2015 ). The idea of ‘looking beyond’ the existing puts the attention to the space dimension of the network pictures which is an issue addressed in the paper by Eriksson et al. ( 2021 ). The authors elaborate on the idea of ‘network horizon’, defined as “how extended one actor’s view of the network is” (Anderson et al., 1994 cited in Eriksson et al., 2021 , p. 1769), and illustrate the negative effect a myopic network horizon can have on bringing forward a change initiative (Eriksson et al., 2021 ). The authors emphasize the need for managers to be aware of how their network horizon overlaps, partly overlaps and does not overlap with other actors’ network horizon, in order to act upon what they perceive. This leads the attention to the issue of the variability in network pictures between individuals involved in the same relationship. Leek and Mason ( 2010 ), found differences in depth and width of network pictures depending on managerial levels and functions within the organization. While an overlap of network pictures is considered to be important, a lack of overlap could also be positively exploited, as it could provide important insights to managers such as helping them in identifying the need for a new communication channel (Leek & Mason, 2010 ). Despite its popularity, the concept of network picture has also attracted some critic for not taking into account the evolving nature of the network. To tackle this weakness and to go beyond the cartesian “picture theory”, Purchase et al. ( 2010 ) contrast the concept of network picture with that of ‘network movies’ to focus the attention on the making of pictures (cinematographic reality) more than the taking (photographic reality). The authors observe that while by adopting the latter perspective researchers aim for stability and order, the cinematographic metaphor “allows researchers to consider industrial networks as evolving complex adaptive systems” (Purchase et al., 2010 , p. 602). In a similar vein, Lowe ( 2022 ) advocates a post-Cartesian focus upon ideas/images and activities as “a dynamically evolving, inter-animating, complex duality, which promotes a practical turn towards polyvalent and situated, imaginative solutions to emergent contextual and often seemingly unmanageable problems and issues within business relationships” (p. 249).
3.2 Managing in business networks
Within the thematic group of papers on managing in business networks (see Table 2 ), we have identified two sub-themes: (1) capabilities, roles and behaviors required for managing (in) business networks and (2) the process of strategizing in business networks. Starting from the first sub-theme, the special issue by Golfetto, Salle, Borghini and Rinallo (2007), brings the attention to one issue, among some others, that has been regularly debate by IMP scholars, namely whether firms are able to ‘manage networks’ or rather can only ‘manage in networks’. Independently from the position taken on this matter (intentional business networks or strategic nets vs. emerging business networks), research seems to converge on the idea that some sort of capabilities are required in order to cope in a context of interconnected relationships. We find two articles in this group of papers that discuss the capabilities required by what has been identified as a ‘network coordinator’ or ‘network mobilizer’. Lemmetyinen and Go ( 2009 ) suggest that the ‘network coordinator’ requires different kind of capabilities such as network orchestration and visioning, and the capacity for joint knowledge creation, but also, towards the end of the life cycle, ‘strong partnering capability’. Also, Hermes and Mainela ( 2014 ), have attempted to be specific on the kind of capabilities and behaviors required in different situations. In their study on a network mobilization process for institutional change in a turbulent context, the authors identify three different behaviors of a ‘peace-building network mobilizers’: incentivizing, reticent and adaptational behaviors. First the authors find that actors become legitimized network mobilizers drawing on incentivizing behavior (offering free consultation and information services) to motivate actors to collaborate. Second, they find that actors in complex crisis situations do not mobilize networks for institutional change through direct, pro-active behavior, as suggested in previous studies, rather they reticently wait for the right moment to get involved. Third, the authors find that peace-building situations are always unique and require a large degree of flexibility and creativity by peace-building actors, which rules out the possibility of adopting long term strategies by network mobilizers who are instead in need of adaptive capabilities (Hermes & Mainela, 2014 ). The other papers of this group take a different perspective compared to the previous mentioned studies: more than focusing on the qualities/behaviors of a single actor and his/her actions, they espouse an interaction perspective on actors. Lowe et al. ( 2012 ), propose a dramaturgical approach to the understanding of business networks and Ramaswamy and Ozcan ( 2020 ) focus on the interactive agency of actors. The idea by Ramaswamy and Ozcan ( 2020 ) is to conceive the actor as an “interacted” actor connected to practices of managerial value creation in interactive platforms that bring together physical and digital artifacts and interfaces, and persons and processes in purpose-built environments. Also, the paper by Cheah ( 2019 ) focuses on how actors interact within a network and how it affects each other’s decision. In their analysis of a triadic interaction in the Malaysian housing market, involving a property developer, states and an NGO, the authors find that the NGO plays both supportive roles (as partner, advisor and mediator) and disruptive roles (as attacker, challenger and influencer) when interacting with the state and property developers (Cheah, 2019 ). Sfandla and Björk ( 2013 ), also take an interactive perspective by proposing a framework for tourism networks - the tourism experience network (TEN) - in which facilitators and tourists are seen as active co-creators of experiences in relational interactive processes. By linking the value as experience logic with the ARA model, the authors define actors as “experience facilitators” who act as connectors, integrators and facilitators in relational bonds processes to include tourists in the network (Sfandla & Björk, 2013 ).
The other set of papers dealing with the issue of managing in business network focuses specifically on the process of strategizing in business networks. The publication of two special issues in Industrial Marketing and Management journal, one in 2004 (Batt & Purchase, 2004 ) and one in 2016 (Freytag, Munksgaard, Clarke & Damgaard, 2016) is an indication of the importance of the topic as well as of the need to better scrutinize this phenomenon. Already in 2009, Harrison and Prenkert ( 2009 ), highlighted a scarcity of studies on how managers in an organization formally develop a strategy in a network context. The authors propose the concept of ‘network strategizing trajectories’ as a way to analyse how a team of strategists considers the effects of network connections while undertaking a planned process within a project setting. Building on the ARA model, the authors identify the actor network strategizing trajectory, the resource network strategizing trajectory and the activities network strategizing trajectory (Harrison & Prenkert, 2009 ). Also the study by Harrison et al. ( 2010 ), focuses on deliberate strategising initiatives putting the attention on how these might vary depending on types of external counterparts, and different periods of development/time: 1) strategising based on network pictures in the absence of direct interaction; 2) strategising in the presence of a network audience; 3) Strategising among deliberate equals; 4) strategising among imaginative equals, and 5) strategising as open and absorptive bystander. In line with other studies within this stream that try to be situational rather than overgeneralize, the paper by Mosch and colleagues ( 2022 ) examines the network roles operated by start ups in a digitalized business network and how they strategize within and across different network roles, identify four network roles -enabler, extender, transformer, and orchestrator- and three main strategizing trajectories: 1) moving to the center, 2) develop strong network ties, and 3) strengthening the current role (Mosch et al., 2022 ).
3.3 Connection of multiple/different networks
From the themes emerged from our sample of articles, the one on the connection of multiple/different networks (see Table 3 ) is characterized by being a recently addressed topic. Indeed, all the 6 papers have been published in the last five years. The papers deal with connection of public-private networks but also networks of object with network of actors and home network with foreign network.
Cheah’s study ( 2019 ) focuses on the link between public and private settings by examining the housing sector which is regulated by a public actor hosting organizations which serve both b2c and b2b customers. The organizations are clearly affected by the public actor in their strategizing process although the authors show that mutual adaptations between the public and private settings are required. The originality of the work lies in the observation that an issue-based net might emerge as a form of collaboration nurtured by the public actor with the goal of reaching a collective purpose – such as public housing initiatives. The concept of issue-based net is also used in the study by Proença et al. ( 2018 ) who adopt that idea to highlight how, in the case of a Portoguese city council, social services networks between public, nonprofit and private organizations have emerged. The peculiarity of the study (if compared to “traditional” studies in the IMP tradition that mainly focus on the emergence of informal, non-planned networks) is that it is focused on the emergence of formally established and ‘planned’ networks.
Also, the paper by Baraldi et al. ( 2022 ), focuses on the connection of public-private networks and, more specifically, on R&D networks in relation to the production of antibiotics. The authors show how the mechanism surrounding the management of the networks is affected, due to the objectives of the project, by the intended social impact of developing and distributing new antibiotics which is in turn affected by the complexity of the R&D networks where multiple and heterogenous actors are involved with different goals and expectations.
Lindkvist et al. ( 2023 ) explore the roles played by actors when a new technology emerges within public and private business network. Distinguishing between the developing setting and the implementing setting, the authors aim to shed light on transition from one network configuration to another. More specifically, the Authors elaborate on transition by analyzing actor’ roles with reference to the acceptance of them over the transition process between developing to implementing networks. Pardo et al. ( 2022 ) propose to consider a new type of network in relation to the Internet of Things. The authors suggest that the connection of Industrial internet of Things (IIoT) physical products creates a sort of network of things which adds to the business network. In the discussion the paper shows that a ‘system of things’ relates to a ‘system of actors’ through changes in connections and in value creation process which in turn affects the way networks can be managed (Pardo et al., 2022 ). The last type of connection between different networks identifiable in this set of papers is the one related to the re-shoring process as analyzed in the paper by Baraldi et al. ( 2018 ). Authors focus their attention to the manufacturing activities which are reshored and so re-embedded in the home country markets and show how the home country network effects guide the entire reshoring process. In other words, the reshoring decision is shaped by not only the business relationships the focal company is embedded in but also through the changes the relocation implies at the home network level.
3.4 Supply networks
A better understanding of the functioning of supply networks has emerged as a key theme and the seven papers discussed in this section (see Table 4 ) aim to provide a contribution in the research area at the intersection of supply chain management and industrial marketing and purchasing research traditions. Most of the papers (5/7 papers) deal with sustainability issues such as the one by Ryan et al. ( 2012 ) that investigates the role of interactions and network for developing sustainable organizations. From a theoretical perspective, the paper advances the understanding of changes – related to dyadic and network levels – for reaching a more comprehensive view about sustainable organizations. In this regard, a conceptual framework is presented which includes the system/network, issue-based or strategic nets, dyadic relationships and the network organization. This framework – based on a multi-actor logic and so against the single actor view – sheds light on how collaborations are fundamental for developing sustainable organizations, and it put an emphasis on the role of suppliers and supply network members when those organizations are emerging. Also, the paper by Frostenson and Prenkert ( 2015 ) aims to demonstrate that supply chains are relational and network-based structures. The work focuses on the risks of taking the focal company as the major and most important actor driving the adaptation of supply chain management to the current sustainability context and scenario.
The article by Meqdadi et al. ( 2017 ) addresses the problem of the ‘spreading of sustainable initiatives’ in supply networks. The Authors show how the coordination mechanisms and capabilities of organizing activities among heterogenous actors is central for spreading green initiatives along the supply network. In this vein, ‘spreading’ seems relating to the concepts of trust and power considered key for orchestrating the diffusion of sustainability. On a similar vein, Rezaei Vandchali et al. ( 2020 ) link the concept of SSCN to the one of relationship management strategies (RMS) to explain how firms should cope with sustainable issues. Their output in terms of theoretical contributions is represented by a network-based framework that leads to the development of 16 propositions aimed to guide companies to identify the sustainability practices and how to implement them. The last paper focusing on sustainability issues – (and the only one adopting a more quantitative methodological perspective) is the study carried out by Wiśniewska-Paluszak and Paluszak ( 2019 ). The authors analyze the concept of network relationships with reference to the agribusiness sector and suggest that ‘network objectives’ are key as they shape the business relationships. With reference to the suppliers and the business relationships of focal firms with them, the Authors point out that the specificities of the agribusiness networks result in the creation of not very long in time supplier relationships. The study shows clearly a big variety of the supplier relationships within agribusiness.
The two remaining articles look at supply networks but from a more traditional (according to the IMP research tradition) perspective. Roseira et al. ( 2010 ) study the supplier networks by focusing on interdependencies which emerge while companies interact. Interdependencies are the unit of analysis in this paper: they are investigated in order to verify what are the effects of them within the supplier networks. For instance, kind of special outsourcing groups are created in which a number of actors get specialized in performing industrial products. Finally, the last paper in this group, by Veludo et al. (2004), shows that partnering and business relationships are key for connecting different research traditions such as IMP, buyer-seller literature and multinational corporation (MNC) literature. The authors utilize the automotive industry as context. In this paper the importance of the network effects is taken into consideration for developing further the MNC literature. The collaborations and their importance between carmakers and suppliers are highlighted as being rather complex due to the potential divergent scopes of the involved parties: these contrasts seem also to increase as consequence of the internationalization of the supply networks.
3.5 Networks structures and dynamics
Network structure and dynamics has been addressed in the IMP literature by considering different subtopics (network structure, networking), perspectives (time, space) and methodological approaches (moving beyond the traditional focus on case research). A central theme is that of the coexistence of stability and change, already highlighted by Håkansson and Snehota ( 1995 ), but dynamics is also related to other themes that may be examined over time or emerge with respect to specific contingencies. However, the heterogeneity of themes and perspectives in the IMP literature generally builds around a significant grip on the underlying themes, helping to build the richness of the IMP approach. Let us look at the identified contributions (see Table 5 ) that testify to this diversity and coherence.To start with an IMP’s core theme - that of stability and change - we can mention the paper by Bondeli and Havenvid ( 2022 ) which puts emphasis on the phenomenon of resilience as the capacity of a firm to survive, adapt and grow in the face of turbulent change, by continuously preparing for and rebounding from setbacks (Hamel & Välikangas, 2003 ; Pettit et al., 2010 ). The authors suggest that a firm’s ability to ‘bounce back’ is dependent on its ability to manage interdependencies with other firms in the network which implies that a firm’s resilience is a function of its relationships. Furthermore, it is suggested that to achieve resilience in a turbulent and uncertain environment, such as described in the paper, firms invest in the development of social capital with business and non-business actors rather than in the development of material resource interfaces (as often underlined in IMP-related studies). Also, the paper by Sutton-Brady ( 2008 ) is focused on the link stability-change in business networks but more than conceiving them as two separate states in the evolution of a network, Sutton-Brady ( 2008 ) stresses their co-existence. The author’s study, based on the analysis of Australian wine industry organizations, identifies and proposes other variables than time (a proxy variable for stability) that may influence the stability of business relationships which includes location, product/service quality, technology, cooperativeness, adaptations and cost. The position of Benson-Rea and Wilson ( 2003 ) on the stability-change problem is different as the authors contest to the IMP approach to adopt a static view of change and suggest taking account of the more dynamic case of network revolution that is the ability to fundamentally change the network focus. Juxtaposing the IMP perspective with the entrepreneurial perspective, Benson-Rea and Wilson ( 2003 ) present a conceptual framework relating evolutionary/emergent and revolutionary/intended networks to learning processes. The question on the emergent vs. intentional nature of business networks has attracted the attention of several scholars. The paper by Matthyssens et al. ( 2013 ) proposes the adoption of a methodological approach of “critical realism” and grapples with an open debate about the nature of business network dynamics. The paper holds together methodological-epistemological aspects and boundary conditions in the IMP debate to either view business network dynamics as an emergent collective phenomenon or as an intentional phenomenon that results from the will of individual actors. From a more empirical point of view, Degbey and Pelto ( 2013 ) have focused on the question of what triggers change and put the attention on the effect of country mergers and acquisitions (M&A) on both incremental and radical network changes. The analysis of their findings shows how changes triggered by an M&A do not only concern the relationship between the merging parties but may spread into connected relationships generating a more extensive network effect. Research in this area has also put the attention on the reconfiguration of business networks resulting from the appearance of new and the disappearance of old actors, resources or activities (Fonfara et al. 2018 ). The paper by Naudé, Zaefarian, Tavani, Neghabi and Zaefarian ( 2014 ), instead of focusing on the effects of network structure and external networking behaviors, examines the antecedents of these two constructs proposing to consider emotional intelligence and entrepreneurial style as key variables. The authors found support to the relationship between emotional intelligence and the two constructs while did not find support to the relationship between entrepreneurial style and external networking. Drawing on the results of the study, the authors conclude that emotional intelligence of CEOs may help them in acquiring a better position in the network as they have better chances to span structural holes and move to a central position in their network.
The topic of time and change is also addressed in the article by Lowe and Rod ( 2018 ) which examines different philosophical and cultural perspectives. The authors distinguish objective (clock time) and subjective dimensions (time marked by events experienced by actors) and examine different concepts of time in different cultures (circular, linear). The paper states that a ‘becoming’ network is an unfolding emergence and therefore this requires researchers to explore “how different contextual conceptions of time in different locales affects different outcomes in terms of uniqueness in behavior, communication and cognition” (Lowe & Rod, 2018 , p. 162). Continuing the debate on change, we find also the study by Brennan ( 2006 ) which examines the relationship between business network research and evolutionary economics research. Brennan ( 2006 ) focuses particularly on the classic and influential contribution of Nelson and Winter ( 1982 ), recognizing some correspondences or parallelisms between evolutionary economics research and the market-as-network approach developed in IMP research. The author hypothesizes advantages that could result from an integration of the two approaches. For the IMP tradition related to market-as-network these advantages would include the study of the dynamics of change, while for evolutionary economics there would be advantages from an extension of the study to interorganizational routines as well as those within synchronic organizations (Brennan, 2006 ).
Networks evolution has been also examined by Guercini and Runfola ( 2012 ) who, by conducting an empirical research on firms producing semi-finished textiles and their long-standing relationships with customers, found two patterns of business network dynamics induced by interaction evolution, which are called “integration” and “substitution.” The four cases examine different circumstances that characterize the evolution of the textile semi-finished product supplier’s interaction with the customer. The analysis of the cases shows how the interactions pose challenges to the relationship which leads two possible consequences: a greater integration into existing relationships in the business network, or a replacement of some relationships with new ones.
The topic of network dynamics and, in particular, network emergence is also discussed by Ramos et al. ( 2013 ) along the following lines: (1) the reasons why networks are formed, that is, why actors need to interact with other actors; (2) how partners are chosen; and (3) how environmental conditions influence the process of network formation. Drawing on the empirical findings, the authors’ conclusion is that there is no one single theory having the power to explain the process of network emergence; instead, a diverse combination of different theories has a good explanatory power at different stages of the process.
While most of the papers in this section deal with the time dimension in relation to business networks, the paper by Törnroos et al. ( 2017 ), exactly acknowledging the prominence of the theme of time in the study of business networks in the IMP literature, highlights a lack of studies on the role of spatial structures in which processes and experiences, as well as mind maps and managerial mindsets, take place. According to the authors the concept of space in research seems to be used in a very broad way, to the point that the theme of space is associated to general concepts such as that of “network structure” or “location”. To fill this gap, the authors propose four dimensions in relation to space for business network research: (1) a structural network dimension; (2) a mental network dimension; (3) a relative network dimension; and (4) a relational dimension. Three notions of space for business network research are then developed: (1) place, (2) location, and (3) distance.
Finally, the last paper in this group, by Andersen et al. ( 2020 ) looks at business network through the tool of metaphor. The authors propose to reevaluate the interaction and process theme in the context of industrial networks by considering different approaches and, in particular, the realist and the constructivist (basically of the social constructivism type) approaches. The contribution appears partly ontological but mainly epistemological to the study of business networks, providing some implications from the discussion of conceptual categories with regard to the study of longitudinal processes of organizations, temporality in processes, and the need to consider different perspectives to better understand interaction in business networks.
4 Conclusions and directions for further research
The aim of our study was to get an overview of the research on business networks produced by researchers belonging to the IMP research community in the last two decades and to use the performed analysis as source of inspiration to generate possible future lines of research which we detail in the following paragraphs. We acknowledge that the reported literature review, although systematic, is not exhaustive as we may have excluded relevant papers on the subject due to the absence in the abstracts of the papers of key words we employed as shortcut to identify research on business networks with an explicit link to the IMP. However, we do not pretend with this paper to provide a comprehensive research agenda on business networks, but rather, we would like to contribute to stimulate the debate on this long-lasting stream of research which continue to appear central also considering the undergoing and impactful economic, environmental and social changes. We thus suggest three lines for future research which revolve around the five sub-themes and insights coming from the underlying studies. The first line of research follows up from the theme of sensemaking, the second line of research comes from intersecting three of the themes identified – managing in business networks, connection of multiple/different networks and supply networks – while the last and third line of research we propose is related to the last theme identified which is network structures and dynamics. Looking at the three research areas it is also possible to envision research that spans across the three lines of research identified as shown in Fig. 1 .
Future lines of research on business networks from an IMP perspective
In relation to the theme of sensemaking, we think that there is plenty of research opportunities starting from concepts identified in the literature and not yet fully exploited. Ideas such as ‘network movies’ (vs. network pictures) and ‘network visioning’ testify the need of looking at business networks with strong processual lenses but also having a forward-looking perspective. From the time perspective, this implies for researchers to account for current sensemaking (usually done retrospectively), but also to make efforts in investigating what’s that managers see as impacting the relevant network in the near future, and how they think they will act upon what they perceive it will be. The challenge for researchers is to produce both theoretical frameworks and managerial tools that really reflect this dynamic and forward-looking perspective. The increasing complexity and uncertainty characterizing markets in the last years (Bocconcelli et al., 2018 ), directs the attention on how managers can be ready to face disruption; by comparing managers’ intentions (forward looking perspective) with subsequent behaviors (reconstructed via sensemaking approach), and by tracking outcomes, might be a way to identify/examine more or less effective patterns. This might also help scrutinizing better the traits/characteristics of individual actors (on which there has been limited attention in IMP-related studies) as well as concepts like resilience which has become very popular but appears often as black-boxed. Also, the ability to see and act in a more extensive network base, also due to an increasing number of actors to relate with (often institutional) and employment of non-human actors in b2b context (Paschen et al., 2021 ), draws the attention on how managers may come (or need to) to question more often their own existing network pictures and perceived network horizons in order to prefigure new/unexpected network configurations. Follow up research questions might be: how do managers get prepared for disruptive events in business networks? what is the role of non-human actors in human actors’ sensemaking process in business network?
A second line of research we believe is still relevant exploring and that we link to the second, third and fourth theme emerged in our literature review, is the one on managing in and across networks. Distancing itself from the conventional view on managerial processes, the IMP suggests that, to the sake of the network itself (its effectiveness and innovativeness), the network should not be controlled; rather, at the core of management in the business landscape there is the networking process (Håkansson et al., 1995 ). Following this seminal line of thought, we have seen, through our literature review, that concepts like ‘network orchestration’ and ‘network mobilization’ have received increasing attention. Again, starting from two key dimensions for the IMP approach – time and space – we see some opportunities for research. From one side, focusing on the space dimension, we see room for research into zooming into the combination of orchestrating mechanisms a company can put in place to manage the multiplicity of relationships it is engaged with. Indeed, concepts like ‘orchestration’ and ‘mobilization’ are often treated as unified mechanisms (toward a network) while there are hints (for instance implied in the concept of ‘trajectories’) that more mechanisms can be used in parallel depending on the specific network (part of a network or sub-network) at hand. Furthermore, the variety of different business and non-business actors, human and non-human actors, as well as the entrance of new actors coming into play due to major transformations brought by the digital transformation and the transition towards sustainable development, might lead to adaptations/modifications to these mechanisms overtime. Furthermore, interactions among actors ‘belonging’ to different networks inevitably increase the possibility of having to cope with contrasting views which poses the attention on topics such as communication and conflict management. This is particular evident in relation to supply networks, especially global, which generally involve actors belonging to different sectors and thus often following different logics. We have seen how supply chain crisis, like the one generated by Covid-19, has led to the re-shaping of global supply networks which make this empirical context particular interest to study changes in orchestration mechanisms. Research on the variety and variability of orchestration/mobilizations mechanisms employed by the same company in and across networks, and over time, is still scant and we thus propose this as a research area for further research on business networks.
The third line of research we propose, and that we see as an overall reflection on the future of research on business networks, is anchored to the last theme discussed in our literature review, network structures and dynamics. The reading of networks proposed by the IMP group is recognizable from that proposed by other scholarly communities in the field of management and more generally in scholarly research in recent decades (strategic networks, social networks, etc.). Indeed, in recent decades the network has been the subject of reading in different disciplinary contexts and with different approaches, from organization to sociology and more generally in the social sciences, from Internet reality to complex systems theory (Barabási, 2013 ). We think that future research comparing these different perspectives to networks, and the peculiar contribution of the IMP approach in comparing these approaches, may be useful for research on approaching markets as networks. IMP research approaches business networks in a context in which the study of interaction and relationships is present. In particular, the study of interaction (La Rocca & Hoholm & Mørk, 2017 ) tends to favor a view of network dynamics as (micro) grounded in the dynamics of interactions in them such as “learning” and “teaching” in interaction (Guercini & Runfola, 2015 ) or interactive decision making (Guercini et al., 2022 ). We believe that the IMP approach to networks candidates it to effectively interpret new contexts in which network actors are emerging from the advancing technological environment such as networks of things or networks with artificial intelligence agents.
5 Appendix A. Papers that deal with concepts/phenomena other than business networks but adopting a business network (IMP) perspective
6 appendix b. overview of the 45 reviewed articles.
Abrahamsen, M., Havenvid, I. M., & La Rocca, A. (2017). Researching the Interactive Business Landscape. In H. Håkansson and I. Snehota (Eds.), No Business is an Island: Making Sense of the Interactive Business World. (pp. 253–273), Emerald.
Andersen, P. H., Medlin, C. J., & Törnroos, J. Å. (2020). Re-appraising interaction and process for industrial network research: The future plunging mirror hall metaphor. Industrial Marketing Management , 91 , 627–638.
Article Google Scholar
Anderson, J. C., Håkansson, H., & Johanson, J. (1994). Dyadic Business relationships within a Business Network Context. Journal of Marketing , 58 (4), 1–15.
Anderson, H., Havila, V., Andersen, P., & Halinen, A. (1998). Position and role-conceptualizing dynamics in business networks. Scandinavian Journal of Management , 14 (3), 167–186.
Aramo-Immonen, H., Carlborg, P., Hasche, N., Jussila, J., Kask, J., Linton, G., & berg, C. (2020). Charting the reach and contribution of IMP literature in other disciplines: A bibliometric analysis. Industrial Marketing Management , 87 , 47–62.
Barabási, A-L. (2013). Network science. Phil Trans R Soc A , 371 , 20120375. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2012.0375 .
Baraldi, E., Ciabuschi, F., Lindahl, O., & Fratocchi, L. (2018). A network perspective on the reshoring process: The relevance of the home- and the host-country contexts. Industrial Marketing Management , 70 , 156–166.
Baraldi, E., Ciabuschi, F., Kronlid, C., & Lindahl, O. (2022). Managing interorganizational interactions for social impact: A study of two antibiotics R&D networks. Journal of Business Research , 141 , 264–278.
Batt, P., & Purchase, S. (2004). Managing collaboration within networks and relationships. Industrial Marketing Management, 33 (3), 169–174.
Benson-Rea, M., & Wilson, H. I. M. (2003). Networks, learning and the lifecycle. European Management Journal , 21 (5), 588–597.
Bocconcelli, R., Cioppi, M., Fortezza, F., Francioni, B., Pagano, A., Savelli, E., & Splendiani, S. (2018). SMEs and marketing: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Management Reviews , 20 , 227–254.
Bondeli, J. V., & Havenvid, M. I. (2022). Bouncing back in turbulent business environments: Exploring resilience in business networks. Industrial Marketing Management , 107 , 383–395.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3 (2), 77–101.
Brennan, R. (2006). Evolutionary economics and the markets-as-networks approach. Industrial Marketing Management , 35 , 829–838.
Cheah, C. W. (2019). The social-political roles of NGOs: A study on a triadic business network. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing , 34 (5), 994–1004.
Cheah, C. W. (2021). Why firms exploit the dual marketing strategy? A network-institutional perspective. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing , 36/12 , 2150–2164.
De Lurdes Veludo, M., Macbeth, D. K., & Purchase, S. (2004). Partnering and relationships within an international network context. International Marketing Review , 21 (2), 142–157.
Degbey, W., & Pelto, E. (2013). Cross-border M&A as a trigger for network change in the Russian bakery industry. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing , 28/3 , 178–189.
Ellis, N., & Hopkinson, G. (2010). The construction of managerial knowledge in business networks: Managers’ theories about communication. Industrial Marketing Management , 39 , 413–424.
Eriksson, V., Hulthén, K., & Pedersen, A. C. (2021). Improving transport performance in supply networks: Effects of (non)overlapping network horizons. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing , 36/10 , 1767–1779.
Fonfara, K., Ratajczak-Mrozek, M., & Leszczyński, G. (2018). Change in business relationships and networks: Concepts and business reality. Industrial Marketing Management, 70 , 1–4.
Ford, D. (1980). The development of buyer-seller relationships in industrial markets. European Journal of Marketing , 14 (5/6), 339–353.
Ford, D., Gadde, L. E., Håkansson, H., & Snehota, I. (2003). Managing Business relationships . Wiley.
Frostenson, M., & Prenkert, F. (2015). Sustainable supply chain management when focal firms are complex: A network perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production , 107 , 85–94.
Guercini, S., & Runfola, A. (2012). Relational paths in business network dynamics: Evidence from the fashion industry. Industrial Marketing Management , 41 (5), 807–815.
Guercini, S., & Runfola, A. (2015). Actors’ roles in interaction and innovation in local systems: A conceptual taxonomy. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing , 30 (3/4), 269–278.
Guercini, S., La Rocca, A., & Snehota, I. (2022). Decisions when interacting in customer-supplier relationships. Industrial Marketing Management , 105 , 380–387.
Hadjikhani, A., & LaPlaca, P. (2013). Development of B2B marketing theory. Industrial Marketing Management , 42 (3), 294–305.
Håkansson, H. (Ed.). (1982). International marketing and purchasing of industrial goods. An interaction approach . Wiley.
Håkansson, H., & Gadde, L. E. (2018). Four decades of IMP research-the development of a research network. IMP Journal , 12 (1), 6–36.
Håkansson, H., & Johanson, J. (1992). A model of Industrial Networks. In Björn, Axelsson, & G. Easton (Eds.), Industrial Networks. A new view of reality . Routledge.
Håkansson, H., & Snehota, I. (1995). Developing relationships in Business networks . Routledge.
Håkansson, H., & Snehota, I. (Eds.). (2017). No business is an island: Making sense of the interactive business world . Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Håkansson, H., Ford, D., Gadde, L. E., Snehota, I., & Waluszewski, A. (2009). Business in networks . Wiley.
Hamel, G., & Välikangas, L. (2003). The quest for resilience. Harvard Business Review, 81 , 52–63.
Harrison, D., & Prenkert, F. (2009). Network strategising trajectories within a planned strategy process. Industrial Marketing Management , 38 , 662–670.
Harrison, D., Holmen, E., & Pedersen, A. C. (2010). How companies strategise deliberately in networks using strategic initiatives. Industrial Marketing Management , 39 (2), 947–955.
Hermes, J. W. S., & Mainela, T. (2014). Mobilizing crisis management networks - entrepreneurial behavior in turbulent contexts. Industrial Marketing Management , 43 (6), 967–976.
Hunt, S. D. (2013). A general theory of business marketing: RA theory, Alderson, the ISBM framework, and the IMP theoretical structure. Industrial Marketing Management , 42 (3), 283–293.
La Rocca, A., Hoholm, T., & Mørk, B. E. (2017). Practice theory and the study of interaction in business relationships - some methodological implications. Industrial Marketing Management , 60 , 187–195.
Laari-Salmela, S., Mainela, T., & Puhakka, V. (2015). Beyond network pictures: Situational strategizing in network context. Industrial Marketing Management , 45 , 117–127.
Leek, S., & Mason, K. (2010). The utilisation of network pictures to examine a company’s employees’ perceptions of a supplier relationship. Industrial Marketing Management , 39 , 400–412.
Lemmetyinen, A., & Go, F. M. (2009). The key capabilities required for managing tourism business networks. Tourism Management , 30 , 31–40.
Lindkvist, H., Lind, F., & Melander, L. (2023). Actor roles and public–private interaction in transitioning networks: The case of geofencing for urban freight transport in Sweden. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 38 (6), 1376–1389.
Lowe, S., & Rod, M. (2018). Business network becoming: Figurations of time, change and process. Industrial Marketing Management , 68 , 156–164.
Lowe, S. (2022). Relationships and networks as a chiasmic mirroring of ideas/images translated in context through ritual embodied activities. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing , 37/2 , 241–251.
Lowe, S., Purchase, S., & Ellis, N. (2012). The drama of interaction within business networks. Industrial Marketing Management, 41 (3), 421–428.
Matthyssens, P., Vandenbempt, K., & Van Bockhaven, W. (2013). Structural antecedents of institutional entrepreneurship in industrial networks: A critical realist explanation. Industrial Marketing Management , 42 (3), 405–420.
Mattsson, L-G. (1987). Management of strategic change in a `markets as networks perspective’. In A. Pettigrew (Ed.), Management of Strategic Change (pp. 234–256). Basil Blackwell.
Meqdadi, O., Johnsen, T. E., & Johnsen, R. E. (2017). The role of power and trust in spreading sustainability initiatives across supply networks: A case study in the bio-chemical industry. Industrial Marketing Management , 62 , 61–76.
Möller, K., & Halinen, A. (2018). IMP thinking and IMM: Co-creating value for business marketing. Industrial Marketing Management , 69 , 18–31.
Möller, K., & Halinen, A. (2022). Clearing the paradigmatic fog—how to move forward in business marketing research. Industrial Marketing Management , 102 , 280–300.
Mosch, P., Winkler, C., Eggert, C. G., Schumann, J. H., Obermaier, R., & Ulaga, W. (2022). Driving or driven by others? A dynamic perspective on how data-driven start-ups strategize across different network roles in digitalized business networks. Industrial Marketing Management , 102 , 381–402.
Naudé, P., Zaefarian, G., Najafi Tavani, Z., Neghabi, S., & Zaefarian, R. (2014). The influence of network effects on SME performance. Industrial Marketing Management , 43 (4), 630–641.
Nelson, R. R., & Winter, S. G. (1982). An evolutionary theory of economic change . Harvard University Press.
Palöatier, R. W., Houston, M. B., & Hulland, J. (2018). Review articles: Purpose, process, and structure. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science , 46 , 1–5.
Pardo, C., Wei, R., & Ivens, B. S. (2022). Integrating the business networks and internet of things perspectives: A system of systems (SoS) approach for industrial markets. Industrial Marketing Management , 104 , 258–275.
Paschen, J., Paschen, U., Pala, E., & Kietzman, J. (2021). Artificial intelligence (AI) and value co-creation in B2B sales: Activities, actors and resources. Australian Journal of Marketing , 29 (3), 243–225.
Pettit, T.J., Fiksel, J. & Croxton, K.L. (2010). Ensuring supply chain resilience: Development of a conceptual framework. Journal of Business Logistics , 31 , 1–21
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Bachrach, D. G., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2005). The influence of management journals in the 1980s and 1990s. Strategic Management Journal , 26 , 473–488.
Proença, T., Proença, J. F., & Costa, C. (2018). Enabling factors for developing a social services network. Service Industries Journal , 38 (5–6), 321–342.
Purchase, S., Lowe, S., & Ellis, N. (2010). From taking network pictures to making network pictures: A new metaphorical manifesto for industrial marketing research. Journal of Organizational Change Management , 23 (5), 595–615.
Ramaswamy, V., & Ozcan, K. (2020). The interacted actor in platformed networks: Theorizing practices of managerial experience value co-creation. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing , 35/7 , 1165–1178.
Ramos, C., Roseira, C., Brito, C., Henneberg, S. C., & Naudé, P. (2013). Business service networks and their process of emergence: The case of the Health Cluster Portugal. Industrial Marketing Management , 42 (6), 950–968.
Rezaei Vandchali, H., Cahoon, S., & Chen, S. L. (2020). Creating a sustainable supply Chain Network by adopting Relationship Management Strategies. Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing , 27 (2), 125–149.
Roseira, C., Brito, C., & Henneberg, S. C. (2010). Managing interdependencies in supplier networks. Industrial Marketing Management , 39 (6), 925–935.
Ryan, G. W., & Bernard, H. R. (2003). Techniques to identify themes. Field Methods , 15 (1), 85–109.
Ryan, A., Mitchell, I. K., & Daskou, S. (2012). An interaction and networks approach to developing sustainable organizations. Journal of Organizational Change Management , 25 (4), 578–594.
Sfandla, C., & Björk, P. (2013). Tourism experience network: Co-creation of experiences in interactive processes. International Journal of Tourism Research , 15 , 495–506.
Snyder, H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research , 104 , 333–339.
Sutton-Brady, C. (2008). As time goes by: Examining the paradox of stability and change in business networks. Journal of Business Research , 61 , 968–973.
Törnroos, J. Å., Halinen, A., & Medlin, C. J. (2017). Dimensions of space in business network research. Industrial Marketing Management , 61 , 10–19.
Tranfield, D., Denyer, D., & Smart, P. (2003). Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. British Journal of Management , 14 , 207–222.
Waluszewski, A., Snehota, I., & La Rocca, A. (2019). What remains to be discovered? Manifesto for researching the interactive business world. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing , 34 (1), 232–239.
Welch, C., & Wilkinson, I. (2002). Idea logics and Network Theory in Business Marketing. Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing , 9 (3), 27–48.
Wiśniewska-Paluszak, J. A., & Paluszak, G. T. (2019). The role of inter-organisational relations and networks in agribusiness: The case for the Polish fruit and vegetable industry. International Journal on Food System Dynamics , 24 (2), 1–30.
Google Scholar
Download references
Open access funding provided by Università Politecnica delle Marche within the CRUI-CARE Agreement.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Dipartimento di Scienze per l’Economia e l’Impresa, Università degli Studi di Firenze, Florence, Italy
Simone Guercini
Department of Management SEGESTA, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Milan, Italy
Antonella La Rocca
Department of Management, Università Politecnica delle Marche, Ancona, Italy
Andrea Perna
Department of Civil and Industrial Engineering, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Andrea Perna .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Guercini, S., Rocca, A.L. & Perna, A. The IMP research on business networks: a systematic literature review and research agenda. Ital. J. Mark. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43039-024-00096-5
Download citation
Received : 21 April 2023
Accepted : 11 May 2024
Published : 24 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s43039-024-00096-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Business networks
- Buyer-seller relationships
- Interdependencies
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 23 May 2024
Systematic literature review of real-world evidence for treatments in HR+/HER2- second-line LABC/mBC after first-line treatment with CDK4/6i
- Veronique Lambert ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6984-0038 1 ,
- Sarah Kane ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0006-9341-4836 2 na1 ,
- Belal Howidi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1166-7631 2 na1 ,
- Bao-Ngoc Nguyen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6026-2270 2 na1 ,
- David Chandiwana ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0002-3499-2565 3 ,
- Yan Wu ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0008-3348-9232 1 ,
- Michelle Edwards ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0001-4292-3140 3 &
- Imtiaz A. Samjoo ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1415-8055 2 na1
BMC Cancer volume 24 , Article number: 631 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) combined with endocrine therapy (ET) are currently recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines and the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) guidelines as the first-line (1 L) treatment for patients with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative, locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer (HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC). Although there are many treatment options, there is no clear standard of care for patients following 1 L CDK4/6i. Understanding the real-world effectiveness of subsequent therapies may help to identify an unmet need in this patient population. This systematic literature review qualitatively synthesized effectiveness and safety outcomes for treatments received in the real-world setting after 1 L CDK4/6i therapy in patients with HR+/ HER2- LABC/mBC.
MEDLINE®, Embase, and Cochrane were searched using the Ovid® platform for real-world evidence studies published between 2015 and 2022. Grey literature was searched to identify relevant conference abstracts published from 2019 to 2022. The review was conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines (PROSPERO registration: CRD42023383914). Data were qualitatively synthesized and weighted average median real-world progression-free survival (rwPFS) was calculated for NCCN/ESMO-recommended post-1 L CDK4/6i treatment regimens.
Twenty records (9 full-text articles and 11 conference abstracts) encompassing 18 unique studies met the eligibility criteria and reported outcomes for second-line (2 L) treatments after 1 L CDK4/6i; no studies reported disaggregated outcomes in the third-line setting or beyond. Sixteen studies included NCCN/ESMO guideline-recommended treatments with the majority evaluating endocrine-based therapy; five studies on single-agent ET, six studies on mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors (mTORi) ± ET, and three studies with a mix of ET and/or mTORi. Chemotherapy outcomes were reported in 11 studies. The most assessed outcome was median rwPFS; the weighted average median rwPFS was calculated as 3.9 months (3.3-6.0 months) for single-agent ET, 3.6 months (2.5–4.9 months) for mTORi ± ET, 3.7 months for a mix of ET and/or mTORi (3.0–4.0 months), and 6.1 months (3.7–9.7 months) for chemotherapy. Very few studies reported other effectiveness outcomes and only two studies reported safety outcomes. Most studies had heterogeneity in patient- and disease-related characteristics.
Conclusions
The real-world effectiveness of current 2 L treatments post-1 L CDK4/6i are suboptimal, highlighting an unmet need for this patient population.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is the most diagnosed form of cancer in women with an estimated 2.3 million new cases diagnosed worldwide each year [ 1 ]. BC is the second leading cause of cancer death, accounting for 685,000 deaths worldwide per year [ 2 ]. By 2040, the global burden associated with BC is expected to surpass three million new cases and one million deaths annually (due to population growth and aging) [ 3 ]. Numerous factors contribute to global disparities in BC-related mortality rates, including delayed diagnosis, resulting in a high number of BC cases that have progressed to locally advanced BC (LABC) or metastatic BC (mBC) [ 4 , 5 , 6 ]. In the United States (US), the five-year survival rate for patients who progress to mBC is three times lower (31%) than the overall five-year survival rate for all stages (91%) [ 6 , 7 ].
Hormone receptor (HR) positive (i.e., estrogen receptor and/or progesterone receptor positive) coupled with negative human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2) expression is the most common subtype of BC, accounting for ∼ 60–70% of all BC cases [ 8 , 9 ]. Historically, endocrine therapy (ET) through estrogen receptor modulation and/or estrogen deprivation has been the standard of care for first-line (1 L) treatment of HR-positive/HER2-negative (HR+/HER2-) mBC [ 10 ]. However, with the approval of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor (CDK4/6i) palbociclib in combination with the aromatase inhibitor (AI) letrozole in 2015 by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), 1 L treatment practice patterns have evolved such that CDK4/6i (either in combination with AIs or with fulvestrant) are currently considered the standard of care [ 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Other CDK4/6i (ribociclib and abemaciclib) in combination with ET are approved for the treatment of HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC; 1 L use of ribociclib in combination with an AI was granted FDA approval in March 2017 for postmenopausal women (with expanded approval in July 2018 for pre/perimenopausal women and for use in 1 L with fulvestrant for patients with disease progression on ET as well as for postmenopausal women), and abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant was granted FDA approval in September 2017 for patients with disease progression following ET and as monotherapy in cases where disease progression occurs following ET and prior chemotherapy in mBC (with expanded approval in February 2018 for use in 1 L in combination with an AI for postmenopausal women) [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 ].
Clinical trials investigating the addition of CDK4/6i to ET have demonstrated significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) and significant (ribociclib) or numerical (palbociclib and abemaciclib) improvement in overall survival (OS) compared to ET alone in patients with HR+/HER2- advanced or mBC, making this combination treatment the recommended option in the 1 L setting [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ]. However, disease progression occurs in a significant portion of patients after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment [ 28 ] and the optimal treatment sequence after progression on CDK4/6i remains unclear [ 29 ]. At the time of this review (literature search conducted December 14, 2022), guidelines by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) recommend various options for the treatment of HR+/HER2- advanced BC in the second-line (2 L) setting, including fulvestrant monotherapy, mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors (mTORi; e.g., everolimus) ± ET, alpelisib + fulvestrant (if phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha mutation positive [PIK3CA-m+]), poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors (PARPi) including olaparib or talazoparib (if breast cancer gene/partner and localizer of BRCA2 positive [BRCA/PALB2m+]), and chemotherapy (in cases when a visceral crisis is present) [ 15 , 16 ]. CDK4/6i can also be used in 2 L [ 16 , 30 ]; however, limited data are available to support CDK4/6i rechallenge after its use in the 1 L setting [ 15 ]. Depending on treatments used in the 1 L and 2 L settings, treatment in the third-line setting is individualized based on the patient’s response to prior treatments, tumor load, duration of response, and patient preference [ 9 , 15 ]. Understanding subsequent treatments after 1 L CDK4/6i, and their associated effectiveness, is an important focus in BC research.
Treatment options for HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC continue to evolve, with ongoing research in both clinical trials and in the real-world setting. Real-world evidence (RWE) offers important insights into novel therapeutic regimens and the effectiveness of treatments for HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC. The effectiveness of the current treatment options following 1 L CDK4/6i therapy in the real-world setting highlights the unmet need in this patient population and may help to drive further research and drug development. In this study, we conducted a systematic literature review (SLR) to qualitatively summarize the effectiveness and safety of treatment regimens in the real-world setting after 1 L treatment with CDK4/6i in patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC.
Literature search
An SLR was performed in accordance with the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions [ 31 ] and reported in alignment with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Literature Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [ 32 ] to identify all RWE studies assessing the effectiveness and safety of treatments used for patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC following 1 L CDK4/6i therapy and received subsequent treatment in 2 L and beyond (2 L+). The Ovid® platform was used to search MEDLINE® (including Epub Ahead of Print and In-Process, In-Data-Review & Other Non-Indexed Citations), Ovid MEDLINE® Daily, Embase, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews by an experienced medical information specialist. The MEDLINE® search strategy was peer-reviewed independently by a senior medical information specialist before execution using the Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies (PRESS) checklist [ 33 ]. Searches were conducted on December 14, 2022. The review protocol was developed a priori and registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Review (PROSPERO; CRD42023383914) which outlined the population, intervention, comparator, outcome, and study design (PICOS) criteria and methodology used to conduct the review (Table 1 ).
Search strategies utilized a combination of controlled vocabulary (e.g., “HER2 Breast Cancer” or “HR Breast Cancer”) and keywords (e.g., “Retrospective studies”). Vocabulary and syntax were adjusted across databases. Published and validated filters were used to select for study design and were supplemented using additional medical subject headings (MeSH) terms and keywords to select for RWE and nonrandomized studies [ 34 ]. No language restrictions were included in the search strategy. Animal-only and opinion pieces were removed from the results. The search was limited to studies published between January 2015 and December 2022 to reflect the time at which FDA approval was granted for the first CDK4/6i agent (palbociclib) in combination with AI for the treatment of LABC/mBC [ 35 ]. Further search details are presented in Supplementary Material 1 .
Grey literature sources were also searched to identify relevant abstracts and posters published from January 2019 to December 2022 for prespecified relevant conferences including ESMO, San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research (ISPOR US), and the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR). A search of ClinicalTrials.gov was conducted to validate the findings from the database and grey literature searches.
Study selection, data extraction & weighted average calculation
Studies were screened for inclusion using DistillerSR Version 2.35 and 2.41 (DistillerSR Inc. 2021, Ottawa, Canada) by two independent reviewers based on the prespecified PICOS criteria (Table 1 ). A third reviewer was consulted to resolve any discrepancies during the screening process. Studies were included if they reported RWE on patients aged ≥ 18 years with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC who received 1 L CDK4/6i treatment and received subsequent treatment in 2 L+. Studies were excluded if they reported the results of clinical trials (i.e., non-RWE), were published in any language other than English, and/or were published prior to 2015 (or prior to 2019 for conference abstracts and posters). For studies that met the eligibility criteria, data relating to study design and methodology, details of interventions, patient eligibility criteria and baseline characteristics, and outcome measures such as efficacy, safety, tolerability, and patient-reported outcomes (PROs), were extracted (as available) using a Microsoft Excel®-based data extraction form (Microsoft Corporation, WA, USA). Data extraction was performed by a single reviewer and was confirmed by a second reviewer. Multiple publications identified for the same RWE study, patient population, and setting that reported data for the same intervention were linked and extracted as a single publication. Weighted average median real-world progression-free survival (rwPFS) values were calculated by considering the contribution to the median rwPFS of each study proportional to its respective sample size. These weighted values were then used to compute the overall median rwPFS estimate.
Quality assessment
The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for nonrandomized (cohort) studies was used to assess the risk of bias for published, full-text studies [ 36 ]. The NOS allocates a maximum of nine points for the least risk of bias across three domains: (1) Formation of study groups (four points), (2) Comparability between study groups (two points), (3) Outcome ascertainment (three points). NOS scores can be categorized in three groups: very high risk of bias (0 to 3 points), high risk of bias (4 to 6), and low risk of bias (7 to 9) [ 37 ]. Risk of bias assessment was performed by one reviewer and validated by a second independent reviewer to verify accuracy. Due to limited methodological data by which to assess study quality, risk of bias assessment was not performed on conference abstracts or posters. An amendment to the PROSPERO record (CRD42023383914) for this study was submitted in relation to the quality assessment method (specifying usage of the NOS).
The database search identified 3,377 records; after removal of duplicates, 2,759 were screened at the title and abstract stage of which 2,553 were excluded. Out of the 206 reports retrieved and assessed for eligibility, an additional 187 records were excluded after full-text review; most of these studies were excluded for having patients with mixed lines of CDK4/6i treatment (i.e., did not receive CDK4/6i exclusively in 1 L) (Fig. 1 and Table S1 ). The grey literature search identified 753 records which were assessed for eligibility; of which 752 were excluded mainly due to the population not meeting the eligibility criteria (Fig. 1 ). In total, the literature searches identified 20 records (9 published full-text articles and 11 conference abstracts/posters) representing 18 unique RWE studies that met the inclusion criteria. The NOS quality scores for the included full-text articles are provided in Table S2 . The scores ranged from four to six points (out of a total score of nine) and the median score was five, indicating that all the studies suffered from a high risk of bias [ 37 ].
Most studies were retrospective analyses of chart reviews or medical registries, and all studies were published between 2017 and 2022 (Table S3 ). Nearly half of the RWE studies (8 out of 18 studies) were conducted in the US [ 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 ], while the remaining studies included sites in Canada, China, Germany, Italy, Japan, and the United Kingdom [ 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ]. Sample sizes ranged from as few as 4 to as many as 839 patients across included studies, with patient age ranging from 26 to 86 years old.
Although treatment characteristics in the 1 L setting were not the focus of the present review, these details are captured in Table S3 . Briefly, several RWE studies reported 1 L CDK4/6i use in combination with ET (8 out of 18 studies) or as monotherapy (2 out of 18 studies) (Table S3 ). Treatments used in combination with 1 L CDK4/6i included letrozole, fulvestrant, exemestane, and anastrozole. Where reported (4 out of 18 studies), palbociclib was the most common 1 L CDK4/6i treatment. Many studies (8 out of 18 studies) did not report which specific CDK4/6i treatment(s) were used in 1 L or if its administration was in combination or monotherapy.
Characteristics of treatments after 1 L CDK4/6i therapy
Across all studies included in this review, effectiveness and safety data were only available for treatments administered in the 2 L setting after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment. No studies were identified that reported outcomes for patients treated in the third-line setting or beyond after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment. All 18 studies reported effectiveness outcomes in 2 L, with only two of these studies also describing 2 L safety outcomes. The distribution of outcomes reported in these studies is provided in Table S4 . Studies varied in their reporting of outcomes for 2 L treatments; some studies reported outcomes for a group of 2 L treatments while others described independent outcomes for specific 2 L treatments (i.e., everolimus, fulvestrant, or chemotherapy agents such as eribulin mesylate) [ 42 , 45 , 50 , 54 , 55 ]. Due to the heterogeneity in treatment classes reported in these studies, this data was categorized (as described below) to align with the guidelines provided by NCCN and ESMO [ 15 , 16 ]. The treatment class categorizations for the purpose of this review are: single-agent ET (patients who exclusively received a single-agent ET after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment), mTORi ± ET (patients who exclusively received an mTORi with or without ET after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment), mix of ET and/or mTORi (patients who may have received only ET, only mTORi, and/or both treatments but the studies in this group lacked sufficient information to categorize these patients in the “single-agent ET” or “mTOR ± ET” categories), and chemotherapy (patients who exclusively received chemotherapy after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment). Despite ESMO and NCCN guidelines indicating that limited evidence exists to support rechallenge with CDK4/6i after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment [ 15 , 16 ], two studies reported outcomes for this treatment approach. Data for such patients were categorized as “ CDK4/6i ± ET ” as it was unclear how many patients receiving CDK4/6i rechallenge received concurrent ET. All other patient groups that lacked sufficient information or did not report outcome/safety data independently (i.e., grouped patients with mixed treatments) to categorize as one of the treatment classes described above were grouped as “ other ”.
The majority of studies reported effectiveness outcomes for endocrine-based therapy after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment; five studies for single-agent ET, six studies for mTORi ± ET, and three studies for a mix of ET and/or mTORi (Fig. 2 ). Eleven studies reported effectiveness outcomes for chemotherapy after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment, and only two studies reported effectiveness outcomes for CDK4/6i rechallenge ± ET. Eight studies that described effectiveness outcomes were grouped into the “other” category. Safety data was only reported in two studies: one study evaluating the chemotherapy agent eribulin mesylate and one evaluating the mTORi everolimus.
Effectiveness outcomes
Real-world progression-free survival
Median rwPFS was described in 13 studies (Tables 2 and Table S5 ). Across the 13 studies, the median rwPFS ranged from 2.5 months [ 49 ] to 17.3 months [ 39 ]. Out of the 13 studies reporting median rwPFS, 10 studies reported median rwPFS for a 2 L treatment recommended by ESMO and NCCN guidelines, which ranged from 2.5 months [ 49 ] to 9.7 months [ 45 ].
Weighted average median rwPFS was calculated for 2 L treatments recommended by both ESMO and NCCN guidelines (Fig. 3 ). The weighted average median rwPFS for single-agent ET was 3.9 months ( n = 92 total patients) and was derived using data from two studies reporting median rwPFS values of 3.3 months ( n = 70) [ 38 ] and 6.0 months ( n = 22) [ 40 ]. For one study ( n = 7) that reported outcomes for single agent ET, median rwPFS was not reached during the follow-up period; as such, this study was excluded from the weighted average median rwPFS calculation [ 49 ].
The weighted average median rwPFS for mTORi ± ET was 3.6 months ( n = 128 total patients) and was derived based on data from 3 studies with median rwPFS ranging from 2.5 months ( n = 4) [ 49 ] to 4.9 months ( n = 25) [ 54 ] (Fig. 3 ). For patients who received a mix of ET and/or mTORi but could not be classified into the single-agent ET or mTORi ± ET treatment classes, the weighted average median rwPFS was calculated to be 3.7 months ( n = 17 total patients). This was calculated based on data from two studies reporting median rwPFS values of 3.0 months ( n = 5) [ 46 ] and 4.0 months ( n = 12) [ 49 ]. Notably, one study of patients receiving ET and/or everolimus reported a median rwPFS duration of 3.0 months; however, this study was excluded from the weighted average median rwPFS calculation for the ET and/or mTORi class as the sample size was not reported [ 53 ].
The weighted average median rwPFS for chemotherapy was 6.1 months ( n = 499 total patients), calculated using data from 7 studies reporting median rwPFS values ranging from 3.7 months ( n = 249) [ 38 ] to 9.7 months ( n = 121) [ 45 ] (Fig. 3 ). One study with a median rwPFS duration of 5.6 months was not included in the weighted average median rwPFS calculation as the study did not report the sample size [ 53 ]. A second study was excluded from the calculation since the reported median rwPFS was not reached during the study period ( n = 7) [ 41 ].
Although 2 L CDK4/6i ± ET rechallenge lacks sufficient information to support recommendation by ESMO and NCCN guidelines, the limited data currently available for this treatment have shown promising results. Briefly, two studies reported median rwPFS for CDK4/6i ± ET with values of 8.3 months ( n = 302) [ 38 ] and 17.3 months ( n = 165) (Table 2 ) [ 39 ]. The remaining median rwPFS studies reported data for patients classified as “Other” (Table S5 ). The “Other” category included median rwPFS outcomes from seven studies, and included a myriad of treatments (e.g., ET, mTOR + ET, chemotherapy, CDK4/6i + ET, alpelisib + fulvestrant, chidamide + ET) for which disaggregated median rwPFS values were not reported.
Overall survival
Median OS for 2 L treatment was reported in only three studies (Table 2 ) [ 38 , 42 , 43 ]. Across the three studies, the 2 L median OS ranged from 5.2 months ( n = 3) [ 43 ] to 35.7 months ( n = 302) [ 38 ]. Due to the lack of OS data in most of the studies, weighted averages could not be calculated. No median OS data was reported for the single-agent ET treatment class whereas two studies reported median OS for the mTORi ± ET treatment class, ranging from 5.2 months ( n = 3) [ 43 ] to 21.8 months ( n = 54) [ 42 ]. One study reported 2 L median OS of 24.8 months for a single patient treated with chemotherapy [ 43 ]. The median OS data in the CDK4/6i ± ET rechallenge group was 35.7 months ( n = 302) [ 38 ].
Patient mortality was reported in three studies [ 43 , 44 , 45 ]. No studies reported mortality for the single-agent ET treatment class and only one study reported this outcome for the mTORi ± ET treatment class, where 100% of patients died ( n = 3) as a result of rapid disease progression [ 43 ]. For the chemotherapy class, one study reported mortality for one patient receiving 2 L capecitabine [ 43 ]. An additional study reported eight deaths (21.7%) following 1 L CDK4/6i treatment; however, this study did not disclose the 2 L treatments administered to these patients [ 44 ].
Other clinical endpoints
The studies included limited information on additional clinical endpoints; two studies reported on time-to-discontinuation (TTD), two reported on duration of response (DOR), and one each on time-to-next-treatment (TTNT), time-to-progression (TTP), objective response rate (ORR), clinical benefit rate (CBR), and stable disease (Tables 2 and Table S5 ).
Safety, tolerability, and patient-reported outcomes
Safety and tolerability data were reported in two studies [ 40 , 45 ]. One study investigating 2 L administration of the chemotherapy agent eribulin mesylate reported 27 patients (22.3%) with neutropenia, 3 patients (2.5%) with febrile neutropenia, 10 patients (8.3%) with peripheral neuropathy, and 14 patients (11.6%) with diarrhea [ 45 ]. Of these, neutropenia of grade 3–4 severity occurred in 9 patients (33.3%) [ 45 ]. A total of 55 patients (45.5%) discontinued eribulin mesylate treatment; 1 patient (0.83%) discontinued treatment due to adverse events [ 45 ]. Another study reported that 5 out of the 22 patients receiving the mTORi everolimus combined with ET in 2 L (22.7%) discontinued treatment due to toxicity [ 40 ]. PROs were not reported in any of the studies included in the SLR.
The objective of this study was to summarize the existing RWE on the effectiveness and safety of therapies for patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment. We identified 18 unique studies reporting specifically on 2 L treatment regimens after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment. The weighted average median rwPFS for NCCN- and ESMO- guideline recommended 2 L treatments ranged from 3.6 to 3.9 months for ET-based treatments and was 6.1 months when including chemotherapy-based regimens. Treatment selection following 1 L CDK4/6i therapy remains challenging primarily due to the suboptimal effectiveness or significant toxicities (e.g., chemotherapy) associated with currently available options [ 56 ]. These results highlight that currently available 2 L treatments for patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC who have received 1 L CDK4/6i are suboptimal, as evidenced by the brief median rwPFS duration associated with ET-based treatments, or notable side effects and toxicity linked to chemotherapy. This conclusion is aligned with a recent review highlighting the limited effectiveness of treatment options for HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC patients post-CDK4/6i treatment [ 56 , 57 ]. Registrational trials which have also shed light on the short median PFS of 2–3 months achieved by ET (i.e., fulvestrant) after 1 L CDK4/6i therapy emphasize the need to develop improved treatment strategies aimed at prolonging the duration of effective ET-based treatment [ 56 ].
The results of this review reveal a paucity of additional real-world effectiveness and safety evidence after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment in HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC. OS and DOR were only reported in two studies while other clinical endpoints (i.e., TTD, TTNT, TTP, ORR, CBR, and stable disease) were only reported in one study each. Similarly, safety and tolerability data were only reported in two studies each, and PROs were not reported in any study. This hindered our ability to provide a comprehensive assessment of real-world treatment effectiveness and safety following 1 L CDK4/6i treatment. The limited evidence may be due to the relatively short period of time that has elapsed since CDK4/6i first received US FDA approval for 1 L treatment of HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC (2015) [ 35 ]. As such, almost half of our evidence was informed by conference abstracts. Similarly, no real-world studies were identified in our review that reported outcomes for treatments in the third- or later-lines of therapy after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment. The lack of data in this patient population highlights a significant gap which limits our understanding of the effectiveness and safety for patients receiving later lines of therapy. As more patients receive CDK4/6i therapy in the 1 L setting, the number of patients requiring subsequent lines of therapy will continue to grow. Addressing this data gap over time will be critical to improve outcomes for patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC following 1 L CDK4/6i therapy.
There are several strengths of this study, including adherence to the guidelines outlined in the Cochrane Handbook to ensure a standardized and reliable approach to the SLR [ 58 ] and reporting of the SLR following PRISMA guidelines to ensure transparency and reproducibility [ 59 ]. Furthermore, the inclusion of only RWE studies allowed us to assess the effectiveness of current standard of care treatments outside of a controlled environment and enabled us to identify an unmet need in this patient population.
This study had some notable limitations, including the lack of safety and additional effectiveness outcomes reported. In addition, the dearth of studies reporting PROs is a limitation, as PROs provide valuable insight into the patient experience and are an important aspect of assessing the impact of 2 L treatments on patients’ quality of life. The studies included in this review also lacked consistent reporting of clinical characteristics (e.g., menopausal status, sites of metastasis, prior surgery) making it challenging to draw comprehensive conclusions or comparisons based on these factors across the studies. Taken together, there exists an important gap in our understanding of the long-term management of patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC. Additionally, the effectiveness results reported in our evidence base were informed by small sample sizes; many of the included studies reported median rwPFS based on less than 30 patients [ 39 , 40 , 41 , 46 , 49 , 51 , 60 ], with two studies not reporting the sample size at all [ 47 , 53 ]. This may impact the generalizability and robustness of the results. Relatedly, the SLR database search was conducted in December 2022; as such, novel agents (e.g., elacestrant and capivasertib + fulvestrant) that have since received FDA approval for the treatment of HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC may impact current 2 L rwPFS outcomes [ 61 , 62 ]. Finally, relative to the number of peer-reviewed full-text articles, this SLR identified eight abstracts and one poster presentation, comprising half (50%) of the included unique studies. As conference abstracts are inherently limited by how much content that can be described due to word limit constraints, this likely had implications on the present synthesis whereby we identified a dearth of real-world effectiveness outcomes in patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC treated with 1 L CDK4/6i therapy.
Future research in this area should aim to address the limitations of the current literature and provide a more comprehensive understanding of optimal sequencing of effective and safe treatment for patients following 1 L CDK4/6i therapy. Specifically, future studies should strive to report robust data related to effectiveness, safety, and PROs for patients receiving 2 L treatment after 1 L CDK4/6i therapy. Future studies should also aim to understand the mechanism underlying CDK4/6i resistance. Addressing these gaps in knowledge may improve the long-term real-world management of patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC. A future update of this synthesis may serve to capture a wider breadth of full-text, peer-reviewed articles to gain a more robust understanding of the safety, effectiveness, and real-world treatment patterns for patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC. This SLR underscores the necessity for ongoing investigation and the development of innovative therapeutic approaches to address these gaps and improve patient outcomes.
This SLR qualitatively summarized the existing real-world effectiveness data for patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment. Results of this study highlight the limited available data and the suboptimal effectiveness of treatments employed in the 2 L setting and underscore the unmet need in this patient population. Additional studies reporting effectiveness and safety outcomes, in addition to PROs, for this patient population are necessary and should be the focus of future research.
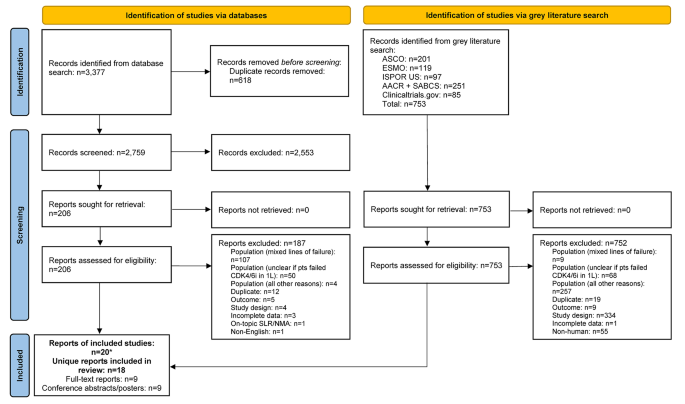
PRISMA flow diagram. *Two included conference abstracts reported the same information as already included full-text reports, hence both conference abstracts were not identified as unique. Abbreviations: 1 L = first-line; AACR = American Association of Cancer Research; ASCO = American Society of Clinical Oncology; CDK4/6i = cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor; ESMO = European Society for Medical Oncology; ISPOR = Professional Society for Health Economics and Outcomes Research; n = number of studies; NMA = network meta-analysis; pts = participants; SABCS = San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium; SLR = systematic literature review.
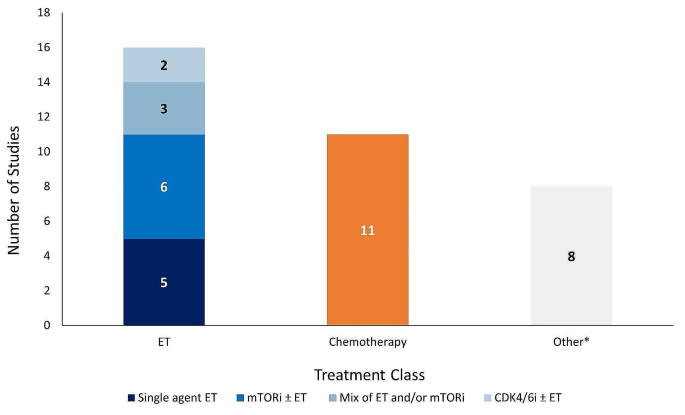
Number of studies reporting effectiveness outcomes exclusively for each treatment class. *Studies that lack sufficient information on effectiveness outcomes to classify based on the treatment classes outlined in the legend above. Abbreviations: CDK4/6i = cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor; ET = endocrine therapy; mTORi = mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor.
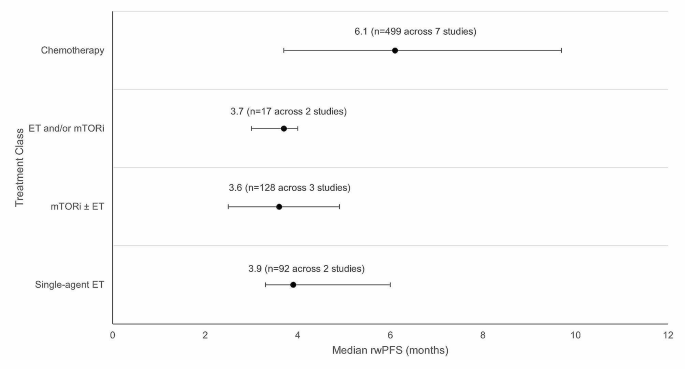
Weighted average median rwPFS for 2 L treatments (recommended in ESMO/NCCN guidelines) after 1 L CDK4/6i treatment. Circular dot represents weighted average median across studies. Horizontal bars represent the range of values reported in these studies. Abbreviations: CDK4/6i = cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor; ESMO = European Society for Medical Oncology; ET = endocrine therapy, mTORi = mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor; n = number of patients; NCCN = National Comprehensive Cancer Network; rwPFS = real-world progression-free survival.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files]. This study is registered with PROSPERO (CRD42023383914).
Abbreviations
Second-line
Second-line treatment setting and beyond
American Association of Cancer Research
Aromatase inhibitor
American Society of Clinical Oncology
- Breast cancer
breast cancer gene/partner and localizer of BRCA2 positive
Clinical benefit rate
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor
Complete response
Duration of response
European Society for Medical Oncology
Food and Drug Administration
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative
Hormone receptor
Hormone receptor positive
Professional Society for Health Economics and Outcomes Research
Locally advanced breast cancer
Metastatic breast cancer
Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online
Medical subject headings
Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor
National Comprehensive Cancer Network
Newcastle Ottawa Scale
Objective response rate
Poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitor
Progression-free survival
Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome, Study Design
Partial response
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Literature Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Patient-reported outcomes
- Real-world evidence
San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium
- Systematic literature review
Time-to-discontinuation
Time-to-next-treatment
Time-to-progression
United States
Łukasiewicz S, Czeczelewski M, Forma A, Baj J, Sitarz R, Stanisławek A, Breast, Cancer—Epidemiology. Risk factors, classification, prognostic markers, and current treatment Strategies—An. Updated Rev Cancers. 2021;13(17):4287.
Google Scholar
World Health Organization (WHO). Breast Cancer Facts Sheet [updated July 12 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer .
Arnold M, Morgan E, Rumgay H, Mafra A, Singh D, Laversanne M, et al. Current and future burden of breast cancer: global statistics for 2020 and 2040. Breast. 2022;66:15–23.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wilkinson L, Gathani T. Understanding breast cancer as a global health concern. Br J Radiol. 2022;95(1130):20211033.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Giaquinto AN, Sung H, Miller KD, Kramer JL, Newman LA, Minihan A et al. Breast Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2022;72(6):524– 41.
National Cancer Institute (NIH). Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer [updated 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html .
American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Breast Cancer [ https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/breast-cancer/about/how-common-is-breast-cancer.html .
Zagami P, Carey LA. Triple negative breast cancer: pitfalls and progress. npj Breast Cancer. 2022;8(1):95.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Matutino A, Joy AA, Brezden-Masley C, Chia S, Verma S. Hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer: redrawing the lines. Curr Oncol. 2018;25(Suppl 1):S131–41.
Lloyd MR, Wander SA, Hamilton E, Razavi P, Bardia A. Next-generation selective estrogen receptor degraders and other novel endocrine therapies for management of metastatic hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: current and emerging role. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022;14:17588359221113694.
Cardoso F, Senkus E, Costa A, Papadopoulos E, Aapro M, André F, et al. 4th ESO-ESMO International Consensus guidelines for advanced breast Cancer (ABC 4)†. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(8):1634–57.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
US Food Drug Administration. Palbociclib (Ibrance) 2017 [updated March 31, 2017. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/palbociclib-ibrance .
US Food Drug Administration. FDA expands ribociclib indication in HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer 2018 [updated July 18. 2018. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-expands-ribociclib-indication-hr-positive-her2-negative-advanced-or-metastatic-breast-cancer .
US Food Drug Administration. FDA approves abemaciclib for HR positive, HER2-negative breast cancer 2017 [updated Sept 28. 2017. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-abemaciclib-hr-positive-her2-negative-breast-cancer .
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®). Breast Cancer 2022 [ https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf .
Gennari A, André F, Barrios CH, Cortés J, de Azambuja E, DeMichele A, et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(12):1475–95.
Beaver JA, Amiri-Kordestani L, Charlab R, Chen W, Palmby T, Tilley A, et al. FDA approval: Palbociclib for the Treatment of Postmenopausal Patients with estrogen Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative metastatic breast Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(21):4760–6.
US Food Drug Administration. Ribociclib (Kisqali) [ https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/ribociclib-kisqali#:~:text=On%20March%2013%2C%202017%2C%20the,hormone%20receptor%20(HR)%2Dpositive%2C .
US Food Drug Administration. FDA approves new treatment for certain advanced or metastatic breast cancers [ https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-treatment-certain-advanced-or-metastatic-breast-cancers .
US Food Drug Administration. FDA expands ribociclib indication in HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer. 2018 [ https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-expands-ribociclib-indication-hr-positive-her2-negative-advanced-or-metastatic-breast-cancer .
US Food Drug Administration. FDA approves abemaciclib as initial therapy for HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer [ https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-abemaciclib-initial-therapy-hr-positive-her2-negative-metastatic-breast-cancer .
Turner NC, Slamon DJ, Ro J, Bondarenko I, Im S-A, Masuda N, et al. Overall survival with Palbociclib and fulvestrant in advanced breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(20):1926–36.
Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, Fasching PA, De Laurentiis M, Im SA, et al. Phase III randomized study of Ribociclib and Fulvestrant in hormone Receptor-Positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-Negative advanced breast Cancer: MONALEESA-3. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(24):2465–72.
Goetz MP, Toi M, Campone M, Sohn J, Paluch-Shimon S, Huober J, et al. MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(32):3638–46.
Gopalan PK, Villegas AG, Cao C, Pinder-Schenck M, Chiappori A, Hou W, et al. CDK4/6 inhibition stabilizes disease in patients with p16-null non-small cell lung cancer and is synergistic with mTOR inhibition. Oncotarget. 2018;9(100):37352–66.
Watt AC, Goel S. Cellular mechanisms underlying response and resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in the treatment of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2022;24(1):17.
Goetz M. MONARCH 3: final overall survival results of abemaciclib plus a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor as first-line therapy for HR+, HER2- advanced breast cancer. SABCS; 2023.
Munzone E, Pagan E, Bagnardi V, Montagna E, Cancello G, Dellapasqua S, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of post-progression outcomes in ER+/HER2– metastatic breast cancer after CDK4/6 inhibitors within randomized clinical trials. ESMO Open. 2021;6(6):100332.
Gennari A, André F, Barrios CH, Cortés J, de Azambuja E, DeMichele A, et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Annals of Oncology. 2021;32(12):1475-95.
European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO). ESMO Metastatic Breast Cancer Living Guideline: ER-positive HER2-negative Breast Cancer [updated May 2023. https://www.esmo.org/living-guidelines/esmo-metastatic-breast-cancer-living-guideline/er-positive-her2-negative-breast-cancer .
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Welch PM VA, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.2 (updated February 2021). www.training.cochrane.org/handbook : Cochrane; 2021.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021;18(3):e1003583.
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, Cogo E, Foerster V, Lefebvre C. PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 Guideline Statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;75:40–6.
Fraser C, Murray A, Burr J. Identifying observational studies of surgical interventions in MEDLINE and EMBASE. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006;6(1):41.
US Food Drug Administration. Palbociclib (Ibrance). Silver Spring, MD: US Food and Drug Administration; 2017.
Book Google Scholar
GA Wells BS, D O’Connell J, Peterson V, Welch M, Losos PT. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses [ https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp .
Lo CK-L, Mertz D, Loeb M. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: comparing reviewers’ to authors’ assessments. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14(1):45.
Martin JM, Handorf EA, Montero AJ, Goldstein LJ. Systemic therapies following progression on first-line CDK4/6-inhibitor treatment: analysis of real-world data. Oncologist. 2022;27(6):441–6.
Kalinsky KM, Kruse M, Smyth EN, Guimaraes CM, Gautam S, Nisbett AR et al. Abstract P1-18-37: Treatment patterns and outcomes associated with sequential and non-sequential use of CDK4 and 6i for HR+, HER2- MBC in the real world. Cancer Research. 2022;82(4_Supplement):P1-18-37-P1-18-37.
Choong GM, Liddell S, Ferre RAL, O’Sullivan CC, Ruddy KJ, Haddad TC, et al. Clinical management of metastatic hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer (MBC) after CDK 4/6 inhibitors: a retrospective single-institution study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022;196(1):229–37.
Xi J, Oza A, Thomas S, Ademuyiwa F, Weilbaecher K, Suresh R, et al. Retrospective Analysis of Treatment Patterns and effectiveness of Palbociclib and subsequent regimens in metastatic breast Cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019;17(2):141–7.
Rozenblit M, Mun S, Soulos P, Adelson K, Pusztai L, Mougalian S. Patterns of treatment with everolimus exemestane in hormone receptor-positive HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer in the era of targeted therapy. Breast Cancer Res. 2021;23(1):14.
Bashour SI, Doostan I, Keyomarsi K, Valero V, Ueno NT, Brown PH, et al. Rapid breast Cancer Disease Progression following cyclin dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitor discontinuation. J Cancer. 2017;8(11):2004–9.
Giridhar KV, Choong GM, Leon-Ferre R, O’Sullivan CC, Ruddy K, Haddad T, et al. Abstract P6-18-09: clinical management of metastatic breast cancer (MBC) after CDK 4/6 inhibitors: a retrospective single-institution study. Cancer Res. 2019;79:P6–18.
Article Google Scholar
Mougalian SS, Feinberg BA, Wang E, Alexis K, Chatterjee D, Knoth RL, et al. Observational study of clinical outcomes of eribulin mesylate in metastatic breast cancer after cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor therapy. Future Oncol. 2019;15(34):3935–44.
Moscetti LML, Riggi L, Sperduti I, Piacentini FOC, Toss A, Barbieri E, Cortesi L, Canino FMA, Zoppoli G, Frassoldati A, Schirone A, Dominici MECF. SEQUENCE OF TREATMENTS AFTER CDK4/6 THERAPY IN ADVANCED BREAST CANCER (ABC), A GOIRC MULTICENTER RETRO/ PROSPECTIVE STUDY. PRELIMINARY RESULTS IN THE RETROSPECTIVE SERIES OF 116 PATIENTS. Tumori. 2022;108(4S):80.
Menichetti AZE, Giorgi CA, Bottosso M, Leporati R, Giarratano T, Barbieri C, Ligorio F, Mioranza E, Miglietta F, Lobefaro R, Faggioni G, Falci C, Vernaci G, Di Liso E, Girardi F, Griguolo G, Vernieri C, Guarneri V, Dieci MV. CDK 4/6 INHIBITORS FOR METASTATIC BREAST CANCER: A MULTICENTER REALWORLD STUDY. Tumori. 2022;108(4S):70.
Marschner NW, Harbeck N, Thill M, Stickeler E, Zaiss M, Nusch A, et al. 232P Second-line therapies of patients with early progression under CDK4/6-inhibitor in first-line– data from the registry platform OPAL. Annals of Oncology. 2022;33:S643-S4
Gousis C, Lowe KMH, Kapiris M. V. Angelis. Beyond First Line CDK4/6 Inhibitors (CDK4/6i) and Aromatase Inhibitors (AI) in Patients with Oestrogen Receptor Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer (ERD MBC): The Guy’s Cancer Centre Experience. Clinical Oncology2022. p. e178.
Endo Y, Yoshimura A, Sawaki M, Hattori M, Kotani H, Kataoka A, et al. Time to chemotherapy for patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast Cancer and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitor use. J Breast Cancer. 2022;25(4):296–306.
Li Y, Li W, Gong C, Zheng Y, Ouyang Q, Xie N, et al. A multicenter analysis of treatment patterns and clinical outcomes of subsequent therapies after progression on palbociclib in HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2021;13:17588359211022890.
Amaro CP, Batra A, Lupichuk S. First-line treatment with a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor plus an aromatase inhibitor for metastatic breast Cancer in Alberta. Curr Oncol. 2021;28(3):2270–80.
Crocetti SPM, Tassone L, Marcantognini G, Bastianelli L, Della Mora A, Merloni F, Cantini L, Scortichini L, Agostinelli V, Ballatore Z, Savini A, Maccaroni E. Berardi R. What is the best therapeutic sequence for ER-Positive/HER2- Negative metastatic breast cancer in the era of CDK4/6 inhibitors? A single center experience. Tumori. 2020;106(2S).
Nichetti F, Marra A, Giorgi CA, Randon G, Scagnoli S, De Angelis C, et al. 337P Efficacy of everolimus plus exemestane in CDK 4/6 inhibitors-pretreated or naïve HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer patients: A secondary analysis of the EVERMET study. Annals of Oncology. 2020;31:S382
Luhn P, O’Hear C, Ton T, Sanglier T, Hsieh A, Oliveri D, et al. Abstract P4-13-08: time to treatment discontinuation of second-line fulvestrant monotherapy for HR+/HER2– metastatic breast cancer in the real-world setting. Cancer Res. 2019;79(4Supplement):P4–13.
Mittal A, Molto Valiente C, Tamimi F, Schlam I, Sammons S, Tolaney SM et al. Filling the gap after CDK4/6 inhibitors: Novel Endocrine and Biologic Treatment options for metastatic hormone receptor positive breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(7).
Ashai N, Swain SM. Post-CDK 4/6 inhibitor therapy: current agents and novel targets. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(6).
Higgins JPTTJ, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). www.training.cochrane.org/handbook : Cochrane; 2022.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Serdar CC, Cihan M, Yücel D, Serdar MA. Sample size, power and effect size revisited: simplified and practical approaches in pre-clinical, clinical and laboratory studies. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2021;31(1):010502.
US Food Drug Administration. FDA approves elacestrant for ER-positive, HER2-negative, ESR1-mutated advanced or metastatic breast cancer [updated January 27 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-elacestrant-er-positive-her2-negative-esr1-mutated-advanced-or-metastatic-breast-cancer .
US Food Drug Administration. FDA approves capivasertib with fulvestrant for breast cancer [updated November 16 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-capivasertib-fulvestrant-breast-cancer .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Joanna Bielecki who developed, conducted, and documented the database searches.
This study was funded by Pfizer Inc. (New York, NY, USA) and Arvinas (New Haven, CT, USA).
Author information
Sarah Kane, Belal Howidi, Bao-Ngoc Nguyen and Imtiaz A. Samjoo contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Pfizer, 10017, New York, NY, USA
Veronique Lambert & Yan Wu
EVERSANA, Burlington, ON, Canada
Sarah Kane, Belal Howidi, Bao-Ngoc Nguyen & Imtiaz A. Samjoo
Arvinas, 06511, New Haven, CT, USA
David Chandiwana & Michelle Edwards
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
VL, IAS, SK, BH, BN, DC, YW, and ME participated in the conception and design of the study. IAS, SK, BH and BN contributed to the literature review, data collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data. VL, IAS, SK, BH, BN, DC, YW, and ME contributed to the interpretation of the data and critically reviewed for the importance of intellectual content for the work. VL, IAS, SK, BH, BN, DC, YW, and ME were responsible for drafting or reviewing the manuscript and for providing final approval. VL, IAS, SK, BH, BN, DC, YW, and ME meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Imtiaz A. Samjoo .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors of this manuscript declare that the research presented was funded by Pfizer Inc. and Arvinas. While the support from Pfizer Inc. and Arvinas was instrumental in facilitating this research, the authors affirm that their interpretation of the data and the content of this manuscript were conducted independently and without bias to maintain the transparency and integrity of the research. IAS, SK, BH, and BN are employees of EVERSANA, Canada, which was a paid consultant to Pfizer in connection with the development of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Lambert, V., Kane, S., Howidi, B. et al. Systematic literature review of real-world evidence for treatments in HR+/HER2- second-line LABC/mBC after first-line treatment with CDK4/6i. BMC Cancer 24 , 631 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-024-12269-8
Download citation
Received : 26 January 2024
Accepted : 16 April 2024
Published : 23 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-024-12269-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- First-line CDK4/6i
ISSN: 1471-2407
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
All Business Strategies Fall into 4 Categories
- Jerome Barthelemy

Some are more creative than others.
The problem with strategy frameworks is that although they can help you determine whether an opportunity is attractive or whether a given strategy is likely to work, they generally don’t help you in the task of identifying the opportunity or crafting the strategy in the first place. This article introduces a framework, built on an in-depth analysis of the creativity literature, that aims to fill that gap by providing a systematic approach to identifying potential strategies. The framework categorizes all strategies into the following four groups, from the least creative to the most creative: adapting an existing industry strategy, combining different existing industry strategies, importing strategies from other industries, and creating a brand new strategy from scratch.
The problem with strategy frameworks is that although they can help you determine whether a given opportunity is attractive or whether a particular strategy is likely to work, they generally don’t help you in the task of identifying the opportunity or crafting the strategy in the first place. As the legendary strategy expert Gary Hamel put it: “ The dirty little secret of the strategy industry is that it doesn’t have any theory of strategy creation .”
- Jérôme Barthélemy is Executive Vice-President, Dean for Post Experience Programs, Corporate Programs and Relations and Professor of Strategy and Management at ESSEC Business School. He is the author of Myths of Strategy (Kogan Page, 2023)
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The introduction to a literature review serves as your reader's guide through your academic work and thought process. Explore the significance of literature review introductions in review papers, academic papers, essays, theses, and dissertations. We delve into the purpose and necessity of these introductions, explore the essential components of literature review introductions, and provide ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Example: Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398 ; Systematic review: "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139).
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing ...
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
This resource is adapted from the Graduate Writing Place's workshop "Tackling a Literature Review & Synthesizing the Work of Others." For more information about our workshops, see Graduate Writing Workshops. INTRODUCTION Compiling and synthesizing literature as a justification for one's own research is a key element of most academic work.
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review - in other words, what you will and won't be covering (the delimitations).This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus.The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically ...
Steps to Completing a Literature Review. Find. Conduct searches for relevant information. Evaluate. Critically review your sources. Summarize. Determine the most important and relevant information from each source, theories, findings, etc. Synthesize. Create a synthesis matrix to find connections between resources, and ensure your sources ...
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
Okay - with the why out the way, let's move on to the how. As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter.
Conducting your literature review by Susanne Hempel. Publication Date: 2020. This book is a step-by-step guide to writing a literature review, and includes tips for modifying the process as needed depending on your audience, purpose, and goals. 7 steps to a comprehensive literature review by Anthony J. Onwuegbuzie; Rebecca K. Frels.
A literature review is much more than an annotated bibliography or a list of separate reviews of articles and books. It is a critical, analytical summary and synthesis of the current knowledge of a topic. ... Introduction - A explanation of the purpose of the study, a statement of the research question(s) the study intends to address;
Fig. 6.1. Introduction chapter as an inverted triangle. Secondly, you may have heard the advice "start broad and narrow the topic down" in your introduction. Imagine your introduction chapter as an inverted triangle (see Fig. 6.1), one that is wide (broad) at the top and pointed (nar-row) at the bottom.
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area. Often part of the introduction to an essay, research report or thesis, the literature review is literally a "re" view or "look again" at what has already been written about the topic, wherein the author analyzes a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior ...
A literature review is a written work that: Compiles significant research published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers; Surveys scholarly articles, books, dissertations, conference proceedings, and other sources; Examines contrasting perspectives, theoretical approaches, methodologies, findings, results, conclusions.
Whatever stage you are at in your academic life, you will have to review the literature and write about it. You will be asked to do this as a student when you write essays, dissertations and theses. Later, whenever you write an academic paper, there will usually be some element of literature review in the introduction. And if you have to
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you. ... Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a ...
Introduction. Your introduction should clearly explain the overall research topic and the depth of the information to be presented; it often also explains the types of sources that will be used. If your literature review is part of a larger research proposal or project, its introduction can be combined with the introduction of your paper. Body.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Introduction: A rapid literature review (RLR) is an alternative to systematic literature review (SLR) that can speed up the analysis of newly published data. The objective was to identify and summarize available information regarding different approaches to defining RLR and the methodology applied to the conduct of such reviews.
To answer to the study's research questions, the Authors decided to rely on a systematic literature review (SLR) method (Tranfield et al., 2003; Snyder, 2019) that helps to reach a reliable evaluation of the existent scientific knowledge of a certain topic.As we are interested - on one hand - to provide an IMP-driven overview of business network research and - on the other hand - to ...
Adeinat and Kassim (2018) tried to retest the model of SPC to address gaps raised in the relevant literature in the Saudi setting. They highlighted two shortages in the relevant literature: namely, first, testing this complex model and interrelationships in only one industry and setting; second, more operational factors such as employees' productivity and achievement require full integration ...
Literature search. An SLR was performed in accordance with the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions [] and reported in alignment with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Literature Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [] to identify all RWE studies assessing the effectiveness and safety of treatments used for patients with HR+/HER2- LABC/mBC following 1 L ...
An initial scoping search on masks and masking in respiratory infections identified thousands of studies and more than 100 reviews. In view of this, our chosen review design was an in-depth narrative review in the hermeneutic tradition, whose primary aim was to make sense of this vast literature . We sought to summarize previous reviews and ...
This article introduces a framework, built on an in-depth analysis of the creativity literature, that aims to fill that gap by providing a systematic approach to identifying potential strategies.
CHAPTER TWO LITERATURE REVIEW 2.0 Introduction This chapter presents a comprehensive review of existing literature related to the design and implementation of final year grading systems in educational institutions. It encompasses studies, theories, and findings relevant to grading systems, educational technology, software development methodologies, and similar topics.