GrammarSimple.Com
40 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Sentences
Table of Contents

Direct And Indirect Speech Examples
While using English, we use direct and indirect speeches quite often. If a sentence is expressed exactly as it came out of the mouth of the person who said it, it becomes a direct speech. However Indirect Speech (also called reported speech) refers to transmitting a sentence that someone has said. It is often used in daily language.
For example,
- Susan told me she ate pizza yesterday. (Indirect Speech)
Susan said, “I ate pizza yesterday.”. (Direct Speech)
- Mathilda told me she had to go out. (Indirect Speech)
Mathilda said: “I have to go out.”. (Direct Speech)
- Julie asked if the train had left when she arrived at the ticket office. (Indirect Speech)
Julie asked: “Did the train leave?” (Direct Speech)
Related Posts
Parallel Structure Sentence Examples, Parallel Structure Definition and Meaning
8 Parts of Speech, Definition and Example Sentences
Using Provided, Definition and Example Sentences
About the author.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
Indirect speech: typical errors.
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
ride off into the sunset
to begin a new, happy life at the end of a story

Apples and oranges (Talking about differences, Part 2)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported speech can be quite challenging for English language learners because in order to change direct speech into reported speech, one must change the perspective and tense of what was said by the original speaker or writer. In this guide, we will explain in detail how to change direct speech into indirect speech and provide lots of examples of reported speech to help you understand. Here are the key aspects of converting direct speech into reported speech.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
- Direct : “I am going to the park.” Reported : He said he was going to the park .
- Direct : “You should try the new restaurant.” Reported : She said that I should try the new restaurant.
- Direct : “We will win the game.” Reported : They said that they would win the game.
- Direct : “She loves her new job.” Reported : He said that she loves her new job.
- Direct : “He can’t come to the party.” Reported : She said that he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct : “It belongs to me.” Reported : He said that it belonged to him .
- Direct : “They are moving to a new city.” Reported : She said that they were moving to a new city.
- Direct : “You are doing a great job.” Reported : He told me that I was doing a great job.
- Direct : “I don’t like this movie.” Reported : She said that she didn’t like that movie.
- Direct : “We have finished our work.” Reported : They said that they had finished their work.
- Direct : “You will need to sign here.” Reported : He said that I would need to sign there.
- Direct : “She can solve the problem.” Reported : He said that she could solve the problem.
- Direct : “He was not at home yesterday.” Reported : She said that he had not been at home the day before.
- Direct : “It is my responsibility.” Reported : He said that it was his responsibility.
- Direct : “We are planning a surprise.” Reported : They said that they were planning a surprise.
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
In reported speech, various reporting verbs are used depending on the nature of the statement or the intention behind the communication. These verbs are essential for conveying the original tone, intent, or action of the speaker. Here are some examples demonstrating the use of different reporting verbs in reported speech:
- Direct: “I will help you,” she promised . Reported: She promised that she would help me.
- Direct: “You should study harder,” he advised . Reported: He advised that I should study harder.
- Direct: “I didn’t take your book,” he denied . Reported: He denied taking my book .
- Direct: “Let’s go to the cinema,” she suggested . Reported: She suggested going to the cinema .
- Direct: “I love this song,” he confessed . Reported: He confessed that he loved that song.
- Direct: “I haven’t seen her today,” she claimed . Reported: She claimed that she hadn’t seen her that day.
- Direct: “I will finish the project,” he assured . Reported: He assured me that he would finish the project.
- Direct: “I’m not feeling well,” she complained . Reported: She complained of not feeling well.
- Direct: “This is how you do it,” he explained . Reported: He explained how to do it.
- Direct: “I saw him yesterday,” she stated . Reported: She stated that she had seen him the day before.
- Direct: “Please open the window,” he requested . Reported: He requested that I open the window.
- Direct: “I can win this race,” he boasted . Reported: He boasted that he could win the race.
- Direct: “I’m moving to London,” she announced . Reported: She announced that she was moving to London.
- Direct: “I didn’t understand the instructions,” he admitted . Reported: He admitted that he didn’t understand the instructions.
- Direct: “I’ll call you tonight,” she promised . Reported: She promised to call me that night.
Reported Speech: Tense Shifts
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
- Direct: “I am eating.” Reported: He said he was eating.
- Direct: “They will go to the park.” Reported: She mentioned they would go to the park.
- Direct: “We have finished our homework.” Reported: They told me they had finished their homework.
- Direct: “I do my exercises every morning.” Reported: He explained that he did his exercises every morning.
- Direct: “She is going to start a new job.” Reported: He heard she was going to start a new job.
- Direct: “I can solve this problem.” Reported: She said she could solve that problem.
- Direct: “We are visiting Paris next week.” Reported: They said they were visiting Paris the following week.
- Direct: “I will be waiting outside.” Reported: He stated he would be waiting outside.
- Direct: “They have been studying for hours.” Reported: She mentioned they had been studying for hours.
- Direct: “I can’t understand this chapter.” Reported: He complained that he couldn’t understand that chapter.
- Direct: “We were planning a surprise.” Reported: They told me they had been planning a surprise.
- Direct: “She has to complete her assignment.” Reported: He said she had to complete her assignment.
- Direct: “I will have finished the project by Monday.” Reported: She stated she would have finished the project by Monday.
- Direct: “They are going to hold a meeting.” Reported: She heard they were going to hold a meeting.
- Direct: “I must leave.” Reported: He said he had to leave.
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
When converting direct speech into reported speech, references to time and place often need to be adjusted to fit the context of the reported speech. This is because the time and place relative to the speaker may have changed from the original statement to the time of reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how time and place references change:
- Direct: “I will see you tomorrow .” Reported: He said he would see me the next day .
- Direct: “We went to the park yesterday .” Reported: They said they went to the park the day before .
- Direct: “I have been working here since Monday .” Reported: She mentioned she had been working there since Monday .
- Direct: “Let’s meet here at noon.” Reported: He suggested meeting there at noon.
- Direct: “I bought this last week .” Reported: She said she had bought it the previous week .
- Direct: “I will finish this by tomorrow .” Reported: He stated he would finish it by the next day .
- Direct: “She will move to New York next month .” Reported: He heard she would move to New York the following month .
- Direct: “They were at the festival this morning .” Reported: She said they were at the festival that morning .
- Direct: “I saw him here yesterday.” Reported: She mentioned she saw him there the day before.
- Direct: “We will return in a week .” Reported: They said they would return in a week .
- Direct: “I have an appointment today .” Reported: He said he had an appointment that day .
- Direct: “The event starts next Friday .” Reported: She mentioned the event starts the following Friday .
- Direct: “I lived in Berlin two years ago .” Reported: He stated he had lived in Berlin two years before .
- Direct: “I will call you tonight .” Reported: She said she would call me that night .
- Direct: “I was at the office yesterday .” Reported: He mentioned he was at the office the day before .
Reported Speech: Question Format
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
- Direct: “Are you coming to the party?” Reported: She asked if I was coming to the party.
- Direct: “What time is the meeting?” Reported: He inquired what time the meeting was.
- Direct: “Why did you leave early?” Reported: They wanted to know why I had left early.
- Direct: “Can you help me with this?” Reported: She asked if I could help her with that.
- Direct: “Where did you buy this?” Reported: He wondered where I had bought that.
- Direct: “Who is going to the concert?” Reported: They asked who was going to the concert.
- Direct: “How do you solve this problem?” Reported: She questioned how to solve that problem.
- Direct: “Is this the right way to the station?” Reported: He inquired whether it was the right way to the station.
- Direct: “Do you know her name?” Reported: They asked if I knew her name.
- Direct: “Why are they moving out?” Reported: She wondered why they were moving out.
- Direct: “Have you seen my keys?” Reported: He asked if I had seen his keys.
- Direct: “What were they talking about?” Reported: She wanted to know what they had been talking about.
- Direct: “When will you return?” Reported: He asked when I would return.
- Direct: “Can she drive a manual car?” Reported: They inquired if she could drive a manual car.
- Direct: “How long have you been waiting?” Reported: She asked how long I had been waiting.
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
In reported speech, quotation marks are not used, differentiating it from direct speech which requires them to enclose the spoken words. Reported speech summarizes or paraphrases what someone said without the need for exact wording. Here are examples showing how direct speech with quotation marks is transformed into reported speech without them:
- Direct: “I am feeling tired,” she said. Reported: She said she was feeling tired.
- Direct: “We will win the game,” he exclaimed. Reported: He exclaimed that they would win the game.
- Direct: “I don’t like apples,” the boy declared. Reported: The boy declared that he didn’t like apples.
- Direct: “You should visit Paris,” she suggested. Reported: She suggested that I should visit Paris.
- Direct: “I will be late,” he warned. Reported: He warned that he would be late.
- Direct: “I can’t believe you did that,” she expressed in surprise. Reported: She expressed her surprise that I had done that.
- Direct: “I need help with this task,” he admitted. Reported: He admitted that he needed help with the task.
- Direct: “I have never been to Italy,” she confessed. Reported: She confessed that she had never been to Italy.
- Direct: “We saw a movie last night,” they mentioned. Reported: They mentioned that they saw a movie the night before.
- Direct: “I am learning to play the piano,” he revealed. Reported: He revealed that he was learning to play the piano.
- Direct: “You must finish your homework,” she instructed. Reported: She instructed that I must finish my homework.
- Direct: “I will call you tomorrow,” he promised. Reported: He promised that he would call me the next day.
- Direct: “I have finished my assignment,” she announced. Reported: She announced that she had finished her assignment.
- Direct: “I cannot attend the meeting,” he apologized. Reported: He apologized for not being able to attend the meeting.
- Direct: “I don’t remember where I put it,” she confessed. Reported: She confessed that she didn’t remember where she put it.
Reported Speech Quiz
Thanks for reading! I hope you found these reported speech examples useful. Before you go, why not try this Reported Speech Quiz and see if you can change indirect speech into reported speech?


50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
In this useful lesson, we’ll explore direct and indirect speech through 50 simple examples. These two ways of speaking help us share what someone else said. Think of direct speech as using the speaker’s exact words, like quoting a friend. Indirect speech , on the other hand, involves changing the original words a bit, as if you’re telling a story about what was said. This lesson is great for anyone looking to get better at English, offering clear examples to make learning easier.
Rules to Make Direct and Indirect Speech
When converting direct speech into indirect speech, it’s important to follow specific rules to ensure the sentence still conveys the original meaning. Here are the key rules:
- Change in Pronouns : Pronouns often need to be changed according to the context and the point of view of the reporting verb. For example, “ I am going ” (direct) might become “ He said he was going ” (indirect).
- Tense Shifts : The tense of the verb in direct speech usually changes when converting to indirect speech. If the reporting verb is in the past tense , the tense in the reported speech shifts back as well. For instance, “ She said, ‘I am eating ‘” changes to “ She said she was eating “.
- Time and Place Words : Words indicating time and place in direct speech are often adjusted in indirect speech. “Here” may change to “there,” “today” to “ that day ,” “tomorrow” to “ the next day ,” etc.
- Question Form : If the direct speech is a question, the indirect form does not use a question format. Instead, it integrates the question into a statement, often using “if” or “whether” for yes/no questions, and ‘wh’ words ( what, when, where, why, who ) for questions that require more detailed answers. For example, “ He asked, ‘Are you coming? ‘” becomes “ He asked if I was coming .”
- No Quotes : In indirect speech, quotation marks are not used. The sentence is integrated into a larger statement, which often starts with verbs like said, asked, or told.
- Exclamations and Commands : Exclamatory sentences and commands in direct speech are transformed into statements or requests in indirect speech. For instance, “He said, ‘How beautiful!'” becomes “He exclaimed that it was beautiful.” Commands like “He said, ‘Sit down!'” change to “He ordered me to sit down.”
- Modal Verbs : Modal verbs can also change in indirect speech, especially might, could, would, and should, depending on the context and the necessity to maintain the original sentence’s meaning.
Remember, the goal of these changes is to maintain the essence of the original statement while adapting it to the grammatical and contextual framework of indirect speech.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
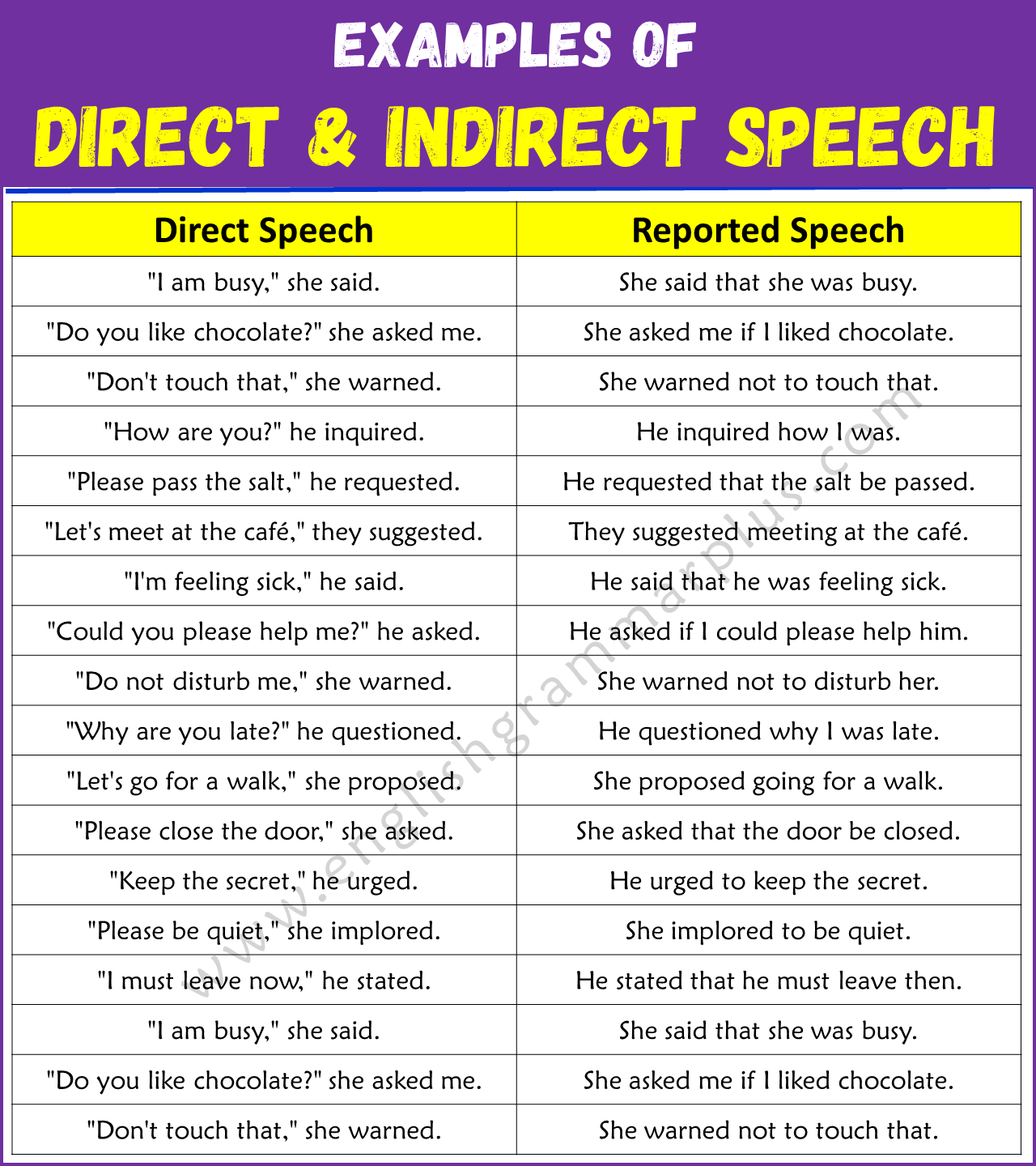
1. Direct: “I am busy,” she said.
Indirect: She said that she was busy.
2. Direct: “We will go tomorrow,” they said.
Indirect: They said that they would go the next day.
3. Direct: “He can play the guitar,” Mike said.
Indirect: Mike said that he could play the guitar.
4. Direct: “Do you like chocolate?” she asked me.
Indirect: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
5. Direct: “Please open the window,” John requested.
Indirect: John requested that the window be opened.
6. Direct: “I have finished my homework,” he announced.
Indirect: He announced that he had finished his homework.
7. Direct: “Don’t touch that,” she warned.
Indirect: She warned not to touch that.
8. Direct: “How are you?” he inquired.
Indirect: He inquired how I was.
9. Direct: “I will help you,” she promised.
Indirect: She promised that she would help me.
10. Direct: “I didn’t see him yesterday,” Tom confessed.
Indirect: Tom confessed that he hadn’t seen him the day before.
11. Direct: “I am going to the market,” Alex said.
Indirect: Alex said that he was going to the market.
12. Direct: “We saw a movie last night,” they told me.
Indirect: They told me that they had seen a movie the night before.
13. Direct: “Can you drive a car?” she questioned.
Indirect: She questioned whether I could drive a car.
14. Direct: “Please pass the salt,” he requested.
Indirect: He requested that the salt be passed.
15. Direct: “I have been to Spain,” she mentioned.
Indirect: She mentioned that she had been to Spain.
16. Direct: “Stay away from the dog,” he cautioned.
Indirect: He cautioned to stay away from the dog.
17. Direct: “Where did you buy this?” she inquired.
Indirect: She inquired where I had bought that.
18. Direct: “I’ll call you tonight,” he promised.
Indirect: He promised that he would call me that night.
19. Direct: “I didn’t take your book,” Sarah insisted.
Indirect: Sarah insisted that she hadn’t taken my book.
20. Direct: “Let’s meet at the café,” they suggested.
Indirect: They suggested meeting at the café.
21. Direct: “I’m feeling sick,” he said.
Indirect: He said that he was feeling sick.
22. Direct: “I won the match,” she exclaimed.
Indirect: She exclaimed that she had won the match.
23. Direct: “Could you please help me?” he asked.
Indirect: He asked if I could please help him.
24. Direct: “Turn off the lights,” she commanded.
Indirect: She commanded that the lights be turned off.
25. Direct: “I’ll see you tomorrow,” he said.
Indirect: He said that he would see me the next day.
26. Direct: “We’re moving to a new city,” they announced.
Indirect: They announced that they were moving to a new city.
27. Direct: “Do not disturb me,” she warned.
Indirect: She warned not to disturb her.
28. Direct: “Why are you late?” he questioned.
Indirect: He questioned why I was late.
29. Direct: “I’ll handle the situation,” she assured.
Indirect: She assured that she would handle the situation.
30. Direct: “I’ve never been to Asia,” he stated.
Indirect: He stated that he had never been to Asia.
31. Direct: “Let’s go for a walk,” she proposed.
Indirect: She proposed going for a walk.
32. Direct: “I am learning Spanish,” he mentioned.
Indirect: He mentioned that he was learning Spanish.
33. Direct: “Please close the door,” she asked.
Indirect: She asked that the door be closed.
34. Direct: “I will join you later,” he promised.
Indirect: He promised that he would join me later.
35. Direct: “I lost my wallet,” she declared.
Indirect: She declared that she had lost her wallet.
36. Direct: “Keep the secret,” he urged.
Indirect: He urged to keep the secret.
37. Direct: “Where is the nearest bank?” she inquired.
Indirect: She inquired where the nearest bank was.
38. Direct: “I might go to the concert,” he speculated.
Indirect: He speculated that he might go to the concert.
39. Direct: “Please be quiet,” she implored.
Indirect: She implored to be quiet.
40. Direct: “I will finish the project by Monday,” he assured.
Indirect: He assured that he would finish the project by Monday.
41. Direct: “Don’t forget to lock the door,” she reminded.
Indirect: She reminded to not forget to lock the door.
42. Direct: “How do you solve this problem?” he pondered.
Indirect: He pondered how to solve that problem.
43. Direct: “I can’t believe I won!” he exclaimed.
Indirect: He exclaimed that he couldn’t believe he had won.
44. Direct: “Would you like some coffee?” she offered.
Indirect: She offered if I would like some coffee.
45. Direct: “I must leave now,” he stated.
Indirect: He stated that he must leave then.
46. Direct: “We’re adopting a puppy,” they shared.
Indirect: They shared that they were adopting a puppy.
47. Direct: “Never speak to me again,” she commanded.
Indirect: She commanded never to speak to her again.
48. Direct: “When will you return the book?” he asked.
Indirect: He asked when I would return the book.
49. Direct: “I’ll think about your offer,” she considered.
Indirect: She considered that she would think about the offer.
50. Direct: “Please bring me a glass of water,” he requested.
Indirect: He requested that a glass of water be brought to him.
Post navigation
Previous post.
No comments yet. Why don’t you start the discussion?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Indirect Speech Definition and Examples
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Indirect speech is a report on what someone else said or wrote without using that person's exact words (which is called direct speech). It's also called indirect discourse or reported speech .
Direct vs. Indirect Speech
In direct speech , a person's exact words are placed in quotation marks and set off with a comma and a reporting clause or signal phrase , such as "said" or "asked." In fiction writing, using direct speech can display the emotion of an important scene in vivid detail through the words themselves as well as the description of how something was said. In nonfiction writing or journalism, direct speech can emphasize a particular point, by using a source's exact words.
Indirect speech is paraphrasing what someone said or wrote. In writing, it functions to move a piece along by boiling down points that an interview source made. Unlike direct speech, indirect speech is not usually placed inside quote marks. However, both are attributed to the speaker because they come directly from a source.
How to Convert
In the first example below, the verb in the present tense in the line of direct speech ( is) may change to the past tense ( was ) in indirect speech, though it doesn't necessarily have to with a present-tense verb. If it makes sense in context to keep it present tense, that's fine.
- Direct speech: "Where is your textbook? " the teacher asked me.
- Indirect speech: The teacher asked me where my textbook was.
- Indirect speech: The teacher asked me where my textbook is.
Keeping the present tense in reported speech can give the impression of immediacy, that it's being reported soon after the direct quote,such as:
- Direct speech: Bill said, "I can't come in today, because I'm sick."
- Indirect speech: Bill said (that) he can't come in today because he's sick.
Future Tense
An action in the future (present continuous tense or future) doesn't have to change verb tense, either, as these examples demonstrate.
- Direct speech: Jerry said, "I'm going to buy a new car."
- Indirect speech: Jerry said (that) he's going to buy a new car.
- Direct speech: Jerry said, "I will buy a new car."
- Indirect speech: Jerry said (that) he will buy a new car.
Indirectly reporting an action in the future can change verb tenses when needed. In this next example, changing the am going to was going implies that she has already left for the mall. However, keeping the tense progressive or continuous implies that the action continues, that she's still at the mall and not back yet.
- Direct speech: She said, "I'm going to the mall."
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she was going to the mall.
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she is going to the mall.
Other Changes
With a past-tense verb in the direct quote, the verb changes to past perfect.
- Direct speech: She said, "I went to the mall."
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she had gone to the mall.
Note the change in first person (I) and second person (your) pronouns and word order in the indirect versions. The person has to change because the one reporting the action is not the one actually doing it. Third person (he or she) in direct speech remains in the third person.
Free Indirect Speech
In free indirect speech, which is commonly used in fiction, the reporting clause (or signal phrase) is omitted. Using the technique is a way to follow a character's point of view—in third-person limited omniscient—and show her thoughts intermingled with narration.
Typically in fiction italics show a character's exact thoughts, and quote marks show dialogue. Free indirect speech makes do without the italics and simply combines the internal thoughts of the character with the narration of the story. Writers who have used this technique include James Joyce, Jane Austen, Virginia Woolf, Henry James, Zora Neale Hurston, and D.H. Lawrence.
- Question Mark Definition and Examples
- Figure of Speech: Definition and Examples
- Indirect Speech in the English Language
- Direct Speech Definition and Examples
- French Grammar: Direct and Indirect Speech
- How to Teach Reported Speech
- Definition and Examples of Direct Quotations
- How to Use Indirect Quotations in Writing for Complete Clarity
- What Is Attribution in Writing?
- Backshift (Sequence-of-Tense Rule in Grammar)
- Indirect Question: Definition and Examples
- Reported Speech
- Using Reported Speech: ESL Lesson Plan
- Constructed Dialogue in Storytelling and Conversation
- The Subjunctive Present in German
- What Are Reporting Verbs in English Grammar?
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples & Worksheet
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
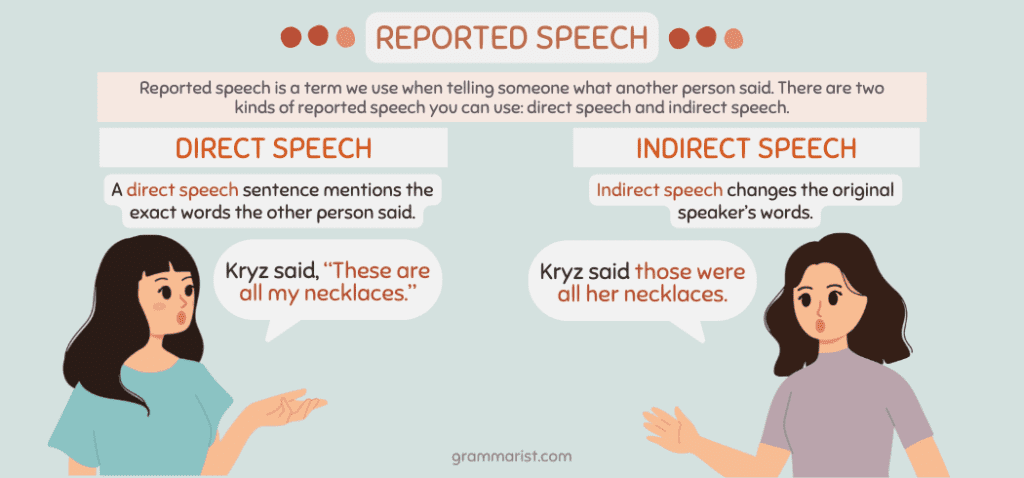
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals
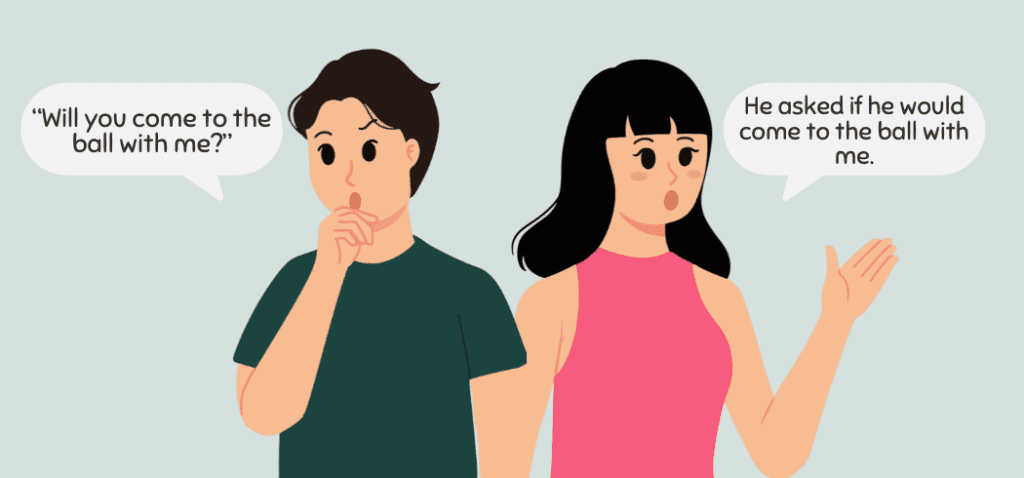

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
Direct and Indirect Speech: Useful Rules and Examples
Are you having trouble understanding the difference between direct and indirect speech? Direct speech is when you quote someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. This can be a tricky concept to grasp, but with a little practice, you’ll be able to use both forms of speech with ease.

Direct and Indirect Speech
When someone speaks, we can report what they said in two ways: direct speech and indirect speech. Direct speech is when we quote the exact words that were spoken, while indirect speech is when we report what was said without using the speaker’s exact words. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I love pizza,” said John. Indirect speech: John said that he loved pizza.
Using direct speech can make your writing more engaging and can help to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion. However, indirect speech can be useful when you want to summarize what someone said or when you don’t have the exact words that were spoken.
To change direct speech to indirect speech, you need to follow some rules. Firstly, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb. Secondly, you need to change the pronouns and adverbs in the reported speech to match the new speaker. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will go to the park,” said Sarah. Indirect speech: Sarah said that she would go to the park.
It’s important to note that when you use indirect speech, you need to use reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked” to indicate who is speaking. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is it?” asked Tom. Indirect speech: Tom asked what time it was.
In summary, understanding direct and indirect speech is crucial for effective communication and writing. Direct speech can be used to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion, while indirect speech can be useful when summarizing what someone said. By following the rules for changing direct speech to indirect speech, you can accurately report what was said while maintaining clarity and readability in your writing.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech
When it comes to reporting speech, there are two ways to go about it: direct and indirect speech. Direct speech is when you report someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. Here are some of the key differences between direct and indirect speech:
Change of Pronouns
In direct speech, the pronouns used are those of the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the pronouns have to be changed to reflect the perspective of the reporter. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John.
- Indirect speech: John said he was going to the store.
In the above example, the pronoun “I” changes to “he” in indirect speech.
Change of Tenses
Another major difference between direct and indirect speech is the change of tenses. In direct speech, the verb tense used is the same as that used by the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the verb tense may change depending on the context. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am studying for my exams,” said Sarah.
- Indirect speech: Sarah said she was studying for her exams.
In the above example, the present continuous tense “am studying” changes to the past continuous tense “was studying” in indirect speech.
Change of Time and Place References
When reporting indirect speech, the time and place references may also change. For example:
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” said Tom.
- Indirect speech: Tom said he would meet you at the park the next day.
In the above example, “tomorrow” changes to “the next day” in indirect speech.
Overall, it is important to understand the differences between direct and indirect speech to report speech accurately and effectively. By following the rules of direct and indirect speech, you can convey the intended message of the original speaker.
Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
When you need to report what someone said in your own words, you can use indirect speech. To convert direct speech into indirect speech, you need to follow a few rules.
Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks
The first step is to remove the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. This is because indirect speech does not use the exact words of the speaker.
Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker
To indicate that you are reporting what someone said, you need to use a reporting verb such as “said,” “asked,” “told,” or “exclaimed.” You also need to use a linker such as “that” or “whether” to connect the reporting verb to the reported speech.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I love ice cream,” said Mary.
- Indirect speech: Mary said that she loved ice cream.
Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb
When you use indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb.
- Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store.
Step 4: Change the Pronouns
You also need to change the pronouns in the reported speech to match the subject of the reporting verb.
- Direct speech: “Are you busy now?” Tina asked me.
- Indirect speech: Tina asked whether I was busy then.
By following these rules, you can convert direct speech into indirect speech and report what someone said in your own words.
Converting Indirect Speech Into Direct Speech
Converting indirect speech into direct speech involves changing the reported speech to its original form as spoken by the speaker. Here are the steps to follow when converting indirect speech into direct speech:
- Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb used in the indirect speech. This will help you determine the tense of the direct speech.
- Change the pronouns: The next step is to change the pronouns in the indirect speech to match the person speaking in the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “She said that she was going to the store,” the direct speech would be “I am going to the store,” if you are the person speaking.
- Change the tense: Change the tense of the verbs in the indirect speech to match the tense of the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “He said that he would visit tomorrow,” the direct speech would be “He says he will visit tomorrow.”
- Remove the reporting verb and conjunction: In direct speech, there is no need for a reporting verb or conjunction. Simply remove them from the indirect speech to get the direct speech.
Here is an example to illustrate the process:
Indirect Speech: John said that he was tired and wanted to go home.
Direct Speech: “I am tired and want to go home,” John said.
By following these steps, you can easily convert indirect speech into direct speech.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and indirect speech are two ways to report what someone has said. Direct speech reports the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech reports the meaning of what was said. Here are some examples of both types of speech:
Direct Speech Examples
Direct speech is used when you want to report the exact words spoken by someone. It is usually enclosed in quotation marks and is often used in dialogue.
- “I am going to the store,” said Sarah.
- “It’s a beautiful day,” exclaimed John.
- “Please turn off the lights,” Mom told me.
- “I will meet you at the library,” said Tom.
- “We are going to the beach tomorrow,” announced Mary.
Indirect Speech Examples
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, is used to report what someone said without using their exact words. It is often used in news reports, academic writing, and in situations where you want to paraphrase what someone said.
Here are some examples of indirect speech:
- Sarah said that she was going to the store.
- John exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
- Mom told me to turn off the lights.
- Tom said that he would meet me at the library.
- Mary announced that they were going to the beach tomorrow.
In indirect speech, the verb tense may change to reflect the time of the reported speech. For example, “I am going to the store” becomes “Sarah said that she was going to the store.” Additionally, the pronouns and possessive adjectives may also change to reflect the speaker and the person being spoken about.
Overall, both direct and indirect speech are important tools for reporting what someone has said. By using these techniques, you can accurately convey the meaning of what was said while also adding your own interpretation and analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech refer to the ways in which we communicate what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, using quotation marks to indicate that you are quoting someone. Indirect speech, on the other hand, involves reporting what someone has said without using their exact words.
How do you convert direct speech to indirect speech?
To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb, such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.” For example, “I love ice cream,” said Mary (direct speech) can be converted to “Mary said that she loved ice cream” (indirect speech).
What is the difference between direct speech and indirect speech?
The main difference between direct speech and indirect speech is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. Direct speech is usually enclosed in quotation marks, while indirect speech is not.
What are some examples of direct and indirect speech?
Some examples of direct speech include “I am going to the store,” said John and “I love pizza,” exclaimed Sarah. Some examples of indirect speech include John said that he was going to the store and Sarah exclaimed that she loved pizza .
What are the rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech?
The rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech include changing the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb and use appropriate reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.”
What is a summary of direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions and introduce a reporting verb.
You might also like:
- List of Adjectives
- Predicate Adjective
- Superlative Adjectives
Related Posts:

This website is AMNAZING
MY NAAMEE IS KISHU AND I WANTED TO TELL THERE ARE NO EXERCISES AVAILLABLEE BY YOUR WEBSITE PLEASE ADD THEM SSOON FOR OUR STUDENTS CONVIENCE IM A EIGHT GRADER LOVED YOUR EXPLABATIO
sure cries l miss my friend
Reported Speech – Free Exercise
Write the following sentences in indirect speech. Pay attention to backshift and the changes to pronouns, time, and place.
- Two weeks ago, he said, “I visited this museum last week.” → Two weeks ago, he said that . I → he|simple past → past perfect|this → that|last …→ the … before
- She claimed, “I am the best for this job.” → She claimed that . I → she|simple present→ simple past|this→ that
- Last year, the minister said, “The crisis will be overcome next year.” → Last year, the minister said that . will → would|next …→ the following …
- My riding teacher said, “Nobody has ever fallen off a horse here.” → My riding teacher said that . present perfect → past perfect|here→ there
- Last month, the boss explained, “None of my co-workers has to work overtime now.” → Last month, the boss explained that . my → his/her|simple present→ simple past|now→ then
Rewrite the question sentences in indirect speech.
- She asked, “What did he say?” → She asked . The subject comes directly after the question word.|simple past → past perfect
- He asked her, “Do you want to dance?” → He asked her . The subject comes directly after whether/if |you → she|simple present → simple past
- I asked him, “How old are you?” → I asked him . The subject comes directly after the question word + the corresponding adjective (how old)|you→ he|simple present → simple past
- The tourists asked me, “Can you show us the way?” → The tourists asked me . The subject comes directly after whether/if |you→ I|us→ them
- The shop assistant asked the woman, “Which jacket have you already tried on?” → The shop assistant asked the woman . The subject comes directly after the question word|you→ she|present perfect → past perfect
Rewrite the demands/requests in indirect speech.
- The passenger requested the taxi driver, “Stop the car.” → The passenger requested the taxi driver . to + same wording as in direct speech
- The mother told her son, “Don’t be so loud.” → The mother told her son . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don’t
- The policeman told us, “Please keep moving.” → The policeman told us . to + same wording as in direct speech ( please can be left off)
- She told me, “Don’t worry.” → She told me . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don’t
- The zookeeper told the children, “Don’t feed the animals.” → The zookeeper told the children . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don’t
How good is your English?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later

Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
English Grammar Here
20 sentences of direct and indirect speech

Direct speech is the ones that the person establishes himself / herself. Usually used in writing language such as novels, stories etc.
Transferring the sentence that someone else says is called indirect speech . It is also called reported speech . Usually, it is used in spoken language . If the transmitted action is done in the past, the sentence becomes the past tense.
Here are 20 examples of direct and indirect speech;
1. Direct : My boyfriend asked, “Do you like horror films?” Indirect : Do you like horror films? my boyfriend asked.
3. Direct : She said, “I might come early.” Indirect : She said she might come early.
4. Direct : I am leaving home now.” Indirect : He said that he left home then.
5. Direct : Are you living here? Indirect : He asked me if I was living here.
6. Direct : I’m going to come. Indirect : She said that she was going to come.
7. Direct : We can communicate smoothly. Indirect : They said that they could communicate smothly.
8. Direct : My mother isn’t very well. Indirect : She said that her mother wasn’t very well.
9. Direct : I need help with my work. Indirect : George said “I need help with my homework.”
10. Direct : I was walking along the Street. Indirect : He said he had been walking along the Street.
11. Direct : I haven’t seen George recently. Indirect : She said that she hadn’t seen George recently.
12. Direct : I would help, but… Indirect : He said he would help but…
13. Direct : I’m waiting for Michael, she said. Indirect : She said (that) she was waiting for Michael”.
14. Direct : They said, “They have taken exercise.” Indirect : They said that they had taken exercise.
15. Direct : I can speak perfect Spanish. Indirect : He said he could speak perfect Spanish.
17. Direct : What is your name? she asked me. Indirect : She asked me what my name was.
18. Direct : I was sleeping when Mary called. Indirect : He said that he had been sleeping when Mary called.
19. Direct : Please help me! Indirect : He asked me to help his.
20. Direct : I have been to France, she told me. Indirect : She told me that she had been to France.
Related Posts

Using Thus in English, Example Sentences with Thus

All English Tenses Example Sentences VIDEOS

Using Until in English, Example Sentences with Until
About the author.
Easy Insightful Literature Notes
Transformation of Sentence: Direct & Indirect Speech
A direct speech can be transformed into an indirect speech and vice versa using a suitable reporting verb and a linker depending on the sentence. Let’s have an example first.
- Tina said to me, “Are you busy now?” [direct speech]
- Tina asked me whether I was busy then. [indirect speech]
Direct Speech
Indirect Speech
- Look, if the reporting verb in direct speech (said) is in past tense, the reporting verb in indirect speech (asked) would also be in past tense. ‘Whether’ is the linker added here as it is a ‘yes-no’ type question (Refer to list 1 below).
- ‘Are’ changes to ‘was’. As the reporting verb was in past tense, the verb in the reported speech will also be in past. (Refer to list 2 below)
- ‘Now’ has become ‘then’. Time and place expressions change if the reporting verb is in past tense. (Refer to list 3 below)
- The question mark (?) has changed to a full stop(.).
- Another important thing, the format of question (v + s + o) has changed to the format of a statement (s + v + o). In indirect speech the pattern always comes to subject + verb + object.
List of Reporting verbs and linkers (list 1)
Verbs of Reported speech (if the reporting verb is in past tense) (list 2) Direct speech → Indirect speech Am / is / are → was / were Was / were → had been Has / have → had Had → had had Shall / will → would Can → could May → might Must, should → must, should Verb1 → verb2 Verb2 → had + verb3
Change of time and place expressions in past tense (list 3) now → then ago → before today → that day yesterday → the previous day tomorrow → the next day last night → the previous night here → there this → that these → those
Narration change of Assertive sentence
- Robin said, “I went to Delhi yesterday.” – Robin said that he had gone to Delhi the previous day .
- She said to her husband, “I want to go with you.” – She told her husband that she wanted to go with him.
Narration change of Interrogative sentence
- He said to me, “Do you know English?” – He asked me whether I knew English.
- She said to me, “Did you go there?” – She wanted to know whether I had gone there.
- I said to him, “What are you doing?” – I asked him what he was doing.
- Rahul said to his mother, “How do you do all these things together?” – Rahul asked his mother how she did all those things together.
Narration change of Imperative sentence
- He said to me, “Go there right now.” – He ordered me to go there right then.
- My teacher said to me, “Obey your parents.” – My teacher asked me to obey my parents.
- She said to me, “Please don’t go there.” – She requested me not to go there.
- He said to her, “Let’s go home.” – He suggested her that they should go home.
- His mother said, “Let him eat whatever he likes.” – His mother suggested that he might be allowed to eat whatever he liked.
Narration change of Optative sentence
- He said to the boy, “May god bless you.” – He prayed that God might bless the boy.
- The girl said, “Had I the wings of a dove.” – The girl wished that she had the wings of a dove.
Narration change of Exclamatory sentence
- “How happy we are here!” said the children. – The children exclaimed in joy that they were very happy there.
- The children said, “How happy we were there!” – The children exclaimed in sorrow that they had been very happy there.
- He said to me, “Good bye!” – He bade me good bye.
- She said to me, “Good evening!”—She wished me good evening.
Narration change of Vocatives
- Teacher said, “ Robin , stand up.” – Teacher asked Robin to stand up.
- The Bishop said to the convict, “Always remember, my son , that the poor body is the temple of the living God.” – The Bishop addressed the convict as his son and advised him to always remember that the poor body is the temple of the living God.
Narration change of question tag
- He said to me, “You went to Kolkata, didn’t you?” – He asked me whether I had gone to Kolkata and assumed that I had.
- I said to him, “Tina didn’t tell a lie, did she?” – I asked him if Tina had told a lie and assumed that she had not.
We serve cookies on this site to offer, protect and improve our services. KNOW MORE OK

English Study Here
100 examples of direct and indirect speech.
100 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech in English, 100 Examples of reported speech in english;
Related Posts

50 Ways to Avoid Using the Word VERY
Transition Words & Phrases Agreement – Addition – Similarity

Phrasal Verbs With SET
About the author.
- Athabasca University
- English Grammar Handbook
- Concise ESL Support
Direct and indirect speech
- Write Site - Home
- Staff and contact info
- Write Site dropbox
- RealTime writing coaching
- Writing forum
- Webinar schedule
- Lessons and videos
- Basic grammar: Parts of speech
- Words often confused and misused
- Recognition of sentence parts
- Transitional devices
- Common sentence errors
- Punctuation
- Word mechanics
- Vocabulary and spelling
- Introduction
- Conditional and hypothetical constructions
- Infinitives and gerunds
- Irregular verbs
- Modals and related expressions
- Passive verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Prepositions
- Pronunciation
- Verb tenses
- Supplementary resources
- Critical thinking, reading and writing
- The writing process
- Research writing
- Writing in the disciplines
- Genres common to academic writing
- Argumentative essay
- Argumentation structure
- Expository writing
- Analytical film review process
- Conducting and writing up interviews
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Library basics
- Studying writing at AU
- Writing resources
- Writing courses
- Assess your writing and language skills
- Marking guide for writing assignments
When using indirect or reported speech, the form changes. Usually indirect speech is introduced by the verb said , as in I said , Bill said , or they said . Using the verb say in this tense, indicates that something was said in the past. In these cases, the main verb in the reported sentence is put in the past. If the main verb is already in a past tense, then the tense changes to another past tense; it can almost be seen as moving even further into the past.
Verb tense changes also characterize other situations using indirect speech. Note the changes shown in the chart and see the table below for examples. With indirect speech, the use of that is optional.
The situation changes if instead of the common said another part of the very to say is used. In that case the verb tenses usually remain the same. Some examples of this situation are given below.
Another situation is the one in which modal constructions are used. If the verb said is used, then the form of the modal, or another modal that has a past meaning is used.
While not all the possibilities have been listed here, there are enough to provide examples of the main rules governing the use of indirect or reported speech. For other situations, try to extrapolate from the examples here, or better still, refer to a good grammar text or reference book.
Some other verbs that can be used to introduce direct speech are ask, report, tell, announce, suggest, and inquire. They are not used interchangeably; check a grammar or usage book for further information.
Updated September 11, 2023 by Digital & Web Operations, University Relations ( [email protected] )
- Phrases and Clauses
- Parts of a Sentence
- Modal Verbs
- Relative Clauses
- Confusing Words
- Online Grammar Quizzes
- Printable Grammar Worksheets
- Courses to purchase
- Grammar Book
- Grammar Blog
- Direct & Indirect Speech
Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and indirect speech grammar rules vary so you need to understand them. We'll start by looking at what each one is. Note that indirect speech is also commonly knows as reported speech.
Definition of Direct Speech
Direct speech is when the words are given in exactly the way that the speaker said them. So in other words they are quoted with no change .
When presenting direct speech, the words are usually placed in quotation marks, with a comma after say(s) / said if it is used to present the speech. Say (s) / said can also be placed at the end of the quotation, in which case a comma comes before it.
Examples of Direct Speech:
- He said, "Don't take the car without asking me".
- John says, "I will help you with your work".
- "We are prepared to revise the law if we can", they said.
- The teacher said, "You must wear the proper uniform".
Definition of Indirect Speech
Indirect speech is also known as reported speech . You may also see it referred to as indirect discourse or indirect narration .
Indirect speech is the reporting of what someone else said in your own words but without changing the meaning of what was said.
Reporting verbs are used to present indirect speech. The common ones are:
- say(s)/said (that)
- told me (that)
That is in brackets as it can be omitted from the sentence, whether spoken or written.

Examples of Indirect Speech:
- He said (that) he would definitely buy it.
- Sheila told me (that) I had to come back in the afternoon.
- The council said (that) they will try and clear the rubbish.
- She told me (that) she was feeling unwell.
So the key difference between direct and indirect speech is that with direct speech the exact words are quoted but in indirect speech it is your own words .
Direct speech is fairly simple to use and understand as it involves just repeating what was said. There is not much to get confused about with the grammar, apart from getting say(s)/said correct.
But indirect or reported speech is more difficult so we will look at that in more detail now.
View more examples of direct and indirect speech >>
Direct and Indirect Speech Conversion
With direct and indirect speech, there are three main things you need to be aware of when converting one to the other:
- Changes in Tense
- Changes in Person and Pronouns
- Changes in Time Phrases
Changing Tenses
The tense of verbs when moving from direct to indirect speech do not necessarily change because if the circumstances of what someone said is the same, then it may be reported as that. For example:
- "I am feeling tired" (= Direct Speech )
- Present Continuous
- She said she is feeling tired (= Indirect Speech )
However, as we are reporting what was said in the past, we often change the tense. This rule for this is related to backshifting, which means shifting back a tense. So the present will go back to the past. Some modals also change.
Here are examples using the previous examples of indirect speech, showing you how they look like in direct speech:
Direct Speech
- "I want to meet you later".
- "You have to come back in the afternoon"
- "We like it a lot"
- "I have been mowing the lawn"
Indirect Speech
- He said he wanted to meet me later.
- Sheila told me I had to come back in the afternoon.
- They said they liked it a lot.
- He said he had been mowing the lawn.
There are more details on the site about changing tenses in indirect / reported speech:
Learn more about changing tenses >>
Changing Pronouns
Pronouns in indirect speech also need to be changed from what they were in the indirect speech, as well as of course adapting the first pronoun to fit the person who said the statement:
- " I want to meet you later".
- " You have to come back in the afternoon"
- " We like it a lot"
- " I have been walking with my wife"
- He said he had been walking with his wife.
Changing Time Phrases
You may also need to change phrases referring to time, though this depends on the context and when you are reporting the speech.
With these examples you have to assume the speech is being reported at a time in the future so the phrases such as 'yesterday' or 'tomorrow' would not makes sense any more in terms of the reported speech.
- She said, "I saw her yesterday ".
- He said, "He will bring the book tomorrow ".
- She said, "I'm going to London today ".
- He said, "We need your assistance now ".
- She said that she had seen her the day before .
- He said that he would bring the book the next day .
- She said she was going to London that day .
- He said they needed my assistance then .
Imperatives
Some different rules apply when turning direct speech using imperatives or commands into indirect speech. Check out the rules here:
Rules for Reported Speech Imperatives >>
More on Reported Speech:

Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
In these examples of direct and indirect speech you are given a sentence in direct speech which is then connected to indirect speech.

Reported Speech Imperatives: Reporting commands in indirect speech
Reported speech imperatives, also known as reported commands, follow a slightly different structure to normal indirect speech. We use imperatives to give orders, advice, or make requests.

Reported Speech Tenses Chart: How to convert tenses
Reported speech tenses may differ from the tense of the direct speech. The general rule for tenses in reported speech is that it changes to the past tense. This is called backshifting.

Reported Speech Quiz - Practice forming indirect speech
This reported speech quiz gives you the chance to practice converting direct speech to reported speech, also known as indirect speech. This involves backshifting with the tenses.
Sign up for free grammar tips, quizzes and lessons, straight into your inbox
New! Comments
Any questions or comments about the grammar discussed on this page?
Post your comment here.

Grammar Rules
Subscribe to grammar wiz:, grammar ebook.

This is an affiliate link
Recent Articles
Modal Verbs of Request
May 18, 24 05:08 AM
Basic Rules of Punctuation in English
May 11, 24 12:42 PM
Modal Verbs of Permission: May, Can, & Could
May 06, 24 10:24 AM
Important Pages
Online Quizzes Grammar Lessons Courses Blog
Connect with Us
Search Site
Privacy Policy / Disclaimer / Terms of Use
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Direct and Indirect Speech: The Ultimate Guide
Direct and Indirect Speech are the two ways of reporting what someone said. The use of both direct and indirect speech is crucial in effective communication and writing. Understanding the basics of direct and indirect speech is important, but mastering the advanced techniques of these two forms of speech can take your writing to the next level. In this article, we will explore direct and indirect speech in detail and provide you with a comprehensive guide that covers everything you need to know.
Table of Contents
What is Direct Speech?
Direct speech is a way of reporting what someone said using their exact words. Direct speech is typically enclosed in quotation marks to distinguish it from the writer’s own words. Here are some examples of direct speech:
- “I am going to the store,” said John.
- “I love ice cream,” exclaimed Mary.
- “The weather is beautiful today,” said Sarah.
In direct speech, the exact words spoken by the speaker are used, and the tense and pronouns used in the quote are maintained. Punctuation is also important in direct speech. Commas are used to separate the quote from the reporting verb, and full stops, question marks, or exclamation marks are used at the end of the quote, depending on the tone of the statement.
What is Indirect Speech?
Indirect speech is a way of reporting what someone said using a paraphrased version of their words. In indirect speech, the writer rephrases the speaker’s words and incorporates them into the sentence. Here are some examples of indirect speech:
- John said that he was going to the store.
- Mary exclaimed that she loved ice cream.
- Sarah said that the weather was beautiful that day.
In indirect speech, the tense and pronouns may change, depending on the context of the sentence. Indirect speech is not enclosed in quotation marks, and the use of reporting verbs is important.
Differences Between Direct and Indirect Speech
The structure of direct and indirect speech is different. Direct speech is presented in quotation marks, whereas indirect speech is incorporated into the sentence without quotation marks. The tenses and pronouns used in direct and indirect speech also differ. In direct speech, the tense and pronouns used in the quote are maintained, whereas, in indirect speech, they may change depending on the context of the sentence. Reporting verbs are also used differently in direct and indirect speech. In direct speech, they are used to introduce the quote, while in indirect speech, they are used to report what was said.
How to Convert Direct Speech to Indirect Speech
Converting direct speech to indirect speech involves changing the tense, pronouns, and reporting verb. Here are the steps involved in converting direct speech to indirect speech:
- Remove the quotation marks.
- Use a reporting verb to introduce the indirect speech.
- Change the tense of the verb in the quote if necessary.
- Change the pronouns if necessary.
- Use the appropriate conjunction if necessary.
Here is an example of converting direct speech to indirect speech:
Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John. Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store.
How to Convert Indirect Speech to Direct Speech
Converting indirect speech to direct speech involves using the same tense, pronouns, and reporting verb as the original quote. Here are the steps involved in converting indirect speech to direct speech:
- Remove the reporting verb.
- Use quotation marks to enclose the direct speech.
- Maintain the tense of the verb in the quote.
- Use the same pronouns as the original quote.
Here is an example of converting indirect speech to direct speech:
Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store. Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John.
Advanced Techniques for Using Direct and Indirect Speech
Using direct and indirect speech effectively can add depth and complexity to your writing. Here are some advanced techniques for using direct and indirect speech:
Blending Direct and Indirect Speech
Blending direct and indirect speech involves using both forms of speech in a single sentence or paragraph. This technique can create a more engaging and realistic narrative. Here is an example:
“Sarah said, ‘I can’t believe it’s already winter.’ Her friend replied that she loved the cold weather and was excited about the snowboarding season.”
In this example, direct speech is used to convey Sarah’s words, and indirect speech is used to convey her friend’s response.
Using Reported Questions
Reported questions are a form of indirect speech that convey a question someone asked without using quotation marks. Reported questions often use reporting verbs like “asked” or “wondered.” Here is an example:
“John asked if I had seen the movie last night.”
In this example, the question “Have you seen the movie last night?” is reported indirectly without using quotation marks.
Using Direct Speech to Convey Emotion
Direct speech can be used to convey emotion more effectively than indirect speech. When using direct speech to convey emotion, it’s important to choose the right tone and emphasis. Here is an example:
“She screamed, ‘I hate you!’ as she slammed the door.”
In this example, the use of direct speech and the exclamation mark convey the intense emotion of the moment.
- When should I use direct speech?
- Direct speech should be used when you want to report what someone said using their exact words. Direct speech is appropriate when you want to convey the speaker’s tone, emphasis, and emotion.
- When should I use indirect speech?
- Indirect speech should be used when you want to report what someone said using a paraphrased version of their words. Indirect speech is appropriate when you want to provide information without conveying the speaker’s tone, emphasis, or emotion.
- What are some common reporting verbs?
- Some common reporting verbs include “said,” “asked,” “exclaimed,” “whispered,” “wondered,” and “suggested.”
Direct and indirect speech are important tools for effective communication and writing. Understanding the differences between these two forms of speech and knowing how to use them effectively can take your writing to the next level. By using advanced techniques like blending direct and indirect speech and using direct speech to convey emotion, you can create engaging and realistic narratives that resonate with your readers.
Related Posts
What is WH Question Words? Definition and Examples
Active Passive Voice: Difference, Usage, and Examples
14 Punctuation Marks With Examples
What Is The Parts of Speech? Definitions, Types & Examples
Rules Articles: a, an, the With Examples
List of Contractions in English With Examples
Add comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
While using English, we use direct and indirect speeches quite often. If a sentence is expressed exactly as it came out of the mouth of the person who said it, it becomes a direct speech. However Indirect Speech (also called reported speech) refers to transmitting a sentence that someone has said. It is often used in daily language. For example ...
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Direct: "I will help you," she promised. Reported: She promised that she would help me. Direct: "You should study harder," he advised. Reported: He advised that I should study harder. Direct: "I didn't take your book," he denied. Reported: He denied taking my book. Direct: "Let's go to the cinema," she suggested.
Indirect: He inquired how I was. 9. Direct: "I will help you," she promised. Indirect: She promised that she would help me. 10. Direct: "I didn't see him yesterday," Tom confessed. Indirect: Tom confessed that he hadn't seen him the day before. 11. Direct: "I am going to the market," Alex said.
In nonfiction writing or journalism, direct speech can emphasize a particular point, by using a source's exact words. Indirect speech is paraphrasing what someone said or wrote. In writing, it functions to move a piece along by boiling down points that an interview source made. Unlike direct speech, indirect speech is not usually placed inside ...
Introduction. In English grammar, we use reported speech to say what another person has said. We can use their exact words with quotation marks, this is known as direct speech, or we can use indirect speech. In indirect speech, we change the tense and pronouns to show that some time has passed. Indirect speech is often introduced by a reporting ...
You can do this while speaking or writing. There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I'll break each down for you. A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example: Kryz said, "These are all my necklaces.". Indirect speech changes the original speaker's words.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech. Change of Pronouns. Change of Tenses. Change of Time and Place References. Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech. Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks. Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker. Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb. Step 4: Change the Pronouns.
Rewrite the demands/requests in indirect speech. The passenger requested the taxi driver, "Stop the car.". → The passenger requested the taxi driver . to + same wording as in direct speech. The mother told her son, "Don't be so loud.". → The mother told her son . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don't.
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
Direct speech is the ones that the person establishes himself / herself.Usually used in writing language such as novels, stories etc. Transferring the sentence that someone else says is called indirect speech.It is also called reported speech.Usually, it is used in spoken language.If the transmitted action is done in the past, the sentence becomes the past tense.
What is indirect speech or reported speech? When we tell people what another person said or thought, we often use reported speech or indirect speech. To do that, we need to change verb tenses (present, past, etc.) and pronouns (I, you, my, your, etc.) if the time and speaker are different.For example, present tenses become past, I becomes he or she, and my becomes his or her, etc.
A direct speech can be transformed into an indirect speech and vice versa using a suitable reporting verb and a linker depending on the sentence. Let's have an example first. Tina said to me, "Are you busy now?" [direct speech] Tina asked me whether I was busy then. [indirect speech] Direct Speech. Speaker. Reporting verb. Direct speech ...
Indirect: She says that she is ill. 2: Direct: I will study", Mary said. Indirect: I will study", said Mary. 3: Direct: She said; "The exam is difficult. Indirect: She said the test was difficult. 4: Direct: I bought a car. Indirect: He said he bought a car. 5: Direct: My parents are very well. Indirect: Alex said that his parents were ...
When using indirect or reported speech, the form changes. Usually indirect speech is introduced by the verb said, as in I said, Bill said, or they said. Using the verb say in this tense, indicates that something was said in the past. In these cases, the main verb in the reported sentence is put in the past. If the main verb is already in a past ...
So the key difference between direct and indirect speech is that with direct speech the exact words are quoted but in indirect speech it is your own words . Direct speech is fairly simple to use and understand as it involves just repeating what was said. There is not much to get confused about with the grammar, apart from getting say (s)/said ...
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
Here is an example of converting indirect speech to direct speech: Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store. Direct speech: "I am going to the store," said John. Advanced Techniques for Using Direct and Indirect Speech. Using direct and indirect speech effectively can add depth and complexity to your writing.
Now consider the different grammatical aspects of both. Reporting Speech: The first part of the direct speech is called reporting speech (she says). Reported Speech: The second part of the sentence, which is enclosed in inverted commas or quotation marks, is called reported speech (I am a little bit nervous). Reporting Verb: The verb of the reporting speech is called the reporting verb (says).
Indirect speech. In linguistics, speech or indirect discourse is a grammatical mechanism for reporting the content of another utterance without directly quoting it. For example, the English sentence Jill said she was coming is indirect discourse while Jill said "I'm coming" would be direct discourse. In fiction, the "utterance" might amount to ...
The 4 Rs of paraphrasing. According to the Virtual Library, here are four steps to paraphrase: Reword the text by using synonyms or different parts of speech; change verb tense or change active verbs to passive and vice versa. Rearrange by moving words to make new sentences or reorganize the sentences in a passage.