Social Media Addiction: Causes and Effects
The causes of sm addiction, the effects of sm addiction.
Problematic or addictive social media (SM) use and its implications for health have become popular research topics in recent years. SM addiction refers to a type of behavioral addiction characterized by an individual’s excessive concern with SM communication that results in an obsessive desire to check SM feedback in a frequent manner. Eventually, those developing this form of addiction start to devote too much time to SM-related matters. In some instances, this approach to priority-setting can impair a person’s activity and success in other crucial areas of life, such as in-person communication, studying, and career progression. The causes and effects of excessive SM use require an in-depth investigation to achieve clarity in formulating a new public health concern and developing resources to address addictions. The issue stems from SM platforms’ technical characteristics and being a source of dopamine and a relief for socially unhappy individuals, and its effects include poorer mental health, physical health issues, and impaired productivity.
The chosen problem can be caused by various interacting factors, including SM sites’ addiction-inducing characteristics, the ability to trigger dopamine release, and offering spaces to compensate for previous relationship-building failures. The first cause refers to modern SM platforms’ addictive features, for example, the promotion of endless scrolling. SM applications’ news feed functions expose the user to an endless and unrestricted stream of information, resulting in immersion combined with distortions to chronoception (Friedman, 2021; Montag et al., 2019). Exposure to such streams of data can create the habit of mindless SM scrolling without realizing how much time has passed. This can give rise to addiction and the symptoms of distress in SM users (Montag et al., 2019; Zenone et al., 2022). The second cause is that rewarding SM experiences can elicit neurotransmitters’ activity, making SM platforms similar to certain drugs. For instance, SM websites are referred to as “dopamine-inducing social environments” as the stream of positive attention, including likes or personal messages, induces pleasure and affects reward pathways in the brain (Hilliard, 2022, para. 3). Getting positive reactions evokes temporary feelings of joy and satisfaction, and this effect is inextricably connected to dopamine release (Burhan & Moradzadeh, 2020). The user can feel the urge to receive even more attention to remain in this positive state. Finally, SM addictions can stem from the individual’s desire to compensate for previous social failures, for instance, insecure attachment. It has been shown that the intensity of Facebook use is positively correlated with the degree of the user’s attachment anxiety (Burhan & Moradzadeh, 2020). The desire to alleviate negative feelings linked with in-person communication might encourage heavier and more addictive SM use (Burhan & Moradzadeh, 2020). Therefore, both neurological and psychological reasons can be involved in the issue.
SM addiction can have various types of negative effects, including a greater likelihood of mental health issues, alterations to individual productivity, and deficiencies in a person’s subjective physical well-being. First, psychological and mental issues become more likely as a result of overusing SM. Specifically, excessive and addictive long-term SM use has been positively associated with developing self-esteem issues, anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and an increased sense of guilt (Rast et al., 2021). Increased SM use limits in-person interaction and physical activity levels while also promoting the fear of being judged during face-to-face communication, thus contributing to the aforementioned conditions (Rast et al., 2021). Second, both academic and workplace performance can decrease due to SM addictions. Specifically, unhealthy SM use has been linked with sleep issues and some reductions in cognitive capacity, as well as extra distractions and time wastage (Priyadarshini et al., 2020; Rast et al., 2021). In combination, these effects can promote barriers to users’ academic and workplace achievements by causing disengagement and information overload (Priyadarshini et al., 2020; Rast et al., 2021). Third, negative physical health outcomes can stem from SM overuse and, more specifically, its effects on the amount of health-promoting physical activity and sleep. For instance, aside from higher C-reactive protein levels, the degree of SM use has a positive relationship with backaches, eye strain, chest pain, and headaches (Lee et al., 2022; Priyadarshini et al., 2020). These consequences are likely to be related to the unhealthy screen staring practices, adopting more sedentary lifestyles, and sleep issues that are the components of SM addictions (Priyadarshini et al., 2020). Thus, the adverse effects of excessive SM use on a person’s life are all-encompassing.
Finally, SM addiction is a complex health issue that can result from the causes of different nature, including the peculiarities of human psychology and neurological functioning, and influence both health and individual productivity. Based on the discussion of hypothetical causes, it is likely that the most popular social networking sites are built in a way to capture and redirect users’ attention. They also offer some illusionary remedies for users’ psychological issues and unmet attachment-related needs. The phenomenon’s outcomes also signify that SM addiction can be more dangerous than it is currently portrayed. These points give support to an opinion that the global healthcare community and researchers should explore the behavioral issue more intensively to develop safe SM use guidelines and effective practices to address the addiction. Additionally, researching how addictive information presentation technologies are used for profit-making might be essential to get at the problem’s root cause.
Burhan, R., & Moradzadeh, J. (2020). Neurotransmitter dopamine (DA) and its role in the development of social media addiction. Journal of Neurology & Neurophysiology , 11 (7), 1-2. Web.
Friedman, E. (2021). Internet addiction: A critical psychology of users . Routledge.
Hilliard, J. (2022). Social media addiction . Addiction Center.
Lee, D. S., Jiang, T., Crocker, J., & Way, B. M. (2022). Social media use and its link to physical health indicators . Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking , 25 (2), 87-93.
Montag, C., Lachmann, B., Herrlich, M., & Zweig, K. (2019). Addictive features of social media/messenger platforms and freemium games against the background of psychological and economic theories. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 16 (14), 1-16.
Priyadarshini, C., Dubey, R. K., Kumar, Y. L. N., & Jha, R. R. (2020). Impact of a social media addiction on employees’ wellbeing and work productivity . The Qualitative Report , 25 (1), 181-196.
Rast, R., Coleman, J. T., & Simmers, C. S. (2021). T he dark side of the like: The effects of social media addiction on digital and in-person communication. The Journal of Social Media in Society , 10 (2), 175-201.
Zenone, M., Kenworthy, N., & Maani, N. (2022). The social media industry as a commercial determinant of health. International Journal of Health Policy and Management , 1-4.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2023, June 21). Social Media Addiction: Causes and Effects. https://studycorgi.com/social-media-addiction-causes-and-effects/
"Social Media Addiction: Causes and Effects." StudyCorgi , 21 June 2023, studycorgi.com/social-media-addiction-causes-and-effects/.
StudyCorgi . (2023) 'Social Media Addiction: Causes and Effects'. 21 June.
1. StudyCorgi . "Social Media Addiction: Causes and Effects." June 21, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/social-media-addiction-causes-and-effects/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Social Media Addiction: Causes and Effects." June 21, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/social-media-addiction-causes-and-effects/.
StudyCorgi . 2023. "Social Media Addiction: Causes and Effects." June 21, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/social-media-addiction-causes-and-effects/.
This paper, “Social Media Addiction: Causes and Effects”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 14, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

Logo Left Content

Logo Right Content
Stanford University School of Medicine blog

Addictive potential of social media, explained
The curious title of Stanford psychiatrist Anna Lembke 's book, Dopamine Nation: Finding Balance in the Age of Indulgence , pays tribute to the crucial and often destructive role that dopamine plays in modern society.
Dopamine , the main chemical involved in addiction, is secreted from certain nerve tracts in the brain when we engage in a rewarding experience such as finding food, clothing, shelter or a sexual mate. Nature designed our brains to feel pleasure when these experiences happen because they increase our odds of survival and of procreation.
But the days when our species dwelled in caves and struggled for survival are long gone. Dopamine Nation explains how living in a modern society, affluent beyond comparison by evolutionary standards, has rendered us all vulnerable to dopamine-mediated addiction . Today, the addictive substance of choice, whether we realize it or not, is often the internet and social media channels, according to Lembke, MD.
"If you're not addicted yet, it's coming soon to a website near you," Lembke joked when I talked to her about the message of Dopamine Nation , which was published in August. This Q&A is abridged from that exchange.
Why did you decide to write this book?

I wanted to tell readers what I'd learned from patients and from neuroscience about how to tackle compulsive overconsumption. Feel-good substances and behaviors increase dopamine release in the brain's reward pathways .
The brain responds to this increase by decreasing dopamine transmission -- not just back down to its natural baseline rate, but below that baseline. Repeated exposure to the same or similar stimuli ultimately creates a chronic dopamine-deficit state, wherein we're less able to experience pleasure.
What are the risk factors for addiction?
Easy access and speedy reward are two of them. Just as the hypodermic needle is the delivery mechanism for drugs like heroin, the smartphone is the modern-day hypodermic needle, delivering digital dopamine for a wired generation.
The hypodermic needle delivers a drug right into our vascular system, which in turn delivers it right to the brain, making the drug more potent. The same is true for the smartphone; with its bright colors, flashing lights and engaging alerts, it delivers images to our visual cortex that are tough to resist. And the quantity is endless. TikTok never runs out.
What makes social media particularly addictive?
We're wired to connect. It's kept us alive for millions of years in a world of scarcity and ever-present danger. Moving in tribes safeguards against predators, optimizes scarce resources and facilitates pair bonding. Our brains release dopamine when we make human connections, which incentivizes us to do it again.
But social connection has become druggified by social-media apps, making us vulnerable to compulsive overconsumption. These apps can cause the release of large amounts of dopamine into our brains' reward pathway all at once, just like heroin, or meth, or alcohol. They do that by amplifying the feel-good properties that attract humans to each other in the first place.
Then there's novelty. Dopamine is triggered by our brain's search-and-explore functions, telling us, "Hey, pay attention to this, something new has come along." Add to that the artificial intelligence algorithms that learn what we've liked before and suggest new things that are similar but not exactly the same, and we're off and running.
Further, our brains aren't equipped to process the millions of comparisons the virtual world demands. We can become overwhelmed by our inability to measure up to these "perfect" people who exist only in the Matrix . We give up trying and sink into depression, or what neuroscientists called "learned helplessness."
Upon signing off, the brain is plunged into a dopamine-deficit state as it attempts to adapt to the unnaturally high levels of dopamine social media just released. Which is why social media often feels good while we're doing it but horrible as soon as we stop.
Is there an antidote to our addiction to social media?
Yes, a timeout -- at least for a day. But a whole month is more typically the minimum amount of time we need away from our drug of choice, whether it's heroin or Instagram, to reset our dopamine reward pathways. A monthlong dopamine fast will decrease the anxiety and depression that social media can induce, and enhance our ability to enjoy other, more modest rewards again.
If and when we return to social media, we can consolidate our use to certain times of the day, avoid certain apps that suck us into the vortex and prioritize apps that connect us with real people in our real lives.
Photo by dole777
Popular posts

Why detecting the earliest biological signs of Parkinson’s disease is so crucial

Are long COVID sufferers falling through the cracks?

Too much social media can be harmful, but it’s not addictive like drugs
Professor of Addictions and Health Psychology, University of South Wales
Senior Lecturer in Psychology of Relationships, University of South Wales
Disclosure statement
Bev John has received funding from European Social Funds/Welsh Government, Alcohol Concern (now Alcohol Change), Research Councils and the personal research budgets of a number of Welsh Senedd members. She is an invited observer of the Cross-Party Group on Problem Gambling at the Welsh Parliament and sits on the “Beat the Odds” steering group that is run by Cais Ltd.
Martin Graff does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of South Wales provides funding as a member of The Conversation UK.
View all partners
If you spend hours of the day on your phone checking social media, you’re not unusual. The average internet user spends two hours a day on various social media sites. But does your habit of checking Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and TikTok every few hours make you a social media “addict”?
The term “social media addiction” is being increasingly used to describe people who spend a lot of time on these websites and apps. Doing so can be harmful to people in a variety of ways – causing low self esteem, bad sleep and increasing stress .
The main focus when considering addiction to substances tends to be on three key elements: compulsion (or loss of control), tolerance (needing to increase amount to achieve the same effect) and withdrawal (unpleasant side effects when use stops). Other factors to consider relate to craving, preoccupation and continuing use despite it causing obvious problems. It’s easy to see how these factors apply to drugs, but what about shopping, gambling or, indeed, social media use?
Increasing interest in these and other behavioural “addictions” – like gaming, sex or the internet – has resulted in broadening definitions of what addiction is. Psychologists talk of excessive appetites and powerful motivational drives to engage in particular behaviours that have the power to do considerable unintended harm .
As researchers in social media and addiction, we have spent the last 25 years understanding different kinds of addiction. Our research tells us that social media addiction is not the same as an addiction to substances, like alcohol and other drugs.
Social media use
Too much social media can certainly be damaging. One major feature of social media is it allows users some control over how they present themselves to others. People can edit their online appearance and sometimes present themselves inaccurately while seeking validation from others.
This can cause all kinds of harm. In a study in 2019, we found when female users looked at the platforms for around one and a half hours per day, this was related to an increased desire to be thin , a heightened awareness of how they think other people judge them and motivation to exercise for the purposes of losing weight.
Read more: Why is celebrity abuse on Twitter so bad? It might be a problem with our empathy
And in 2016, we investigated the ways people seek validation on social media. We looked at how often people manipulate posts to increase the number of likes received, use social media to boost spirits or blindly post about issues with which they did not necessarily agree.
We found when this kind of online behaviour increased, self-esteem decreased. But our findings didn’t necessarily show a compulsion to use social media – something key in making it an addiction. Other social factors, such as fear of missing out and narcissistic personality traits, may drive the need to use social media to an unhealthy degree.
Social media addiction
In 2020, we undertook a study into harmful gambling that might help answer the question of whether social media addiction is real.
We found that rapid technological developments in the ease and speed of access of phone and tablet apps are leading to increased levels of gambling harm. Similar psychological processes may be at work on social media platforms, where need for validation, craving and checking likes is amplified.
Behavioural explanations for how addictions develop emphasise the power of reinforcement. Gambling products often use the most powerful form of reinforcement: random pay outs . This, again, is potentially similar to the way users receive validation in the form of “likes” on social media.

There are some who might argue that chronic overuse of social media can be seen as an addiction, but it not is currently recognised as such by the American Psychiatric Association .
There are important differences between excessive social media use and substances in terms of addiction. For example, withdrawal from the latter is often physically unpleasant and sometimes dangerous without medical supervision. Users often suffer stigma, which can be a barrier to seeking help. In comparison, it hasn’t yet been established that there are physical withdrawal effects when people stop using social media.
Considering social media use more as a continuum of possible harm might allow more scope for appropriately targeted messages that could prevent problems developing in the first place.
There are clearly elements of social media use that resonate with certain characterisations of addiction, such as psychological notions of excessive appetites or powerful motivations, and the built-in platform mechanisms of reinforcement through random affirmations or “likes”. It’s also clear that this can be harmful in terms of negative impact on some users’ self-esteem and body image.
But despite these factors, the most useful question might be how to create a healthy balance of interaction in our virtual and real worlds.
It’s worth remembering that behavioural addictions, like those to substances, often occur alongside other mental health issues such as anxiety and depression, suggesting that vulnerability may be multifaceted. This may also be true of excessive social media use.
- Social media
- Digital addiction

Research Fellow – Beyond The Resource Curse

Audience Development Coordinator (fixed-term maternity cover)

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF
Subscribe or renew today
Every print subscription comes with full digital access
Science News
Social media harms teens’ mental health, mounting evidence shows. what now.
Understanding what is going on in teens’ minds is necessary for targeted policy suggestions

Most teens use social media, often for hours on end. Some social scientists are confident that such use is harming their mental health. Now they want to pinpoint what explains the link.
Carol Yepes/Getty Images
Share this:
By Sujata Gupta
February 20, 2024 at 7:30 am
In January, Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook’s parent company Meta, appeared at a congressional hearing to answer questions about how social media potentially harms children. Zuckerberg opened by saying: “The existing body of scientific work has not shown a causal link between using social media and young people having worse mental health.”
But many social scientists would disagree with that statement. In recent years, studies have started to show a causal link between teen social media use and reduced well-being or mood disorders, chiefly depression and anxiety.
Ironically, one of the most cited studies into this link focused on Facebook.
Researchers delved into whether the platform’s introduction across college campuses in the mid 2000s increased symptoms associated with depression and anxiety. The answer was a clear yes , says MIT economist Alexey Makarin, a coauthor of the study, which appeared in the November 2022 American Economic Review . “There is still a lot to be explored,” Makarin says, but “[to say] there is no causal evidence that social media causes mental health issues, to that I definitely object.”
The concern, and the studies, come from statistics showing that social media use in teens ages 13 to 17 is now almost ubiquitous. Two-thirds of teens report using TikTok, and some 60 percent of teens report using Instagram or Snapchat, a 2022 survey found. (Only 30 percent said they used Facebook.) Another survey showed that girls, on average, allot roughly 3.4 hours per day to TikTok, Instagram and Facebook, compared with roughly 2.1 hours among boys. At the same time, more teens are showing signs of depression than ever, especially girls ( SN: 6/30/23 ).
As more studies show a strong link between these phenomena, some researchers are starting to shift their attention to possible mechanisms. Why does social media use seem to trigger mental health problems? Why are those effects unevenly distributed among different groups, such as girls or young adults? And can the positives of social media be teased out from the negatives to provide more targeted guidance to teens, their caregivers and policymakers?
“You can’t design good public policy if you don’t know why things are happening,” says Scott Cunningham, an economist at Baylor University in Waco, Texas.
Increasing rigor
Concerns over the effects of social media use in children have been circulating for years, resulting in a massive body of scientific literature. But those mostly correlational studies could not show if teen social media use was harming mental health or if teens with mental health problems were using more social media.
Moreover, the findings from such studies were often inconclusive, or the effects on mental health so small as to be inconsequential. In one study that received considerable media attention, psychologists Amy Orben and Andrew Przybylski combined data from three surveys to see if they could find a link between technology use, including social media, and reduced well-being. The duo gauged the well-being of over 355,000 teenagers by focusing on questions around depression, suicidal thinking and self-esteem.
Digital technology use was associated with a slight decrease in adolescent well-being , Orben, now of the University of Cambridge, and Przybylski, of the University of Oxford, reported in 2019 in Nature Human Behaviour . But the duo downplayed that finding, noting that researchers have observed similar drops in adolescent well-being associated with drinking milk, going to the movies or eating potatoes.
Holes have begun to appear in that narrative thanks to newer, more rigorous studies.
In one longitudinal study, researchers — including Orben and Przybylski — used survey data on social media use and well-being from over 17,400 teens and young adults to look at how individuals’ responses to a question gauging life satisfaction changed between 2011 and 2018. And they dug into how the responses varied by gender, age and time spent on social media.
Social media use was associated with a drop in well-being among teens during certain developmental periods, chiefly puberty and young adulthood, the team reported in 2022 in Nature Communications . That translated to lower well-being scores around ages 11 to 13 for girls and ages 14 to 15 for boys. Both groups also reported a drop in well-being around age 19. Moreover, among the older teens, the team found evidence for the Goldilocks Hypothesis: the idea that both too much and too little time spent on social media can harm mental health.
“There’s hardly any effect if you look over everybody. But if you look at specific age groups, at particularly what [Orben] calls ‘windows of sensitivity’ … you see these clear effects,” says L.J. Shrum, a consumer psychologist at HEC Paris who was not involved with this research. His review of studies related to teen social media use and mental health is forthcoming in the Journal of the Association for Consumer Research.
Cause and effect
That longitudinal study hints at causation, researchers say. But one of the clearest ways to pin down cause and effect is through natural or quasi-experiments. For these in-the-wild experiments, researchers must identify situations where the rollout of a societal “treatment” is staggered across space and time. They can then compare outcomes among members of the group who received the treatment to those still in the queue — the control group.
That was the approach Makarin and his team used in their study of Facebook. The researchers homed in on the staggered rollout of Facebook across 775 college campuses from 2004 to 2006. They combined that rollout data with student responses to the National College Health Assessment, a widely used survey of college students’ mental and physical health.
The team then sought to understand if those survey questions captured diagnosable mental health problems. Specifically, they had roughly 500 undergraduate students respond to questions both in the National College Health Assessment and in validated screening tools for depression and anxiety. They found that mental health scores on the assessment predicted scores on the screenings. That suggested that a drop in well-being on the college survey was a good proxy for a corresponding increase in diagnosable mental health disorders.
Compared with campuses that had not yet gained access to Facebook, college campuses with Facebook experienced a 2 percentage point increase in the number of students who met the diagnostic criteria for anxiety or depression, the team found.
When it comes to showing a causal link between social media use in teens and worse mental health, “that study really is the crown jewel right now,” says Cunningham, who was not involved in that research.
A need for nuance
The social media landscape today is vastly different than the landscape of 20 years ago. Facebook is now optimized for maximum addiction, Shrum says, and other newer platforms, such as Snapchat, Instagram and TikTok, have since copied and built on those features. Paired with the ubiquity of social media in general, the negative effects on mental health may well be larger now.
Moreover, social media research tends to focus on young adults — an easier cohort to study than minors. That needs to change, Cunningham says. “Most of us are worried about our high school kids and younger.”
And so, researchers must pivot accordingly. Crucially, simple comparisons of social media users and nonusers no longer make sense. As Orben and Przybylski’s 2022 work suggested, a teen not on social media might well feel worse than one who briefly logs on.
Researchers must also dig into why, and under what circumstances, social media use can harm mental health, Cunningham says. Explanations for this link abound. For instance, social media is thought to crowd out other activities or increase people’s likelihood of comparing themselves unfavorably with others. But big data studies, with their reliance on existing surveys and statistical analyses, cannot address those deeper questions. “These kinds of papers, there’s nothing you can really ask … to find these plausible mechanisms,” Cunningham says.
One ongoing effort to understand social media use from this more nuanced vantage point is the SMART Schools project out of the University of Birmingham in England. Pedagogical expert Victoria Goodyear and her team are comparing mental and physical health outcomes among children who attend schools that have restricted cell phone use to those attending schools without such a policy. The researchers described the protocol of that study of 30 schools and over 1,000 students in the July BMJ Open.
Goodyear and colleagues are also combining that natural experiment with qualitative research. They met with 36 five-person focus groups each consisting of all students, all parents or all educators at six of those schools. The team hopes to learn how students use their phones during the day, how usage practices make students feel, and what the various parties think of restrictions on cell phone use during the school day.
Talking to teens and those in their orbit is the best way to get at the mechanisms by which social media influences well-being — for better or worse, Goodyear says. Moving beyond big data to this more personal approach, however, takes considerable time and effort. “Social media has increased in pace and momentum very, very quickly,” she says. “And research takes a long time to catch up with that process.”
Until that catch-up occurs, though, researchers cannot dole out much advice. “What guidance could we provide to young people, parents and schools to help maintain the positives of social media use?” Goodyear asks. “There’s not concrete evidence yet.”
More Stories from Science News on Science & Society

What Science News saw during the solar eclipse

During the awe of totality, scientists studied our planet’s reactions

Your last-minute guide to the 2024 total solar eclipse

Protein whisperer Oluwatoyin Asojo fights neglected diseases

How a 19th century astronomer can help you watch the total solar eclipse

Timbre can affect what harmony is music to our ears

Not all cultures value happiness over other aspects of well-being

‘Space: The Longest Goodbye’ explores astronauts’ mental health
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber? Become one now .
Advertisement

Social Media Addiction and Its Impact on College Students' Academic Performance: The Mediating Role of Stress
- Regular Article
- Published: 01 November 2021
- Volume 32 , pages 81–90, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
- Lei Zhao ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7337-3065 1 , 2
6761 Accesses
12 Citations
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
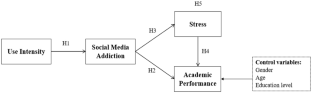
Social media use can bring negative effects to college students, such as social media addiction (SMA) and decline in academic performance. SMA may increase the perceived stress level of college students, and stress has a negative impact on academic performance, but this potential mediating role of stress has not been verified in existing studies. In this paper, a research model was developed to investigate the antecedent variables of SMA, and the relationship between SMA, stress and academic performance. With the data of 372 Chinese college students (mean age 21.3, 42.5% males), Partial Least Squares, Structural Equation Model was adopted to evaluate measurement model and structural model. The results show that use intensity is an important predictor of SMA, and both SMA and stress have a negative impact on college students’ academic performance. In addition, we further confirmed that stress plays a mediating role in the relationship between SMA and college students’ academic performance.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
An investigation of the social media overload and academic performance
Xiongfei Cao, Yuntao Wu, … Ahsan Ali
A serial mediation model of social media addiction and college students’ academic engagement: the role of sleep quality and fatigue
Jie Zhuang, Qiaoxing Mou, … Miaomiao Zhao
Associations Between Academic Motivation, Academic Stress, and Mobile Phone Addiction: Mediating Roles of Wisdom
Abolghasem Yaghoobi, Kambiz Karimi, … Sahar Mohammadi
Al-Yafi, K., El-Masri, M., & Tsai, R. (2018). The effects of using social network sites on academic performance: The case of Qatar. Journal of Enterprise Information Management , 31 (3), 446–462. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-08-2017-0118 .
Andreassen, C. S., & Pallesen, S. (2014). Social network site addiction—an overview. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 20 , 1–9.
Article Google Scholar
Andreassen, C. S., Pallesen, S., & Griffiths, M. D. (2017). The relationship between addictive use of social media, narcissism, and self-esteem: Findings from a large national survey. Addictive Behaviors, 64 , 287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.03.006
Andreassen, C. S., Torsheim, T., Brunborg, G. S., & Pallesen, S. (2012). Development of a facebook addiction scale. Psychological Reports, 110 (2), 501–517.
Argyris, Y. E., & Xu, J. (2016). Enhancing self-efficacy for career development in Facebook. Computers in Human Behavior, 55 (2), 921–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.10.023
Arnett, J. J. (2000). Emerging adulthood: A theory of development from the late teens through the twenties. American Psychologist, 55 (5), 469–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.10.023
Bano, S., Cisheng, W., Khan, A., & Khan, N. A. (2019). WhatsApp use and student’s psychological well-being: Role of social capital and social integration. Children and Youth Services Review, 103 , 200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2019.06.002
Barclay, D., Higgins, C., & Thompson, R. (1995). The partial least squares (PLS) approach to causal modeling: Personal computer adoption and use as an illustration. Technology Studies, 2 (2), 285–309.
Google Scholar
Bijari, B., Javadinia, S. A., Erfanian, M., Abedini, M. R., & Abassi, A. (2013). The impact of virtual social networks on students’ academic achievement in Birjand University of Medical Sciences in East Iran. Procedia Social and Behavioural Sciences, 83 , 103–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.06.020
Błachnio, A., Przepiorka, A., & Pantic, I. (2016). Association between facebook addiction, self-esteem and life satisfaction: A cross-sectional study. Computers in Human Behavior, 55 , 701–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.10.026
Brailovskaia, J., Rohmann, E., Bierhoff, H. W., Schillack, H., & Margraf, J. (2019). The relationship between daily stress, social support and Facebook addiction disorder. Psychiatry Research, 276 , 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2019.05.014
Brailovskaia, J., Schillack, H., & Margraf, J. (2018). Facebook addiction disorder in Germany. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 21 (7), 450–456. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2018.0140
Buil, I., Martínez, E., & Matute, J. (2016). From internal brand management to organizational citizenship behaviors: Evidence from frontline employees in the hotel industry. Tourism Management, 57 (12), 256–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.06.009
Busalim, A. H., Masrom, M., & Zakaria, W. N. B. W. (2019). The impact of Facebook addiction and self-esteem on students’ academic performance: A multi-group analysis. Computers & Education, 142 , 103651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103651
Carolus, A., Binder, J. F., Muench, R., Schmidt, C., Schneider, F., & Buglass, S. L. (2019). Smartphones as digital companions: Characterizing the relationship between users and their phones. New Media & Society, 21 , 914–938. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444818817074
China Internet Network Information Center (CNNIC), 2020. The 44th Statistical Report on Internet Development in China (in Chinese). Retrieved August 28, 2020, from http://www.cac.gov.cn/2020-08/30/c_1124938750.htm
Cohen, S., Kamarck, T., & Mermelstein, R. (1983). A global measure of perceived stress. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 24 (4), 385–396. https://doi.org/10.2307/2136404
Dendle, C., Baulch, J., Pellicano, R., Hay, M., Lichtwark, I., Ayoub, S., & Horne, K. (2018). Medical student psychological distress and academic performance. Medical Teacher . https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2018.99099
Doleck, T., & Lajoie, S. (2018). Social networking and academic performance: A review. Education and Information Technologies, 23 (1), 435–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-017-9612-3
Griffths, M. D., Kuss, D. J., & Demetrovics, Z. (2014). Social networking addictions: An overview of preliminary findings. Behavioral Addictions Criteria, Evidence, and Treatment , 119–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-407724-9.00006-9 .
Hair, J. F. J., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) . Sage Publication.
Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., & Ringle, C. M. (2019). When to use and how to report the results of pls-sem. European Business Review, 31 (1), 2–24. https://doi.org/10.1108/EBR-11-2018-0203
Hayes, A. F. (2009). Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Communication Monographs, 76 (4), 408–420. https://doi.org/10.1080/03637750903310360
Hormes, J. M., Kearns, B., & Timko, C. A. (2014). Craving Facebook? Behavioral addiction to online social networking and its association with emotion regulation deficits. Addiction, 109 (12), 2079–2088. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.12713
Hsiao, K. L., Shu, Y., & Huang, T. C. (2017). Exploring the effect of compulsive social app usage on technostress and academic performance: Perspectives from personality traits. Telematics and Informatics, 34 , 679–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2016.11.001
Jie, T., Yizhen, Y., Yukai, D., Ying, M., Dongying, Z., & Jiaji, W. (2014). Addictive behaviors prevalence of internet addiction and its association with stressful life events and psychological symptoms among adolescent internet users. Addictive Behaviors, 39 (3), 744–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.07.012
Juana, I., Serafín, B., Jesús, L., et al. (2020). Effectiveness of music therapy and progressive muscle relaxation in reducing stress before exams and improving academic performance in nursing students: A randomized trial. Nurse Education Today, 84 , 104217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2019.104217
Kimberly, Y. (2009). Facebook addiction disorder . The Center for Online Addiction.
Lau, W. W. F. (2017). Effects of social media usage and social media multitasking on the academic performance of university students. Computers in Human Behavior, 68 (3), 286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.11.043
Lazarus, R. S., & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, appraisal, and coping . Springer.
Lee, W. W. S. (2017). Relationships among grit, academic performance, perceived academic failure, and stress in associate degree students. Journal of Adolescence, 60 , 148–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2017.08.006
Leung, L. (2007). Stressful life events, motives for Internet use, and social support among digital kids. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 10 (2), 204–214. https://doi.org/10.1089/cpb.2006.9967
Liang, C., Gu, D., Tao, F., Jain, H. K., Zhao, Y., & Ding, B. (2017). Influence of mechanism of patient-accessible hospital information system implementation on doctor-patient relationships: A service fairness perspective. Information & Management, 54 (1), 57–72.
Lim, K., & Jeoung, Y. S. (2010). Understanding major factors in taking Internet based lectures for the national college entrance exam according to academic performance by case studies. The Journal of the Korea Contents Association, 10 (12), 477–491. https://doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2010.10.12.477
Lim, Y., & Nam, S.-J. (2016). Time spent on the Internet by multicultural adolescents in Korea. Asia Pacific Journal of Education, 37 (1), 55–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/02188791.2016.1169994
Lin, C. L., Jin, Y. Q., Zhao, Q., Yu, S. W., & Su, Y. S. (2021). Factors influence students’ switching behavior to online learning under covid-19 pandemic: A push-pull-mooring model perspective. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 30 (3), 229–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00570-0
Lovibond, P. F., & Lovibond, S. H. (1995). The structure of negative emotional states: Comparison of the depression anxiety stress scales (DASS) with the Beck depression and anxiety inventories. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 33 (3), 335–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.12.004
Marino, C., Gini, G., Vieno, A., & Spada, M. M. (2018). A comprehensive meta-analysis on problematic Facebook use. Computers in Human Behavior, 83 , 262–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.02.009
Masood, A., Luqman, A., Feng, Y., & Ali, A. (2020). Adverse consequences of excessive social networking site use on academic performance: Explaining underlying mechanism from stress perspective. Computers in Human Behavior . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106476
McDaniel, B. (2015). ‘Technoference’: Everyday intrusions and inter-ruptions of technology in couple and family relationships. In C. Bruess Içinde (Ed.), Family communication in the age of digital and social media. Peter Lang Publishing.
Nayak, J. K. (2018). Relationship among smartphone usage, addiction, academic performance and the moderating role of gender: A study of higher education students in India. Computers and Education, 123 (5), 164–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.05.007
O'Brien, L. (2012). Six ways to use social media in education. Retrieved from https://cit.duke.edu/blog/2012/04/six-ways-to-use-social-media-in-education/
Orosz, G., Istvan, T., & Beata, B. (2016). Four facets of Facebook intensity—the development of the multidimensional facebook intensity scale. Personality and Individual Differences, 100 , 95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.11.038
Oye, N. D., Adam, M. H., & Nor Zairah, A. R. (2012). Model of perceived influence of academic performance using social networking. International Journal of Computers and Technology, 2 (2), 24–29. https://doi.org/10.24297/ijct.v2i1.2612
Pang, H. (2018). How does time spent on WeChat bolster subjective well-being through social integration and social capital? Telematics and Informatics, 25 , 2147–2156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2018.07.015
Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 28 (6), 2117–2127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.06.016
Peng, Y., & Li, J. (2021). The effect of customer education on service innovation satisfaction: The mediating role of customer participation. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 47 (5), 326–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2020.12.014
Phu, B., & Gow, A. J. (2019). Facebook use and its association with subjective happiness and loneliness. Computers in Human Behavior, 92 , 151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.11.020
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J.-Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology , 88 (5), 879–903. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879 .
Prato, C. A., & Yucha, C. B. (2013). Biofeedback-assisted relaxation training to decrease test anxiety in nursing students. Nursing Education Perspectives, 34 (2), 76–81. https://doi.org/10.1097/00024776-201303000-00003
Rouis, S. (2012). Impact of cognitive absorption on facebook on students’ achievement. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 15 (6), 296–303. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2011.0390
Ryan, T., Chester, A., Reece, J., & Xenos, S. (2014). The uses and abuses of facebook: A review of facebook addiction. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 3 (3), 133–148. https://doi.org/10.1556/JBA.3.2014.016
Sandra, K., Dawans, B. V., Heinrichs, M., & Fuchs, R. (2013). Does the level of physical exercise affect physiological and psychological responses to psychosocial stress in women. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 14 , 266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychsport.2012.11.003
Shaw, M., & Black, D. W. (2008). Internet addiction . Springer.
Shi, C., Yu, L., Wang, N., Cheng, B., & Cao, X. (2020). Effects of social media overload on academic performance: A stressor–strain–outcome perspective. Asian Journal of Communication, 30 (2), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/01292986.2020.1748073
Statista (2020). Number of social media users worldwide from 2010 to 2021 (in billions). Retrieved from https://www.statista.com/statistics/278414/number-of-worldwide-social-network-users/
Tang, J. H., Chen, M. C., Yang, C. Y., Chung, T. Y., & Lee, Y. A. (2016). Personality traits, interpersonal relationships, online social support, and Facebook addiction. Telematics and Informatics, 33 (1), 102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2015.06.003
Wang, J. L., Wang, H. Z., Gaskin, J., & Wang, L. H. (2015). The role of stress and motivation in problematic smartphone use among college students. Computers in Human Behavior, 53 , 181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.07.005
Wartberg, L., Kriston, L., & Thomasius, R. (2020). Internet gaming disorder and problematic social media use in a representative sample of German adolescents: Prevalence estimates, comorbid depressive symptoms and related psychosocial aspects. Computers in Human Behavior, 103 , 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.09.014
Xu, X. A., Xue, K. N., Wang, L. L., Gursoy, D., & Song, Z. B. (2021). Effects of customer-to-customer social interactions in virtual travel communities on brand attachment: the mediating role of social well-being. Tourism Management Perspectives, 38 , 100790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2021.100790
Zhao, L. (2021). The impact of social media use types and social media addiction on subjective well-being of college students: A comparative analysis of addicted and non-addicted students. Computers in Human Behavior Reports, 4 (2), 100122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbr.2021.100122
Zhao, L., Liang, C., & Gu, D. (2021). Mobile social media use and trailing parents’ life satisfaction: Social capital and social integration perspective. International Journal of Aging and Human Development, 92 (3), 383–405. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091415020905549
Download references
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the Planning Subject for the 14th Five-year Plan of National Education Sciences (Grant No. EIA210425).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Management, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, 230009, Anhui, China
Wendian College, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601, Anhui, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lei Zhao .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declared no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Zhao, L. Social Media Addiction and Its Impact on College Students' Academic Performance: The Mediating Role of Stress. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 32 , 81–90 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00635-0
Download citation
Accepted : 21 October 2021
Published : 01 November 2021
Issue Date : February 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00635-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Use intensity
- Social media addiction
- Academic performance
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Likes, Shares, and Beyond: Exploring the Impact of Social Media in Essays
Table of contents
- 1 Definition and Explanation of a Social Media Essay
- 2.1 Topics for an Essay on Social Media and Mental Health
- 2.2 Social Dynamics
- 2.3 Social Media Essay Topics about Business
- 2.4 Politics
- 3 Research and Analysis
- 4 Structure Social Media Essay
- 5 Tips for Writing Essays on Social Media
- 6 Examples of Social Media Essays
- 7 Navigating the Social Media Labyrinth: Key Insights
In the world of digital discourse, our article stands as a beacon for those embarking on the intellectual journey of writing about social media. It is a comprehensive guide for anyone venturing into the dynamic world of social media essays. Offering various topics about social media and practical advice on selecting engaging subjects, the piece delves into research methodologies, emphasizing the importance of credible sources and trend analysis. Furthermore, it provides invaluable tips on structuring essays, including crafting compelling thesis statements and hooks balancing factual information with personal insights. Concluding with examples of exemplary essays, this article is an essential tool for students and researchers alike, aiding in navigating the intricate landscape of its impact on society.
Definition and Explanation of a Social Media Essay

Essentially, when one asks “What is a social media essay?” they are referring to an essay that analyzes, critiques, or discusses its various dimensions and effects. These essays can range from the psychological implications of its use to its influence on politics, business strategies, and social dynamics.
A social media essay is an academic or informational piece that explores various aspects of social networking platforms and their impact on individuals and society.
In crafting such an essay, writers blend personal experiences, analytical perspectives, and empirical data to paint a full picture of social media’s role. For instance, a social media essay example could examine how these platforms mold public opinion, revolutionize digital marketing strategies, or raise questions about data privacy ethics. Through a mix of thorough research, critical analysis, and personal reflections, these essays provide a layered understanding of one of today’s most pivotal digital phenomena.
Great Social Media Essay Topics
When it comes to selecting a topic for your essay, consider its current relevance, societal impact, and personal interest. Whether exploring the effects on business, politics, mental health, or social dynamics, these social media essay titles offer a range of fascinating social media topic ideas. Each title encourages an exploration of the intricate relationship between social media and our daily lives. A well-chosen topic should enable you to investigate the impact of social media, debate ethical dilemmas, and offer unique insights. Striking the right balance in scope, these topics should align with the objectives of your essays, ensuring an informative and captivating read.
Topics for an Essay on Social Media and Mental Health
- The Impact of Social Media on Self-Esteem.
- Unpacking Social Media Addiction: Causes, Effects, and Solutions.
- Analyzing Social Media’s Role as a Catalyst for Teen Depression and Anxiety.
- Social Media and Mental Health Awareness: A Force for Good?
- The Psychological Impacts of Cyberbullying in the Social Media Age.
- The Effects of Social Media on Sleep and Mental Health.
- Strategies for Positive Mental Health in the Era of Social Media.
- Real-Life vs. Social Media Interactions: An Essay on Mental Health Aspects.
- The Mental Well-Being Benefits of a Social Media Detox.
- Social Comparison Psychology in the Realm of Social Media.
Social Dynamics
- Social Media and its Impact on Interpersonal Communication Skills: A Cause and Effect Essay on Social Media.
- Cultural Integration through Social Media: A New Frontier.
- Interpersonal Communication in the Social Media Era: Evolving Skills and Challenges.
- Community Building and Social Activism: The Role of Social Media.
- Youth Culture and Behavior: The Influence of Social Media.
- Privacy and Personal Boundaries: Navigating Social Media Challenges.
- Language Evolution in Social Media: A Dynamic Shift.
- Leveraging Social Media for Social Change and Awareness.
- Family Dynamics in the Social Media Landscape.
- Friendship in the Age of Social Media: An Evolving Concept.
Social Media Essay Topics about Business
- Influencer Marketing on Social Media: Impact and Ethics.
- Brand Building and Customer Engagement: The Power of Social Media.
- The Ethics and Impact of Influencer Marketing in Social Media.
- Measuring Business Success Through Social Media Analytics.
- The Changing Face of Advertising in the Social Media World.
- Revolutionizing Customer Service in the Social Media Era.
- Market Research and Consumer Insights: The Social Media Advantage.
- Small Businesses and Startups: The Impact of Social Media.
- Ethical Dimensions of Social Media Advertising.
- Consumer Behavior and Social Media: An Intricate Relationship.
- The Role of Social Media in Government Transparency and Accountability
- Social Media’s Impact on Political Discourse and Public Opinion.
- Combating Fake News on Social Media: Implications for Democracy.
- Political Mobilization and Activism: The Power of Social Media.
- Social Media: A New Arena for Political Debates and Discussions.
- Government Transparency and Accountability in the Social Media Age.
- Voter Behavior and Election Outcomes: The Social Media Effect.
- Political Polarization: A Social Media Perspective.
- Tackling Political Misinformation on Social Media Platforms.
- The Ethics of Political Advertising in the Social Media Landscape.
- Memes as a Marketing Tool: Successes, Failures, and Pros of Social Media.
- Shaping Public Opinion with Memes: A Social Media Phenomenon.
- Political Satire and Social Commentary through Memes.
- The Psychology Behind Memes: Understanding Their Viral Nature.
- The Influence of Memes on Language and Communication.
- Tracing the History and Evolution of Internet Memes.
- Memes in Online Communities: Culture and Subculture Formation.
- Navigating Copyright and Legal Issues in the World of Memes.
- Memes as a Marketing Strategy: Analyzing Successes and Failures.
- Memes and Global Cultural Exchange: A Social Media Perspective.
Research and Analysis
In today’s fast-paced information era, the ability to sift through vast amounts of data and pinpoint reliable information is more crucial than ever. Research and analysis in the digital age hinge on identifying credible sources and understanding the dynamic landscape. Initiating your research with reputable websites is key. Academic journals, government publications, and established news outlets are gold standards for reliable information. Online databases and libraries provide a wealth of peer-reviewed articles and books. For websites, prioritize those with domains like .edu, .gov, or .org, but always critically assess the content for bias and accuracy. Turning to social media, it’s a trove of real-time data and trends but requires a discerning approach. Focus on verified accounts and official pages of recognized entities.
Analyzing current trends and user behavior is crucial for staying relevant. Platforms like Google Trends, Twitter Analytics, and Facebook Insights offer insights into what’s resonating with audiences. These tools help identify trending topics, hashtags, and the type of content that engages users. Remember, it reflects and influences public opinion and behavior. Observing user interactions, comments, and shares can provide a deeper understanding of consumer attitudes and preferences. This analysis is invaluable for tailoring content, developing marketing strategies, and staying ahead in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Structure Social Media Essay
In constructing a well-rounded structure for a social media essay, it’s crucial to begin with a strong thesis statement. This sets the foundation for essays about social media and guides the narrative.
Thesis Statements
A thesis statement is the backbone of your essay, outlining the main argument or position you will explore throughout the text. It guides the narrative, providing a clear direction for your essay and helping readers understand the focus of your analysis or argumentation. Here are some thesis statements:
- “Social media has reshaped communication, fostering a connected world through instant information sharing, yet it has come at the cost of privacy and genuine social interaction.”
- “While social media platforms act as potent instruments for societal and political transformation, they present significant challenges to mental health and the authenticity of information.”
- “The role of social media in contemporary business transcends mere marketing; it impacts customer relationships, shapes brand perception, and influences operational strategies.”
Social Media Essay Hooks
Social media essay hooks are pivotal in grabbing the reader’s attention right from the beginning and compelling them to continue reading. A well-crafted hook acts as the engaging entry point to your essay, setting the tone and framing the context for the discussion that will follow.
Here are some effective social media essay hooks:
- “In a world where a day without social media is unimaginable, its pervasive presence is both a testament to its utility and a source of various societal issues.”
- “Each scroll, like, and share on social media platforms carries the weight of influencing public opinion and shaping global conversations.”
- “Social media has become so ingrained in our daily lives that its absence would render the modern world unrecognizable.”
Introduction:
Navigating the digital landscape, an introduction for a social media essay serves as a map, charting the terrain of these platforms’ broad influence across various life aspects. This section should briefly summarize the scope of the essay, outlining both the benefits and the drawbacks, and segue into the thesis statement.
When we move to the body part of the essay, it offers an opportunity for an in-depth exploration and discussion. It can be structured first to examine the positive aspects of social media, including improved communication channels, innovative marketing strategies, and the facilitation of social movements. Following this, the essay should address the negative implications, such as issues surrounding privacy, the impact on mental health, and the proliferation of misinformation. Incorporating real-world examples, statistical evidence, and expert opinions throughout the essay will provide substantial support for the arguments presented.
Conclusion:
It is the summit of the essay’s exploration, offering a moment to look back on the terrain covered. The conclusion should restate the thesis in light of the discussions presented in the body. It should summarize the key points made, reflecting on the multifaceted influence of social media in contemporary society. The essay should end with a thought-provoking statement or question about the future role of social media, tying back to the initial hooks and ensuring a comprehensive and engaging end to the discourse.
Tips for Writing Essays on Social Media
In the ever-evolving realm of digital dialogue, mastering the art of essay writing on social media is akin to navigating a complex web of virtual interactions and influences. Writing an essay on social media requires a blend of analytical insight, factual accuracy, and a nuanced understanding of the digital landscape. Here are some tips to craft a compelling essay:
- Incorporate Statistical Data and Case Studies
Integrate statistical data and relevant case studies to lend credibility to your arguments. For instance, usage statistics, growth trends, and demographic information can provide a solid foundation for your points. Case studies, especially those highlighting its impact on businesses, politics, or societal change, offer concrete examples that illustrate your arguments. Ensure your sources are current and reputable to maintain the essay’s integrity.
- Balance Personal Insights with Factual Information
While personal insights can add a unique perspective to your essay, balancing them with factual information is crucial. Personal observations and experiences can make your essay relatable and engaging, but grounding these insights in factual data ensures credibility and helps avoid bias.
- Respect Privacy
When discussing real-world examples or case studies, especially those involving individuals or specific organizations, be mindful of privacy concerns. Avoid sharing sensitive information, and always respect the confidentiality of your sources.
- Maintain an Objective Tone
It is a polarizing topic, but maintaining an objective tone in your essay is essential. Avoid emotional language and ensure that your arguments are supported by evidence. An objective approach allows readers to form opinions based on the information presented.
- Use Jargon Wisely
While using social media-specific terminology can make your essay relevant and informed, it’s important to use jargon judiciously. Avoid overuse and ensure that terms are clearly defined for readers who might not be familiar with their lingo.
Examples of Social Media Essays
Title: The Dichotomy of Social Media: A Tool for Connection and a Platform for Division
Introduction
In the digital era, social media has emerged as a paradoxical entity. It serves as a bridge connecting distant corners of the world and a battleground for conflicting ideologies. This essay explores this dichotomy, utilizing statistical data, case studies, and real-world examples to understand its multifaceted impact on society.
Section 1 – Connection Through Social Media:
Social media’s primary allure lies in its ability to connect. A report by the Pew Research Center shows that 72% of American adults use some form of social media, where interactions transcend geographical and cultural barriers. This statistic highlights the platform’s popularity and role in fostering global connections. An exemplary case study of this is the #MeToo movement. Originating as a hashtag on Twitter, it grew into a global campaign against sexual harassment, demonstrating its power to mobilize and unify people for a cause.
However, personal insights suggest that while it bridges distances, it can also create a sense of isolation. Users often report feeling disconnected from their immediate surroundings, hinting at the platform’s double-edged nature. Despite enabling connections on a global scale, social media can paradoxically alienate individuals from their local context.
Section 2 – The Platform for Division
Conversely, social media can amplify societal divisions. Its algorithm-driven content can create echo chambers, reinforcing users’ preexisting beliefs. A study by the Knight Foundation found that it tends to polarize users, especially in political contexts, leading to increased division. This is further exacerbated by the spread of misinformation, as seen in the 2016 U.S. Presidential Election case, where it was used to disseminate false information, influencing public opinion and deepening societal divides.
Respecting privacy and maintaining an objective tone, it is crucial to acknowledge that social media is not divisive. Its influence is determined by both its usage and content. Thus, it is the obligation of both platforms to govern content and consumers to access information.
In conclusion, it is a complex tool. It has the unparalleled ability to connect individuals worldwide while possessing the power to divide. Balancing the personal insights with factual information presented, it’s clear that its influence is a reflection of how society chooses to wield it. As digital citizens, it is imperative to use it judiciously, understanding its potential to unite and divide.
Delving into the intricacies of social media’s impact necessitates not just a keen eye for detail but an analytical mindset to dissect its multifaceted layers. Analysis is paramount because it allows us to navigate through the vast sea of information, distinguishing between mere opinion and well-supported argumentation.
This essay utilizes tips for writing a social media essay. Statistical data from the Pew Research Center and the Knight Foundation lend credibility to the arguments. The use of the #MeToo movement as a case study illustrates its positive impact, while the reference to the 2016 U.S. Presidential Election demonstrates its negative aspects. The essay balances personal insights with factual information, respects privacy, maintains an objective tone, and appropriately uses jargon. The structure is clear and logical, with distinct sections for each aspect of its impact, making it an informative and well-rounded analysis of its role in modern society.
Navigating the Social Media Labyrinth: Key Insights
In the digital age, the impact of social media on various aspects of human life has become a critical area of study. This article has provided a comprehensive guide for crafting insightful and impactful essays on this subject, blending personal experiences with analytical rigor. Through a detailed examination of topics ranging from mental health and social dynamics to business and politics, it has underscored the dual nature of social media as both a unifying and divisive force. The inclusion of statistical data and case studies has enriched the discussion, offering a grounded perspective on the nuanced effects of these platforms.
The tips and structures outlined serve as a valuable framework for writers to navigate the complex interplay between social media and societal shifts. As we conclude, it’s clear that understanding social media’s role requires a delicate balance of critical analysis and open-mindedness. Reflecting on its influence, this article guides the creation of thoughtful essays and encourages readers to ponder the future of digital interactions and their implications for the fabric of society.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Advertisement
Supported by
Is Social Media Addictive? Here’s What the Science Says.
A major lawsuit against Meta has placed a spotlight on our fraught relationship with online social information.
- Share full article

By Matt Richtel
A group of 41 states and the District of Columbia filed suit on Tuesday against Meta , the parent company of Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp and Messenger, contending that the company knowingly used features on its platforms to cause children to use them compulsively, even as the company said that its social media sites were safe for young people.
“Meta has harnessed powerful and unprecedented technologies to entice, engage and ultimately ensnare youth and teens,” the states said in their lawsuit filed in federal court. “Its motive is profit.”
The accusations in the lawsuit raise a deeper question about behavior: Are young people becoming addicted to social media and the internet? Here’s what the research has found.
What Makes Social Media So Compelling?
Experts who study internet use say that the magnetic allure of social media arises from the way the content plays to our neurological impulses and wiring, such that consumers find it hard to turn away from the incoming stream of information.
David Greenfield, a psychologist and founder of the Center for Internet and Technology Addiction in West Hartford, Conn., said the devices lure users with some powerful tactics. One is “intermittent reinforcement,” which creates the idea that a user could get a reward at any time. But when the reward comes is unpredictable. “Just like a slot machine,” he said. As with a slot machine, users are beckoned with lights and sounds but, even more powerful, information and reward tailored to a user’s interests and tastes.
Adults are susceptible, he noted, but young people are particularly at risk, because the brain regions that are involved in resisting temptation and reward are not nearly as developed in children and teenagers as in adults. “They’re all about impulse and not a lot about the control of that impulse,” Dr. Greenfield said of young consumers.
Moreover, he said, the adolescent brain is especially attuned to social connections, and “social media is all a perfect opportunity to connect with other people.”
Meta responded to the lawsuit by saying that it had taken many steps to support families and teenagers. “We’re disappointed that instead of working productively with companies across the industry to create clear, age-appropriate standards for the many apps teens use, the attorneys general have chosen this path,” the company said in a statement.
Does Compulsion Equal Addiction?
For many years, the scientific community typically defined addiction in relation to substances, such as drugs, and not behaviors, such as gambling or internet use. That has gradually changed. In 2013, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, the official reference for mental health conditions, introduced the idea of internet gaming addiction but said that more study was warranted before the condition could be formally declared.
A subsequent stud y explored broadening the definition to “internet addiction.” The author suggested further exploring diagnostic criteria and the language, noting, for instance, that terms like “problematic use” and even the word “internet” were open to broad interpretation, given the many forms the information and its delivery can take.
Dr. Michael Rich, the director of the Digital Wellness Lab at Boston Children’s Hospital, said he discouraged the use of the word “addiction” because the internet, if used effectively and with limits, was not merely useful but also essential to everyday life. “I prefer the term ‘Problematic Internet Media Use,” he said, a term that has gained currency in recent years.
Dr. Greenfield agreed that there clearly are valuable uses for the internet and that the definition of how much is too much can vary. But he said there also were clearly cases where excessive use interferes with school, sleep and other vital aspects of a healthy life. Too many young consumers “can’t put it down,” he said. “The internet is a giant hypodermic, and the content, including social media like Meta, are the psychoactive drugs.”
Matt Richtel is a health and science reporter for The Times, based in Boulder, Colo. More about Matt Richtel
A Parent’s Guide to Kids and Social Media
Does your child have an unhealthy relationship with social media? This is what problematic use could look like .
We asked experts for one practical strategy that parents can use with their kids to help mitigate the harms of social media. Here’s what they told us .
There are many tools that allow parents to monitor and set limits on their children’s screen time. Here’s what to know about them .
If you’ve already given your teen full access to social media, these three strategies can help them cut back .
Is social media addictive? Here is what the science says .
A new book argues that banning social media isn’t the answer to online safety. Instead, the author says parents should emphasize the importance of digital literacy and privacy .
Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Social Media — The Impact of Social Media: Causes and Effects
The Impact of Social Media: Causes and Effects
- Categories: Effects of Social Media Social Media
About this sample

Words: 1226 |
Published: Feb 7, 2024
Words: 1226 | Pages: 3 | 7 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, cause 1: increased connectivity and communication, cause 2: promotion of self-expression and individuality, cause 3: access to information and awareness, effect 1: impacts on mental health, effect 2: influence on societal norms and values, effect 3: privacy and security concerns.

COMMENTS
The Effects of SM Addiction. SM addiction can have various types of negative effects, including a greater likelihood of mental health issues, alterations to individual productivity, and deficiencies in a person's subjective physical well-being. First, psychological and mental issues become more likely as a result of overusing SM.
One of the main causes of this addiction is the extensive use of social media. According to a 2018 Pew Research Center survey, 95% of all teens (ages 13-17) have access to a smartphone. In the same survey, 45% of teens say that they are online almost constantly. Anytime I go anywhere, I can find someone completely hooked into their phone.
Social media addiction (SMA) led to the formation of health-threatening behaviors that can have a negative impact on the quality of life and well-being. Many factors can develop an exaggerated tendency to use social media (SM), which can be prevented in most cases. This study aimed to explore the reasons for SMA.
This meta‐analysis examines the relations between social media addiction and Big Five traits, together with moderating effects on the associations. Sixty‐three studies comprising 74 samples (N ...
Addictive potential of social media, explained. The curious title of Stanford psychiatrist Anna Lembke 's book, Dopamine Nation: Finding Balance in the Age of Indulgence, pays tribute to the crucial and often destructive role that dopamine plays in modern society. Dopamine, the main chemical involved in addiction, is secreted from certain nerve ...
social media addiction scales, or general addiction in a population, and theories or models that have been applied in studies of social media addiction. Yet, it appears that 70 these reviews have a limited focus and narrow perspective. They do not cover up-to-date facets of social media addiction among young users. For example, Sun and Zhang
Social Media Addiction (SMA) is a behavioral addiction that hinders one's individual life and function due to an extreme level of dependence on social media platforms [1]. It could be ...
Excessive and compulsive use of social media may lead to social media addiction (SMA). The main aim of this study was to investigate whether demographic factors (including age and gender), impulsivity, self-esteem, emotions, and attentional bias were risk factors associated with SMA. The study was conducted in a non-clinical sample of college ...
Most studies have looked at the connection between social media use and its effects (such as social media addiction) and a number of different psychosomatic disorders. ... A keyword search for "social media addiction" OR "problematic social media use" yielded 553 papers, which were downloaded from Scopus. The information was gathered in ...
The term "social media addiction" is being increasingly used to describe people who spend a lot of time on these websites and apps. Doing so can be harmful to people in a variety of ways ...
Social media. The term 'social media' refers to the various internet-based networks that enable users to interact with others, verbally and visually (Carr & Hayes, Citation 2015).According to the Pew Research Centre (Citation 2015), at least 92% of teenagers are active on social media.Lenhart, Smith, Anderson, Duggan, and Perrin (Citation 2015) identified the 13-17 age group as ...
First, set a good example by putting your own screens down when interacting with your children. Talk to your teen about the pros and cons of social media: while it can be fun, it can also become a distraction. Set limits on your child's social media use. Most importantly, talk to your children about their experiences, including who they are ...
Previous systematic reviews on social media addiction among young people during the COVID-19 pandemic have indicated that poor real-life social relationships may inadvertently cause young adults ...
The concern, and the studies, come from statistics showing that social media use in teens ages 13 to 17 is now almost ubiquitous. Two-thirds of teens report using TikTok, and some 60 percent of ...
Social media use can bring negative effects to college students, such as social media addiction (SMA) and decline in academic performance. SMA may increase the perceived stress level of college students, and stress has a negative impact on academic performance, but this potential mediating role of stress has not been verified in existing studies. In this paper, a research model was developed ...
Social media addiction has numerous detrimental effects on individuals and communities. This addiction can negatively impact mental health, leading to increased feelings of depression, anxiety, and loneliness. The constant exposure to carefully curated images and narratives can breed envy and dissatisfaction with one's own life, further ...
Abstract. Social media are responsible for aggravating mental health problems. This systematic study summarizes the effects of social network usage on mental health. Fifty papers were shortlisted from google scholar databases, and after the application of various inclusion and exclusion criteria, 16 papers were chosen and all papers were ...
Social Media Addiction. Social media addiction, also known as social media dependency or problematic social media use, refers to a compulsive and excessive engagement with social media platforms, to the extent that it interferes with one's daily life, relationships, and well-being. Individuals who are addicted to social media often exhibit ...
Unpacking Social Media Addiction: Causes, Effects, and Solutions. Analyzing Social Media's Role as a Catalyst for Teen Depression and Anxiety. ... Social Media Essay Hooks. Social media essay hooks are pivotal in grabbing the reader's attention right from the beginning and compelling them to continue reading. A well-crafted hook acts as the ...
Here is what the science says. A new book argues that banning social media isn't the answer to online safety. Instead, the author says parents should emphasize the importance of digital literacy ...
41%. Percentage of teens with the highest social media use who rate their overall mental health as poor or very poor, compared with 23% of those with the lowest use. For example, 10% of the highest use group expressed suicidal intent or self-harm in the past 12 months compared with 5% of the lowest use group, and 17% of the highest users expressed poor body image compared with 6% of the lowest ...
October 19, 2021 by Prasanna. Causes and Effects of Social Media Essay: Today we will learn about the cause and effect of social media on youth, teenagers and adults. How this term social media is affecting today's world with good or bad learnings. In earlier days the mode of communication was sending letters to communicate with someone.
Social media can contribute to feelings of anxiety and depression by creating a constant need for validation and comparison. The curated nature of social media feeds can lead individuals to develop unrealistic expectations and feelings of inadequacy. 3. Impact of social media on overall well-being and relationships.