- Resume Writing
- Resume Examples
- Cover Letter
- Remote Work
- Famous Resumes
- Try Kickresume

Cover Letter for PhD Application: Guide for Writing One & Example From a Real PhD Student
- Klara Cervenanska ,
- Updated March 27, 2023 9 min read
When applying for a PhD research position, you usually need to submit certain documents, including an academic CV and a cover letter for PhD application .
A PhD cover letter, also referred to as an academic cover letter, should be carefully crafted, well-formatted, and contain specific sections.
We'll show you how to do exactly that, along with a sample of an academic cover letter from a real person admitted to a PhD program at Lyon University in France.
And if you're not sure how to go about writing your PhD CV, check out this article: CV for PhD Application: How to Write One Like a True Scholar (+CV Example) .
Table of Contents
Click on a section to skip
What is an academic cover letter?
What to include in a cover letter for phd application, how to write a cover letter for phd application, how to format an academic cover letter, phd cover letter sample.
An academic cover letter is a document that PhD candidates submit alongside their academic CV when applying for a PhD.
Essentially, it's a cover letter for a PhD application.
It's not exactly the same as your regular business cover letter. Nor is it the same as a personal statement or a motivation letter .
The purpose of a cover letter for PhD application is to explain to the reader, who's likely a researcher or a professor, what you can contribute to their institution and/or field.
Moreover, in a PhD application cover letter, you should explain why you're a good match for the research position on the program.
Differences between academic cover letter and business cover letter
Both these documents serve different purposes and people use them in different settings:
- Academic cover letter is used when applying for positions in academia — most often for a PhD. More emphasis should be on education, research background and scholarly accomplishments. Moreover, it should explain what your contribution to the institution or field could be. It should also point the reader to your academic CV.
- Regular (business) cover letter is normally used when applying for any kind of job . Hence, more emphasis should be on skills and past experience while being tailored to a specific job position. You should also explain why you're a good fit for the position at the given company. It should point the reader to your resume.
There are also other documents people often mistake for an academic cover letter. These include:
- Motivation letter is especially relevant for fresh graduates when applying to a university, a non-profit organization, or voluntary work. A motivation letter focuses more on your interests and motives for applying.
- Personal statement. Also used in an academic setting. It's always written by an applicant, often a prospective student, applying to college, university, or graduate school. You explain why you've chosen a particular course and why you'd be good at it. Other names include a statement of purpose or a letter of intent .
Like every cover letter, an academic one also needs to include specific elements and content sections. These are:
- Header. Here, provide your contact information, such as your name, address, phone number, and email in the header of the document.
- Formal salutation. In an official letter like this one, you should address the reader in a professional and formal way. If you know who'll be reading your cover letter, go with Dear Dr. [Surname] or Dear Professor [Surname] . If you don't, go with Dear Sir/Madam .
- The specific PhD program or position. Clearly state in your letter which research position you're applying for or the name of the PhD program. A cover letter is usually read before a CV, so you need to make sure everything is clear.
- Your motivation. Explain why you're interested in the specific PhD position — it's one of the key elements you should include.
- Your academic background. Now, we don't mean you should list in detail every single university course you ever took. Instead, focus on the most relevant course for the PhD and describe in detail what you learned, any projects you worked on, why it was interesting (and optionally, what knowledge gap you identified). In this way, you also show a certain level of understanding of the field.
- Your ambition. Briefly mention what your ambitions, intentions, and plans are regarding your contribution to the field when securing your PhD position. How is your research going to enrich the field? How will the institution benefit from it?
- Conclusion. Keep the conclusion short. Contrary to a regular cover letter ending , there's no place for reiterating everything here. Simply thank the reader for your consideration and prompt them to read your academic CV.
- Formal sign-off. Just pick from the usual: Sincerely, Respectfully, Regards... Then throw in your full name in the following line.
And that's all you need to include!
Now, let's take a look at how to write your cover letter step-by-step.
Applying for a PhD will be a lot less stressful if you follow these tips on how to write a cover letter for a research position:
Consider researching the background of the organization, department, ongoing research projects, and their past and current projects. All that before you start writing your cover letter. Knowing these things will help you tailor your letter to the specific PhD opening.
Before you actually start writing, try to sit down and take a moment to think first. Assess how your past experiences helped you prepare for the PhD position and scribble down those that are most relevant and significant for the specific program. These include any research experiences, research projects, courses, or internships.
In the first few sentences of your letter, you need to convey some basic information about yourself and what specific position you're applying for. The opening should also state firmly why you're a strong candidate for the position/program, by using a persuasive and convincing wording. Here's an example: "As an MChem Chemistry graduate with a narrow focus on the sustainable synthesis of biologically active molecules from the University of Dundee, I am excited to apply to a "Synthesis Of Small Molecule Inhibitors Using Enzymes" PhD programme at an institution with such a strong foundation and numerous research groups in this field."
This is the place where you may explore more extensively on the educational journey that brought you here. Set the foundation for demonstrating how your Master's degree and research experience seamlessly translate into the next phase — the PhD program. Emphasize how your thesis contributes to the field's body of knowledge. Mention any other publications that support your thesis. And, if you can, identify any knowledge gaps or topics that can be explored further.
This paragraph provides the opportunity to neatly tie in together everything the reader has learned about you so far. You can show how your previous experience, coupled with what you'll learn during the PhD program, will come together to produce something novel to enrich the field. First, identify the courses or topics within the PhD program that interest you the most and how they relate to you developing your research further. Second, introduce your future research aspirations and goals. Third, point out how this future work will enrich the field and what will the intellectual merit be.
When ending your PhD cover letter, briefly refer your reader to your academic CV and encourage them to examine all of the remaining projects, courses, publications, or references . Finally, thank the reader for their time and consideration and let them know you look forward to hearing from them. Sign off.
Put the letter in a drawer and don't think about it for a day or two. Then, when you read it again, you'll have a fresh pair of eyes to see the cover letter in a new light. Maybe you decide some things are redundant, or you think of something that's more relevant. Or you know, find a typo here and there.
Just like an academic cover letter needs to contain certain content components, the formatting should also align with the structural expectations for this type of document.
How long should a cover letter be? How to finish a cover letter? And what about the cover letter font and spacing?
Here's a recommended academic cover letter format:
- Length. While STEM PhD candidates should aim for half a page to one page, humanities candidates can do 1–2 pages.
- Font. Use one of the classics: Times New Roman, Calibri, or Arial. Just no Comic Sans, we beg you. Keep the size between 10–12 points. Also remember to keep the text clean — no underlining, no bolding, and no color. However, you can use italics if appropriate.
- Spacing. Cover letter spacing isn't complicated. Just single-space your text, make sure there's a space between each paragraph, and leave a space between the concluding paragraph and your formal sign-off.
- Margins. The only rule here is that the margins on your cover letter should match those on your CV.
- Consistence with your CV. Your academic cover letter should match your academic CV in all formatting aspects — including the cover letter font and spacing. For example, Kickresume lets you choose a matching template for your CV and your cover letter, so no need to worry about this.
If the institution provided any instructions for formatting your academic cover letter, don’t get creative and follow their guidelines.
Finally, to help you tie everything we talked about together, here's a cover letter sample from a real person admitted to a PhD program at Lyon University in France.
These things ensured Herrera's cover letter was successful:
- She clearly states her motivation in the opening. In the first two paragraphs, Herrera introduces herself and her motivation to apply for the given PhD program.
- She describes educational and research background thoroughly. The main body of the letter is dedicated to describing Herrera's educational background, research projects, internships, and skills acquired throughout the way.
- She presents research aspirations in the letter. Herrera writes: "I have a history of proven results and profound findings. Given opportunity, I’m confident in my abilities to earn similar ground-breaking results while being part of your team."
Even though this example lacks some of the key elements, such as mentioning the specific PhD program or identifying the topics within the PhD program that interest her the most, this PhD cover letter still managed to impress the University of Lyon.
Lyon University PhD Student Cover Letter Sample
Klara graduated from the University of St Andrews in Scotland. After having written resumes for many of her fellow students, she began writing full-time for Kickresume. Klara is our go-to person for all things related to student or 'no experience resumes'. At the same time, she has written some of the most popular resume advice articles on this blog. Her pieces were featured in multiple CNBC articles. When she's not writing, you'll probably find her chasing dogs or people-watching while sipping on a cup of coffee.
Related Posts
10 cover letter samples by people who got hired at volvo, t-mobile or hubspot, cover letter analysis: junior product manager hired by ibm, share this article, join our newsletter.
Every month, we’ll send you resume advice, job search tips, career hacks and more in pithy, bite-sized chunks. Sounds good?
PHD Application cover letter examples
As the highest postgraduate qualification you can achieve, it’s no wonder that most PhD programs require a cover letter as part of the application process.
So, if you’re hoping to complete your doctorate, you need to brush up on your writing skills and prove why you deserve a place in the program.
To help you do that, we’ve put together this comprehensive guide, complete with PhD cover letter examples to support your application.
CV templates
PHD Application cover letter example 1

PHD Application cover letter example 2

PHD Application cover letter example 3

The example cover letters here should give you a good general idea on how your PHD Application cover letter should be formatted and written.
The rest of this guide gives more specific guidance on how to create your own cover letter in this format, and even includes some templates you can copy and paste.
How to write a PHD Application cover letter
A simple step-by-step guide to writing your very own winning cover letter.
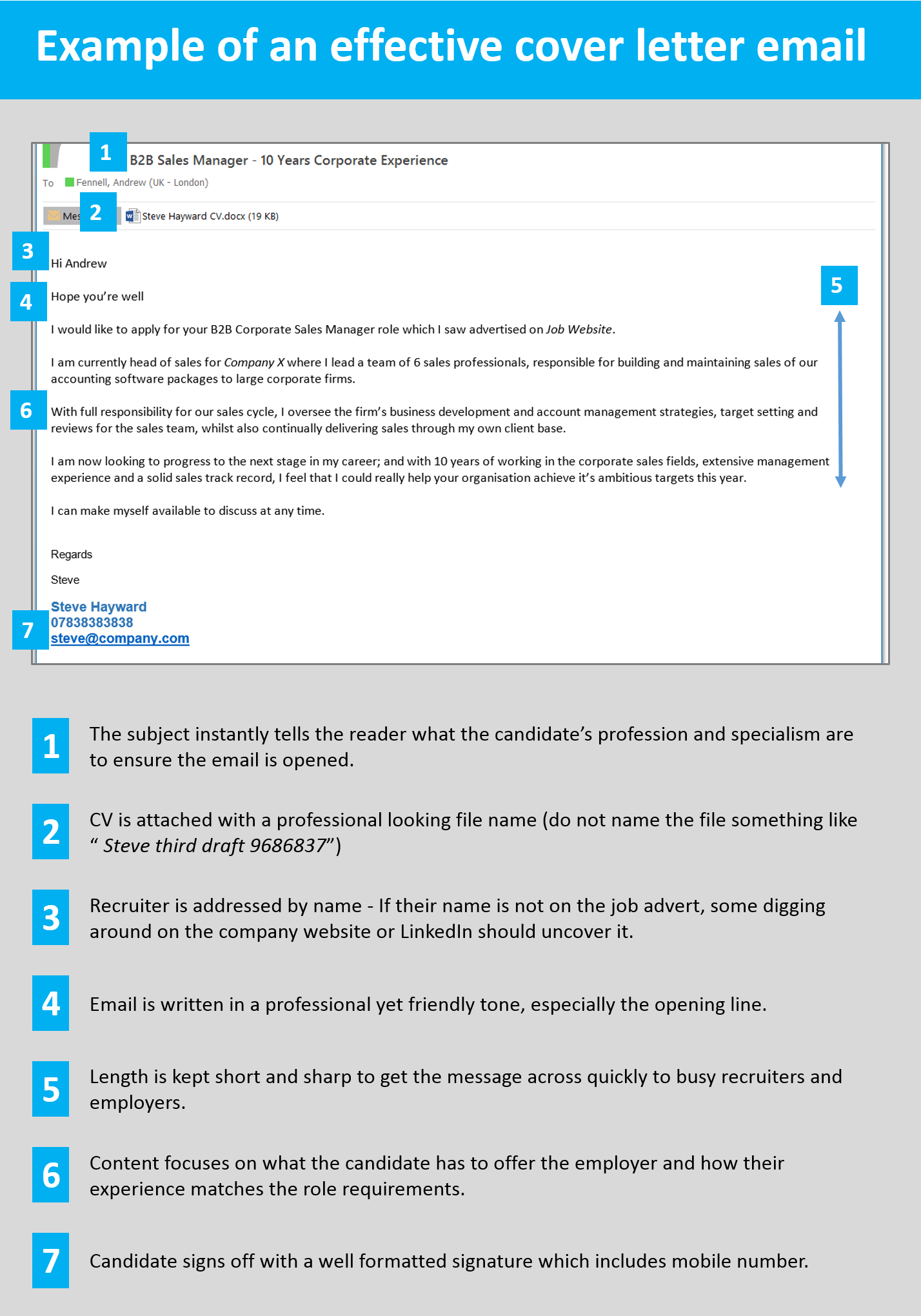
Write your cover letter in the body of an email/message
When writing your PHD Application cover letter, it’s best to type the content into the body of your email (or the job site messaging system) and not to attach the cover letter as a separate document.
This ensures that your cover letter gets seen as soon as a recruiter or employer opens your message.
If you attach the cover letter as a document, you’re making the reader go through an unnecessary step of opening the document before reading it.
If it’s in the body of the message itself, it will be seen instantly, which hugely increases the chances of it being read.
Start with a friendly greeting

Start you cover letter with a greeting that is professional but friendly.
This will build rapport with the recruiter whilst showing your professionalism.
- Hi, hope you’re well
- Hi [insert recruiter name]
- Hi [insert department/team name]
Avoid overly formal greetings like “Dear sir/madam ” unless applying to very traditional companies.
How to find the contact’s name?
Addressing the recruitment contact by name is an excellent way to start building a strong relationship. If it is not listed in the job advert, try these methods to find it.
- Check out the company website and look at their About page. If you see a hiring manager, HR person or internal recruiter, use their name. You could also try to figure out who would be your manager in the role and use their name.
- Head to LinkedIn , search for the company and scan through the list of employees. Most professionals are on LinkedIn these days, so this is a good bet.
Identify the role you are applying for
Once you’ve opened up the cover letter with a warm greeting to start building a relationship, it is time to identify which role you want to apply for.
Recruiters are often managing multiple vacancies, so you need to ensure you apply to the correct one.
Be very specific and use a reference number if you can find one.
- I am interested in applying for the position of *specialist field PHD Applicant* with your company.
- I would like to apply for the role of Sales assistant (Ref: 406f57393)
- I would like to express my interest in the customer service vacancy within your retail department
- I saw your advert for a junior project manager on Reed and would like to apply for the role.
See also: CV examples – how to write a CV – CV profiles
Highlight your suitability
The main purpose of your cover letter is to excite recruiters and make them eager to open your CV. And you achieve this by quickly demonstrating your suitability to the job you are applying for.
Take a look at the job adverts you are applying for, and make note of the most important skills being asked for.
Then, when you write your cover letter, make your suitability the focal point.
Explain how you meet the candidate requirements fully, and why you are so well suited to carry out the job.
This will give recruiters all the encouragement they need to open your CV and consider your application.

Keep it short and sharp
A good cover letter is short and sharp, getting to the point quickly with just enough information to grab the attention of recruiters.
Ideally your cover letter should be around 4-8 sentences long – anything longer will risk losing the attention of time-strapped recruiters and hiring managers .
Essentially you need to include just enough information to persuade the reader to open up your CV, where the in-depth details will sit.
Sign off professionally
To round of your CV, you should sign off with a professional signature.
This will give your cover letter a slick appearance and also give the recruiter all of the necessary contact information they need to get in touch with you.
The information to add should include:
- A friendly sign off – e.g. “Kindest regards”
- Your full name
- Phone number (one you can answer quickly)
- Email address
- Profession title
- Professional social network – e.g. LinkedIn
Here is an example signature;
Warm regards,
Jill North IT Project Manager 078837437373 [email protected] LinkedIn
Quick tip: To save yourself from having to write your signature every time you send a job application, you can save it within your email drafts, or on a separate documents that you could copy in.

What to include in your PHD Application cover letter
Here’s what kind of content you should include in your PHD Application cover letter…
The exact info will obviously depend on your industry and experience level, but these are the essentials.
- Your relevant experience – Where have you worked and what type of jobs have you held?
- Your qualifications – Let recruiters know about your highest level of qualification to show them you have the credentials for the job.
- The impact you have made – Show how your actions have made a positive impact on previous employers; perhaps you’ve saved them money or helped them to acquire new customers?
- Your reasons for moving – Hiring managers will want to know why you are leaving your current or previous role, so give them a brief explanation.
- Your availability – When can you start a new job ? Recruiters will want to know how soon they can get you on board.
Don’t forget to tailor these points to the requirements of the job advert for best results.
PHD Application cover letter templates
Copy and paste these PHD Application cover letter templates to get a head start on your own.
Dear Admissions Committee
I am writing to express my strong interest in the Ph.D. in Physics programme at the University of London. As a highly motivated and dedicated individual with a deep fascination with the fundamental principles of physics, I am eager to contribute my academic background and research experience to your faculty.
I hold an MSc in Physics from the University of Birmingham, where I achieved distinctions for quantum mechanics, thermodynamics, and atomic & molecular physics. During this period, I was involved in evaluating quantum phenomena using computational methods, which honed my analytical skills and provided insights into the intricate nature of quantum systems. My passion for research has also led me to publish two peer-reviewed papers in reputable journals.
I am enthusiastic about continuing my journey in addressing challenges in the field of physics and have previously collaborated with renowned experts in securing £10M in funding to support projects, as well as improving experimental efficiency by 40% through implementing state-of-the-art quantum optics equipment. I have also delivered presentations to share research on condensed matter systems.
I am thrilled at the possibility of joining your institution. Thank you for considering me for the programme.
Kind regards
Matt Turner
I am writing to you concerning the Ph.D. program in Chemical Engineering at the University of Oxford. I possess a profound passion for advanced research and innovation in chemical engineering, with an eagerness to contribute my academic background and problem-solving abilities to your institution.
I hold an MSc in Chemical Engineering from Imperial College London and had the opportunity to delve into cutting-edge projects alongside esteemed experts. We focused on sustainable practices in chemical manufacturing, as well as the efficient production, transformation, and transportation of various products. I helped design and conduct experiments to improve chemical operations and reduce environmental impacts, where my findings were published in two peer-reviewed journals.
Some key accomplishments during master’s studies include, obtaining research funding worth £2M to conduct experiments in catalysis and reaction engineering, and playing a role in improving industrial processes by 50%. In addition, I delivered five oral presentations at international conferences to share information on driving sustainable practices.
Thank you for considering my application, and I am available at your convenience for further discussions.
Sable Norris
Dear Members of the Graduate Admissions Committee
I am writing to express my interest in the Ph.D. programme in Archaeology at the University of Cambridge. I possess a profound fascination for uncovering the mysteries of the past, and I am focused on contributing my academic background, fieldwork experience, and research skills to your institution.
I obtained a master’s degree in Archaeology from the University of Manchester, where I had the privilege of working closely with esteemed faculty and engaged in research that ignited my passion for understanding the Sumerian civilisation.
During my studies I conducted original research on the excavation and analysis of burial sites to shed light on their ancient practices and cultural beliefs, completing 95 excavation seasons, which was 30+ more than any other student, co-authoring two research papers published in reputable journals, and securing £500K from the UK government to conduct a 3-month research trip in the Middle East.
My experience coupled with advanced coursework in archaeological methodologies and artefact analysis have equipped me with the skills to excel in the programme. Thank you for considering my application.
Dominic Ferdinand
Writing an impressive cover letter is a crucial step in landing a place on a PHD, so taking the time to perfect it is well worth while.
By following the tips and examples above you will be able to create an eye-catching cover letter that will wow recruiters and ensure your CV gets read – leading to more job interviews for you.
Good luck with your job search!

- Writing an Academic Cover Letter for a PhD Application
- Applying to a PhD
- The aim of an academic cover letter is to convince the supervisor that you are a strong candidate for the PhD position on offer.
- Your cover letter should be half a page to a full page in length; it should be concise and to the point.
- Your PhD cover letter should include your personal details , the position you’re applying for, your motivation for applying, what you know about the project, what relevant experience you have and what makes you suited for the position.
The two documents crucial to get right when applying to a PhD are your CV and covering letter.
In this article, we’ll set out the core guidelines you should follow to create an effective academic cover letter.
What Is An Academic Cover Letter?
An academic cover letter is a written document that accompanies your CV and application form when applying for a PhD.
It’s different from a CV as instead of being a structured summary of your skills and experience, it is a summary of why you believe you are suited for a particular PhD programme. As a result, all academic covering letters should be tailored for the specific position you are applying for and addressed to the supervisor who is overseeing the project. They also shouldn’t repeat what is already stated in your CV, but rather expand on the details most related to the position you are applying to.
Note: An academic cover letter is sometimes referred to as a PhD application letter, but never a motivation letter. The latter is different in that it concerns the reasons as to why you want to undertake research, while a cover letter focuses on demonstrating your suitability for a programme. This is an important distinction to note.
What Is the Purpose of An Academic Cover Letter?
The aim of an academic cover letter is to convince the PhD supervisor that you are the perfect candidate for the PhD project.
Academic cover letters should complement your CV and sell you as a person – will your potential supervisor be excited to work with you after having read your cover letter?
What Should I Include in My Academic Cover Letter?
You should demonstrate that you have the skills which make you suited for research. It is essential that you recognise these skills in you and that you use them to promote yourself.
1. Your Personal Details
Include your name, address, email address and phone number in the top right corner of the letter. This is so the supervisor can reach you should they have questions or require any further information.
2. The Position You’re Applying For
Help the supervisor establish exactly which PhD position you are applying for as there may be several positions being advertised at one time. If they provide a reference number as part of the project description, it would be a good idea to include it in brackets.
3. Why You’re Interested in The Position
Use this section to explain your motivations for applying to the specific PhD and where your research interests stem from. Is it related to the dissertation you produced as part of your final year undergraduate dissertation, etc?
Whatever your motivation for applying to the PhD, make sure that your enthusiasm comes across clearly. The supervisor will appreciate how great a role self-drive plays in completing PhD projects and you will want to convince them you have the level of drive required to be successful.
4. What You Understand About the Project
Besides explaining your motivations for undertaking the project, show that you possess a basic understanding of it. In doing so, make sure you reinforce each point with some level of evidence; avoid making general statements or talking loosely around the research subject. This will show the PhD supervisor that you’ve taken the time to research the background to the project.
5. What Relevant Experience You Have
In this section, briefly discuss your academic background and any relevant experience you have within the field of research. Don’t worry if you have little experience in this area as this will be the case for most applicants. If this the case, then use this section to explain how you will be committed to the PhD research project. If you have experience in conducting research, explain what your role was, the analytical methods you used and any other aspects of your work which may be relevant. Similarly, discuss any teaching experience if you happen to have it.
6. Closing Statement
Keep this short and concise. Thank the supervisor for taking the time to read your application and let them know that you’re looking forward to hearing from them.
How Long Should My Academic Cover Letter Be?
Your academic cover letter should be between half a page to one full page .
To keep it effective, make it as concise as possible and only discuss points which are either relevant to the project or the aspect of being a doctoral research student. This may feel difficult to do, especially if you have much you want to include, but keep in mind that your cover letter can also be used as evidence of your communication skills, more specifically, whether you can convey important information in a clear and logical manner. As this will be a key skill of any research candidate, the prospective supervisor will take it into account when evaluating your capabilities.
How to Format an Academic Cover Letter for A PhD Application
Your cover letter should be written in paragraph format, with bullet points only reserved for situations where a list would improve clarity. This is because a cover letter is one of the few places where you are expected to show your personality, so using too many bullet points will diminish your ability to do this. The best way to approach writing your application letter is to see it as a very short personal essay.
Use a common font like Times New Roman or Calibri, and if possible, avoid the use of highlighting, underlining and tables as they become too distracting. Keep your font size between 10 to 12 points and your margins to at least 0.5 inches around all edges. Try to match the font size, type, line spacing and margin size to your academic CV for neat and consistent presentation.
Your cover letter should be addressed to the PhD supervisor, starting with a “Dear [academic title] [surname]”, for example, “Dear Professor Williams”.
Hopefully, you now know what it takes to write a successful cover letter for a PhD application. While a strong cover letter will go a long way to helping you stand out, you will need to learn how to create an equally strong CV if you really want your application form to excel. To this effect, we recommend you next read our step-by-step guide for creating effective academic CVs .
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Professional PhD Cover Letter Examples for 2024
Your PhD cover letter must immediately highlight your main thesis contribution. Draw the reader's attention with a succinct explanation of your research significance and uniqueness. Demonstrate how your expertise aligns with the department or institution's academic focus. Your cover letter should create a compelling narrative that weaves your skills into their ongoing projects and goals.
Cover Letter Guide
PhD Cover Letter Sample
Cover Letter Format
Cover Letter Salutation
Cover Letter Introduction
Cover Letter Body
Cover Letter Closing
No Experience PhD Cover Letter
Key Takeaways

Embarking on your job search, you've likely discovered the need to craft a compelling PhD cover letter—a document that can stump even the most accomplished professionals. This crucial letter shouldn't just echo your resume; it must weave the narrative of your proudest professional triumph. With formal language minus the clichés, and conciseness that caps at one page, we'll guide you through the intricacies of creating a cover letter that stands out, ensuring your application demands attention.
- Write a phd cover letter that helps you stand out (and get the job);
- Understand how to start and end your phd cover letter with the appropriate greeting;
- What to include in the body of your phd cover letter to put your best foot forward;
- Your most important achievements - how to present them as part of your phd cover letter.
And if you want to make your life even easier, simply drag and drop your phd resume into Enhancv's AI cover letter generator, and it will write your cover letter for you in just a few moments.
If the phd isn't exactly the one you're looking for we have a plethora of cover letter examples for jobs like this one:
- PhD resume guide and example
- Educational Consultant cover letter example
- Librarian cover letter example
- Special Education Teacher cover letter example
- Undergraduate Teaching Assistant cover letter example
- Bilingual Teacher cover letter example
- Piano Teacher cover letter example
- Early Childhood Teacher cover letter example
- Substitute Teacher cover letter example
- High School Teacher cover letter example
- Kindergarten Teacher Assistant cover letter example
PhD cover letter example
PETER CONNOLLY
Clarksville, TN
+1-(234)-555-1234
- Highlighting Significant Achievements: By mentioning the accomplishment of improving blockchain security by 65% and securing $16 million in funding, the candidate effectively showcases their capability to deliver impactful and quantifiable results that can resonate with the prospective employer's desire for competent professionals.
- Matching Skills to Job Requirements: Specifically addressing expertise in areas of cybersecurity and software engineering indicates the applicant's understanding of the technical skills required and showcases their proficiency in those areas, which are likely essential for the role being applied for.
- Demonstrating Value Addition: The author prompts a forward-looking discussion by suggesting a meeting to explore how their background can contribute to the company, implying a readiness to tailor their skills and past experiences to meet the employer's specific needs.
What are the basics of the design or format of your phd cover letter?
To start, here's a reminder for you: the Applicant Tracker System (or software that is used to assess candidate profiles), won't be reading your phd cover letter.
Recruiters enjoy reading phd cover letters with a standardized format that uses:
- the same font as the resume (e.g. modern ones like Raleway or Volkhov are prefered over the clichéd Times New Roman or Arial);
- single spacing to keep the content concise and organized (this is all ready for you in our cover letter templates );
- a one-inch margin to wrap around the text, like in our cover letter builder ;
- PDF as a file format, as it allows your design (and visual element) to stay the same.
Finally, we can't go on without mentioning the key sections of your phd cover letter.
In the top one-third, make sure to include a header (with your contact information, name, role, and date), a salutation, and an introduction.
Next, follows the heart and soul of your phd cover letter or its body.
End your phd cover letter with a closing paragraph and, if you wish, a signature.
The top sections on a phd cover letter
Header: This includes your contact information, the date, and the recipient's details; it's essential for providing immediate visibility of your identity and for professional correspondence formatting.
Opening Salutation/Greeting: A formal greeting addresses the recipient properly and sets a respectful and professional tone for the cover letter, which is important for making a good first impression.
Introduction: This section should capture the recruiter's attention by briefly introducing your background, your interest in the PhD program, and the specific reasons you are drawn to this particular opportunity.
Research Interests and Academic Background: Tailor this part to showcase your relevant educational and research experiences, current interests, and how it aligns with the department’s work, demonstrating your fit for the program.
Closing and Call to Action: Conclude by summarizing your suitability for the role, reiterating your enthusiasm, and inviting further discussion, showing proactivity and eagerness to engage with the academic community.
Key qualities recruiters search for in a candidate’s cover letter
- Deep expertise in the specific research field: Demonstrates the ability to contribute valuable insights and drive the research forward.
- Strong analytical and critical thinking skills: Essential for designing experiments, analyzing data, and drawing meaningful conclusions.
- Proven track record of academic accomplishments: Indicates the capability to undertake and complete challenging research projects.
- Excellent communication skills (written and verbal): Vital for writing research papers, grant proposals, and collaborating with peers and mentors.
- Self-motivation and independence: Necessary for driving one's own research and overcoming the inevitable challenges of a PhD program.
- Demonstrated perseverance and commitment: Shows that the candidate can see long-term projects through to completion despite obstacles.
What matters most when tailoring your phd cover letter salutation
Your phd cover letter greeting should feel welcoming to recruiters.
Use their first name (e.g. "Dear Marshall" or "Dear Sara"), if you've previously been in touch with the hiring manager and are on a more friendly basis.
If this is the first time you're contacting the recruiters, start your phd cover letter with:
- their last name (e.g. "Dear Ms. Ali" or "Dear Mr. Stevens") - look up who's the hiring manager for the role on social media or the company website;
- generalized greeting (e.g. "Dear HR Team") - just don't use "To whom it may concern" or "Dear Sir/Madam".
List of salutations you can use
- Dear Dr. [Last Name],
- Dear Professor [Last Name],
- Dear Dr. [First Name] [Last Name],
- Dear Search Committee,
- Dear Hiring Committee,
- Dear [Department Name] Selection Committee,
The phd cover letter intro: aligning your interest with the company culture
You only have one chance at making a memorable first impression on recruiters with your phd cover letter.
Structure your introduction to be precise and to include no more than two sentences.
Here are some ideas on how to write a job-winning phd cover letter introduction:
- get creative - show off your personality from the get-go (if this aligns with the company culture);
- focus on your motivation - be specific when you say what gets you excited about this opportunity.
What to write in the middle or body of your phd cover letter
Here's where it gets tricky.
Your phd cover letter body should present you in the best light possible and, at the same time, differ from your resume.
Don't be stuck in making up new things or copy-pasting from your resume. Instead, select just one achievement from your experience.
Use it to succinctly tell a story of the job-crucial skills and knowledge this taught you.
Your phd cover letter is the magic card you need to further show how any organization or team would benefit from working with you.
Closing paragraph basics: choose between a promise and a call to action
You've done all the hard work - congratulations! You've almost reached the end of your phd cover letter .
But how do you ensure recruiters, who have read your application this far, remember you?
Most phd professionals end their cover letter with a promise - hinting at their potential and what they plan on achieving if they're hired.
Another option would be to include a call for follow-up, where you remind recruiters that you're very interested in the opportunity (and look forward to hearing from them, soon).
Choose to close your phd cover letter in the way that best fits your personality.
Which story should you tell in your phd cover letter when you have zero experience
Candidates, lacking professional experience in the field - this one is for you.
Your phd cover letter is an exercise of integrity, honesty, and, above all, spinning a positive narrative around your strengths.
And what better way to capture recruiters' attention than with your most job-relevant achievement (this could be from your internship or volunteering experience)?
Make sure to back up your success with transferrable skills that are relevant to the job (e.g. how your year, studying abroad, has taught you to be more motivated and handle multicultural environments).
Another safe card you can bet on is your career dream: in the body of your phd cover letter, go into the details of how your ambitions would help make the company you're applying for better.
Key takeaways
Your phd cover letter is your best shot at standing out by showing your motivation and the unique skills you'd bring to the job:
- Chose no more than one achievement, which you'd be talking about in the body of your phd cover letter, by focusing on skills and outcomes;
- Address recruiters with their first or last name, or "Dear Hiring Manager" in your phd cover letter greeting;
- Introduce in no more than two sentences what makes your profile unique (perhaps it's your motivation, enthusiasm, or appreciation of the company you're applying for);
- Select the same font you have used in your resume (avoid Times New Roman and Arial, as most candidates tend to invest in them);
- Close your phd cover letter with a promise of how you see yourself growing in the company and the benefits you'd bring about.

Cover letter examples by industry
AI cover letter writer, powered by ChatGPT
Enhancv harnesses the capabilities of ChatGPT to provide a streamlined interface designed specifically focused on composing a compelling cover letter without the hassle of thinking about formatting and wording.
- Content tailored to the job posting you're applying for
- ChatGPT model specifically trained by Enhancv
- Lightning-fast responses

Are There Enough Remote Entry-Level Jobs? Here’s What 10 800 Postings Say
Should you include citizenship on your resume, note to recruiters on linkedin: how to write a professional note that gets noticed, should i put my resume on linkedin, what are you passionate about: best interview answers, how to answer the "why do you want to change your career path" interview question.
- Create Resume
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Preferences
- Resume Examples
- Resume Templates
- AI Resume Builder
- Resume Summary Generator
- Resume Formats
- Resume Checker
- Resume Skills
- How to Write a Resume
- Modern Resume Templates
- Simple Resume Templates
- Cover Letter Builder
- Cover Letter Examples
- Cover Letter Templates
- Cover Letter Formats
- How to Write a Cover Letter
- Resume Guides
- Cover Letter Guides
- Job Interview Guides
- Job Interview Questions
- Career Resources
- Meet our customers
- Career resources
- English (UK)
- French (FR)
- German (DE)
- Spanish (ES)
- Swedish (SE)
© 2024 . All rights reserved.
Made with love by people who care.
- Undergraduate Students
- Masters Students
- PhD/Doctoral Students
- Postdoctoral Scholars
- Faculty & Staff
- Families & Supporters
- Prospective Students
- Explore Your Interests / Self-Assessment
- Build your Network / LinkedIn
- Search for a Job / Internship
- Create a Resume / Cover Letter
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Prepare for Graduate School
- Find Funding Opportunities
- Prepare for the Academic Job Market
- Search for a Job or Internship
- Advertising, Marketing, and Public Relations
- Arts & Entertainment
- Consulting & Financial Services
- Engineering & Technology
- Government, Law & Policy
- Hospitality
- Management & Human Resources
- Non-Profit, Social Justice & Education
- Retail & Consumer Services
- BIPOC Students & Scholars
- Current & Former Foster Youth
- Disabled Students & Scholars
- First-Generation Students & Scholars
- Formerly Incarcerated Students & Scholars
- International Students & Scholars
- LGBTQ+ Students & Scholars
- Students & Scholars with Dependents
- Transfer Students
- Undocumented Students & Scholars
- Women-Identifying Students & Scholars
Academic Cover Letter for Doctoral Students
- Share This: Share Academic Cover Letter for Doctoral Students on Facebook Share Academic Cover Letter for Doctoral Students on LinkedIn Share Academic Cover Letter for Doctoral Students on X
The academic cover letter communicates your scholarly fit with the position, organization and department. The cover letter should be no longer than 2 pages and should expand on your most relevant accomplishments and situate your work in the context outlined by the position. It should also outline your research agenda and future trajectory. All academic positions will require a cover letter and because the academic job market is so competitive, it has become common for search committees to ask just for a cover letter and CV. If this is the case you need to include paragraphs that provide information similar to teaching and research statements, highlighting what is not articulated on your CV. Some disciplines have a very specific format, so be sure to work with your department to align your cover letter with disciplinary standards. Avoid overly verbose or overly humble language.
Tips for condensing research and teaching statements into the academic cover letter:
- Your materials should create an overall picture of you as a scholar. This means that you should consider each document within the context of the other materials required.
- Begin by drafting longer statements about teaching (the teaching statement) and research (dissertation abstract, research statement).
- Pare down these statements for different lengths: one page, one paragraph.
- For the cover letter, take your one-paragraph versions of your teaching and research statements and edit them to market yourself as a scholar and teacher – how do you want the committee to perceive you? What’s the main take-away you want them to know about you?
- Because the materials required vary widely, keep in mind that the cover letter should be able to act as a standalone document – any other materials should expand and reinforce the cover letter.
- Your Job Search
- Developing Application Materials
- Academic Job Market
Academic Cover Letters
The cover letter is a single spaced, two-page introductory document that creates a narrative for your application package. It introduces the search committee to your:
- Enthusiasm for the position and your expected availability (e.g., expected defense date)
- Teaching and teaching assistantships
- Other relevant experience (internships, previous professional experience, etc.)
- Fit (why you are the right person for the position, understanding of campus culture and values, etc.)
Because no cover letter can convey all this information appropriately in only two pages, you will need to tailor your letter depending on the department, the university, the requirements specified in the job call, your application package, etc.
Keep in mind, the cover letter should not directly lift content from other supporting material. For example, if a job call also asks for a Teaching Statement or Philosophy, you should not feel pressure to condense all of that content into a paragraph. Rather use the cover letter to illustrate how your teaching fits into your scholarly identity. Consider how it is informed by your research, commitment to equity and inclusion, etc.
- How the job call is written, which responsibilities are presented and in what order – is teaching prioritized over research?
- What application documents are requested – is there something not requested that you could elaborate on in the cover letter?
- What student populations would you engage with as a faculty member in the department – undergraduate? graduate? both?
- Is the institution mission-driven – how does that impact your professional narrative?
The cover letter could include a combination of the following paragraphs:
Opening Paragraph
Just like articles and dissertations have a central “thesis” or research question, this paragraph gives the letter’s thesis statement, clarifying how your mix of experience makes you the best candidate for the job. This paragraph lists the basics of the cover letter:
- Introduce yourself
- Explain your interest in the position and institution
- Basic rundown of who you are as a scholar in relation to the role
Body Paragraphs
This content could address your research project(s), areas of interest, methodological training, and future research agendas. Think about how you would fit into the department and the expertise you would provide. If you are applying to a research institution, your research paragraphs should come first.
You will want to include some of the following points:
- Your current research project (dissertation)
- Potential future projects (dissertation to book, next research project, etc.)
- Impact of your project(s) (publications, conference or poster presentations, public lectures, etc.)
- Other achievements (grants and funding won, awards earned, public-facing work, etc.)
- Potential collaborations within the department and/or across the institution, depending on the interdisciplinary nature of the position.
This content discusses your teaching experience, whether as an instructor of record or a TA, your pedagogical training, and any mentoring/advising. If the job is teaching-focused, this should be where you start. Use this space to introduce how your teaching is a part of who you are as a scholar.
- Your approach to teaching
- Other ways you have engaged with and/or mentored students (office hours, summer research opportunities, etc.)
- Expertise in relation to courses you are prepared to teach
This content communicates how you contribute to the collegial nature of the institution or department to which you are applying. It might range from a full paragraph to a few sentences supplementing your research or teaching paragraphs.
You can pull from:
- Graduate Assistantships or other service you have done within your department (e.g., serving on committees), the institution, or professional organizations
- Conference volunteering and service
- Search committee participation
- Other volunteer work and community involvement
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
This content discusses how your current and future experiences consider diversity, equity, inclusivity, and accessibility. Commitment to DEI can be shown through:
- Research areas, pedagogical applications, or service in and outside of institutions
- Where you align with the mission statement of the institution and/or department
- How you can contribute to the student population or wider community
These considerations are communicated most seamlessly not as stand-alone paragraphs, but woven into your document as a whole.
Closing Paragraph
Think back to your thesis statement and reinforce your excitement about the role. Keep it short and to the point – thank them for their time and consideration, ending with a professional sign off and full name.
General Tips Before Submission
- Prior to submitting, double check that the cover letter is signed and saved as a PDF (preferably on Northwestern letterhead).
- As with all application documents, make sure to have multiple eyes on the content before submitting it to the hiring committee.
- Take advantage of the support Northwestern provides from the Graduate Writing Place and Northwestern Career Advancement.
- Postdocs can make appointments for individualized feedback with the Office of Postdoctoral Affairs.

What Is a PhD Cover Letter?
What key points should i include within my phd application letter, tips to improve your phd application letter, example phd cover letter, final thoughts, phd cover letters.
Updated October 11, 2023

All products and services featured are independently selected by WikiJob. When you register or purchase through links on this page, we may earn a commission.
A PhD cover letter is an important part of your PhD application. Your cover letter (which may also be referred to as a motivational letter) focuses upon what makes you a great candidate and why you should be invited for interview.
This article will cover what a PhD cover letter is, when it would be used and how you can write a notable cover letter for your PhD application.
Your cover letter is your first opportunity to explain to the committee why you should be selected to study for your postgraduate doctorate. It not only demonstrates your personality, but it can also explain in your own words why the hiring panel should choose you as a PhD student.
Like most cover letters , your PhD application letter should complement, but not repeat, your CV. It should explain and expand on the details referenced within your CV or application form .
You should tailor the content to your chosen PhD topic – this will enable you to focus your specific expertise and academic achievements on your learning capabilities.
It should be noted that when it comes to submitting your application to study for a PhD, you may be required to submit a personal statement as well as a cover letter. Each university will have its own criteria, but note that a cover letter is different from a personal statement.
Your personal statement will focus upon your interests and your ambitions, whilst your PhD cover letter will be looking at your tangible achievements , such as your academic and professional experience.
If you are required to draft both statements, then try to keep this in mind during the writing process.

There are no rules for what to include within your PhD cover letter but, broadly speaking, your submission should include references to the following:
Who you are – what your personality is and what sets you apart from other potential PhD candidates. Your cover letter should be a sales tool that should make any committee want to choose you to join their team.
Your skills and achievements (along with any evidence to substantiate your claims).
Your research into the specific academic institution (why you want to attend that specific school and what makes it a good fit for you).
Your understanding of your research project and what you believe its impact may be upon your sector (this will demonstrate not just your knowledge of the research but will showcase your passion and motivation for the project).
How your specific skills are relevant to the application. Have you undertaken any work experience relevant to that field? Have you been inspired by what previous alumni have achieved?
As with all applications, writing a great cover letter is a skill. It requires you to tread the balance between explaining in detail who you are and why you should be chosen, while remaining concise. It needs to showcase your personality while remaining professional.
It’s a difficult writing skill and one which shouldn’t be rushed. You should take your time to craft your application letter – the more time that is spent on it, the greater your chance of success.
A practical tip is to use the ‘top-down’ approach . This is a writing skill often used by marketers and PR professionals whereby you incorporate the strongest arguments/details at the top and work your way down.
You need to ensure that if a committee member stops reading your cover letter at any point, then they have already noted the most pressing details.
How Do I Write My PhD Cover Letter?
An easy way to focus your thoughts when writing your application letter is to consider it as a way of telling your story, at least in relation to the PhD you are applying for. By this, we mean that your letter should have a clear beginning, middle and end.
Using this format as a guide, here are some examples of how to start writing your PhD cover letter.
Starting Your Cover Letter
As with any form of professional correspondence, do your due diligence and be confident that you know who to send your application to.
As previously mentioned, each school will have its own application criteria – for some, it may need to be addressed to a specific professor, whilst others may direct you to a department or someone responsible for all recruitment.
Make sure you find out their name – along with correct spellings and titles. This is your first chance to make a good impression, so you must pay attention to the details.
Introducing Yourself
A good place to start is to introduce yourself first. Ask yourself, who are you and why should the committee continue to read your application letter?
This is your opportunity to explain what PhD you are applying for and why you want to study further. You may want to start your storytelling in this section.
For example:
I became interested in this subject when I met [name], who is one of your alumni. They inspired me to want to continue my learning and further my knowledge, which has been developed through my professional experience at [company name].
As you can see from this example, the letter is starting to explain why the candidate wants to apply for the application, what inspires them to continue their learning and gives a look into their achievements. The result is that it makes the reader want to continue reading the letter.
Showcasing Your Skills and Achievements
The middle section is where you talk about what you have achieved and how you want to further your development and make an impact on your field of study.
This section should refer to your CV and provide greater insights into what you already know and why you would be a great candidate for the PhD programme.
You could use this section to briefly introduce what topic you believe would make a great research project.
As you can see from my enclosed CV, I have an extensive professional history within my sector. From my experience at [company name], I was able to focus upon my key specialisms, which led me to develop an interest in [project]. I believe that, due to the ever-changing nature of the profession, there is scope to continue the research into [subject] and I’m keen to combine my practical and theoretical knowledge in my research. I believe this is of value to not just myself and my peers but also my wider profession because of [detail].
Again, this is demonstrating a level of professionalism while starting to showcase exactly why you should be chosen to join the PhD programme. It shows that you’re not just thinking of yourself, you’re also considering the wider implications that your research may have upon your field of study.
Ending Your Cover Letter
As you draw towards the end of your cover letter, you may wish to reiterate why you want to study at this specific institution. Showing you have researched the university’s research reputation can go a long way to impressing hiring panels.
It may be globally renowned, or perhaps it’s a good fit for your specific area of interest. Maybe there’s a specific professor you would like to work alongside or maybe you’ve seen the career advancement of previous alumni. If you have a personal reason why you are a good fit for the school, then state it here.
Additionally, we would also recommend explaining what you plan to do with your research upon its completion. Hiring panels will be keen to find out how you plan to use your expertise and what your long term ambitions are.
I am particularly interested in joining the PhD programme at [school] because of your reputation as global research leaders. Throughout my career, I have strived to work alongside the best because I believe in the importance of peer learning. I am keen to work alongside your distinguished professors to carry out my research in [subject]. I believe that I am the right fit for your institution because of [x,y,z] and through my correspondence with [named contact of the previous alumni], I am aware of the help and support that you provide to your PhD applicants. Following on from the completion of my doctorate, I plan to use my knowledge to do [x,y,z].
As you sign off your cover letter, make sure you include a call to action. Encourage the panel to get in touch with you to arrange a formal interview or direct them to your CV so that they can be reminded of your experience.
You need to end the letter with no doubt that you are a good fit for the PhD programme and that you are an ideal candidate that they need to snap up.
I hope that this letter has given you some insight into my dedication to my learning and that you will consider my application. I would like to draw your attention back to my CV which is enclosed with this letter, which demonstrates my professional and academic history. I look forward to hearing from you in due course.
If you have addressed the letter to a named contact, use ‘Yours sincerely’. If you have been directed to address your letter to a general department, then formalities suggest that you should use the sign off ‘Yours faithfully’.
Keep it concise . Where possible, it shouldn’t exceed two pages of A4. They can find out more detail about who you are during the interview stage; this is merely to whet their appetite and excite them to want to find out more about you.
Don’t reiterate what has already been written on your CV . Instead, they want to know how the experience on your CV has made you a more rounded individual. How has it shaped your interest in your chosen study and what is compelling you to continue to further your learning?
Provide evidence . If you are highly regarded within your professional sector, then demonstrate this – are you involved in any sector groups or have you been recognised with any awards? The whole purpose of your potential research project is to provide evidentiary proof of your hypothesis so if you are going to make bold statements about your career history, then the first thing any PhD supervisor will want to know, is 'Where is the evidence?'.
Check for errors . Remember that your letter is a professional representation of who you are. Before submitting your PhD application, make sure that your cover letter is free from grammatical errors and spelling mistakes. It’s a sister document to your CV so try to ensure consistency between the two documents – use similar formatting, a professional font (Ariel or Calibri are good choices) and ensure that your margins are coherent.

Below, is an example of a cover letter for your PhD application. We hope that it inspires you and helps you to understand more about what you should be including when it comes to writing your own letter.
Remember that this is an example only and your cover letter should be tailored to your circumstances.
Recipient Name Recipient Job Title Recipient Address Date Dear [name] Cover letter for application to join the PhD programme at [school]. I am writing to you to showcase my interest in continuing my academic study through the PhD programme in [subject] at [University]. I am keen to join the doctoral programme within your [department] because I believe that its rich history of academic research is a perfect match for my academic aptitude and my extensive career history. I’ve long been interested in [subject] and I recently met with [name], who is one of your alumni. They inspired me to take the leap and submit this application because I’ve long been interested in developing my knowledge honed through my professional experience at [company name]. I studied [subject] at [university] and throughout my academic history and work experience, I’ve developed a strong interest in the niche field of [topic]. My BA thesis was based upon [subject] and since completing my undergraduate studies, I’ve been able to put my theoretical knowledge into practice through my work at [company name]. As you can see from my enclosed CV, I’ve been able to hone my skills into key specialisms which have led me to develop an interest in [project]. I believe that there is scope to continue the research into [subject] due to the ever-changing nature of the profession and I’m keen to combine my practical and theoretical knowledge with my research. I believe this is of value to not just myself and my peers but also my wider profession, since it could help others to understand the importance of [subject]. I wish to continue my academic career by completing my doctorate, which has always been a long-term ambition of mine. I cannot imagine a better place to study than [university]. I have always been inspired by the achievements of this academic institution and I wish to work alongside your teaching staff to research my hypothesis which is [details]. In particular, I would like to work alongside Professor [name], who was highly regarded by our mutual acquaintance [alumni name]. With my theoretical knowledge and my professional expertise, I am confident that I can complete my chosen research project to a high standard. I am a dedicated hard worker and have long been regarded within my sector through my involvement with [professional bodies]. I have also been recognised along with my peers for our work through the achievements of many industry awards including [details]. Following on from the completion of my doctorate, I plan to use my knowledge to help educate fellow professionals, and thus improve awareness and understanding of our sector. I hope that this letter has given you some insight into my dedication to my learning and that you will consider my application. I would like to draw your attention back to my CV which is enclosed with this letter, which will demonstrate my professional and academic history. I look forward to hearing from you in due course. Yours sincerely, [Signature] [Name] Encl. Curriculum Vitae
This article has been designed to give you some insights into what to expect from your PhD application.
To read more about PhDs, we recommend that you read our postgraduate pages , which contain numerous articles about PhDs, MBAs and further study.
You might also be interested in these other Wikijob articles:

Or explore the Postgraduate / PHD sections.
Ultimate Letter
Letter For Everyone

Cover Letter For PhD Application | Samples and Templates
Would you like to see a sample cover letter of application for PhD position? Here are some professionally designed patterns and also a sample cover letter for PhD application.
It doesn’t matter if you’re trying to keep your student discounts up to age 30 or answering questions that no one in the history of mankind has ever answered. All this is possible with a well-designed PhD application.
There are very few vacancies, and there are dozens of equally qualified candidates. This guide to writing a PhD admission letter or motivational letter will go over some of the important steps to consider when writing a letter.
The first thing you should do is check the requirements of the institution you are applying to, first make sure a cover letter is required, and then see which sections they would like you to cover.
They differ from one institute to another and from one course to another. A sample academic cover letter of application for a PhD position is your best chance of being accepted.
This article is a complete guide on how to write application letters for PhD positions. It also contains a sample PhD application letter and templates to help you write the best.
Table of Contents

What is a PhD Admission Letter?
The letter of application is your first chance to tell the committee why you should be selected for graduate studies. Not only does this show your personality, but it can also explain why a recruiting board should choose you as a PhD student in his own words.
Your PhD application letter, like most others, should complement, not duplicate, your resume. It should explain and expand on the information on your resume or application form. You must adapt the content to your chosen PhD thesis. A theme that allows you to focus your specific experience and academic achievement on your learning abilities.
It should be noted that when applying for a PhD, you may be required to submit a personal statement as well as a cover letter. Each university will have its own set of requirements, but keep in mind that a cover letter is not the same as a personal statement.
Your statement will highlight your interests and goals while your PhD the cover letter will highlight your material accomplishments such as academic and professional experience.
If you need to prepare both statements, try to keep this in mind when writing. Having a sample PhD application letter is also another way to make sure you’re writing something compelling.
What are the key points I should include in my PhD admission letter?
There are no rules about what we must include in your PhD cover letter, but in general, your application must include references to the following:
Who you are – your personality and what sets you apart from other potential PhDs. Your cover letter should be a sales tool that will encourage any committee to select you for their team. The successful cover letter should contain the following
- Your abilities and accomplishments (along with any evidence to support your claims).
- In addition, your study of a particular institution for your doctoral program(why you want to attend this particular institution and what makes it suitable for you).
- Your understanding of your research project and your expectations regarding its impact on your industry (this will show not only your knowledge of the research but also your passion and motivation for the project).
- How do your specific skills apply to the post? Have you gained any relevant experience in this area? Have you been inspired by the achievements of previous bachelor’s degree and master’s degree?
Writing a great motivation letter is a skill, just like any other part of the application process. This requires you to explain in a balanced way who you are and why you should be selected, in detail while remaining concise.
While remaining professional, it should reflect your personality. This is a difficult writing skill that should not be rushed.
Don’t rush into writing your application letter; the more time you spend on it, the higher your chances of you becoming a successful PhD student. Use the top-down approach as a practical tip.
You can use a sample PhD cover letter to make sure you don’t make mistakes and are on the right track. Continue reading to learn more about Cover Letter Sample and Templates for PhD application. This will help you write a cover letter for PhD application.
What is the purpose of a PhD Statement?
If you are a PhD candidate, an academic letter of the application allows you to explain to the reader, who is likely the professor or director in charge of reviewing PhD applicants, what you can offer to the program and why they should select you for a place.
You can use your cover letter to fill in any gaps on your resume (CV), tailor your application to a specific program, and showcase your communication skills and passion.
This is your chance to impress a PhD program director with your identity and the assets you will bring to their institution.
How to write a PhD Statement?
Follow these steps to write a PhD statement:
1. Learn the details of the program and organization
Review the information you have about the program you are applying for before writing your application letter. Use a different application letter for each organization because they may be looking for unique qualities in candidates.
Analyze your qualities, as well as those of the ideal candidate, and tailor your application letter to the areas where they overlap.
2. Create a formal letter of application.
A STEM-focused application letter should be one page, while a liberal arts-focused application letter can be two pages. Always check with the organization and adhere to any formatting rules they may have for the application material.
Use a professional font and font size, pay attention to clear formatting, and avoid adding extra elements such as pictures or frames.
3. Provide your most recent contact information.
It is especially important to provide up-to-date and correct contact information when contacting several organizations at once. If the organization needs more information or wants to schedule an interview, you should make sure they can contact you.
The presence of up-to-date and accurate information indicates professionalism and reliability.
4. Create an introduction
Write an introduction after you’ve completed the body of your cover letter. The introduction should clearly state what you are applying for. You can also use this space to briefly mention future ambitions or goals.
5. In the first paragraph of the main body, highlight your strengths and experience.
Write the first paragraph of your cover letter highlighting your education, strengths, and experience. This paragraph should describe who you are academically and what you hope to achieve while participating in the program. Tell us about your specific interests in this area, what sparked your interest, and any research you’ve done on those specific interests.
6. In the second main paragraph, describe your distinctive features.
Focus on your passion, drive, and unique qualities that set you apart from other candidates in the second paragraph of your cover letter. You want to show not only how the program can help you, but also how you can improve the program if accepted. Consider overlaps between your qualifications and what the program is looking for in an ideal candidate.
7. Complete your application letter.
End the application letter by thanking the reader for their time and expressing appreciation for the opportunity. The conclusion should complement the rest of your application letter, demonstrating your enthusiasm for your field and commitment to the organization.
Your conclusion should also encourage the reader to contact you for more information, discussion, or to schedule an interview.
8. Include a formal closure and signature.
Your closing and signature are the final elements of your academic cover letter. In most cases, you may not need to physically sign the document; a printed name will suffice.
Avoid using intimate closing phrases and use more professional ones instead. Here are some examples of professional closing statements. The sample PhD application letter written below will serve as a great guide to make sure you get it right.
Tips for writing an effective PhD thesis Statement
You can use the following guidelines to write your PhD statement:
Start at the very beginning of the process. Preparing an application for graduate school requires careful planning. Set aside enough time to write, edit, and proofread your cover letter.
Take a break between writing and editing. When you’ve finished writing your application letter, save it and wait a few days before editing to make sure you notice ways to improve or correct your work.
Make the most of your resources. If you are still in college, you can use the writing or career centers to craft an effective cover letter. Talk to your favorite professors or lecturers, ask them questions and listen to their advice.
Carefully review your PhD thesis. statement. You want to present yourself professionally in your application letter because this is one of your first points of contact with a potential school. Use proofreading software, read your cover letter aloud, and ask friends and colleagues to read it for you to create a flawless application letter.
Make your points clear. You must provide evidence for every claim you make about yourself. Tell us as much as possible about your achievements and hobbies.
Focus on your true self. Demonstrate why you are the best candidate for your chosen school by emphasizing how your uniqueness will benefit the program. Concentrate on articulating your important accomplishments.
Samples and Templates Of Academic Cover Letters for PhD Statement
Academic Cover Letter Sample for PhD Position
Receiver name
Recipient’s position
Address of the recipient
Dear [name]
Cover letter for the PhD program at [institution name].
I am writing to express my research interests in continuing my academic studies at [university] through a PhD program in [topic].
I am very eager to join your [Faculty Postgraduate] program because I consider that its prosperous history of academic research is an ideal match for my academic abilities and extensive career experience. I have been interested in [the topic] for a long time and recently met with [name], one of your alumni. And they inspired me to take a chance and submit this letter because I have long wanted to expand on the knowledge I gained through my experience at [your company name].
I studied [mention subject] at [mention university], and throughout my academic history and work experience, I grew a strong interest in this niche area [your topic]. My thesis was on [subject], and I was able to put my academic knowledge into practice while working at [your company name where you work/worked] since graduating from my undergraduate studies.
As you can see from my attached academic CV, I was able to sharpen my skills in key specializations, which led to my interest in [the project]. Because of the ever-changing nature of my profession, I believe there are opportunities for further study [of the subject] and I am eager to combine my theoretical and practical knowledge with my research PhD project.
I believe that this is valuable not only for me and my colleagues but for my profession as a whole because it can help others understand the meaning [of the subject].
I hope to continue my academic career with a PhD, which has long been my goal. I can’t think of a better university to study than [the university you are wishing to complete your PhD from]. I’ve always been motivated by the accomplishments of this institution and would like to collaborate with your teaching staff to explore my hypothesis, namely [details]. I would especially like to work with Professor [mention name], who was admiringly regarded by our mutual understanding [name of alumnus].
Thus, I am sure that with my theoretical knowledge and professional experience I will be able to complete the research project I have chosen at a high level. I am a dedicated, hardworking individual who has long been respected in my industry through my involvement in [professional organizations]. I have also been recognized for my work, along with my peers, through many industry awards, including [details].
After completing my PhD, I intend to use my knowledge to educate fellow professionals, thereby increasing awareness and understanding of our industry.
I hope this letter has given you some idea of my commitment to my education and that you will consider my application.
I would like to once again draw your attention to my CV, which is attached to this letter and describes in detail my professional and academic background.
I look forward to hearing from you shortly.
[Signature]
FINAL WORDS
Your cover letter for PhD application should contain a brief introduction to the program you want to apply for in the text of the application. This should be included in any cover letter. You need to write down the letter to the PhD supervisor.
First, state a clear career goal for your future project, as well as the reasons why you chose this particular PhD program. Mention in detail your previous professional and academic history. Also mention if you are applying for professional scientific research or anything else.
Q. How do I write a cover letter for a PhD admission?
A. Your cover letter for PhD application should contain a brief introduction to the program you want to apply for in the text of the application. This should be included in any cover letter. You need to write down the letter to the PhD supervisor.
Q. How do I write a good PhD application?
A. First, state a clear career goal for your future project, as well as the reasons why you chose this particular PhD program. Mention in detail your previous professional and academic history. Also mention if you are applying for professional scientific research or anything else.
Related Articles:-
5 Samples Of Accident Leave Letter
9 Easy Samples Of Leave Application For Surgery
Leave Application For Cousin Marriage
Leave Application For Surgery Samples
Format And Samples Of Writing Absent Application Letter

Academic Cover Letters
What is this handout about.
The long list of application materials required for many academic teaching jobs can be daunting. This handout will help you tackle one of the most important components: the cover letter or letter of interest. Here you will learn about writing and revising cover letters for academic teaching jobs in the United States of America.
What is an academic cover letter?
An academic cover letter describes your experiences and interest as a candidate for a specific position. It introduces you to the hiring committee and demonstrates how your academic background fits with the description of the position.
What do cover letters for academic teaching jobs typically contain?
At their most basic level, academic cover letters accomplish three things: one, they express your interest in the job; two, they provide a brief synopsis of your research and teaching; and three, they summarize your past experiences and achievements to illustrate your competence for the job. For early-career scholars, cover letters are typically no more than two pages (up to four pages for senior scholars). Occasionally, a third page may make sense for an early-career scholar if the application does not require a separate teaching statement and/or research statement. Digital versions of cover letters often contain hyperlinks to your CV or portfolio page. For some fields, cover letters may also include examples of your work, including music, popular articles, and other multimedia related to your research, service, or teaching available online. Typically, letters appear on departmental or university letterhead and include your signature. Above all, a strong cover letter presents your accomplishments and your familiarity with the institution and with the position.
How should I prepare to write my academic cover letter?
Like all writing, composing a cover letter is a process. The process may be as short as a few hours or as long as several weeks, but at the end the letter should present you as a strong candidate for the job. The following section has tips and questions for thinking through each stage of this writing process. You don’t need to answer all of these questions to write the letter; they are meant to help you brainstorm ideas.
Before you begin writing your cover letter, consider researching the institution, the department, and the student population. Incorporating all three aspects in your letter will help convey your interest in the position.
Get to know the institution. When crafting your cover letter, be aware of the type of institution to which you are applying. Knowing how the institution presents itself can help you tailor your letter and make it more specific.
- Where is the institution located?
- Is it on a quarter-system or semester-system?
- What type of institution is it? Is it an R1? Is it an R2? Is it a liberal arts college? Is it an HBCU? Is it a community college? A private high school?
- What is the institution’s culture? Is it teaching-focused or research-focused? Does it privilege experiential learning? Does it value faculty involvement outside the classroom? Is it affiliated with a specific religious tradition?
- Does it have any specific institutional commitments?
- How does the institution advocate for involvement in its local community?
- What are the professional development opportunities for new and junior faculty?
Learn about the department. Knowing the specific culture and needs of the department can help you reach your audience: the department members who will be reading your documents and vetting you as a candidate.
- Who is on the search committee? Who is the search committee chair?
- What is the official name of the department?
- Which different subfields make up the department?
- Is it a dual appointment or a position in a dual department?
- How does the department participate in specific types of student outreach?
- Does the department have graduate students? Does it offer a terminal Master’s degree, Ph.D., or both? How large are the cohorts? How are they funded?
- Does the department encourage or engage in interdisciplinary work?
- Does the majority of the department favor certain theoretical or methodological approaches?
- Does the department have partnerships with local institutions? If so, which ones?
- Is the department attempting to fill a specific vacancy, or is it an entirely new position?
- What are the typical course offerings in the department? Which courses might you be expected to teach? What courses might you be able to provide that are not currently available?
Consider the students. The search committee will often consider how you approach instructing and mentoring the student body. Sometimes committees will even reserve a position for a student or solicit student feedback on a candidate:
- What populations constitute the majority of the undergraduate population?
- Have there been any shifts in the student population recently?
- Do students largely come from in-state or out-of-state?
- Is there an international student population? If so, from which countries?
- Is the university recruiting students from traditionally underrepresented populations?
- Are students particularly active on campus? If so, how?
Many answers to these questions can be found both in the job description and on the institution’s website. If possible, consider contacting someone you know at the institution to ask about the culture directly. You can also use the institution’s course catalog, recruitment materials, alumni magazine, and other materials to get answers to these questions. The key is to understand the sort of institution to which you are applying, its immediate needs, and its future trajectory.
Remember, there is a resource that can help you with all three aspects—people. Reach out to your advisor, committee members, faculty mentors, and other contacts for insight into the prospective department’s culture and faculty. They might even help you revise your letter based on their expertise. Think of your job search as an opportunity to cultivate these relationships.
After you have done some initial research, think about how your experiences have prepared you for the job and identify the ones that seem the most relevant. Consider your previous research, internships, graduate teaching, and summer experiences. Here are some topics and questions to get you started thinking about what you might include.
Research Experiences. Consider how your research has prepared you for an academic career. Since the letter is a relatively short document, select examples of your research that really highlight who you are as a scholar, the direction you see your work going, and how your scholarship will contribute to the institution’s research community.
- What are your current research interests?
- What topics would you like to examine in the future?
- How have you pursued those research interests?
- Have you traveled for your research?
- Have you published any of your research? Have you presented it at a conference, symposium, or elsewhere?
- Have you worked or collaborated with scholars at different institutions on projects? If so, what did these collaborations produce?
- Have you made your research accessible to your local community?
- Have you received funding or merit-based fellowships for your research?
- What other research contributions have you made? This may include opinion articles, book chapters, or participating as a journal reviewer.
- How do your research interests relate to those of other faculty in the department or fill a gap?
Teaching Experience. Think about any teaching experience you may have. Perhaps you led recitations as a teaching assistant, taught your own course, or guest lectured. Pick a few experiences to discuss in your letter that demonstrate something about your teaching style or your interest in teaching.
- What courses are you interested in teaching for the department? What courses have you taught that discussed similar topics or themes?
- What new courses can you imagine offering the department that align with their aim and mission?
- Have you used specific strategies that were helpful in your instruction?
- What sort of resources do you typically use in the classroom?
- Do you have anecdotes that demonstrate your teaching style?
- What is your teaching philosophy?
- When have you successfully navigated a difficult concept or topic in the classroom, and what did you learn?
- What other opportunities could you provide to students?
Internships/Summer/Other Experiences. Brainstorm a list of any conferences, colloquiums, and workshops you have attended, as well as any ways you have served your department, university, or local community. This section will highlight how you participate in your university and scholarly community. Here are some examples of things you might discuss:
- Professional development opportunities you may have pursued over the summer or during your studies
- International travel for research or presentations
- Any research you’ve done in a non-academic setting
- Presentations at conferences
- Participation in symposia, reading groups, working groups, etc.
- Internships in which you may have implemented your research or practical skills related to your discipline
- Participation in community engagement projects
- Participation in or leadership of any scholarly and/or university organizations
In answering these questions, create a list of the experiences that you think best reflect you as a scholar and teacher. In choosing which experiences to highlight, consider your audience and what they would find valuable or relevant. Taking the time to really think about your reader will help you present yourself as an applicant well-qualified for the position.
Writing a draft
Remember that the job letter is an opportunity to introduce yourself and your accomplishments and to communicate why you would be a good fit for the position. Typically, search committees will want to know whether you are a capable job candidate, familiar with the institution, and a great future addition to the department’s faculty. As such, be aware of how the letter’s structure and content reflect your preparedness for the position.
The structure of your cover letter should reflect the typical standards for letter writing in the country in which the position is located (the list below reflects the standards for US letter writing). This usually includes a salutation, body, and closing, as well as proper contact information. If you are affiliated with a department, institution, or organization, the letter should be on letterhead.
- Use a simple, readable font in a standard size, such as 10-12pt. Some examples of fonts that may be conventional in your field include Arial, Garamond, Times New Roman, and Verdana, among other similar fonts.
- Do not indent paragraphs.
- Separate all paragraphs by a line and justify them to the left.
- Make sure that any included hyperlinks work.
- Include your signature in the closing.
Before you send in your letter, make sure you proofread and look for formatting mistakes. You’ll read more about proofreading and revising later in this handout!
The second most important aspect of your letter is its content. Since the letter is the first chance to provide an in-depth introduction, it should expand on who you are as a scholar and possible faculty member. Below are some elements to consider including when composing your letter.
Identify the position you are applying to and introduce yourself. Traditionally, the first sentence of a job letter includes the full name of the position and where you discovered the job posting. This is also the place to introduce yourself and describe why you are applying for this position. Since the goal of a job letter is to persuade the search committee to include you on the list of candidates for further review, you may want to include an initial claim as to why you are a strong candidate for the position. Some questions you might consider:
- What is your current status (ABD, assistant professor, post-doc, etc.)?
- If you are ABD, have you defended your dissertation? If not, when will you defend?
- Why are you interested in this position?
- Why are you a strong candidate for this position?
Describe your research experience and interests. For research-centered positions, such as positions at R1 or other types of research-centered universities, include information about your research experience and current work early in the letter. For many applicants, current work will be the dissertation project. If this is the case, some suggest calling your “dissertation research” your “current project” or “work,” as this may help you present yourself as an emerging scholar rather than a graduate student. Some questions about your research that you might consider:
- What research experiences have you had?
- What does your current project investigate?
- What are some of the important methods you applied?
- Have you collaborated with others in your research?
- Have you acquired specific skills that will be useful for the future?
- Have you received special funding? If so, what kind?
- Has your research received any accolades or rewards?
- What does your current project contribute to the field?
- Where have you presented your research?
- Have you published your research? If so, where? Or are you working on publishing your work?
- How does your current project fit the job description?
Present your plans for future research. This section presents your research agenda and usually includes a description of your plans for future projects and research publications. Detailing your future research demonstrates to the search committee that you’ve thought about a research trajectory and can work independently. If you are applying to a teaching-intensive position, you may want to minimize this section and/or consider including a sentence or two on how this research connects to undergraduate and/or graduate research opportunities. Some questions to get you started:
- What is your next research project/s?
- How does this connect to your current and past work?
- What major theories/methods will you use?
- How will this project contribute to the field?
- Where do you see your specialty area or subfield going in the next ten years and how does your research contribute to or reflect this?
- Will you be collaborating with anyone? If so, with whom?
- How will this future project encourage academic discourse?
- Do you already have funding? If so, from whom? If not, what plans do you have for obtaining funding?
- How does your future research expand upon the department’s strengths while simultaneously diversifying the university’s research portfolio? (For example, does your future research involve emerging research fields, state-of-the-art technologies, or novel applications?)
Describe your teaching experience and highlight teaching strategies. This section allows you to describe your teaching philosophy and how you apply this philosophy in your classroom. Start by briefly addressing your teaching goals and values. Here, you can provide specific examples of your teaching methods by describing activities and projects you assign students. Try to link your teaching and research together. For example, if you research the rise of feminism in the 19th century, consider how you bring either the methodology or the content of your research into the classroom. For a teaching-centered institution, such as a small liberal arts college or community college, you may want to emphasize your teaching more than your research. If you do not have any teaching experience, you could describe a training, mentoring, or coaching situation that was similar to teaching and how you would apply what you learned in a classroom.
- What is your teaching philosophy? How is your philosophy a good fit for the department in which you are applying to work?
- What sort of teaching strategies do you use in the classroom?
- What is your teaching style? Do you lecture? Do you emphasize discussion? Do you use specific forms of interactive learning?
- What courses have you taught?
- What departmental courses are you prepared to teach?
- Will you be able to fill in any gaps in the departmental course offerings?
- What important teaching and/or mentoring experiences have you had?
- How would you describe yourself in the classroom?
- What type of feedback have you gotten from students?
- Have you received any awards or recognition for your teaching?
Talk about your service work. Service is often an important component of an academic job description. This can include things like serving on committees or funding panels, providing reviews, and doing community outreach. The cover letter gives you an opportunity to explain how you have involved yourself in university life outside the classroom. For instance, you could include descriptions of volunteer work, participation in initiatives, or your role in professional organizations. This section should demonstrate ways in which you have served your department, university, and/or scholarly community. Here are some additional examples you could discuss:
- Participating in graduate student or junior faculty governance
- Sitting on committees, departmental or university-wide
- Partnerships with other university offices or departments
- Participating in community-partnerships
- Participating in public scholarship initiatives
- Founding or participating in any university initiatives or programs
- Creating extra-curricular resources or presentations
Present yourself as a future faculty member. This section demonstrates who you will be as a colleague. It gives you the opportunity to explain how you will collaborate with faculty members with similar interests; take part in departmental and/or institution wide initiatives or centers; and participate in departmental service. This shows your familiarity with the role of faculty outside the classroom and your ability to add to the departmental and/or institutional strengths or fill in any gaps.
- What excites you about this job?
- What faculty would you like to collaborate with and why? (This answer may be slightly tricky. See the section on name dropping below.)
- Are there any partnerships in the university or outside of it that you wish to participate in?
- Are there any centers associated with the university or in the community that you want to be involved in?
- Are there faculty initiatives that you are passionate about?
- Do you have experience collaborating across various departments or within your own department?
- In what areas will you be able to contribute?
- Why would you make an excellent addition to the faculty at this institution?
Compose a strong closing. This short section should acknowledge that you have sent in all other application documents and include a brief thank you for the reader’s time and/or consideration. It should also state your willingness to forward additional materials and indicate what you would like to see as next steps (e.g., a statement that you look forward to speaking with the search committee). End with a professional closing such as “Sincerely” or “Kind Regards” followed by your full name.
If you are finding it difficult to write the different sections of your cover letter, consider composing the other academic job application documents (the research statement, teaching philosophy, and diversity statement) first and then summarizing them in your job letter.
Different kinds of letters may be required for different types of jobs. For example, some jobs may focus on research. In this case, emphasize your research experiences and current project/s. Other jobs may be more focused on teaching. In this case, highlight your teaching background and skills. Below are two models for how you could change your letter’s organization based on the job description and the institution. The models offer a guide for you to consider how changing the order of information and the amount of space dedicated to a particular topic changes the emphasis of the letter.
Research-Based Position Job Letter Example:
Teaching-based position job letter example:.
Remember your first draft does not have to be your last. Try to get feedback from different readers, especially if it is one of your first applications. It is not uncommon to go through several stages of revisions. Check out the Writing Center’s handout on editing and proofreading and video on proofreading to help with this last stage of writing.
Potential pitfalls
Using the word dissertation. Some search committee members may see the word “dissertation” as a red flag that an applicant is too focused on their role as a graduate student rather than as a prospective faculty member. It may be advantageous, then, to describe your dissertation as current research, a current research project, current work, or some other phrase that demonstrates you are aware that your dissertation is the beginning of a larger scholarly career.
Too much jargon. While you may be writing to a specific department, people on the search committee might be unfamiliar with the details of your subfield. In fact, many committees have at least one member from outside their department. Use terminology that can easily be understood by non-experts. If you want to use a specific term that is crucial to your research, then you should define it. Aim for clarity for your reader, which may mean simplification in lieu of complete precision.
Overselling yourself. While your job letter should sell you as a great candidate, saying so (e.g., “I’m the ideal candidate”) in your letter may come off to some search committee members as presumptuous. Remember that although you have an idea about the type of colleague a department is searching for, ultimately you do not know exactly what they want. Try to avoid phrases or sentences where you state you are the ideal or the only candidate right for the position.
Paying too much attention to the job description. Job descriptions are the result of a lot of debate and compromise. If you have skills or research interests outside the job description, consider including them in your letter. It may be that your extra research interests; your outside skills; and/or your extracurricular involvements make you an attractive candidate. For example, if you are a Latin Americanist who also happens to be well-versed in the Spanish Revolution, it could be worth mentioning the expanse of your research interests because a department might find you could fill in other gaps in the curriculum or add an additional or complementary perspective to the department.
Improper sendoff. The closing of your letter is just as important as the beginning. The end of the letter should reflect the professionalism of the document. There should be a thank-you and the word sincerely or a formal equivalent. Remember, it is the very last place in your letter where you present yourself as a capable future colleague.
Small oversights. Make sure to proofread your letter not just for grammar but also for content. For example, if you use material from another letter, make sure you do not include the names of another school, department, or unassociated faculty! Or, if the school is in Chicago, make sure you do not accidentally reference it as located in the Twin Cities.
Name dropping. You rarely know the internal politics of the department or institution to which you are applying. So be cautious about the names you insert in your cover letters. You do not want to unintentionally insert yourself into a departmental squabble or add fire to an interdepartmental conflict. Instead, focus on the actions you will undertake and the initiatives you are passionate about.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Ball, Cheryl E. 2013. “Understanding Cover Letters.” Inside Higher Ed , November 3, 2013. https://www.insidehighered.com/advice/2013/11/04/essay-cover-letter-academic-jobs .
Borchardt, John. 2014. “Writing a Winning Cover Letter.” Science Magazine , August 6, 2014. https://www.sciencemag.org/careers/2014/08/writing-winning-cover-letter# .
Helmreich, William. 2013. “Your First Academic Job.” Inside Higher Ed , June 17, 2013. https://www.insidehighered.com/advice/2013/06/17/essay-how-land-first-academic-job .
Kelsky, Karen. 2013. “How To Write a Journal Article Submission Cover Letter.” The Professor Is In (blog), April 26, 2013. https://theprofessorisin.com/2013/04/26/how-to-write-a-journal-article-submission-cover-letter/ .
Tomaska, Lubomir, and Josef Nosek. 2008. “Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Cover Letter to Accompany a Job Application for an Academic Position.” PLoS Computational Biology 14(5). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006132 .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
404 Not found
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

Campus protests over the Gaza war
How some faculty members are defending student protesters, in actions and in words.
Rachel Treisman

Columbia University faculty and staff gather on the campus in solidarity with student protesters on Monday. Stefan Jeremiah/AP hide caption
Columbia University faculty and staff gather on the campus in solidarity with student protesters on Monday.
Sarah Phillips was on the Indiana University campus in Bloomington for meetings Saturday when she saw social media posts calling for help protecting students' free speech rights.
When Phillips, an anthropology professor at IU, arrived at the site of the campus protest she recognized some of her students, "completely peaceful," standing face-to-face with what she described as heavily armed riot police. Reflexively, she started walking toward them.
"My instincts just kicked in," she told NPR on Monday. "And a few moments later, I found myself on the ground, handcuffed and being marched with some students and other faculty to a bus that was ready to take us away to the local jail."
The students were protesting at Dunn Meadow, a university-designated assembly area since 1969 and the site of an encampment that the school administration banned in a widely criticized last-minute policy change .
A few days earlier, on Thursday, Indiana state and university police had arrested 33 people as they tried to disperse the crowd. Protesters quickly regrouped, and Phillips was alarmed to hear on Saturday that armed police were once again gathering at the park.
She was one of four faculty members and 19 students arrested that day alone — among the hundreds of people who have been arrested at pro-Palestinian campus protests across the country in the last two weeks.
Demonstrators at Indiana, as in many other states, are calling for a cease-fire in Gaza and an end to both university investment in Israeli-affiliated companies and its partnership with a nearby U.S. Navy installation.
And professors are increasingly standing with students, in what many describe as an effort to safeguard the students' right to protest.

Middle East crisis — explained
As student protesters get arrested, they risk being banned from campus too.
"As a faculty member who cares about freedom of speech — who sees freedom of speech as the bedrock of democracy and really as the foundation for a public education — I see it as my responsibility to speak up when I see harm being done to students and their rights being violated," Phillips said. "And if my voice isn't enough, then I'm going to have to speak up, so to say, for them in other ways."
Most of the people arrested on Saturday, including Phillips, were hit with the misdemeanor charge of criminal trespass. All were also handed slips of paper by university police banning them from school property for one year (with the exception of one organizer who was banned for five years ).
The administration later said that students and faculty who were arrested can appeal their trespass warnings with university police, and will be allowed on campus to finish the semester while that process is underway.
Phillips plans to do so. But, she says, this last week of classes is especially important for professors in terms of meeting with students and administering finals — and that experience has already been disrupted. On Monday, her students presented their final projects on Zoom rather than in their classroom.
"I know we're all being very careful to not violate the terms of that trespass ban, because we've been informed that, should we do so, that the consequences could ramp up and be even worse than they are right now," she said.
Protests at Indiana have continued, with demonstrators now also calling for the university's president and provost to step down. More than 800 current and emeritus faculty members from the school have also signed an open letter calling for their resignation or removal.

As pro-Palestinian protests spread, more university leaders weigh police involvement
It's one of several schools around the country where professors are getting arrested at demonstrations, circulating letters in support of arrested protesters and holding no-confidence votes in their administrations.
At Columbia University, for example, faculty members in orange vests linked arms , forming a human wall at the entrance to students' encampment as police arrived to break it up on Monday. Professors at Emory University staged a campus walkout that same day, chanting "hands off our students."
Many faculty members, disturbed by the forceful police response to protests, are increasingly standing up for students' academic freedom — and pushing back against university leadership that they see as infringing on it.
"I feel like faculty are in triage mode right now," said Irene Mulvey, president of the American Association of University Professors (AAUP). "They're helping the students, putting their bodies on the line ... they're dealing with the administration with no-confidence votes, but also trying to deal with the administration directly to get them to back off and do the right thing."
Faculty are attending — and getting arrested at — protests

Indiana State Police riot squad arrested dozens of people during a pro-Palestinian protest in Dunn Meadow in Bloomington on Thursday. Jeremy Hogan/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images hide caption
Indiana State Police riot squad arrested dozens of people during a pro-Palestinian protest in Dunn Meadow in Bloomington on Thursday.
Hundreds of students have been arrested at campus protests within the last week. There is no exact tally of how many professors have been arrested, according to the AAUP, but news stories and social media reports suggest the numbers are steadily mounting.
Steve Tamari, a history professor at Southern Illinois University Edwardsville, was among the protesters arrested at a campus demonstration on Saturday at Washington University in St. Louis, with video showing several officers slamming him to the ground.
In a statement read by a student on Tuesday, Tamari said he was "body slammed and crushed by the weight of several St. Louis County Police officers and then dragged across campus by the police," and remains hospitalized with broken ribs and a broken hand.
Two professors were among the 28 people arrested at Emory University on Thursday, after the administration called in city and state police to disperse a protest. Both high-profile arrests were captured on bystander videos.
In one, economics professor Caroline Fohlin approaches several police officers as they wrestle a protester to the ground, asking "what are you doing?" and telling them to get away. As she approaches, one officer grabs her by the wrist and flips her onto the sidewalk. Another comes over to help zip-tie her hands behind her back, as she protests: "I am a professor!"

Nearly 300 people arrested at campus protests against the war in Gaza this weekend
Fohlin was later charged with battery against a police officer. Her lawyer, Gregory Clement, later told the Atlanta Journal-Constitution that the arrest was misguided.
"Caroline Fohlin was not a protester at Emory on April 25," Clement said. "She emerged from her office, concerned only about the treatment of students on the quad."
The other professor arrested, Noëlle McAfee, was captured on video urging bystanders to notify the philosophy department — of which she is the chair — of her arrest as she is led away in handcuffs.
McAfee later told 11Alive News that she was passing through the area of the protest when she came across cops "pummeling" a young protester, and stood nearby asking them to stop. She didn't leave when police told her to, and was charged with disorderly conduct.
Twenty years ago, she said, she probably would have been one of those protesters. Today, she's focused less on the Israel-Hamas conflict at the heart of the demonstrations and more on what she calls the issue of "issue of higher education administrators clamping down on free expression and delegitimizing any kind of dissent."
"At this season of my life my job is to protect the students and to protect ... academic freedom. I can do that better than they can do that," she said. "And I think that's what we're seeing with faculty all over, both wanting to protect the students and wanting to call out administrations that are actually putting the students at risk."

Top companies are on students' divest list. But does it really work?
But some faculty members are participating in protests themselves, joining students in calling for a cease-fire in Gaza and divestment from companies that do business with Israel.
Steven Thrasher, a journalism professor and chair of social justice in reporting at Northwestern University's Medill School, has been acting in what he calls a role of faculty support for the student encampment on its Illinois campus.
When the encampment started last week, he and other members of the group Educators for Justice in Palestine mobilized to make sure there would be faculty members available for bail support, university negotiations and physically defending student protesters, including by signing up for four-hour shifts on site.

Columbia University protesters occupy a campus building, echoing 1968
"We're making sure that there's always four of us who are there, that the students know that we're there," Thrasher told NPR on Friday. "But ... we did not expect to be in a human barricade position in the first 10 minutes, which is what happened [Thursday] morning."
At protests, Thrasher identifies himself as someone who is willing to be arrested. He hopes that doesn't happen, but says he feels "quite committed to, if there's violence that can happen between the students and the administration or cops, that I'm going to put my body in that space when I'm there."
Thrasher acknowledges he's motivated by more than just protecting students' free speech.
"I would think that if I saw students who disagreed with me politically ... I would also intervene" on their behalf, he said. "But for me, it's also, I'm supporting them in something that I think is very righteous, and I'm very proud of them."
On Monday, Northwestern students and administrators reached an agreement to end the campus encampment.
Several faculty members have said in speeches and social media posts that they fear they will lose their jobs or face other repercussions for speaking out.
Mulvey, of the AAUP, says it's riskier for non-tenured professors to take a stand — and the long-term decline in tenure at American universities means that most do not have it . She said those dynamics are damaging not only to higher education institutions but democracy itself.
"If higher education faculty are beholden to saying what powerful people want them to say, and if they stray out of the line they're going to get fired, we are living in an authoritarian society," she said.
Faculty members are making demands — including resignations — of leadership

Emory University professors held a walkout on Monday in support of student protesters. Elijah Nouvelage/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Emory University professors held a walkout on Monday in support of student protesters.
Faculty members at a growing list of schools are also making their opinions and demands known in writing.
Some are speaking up based on their subject matter expertise, like history professors at the University of Southern California and media school professors at Indiana University .
"As a faculty expressly charged with teaching our students about these values in the pursuit of journalism and other expressions of public communication, we strongly dissent from these anti-democratic acts," the Indiana professors wrote.
Professors at Northeastern University , where over 100 people were arrested on Saturday , sent university leaders a letter urging them to drop charges against protesters and issue a public apology and retraction of false allegations of antisemitism, among other demands. At least 144 Vanderbilt University professors signed a letter expressing support for student protesters and criticizing its "excessive and punitive" response.

In Columbia University's protests of 1968 and 2024, what's similar — and different
At Princeton, where two graduate students were arrested and suspended from campus for setting up tents, faculty members signed a letter condemning their punishment and demanding their reinstatement. Over 300 Yale professors signed a similar letter pressing university leaders to call on authorities to drop charges against all 48 protesters arrested and take no further disciplinary action against them.
"The use of policing, penalization and retribution to avoid protest or dialogue with students cannot stand, as this is no model for an educational institution," the Yale professors wrote.
And faculty members at some schools — including Barnard , Emory , UT-Austin and Cal Poly Humboldt — are issuing votes and statements of no confidence in their presidents, over their response to campus protests.

Consider This from NPR
How today's college protests echo history.
The principle of shared governance — which the AAUP defines as the "joint responsibility of faculty, administrations, and governing boards to govern colleges and universities" — is key to helping campuses move forward, Mulvey says.
She says most schools already have mechanisms — like faculty senates and academic councils — through which faculty members and administrators can engage with each other over what's happening and how to respond. But at many schools, she says, administrations are currently ignoring that structure.
"If you're not upholding it when it's needed, then it means nothing," she says. "The first thing is going to have to be a rebuilding of trust. And that trust takes a long time to build and repair."
Education and community as a path forward

Students work on their class assignments at a demonstration at George Washington University on Sunday. Cliff Owen/AP hide caption
Students work on their class assignments at a demonstration at George Washington University on Sunday.
Campus protests, occupations and mass arrests are continuing, even as many schools wrap up classes and final exams.
Despite the frenzy, Mulvey believes professors generally will do their best to help students complete the term.
"My feeling is that the vast majority of faculty will bend over backwards to fulfill their academic obligations to the students ... whether it means a written final instead of an in-class final, whether it means extensions on projects, whether it means additional office hours," she said.

Enlighten Me with Rachel Martin
This palestinian american professor leans on his quaker faith during conflict.
Mulvey sees the way forward as through education both inside and beyond the classroom. Thrasher, at Northwestern, agrees. He's currently teaching a graduate seminar called "The Theater of Protest," and accompanied his students to the encampment for a field trip during Monday's class.
Thrasher, who has reported on various Occupy Wall Street and Black Lives Matter protests over the years, says these sorts of encampments are "really amazing pedagogical spaces" where lots of valuable learning can happen, from interfaith prayers to lending libraries.
Phillips, the Indiana professor who was arrested, agrees that students are "our best teachers right now."
Like Thrasher, she says the best thing to come out of this turmoil is the deepening of solidarities within the community — she says she's spent time with colleagues in ways she hasn't in her more than two decades at the university, and seeing many newly emboldened to stand up for their beliefs.
"There's definitely no more business as usual," she says. "We have really come together in a way that has shown how fragile community can be, but also how important community is."
- faculty members
- Israel-Hamas war
- campus protests

Cover Letter for a Transcriptionist 2024 (With Free Example)
- May 8, 2024
Before writing a cover letter for a transcriptionist, we must have an idea about the job of a transcriptionist. So, any professional who listens converts an audio recording to text is a transcriptionist. They basically produce texts from audios and make it suitable for use in a document. In this blog, we would provide you sample cover letters for a transcriptionist job.
Who would hire a transcriptionist?
Well, it could be an individual with hearing issues or it could be an organization requiring written record of proceedings. To get a good job, a decent cover letter is required that highlights your passion, competencies, and credentials.
Transcriptionist job covers a large number of working areas like business , education, entertainment, insurance, web content, etc. But the two most common transcription work medicine and law.
Elements of Cover Letter for a Transcriptionist
While writing a cover letter for a transcriptionist you need to make sure to add such information that look appealing to hiring managers and highlights what value you can provide to the company. Below are some elements that you must include:
Header : Your contact information, date, and the recipient’s details.
Salutation : Address the hiring manager or relevant person if known.
Introduction : State the position you’re applying for and express your interest.
Skills and Experience : Highlight your transcription skills, software proficiency, attention to detail, and any relevant experience.
Accomplishments : Share specific achievements or projects that demonstrate your abilities.
Why You’re a Fit : Explain why you’re a good fit for the role and the company.
Closing Paragraph : Reiterate your interest, express gratitude, and suggest the next steps.
Closing : End with a professional sign-off (e.g., “Sincerely”) and your name.
Optional Elements : Include a postscript, references, or additional information if relevant.
Writing a Cover Letter for a Transcriptionist
- Study the Job Description : Carefully read the job description to understand the specific skills and qualifications the employer is looking for in a transcriptionist.
- Format Your Cover Letter : Use a professional format with clear headings and a clean layout. Choose a standard font and keep the formatting consistent throughout the document.
- Header : Include your contact information and the date at the top of the page. Below that, include the recipient’s details (name, title, company, address).
- Salutation : Address the hiring manager or relevant person using their name if possible (e.g., “Dear Mr./Ms. [Last Name],”).
- Introduction : Start by mentioning the position you’re applying for and where you found the job listing. Express genuine enthusiasm for the opportunity.
- Skills and Experience : Highlight your transcription skills, including typing speed, accuracy, and familiarity with transcription software. Discuss any specialized training or certifications you have that are relevant to the role.
- Accomplishments : Provide specific examples of your achievements in transcription, such as meeting tight deadlines, maintaining accuracy in challenging situations, or improving transcription processes.
- Why You’re a Fit : Explain how your skills and experience align with the job requirements outlined in the job description. Emphasize what sets you apart from other candidates and how you can contribute to the company’s success.
- Closing Paragraph : Reiterate your interest in the position and your enthusiasm for the opportunity to join the company. Thank the hiring manager for considering your application and express your willingness to provide further information or schedule an interview.
- Closing : End with a professional sign-off (e.g., “Sincerely” or “Best regards”) followed by your name.
- Optional Elements : Consider including a postscript to highlight a key point or add a personal touch. You can also mention that you’ve attached your resume for further reference.
Cover Letter Template for a Transcriptionist
[Your Name]
[Your Address]
[City, State, Zip Code]
[Your Email Address]
[Your Phone Number]
[Hiring Manager’s Name]
[Company Name]
[Company Address]
Dear [Hiring Manager’s Name],
I am writing to express my interest in the transcriptionist position at [Company Name], as advertised on [where you found the job listing]. With [number] years of experience in transcription and a passion for linguistic precision, I am confident in my ability to contribute effectively to your team.
In my previous role at [Previous Company], I honed my transcription skills, achieving a typing speed of [typing speed] words per minute with exceptional accuracy. I am proficient in using a variety of transcription software and have experience transcribing audio files across various industries, including [mention any relevant industries]. Additionally, my attention to detail and ability to maintain confidentiality ensure that I consistently deliver high-quality transcriptions on time.
I am particularly impressed by [mention something specific about the company or job posting], and I am eager to bring my skills and expertise to [Company Name]. I am excited about the opportunity to contribute to your team and help elevate transcription standards within your organization.
Thank you for considering my application. I am looking forward to the possibility of discussing how my skills align with your needs further. Please find my resume attached for your reference.
Cover Letter Example for Transcriptionist
Certainly! Here’s a more specific example of a cover letter for a transcriptionist position:
Isabella Thompson 123 Main Street Anytown, USA 12345 [email protected] (555) 123-4567 [Date]
Ms. Emily Johnson Hiring Manager ABC Transcription Services 456 Oak Avenue Anytown, USA 54321
Dear Ms. Johnson,
I am writing to express my interest in the transcriptionist position at ABC Transcription Services, as advertised on your company website. With over five years of experience in transcription and a strong dedication to accuracy and efficiency, I am confident in my ability to contribute effectively to your team.
During my tenure at XYZ Transcription Solutions, I transcribed a wide variety of audio files, including medical dictations, legal proceedings, and business meetings. My typing speed of 80 words per minute, combined with meticulous attention to detail, allowed me to consistently produce accurate and error-free transcripts. I am proficient in using transcription software such as Express Scribe and have experience working with different audio formats.
What excites me most about the opportunity at ABC Transcription Services is your commitment to providing high-quality transcription services to clients in the healthcare industry. I am eager to leverage my experience in medical transcription to contribute to your team’s success and uphold your company’s reputation for accuracy and professionalism.
Thank you for considering my application. I am enthusiastic about the possibility of joining ABC Transcription Services and contributing to your team. I look forward to the opportunity to discuss how my skills and experiences align with the needs of your company. Please find my resume attached for your review.
Isabella Thompson
Is it hard to be a transcriptionist?
Well, the work of a transcriptionist may be hard because sometimes the audio files are not clear even some are with background noise and hard to transcribe. And the work should be precise means need utmost focus and attention.
Is transcriptionist a paying job?
You can earn more than $30 per hour as an experienced transcriptionist.

- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
The Definitive Voice of Entertainment News
Subscribe for full access to The Hollywood Reporter
site categories
John mayer sets the record straight on his friendship with andy cohen.
In a letter to The Hollywood Reporter, the rocker takes exception to a "flawed" question in this week’s cover interview with the Bravo host.
By THR Staff
- Share this article on Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter
- Share this article on Flipboard
- Share this article on Email
- Show additional share options
- Share this article on Linkedin
- Share this article on Pinit
- Share this article on Reddit
- Share this article on Tumblr
- Share this article on Whatsapp
- Share this article on Print
- Share this article on Comment

It’s no surprise that this week’s The Hollywood Reporter cover story on Andy Cohen would garner some attention — in it, the Watch What Happens Live host and Bravo producer spoke candidly with co-editor in chief Maer Roshan about the accusations that had been swirling around the Real Housewives franchise, from on-set sexism to racism to alcohol and drug abuse, breaking his long silence about the controversy .
Related Stories
So many 'real housewives' returning to bravo, andy cohen finally speaks out on 'real housewives' reckoning: "it's hurtful. but i have no regrets".
“Your friendship with Mayer has been the subject of intense speculation,” Roshan noted. “People seem dubious that a straight rock star can have a close, platonic relationship with a gay TV personality.”
“Let them speculate” Cohen replied. “I honestly love John Mayer, and he loves me. But because we are so affectionate to each other, people don’t know what box to put that in. They assume we are sleeping with each other, which we are most definitely not.”
That brief snippet in a 5,000-word interview quickly went viral, with dozens of news outlets, from CNN to the Daily Mail to Yahoo News, picking it up. More surprisingly, the question caught the eye of a certain rock guitarist — Mayer himself — who was moved to write THR the following response, which is printed here in full:
Hi Mr. Roshan,
I read your interview with Andy Cohen , and was intrigued by your line of questioning regarding our friendship. You posited that “your friendship with Mayer has been a subject of intense speculation. People seem dubious that a straight rock star can have a close platonic relationship with a gay TV personality.”
I think this is somewhat of a specious premise. First, there is a long and storied history of “rock stars” (not mocking, just won’t refer to myself as one) befriending gay icons and artists.
I love intelligent discourse — as I hope you’ll find this email to be — but I bristle at your selectively flimsy logic meant to coax an answer, when the premise itself is so deeply flawed — and quite possibly not even quantitatively true.
Quite simply, if someone is dubious of a platonic relationship between a straight man and a gay man, I don’t think that shallow a view deserves clarification by anyone with self respect, be it Andy or your publication. Reinforcing the idea that any gay/straight relationship needs qualification that it’s not sexual devoids everyone involved of their dignity.
Respectfully,
John Mayer
THR Newsletters
Sign up for THR news straight to your inbox every day
More from The Hollywood Reporter
‘rhobh’ stars dorit and pk kemsley announce separation after nine years of marriage, tom brady roast comic says robert kraft massage jokes were off-limits, andy cohen cleared as bravo completes investigation, paving way for ‘wwhl’ renewal, streaming ratings: ‘fallout’ has amazon’s biggest opening ever, so many ‘real housewives’ returning to bravo, ‘deadly influence’ docuseries on social media murders set at id (exclusive).
May 6, 2024

The following message was sent to the Emory community by President Gregory L. Fenves on May 6, 2024.
Dear Emory Community,
I have been firm in my commitment that Emory will celebrate our graduating students at Commencement. While that commitment has not changed, concerns about safety and security require us to adjust the plans.
Emory will relocate Commencement activities to the Gas South District in Duluth, Georgia, an indoor complex that includes the Gas South Arena and the Gas South Convention Center. This change in venue impacts Emory’s university-wide Commencement celebration as well as the diploma ceremonies for all nine schools, including Oxford College. Details of the revised Commencement plans, including those for related events and receptions, have been added to the Commencement website . This site will be updated as additional details become available.
Please know that this decision was not taken lightly. It was made in close consultation with the Emory Police Department, security advisors, and other agencies — each of which advised against holding Commencement events on our campuses.
I know that this news will be deeply disappointing to many of you. The FAQs included on the Commencement site provide answers to some of the many questions related to this change.
I want to end by congratulating the Emory Class of 2024 — a class like no other. For many of you, the pandemic interrupted your high school graduations, and you began your Emory experience online. Next Monday, we will celebrate all that you have accomplished since then. You will have your moment together, in person, alongside the people who matter to you the most. Each of your names will be read aloud, and each of you will be conferred an Emory degree. We will applaud your dedication, your accomplishments, and your resilience. You will become graduates of Emory University, ready to enter a world that needs your talents, your wisdom, and your leadership.
Gregory L. Fenves President
- Commencement
- University Announcements
Recent News
Download emory news photo.
By downloading Emory news media, you agree to the following terms of use:
Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License
By exercising the Licensed Rights (defined below), You accept and agree to be bound by the terms and conditions of this Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License ("Public License"). To the extent this Public License may be interpreted as a contract, You are granted the Licensed Rights in consideration of Your acceptance of these terms and conditions, and the Licensor grants You such rights in consideration of benefits the Licensor receives from making the Licensed Material available under these terms and conditions.
Section 1 – Definitions.
- Adapted Material means material subject to Copyright and Similar Rights that is derived from or based upon the Licensed Material and in which the Licensed Material is translated, altered, arranged, transformed, or otherwise modified in a manner requiring permission under the Copyright and Similar Rights held by the Licensor. For purposes of this Public License, where the Licensed Material is a musical work, performance, or sound recording, Adapted Material is always produced where the Licensed Material is synched in timed relation with a moving image.
- Copyright and Similar Rights means copyright and/or similar rights closely related to copyright including, without limitation, performance, broadcast, sound recording, and Sui Generis Database Rights, without regard to how the rights are labeled or categorized. For purposes of this Public License, the rights specified in Section 2(b)(1)-(2) are not Copyright and Similar Rights.
- Effective Technological Measures means those measures that, in the absence of proper authority, may not be circumvented under laws fulfilling obligations under Article 11 of the WIPO Copyright Treaty adopted on December 20, 1996, and/or similar international agreements.
- Exceptions and Limitations means fair use, fair dealing, and/or any other exception or limitation to Copyright and Similar Rights that applies to Your use of the Licensed Material.
- Licensed Material means the artistic or literary work, database, or other material to which the Licensor applied this Public License.
- Licensed Rights means the rights granted to You subject to the terms and conditions of this Public License, which are limited to all Copyright and Similar Rights that apply to Your use of the Licensed Material and that the Licensor has authority to license.
- Licensor means the individual(s) or entity(ies) granting rights under this Public License.
- Share means to provide material to the public by any means or process that requires permission under the Licensed Rights, such as reproduction, public display, public performance, distribution, dissemination, communication, or importation, and to make material available to the public including in ways that members of the public may access the material from a place and at a time individually chosen by them.
- Sui Generis Database Rights means rights other than copyright resulting from Directive 96/9/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 March 1996 on the legal protection of databases, as amended and/or succeeded, as well as other essentially equivalent rights anywhere in the world.
- You means the individual or entity exercising the Licensed Rights under this Public License. Your has a corresponding meaning.
Section 2 – Scope.
- reproduce and Share the Licensed Material, in whole or in part; and
- produce and reproduce, but not Share, Adapted Material.
- Exceptions and Limitations . For the avoidance of doubt, where Exceptions and Limitations apply to Your use, this Public License does not apply, and You do not need to comply with its terms and conditions.
- Term . The term of this Public License is specified in Section 6(a) .
- Media and formats; technical modifications allowed . The Licensor authorizes You to exercise the Licensed Rights in all media and formats whether now known or hereafter created, and to make technical modifications necessary to do so. The Licensor waives and/or agrees not to assert any right or authority to forbid You from making technical modifications necessary to exercise the Licensed Rights, including technical modifications necessary to circumvent Effective Technological Measures. For purposes of this Public License, simply making modifications authorized by this Section 2(a)(4) never produces Adapted Material.
- Offer from the Licensor – Licensed Material . Every recipient of the Licensed Material automatically receives an offer from the Licensor to exercise the Licensed Rights under the terms and conditions of this Public License.
- No downstream restrictions . You may not offer or impose any additional or different terms or conditions on, or apply any Effective Technological Measures to, the Licensed Material if doing so restricts exercise of the Licensed Rights by any recipient of the Licensed Material.
- No endorsement . Nothing in this Public License constitutes or may be construed as permission to assert or imply that You are, or that Your use of the Licensed Material is, connected with, or sponsored, endorsed, or granted official status by, the Licensor or others designated to receive attribution as provided in Section 3(a)(1)(A)(i) .
Other rights .
- Moral rights, such as the right of integrity, are not licensed under this Public License, nor are publicity, privacy, and/or other similar personality rights; however, to the extent possible, the Licensor waives and/or agrees not to assert any such rights held by the Licensor to the limited extent necessary to allow You to exercise the Licensed Rights, but not otherwise.
- Patent and trademark rights are not licensed under this Public License.
- To the extent possible, the Licensor waives any right to collect royalties from You for the exercise of the Licensed Rights, whether directly or through a collecting society under any voluntary or waivable statutory or compulsory licensing scheme. In all other cases the Licensor expressly reserves any right to collect such royalties.
Section 3 – License Conditions.
Your exercise of the Licensed Rights is expressly made subject to the following conditions.
Attribution .
If You Share the Licensed Material, You must:
- identification of the creator(s) of the Licensed Material and any others designated to receive attribution, in any reasonable manner requested by the Licensor (including by pseudonym if designated);
- a copyright notice;
- a notice that refers to this Public License;
- a notice that refers to the disclaimer of warranties;
- a URI or hyperlink to the Licensed Material to the extent reasonably practicable;
- indicate if You modified the Licensed Material and retain an indication of any previous modifications; and
- indicate the Licensed Material is licensed under this Public License, and include the text of, or the URI or hyperlink to, this Public License.
- You may satisfy the conditions in Section 3(a)(1) in any reasonable manner based on the medium, means, and context in which You Share the Licensed Material. For example, it may be reasonable to satisfy the conditions by providing a URI or hyperlink to a resource that includes the required information.
- If requested by the Licensor, You must remove any of the information required by Section 3(a)(1)(A) to the extent reasonably practicable.
Section 4 – Sui Generis Database Rights.
Where the Licensed Rights include Sui Generis Database Rights that apply to Your use of the Licensed Material:
- for the avoidance of doubt, Section 2(a)(1) grants You the right to extract, reuse, reproduce, and Share all or a substantial portion of the contents of the database, provided You do not Share Adapted Material;
- if You include all or a substantial portion of the database contents in a database in which You have Sui Generis Database Rights, then the database in which You have Sui Generis Database Rights (but not its individual contents) is Adapted Material; and
- You must comply with the conditions in Section 3(a) if You Share all or a substantial portion of the contents of the database.
Section 5 – Disclaimer of Warranties and Limitation of Liability.
- Unless otherwise separately undertaken by the Licensor, to the extent possible, the Licensor offers the Licensed Material as-is and as-available, and makes no representations or warranties of any kind concerning the Licensed Material, whether express, implied, statutory, or other. This includes, without limitation, warranties of title, merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, non-infringement, absence of latent or other defects, accuracy, or the presence or absence of errors, whether or not known or discoverable. Where disclaimers of warranties are not allowed in full or in part, this disclaimer may not apply to You.
- To the extent possible, in no event will the Licensor be liable to You on any legal theory (including, without limitation, negligence) or otherwise for any direct, special, indirect, incidental, consequential, punitive, exemplary, or other losses, costs, expenses, or damages arising out of this Public License or use of the Licensed Material, even if the Licensor has been advised of the possibility of such losses, costs, expenses, or damages. Where a limitation of liability is not allowed in full or in part, this limitation may not apply to You.
- The disclaimer of warranties and limitation of liability provided above shall be interpreted in a manner that, to the extent possible, most closely approximates an absolute disclaimer and waiver of all liability.
Section 6 – Term and Termination.
- This Public License applies for the term of the Copyright and Similar Rights licensed here. However, if You fail to comply with this Public License, then Your rights under this Public License terminate automatically.
Where Your right to use the Licensed Material has terminated under Section 6(a) , it reinstates:
- automatically as of the date the violation is cured, provided it is cured within 30 days of Your discovery of the violation; or
- upon express reinstatement by the Licensor.
- For the avoidance of doubt, the Licensor may also offer the Licensed Material under separate terms or conditions or stop distributing the Licensed Material at any time; however, doing so will not terminate this Public License.
- Sections 1 , 5 , 6 , 7 , and 8 survive termination of this Public License.
Section 7 – Other Terms and Conditions.
- The Licensor shall not be bound by any additional or different terms or conditions communicated by You unless expressly agreed.
- Any arrangements, understandings, or agreements regarding the Licensed Material not stated herein are separate from and independent of the terms and conditions of this Public License.
Section 8 – Interpretation.
- For the avoidance of doubt, this Public License does not, and shall not be interpreted to, reduce, limit, restrict, or impose conditions on any use of the Licensed Material that could lawfully be made without permission under this Public License.
- To the extent possible, if any provision of this Public License is deemed unenforceable, it shall be automatically reformed to the minimum extent necessary to make it enforceable. If the provision cannot be reformed, it shall be severed from this Public License without affecting the enforceability of the remaining terms and conditions.
- No term or condition of this Public License will be waived and no failure to comply consented to unless expressly agreed to by the Licensor.
- Nothing in this Public License constitutes or may be interpreted as a limitation upon, or waiver of, any privileges and immunities that apply to the Licensor or You, including from the legal processes of any jurisdiction or authority.
Creative Commons is not a party to its public licenses. Notwithstanding, Creative Commons may elect to apply one of its public licenses to material it publishes and in those instances will be considered the “Licensor.” The text of the Creative Commons public licenses is dedicated to the public domain under the CC0 Public Domain Dedication . Except for the limited purpose of indicating that material is shared under a Creative Commons public license or as otherwise permitted by the Creative Commons policies published at creativecommons.org/policies , Creative Commons does not authorize the use of the trademark “Creative Commons” or any other trademark or logo of Creative Commons without its prior written consent including, without limitation, in connection with any unauthorized modifications to any of its public licenses or any other arrangements, understandings, or agreements concerning use of licensed material. For the avoidance of doubt, this paragraph does not form part of the public licenses.
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS. A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Dear Colleague Letter: Non-Academic Research Internships for Graduate Students in Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies (Hydrogen INTERN) Supplemental Funding Opportunity
May 6, 2024
Dear Colleague:
Fostering the growth of a globally competitive and diverse research workforce and advancing the scientific and innovation skills of U.S. students are strategic objectives of the National Science Foundation (NSF). Supporting the development of a skilled workforce in energy efficiency and renewable energy is a strategic objective of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). The NSF and DOE's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) have established a partnership to support internship and training opportunities to meet these strategic objectives with a focus on hydrogen and fuel cell technologies. A new generation of skilled workforce is needed to drive research and development of hydrogen production, delivery, infrastructure, storage, fuel cells, and multiple end uses across transportation, industrial, and stationary power applications. For more information on DOE-EERE's priorities for hydrogen energy research, please see the DOE's Hydrogen Program Areas and the U.S. National Clean Hydrogen Strategy Roadmap .
This Dear Colleague Letter (DCL) describes this unique partnership with DOE EERE's Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies Office (HFTO) and is aligned with and conforms with the NSF INTERN opportunity described in the Dear Colleague Letter: Non-Academic Research Internships for Graduate Students (INTERN) Supplemental Funding Opportunity . This DCL is referred to as the Hydrogen INTERN DCL.
SUPPLEMENTAL FUNDING OPPORTUNITY
NSF will consider supplemental funding requests in the broad area of hydrogen and fuel cell technologies that enable PIs (or Co-PIs) to request supplemental support of up to $55,000 and six months for graduate students supported on active NSF grants with the following goals:
- To provide graduate students with the opportunity to augment their research assistantships or NSF Graduate Research Fellowship Program (GRFP) fellowships with research internship activities and training opportunities that will complement their academic research training.
- To allow graduate students to pursue new activities aimed at acquiring professional development experience that will enhance their preparation for multiple career pathways after graduation.
- To encourage the participation of the full spectrum of diverse talent in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).
DESCRIPTION OF THE ACTIVITIES SUPPORTED
The PI/co-PI of an active NSF award may request supplemental funding for one or more graduate students to gain knowledge, skills, training, and experiences in hydrogen and fuel cell technologies and their application areas.
Internship hosts include, but are not limited to:
- Private sector companies, laboratories, or industry research and development groups.
- Start-up businesses such as, but not limited to, those funded through the NSF's Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program and Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) programs.
- Department of Energy Laboratories, other government agencies (all levels), and National Laboratories.
- Museums, science centers, and other informal learning settings that educate the public.
- Policy think-tanks.
- Non-profit organizations.
Prior to submission, PIs are encouraged to discuss possible INTERN supplements with the cognizant NSF Program Director Points of Contact listed in this DCL to ensure the proposed internship and its topic are a good fit for this DCL. It is expected that the graduate student and the PI on the NSF grant will work together to identify experiences that add the most educational value for the graduate student through activities that are not already available at the student's academic institution. Further, it is expected that the internship will be research-focused and will be on-site at the host organization unless a specific exception to this is granted by the cognizant Program Director due to extenuating circumstances.
ELIGIBILITY
To be eligible for this opportunity, graduate students must have completed at least one academic year in their graduate program (master's or doctoral) prior to commencement of the proposed INTERN activity and be making satisfactory progress toward completion of their degree.
SUPPLEMENTAL FUNDING REQUEST PREPARATION INSTRUCTIONS
Information about requesting supplemental support is contained in the NSF PAPPG ), Chapter VI.E.5. In addition to the PAPPG requirements for supplemental support, the following materials must be included.
- A two-page summary that describes the internship
- A one-page personal statement from the graduate student describing career goals, accomplishments, and how the activity will better prepare the individual to enter the workforce.
- Research summary to include contribution(s) to research discipline
- Institution(s)
- Year of study (1st year, 2nd year, etc.)
- Completed coursework
- Employment and volunteer/outreach history
- Publications (accepted only)
- Other information relevant to the proposed internship
- A letter of collaboration from an authorized official at the host organization that describes the internship opportunity and mentoring the student will experience during the internship. The letter should include a statement confirming that neither the graduate student nor the PI has a financial interest in the organization hosting the internship.
- An endorsement letter from the PI that confirms that the student meets the eligibility requirements specified in this DCL. The letter must describe how the proposed internship activity will contribute to the student's graduate education experience and how it may impact time to degree.
- The NSF recipient and Host Organization must agree in advance as to how intellectual property (IP) rights will be handled. A signed agreement on IP (including publication and patent rights) must be submitted either as a supplementary document or, via email to the cognizant Program Director after submission of the supplementary funding request and prior to the award of the supplemental funding. NSF is responsible neither for the agreement reached nor the IP information exchanged between the NSF recipient and Host Organization.
- A budget and budget justification.
SUPPLEMENTAL FUNDING AMOUNT
The total amount of funding requested must not exceed $55,000 per student per six-month period. NSF plans to fund up to approximately 10 or more supplements in each fiscal year starting with FY 2024, depending on availability of funds.
ALLOWABLE COSTS UNDER THIS DCL
Funds may be used to support travel, tuition and fees, health insurance, additional stipend, and temporary relocation costs for the graduate student. Additional stipends are not allowed for GRFP fellows "on tenure" (currently receiving a GRFP stipend), but a stipend will be considered for fellows "on reserve" (not currently receiving a GRFP stipend) equal to the monthly rate of the GRFP stipend. Up to $2,500 may be used for the PI or the graduate research fellow's advisor to travel to work with the host organization in co-mentoring the student during the internship. Up to $2,500 may be used for materials and supplies to support the student during the internship. Travel costs must be allocated in the budget request for the graduate student to travel once to Washington DC, to present the outcomes of the INTERN project at the DOE's Annual Merit Review meeting. The recipient is permitted to request indirect costs in accordance with their approved/negotiated indirect cost rate. The total requested budget cannot exceed the limits listed under the "Supplement funding amount" section above. Note: Spousal and dependent travel are not supported.
PERIOD OF SUPPORT
The supplement funding will provide up to six months of support for an internship. Up to two supplemental funding requests may be submitted on a grant per student. This would allow the student up to two internship periods of up to six months each (i.e., a maximum of 12 months per student).
Supplemental funding requests may be submitted at any time with a target date of June 15 for Fiscal Year 2024 and April 15 for future Fiscal Years.
SUBMISSION & REVIEW
Requests for supplemental funding must be submitted electronically via Research.gov. A PI or co-PI on an NSF award must contact his/her cognizant program director prior to submission. GRFP INTERN supplement requests are submitted by the GRFP PI, not by the GRFP fellow or the fellow's research advisor. Requests for supplemental funding submitted in response to this DCL will be reviewed internally by NSF Program Officers. All supplements are subject to (a) the availability of funds, and (b) merit review of the supplemental funding request.
- Dr. Prakash Balan, [email protected] - Directorate for Engineering
- Dr. Barbara Ransom, [email protected] - Directorate for Geosciences
SPECIAL AWARD CONDITION
Intellectual Property Rights: Internships under this DCL are considered equivalent to traineeships. The National Science Foundation claims no rights to any inventions or writings that might result from its traineeship awards. However, trainees should be aware that NSF, another Federal agency, or some private party may acquire such rights through other support for particular research. Also, trainees should note their obligation to include an Acknowledgment and Disclaimer in any publication.
POLICY OR CODE ADDRESSING HARASSMENT
Recipients are required to have a policy or code of conduct that addresses sexual harassment, other forms of harassment, and sexual assault. The recipient should work with the Host Organization to ensure that the Host Organization also has a policy or code of conduct that addresses sexual harassment, other forms of harassment, and sexual assault including reporting and complaint procedures and to confirm that such policy both covers and protects INTERN students interacting with the Host Organization. The recipient should also coordinate with the Host Organization to provide orientation to graduate students to cover expectations of behavior to ensure a safe and respectful environment, and to review the recipient and host organization's policy or code of conduct addressing sexual harassment, other forms of harassment, and sexual assault, including reporting and complaint procedures. For additional information, see the NSF policies at https://new.nsf.gov/stopping-harassment .
Susan Marqusee, Assistant Director Directorate for Biological Sciences (BIO)
Dilma Da Silva, Acting Assistant Director Directorate for Computer and Information Science and Engineering (CISE)
James L. Moore III, Assistant Director Directorate for Education and Human Resources (EDU)
Susan Margulies, Assistant Director Directorate for Engineering (ENG)
Alexandra Isern, Assistant Director Directorate for Geosciences (GEO)
C. Denise Caldwell, Acting Assistant Director Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences (MPS)
Alicia Knoedler, Office Head Office of Integrative Activities (OIA)
Kendra Sharp, Office Head Office of International Science and Engineering (OISE)
Kaye Husbands Fealing, Assistant Director Directorate for Social, Behavioral and Economic Sciences (SBE)
Erwin Gianchandani, Assistant Director Directorate for Technology, Innovation and Partnership (TIP)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to write a cover letter for your Ph.D. application. Follow these steps to write your academic cover letter: 1. Review the program and organization information. Before crafting your academic cover letter, review the information you have about the program you're applying for. Avoid using the same cover letter for each organization, as they ...
A cover letter should be addressed to a named person i.e. "Dear Professor Smith". For a PhD application, this will usually be the PhD supervisor, but may be a specific person in charge of recruitment. If you are still unsure who to address the cover letter to, it should be directed to the Head of Department.
A PhD cover letter, also referred to as an academic cover letter, should be carefully crafted, well-formatted, and contain specific sections. We'll show you how to do exactly that, along with a sample of an academic cover letter from a real person admitted to a PhD program at Lyon University in France.
Copy and paste these PHD Application cover letter templates to get a head start on your own. Template 1. Dear Admissions Committee. I am writing to express my strong interest in the Ph.D. in Physics programme at the University of London. As a highly motivated and dedicated individual with a deep fascination with the fundamental principles of ...
Try to match the font size, type, line spacing and margin size to your academic CV for neat and consistent presentation. Your cover letter should be addressed to the PhD supervisor, starting with a "Dear [academic title] [surname]", for example, "Dear Professor Williams". Tip: Make sure to get the title of the supervisor correct.
1. Greeting. Like any application letter, a cover letter for PhD a position should have a polite and professional greeting. It's best to address your PhD cover letter to a specific person, such as the head of the department or the admission team. 2.
Your phd cover letter is the magic card you need to further show how any organization or team would benefit from working with you. Body Paragraph During my tenure at Acme Corp, I spearheaded a project that improved our data analysis workflow, reducing processing time by 40%.
Embarking on a PhD journey is a significant academic milestone, and the first step often begins with articulating your research goals and aspirations in a PhD cover letter. This document serves as a window into your academic pursuits , highlighting the depth of your research and the contributions you envision for your scientific field.
A successful cover letter "hooks" an employer in the first paragraph. The first few sentences should show that you've done your research about the job or internship and the organization and should make an employer want to learn more about you. A cover letter is also the first writing sample that an employer sees from you.
A cover letter introduces you to a potential employer and should accompany your résumé, unless the employer requests otherwise. If there is an option to include a cover letter, we always recommend doing so. While a résumé provides a summary of your relevant skills, experiences, and achievements ...
The academic cover letter communicates your scholarly fit with the position, organization and department. The cover letter should be no longer than 2 pages and should expand on your most relevant accomplishments and situate your work in the context outlined by the position. It should also outline your. research agenda and future trajectory.
A PhD cover letter is a document sent along with your PhD application, whether it's for a doctoral programme or a research position. A PhD cover letter introduces you to the committee and explains your sincere interest and motivation in pursuing the chosen field of study.
Academic Cover Letters. The cover letter is a single spaced, two-page introductory document that creates a narrative for your application package. It introduces the search committee to your: Enthusiasm for the position and your expected availability (e.g., expected defense date) Research. Teaching and teaching assistantships.
Example PhD Cover Letter. Below, is an example of a cover letter for your PhD application. We hope that it inspires you and helps you to understand more about what you should be including when it comes to writing your own letter. Remember that this is an example only and your cover letter should be tailored to your circumstances.
Although a PhD cover letter has a more academic focus, it is as much of a sales pitch as any other cover letter. Here is what we cover in the PhD cover letter example and writing guide: Understanding how to structure your cover letter, with each part serving a purpose: header, greeting, introduction, body and conclusion.
Cover letter for the PhD program at [institution name]. I am writing to express my research interests in continuing my academic studies at [university] through a PhD program in [topic]. I am very eager to join your [Faculty Postgraduate] program because I consider that its prosperous history of academic research is an ideal match for my ...
A comprehensive guide to the world of Resumes and Cover Letters, written and presented specifically for PhD students by the Harvard FAS Office of Career Services. Click here to access the handbook.
At their most basic level, academic cover letters accomplish three things: one, they express your interest in the job; two, they provide a brief synopsis of your research and teaching; and three, they summarize your past experiences and achievements to illustrate your competence for the job. For early-career scholars, cover letters are ...
An bookish cover letter is a document that PhD candidates submit alongside their academic CV whereas applying for one PhD. Essentially, it's a cover letter for a PhD application. It's don exactly this equivalent as your regular business cover zuschriften. Nor is it the same as a personalization description or a motivational letter.
Faculty members are making demands — including resignations — of leadership. Emory University professors held a walkout on Monday in support of student protesters. Faculty members at a growing ...
Format Your Cover Letter: Use a professional format with clear headings and a clean layout. Choose a standard font and keep the formatting consistent throughout the document. Header: Include your contact information and the date at the top of the page. Below that, include the recipient's details (name, title, company, address).
In a letter to The Hollywood Reporter, the rocker takes exception to a "flawed" question in this week's cover interview with the Bravo host. By THR Staff It's no surprise that this week's ...
Emory will relocate Commencement activities to the Gas South District, an indoor complex in Duluth, Georgia. This change impacts Emory's university-wide Commencement celebration as well as the diploma ceremonies for all nine schools.
A letter of collaboration from an authorized official at the host organization that describes the internship opportunity and mentoring the student will experience during the internship. The letter should include a statement confirming that neither the graduate student nor the PI has a financial interest in the organization hosting the internship.
Pursuant to that letter, the Department recently produced classified documents to the Select Subcommittee that were previously released in an unclassified and highly redacted Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) production to U.S. Right to Know. 3. These documents contain highly pertinent information that credibly suggests:
Nauta's grand jury testimony could become a notable part of an eventual trial against Trump. Even if Nauta refuses to testify, prosecutors could seek to use his grand jury statements about Trump ...