- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file

People also looked at
Original research article, “i just want to stay out there all day”: a case study of two special educators and five autistic children learning outside at school.

- 1 Department of Education and Wellness, Elon University, Elon, NC, United States
- 2 Department of Psychology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom
School is often stressful for autistic students. Similarly, special educators are susceptible to burnout because of the unique demands of their jobs. There is ample evidence that spending time outside, particularly in nature, has many positive effects on mental, emotional, and physical wellbeing. In this case study of two special educators and five autistic students in a social skills group at an elementary school in the southeastern United States, we sought to identify the effects of moving the class outside several times per week. Findings indicated that while there were challenges, the autistic children experienced numerous affordances that supported development toward achieving Individualized Education Plan goals. Moreover, there were also notable positive effects for the special educators. We found that even with little prior experience, learning outside is possible and beneficial to everyone involved.
Introduction
The first time Jacob, an autistic 1 elementary student with selective mutism, ventured into an outdoor environment at his rural school, he spoke to his friend while they were in the midst of an activity. His special education teachers were shocked. They told us they had never heard him verbalize anything due to selective mutism, an anxiety disorder that inhibits individuals from speaking in certain social situations despite an ability to speak in more familiar or comfortable settings ( American Psychiatric Association, 2013 ). As the year progressed and Jacob went outside more often with his social skills class, he spoke spontaneously with greater frequency, sometimes asking questions and interacting with his peers. Toward the end of the year, Jacob approached a brick wall near the outdoor learning environment that the class was using that day. He noticed a spider spinning a web on the wall. “Look at this!” he called to his friends. Several other children in the group gathered around, and they discussed what the spider was doing and why it was there. Jacob was an active participant in the conversation, engaged and curious.
Since Jacob was a participant in our case study, we were able to observe the ways that he and his autistic peers interacted with their teachers, with each other, and with the environment. Autism is a neurodevelopmental condition that consists of several typical behaviors or traits. These include repetitive, stereotyped behaviors and difficulties or impairments with social interaction and communication ( World Health Organization, 1992 ; American Psychiatric Association, 2013 ). As it is a spectrum, the needs, abilities, and outcomes of autistic individuals varies greatly. There is limited research on how nature might affect autistic children, especially at school, but there are many anecdotal accounts, which is what inspired our investigation. Higashida (2007) , an autistic Japanese teenager who communicates through a letterboard and computer, shared that nature has the ability to alter his emotions: “Just by looking at nature, I feel as if I’m being swallowed up into it … Nature calms me down when I’m furious and laughs with me when I’m happy” (p. 124). Gordon (2013) wrote about a non-speaking autistic four-year-old child spelling his name for the first time ever while outside using sticks as props. The teacher in Gordon’s article believes that spending time outdoors every day helps children with additional needs accomplish tasks previously believed to be beyond their capabilities. Brewer (2016) highlighted two schools in England that offered opportunities for students with additional education needs to spend time outdoors. According to a teacher at one of the schools, being outside is calming and stress-relieving, especially for autistic students. James (2018) , a British forest school leader, felt so strongly regarding the benefits he saw from taking autistic people into nature that he authored Forest School and Autism: A Practical Guide to encourage others to follow suit. James wrote that there is a lack of research available supporting the use of outdoor spaces with autistic people despite the wealth of anecdotal accounts, including those he details in his book.
Evidence continues to mount that spending time in nature is good for everyone (e.g., Chawla, 2015 ; Williams, 2017 ). While there are numerous studies that demonstrate benefits for typically developing children and adults (e.g., Wells and Evans, 2003 ; Fjørtoft, 2004 ; Swarbrick et al., 2004 ; Morita et al., 2007 ; Berman et al., 2008 ; Abraham et al., 2010 ; Berman et al., 2012 ; Kuo et al., 2018a ), there is limited research on the effects of nature for those with autism. Moreover, using outdoor environments as an accommodation to support autistic students at school is understudied. Therefore, in this case study of two special educators and five autistic students in a social skills group, we addressed the following research questions: What are the challenges and affordances of outdoor learning for autistic children? What are the special educators’ perspectives on outdoor learning with autistic children?
Literature Review
There is growing interest in the use of outdoor environments to benefit children. For instance, the North American Association for Environmental Education (2017) reported that there were 250 nature-based preschools and kindergartens in the United States, a notable increase. Learning outside can serve various educational purposes. The Institute for Outdoor Learning (n.d.) emphasizes “discovery, experimentation, learning about and connecting to the natural world, and engaging in environmental and adventure activities,” which can happen through multi-day trips, residential experiences, and adventure sports. Relatedly, nature-based learning (NBL) is “an educational approach that uses the natural environment as the context for learning” ( Chawla, 2018 , p. xxvii). Forest School (FS) is one example of NBL. The Forest School Association, 2011 , a professional body in the United Kingdom, provides six principles to guide and support FS practitioners. For example, FS takes place in an immersive wooded or natural environment, and learning is child-led. Recent research suggests that FS may facilitate feelings of affinity or ownership over natural spaces, thus encouraging pro-environmental behaviors ( Harris, 2021 ). NBL can, in practice, look many different ways. Access to an immersive wooded or natural environment is not necessary, however. Outdoor learning can occur in urban areas where children explore sidewalks, subways, stores, and parks (e.g., Whitlock, 2020 ).
The effects of engaging with nature are diverse. There are benefits to mental health, including lower stress levels ( Wells and Evans, 2003 ; Morita et al., 2007 ), improved social and emotional wellbeing ( Abraham et al., 2010 ; Berman et al., 2012 ), and feelings of belonging and sense of self ( Swarbrick et al., 2004 ; Cummings and Nash, 2015 ). Interpersonal skills seem to be positively impacted ( Dillon et al., 2005 ), including increased expressions of sympathy toward others and the environment ( Barthel et al., 2018 ). Even nearby nature has notable implications for cognition, intelligence, and development in both educational and residential contexts. Wells (2000) found that, in a study of low-income families with children aged 7–12 years old, moving from a “low naturalness” area to a “high naturalness” area had significant effects for child cognitive function. Similarly, Wells and Evans (2003) , using a four-item naturalness scale, reported that nearby nature may be a buffer for stressful life events for children with a mean age of 9.2 years in rural residential contexts. In a study of adults in Australia, Astell-Burt and Feng (2019) reported that higher amounts of tree canopy (30%) as well as total green space were associated with lower psychological distress and better general health. Bijnens et al. (2020) found that residential green space could have positive impacts on intelligence for children ranging in age from 7 to 15 years old in urban settings.
The benefits of nature for educational purposes have also been documented. Dadvand et al. (2015) , in their study of over 2,500 7 to 10-year-olds in Barcelona, suggested the possibility of improvements in cognitive development associated with surrounding greenness, particularly greenness of schools. Kuo et al., 2018b studied grass and tree cover in a sample of over 318 public schools in Chicago in relation to achievement on state-level assessments. Tree cover was related to academic achievement, particularly for math, while grass cover was not related. Thus, the presence of green spaces in and around schools seems to offer benefits to children. Additionally, Kuo et al., 2018a concluded that classroom engagement from 9 to 10-year-old children increased following lessons that took place in nature, suggesting the potential for what the authors refer to as “refueling in flight” for student focus. This reinforces Kuo et al.'s (2019) sentiment that “it is time to take nature seriously as a resource for learning and development” (p. 6). Considering the existing research, could the same be true for engaging autistic students with nature?
The accommodations and supports each autistic individual requires, if any, are highly variable. A large number of interventions exist to address supposed impairments in autistic populations; these include commonly known interventions such as Applied Behavior Analysis ( Baer et al., 1968 ), TEACHH (Treatment and Education of Autistic and Communications - Handicapped Children; Mesibov et al., 2005 ), and intensive interaction ( Nind and Hewett, 1988 ). The type of intervention or support that an autistic school-age child will receive is dependent on the specifications of that individual's Individualized Education Plan (IEP); the IEP, when used correctly, serves as a roadmap of interventions and supports to attain specific, measurable goals ( Blackwell and Rossetti, 2014 ). Difficulties with social interactions, for example, may prompt the use of an intervention like a social skills group. Group social skills training involves the teaching and practice of social skills among peers. This is the context of our case study. The worthwhileness of such an intervention for targeting the social skills of autistic children remains unclear, with some evidence of effectiveness ( Hotton and Coles, 2016 ) and other authors concluding that the intervention has little impact ( Bellini et al., 2007 ); despite this, the teaching and practicing of social skills in a group setting remains a common practice in special education ( DeRosier et al., 2011 ).
School experiences can be difficult for autistic children, leading to increased mental health issues and additional support needs. Due to the differences or difficulties in social communication common in autistic people, interactions with peers can be complex and challenging, causing stress and anxiety. Autistic children are also more likely to be bullied at school because of their behavioral differences ( Rowley et al., 2012 ). In fact, autistic children and teenagers are more likely to experience bullying and victimization than typically developing peers and peers with intellectual disability. Additionally, autistic children may experience gaps in academic achievement as well due to social impairments and other difficulties not related to intellect or ability ( Estes et al., 2011 ). It is not surprising, then, that mental health issues are more prevalent among the autistic population than the general population, with some researchers reporting estimates of 20% of the autistic population experience co-occurring anxiety disorders ( Lai et al., 2019 ). Confounded with the usual difficulties of childhood and adolescence, school can be a tumultuous time for autistic students.
One potential avenue of support for autistic individuals that is underutilized and understudied is the use of outdoor environments. While there is extensive research showing that time spent in nature offers benefits for wellbeing, particularly mental health, and even cognition and intelligence in typically developing populations or those with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), there is far less research on what nature might offer autistic people, especially children. According to Blakesley et al. (2013) , gardening projects, summer camps, field visits, and animal therapy have shown to have positive effects for autistic children; however, more research on the potential of outdoor learning for autistic children at school is needed.
The research that does exist is promising. Bradley and Male (2017) interviewed four autistic children, ages 6–8 years old, who participated in FS as well as their parents. Despite the small sample size, several benefits were identified from the interviews; these included friends/friendship development, challenges and risk taking, learning outcomes, and experiencing success. Zachor et al. (2016) utilized quantitative methods to study the impact of an outdoor adventure program on the autistic symptomatology of 51 autistic children between the ages of 3–7 years, with findings indicating a reduction of symptomatology after participation in the outdoor group when compared to a control group. Additionally, Li et al. (2019) interviewed caregivers of autistic children in China, who ranged in age from 4 to 17 years old, and “identified multiple sensory-motor, emotional, and social benefits of nature for children with autism” (p. 78). The findings from these three studies demonstrate that learning outdoors may need to be considered an accommodation and intervention for autistic children. Further evidence, especially in a school context, would bolster the research base and potentially lead to nature-based accommodations for autistic children.
Theoretical Framework
This study is framed by the theory of stress recovery put forward by Ulrich et al. (1991) . Stress recovery theory (SRT) suggests that following a bout of stress, individuals who are exposed to natural settings are able to reduce that stress more quickly than those who were not exposed to natural settings, demonstrated even at a parasympathetic level. The authors noted that the idea of stress recovery occurring in natural settings is not a new one; it has been documented throughout history, including in evolutionary theories. Stress reduction has also been observed in a study using nature sounds rather than visual natural scenes ( Alvarsson et al., 2010 ). Decades of research show that natural settings contribute to decreased stress and associated mental health issues ( Wells and Evans, 2003 ; Morita et al., 2007 ; Abraham et al., 2010 ; Berman et al., 2012 ).
SRT has also been applied in a sample of 18 11-year-olds, some of whom were considered to have “bad” behavior. Roe and Aspinall (2011) measured mood and reflection on personal development before and after a typical indoor lesson and a FS session. The authors reported that greater positive behavioral change occurred after time in the forest environment, suggesting that the restorative potential of nature may have been at play. Additionally, SRT underpinned work conducted by Shao et al. (2020) in which 26 elementary-aged children performed first an electronic gardening task followed by a real-life horticultural activity. Various physiological measurements (e.g., heart rate variability and skin conductance) indicated that the children experienced positive impacts from the real-life horticultural activity, including a decrease in sympathetic nervous activity. Thus, SRT has been applied to work with a range of ages, including younger children.
As previously noted, autistic individuals have a more difficult school experience. Additionally, the levels of mental health issues among the autistic population is much higher than that of typically developing peers ( Lai et al., 2019 ). It is likely that those challenging and sometimes traumatic school experiences are among several factors contributing to increased mental health issues among school-age autistic children. Due to its significant and continued impact upon wellbeing and various outcomes, the school experience and associated mental health issues should be of focus for teachers, caregivers, counselors, interventionists, and other practitioners who engage with this population. Stress recovery offered by educational activities occurring in nature could be beneficial, then, by mitigating the stressful experiences of attending school or interacting socially with others.
Research Methods
As a case study, this is a preliminary investigation of a phenomenon over which we had little control ( Yin, 2017 ). According to Miles et al. (2019) , a case is “a phenomenon of some sort occurring in a bounded context” (p. 44). Thus, our case is a social skills group consisting of two special educators and five autistic students who used both indoor and outdoor environments at an elementary school in the southeastern United States. Furthermore, this is an exploratory case study given that it was not intended to test a particular hypothesis ( Yin, 2017 ). As noted by Hancock and Algozzine (2011) , exploratory case studies serve as a prelude for more expansive investigations that might seek to confirm a hypothesis or work with a concept in a more in-depth manner. Given the small sample size, our findings are not generalizable.
The case study was carried out at a public K-5 elementary school with approximately 600 students, an estimated 47% of whom are eligible for free or reduced price lunch. The school, which we will call Belington Elementary (pseudonym), has a special education department consisting of two teachers, both of whom participated in this study. They provide both push-in and pull-out support for students with IEPs, and they also co-facilitated a 30-min social skills group with five autistic students every day.
The purpose of this social skills group was to offer guidance and practice for communicating and interacting with peers through a variety of lessons. Sometimes the teachers provided direct instruction regarding specific concepts. For example, the teachers might read a book in which one of the characters demonstrates emotion regulation, or they might facilitate a matching activity that required students to align particular situations, as stated by the teacher, to the coordinating emotions that the individual in the fictional situation was likely feeling. Sometimes the teachers prompted the students to engage with each other through games and free play. For example, the teachers invited the students to build well-known international monuments using materials found outside in small groups, which required cooperation and collaboration. Social skills interventions are commonly used for autistic children, particularly those in mainstream environments, as they teach the social interaction behaviors that would be considered “typical” in society. The behaviors may include maintaining eye contact, reducing atypical speech patterns, and expressing interest in what other conversation partners are saying ( White et al., 2010 ). Social skills training programs have been reported to be effective in targeting perceived “deficits” or differences in social interaction (e.g., Kamps et al., 1992 ; Webb et al., 2004 ; Cappadocia and Weiss, 2011 ).
There were four outdoor environments generally used by the teachers for this case study (see Figure 1 ). First was a small pavilion situated very close to the school building. Next to the pavilion was a small garden, but it was overgrown and not actively used by anyone at the school. The second area was referred to as “the outdoor classroom” and was located in a more open area next to the school. The outdoor classroom consisted of several picnic tables under a large covering. Both the pavilion and the outdoor classroom were located just outside the door from the special education classroom, which both teachers shared. The third area was the playground, blacktop, and field located at the back of the school. Finally, there was a nature trail that led to a small clearing in a wooded area. There were wooden benches that formed a circle in the clearing. Accessing the nature trail required a slightly longer walk out of the building, across the parking lot, and over a small patch of grass. For the purposes of our research, we considered the pavilion, outdoor classroom, and playground/blacktop/field areas to be sites for outdoor learning; activities that took place in the nature trail and clearing in the wooded area were considered NBL due to the more immersive setting.
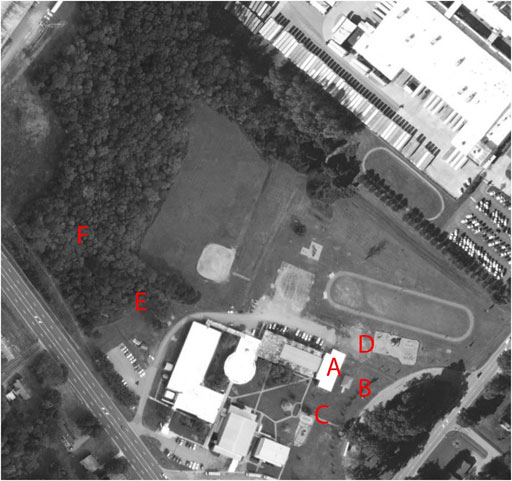

FIGURE 1 . Belington elementary campus. A = Indoor Classroom, B = Outdoor Classroom, C = Pavilion, D = Playground and Blacktop Area, E = Nature Trail, F = Forest Classroom
Participants
Participants included two special educators and five autistic students. The teachers, Mrs. Barrett and Ms. Smith (pseudonyms), were both in the early stages of their careers in special education. While Ms. Smith graduated from university two years prior, Mrs. Barrett worked for over 10 years in several other education and childcare contexts before seeking a special education qualification. Both teachers had minimal experience taking autistic children outside the classroom and no formal training or experience with outdoor learning. The social skills group was composed of five students from 2nd, 3rd, and 4th grades. All of them identified as male and white, had autism diagnoses, and spoke English as their first language. Basic descriptive information regarding the participants can be found in Table 1 .
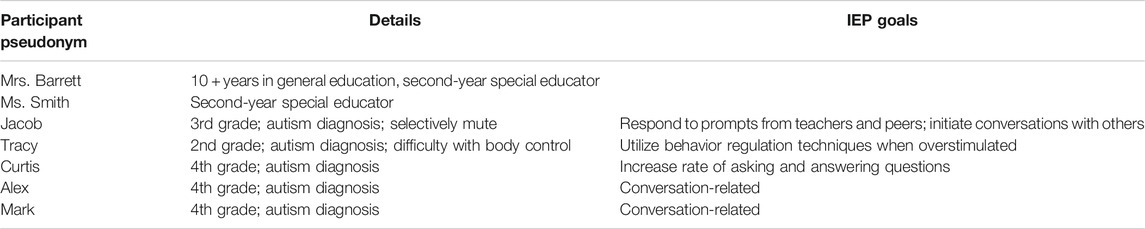
TABLE 1 . Participant information.
Data Collection
A total of 31 visits were carried out, with 26 observations taking place outside and 5 taking place indoors. One visit was completed at the end of January while 7–8 visits were completed per month from February to May. Visits were typically on Mondays and Wednesdays, though seven of the visits were on other days of the week due to events at the elementary school, which meant the class was unable to meet, or to observe the children indoors. The 30-minute social skills classes met in the afternoon each day during the last lesson block of the day. At the start of the study, the teachers agreed among themselves that they would take the children outside on Mondays and Wednesdays. This plan sometimes changed due to weather or a change in lesson plans. Thus, the decision regarding which days to go outside was predetermined, but the teachers had the autonomy to make adjustments day-to-day. We did not observe the students during other subjects.
Field notes were handwritten when at the school and later typed on a shared document. We elaborated on the field notes on the shared document, which resulted in longer narratives. We also tracked the frequency of certain behaviors exhibited by three of the students (Curtis, Jacob, and Tracy; pseudonyms) in our field notes. The target behaviors were related to the IEP goals for each student; the purpose of focusing on IEP goals was to observe if an outdoor environment facilitated any progress or development in regards to those particular goals. Behavior frequency was noted throughout the entire class period, with tally marks indicating the presence of the target behavior. Further details denoting the content of the behaviors were recorded as well. For example, if Curtis asked a question, we would write down what he asked. The decision to track behaviors for only three of the five students was made due to the other two children’s IEP goals. That is, their goals were generally conversation-related but difficult to track using frequencies. Thus, we focused on tracking behaviors of three students with goals that could be more easily quantified.
Finally, we conducted semi-structured interviews with both teachers at the beginning, middle, and end of the data collection period. Interviews lasted 30–45 min and were carried out in person at the school. The first two interviews were with each teacher separately (i.e., two interviews for each) and the final interview was with both teachers together in an effort to provide a space for reflection and discussion between them. In the first interview, questions focused on their previous experiences working with children (both indoors and outdoors), their own relationship with nature, their feelings about incorporating outdoor learning, and their initial impressions or observations of their first few sessions outdoors. The second interview included questions regarding outdoor lesson planning inspiration, how the teachers felt the group was managing with outdoor lessons, how they themselves were impacted by taking their lessons outside, any difficulties they encountered, and how they were beginning to use outdoor learning with their other groups throughout the day. The final interview focused on reflections from both teachers regarding the challenges they faced throughout the experience and what they felt they did to be successful in outdoor environments. All interviews were audio recorded and transcribed.
Data Analysis
We followed Miles et al.'s (2019) guidance regarding qualitative data analysis. To start, we conducted two phases of coding on the interviews and field notes. Coding served to categorize like pieces of data. The first cycle of coding utilized several of the many types of coding, including descriptive, in vivo , and emotions coding. The purpose of the first cycle of coding was to summarize two of the available data sources. The second cycle of coding served to identify patterns in those codes. Codes were then grouped together into categories or themes.
Next, we completed a round of jottings. Jottings documented our thinking as we analyzed the data. These brief notes were written directly into the interview and field note documents to ensure continuity between the data that prompted the thought and the thought itself. Following the use of jottings, analytic memoing then served to “synthesize (descriptive summaries of data) into higher level analytic meanings” ( Miles et al., 2019 , p. 97). Beyond just noting thoughts about the data, analytic memos extend and connect various data with theory and researcher perception.
To formalize and organize our thoughts and findings, we produced assertions and propositions based on all sources of data. According to Miles et al. (2019) , assertions are declarative statements while propositions are conditional statements that serve to predict. These statements allowed us to look at the findings comprehensively and better determine the entire picture of what occurred throughout the study, based upon the available data. To summarize and conclude the process, we carried out a within-case analysis to describe what occurred within the single case of focus in our study.
Limitations
Case studies, particularly those that are exploratory and utilizing within-case analysis, are not generalizable as they focus in depth on one particular case to better understand some aspect of that case. More time observing the participants and conducting the study over a longer period of time would have given us a more robust set of data. Finally, the special educators in this case study were not experts in outdoor learning and had very limited experience taking students outside. Therefore, the challenges and affordances we found may be unique to this context.
When Mrs. Barrett and Ms. Smith agreed to participate in this case study, we had to rely on their willingness, creativity, and resilience to regularly use outdoor environments with their social skills group. Our first research question pertained to the effects of being outside on autistic students, but the second research question about special educators’ perceptions of outdoor learning was perhaps more significant. Mrs. Barrett and Ms. Smith decided what days they would go outside, where on the school campus they might go, what concepts and topics to integrate into their lessons, whether they were adequately meeting IEP goals, and how to respond to autistic students’ needs during transitions and disruptions to their routines. They were the conduits for the entire case study. If for any reason they were not comfortable using outdoor environments, we would not have been able to observe their students.
Neither of the special educators had significant prior experience or training with NBL. During our first interview, Ms. Smith said that she had not used the outdoor environments at her school very often, “just taking them out a few times last year.” She continued, “I would take them out to the outdoor classroom... sometimes on a nice sunny day” but confessed she did not have “a lot of experience incorporating, like, outdoor instruction or environmental education.” When we asked what inspired her to use the outdoor environments a few times, she said,
I thought that was really cool, and I kind of wanted to explore them too, um, just 'cause I knew we had a trail. I knew we had the outdoor classroom there for a reason, and I enjoyed it outside, especially like when the weather was nicer, and I figured it was a fun break for my students, too.
Even without much prior experience or training, both Ms. Smith and Mrs. Barrett found going outside to be appealing enough to participate in this study, and their comfort levels increased the more they used the outdoor environments. Mrs. Barrett noted during her second interview, “We were kind of hesitant before (about) going outside,” but then quickly followed with, “Now that we (are more) experienced... it's just like, calmer. It's peaceful. I just want to stay out there all day.” Both special educators found that outdoor environments offered more than just a fun break for students.
Before we began observing the social skills group, Ms. Smith and Mrs. Barrett shared with us the general IEP goals for their five autistic students. In an email, they highlighted the specific skills they would be working on during the study:
• Engaging in appropriate conversation with others (listening to others, asking relevant questions, using a “social filter”)
• Using “appropriate verbalizations” to express feelings and needs rather than shutting down or using aggressive/physical behaviors
• Identifying others’ perspectives and feelings
• Identifying the problem in a social situation and creating a solution to meet both party’s needs (problem-solving skills)
• Completing non-preferred tasks
• Asking for a break when frustrated
• Demonstrating verbal control in different social situations
They also stressed that there was not a set curriculum that they were required to follow, which allowed them the flexibility of creating their own lessons in ways that would meet their students’ needs and IEP goals. In fact, they were used to developing their own curriculum. “Last year we didn’t have any type of curriculum (provided),” they wrote in the email, “so we pulled from a lot of online resources.” From the beginning, Mrs. Barrett and Ms. Smith were both cautiously optimistic about regularly using outdoor environments with their autistic students. Their lack of experience and training was not insurmountable. Rather, they displayed a growth mindset throughout the study. This was especially apparent in the lessons they developed.
The first outdoor lesson we observed took place in the blacktop area just outside of their classroom (location D on Figure 1 ). The main objective was to support students’ identification of emotion states, so Ms. Smith wrote “happy,” “sad,” “angry,” and “afraid” on four distinct spaces on the blacktop in chalk. The students were then tasked with drawing pictures or writing words with chalk that they associated with the emotion words. The spaces for drawing were approximately five feet away from each other; the children worked in pairs, rotating to the various spaces as the lesson progressed. Throughout the lesson, students were observed laughing and smiling. Some children found nearby rocks on the ground and threw them toward the field while they were taking breaks from drawing. At the end of the activity, everyone sat on the ground in a circle to summarize what they learned. The students were largely engaged in the activity, though some noted that sitting on the hard ground hurt their hand or that the cracks in the asphalt got in the way of their drawing. Despite the colder weather on this day, the only comments about feeling cold came from adults present.
During the second outdoor lesson we observed, the children were noticeably different in their expressions of emotion and interactions with one another compared to their behavior at the start of the class indoors. When observation began at the start of class, before the group had moved outside, the children were being kept on the carpet because the teachers felt they were not following instructions to be quiet and still. Once outside, the activity, which involved running to various parts of the playground to select an emotion word that described the scenario being read aloud (e.g., happy, sad, angry), prompted smiles, laughter, happy screaming, and talking among the students. This was true for Jacob as well, which caused Ms. Smith to comment that she’d never before seen Jacob speak to peers unprompted during an activity.
Several days later, they took a book about emotion regulation outside to the picnic tables to read as a group. While Ms. Smith read aloud, many of the students moved their bodies, tapping on the tables and alternating between standing and sitting. At one point during the lesson, Jacob was moving around rocks and items he found on the ground. Ms. Smith asked a question specifically addressed to him in what appeared to be an attempt to re-engage him in the story. During the following outdoor lesson, the group reviewed the book. Then, to enhance their understanding of the book, Mrs. Barrett and Ms. Smith showed the students a container of bubbles, pulled out the plastic wand, and blew a few into the air. The bubbles were meant to indicate feelings of anger that eventually build up until they pop. The students provided answers to the question, “What makes you angry?” and then were to chase a bubble and “pop” it. Jacob and Tracy in particular seemed to enjoy the opportunity to run after and pop bubbles, as they laughed and smiled throughout this portion of the activity. Mark seemed eager to help Ms. Smith with blowing the bubbles.
During the next outdoor lesson, the concept was advanced further through the use of a liter bottle of soda. The lesson began with a discussion of what they learned about being angry or frustrated from the bubble popping activity. During this review, Tracy and Jacob were moving around, displaying stimming behaviors, and standing up. The teachers shook the bottle to indicate the process of getting angry. The bottle was then opened, and some of its contents spilled out, much to the delight of the children. This prompted a conversation about what strategies could have been used to prevent the spill. The students suggested taking a break while shaking the bottle to allow the fizzing to calm down, which they demonstrated with another bottle of soda. They waited a few minutes after shaking the bottle, and the students discussed whether this was a long enough break to prevent another explosion. During this portion of the lesson, Tracy was corrected by the teachers for not paying attention. This was then related to strategies that they could use to defuse anger. These strategies were demonstrated through the use of skits; the students were put into two groups and tasked with acting out a situation where someone was upset and had to employ a strategy to diffuse their anger. The children largely participated in the skits, though Tracy commented that he was cold and spent some time zipping and unzipping his jacket. Additionally, Jacob was not taking part in this activity, as he was slightly away from the group, touching one of the gazebo’s columns. This was not acknowledged by the teacher.
Continuing with the theme of emotion regulation, another activity on a particularly warm and sunny day included four hula hoops with colors coordinating to the Zones of Regulation, an emotional control system created by Leah Kuypers. The four colors help to categorize different emotions, with blue indicating low alertness, green indicating calm states, yellow indicating elevated emotions, and red indicating extremely elevated emotions. One of the teachers read a scenario, and the children responded by moving to the hula hoop that corresponded to the regulation zone they felt was represented by the scenario. For instance, one scenario was, “Tommy was walking to his table in the cafeteria when he dropped his tray of food. All of his food went on the ground. What zone do you think Tommy was in when this happened?” At first, all of the children moved together, seeming to make the same decisions. Eventually, students broke off and made their own choices about what zone matched best. Throughout the activity, Alex appeared to be dancing as he participated. When students did choose a hula hoop that no one else went to, the teachers asked them to justify their choice, prompting a discussion. For instance, toward the end of the activity, Jacob broke off from the group and went to a different hoop than his peers. The teachers then asked him to explain why he made that choice.
After several months of incorporating outdoor environments into their instruction, the teachers planned a series of lessons to develop teamwork skills. During an indoor class lesson, the students began to work on a small group project. The groups were tasked with building well-known structures out of Legos (e.g., Statue of Liberty, Sphinx, Great Wall of China). The next day, the class took their Lego projects outside to work at the outdoor classroom under the pavilion. Several classes later, the teachers told the students that they would be repeating the same process of building famous structures in small groups; this time, though, the students would be utilizing whatever natural materials they could find outside. Over the course of several outdoor lessons, the students, in their groups, brainstormed what types of materials they would need, where they could get those materials outside, and how they would build the structures. One day was spent on the nature trail collecting materials in a bucket to take back inside. Then, several lessons, both indoor and outdoor, were spent creating their structures. The outdoor lessons to prepare for making a famous structure out of natural materials were interspersed with indoor lessons teaching, reviewing, and discussing what teamwork looks like. That is, concepts were taught inside that were then immediately incorporated into outdoor activities, creating an indoor-outdoor transfer of skills and knowledge.
The aforementioned are only a small sample of the lessons planned and executed by Ms. Smith and Mrs. Barrett for their social skills group with autistic students. Table 2 presents details about all of the lessons that were observed during the study.
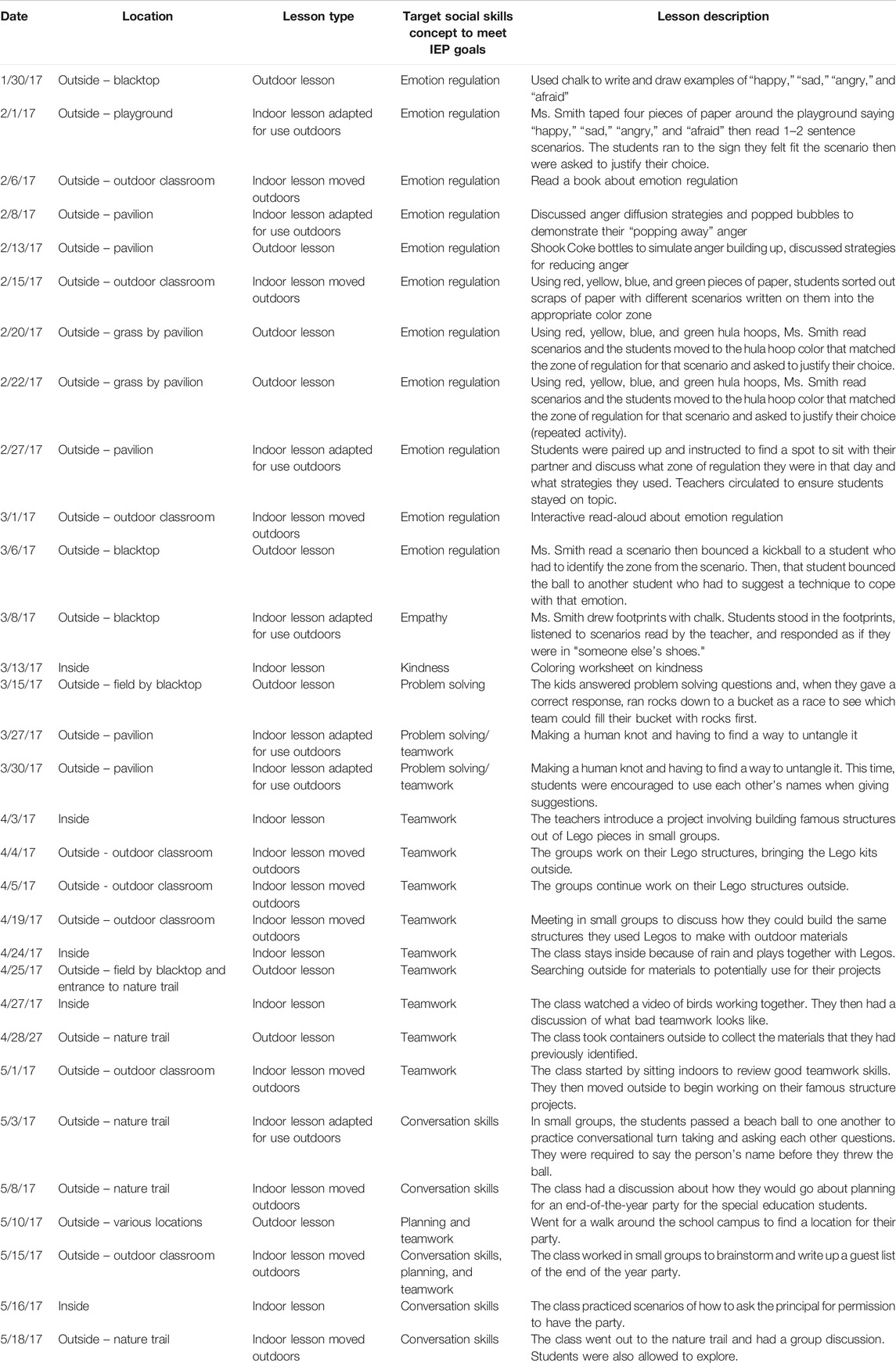
TABLE 2 . Descriptions of lessons.
Our analysis of the data revealed the challenges experienced by the special educators and their students, the adaptations the teachers made in response to the challenges, and the affordances for everyone in the case study.
Not surprisingly, taking autistic children into new learning environments has its challenges. To begin, there were several reasons why the teachers, who taught at a school with several well-developed outdoor spaces, had never utilized these locations before. The main barrier was timing; the teachers had only 30 min with their social skills group and were hesitant to use some of that limited time to travel to and from the outdoor environments. Once the teachers tried taking their group out, they realized that “it didn’t take as long to get out there as I thought it would.” Importantly, they used that transition time effectively, as we explain below, incorporating it into their lesson so that travel time was not “wasted” time.
Once the group started going outside more regularly, the teachers found that an additional barrier was the weather; more specifically, a lack of appropriate clothing and footwear for adverse weather conditions sometimes stopped the class from going outside. On one day, the teachers changed the plans to go outside “because it was raining and cold, and we didn't want anybody getting sick.” Another day, the class decided to stay inside because one of the students had new shoes on and didn’t want to get them muddy on the nature trail.
Over the course of the study, the teachers also came to realize that not all of the outdoor spaces available to them were equal. That is, the class had several options, including a pavilion close to the school that had a view of the front parking lot, where buses and parents would line up at the end of the school day; the playground, blacktop, and field behind the school that had a view of a road; and the nature trail and outdoor classroom that was secluded from any views of the road or the school. Ms. Smith quickly found that “they’re able to focus more when we're in areas further away from the road.” Both teachers agreed that the students were less “distracted” when they were in the nature trail and forest classroom, leading them to prefer taking the students there.
It seems that this preference was shared by the students as well; during one lesson, Ms. Smith told the students they would be going to the pavilion, and several students groaned and expressed that they felt that space was boring because “it’s just land.” When outside at the pavilion or on the field that had views of the road, there were several instances of children becoming noticeably “distracted” when large trucks passed by, often commenting on what they saw. Additionally, several of the children experienced anxiety related to knowing what time it was and having sufficient time to prepare for going home. Thus, when the class was at the outdoor pavilion and the students could see parents and buses arriving for pickup, this anxiety increased and became disruptive to the lesson.
Despite the clear barriers that existed, the teachers persisted in incorporating outdoor learning into their social skills class. This persistence necessitated a willingness by the teachers to adapt accordingly.
Adaptations
On a larger scale, both teachers underwent a transition in their approach to teaching this particular social skills group. As mentioned previously, neither teacher had experience taking children, particularly autistic children, outside for educational purposes. Throughout the study, both became more confident and comfortable with taking autistic children, and children with other additional needs, into outdoor environments. They became so comfortable, in fact, that they began taking children from their other groups, including reading and math support groups, outside. This was not an expectation of the study; rather, the teachers noticed the effects on themselves and their students and were compelled to try it on their own.
In a more literal sense, the importance of transitions to the success of the group’s outdoor lessons was quickly apparent. An initial apprehension existed with both teachers regarding the amount of time that would be spent walking to the outdoor environments in use for that lesson. Because of this, the teachers often opted for closer locations when going outside, such as the playground, grass field behind the school, or pavilion that was right next to the building; the students often complained when they were told this was their destination for the day, however. Additionally, there were downsides to these more easily accessible outdoor environments such as proximity to roads and parking lots and the presence of other classes. This challenged the teachers to find a way to access a more secluded outdoor location and deliver a meaningful lesson within the 30-minute time frame of the class session.
To do this, Ms. Smith found that transition time could be effectively harnessed so that the five-minute walk to the more secluded outdoor environment on the nature trail became a feasible option for the class. During several sessions, Ms. Smith used the time spent walking back into the building to have individual “check-outs” with the students. Describing her thought process for doing this, Ms. Smith said, “That’s why I was like, let’s just do individual check-outs as we walk back instead, where I just talk to them one-on-one, because they’re not listening to each other as a group … I just checked in with a couple as we walked to ask them, ‘Hey, do you think you met your goal today, and how did you do that?’ I talked to at least three or four of them.” On trips from the building out to the nature trail, the teachers sometimes explained rules, procedures, and expectations for the day, told the class what the planned activity was, or asked individual students what emotion regulation zone they felt they were in at that time. On other days, transition time was used to play “I Spy” to encourage students to pay attention to their surroundings. With their newfound realization of the impact that effective transitions can have, both teachers felt that “trying to plan for those transitions” during lesson planning was particularly crucial to increasing the chances for success.
While we offered the teachers support with brainstorming ideas and developing lesson plans, they did not ask for this help and were insistent on using their own ideas. To start, the teachers often opted to take the lessons they would use indoors and simply move them to an outdoor environment. For instance, they did this several times with read-aloud books and post-reading discussions. Early in the study, Ms. Smith mentioned that she was “very comfortable taking indoor activities outside. But I don’t necessarily feel like I’m great at using what’s outside for the lesson.” After observing this, we found that lessons could be categorized in four ways: indoor lessons delivered inside, indoor lessons that are simply moved into an outdoor setting, indoor lessons that are adapted to utilize some element of the outdoor setting, and lessons designed for use only outdoors.
An added difficulty was the topic that this particular group needed to cover: social skills. Ms. Smith found this more difficult as “social skills was something like, I don't know if I was, if I would say I was necessarily, like, really taught how to teach necessarily.” In an effort to utilize the outdoors for social skills lessons more effectively, the teachers found that it was easiest to search for one of those elements -- outdoor learning or social skills -- and then adapt the idea they’ve found to include the other element. Thus, they avoided the frustration of trying to find ideas for “social skills lessons outdoors,” which may not readily exist online.
To source ideas for their outdoor lessons, the teachers utilized online searches and platforms like Pinterest as well as asking their colleagues for input, and they had success with these methods. Lesson planning required a learning curve, though, as Ms. Smith noted that she had to realize that “it’s okay to, like, go back to something that's worked because it's familiar and it's good … good for them, too. Because I think some, at the beginning, I was just feeling pressured to like come up with something new every time, too.” Additionally, the teachers had to remember that going outside meant they were able to utilize an entirely new set of materials. Ms. Smith found that her “normal frame of mind is worksheets. Videos … maybe a game inside. But now, it's like I need to think about a different space, different materials and what not.” With this, Ms. Smith demonstrated how she adapted her approach to lesson planning during the study.
Adaptations were evident throughout the five months of the study. For instance, the teachers learned that their class responded best when new concepts were introduced indoors and follow-up activities were conducted outside, rather than trying to teach new concepts in the outdoor environment. The teachers believed that this was the case because “when you’re outside, you don’t want to just be sitting and listening. They’re ready to move and be active.” Allowing for movement and physical activity -- taking advantage of having more space outdoors -- was another key to success for the class as the teachers focused on “trying to incorporate more movement, so we've done a lot of games.” Additionally, understanding that lessons don’t have to be complicated to be impactful meant that outdoor lessons felt more approachable for the teachers. Ms. Smith stated that “coming up with your own ideas is a little bit easier now. Like, just thinking of the spaces that we have and … just it's easier to think about. I was like, ‘Well, we can take a walk outside,’ like even just something as simple as taking a walk outside to see all the different places.”
The teachers also expressed that flexibility, both in carrying out lesson plans and in expectations, was key when taking their autistic students outside. For instance, on one day that was intended to be an indoor lesson, the class took a vote to decide where they would prefer to work; four of the students voted to work outside, so the class moved locations and simply took the indoor lesson into the outdoor classroom. This happened quite frequently, as Ms. Smith noted that the class was spending more time outside than what was required from the study because “the kids have been asking to.” During another lesson, Mrs. Barrett realized that she had forgotten one of the key materials, a small whiteboard, inside. She adapted the lesson to account for this, having the children act out the scenarios she was going to draw instead, resulting in a successful lesson.
While the class certainly discussed and adhered to rules and procedures for being outside in order to keep all of the students as safe as possible, the expectations that students were held to evolved as the class spent more time outside. Certain behaviors were discouraged in any setting, such as interrupting teachers or classmates by speaking out of turn. Others, however, were allowed in the outdoor space as the teachers noticed that they adapted their own attitudes toward what constituted acceptable behavior while outdoors. Mrs. Barrett admitted that, when taking the class outside, she was “more flexible with [them]... I don’t expect them to sit still.” She also shared that while she still expected students to listen to her as she teaches, those specific listening behaviors that she is looking out for are also different outside, noting that “I can tell. I can say, ‘Okay. So who … ’ And they say it right back. I know they're listening.” Additionally, observations of the class and teachers indoors showed that sitting still and showing body language that was indicative of focus on the teacher were expectations; children who deviated from these expectations were given reminders of “proper” behavior. When outdoors, however, bodily movement became more accepted, with Mrs. Bartlett sharing, “One chose to sit on the boardwalk and the other three sat on the bench. Well, one started off on the bench and he went off, under the bench. Like, okay. Whatever. As long as you're listening, I'm good.”
Despite the adaptations that the teachers made toward more accepting and flexible behavioral expectations when outside, styles of instruction that would align more closely with NBL or FS, the lessons remained fairly “traditional” in that they were teacher-centered and lesson-centered. Each lesson focused on a particular skill that was addressed; these skills aligned with expectations of what a social skills group should cover and included, during the time of the study, constructs such as emotion regulation, teamwork, problem solving, and conversational turn-taking. A further shift toward an embrace of NBL or FS would result in lessons being more child-centered, child-led, and inquiry-based. These adaptations were not observed during the study.
Affordances
During our observations, we tracked the frequency of certain behaviors exhibited by three of the students, Jacob, Tracy, and Curtis; the target behaviors were selected based upon the students’ IEP goals. Jacob’s goal involved “being able to communicate basic wants and needs and … asking and answering questions.” Tracy’s IEP goal was to utilize self-regulation skills to identify and remove himself from situations that made him over-stimulated, and Curtis’ goal was to ask questions to elicit more information, rather than staying silent, which can then lead to frustration. We wanted to see if being outside might help these students meet the goals in their IEPs.
In tracking Curtis’ goal, we found that his question asking increased more indoors compared to outdoors. Those indoor questions, however, pertained to going outside. For instance, during one session, Curtis asked about a specific material that was being brought outside and if he could help carry it. In another, he asked if he could wear his sunglasses outside. While outdoors, Curtis noticed a helicopter leaf on the ground. After he asked what it was, Ms. Smith helped him to pick it up and throw it in the air to watch how it floated to the ground. The number of times Curtis asked questions certainly increased overall, and it appeared that his interest or enjoyment in going outside prompted those questions.
During the study, Tracy did not utilize any self-regulation techniques. We did not observe him reach a point of being over-stimulated during any of the outdoor or indoor sessions that we observed. This suggests that, despite some fears from the teachers, the outdoor environments did not overwhelm or worsen any feelings for Tracy. To the contrary, we noticed that Tracy enjoyed being outside and looked forward to learning in the outdoor environments. In fact, several situations occurred while outdoors that reasonably could have led to conflict or feeling overwhelmed but did not. For instance, during the lesson where the class read a book about diffusing anger, one of his peers seemed to become annoyed with Tracy’s movements (stomping on the ground) and yelled, “Stop!” In response, Tracy stopped what he was doing and further conflict was avoided. In several other instances, Tracy was directed to pay attention or stop a certain behavior; in each case, Tracy effectively followed the teacher or peer’s directions and re-engaged with the activity. This was in contrast to the indoor lessons, where his behavior was observed to be more chaotic and unsettled. During one indoor lesson, Tracy interrupted the lesson by whispering, “Tornado!” unprompted. He then pretended to play the drums on his legs and moved his body and mouth throughout the rest of instruction. In another indoor lesson that required the students to sit on the carpet and watch a video, Tracy repeatedly spoke aloud during the video.
Perhaps most strikingly, Jacob’s goal of increasing his utterances as well as his responses to questions was clearly and certainly addressed while outside. Jacob spoke and responded to prompts more frequently while outside compared to inside; it also seemed that teachers and peers prompted Jacob to speak more frequently while outside as well. Reflecting on this, Ms. Smith said, “[Jacob] speaks up more. He speaks up more to his classmates, I would say, outside. Like, I think, ‘cause … he feels like there’s more space between him and the teacher … but he does initiate more conversation to his peers outside than he does inside.” Mrs. Barrett attributed this to the outdoor environment, noting, “[Ms. Smith] told me that he talked, had a conversation with another student in front of her, and he asked a question, point blank, to her … Very unusual. That’s where we see him, like, even after school, when they're outside playing, that's when we see him really interacting, is outside. That's when he … That’s his forte, I guess.” This was evident from the first outdoor lesson, when Ms. Smith noted that Jacob was speaking to his peers as she’d never observed before, through to one of the last sessions that we observed when Jacob and his peers found a spider on its web. When asked if he preferred the classroom or being outdoors, Jacob replied, “Outdoors.”
Separate from the frequency tracking of specific IEP goals, the group also experienced additional affordances from spending time outside. Ms. Smith observed “a higher energy level outside, just in more of an eagerness to participate because it's almost like it’s a surprise, what we're gonna, like, what are we gonna do now? And the kids really do look forward to it every time they come in.” The unpredictability of the use of outdoor environments excited and interested the students.
Both teachers repeatedly mentioned that all of their students were more focused while outside and exhibited clearer signs of listening during activities. Additionally, several students who were more prone to shouting out or interrupting other speakers inside were noticeably calmer and shouted out far less while outside. This was particularly true for Mark; according to Ms. Smith, “(Mark) doesn't call out as much outside. He listens more. I don't know why, but he does. I don't know if it's the environment or he knows we're doing something new so he has to pay attention more.” One of Mark’s daily behavioral goals was to reduce instances of blurting out in class; thus, these observations were particularly significant to the teachers.
Finally, the students seemed to benefit from the fresh air, the ability to more freely move around, and the ability to fidget or move when necessary while still listening without disrupting their peers’ learning. Additionally, while instances of the students struggling with behavior outside were very infrequent, Mrs. Barrett did note that the class “did have one incident out there where (a student) shut down, but after the … incident, like, he refused to move. So, we just calmly had everyone come back in because it was at the end. I let him sit there … He got up. Because usually before in the classroom, he would throw chairs, desks, things.” Thus, students potentially had more space to safely work through the process of regulating their emotions when outside. Most importantly, perhaps, in assuaging any fears that teachers may have about taking their autistic students into a new environment is Ms. Smith’s view that “no one’s (behavior has) gotten worse outside.”
The students were not the only participants who experienced clear positive effects from spending time outside. Both teachers repeatedly noted ways that they benefited from the experience as well. The teachers felt that the outdoor environments required them to be more creative in lesson planning. While this may have been challenging at times, they also noted that it made them “more thoughtful about the space we use and how we use it.” Additionally, the teachers seemed to harness the feelings of being challenged by their mission to use the outdoor environments in a productive way, sharing that while it was sometimes intimidating, they found the experience exciting as well. The other main impact that the teachers experienced was increasing feelings of peacefulness and calm while taking the students outside. Ms. Smith said that she doesn’t “feel quite as drained after being outside. I think it’s more refreshing because it's a break from the usual.
Nature can serve as an accommodation to support autistic students in meeting IEP goals, particularly due to the positive impact time outside has on stress reduction ( Ulrich et al., 1991 ). Our observations suggest that the outdoor environments did not hinder progress in meeting IEP goals and, in some cases, may have facilitated opportunities to work toward those goals due to lower stress levels.
Jacob, for instance, did not speak unprompted in the social skills class for the first half of the year when the class was inside, likely due to selective mutism. Selective mutism is reported as being connected to stressful life experiences, including those occurring at school ( Muris and Ollendick, 2015 ), though some autistic individuals with selective mutism are reported as not speaking due to a lack of interest in the social context rather than shyness or anxiety ( Steffenburg et al., 2018 ). It is possible that this was a factor for Jacob as well. During the first trip outside and in many subsequent sessions, Jacob participated verbally. There could be a number of reasons that Jacob felt more able to speak while outside; these include having physical distance from the teachers, feeling more relaxed and enjoying class more, or the different style of activities used in some instances outside (e.g., incorporating more physical movement). Additionally, the stress reduction that occurs in nature might have allowed Jacob to feel comfortable enough to speak. Whatever the reason, it was evident from tracking Jacob’s utterances, both prompted and unprompted, that being outside led to an increase in utterances, moving him closer to that specific IEP goal.
In the case of Tracy, the outdoor environments did not cause him to feel overstimulated to the point of having difficulty regulating his feelings or behavior. While we are not able to conclude whether this was from being in an outdoor space or if another alternative education space that was indoors would have had a similar effect on him, it is possible that the stress reduction from being outdoors minimized feelings of overstimulation. Regardless, the impact of the outdoor environments on Tracy was not a negative one. Both Jacob and Tracy’s suspected experiences of lower stress levels outdoors are supported by prior research (e.g., Wells and Evans, 2003 ; Chawla, 2015 ).
Finally, the outdoors seemed to provide a topic of conversation for Curtis, as he asked several questions regarding the details of his class going outside. In the case of all three students, being outside did not hinder their progress toward addressing their IEP goals; rather, our data suggest that outdoor environments moved them closer to reaching those goals. Given the well documented negative effects that poorly designed indoor classrooms can have on autistic children ( McAllister and Maguire, 2012 ), accessing an educational space that does not have those same detrimental impacts could have additional beneficial effects and should be considered as a relatively accessible support or accommodation. Despite the aforementioned benefits, it is important to avoid romanticizing the positive impacts of time outdoors for autistic children. It is unreasonable to expect that all people, including all autistic children, will enjoy being outdoors all of the time or respond positively; in some cases, time in or near nature may increase anxiety ( Larson et al., 2018 ).
While this began as a study focused on how outdoor environments might affect autistic students, the picture that emerged following five months of data collection placed the teachers’ experiences front and center as well. The two special educators demonstrated a growth mindset; they began the study with no outdoor learning experience, confronted the barriers that they came across throughout the process, and appreciated the benefits that outdoor learning offered to themselves and their students. This growth mindset was likely supported by the impacts to teachers that we did not expect. There are many legitimate reasons why teachers may be hesitant to take their students outside; these include time constraints, safety concerns, lack of confidence, or rigidity in developing lessons to adhere to standards ( Rickinson et al., 2004 ; Dyment, 2005 ). Several of these barriers were factors for the teachers in the study, particularly the lack of confidence and feelings of having insufficient time. Despite the presence of these challenges, Ms. Smith and Mrs. Barrett persisted and continued to take their students outside. Thus began what seemed to be a feedback loop: the more the teachers took their students outside, the more the students looked forward and expected to go outside. Furthermore, as the teachers gained more experience taking their social skills group outside, their confidence increased to the point that, unprompted, they began taking their other classes outside as well.
Additionally, teachers are undoubtedly under a tremendous amount of stress, which can lead to burnout and negative impacts to wellbeing ( Richards et al., 2018 ). While we initially expected Ulrich et al.'s (1991) SRT to be a factor influencing how autistic students responded in the outdoor environment due to reported stressful school experiences, it is possible that the teachers equally benefited from stress reduction while outside, evidenced by continued mention of feelings of calm, enjoying the peace of the outdoors, and feeling less drained. It would seem that in the midst of a chaotic school day, spending time outside offered a reprieve for the teachers that outweighed the difficulties of identifying and planning lessons to execute outside. Feelings of lowered stress and increased relaxation are among the most commonly noted positive effects of exposure to nature for adults ( Maller et al., 2006 ; Morita et al., 2007 ; Cole and Hall, 2010 ).
In particular, Mrs. Barrett seemed to undergo a stark transformation. When approached about the research, we received a more reluctant acceptance from Mrs. Barrett; it seemed that Ms. Smith naturally took the lead, likely due to a higher comfort level with the topic or more motivation to tackle the opportunity. Whatever the reason, it is due to this initial hesitance that Mrs. Barrett’s experience taking her students outside is more striking. When interviewing her at the end of the study, she reported having opted to take her other special education classes outdoors as well, citing the positive feelings that she got from the experience as a driving factor. She made at least three references to feeling peaceful and calm while outdoors in her second interview. Mrs. Barrett also seemed to evolve in her expectations of her students while outside, mentioning that as long as she knew her students were listening, she did not mind them moving around or choosing to stand or lay down while she taught outside. This contrasted with her teaching style inside, which was far more structured and emphasized traditional listening cues such as sitting upright, being quiet, and maintaining eye contact.
Future Research
Despite our initial focus on the development of the students, the teachers in our study, Ms. Smith and Mrs. Barrett, became crucially important to the overall case. The evolution and impacts that they experienced suggest that future research should explore the wellbeing effects for teachers who take their students outside as well as the implications this may have for job satisfaction, teacher retention, and reducing burnout.
In our observations of a social skills class consisting of five autistic students and their two special education teachers who incorporated outdoor learning into their day for five months, we saw a range of affordances available to teachers and students alike and ample evidence of their enjoying these affordances. Harnessing such benefits in an educational context requires teachers who are willing and capable of supporting students in engaging with the outdoors. Ms. Smith and Mrs. Barrett, neither of whom had any previous experience or training with taking autistic children outside to learn, were able to adapt their existing knowledge and skills to support their students in learning in the new environment. Additionally, there was no evidence of students experiencing negative outcomes or feeling worse while outside. Coupled with the progress that students such as Jacob showed during the outdoor lessons, this suggests that nature should be considered as an option to meet the needs of autistic children during the school day. This case study serves to demonstrate that, even for teachers with no prior experience taking children into nature, outdoor learning is possible and beneficial to everyone involved.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Elon University Institutional Review Board. Written informed consent to participate in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardian/next of kin.
Author Contributions
SF and SM contributed to conception, design, and recruitment for the study. SF collected data. Both SF and SM contributed to analysis. SF wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and both SF and SM revised and approved the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jessica Wery and Maddie Craft for their assistance on this study.
1 Following Kenny et al.’s (2016) study of preferred terminology in the autism community, we are using identity-first language throughout.
Abraham, A., Sommerhalder, K., and Abel, T. (2010). Landscape and Well-Being: A Scoping Study on the Health-Promoting Impact of Outdoor Environments. Int. J. Public Health 55 (1), 59–69. doi:10.1007/s00038-009-0069-z
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Alvarsson, J. J., Wiens, S., and Nilsson, M. E. (2010). Stress Recovery during Exposure to Nature Sound and Environmental Noise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 7 (3), 1036–1046. doi:10.3390/ijerph7031036
American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . 5th ed. Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing .
Astell-Burt, T., and Feng, X. (2019). Association of Urban Green Space with Mental Health and General Health Among Adults in Australia. JAMA Netw. Open 2 (7), e198209. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8209
Baer, D. M., Wolf, M. M., and Risley, T. R. (1968). Some Current Dimensions of Applied Behavior Analysis1. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 1, 91–97. doi:10.1901/jaba.1968.1-91
Barthel, S., Belton, S., Raymond, C. M., and Giusti, M. (2018). Fostering Children’s Connection to Nature through Authentic Situations: The Case of Saving Salamanders at School. Front. Psychol. 9, 928. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00928
Bellini, S., Peters, J. K., Benner, L., and Hopf, A. (2007). A Meta-Analysis of School-Based Social Skills Interventions for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Remedial Spec. Edu. 28 (3), 153–162. doi:10.1177/07419325070280030401
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Berman, M. G., Jonides, J., and Kaplan, S. (2008). The Cognitive Benefits of Interacting with Nature. Psychol. Sci. 19 (12), 1207–1212.
Berman, M. G., Kross, E., Krpan, K. M., Askren, M. K., Burson, A., Deldin, P. J., et al. (2012). Interacting with Nature Improves Cognition and Affect for Individuals with Depression. J. Affective Disord. 140 (3), 300–305. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2012.03.012
Bijnens, E. M., Derom, C., Thiery, E., Weyers, S., and Nawrot, T. S. (2020). Residential Green Space and Child Intelligence and Behavior across Urban, Suburban, and Rural Areas in Belgium: A Longitudinal Birth Cohort Study of Twins. Plos Med. 17 (8), e1003213. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003213
Blackwell, W. H., and Rossetti, Z. S. (2014). The Development of Individualized Education Programs: Where Have We Been and where Should We Go Now? SAGE Open 4 (2), 1–15. doi:10.1177/2158244014530411
Blakesley, D., Rickinson, M., and Dillon, J. (2013). Engaging Children on the Autistic Spectrum with the Natural Environment: Teacher Insight Study and Evidence Review . Natural England Commissioned Reports, NECR116 .
Bradley, K., and Male, D. (2017). ‘Forest School Is Muddy and I like it’: Perspectives of Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder, Their Parents and Educational Professionals. Educ. Child Psychol. 34 (2), 80–93.
Google Scholar
Brewer, K. (2016). Nature Is the Best Way to Nurture Pupils with Special Educational Needs. The Guardian. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/teacher-network/2016/may/01/nature-nurture-pupils-special-educational-needs-outdoor-education (Accessed May 1, 2016).
Cappadocia, M. C., and Weiss, J. A. (2011). Review of Social Skills Training Groups for Youth with Asperger Syndrome and High Functioning Autism. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 5 (1), 70–78. doi:10.1016/j.rasd.2010.04.001
Chawla, L. (2015). Benefits of Nature Contact for Children. J. Plann. Lit. 30 (4), 433–452. doi:10.1177/0885412215595441
Chawla, L. (2018). Nature-based Learning for Student Achievement and Ecological Citizenship. Curriculum Teach. Dialogue 20 (1&2), xxv–xxxix.
Cole, D. N., and Hall, T. E. (2010). Experiencing the Restorative Components of Wilderness Environments: Does Congestion Interfere and Does Length of Exposure Matter? Environ. Behav. 42, 806–823. doi:10.1177/0013916509347248
Cumming, F., and Nash, M. (2015). An Australian Perspective of a Forest School: Shaping a Sense of Place to Support Learning. J. Adventure Edu. Outdoor Learn. 15 (4), 296–309. doi:10.1080/14729679.2015.1010071
Dadvand, P., Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J., Esnaola, M., Forns, J., Basagaña, X., Alvarez-Pedrerol, M., et al. (2015). Green Spaces and Cognitive Development in Primary Schoolchildren. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112 (26), 7937–7942. doi:10.1073/pnas.1503402112
DeRosier, M. E., Swick, D. C., Davis, N. O., McMillen, J. S., and Matthews, R. (2011). The Efficacy of a Social Skills Group Intervention for Improving Social Behaviors in Children with High Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 41 (8), 1033–1043. doi:10.1007/s10803-010-1128-2
Dillon, J., Morris, M., O'Donnell, L., Reid, A., Rickinson, M., and Scott, W. (2005). Engaging and Learning with the Outdoors - The Final Report of the Outdoor Classroom in a Rural Context Action Research Project. National Foundation for Education Research. Available at: http://www.bath.ac.uk/cree/resources/OCR.pdf (Accessed July 2, 2018).
Dyment, J. E. (2005). Green School Grounds as Sites for Outdoor Learning: Barriers and Opportunities. Int. Res. Geographical Environ. Edu. 14 (1), 28–45. doi:10.1080/09500790508668328
Estes, A., Rivera, V., Bryan, M., Cali, P., and Dawson, G. (2011). Discrepancies between Academic Achievement and Intellectual Ability in Higher-Functioning School-Aged Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 41 (8), 1044–1052. doi:10.1007/s10803-010-1127-3
Fjørtoft, I. (2004). Landscape as Playscape: The Effects of Natural Environments on Children’s Play and Motor Development. Child. Youth Environments 14 (2), 21–44.
Forest School Association (2011). What Is Forest School? Available at: https://www.forestschoolassociation.org/what-is-forest-school/ . (Accessed September 15, 2018)
Gordon, A. (2013). Kids with Autism Benefit from Outdoor Classroom. Toronto Star. Available at: https://www.thestar.com/life/parent/2013/07/05/kids_with_autism_benefit_from_outdoor_classroom.html (Accessed July 5, 2013).
Hancock, D. R., and Algozzine, B. (2011). Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers . 2nd ed. New York: Teachers College Press . doi:10.1201/b11430
CrossRef Full Text
Harris, F. (2021). Developing a Relationship with Nature and Place: The Potential Role of Forest School . Environmental Education Research, ahead-of-print . doi:10.1080/13504622.2021.1896679
Higashida, N. (2007). The Reason I Jump . (Yoshida, K. A. & Mitchell, D., Trans.) . New York: Penguin Random House .
Hotton, M., and Coles, S. (2016). The Effectiveness of Social Skills Training Groups for Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 3, 68–81. doi:10.1007/s40489-015-0066-5
Institute for Outdoor Learning (n.d.). About Outdoor Learning. Available at: https://www.outdoor-learning.org/Good-Practice/Research-Resources/About-Outdoor-Learning . (Accessed July 12, 2018)
James, M. (2018). Forest School and Autism: A Practical Guide . London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers .
Kamps, D. M., Leonard, B. R., Vernon, S., Dugan, E. P., Delquadri, J. C., Gershon, B., et al. (1992). Teaching Social Skills to Students with Autism to Increase Peer Interactions in an Integrated First-Grade Classroom. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 25, 281–288. doi:10.1901/jaba.1992.25-281
Kenny, L., Hattersley, C., Molins, B., Buckley, C., Povey, C., and Pellicano, E. (2016). Which Terms Should be Used to Describe Autism? Perspectives from the UK Autism Community. Autism 20 (4), 442–462. doi:10.1177/1362361315588200
Kuo, M., Barnes, M., and Jordan, C. (2019). Do experiences with Nature Promote Learning? Converging Evidence of a Cause-And-Effect Relationship. Front. Psychol. 10, 305. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00305
Kuo, M., Browning, M. H. E. M., and Penner, M. L. (2018a). Do lessons in Nature Boost Subsequent Classroom Engagement? Refueling Students in Flight. Front. Psychol. 8, 2253. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02253
Kuo, M., Browning, M. H. E. M., Sachdeva, S., Lee, K., and Westphal, L. (2018b). Might School Performance Grow on Trees? Examining the Link between “Greenness” and Academic Achievement in Urban, High-Poverty Schools. Front. Psychol. 9, 1669. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01669
Lai, M.-C., Kassee, C., Besney, R., Bonato, S., Hull, L., Mandy, W., et al. (2019). Prevalence of Co-occurring Mental Health Diagnoses in the Autism Population: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. The Lancet Psychiatry 6 (10), 819–829. doi:10.1016/s2215-0366(19)30289-5
Larson, L. R., Barger, B., Ogletree, S., Torquati, J., Rosenberg, S., Gaither, C. J., et al. (2018). Gray Space and Green Space Proximity Associated with Higher Anxiety in Youth with Autism. Health & Place 53, 94–102. doi:10.1016/j.healthplace.2018.07.006
Li, D., Larsen, L., Yang, Y., Wang, L., Zhai, Y., and Sullivan, W. C. (2019). Exposure to Nature for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Benefits, Caveats, and Barriers. Health & Place 55, 71–79. doi:10.1016/j.healthplace.2018.11.005
Maller, C., Townsend, M., Pryor, A., Brown, P., and St Leger, L. (2006). Healthy Nature Healthy People: 'contact with Nature' as an Upstream Health Promotion Intervention for Populations. Health Promot. Int. 21 (1), 45–54. doi:10.1093/heapro/dai032
McAllister, K., and Maguire, B. (2012). Design Considerations for the Autism Spectrum Disorder-Friendly Key Stage 1 Classroom. Support Learn. 27 (3), 103–112. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9604.2012.01525.x
Mesibov, G. B., Shea, V., and Schopler, E. (2005). The TEACCH Approach to Autism Spectrum Disorders . New York: Springer Science + Business Media .
Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., and Saldaña, J. (2019). Qualitative Data Analysis: A Methods Sourcebook . Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications .
Morita, E., Fukuda, S., Nagano, J., Hamajima, N., Yamamoto, H., Iwai, Y., et al. (2007). Psychological Effects of Forest Environments on Healthy Adults: Shinrin-Yoku (Forest-air Bathing, Walking) as a Possible Method of Stress Reduction. Public Health 121 (1), 54–63. doi:10.1016/j.puhe.2006.05.024
Muris, P., and Ollendick, T. H. (2015). Children Who Are Anxious in Silence: A Review on Selective Mutism, the New Anxiety Disorder in DSM-5. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 18, 151–169. doi:10.1007/s10567-015-0181-y
Nind, M., and Hewett, D. (1988). Interaction as Curriculum. Br. J. Spec. Edu. 15 (2), 49–89. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8578.1988.tb00314.x
North American Association for Environmental Education (NAAEE) (2017). Nature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: 2017 National Survey . Washington, DC: NAAEE .
Richards, K. A. R., Hemphill, M. A., and Templin, T. J. (2018). Personal and Contextual Factors Related to Teachers’ Experience with Stress and Burnout. Teach. Teach. 24 (7), 768–787. doi:10.1080/13540602.2018.1476337
Rickinson, M., Dillon, J., Teamey, K., Morris, M., Choi, M. Y., Sanders, D., et al. (2004). A Review of Research on Outdoor Learning . Telford: Field Studies Council .
Roe, J., and Aspinall, P. (2011). The Restorative Outcomes of Forest School and Conventional School in Young People with Good and Poor Behaviour. Urban For. Urban Green. 10, 205–212. doi:10.1016/j.ufug.2011.03.003
Rowley, E., Chandler, S., Baird, G., Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Loucas, T., et al. (2012). The Experience of Friendship, Victimization and Bullying in Children with an Autism Spectrum Disorder: Associations with Child Characteristics and School Placement. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 6 (3), 1126–1134. doi:10.1016/j.rasd.2012.03.004
Shao, Y., Elsadek, M., and Liu, B. (2020). Horticultural Activity: Its Contribution to Stress Recovery and Wellbeing for Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17 (4), 1229. doi:10.3390/ijerph17041229
Steffenburg, H., Steffenburg, S., Gillberg, C., and Billstedt, E. (2018). Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders and Selective Mutism. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 14, 1163–1169. doi:10.2147/ndt.s154966
Swarbrick, N., Eastwood, G., and Tutton, K. (2004). Self-esteem and Successful Interaction as Part of the Forest School Project. Support Learn. 19 (3), 142–146. doi:10.1111/j.0268-2141.2004.00337.x
Ulrich, R. S., Simons, R. F., Losito, B. D., Fiorito, E., Miles, M. A., and Zelson, M. (1991). Stress Recovery during Exposure to Natural and Urban Environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 11 (3), 201–230. doi:10.1016/s0272-4944(05)80184-7
Webb, B. J., Miller, S. P., Pierce, T. B., Strawser, S., and Jones, W. P. (2004). Effects of Social Skill Instruction for High-Functioning Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabl 19 (1), 53–62. doi:10.1177/10883576040190010701
Wells, N. M. (2000). At Home with Nature. Environ. Behav. 32 (6), 775–795. doi:10.1177/00139160021972793
Wells, N. M., and Evans, G. W. (2003). Nearby Nature. Environ. Behav. 35 (3), 311–330. doi:10.1177/0013916503035003001
White, S. W., Koenig, K., and Scahill, L. (2010). Group Social Skills Instruction for Adolescents with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorders. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabl 25 (4), 209–219. doi:10.1177/1088357610380595
Whitlock, A. M. (2020). Walking the City: Developing Place-Consciousness through Inquiry. Social Stud. Young Learner 33 (2), 20–24.
Williams, F. (2017). The Nature Fix . W. W. Norton & Company .
World Health Organization (1992). The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines . Geneva: World Health Organization .
Yin, R. K. (2017). Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . 6th ed. Los Angeles: Sage .
Zachor, D. A., Vardi, S., Baron-Eitan, S., Brodai-Meir, I., Ginossar, N., and Ben-Itzchak, E. (2016). The Effectiveness of an Outdoor Adventure Programme for Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Controlled Study. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 59, 550–556. doi:10.1111/dmcn.13337
Keywords: outdoor learning, nature-based learning, special education, case study, autism
Citation: Friedman S and Morrison SA (2021) “I just want to stay out there all day”: A Case Study of Two Special Educators and Five Autistic Children Learning Outside at School. Front. Educ. 6:668991. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.668991
Received: 17 February 2021; Accepted: 30 April 2021; Published: 20 May 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Friedman and Morrison. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Samantha Friedman, [email protected]
- Case report
- Open access
- Published: 11 September 2017
A case of a four-year-old child adopted at eight months with unusual mood patterns and significant polypharmacy
- Magdalena Romanowicz ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4916-0625 1 ,
- Alastair J. McKean 1 &
- Jennifer Vande Voort 1
BMC Psychiatry volume 17 , Article number: 330 ( 2017 ) Cite this article
43k Accesses
2 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Long-term effects of neglect in early life are still widely unknown. Diversity of outcomes can be explained by differences in genetic risk, epigenetics, prenatal factors, exposure to stress and/or substances, and parent-child interactions. Very common sub-threshold presentations of children with history of early trauma are challenging not only to diagnose but also in treatment.
Case presentation
A Caucasian 4-year-old, adopted at 8 months, male patient with early history of neglect presented to pediatrician with symptoms of behavioral dyscontrol, emotional dysregulation, anxiety, hyperactivity and inattention, obsessions with food, and attachment issues. He was subsequently seen by two different child psychiatrists. Pharmacotherapy treatment attempted included guanfacine, fluoxetine and amphetamine salts as well as quetiapine, aripiprazole and thioridazine without much improvement. Risperidone initiated by primary care seemed to help with his symptoms of dyscontrol initially but later the dose had to be escalated to 6 mg total for the same result. After an episode of significant aggression, the patient was admitted to inpatient child psychiatric unit for stabilization and taper of the medicine.
Conclusions
The case illustrates difficulties in management of children with early history of neglect. A particular danger in this patient population is polypharmacy, which is often used to manage transdiagnostic symptoms that significantly impacts functioning with long term consequences.
Peer Review reports
There is a paucity of studies that address long-term effects of deprivation, trauma and neglect in early life, with what little data is available coming from institutionalized children [ 1 ]. Rutter [ 2 ], who studied formerly-institutionalized Romanian children adopted into UK families, found that this group exhibited prominent attachment disturbances, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), quasi-autistic features and cognitive delays. Interestingly, no other increases in psychopathology were noted [ 2 ].
Even more challenging to properly diagnose and treat are so called sub-threshold presentations of children with histories of early trauma [ 3 ]. Pincus, McQueen, & Elinson [ 4 ] described a group of children who presented with a combination of co-morbid symptoms of various diagnoses such as conduct disorder, ADHD, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression and anxiety. As per Shankman et al. [ 5 ], these patients may escalate to fulfill the criteria for these disorders. The lack of proper diagnosis imposes significant challenges in terms of management [ 3 ].
J is a 4-year-old adopted Caucasian male who at the age of 2 years and 4 months was brought by his adoptive mother to primary care with symptoms of behavioral dyscontrol, emotional dysregulation, anxiety, hyperactivity and inattention, obsessions with food, and attachment issues. J was given diagnoses of reactive attachment disorder (RAD) and ADHD. No medications were recommended at that time and a referral was made for behavioral therapy.
She subsequently took him to two different child psychiatrists who diagnosed disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD), PTSD, anxiety and a mood disorder. To help with mood and inattention symptoms, guanfacine, fluoxetine, methylphenidate and amphetamine salts were all prescribed without significant improvement. Later quetiapine, aripiprazole and thioridazine were tried consecutively without behavioral improvement (please see Table 1 for details).
No significant drug/substance interactions were noted (Table 1 ). There were no concerns regarding adherence and serum drug concentrations were not ordered. On review of patient’s history of medication trials guanfacine and methylphenidate seemed to have no effect on J’s hyperactive and impulsive behavior as well as his lack of focus. Amphetamine salts that were initiated during hospitalization were stopped by the patient’s mother due to significant increase in aggressive behaviors and irritability. Aripiprazole was tried for a brief period of time and seemed to have no effect. Quetiapine was initially helpful at 150 mg (50 mg three times a day), unfortunately its effects wore off quickly and increase in dose to 300 mg (100 mg three times a day) did not seem to make a difference. Fluoxetine that was tried for anxiety did not seem to improve the behaviors and was stopped after less than a month on mother’s request.
J’s condition continued to deteriorate and his primary care provider started risperidone. While initially helpful, escalating doses were required until he was on 6 mg daily. In spite of this treatment, J attempted to stab a girl at preschool with scissors necessitating emergent evaluation, whereupon he was admitted to inpatient care for safety and observation. Risperidone was discontinued and J was referred to outpatient psychiatry for continuing medical monitoring and therapy.
Little is known about J’s early history. There is suspicion that his mother was neglectful with feeding and frequently left him crying, unattended or with strangers. He was taken away from his mother’s care at 7 months due to neglect and placed with his aunt. After 1 month, his aunt declined to collect him from daycare, deciding she was unable to manage him. The owner of the daycare called Child Services and offered to care for J, eventually becoming his present adoptive parent.
J was a very needy baby who would wake screaming and was hard to console. More recently he wakes in the mornings anxious and agitated. He is often indiscriminate and inappropriate interpersonally, unable to play with other children. When in significant distress he regresses, and behaves as a cat, meowing and scratching the floor. Though J bonded with his adoptive mother well and was able to express affection towards her, his affection is frequently indiscriminate and he rarely shows any signs of separation anxiety.
At the age of 2 years and 8 months there was a suspicion for speech delay and J was evaluated by a speech pathologist who concluded that J was exhibiting speech and language skills that were solidly in the average range for age, with developmental speech errors that should be monitored over time. They did not think that issues with communication contributed significantly to his behavioral difficulties. Assessment of intellectual functioning was performed at the age of 2 years and 5 months by a special education teacher. Based on Bailey Infant and Toddler Development Scale, fine and gross motor, cognitive and social communication were all within normal range.
J’s adoptive mother and in-home therapist expressed significant concerns in regards to his appetite. She reports that J’s biological father would come and visit him infrequently, but always with food and sweets. J often eats to the point of throwing up and there have been occasions where he has eaten his own vomit and dog feces. Mother noticed there is an association between his mood and eating behaviors. J’s episodes of insatiable and indiscriminate hunger frequently co-occur with increased energy, diminished need for sleep, and increased speech. This typically lasts a few days to a week and is followed by a period of reduced appetite, low energy, hypersomnia, tearfulness, sadness, rocking behavior and slurred speech. Those episodes last for one to 3 days. Additionally, there are times when his symptomatology seems to be more manageable with fewer outbursts and less difficulty regarding food behaviors.
J’s family history is poorly understood, with his biological mother having a personality disorder and ADHD, and a biological father with substance abuse. Both maternally and paternally there is concern for bipolar disorder.
J has a clear history of disrupted attachment. He is somewhat indiscriminate in his relationship to strangers and struggles with impulsivity, aggression, sleep and feeding issues. In addition to early life neglect and possible trauma, J has a strong family history of psychiatric illness. His mood, anxiety and sleep issues might suggest underlying PTSD. His prominent hyperactivity could be due to trauma or related to ADHD. With his history of neglect, indiscrimination towards strangers, mood liability, attention difficulties, and heightened emotional state, the possibility of Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder (DSED) is likely. J’s prominent mood lability, irritability and family history of bipolar disorder, are concerning for what future mood diagnosis this portends.
As evidenced above, J presents as a diagnostic conundrum suffering from a combination of transdiagnostic symptoms that broadly impact his functioning. Unfortunately, although various diagnoses such as ADHD, PTSD, Depression, DMDD or DSED may be entertained, the patient does not fall neatly into any of the categories.
This is a case report that describes a diagnostic conundrum in a young boy with prominent early life deprivation who presented with multidimensional symptoms managed with polypharmacy.
A sub-threshold presentation in this patient partially explains difficulties with diagnosis. There is no doubt that negative effects of early childhood deprivation had significant impact on developmental outcomes in this patient, but the mechanisms that could explain the associations are still widely unknown. Significant family history of mental illness also predisposes him to early challenges. The clinical picture is further complicated by the potential dynamic factors that could explain some of the patient’s behaviors. Careful examination of J’s early life history would suggest such a pattern of being able to engage with his biological caregivers, being given food, being tended to; followed by periods of neglect where he would withdraw, regress and engage in rocking as a self-soothing behavior. His adoptive mother observed that visitations with his biological father were accompanied by being given a lot of food. It is also possible that when he was under the care of his biological mother, he was either attended to with access to food or neglected, left hungry and screaming for hours.
The current healthcare model, being centered on obtaining accurate diagnosis, poses difficulties for treatment in these patients. Given the complicated transdiagnostic symptomatology, clear guidelines surrounding treatment are unavailable. To date, there have been no psychopharmacological intervention trials for attachment issues. In patients with disordered attachment, pharmacologic treatment is typically focused on co-morbid disorders, even with sub-threshold presentations, with the goal of symptom reduction [ 6 ]. A study by dosReis [ 7 ] found that psychotropic usage in community foster care patients ranged from 14% to 30%, going to 67% in therapeutic foster care and as high as 77% in group homes. Another study by Breland-Noble [ 8 ] showed that many children receive more than one psychotropic medication, with 22% using two medications from the same class.
It is important to note that our patient received four different neuroleptic medications (quetiapine, aripiprazole, risperidone and thioridazine) for disruptive behaviors and impulsivity at a very young age. Olfson et al. [ 9 ] noted that between 1999 and 2007 there has been a significant increase in the use of neuroleptics for very young children who present with difficult behaviors. A preliminary study by Ercan et al. [ 10 ] showed promising results with the use of risperidone in preschool children with behavioral dyscontrol. Review by Memarzia et al. [ 11 ] suggested that risperidone decreased behavioral problems and improved cognitive-motor functions in preschoolers. The study also raised concerns in regards to side effects from neuroleptic medications in such a vulnerable patient population. Younger children seemed to be much more susceptible to side effects in comparison to older children and adults with weight gain being the most common. Weight gain associated with risperidone was most pronounced in pre-adolescents (Safer) [ 12 ]. Quetiapine and aripiprazole were also associated with higher rates of weight gain (Correll et al.) [ 13 ].
Pharmacokinetics of medications is difficult to assess in very young children with ongoing development of the liver and the kidneys. It has been observed that psychotropic medications in children have shorter half-lives (Kearns et al.) [ 14 ], which would require use of higher doses for body weight in comparison to adults for same plasma level. Unfortunately, that in turn significantly increases the likelihood and severity of potential side effects.
There is also a question on effects of early exposure to antipsychotics on neurodevelopment. In particular in the first 3 years of life there are many changes in developing brains, such as increase in synaptic density, pruning and increase in neuronal myelination to list just a few [ 11 ]. Unfortunately at this point in time there is a significant paucity of data that would allow drawing any conclusions.
Our case report presents a preschool patient with history of adoption, early life abuse and neglect who exhibited significant behavioral challenges and was treated with various psychotropic medications with limited results. It is important to emphasize that subthreshold presentation and poor diagnostic clarity leads to dangerous and excessive medication regimens that, as evidenced above is fairly common in this patient population.
Neglect and/or abuse experienced early in life is a risk factor for mental health problems even after adoption. Differences in genetic risk, epigenetics, prenatal factors (e.g., malnutrition or poor nutrition), exposure to stress and/or substances, and parent-child interactions may explain the diversity of outcomes among these individuals, both in terms of mood and behavioral patterns [ 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Considering that these children often present with significant functional impairment and a wide variety of symptoms, further studies are needed regarding diagnosis and treatment.
Abbreviations
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder
Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Reactive Attachment disorder
Norman RE, Byambaa M, De R, Butchart A, Scott J, Vos T. The long-term health consequences of child physical abuse, emotional abuse, and neglect: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2012;9(11):e1001349. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001349 . Epub 2012 Nov 27
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kreppner JM, O'Connor TG, Rutter M, English and Romanian Adoptees Study Team. Can inattention/overactivity be an institutional deprivation syndrome? J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2001;29(6):513–28. PMID: 11761285
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Dejong M. Some reflections on the use of psychiatric diagnosis in the looked after or “in care” child population. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2010;15(4):589–99. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359104510377705 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Pincus HA, McQueen LE, Elinson L. Subthreshold mental disorders: Nosological and research recommendations. In: Phillips KA, First MB, Pincus HA, editors. Advancing DSM: dilemmas in psychiatric diagnosis. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2003. p. 129–44.
Google Scholar
Shankman SA, Lewinsohn PM, Klein DN, Small JW, Seeley JR, Altman SE. Subthreshold conditions as precursors for full syndrome disorders: a 15-year longitudinal study of multiple diagnostic classes. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2009;50:1485–94.
AACAP. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with reactive attachment disorder of infancy and early childhood. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2005;44:1206–18.
Article Google Scholar
dosReis S, Zito JM, Safer DJ, Soeken KL. Mental health services for youths in foster care and disabled youths. Am J Public Health. 2001;91(7):1094–9.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Breland-Noble AM, Elbogen EB, Farmer EMZ, Wagner HR, Burns BJ. Use of psychotropic medications by youths in therapeutic foster care and group homes. Psychiatr Serv. 2004;55(6):706–8.
Olfson M, Crystal S, Huang C. Trends in antipsychotic drug use by very young, privately insured children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2010;49:13–23.
PubMed Google Scholar
Ercan ES, Basay BK, Basay O. Risperidone in the treatment of conduct disorder in preschool children without intellectual disability. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2011;5:10.
Memarzia J, Tracy D, Giaroli G. The use of antipsychotics in preschoolers: a veto or a sensible last option? J Psychopharmacol. 2014;28(4):303–19.
Safer DJ. A comparison of risperidone-induced weight gain across the age span. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2004;24:429–36.
Correll CU, Manu P, Olshanskiy V. Cardiometabolic risk of second-generation antipsychotic medications during first-time use in children and adolescents. JAMA. 2009;302:1765–73.
Kearns GL, Abdel-Rahman SM, Alander SW. Developmental pharmacology – drug disposition, action, and therapy in infants and children. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1157–67.
Monk C, Spicer J, Champagne FA. Linking prenatal maternal adversity to developmental outcomes in infants: the role of epigenetic pathways. Dev Psychopathol. 2012;24(4):1361–76. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579412000764 . Review. PMID: 23062303
Cecil CA, Viding E, Fearon P, Glaser D, McCrory EJ. Disentangling the mental health impact of childhood abuse and neglect. Child Abuse Negl. 2016;63:106–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2016.11.024 . [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 27914236
Nemeroff CB. Paradise lost: the neurobiological and clinical consequences of child abuse and neglect. Neuron. 2016;89(5):892–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.019 . Review. PMID: 26938439
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are also grateful to patient’s legal guardian for their support in writing this manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Mayo Clinic, Department of Psychiatry and Psychology, 200 1st SW, Rochester, MN, 55901, USA
Magdalena Romanowicz, Alastair J. McKean & Jennifer Vande Voort
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MR, AJM, JVV conceptualized and followed up the patient. MR, AJM, JVV did literature survey and wrote the report and took part in the scientific discussion and in finalizing the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final document.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Magdalena Romanowicz .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication.
Written consent was obtained from the patient’s legal guardian for publication of the patient’s details.
Competing interests
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Romanowicz, M., McKean, A.J. & Vande Voort, J. A case of a four-year-old child adopted at eight months with unusual mood patterns and significant polypharmacy. BMC Psychiatry 17 , 330 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-017-1492-y
Download citation
Received : 20 December 2016
Accepted : 01 September 2017
Published : 11 September 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-017-1492-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Polypharmacy
- Disinhibited social engagement disorder
BMC Psychiatry
ISSN: 1471-244X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Case study: ‘He’s a 10-year-old child with disabilities . . . I can’t see how isolating helps’
Debbie kennedy says the regular use of seclusion has worsened her son’s behaviour.
Dylan Kennedy (10) with his mother Debbie Kennedy at home in Dublin. Photograph: The Irish Times
Debbie Kennedy accepts her 10-year-old son can be difficult to handle on occasion.
He’s autistic and has been diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
There are times when he gets frustrated, angry and stressed. Equally, she says, he can be calmed down quickly with simple interventions.
“He’s very intelligent,” says Kennedy.”He could tell you anything about any car. He loves Top Gear . . . when he does act out, I can control him with one hand or distract him.”
But she says the past past two years have been marked by a sharp deterioration in his behaviour. She puts much of this down to what she says was the overuse of seclusion at school to control his behaviour.
In all, she estimates he was placed in a seclusion or “time-out” room on more than 30 occasions over a two-year period.
While in most cases she was told they were for short periods of time, she maintains that on a several occasions he was placed there for up to two hours at a time.
“In order to help a vulnerable child like Dylan manage his emotions and control his behaviour, he needs support, guidance and explanation,” she says.
“If he’s isolated from others, without guidance or support, I can’t see how that helps. In fact, it’s a more frightening experience – especially for a child with disabilities.”
Benincasa Special School in Blackrock, Co Dublin, said that while it was not in a position to comment on Dylan's individual case, the school had always acted "properly and in accordance with good practice at all times".
In line with its policies, seclusion was only ever used as a measure of last resort and where a child was disruptive to the point of posing an imminent danger to themselves or others.
Kennedy, however, feels the school was too quick to seclude her son and says he regularly came home in tears after being placed in the room, or isolated from the wider class.
“He would spend hours crying, saying how much he wanted to die and felt he wasn’t good enough.”
She also feels he was placed in the room on foot of relatively minor incidents, like throwing a pencil against a blackboard or refusing to do work.
School records, however, show there were occasions when he kicked or punched staff. On one occasion, he is said to have raised a chair in the air, before it was taken from him.
The seclusion room – based on photographs taken by Dylan’s mother – is a small bare room with no furniture.
There is a window with metal bars on the outside. The door has no handle on the inside and there is a peephole for staff.
The school said a staff member was present outside the seclusion room, monitoring the student, at all times.
“The seclusion room is designed with regards to the health and safety of the student in question. The room does not contain certain furniture as such items are often considered safety hazards to both the student or staff members,” it said.
Kennedy ended up withdrawing permission for her son to be placed in the room. Afterwards, she says she would receive phone calls from 9.10am onwards asking her to collect him.
He ended up being taught at home by his mother for long periods and resumed school on a limited basis.
She is careful to say Dylan enjoyed several successful years at his special school prior to this and many staff went out of their way to help and support him. “I couldn’t speak highly enough of them.”
But she feels the use of seclusion has left a damaging legacy which Dylan is still coming to terms with.
“He needs therapy after all that’s happened. We can be out having fun and he’ll mention what happened to him,” she says.
“He is the most caring and affectionate boy. He’s clever and funny and has a huge obsession with cars. I wouldn’t change him for anything.”
Carl O'Brien
Carl O'Brien is Education Editor of The Irish Times. He was previously chief reporter and social affairs correspondent
IN THIS SECTION
‘in every school there are students like john who hunger for fewer disruptions to their timetabled week’, how to make the most of the leaving cert run-in: study tips, social media and taking breaks, my 19-year-old college-going son is depressed and anxious, rise in school absenteeism: ‘some stay up too late on their phones until 3 or 4am’, unregulated student digs: a home away from home or an isolating experience, bruce springsteen in croke park review: blockbuster performance closes irish tour on an emotion-filled evening, tony o’reilly’s secret past shaped his need to play the life of an ascendancy landlord, ireland’s two-tier cancer drug system: ‘i can give one drug to one lot of patients, not to another’, iran declares five days of mourning after president ebrahim raisi (63) killed in helicopter crash, blue flags 2024: beaches in dublin, wexford and waterford lose out. check how your local area fared, latest stories, connacht look to sign sam prendergast on loan from leinster, european election midlands-north-west debate: migration a heated topic, but winning candidates hard to pick, unfilled psychiatric posts leaving young people on ‘unacceptably long waiting lists’, ‘it’s hard to aspire to something you cannot see’, healthcare workers to get quick digital access to patients’ medical records under new national system.
:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/sandbox.irishtimes/ZNXTZ2DRXNFU5MTNZFDVCVJJNE.png)
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Information
- Cookie Settings
- Community Standards
- Armenia response
- Gaza response

- High contrast
- Press centre

Search UNICEF
Case studies on disability and inclusion.
To document UNICEF’s work on disability and inclusion in Europe and Central Asia region, UNICEF Regional Office for Europe and Central Asia has developed a set of five case studies.
UNICEF takes a comprehensive approach to inclusion, working to ensure that all children have access to vital services and opportunities. When UNICEF speaks about “inclusion” this encompasses children with and without disabilities, marginalized and vulnerable children, and children from minority and hard-to-reach groups.
The case studies have a specific focus on children with disabilities and their families. However, many of the highlighted initiatives are designed for broad inclusion and benefit all children. In particular, this case study, covers such topics as: Inclusive Preschool, Assistive Technologies (AT), Early Childhood intervention (ECI), Deinstitutionalisation (DI).
Case studies

Case study 1: “Open source AAC in the ECA Region”
Files available for download (1).

Case study 2: “Inclusive Preschool in Bulgaria”


Case study 3: “Assistive technology in Armenia"

Case study 4: “Early childhood intervention in the ECA region”

Case study 5: “Deinstitutionalization in the ECA region”
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

A CASE STUDY OF A CHILD WITH SPECIAL NEED/LEARNING DIFFICULTY Researcher

2018, INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CREATIVE RESEARCH THOUGHTS(IJCRT)
The study has been conducted to investigate the levels and kind of difficulty the child/student is facing in learning things in or outside the classroom. It also examines the relationship between the school and home environment of the student with special needs who is facing difficulty in learning i.e. reading, writing listening or speaking. The case study was conducted by keen observations of the special needed child by involving and getting information directly from different reliable sources like,concerned teachers, peer groups from the school, parents, family members and peer groups of the child from the home environment. The tools used in the study were 1. Qustionnaire. 2. Direct observation. Etc.The study reveals the fact that the actually the child not having any slow learners like problem nor she is shy or un interested in learning by nature but she loves to read , learn , take part in different activities, she is having a creative mind by birth or nature but only the problem of her difficulties in learning is because of the depression she has laid in her mind of part of the home environment and improper treatment given to her by parents,family,teacher' s, elder' s in the school or at home.
Related Papers
The main purpose of this study was to find out the contributions and challenges of Sebeta Special School for the students with visual impairments. The research design used was qualitative case study method as this would enable the researcher to make in-depth study of the case from different perspectives. For responding to this main purpose of the study, purposive sampling was used and the subjects of the study were selected by purposive sampling technique as they were taught to have the necessary information for the problem under study. Accordingly, twelve teachers, (six males and six females), ten members of the support staff (five males and five females) and twelve students of grades five to eight (six males and six females) were selected for focus group discussions. Besides, interview was conducted with the director and vice-director of the school and two teachers (a male and a female) and two students of grades five to eight (a male and a female).Relevant documents and observation checklists were also used as data sources. Finally, the data collected were organized, thematically analyzed and presented. Regarding the contributions made, the findings revealed that the school has been serving the students as school to learn in and succeed, home to live in and family to leave with. There were also services being delivered for the students and different resources were also available in the special school. Findings displayed that challenges to the special school as manpower assignment was not need based and there were lack of skills necessary to run activities in the special school as reading and writing braille, inadequate budget and resources like student textbooks transcribed in to braille and wastages in usage of the available resources. Besides, there were conditions that violate the safety of students. The recommendations made included such things as alleviating the challenges the school encountered such as appropriate use of resource, availing the necessary resources as braille textbooks, budget and others.
CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research - Zenodo
Arpeeta Anand
IOSR Journals
" The ramification and still over effect of learning disability affect so much that education of school children find hard reality to attain its universal character. At the same time the problem continues to be the most baffling one for the state thriving for universalization of elementary education and ensuring right to education for all. Many interventions and policy measures although were initiated to increase the achievement level of students but at the Psycho-social level addressing the problem still remained attempted. Providing appropriate literacy and innumeracy learning opportunities especially, continues to be a challenge both for the teachers so also parents. Observing the gravity of the problem an earnest attempt has been made in this paper to understand the conflicting currents of the problem from a psycho-social perspective. A diagnosis also has been made to address the challenges of learning disability among school children, so that the objective of universalization of education could be well attained with.
Croatian Journal of Education - Hrvatski časopis za odgoj i obrazovanje
Jasna Kudek
Journal of emerging technologies and innovative research
Masrat Majeed
Learning Disorder is not single disorder but include disabilities in any of seven areas related to Reading, Language and Mathematics. These separate types of learning disabilities frequently co-occur with one-another and with Social Skill Deficits and Emotional or Behavioral Disorder. Approximately 7% of all school children under the age group of 3-6 years are identified as Learning Disability in the Composite Regional Centre (CRC) according the Survey done during the period of 2018. Using many tests and assessments, it was found that these children with LD are also attributed to other emotional or behavioral disorders. While learning disability, learning disorder and learning difficulty are often used interchangeably, they differ in many ways. Disorder refers to significant learning problems in an academic area. These problems, however, are not enough to warrant an official diagnosis. Learning disability, on the other hand, is an official clinical diagnosis, whereby the individual ...
SHODH SARITA
Arpeeta Anand , Mohd. Faijullah Khan (Asstt. Prof., IASE)
Specific Learning Disability (SLD) is a neurological problem which creates lots of challenges in the life of children. Academic challenges are the most significant one when it comes to SLD. Aims: To realize the academic challenges that children experienced with Specific Learning Disability. Setting and Design: Phenomenological method with purposive sampling technique was used to understand the perspective of children. Materials and Methods: Semi-structured Interview Schedule was administered on 10 SLD children who are already diagnosed by clinical psychologist studying in elementary grade i.e. 6th grade to 8th grade of private inclusive schools of Delhi. Analysis Used: Content Analysis was used to elicit the data from open-ended questions. Results: (i) Children with learning disability are not lazy & dumb, they perceive and process information in a different manner. (ii) They encounter difficulty in comprehending what they have read, experience making mistakes while reading, repeating the sentences, taking pause, trouble in remembering & mispronouncing same sounding words. (iii)Children doesn’t want to write because of the fright behind committing spelling mistakes. (iv) Many children experience problem of illegible writing, pain in hand, extra efforts & longer time for writing and trouble in expressing their own ideas & feelings in writing. (v)They struggle while comprehending & solving the word problems, issues of learning formulas, making things in order of operations, basic calculations, understanding time, directions, money related work and difficulty in keeping scores of games & matches. (vi) Have trouble in adjusting to new situations, take time to adapt new changes in their life, demand lots of coordination & organization, face problem in rote learning & remembering, comprehending meaning from text and thinking out of box (vii) Complained about inability to perform activities that require sequential order, meeting deadlines, following schedules, arranging things, setting priorities and managing time for themselves. (viii) Experience inability to interpret their own environment as a consequence react inappropriately, misunderstood situation and comprehend different meaning with incorrect interpretation. (ix) Trouble in understanding what they hear and making differences in sound, difficulty in comprehending meaning from sounds, require frequent repetition and struggle in remembering what they heard. (x) The foremost problem of misunderstanding in analyzing and synthesizing visually presented information. (xi)They experience inability to differentiate between same sounding words, struggle while copying from writing board, mispronouncing the words while reading, difficulty in comprehending meaning out of what they read and figuring out what is there in pictures & graphs. Conclusions: The present study has identified various challenges faced by children academically. Proper support & motivation of parents & teachers can help children in developing positive attitude towards learning. Keywords: Specific Learning Disability, Children, Education, Academic Challenges, Phenomenological Analysis
Science Park Research Organization & Counselling
This study aims to obtain problems encountered in special education in the direction of opinions of parents attending to Special Training and Rehabilitation Institution and develop solution suggestions compansating these problems. In the scope of study parents of 20 students were interviewed. Tha datas that were obtained as a result of qualitative semi-structured interview form, were analysed by descriptive analysis method. The participant parents were asked 7 questions about education period, physical conditions, difficulties they encountered regarding their children in the scope of relations of teachers with parents and managers and point of view of society. Most of the participants expressed problems such as most of the problems should be solved by top levels, training hours are insufficient and rejection of society.
Sara Sadiki , Fitore Bajrami
The qualitative method was the research method used in this study as the most appropriate to the purpose, objectives, and research questions of the study. The purpose of this study is to examine the experiences of parents during education of their children with special needs. The research question of this study was: What experiences have parents had during the education of their children with special needs? The sample in this paper consists of 13 respondents, citizens of Debar parents of children with special needs. The interviewed sample consisted of 10 mothers and 3 fathers. From the analyzes made, it appears that 99% of parents regarding the inclusion of children answered that it is very necessary, they hope that these laws and rules are respected in schools, that there are no differences and discriminations with children, but that everyone is equal in the classroom and have maximum care, especially children with special needs. 46% of the parents answered that they got enough help from the school, they were not underestimated by others, the teacher supported them and helped them adapt, showing that the children were calmer and more productive. While 53.8% of parents answered that the school does not have help with their child, they express dissatisfaction and non-fulfillment of the conditions for work with children with special needs. Based on the analyzes carried out, 75% of the parents answered that they had difficulties with their child's adaptation to school, and the parents were also forced to stay with them in the classroom for several months.
Dr. Muhammad Irfan Arif
Authors: Kafiat Ullah Khan Research Scholar Allama Iqbal Open University Islamabad E-mail: [email protected] Ameer Hasan MS(Management Sciences) Riphah International University Islamabad E-mail: [email protected] Muhammad Irfan Arif Ph.D Scholar University of Education Lahore E-mail: [email protected] "ABSTRACT The purpose of the study was to explore and measure the perception and satisfaction level of parents of special children about the role of special education institutes in the adjustment of special children in their families. The researcher used two self developed questionnaires to collect the data about the problem under investigation, one questionnaire to explore the perception of parents of special children about the role of special education school in the adjustment of special children in their families and the other questionnaire to measure the satisfaction level of parents. All special children of District Bhakkar were constituted as target population for the study. The special children of Special Education School Bhakkar were assessable population for the study. Parents of sixty special children from Special Education School Bhakkar conveniently selected as a sample for the study. Simple descriptive statistical techniques such as mean and percentages were used to analyze the collected data. After careful data analysis the researchers concluded that the special education schools may play very vital role in the adjustment of special children in their family but unfortunately due to lack of resources and infrastructure they are not fulfilling the needs of special children and there is also some lack in the awareness about the importance of social adjustment of special children in their families. The researcher identified very important needs, problems, self concept, and adjustment problems of special children through review of literature and research. Key Words: Special Education , Special Children , Family Adjustment "
The International Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities Invention
Ermira Tati
RELATED PAPERS
Australasian Journal of Philosophy
Garrett Cullity
Dhita Safitri
Gastroenterology
Nikoo Fattahi
Oxford Medicine Online
Revista de Artes Marciales Asiáticas
Stephan Berwick
BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology
Josaphat K Byamugisha
Moscow University Biological Sciences Bulletin
Vladimir Aleoshin
Rev Colomb Cardiol
JUAN PABLO LEON MONTENEGRO
Medical Informatics Europe
Andrew James
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal
Gökçen Çoban
La innovación docente como misión del profesorado : Congreso Internacional Sobre Aprendizaje, Innovación y Competitividad
isabel chiyon
Proceedings of 7th International Seminar on Ecology, Human Habitat and Environmental Change in the Malay World
Mashitoh Yaacob
New Journal of Physics - NEW J PHYS
Serkan Karabacak
Revista brasileira de parasitologia veterinária = Brazilian journal of veterinary parasitology : Órgão Oficial do Colégio Brasileiro de Parasitologia Veterinária
Anderson Cezar
in diritto&diritti
Giuseppe Melchiorre Napoli
Educação & Realidade
Claudemir Belintane
Chemosphere
Muhammad Lukman
2024–Il problema della gurerra e le vie della pace
Tecla Mazzarese
Miguel Guzman Muñoz
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Children's mental health case studies
- Food, health and nutrition
- Mental wellbeing
- Mental health
Explore the experiences of children and families with these interdisciplinary case studies. Designed to help professionals and students explore the strengths and needs of children and their families, each case presents a detailed situation, related research, problem-solving questions and feedback for the user. Use these cases on your own or in classes and training events
Each case study:
- Explores the experiences of a child and family over time.
- Introduces theories, research and practice ideas about children's mental health.
- Shows the needs of a child at specific stages of development.
- Invites users to “try on the hat” of different specific professionals.
By completing a case study participants will:
- Examine the needs of children from an interdisciplinary perspective.
- Recognize the importance of prevention/early intervention in children’s mental health.
- Apply ecological and developmental perspectives to children’s mental health.
- Predict probable outcomes for children based on services they receive.
Case studies prompt users to practice making decisions that are:
- Research-based.
- Practice-based.
- Best to meet a child and family's needs in that moment.
Children’s mental health service delivery systems often face significant challenges.
- Services can be disconnected and hard to access.
- Stigma can prevent people from seeking help.
- Parents, teachers and other direct providers can become overwhelmed with piecing together a system of care that meets the needs of an individual child.
- Professionals can be unaware of the theories and perspectives under which others serving the same family work
- Professionals may face challenges doing interdisciplinary work.
- Limited funding promotes competition between organizations trying to serve families.
These case studies help explore life-like mental health situations and decision-making. Case studies introduce characters with history, relationships and real-life problems. They offer users the opportunity to:
- Examine all these details, as well as pertinent research.
- Make informed decisions about intervention based on the available information.
The case study also allows users to see how preventive decisions can change outcomes later on. At every step, the case content and learning format encourages users to review the research to inform their decisions.
Each case study emphasizes the need to consider a growing child within ecological, developmental, and interdisciplinary frameworks.
- Ecological approaches consider all the levels of influence on a child.
- Developmental approaches recognize that children are constantly growing and developing. They may learn some things before other things.
- Interdisciplinary perspectives recognize that the needs of children will not be met within the perspectives and theories of a single discipline.
There are currently two different case students available. Each case study reflects a set of themes that the child and family experience.
The About Steven case study addresses:
- Adolescent depression.
- School mental health.
- Rural mental health services.
- Social/emotional development.
The Brianna and Tanya case study reflects themes of:
- Infant and early childhood mental health.
- Educational disparities.
- Trauma and toxic stress.
- Financial insecurity.
- Intergenerational issues.
The case studies are designed with many audiences in mind:
Practitioners from a variety of fields. This includes social work, education, nursing, public health, mental health, and others.
Professionals in training, including those attending graduate or undergraduate classes.
The broader community.
Each case is based on the research, theories, practices and perspectives of people in all these areas. The case studies emphasize the importance of considering an interdisciplinary framework. Children’s needs cannot be met within the perspective of a single discipline.
The complex problems children face need solutions that integrate many and diverse ways of knowing. The case studies also help everyone better understand the mental health needs of children. We all have a role to play.
These case has been piloted within:
Graduate and undergraduate courses.
Discipline-specific and interdisciplinary settings.
Professional organizations.
Currently, the case studies are being offered to instructors and their staff and students in graduate and undergraduate level courses. They are designed to supplement existing course curricula.
Instructors have used the case study effectively by:
- Assigning the entire case at one time as homework. This is followed by in-class discussion or a reflective writing assignment relevant to a course.
- Assigning sections of the case throughout the course. Instructors then require students to prepare for in-class discussion pertinent to that section.
- Creating writing, research or presentation assignments based on specific sections of course content.
- Focusing on a specific theme present in the case that is pertinent to the course. Instructors use this as a launching point for deeper study.
- Constructing other in-class creative experiences with the case.
- Collaborating with other instructors to hold interdisciplinary discussions about the case.
To get started with a particular case, visit the related web page and follow the instructions to register. Once you register as an instructor, you will receive information for your co-instructors, teaching assistants and students. Get more information on the following web pages.
- Brianna and Tanya: A case study about infant and early childhood mental health
- About Steven: A children’s mental health case study about depression
Cari Michaels, Extension educator
Reviewed in 2023
© 2024 Regents of the University of Minnesota. All rights reserved. The University of Minnesota is an equal opportunity educator and employer.
- Report Web Disability-Related Issue |
- Privacy Statement |
- Staff intranet

Early Childhood Education: How to do a Child Case Study-Best Practice
- Creating an Annotated Bibliography
- Lesson Plans and Rubrics
- Children's literature
- Podcasts and Videos
- Cherie's Recommended Library
- Great Educational Articles
- Great Activities for Children
- Professionalism in the Field and in a College Classroom
- Professional Associations
- Pennsylvania Certification
- Manor's Early Childhood Faculty
- Manor Lesson Plan Format
- Manor APA Formatting, Reference, and Citation Policy for Education Classes
- Conducting a Literature Review for a Manor education class
- Manor College's Guide to Using EBSCO Effectively
- How to do a Child Case Study-Best Practice
- ED105: From Teacher Interview to Final Project
- Pennsylvania Initiatives
Description of Assignment
During your time at Manor, you will need to conduct a child case study. To do well, you will need to plan ahead and keep a schedule for observing the child. A case study at Manor typically includes the following components:
- Three observations of the child: one qualitative, one quantitative, and one of your choice.
- Three artifact collections and review: one qualitative, one quantitative, and one of your choice.
- A Narrative
Within this tab, we will discuss how to complete all portions of the case study. A copy of the rubric for the assignment is attached.
- Case Study Rubric (Online)
- Case Study Rubric (Hybrid/F2F)
Qualitative and Quantitative Observation Tips
Remember your observation notes should provide the following detailed information about the child:
- child’s age,
- physical appearance,
- the setting, and
- any other important background information.
You should observe the child a minimum of 5 hours. Make sure you DO NOT use the child's real name in your observations. Always use a pseudo name for course assignments.
You will use your observations to help write your narrative. When submitting your observations for the course please make sure they are typed so that they are legible for your instructor. This will help them provide feedback to you.
Qualitative Observations
A qualitative observation is one in which you simply write down what you see using the anecdotal note format listed below.
Quantitative Observations
A quantitative observation is one in which you will use some type of checklist to assess a child's skills. This can be a checklist that you create and/or one that you find on the web. A great choice of a checklist would be an Ounce Assessment and/or work sampling assessment depending on the age of the child. Below you will find some resources on finding checklists for this portion of the case study. If you are interested in using Ounce or Work Sampling, please see your program director for a copy.
Remaining Objective
For both qualitative and quantitative observations, you will only write down what your see and hear. Do not interpret your observation notes. Remain objective versus being subjective.
An example of an objective statement would be the following: "Johnny stacked three blocks vertically on top of a classroom table." or "When prompted by his teacher Johnny wrote his name but omitted the two N's in his name."
An example of a subjective statement would be the following: "Johnny is happy because he was able to play with the block." or "Johnny omitted the two N's in his name on purpose."
- Anecdotal Notes Form Form to use to record your observations.
- Guidelines for Writing Your Observations
- Tips for Writing Objective Observations
- Objective vs. Subjective
Qualitative and Quantitative Artifact Collection and Review Tips
For this section, you will collect artifacts from and/or on the child during the time you observe the child. Here is a list of the different types of artifacts you might collect:
Potential Qualitative Artifacts
- Photos of a child completing a task, during free play, and/or outdoors.
- Samples of Artwork
- Samples of writing
- Products of child-led activities
Potential Quantitative Artifacts
- Checklist
- Rating Scales
- Product Teacher-led activities
Examples of Components of the Case Study
Here you will find a number of examples of components of the Case Study. Please use them as a guide as best practice for completing your Case Study assignment.
- Qualitatitive Example 1
- Qualitatitive Example 2
- Quantitative Photo 1
- Qualitatitive Photo 1
- Quantitative Observation Example 1
- Artifact Photo 1
- Artifact Photo 2
- Artifact Photo 3
- Artifact Photo 4
- Artifact Sample Write-Up
- Case Study Narrative Example Although we do not expect you to have this many pages for your case study, pay close attention to how this case study is organized and written. The is an example of best practice.
Narrative Tips
The Narrative portion of your case study assignment should be written in APA style, double-spaced, and follow the format below:
- Introduction : Background information about the child (if any is known), setting, age, physical appearance, and other relevant details. There should be an overall feel for what this child and his/her family is like. Remember that the child’s neighborhood, school, community, etc all play a role in development, so make sure you accurately and fully describe this setting! --- 1 page
- Observations of Development : The main body of your observations coupled with course material supporting whether or not the observed behavior was typical of the child’s age or not. Report behaviors and statements from both the child observation and from the parent/guardian interview— 1.5 pages
- Comment on Development: This is the portion of the paper where your professional analysis of your observations are shared. Based on your evidence, what can you generally state regarding the cognitive, social and emotional, and physical development of this child? Include both information from your observations and from your interview— 1.5 pages
- Conclusion: What are the relative strengths and weaknesses of the family, the child? What could this child benefit from? Make any final remarks regarding the child’s overall development in this section.— 1page
- Your Case Study Narrative should be a minimum of 5 pages.
Make sure to NOT to use the child’s real name in the Narrative Report. You should make reference to course material, information from your textbook, and class supplemental materials throughout the paper .
Same rules apply in terms of writing in objective language and only using subjective minimally. REMEMBER to CHECK your grammar, spelling, and APA formatting before submitting to your instructor. It is imperative that you review the rubric of this assignment as well before completing it.
Biggest Mistakes Students Make on this Assignment
Here is a list of the biggest mistakes that students make on this assignment:
- Failing to start early . The case study assignment is one that you will submit in parts throughout the semester. It is important that you begin your observations on the case study before the first assignment is due. Waiting to the last minute will lead to a poor grade on this assignment, which historically has been the case for students who have completed this assignment.
- Failing to utilize the rubrics. The rubrics provide students with guidelines on what components are necessary for the assignment. Often students will lose points because they simply read the descriptions of the assignment but did not pay attention to rubric portions of the assignment.
- Failing to use APA formatting and proper grammar and spelling. It is imperative that you use spell check and/or other grammar checking software to ensure that your narrative is written well. Remember it must be in APA formatting so make sure that you review the tutorials available for you on our Lib Guide that will assess you in this area.
- << Previous: Manor College's Guide to Using EBSCO Effectively
- Next: ED105: From Teacher Interview to Final Project >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2024 2:53 PM
- URL: https://manor.libguides.com/ece

Manor College Library
700 fox chase road, jenkintown, pa 19046, (215) 885-5752, ©2017 manor college. all rights reserved..
Case studies in child welfare
About this guide, child welfare case studies, real-life stories, and scenarios, social services and organizational case studies, other case studies, using case studies.
This guide is intended as a supplementary resource for staff at Children's Aid Societies and Indigenous Well-being Agencies. It is not intended as an authority on social work or legal practice, nor is it meant to be representative of all perspectives in child welfare. Staff are encouraged to think critically when reviewing publications and other materials, and to always confirm practice and policy at their agency.
Case studies and real-life stories can be a powerful tool for teaching and learning about child welfare issues and practice applications. This guide provides access to a variety of sources of social work case studies and scenarios, with a specific focus on child welfare and child welfare organizations.
- Real cases project Three case studies, drawn from the New York City Administration for Children's Services. Website also includes teaching guides
- Protective factors in practice vignettes These vignettes illustrate how multiple protective factors support and strengthen families who are experiencing stress. From the National Child Abuse Prevention Month website
- Child welfare case studies and competencies Each of these cases was developed, in partnership, by a faculty representative from an Alabama college or university social work education program and a social worker, with child welfare experience, from the Alabama Department of Human Resources
- Immigration in the child welfare system: Case studies Case studies related to immigrant children and families in the U.S. from the American Bar Association
- White privilege and racism in child welfare scenarios From the Center for Advanced Studies in Child Welfare more... less... https://web.archive.org/web/20190131213630/https://cascw.umn.edu/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/WhitePrivilegeScenarios.pdf
- You decide: Would you remove these children from their families? Interactive piece from the Australian Broadcasting Corporation featuring cases based on real-life situations
- A case study involving complex trauma This case study complements a series of blog posts dedicated to the topic of complex trauma and how children learn to cope with complex trauma
- Fostering and adoption: Case studies Four case studies from Research in Practice (UK)
- Troubled families case studies This document describes how different families in the UK were helped through family intervention projects
- Parenting case studies From of the Pennsylvania Child Welfare Resource Center's training entitled "Understanding Reactive Attachment Disorder"
- Children’s Social Work Matters: Case studies Collections of narratives and case studies
- Race for Results case studies Series of case studies from the Annie E. Casey Foundation looking at ways of addressing racial inequities and supporting better outcomes for racialized children and communities
- Systems of care implementation case studies This report presents case studies that synthesize the findings, strategies, and approaches used by two grant communities to develop a principle-guided approach to child welfare service delivery for children and families more... less... https://web.archive.org/web/20190108153624/https://www.childwelfare.gov/pubPDFs/ImplementationCaseStudies.pdf
- Child Outcomes Research Consortium: Case studies Case studies from the Child Outcomes Research Consortium, a membership organization in the UK that collects and uses evidence to improve children and young people’s mental health and well-being
- Social work practice with carers: Case studies
- Social Care Institute for Excellence: Case studies
- Learning to address implicit bias towards LGBTQ patients: Case scenarios [2018] more... less... https://web.archive.org/web/20190212165359/https://www.lgbthealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/Implicit-Bias-Guide-2018_Final.pdf
- Using case studies to teach
- Last Updated: Aug 12, 2022 11:21 AM
- URL: https://oacas.libguides.com/case-studies
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- About Mild TBI and Concussion
- After a Mild TBI or Concussion
- Health Disparities in TBI
- Comparing Head Impacts
- Clinical Guidance
- Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Management Guideline
- Resources for Health Care Providers
Traumatic Brain Injury & Concussion
About Moderate and Severe TBI

Preventing TBI
Symptoms of Mild TBI and Concussion

Where to Get Help

Facts About TBI
For Medical Professionals

Clinical Guidance for Pediatric mTBI

Health Care Provider Resources
CDC Programs

HEADS UP Online Training Courses
National Concussion Surveillance System
Core State Injury Prevention Program (Core SIPP)
A traumatic brain injury, or TBI, is an injury that affects how the brain works. TBI is a major cause of death and disability in the United States.
For Everyone
Health care providers.
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the liver after adrenal neuroblastoma surgery: a case report
- Case Report
- Open access
- Published: 18 May 2024
- Volume 15 , article number 174 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Qiyang Shen 1 ,
- Xingyu Liu 2 ,
- Lijie Zhang 3 ,
- Tao Li 1 &
- Jianfeng Zhou 1
12 Accesses
Explore all metrics
A boy aged 55 months was diagnosed with stage IV Neuroblastoma (NB) of the right adrenal gland 2 years ago. Preoperative chemotherapy was given and he was then treated with retroperitoneal tumor resection and lymph node dissection. After surgery, the children were transferred to the Hemato-Oncology Department for chemotherapy according to the high-risk group NB, with outpatient follow-up every 6 months. In the second postoperative year, abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan revealed a rounded hypodense area in the upper part of the right posterior lobe of the liver, with marked inhomogeneous enhancement in the venous phase after enhancement, which was surgically resected, and postoperative pathology confirmed inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) of liver. The patient was not given any special treatment after surgery. In this study, whole transcriptome sequencing was performed on the postoperative specimen of adrenal NB and the specimen of IMT of liver. This unusual case emphasizes the need for close monitoring of second tumor development in NB survivors even in the absence of known predisposing factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
HIV-related bilateral inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the adrenal gland: a case report and literature review

Crizotinib combined with bronchoscopic interventional treatment in ALK-positive inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of left main stem bronchus: a case report

Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour arising in the adrenal gland: a case report
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Background
With improved diagnostic and treatment modalities for neuroblastoma (NB), the prognosis for patients is getting better, but the risk of patients developing a second tumor remains [ 1 ]. A so-called second tumor is another tumor that develops near or away from the primary tumor [ 2 ]. The appearance of a mass in the organism after the complete cure of a malignant tumor does not necessarily mean the recurrence of the tumor or the development of another malignant tumor [ 3 ]. In addition, the development of a second tumor may or may not be related to the treatment of the prior tumor, as genetic risk factors or other external carcinogens may also be involved [ 4 ]. The development of a second malignant tumor is one of the most devastating events affecting the survival of these patients [ 5 , 6 ]. Studies suggest that the younger the cancer survivor, the more deadly the second primary malignancy [ 7 ]. Another study reported malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumour as the second primary malignant tumor after pediatric NB treatment [ 8 ]. IMT is a rare inert tumor that has been less frequently reported as a second tumor occurring after treatment of malignancy in pediatric patients, with cases of IMT occurring after treatment of pediatric nephroblastoma reported [ 9 ]. Characterized by spindle cell proliferation and inflammatory cell infiltration, IMT is an intermediate state tumor with malignant potential, and therefore should be given adequate attention when it appears as a second tumor [ 10 ]. This study reports a case of a child who developed liver inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) after NB.
This study was reviewed by the ethics committee of the Children’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, batch number: NJCH2020137. The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The legal guardians/next of kin of the participants provided written informed consent for participation in this study. Written informed consent for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data contained herein was obtained from the legal guardian/next of kin of the minor.
2.1 Case presentation
A male child, aged 28 months, was admitted to the hospital for examination in 2018 when he was found to have a frontal parietal mass with fever for 6 days. Chest and whole abdomen CT scan showed soft tissue density mass shadow of the right adrenal gland, with multiple small nodular calcified foci seen internally; multiple nodular calcified foci seen in the retroperitoneum and pelvis, which was considered as NB with possible retroperitoneal pelvic multiple lymph node metastases (Fig. 1 A). Cranial CT scan revealed thickening of the cranial plate of the frontal parietal bone on both sides, radiolucent periosteal reaction was seen in the inner plate, and soft tissue mass formation was seen in the surrounding area, metastasis was considered (Fig. 1 B). The child underwent cranial tumor biopsy on 3/23/2018, and postoperative pathology showed a small round cell malignancy, and NB metastasis was considered in conjunction with the child’s clinical history and immunohistochemistry results. In this study, we used fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to detect the amplification rate of the MYCN gene, and a MYCN (green signal)/CEP2 (orange signal) ratio > 4 was considered positive, i.e., MYCN amplification; a MYCN/CEP2 ratio ≥ 1 and < 4 was considered gain; and a MYCN/CEP2 ratio < 1 was considered negative. MYCN gene test result was gain (Fig. 2 ).

The patient’s first physical examination. A A whole-body CT shows a suspicious mass in the right adrenal gland. B CT scan of the head showed bony abnormalities of the frontal parietal bone with soft tissue masses on both sides, metastasis was considered

FISH assay to detect MYCN gene amplification, green signal for MYCN gene and orange gene for CEP2, × 1000. MYCN gene test result was gain. (Among the counted tumor cells, the MYCN/CEP2 ratio was 1.07, the mean MYCN signal was 2.45, and the mean CEP2 signal was 2.3)
The child was diagnosed with NB, stage IV, and was included in the ultra-high-risk group because of cranial, dural, and multiple vertebral metastases, and was subsequently transferred to the Hemato-Oncology Department for chemotherapy. Since 11/04/2018 patient was given 3 courses of chemotherapy in the ultra-high risk group regimen for NB (Course I: cyclophosphamide, topotecan; Course II: topotecan, cyclophosphamide; Course III: pedialyte glycosides, cisplatin). On June 29, 2018, the patient underwent retroperitoneal tumor resection and retroperitoneal lymph node dissection in the Department of General Surgery of Nanjing Children’s Hospital. Postoperative pathology revealed post-chemotherapy changes in NB (differentiated type) with lymph node metastasis (Fig. 3 ). Transferred to Hemato-Oncology for chemotherapy after surgery (Course 1: CTX + TOPO; Course 2: CTX + TOPO; Course 3: CDDP + VP16; Course 4: CTX + DOXO + VCR + MESNA; Course 5: CDDP + VP16; Course 6: CTX + DOXO + VCR + MESNA; Course 7: CTX + TOPO; Course 8: CDDP + VP16; Course 9: CTX + DOXO + VCR + MESNA; Course 10: CTX + TOPO) and the abdominal CT was reviewed regularly.

Hematoxylin and eosin stain of the mass. The patient had preoperative chemotherapy, and the postoperative NB pathological section results showed differentiated type ( A : 40 × ; B : 100 ×)
The child underwent a routine postoperative thoracic and abdominal CT review in June 2020, which revealed an abnormal occupancy in the upper right posterior lobe of the liver. Further examination of the whole abdomen using CT scan with contrast showed that the right lobe of the liver was visible as a classically rounded low-density area with an extent of about 22 × 24 mm, and enhancement reveals inhomogeneous enhancement, which is evident in the venous phase, within which enhanced nodules are also seen.; NB liver metastasis is considered (Fig. 4 ). Subsequently, hepatic anomalous occupancy resection was performed in our General Surgery Department, and the occupancy was anatomically resected using indocyanine green fluorescence navigated hepatic occupancy resection, and postoperative pathology showed IMT (Fig. 5 A). Ventana D5F3 immunohistochemical staining showed positive anaplastic lymphoma kinas (ALK), consistent with the diagnosis of IMT (Fig. 5 B). Whole transcriptome sequencing of the adrenal NB specimen and the IMT of liver revealed a large number of differentially expressed genes (Fig. 6 ). A VIT chemotherapy regimen (Vincristine, Irinotecan and Temozolomide) was used postoperatively with outpatient follow-up.
Abdominal CT showed that the liver was normal in shape and size, and the right lobe of the liver could be seen as a rounded hypodense area, with inhomogeneous enhancement seen in the venous phase, within which enhancement nodules could be seen

A Hematoxylin and eosin stain of the mass, postoperative pathology shows inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (40 × ; 100 ×); B Immunohistochemistry for ALK shows strong positivity (100 × ; 200 ×)
Whole transcriptome sequencing of adrenal NB specimens and liver IMT specimens revealed a large number of differential genes
3 Discussion
Comprehensive treatment of NB is associated with multiple complications, including cognitive deficits, cardiotoxicity, and chronic kidney disease [ 1 , 11 , 12 ]. In addition, many individual cases have reported a second tumor after treatment [ 13 , 14 ]. IMT of the Liver is a tumor-like lesion characterized by fibrous tissue, capillary hyperplasia, and local tissue inflammatory cell infiltration following necrosis of liver tissue caused by various inflammatory factors. The condition as a second tumor is reported for the first time [ 15 ].
When two tumors appear in adjacent locations at different times, multiple etiologies may be involved [ 16 ]. The second tumor may represent an extension or metastasis of the primary tumor [ 17 ]. Irradiation and drug therapy used as adjuvant modalities during the preoperative and postoperative period may have contributed to the development of the new tumor [ 18 ]. In addition, a patient’s genetic susceptibility to cancer, other environmental factors, or unknown causes may also lead to the development of a second tumor [ 19 , 20 ]. Low-dose irradiation is known to induce a second tumor [ 21 ]. In general, the following criteria should be followed for the diagnosis of radiation tumors [ 22 ]: the new lesion appears in the radiated area; it is histologically distinct from the first tumor; it develops after a latent period that reasonably allows for the development of a secondary tumor, and there are no other conditions that predispose to tumor development. And the patient's medical records showed no other genetic or environmental factors predisposing him to cancer. Based on the fact that the patient received prior chemotherapy, the authors of this article do not exclude the possibility that chemotherapy may have acted as a causative factor in the development of hepatic IMT. However, it is not entirely clear whether this is the case.
In addition, in this study, whole transcriptome next-generation sequencing of adrenal NB specimens and IMT of liver specimens were performed. Whole transcriptome sequencing showed complete discordance in gene expression between adrenal NB specimens and liver IMT specimens, this transcriptomic level analysis again validated the non-homologous nature of the patient's two successive tumors. Genetic studies have similarly shown that rearrangement of the ALK gene may contribute to tumorigenesis, suggesting that IMT is likely to occur as a tumor entity and is not a reactive progression due to a particular disease [ 9 ]. Our immunohistochemistry results also showed strong positivity for ALK, which can be used to differentiate from NB. It is more likely that radiotherapy and medication used as adjuvant modalities during the preoperative and postoperative period contributed to the development of IMT of liver after adrenal NB surgery. Overall, the association between the two tumors awaits further study.
Data availability
The datasets for this article are not publicly available due to concerns regarding participant/patient anonymity. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to the corresponding author.
Castle JT, Levy BE, Rodeberg DA. Abdominal tumors: wilms, neuroblastoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, and hepatoblastoma [J]. Surg Clin North Am. 2022;102(5):715–37.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Baird DC, Meyers GJ, Hu JS. Testicular cancer: diagnosis and treatment [J]. Am Fam Phys. 2018;97(4):261–8.
Google Scholar
Breslow NE, Lange JM, Friedman DL, et al. Secondary malignant neoplasms after Wilms tumor: an international collaborative study [J]. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(3):657–66.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Guan X, Wei R, Yang R, et al. Association of radiotherapy for rectal cancer and second gynecological malignant neoplasms [J]. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2031661.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Attarbaschi A, Carraro E, Ronceray L, et al. Second malignant neoplasms after treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma-a retrospective multinational study of 189 children and adolescents [J]. Leukemia. 2021;35(2):534–49.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Fabius AWM, van Hoefen WM, van Leeuwen FE, et al. Subsequent malignant neoplasms in retinoblastoma survivors [J]. Cancers. 2021;13(6):1200.
Keegan THM, Bleyer A, Rosenberg AS, et al. Second primary malignant neoplasms and survival in adolescent and young adult cancer survivors [J]. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(11):1554–7.
Ottaviano M, Maddalena C, D’Armiento M, et al. Systemic treatment of malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumour after childhood neuroblastoma: chemotherapy in malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumour [J]. Anticancer Drugs. 2019;30(9):959–63.
Li YP, Han WW, He LJ, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor after treatment of wilms tumor in a 6-year-old boy: a case report and literature review [J]. Urology. 2021;149:e25–8.
Webb TR, Slavish J, George RE, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: role in cancer pathogenesis and small-molecule inhibitor development for therapy [J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009;9(3):331–56.
Cairo SB, Urias AR, Murphy JT. Pediatric abdominal malignancies and intravascular extension: contemporary single-center experience [J]. J Surg Res. 2022;280:396–403.
Uttinger KL, Riedmeier M, Reibetanz J, et al. Adrenalectomies in children and adolescents in Germany—a diagnose related groups based analysis from 2009–2017 [J]. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:914449.
Article Google Scholar
Martin A, Schneiderman J, Helenowski IB, et al. Secondary malignant neoplasms after high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell rescue for high-risk neuroblastoma [J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014;61(8):1350–6.
Applebaum MA, Vaksman Z, Lee SM, et al. Neuroblastoma survivors are at increased risk for second malignancies: a report from the international neuroblastoma risk group project [J]. Eur J Cancer. 2017;72:177–85.
Filips A, Maurer MH, Montani M, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the liver: a case report and review of literature [J]. World J Hepatol. 2020;12(4):170–83.
Applebaum MA, Henderson TO, Lee SM, et al. Second malignancies in patients with neuroblastoma: the effects of risk-based therapy [J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62(1):128–33.
Westerveld ASR, van Dalen EC, Asogwa OA, et al. Neuroblastoma survivors at risk for developing subsequent neoplasms: a systematic review [J]. Cancer Treat Rev. 2022;104:102355.
Zhen H, Guan H, Ma J, et al. Risk of developing second malignant neoplasms in patients with neuroblastoma: a population study of the US SEER database [J]. Radiat Oncol. 2021;16(1):228.
Lee JS, Dubois SG, Coccia PF, et al. Increased risk of second malignant neoplasms in adolescents and young adults with cancer [J]. Cancer. 2016;122(1):116–23.
Yalcin B, Kremer LC, van Dalen EC. High-dose chemotherapy and autologous haematopoietic stem cell rescue for children with high-risk neuroblastoma [J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;12(5):CD006301.
Hawkins M, Bhatia S, Henderson TO, et al. Subsequent primary neoplasms: risks, risk factors, surveillance, and future research [J]. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2020;67(6):1135–54.
Park KJ, Kang SH, Lee HG, et al. Olfactory neuroblastoma following treatment for pituitary adenoma [J]. J Neurooncol. 2008;90(2):237–41.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank the patient and her parents for their participation in this research.
The study was based on the Pediatric Solid Tumor Cohort of Nanjing Children’s Hospital.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Pediatric Surgery, Children’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Qiyang Shen, Tao Li & Jianfeng Zhou
Department of Pediatric Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu, Anhui, China
Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China
Lijie Zhang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Qiyang Shen and Xingyu Liu conducted the research. Qiyang Shen, Tao Li and Jianfeng Zhou are responsible for tumor resection and pathology specimen collection. Xingyu Liu and Lijie Zhang analyzed data. Qiyang Shen and Xingyu Liu drafted the manuscript. Tao Li and Jianfeng Zhou reviewed the draft. All authors contribute to the article and approve the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Tao Li or Jianfeng Zhou .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study involving human participants was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee. The legal guardians/next of kin of the participants provided written informed consent for participation in this study. Written informed consent for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data contained herein was obtained from the legal guardian/next of kin of the minor.
Competing interests
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Shen, Q., Liu, X., Zhang, L. et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the liver after adrenal neuroblastoma surgery: a case report. Discov Onc 15 , 174 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12672-024-01039-4
Download citation
Received : 30 September 2023
Accepted : 15 May 2024
Published : 18 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12672-024-01039-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Neuroblastoma
- Secondary tumor
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor
- Whole transcriptome sequencing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The following case studies present three different children with ASD and describe the SLP's strategies to enhance communication and quality of life. The three case studies demonstrate various options in AAC intervention that can be used by children of different ages. —Ann-Mari Pierotti, MS, CCC-SLP. Case Study 1: Anderson | Case Study 2 ...
Handout #2 provides case histories of four students: Chuck, a curious, highly verbal, and rambunctious six-year-old boy with behavior disorders who received special education services in elementary school. Juanita, a charming but shy six-year-old Latina child who was served as an at-risk student with Title 1 supports in elementary school.
CASE STUDY EXAMPLE effective instructional strategy and parents of children with ASD have used this strategy to successfully teach requesting. Additionally, naturalistic intervention is designed to be conducted within natural routines. Next, Mrs. Dell creates a data collection system that is succinct and easy to implement
The case study was conducted by keen observations of the special needed child by involving and getting information directly from different reliable sources like,concerned teachers, peer groups from the school, parents, family members and peer groups of the child from the home environment. The tools used in the study were 1. Qustionnaire. 2.
Keywords: outdoor learning, nature-based learning, special education, case study, autism. Citation: Friedman S and Morrison SA (2021) "I just want to stay out there all day": A Case Study of Two Special Educators and Five Autistic Children Learning Outside at School. Front. Educ. 6:668991. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.668991
Special education inclusion services differ greatly by school, by town, and by state. A special education inclusion teacher can be in a classroom and work as a helper, or the special education teacher can be act as a co-teacher, with both teachers working collaboratively to instruct their diverse students of different abilities.
It can be challenging to have a special needs child but finding the right educational setting is probably the biggest challenge special needs families face, however we count ourselves very lucky to have found the Circle Centre." Harrison's story Harrison was diagnosed with autism when he was just over 2 years old.
A Case Study of a School Child with Emotional and Behavior Problems treated using Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. August 2022; ... early childhood special education, 13 (1), 82-105.
children with special educational needs are catered for. In order to pursue this enquiry a case study research design was used to ascertain multiple perspectives through interviews in Rose Hill Primary School. Four groups of people were interviewed in the school - the principal, eight teachers, two special needs assistants ...
A Journey to Stare Then Reach - a case study of a special child. This is a story of a little angel of in the school Durgabhai Deshmukh Vocational Training and Rehabilitation Centre. The mother of the little angel is a homemaker while her father was working at a press. Little angel was the first child of her parents and was born on 19th March 2012.
A Case Study Approach to Writing Individualized Special Education Documents: From Preschool to Graduation will follow one child, Rochelle, throughout her life in special education. For each primary special education document, you will be given a glimpse into Rochelle's life and needs. Given this information, you can then
Background Long-term effects of neglect in early life are still widely unknown. Diversity of outcomes can be explained by differences in genetic risk, epigenetics, prenatal factors, exposure to stress and/or substances, and parent-child interactions. Very common sub-threshold presentations of children with history of early trauma are challenging not only to diagnose but also in treatment. Case ...
Case study: 'He's a 10-year-old child with disabilities . . . ... especially for a child with disabilities." Benincasa Special School in Blackrock, Co Dublin, said that while it was not in a ...
The case studies have a specific focus on children with disabilities and their families. However, many of the highlighted initiatives are designed for broad inclusion and benefit all children. In particular, this case study, covers such topics as: Inclusive Preschool, Assistive Technologies (AT), Early Childhood intervention (ECI ...
It adopted a mixed method research approach and a case study design. Participating in the study were one head teacher, five preschool staff members and five children with attachment difficulties/an attachment disorder. ... Six more types are activity simplification, child preferences, special equipment, adult support, peer support and invisible ...
This study aimed at exploring the influence of a structured field experience in the form of a child case study on the beliefs and practices of student-teachers with respect to inclusive education using qualitative research design (Creswell, 2013 ). This structured field experience is based on the experiential learning approach to teacher ...
PDF | On Jan 10, 2009, Anna Ksigou published CHILD CASE STUDY-ASSESSMENT AND INTERVENTION | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
I- Research proposed / Case Study: A Case Study on a actual situation:In this activity I Mr Vipan Raj Sardar Patel University Balaghat,{MP} have taken a real situation of a student/ child of a village, Jagota of tehsil Bhella , District Doda Jammu & Kashmir (India) from class 6th from a government school with special need/learning difficulty ...
This study explored the impact of combining direct instruction with structured field experience, in the form of a child case study, on the beliefs and practices of teacher participants.Seventeen Master of Education candidates, who enrolled in a 'Special Needs and Inclusion' course, conducted child case studies in private schools in the United Arab Emirates and reported deeper understanding ...
Preschool (Section 619) Child Example Case Study: "Kim" at 35 Months of Age 2 list of foods she is gradually introducing in small bites to increase Kim's ability to accept the foods the family typically eats. Kim was able to assist with dressing (raise an arm, step into a pants leg when held).
Mental health. Children's mental health case studies. Explore the experiences of children and families with these interdisciplinary case studies. Designed to help professionals and students explore the strengths and needs of children and their families, each case presents a detailed situation, related research, problem-solving questions and ...
The Narrative portion of your case study assignment should be written in APA style, double-spaced, and follow the format below: Introduction: Background information about the child (if any is known), setting, age, physical appearance, and other relevant details.There should be an overall feel for what this child and his/her family is like. Remember that the child's neighborhood, school ...
Case studies and real-life stories can be a powerful tool for teaching and learning about child welfare issues and practice applications. This guide provides access to a variety of sources of social work case studies and scenarios, with a specific focus on child welfare and child welfare organizations.
View recommendations for diagnosis and management of children with mild TBI. Nov. 6, 2023. Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Management Guideline. View clinical recommendations for diagnosis and management of adults with mild TBI. Apr. 29, 2024. Health Care Provider Resources. View resources to manage and prevent concussions.
A boy aged 55 months was diagnosed with stage IV Neuroblastoma (NB) of the right adrenal gland 2 years ago. Preoperative chemotherapy was given and he was then treated with retroperitoneal tumor resection and lymph node dissection. After surgery, the children were transferred to the Hemato-Oncology Department for chemotherapy according to the high-risk group NB, with outpatient follow-up every ...