
- Book Solutions
- State Boards

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Life Processes
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 6 life processes.

At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 6
CASE STUDY : 1
Carbon and energy requirements of the autotrophic organism are fulfilled by photosynthesis. It is the process by which autotrophs take in substances from the outside and convert them into stored forms of energy. This material is taken in the form of carbon dioxide and water which is converted into carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. Carbohydrates are utilised for providing energy to the plant.
i) Write a chemical reaction which occur during photosynthesis?
Ans: 6CO2 +12H2O + Chlorophyll & sunlight👉 C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
ii) In which form of carbohydrates does the plant stored in them?
Ans: The carbohydrates are stored in the form of starch as the internal energy.
iii) What is stomata?
Ans: The process present in the surface of a leaf or the stem of a plant to allow the exchange of gases.
iv) What are the functions of stomata?
Ans: i) Exchange of gases i.e oxygen and CO2
ii) Transpiration
v) What is Chloroplast?
Ans: Chloroplast is a cell organelles which contains photosynthetic pigment called as chlorophyll which help in the absorption of sunlight.
CASE STUDY : 2
The alimentary canal is basically a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus. In Fig. 6.6, we can see that the tube has different parts. Various regions are specialised to perform different functions.
We eat various types of food which has to pass through the same digestive tract. Naturally the food has to be processed to generate particles which are small and of the same texture. This is achieved by crushing the food with our teeth
i) Which enzyme is present in our mouth to digest starch?
Ans: Salivary amylase from salivary glands.
ii) What are the types of enzymes released by our stomach?
Ans: Hydrochloric acid, pepsin and a mucus.
iii) Which is the longest part of our alimentary canal in our body?
Ans: Small intestine
iv) What are villi?
Ans: Villi are finger like projection present inside the inner lining of the small intestine which increases the surface area for absorption.
v) What are the enzymes that are released by pancreas?
Ans: Enzyme released by pancreas – • trypsin- Digestion of protein
lipase – breakdown of emulsified fats
CASE STUDY : 3
The food material taken in during the process of nutrition is used in cells to provide energy for various life processes. Diverse organisms do this in different ways – some use oxygen to break-down glucose completely into carbon dioxide and water, some use other pathways that do not involve oxygen (Fig. 6.8). In all cases, the first step is the break-down of glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm.
i) What is anaerobic respiration?
Ans: The conversion of pyruvate into ethanol, CO2 & energy take place in the absence of air(oxygen), it is called anaerobic respiration.
ii) Explain the process which happen in our muscle cells?
Ans- The conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid( 3 carbon molecule) and energy due to the lack of oxygen.
iii) In which form our body used the energy?
Ans: It is in the form of ATP molecule i.e Adenosine Triphosphate.
iv) Why there is a faster breathing rate of aquatic animals then the terrestrial animals?
Ans- The amount of O2 dissolved in water is low as compared to amount of O2 present in air. Therefore, aquatic animals have faster breathing rate.
v) Write the name of organ used for respiration by different organism- fish, frog?
Ans- i) fish- gills
ii) frog- skin, lungs
CASE STUDY : 4
The excretory system of human beings includes a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra. Kidneys are located in the abdomen, one on either side of the backbone. Urine produced in the kidneys passes through the ureters into the urinary bladder where it is stored until it is released through the urethra.
i) What is the purpose of making urine?
Ans: Urine is to filter out the blood i e to remove waste product from the blood such as urea.
ii) What is Bowman’s capsule?
Ans: A cup shaped end of a coiled tube which is associated with capillaries to collect filterate.
iii) What is dialysis?
Ans: To remove nitrogenous waste from your blood by using machine when kidney does not its function i.e in case of kidney failure.
iv) What is the function of urinary bladder?
Ans: It is used to stored urine until the pressure comes from the brain to pass it out.
v) What are the different parts of nephrons?
Ans: Renal artery, Bowman’s capsule, glomerulus, tubular part of nephron and a collecting duct.
CASE STUDY : 5
The heart is a muscular organ which is as big as our fist. Because both oxygen and carbon dioxide have to be transported by the blood, the heart has different chambers to prevent the oxygen-rich blood from mixing with the blood containing carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide-rich blood has to reach the lungs for the carbon dioxide to be removed, and the oxygenated blood from the lungs has to be brought back to the heart. This oxygen-rich blood is then pumped to the rest of the body.
i) How many chambers are present in the heart of mammals and reptiles?
Ans: Mammals- 4 chamber heart and reptiles- 3 chambered heart
ii) Who carry deoxygenated blood from body to heart?
Ans: Vena cava carries deoxygenated blood from body to heart.
iii) What do you meant by the term double circulation?
Ans: The blood goes through the heart twice during each cycle known as double circulation.
iv) What is hypertension?
Ans: The force that blood experts against the wall of a vessels is called hypertension or high blood pressure.
V) Which device measured blood pressure?
Ans: Sphygmomanometer
CASE STUDY : 6
Plant transport systems will move energy stores from leaves and raw materials from roots. These two pathways are constructed as independently organised conducting tubes. One, the xylem moves water and minerals obtained from the soil. The other, phloem transports products of photosynthesis from the leaves where they are synthesised to other parts of the plant
i) What are the different parts of xylem?
Ans: vessels, tracheids, xylem parenchyma and fibres.
ii) What do you meant by the term transpiration?
Ans: The loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plant.
iii) What are the advantages of transpiration?
Ans: i) help in the absorption and the upward movement of water
ii) temperature regulation
iv) What is translocation?
Ans: The transport of soluble products of photosynthesis is called translocation.
v) How does plant remove their waste product?
Ans: They remove their waste product in the form of fallen leaves, resins and gums.
For more update follow net explanations page
Wonderful..
It’s helpful thank u
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Sikkim scert class 4 evs chapter 2 games we play solution, sikkim scert class 4 evs chapter 1 changing families solution, assam scert class 8 geography and economics chapter 1 solutions, tripura board class 6 bengali solutions chapter 2 তালগাছ.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Last modified on: 3 years ago
- Reading Time: 7 Minutes
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes .
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v).
All living cells need nutrients, O, and other essential substances. Also, the waste and harmful substances need to be removed continuously for healthy functioning of cells. So, a well developed transport system is mandatory for living organisms. Complex organisms have special fluids within their bodies to transport such materials. Blood is the most commonly used body fluid by most of the higher organisms. Lymph also helps in the transport of certain substances.
(i) Which of the following does not exhibit phagocytic activity? (a) Monocytes (b) Neutrophils (c) Basophil (d) Macrophage
(ii) Amount of blood corpusles in changed in dengue fever. One of the common symptoms observed in people infected with dengue fever is (a) significant decrease in RBC count (b) significant decrease in WBC count (c) significant decrease in platelets count (d) significant increase in platelets count.
(iii) Why are WBCs called soldiers of the body? (a) They are capable of squeezing out of blood capillaries. (b) They are manufactured in bone marrow. (c) They fight against disease causing germs. (d) They have granular cytoplasm with lobed nucleus.
(iv) Name the blood cells, whose reduction in number can cause clotting disorder, leading to excessive loss of blood from the body. (a) Erythrocytes (b) Neutrophils (c) Leucocytes (d) Thrombocytes
(v) Which of the following is the correct feature of lymph? (a) It is similar to the plasma of blood, but is colourless and contains less proteins. (b) It is similar to the WBCs of blood, but is colourless and contain more proteins. (c) It is similar to the RBCs of blood and red in colour. (d) It contains more fats.
Question 2:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed? (a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite? (a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph? (a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through (a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostome
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 6 Life Processes PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes Case Study Questions, by practicing this Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 6 Life Processes
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in transpiration, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through pores called stomata. Normally stomata remain open in the daytime and close during the night
(i) Which of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
Answer: (d) Chlorophyll content of leaves
(ii) Water vapour comes out from the plant leaf through the stomatal opening. Through the same stomatal opening, carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant during photosynthesis. Reason out the above statements . using one of following options. (a) The above processes happen only during night time. (b) One process occurs during day time and the other at night. (c) Both processes cannot happen Simultaneously. (d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
Answer: (d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
(iii) Which of the following statements is not true for stomatal apparatus? (a) Guard cells invariably possess chloroplasts and mitochondria. (b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells. (c) Stomata are involved in gaseous exchange. (d) Inner wall of guard cells are thick.
Answer: (b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells.
(iv) Which of the following is not a purpose of transpiration? (a) Helps in absorption and transport in plants (b) Prevents loss of water (c) Maintains shape and structure of plants by keeping the cells turgid (d) Supplies water for photosynthesis
Answer: (b) Prevents loss of water
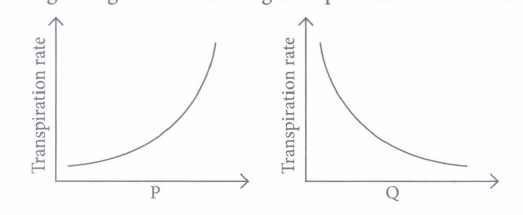
Answer: (a) P-Atmospheric temperature; Q-Atmospheric pressure
Question 2:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic, and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed? (a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Answer: (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite? (a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm
Answer: (b) Taenia
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph? (a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium
Answer: (b) Mushroom
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
Answer: (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through (a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostom
Answer: (d) cytostom
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Life Processes Case Study Based Questions Class 10
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the Life Processes Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter Life Processes. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
With the help of Life Processes Case Study Based Questions, students don’t need to memorise each answer. As answers for these case studies are already available in the given passage. Questions are asked through MCQs so student’s won’t take time to mark the answers. These multiple choice questions can help students to score the weightage of Life Processes.
Life Processes Case Study Based Questions with Solutions
Selfstudys provides case studies for the Class 10 Science chapter Life Processes with solutions. The Solutions can be helpful for students to refer to if there is a doubt in any of the case studies problems. The solutions from the Selfstudys website are easily accessible and free of cost to download. This accessibility can help students to download case studies from anywhere with the help of the Internet.
Life Processes Case Study Based Questions with solutions are in the form of PDF. Portable Document Format (PDF) can be downloaded through any of the devices: smart phone, laptop. Through this accessibility, students don't need to carry those case based questions everywhere.
Features of Life Processes Case Study Based Questions
Before solving questions, students should understand the basic details of Life Processes. Here are the features of case based questions on Life Processes are:
- These case based questions start with short or long passages. In these passages some concepts included in the chapter can be explained.
- After reading the passage, students need to answer the given questions. These questions are asked in the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ).
- These case based questions are a type of open book test. These case based questions can help students to score well in the particular subject.
- These Life Processes Case Study Based Questions can also be asked in the form of CBSE Assertion and Reason .
Benefits of Solving Life Processes Case Study Based Questions
According to the CBSE board, some part of the questions are asked in the board exam question papers according to the case studies. As some benefits of solving Life Processes Case Study Based Questions can be obtained by the students. Those benefits are:
- Through solving case studies students will be able to understand every concept included in the chapter Life Processes
- Passages included in the case study are seen passages, so students don’t need to struggle for getting answers. As these questions and answers can be discussed by their concerned teacher.
- Through these students can develop their observation skills. This skill can help students to study further concepts clearly.
- Case studies covers all the concepts which are included in the Life Processes
How to Download Life Processes Case Based Questions?
Students studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to solve questions based on case study. It is necessary for students to know the basic idea of Life Processes Case Study Based Questions. Students can obtain the basic idea of case based questions through Selfstudys website. Easy steps to download it are:
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which is visible in the navigation bar.
- A pop-up menu will appear, Select case study from the list.
- New page will appear, select 10 from the list of classes.
- Select Science from the subject list.
- And in the new page, you can access the Life Processes Case Study Based Questions.
Tips to solve Life Processes Case Study Questions-
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Life Processes Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science.
- Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
- Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
- Identify the questions and give the answers according to the case given.
- Read the passage again, so that you can easily answer the complex questions.
- Answer according to the options given below the questions provided in the Life Processes Case Study Based Questions.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Case Based Questions - Life Processes
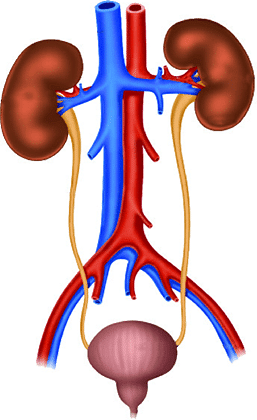
Question 1: Which of these is the structural and functional unit of part 2? (a) Alveoli (b) Nephron (c) Neuron (d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (b) A nephron is the basic functional unit of kidneys that consists of a glomerulus and its associated tubules through which the glomerular filtrate passes before it emerges as urine. They are the microscopic structure composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.
Question 2: Choose the correct path of urine in our body: (a) kidney → ureter → urethra → urinary bladder (b) kidney → urinary bladder → urethra → ureter (c) kidney → ureters → urinary bladder → urethra (d) urinary bladder → kidney → ureter → urethra
Correct Answer is Option (c) Kidneys are the paired organs where urine formation takes place. Small muscular tube, called as ureter, extend from kidneys and carries urine to urinary bladder. The urethra is a small tube that extends from the urinary bladder to an external opening.
Read the given passage and answer the questions from. Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs comes to the thin-walled upper chamber of the heart on the left. The left upper chamber (A) then relaxes. It then contracts and the blood is allowed to enter the next chamber (B), as it expands. When the muscular left lower chamber of heart contracts the blood is pumped out to the body via aorta. Deoxygenated blood reaches from the body to the upper chamber on the right side of heart (C) and it expands. As this part contracts, the corresponding lower chamber (D) dilates. This transfers the blood to right ventricle, which in turn pumps it to the lungs for oxygenated. Question 3: Which of these correctly represents the label A, B, C and D in the above passage? (a) A - Left atrium, B- Left Ventricle, C- Right atrium, D- Right ventricle (b) A - Right ventricle, B- Left atrium, C- Left Ventricle, D- Right atrium (c) A- Right atrium, B- Right ventricle, C- Left atrium, D- Left ventricle (d) A- Left ventricle, B- Right atrium, C- Right ventricle, D- Left atrium
Correct Answer is Option (a) A- Left atrium, B- Left Ventricle, C- Right atrium, D- Right ventricle
Question 4: What is the correct route of blood in a human? (a) A → B → Lungs → C → D (b) A → B → D → C → Lungs (c) C → D → B → A → Lungs (d) C → D → Lung → A → B
Correct Answer is Option (d) C (Right atrium) → D (Right ventricle) → Lungs → A (Left atrium) → B (Left ventricle).
Question 5: What prevents backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction? (a) Valves in heart (b) Thick muscular walls of ventricles (c) Thin walls of atria (d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a) False. Valves prevent the back flow of blood inside the heart during contraction of heart chambers (atria or ventricles).
Read the passage and answer the questions. Some experiments were carried out using Croton sp. plants to understand the process of photosynthesis. It was observed that the leaves of the plant exposed to light for longer duration accumulated more starch. However, due to presence of pre-formed starch in the leaves, it was difficult to find the net productivity on a fixed exposure to light source. Therefore, it was necessary to obtain starch free leaves in the plant before starting the experiment. Question 6: Which of the following would help obtain starch free leaves in the plant? (a) Expose the leaves to blue light for 48 hours before starting the experiment. (b) Keep the plant in dark for about 48 hours before starting the experiment. (c) Remove starch from the leaves by exosmosis, 48 hours before starting the experiment. (d) Keep the leaves to red light for 48 hours before starting the experiment.
Correct Answer is Option (b) The starch free leaves can be obtained by keeping the plant in dark, so that already present starch is utilized in 48 hrs.
Question 7: After a period of illumination, the leaves were boiled in alcohol to make them colourless. Which of the following could be used to test the end product stored in the leaves? (a) Cobalt chloride paper (b) Litmus paper (c) Iodine solution (d) Copper sulphate solution
Correct Answer is Option (c) Starch presence can be tested by adding iodine solution which gives bluish black colour of starch – iodine mixture.
Question 8: Some of the starch free leaves were coated with wax on both the surfaces. The plant was maintained under normal environmental conditions. At the end of the experiment, the wax coated leaves are likely to show _____. (a) Accumulation of more water. (b) Wilting of the wax coated leaves. (c) Increase in sucrose accumulation. (d) Decrease in number of chloroplasts
Correct Answer is Option (b) Wilting occurs due to wax blocks the transpiration so water transportation inhibits.
Question 9: During the morning hours, using a fine blade, an incision was made to the leaves such that the phloem tissue was cut open. Analysis of the liquid oozing out was found to contain high amount of: (a) Xylose (b) Ribose (c) Sucrose (d) Galactose
Correct Answer is Option (c) The transport of glucose, occurs in the form of sucrose, in phloem therefore, when cell sap oozes out, liquid contains sucrose.
Top Courses for Class 10
Faqs on class 10 science chapter 5 case based questions - life processes, important questions, shortcuts and tricks, past year papers, extra questions, practice quizzes, previous year questions with solutions, sample paper, semester notes, study material, mock tests for examination, objective type questions, viva questions, video lectures.

Case Based Type Practice Questions: Life Processes Free PDF Download
Importance of case based type practice questions: life processes, case based type practice questions: life processes notes, case based type practice questions: life processes class 10, study case based type practice questions: life processes on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 1: Life processes
About this unit.
In this unit, we learn about basic life processes such as photosynthesis, nutrition, transportation and excretion.
What are life processes?
- Intro to life processes (Opens a modal)
Nutrition & types
- Autotrophs & heterotrophs (nutrition modes) (Opens a modal)
- Types of nutrition Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Autotrophic nutrition
- Photosynthesis (Opens a modal)
- Guard cells and stomata Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Photosynthesis and respiration Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Nutrition in human beings
- Digesting Food (Opens a modal)
- Digestion in Intestines Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Human digestion Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Respiration
- Aerobic & anaerobic respiration (Opens a modal)
- Respiration site & ATP (Opens a modal)
- Meet the lungs! (Opens a modal)
- The lungs and pulmonary system (Opens a modal)
- Inhaling and exhaling (Opens a modal)
- How does lung volume change? (Opens a modal)
- The respiratory system review (Opens a modal)
- Types of respiration Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Breathing in animals Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
Transportation in plants
- Intro to vascular tissues (xylem & phloem) (Opens a modal)
- Xylem & transpiration (Opens a modal)
- Phloem & translocation (Opens a modal)
- Transportation in plants Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Transportation in animals
- Meet the heart! (Opens a modal)
- Flow through the heart (Opens a modal)
- Two circulations in the body (Opens a modal)
- Arteries vs. veins - what's the difference? (Opens a modal)
- Lymph & lymphatic system (Opens a modal)
- The circulatory system review (Opens a modal)
- Transportation in human beings Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Blood vessels and their maintenance Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Meet the kidneys! (Opens a modal)
- Parts of a nephron (Opens a modal)
- Excretion in human beings Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Study Questions Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study and Passage Based Questions that will come in CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exams.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Re a son . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Life Processes Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in transpiration, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through pores called stomata. Normally stomata remain open in the daytime and close during the night
(i) Which of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
Answer: (d) Chlorophyll content of leaves
(ii) Water vapour comes out from the plant leaf through the stomatal opening. Through the same stomatal opening, carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant during photosynthesis. Reason out the above statements . using one of following options. (a) The above processes happen only during night time. (b) One process occurs during day time and the other at night. (c) Both processes cannot happen Simultaneously. (d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
Answer: (d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
(iii) Which of the following statements is not true for stomatal apparatus? (a) Guard cells invariably possess chloroplasts and mitochondria. (b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells. (c) Stomata are involved in gaseous exchange. (d) Inner wall of guard cells are thick.
Answer: (b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells.
(iv) Which of the following is not a purpose of transpiration? (a) Helps in absorption and transport in plants (b) Prevents loss of water (c) Maintains shape and structure of plants by keeping the cells turgid (d) Supplies water for photosynthesis
Answer: (b) Prevents loss of water

Answer: (a) P-Atmospheric temperature; Q-Atmospheric pressure
Question 2:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic, and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed? (a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Answer: (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite? (a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm
Answer: (b) Taenia
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph? (a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium
Answer: (b) Mushroom
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
Answer: (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through (a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostom
Answer: (d) cytostom
Case Study 3: Life processes are the essential functions that living organisms perform to maintain their existence. These processes include nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion, and reproduction. Nutrition involves the intake of food and its utilization by the body for energy and growth. It can be classified into two types: autotrophic and heterotrophic. Autotrophic nutrition is the process by which organisms, such as plants, produce their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. Heterotrophic nutrition is the process by which organisms obtain nutrients by consuming other organisms. Respiration is the process of releasing energy from food through the oxidation of glucose molecules. Transportation involves the movement of materials, such as nutrients, water, and gases, within the body. Excretion is the removal of waste products generated by metabolic activities. Reproduction is the process by which organisms produce offspring of their own kind. Understanding life processes is crucial for studying the functioning and survival of living organisms.
What are the essential functions that living organisms perform to maintain their existence called? a) Life processes b) Metabolic activities c) Cellular respiration d) Photosynthesis Answer: a) Life processes
What is autotrophic nutrition? a) The process of consuming other organisms for nutrients b) The process of producing food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide through photosynthesis c) The process of releasing energy from food through oxidation d) The process of removing waste products from the body Answer: b) The process of producing food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide through photosynthesis
What is the process of releasing energy from food through the oxidation of glucose molecules called? a) Respiration b) Photosynthesis c) Transportation d) Reproduction Answer: a) Respiration
What does transportation involve? a) The intake of food and its utilization by the body b) The movement of materials within the body c) The removal of waste products generated by metabolic activities d) The process of producing offspring Answer: b) The movement of materials within the body
What is reproduction? a) The intake of food and its utilization by the body b) The movement of materials within the body c) The removal of waste products generated by metabolic activities d) The process of producing offspring of their own kind Answer: d) The process of producing offspring of their own kind
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Life Processes Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Extra questions of class 10 social science economics chapter 1 development pdf download, extra questions of class 10 maths chapter 10 circles pdf download, mcq class 10 english for anne gregory questions with answers english poem 11, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 6 Class 10 - Life Processes
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Chapter 6 of Class 10, Life Processes, is going to teach you about the life processes of plants and animals that occur in their body at each and every second. These processes are the essence of a living being.
We, at Teachoo , will provide you with all the necessary sources such as concepts , NCERT questions along with extra questions made by our experts which will help you in clarifying all the concepts easily.
The life processes that you are going to learn about, both for plants and human beings are -
- Nutrition (Autotrophic or Heterotrophic)
- Respiration
- Transportation (Blood or other life sustaining substances)
NCERT Questions
Questions from inside the book, teachoo questions, case based questions (mcq), assertion reasoning questions (mcq), mcqs from ncert exemplar.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes

Chapter 6 Life Processes Class 10 NCERT Solutions
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapters:, how does amoeba engulf its food, which part of the roots is involved in exchange of respiratory gases, define photolysis., what are chemotrophs, what is the mode of nutrition in fungi, contact form.
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 10th standard science subject life processes case study questions 2021.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Digestion is a catabolic process in which complex and large components of food are broken down into their respective simpler and smaller forms with the help of various hydrolytic enzymes. In human, the process of intake of essential nutrients in the form of food takes place through an entire system known as digestive system. The digestive system in human includes alimentary canal and its associated digestive glands. (i) Identify the cells whose secretion protects the lining of gastro-intestinal tract from various enzymes.
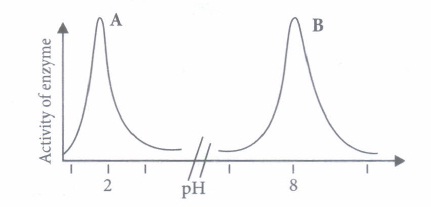
(ii) Digestion of proteins is incomplete in the absence of enterokinase, because (a) trypsinogen is not converted into trypsin (b) pepsinogen is not converted into pepsin (c) prorennin is not converted into rennin (d) chymotrypsinogen is not converted into chymotrypsin (iii) Match the column I with column II and column III. Choose the correct option.
(v) If the inner surface of the ileum in the human small intestine was smooth, rather than being folded and subdivided into villi, which of the following statements would be true? (a) The rate of absorption of digested food molecules would be higher, because the digested food would pass more easily through the digestive tract. (b) Digestion would not be as effective, because there would be fewer cells secreting trypsin (a proteindigesting enzyme). (c) Humans would have needed to evolve a much longer small intestine to absorb sufficient nutrients from their food. (d) Humans would not be able to survive, because the digestive tract would be more susceptible to damage.
Respiration is an energy releasing enzymatically controlled process which involves a stepwise oxidative breakdown of food substances inside living cells. The oxidative breakdown of respiratory substrates with the help of atmospheric oxygen is aerobic respiration. Glucose is completely broken down into CO 2 and H 2 O by this process of oxidation and large amount of energy is produced. (i) Site of Krebs' cycle is
(ii) The pathway of respiration common in all living organisms is X ;it occurs in the Y and the products formed are two molecules of Z . Identify X, Y and Z in the above paragraph and select the correct answer.
(iii) Number of oxygen molecules utilised in glycolysis is ____________.
(iv) How many ATP molecules could maximally be generated from one molecule of glucose, if the complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose to CO 2 and H 2 O yields 686 kcal and the useful chemical energy available in the high energy phosphate bond of one molecule of ATP is 12 kcal?
(v) The end product of aerobic respiration is
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic nutrition. (i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed?
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite?
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph?
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through
The food which is prepared by the process of photosynthesis in the leaves of a plant has to be transported to other parts like stem, roots, branches, etc. Therefore this food is transported to other parts of the plant through phloem. (i) A few drops of sap were collected by cutting across a plant stem by a suitable method. The sap was tested chemically. Which one of the following test results indicates that it is phloem sap?
(ii) What is the direction of movement of sugars in phloem?
(iv) A girdled plant (upto bast) may survive for some time but it will eventually die, because (a) water will not move downwards (b) water will not move upwards (c) sugars and other organic materials will not move downwards (d) sugars and other organic materials will not move upwards (v) Phloem sap is mainly made of
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject life processes case study questions 2021 answer keys.
(i) (c): Goblet cells or mucous cells are present throughout the epithelium of gastric glands and secrete mucus, which protects gastro-intestinallining from enzymatic action. (ii) (a) (iii) (c) (iv) (b): Pepsin and trypsin both are protein digesting enzymes, but they work at different locations and different pH in alimentary canal. Pepsin, which is most active at pH of 1.5 to 2.5, is an important peptic enzyme in stomach. Trypsin, which is a pancreatic protease, acts mostly in upper small intestine (duodenum and jejunum), works at an optimum pH of 7.5 - 8.5. (v) (c): The absorptive surface of small intestinal mucosa have many folds, which increase its surface area. Also located on epithelial surface of small intestine are millions of small villi. Intestinal epithelial cell on each villus is characterised by a brush- border which further increases the surface area. Thus, to compensate for this and to have effective absorption of nutrients, intestine would need to be much longer in length.
(i) Krebs' cycle takes place in mitochondrial matrix. (ii) (b) (iii) (a) : Glycolysis does not utilise any oxygen as it is an anaerobic process. (iv) (d) (v) (d): In aerobic respiration, glucose is completely broken down to CO 2 and H 2 O with the production of a large amount of energy (ATP).
(i) (b): Yeast, mushroom and bread mould have a saprophytic mode of nutrition which is chemoheterotrophic in nature. They breakdown complex organic substances by secreting digestive enzyme outside their body and absorb simple molecules as nutrients. (ii) (b) (iii) (b): Yeast, mushroom and bread mould have a saprophytic mode of nutrition which is chemoheterotrophic in nature. They breakdown complex organic substances by secreting digestive enzyme outside their body and absorb simple molecules as nutrients. (iv) (c): Heterotrophic nutrition is mode of nutrition in which an organism depends on other living organisms for food. (v) (a)
(i) (d) (ii) (c): Baked potatoes consist of starch which is a polysaccharide. In oral cavity, the food is mixed with saliva that contains an enzyme salivary amylase which converts starch into maltose, isomaltose and small dextrins. The pancreatic juice (present in small intestine) contains pancreatic amylase which converts starch into maltose, isomaltose and \(\alpha\) -dextrins. \(\text { Starch } \frac{\text { Pancreatic }}{\alpha \text { -amylase }}>\text { Maltose }+\text { Isomaltose }+\alpha \text { -Dextrins }\) Further, disaccharidases such as maltase (present in intestinal juice in small intestine) break down disaccharides such as maltose into monosaccharides or simpler sugars. (iii) (d): After removal of gall bladder, bile could no longer to be stored and hence fat metabolism would be affected. Therefore, fat intake should be restricted. (iv) (d) (v) (c)
(i) (b) (ii) (a): Food is transported by vascular tissue phloem from source to sink. Source is a part that synthesise food and sink is a part that stores or needs the food. Since source and sink can be reversed depending on plant's need, therefore direction of movement of sugar in phloem can be bidirectional, i.e., both upwards or downwards. (iii) (b) (iv) (c)
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects
Study Material
.webp)
Home > Class 10 Science Subject-wise Material
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes

From Class 10 Science Chapter 6, the final examination paper includes questions weighing 9 out of the total marks. The purpose of including life processes is to teach people about metabolism, how the human body functions properly, reproduction, excretion, and many more. Students get a comprehensive understanding of how life existed on Earth and why it is mandatory for any living being to function when it is at rest.
Biology isn’t an easy subject to understand but with the help of the Class Xth NCERT textbook and the right study material, the student can grasp it. At Educart, students as well as teachers can access study materials like class 10 life process notes, question banks, practice worksheets, mind maps, and other study material to improve the exam preparation.
CBSE Class 10 Life Processes Notes
Below, we have provided the links to downloadable PDFs of chapter-wise Notes for Ch 6 science class 10 notes and get an in-depth explanation and understanding of the chapter.
<red> ➜ <red>Class 10 Life Process Notes Part-1
<red> ➜ <red>class 10 life process notes part-2.
📈 Trending: Class 10 CBSE Syllabus 2024-25
📺 Recommended: Educart One Shots for Class 10
📚 Don't Miss: CBSE Class 10 Open Book Test

CBSE Class 10 Life Processes DoE Worksheet
Below, we have provided the links to downloadable PDFs of DoE Worksheets for Life Processes Class 10 to practice more questions.
<red> ➜ <red>Worksheet 22
<red> ➜ <red>worksheet 23, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 24, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 25, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 26, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 27, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 28, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 29, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 30, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 31, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 83em, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 84em, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 85em, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 86e, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 87e, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 88e, cbse class 10 life processes experiential activities.
Below, we have provided the links to downloadable PDFs of Experiential Learning Activity for ch 6 class 10 Science to help students implement their acquired knowledge in the real world.

<red> ➜ <red>Life Processes Experiential Activities
Cbse class 10 life processes important questions.
Below, we have provided Class 10 Science Important Questions that cover all the important questions in Life Processes.
<red> ➜ <red>Life Processes Important Questions(View)
Cbse class 10 life processes mind maps.
Below, we have provided Class 10 Science Mind maps that include mind maps of the related concepts in Life Processes.
<red> ➜ <red>Life Processes Mind Maps
Cbse class 10 life processes question bank.
Below, we have provided Class 10 Science Question Banks that cover every typology question with detailed explanations from various resources in one place.
<red> ➜ <red>Class 10 Life Processes CBSE Question Bank
<red> ➜ <red>class 10 life processes kendriya vidyalaya question bank, cbse class 10 life processes support material.
Below, we have provided Class 10 Science Support Materials that cover Case Study-based questions from the various concepts explained in Science NCERT chapters.
<red> ➜ <red>Life Processes Support Material
Why download these chapter-wise pdfs.
With the right study material along with the NCERT, students can score high in board exams or any other exam at school and for college entrance. Studying from these chapter-wise PDFs for ch 6 life processes class 10 can help in developing a strong conceptual base for students. Downloading these life processes class 10 PDFs can offer significant benefits to teachers and students.
- The study material PDF provides a structured way of learning and students can create a schedule. Creating a study schedule can help in allotting significant time to every subject and students can focus on one subject at a time.
- Now students won’t have to carry these heavy textbooks, instead, they can have the complete study material in one place that can be accessed at any time.
- Downloading PDFs is efficient since the content can be downloaded on any device and can be accessed from anywhere.
- Students can print the study material for the note-making process and prepare better for the exams.
How Can This Chapter-wise Material Help Students?
The chapter-wise material for Science Life Processes will help in preparing the chapter from the 10th NCERT textbook along with the additional right study material. After downloading chapter notes, DoE worksheets, question banks, important questions, and many other study materials, students can prepare for the chapter effectively.
- The class 10 science chapter 6 note covers the chapter comprehensively and includes all the important concepts. Students can understand the chapter better and in detail.
- Mind maps created will help students connect the concepts of what they have learned. It will help significantly in aligning your already existing knowledge with the newly acquired knowledge thus improving the understanding of the chapter.
- The DoE worksheets and question banks can help in preparing every typology included in the 10th board exams. Students can prepare a timetable and practice related questions after thoroughly understanding the concept.
- The Class 10 CBSE important questions include not only the must-prepare concept questions for the exam but the recurring questions also. Practicing important questions will increase the likelihood of scoring better marks on the exam.
At Educart we have provided these questions and other support materials, so teachers can help the students practice these types of questions thoroughly. These PDFs can be downloaded just with a click and user authentication.
Extra 10% Discount

CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
Class 10 subject-wise material, ncert books for class 10.
Buy Latest Books
Teacher's Corner
To Download PDF
Please verify your Whatsapp number first, so you can download this pdf immediately
Please type a valid 10 digit whatsapp number

OTP sent, check your whatsapp
Your OTP is incorrect, Please enter valid OTP

- Mathematics (Standard)
- Mathematics (Basic)
- Social Science
- Computer Application
- Information Technology
- English Core
- Mathematics
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political Science
- Science (Hindi )
- Maths (Hindi)
- Social Science (Hindi )
- Applied Maths
- Physical Education
- English Language
- History & Civics
- 10 Year Solved Papers
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 English
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Math Standard
- Computer Applications
- Class 12 PCB Combo
- Class 12 PCM Combo
- Entrance Exam
- K-8 Raspberry Solutions
- K-8 Kiwi Solutions
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Get extra questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes with PDF. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These extra questions will be helpful to revise the important topics and concepts. You can easily download all the questions and answers in PDF format from our app.
Life Processes Class 10 Science Extra Questions with Answers
Question 1: Mention the raw materials required for photosynthesis.
Answer: The following raw materials are required for photosynthesis: (i) Carbon Dioxide: Plants get CO 2 from atmosphere through stomata. (ii)Water: Plants absorb water from soil through roots and transport to leaves. (iii) Sunlight: Sunlight, which is absorbed by the chlorophyll and other green parts of the plant.
Question 2: What would be the consequences of deficiency of haemoglobin in your body?
Answer: The deficiency of haemoglobin in our body is called anaemia. In anaemia, the blood is unable to carry the sufficient amount of oxygen required by the body. So, respiration would be less and less energy will be available to the body. The haemoglobin deficient person will feel weak, pale, lethargic and will be unable to perform heavy physical work.
Question 3: Name the green dot like structures in some cells observed by a student when a leaf peel was viewed under a microscope. What is this green colour due to?
Answer: The green dot-like structures in some cells observed by a student when a leaf peel is viewed under a microscope are chloroplasts. The green colour is due to the presence of green pigment, chlorophyll.
Question 4: State any one difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
Answer: In autotrophic nutrition, organisms obtain their food from inorganic substances. In heterotrophic nutrition, organisms derive their food from organic substances.
Question 5: A Give one reason why multicellular organisms require special organs for exchange of gases between their body and their environment.
Answer: In unicellular organisms the entire body of the organism is in contact with the environment hence exchange of materials can take place but, in multicellular organisms the entire body of the organism is not in contact with the environment and hence simple diffusion is not helpful.
Question 6: Name the process in plants where water is lost as water vapour. :
Answer: Transpiration is the process when plants loose water as vapour.
Question 7: What is translocation in plants?
Answer: Translocation is the movement of soluble materials, products of photosynthesis from leaves to other tissues throughout the plant.
Question 8: State the basic difference between the process of respiration and photosynthesis.
Question 9: In the experiment “Light is essential for photosynthesis”, why does the uncovered part of the leaf turn blue-black after putting iodine solution?
Answer: Starch is produced in the uncovered part of the leaf because it is exposed to sunlight allowing it to photosynthesize, which turns blue-black in presence of iodine solution.
Question 10: Name the component of blood that helps in the formation of blood clot in the event of a cut.
Answer: Platelets help in clotting of blood in the event of a cut.
Question 111: Mention how organisms like bread moulds and mushrooms obtain their food.
Answer: Organisms like bread moulds and mushrooms breakdown the food materials outside the body and then absorb the nutrients of the bread.
Question 12: What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed?
Answer: Xylem in plant transports water and dissolved mineral nutrients from the roots to all parts of the vascular plant. So, if xylem is removed from the plant, the water and mineral supply to the plant will stop and therefore, the plant will die.
Question 13: Where does digestion of fat take place in our body?
Answer: Digestion of fat takes place in the small intestine of our body.
Question 14: What is the mode of nutrition in human beings?
Answer: Holozoic nutrition.
Question 15: What are enzymes? Name any one enzyme of our digestive system and write its function.
Answer: Enzymes are biological catalysts. Catalysts are proteins that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being used up. For example: Amylase catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars in the mouth and small intestine
Question 16: (i) Write the balanced chemical equation for the process of photosynthesis,
(ii) When do the desert plants take up carbon dioxide and perform photosynthesis?
Answer: (i) Photosynthesis can be represented using a chemical equation. The overall balanced equation is
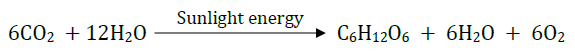
(ii) Desert plants open up their stomata during night and take in CO 2 . Stomata remains close during the day time to prevent the loss of water by i transpiration. They store the CO 2 in their cells until the sun comes out and they can carry on with photosynthesis during the day time.
Question 17: Why do herbivores have longer, small intestine than carnivores?
Answer: Digestion of cellulose takes a longer time. Hence, herbivores eating grass need a longer small intestine to allow complete digestion of cellulose. Carnivorous animals cannot digest cellulose due to the absence of enzyme cellulose hence they have a shorter intestine.
Question 18: Why do the walls of the trachea not collapse when there is less air in it?
Answer: Rings of cartilages are present in trachea. These rings support the trachea and do not allow the trachea to collapse when there is less air in it.
Question 19: What are the final products after digestion of carbohydrates and proteins?
Answer: The final product produced after digestion of carbohydrates is glucose and of proteins is amino acids.
Question 20: What is saliva? State its role in the digestion of food.
Answer: Saliva is a watery fluid secreted by the salivary glands in the mouth. The digestive functions of saliva include moistening food, and helping to create a food bolus, so it can be swallowed easily. Saliva contains the enzyme amylase that breaks some starches down into maltose and dextrin.
Question 21: Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba.
Answer: Amoeba is a protozoan found in fresh water. It feeds on microscopic plants and animals present in water. The mode of nutrition in amoeba is Holozoic. And the process of obtaining food by amoeba is called phagocytosis. The different processes involved in the nutrition of amoeba are:
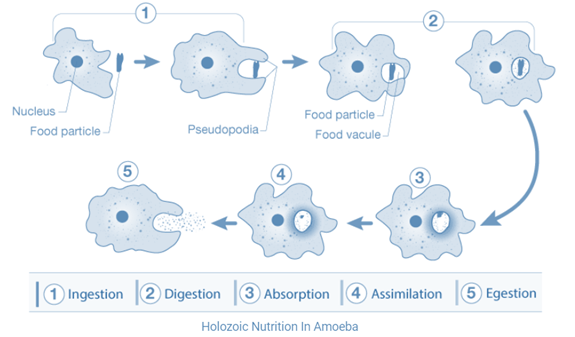
Ingestion: Ingestion is the process of taking food in the body. Amoeba is a unicellular animal, so it doesn’t have a mouth for ingestion of food. Amoeba ingests the food by encircling it by forming pseudopodia. When the food is completely encircled, the food is engulfed in the form of a bag called food vacuole.
Digestion: Digestion is the process of breaking the large and insoluble molecules in small and water soluble molecules. In amoeba, several digestive enzymes react on the food present in the food vacuoles and break it down into simple and soluble molecules.
Absorption: The food digested by digestive enzymes is then absorbed in the cytoplasm by the process of diffusion. While the undigested food remains in the food vacuole. If a large amount of food is absorbed by amoeba, the excess food is stored in the cytoplasm in the form of glycogen and lipids.
Assimilation: During this step the food absorbed by the cytoplasm is used to obtain energy, growth and repair. This process of utilizing absorbed food for obtaining energy, repair and growth is called assimilation.
Egestion: When a sufficient amount of undigested food gets collected in the food vacuole, it is thrown out of the body by rupturing cell membrane. The process of removal of undigested food from the body is called egestion.
Question 22: State differences between arteries and veins.
Question 23: How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Answer: Alveoli are small pouches or sacs like structure. They are surrounded by blood capillaries. Thus a large amount of air is brought in contact with the air in the lungs. More than millions of alveoli are present in the lungs. The presence of millions of alveoli in the lungs provides a very large surface area for the exchange of gases. The availability of large surface area maximises the exchange of gases.
Question 24: Name two excretory products other than O 2 and CO 2 in plants.
Answer: The two excretory products other than O 2 and CO 2 in plants are resins and gums.
Question 25: In single celled organisms diffusion is sufficient to meet all their requirements of food, exchange of gases or removal of wastes but it is not in case of multicellular organisms. Explain the reason for this difference.
Answer: Unicellular organisms can absorb sufficient oxygen because of its complete
contact with the atmosphere, but in multicellular organisms the rate of absorption and diffusion becomes very less because all cells are not in direct contact with the atmosphere. Multicellular organisms require greater amount of oxygen to sustain life processes which cannot be fulfilled by the process of diffusion.
Question 26: Draw a diagram of human excretory system and label kidneys, ureters on it.
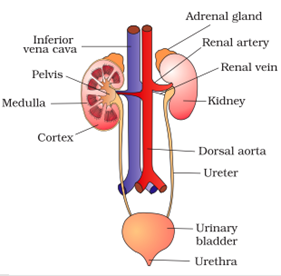
Question 27: Name the acid presents in the following:
(i) Tomato (ii) Vinegar (iii) Tamarind
Answer: (i) Oxalic acid (ii) citric acid (iii) Tartaric acid.
Question 28: State the role of the following in human digestive system:
(i) Digestive enzymes (ii) Hydrochloric acid (iii) Villi
Answer: (i) Digestive enzymes – Foods need to be broken into their small or simpler molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. However, the physical breakdown of food is not enough. Enzymes are hence needed for the chemical breakdown of food and speeding up the digestive process. The products of digestion can hence be small enough to be absorbed.
(ii) Hydrochloric acid – Hydro chloric acid helps to kill the germs which might have entered in to the system through food. It creates acidic medium for the pepsin to act on food to breakdown proteins.
(iii) Villi – Villi are finger like projections in the small intestine. They help to increase the surface area for absorption of the digested food. Villi are richly supplied with blood vessel which help to absorb digested food in to the blood stream.
Question 29: In mammals and birds why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood?
Answer: Mammals and birds are warm blooded animals. This means they can control their body temperature and do not have to depend on environment for their body temperature regulation. Because of this birds and mammals require optimum oxidization of glucose which would be possible with good supply of oxygen. So it is required to have separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood to supply the required amount of oxygen.
Question 30: Draw a diagram of human respiratory system and label it.
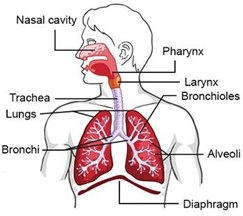
Question 31: (a) Name the site of exchange of material between the blood and surrounding cells.
(b) Draw a schematic representation of transport and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in human body.
Answer: (a) Capillaries
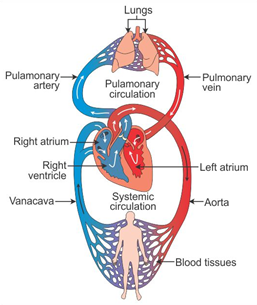
Question 32: List three characteristics of lungs which make it an efficient respiratory surface.
Answer: These features which particularly make our lungs efficient for gas exchange.
- Thin: the air sac walls are very thin so that gases can quickly diffuse through them. Oxygen is absorbed in to the blood and carbon dioxide is given out in to the lungs to be exhaled out.
- Moist: the air sacs are moist with mucus so that gases can dissolve before diffusing.
- Large surface area: the surface area for gases to diffuse through in human lungs is roughly the same as a tennis court. The alveoli help to increase the surface area for absorption of oxygen.
- Good blood supply: the air sacs or the alveoli have a large capillary network so that large volumes of gases can be exchanged. More the flow of blood more exchange.
Question 33: (a) What is the role of HCl in our stomach? (b) What is emulsification of fats? (c) Which protein digesting enzyme is present in pancreatic juice?
Answer: (a)(i) It sterilises food by killing pathogens and other microbes.
(ii) It has a pH of 2, which is perfect for entyaus such as pepsin to break down proteins as effectively as possible.
(iii) Helps emulsify food (digestion of protein and stimulates the pancreas to produce digestive enzymes and bile) and protects against harmful bacteria.
(b) Breakdown of large globule fats into smaller fats droplets is known as emulsification.
(c) Trypsin is the enzyme secreted by the pancreas which aids in digestion of proteins.
Question 34: In human alimentary canal, name the site of complete digestion of various components of food. Explain the process of digestion.
Answer: In small intestine, complete digestion of various components of food take place. The process of digestion of food in mouth, stomach and small intestine in human body are as follows:
Mouth: Digestion of food begins in the mouth. Saliva present in mouth contains a digestive enzyme, called salivary amylase, maltose and dextrin, which breaks down starch into sugar.
Stomach: Stomach stores and mixes the food received from the oesophagus with gastric juices. The main components of gastric juice are hydrochloric acid, mucus and pepsinogen. Hydrochloric acid dissolves bits of food and creates an acidic medium. In this medium, pepsinogen is converted to pepsin which is a protein-digesting enzyme. Mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of HCl.
Small Intestine: Small intestine is the site of complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Small intestine produces intestinal juice from the glands present in its wall. The intestinal juice helps in further digestion of food. Small intestine also obtains digestive juices from liver and pancreas. The liver produces bile juice that causes emulsification of fats and the pancreas produces pancreatic juice for digesting proteins and emulsified fats. This digested food is finally absorbed through the intestinal walls.
Question 35: (a) “The breathing cycle is rhythmic whereas exchange of gases is a continuous process”. Justify this statement.
(b) What happens if conducting tubes of circulatory system develops a leak? State in brief, how could this be avoided?
(c) How opening and closing of stomata takes place?
Answer: (a) The breathing cycle involves inhalation and exhalation of air due to alternate expansion and contraction of thoracic cavity. Thus, it is a rhythmic process. But exchange of gases is a continuous process as it takes place between the blood and each and every cell, by diffusion.
(b) The circulatory system will become inefficient if it develops a leak. This could be avoided by maintaining a normal blood pressure.
(c) When water flows into the guard cells, the guard cells swell and the stomatal pore opens up. When water moves out the guard cells shrinks and the stomatal pore closes.
Question 36: Describe in brief the function of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra.
Answer: The Kidneys filter the blood and concentrate the filtrate to make urine. They also help regulate blood pressure. Ureters transport the urine to the urinary bladder. Urinary bladder is like a holding tank for the urine until it’s ready to be excreted. Urethra is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the outside of the body for excretion.
Question 37: Explain the process of breakdown of glucose in a cell (ii) in the absence of oxygen.
Answer: The process of breakdown of glucose in a cell are as follows:
The first step in the breakdown of glucose both in presence of O 2 and in absence of O 2 is same. In this step, glucose is broken down into pyruvate.
Second step which involves further breakdown of private into simple compounds can take place in two different ways:
(i) In presence of O 2 : In the presence of O 2 , private is converted into CO 2 and water. Energy released during aerobic respiration is much greater than that released during an anaerobic respiration.
(ii) In absence of O 2 : In the absence of O 2 in yeast, pyruvate is converted into ethanol and CO 2 and the process is called fermentation. In absence of O 2 , in our muscle cells, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid. The build up of lactic acid in muscle cells causes cramps.
Question 38: (a)Explain how does the exchange of gases occur in plants across the surface of stems, roots and leaves. (b) How are water and minerals transported in plants?
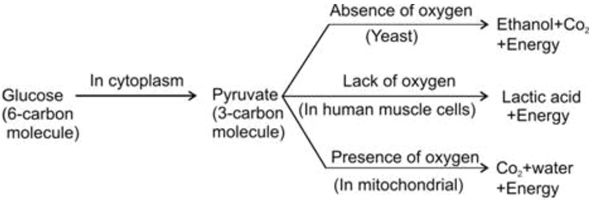
(a) In plants there are tiny pores called stomata on leaves and lenticels in stem which facilitate the exchange of gases. Carbon dioxide is taken in and oxygen given out {during photosynthesis} and vice versa during respiration.
(b) Water and minerals are transported within the plant by the Xylem vessels (mainly in an upward direction); these are part of the vascular system which also includes Phloem vessels. Phloem transports the products of photosynthesis within the plant, to all parts like the stem, roots, fruits etc. in all directions.
Question 39: State in brief the function of: 1. renal artery 2. kidney 3. ureter 4. urinary bladder
Answer: Renal artery: The renal artery carries blood to the kidneys from the abdominal aorta. This blood comes directly from the heart and is sent to the-kidneys to be filtered before it passes through the rest of the body. Up to one-third of the total cardiac output per heartbeat is sent to the renal arteries to be filtered by the kidneys. Each kidney has one renal artery that supplies it with blood. The filtered blood then can exit the renal vein.
Kidney: The kidneys perform the essential function of removing waste products from the blood and regulating the water fluid levels. The kidneys regulate the body’s fluid volume, mineral composition and acidity by excreting and reabsorbing water and inorganic electrolytes.
Ureter: The ureter is a tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.’ There are two ureters, one attached to each kidney.
Urinary bladder: The urinary bladder is an expandable muscular sac that stores urine before it is excreted out of the body through the urethra.
Question 40: How is urine produced and eliminated?
Answer: Blood from the heart comes into the kidneys afferent and efferent arteriole from the renal arteries where it enters about 2-3 million nephrons per kidney. Then, it goes through the glomerulus a tuft or bunch of blood capillaries and get rid of some of the unwanted substances like urea, uric acid, creatinine in the blood and then continues through the renal tubules. The loop of Henley, reabsorb certain substances such as water (actually if body is dehydrated, body will send antidiuretic hormone (ADH) to kidneys to prevent extra water from going into urine and thus saving water for body and get rid of anything else that isn’t wanted, then the urine goes through ureters to bladder and then to urethra where it is excreted out of body as urine.
Question 41: (a) Draw a diagram to show open stomatal pore and label on it: (i) guard cells (ii) chloroplast (b) State two functions of stomata. (c) How do guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomatal pore?
Answer: (a)
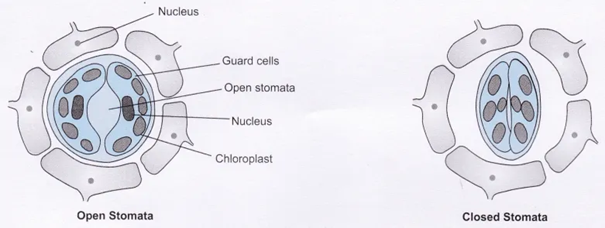
(b) Two functions of stomata are: (i) Exchange of gases between the plant and the atmosphere takes place through stomata. (ii)Transpiration in plants takes place through stomata.
(c) Opening and Closing of Stomatal Pore: The opening and closing of the pore is a function of the guard cells. The guard cells swell when water flows into them causing the stomatal pore to open. Similarly, the pore closes if the guard cells shrink. As large amount of water is lost through these stomata, the plant closes these pores when it does not require carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
Question 42: Why is the rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms?
Answer: Quantity of dissolved oxygen is fairly low in water as compared to the amount of oxygen in air. Aquatic organisms therefore have to breath faster than terrestrial organisms to absorb the required amount of oxygen from the water.
- NCERT Exemplar
- Science Exemplar Class 10
- Life Processes
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Solutions for Chapter 6 - Life Processes
Ncert exemplar solutions class 10 science chapter 6 – free pdf download.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes are premier study material required for the students to score good marks in Class 10 CBSE examinations as well as to avoid difficulty in understanding the concepts to be taught in higher secondary and graduation courses. The Class 10 Exemplar provided here consists of MCQs, fill in the blanks, practice questions, value-based questions, and previous years’ questions on Life Processes.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 mainly deals with the maintenance processes in living organisms. In this chapter, students will learn to identify vital life processes and understand different types of nutrition as well as the respiratory organs and their mechanism, excretion, digestion, etc. To make learning more interesting and easy, we provide NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes in PDF here.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes

Access Answers to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – Life Processes
Multiple-choice questions.
1. Which of the following statements about autotrophs is incorrect?
(a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll
(b) They store carbohydrates in the form of starch
(c) They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight
(d) They constitute the first trophic level in food chains
The answer is (c) They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight
Explanation:
They need sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates.
2. In which of the following groups of organisms, food material is broken down outside the body and absorbed?
(a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba
(b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta
(d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
The answer is (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
Yeast, mushroom and bread moulds are saprophytes, and Saprophytes break the food material outside their body and absorbed it.
3. Select the correct statement
(a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
(b) Heterotrophs utilise solar energy for photosynthesis
(c) Heterotrophs synthesise their own food
(d) Heterotrophs are capable of converting carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates
The answer is (a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
Heterotrophs are either dependent on Phototrophs or other organisms for their food.
4. Which is the correct sequence of parts in the human alimentary canal?
(a) Mouth → stomach → small intestine → oesophagus → large intestine
(b) Mouth →oesophagus → stomach → large intestine → small intestine
(c) Mouth → stomach → oesophagus → small intestine → large intestine
(d) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
The answer is (d) Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
5. If salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva, which of the following events in the mouth cavity will be affected?
(a) Proteins breaking down into amino acids
(b) Starch breaking down into sugars
(c) Fats breaking down into fatty acids and glycerol
(d) Absorption of vitamins
The answer is (b) Starch breaking down into sugars
The Salivary Amylase enzyme present in the saliva breaks down Starch into simpler sugar and helps in digesting them. Hence the breakdown of starch will be affected if salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva.
6. The inner lining of the stomach is protected by one of the following from hydrochloric acid. Choose the correct one (a) Pepsin
(c) Salivary amylase
The answer is (b) Mucus
7. Which part of the alimentary canal receives bile from the liver?
(a) Stomach
(b) Small intestine
(c) Large intestine
(d) Oesophagus
The answer is (b) Small intestine
Bile goes to the small intestine from the gall bladder through hepta pancreatic duct.
8. A few drops of iodine solution were added to rice water. The solution turned blue-black in colour. This indicates that rice water contains
(a) complex proteins
(b) simple proteins
The answer is (d) starch
Explanation
Starch is made up of two components Amylose and Amylopectin. When we add iodine to starch-containing water Amylose reacts with iodine to form a blue colour complex. Here solution gives blue-black colour on adding Iodine which confirms the presence of starch in the rice water.
9. In which part of the alimentary canal is food finally digested?
(b) Mouth cavity
(d) Small intestine
The answer is (d) Small intestine
Although the primary digestion process is conducted in mouth and stomach most of the digestion process occurs in the small intestine and large intestine digestion process will not take place.
10. Choose the function of the pancreatic juice from the following
(a) trypsin digests proteins and lipase carbohydrates
(b) trypsin digests emulsified fats and lipase proteins
(c) trypsin and lipase digest fats
(d) trypsin digests proteins and lipase emulsified fats
The answer is (d) trypsin digests proteins and lipase emulsified fats
Trypsin breaks down proteins into polypeptides and Lipase digest emulsified fat molecules into fatty acids and glycerol.
11. When air is blown from the mouth into a test-tube containing lime water, the lime water is turned milky due to the presence of
(b) carbon dioxide
(c) nitrogen
(d) water vapour
The answer is (b) carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide reacts with lime water and turns the lime water milky.
12. The correct sequence of anaerobic reactions in yeast is

The answer is d)
In Yeast cytoplasm, Glucose is breakdown in anaerobic condition to produce Pyruvate which is further breakdown to Ethanol and carbon-di-oxide
13. Which of the following is most appropriate for aerobic respiration?

Soln: Answer is Option (B)
14. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true about respiration?
(i) During inhalation, ribs move inward and diaphragm is raised
(ii) In the alveoli, exchange of gases takes place i.e., oxygen from alveolar air diffuses into blood and carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveolar air
(iii) Haemoglobin has a greater affinity for carbon dioxide than oxygen
(iv) Alveoli increase surface area for exchange of gases
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
The answer is (d) (ii) and (iv)
Statement i) is wrong because ribs move outward and the diaphragm is lowered during inhalation. Similarly Option iii) is wrong because Hemoglobin has greater affinity for Oxygen than CO 2.
15. Which is the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
(a) Nostrils →larynx →pharynx →trachea →lungs
(b) Nasal passage →trachea →pharynx →larynx →alveoli
(c) larynx →nostrils →pharynx →lungs
(d) Nostrils →pharynx →larynx →trachea →alveoli
The answer is (d) Nostrils →pharynx →larynx →trachea→alveoli
Air enter respiratory system through nostrils, passes to pharynx, larynx, trachea and then to alveoli. After inhalation diaphragm and intercoastal muscles contract along with expansion of thoracic muscles which creates enough space for the air to enter into the lungs.
16. During respiration exchange of gases take place in
(a) trachea and larynx
(b) alveoli of lungs
(c) alveoli and throat
(d) throat and larynx
The answer is (b) alveoli of lungs
Trachea, Larynx provide a passage for the movement of air. Gas exchange takes place in Alveoli of lungs. From alveoli, oxygen diffuses into blood and Carbon-di-oxide exhaled out of blood.
17. Which of the following statement (s) is (are) true about the heart?
(i) The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from different parts of the body while the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from lungs
(ii) Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different body parts while right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
(iii) Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to the right ventricle which sends it to different body parts
(iv) The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body while the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different parts of the body
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
The answer is (c) (ii) and (iv)
Oxygenated blood circulates through the left part of the heart whereas deoxygenated blood circulates through the right part of the heart. Atrium receives blood and ventricle pumps the blood out of the heart.
18. What prevents backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction?
(a) Valves in heart
(b) Thick muscular walls of ventricles
(c) Thin walls of atria
(d) All of the above
The answer is (a) Valves in the heart
Walls in the heart are responsible for only pumping of the blood and they are not responsible for blocking backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction.
19. Single circulation i.e., blood flows through the heart only once during one cycle of passage through the body, is exhibited by
(a) Labeo, Chameleon, Salamander
(b) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
(c) Hyla, Rana, Draco
(d) Whale, Dolphin, Turtle
The answer is (b) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
In Option a) Chameleon is a reptile and Salamander is an amphibian which has 3 chambered hearts and shows partial double circulation. In Option c) all are Amphibians and they show partial double circulation. In option d) Whale is a mammal, but a turtle is a reptile hence option d) is wrong.
20. In which of the following vertebrate group/groups, the heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body?
(a) Pisces and amphibians
(b) Amphibians and reptiles
(c) Amphibians only
(d) Pisces only
The answer is (d) Pisces only
This is because of the single circulation where deoxygenated blood from all part of the body is pumped into the heart. From the heart, it is pumped to gills where it gets oxygenated and gets transferred to all parts of the body. Hence it proves Pisces will not receive oxygenated blood.
21. Choose the correct statement that describes arteries.
(a) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under high pressure; collect blood from different organs and bring it back to the heart
(b) They have thin walls with valves inside, blood flows under low pressure and carries blood away from the heart to various organs of the body
(c) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under low pressure; carry blood from the heart to various organs of the body
(d) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carry blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
The answer is (d) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high pressure and carries blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
22. The filtration units of kidneys are called
(b) urethra
(c) neurons
(d) nephrons
The answer is (d) nephrons
Nephron is called as the functional unit of the kidney. It helps in removing the waste products and excess substances from our body.
23. Oxygen liberated during photosynthesis comes from
(b) chlorophyll
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) glucose
The answer is (a) water
During photosynthesis, water molecule splits to produce Oxygen and Hydrogen Ions. Oxygen is expelled out of plants and Hydrogen is used to reduce Carbon-di-oxide to produce carbohydrates.
24. The blood leaving the tissues becomes richer in
(a) carbon dioxide
(c) haemoglobin
The answer is (a) carbon dioxide
Because of respiration Carbon-di-oxide gets accumulated in tissues. Hence blood leaving the tissues becomes richer in Carbon-di-oxide.
25. Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
(a) Organisms grow with time
(b) Organisms must repair and maintain their structure
(c) Movement of molecules does not take place among cells
(d) Energy is essential for life processes
The answer is (c) Movement of molecules does not take place among cells
Movement of molecule is a vital process. Movement of molecules in cells take place in active and passive modes such as Diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion etc.
26. The internal (cellular) energy reserve in autotrophs is
(a) glycogen
(b) protein
(d) fatty acid
The answer is (c) starch
Glycogen is the stored energy in animals, Plants stores energy in the form of Starch.
27. Which of the following equations is the summary of photosynthesis?
(a) 6CO 2 + 12H2O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2 O
(b) 6CO 2 +H 2 O + Sunlight→C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 + 6H 2 O
(c) 6CO 2 + 12H 2 O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight→ C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O2 + 6H 2 O
(d) 6CO 2 + 12H 2 O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight→ C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O
Answer is (c) 6CO 2 + 12H 2 O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight→ C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2 O
Option a does not show the factors responsible for photosynthesis. Option b) is not a balanced equation. Option d) is wrong as it has CO2 in the products.
28. Choose the event that does not occur in photosynthesis
(a) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
(b) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
(c) Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
(d) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy
Answer is (c) Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
29. The opening and closing of the stomatal pore depend upon
(b) temperature
(c) water in guard cells
(d) concentration of CO2 in stomata
The answer is (c) water in guard cells
Opening of guard cells is facilitated by the entry of water inside guard cells. This makes the guard cell turgid. The closing of guard cells is facilitated by water coming out of guard cells. This will make the guard cells flaccid.
30. Choose the forms in which most plants absorb nitrogen
(i) Proteins
(ii) Nitrates and Nitrites
(iv) Atmospheric nitrogen
(a) (i) and (ii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
The answer is (b) (ii) and (iii)
Plants cannot absorb atmospheric Nitrogen. They can absorb Nitrogen in the form of Nitrates, Nitrites and Urea present in the soil.
31. Which is the first enzyme to mix with food in the digestive tract?
(b) Cellulase
(c) Amylase
(d) Trypsin
Answer is (c) Amylase
Amylase is secreted in mouth and acts on the starch to convert into simpler molecules. Hence Amylase is the first enzyme to mix with food in the digestive tract.
32. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) Pyruvate can be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide by yeast
(ii) Fermentation takes place in aerobic bacteria
(iii) Fermentation takes place in mitochondria
(iv) Fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
The answer is(c) (i) and (iv)
Fermentation is carried out by anaerobes in the cytoplasm. Hence option ii) and iii) are wrong.
33. Lack of oxygen in muscles often leads to cramps among cricketers. This results due to
(a) conversion of pyruvate to ethanol
(b) conversion of pyruvate to glucose
(c) non-conversion of glucose to pyruvate
(d) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid
The answer is (d) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid
The breakdown of Pyruvate in the presence of oxygen takes place in mitochondria leading to the formation of Lactic acid. Due to workout oxygen is used for the production of energy leading to the lack of oxygen and production of lactic acid.
34. Choose the correct path of urine in our body
(a) kidney → ureter → urethra → urinary bladder
(b) kidney → urinary bladder → urethra → ureter
(c) kidney → ureters → urinary bladder → urethra
(d) urinary bladder → kidney → ureter → urethra
Answer is (c) kidney → ureters → urinary bladder → urethra
Urine from nephron is brought to the collecting duct of kidneys where the urine enters the ureters. There are 2 ureters, each opening from one kidney into the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder stores urine and its size increases as the amount of urine collected increases. When the CNS gives a voluntary message the muscles of bladder contract and the bladder sphincter relaxes thus excreting urine out through the urethra.
35. During deficiency of oxygen in tissues of human beings, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in the
(a) cytoplasm
(b) chloroplast
(c) mitochondria
(d) Golgi body
Answer is (a) cytoplasm
When there is lack of oxygen Breakdown of Pyruvate takes place in the cytoplasm of muscle cells leading to the formation of Lactic acid.
Short Answer Questions
36. Name the following
(a) The process in plants that links light energy with chemical energy
(b) Organisms that can prepare their own food
(c) The cell organelle where photosynthesis occurs
(d) Cells that surround a stomatal pore
(e) Organisms that cannot prepare their own food
(f) An enzyme secreted from gastric glands in the stomach that acts on proteins.
- Photosynthesis
- Chloroplasts
- Guard cells
- Heterotrophs
37. “All plants give out oxygen during day and carbon dioxide during the night”. Do you agree with this statement? Give reason.
The statement is wrong because plants respire every time and expel out Carbon-di-oxide every time but they give out oxygen only in the daytime as the photosynthesis process can take place only in the presence of sunlight.
38. How do the guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomatal pores?
Opening of guard cells is facilitated by the entry of water inside guard cells. This make the guard cell turgid. The closing of guard cells is facilitated by water coming out of guard cells. This will make the guard cells flaccid.
Entry of water inside guard cells will make the cell turgid leading to the opening of stomata. Similarly, the cell becomes flaccid when water comes out of guard cells, this leads to the closing of the stomata.
39. Two green plants are kept separately in oxygen-free containers, one in the dark and the other in continuous light. Which one will live longer? Give reasons.
The plant kept in continuous light live longer because plants release CO 2 during respiration. In the case of the plant kept in the dark, CO 2 resulting in lack of oxygen and the plant will die earlier.
40. If a plant is releasing carbon dioxide and taking in oxygen during the day, does it mean that there is no photosynthesis occurring? Justify your answer.
If a plant is releasing carbon dioxide and taking in oxygen during the day means plant is respiring; it does not mean that there is no photosynthesis occurring in the plant. This is because Photosynthesis and respiration are two independent processes.
41. Why do fishes die when taken out of water?
Fishes can respire only by using dissolved oxygen. When we take fish out of the water it cannot respire due to lack of dissolved oxygen and they die.
42. Differentiate between an autotroph and a heterotroph
43. Is ‘nutrition’ a necessity for an organism? Discuss.
Nutrition is an absolute necessity for the organisms because nutrition provides energy for carrying out metabolic activities.
44. What would happen if green plants disappear from earth?
Green plants are the sources of energy for all the heterotrophs on earth. Plants convert solar and chemical energy into viable food sources. If plants get disappeared from the earth, it leads to an imbalance in the ecosystem and heterotrophs may die without food.
45. Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with vaseline. Will this plant remain healthy for long? Give reasons for your answer.
Coating vaseline to the leaves of a healthy plant will clog its stomata pores and stops the respiration of plants and the plants die.
46. How does aerobic respiration differ from anaerobic respiration?
47. Match the words of Column (A) with that of Column (B)
48. Differentiate between an artery and a vein.
Artery has thick walls whereas Veins has thin walls.
Arteries carry blood away from the heart but veins carry blood to the heart.
In arteries valves are absent and in veins they are present
In arteries, blood flows under pressure but in veins, there will be no pressure.
49. What are the adaptations of leaf for photosynthesis?
Adaptation of leaf for photosynthesis are as follows
- The surface of the leaf is flat to allow greater exposure of light.
- Presence of chlorophyll to trap sunlight
- Presence of stomata on the lower surface for easy transpiration
50. Why is small intestine in herbivores longer than in carnivores?
Food of herbivores contains mostly cellulose. To digest cellulose herbivores need help of certain bacteria. To accommodate the microbes and to facilitate digestion of food herbivores has longer small intestine than carnivores.
51. What will happen if the mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands?
Mucus prevent the inner lining of the stomach from HCL. Mucus prevents drying of the inner lining of the stomach. Mucus helps in easy movement of food particles through the digestive system. If the mucus is not secreted food will not easily be moved through the digestive system. HCL will damage the stomach lining and the digestion process will not take place.
52. What is the significance of the emulsification of fats?
Emulsification is a process of breakage of larger fats molecules into digestible fat globules. Emulsification aids action enzymes on fats by breaking larger fat molecules.
53. What causes movement of food inside the alimentary canal?
Peristalsis is the process that cause movement of food inside the alimentary canal.
54. Why does the absorption of digested food occur mainly in the small intestine?
Small intestine has specialized structures that facilitate the absorption of digested food. Small intestine has several folds that increase the area of absorption. Small intestine also has fingerlike projection called microvilli which are richly supplied by blood vessels.
55. Match Group (A) with Group (B)
56. Why is the rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms?
Rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than in terrestrial organisms because the availability of oxygen is less in water than on land, hence to obtain required oxygen aquatic organisms has to work hard.
57. Why is blood circulation in the human heart called double circulation?
In Humans blood flow in two directions simultaneously in one cardiac cycle. Oxygenated blood comes to the heart from the lungs and at the same time, de-oxygenated blood goes from Heart towards the lungs. Because of this double movement is blood circulation in the human heart called double circulation.
58. What is the advantage of having a four-chambered heart?
Four chambered heart has the following advantages
- Clear cut division of labours among different chambers
- Segregation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart.
- Efficiency of the heart will increase.
59. Mention the major events during photosynthesis
Major events of Photosynthesis are
- Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
- Conversion of light energy into chemical energy
- Splitting of water molecules into Hydrogen and Oxygen
- Reduction of CO2 to form carbohydrates.
60. In each of the following situations what happens to the rate of photosynthesis?
(a) Cloudy days
(b) No rainfall in the area
(c) Good manuring in the area
(d) Stomata get blocked due to dust
- Rate of photosynthesis will reduce due to the availability of sunlight.
- Rainfall will not affect the rate of Photosynthesis
- Manuring will not affect the rate of Photosynthesis
- Blockage of stomata will reduce the rate of photosynthesis because blockage will affect availability pf Carbon-di-oxide.
61. Name the energy currency in the living organisms. When and where is it produced?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency in the living organisms. It is produced in Mitochondria during respiration.
62. What is common for Cuscuta, ticks and leeches?
These all are parasite. They live on or inside another body to obtain food from the host. In obtaining food parasites always harm their host.
63. Explain the role of the mouth in digestion of food.
Role of mouth in digestion of food.
- Ingestion of food
- Breakage of food by Mastication
- Saliva aids easy swallowing of food
- Salivary amylase breaks starch into simpler carbohydrates.
64. What are the functions of gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach?
Hydrochloric acid, pepsin and mucus are secreted by gastric gland present in the stomach. They have following functions.
HCL Kills germs present in the food and it decreases P H of the stomach which is essential for the working of digestive enzymes.
Pepsin digests protein.
Mucus protects the stomach’s inner line from HCL.
65. Match the terms in Column (A) with those in Column (B)
66. Name the correct substrates for the following enzymes
(a) Trypsin
(b) Amylase
67. Why do veins have thin walls as compared to arteries?
Blood flow through veins does not exert pressure on walls of veins hence they have thin walls. Blood flow in arteries exerts high pressure on arterial walls hence they need thick walls.
68. What will happen if platelets were absent in the blood?
Platelets are responsible for the clotting of the blood. If platelets are absent blood will not clot. In case of injuries, blood flow cannot be stopped without clotting and this may prove fatal for the person.
69. Plants have low energy needs as compared to animals. Explain.
Most of the transport in plants occurs through passive transport which does not require energy and plants standstill at one place and they will not travel in search of food Hence Plants require low energy compared to animals.
70. Why and how does water enter continuously into the root xylem?
Water should enter the root xylem continuously to assist the various process such as photosynthesis. Continuous flow of water into root xylem is due to transpiration pull.
71. Why is transpiration important for plants?
Transpiration is important for plants because of the following reasons.
(a) It creates transpiration pull to facilitate the ascent of sap.
(b) Ascent of sap is necessary to make water available for photosynthesis.
(c) It helps a plant to get rid of excess water.
72. How do leaves of plants help in excretion?
Leaves plays an important role in excretion in plants because CO 2 is expelled out through pores of stomata present in the leaf. Plants shed leaves to get rid of excretory products deposited on them.
Long Answer Questions
73. Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba.
Amoeba shows holozoic nutrition which is comprised of Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption, Assimilation and Egestion.
Ameoba traps food particles through fingerlike projections called pseudopodia. Pseudopodia present outside its body and helps in taking food along with water
Food vacuoles are made after ingesting the food. Enzymes are released in the food vacuole for digestion.
Absorption:
After digestion, nutrients enter the cytoplasm through osmosis.
Assimilation:
Nutrients are utilized by the cell for various purposes.
Food vacuole goes near the cell membrane to empty its contents outside the cell. This results in the expulsion of waste materials from the cell.
74. Describe the alimentary canal of man.

Human Alimentary canal has the following parts
Buccal Cavity:
Generally called as mouth and it consists of tongue, teeth and salivary gland. It is the entry site for the food to the digestive system. Food is breakdown into simpler molecules by mastication in the buccal cavity and salivary amylase breaks Starch into simpler carbohydrates in the Buccal cavity.
Oesophagus:
Buccal cavity is connected to the long tube-like structure called as Oesophagus. Oesophagus connects the buccal cavity to the stomach and assists the inflow of food towards the stomach. Oesophagus has a valve to prevent backflow of food particles.
Stomach is a J Shaped organ which has gastric glands in it. Gastric glands secrets Hydrochloric acid, Pepsin and Mucus that helps in the digestion of food.
Small Intestine:
Small intestine is highly coiled long structure. Small intestine performs major of the food absorption. Small intestine has specialized structures that facilitate the absorption of digested food. Small intestine has several folds that increase the area of absorption. Small intestine also has fingerlike projection called microvilli which are richly supplied by blood vessels.
Large Intestine :
This is shorter than the small intestine and its lumen is larger than that of Small intestine. The major function of the large intestine is to absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter and transmit the useless waste material from the body.
Large Intestine open into rectum. Waste materials and undigested food are stored in the rectum.
It is the opening at the end of the alimentary canal. Solid waste materials leave the body through Anus.
75. Explain the process of breathing in man
Breathing in Humans has two processes 1) Inhalation 2) Exhalation
Inhalation:
Inhalation is the process of taking oxygen. During this process, ribs come out and the diaphragm moves down. This increases the volume of the lungs and decreases the pressure. This will make the air move towards the lungs.
Exhalation:
Exhalation is a process of throwing out carbon-dioxide. During this process, ribs go down and the diaphragm moves up. This decreases the volume of the lungs and increases the pressure. As a result, air moves out of the lungs.
76. Explain the importance of soil for plant growth.
Soil is very important for the growth of the plant for the following reasons.
- Soil provides the base for the growth of the plants and provides a platform for the penetration of roots.
- It acts as a reservoir of the water.
- Soil has different minerals essential for the growth of the plant. Soil is the only medium from which soil obtain nutrients.
- Soil has organic materials essential for the growth of the plants.
- Soil has microorganisms that have a symbiotic relationship with the plant and these microbes assist the plant in their growth and life processes.
77. Draw the diagram of the alimentary canal of man and label the following parts. Mouth, Oesophagus, Stomach, Intestine

78. How do carbohydrates, proteins and fats get digested in human beings?
Carbohydrate Digestion
Digestion of carbohydrates starts with buccal cavity where salivary enzymes break down the starch into simple sugar molecules. Other sugar molecules are breakdown to glucose in the small intestine.
Protein digestion
Proteins are partially digested by pepsin secreted by gastric glands present in the stomach. Then Pancreatic juice secrets trypsin and chymotrypsin enzymes in the small intestine where complete digestion of proteins takes place.
Fat Digestion
Fats are digested in the small intestine. Bile juice present in the liver emulsifies the fat which breaks fats into small globules. These small fat globules are converted into glycerol and fatty acids by Lipase enzyme.
79. Explain the mechanism of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants produce their own food by utilizing sunlight, CO2 and water. CO@ and water are converted to carbohydrates with the evolution of oxygen. Photosynthesis reaction can be given by the following reaction.
6CO 2 + 6H 2 O Sunlight energy C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2
Process of Photosynthesis is divided into 4 processes
- Reduction of CO2 to produce carbohydrates
80. Explain the three pathways of breakdown in living organisms.

Glucose is first broken down to 3 carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of all organisms. Pyruvate is further broken down by the flowing steps.
Pyruvate is broken down in the absence of oxygen and the process is called anaerobic respiration. In yeasts, pyruvate is broken down to produce CO 2 and ethanol.
In Muscle Cells:
During rigorous physical activity, the energy demand of our muscles cells increases rapidly. This is compensated by anaerobic respiration in muscle cells. In muscle cells, pyruvate is broken down into lactic acid.
In Mitochondria:
In case of aerobic respiration( in presence of oxygen) pyruvate is broken down in mitochondria. Here Pyruvate is broken down to produce H 2 O and CO 2. Aerobic respiration is most common in most of the organisms.
81. Describe the flow of blood through the heart of human beings

• Deoxygenated blood from different organs comes to the right atrium through the vena cava.
• From the right atrium, blood goes to the right ventricle. The tricuspid valve between the right atrium and right ventricle prevents the backflow of blood.
• From the right ventricle, blood goes to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. Inside the lungs, carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and oxygen enters the blood.
• From the lungs, blood goes to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein.
• From the left atrium, blood goes to the left ventricle.
• From the left ventricle, blood is pumped into the aorta so that it can be supplied to different organs.
82. Describe the process of urine formation in kidneys

The basic filtration unit in the kidneys is a cluster of very thin-walled blood capillaries. Each capillary cluster in the kidney is associated with the cup-shaped end of a coiled tube called Bowman’s capsule that collects the filtrate (Fig. 6.14). Each kidney has large numbers of these filtration units called nephrons packed close together.
Some substances in the initial filtrate, such as glucose, amino acids, salts and a major amount of water, are selectively re-absorbed as the urine flows along the tube. The amount of water re-absorbed depends on how much
excess water is there in the body and on how much of dissolved waste there is to be excreted. The urine forming in each kidney eventually enters a long tube, the ureter, which connects the kidneys with the urinary bladder.
Urine is stored in the urinary bladder until the pressure of the expanded bladder leads to the urge to pass it out through the urethra. The bladder is muscular, so it is under nervous control.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NCERT Exemplar
These Exemplars will help students gain insights into all the important chapter questions as well as develop a better understanding of each topic. Additionally, using these exemplars will enable students to study effectively and be well-prepared to answer any type of question that can be asked in the board exam.
Class 10 Science NCERT Life Process Important Topics
- What Is Life Process?
- Autotrophic Nutrition
- Heterotrophic Nutrition
- How Do Organisms Obtain Their Nutrition?
- Nutrition in Human Beings
- Respiration
- Transportation
- Excretion in Human Beings
- Excretion in Plants
NCERT Exemplar Solutions, provided on BYJU’S website, will boost your exam preparation by providing you with the additional knowledge required to understand the concepts clearly. Students are recommended to study these Exemplar Solutions and NCERT Solutions thoroughly to excel in CBSE Class 10 examination. To score good marks in the Class 10 examinations, students can access and download the study materials provided at BYJU’S in PDFs for free. To access the study material, you can visit BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S – The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6
Why are byju’s ncert exemplar solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 important, what concepts will i learn from the ncert exemplar solutions for class 10 science chapter 6, what are the advantages of using the ncert exemplar solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 from byju’s, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Weekend Edition Sunday
- Latest Show
Sunday Puzzle
- Corrections
Listen to the lead story from this episode.
Politics chat: Biden and Trump pin their hopes on debate to give them an edge
by Tamara Keith , Mara Liasson
Meet the woman who escaped two conflicts — as a Palestinian refugee, then in Ukraine
by Tamara Keith , Eleana Tworek
Biden will address the commencement ceremony at Morehouse College. Protests are expected
by Tamara Keith , Stephen Fowler

These teens were missing too much school. Here's what it took to get them back
by Leigh Paterson , Elizabeth Miller
Plant-based restaurants are adding beef. Does the climate math add up?
by Tamara Keith , Julia Simon
An iconic chocolate factory shuts shop in Chicago
by Michael Puente

Sunday Puzzle NPR hide caption
Sunday Puzzle: Complete the compound with these animal connections!
by Will Shortz
Tree seeds that flew around the moon are now being planted across the U.S.
by William Joseph Hudson
Music Interviews
Sudanese musician sinkane on his new album 'we belong'.
by Tamara Keith
The Supreme Court ruled to protect the CFPB. Here's why it matters for your money
Middle east, anger at netanyahu cuts through a somber tel aviv rally to bring home the hostages.
by Hadeel Al-Shalchi
Trump addresses NRA's annual meeting, urges them to vote
by Tamara Keith , Caroline Love
A London court will rule on Julian Assange's extradition to the U.S.
by Tamara Keith , Willem Marx
Rock icon or a victim of exploitation? Examining Amy Winehouse's legacy
by Tamara Keith , Stephen Thompson
Scientists at Berkeley develop a tool to help cities measure carbon emissions
by Kevin Stark / KQED
Furiosa makes a splash at the 2024 Cannes Film Festival
Environment, on a trail in the adirondack mountains, runners appreciate the spring season.
by Emily Russell, NCPR

Author Interviews
Hold on to your wishes — there's a 'spider in the well'.
by Tamara Keith , Samantha Balaban , Melissa Gray
Searching for a song you heard between stories? We've retired music buttons on these pages. Learn more here.
Press Herald
Account Subscription: ACTIVE
Questions about your account? Our customer service team can be reached at [email protected] during business hours at (207) 791-6000 .
- Local & State
Observe Memorial Day with these events in southern Maine
Tons of towns have parades and ceremonies happening Monday.

You are able to gift 5 more articles this month.
Anyone can access the link you share with no account required. Learn more .
With a Press Herald subscription, you can gift 5 articles each month.
It looks like you do not have any active subscriptions. To get one, go to the subscriptions page .
Loading....

Kids and adults gather at a Memorial Day parade to honor and celebrate veterans in South Portland. Sofia Aldinio/ Staff Photographer
BATH 10 a.m. Monday. Parade begins at 200 Congress Ave. and concludes at Library Park and will be followed by a wreath-laying service at 11 a.m.
BERWICK 11 a.m. Monday. Parade begins at Berwick Town Hall/Sullivan Square and proceeds to Lord’s Cemetery by way of Wilson and Allen streets. After a ceremony there, the parade will continue down Saw Mill Hill Street with a pause at the Somersworth-Berwick Bridge for a brief memorial service for those lost at sea. The parade ends at Sullivan Square with a memorial service honoring area veterans.
BIDDEFORD-SACO Opening ceremony at 9:55 a.m. Monday at Saco City Hall. Parade starts at 10 a.m. from Saco City Hall and proceeds along Main Street and down York Hill into Biddeford, continues along Main Street, onto Alfred Street and finishes at Veteran’s Memorial Park with a closing ceremony at 10:45 a.m.
BRUNSWICK-TOPSHAM 9 a.m. Monday. Parade proceeds from Topsham Town Hall, pauses for observances while crossing the Brunswick-Topsham bridge, and concludes at the Brunswick Mall.
CAPE ELIZABETH 9 a.m. Monday. Parade begins at the middle school parking lot, turns right on Scott Dyer Road, right onto Route 77 and ends at the village green adjacent to the town hall. A brief ceremony and laying of the wreath will be held at the Village Green after the parade.
CUMBERLAND 8 a.m. Monday. Kids run at Greely High School followed by 5K Run and Remember race at 8:30 a.m. Parade starts at 10 a.m. at Mabel I. Wilson School and ends at the veterans’ monument in Moss Side Cemetery in Cumberland Center, where a ceremony will be held at 10:30 a.m. Advertisement
FALMOUTH 10 a.m. Monday. Parade proceeds from 65 Depot Road (Falmouth American Legion) to Pine Grove Park, where a ceremony will be held.
FREEPORT 9:30 a.m. Monday. Parade proceeds from Holbrook Street, heads north on Main and makes a right onto School Street, then right onto Park Street, ending in Memorial Park. There will be a small ceremony in Memorial Park starting at 10 a.m.
GORHAM 11 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Village School (12 Robie St.) and ends at Eastern Cemetery on Johnson Road.
GRAY 11:30 a.m. Monday. Parade leaves the Russell School (8 Gray Park), proceeds to Shaker Road and continues to the Soldiers Monument at the intersection of Routes 26 and 3 for a wreath-laying ceremony. Parade continues north to the American Legion Post (15 Lewiston Road) for a closing ceremony.
LYMAN 1 p.m. Monday. Parade starts at Waterhouse Road/Mill Pond in Goodwins Mills and ends at the Lyman Town Hall on South Waterboro Road.
NEW GLOUCESTER 9 a.m. Monday. Parade leaves from Memorial Elementary School (86 Intervale Road) and heads down Intervale Road to Route 100/202 to Veterans Park for a memorial service. The parade will reconvene and go down Peacock Hill Road, then take a left on Gilmore Road. Advertisement
OLD ORCHARD BEACH 1 p.m. Monday. Parade starts at the corner of Ballpark Way and E. Emerson Cumming Boulevard and proceeds down Saco Avenue, Old Orchard Beach Street to First Street and ends at Veteran’s Memorial Park.
PORTLAND 2 p.m. Monday. The procession starts at Longfellow School (432 Stevens Ave.) and ends at Evergreen Cemetery for a commemoration ceremony.
SANFORD 10 a.m. Monday. The parade starts at the Sanford Armory (88 William Oscar Emery Drive), proceeds up Gowen Park Drive and ends at Central Park.
SCARBOROUGH 10 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Scarborough High School, turns onto Route 114 and then Route 1, past town offices to the Maine Veterans Home and concludes with a ceremony there.
SOUTH PORTLAND 10:30 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Southern Maine Community College parking lot, proceeds down Broadway to the Veterans Monument for a short Memorial Day recognition service.
WELLS 9 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Wells High School (200 Sanford Road) and proceeds to Ocean View Cemetery for a ceremony and musical performances. Advertisement
WESTBROOK 10 a.m. Monday. Parade proceeds down Main Street and will be followed by a ceremony in Riverbank Park.
WINDHAM 9 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Windham Town Hall and proceeds onto Route 202 toward Windham High School. At 10 a.m., there will be a ceremony in front of Windham’s Veterans Memorial Flagpole at Windham High School.
YARMOUTH 10 a.m. Monday. Parade leaves from Yarmouth High School (286 West Elm St.) and proceeds to the Memorial Green at Town Hall for a ceremony.
YORK 10 a.m. Monday. Parade starts near St. Christopher’s Church (4 Barrell Lane) and proceeds down York Street to York Town Hall.
Success. Please wait for the page to reload. If the page does not reload within 5 seconds, please refresh the page.
Enter your email and password to access comments.
Forgot Password?
Don't have a commenting profile? Create one.
Hi, to comment on stories you must create a commenting profile . This profile is in addition to your subscription and website login. Already have a commenting profile? Login .
Invalid username/password.
Please check your email to confirm and complete your registration.
Create a commenting profile by providing an email address, password and display name. You will receive an email to complete the registration. Please note the display name will appear on screen when you participate.
Already registered? Log in to join the discussion.
Only subscribers are eligible to post comments. Please subscribe or login first for digital access. Here’s why .
Use the form below to reset your password. When you've submitted your account email, we will send an email with a reset code.
Send questions/comments to the editors.
Report says former Maine Turnpike executive threatened and intimidated employees for years
Opinion: we can do way better than the gorham connector, the wrap: farmers to return to monument square; hobbit-core restaurant planned for brunswick, complaint may halt changes to casco bay ferry ticket prices, skeletal remains found on gorham property, daily headlines.
- Email address
- Hidden Untitled
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Member Log In
Please enter your username and password below. Already a subscriber but don't have one? Click here .
Not a subscriber? Click here to see your options
Assessing environmental impacts of a textile company using life cycle assessment approach—a case study
- Environmental Sustainability: Challenges and Solutions
- Published: 22 May 2024
Cite this article

- Hetvi Dani 1 &
- M. A. Shabiimam ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8857-4903 1
The textile industry is known for its significant environmental impact, and as such, there is a growing need to assess the industry’s production practices. Life cycle assessment (LCA) is an effective tool for measuring the environmental impact of textile products from raw material production to end-of-life disposal. Surat city, known as textile hub of India, has multiple industrial clusters that play host to different elements of the textile value chain. This research aims to evaluate the environmental performance of a Surat-based textile company. The study involves the collection of data from textile manufacturing facilities, including gray cloth production and wet processes (gate-to-gate approach). The data collected has been analyzed using the GABI (9.2.1 version) software. The study provides potential environmental impact data on present textile technology and production situation. Significant hotspots have been determined throughout supply chain and the associated drivers identified. However, the industry’s environmental impact can be reduced by practicing ecoefficiency, immaterialization, and recycling textile waste. This research highlights the importance of LCA in identifying the environmental impact of the textile industry and provides a basis for developing sustainable practices to minimize the industry’s environmental impact.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Data Availability
The data are obtained from industry which is not possible to share.
Ammayappan L, Jose S, Arputha Raj A (2016) Sustainable production processes in textile dyeing, Environ. Footpr Eco-Des Prod Process. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0111-6_8
Bergerson JA et al (2020) Life cycle assessment of emerging technologies: evaluation techniques at different stages of market and technical maturity. J Ind Ecol 24(1):11–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/jiec.12954
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bhawan U (2022) Ministry of textiles government of India 21–22. Annual report ministry of textiles. https://texmin.nic.in/sites/default/files/AR_Ministry_of_Textiles_%202021-22_Eng.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2023
Curran MA (2013) Life Cycle Assessment: A review of the methodology and its application to sustainability’. Curr Opin Chem Eng 2(3):273–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2013.02.002
Article Google Scholar
Dhonde B, Patel CR (2020) Implementing circular economy concepts for sustainable urban freight transport: case of textile manufacturing supply chain. Acta Logist 7(2):131–143. https://doi.org/10.22306/al.v7i2.172
FICCI (2014) India LCA directory. http://ficci.in/study-page.asp?spid=20426§orid=52 . Accessed on 15 May 2023
Hari D and Mitra R (2022) Circular textile and apparel in India policy intervention priorities and ideas. Centre for Responsible Business. https://c4rb.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Circular_Apparel_Status_Paper_140422.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2023
Hasanuzzaman, Bhar C (2016) Indian textile industry and its impact on the environment and health: a review. Int J Inf Syst Serv Sect 8(4):33–46. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJISSS.2016100103
Kalliala E, Talvenmaa P (2000) Environmental profile of textile wet processing in Finland. J Clean Prod 8(2):143–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-6526(99)00313-3
Khurana K (2022) The Indian fashion and textile sector in and post COVID-19 times. Fash Text 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40691-021-00267-4
Moreira Cardoso AA (2013) Life cycle assessment of two textile products wool and cotton. Dissertation, Porto University. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/143413631.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2023
Munasinghe P, Druckman A, Dissanayake DGK (2021) A systematic review of the life cycle inventory of clothing. J Clean Prod 320:128852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128852
Niinimaki K et al (2020) The environmental price of fast fashion. Nat Rev Earth Environ 1(4):189–200. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-020-0039-9
Baitz et al (2012) GaBi database & modelling principles 2012, version 6.0. https://gabi-6-lci-documentation.gabi-software.com/xml-data/external_docs/GaBiModellingPrinciples.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2023
Roos S (2016) Advancing life cycle assessment of textile products to include textile chemicals. Dissertation, Chalmers University of Technology. https://publications.lib.chalmers.se/records/fulltext/246361/246361.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2023
Roy Choudhury AK (2014) Environmental impacts of the textile industry and its assessment through life cycle assessment. In: Roadmap to Sustainable Textiles and Clothing pp 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-287-110-7_1 . Accessed 15 May 2023
Saurabh E et al (2022) Carbon footprint assessment of textile industry. Int Res J Eng Technol 391–402. https://www.irjet.net/archives/V9/i8/IRJET-V9I865.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2023
Sharpe S, Dominish E, Martinez Fernandez MC (2022) Taking climate action: measuring carbon emissions in the garment sector in Asia. https://www.ilo.org/global/publications/working-papers/WCMS_838031/lang--en/index.htm . Accessed 15 May 2023
Yuan ZW et al (2013) Life-cycle assessment of continuous pad-dyeing technology for cotton fabrics. Int J LCA 18(3):659–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-012-0470-3
Zhang Y et al (2015) Life cycle assessment of cotton T-shirts in China. Int J LCA 20(7):994–1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-015-0889-4
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Civil Engineering Department, School of Technology, Pandit Deendayal Energy University, Gandhinagar, Gujarat, 382426, India
Hetvi Dani & M. A. Shabiimam
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection and analysis were performed by Hevi Dani, and Shabiimam M. A. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Hetvi Dani and edited by Shabiimam M. A. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to M. A. Shabiimam .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
This work does not contain any research involving humans or animals.
Consent to participate
The work described has not been published before; that it is not under consideration for publication anywhere else; that written informed consent was obtained from individual or guardian participants.
Consent for publication
The publication consent was obtained from all co-authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Loubet
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Dani, H., Shabiimam, M.A. Assessing environmental impacts of a textile company using life cycle assessment approach—a case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33719-7
Download citation
Received : 01 August 2023
Accepted : 14 May 2024
Published : 22 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33719-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Life cycle assessment
- Textile industry
- GABI software
- Environment
- Sustainability
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CBSE Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 6. CASE STUDY : 1. Carbon and energy requirements of the autotrophic organism are fulfilled by photosynthesis. It is the process by which autotrophs take in substances from the outside and convert them into stored forms of energy. This material is taken in the form of carbon dioxide ...
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys. (i) (c): In the test tube full of mercury (figure A) there is no air and, therefore, the introduced soaked seeds do not get air for aerobic respiration. But they are capable of respiration in the absence of oxygen as is indicated by the ...
There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes. Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to ...
These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations. Case Study Questions Chapter 6 Life Processes. Case/Passage - 1. There is a pair of bean-shaped organs P in the human body towards the back, just above the ...
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in transpiration, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through pores called stomata. Normally stomata remain open in the daytime ...
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Life Processes Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science. Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
Life Processes - Case Based Questions - CBSE 10 | CBSE Class 10 Biology | Class 10 Science Chapter 6 | NCERT Solution for Class 10 Biology | Vedantu Class 9 ...
To watch the most important Questions Click here: https://youtu.be/PfAcjMvGY50To watch Assertion & Reason questions Click here: https://youtu.be/oHOJmO6eMOcT...
Life Processes Case Study Questions (CSQ's) Practice Tests. Timed Tests. Select the number of questions for the test: Select the number of questions for the test: TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Biology Life Processes chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem ...
Explain the concept of Aerobic respiration covered in Chapter 6 of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science. 1. The process occurs in the presence of oxygen. 2. CO 2, water and energy are the products of aerobic respiration. 3. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm first step, followed by mitochondria in the second step.
The Case Based Type Practice Questions: Life Processes is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 10 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
Learn about the basic life processes that sustain living organisms, such as photosynthesis, nutrition, transportation and excretion. Khan Academy Class 10 Biology (India).
The Class 10 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 6 Life Processes includes all the intext and exercise questions. Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NCERT questions and answers help students to clear their doubts and to obtain good marks in Class 10 board exam. All the solutions provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE ...
4. The assimilation process involves: (a) Breakdown of glucose (b) Removal of nitrogenous waste (c) Obtaining energy from absorbed food ( d) Both a and b 5. The food to be egested is temporarily stored in: (a) Anus (b) Caecum (c) Vermiform appendix (d) Rectum Question 2 The food that we eat gets broken down into simpler compounds for absorption.
Life Processes Case Study Questions With Answers. Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in ...
Chapter 6 of Class 10, Life Processes, is going to teach you about the life processes of plants and animals that occur in their body at each and every second. These processes are the essence of a living being. We, at Teachoo, will provide you with all the necessary sources such as concepts, NCERT questions along with extra questions made by our ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Textbook Chapter End Questions. Question 1. The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for. (i) nutrition. (ii) respiration. (iii) excretion. (iv) transportation. Answer: (iii) Excretion.
Answer. The following raw materials are required for photosynthesis: → Carbon Dioxide: Plants get CO from atmosphere through stomata. → Water: Plants absorb water from soil through roots and transport to leaves. → Sunlight: Sunlight, which is absorbed by the chlorophyll and other green parts of the plant. 3.
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Case Study Questions 2021. 10th Standard CBSE. Reg.No. : Science. Time : 00:30:00 Hrs. Total Marks : 20. Digestion is a catabolic process in which complex and large components of food are broken down into their respective simpler and smaller forms with the help of various hydrolytic enzymes.
Life Processes 85. Activity 5.3. nTake 1 mL starch solution (1%) in two test tubes (A and B). nAdd 1 mL saliva to test tube A and leave both test tubes undisturbed for 20-30 minutes. nNow add a few drops of dilute iodine solution to the test tubes.
Studying from these chapter-wise PDFs for ch 6 life processes class 10 can help in developing a strong conceptual base for students. Downloading these life processes class 10 PDFs can offer significant benefits to teachers and students. The study material PDF provides a structured way of learning and students can create a schedule.
Life Processes Class 10 Science Extra Questions with Answers. Question 1: Mention the raw materials required for photosynthesis. Answer: The following raw materials are required for photosynthesis: (i) Carbon Dioxide: Plants get CO 2 from atmosphere through stomata. (ii)Water: Plants absorb water from soil through roots and transport to leaves.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Free PDF Download. NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes are premier study material required for the students to score good marks in Class 10 CBSE examinations as well as to avoid difficulty in understanding the concepts to be taught in higher secondary and graduation courses.
Meet the woman who escaped two conflicts — as a Palestinian refugee, then in Ukraine. by Tamara Keith, Eleana Tworek. 6 min.
Parade starts at Southern Maine Community College parking lot, proceeds down Broadway to the Veterans Monument for a short Memorial Day recognition service. 9 a.m. Monday. Parade starts at Wells ...
The textile industry is known for its significant environmental impact, and as such, there is a growing need to assess the industry's production practices. Life cycle assessment (LCA) is an effective tool for measuring the environmental impact of textile products from raw material production to end-of-life disposal. Surat city, known as textile hub of India, has multiple industrial clusters ...