

100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported speech can be quite challenging for English language learners because in order to change direct speech into reported speech, one must change the perspective and tense of what was said by the original speaker or writer. In this guide, we will explain in detail how to change direct speech into indirect speech and provide lots of examples of reported speech to help you understand. Here are the key aspects of converting direct speech into reported speech.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
- Direct : “I am going to the park.” Reported : He said he was going to the park .
- Direct : “You should try the new restaurant.” Reported : She said that I should try the new restaurant.
- Direct : “We will win the game.” Reported : They said that they would win the game.
- Direct : “She loves her new job.” Reported : He said that she loves her new job.
- Direct : “He can’t come to the party.” Reported : She said that he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct : “It belongs to me.” Reported : He said that it belonged to him .
- Direct : “They are moving to a new city.” Reported : She said that they were moving to a new city.
- Direct : “You are doing a great job.” Reported : He told me that I was doing a great job.
- Direct : “I don’t like this movie.” Reported : She said that she didn’t like that movie.
- Direct : “We have finished our work.” Reported : They said that they had finished their work.
- Direct : “You will need to sign here.” Reported : He said that I would need to sign there.
- Direct : “She can solve the problem.” Reported : He said that she could solve the problem.
- Direct : “He was not at home yesterday.” Reported : She said that he had not been at home the day before.
- Direct : “It is my responsibility.” Reported : He said that it was his responsibility.
- Direct : “We are planning a surprise.” Reported : They said that they were planning a surprise.
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
In reported speech, various reporting verbs are used depending on the nature of the statement or the intention behind the communication. These verbs are essential for conveying the original tone, intent, or action of the speaker. Here are some examples demonstrating the use of different reporting verbs in reported speech:
- Direct: “I will help you,” she promised . Reported: She promised that she would help me.
- Direct: “You should study harder,” he advised . Reported: He advised that I should study harder.
- Direct: “I didn’t take your book,” he denied . Reported: He denied taking my book .
- Direct: “Let’s go to the cinema,” she suggested . Reported: She suggested going to the cinema .
- Direct: “I love this song,” he confessed . Reported: He confessed that he loved that song.
- Direct: “I haven’t seen her today,” she claimed . Reported: She claimed that she hadn’t seen her that day.
- Direct: “I will finish the project,” he assured . Reported: He assured me that he would finish the project.
- Direct: “I’m not feeling well,” she complained . Reported: She complained of not feeling well.
- Direct: “This is how you do it,” he explained . Reported: He explained how to do it.
- Direct: “I saw him yesterday,” she stated . Reported: She stated that she had seen him the day before.
- Direct: “Please open the window,” he requested . Reported: He requested that I open the window.
- Direct: “I can win this race,” he boasted . Reported: He boasted that he could win the race.
- Direct: “I’m moving to London,” she announced . Reported: She announced that she was moving to London.
- Direct: “I didn’t understand the instructions,” he admitted . Reported: He admitted that he didn’t understand the instructions.
- Direct: “I’ll call you tonight,” she promised . Reported: She promised to call me that night.
Reported Speech: Tense Shifts
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
- Direct: “I am eating.” Reported: He said he was eating.
- Direct: “They will go to the park.” Reported: She mentioned they would go to the park.
- Direct: “We have finished our homework.” Reported: They told me they had finished their homework.
- Direct: “I do my exercises every morning.” Reported: He explained that he did his exercises every morning.
- Direct: “She is going to start a new job.” Reported: He heard she was going to start a new job.
- Direct: “I can solve this problem.” Reported: She said she could solve that problem.
- Direct: “We are visiting Paris next week.” Reported: They said they were visiting Paris the following week.
- Direct: “I will be waiting outside.” Reported: He stated he would be waiting outside.
- Direct: “They have been studying for hours.” Reported: She mentioned they had been studying for hours.
- Direct: “I can’t understand this chapter.” Reported: He complained that he couldn’t understand that chapter.
- Direct: “We were planning a surprise.” Reported: They told me they had been planning a surprise.
- Direct: “She has to complete her assignment.” Reported: He said she had to complete her assignment.
- Direct: “I will have finished the project by Monday.” Reported: She stated she would have finished the project by Monday.
- Direct: “They are going to hold a meeting.” Reported: She heard they were going to hold a meeting.
- Direct: “I must leave.” Reported: He said he had to leave.
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
When converting direct speech into reported speech, references to time and place often need to be adjusted to fit the context of the reported speech. This is because the time and place relative to the speaker may have changed from the original statement to the time of reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how time and place references change:
- Direct: “I will see you tomorrow .” Reported: He said he would see me the next day .
- Direct: “We went to the park yesterday .” Reported: They said they went to the park the day before .
- Direct: “I have been working here since Monday .” Reported: She mentioned she had been working there since Monday .
- Direct: “Let’s meet here at noon.” Reported: He suggested meeting there at noon.
- Direct: “I bought this last week .” Reported: She said she had bought it the previous week .
- Direct: “I will finish this by tomorrow .” Reported: He stated he would finish it by the next day .
- Direct: “She will move to New York next month .” Reported: He heard she would move to New York the following month .
- Direct: “They were at the festival this morning .” Reported: She said they were at the festival that morning .
- Direct: “I saw him here yesterday.” Reported: She mentioned she saw him there the day before.
- Direct: “We will return in a week .” Reported: They said they would return in a week .
- Direct: “I have an appointment today .” Reported: He said he had an appointment that day .
- Direct: “The event starts next Friday .” Reported: She mentioned the event starts the following Friday .
- Direct: “I lived in Berlin two years ago .” Reported: He stated he had lived in Berlin two years before .
- Direct: “I will call you tonight .” Reported: She said she would call me that night .
- Direct: “I was at the office yesterday .” Reported: He mentioned he was at the office the day before .
Reported Speech: Question Format
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
- Direct: “Are you coming to the party?” Reported: She asked if I was coming to the party.
- Direct: “What time is the meeting?” Reported: He inquired what time the meeting was.
- Direct: “Why did you leave early?” Reported: They wanted to know why I had left early.
- Direct: “Can you help me with this?” Reported: She asked if I could help her with that.
- Direct: “Where did you buy this?” Reported: He wondered where I had bought that.
- Direct: “Who is going to the concert?” Reported: They asked who was going to the concert.
- Direct: “How do you solve this problem?” Reported: She questioned how to solve that problem.
- Direct: “Is this the right way to the station?” Reported: He inquired whether it was the right way to the station.
- Direct: “Do you know her name?” Reported: They asked if I knew her name.
- Direct: “Why are they moving out?” Reported: She wondered why they were moving out.
- Direct: “Have you seen my keys?” Reported: He asked if I had seen his keys.
- Direct: “What were they talking about?” Reported: She wanted to know what they had been talking about.
- Direct: “When will you return?” Reported: He asked when I would return.
- Direct: “Can she drive a manual car?” Reported: They inquired if she could drive a manual car.
- Direct: “How long have you been waiting?” Reported: She asked how long I had been waiting.
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
In reported speech, quotation marks are not used, differentiating it from direct speech which requires them to enclose the spoken words. Reported speech summarizes or paraphrases what someone said without the need for exact wording. Here are examples showing how direct speech with quotation marks is transformed into reported speech without them:
- Direct: “I am feeling tired,” she said. Reported: She said she was feeling tired.
- Direct: “We will win the game,” he exclaimed. Reported: He exclaimed that they would win the game.
- Direct: “I don’t like apples,” the boy declared. Reported: The boy declared that he didn’t like apples.
- Direct: “You should visit Paris,” she suggested. Reported: She suggested that I should visit Paris.
- Direct: “I will be late,” he warned. Reported: He warned that he would be late.
- Direct: “I can’t believe you did that,” she expressed in surprise. Reported: She expressed her surprise that I had done that.
- Direct: “I need help with this task,” he admitted. Reported: He admitted that he needed help with the task.
- Direct: “I have never been to Italy,” she confessed. Reported: She confessed that she had never been to Italy.
- Direct: “We saw a movie last night,” they mentioned. Reported: They mentioned that they saw a movie the night before.
- Direct: “I am learning to play the piano,” he revealed. Reported: He revealed that he was learning to play the piano.
- Direct: “You must finish your homework,” she instructed. Reported: She instructed that I must finish my homework.
- Direct: “I will call you tomorrow,” he promised. Reported: He promised that he would call me the next day.
- Direct: “I have finished my assignment,” she announced. Reported: She announced that she had finished her assignment.
- Direct: “I cannot attend the meeting,” he apologized. Reported: He apologized for not being able to attend the meeting.
- Direct: “I don’t remember where I put it,” she confessed. Reported: She confessed that she didn’t remember where she put it.
Reported Speech Quiz
Thanks for reading! I hope you found these reported speech examples useful. Before you go, why not try this Reported Speech Quiz and see if you can change indirect speech into reported speech?

Reported Speech – Rules, Examples & Worksheet
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
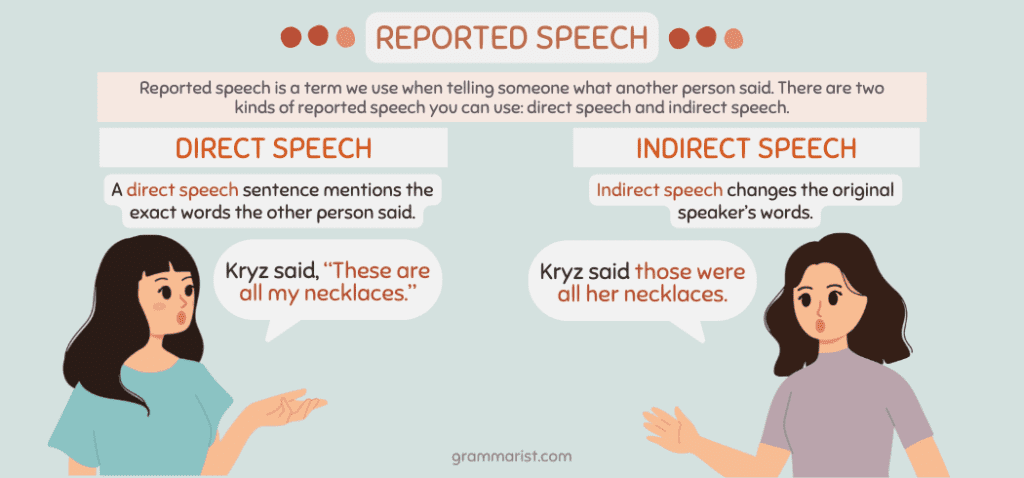
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
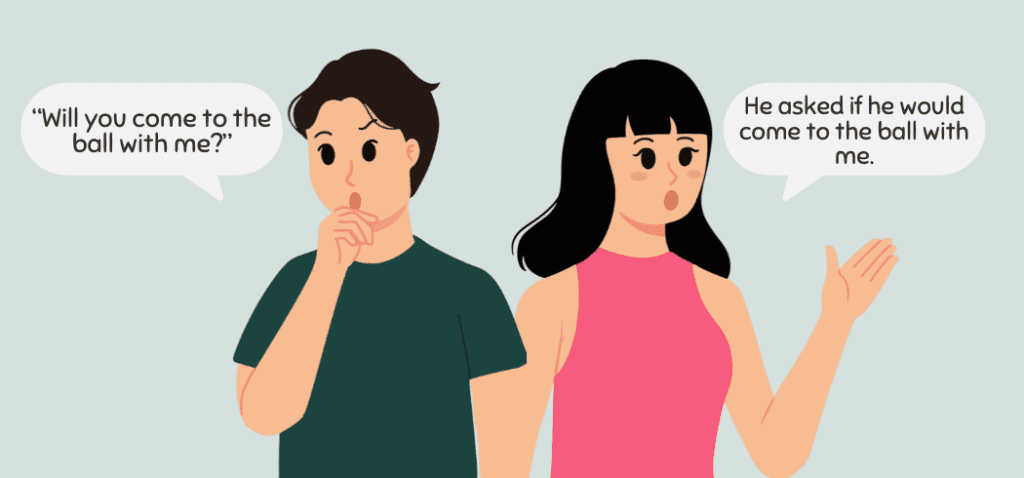
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
Reported Speech: Rules, Examples, Exceptions

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course
What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to backshift in reported speech.
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

He said he HAS three children
But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:

More Espresso English Lessons:
About the author.
Shayna Oliveira
Shayna Oliveira is the founder of Espresso English, where you can improve your English fast - even if you don’t have much time to study. Millions of students are learning English from her clear, friendly, and practical lessons! Shayna is a CELTA-certified teacher with 10+ years of experience helping English learners become more fluent in her English courses.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
Reported Speech in English
“Reported speech” might sound fancy, but it isn’t that complicated.
It’s just how you talk about what someone said.
Luckily, it’s pretty simple to learn the basics in English, beginning with the two types of reported speech: direct (reporting the exact words someone said) and indirect (reporting what someone said without using their exact words ).
Read this post to learn how to report speech, with tips and tricks for each, plenty of examples and a resources section that tells you about real world resources you can use to practice reporting speech.
How to Report Direct Speech
How to report indirect speech, reporting questions in indirect speech, verb tenses in indirect reported speech, simple present, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, simple past, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, simple future, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, authentic resources for practicing reported speech, novels and short stories, native english videos, celebrity profiles.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Direct speech refers to the exact words that a person says. You can “report” direct speech in a few different ways.
To see how this works, let’s pretend that I (Elisabeth) told some people that I liked green onions.
Here are some different ways that those people could explain what I said:
Direct speech: “I like green onions,” Elisabeth said.
Direct speech: “I like green onions,” she told me. — In this sentence, we replace my name (Elisabeth) with the pronoun she.
In all of these examples, the part that was said is between quotation marks and is followed by a noun (“she” or “Elisabeth”) and a verb. Each of these verbs (“to say,” “to tell [someone],” “to explain”) are ways to describe someone talking. You can use any verb that refers to speech in this way.
You can also put the noun and verb before what was said.
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, “I like spaghetti.”
The example above would be much more likely to be said out loud than the first set of examples.
Here’s a conversation that might happen between two people:
1: Did you ask her if she liked coffee?
2: Yeah, I asked her.
1: What did she say?
2. She said, “Yeah, I like coffee.” ( Direct speech )
Usually, reporting of direct speech is something you see in writing. It doesn’t happen as often when people are talking to each other.
Direct reported speech often happens in the past. However, there are all kinds of stories, including journalism pieces, profiles and fiction, where you might see speech reported in the present as well.
This is sometimes done when the author of the piece wants you to feel that you’re experiencing events in the present moment.
For example, a profile of Kristen Stewart in Vanity Fair has a funny moment that describes how the actress isn’t a very good swimmer:
Direct speech: “I don’t want to enter the water, ever,” she says. “If everyone’s going in the ocean, I’m like, no.”
Here, the speech is reported as though it’s in the present tense (“she says”) instead of in the past (“she said”).
In writing of all kinds, direct reported speech is often split into two or more parts, as it is above.
Here’s an example from Lewis Carroll’s “ Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland ,” where the speech is even more split up:
Direct speech: “I won’t indeed!” said Alice, in a great hurry to change the subject of conversation. “Are you—are you fond—of—of dogs?” The Mouse did not answer, so Alice went on eagerly: “There is such a nice little dog near our house I should like to show you!”
Reporting indirect speech is what happens when you explain what someone said without using their exact words.
Let’s start with an example of direct reported speech like those used above.
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, “I like coffee.”
As indirect reported speech, it looks like this:
Indirect speech: Elisabeth said she liked coffee.
You can see that the subject (“I”) has been changed to “she,” to show who is being spoken about. If I’m reporting the direct speech of someone else, and this person says “I,” I’d repeat their sentence exactly as they said it. If I’m reporting this person’s speech indirectly to someone else, however, I’d speak about them in the third person—using “she,” “he” or “they.”
You may also notice that the tense changes here: If “I like coffee” is what she said, this can become “She liked coffee” in indirect speech.
However, you might just as often hear someone say something like, “She said she likes coffee.” Since people’s likes and preferences tend to change over time and not right away, it makes sense to keep them in the present tense.
Indirect speech often uses the word “that” before what was said:
Indirect speech: She said that she liked coffee.
There’s no real difference between “She said she liked coffee” and “She said that she liked coffee.” However, using “that” can help make the different parts of the sentence clearer.
Let’s look at a few other examples:
Indirect speech: I said I was going outside today.
Indirect speech: They told me that they wanted to order pizza.
Indirect speech: He mentioned it was raining.
Indirect speech: She said that her father was coming over for dinner.
You can see an example of reporting indirect speech in the funny video “ Cell Phone Crashing .” In this video, a traveler in an airport sits down next to another traveler talking on his cell phone. The first traveler pretends to be talking to someone on his phone, but he appears to be responding to the second traveler’s conversation, which leads to this exchange:
Woman: “Are you answering what I’m saying?”
Man “No, no… I’m on the phone with somebody, sorry. I don’t mean to be rude.” (Direct speech)
Woman: “What was that?”
Man: “I just said I was on the phone with somebody.” (Indirect speech)
When reporting questions in indirect speech, you can use words like “whether” or “if” with verbs that show questioning, such as “to ask” or “to wonder.”
Direct speech: She asked, “Is that a new restaurant?”
Indirect speech: She asked if that was a new restaurant.
In any case where you’re reporting a question, you can say that someone was “wondering” or “wanted to know” something. Notice that these verbs don’t directly show that someone asked a question. They don’t describe an action that happened at a single point in time. But you can usually assume that someone was wondering or wanted to know what they asked.
Indirect speech: She was wondering if that was a new restaurant.
Indirect speech: She wanted to know whether that was a new restaurant.
It can be tricky to know how to use tenses when reporting indirect speech. Let’s break it down, tense by tense.
Sometimes, indirect speech “ backshifts ,” or moves one tense further back into the past. We already saw this in the example from above:
Direct speech: She said, “I like coffee.”
Indirect speech: She said she liked coffee.
Also as mentioned above, backshifting doesn’t always happen. This might seem confusing, but it isn’t that difficult to understand once you start using reported speech regularly.
What tense you use in indirect reported speech often just depends on when what you’re reporting happened or was true.
Let’s look at some examples of how direct speech in certain tenses commonly changes (or doesn’t) when it’s reported as indirect speech.
To learn about all the English tenses (or for a quick review), check out this post .
Direct speech: I said, “I play video games.”
Indirect speech: I said that I played video games (simple past) or I said that I play video games (simple present).
Backshifting into the past or staying in the present here can change the meaning slightly. If you use the first example, it’s unclear whether or not you still play video games; all we know is that you said you played them in the past.
If you use the second example, though, you probably still play video games (unless you were lying for some reason).
However, the difference in meaning is so small, you can use either one and you won’t have a problem.
Direct speech: I said, “I’m playing video games.”
Indirect speech: I said that I was playing video games (past continuous) or I said that I’m playing video games (present continuous).
In this case, you’d likely use the first example if you were telling a story about something that happened in the past.
You could use the second example to repeat or stress what you just said. For example:
Hey, want to go for a walk?
Direct speech: No, I’m playing video games.
But it’s such a nice day!
Indirect speech: I said that I’m playing video games!
Direct speech: Marie said, “I have read that book.”
Indirect speech: Marie said that she had read that book (past perfect) or Marie said that she has read that book (present perfect).
The past perfect is used a lot in writing and other kinds of narration. This is because it helps point out an exact moment in time when something was true.
The past perfect isn’t quite as useful in conversation, where people are usually more interested in what’s true now. So, in a lot of cases, people would use the second example above when speaking.
Direct speech: She said, “I have been watching that show.”
Indirect speech: She said that she had been watching that show (past perfect continuous) or She said that she has been watching that show (present perfect continuous).
These examples are similar to the others above. You could use the first example whether or not this person was still watching the show, but if you used the second example, it’d probably seem like you either knew or guessed that she was still watching it.
Direct speech: You told me, “I charged my phone.”
Indirect speech: You told me that you had charged your phone (past perfect) or You told me that you charged your phone (simple past).
Here, most people would probably just use the second example, because it’s simpler, and gets across the same meaning.
Direct speech: You told me, “I was charging my phone.”
Indirect speech: You told me that you had been charging your phone (past perfect continuous) or You told me that you were charging your phone (past continuous).
Here, the difference is between whether you had been charging your phone before or were charging your phone at the time. However, a lot of people would still use the second example in either situation.
Direct speech: They explained, “We had bathed the cat on Wednesday.”
Indirect speech: They explained that they had bathed the cat on Wednesday. (past perfect)
Once we start reporting the past perfect tenses, we don’t backshift because there are no tenses to backshift to.
So in this case, it’s simple. The tense stays exactly as is. However, many people might simplify even more and use the simple past, saying, “They explained that they bathed the cat on Wednesday.”
Direct speech: They said, “The cat had been going outside and getting dirty for a long time!”
Indirect speech: They said that the cat had been going outside and getting dirty for a long time. (past perfect continuous)
Again, we don’t shift the tense back here; we leave it like it is. And again, a lot of people would report this speech as, “They said the cat was going outside and getting dirty for a long time.” It’s just a simpler way to say almost the same thing.
Direct speech: I told you, “I will be here no matter what.”
Indirect speech: I told you that I would be here no matter what. (present conditional)
At this point, we don’t just have to think about tenses, but grammatical mood, too. However, the idea is still pretty simple. We use the conditional (with “would”) to show that at the time the words were spoken, the future was uncertain.
In this case, you could also say, “I told you that I will be here no matter what,” but only if you “being here” is still something that you expect to happen in the future.
What matters here is what’s intended. Since this example shows a person reporting their own speech, it’s more likely that they’d want to stress the truth of their own intention, and so they might be more likely to use “will” than “would.”
But if you were reporting someone else’s words, you might be more likely to say something like, “She told me that she would be here no matter what.”
Direct speech: I said, “I’ll be waiting for your call.”
Indirect speech: I said that I would be waiting for your call. (conditional continuous)
These are similar to the above examples, but apply to a continuous or ongoing action.
Direct speech: She said, “I will have learned a lot about myself.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would have learned a lot about herself (conditional perfect) or She said that she will have learned a lot about herself (future perfect).
In this case, using the conditional (as in the first example) suggests that maybe a certain event didn’t happen, or something didn’t turn out as expected.
However, that might not always be the case, especially if this was a sentence that was written in an article or a work of fiction. The second example, however, suggests that the future that’s being talked about still hasn’t happened yet.
Direct speech: She said, “By next Tuesday, I will have been staying inside every day for the past month.”
Indirect speech: She said that by next Tuesday, she would have been staying inside every day for the past month (perfect continuous conditional) or She said that by next Tuesday, she will have been staying inside every day for the past month (past perfect continuous).
Again, in this case, the first example might suggest that the event didn’t happen. Maybe the person didn’t stay inside until next Tuesday! However, this could also just be a way of explaining that at the time she said this in the past, it was uncertain whether she really would stay inside for as long as she thought.
The second example, on the other hand, would only be used if next Tuesday hadn’t happened yet.
Let’s take a look at where you can find resources for practicing reporting speech in the real world.
One of the most common uses for reported speech is in fiction. You’ll find plenty of reported speech in novels and short stories . Look for books that have long sections of text with dialogue marked by quotation marks (“…”). Once you understand the different kinds of reported speech, you can look for it in your reading and use it in your own writing.
Writing your own stories is a great way to get even better at understanding reported speech.
One of the best ways to practice any aspect of English is to watch native English videos. By watching English speakers use the language, you can understand how reported speech is used in real world situations.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Try FluentU for FREE!
Celebrity profiles, which you can find in print magazines and online, can help you find and practice reported speech, too. Celebrity profiles are stories that focus on a famous person. They often include some kind of interview. The writer will usually spend some time describing the person and then mention things that they say; this is when they use reported speech.
Because many of these profiles are written in the present tense, they can help you get used to the basics of reported speech without having to worry too much about different verb tenses.
While the above may seem really complicated, it isn’t that difficult to start using reported speech.
Mastering it may be a little difficult, but the truth is that many, many people who speak English as a first language struggle with it, too!
Reported speech is flexible, and even if you make mistakes, there’s a good chance that no one will notice.
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

Search form
- B1-B2 grammar
Reported speech
Daisy has just had an interview for a summer job.
Instructions
As you watch the video, look at the examples of reported speech. They are in red in the subtitles. Then read the conversation below to learn more. Finally, do the grammar exercises to check you understand, and can use, reported speech correctly.
Sophie: Mmm, it’s so nice to be chilling out at home after all that running around.
Ollie: Oh, yeah, travelling to glamorous places for a living must be such a drag!
Ollie: Mum, you can be so childish sometimes. Hey, I wonder how Daisy’s getting on in her job interview.
Sophie: Oh, yes, she said she was having it at four o’clock, so it’ll have finished by now. That’ll be her ... yes. Hi, love. How did it go?
Daisy: Well, good I think, but I don’t really know. They said they’d phone later and let me know.
Sophie: What kind of thing did they ask you?
Daisy: They asked if I had any experience with people, so I told them about helping at the school fair and visiting old people at the home, that sort of stuff. But I think they meant work experience.
Sophie: I’m sure what you said was impressive. They can’t expect you to have had much work experience at your age.
Daisy: And then they asked me what acting I had done, so I told them that I’d had a main part in the school play, and I showed them a bit of the video, so that was cool.
Sophie: Great!
Daisy: Oh, and they also asked if I spoke any foreign languages.
Sophie: Languages?
Daisy: Yeah, because I might have to talk to tourists, you know.
Sophie: Oh, right, of course.
Daisy: So that was it really. They showed me the costume I’ll be wearing if I get the job. Sending it over ...
Ollie: Hey, sis, I heard that Brad Pitt started out as a giant chicken too! This could be your big break!
Daisy: Ha, ha, very funny.
Sophie: Take no notice, darling. I’m sure you’ll be a marvellous chicken.
We use reported speech when we want to tell someone what someone said. We usually use a reporting verb (e.g. say, tell, ask, etc.) and then change the tense of what was actually said in direct speech.
So, direct speech is what someone actually says? Like 'I want to know about reported speech'?
Yes, and you report it with a reporting verb.
He said he wanted to know about reported speech.
I said, I want and you changed it to he wanted .
Exactly. Verbs in the present simple change to the past simple; the present continuous changes to the past continuous; the present perfect changes to the past perfect; can changes to could ; will changes to would ; etc.
She said she was having the interview at four o’clock. (Direct speech: ' I’m having the interview at four o’clock.') They said they’d phone later and let me know. (Direct speech: ' We’ll phone later and let you know.')
OK, in that last example, you changed you to me too.
Yes, apart from changing the tense of the verb, you also have to think about changing other things, like pronouns and adverbs of time and place.
'We went yesterday.' > She said they had been the day before. 'I’ll come tomorrow.' > He said he’d come the next day.
I see, but what if you’re reporting something on the same day, like 'We went yesterday'?
Well, then you would leave the time reference as 'yesterday'. You have to use your common sense. For example, if someone is saying something which is true now or always, you wouldn’t change the tense.
'Dogs can’t eat chocolate.' > She said that dogs can’t eat chocolate. 'My hair grows really slowly.' > He told me that his hair grows really slowly.
What about reporting questions?
We often use ask + if/whether , then change the tenses as with statements. In reported questions we don’t use question forms after the reporting verb.
'Do you have any experience working with people?' They asked if I had any experience working with people. 'What acting have you done?' They asked me what acting I had done .
Is there anything else I need to know about reported speech?
One thing that sometimes causes problems is imperative sentences.
You mean like 'Sit down, please' or 'Don’t go!'?
Exactly. Sentences that start with a verb in direct speech need a to + infinitive in reported speech.
She told him to be good. (Direct speech: 'Be good!') He told them not to forget. (Direct speech: 'Please don’t forget.')
OK. Can I also say 'He asked me to sit down'?
Yes. You could say 'He told me to …' or 'He asked me to …' depending on how it was said.
OK, I see. Are there any more reporting verbs?
Yes, there are lots of other reporting verbs like promise , remind , warn , advise , recommend , encourage which you can choose, depending on the situation. But say , tell and ask are the most common.
Great. I understand! My teacher said reported speech was difficult.
And I told you not to worry!
Check your grammar: matching
Check your grammar: error correction, check your grammar: gap fill, worksheets and downloads.
What was the most memorable conversation you had yesterday? Who were you talking to and what did they say to you?

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
What is Reported Speech and how to use it? with Examples
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said. Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker's exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions. 1. Reported Statements: In reported statements, the reporting verb is usually "said." The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and any pronouns referring to the speaker or listener are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. For example, "I am going to the store," becomes "He said that he was going to the store." 2. Reported Questions: In reported questions, the reporting verb is usually "asked." The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and the word order changes from a question to a statement. For example, "What time is it?" becomes "She asked what time it was." It's important to note that the tense shift in reported speech depends on the context and the time of the reported speech. Here are a few more examples: ● Direct speech: "I will call you later." Reported speech: He said that he would call me later. ● Direct speech: "Did you finish your homework?" Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework. ● Direct speech: "I love pizza." Reported speech: They said that they loved pizza.
When do we use reported speech?
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly. Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation. Some common situations where reported speech is used include: News reports: Journalists often use reported speech to quote what someone said in an interview or press conference. Business and professional communication: In professional settings, reported speech can be used to summarize what was discussed in a meeting or to report feedback from a customer. Conversational English: In everyday conversations, reported speech is used to relate what someone else said. For example, "She told me that she was running late." Narration: In written narratives or storytelling, reported speech can be used to convey what a character said or thought.
How to make reported speech?
1. Change the pronouns and adverbs of time and place: In reported speech, you need to change the pronouns, adverbs of time and place to reflect the new speaker or point of view. Here's an example: Direct speech: "I'm going to the store now," she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then. In this example, the pronoun "I" is changed to "she" and the adverb "now" is changed to "then." 2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here's an example: Direct speech: "I will meet you at the park tomorrow," he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day. In this example, the present tense "will" is changed to the past tense "would." 3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as "say," "tell," "ask," or "inquire" depending on the context of the speech. Here's an example: Direct speech: "Did you finish your homework?" she asked. Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework. In this example, the reporting verb "asked" is changed to "said" and "did" is changed to "had." Overall, when making reported speech, it's important to pay attention to the verb tense and the changes in pronouns, adverbs, and reporting verbs to convey the original speaker's message accurately.
How do I change the pronouns and adverbs in reported speech?
1. Changing Pronouns: In reported speech, the pronouns in the original statement must be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. Generally, the first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours) are changed according to the subject of the reporting verb, while the second and third person pronouns (you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are changed according to the object of the reporting verb. For example: Direct speech: "I love chocolate." Reported speech: She said she loved chocolate. Direct speech: "You should study harder." Reported speech: He advised me to study harder. Direct speech: "She is reading a book." Reported speech: They noticed that she was reading a book. 2. Changing Adverbs: In reported speech, the adverbs and adverbial phrases that indicate time or place may need to be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. For example: Direct speech: "I'm going to the cinema tonight." Reported speech: She said she was going to the cinema that night. Direct speech: "He is here." Reported speech: She said he was there. Note that the adverb "now" usually changes to "then" or is omitted altogether in reported speech, depending on the context. It's important to keep in mind that the changes made to pronouns and adverbs in reported speech depend on the context and the perspective of the new speaker. With practice, you can become more comfortable with making these changes in reported speech.
How do I change the tense in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense of the reported verb usually changes to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here are some guidelines on how to change the tense in reported speech: Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I like pizza." Reported speech: She said she liked pizza. Present continuous in direct speech changes to past continuous in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I am studying for my exam." Reported speech: He said he was studying for his exam. Present perfect in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I have finished my work." Reported speech: She said she had finished her work. Past simple in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I visited my grandparents last weekend." Reported speech: She said she had visited her grandparents the previous weekend. Will in direct speech changes to would in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I will help you with your project." Reported speech: He said he would help me with my project. Can in direct speech changes to could in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I can speak French." Reported speech: She said she could speak French. Remember that the tense changes in reported speech depend on the tense of the verb in the direct speech, and the tense you use in reported speech should match the time frame of the new speaker's perspective. With practice, you can become more comfortable with changing the tense in reported speech.
Do I always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech?
No, you do not always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech. However, using a reporting verb can help to clarify who is speaking and add more context to the reported speech. In some cases, the reported speech can be introduced by phrases such as "I heard that" or "It seems that" without using a reporting verb. For example: Direct speech: "I'm going to the cinema tonight." Reported speech with a reporting verb: She said she was going to the cinema tonight. Reported speech without a reporting verb: It seems that she's going to the cinema tonight. However, it's important to note that using a reporting verb can help to make the reported speech more formal and accurate. When using reported speech in academic writing or journalism, it's generally recommended to use a reporting verb to make the reporting more clear and credible. Some common reporting verbs include say, tell, explain, ask, suggest, and advise. For example: Direct speech: "I think we should invest in renewable energy." Reported speech with a reporting verb: She suggested that they invest in renewable energy. Overall, while using a reporting verb is not always required, it can be helpful to make the reported speech more clear and accurate.
How to use reported speech to report questions and commands?
1. Reporting Questions: When reporting questions, you need to use an introductory phrase such as "asked" or "wondered" followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here's an example: Direct speech: "What time is the meeting?" Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was. Note that the question mark is not used in reported speech. 2. Reporting Commands: When reporting commands, you need to use an introductory phrase such as "ordered" or "told" followed by the person, to + infinitive, and any additional information. Here's an example: Direct speech: "Clean your room!" Reported speech: She ordered me to clean my room. Note that the exclamation mark is not used in reported speech. In both cases, the tense of the reported verb should be changed accordingly. For example, present simple changes to past simple, and future changes to conditional. Here are some examples: Direct speech: "Will you go to the party with me?" Reported speech: She asked if I would go to the party with her. Direct speech: "Please bring me a glass of water." Reported speech: She requested that I bring her a glass of water. Remember that when using reported speech to report questions and commands, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
How to make questions in reported speech?
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as "asked" or "wondered" followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech: Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include "asked," "inquired," "wondered," and "wanted to know." Change the tense and pronouns: Next, you need to change the tense and pronouns in the sentence to reflect the shift from direct to reported speech. The tense of the verb is usually shifted back one tense (e.g. from present simple to past simple) in reported speech. The pronouns should also be changed as necessary to reflect the shift in perspective from the original speaker to the reporting speaker. Use an appropriate question word: If the original question contained a question word (e.g. who, what, where, when, why, how), you should use the same question word in the reported question. If the original question did not contain a question word, you can use "if" or "whether" to introduce the reported question. Change the word order: In reported speech, the word order of the question changes from the inverted form to a normal statement form. The subject usually comes before the verb, unless the original question started with a question word. Here are some examples of reported questions: Direct speech: "What time is the meeting?" Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was. Direct speech: "Did you finish your homework?" Reported speech: He wanted to know if I had finished my homework. Direct speech: "Where are you going?" Reported speech: She wondered where I was going. Remember that when making questions in reported speech, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately. Here you can find more examples of direct and indirect questions
What is the difference between reported speech an indirect speech?
In reported or indirect speech, you are retelling or reporting what someone said using your own words. The tense of the reported speech is usually shifted back one tense from the tense used in the original statement. For example, if someone said, "I am going to the store," in reported speech you would say, "He/she said that he/she was going to the store." The main difference between reported speech and indirect speech is that reported speech usually refers to spoken language, while indirect speech can refer to both spoken and written language. Additionally, indirect speech is a broader term that includes reported speech as well as other ways of expressing what someone else has said, such as paraphrasing or summarizing.
Examples of direct speech to reported
1. Direct speech: "I am hungry," she said. Reported speech: She said she was hungry. 2. Direct speech: "Can you pass the salt, please?" he asked. Reported speech: He asked her to pass the salt. 3. Direct speech: "I will meet you at the cinema," he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet her at the cinema. 4. Direct speech: "I have been working on this project for hours," she said. Reported speech: She said she had been working on the project for hours. 5. Direct speech: "What time does the train leave?" he asked. Reported speech: He asked what time the train left. 6. Direct speech: "I love playing the piano," she said. Reported speech: She said she loved playing the piano. 7. Direct speech: "I am going to the grocery store," he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to the grocery store. 8. Direct speech: "Did you finish your homework?" the teacher asked. Reported speech: The teacher asked if he had finished his homework. 9. Direct speech: "I want to go to the beach," she said. Reported speech: She said she wanted to go to the beach. 10. Direct speech: "Do you need help with that?" he asked. Reported speech: He asked if she needed help with that. 11. Direct speech: "I can't come to the party," he said. Reported speech: He said he couldn't come to the party. 12. Direct speech: "Please don't leave me," she said. Reported speech: She begged him not to leave her. 13. Direct speech: "I have never been to London before," he said. Reported speech: He said he had never been to London before. 14. Direct speech: "Where did you put my phone?" she asked. Reported speech: She asked where she had put her phone. 15. Direct speech: "I'm sorry for being late," he said. Reported speech: He apologized for being late. 16. Direct speech: "I need some help with this math problem," she said. Reported speech: She said she needed some help with the math problem. 17. Direct speech: "I am going to study abroad next year," he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to study abroad the following year. 18. Direct speech: "Can you give me a ride to the airport?" she asked. Reported speech: She asked him to give her a ride to the airport. 19. Direct speech: "I don't know how to fix this," he said. Reported speech: He said he didn't know how to fix it. 20. Direct speech: "I hate it when it rains," she said. Reported speech: She said she hated it when it rained.
What is Direct and Indirect Speech?
Direct and indirect speech are two different ways of reporting spoken or written language. Let's delve into the details and provide some examples. Click here to read more
Fluent English Grammar
Created by Fluent English Grammar
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service
Time and Place in Reported Speech
When we report something, we may need to make changes to:
- time (now, tomorrow)
- place (here, this room)
If we report something around the same time, then we probably do not need to make any changes to time words . But if we report something at a different time, we need to change time words. Look at these example sentences:
- He said: "It was hot yesterday ." → He said that it had been hot the day before .
- He said: "We are going to swim tomorrow ." → He said they were going to swim the next day .
Here is a list of common time words, showing how you change them for reported speech:

Place words
If we are in the same place when we report something, then we do not need to make any changes to place words . But if we are in a different place when we report something, then we need to change the place words. Look at these example sentences:
- He said: "It is cold in here ." → He said that it was cold in there .
- He said: "How much is this book ?" → He asked how much the book was.
Here are some common place words, showing how you change them for reported speech:

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
Indirect speech: typical errors.
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
to try to persuade a customer who is already buying something to buy more, or to buy something more expensive

Searching out and tracking down: talking about finding or discovering things

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Reported Speech Exercises
Perfect english grammar.

Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site:
( Click here to read the explanations about reported speech )
Reported Statements:
- Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Past Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Present Perfect Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Future Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Mixed Tense Reported Statement Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- 'Say' and 'Tell' (quite easy) (in PDF here)
Reported Questions:
- Present Simple Reported Yes/No Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Present Simple Reported Wh Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Mixed Tense Reported Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
Reported Orders and Requests:
- Reported Requests and Orders Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Reported Speech Mixed Exercise 1 (difficult) (in PDF here)
- Reported Speech Mixed Exercise 2 (difficult) (in PDF here)

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
Reported Speech – Free Exercise
Write the following sentences in indirect speech. Pay attention to backshift and the changes to pronouns, time, and place.
- Two weeks ago, he said, “I visited this museum last week.” → Two weeks ago, he said that . I → he|simple past → past perfect|this → that|last …→ the … before
- She claimed, “I am the best for this job.” → She claimed that . I → she|simple present→ simple past|this→ that
- Last year, the minister said, “The crisis will be overcome next year.” → Last year, the minister said that . will → would|next …→ the following …
- My riding teacher said, “Nobody has ever fallen off a horse here.” → My riding teacher said that . present perfect → past perfect|here→ there
- Last month, the boss explained, “None of my co-workers has to work overtime now.” → Last month, the boss explained that . my → his/her|simple present→ simple past|now→ then
Rewrite the question sentences in indirect speech.
- She asked, “What did he say?” → She asked . The subject comes directly after the question word.|simple past → past perfect
- He asked her, “Do you want to dance?” → He asked her . The subject comes directly after whether/if |you → she|simple present → simple past
- I asked him, “How old are you?” → I asked him . The subject comes directly after the question word + the corresponding adjective (how old)|you→ he|simple present → simple past
- The tourists asked me, “Can you show us the way?” → The tourists asked me . The subject comes directly after whether/if |you→ I|us→ them
- The shop assistant asked the woman, “Which jacket have you already tried on?” → The shop assistant asked the woman . The subject comes directly after the question word|you→ she|present perfect → past perfect
Rewrite the demands/requests in indirect speech.
- The passenger requested the taxi driver, “Stop the car.” → The passenger requested the taxi driver . to + same wording as in direct speech
- The mother told her son, “Don’t be so loud.” → The mother told her son . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don’t
- The policeman told us, “Please keep moving.” → The policeman told us . to + same wording as in direct speech ( please can be left off)
- She told me, “Don’t worry.” → She told me . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don’t
- The zookeeper told the children, “Don’t feed the animals.” → The zookeeper told the children . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don’t
How good is your English?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
English EFL
Reported speech
Tense changes in reported speech
Indirect speech (reported speech) focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech, the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Normally, the tense in reported speech is one tense back in time from the tense in direct speech: She said, "I am tired." = She said that she was tired.
You do not need to change the tense if the reporting verb is in the present, or if the original statement was about something that is still true (but this is only for things which are general facts, and even then usually we like to change the tense) , e.g.
- He says he has missed the train but he'll catch the next one.
- We explained that it is very difficult to find our house.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
These modal verbs do not change in reported speech: might, could, would, should, ought to :
- We explained, "It could be difficult to find our house." = We explained that it could be difficult to find our house.
- She said, "I might bring a friend to the party." = She said that she might bring a friend to the party.
Course Curriculum
- Direct and indirect speech 15 mins
- Tense changes in reported speech 20 mins
- Changing time and place in reported speech 20 mins
- Reported questions 20 mins
- Reporting verbs 20 mins
- Reporting orders and requests 15 mins
- Reporting hopes, intentions and promises 20 mins
- Grammar Lessons
- Grammar Exercises
- Grammar Quizzes
- Mixed Tests
- PDF Worksheets
- Beginners Lessons
- Easy Worksheets
- Beginners Tests
- Reading Exercises
- Drag & Drop Grammar
- English For Kids
- Kids Word Games
- Picture Vocabulary
- Reading Tests
- Short Dialogues
- Short Sentences
- Closest in Meaning
- Irrelevant Sentence
- ESL Paragraphs
- GRE Reading
- Text Completion
- GRE Equivalence
- SAT Sentence
- Essay Writing
- Vocabulary Exercises
- Study Skills Tips
- Drag & Drop Vocab
Reported Speech Examples

See the Video Exercise

GrammarSimple.Com
40 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Sentences
Table of Contents
Direct And Indirect Speech Examples
While using English, we use direct and indirect speeches quite often. If a sentence is expressed exactly as it came out of the mouth of the person who said it, it becomes a direct speech. However Indirect Speech (also called reported speech) refers to transmitting a sentence that someone has said. It is often used in daily language.
For example,
- Susan told me she ate pizza yesterday. (Indirect Speech)
Susan said, “I ate pizza yesterday.”. (Direct Speech)
- Mathilda told me she had to go out. (Indirect Speech)
Mathilda said: “I have to go out.”. (Direct Speech)
- Julie asked if the train had left when she arrived at the ticket office. (Indirect Speech)
Julie asked: “Did the train leave?” (Direct Speech)
Related Posts
Parallel Structure Sentence Examples, Parallel Structure Definition and Meaning
8 Parts of Speech, Definition and Example Sentences
Using Provided, Definition and Example Sentences
About the author.
Trump Seemed To Have Had Some Sort of...Episode at a Rally In New Jersey
The way various outlets covered it ought to be taught in journalism schools as an example of what never to do.

“Al Capone was so mean that if you went to dinner with him and he didn’t like you, you’d be dead the next morning. And I got indicted more than him. On bullshit, too. Just bullshit.”
“The enemies from within are more dangerous to me than the enemies on the outside. Russia and China we can handle, but these lunatics within our government that are going to destroy our country, we have to get it stopped. They’re not on the right; they’re on the left.”
“Fat Alvin, corrupt guy.”
“You could take the ten worst presidents in the history of our country and add them up...and they haven’t done the damage to our country that this total moron has done. He’s a fool; he’s not a smart man. He never was. He was considered stupid. I talk about him differently now because now the gloves are off. He’s a bad guy…he’s the worst president ever, of any country. The whole world is laughing at him; he’s a fool.”
“They’re emptying out their mental institutions into the United States, our beautiful country. And now the prison populations all over the world are down. They don’t want to report that the mental-institution population is down because they’re taking people from insane asylums and from mental institutions.”
“Has anyone ever seen The Silence of the Lambs ? The late, great Hannibal Lecter. He’s a wonderful man. He oftentimes would have a friend for dinner. Remember the last scene? ‘Excuse me, I’m about to have a friend for dinner,’ as this poor doctor walked by. ‘I’m about to have a friend for dinner.’ But Hannibal Lecter. Congratulations. The late, great Hannibal Lecter. We have people that have been released into our country that we don’t want in our country, and they’re coming in totally unchecked, totally unvetted. And we can’t let this happen. They’re destroying our country, and we’re sitting back and we better damn well win this election, because if we don’t, our country is going to be doomed. It’s going to be doomed.”
(Not to be pedantic, but the fictional Mr. Lecter is still fictionally alive, and not fictionally dead. He has accomplished this despite, you know, not being a real person.)
The only story to be written about this event is that a huge crowd gathered to see and hear the presumptive presidential candidate have some sort of episode in public. That is a major news story. Half the electorate has turned into a banana farm. The following, from The New York Times, is not the way to do this.
But if Mr. Trump’s speech largely consisted of what has become his standard fare, the setting stood out. Though New Jersey has voted for Democratic presidential candidates in every election since 1992, and Mr. Trump lost the state by double-digit margins in both 2016 and 2020, he insisted that he could win there in November. “We’re expanding the electoral map, because we are going to officially play in the state of New Jersey,” Mr. Trump said to a packed crowd on the beach. “We’re going to win the state of New Jersey.”
Neither is this.
Mr. Trump, who once owned casinos in Atlantic City, N.J., and who often spends summers at his golf club in Bedminster, N.J., has been publicly bullish on his chances in New Jersey for months. Political experts, and even some of his advisers, are skeptical. Still, parts of the state are deeply conservative, including the area around Wildwood, a boardwalk town on the southern end of the Jersey Shore and a beach destination popular with working-class families. Many visitors come from Pennsylvania, a battleground state that backed Mr. Trump in 2016 but swung to Mr. Biden in 2020.
And, finally, this isn’t, either.
Against the backdrop of classic Americana, Mr. Trump repeated his typical criticism that Mr. Biden’s economic policies were hurting the middle class. With an amusement park operating rides in the background, he insisted that only he could preserve the summer shore tradition. “The choice for New Jersey and Pennsylvania is simple,” Mr. Trump said, telling supporters to vote for him if they wanted “lower costs, higher income and more weekends down at the shore.” (The area’s locals usually say “down the shore,” but judging by the cheers of the crowd, the point was well received.) The rally was a stark contrast to the scene at the Manhattan courthouse, where proceedings are more sober and Mr. Trump’s comments are limited to remarks to reporters before he enters and leaves the courtroom.
This is normalization that ought to be taught in journalism schools as an example of what never to do. And the comparisons drawn between Trump in Court and Trump on the Stump are dangerously facile. His criminal trial isn’t just another bump on the campaign trail, like a freak snowstorm in Iowa or a washed-out bridge in New Hampshire. The odds are better than 50–50 that the presumptive Republican presidential candidate will be a convicted criminal going into his party’s convention. That’s a black-swan event in American history, and it ought to be covered like one every day.

Charles P Pierce is the author of four books, most recently Idiot America , and has been a working journalist since 1976. He lives near Boston and has three children.

@media(max-width: 73.75rem){.css-1ktbcds:before{margin-right:0.4375rem;color:#FF3A30;content:'_';display:inline-block;}}@media(min-width: 64rem){.css-1ktbcds:before{margin-right:0.5625rem;color:#FF3A30;content:'_';display:inline-block;}} Politics With Charles P. Pierce Exclusives

Mike Johnson Took a Field Trip to Court

Aww, Trump Brought Some Buddies to Court

We Have to Talk About Brain Worms

Trump Put a Literal Price on the Future

The Stormy Has Passed

RFK Jr. Has A Medieval-Sounding Medical History

Stormy Daniels' Testimony Was Something Else

Matt Gaetz and MTG Are Theologians Now?

What the Heck Happened to the Film ‘The Sixth’?

Justice Amy Coney Barrett Is Not Some Kind of Hero

Trump’s Right About One Thing
Ukraine war latest: Two dead in airstrike on Kharkiv; Russia says UK is 'de facto' participant in war
At least two people have been killed and more than a dozen injured in a reported Russian attack on Ukraine's second-largest city. Russia's ambassador to the UK says Britain's sharing of weapons and intelligence with Kyiv has effectively drawn it into the war.
Friday 17 May 2024 15:19, UK
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
- Two dead and 13 injured in Kharkiv attack
- Russia claims UK is 'de facto participant' in conflict | Moscow official warns US it is 'playing with fire' in 'indirect war'
- Russian troops advance - but situation 'stabilised', says Zelenskyy
- Putin: Capturing major city 'not part of plan'
- Kharkiv 'attacked' in 16-hour air raid alert - longest since war began
- Footage shows oil refinery fire and burning fuel depots after 'massive' overnight attack
- Analysis: Great power politics on display in China visit
- Were Putin and Xi really pictured with their 'nuclear footballs'?
- Live reporting by Narbeh Minassian
Ask a question or make a comment
Moscow says it sees the US and UK as responsible for recent attacks because they are allowing Ukraine to use Western weapons against Russian targets.
The Russian foreign ministry said the UK, US, EU and Kyiv were "playing with fire" over attacks on Russian soil, state news agency Tass reports.
Such actions will not go unanswered, it warned.
"Once again, we should like to unequivocally warn Washington, London, Brussels and other Western capitals, as well as Kyiv, which is under their control, that they are playing with fire. Russia will not leave such encroachments on its territory unanswered."
Earlier today, Russia's ambassador to the UK said the UK was a de facto participant in the war.
This was because it has supplied Kyiv with weapons and shared real-time intelligence, said Andrei Kelin.
The number of victims from a reported Russian airstrike has risen, officials say.
At least two people are now said to have died, with another 13 injured - four of whom are in a "serious condition", regional governor Oleh Syniehubov said.
It is not clear what the attack targeted, but Mr Syniehubov said those injured are civilians.
Reports had initially claimed one person had died and four injured.
Kharkiv, Ukraine's second largest city, and the surrounding region have long been targeted by Russian attacks but the strikes have become more intense in recent months.
Ukraine President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has accused Moscow of seeking to reduce the city to rubble.
A Ukrainian drone hit another oil terminal this morning, this time in the Russian Black Sea port of Novorossiisk, according to sources and footage shared on social media.
The Importpischeprom oil products terminal and Sheskharis oil harbour were struck, with the port shut soon after the attack.
Oil loadings resumed later from Sheskharis, according to industry sources and LSEG data, while activity at Importpischeprom remains suspended.
It came as Russian officials reported another drone attack on an oil refinery, causing a fire in Tuapse, which is roughly 150km southeast of Novorossiisk.
Both are in the Krasnodar region.
Russian oil pipeline monopoly Transneftdid not reply to a request for comment. Its subsidiary, Novorossiisk Commercial Sea Port Group (NCSP), which operates the Sheskharis oil terminal, declined to comment.
Novorossiisk is Russia's largest port on the Black Sea and is a key oil outlet for crude oil and transit in country's south. It also handles grain, coal, mineral fertilisers, timber, containers, food and chemical cargoes.
Four people have been hurt and at least one has died in an airstrike on the city of Kharkiv, according to local officials.
The regional governor says some of those injured are civilians, while it's reported Russia used guided bombs in the attack.
It's not immediately clear what exactly came under attack.
More now on the comments made earlier by the Ukrainian army's commander-in-chief Oleksandr Syrskyi (see our 10.21am post).
He said he expects fighting to intensify as Russia continues to attack Kharkiv - with Sumy the next possible target, roughly 170km northwest.
Russia's attack on Kharkiv has expanded the area of active fighting by almost 70km, he added, which was designed to force Ukraine to divert stretched resources to the region.
In comments on the Telegram messaging app, he said the main focus of Russia's attack is towards the area of Lyptsi and further east in Vovchansk - as our military analyst Michael Clarke reported earlier (1.27pm).
Mr Syrskyi said Russia attacked early after noticing a change in troops, but they "failed to break through".
He added Ukraine "must prevent further advance" by "inflicting maximum losses with air strikes, missile systems, artillery and tank fire".
Russia's defence ministry claims Russian forces have taken control of 12 settlements in Ukraine's northeastern Kharkiv region in the past week.
Moscow has claimed a series of gains since its forces launched a new offensive in Kharkiv's north last Friday - in a move which surprised Ukrainian soldiers stationed in the area.
As we've been reporting, Vladimir Putin said earlier that his troops were creating a "buffer zone" in Kharkiv to protect Russian border regions.
Earlier we reported Vladimir Putin's claims that there are no plans to capture the city of Kharkiv as his forces continue to attack the region (see 11.17am post).
Our defence and security analyst Michael Clarke says Russian forces would not be able to take the city even if they tried as they "just don't have the forces to concentrate on big cities".
"It would take them months of grinding warfare to actually conquer Kharkiv," he said.
"Unless the Ukrainians somehow open the gates and let them in, which they won't."
Moscow's forces are pushing towards the village of Lyptsi, he says, which is about 15 miles from Kharkiv city and well within artillery range.
"If they get there, they could certainly start to bombard the city and Ukrainians would have to do something about that," he said, adding they are also targeting the key town of Vovchansk, possibly to try to link up with forces further south.
While capturing the city of Kharkiv remains a remote possibility, Clarke says they can draw Ukrainian forces away from the south, as they "already have done".
Buffer zone 'propaganda'
Mr Putin claims the Kharkiv offensive is to create a buffer zone between the two countries, so Ukraine cannot attack regions within Russia.
Belgorod, in particular, has reportedly been the target of Ukrainian drone attacks in recent weeks, but Clarke says any buffer zone is unlikely to make much difference.
"At the moment, he's got a boundary of about three miles and the Ukrainians are getting American missiles," Clarke says.
"The missiles come with maximum ranges of about 170, 180 miles. It's neither here nor there."
The Ukrainians have got "many ways" of attacking Belgorod and Rostov, he said.
"So, I think it's more for propaganda purposes inside Russia - that Putin is saying 'we're having a border area to reassure the public in Belgorod and Rostov that these cross-border raids and these missile strikes might not take place in the future'."
UK is 'de facto' participant
Meanwhile, Russia's ambassador to the UK has said Britain is a de facto a participant in the Ukraine war (see our 12.32pm post).
Clarke says this is the "truest thing he's said today".
"The British government has made it very clear we're helping the Ukrainians with intelligence and, where appropriate, we've done it with our aerial intelligence," he said.
"So, the Russian ambassador is telling me something I've known for about the last two and a bit years."
Volodymyr Zelenskiy has waved through two potentially key bits of legislation around service in the military.
Firstly, the Ukraine president has this afternoon signed a law allowing some categories of convicts to serve in the army.
He also signed off a separate law increasing fines for those not abiding by army mobilisation rules.
Ukraine is trying to fill a shortfall in manpower some military analysts say is Kyiv's biggest challenge against a much larger enemy.
Recruiting convicts is only expected to boost numbers by around several thousand, from a possible pool of up to 20,000 convicts, senior lawmaker David Arakhamia said earlier this month.
Serious criminals barred
The bill would not allow people convicted of the most serious crimes to enlist, lawmaker Oleksiy Honcharenko said.
People convicted of the premeditated murder of two or more people, rape, sexual violence, crimes against national security and serious corruption violations would remain barred.
"It's no secret that the mobilisation resource of our enemy is huge, and therefore we should use all available opportunities to fight back armed aggression," a note attached to the bill said.
"Some of these people are motivated and patriotic citizens who are ready to redeem themselves before society on the battlefield."
Russia's ambassador to the UK has just said Britain is a de facto participant in the Ukraine war.
Andrei Kelin told Russia's Rossiya-24 state TV channel the UK is considered as such because it supplies Kyiv with weapons and shares real-time intelligence.
Former Russian president Dmitry Medvedev has made a similar claim previously.
The US is "playing with fire" over its "indirect war" with Russia, a top diplomat has warned.
Russian deputy foreign minister Sergei Ryabkov told the TASS news agency: "We warn that they are playing with fire. They have long been in a state of indirect war with the Russian Federation."
His comments reflect Russian concern over the West's ongoing support for Ukraine, with recent comments viewed by Moscow as an aggressive shift.
The UK's foreign secretary Lord Cameron said earlier this month Ukraine has a right to use the weapons provided by Britain to strike targets inside Russia - while US secretary of state Antony Blinken made similar comments during a visit this week in Kyiv.
"They somehow fail to realise that, in order to satisfy their own geopolitical ideas, they are approaching a phase in which it will be very difficult to control what is happening and to prevent a dramatic crisis," Mr Ryabkov added, referring to the US.
"This rhetoric, this drumming, this constant baiting of their allies to help Ukraine even more, to expand their support, shows only one thing: people are living, as they themselves say, 'in a box'," he said.
He said this is a "great risk" as it is "impossible to get through" to the Americans.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

Man who crashed U-Haul near White House pleads guilty
Sai Varshith Kandula, 20, told the Secret Service he planned to seize power. A defense attorney raised mental health issues.

A St. Louis-area man who crashed his rented U-Haul truck into Lafayette Square last year, with the apparent intention of entering the White House and overthrowing the government, pleaded guilty in federal court in the District on Monday to damaging federal property.
As part of a plea agreement, prosecutors added a “terrorism” enhancement for Sai Varshith Kandula, which exposed him to a sentence of 12 to 15 years in prison. But the maximum sentence for federal property damage is 10 years, and prosecutors agreed to seek a term of eight years for Kandula when he appears for sentencing on Aug. 23.
Kandula, 20, has been in the D.C. jail since the brief incident in the park last May. Surveillance footage from the park showed the U-Haul driving east on H Street, then turning into the park and nearly hitting two pedestrians before he slammed into a barrier of security bollards. The Secret Service said Kandula backed up the U-Haul and drove it into the bollards a second time before climbing out of the truck and unfurling a flag with a Nazi swastika.
When agents questioned him, Kandula reported that he had been planning his journey for six months, according to a detention memo filed by federal prosecutors. Kandula allegedly said that his goal was to “get to the White House, seize power, and be put in charge of the nation.”
Asked how this might work, Kandula reportedly replied, “Kill the president if that’s what I have to do and would hurt anyone that would stand in my way.” Asked about his flag, Kandula is said to have answered that “Nazis have a great history” and that he admired their authoritarian nature. He said he looked up to Adolf Hitler “because he was a strong leader,” according to the memo from Assistant U.S. Attorney Alexander R. Schneider.
Kandula, who lived with his parents in Chesterfield, Mo., was ordered held in jail until his trial by U.S. Magistrate Judge Moxila A. Upadhyaya. Court records show that Kandula’s lawyers have struggled to have the D.C. jail provide him with appropriate mental health treatment.
At the plea hearing Monday, defense attorney N. Scott Rosenblum said that Kandula had been seen by mental health specialists and “diagnosed with schizophrenia.” Kandula told U.S. District Judge Dabney L. Friedrich that he was taking medication for his illness but did not know what it was.
Kandula also said he was born in India and is not an American citizen. He acknowledged he could face deportation when he is finished serving his sentence.
Authorities said Kandula flew from St. Louis to Washington Dulles International Airport on May 22, 2023, then rented the U-Haul truck and drove directly to D.C. and the White House.
After Kandula slammed into the bollards twice, he immediately surrendered when U.S. Park Police officers ordered him to the ground, court records show. He also supplied a “green book” with handwritten entries about harming his family and taking over the country.
“My fellow citizens of United States,” Kandula allegedly wrote in a speech to be delivered after he seized power. “There shall be consequence if civil unrest happens. Any opposition will be met with death penalty … We will rebuild this world, and put a new system in place once the objective has been achieved. Sieg hail [sic].”
The judge asked Kandula, “Is it true you drove a U-Haul truck into the metal bollards at 16th and H streets?”
“Yes,” Kandula answered.
“Is it true you backed up and did it a second time?” Friedrich asked.
“Uh, yep,” Kandula said.
The collision caused $4,322 in damage to the bollards and $52,405 in damage to the U-Haul, Schneider said. Kandula may be ordered to pay restitution for both amounts at his sentencing.

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Chiefs kicker Butker congratulates women graduates and says most are more excited about motherhood
FILE - Kansas City Chiefs kicker Harrison Butker speaks to the media during NFL football Super Bowl 58 opening night Monday, Feb. 5, 2024, in Las Vegas. Butker railed against Pride month along with President Biden’s leadership during the COVID-19 pandemic and his stance on abortion during a commencement address at Benedictine College last weekend. (AP Photo/Charlie Riedel, File)
The Benedictine College sign is seen Wednesday, May 15, 2024, in Atchison, Kan., days after Kansas City Chiefs kicker Harrison Butker gave a commencement speech that has been gaining attention. Butker’s speech has raised some eyebrows with his proclamations of conservative politics and Catholicism, but he received a standing ovation from graduates and other attendees of the commencement ceremony on Saturday, May 11. (AP Photo/Nick Ingram)
- Copy Link copied
KANSAS CITY, Mo. (AP) — The commencement speaker at Kansas’ Benedictine College , a private Catholic liberal arts school, congratulated the women receiving degrees — and said most of them were probably more excited about getting married and having children.
Harrison Butker, the kicker for the Super Bowl champion Kansas City Chiefs, is getting attention for those and other comments last weekend in which he said some Catholic leaders were “pushing dangerous gender ideologies onto the youth of America.”
Butker, who’s made his conservative Catholic beliefs well known, also assailed Pride month , a particularly important time for the LGBTQ+ rights movement, and President Joe Biden’s stance on abortion.
“I think it is you, the women, who have had the most diabolical lies told to you,” Butker said.
AP AUDIO: Chiefs kicker Butker congratulates women graduates and says most are more excited about motherhood
A Super Bowl champion kicker is in hot water after comments he made during a college commencement speech. Correspondent Gethin Coolbaugh reports.
“Some of you may go on to lead successful careers in the world, but I would venture to guess that the majority of you are most excited about your marriage and the children you will bring into this world. I can tell you that my beautiful wife Isabelle would be the first to say that her life truly started when she started living her vocation as a wife and as a mother,” he said.
Butker said that his wife embraced “one of the most important titles of all. Homemaker.“
“Harrison Butker gave a speech in his personal capacity,” NFL senior vice president and chief diversity and inclusion officer Jonathan Beane said in a statement. “His views are not those of the NFL as an organization. The NFL is steadfast in our commitment to inclusion, which only makes our league stronger.”
Butker also criticized as disparaging to the Catholic Church an article by The Associated Press highlighting a shift toward conservativism in some parts of the church.
The three-time Super Bowl champion delivered his roughly 20-minute address Saturday at the Catholic private liberal arts school in Atchison, Kansas, which is located about 60 miles (97 kilometers) miles north of Kansas City. He received a standing ovation from graduates and other attendees.
Butker, 28, referred to a “deadly sin sort of pride that has a month dedicated to it” in an oblique reference to Pride month. Butker also took aim at Biden’s policies, including his condemnation of the Supreme Court’s reversal of the 1973 Roe v. Wade decision and advocacy for freedom of choice — a key campaign issue in the 2024 presidential race.
Biden, who is Catholic, has a fraught history on the issue. He initially opposed the Roe v. Wade decision, saying it went too far . He also opposed federal funding for abortions and supported restrictions on abortions later in pregnancy.
Butker also tackled Biden’s response to COVID-19, which has killed nearly 1.2 million people in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“While COVID might have played a large role throughout your formative years, it is not unique,” he said. “Bad policies and poor leadership have negatively impacted major life issues. Things like abortion, IVF, surrogacy, euthanasia, as well as a growing support for degenerate cultural values and media all stem from pervasiveness of disorder.”
Graduates had mixed views on the speech. ValerieAnne Volpe, 20, who graduated with an art degree, lauded Butker for saying things that “people are scared to say.”
“You can just hear that he loves his wife. You can hear that he loves his family,” she said.
Elle Wilbers, 22, who is heading to medical school, said she was shocked by Butker’s criticism of priests and bishops and his reference to the LGBTQ+ community, one that she described as “horrible.”
“We should have compassion for the people who have been told all their life that the person they love is like, it’s not OK to love that person,” Wilbers said.
Kassidy Neuner, 22, who will spend a gap year teaching before going to law school, said being a stay-at-home parent is “a wonderful decision.”
“And it’s also not for everybody,” Neuner added, saying, “I think that he should have addressed more that it’s not always an option. And, if it is your option in life, that’s amazing for you. But there’s also the option to be a mother and a career woman.”
The Chiefs declined to comment on Butker’s commencement address.
The 2017 seventh-round pick out of Georgia Tech has become of the NFL’s best kickers, breaking the Chiefs’ franchise record with a 62-yard field goal in 2022. Butker helped them win their first Super Bowl in 50 years in 2020, added a second Lombardi Trophy in 2023, and he kicked the field goal that forced overtime in a Super Bowl win over San Francisco in February.
It has been an embarrassing offseason for the Chiefs, though.
Last month, voters in Jackson County, Missouri, soundly rejected a ballot initiative that would have helped pay for an $800 million renovation to Arrowhead Stadium, home of the Chiefs. Many voters criticized the plan put forward by the Chiefs as catering primarily to VIPs and the wealthy.
The same week, wide receiver Rashee Rice turned himself in to Dallas police on multiple charges, including aggravated assault, after he was involved in a high-speed crash that left four people with injuries. Rice has acknowledged being the driver of one of the sports cars that was going in excess of 100 mph (160 kph).
Last week, law enforcement officials told The Dallas Morning News that Rice also was suspected of assaulting a person at a downtown nightclub. Dallas police did not name Rice as the suspect in detailing a report to The Associated Press.
Chiefs coach Andy Reid said he had spoken to the receiver and the team was letting the legal process play out.
Associated Press writer Heather Hollingsworth in Mission, Kansas, contributed to this story.
AP NFL: https://apnews.com/hub/nfl
Advertisement
Supported by
At a Dinner, Trump Assailed Climate Rules and Asked $1 Billion From Big Oil
At a private meeting at Mar-a-Lago, the former president said fossil fuel companies should donate to help him beat President Biden.
- Share full article

By Lisa Friedman , Coral Davenport , Jonathan Swan and Maggie Haberman
Former President Donald J. Trump told a group of oil executives and lobbyists gathered at a dinner at his Mar-a-Lago resort last month that they should donate $1 billion to his presidential campaign because, if elected, he would roll back environmental rules that he said hampered their industry, according to two people who were there.
About 20 people attended an April 11 event billed as an “energy round table” at Mr. Trump’s private club, according to those people, who asked not to be identified in order to discuss the private event. Attendees included executives from ExxonMobil, EQT Corporation and the American Petroleum Institute, which lobbies for the oil industry.
The event was organized by the oil billionaire Harold Hamm, who has for years helped to shape Republican energy policies. It was first reported by The Washington Post.
Mr. Trump has publicly railed for months against President Biden’s energy and environmental agenda, as Mr. Biden has raced to restore and strengthen dozens of climate and conservation rules that Mr. Trump had weakened or erased while in office. In particular, Mr. Trump has promised to eliminate Mr. Biden’s new climate rules intended to accelerate the nation’s transition to electric vehicles, and to push a “drill, baby, drill” agenda aimed at opening up more public lands to oil and gas exploration.
Mr. Biden has called climate change an existential threat and has moved to cut the pollution that is dangerously heating the planet and supercharging storms, heat waves and drought.
Over a dinner of chopped steak, Mr. Trump repeated his public promises to delete Mr. Biden’s pollution controls, telling the attendees that they should donate heavily to help him beat Mr. Biden because his policies would help their industries.
“That has been his pitch to everybody,” said Michael McKenna, who worked in the Trump White House but did not attend the event in Florida.
Mr. McKenna said the former president’s appeal to the fossil fuel industry could be summed up as: “Look, you want me to win. You might not even like me, but your other choice is four more years of these guys,” referring to the Biden administration. He added, “The uniform sentiment of guys in the business community is ‘We don’t want four more years of Team Biden.’”
Karoline Leavitt, a spokeswoman for the Trump campaign, did not address the specifics of what Mr. Trump was described as saying at the dinner. In a statement, she attacked President Biden as controlled “by environmental extremists who are trying to implement the most radical energy agenda in history and force Americans to purchase electric vehicles they can’t afford,” and that Mr. Trump is “supported by people who share his vision of American energy dominance to protect our national security and bring down the cost of living for all Americans.”
Mr. Biden’s presidential campaign on Thursday accused Mr. Trump of “straight up selling out working families for campaign donations from oil barons.”
Mr. Biden has frustrated the fossil fuel industry by pursuing the most ambitious climate agenda in the nation’s history. He has signed a sweeping law that pumps $370 billion into incentives for clean energy and electric vehicles and has enacted a suite of tough regulations designed to sharply reduce emissions from the burning of oil, gas and coal.
This year, the Biden administration paused the permitting process for new facilities that export liquefied natural gas in order to study their impact on climate change, the economy and national security.
But the fossil fuel industry has also enjoyed record profits under the Biden administration. Last year, the United States produced record amounts of oil . And even with the pause in new permits for gas export terminals, the United States is the world’s leading exporter of natural gas and is still on track to nearly double its export capacity by 2027 because of projects already permitted and under construction.
Mr. Biden has also approved several oil and gas projects sought by the fossil fuel industry.
He has authorized an enormous $8 billion oil development in Alaska known as the Willow project. He also granted a crucial permit for the Mountain Valley Pipeline, a project championed by Senator Joe Manchin III, a West Virginia Democrat, despite opposition from climate experts and environmental groups. Last month, undeterred by opposition from climate activists, the Biden administration also gave approval for an oil export project in Texas known as the Sea Port Oil Terminal.
Some oil and gas executives have said that they would prefer some of Mr. Biden’s regulations to remain, such as a rule requiring companies to detect and stop methane leaks from oil and gas wells. They said they wanted consistency rather than an endless pattern of regulatory whiplash in which rules are enacted by one administration, repealed by the next and restored by the one after that.
Many, however, have attacked Mr. Biden’s policies, and the industry has contributed heavily to Mr. Trump’s presidential campaign.
Although attendees were told that Mr. Trump’s event was an energy round table, waiting on the chairs of executives and lobbyists at Mar-a-Lago were printouts of PowerPoint slides about migrants at the southern border.
Part of the meeting dwelled on migration, and Mr. Trump declared he wanted separate divisions of Ultimate Fighting Championship fighters: one designated for immigrants who came across the border illegally, and the other for “Americans.”
The room was filled predominantly with oil and gas executives, including Mike Sabel, the chief executive and founder of Venture Global LNG; Toby Rice, the president and chief executive of EQT Corporation; Jack Fusco, the chief executive of Cheniere Energy; and Nick Dell’Osso, the president of Chesapeake Energy.
Also in the room were Doug Burgum, the governor of North Dakota and a former Republican presidential candidate who has been acting as Mr. Trump’s point man on energy issues; and Mr. Hamm, the billionaire executive chairman of Continental Resources, which is among the biggest oil and gas drilling companies in Oklahoma and North Dakota.
Accompanied by Susie Wiles, his top political adviser; Taylor Budowich, a former aide; and Meredith O’Rourke, a fund-raiser, Mr. Trump asked the executives to detail their concerns on energy issues, according to the two attendees.
The American Petroleum Institute, the nation’s top fossil fuel industry group, is running an eight-figure national advertising campaign to promote fossil fuels and “dismantle policy threats,” Mike Sommers, the chief executive of the trade group, has said. Separately, the American Fuel & Petrochemical Manufacturers, which represents petroleum refiners, has started to buy ads in nine battleground states urging Americans to fight Mr. Biden’s regulation on tailpipe emissions.
And states with Republican attorneys general have filed legal challenges against most if not all of Mr. Biden’s regulations, including a suit announced on Thursday by 27 states arguing that the administration overstepped its authority in cracking down on smokestack pollution from power plants.
But Mr. Trump told executives they were not fighting hard enough. He also went on a rant about windmills, the attendees said. Mr. Trump has falsely claimed that wind turbines cause cancer and that offshore wind farms are “driving whales crazy .”
Mr. Trump did not request money in exchange for killing Mr. Biden’s climate regulations, the two people in the room maintained. Rather, the former president told executives that he was determined to squash what he considered anti-business policies, and that the oil industry should therefore want him to win and should raise $1 billion to ensure his success.
He told the executives that the amount of money they would save in taxes and legal expenses after he repealed regulations would more than cover a billion dollar contribution, the people said.
Mr. Hamm has had Mr. Trump’s ear on energy issues dating back to the former president’s 2016 campaign and pushed him to appoint Scott Pruitt to run the Environmental Protection Agency, where Mr. Pruitt denied the established science of climate change and unraveled environmental protections.
After Mr. Trump lost the 2020 election, Mr. Hamm briefly supported some of the former president’s rivals, including Gov. Ron DeSantis of Florida and former United Nations Ambassador Nikki Haley. But the oil tycoon appeared to have had a change of heart. Mr. Hamm donated $3,300 to Mr. Trump’s campaign last year, the maximum allowed for a primary contribution, and another $3,300 in March, according to campaign filings.
Mr. Hamm did not immediately respond to a request for comment. Mr. McKenna said Mr. Hamm continued to play an outsize role in Mr. Trump’s energy policy. “If Harold has an idea, the rest of us have to chase it around,” he said. “Harold Hamm wants that L.N.G. pause gone, he wants the California waiver and the tailpipe rule gone.”
California has for decades received waivers under the Clean Air Act that authorize it to set environmental rules that are tougher than federal regulations. To do business in California, automakers and other industries must comply with its rules. Mr. Trump has promised to revoke California’s waivers.
An earlier version of a picture caption with this article misstated the location of Mar-a-Lago. It is in Palm Beach, Fla., not West Palm Beach.
How we handle corrections
Lisa Friedman is a Times reporter who writes about how governments are addressing climate change and the effects of those policies on communities. More about Lisa Friedman
Coral Davenport covers energy and environment policy, with a focus on climate change, for The Times. More about Coral Davenport
Jonathan Swan is a political reporter covering the 2024 presidential election and Donald Trump’s campaign. More about Jonathan Swan
Maggie Haberman is a senior political correspondent reporting on the 2024 presidential campaign, down ballot races across the country and the investigations into former President Donald J. Trump. More about Maggie Haberman
Our Coverage of the 2024 Election
Presidential Race
President Biden and Donald Trump have agreed to two debates on June 27 on CNN and Sept. 10 on ABC News, raising the likelihood of the earliest general-election debate in modern history.
The early-debate gambit from Biden amounted to a public acknowledgment that he is trailing in his re-election bid , and a bet that an accelerated debate timeline will force voters to confront the possibility of Trump returning to power .
Robert F. Kennedy Jr.’s running mate, the Silicon Valley investor Nicole Shanahan, said that she had given another $8 million to their independent campaign.
Biden’s Investments in Battlegrounds: Biden’s economic policies have helped spur billions of dollars in new investments in Arizona and Georgia, yet Trump has maintained a significant lead over Biden in both states .
Warming to Trump: In an about-face, big financiers on Wall Street, in Silicon Valley and elsewhere are increasingly on board for a second Trump term after the first one alienated them.
Russian Disinformation: Ahead of the election, Russian disinformation videos are trying to appeal to right-wing voters with fake messages about Biden , experts say.
Black Women in the Senate: The Democratic Party has taken heat for not backing Black female candidates in statewide races. But in November, voters could double the number of Black women ever elected to the Senate .
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Remarks by President Biden at a Campaign Reception | Seattle, WA
6:22 P.M. PDT
THE PRESIDENT: Folks, thank you. (Applause.) I’ll tell you something else — (inaudible) get up here. I want to tell you something else. When we win, he ain’t staying in Washington State. (Applause.)
GOVERNOR INSLEE: Uh oh! (Laughter and applause.)
THE PRESIDENT: Go talk to Trudi. (Laughs.)
GOVERNOR INSLEE: Go get it. Have fun tonight.
THE PRESIDENT: Thank you.
Hello, Seattle! (Applause.) And thank you for the warm welcome. But please keep it down because — (laughter) — Donald Trump is sleeping. (Laughter.) “Sleepy Don,” I kind of like that these days. (Laughter.)
You know, I have — look, Governor Inslee, Jay, you are the leader in the country on climate change. You really are. You’ve done more as a governor in your state than any governor has in anywhere in America. (Applause.)
When they told us we couldn’t possibly get a bipartisan agreement to spend money on climate change, we got $369 billion. (Applause.) When I think climate change, I think jobs.
One of the things that I know we got a little — some people got a little worried because right after I got the nomination and was elected, I didn’t — I w- — made sure I didn’t introduce my entire climate change policy for a simple reason. I wanted to bring along organized labor. Labor always thought of climate as causing them jobs — costing them jobs. But I spent time with the IBEW, starting with them, and every other major labor union in America has endorsed our climate policy, embraced it, and made it work. So — (applause) —
And, Trudi, as my mother would say, no purgatory for you, (inaudible), straight to heaven — straight to heaven.
There’s no such thing as being the “First Spouse.” There’s no such thing. It’s about — when you’re the wife or the husband of a governor, you’re the governor too. So, thank you very much. (Applause.) No, no. You know I’m telling you the truth.
They know where you can show up. They know where you live without — “Why did we do this? Why’d we do that?”
Anyway, thank you very much.
And, look, I also want to thank the Governor. The previous Governor has become a great friend of mine, and I have great faith that he ain’t going nowhere either, if I make it. And that’s Gary — Governor Gary Locke. Where are you, Gary? (Applause.)
And you want a fighter on your side, you want someone who knows what she’s talking about, someone who does what she says and says what she does, Congresswoman Jayapal, who’s right here. (Applause.)
I want to thank Nick and Lisa and all the co-hosts here tonight.
Just let me say I — you know, I should have the Head and the Heart perform before every — every program I have, because this is — this is an incredible crowd. (Applause.)
My dad, when he was high school age — he was from Baltimore — he had a band. He got into Johns Hopkins, but because of the war, he never got to go, make a long story short. But my dad played the saxophone and the clarinet. He could sing a little bit, and he could dance. He had a band.
And he said, “Joey, I don’t know where the hell you came from. You have no lip, you can’t play a reed instrument.” (Laughter.) “You have two left feet and can’t dance. And you can’t carry a tune in the wheelbarrow. But I still love you.”
So, I — (laughter) — I’m always appreciative when anybody with musical talent says something nice about me. Charity and Matthew, you’re incredible. Thank you for all you do.
Look, folks — (applause) — as we go into spring, we genuinely feel the excitement and momentum we’re building in the campaign, and I mean that sincerely.
I think most of the members of Congress that I’ve served with so long will tell you no one ever doubts I — what — I mean what I say. The problem is that I sometimes say all that I mean. (Laughter.) But I’m optimistic. I’m feeling good. Feeling good about the country. We’re moving. So far, over 1.6 million individuals have contributed to our campaign — five hundred and fifty thous- — fifty-five thousand of them in just sin- — ma- — new since the last campaign, new contributions. And 90 percent of those contributions are under $200 — people contributing $5, $10, $20, $50 dollars a month helping this campaign.
There’s a genuine groundswell. People are engaged, no matter what the polling data says. And we’ve opened over 150 offices in — 150 — 1-5-0 — in battleground states. And that as — and Trump has his zero in those states. And while the press doesn’t write about it — (applause) — the momentum is clearly in our favor, with the polls moving towards us and away from Trump. Earlier this week, I was in Wisconsin. The Quinnimac [Quinnipiac] Poll had up 6 points with registered voters. The — the IPSOS/ABC poll has us 4 percent up. But it’s awful hard to judge the polls these days because they’re so difficult to take. They don’t have — most people don’t answer their landlines, and so it’s really up in the air. But I can tell you, we’re out around the country, we’re out around a lot. There’s some enthusiasm. People want to get things done. Things are beginning to move. And people are beginning to focus.
And those of you who’ve been involved in — in partisan politics and going door to door and those kinds of things, people really don’t get juiced until somewhere toward the end of the summer and the beginning of the fall. But we’re — we’re really optimistic.
I know everyone is feeling that enthusi- — I know not everyone is feeling that enthusiasm. The other day, a defeated-looking man came up to me and said, “Mr. President, I’m being crushed by debt, and I’m completely wiped out.” I had to say to him, “I’m sorry, Donald, I can’t help you.” (Laughter and applause.) “Nothing I can do to help.” (Applause.) Look, Trump knows he’s in trouble. You know, he has bragged about he’s the reason why Roe v. Wade was overturned, and now he’s worried the voters are going to remind him of that and all the cruelty and chaos that has caused.
Well, let me ask you: Are we going to hold him accountable or not? We are, right? (Applause.) Trump did a long interview in TIME Magazine. You ought to read — I’m being deadly earnest about this. You ought to read it.
He said, quote, “states should monitor women’s pregnancies and prosecute those who violate the bans.”
Monitor women’s pregnancies? What have we become here?
But, look, chaos is nothing new to Trump. His presidency was a chaos. Trump is trying to make the country forget how dark and unsettling things were when he was president. But we’re never going to forget. We’ll never forget the fact — him lying about the pandemic. He knew how dangerous it was, but he didn’t want to — he wouldn’t say it to anybody. He said, “Just go inject a little bleach in your arm.” (Laughter.) Too bad he didn’t. (Laughter and applause.)
Look — all kidding aside, it was bizarre. We lost a million people. And all the data shows those million, every one of them had eight people that were significant to them — brothers, sisters, uncle, aunts, mothers, fathers, wives, children.
We’re never going to gret [forget] the love le- — his love letters to Kim Jong Un of North Korea, talking about what a — how he could work with him, he’s a good man, or his administration — his admiration for Putin, standing with Putin at a press conference after a meeting and talking about how he believed Putin, he didn’t believe his own security people. And here’s what he said in that TIME Magazine article. He said he — and he may — he said — straight up, I really urge you to read it so I’m not — I’m not putting words in his mouth (inaudible). His words. No, I — I really mean it. Because he means what he says.
He said he wouldn’t — wouldn’t — may not come to an aid of an ally in Europe or Asia if attacked if he felt that country hadn’t been spending enough money on its own defense system — would not come to the aid.
Look, folks, I don’t want any part of that. And I spent a lot of time — my reg- — expertise is American foreign policy and climate, the two things that I’ve worked on the most. And, you know, I go to these international meetings, because I know personally the vast majority of the world leaders, and the new ones as well.
And every — whether it’s a G7 meeting or G20 in any — wherever it is — and I mean this from the bottom of my heart — it’s disturbing, because what will happen, as we’re leaving the meetings, one of the leaders — many of them — will grab me by the arm and say, “He can’t win again. Please. My d-” — meaning their — “My democracy is at stake.”
Look, folks, Madeleine Albright was right. We are the essential nation. If we don’t stand up, who does? Who does? If we don’t unite the world, who can — in our interest?
But look how far we’ve come: 15 million brand new jobs, a record, just in three and a half years. (Applause.) More people have health insurance today than ever before in the history of this country. (Applause.)
We took on Big Pharma, which I’ve been fighting since I was a senator, and we finally won. Anybody knows they need insulin for their serious problems they have, it’d cost them — instead of costing them 400 bucks a month, now it costs 15 bucks a month. (Applause.) And it’s only just beginning.
And, folks, it not only saves lives, it saves taxpayers $160 billion — (applause) — because Medicare doesn’t have to pay the price. That’s a fact.
And with your governor’s help, we’re making the most significant investment ever in climate.
I’m so proud to report that co- — that wh- — they co-released by 20 major climate organizations, from the Sierra Club to the Sunrise Movement, it credited our administration with making more than 300 actions related to climate, conservation, public health, and clean energy.
In their words — in an endorsement: “Biden does more to take action to protect, restore, and secure health and environment in America than any president in American history, and he’s not done yet.” (Applause.) We are not done yet. (Applause.)
And as Jay will tell you, every time I had a tough decision, I’d call him, I — for get his opinion. And I’m not joking.
Jay, there’s no place to hide, if I make it. (Laughter.) (Inaudible) — no, I’m serious. He’s the best in the country.
I signed the most significant gun safety law in 30 years. (Applause.) The idea our children are going to school and learning how to duck and cover is sick. It’s sick.
More children killed because of a bullet than any other reason. Think of that, in America — the United States of America. And the [former] President is saying — thanking the — telling the National Rifle Association that, you know, he’s their best friend, nothing is going to happen when he’s there.
Well, guess what? Thirty years ago — it’s not going to stop until we ban assault weapons again. (Applause.)
I apologize. I’m going on too long.
But, look, the point is: We’re lowering costs, expanding opportunities, and protecting freedoms. But it’s all at stake. It really is all at stake.
Trump is still determined, in his words, to “terminate” the Affordable Care Act, which will kick millions of people off insurance. You know, it’s the only reason why people with a pre-existing condition are able to get insurance — tens of thousands of them.
He’s determined to get rid of my climate law, and he’s just flat out saying it, because the oil companies hate it.
In fact, it’s been reported — you probably saw it on television. He said it in his — in — in the TIME Magazine article that’s on the front — he’s on the front cover of.
He said that he asked Big Oil, quote, “to direct a billion dollars to his campaign.” He said it would be a good “deal” for them.
No, I’m serious. I’m not making this stuff up. Just read it. His own words. He’d repeal everything we’re doing on climate. And he said in the TIME article he wants to drill, drill, drill.
Well, folks, look, during his presidency, he exploded the federal deficit more than any other president had in a term — (inaudible) the federal deficit than any pre- — any previous president.
And he’s determined to cut Social Security and Medicare. His own words: “There’s a lot you can do in terms of cutting,” he says.
Nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office just released a study, j- — this is noth- — nothing out of my office — showing his plan for what he wants to spend the next four years. And he’s — he laid it out, as did the MAGA Republicans in the House. It would cost $5 trillion over the next decade. It’s fiscally recke- — it’s just totally reckless.
And, folks, there’s so much at stake.
You know, I proposed the strongest border bill ever — the most — most fair and humane immigration reform in decades. It includes a pathway to citizenship for DREAMers and more.
And, by the way — (applause) — and, by the way, I’m proud that my administration announced that DREAMers are finally able to get healthcare under the Affordable Care Act now. (Applause.)
If the team would just hold a second, I want to tell you — look, there’s a reason why we have the most advanced economy in the world today, right now: Because we’re not xenophobic. We allow people to come in and work. We grow our economy.
Look at China. China’s in a situation where they have more retired than working. They ha- — they don’t know what to do about it. Many other countries in the same position.
Meanwhile, in the same Trump TIME interview, he vowed to use the U.S. military — saying this, straight up. He’s vowed to use the U.S. military to comb the country and deport 11 million people here in America who are waiting to have their cases determined.
I mean — and he calls — and he calls immigrants — and he means it — he calls them “rapists” and “murderers.” And he said, quote, “They are not people.” “They are not people.”
I wonder what would happen when my Irish ancestors were trying to get here, what he would have thought of.
Trump says immigrants “poison the blood of America.”
Folks, just look at the audience. We are a nation that’s integrated with all kinds of denominations, all kinds of backgrounds, all kinds of — look, it’s not who we are. That’s not America.
But, folks, the biggest threat Trump poses is straight to our democracy — literally, not figure- — our democracy.
The same TIME article, he said what I’ve heard him say other times. He said, “A lot of people liked it when I said I’d be a dictator on day one.”
Well, there were some MAGA Republicans who probably did like it, but I sure in hell didn’t, and I’m going to make sure it doesn’t happen. (Applause.)
Folks, when asked if he thought — he was asked if he thought — asked if he thought if violence would occur if he lost. You know what his response was? Straight up. “It depends.”
He calls the insurrectionists who are now in prison — he calls them “patriots.” And if reelected, he wants to pardon “every one” of them, he says.
Trump says when he loses again — if he — he says “if,” I say “when” — (laughter and applause) — he loses again, he says there will be a “bloodbath.” His words. A “bloodbath.” He means it.
Look, let me ask you a question. Do you see every — all these people vying to become his vice president? They’re being asked will they accept the outcome of the election. They’re all afraid to say they would. They’re all hedging the bet because they want to be his vice presidential nominee.
And, folks, look, the fact is that we’re in a position where the MAGA candidates auditioning for vice president are saying they aren’t sure, if they lose, whether they’d accept the outcome. And he says, “It depends.”
Folks, look, let me close with this. What’s at risk in 2024 are our freedoms and our very democracy.
I never thought I’d say that. As a student of history, someone who’s been doing this job for a long time, I never, ever thought I would say that.
Look at the presidential historians — conservative presidential historians, what they’re saying. You find anybody that doesn’t take it serious, who knows what they’re talking about?
That’s why I need you so badly. So, let me ask you: Are you with me? (Applause.)
I need your help. And I’m fed up. And I’ve never — (applause) — I’ve never been more — (applause) — I’ve never been more optimistic about our future. We just have to remember — we have to remember who we are.
We’re the United States of America. (Applause.) We’re the only nation in the world that’s come out of every crisis we’ve gone into stronger than we went in. And there’s nothing — and I mean this from the bottom of my heart — there’s nothing beyond our capacity when we act together.
So, God bless you all. And let’s protect these troops. (Applause.) Let’s go, (inaudible). (Applause.) Really. (Inaudible.)
Thank you, thank you, thank you. (Applause.)
Don’t jump.
Thank you all. Thank you. (Applause.)
Thank you all. (Applause.)
6:42 P.M. EDT
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Direct: "I will help you," she promised. Reported: She promised that she would help me. Direct: "You should study harder," he advised. Reported: He advised that I should study harder. Direct: "I didn't take your book," he denied. Reported: He denied taking my book. Direct: "Let's go to the cinema," she suggested.
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please. Instead, say request or say. For example: "Please don't interrupt the event," said the host.
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, "I like coffee.". As indirect reported speech, it looks like this: Indirect speech: Elisabeth said she liked coffee. You can see that the subject ("I") has been changed to "she," to show who is being spoken about. If I'm reporting the direct speech of someone else, and this person says "I," I'd ...
Introduction. In English grammar, we use reported speech to say what another person has said. We can use their exact words with quotation marks, this is known as direct speech, or we can use indirect speech.In indirect speech, we change the tense and pronouns to show that some time has passed.Indirect speech is often introduced by a reporting verb or phrase such as ones below.
We use reported speech when we want to tell someone what someone said. We usually use a reporting verb (e.g. say, tell, ask, etc.) and then change the tense of what was actually said in direct speech. ... Sentences that start with a verb in direct speech need a to + infinitive in reported ... 20:36. The last most memorable conversation that I ...
Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later. In the direct speech example you can see the modal verb 'will' being used to ask a question. Notice how in reported speech the modal verb 'will' and the reporting verb 'ask' are both written in the past tense. So, 'will' becomes 'would' and 'ask' becomes 'asked'.
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said. ... The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include "asked," "inquired," "wondered," and "wanted to know." ... 20. Direct speech ...
Time and Place in Reported Speech. When we report something, we may need to make changes to: time (now, tomorrow) place (here, this room) direct speech. reported speech. She said, "I saw Mary yesterday." She said she had seen Mary the day before. He said: "My mother is here."
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site: (Click here to read the explanations about reported speech) Reported Statements: Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here) Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here) Past Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in ...
Rewrite the demands/requests in indirect speech. The passenger requested the taxi driver, "Stop the car.". → The passenger requested the taxi driver . to + same wording as in direct speech. The mother told her son, "Don't be so loud.". → The mother told her son . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don't.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
In indirect speech, the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command. Normally, the tense in reported speech is one tense back in time from the tense in direct speech: She said, "I am tired." = She said that she was tired. Phrase in Direct Speech. Equivalent in Reported Speech.
What is indirect speech or reported speech? When we tell people what another person said or thought, we often use reported speech or indirect speech. To do that, we need to change verb tenses (present, past, etc.) and pronouns (I, you, my, your, etc.) if the time and speaker are different.For example, present tenses become past, I becomes he or she, and my becomes his or her, etc.
See the sentences below with direct and indirect speech forms, these are great references to understand the difference. Also See: Say vs Tell Exercises Subjunctive That Clause Reported Speech Examples 1 1. "Don't play with matches," his mother said. 1. His mother told him not to play with matches. 2. "I've forgotten to bring my lunch with me ...
ESL Reporting Modal Verbs Worksheet - Grammar Exercises: Identifying, Matching, Gap-fill, Rewriting Sentences, Writing a Paragraph - Intermediate (B1) - 30 minutes. In this useful reported speech worksheet, students learn the indirect form of four modal verbs and practice using them in reported speech. First, students read a short dialogue and ...
However Indirect Speech (also called reported speech) refers to transmitting a sentence that someone has said. It is often used in daily language. For example, Susan told me she ate pizza yesterday. (Indirect Speech) Susan said, "I ate pizza yesterday.". (Direct Speech) Mathilda told me she had to go out. (Indirect Speech) Mathilda said ...
Michael M. Santiago // Getty Images. Over the weekend, the de facto Republican presidential candidate gave a speech in New Jersey in which he sounded like a raving lunatic. To wit: "Al Capone ...
We have reported this morning Russia claimed a Ukrainian drone attack caused a fire at an oil refinery in Krasnodar (see our 6.44am post). Footage shared by The Wall Street Journal's chief foreign ...
Friedrich asked. "Uh, yep," Kandula said. The collision caused $4,322 in damage to the bollards and $52,405 in damage to the U-Haul, Schneider said. Kandula may be ordered to pay restitution ...
PHOENIX — Justice Department officials said reports of widespread threats against officials running the 2020 and 2022 elections have resulted in charges against roughly 20 people, with more than ...
Chiefs kicker Butker congratulates women graduates and says most are more excited about motherhood. FILE - Kansas City Chiefs kicker Harrison Butker speaks to the media during NFL football Super Bowl 58 opening night Monday, Feb. 5, 2024, in Las Vegas. Butker railed against Pride month along with President Biden's leadership during the COVID ...
May 9, 2024. Former President Donald J. Trump told a group of oil executives and lobbyists gathered at a dinner at his Mar-a-Lago resort last month that they should donate $1 billion to his ...
Slovakia's Prime Minister Robert Fico walks during the European Council summit at the EU headquarters in Brussels, on April 18, 2024. Slovakia's Prime Minister Robert Fico was shot at after a ...
Hello, Seattle! (Applause.) And thank you for the warm welcome. But please keep it down because — (laughter) — Donald Trump is sleeping. (Laughter.) "Sleepy Don," I kind of like that these ...
The political rawness of the moment, as Israel pounds Gaza and outrage rocks American college campuses, means President Joe Biden's big speech Tuesday condemning antisemitism is most notable for ...
Provide a brief description (1-2 sentences) of the asset condition assessment used to determine the condition ratings reported below. Start Printed Page 42585 For each of the following asset types, indicate whether replacement, rehabilitation, or repair will occur under this project.