Unemployment Essay
500+ words essay on unemployment.
Unemployment is a serious problem among young people. There are thousands of people who do not have any work to do and cannot find work for themselves. Unemployment refers to the situation where a person wants to work but cannot find employment in the labour market. One of the major reasons that contribute to unemployment is the large population of India and the limited availability of resources. In this essay on unemployment, we will discuss all these issues responsible for unemployment in India and how we can overcome this problem. Students must go through this unemployment essay to get ideas on how to write an effective essay on the topic related to unemployment. Also, they can practice more CBSE essays on different topics to boost their writing skills.
Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, defined as the number of people actively looking for a job as a percentage of the labour force. The unemployment rate for the year 2013-14 in rural India was 4.7%, whereas it was 5.5% for urban India. In the short term, unemployment significantly reduces a person’s income and, in the long term, it reduces their ability to save for retirement and other goals. Unemployment is a loss of valuable productive resources to the economy. The impact of job loss in rural and regional areas flows through the local community, damaging businesses.

Reason for Unemployment
An unemployed person is one who is an active member of the labour force and is seeking work but is unable to find any work for himself. There are multiple reasons behind the unemployment of a person. One of them is the slow economic growth, due to which jobs in adequate numbers are not created. Excessive dependence on agriculture and slow growth of non-farm activities also limit employment generation. Unemployment in urban areas is mainly the result of substantial rural migration to urban areas. This has also resulted in a labour workforce in cities. The lack of technology and proper machinery has also contributed to unemployment.
The present educational system is based on theoretical knowledge instead of practical work. Thus, it lacks the development of aptitude and technical qualifications required for various types of work among job seekers. This has created a mismatch between the need and availability of relevant skills and training. This results in unemployment, especially among the youth and educated people with high degrees and qualifications. Apart from it, the lack of investment and infrastructure has led to inadequate employment opportunities in different sectors.
Steps to Eliminate Unemployment
Various strategies and proposals have been implemented to generate employment. Many Employment programmes and policies have been introduced and undertaken to boost self-employment and help unemployed people engage in public works. The Government of India has taken several policy measures to fight the problem of unemployment. Some of the measures are the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), National Skill Development Mission, Swarna Jayanti Shahari Rozgar Yojana (SJSRY), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs).
Despite the measures taken by the government, India remains a country experiencing severe unemployment problems. It can be resolved by imparting education in such a way that youth get the necessary skills so as to get employment easily. Setting up various vocational training and vocational courses for undergraduate and postgraduate students will help in finding employment for youth. The government needs to emphasise these courses at the primary level and make them a compulsory part of the curriculum to make students proficient in their early stages of life. Career counselling should be provided within schools and colleges so that students can choose a better career option based on their interests and ability. Government should create more job opportunities for the youth and graduates.
India is a fast-growing economy. There is an enormous scope for improvement in the unemployment sector. The various measures and steps taken by the government to increase the employment rate have succeeded to a great extent. The widespread skill development programmes have gained popularity across the nation. With better enforcement of the strategies, the employment level can be significantly improved. Although, we have to go a long way before we can say that all the people in India will get employment.
We hope this essay on unemployment must have helped students in boosting their essay-writing skills. Keep learning and visiting the BYJU’S website for more study material.
Frequently Asked Questions on Unemployment Essay
Is unemployment still an existing problem in india.
Yes, unemployment is still a serious issue in our country. Steps need to be taken by the government and also by the youngsters in India to improve this situation.
Is it necessary for schoolchildren to be informed about unemployment?
Students at this young age should definitely be informed about this topic as it will motivate them to study and aim for higher scores in exams.
What points are to be added to an essay topic on Unemployment?
Add details about different age groups of people suffering from this state of employment. You can focus on the fact that poverty is an indirect reason for unemployment and vice-versa. Then, suggest steps that can be taken to bring about an improvement in education and increase the percentage of literacy.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
Unemployment Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on unemployment.
Unemployment is a very serious issue not only in India but in the whole world. There are hundreds and thousands of people out there who do not have employment . Besides, the problems of unemployment are very severe in India because of the growing population and demand for jobs. Moreover, if we neglect this problem then it will be going to become the reason for the doom of the nation.

What is Unemployment?
Unemployment refers to a situation in which a skilled and talented people wanted to do a job. But cannot find a proper job due to several reasons.
Types of Unemployment
Now we know what is unemployment but unemployment does not only mean that the person does not have a job. Likewise, unemployment also includes people working in areas out of their expertise.
The various types of unemployment include disguised unemployment, seasonal unemployment, open unemployment, technological unemployment, structural unemployment. Besides, some other unemployment is cyclic unemployment, educated unemployment, underemployment, frictional unemployment, chronic unemployment, and casual unemployment.
Above all, seasonal unemployment, under unemployment, and disguised unemployment are the most common unemployment that is found in India.
Reasons for Unemployment
In a country like India, there is much reason for a large section of the population for being unemployed. Some of these factors are population growth, slow economic growth , seasonal occupation, slow growth of the economic sector, and fall in the cottage industry.
Moreover, these are the major reason for unemployment in India. Also, the situation has become so drastic that highly educated people are ready to do the job of a sweeper. Besides, the government is not doing his work seriously.
Apart from all these, a large portion of the population is engaged in the agricultural sector and the sector only provides employment in harvest or plantation time.
In addition, the biggest reason of unemployment in India is its vast population which demands a large number of jobs every year which the government and authorities are unable to provide.
Consequences of Unemployment
If things will go on like the current scenario then unemployment will become a major issue. Apart from this, the following things happen in an economy which is an increase in poverty, an increase in crime rate, exploitation of labor, political instability, mental health, and loss of skills. As a result, all this will eventually lead to the demise of the nation.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Initiative by Government
The government has taken the problem very seriously and have taken measures to slowly reduce unemployment. Some of these schemes includes IRDP (Integrated Rural Development Programme), DPAP (Drought Prone Area Programme), Jawahar Rozgar Yojana, Employment Assurance Scheme, NRY (Nehru Rozgar Yojana), Training for self-Employment, PMIUPEP (Prime Minister’s Integrated Urban Poverty Eradication Program), employment exchange, Employment Guarantee Scheme, development of organized sector, small and cottage industries, employment in forging countries, and Jawahar Gram Samridhi Yojana and few more.
Besides, these schemes the government also make some rules flexible, so that employment can be created in the private sector also.
To conclude, we can say that the problem of unemployment in India has reached a critical stage. But, now the government and local authorities have taken the problem seriously and working on it to reduce unemployment. Also, to completely solve the issue of unemployment we have to tackle the main issue of unemployment that is the vast population of India.
FAQs about Unemployment
Q.1 Why there is a problem of unemployment in India? A.1 Due to overpopulation and lack of proper skills there is a problem of unemployment in India.
Q.2 Define Disguised unemployment? A.2 Disguised unemployment refers to a form of employment in which more than the required numbers of people work in industry or factory. And removing some employee will not affect productivity.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Unemployment Essay
Introduction.
Unemployment can be defined as the condition where citizens of a country are jobless and have in the recent past been involved in searching work without a success. Unemployment rate can be defined as the prevalence of unemployment opportunities in a country. The unemployment index is calculated by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by the number of individuals in the labour force (Arestis & John 15).
I have chosen the unemployment situation because of the increasing and prevalent unemployment rates in various countries.
Recent statistics indicate that, the rate of unemployment is on the increase and there is a lot of information to cover the complex area of unemployment. There are various reasons which cause unemployment in a country. The following are some of the reasons that cause unemployment rate in a country (Arestis & John 20).
- Advances in new technologies. New technologies to a large extent replace the human labour force which renders most human beings as unemployed.
- Population increase. The level of unemployment is believed to go up as population in a country increases. Increase in population leads to an increased pressure on the available resources. These limited resources are few and cannot accommodate the increasing demands of the population
- National policies. Some countries have stringent national policies that favour the increase in the unemployment levels in a country. These national policies will always restrict the participation of certain gender groups in specific employment sectors. For example, some countries restricts the participation of women in many employment sectors especially the building, and construction sector.
- Political environments also play a major role towards increasing the rate of unemployment. Political environments that increase the rate of unemployment are quite dominant especially in the developing countries. Such environments will enhance political vices such as nepotism and corruption which undermines the possibility of having fair distribution of employment opportunities to citizens.
- Economic depression. Economic depression is a form of economic recession that is long-term which is characterized by a downturn in the various economic activities in a country.
In analyzing this complex situation of unemployment, it is of vital importance to consider the application of various system analyzing tools such as “tools, methods, methodology and many techniques”. This will make the analysis of the complex situation being analyzed to be understood easily.
In my research I will analyze the complex process of unemployment with the aim of creating a sustainable environment in the employment sector.
The research will encompass the various causes of unemployment rates, the challenges being encountered in the process of reducing unemployment rates. The research will critically analyze the various types of unemployment and, the mechanisms which can be adopted in order to reduce the prevalent rates of unemployment.
Unemployment is a complex problem facing many countries presently. The process of reducing unemployment rates can be a daunting process fraught with disappointments. As a summary of the major findings of the research, the major cause of unemployment is lack of information among citizens, and poor governance policies in a country (Arestis & John 30).
Various citizens are ignorant on how to effectively utilize the available natural and human resources to create employment. They lack a sense of creativity which could possibly create employment opportunities. Also, most citizens are ignorant on how to effectively participate in democratic governance process.
This ignorance eventually creates autocratic governance regimes which fosters nepotism and corruption. These political vices reduce the availability of employment opportunities in a country, leading to unemployment (Arestis & John 15).
One key requirement of a good system practitioner is the ability of the system practitioner to apply the various models, methods and theories of system practitioner into the real life.
My undertaking of this project will assist me to apply the various system practitioner concepts learnt in class to the real life complex scenario of unemployment (Jacques & Stephen, 1994, pg. 21). In analyzing the complexity associated with unemployment, I will consider the various theories of complex management which I will discuss along with the development of this paper.
Applying hard systems method
Before analyzing the complex process of unemployment, it is important to make a distinction between hard and soft systems. Hard systems can be defined as those problems that deal with the “how” questions. For example, the question of how to increase the rate of employment is an example of a hard problem.
A hard problem is always characterized by the fact that there is a distinct solution, and there are a number of defined goals that are well defined which should be accomplished. On the other hand, a soft system is a problem that encompasses both the “how” and “what” questions (Jacques & Stephen, 1994, pg. 27)
The complex process of unemployment could be well analyzed using the hard system method of approach. The hard system method tries to analyze a complex problem through many stages which will be discussed in this paper.
There are various advantages that are associated with the use of the hard system methodology of concept analysis. The following are some of the advantages of using the hard system method (Jacques & Stephen, 1994, pg. 35)
- It provides a deeper understanding and analysis of the problem of unemployment and answers the question of how to mitigate the unemployment problem.
- Hard system analysis provides answers to other complex problems related to unemployment like how to use technology to increase the rate of employment.
The following diagram indicates the application of hard system in the analysis of unemployment.
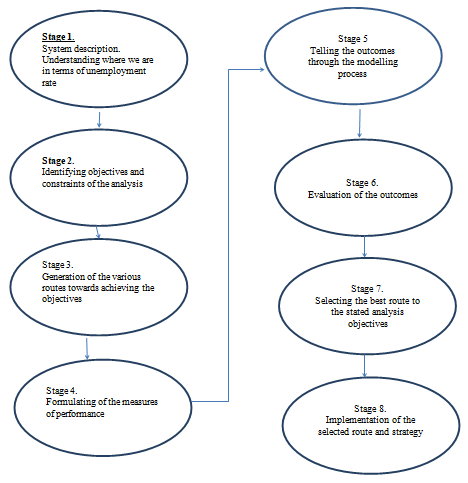
The above diagram indicates the various processes that will be undertaken in the analysis of the unemployment problem.
Stage 1. System description
System description will always indicate the current position and status of the problem being analyzed. Currently we are experiencing a high rate of unemployment which is characterized by the increasing population rate. The world population is estimated at 7 billion people.
The available limited employment resources are not sufficient to carter for the demands of the 7 billion individuals. This eventually piles up pressure on the resources that could be used to create employment opportunities, hence leading to an increased level of unemployment (Steger, Maznevski & Wolfgang 39).
The following table illustrates the world population by continent by 2011.
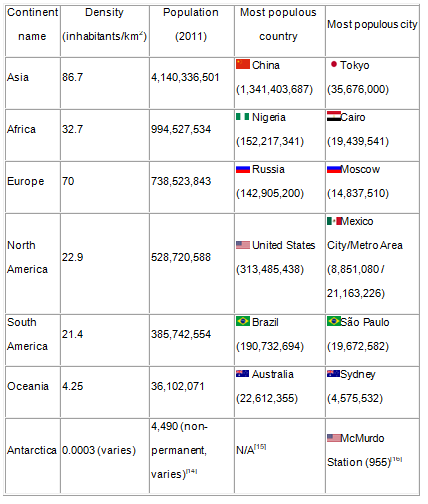
The alarming increase in the level of unemployment creates a need for analyzing the complex concept of unemployment with the aim of unmasking the strategies to be adopted in order to reduce unemployment rates (Arestis & John 55).
The following table indicates the world top ten countries by unemployment rate
The above data directly underpins the fact that unemployment is a complex prevalent issue. If much is not done to contain the issue, then, the issue will become out of control and cause adverse effects to the limited human, and natural resources available (Arestis & John 60).
Stage 2. Identification of constraints and objectives
The main objective of this sturdy is to identify the various causes of unemployment and any relevant measure that can be adopted to mitigate the problem of unemployment. Also, the sturdy is aimed at identifying the reasons as to why there is a huge gap between the unemployment rates in developed countries and the developing countries (Steger, Maznevski & Wolfgang 40).
The major projected constrain is the political environments and government policies and ideologies governing the utilization of resources, and the creation of employment opportunities.
Stage 3. Generation of routes to objectives
- Governments and relevant stakeholders should ensure that, there is gender equity and equality in the allocation of employment opportunities.
- Governments should adopt various strategies that will involve the citizens in the creation of employment opportunity for self-sustainability. A self-sustenance economy should be adopted which can be achieved through promotion of innovation and creativity.
- Removal of political and governance ideologies that promote nepotism, and corruption.
- Creation of public awareness and increased public participation in the governance process.
Stage 4. Formulating measures for performance
Measures of performance will measure to what extent has the research objectives been met. In order to measure the performance, the unemployment index will be recorded for the next five years after the activities stipulated in the routes to objectives have been undertaken.
The unemployment index obtained will then be compared to unemployment index done before undertaking this research. The comparison will give vital information as to whether there is been an improvement in the unemployment index after the adoption of the routes to objectives (Zimmer & Jake 44).
Stage 5. Modeling
The modeling process will involve those activities that are geared towards determining the outcomes of the research (Zimmer & Jake 51). In order to identify the outcomes, a survey will be carried out after every year for the next five years to find out the rate of unemployment.
This will be calculated by dividing the number of employed individuals by the number of unemployed individuals. The index obtained will then be compared in order to determine whether there is an improvement or a decline in the unemployment rate (Arestis & John 31).
Stage 6. Evaluation
The evaluation stage is the most important stage in the analysis of the complex issue. Evaluation will involve the analysis of the outcomes obtained from the modelling stage. The evaluation will involve the analysis of the disparities that will be recorded in the research.
This will involve the sturdy of what factors are causing the disparity and how to re-align and reconfigure the process routes in order to achieve the research objectives. Evaluation process might also include the prototyping technique where the routes are tested, and retested in order to determine their viability before being fully implemented (Zimmer & Jake 71).
Stage 7. Selecting the best routes to objectives
After the evaluation process, the best route towards achieving the objectives should be selected. The route chosen should ensure that the research objectives have been met to a large extent. In the analysis of unemployment, the best route that was identified was the creation of awareness and involving the individuals in the governance process (Steger, Maznevski & Wolfgang 59).
This route will increase the level of democracy in a country hence creating equal employment opportunities for both women and men. Also, creating public awareness will ensure that citizens are well equipped with knowledge of how to effective utilize resources and create employment opportunities.
Also, public participation in the governance process will ensure that the governance policies adopted foster democracy which is a key ingredient towards reducing the rate of unemployment (Arestis & John 75).
Stage 8. Implementation of the selected routes
The implementation process will involve the process of adopting and enrolling the best selected route. In the case of unemployment, the selected route of creating awareness and increasing public participation in the governance process will be adopted.
Creating awareness will involve conducting of seminars to enlighten the public on how to effectively use the available resources, and how to create employment opportunities through innovation (Steger, Maznevski & Wolfgang 69).
Public participation in the process of policy formulation will be achieved through promotion of civic education among citizens on how to carefully vote and chose leaders with integrity.
Also, the civic education will be aimed at increasing public participation in government related projects, and governance processes starting from the grassroots government structures. Also, the civic education will aim at educating citizens on how they can get access to public funds and amenities.
Stakeholders involved
Stakeholders can be described as those people who are in one way or the other affected by the problem of unemployment. Also, stakeholders in one way or the other affect the entire problem of unemployment. Stakeholders can negatively or positively be affected by the unemployment concept.
On the other hand, stakeholders can positively or negatively influence the prevalence of unemployment concept (Jacques & Stephen, 1994, pg. 75)
The following tables indicates a summary of the how stakeholders are affected/affect the unemployment concept
Ethicality statement
As a system practitioner I fully commit myself to the various ethical guidelines that should be followed whenever undertaking any research work. I will consider the following ethical consideration I my research undertaking:
- The data collected will be solely used for the purpose of the research, and no client data will be used for any other purposes not stipulated in the research.
- The clients will be fully informed on the purpose of the research, and the duration the research is going to take.
- The participation of subjects in the research will be voluntary, and out of consent. Where approval is required, then, the relevant approving bodies will be sought.
Conclusion and recommendations
In conclusion, it is evident from the research that unemployment is a complex issue that can be solved abstractly. With the increasing levels of unemployment, much has to be done in order to mitigate and reduce the rate of unemployment. This calls for public awareness, and participation in the entire process of creating employment. Such a complex issue should not be entrusted in the hands of greedy and selfish leaders.
Project log
The entire project will be spread over a period of six weeks with the first two weeks dealing with the preparation process and the last four weeks dealing with the data collection and analysis. The five weeks have been broken into three phases.
The following table indicates the project log phases.
Week 1 and week 2
During the first two weeks, I was involved in the process of consulting my colleagues and tutor to try and sought out their opinion about the topic. This gave a chance to discuss the various available methodologies that could be used in the sturdy. Also, this gave a chance to identify whether unemployment is a complex process or not.
Also, during the first week, I was able to undertake a literature review in order to determine what other researchers have done about the unemployment concept. The literature review sufficed me with relevant information about the unemployment concept.
Also, the information obtained was useful in avoiding mistakes done by previous researchers. The literature review involved researching the relevant literature materials like the internet, books, journals, and articles. I also obtained a chance of visiting various libraries in order to find out more information about the unemployment concept.
Week 3, 4 and 5
Most of the research work was conducted during the third, fourth and the fifth week. Various data was collected about the unemployment rate of individuals. Also, clients were required to fill in a survey form and a questionnaire in order to determine the causes of unemployment. Also, the subjects were required to give their individual opinions about what could be done in order to reduce the rate of unemployment.
Various data collections methods were employed in the process of data collection which includes the following methods; survey forms, questionnaires, and interviews.
Subjects were required to fill in questionnaires which sought to find out what were the causes of unemployment and what could be done to reduce the unemployment rates. Subjects were also required to fill in a survey form to determine whether the government is doing much to contain the problem of unemployment.
A series of interviews were also conducted with the aim of finding more first-hand information about the problem of unemployment. A total of three interviews were conducted during the entire period of the project. The following are the interviews that were conducted during the time of research.
The sixth week of the research was purely dedicated to data analysis and the sturdy of the findings. The data collected was analyzed and compared to previous data that was collected by other researchers on the same subject. The data analysis stage involved the application of the hard system on the complex process of unemployment. Various stages of the hard system methodology were studied in respect to unemployment.
Also, the compilation of the results obtained was done on the sixth week. This was the last week of the project undertaking, and due consultation was made to ensure that the project is up to date and with the relevant requirements.
I also, spent some time with my project supervisor in order to discuss the application of TMA in the complex process of unemployment. My supervisor advice helped a lot in the development of the project in the sense that, the information I was given largely assisted in the ensuring the realization of the research objectives.
Summary of the project log
In this section of the report, I will cover a brief summary of what I have been able to undertake during my six weeks of undertaking the project.
Undertaking the T306 course has largely helped build more on the concept that I learnt in my previous course, T205-An approach to system thinking. Managing complexity has equipped me with knowledge of how to apply various managing complexity theories, systems, and methodology in analyzing complex situations.
During the first five weeks of my project undertaking, I was extensively involved in the process of data collection and literature review. This introduced me to a number of literature and concept regarding the problem of unemployment. It also introduced me to a wide range of knowledge regarding data collection methods like interviews, questionnaires, and surveys.
The last week of the project was dedicated to data analysis. During this period of data analysis, various data analysis techniques were employed to analyze the data. This introduced me to a wide range of scientific data analysis methods of analyzing data.
Client report
The major client in the above research is the unemployed citizen or individual. They are the ones who are largely affected by the rising unemployment rate. Most of the unemployed individuals or citizens have the common ideology that it is the responsibility of government and private sectors to create employment.
Such an ideology is wrong because the process of creating employment opportunities is neither a government responsibility nor the responsibility of the private sector. It is a collective responsibility that has to be done by the collaboration of the citizens, the private sector, and the government.
There are various forms of employment that currently exists. One can be self employed which means that, they are their own employers. This form of employment fosters renovation and a spirit of entrepreneurship among citizens. This spirit eventually promotes innovation and creativity which eventually creates employment opportunities.
Also, citizens should be made to understand that, democracy plays a major role towards creation of employment opportunities. Democracy ensures accountability and transparency towards the use of resources, hence creating avenues for more employment opportunities. On the other hand, corruption, nepotism, and violence lead to misuse of resources which eventually blocks avenues for creating employment opportunities.
In order to reduce the adverse effects associated with unemployment, citizens should engage in innovation and creative activities. This will enhance the proper utilization of resources and eventually creating employment opportunities. One major desirable aspect of a good economy is the ability to be self sustainable.
A self sustainable economy will ensure that citizens have the services and products they require. One way of ensuring a self sustaining economy is by having citizens engage in innovative and creative activities. Such activities will lead to specialization, and creation of more job, and employment opportunities.
Works Cited
Arestis, Philip & McCombie, John. Unemployment: Past and Present . Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan, 2009. Print.
Jaques, Elliott, and Stephen, Clement. Executive Leadership: A Practical Guide to Managing Complexity . Malden, Mass: Blackwell, 1994. Print.
Steger, Ulrich & Maznevski, Martha & Wolfgang, Amann. Managing Complexity in Global Organizations . Chichester, West Sussex, England: John Wiley & Sons, 2007. Print.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 27). Unemployment. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-essay/
"Unemployment." IvyPanda , 27 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Unemployment'. 27 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Unemployment." February 27, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Unemployment." February 27, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Unemployment." February 27, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-essay/.
- Unemployment Effects on Lithuania Individuals
- Being Unemployed and the Impact of Unemployment as a Broad Issue
- Measuring Unemployment Issues in Society
- Unemployment in the US: Job Favoritism
- Business Cycle and Unemployment
- Macroeconomics in Unemployment
- Unemployment Rates in the U.S.
- Unemployment in Sweden: Causes and Solutions
- Work and Good Health of the Employed and the Unemployed
- Unemployment Rate as the Biggest National Economy Challenge
- Cuban Model as a Solution to Economic Problems in the Third World?
- US Problems: Medicare Program Ineffectiveness
- Labor Unions Negative Effects on Economics
- The Economic Problem for Marx
- Critical Analysis: Does Cultural Capital Structure American Consumption

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Unemployment: 100 to 300 Words
- Updated on
- Mar 30, 2024

Writing an essay on unemployment provides an opportunity to explore a critical issue affecting societies worldwide. Unemployment, a multifaceted problem, has far-reaching consequences that touch upon various aspects of individuals, families, and nations. In this essay, we will delve into the complexities of unemployment, examine its causes and consequences, discuss government initiatives, and shed light on potential solutions.

Table of Contents
- 1 What is Unemployment?
- 2 Essay on Unemployment in 100 words
- 3 Essay on Unemployment in 200 words
- 4 Essay on Unemployment in 300 words
- 5 Tips to Ace in Writing An Essay
Must Read: The Beginner’s Guide to Writing an Essay
What is Unemployment?
Lack of jobs leads to unemployment. It is a very serious economic and social concern that is happening all around the globe leading to many social ills. This issue is a major one and hence many governments are trying to address it. When people of a nation are employed, that leads to the economic and social well-being of that nation. To address it, the education system needs to be modeled differently so as to increase the employability of people. In democracies, political parties use unemployment as a core issue in their election manifestos.
Essay on Unemployment in 100 words
Unemployment refers to the condition when individuals, capable and willing to work, are unable to secure gainful employment. It is a pervasive issue across the globe, with varying degrees of impact on societies. Unemployment results in financial instability, and emotional distress, and hampers individual growth. Governments and organizations must collaborate to create opportunities for employment through skill development and policy implementation.
Essay on Unemployment in 200 words
Unemployment, a pressing concern globally, stems from multiple factors that hinder the workforce’s engagement in productive activities. It affects both developed and developing nations, contributing to economic imbalances and social disparities. The consequences of unemployment include reduced income levels, increased poverty rates, and strained government resources. Moreover, the psychological toll it takes on individuals and families can be severe, leading to stress, depression, and strained relationships.
Essay on Unemployment in 300 words
The intricate web of unemployment is spun from a mix of causes, ranging from economic fluctuations to structural shifts in industries. Cyclical unemployment, driven by economic downturns, and structural unemployment, resulting from a mismatch between skills and job openings, are widespread forms. Additionally, technological advancements lead to technological unemployment as machines replace human labour.
Unemployment has cascading effects on societies. Diminished purchasing power affects market demand, thereby impacting economic growth. As unemployment rates rise, so does the burden on social welfare programs and the healthcare system. The phenomenon also fuels social unrest and political instability, making it a challenge governments cannot ignore.
Governments worldwide have initiated strategies to tackle unemployment. Skill development programs, vocational training, and entrepreneurship initiatives are designed to equip individuals with market-relevant skills. Furthermore, promoting labour-intensive industries and investing in sectors with growth potential can generate employment opportunities.
In conclusion, unemployment is a complex issue that necessitates a multi-pronged approach. Governments, industries, and individuals must collaborate to alleviate its impact. Effective policy implementation, education reforms, and the cultivation of entrepreneurial spirit can pave the way towards reducing unemployment rates and fostering a more stable and prosperous society.
Tips to Ace in Writing An Essay
Before we dive into the specifics of unemployment, let’s briefly discuss some tips to enhance your essay-writing skills:
- Understand the Prompt: Ensure a clear understanding of the essay prompt to address all its components effectively.
- Research Thoroughly: Gather relevant information from credible sources to build a comprehensive and informed essay.
- Organize Your Thoughts: Create an outline to structure your essay logically, allowing your ideas to flow coherently.
- Introduction and Conclusion: Craft a compelling introduction to engage your readers, and a succinct conclusion to summarize your key points.
- Use Clear Language: Express your ideas using clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or overly complex vocabulary.
- Provide Examples: Illustrate your points with real-life examples to enhance understanding and credibility.
- Edit and Proofread: Revise your essay for grammar, punctuation, and coherence to ensure a polished final draft.
Also Read: Unemployment v/s Underemployment – What’s Worse?
Related Reads:-
Unemployment refers to the state in which individuals who are willing and able to work are without gainful employment opportunities. It is a condition where individuals seek jobs but are unable to secure them, leading to financial instability and societal challenges.
Unemployment, as discussed in the essay, is a multifaceted issue encompassing the lack of employment opportunities for willing and capable individuals. It explores various forms of unemployment, its causes, far-reaching consequences on economies and societies, and the role of governments in implementing solutions to mitigate its impact.
Unemployment is the term used to describe the situation where individuals of working age are actively seeking employment but are unable to find suitable job opportunities. It signifies a gap between the available workforce and available jobs, often leading to economic and social challenges within a society.
Unemployment emerges as a prominent thread, influencing economic, social, and psychological realms. As we’ve explored in this essay, comprehending the causes and consequences of unemployment is pivotal in devising solutions. Governments, institutions, and individuals must strive collectively to unravel this issue’s complexities and weave a fabric of employment opportunities, stability, and progress. We hope that this essay blog on Unemployment helps. For more amazing daily reads related to essay writing , stay tuned with Leverage Edu .
Manasvi Kotwal
Manasvi's flair in writing abilities is derived from her past experience of working with bootstrap start-ups, Advertisement and PR agencies as well as freelancing. She's currently working as a Content Marketing Associate at Leverage Edu to be a part of its thriving ecosystem.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Essays About Unemployment: Top 6 Examples and 5 Prompts
Read our guide to see helpful essay examples and prompts to further your understanding and write essays about unemployment.
Unemployment is an unfortunate circumstance many find themselves in; it is a challenge that civilized society faces today. When people are unemployed, they look for jobs but cannot get them. As a result, they are left without a source of income and cannot adequately provide for themselves and their families. This, in turn, can lead to various issues, including depression.
Unemployment is a social, economic, and political issue. It leaves many people in poverty and prevents people from obtaining a source of income. As a result, politicians capture the eyes of voters by promising to lower the unemployment rate to get elected.
You can get started by reading these essay examples if you are writing essays about unemployment.
6 Examples of Essays About Unemployment
1. unemployment reflection by christopher haynes, 2. what i learned from nearly a year of unemployment by becca slaughter, 3. why aren’t europe and canada in the same boat as u.s. for unemployment by glen hendrix, 4. a global dilemma: how unemployment creates poverty by tess hinteregger, 5. why has covid-19 been especially harmful for working women by nicole bateman and martha ross, 6. youth day and ordeal of nigerian youth by utomi jerome-mario, essay prompts about unemployment, 1. unemployment during the covid-19 pandemic, 2. the connection between unemployment and crime, 3. unemployment: whose fault is it, 4. the causes of unemployment, 5. the effects of unemployment.
“In order to secure work, we must be prepared to change or upgrade our skills and be willing to relocate if necessary. But some people are not interested in retraining to find work in another field, some people do not have the confidence to go out and look for work, and some refuse to accept a job they feel is below their level. Unless people like this change their attitudes, they will not be able to find work.”
Haynes provides two perspectives on unemployment; first, that the government should do more to address it, and second, that if people want work, they must adjust to make a living. He believes that many are unemployed because they are unwilling to change their skillset or relocate to get a job. Therefore, more should be done to reduce unemployment, but it goes both ways; everyone must put in the effort.
“I remember feeling embarrassed and powerless. I was angry it wasn’t my decision. I was happy I didn’t have to go back there, yet I was stressed about not having anywhere to go. Ultimately, I felt an overwhelming sadness that left me terrified. While I was overflowing with confusing and contradicting emotions, I somehow felt empty.”
In her essay, Slaughter reflects on her unemployed time and how it changed her. Her previous job was long and stressful, but whenever someone would ask her what she did for a living, she was embarrassed and regretful for not being there anymore. In addition to losing her job, she feels like she lost a part of herself at that time. Thankfully, she got a new job, one less taxing than her previous one.
“You would think paying all that money year after year to a government whose purpose is to “establish justice, insure domestic tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general welfare, and secure the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our posterity” would entitle that person to a modicum of “blessings” to insure his “tranquility” and “general welfare” in case of some stupid virus pandemic. It would certainly be the “just” thing to do. And that person’s “posterity” might look a bit less bleak. European governments and Canada did just that. And it’s not even explicitly stated in the preamble to their constitution.”
Hendrix criticizes the United States’ response to the unemployment problem caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, saying that Canada and European nations have done a much better job. He discusses how much better their unemployment benefit system is compared to the U.S. and how it is ironic that the United States, whose constitution says all of these things promoting justice and wellbeing, cannot provide that for its citizens during a global pandemic.
“While unemployment can create poverty, poverty also reduces the chance of being employed. To ensure that those who are affected by unemployment do not fall into the negative cycle, researchers believe that governments should focus on improving quality education and training all young people so they remain in school.”
Hinteregger, in her essay, explains the link between unemployment and poverty, writing that it leads to the loss of income. People will also have to raise their families in poverty, which perpetuates the cycle of poverty. In addition, the poor may resort to violence to make a living. She points out the sheer irony of this issue, as unemployment causes poverty while poverty may also reduce the chance of being employed.
“COVID-19 is hard on women because the U.S. economy is hard on women, and this virus excels at taking existing tensions and ratcheting them up. Millions of women were already supporting themselves and their families on meager wages before coronavirus-mitigation lockdowns sent unemployment rates skyrocketing and millions of jobs disappeared. And working mothers were already shouldering the majority of family caregiving responsibilities in the face of a childcare system that is wholly inadequate for a society in which most parents work outside the home.”
Bateman and Ross write about the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on women. Many women are forced to go through so much to provide for their families; however, the lockdowns led to many of them losing their jobs. The unemployment rate for women rose dramatically, by 12 percent, from February to April of 2020. It has been difficult for them to balance work with taking care of their families, women’s primary role as dictated by society.
“Youth unemployment is potentially dangerous as it sends a signal to all segments of the Nigerian Society. Here in Nigeria, the rate of youth unemployment is high, even at the period of economic normalcy i.e. the oil boom of the 1970s (6.2 per cent); 1980s (9.8 per cent) and the 1990s (11.5 per cent). Youth unemployment therefore is not a recent phenomenon. But if what happened in the 1980s/90s were a challenge of sorts, what is happening presently, going by the latest report by the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), is a challenge.”
Jerome-Mario’s essay focuses on several issues affecting the Nigerian youth, including unemployment. The country has a high unemployment rate; over a fourth of the youth population is unemployed. He stresses the importance of the youth using their voice to make a change and to persuade the government to care for its citizens more.

The pandemic and its lockdown policies have undoubtedly caused many people to lose jobs. Look into the impact of COVID-19 on the unemployment rate, particularly during the early months of the pandemic. Which sectors were most affected? Pull data and statistics to show how the public was affected by the covid-19 pandemic in terms of unemployment.
Many say that unemployment leads to higher crime rates. Do you believe this is true? Research how unemployment is linked to crime; examine the effects of unemployment on mental health; and conclude whether this may contribute to the increased likelihood of committing a crime.
In Haynes’ essay, he claims that employers/the government, and workers are to blame for unemployment. After reading his essay and both arguments, who do you believe is at fault? Explain your response in detail, and make sure to provide a solid base of evidence.
Unemployment has many contributing causes. Assuming a non-pandemic setting, research what causes unemployment and list them down in your essay. Elaborate on each one and, if you can draw connections, explain them as well.
As a grave issue, unemployment has many severe effects, notably poverty. For your essay, write about the effects of unemployment on a person, both physical and mental. How are they connected? What secondary effects might they produce? For a compelling and argumentative essay, answer these questions using research material and interview data.
For help with this topic, read our guide explaining what is persuasive writing ?If you are interested in learning more, check out our essay writing tips !

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
Unemployment in the Country
How it works
An adage says “an idle hand is a devil’s workshop”. The enormous growth of unemployment in our society today calls for alarm, and it is expedient for all nations to figure out what leads to this great dilemma. Unemployment has messed up our society because of three major factors, such as increase in population, lack of encouragement for self-employment, and change in technology.
One of the major causes of unemployment is increase in population. Increase in population is an event experienced when the number of people in a particular place exceeds the available resources to sustain them sufficiently.
The number of people who are seeking employment is daily increasing, and it is more burdensome to make jobs available for all these large number of job seekers. For example, if a government project is projected to cover 50,000 unemployed people in next five years, the increase in population before that time will leave other set of people unemployed. A situation like this makes demands for job to be more than the available jobs. Undoubtedly, all these will end up in increased number of unemployed people. The unemployment condition will linger as long as the demand and supply gap persists. This is currently happening in Asian countries.
Another cause of unemployment is lack of encouragement for self-employment. Many popular industries we see today are products of self-employment. If governments don’t encourage people by providing what they need to be self-employed, unemployment will definitely persist. Nigeria, for instance, is a country blessed with talented young people, but she doesn’t encourage the talented young ones by providing constant electricity which is vital in self-employment. When vocational skills are tagged tuition free, many will learn to be self-employed which will turn out to put unemployment to flight. Our system of education has failed in developing or encouraging the zeal of self-employment among our youths. When self-employment is not encouraged, unemployment will remain.
Finally, unemployment is not just caused by increase in population and lack of encouragement for self-employment alone but also caused by the change in technology (advanced technology). This is a situation whereby technology has advanced and begins to compete with man. A typical example is when a firm lays off machinery workers and substitutes them with robots. There is need for workers to add more knowledge and skills in order for them not to be replaced by the advanced technology. Those that don’t surpass the function of the advanced technology will ultimately become unemployed at the end. Labor saving machine is another example of what industries are using in place of man in order to maximize production and profit. As technology is changing, it is also changing other things.
To sum up, causes of unemployment vary from country to country, and its effects include psychological and financial problem. The major causes of unemployment are increase in population, lack of encouragement for self-employment, and change in technology. Unemployment has totally become a major problem which affects our community. Therefore, countries should construct more industries so as to give more opportunities to meet the needs of the increased population. They should also minimize the involvement of the advanced technology that replaces man and encourage self-employment.

Cite this page
Unemployment in the country. (2020, Feb 15). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/unemployment-in-the-country/
"Unemployment in the country." PapersOwl.com , 15 Feb 2020, https://papersowl.com/examples/unemployment-in-the-country/
PapersOwl.com. (2020). Unemployment in the country . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/unemployment-in-the-country/ [Accessed: 27 Apr. 2024]
"Unemployment in the country." PapersOwl.com, Feb 15, 2020. Accessed April 27, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/unemployment-in-the-country/
"Unemployment in the country," PapersOwl.com , 15-Feb-2020. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/unemployment-in-the-country/. [Accessed: 27-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2020). Unemployment in the country . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/unemployment-in-the-country/ [Accessed: 27-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

19.4: Causes of Unemployment around the World
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 164359

Learning Objectives
- Explain the nature and causes of unemployment
- Analyze the natural rate of unemployment and the factors that affect it
- Identify how undeveloped labor markets can result in the same hardships as unemployment
We can categorize the causes of unemployment in the world's high-income countries in two ways: either cyclical unemployment caused by the economy when in a recession, or the natural rate of unemployment caused by factors in labor markets, such as government regulations regarding hiring and starting businesses.
Unemployment from a Recession
For unemployment caused by a recession, the Keynesian economic model points out that both monetary and fiscal policy tools are available. The monetary policy prescription for dealing with recession is straightforward: run an expansionary monetary policy to increase the quantity of money and loans, drive down interest rates, and increase aggregate demand . In a recession , there is usually relatively little danger of inflation taking off, and so even a central bank, with fighting inflation as its top priority, can usually justify some reduction in interest rates.
With regard to fiscal policy , the automatic stabilizers that we discussed in Government Budgets and Fiscal Policy should be allowed to work, even if this means larger budget deficits in times of recession. There is less agreement over whether, in addition to automatic stabilizers, governments in a recession should try to adopt discretionary fiscal policy of additional tax cuts or spending increases. In the case of the Great Recession, the case for this kind of extra-aggressive expansionary fiscal policy is stronger, but for a smaller recession, given the time lags of implementing fiscal policy, countries should use discretionary fiscal policy with caution.
However, the aftermath of the Recession emphasizes that expansionary fiscal and monetary policies do not turn off a recession like flipping a switch turns off a lamp. Even after a recession is officially over, and positive growth has returned, it can take some months—or even a couple of years—before private-sector firms believe the economic climate is healthy enough that they can expand their workforce.
The Natural Rate of Unemployment
Unemployment rates in European nations have typically been higher than in the United States. In 2020, before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic , the U.S. unemployment rate was 3.5%, compared with 8.5% in France, 10% in Italy, and 7.1% in Sweden. We can attribute the pattern of generally higher unemployment rates in Europe, which dates back to the 1970s, to the fact that European economies have a higher natural rate of unemployment because they have a greater number of rules and restrictions that discourage firms from hiring and unemployed workers from taking jobs.
Addressing the natural rate of unemployment is straightforward in theory but difficult in practice. Government can play a useful role in providing unemployment and welfare payments, for example, by passing rules about where and when businesses can operate, and assuring that the workplace is safe. However, these well-intentioned laws can, in some cases, become so intrusive that businesses decide to place limits on their hiring.
For example, a law that imposes large costs on a business that tries to fire or lay off workers will mean that businesses try to avoid hiring in the first place, as is the case in France. According to Business Week , “France has 2.4 times as many companies with 49 employees as with 50 ... according to the French labor code, once a company has at least 50 employees inside France, management must create three worker councils, introduce profit sharing, and submit restructuring plans to the councils if the company decides to fire workers for economic reasons.” This labor law essentially limits employment (or raises the natural rate of unemployment).
Undeveloped and Transitioning Labor Markets
Low-income and middle-income countries face employment issues that go beyond unemployment as it is understood in the high-income economies. A substantial number of workers in these economies provide many of their own needs by farming, fishing, or hunting. They barter and trade with others and may take a succession of short-term or one-day jobs, sometimes receiving pay with food or shelter, sometimes with money. They are not “unemployed” in the sense that we use the term in the United States and Europe, but neither are they employed in a regular wage-paying job.
The starting point of economic activity, as we discussed in Welcome to Economics!, is the division of labor, in which workers specialize in certain tasks and trade the fruits of their labor with others. Workers who are not connected to a labor market are often unable to specialize very much. Because these workers are not “officially” employed, they are often not eligible for social benefits like unemployment insurance or old-age payments—if such payments are even available in their country. Helping these workers to become more connected to the labor market and the economy is an important policy goal. Recent research by development economists suggests that one of the key factors in raising people in low-income countries out of the worst kind of poverty is whether they can make a connection to a somewhat regular wage-paying job.
Economist Sir W. Arthur Lewis examined such transitions of labor and the impact on economic development. His core theoretical framework—the dual sector economy—proposes that, essentially, the marginal product of low-skilled workers is greater in the manufacturing sector than it is in the agricultural sector. That’s because most agricultural societies are both mature and have fixed inputs (land, water, and related resources); the marginal product of additional farmers on that land is nearly zero, creating what Lewis termed “surplus workers.” Early-stage manufacturing sectors, however, have great need for low-skilled workers, and can make better use (greater marginal product) of them. Their wages will remain low, but as stated above, the wages are more likely to be consistent and therefore move toward a large-scale transition of the labor force.
We have seen this practically in many nations experiencing a shift in labor, particularly in China. In many regions, it is marked by a level of migration—people leaving rural areas for cities or manufacturing zones. At some point, nations achieve what economists call the Lewis turning point, in which the surplus agricultural labor is fully absorbed into the manufacturing sector. Typically, when this occurs, wages in both agricultural and manufacturing sectors begin to rise in a sustainable manner. Despite massive transformation in the Chinese economy over the past decades, economists dispute whether China has actually reached the Lewis turning point.
Economic transition is not without its downsides. Many manufacturing-focused countries still rely heavily on their agricultural sectors for their own sustenance and as a core part of international trade. As the agricultural sector faces competition from manufacturing, and as people physically leave rural areas, farming economies can suffer downturns and unpredictability. Finally, countries or individual farmers seeking to make up for their missing labor may encourage migration and/or immigration that may cause political or financial conflict.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Costs to the Individual
Costs to society, costs to the country, the bottom line, the cost of unemployment to the economy.
It’s not just the price of paying out benefits
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
While economists and academics make convincing arguments that a certain natural level of unemployment cannot be erased, elevated unemployment imposes high costs on the individual, society, and the country.
Worse yet, most of the costs are of the dead loss variety, where there are no offsetting gains to the costs that everyone must bear. Depending on how it’s measured, the unemployment rate is open to interpretation. In addition, underemployment can be extremely detrimental to the economy of society as well. Unemployment numbers include people who are working at low-paying or low-skill jobs that do not provide enough full-time hours for benefits or enough to earn a living wage.
Global and national emergencies can trigger both unemployment and underemployment. For example, when the COVID-19 pandemic hit, it left more than 10 million Americans jobless in its first two weeks. The situation was so serious that the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act expanded unemployment benefits to self-employed and part-time workers through Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Assistance and provided up to 39 weeks of benefits beginning on or after Jan. 27, 2020, and ending on or before Dec. 31, 2020.
Key Takeaways
- Unemployment has costs to a society that are more than just financial.
- Unemployed individuals not only lose income but also face challenges to their physical and mental health.
- There are societal costs of high unemployment.
- Governmental costs go beyond the payment of benefits to the loss of the production of workers, which reduces the gross domestic product (GDP).
- Unemployment affects not on the individual but also their spouses, partners, and children.
The costs of unemployment to the individual are not hard to imagine. When a person loses their job, there is often an immediate impact on their standard of living. Before the Great Recession , the average savings rate in the U.S. had been drifting down toward zero (and sometimes below). There are anecdotal reports that the average person is only a few weeks away from serious financial trouble without a paying job.
Even those eligible for unemployment benefits and other forms of government assistance find it is not enough as these benefits often only replace 50% or less of their regular income. That means these people are consuming far less than usual. However, the economic consequences can go beyond just less consumption. Many people will turn to retirement savings in a pinch, and draining these savings has long-term ramifications.
Prolonged unemployment may lead to an erosion of skills, basically robbing the economy of otherwise useful talents. At the same time, the experience of unemployment (either direct or indirect) may alter how workers plan for their futures—prolonged unemployment can lead to greater skepticism and pessimism. On a similar note, the absence of income created by unemployment can force families to deny educational opportunities to their children and deprive the economy of those future skills.
Last but not least, there are other costs to the individual. Studies have shown that prolonged unemployment harms workers' mental health and can worsen physical health, and shorten lifespans.
The social costs of unemployment are difficult to calculate but no less real. When unemployment becomes a pervasive problem, there are often increased calls for protectionism and severe restrictions on immigration.
Protectionism can not only lead to destructive tit-for-tat retaliation among countries but reductions in trade harm the economic well-being of all trading partners.
Other social costs include how people interact with each other. Studies have shown that times of elevated unemployment may correlate both with less volunteerism and higher crime.
The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act expanded unemployment benefits to self-employed and part-time workers and helped keep individuals and families solvent during a global pandemic.
The economic costs of unemployment are probably more obvious when viewed through the lens of the national checkbook. Unemployment may lead to higher payments from state and federal governments for unemployment benefits, food assistance, and Medicaid.
Unemployment is also a dangerous state for the U.S. economy. Almost 70% of what the U.S. economy produces goes to personal consumption and unemployed workers.
Even those receiving government support cannot spend at prior levels. The production of those workers leaves the economy, which reduces the gross domestic product (GDP) and moves the country away from the efficient allocation of its resources. For those who subscribe to Jean-Baptiste Say’s theory that the production of goods creates its own demand, that is a serious issue.
It is also worth noting that companies pay a price for high unemployment as well. Unemployment benefits are financed largely by taxes assessed on businesses.
How Does a High Unemployment Rate Affect the Economy?
A high unemployment rate affects the economy in many ways. Unemployed people tend to spend less, may accrue more debt, and unemployment may lead to higher payments from state and federal governments for things like food stamps.
How Do I Get Unemployment Benefits?
You have to apply for unemployment benefits through your state. You can find your state's guidelines via the U.S. Department of Labor website, CareerOneStop . Some states will allow you to file a claim over the phone or online, other states make you file a claim in person. Make sure to have your contact information, like your social security number and information about your former employer on hand.
Should I Use My Retirement Savings if I Am Unemployed?
If you find your unemployment benefits running out or your benefits don't stretch enough to pay the bills, you could be tempted to pull money out of a retirement account. However, it isn't always the best idea. If you withdraw early, you will be hit with a 10% percent penalty tax, plus state and federal taxes, unless you meet certain eligibility requirements to waive the penalty tax. You could consider a loan from your retirement account, which does not incur penalities.
Governments worry about the consequences of inflation, but unemployment is likewise a serious issue. Apart from the social unrest and disgruntlement that unemployment can produce in the electorate, high unemployment can have a self-perpetuating negative impact on businesses and the country's economic health.
Worse still, some of the more pernicious effects of unemployment are subtle and long-lasting. Consumer and business confidence are key to economic recoveries, and workers must feel confident in their future to invest in developing the skills—and building the savings —that the economy needs to grow in the future. The unemployment costs go far beyond the accumulated sums handed out as unemployment insurance benefits.
International Monetary Fund. " Unemployment: The Curse of Joblessness ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Monthly Labor Review: Unemployment rises in 2020, as the Country Battles the COVID-19 Pandemic ."
U.S. Department of Labor. " Advisory: Unemployment Insurance Program Letter NO. 14-20 ," Page 3.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Monthly Labor Review: Great Recession, Great Recovery? Trends from the Current Population Survey ."
Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis, FRED. " Personal Saving Rate ."
American Psychological Association (APA). " The Toll of Job Loss ."
US National Library of Medicine. " Effects of unemployment on mental and physical health ."
American Immigration Council. " The Economic Blame Game: Immigration and Unemployment ."
Urban Institute. " Consequences of Long-Term Unemployment ," Pages 4 and 5.
U.S. Department of Labor. " Unemployment Insurance Relief During COVID-19 Outbreak ."
Bureau of Economic Analysis. “ National Income and Product Accounts Tables: Table 1.1.6. Real GDP ,” Select “Modify,” Select “First Year 2019,” Select “Series Annual,” Select “Refresh Table.”
Mises Institute. " Say's Law in Context ."
Internal Revenue Service. " Understanding Employment Taxes ," Page 7.
- What Is Unemployment? Causes, Types, and Measurement 1 of 43
- What Does Termination of Employment Mean? 2 of 43
- What Is an Unemployment Claim? 3 of 43
- Unemployment Compensation: Definition, Requirements, and Example 4 of 43
- What Is Severance Pay? Definition and Why It's Offered 5 of 43
- The Layoff Payoff: A Severance Package 6 of 43
- 7 Considerations When You Negotiate Severance 7 of 43
- 7 Effective Ways to Prepare for a Layoff 8 of 43
- Unemployment Insurance (UI): How It Works, Requirements, and Funding 9 of 43
- How to Apply for Unemployment Insurance Now 10 of 43
- Who Doesn't Get Unemployment Insurance? 11 of 43
- What Was Private Unemployment Insurance? 12 of 43
- How to Pay Your Bills When You Lose Your Job 13 of 43
- Can I Access Money in My 401(k) If I Am Unemployed? 14 of 43
- All About COBRA Health Insurance 15 of 43
- Medical Debt: What to Do When You Can’t Pay 16 of 43
- Help, My Unemployment Benefits Are Running Out 17 of 43
- What Is the Unemployment Rate? Rates by State 18 of 43
- How Is the U.S. Monthly Unemployment Rate Calculated? 19 of 43
- Unemployment Rates: The Highest and Lowest Worldwide 20 of 43
- What You Need to Know About the Employment Report 21 of 43
- U-3 vs. U-6 Unemployment Rate: What's the Difference? 22 of 43
- Participation Rate vs. Unemployment Rate: What's the Difference? 23 of 43
- What the Unemployment Rate Does Not Tell Us 24 of 43
- How the Unemployment Rate Affects Everybody 25 of 43
- How Inflation and Unemployment Are Related 26 of 43
- How the Minimum Wage Impacts Unemployment 27 of 43
- The Cost of Unemployment to the Economy 28 of 43
- Okun’s Law: Economic Growth and Unemployment 29 of 43
- What Can Policymakers Do To Decrease Cyclical Unemployment? 30 of 43
- What Happens When Inflation and Unemployment Are Positively Correlated? 31 of 43
- The Downside of Low Unemployment 32 of 43
- Frictional vs. Structural Unemployment: What’s the Difference? 33 of 43
- Structural vs. Cyclical Unemployment: What's the Difference? 34 of 43
- Cyclical Unemployment: Definition, Cause, Types, and Example 35 of 43
- Disguised Unemployment: Definition and Different Types 36 of 43
- Employment-to-Population Ratio: Definition and What It Measures 37 of 43
- Frictional Unemployment: Definition, Causes, and Quit Rate Explained 38 of 43
- Full Employment: Definition, Types, and Examples 39 of 43
- Labor Force Participation Rate: Purpose, Formula, and Trends 40 of 43
- Labor Market Explained: Theories and Who Is Included 41 of 43
- What Is the Natural Unemployment Rate? 42 of 43
- Structural Unemployment: Definition, Causes, and Examples 43 of 43
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/job_classifieds-5845c9e43df78c0230262b71.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Essay on Unemployment Rate
Introduction
The essay is focused on examining the issue of unemployment among people in various societies and countries around the world, the reasons for unemployment, types of unemployment, ways to overcome the issue of unemployment and examine the costs associated with unemployment. Unemployment is a major social issue among people in the economic market today, there are several reasons for unemployment in economics depending on the type of unemployment available, these can be directed to government, employer, supply of labor, among others. The types of unemployment can be directed to frictional unemployment, structural unemployment, cyclical unemployment, and seasonal unemployment. There is a need to solve the unemployment problem in the social economies, this can be done in several ways including enhancing political stability, promoting education, controlling the growth of population, among others. The issue of unemployment in the social economies has several costs ranging from loss of income among individuals, low standard of living among unemployed people, low production, and economic growth, among other costs.
Unemployment and reasons for unemployment
Unemployment is a major problem in various countries around the world, this is a situation whereby people do not have any work that can generate income and are actively searching for a job (Hauser & Burrows, 2018). Individuals in this situation are mostly employable and are actively searching for jobs. This can also include people who are working in jobs that are below their qualifications, experience, and satisfaction. The situation where there is a high level of unemployment will result in several economic distress and problems. The situation of unemployment hinders people to engage in productive work to facilitate development in the country. This will result in a decrease in economic productivity and development (Hauser & Burrows, 2018).
The two categories of unemployment are voluntary and involuntary unemployment, the situation where one moves out from a job to search for another is known as voluntary unemployment, and a situation where a person is laid off and now looking for a job is known as involuntary unemployment. Wolcott et al., (2020) in 2020, the coronavirus pandemic affected Singapore and the world, causing a high level of involuntary unemployment. There are several reasons for unemployment, inadequate job opportunities in a country can cause unemployment in the country. The slow economic development issue can result in unemployment, especially when the population growth is increasing.
The high growth of the population can result in unemployment challenges when the country is not developing and when fewer job opportunities are in the country. Also, people who depend on agriculture production work can become unemployed when the season is not favorable for plant growth. A decrease in industrialization and investment can account for unemployment in several countries that are not developing, the situation where there are few industries and investments are not available will have a severe influence on the employment of people in a developing country. Improper economic planning can also result in unemployment challenges, situations, where there is a gap between supply and demand of labor, which will result in unemployment.
Various types of unemployment
Hauser & Burrows, (2018) Types of unemployment can include frictional, cyclical, structural, institutional, and seasonal unemployment. These types of unemployment are based on voluntary and involuntary unemployment. Frictional unemployment is a situation where a person voluntarily moves from one job to another in a country. The time spent to get another job can be linked to unemployment, it may take some time before the person gets another job. Some people move to another location to search for a new job which can take some time before getting the desired job. When fresh graduate students’ transit to search for a job, the time spent before getting a job is also linked to frictional unemployment. The time can be very short or longer depending on the availability of the job the applicant is seeking (Hwang, 2019).
Hwang, (2019) cyclical unemployment is another type of unemployment where the decrease in production and demand for products results in a decrease in employment of new workers. The situation where a company is not getting enough purchases of goods from the market will decrease income level and ability to pay workers. This can lead to a decrease in salary, and an increase in savings. People will not be able to buy enough goods when their salary is decreased and savings are increased. The situation is cyclical in nature but can be resolved when economic growth and investment are facilitated in the country.
Structural unemployment is when there is a new change in the operation of a business, technology, and production. The situation whereby a company adapts to a new technological system or process will result in laying off workers who do not have the relevant skills for the new changes. There will be a need for retraining of staffs or workers to understand how to use new systems in the company (Wolcott et al., 2020).
Institutional unemployment occurs when there are changes in policies, institutional incentives, and interference of the free market condition in a country. The change in employment policies and strategies can result in laying off some workers in order to regulate the new policies.
Seasonal unemployment is a situation whereby workers that depend on jobs that operate in different seasons are not having jobs due to the unfavorable season or weather conditions to engage in such jobs. An example is farming, among others.
Various ways to overcome unemployment
Education is very important in solving the problem of unemployment, educating people will help increase their skills and ability to be employed and start their own businesses. Education will enable workers to advance their skills and employability level. The education system has to be improved in order to enhance the admission of students into higher studies in colleges and universities. The availability and improvement of vocational institutions can also facilitate the development of skills among students in the higher level of education. Students from these training institutions can start their own businesses after completion and reduce the unemployment rate in the country. The industrial technique can be enhanced to identify the employment needs of the country and improve labor-intensive technology in order to employ more people instead of using machines and other fully technological systems (Sari, 2019).
There is a need to design a policy to solve seasonal unemployment issues, mostly in the agriculture sector, the provision of alternative job opportunities for workers who depend on seasonal jobs will help reduce the unemployment rate during unfavorable seasons. Also, the use of multiple cropping can be encouraged in order to facilitate the production of crops favorable in any given season. The addition of varied plantations, animal husbandry, food processing, and other farming practices will enhance employment.
The use of communication and employment exchanges can be provided to enhance the dissemination of information regarding job opportunities available anytime. This will alert the public in order to enhance the employment rate and reduce frictional unemployment. There is a need to assist self-employed individuals in order to facilitate their work and production. This can be in a form of financial support, technical training, and raw material support in order to improve self-employed businesses.
The development and implementation of policies that encourage the development of more jobs in a country will help reduce unemployment. There is a need to increase development of jobs in a country and increase employment of labor in order to help them gain benefits and contribute towards societal development. There can also, be enhanced employment program facilitation, this is done by setting plans to develop infrastructure, power supply, roads, and other facilities that encourage production (Sari, 2019).
Costs associated with unemployment
There are some costs associated with unemployment which include individual and societal costs; the major cost to unemployed individuals is income lost, this is the situation where a person does not get any income due to unemployment. Unemployment affects people’s ability to earn money. The situation can hinder people’s ability to finance and take good care of themselves. The well-being of people becomes disrupted due to a lack of income to support themselves. The cost to society is a reduction in productivity through a decrease in goods and services, the people do not have money to purchase goods and services, this also affects the performance of companies and organizations in the society. The situation also causes waste of resources including labor, since the economy does not utilize these resources efficiently. The situation, when people take up jobs below their qualifications, brings about inefficient use of labor. This also results in the loss of skills and labor capital in the economy (Alrasheedy, 2019).
The situation of unemployment can affect the health of people in the country, this includes the mental and physical wellbeing of individuals in the country. There is an incidence of family and social unrest, an increase in the crime rate, and other bad practices in society. The situation of unemployment can cause disruption on confidence and self-esteem among people who are unemployed (Alrasheedy, 2019). The situation can drastically deplete the skills, motivation, and well-being of people in the country. The situation of unemployment also causes loss of tax and revenue to the government, development of the country will be slowed and hindered. The expenditure incurred by the government increases as a result of providing support to unemployed people in the country. The situation of a high rate of unemployment will bring about severe problems to individuals, the situation where the unemployment problem takes longer duration, the country resort to borrowing from other countries and becoming indebted to those countries.
Unemployment is a major social issue in many countries in the world, the situation of unemployment is a challenge to the government, employers, and individuals in the society. The types of unemployment can be directed to frictional unemployment, structural unemployment, cyclical unemployment, and seasonal unemployment. The situation of unemployment can be identified when a person is actively seeking a job but does not get any available. This can also include people who are working in jobs that are below their qualifications, experience, and satisfaction. The situation where there is a high level of unemployment will result in several economic distress and problems. The situation of unemployment hinders people to engage in productive work to facilitate development in the country. This will result in a decrease in economic productivity and development.
The two categories of unemployment are voluntary and involuntary unemployment, the situation where one moves out from a job to search for another is known as voluntary unemployment, and a situation where a person is laid off and now looking for a job is known as involuntary unemployment. There are several causes of unemployment, including population growth, slow economic development, people who depend on seasonal jobs such as agriculture production work can become unemployed. A decrease in industrialization and investment can account for unemployment, improper economic planning can also result in unemployment challenges. The situation of unemployment can result in social unrest, an increase in the crime rate, and other bad practices in society. The situation of unemployment can cause disruption on confidence and self-esteem among people who are unemployed. Unemployment can be solved when there is education, development of new jobs, investment, and support of self-employed workers.
Alrasheedy, A. (2019). The cost of unemployment in Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 11 (11), 1-30.
Hauser, M. M., & Burrows, P. (2018). The Economics of Unemployment Insurance (1st ed.). London: Routledge.
Hwang, G. J. (2019). How fair are unemployment benefits? The experience of East Asia. International Social Security Review, 72 (2), pp.49-73.
Sari, A. I. (2019). Social Entrepreneurs and Innovation for the Unemployment. International Journal of Economics and Management, 1 (3), pp.72-79.
Wolcott, E., Ochse, M. G., Kudlyak, M., & Kouchekinia, N. A. (2020). Temporary Layoffs and Unemployment in the Pandemic. FRBSF Economic Letter , p.34.
Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- Electron transfer theory
- Smoking In Pregnant Women in the United Kingdom
- Essay on Globalization
- Essay on Social Forces That Shaped America
- Essay on Vision
- Essay on Plagiarism
Unemployment Essay Sample
Unemployment is the state of being jobless and seeking employment, or not having a job. It’s one of the most terrifying things that can happen to an individual. The number of unemployed people in the US is increasing and it’s time we took a closer look at what this means for our society. This essay will explore its causes and inferences.
Here is a sample essay on unemployment given by the experts to students. It could be used as a standard essay to write such other essays for the assignments.
Essay Example on Unemployment
- Thesis Statement of Unemployment Essay
- Introduction of Unemployment Essay
- Cause of Unemployment in the World
- Inferences of the Unemployment in a society of Nation
- How to deter the Problem of Unemployment at Global Scale
Thesis Statement of Unemployment Essay Unemployment gives rise to anarchy, terrorism, and a threat to the internal security of a nation. I ntroduction of Unemployment Essay Today the most fundamental problem that is engulfing society is the issue of unemployment. People are not able to manage two squares of meals per day. This issue cannot be ignored by us at any point as it is eating the structure of our society like a termite thus making it hollow from the inside. There are many problems that arise due to unemployment like terrorism in society which is dangerous for humankind. The issue could be addressed at the most be getting solutions on the problem of unemployment in society, which acts as the causing effect of terrorism and other problems. Main Body of Unemployment Essay Cause of Unemployment in the World The major cause of unemployment in society is the improper management of resources and giving unequal status to the people of society. Here are some major causes of unemployment given below. Unequal Distribution of resources The economic resources are unequally distributed among the people in a society of the nation at large. As a consequence of which some sections get mighty wealth as compared to others. Excessive deflation Another biggest cause that lies behind the cause of unemployment in society is the excessive deflation in the country. When people have to sell their products below the manufacturing cost they find no profit in the business. There comes a time when this business is closed by the businessmen due to lack of profit in the work. Many people lose their employment due to this reason. Mismanagement of the Banking and Financial Institution Loan and other Financial Help are given to the businessmen easily as compared to the common masses. As a result of which there is not a development of the poor people as they cannot invest money for any innovative purpose by owing a loan from the bank. This corruption is the cause of unemployment in a poor section of society. Get Non-Plagiarized Custom Essay on Unemployment in USA Order Now Inferences of the Unemployment in a society of Nation Here are the main results of unemployment in a given nation of a particular society. Students become the enemy of other’s lives in these states. Terrorism – In the scarcity of jobs youth people join many terrorist groups for the sake of earning livelihood for their families. Thus the rise of terrorism could be backed by the unemployment problem. Human Trafficking – The biggest issue of human trafficking is unemployment; many women and men are being transferred across the national and international boundaries for this reason. People do not have enough money to rare their families and thus get involved in such anti-social practices to earn money. Social Riots – Social riots are also the conclusion of unemployment as communities get irritated when other people from a different community get employment. This emotion of wrath and jealously is very strong which even kills the lives of many innocent. Communal Issues – Many times it also gives rise to the communal issue when social riots take their final destination. It could be the most serious result of unemployment in any society. How to deter the Problem of Unemployment at Global Scale The issue of unemployment is not a small problem that could be easily uprooted by society. Its roots had gone very deep into society and it is very difficult to eradicate them. It could be done by making certain efforts by every person in the world. Here are some points that could be considered by the people to eradicate the unemployment problem from society or the world at large. Equal Distribution of Economic Resources The economic resources must be equally distributed among the people so that this issue of unemployment and accumulation of wealth could be solved. Though it is a difficult thing to do but still if we make some plans for it, success could be achieved in it. Reduction in Corruption Corruption is a major issue that causes a huge part of the unemployment problems. This could be reduced by the efficient bureaucrats of the nation. Skill Oriented study The education should be skilled oriented so that people can work easily to save their livelihood. The education system should also encourage students to create new jobs and employment generation. Buy Customized Essay on Unemployment At Cheapest Price Order Now Conclusion The above discussions and arguments about unemployment draw a conclusion that though the issue is very big it could be solved by making efforts. Certain plans and strategies are needed to achieve the dream of eradicating the unemployment issue from society. Intelligentsia of the society needs to pay big attention towards this field of unemployment. Thus we can save our world from ill practices like terrorism and riots.
Hire essay writers to get professional essay writing at an affordable price
This essay has attempted to provide an overview of the causes and consequences of unemployment.
Looking for a professional essay writer to write your assignment? Hire our USA based essay writers to get excellent services with no plagiarism and affordable rates.
Students can get free essay samples to understand how to write an effective essay. Some of the essay samples are Space Exploration Essay , Capital Punishment Essay Example , Nuclear Power Essay Sample , and so on.
Students Assignment Help also offers multiple academic writing help and services for USA students such as custom writing services , assignment proofreading services , report writing help , etc. You can contact our experts any time to get instant and fastest academic help.
Explore More Relevant Posts
- Nike Advertisement Analysis Essay Sample
- Mechanical Engineer Essay Example
- Reflective Essay on Teamwork
- Career Goals Essay Example
- Importance of Family Essay Example
- Causes of Teenage Depression Essay Sample
- Red Box Competitors Essay Sample
- Deontology Essay Example
- Biomedical Model of Health Essay Sample-Strengths and Weaknesses
- Effects Of Discrimination Essay Sample
- Meaning of Freedom Essay Example
- Women’s Rights Essay Sample
- Employment & Labor Law USA Essay Example
- Sonny’s Blues Essay Sample
- COVID 19 (Corona Virus) Essay Sample
- Why Do You Want To Be A Nurse Essay Example
- Family Planning Essay Sample
- Internet Boon or Bane Essay Example
- Does Access to Condoms Prevent Teen Pregnancy Essay Sample
- Child Abuse Essay Example
- Disadvantage of Corporate Social Responsibilities (CSR) Essay Sample
- Essay Sample On Zika Virus
- Wonder Woman Essay Sample
- Teenage Suicide Essay Sample
- Primary Socialization Essay Sample In USA
- Role Of Physics In Daily Life Essay Sample
- Are Law Enforcement Cameras An Invasion of Privacy Essay Sample
- Why Guns Should Not Be Banned
- Neolithic Revolution Essay Sample
- Home Schooling Essay Sample
- Cosmetology Essay Sample
- Sale Promotion Techniques Sample Essay
- How Democratic Was Andrew Jackson Essay Sample
- Baby Boomers Essay Sample
- Veterans Day Essay Sample
- Why Did Japan Attack Pearl Harbor Essay Sample
- Component Of Criminal Justice System In USA Essay Sample
- Self Introduction Essay Example
- Divorce Argumentative Essay Sample
- Bullying Essay Sample
Get Free Assignment Quote
Enter Discount Code If You Have, Else Leave Blank

Understanding how unemployment impacts the economy
Published: 10/03/2023 Updated: 01/10/2024
Workforce availability is an important indicator of economic health
by Kristen Stephenson
Earlier this year, GPEC launched the Economic Monitor, a comprehensive web tool designed to provide timely, actionable insights into the state of the economy. Through an exploration of key economic indicators, the Economic Monitor offers a concise picture of health at both national and regional levels.
Each month, I’m diving into one of the indicators from the Monitor to share in greater detail what the metric measures are, why it matters to the economy and what the current numbers tell us. This month, we’re talking about unemployment rate.
What does unemployment rate measure?
The unemployment rate measures the percentage of people in the labor force who are not employed but are actively looking and available for work. People who have not actively looked for work in the last four weeks are excluded from the labor force, and therefore the unemployment rate. The Bureau of Labor Statistics measures other indicators of labor utilization that take into account discouraged workers, marginally attached workers and part time workers, but the aforementioned indicator is the official “unemployment rate.”
Why does unemployment rate matter?
The unemployment rate is one of the most well-known and reported indicators of the economy. The unemployment rate shows the available capacity of the workforce. It can also indicate financial stress – when an individual is jobless, they are much more likely to reduce their expenditures, which impacts overall consumer spending, another key economic indicator.
It's important not to look at unemployment rates in a vacuum but to consider it along with the current size of the labor force and the labor force participation rate. If the unemployment rate remains steady or decreases while the labor force is shrinking it can be a sign that workers are becoming discouraged and are no longer looking for employment opportunities.
What do the current numbers say?
The United States unemployment rate was 3.8% as of August 2023. This rate is nearly unchanged compared to the same time last year when it was 3.7%. The rate has been persistently near historic lows for the last couple of years, even as inflation and other external pressures have affected the market. At the same time the labor force and employment levels have continued to grow. By all accounts we should be seeing an increase in unemployment and a decrease in hiring, yet that has not been the case.
The story is much the same in Arizona as it also continues to see near-historic lows in unemployment rates. As of August 2023, the State’s unemployment rate was also 3.8%. This was a slight increase (0.2%) from the same time in July 2023 but down from 4.0% a year ago. In the same year-over-year comparison, our labor force increased by 1.8%, indicating a robust employment situation.
However, there are factors to continue to watch for which could affect the employment situation. Additional interest rate increases by the federal reserve or a potential government shutdown could pause hiring and drive the unemployment rate up. As always, we will continue to monitor the unemployment rate and share insights as correlated factors impact the numbers.
Track trends in the Economic Monitor
To monitor unemployment rate trends in real time along with me, mapped alongside 13 other key indicators of health, visit gpec.org/monitor. We hope you find the Monitor a valuable tool in understanding the ever-changing economic landscape.
See Economic Monitor
Meet the Author

Kristen Stephenson Senior Vice President, Research & Analytics Greater Phoenix Economic Council
Recent News
Xnrgy breaks ground on manufacturing facility and u.s. headquarters in mesa, content at scale announces new headquarters in scottsdale, arizona amidst remarkable first-year growth, what makes greater phoenix so great: chelsey ogles, ambassador event: the next era of semicon, tsmc arizona, u.s. department of commerce announce up to $6.6b in proposed chips act direct funding; company plans third leading-edge fab in phoenix, freeway’s new startup ecosystem dashboard gives entrepreneurs, investors real-time data, what makes greater phoenix so great: irelan griner, measuring real manufacturing and trade industry sales, celebrating the connection of art and economy: a recap of artlink’s annual gala, what makes greater phoenix so great: andrew goodwin from pps.
Unemployment in Our Country Essay in English

Unemployment Essay
Unemployment is a very serious problem all over the world. There are hundreds and thousands of people who are unemployed. Also, the problem of unemployment is very serious due to the growing population and the demand for jobs.
There are many reasons of unemployment.
Bribery has become a norm for employment. People who are not able to pay bribes are always unemployed. Our economy is lagging behind and the role of economic growth is very slow. Rapid population growth has been a major problem in our country. This is one of the main causes of unemployment. Backward business sectors are not yet as attractive to students as the field of agriculture and cottage industries.
Rapid population growth should be monitored. The family planning program should be more popular in rural areas. All efforts should be made in this direction. The education system needs to change. Career and technical education should be given importance. Education should be solid and practical.
The national unemployment crisis is affecting a large population of our country, especially a generation of young people who are the future leaders of our country. Unemployment results in the underdevelopment of the nation. However, the government has taken many steps to address this issue.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Unemployment Speech

Long and Short Speeches on Unemployment
Any individual who is deprived of earning a living and faces difficulty in getting a paid job is known as unemployed and the condition is termed as unemployment. With India being a highly populated country, unemployment has always been a major problem in our country. And this problem has been increasing at a major rate.
Here, we have provided a long speech as well as a short unemployment speech in English for the students of all categories. Students can easily refer to our speech on unemployment for any exam preparation and can also gather information on this topic to prepare their own speech.
There is also a 10 Lines Speech provided by us especially for the students of Class 1 and Class 2.
Long Speech on Unemployment
This long speech on unemployment has been provided as a reference for the students of Class 7 To Class 12 for their exam preparation.
Warm greetings to everyone! I firstly appreciate everyone who has gathered here to discuss the problem of unemployment. I am thankful enough for providing me with an opportunity to deliver a speech on unemployment.
Unemployment has become a major concern among the people of India today. With the increasing population, the job sectors fail to provide a full-time job to all the people. This, as a result, has increased the rate of unemployment in our country. Thus, unemployment can be defined as the condition where an individual is deprived of a paid job or self-employment and is unable to find a suitable job for employment.
The fear of unemployment has caused a level of depression and mental stress on the youth today. In spite of getting a degree and having the highest qualifications, they still have to go through the process of unemployment. Many individuals, being the sole bread earner of the family, struggle day and night to earn a living. Unemployment not only refers to being jobless, but it also refers to the state where an individual is being underpaid as per their experience and qualifications. Several individuals are unsatisfied with the jobs they are in and are sticking to their jobs due to unemployment problems.
Implementation of various government programs to improve the practical skills of the students must be done in every school and college. Although the government of India has introduced several employment schemes to offer jobs to the unemployed, many more steps must be taken to reduce the unemployment rate in our country. People must be made aware of self-employment and proper fundings for these government programs and projects must be implemented by the government.
Lastly, I would like to thank all of you for your patience and for coming here to discuss this issue.
Short Speech on Unemployment in English
Given below is a short unemployment speech in English for the students of Class 3 to Class 6.
Greetings everyone! Today I am here to deliver a speech on the topic of unemployment.
With the fast-growing industries and economic system, our country India still lags behind in the field of employment. In spite of having a higher degree and qualification, many people have to suffer through the process of unemployment. The main reason behind this major issue is the growing population and demand for a full-time job. Many citizens of the country are still deprived of paid jobs and are struggling to earn a living. This has also eventually led to mental pressures and depression among the youth. Although there has been an increase in the literacy rate of the people that has also increased the demand for new jobs.
It is high time that the government should take up initiatives to provide employment to the people. There are several government programs and schemes that have been introduced by the Prime Minister to help the unemployed to get a paid job. New training programs should be introduced in schools and colleges for the better development of the students. People should be made familiar with the self-employment scheme and initiatives must be implemented by the government for funding these programs.
Lastly, I would like to end my speech by saying that unemployment has become a major problem in India today and necessary steps must be taken to reduce the unemployment rate.
10 Lines Speech on Unemployment
Here is a 2-minute long speech on unemployment for the students of Class 1 and Class 2.
Good morning everyone! Today I am here to deliver a speech on unemployment.
Unemployment is a serious problem faced by many people in our country.
The increasing population and higher demands for jobs give rise to unemployment.
India being a populated country faces a higher unemployment rate due to limited job sectors.
There are several people who do not have a paid job and are surviving unemployment.
Unemployment also counts those individuals who are being underpaid in their jobs and are working outside their area of interest.
Even people having higher degrees and qualifications have to go through the process of unemployment.
This causes a high level of mental pressure and depression to the individuals as they struggle day and night to earn a living.
Due to slow economic growth and small job sectors, this problem has given rise to many unemployed people.
Lastly, I would like to say that unemployment is becoming a major concern of the youth of our country and if not solved in time, it will also bring down the economic rate of our country.

FAQs on Unemployment Speech
1. How can you include initiatives taken by the government to curb unemployment in your speech?
This problem is taken very seriously by the government, and a number of schemes are being implemented to reduce unemployment. Among these schemes are IRDP (Integrated Rural Development Programme), DPAP (Drought Prone Area Programme), Jawahar Rozgar Yojana, Training for self-employment, PMIUPEP (Prime Minister's Integrated Urban Poverty Eradication Program), employment exchange, Employment Guarantee Scheme, development of organized sector, small and cottage industries, employment in forging countries, and others.
2. What are the reasons for unemployment that I can include in my unemployment speech?
There are numerous reasons for a large section of the population of our country to be facing the problem of unemployment. Some of these reasons are population growth, slow economic growth, seasonal occupations, slow economic growth and a decrease in the cost of living in our country. Additionally, the large population of the country adds to the unemployment problem in India. The country's population demands a huge number of jobs and occupations every year, which the government is unable to supply.
3. What are the types of unemployment?
All of us today are aware of what unemployment is. However, it does not just mean that any person is unemployed. Likewise, unemployment also refers to people working in areas that are outside of their expertise or mastery. Some of the various types of unemployment include disguised unemployment, seasonal unemployment, open unemployment, technological unemployment, and structural unemployment. Other types of unemployment include cyclical unemployment, educated but unemployed, underemployment, frictional unemployment, chronic unemployment and casual unemployment. Presently, in India, among the most prevalent types of unemployment are seasonal unemployment, underemployment, and disguised unemployment.
4. What type of unemployment can be found in developed countries?
Mostly in developed countries, cyclical and frictional unemployment exist. The period of cyclical unemployment is the period in which the unemployment rate rises and falls according to cycles of economic ups and downs. It is vital to minimize cyclical unemployment during recessions. In an economy, frictional unemployment arises from voluntary job transitions. Frictional unemployment is a fact of life, even in a growing, stable economy. The frictional unemployment that occurs when workers leave their current jobs in search of new jobs and when workers enter the workforce for the first time does not include those workers who remain in their current job until they find a new one, since they are never unemployed.
5. How to define different types of unemployment in india?
Open or Structural Unemployment- The phenomenon of open or structural unemployment occurs when a number of people desire to work but are unable to find jobs for themselves. It is a result of a growing population and people migrating to larger cities.
Disguised Unemployment - Under this type of unemployment, people seem employed, yet their productivity is zero and they do not receive any assistance to increase their output.
Seasonal Unemployment - During some seasons in India, farming is not practiced year-round, which results in farmers being jobless for a few months. Seasonal unemployment is also observed in the sugarcane industry, cold drinks industry, and crackers industry.
The Reporter
Unemployment in Informal Labor Markets in Developing Countries
Developing countries typically exhibit low rates of rural wage employment. For example, in India, male workers whose primary source of earnings is wage labor report working on only 46 percent of days per year. 1 Bangladesh has a similarly low 55 percent rate of employment among landless males, and the rates are even lower in sub-Saharan Africa. 2
What do these low employment rates mean? One possibility is that they reflect extremely high involuntary unemployment. Alternatively, the rates could be an outcome of reasonably well functioning labor markets in which workers are simply choosing self-employment, which tends to be high in poor countries. These two possibilities have drastically different implications for understanding how well labor markets work and what role, if any, there is for policy intervention.
Our work has sought to characterize the functioning of labor markets in developing countries and examine microfoundations for why markets might not always be clear. In this summary, we focus on rural labor markets, with evidence primarily drawn from India. These markets are of intrinsic interest: they are the primary source of wage employment for over a billion people worldwide, including the world’s poorest, and their features — informal, decentralized spot markets for labor, where workers and employers match for short-term contracts — are ubiquitous in both rural and urban areas of poor countries. Consequently, many, though not all, lessons from this work likely apply more broadly in developing-country settings.
Staggering Involuntary Unemployment
We begin with the central question of whether low employment rates reflect involuntary or voluntary unemployment. We tackle this question with Yogita Shamdasani by developing a new empirical approach. 3 We induce transitory hiring shocks in randomly selected Indian local labor markets — villages — by “removing” on average 24 percent of male workers by giving them factory jobs in sites outside of the village for two to four weeks. This shock substantively reduces the number of workers in the local village economy without changing labor demand within the village. Looking at the local labor market response to our hiring shock enables us to learn how many people wanted a job at the prevailing wage but could not find one before we intervened. Importantly, we learn this simply by observing the employment behavior of the remaining workers and employers.
We find distinctly different patterns of effects in “lean” versus “peak” months, reflecting seasonality in agricultural hiring. In lean months we detect severe rationing: at least one in four workers in the economy wants a wage job but cannot find one. Excluding our external factory jobs, removing a quarter of the labor force has no effect on lean season wages or aggregate employment. This is consistent with rationed workers filling the newly vacated job slots, leaving the total number of people holding a job unchanged. In contrast, in peak months the impact of our hiring shock matches a textbook supply and demand model: wages rise quickly — within a week — and aggregate employment in the village falls, so that each new job created in the external factory jobsites generates only 0.74 days of new work for laborers in the economy overall. Together, these findings present a more nuanced picture of informal labor markets: they have the capacity to be extremely agile and responsive, but also exhibit extremely high levels of labor rationing in lean months.
Our approach contrasts with how economists have typically measured unemployment to date: asking people in surveys whether they were looking for work but could not find it. It is unclear whether such survey self-reports are reliable. 4 By basing our measurement on whether workers actually choose to work when job slots in the local economy open up, we obtain revealed preference estimates of rationing.
Our approach also lets us learn about self-employment. We find that many rationed workers are disguised as entrepreneurs: as soon as job slots open up in their village, entrepreneurs readily abandon their agricultural and nonagricultural businesses in order to take a wage job with a local employer. In lean months, at least 24 percent of self-employment stems from workers being rationed out of wage labor. Among farmers with small landholdings, this shift to self-employment is especially high: in lean months, at least 64 percent of work on small farms would not occur if those farmers could find wage jobs instead. Consequently, our results indicate that a substantial fraction of self-employment stems from poor labor market prospects rather than high growth opportunities. This can help us understand why broadly targeted interventions such as credit, wage subsidies, and training for microenterprises tend to generate low average returns.
These patterns indicate why answers to standard involuntary unemployment questions can be unreliable in developing countries, and more broadly in settings with self-employment or informal work like gig jobs. In employment surveys run by governments — in India, the US, and most other settings — workers are only classified as involuntarily unemployed if they are not engaged in any work activity. Since a rationed worker who cannot find wage work can turn to self-employment or a gig economy job to make some extra money, focusing on these standard questions can lead to drastic underestimation of labor rationing in the economy. We show that alternate employment status questions that take this into account can yield more accurate estimates.
But why is there so much labor rationing? If there are more workers who want jobs than there are jobs available, we would expect wages to fall until the supply of workers equals demand. Kaur documents that in rural India, wages are downwardly rigid. 5 Specifically, while they rise in response to positive shocks, they do not fall in response to negative shocks, such as droughts. Kaur’s study shows that downward rigidity causes increased unemployment — arguably the first direct evidence of employment effects of wage rigidity in any setting.
In addition to wage rigidity, wage compression also seems to be exhibited in labor markets in this setting: workers of varying abilities are paid the same wage. As we show in Figure 1, there tends to be a single prevailing wage for a given type of task in the economy, which most workers are paid despite differences in underlying ability. One consequence is that all workers agree on what the prevailing wage is for a task, a feature that plays an important role in labor market dynamics.
Market Power, Unemployment, and Social Forces
Informal labor markets often embody features we might associate with competitiveness and flexibility: there are many decentralized workers and employers, the short duration of contracts means that wages could quickly reflect changes in market conditions, there are no formal unions or institutions, and minimum wage laws are generally ignored. Why, then, do wages seem inflexible — over time, across people, and in response to shocks? Understanding this is key for understanding the high levels of unemployment.
Our research indicates that it is essential to account for one additional feature of these markets: workers are not anonymous to one another. 6 They live in close-knit communities and are dependent on each other socially and economically — for example, through job referrals and informal insurance. This creates scope for individuals to use the threat of sanctions to sustain norms that are perceived to be in their collective interest.
In work with Nandita Krishnaswamy, we document norms against accepting wage or price cuts in a range of markets in India and Kenya. 7 In Figure 2, we show evidence from rural agricultural workers, construction workers at urban labor stands, taxi drivers, food vendors, and butchers. In each case, respondents state that undercutting the prevailing price is considered unacceptable [Panel A]. Doing so would result in a range of sanctions, from being socially ostracized to losing one’s source of livelihood [Panel B]. For example, 90 percent of rural workers respond that others would get angry with an individual who accepted a job below the prevailing wage and 59 percent believe others would impede the labor market prospects of that individual by means such as withholding referrals.
We then use a field experiment to examine whether norms against accepting wage cuts can help us understand the presence of wage floors in rural labor markets. Specifically, we hypothesize that during times of unemployment, at least some workers would prefer to work below the prevailing wage rather than remaining jobless, but do not due to the threat of sanctions from other workers.
We partner with local employers who make job offers for lean season agricultural work. Employers follow the typical process for agricultural hiring: traveling to the neighborhood where the majority of workers live and making job offers to workers at their homes. We randomize both the wage level of the offer and the degree of observability.
In the “public” treatment, which is the status quo for our setting, the employer offers the job outside on the street where neighbors, who are typically other workers, can overhear the offer, and could then tell other workers in the community. In the “employer” treatment, the wage offer is observable to the employer but not to others in the community. In the “private” condition, the job is offered inside the worker’s home and consequently is not directly observable to others in the community. After the conclusion of the experiment, participants received a supplement so that no one actually worked below the prevailing wage.
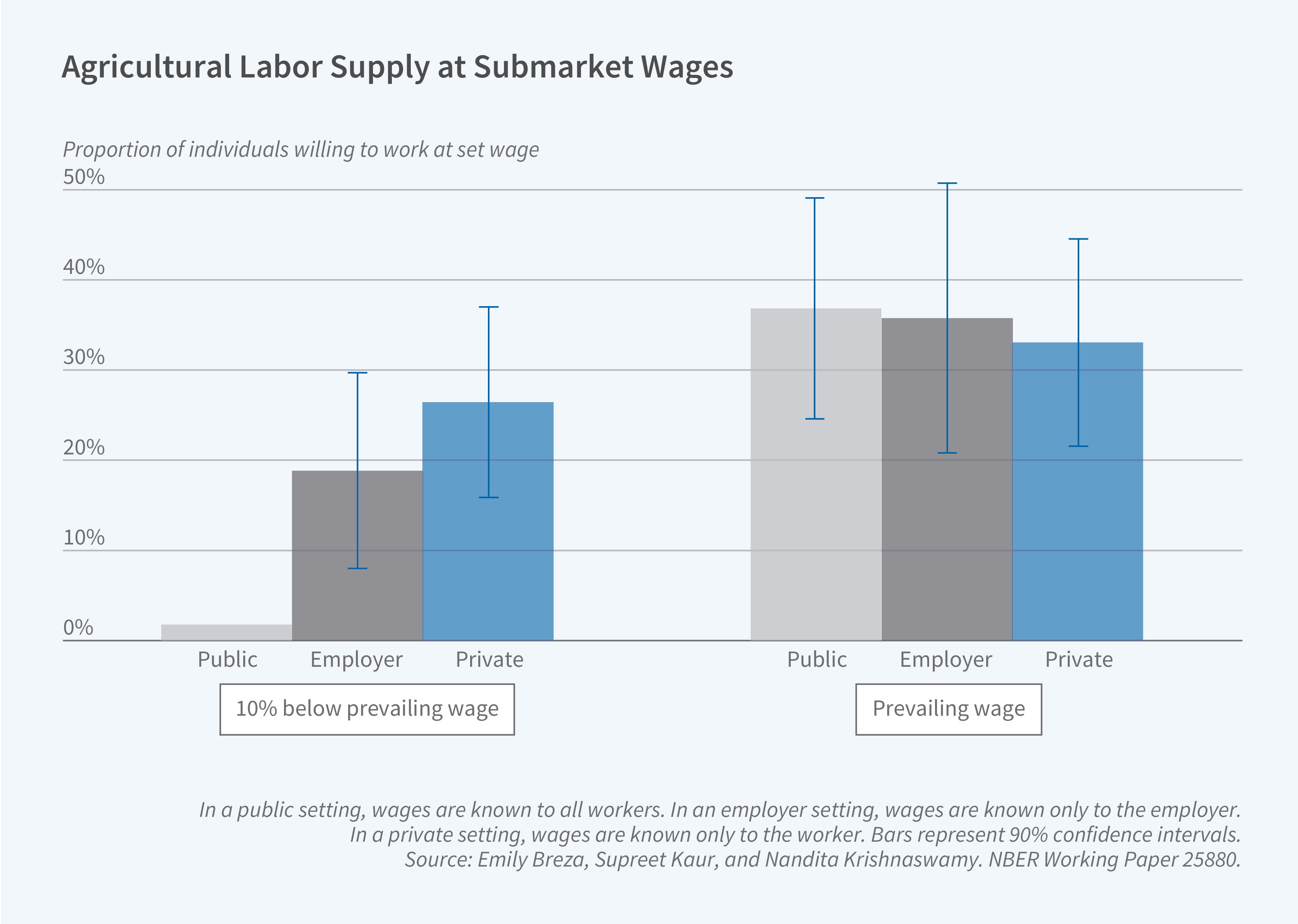
Despite high unemployment, only 1.8 percent of agricultural workers are willing to accept jobs below the prevailing wage under the status quo. However, this number jumps to 26 percent when this choice is not observable to other workers. In contrast, for prevailing-wage job offers, social observability has no detectable impact on job take-up. This is consistent with the idea that social observability only matters when there are norm violations.
These findings are consistent with substantial distortions in the aggregate supply curve. At low wages, social pressure leads to a restriction in labor supply, making it appear that below the prevailing wage, labor supply falls to close to zero. However, absent social considerations, unemployed workers would prefer working below the prevailing wage to remaining jobless. Whether the norm among workers increases or decreases, total employment depends on whether employers have market power. Regardless, a back-of-the-envelope calculation suggests that maintaining a wage floor is beneficial for worker earnings as a whole.
Overall, our findings suggest that market power can arise in many decentralized markets and may be more widespread in developing countries than has been previously thought.
Wage Compression: Social Forces
Social forces also have relevance for explaining wage compression. With Shamdasani, we explore whether and under what circumstances workers care about their pay relative to that of their coworkers. 8 If relative pay differences cause workers to withdraw labor supply or effort, employers may prefer offering compressed wage contracts.
We conduct an experiment with workers in seasonal, month-long, low-skilled manufacturing jobs in India. Workers are randomly organized into three-person production units, each of which is randomized to one of four different pay structures. In the pay disparity condition, each unit member is paid a different wage — w High , w Med , or w Low — in accordance with his respective productivity rank within the unit determined by baseline productivity levels. In the three compressed pay conditions, all unit members are paid the same wage, which we randomly assign to be w High , w Med , or w Low . This allows us to compare, for example, workers with the same average baseline productivity who both earn an absolute wage of w Low , but differ in whether they are paid less than their peers under the pay disparity treatment or the same as their peers under the compressed low wage treatment.
Figure 4 shows the impacts of pay disparity on standardized output holding own wage fixed. Prior to “Day 0” of the experiment, all workers were paid identical training wages. For low-ranked workers earning w Low , output declines by 0.33 standard deviations (22 percent) on average after a worker begins earning less than both his coworkers, and attendance declines by 12 percentage points. Perhaps surprisingly, the high-ranked workers in pay disparity units, who earn more than both their coworkers, also experience a reduction in output and labor supply.
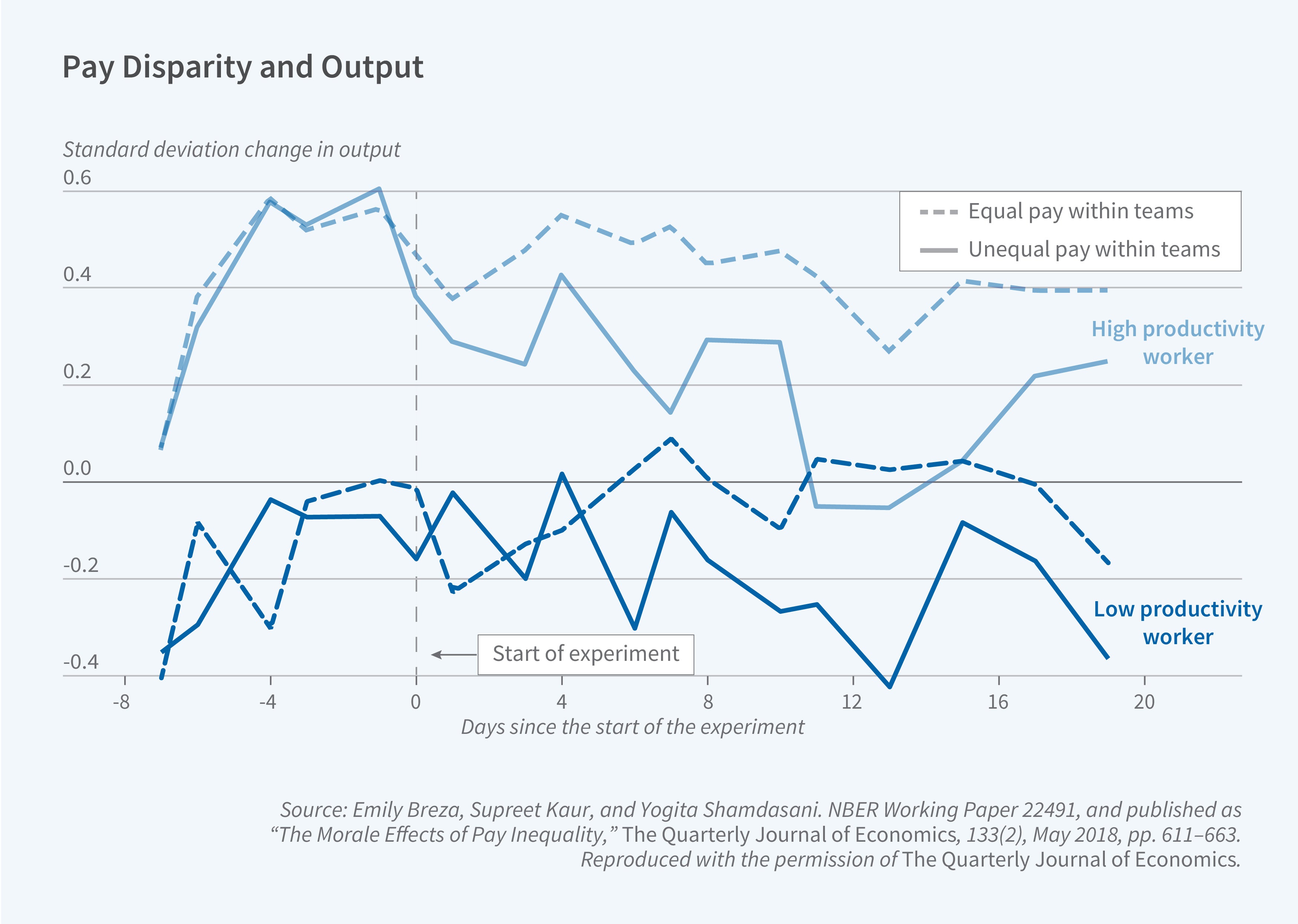
We find that perceived justifications play an important role in mediating the effects. When workers can clearly perceive that their higher-paid peers are more productive than themselves, pay disparity has no discernible negative effects on output or labor supply. That workers tolerate pay inequality only when productivity differences are extremely transparent can help explain why we observe piece rates in practice where output is fully observable but do not often observe other forms of pay dispersion.
Finally, we show that these morale effects likely operate through resentment and hostility in the workplace, reducing social cohesion among unit members. In two incentivized, cooperative games, members of pay disparity units are less able to work together than members of compressed units, even when it’s in their own interest. However, in both cases, when pay disparity is clearly justified, these effects disappear.
Together, this body of work makes progress toward understanding the functioning of rural labor markets in developing countries. It shows that while these markets embody remarkable flexibility and agility, wages are rigid and involuntary unemployment is extremely high, particularly during months when agricultural labor demand is low. This changes the logic of labor market analysis. For example, because wages do not always play an allocative role, analyses that assume wages tell us something about labor productivity will be misleading. In addition, our findings are relevant for poverty alleviation policies. For example, they suggest that workfare programs that offer jobs to unemployed workers — a popular policy tool in developing countries — are least likely to crowd out private sector jobs if implemented in lean seasons, but may do so in shoulder or peak seasons.
Why such high levels of unemployment exist in this setting remains an open question. Researchers have failed to find support for the traditional microfoundations that were discussed in the early development literature, such as nutrition efficiency wages. Our work makes progress on this puzzle by highlighting a microfoundation not previously considered: the centrality of social forces in determining market outcomes. Because markets are made up of people, they are underpinned by social relationships that can drastically alter their functioning.
Researchers
More from nber.
“ India - National Sample Survey 2009–2010, ” Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. International Labour Organization, January 21, 2024.
“ Effects of Emigration on Rural Labor Markets, ” Akram AA, Chowdhury S, Mobarak AM. NBER Working Paper 23929, October 2017. Accelerating Poverty Reduction in Africa , Beegle K, Christiaensen L, editors. Washington, DC: The World Bank, October 2019.
“ Labor Rationing, ” Breza E, Kaur S, Shamdasani Y. NBER Working Paper 28643, April 2021, and American Economic Review 111(10), October 2021, pp. 3184–3224.
“ Measurement Error in Survey Data, ” Bound J, Brown C, Mathiowetz N. In Handbook of Econometrics , volume 5, Heckman J, Leamer E, editors, pp. 3705–3843. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2001. “ Involuntary Unemployment, ” Taylor JB. In The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics . London: Palgrave Macmillan, 2008.
“ Nominal Wage Rigidity in Village Labor Markets, ” Kaur S. NBER Working Paper 20770, November 2017, and American Economic Review 109(10), October 2019, pp. 3585–3616.
“ The Morale Effects of Pay Inequality, ” Breza E, Kaur S, Shamdasani Y. NBER Working Paper 22491, August 2016, and The Quarterly Journal of Economics 133(2), May 2018, pp. 611–663.
“ Social Norms as a Determinant of Aggregate Labor Supply, ” Breza E, Kaur S, Krishnaswamy N. NBER Working Paper 25880, February 2024.
NBER periodicals and newsletters may be reproduced freely with appropriate attribution.
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

© 2023 National Bureau of Economic Research. Periodical content may be reproduced freely with appropriate attribution.
Unemployment biggest worry in India, world's fastest growing economy: Reuters poll
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Milounee Purohit; Polling by Veronica Khongwir, Susobhan Sarkar; Editing by Hari Kishan and Jonathan Oatis
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

India's Yes Bank reported a bigger-than-expected rise in net profit for the January-March quarter on Saturday, helped by a drop in loan-loss provisions and higher non-interest income.

World Chevron

Russian missiles pound Ukrainian power plants in escalating campaign
A Russian missile attack pounded power facilities in the centre and west of Ukraine on Saturday, mounting pressure on the ailing energy system as the country faces a shortage of air defences despite a breakthrough in U.S. military aid.

- Share full article
Advertisement
The Morning
After apartheid.
Thirty years after apartheid ended, South Africa will vote again.

By John Eligon
South Africa’s apartheid government died in an election 30 years ago tomorrow. For the first time, Black South Africans were among those casting ballots. In the regime’s place, voters inaugurated a democracy led by people who look like the country’s majority. Hopes ran high: Nelson Mandela became president and vowed to help Black communities prosper by giving them access to the wealth, land and mines — South Africa is rich in gold and diamonds — colonizers had taken.
Toppling the racist regime, it turns out, was just the beginning.
Three decades later, Mandela’s vision is far from realized. Most Black South Africans don’t earn enough to meet their basic needs, and many lack reliable services like electricity and water. Racial disparities in employment, education and income are still massive. Communities where people live in tin shacks and use latrines sit alongside suburbs with swimming pools and electrified walls.
With a major national election next month, my colleague Lynsey Chutel and I have been reporting to understand how South Africa got here. We’ve sifted through data, interviewed experts and chatted with dozens of residents from every walk of life. ( Read our story here .) Today’s newsletter will explain what happened.
Joyful progress
For all its problems, South Africa has still achieved something remarkable. After apartheid, its democratic government, led by the liberation movement, the African National Congress, drafted a constitution that enshrines equal rights for everyone. Since 1994, the country has held six peaceful and credible democratic elections. Even though the A.N.C. has had a grip on power, the political arena is fierce and combative. This year, a record 52 parties will be on the national ballot.
In many places, you see an inclusive joy these days that would not have been possible under apartheid. On any given night, you’ll find Black partygoers in swanky nightclubs or high-end restaurants, sucking on hookah pipes or posing for Instagram snapshots. Some townships, which the apartheid government had designed to keep the Black population ostracized, have vibrant arts and culture scenes. Festivals are frequently held in all parts of the country and draw multiracial crowds. Many thump with amapiano, a South African brand of house music, and revelers doing smooth robotic jiggles.
The economic situation is not uniformly bleak. The upscale shopping malls and modern office towers are no longer the preserve of white South Africans. In 2022, there were 16 times more Black South Africans living in households among the top 15 percent of earners than there were in 1995.
Even when it comes to venting frustrations with the government, there is a lively protest culture, with people of all shades and socioeconomic backgrounds taking to the streets. Civil society thrives: Many human rights organizations advocate for the most vulnerable. A robust and independent press calls out government wrongdoing.
A stubborn legacy
Mandela’s government raced to provide homes, electricity and water to the millions of Black South Africans deprived of those basics under apartheid. Over time, though, progress slowed.
Some advocates argued that the government should quickly seize banks, mines and land. But policymakers worried about scaring international investors and institutions. So they often took a gentler approach. Instead of nationalizing corporations, the government mandated greater Black representation among business owners in order for companies to get contracts from the state. Instead of taking land from white owners, the government simply urged them to sell some of it. Some did, and a few Black buyers — mostly with government support — had the means to purchase land, but not nearly enough to transform the economy.
Gap between unemployment rates of Black and white South Africans

Black unemployment rate
White unemployment rate

Today, white people, who are 7 percent of the population, still own most land and big business. Black South Africans have made some inroads. But the benefits have mostly gone to a small number of politically connected Black people at the top of the economic ladder.
This elite enrichment is tied to the country’s persistent corruption, which began even as the new country took shape. The A.N.C. back then was filled with revolutionaries who had been tortured, imprisoned or exiled by the white-led regime. Suddenly, many of those same liberation fighters became top government officials. They had access to resources and power they’d never known before. Multiple A.N.C. veterans have told me that some party members couldn’t resist grabbing the spoils. They felt that they had sacrificed so much and it was time for them to eat.
South Africans today live with the consequences. The state-owned power company, for instance, was pilfered and now struggles to keep plants working, leading to frequent blackouts. Commercial ships and trucks have been backed up at South Africa’s vital shipping ports because of the dysfunctional state-owned logistics company.
A young nation’s future
South Africa, like other African nations and even the United States, has not figured out how to undo economic inequities created by hundreds of years of racial oppression.
But history is not destiny. Frustrated South Africans head to the polls next month. For the first time since full democracy began in 1994, the A.N.C. may lose its majority in Parliament. If it does, voters will be exercising a freedom they gained that is not in question: to choose, and dispatch, leaders as they wish.
Related: Read John’s guide to the South African election.
THE LATEST NEWS
Supreme court.
The Supreme Court’s conservative majority appears likely to rule that ex-presidents have some immunity from prosecution .
That would narrow the federal Jan. 6 case against Donald Trump, and make it less likely that he would face trial before the 2024 election.
The court usually issues major rulings in late June or early July. Even that could be enough to delay Trump’s trial past the election, The Times’s Adam Liptak explains .
During arguments, several justices focused on presidential power generally rather than Trump. “We’re writing a rule for the ages,” Justice Neil Gorsuch said.
Trump’s lawyer suggested that criminal immunity could apply even if a president ordered the military to kill a rival or stage a coup .
Trump on Trial
David Pecker, the former publisher of The National Enquirer, told the jury in Trump’s Manhattan criminal trial that he helped buy and bury three scandalous stories about Trump during the 2016 election.
Pecker heard in October 2016 that the adult film star Stormy Daniels was trying to sell her story of a tryst with Trump and suggested that Michael Cohen, Trump’s former lawyer, buy it. That hush money, which Trump reimbursed Cohen for, is now central to prosecutors’ case .
Pecker acknowledged that the hush money was effectively an illegal donation to Trump’s campaign and said that Trump was worried about how the stories could affect the race, not about his family finding out. That may help prosecutors argue that Trump sought to win the election through illegal means.
Pecker testified that after Trump won, he attended a meeting at Trump Tower in which Trump thanked him for purchasing the stories in front of James Comey , the F.B.I. director.
Harvey Weinstein
New York’s highest court overturned Harvey Weinstein’s 2020 conviction for sex crimes. It said the judge had erred by allowing witnesses unrelated to the charges.
The Manhattan district attorney must decide whether to seek a retrial. Weinstein will be moved to a prison in California, where he was separately sentenced to 16 years for rape.
“The criminal case against him has been fragile since the day it was filed,” wrote Jodi Kantor , whose reporting revealed decades of accusations against Weinstein and helped kick off the #MeToo movement. Read the full ruling .
Campus Protests
Pro-Palestinian encampments have spread across the country, and hundreds of people have been arrested. This map shows where .
U.S.C. canceled its main graduation ceremony because of the protests. Demonstrations are rare in the school’s 144-year history .
Israel-Hamas War
Biden and the leaders of 17 other nations called on Hamas to release all its hostages, in an effort to raise pressure on the group to agree to a cease-fire.
Western aid groups in Gaza have repeatedly come under fire from the Israeli military , even after they shared their locations with officials, a Times video investigation found.
Antony Blinken, the secretary of state, met with Xi Jinping .
A Chinese company is Americans’ favorite drone maker. The U.S. government considers it a security threat .
More International News
A ruling council took office in Haiti as Prime Minister Ariel Henry resigned . The country faces widespread gang violence and a humanitarian crisis.
The U.S. said it would withdraw troops from Chad, days after saying the same about Niger. Both African countries have been strengthening ties with Russia .
Other Big Stories
About 20 percent of milk sampled nationwide showed genetic traces of bird flu , the F.D.A. found. There was no sign the milk was unsafe to drink, but it suggests the outbreak is widespread in cows.
A high school athletic director in Maryland was arrested on charges that he used A.I. to fake an audio clip of the principal making racist and antisemitic remarks.
The authorities in Mississippi have issued playing cards depicting victims of unsolved murders , hoping for leads.
Toby Kiers had a choice between being a bad scientist or a bad mother . She chose defiance, she writes, and brought her children with her on expeditions.
Mike Johnson deserves praise for standing up against his party to pass aid for Ukraine, Israel and Taiwan, Frank Bruni writes.
You’ve been wronged. That doesn’t mean your complaints are right , Pamela Paul argues.
Here are columns by David Brooks on rising federal debt and Paul Krugman on the progress of unions .
MORNING READS
Check mate: The next world chess champion could be the youngest ever .
Teddy’s here, too: Sharing a bed with a partner sometimes means making room for their stuffed animal .
Fines: A Wyoming town penalized a 13-year-old for selling Girl Scout cookies in the wrong place , The Cowboy State Daily reports.
Homes: A study suggests that Gen Z has it better in the housing market than the millennials who came before.
Lives Lived: Carrie Robbins made a classic wig and poodle skirt for “Grease” — using a bath mat and a toilet cover — and turned other actors into Spanish inquisitors, British highwaymen and more. She died at 81 .
N.F.L. Draft: U.S.C.’s Caleb Williams went No. 1 to the Chicago Bears, as expected, in the first round of the draft. The Atlanta Falcons’ selection of the Washington quarterback Michael Penix Jr. shocked league insiders .
N.B.A.: Joel Embiid, recently diagnosed with Bell’s palsy , scored 50 points to power the 76ers past the Knicks and narrow their series lead to 2-1.
N.H.L.: The New York Islanders face a 3-0 series deficit after losing 3-2 to the Carolina Hurricanes at home.
ARTS AND IDEAS
Young people are spending more time on TikTok and YouTube. To stay relevant, many podcast hosts have started recording their conversations in video as well as audio.
While a “video podcast” might seem contradictory, people watch . Interview-driven series like “The Joe Rogan Experience,” “Conan O’Brien Needs a Friend” and “Drink Champs” reach millions of subscribers on YouTube and Spotify, which added support for video in 2020.
More on culture
The Onion was sold to a group of media veterans whose firm — Global Tetrahedron — took its name from an Onion joke .
Artifacts from the Titanic — including its bandleader’s violin case — are up for auction this weekend in England, 112 years after the ship sank.
A new production of “The Great Gatsby” on Broadway is a lot of fun, our critic writes, but it falters in serious moments.
Ahead of the White House Correspondents Dinner, the comedian Roy Wood Jr. — who hosted last year — discussed humor and the 2024 election on “The Run-Up” podcast. Listen here .
THE MORNING RECOMMENDS …
Mix six ingredients for a quick miso-mascarpone pasta .
Make your shower more luxurious .
Learn the new rules for visiting Venice.
Pack a sleeping pad for your car camping trip.
Refresh your bathroom for $50 or less .
Take our news quiz .
Here is today’s Spelling Bee . Yesterday’s pangram was blithely .
And here are today’s Mini Crossword , Wordle , Sudoku , Connections and Strands .
Thanks for spending part of your morning with The Times. See you tomorrow.
Sign up here to get this newsletter in your inbox . Reach our team at [email protected] .
John Eligon is the Johannesburg bureau chief for The Times, covering a wide range of events and trends that influence and shape the lives of ordinary people across southern Africa. More about John Eligon

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Unemployment is one of the fundamental economic and social problems in the world. Every country once in a while experiences a lack of working places available on the labor market. It could be said that unemployment rate is constantly changing, as it depends on the variety of social and economic factors. It could be assumed that unemployment is ...
The unemployment rate for the year 2013-14 in rural India was 4.7%, whereas it was 5.5% for urban India. In the short term, unemployment significantly reduces a person's income and, in the long term, it reduces their ability to save for retirement and other goals. Unemployment is a loss of valuable productive resources to the economy.
500+ Words Essay on Unemployment. Unemployment is a very serious issue not only in India but in the whole world. There are hundreds and thousands of people out there who do not have employment. Besides, the problems of unemployment are very severe in India because of the growing population and demand for jobs.
Unemployment rate can be defined as the prevalence of unemployment opportunities in a country. The unemployment index is calculated by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by the number of individuals in the labour force (Arestis & John 15). We will write a custom essay on your topic. 809 writers online.
Essay on Unemployment in 100 words. Unemployment refers to the condition when individuals, capable and willing to work, are unable to secure gainful employment. It is a pervasive issue across the globe, with varying degrees of impact on societies. Unemployment results in financial instability, and emotional distress, and hampers individual growth.
This essay will explore the primary reasons for unemployment, examining how economic conditions, technological advancements, education levels, and government policies all play a role in shaping the job market. By analyzing these factors, we can gain a deeper insight into the root causes of unemployment and develop strategies to address this ...
Mental health issues: Unemployment can cause stress, anxiety, and depression, which can negatively impact an individual's mental health. Strained relationships and family instability: Unemployment may cause financial strain and tension within families, leading to relationship problems and instability. These effects of unemployment can have ...
6 Examples of Essays About Unemployment. 1. Unemployment Reflection by Christopher Haynes. "In order to secure work, we must be prepared to change or upgrade our skills and be willing to relocate if necessary. But some people are not interested in retraining to find work in another field, some people do not have the confidence to go out and ...
Essay Example: An adage says "an idle hand is a devil's workshop". The enormous growth of unemployment in our society today calls for alarm, and it is expedient for all nations to figure out what leads to this great dilemma. ... To sum up, causes of unemployment vary from country to country, and its effects include psychological and financial ...
Understanding the causes and types of unemployment is crucial for developing effective solutions. Unemployment can take various forms, influenced by different factors in society. It is caused by a combination of economic forces, technological advancements, seasonal fluctuations, and policy changes. Addressing unemployment requires comprehensive ...
The Natural Rate of Unemployment. Unemployment rates in European nations have typically been higher than in the United States. In 2020, before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. unemployment rate was 3.5%, compared with 8.5% in France, 10% in Italy, and 7.1% in Sweden.We can attribute the pattern of generally higher unemployment rates in Europe, which dates back to the 1970s, to the ...
However, the most recent economic survey shows that the rate of unemployment in the US has been on the decline and stood at 8.10% in August 2012 down from 8.30% in July and 9.10% in the year 2011 according to the US economic survey 2012 (Yates, 1994). Data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics on August 2012 also shows varying rates of ...
Global and national emergencies can trigger both unemployment and underemployment. For example, when the COVID-19 pandemic hit, it left more than 10 million Americans jobless in its first two weeks.
Essay on Unemployment Rate. Published: 2021/11/23. Number of words: 1986. Introduction. The essay is focused on examining the issue of unemployment among people in various societies and countries around the world, the reasons for unemployment, types of unemployment, ways to overcome the issue of unemployment and examine the costs associated ...
Here are the main types of unemployment: 1. Structural Unemployment. Structural unemployment occurs when there is a discrepancy between the skills and qualifications of workers and the demands of available jobs. Causes: Changes in technology, shifts in consumer preferences, and structural changes in industries can render specific skills ...
The major cause of unemployment in society is the improper management of resources and giving unequal status to the people of society. Here are some major causes of unemployment given below. Unequal Distribution of resources. The economic resources are unequally distributed among the people in a society of the nation at large.
Essay on Unemployment. The three basic needs of human beings are - food, home and clothing. All these needs can be properly fulfilled only if a person has money. And to earn this money, the person must be employed, that is, he or she must have a paid occupation. However, there are many people in the world and our country too who have failed to ...
As of August 2023, the State's unemployment rate was also 3.8%. This was a slight increase (0.2%) from the same time in July 2023 but down from 4.0% a year ago. In the same year-over-year comparison, our labor force increased by 1.8%, indicating a robust employment situation. However, there are factors to continue to watch for which could ...
This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Unemployment has been an issue and a concern in most counties across the world, including the US, but unemployment is at the lowest it has ever been in 50 years. The factors include demographics, level ...
The national unemployment crisis is affecting a large population of our country, especially a generation of young people who are the future leaders of our country. Unemployment results in the underdevelopment of the nation. However, the government has taken many steps to address this issue.
Short Speech on Unemployment in English. Given below is a short unemployment speech in English for the students of Class 3 to Class 6. Greetings everyone! Today I am here to deliver a speech on the topic of unemployment. With the fast-growing industries and economic system, our country India still lags behind in the field of employment.
Unemployment among 15- to 24-year-olds in the European Union was 14.5% last year, down from 22.4% in 2015. In Germany it was just 5.8%. In such tight labour markets, armies have a hard time ...
Developing countries typically exhibit low rates of rural wage employment. For example, in India, male workers whose primary source of earnings is wage labor report working on only 46 percent of days per year. 1 Bangladesh has a similarly low 55 percent rate of employment among landless males, and the rates are even lower in sub-Saharan Africa. 2 What do these low employment rates mean?
The biggest economic challenge for the government after the ongoing election is unemployment, according to economists polled by Reuters who expected the world's most populous country to grow a ...
A chart shows the unemployment rates of Black and white South Africans. The gap in unemployment rates between the two groups has grown from 30 percentage points in 2000 to 35 points in 2023. 50%
Discretionary fiscal policy changes, in turn, account for less than 20% of the observed changes. The analysis also finds the primary balance multiplier on GDP to be very small. We reconcile our results with the literature, underscoring the importance of accurate shock identification and accounting for cross-country heterogeneity. Series: