Top Science News
Latest top headlines.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces
- Brain Tumor
- Intelligence
- Molecular Biology
- Cell Biology
- Mental Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Consumer Electronics
- Oceanography
- Space Telescopes
- Space Exploration
- Space Missions
- Food and Agriculture
- New Species
- Evolutionary Biology
- Dolphins and Whales
- Connecting Lab-Grown Brain Cells
- How We Perceive Bitter Taste
- Friendly Pat On the Back: Free Throws
- A Welcome Hug Is Good for Your Health

Top Physical/Tech
- Next-Generation Digital Displays
- Tiny Plastic Particles Are Found Everywhere
- Unprecedented Behavior from Nearby Magnetar
- How the Moon Turned Itself Inside Out
Top Environment
- 3D Mouth of an Ancient Jawless Fish
- Do Odd Bones Belong to Gigantic Ichthyosaurs?
- Big-Eyed Marine Worm: Secret Language?
- Toothed Whale Echolocation and Jaw Muscles
Health News
Latest health headlines.
- Liver Disease
- Infectious Diseases
- Prostate Cancer
- Men's Health
- Medical Imaging
- Medical Devices
- Patient Education and Counseling
- Today's Healthcare
- Heart Disease
- Sleep Disorder Research
- Insomnia Research
- Gender Difference
- K-12 Education
- STEM Education
- Diet and Weight Loss
- Children's Health
- Computer Modeling
- Mathematical Modeling
- Mathematics
- Breast Cancer
- Diseases and Conditions
- Consumer Behavior
- Racial Issues
Health & Medicine
- Protein That Controls CAR T Cell Longevity
- The Genesis of Our Cellular Skeleton
- Hepatitis B and D Virus Cell Entry Inhibitor
- Combating Drug-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Mind & Brain
- AI Makes Retinal Imaging 100 Times Faster
- Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
- Sleep, Circadian Rhythms and Metabolism
- Evolving Attitudes of Gen X Toward Evolution
Living Well
- Obese and Overweight Children: Iron Deficiency
- How to Prevent Toxic Answers from AI Chatbots
- AI-Assisted Breast-Cancer Screening
- Helping People Improve Self-Control
Physical/Tech News
Latest physical/tech headlines.
- Spintronics Research
- Spintronics
- Quantum Computers
- Organic Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Wearable Technology
- Extrasolar Planets
- Astrophysics
- Asteroids, Comets and Meteors
- Dark Matter
- Global Warming
- Telecommunications
- Computers and Internet
- Human Biology
Matter & Energy
- When Light Makes Materials Magnetic
- Qubits: Evading Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
- Assessing the Applicability of Reactions
- Waterproof 'E-Glove' Helps Scuba Divers Talk
Space & Time
- Assessing Liveability of Other Planets
- Neutron Stars and Elusive Dark Matter
- Inexplicable Flying Fox in Hydra Galaxy Cluster
- Climate Change Threatens Antarctic Meteorites
Computers & Math
- Curving Light for Better Wireless Communication
- Resistance-Free Electron Channels
- Understanding Neurons: Spike-Sorting Software
- Can Language Models Read the Genome?
Environment News
Latest environment headlines.
- Rainforests
- Environmental Awareness
- Biochemistry Research
- Biotechnology
- Developmental Biology
- Endangered Plants
- Ecology Research
- Agriculture and Food
- Marine Biology
- Air Quality
- Air Pollution
- Environmental Issues
- Sustainability
- Energy and the Environment
- Renewable Energy
- Solar Energy
- Ancient Civilizations
- Archaeology
- Anthropology
- Early Birds
- Bird Flu Research
- Biodiversity
- Geomagnetic Storms
Plants & Animals
- Climate: Forest Adaptation Strategies
- Cellular DNA Repair Mechanism
- Amazon's Orchid Bees and Deforestation
- Algae Shifts With Climate
Earth & Climate
- Novel Spectrometer for Air Pollutant Analysis
- Microplastic 'Hotspots' in Open Waters
- Microbial Plastic Factory for Quality Plastic
- More Efficient Organic Solar Cells
Fossils & Ruins
- Early Medieval Money Mystery Solved
- Birdfeeders Are for the Birds
- Humans Can Increase Biodiversity
- Tracing the Largest Solar Storm in Modern Times
Society/Education News
Latest society/education headlines.
- Health Policy
- Infant's Health
- Disaster Plan
- Social Issues
- Natural Disasters
- Environmental Policies
- Child Development
- Infant and Preschool Learning
- Language Acquisition
- Child Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Relationships
- Energy Issues
- Educational Psychology
Science & Society
- Parental Leave Policy and Premature Babies
- Social Media Use During Disasters
- Atmospheric, Economic Drivers of Air Pollution
- Are Lab-Grown Brain Tissues Ethical?
Education & Learning
- Talk to Your Baby: It Matters
- Exercise Habits in Youth, Good Health Later
- Universities Connected to Local Sustainability?
- Early Detection of Language Disorders Key
Business & Industry
- Active Workstations and Cognitive Performance
- Suppressing Boredom at Work Hurts Productivity
- Pairing Crypto Mining With Green Hydrogen
- Feeling Apathetic? There May Be Hope
- Device: Self-Healing Materials, Drug Delivery
- Feeling Insulted? How to Rid Yourself of Anger
- Pregnancy Accelerates Biological Aging
- What's Quieter Than a Fish? A School of Them
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat, about this site.
ScienceDaily features breaking news about the latest discoveries in science, health, the environment, technology, and more -- from leading universities, scientific journals, and research organizations.
Visitors can browse more than 500 individual topics, grouped into 12 main sections (listed under the top navigational menu), covering: the medical sciences and health; physical sciences and technology; biological sciences and the environment; and social sciences, business and education. Headlines and summaries of relevant news stories are provided on each topic page.
Stories are posted daily, selected from press materials provided by hundreds of sources from around the world. Links to sources and relevant journal citations (where available) are included at the end of each post.
For more information about ScienceDaily, please consult the links listed at the bottom of each page.

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

- 26 Mar 2024
- Research & Ideas
How Humans Outshine AI in Adapting to Change
Could artificial intelligence systems eventually perform surgeries or fly planes? First, AI will have to learn to navigate shifting conditions as well as people do. Julian De Freitas and colleagues pit humans against machines in a video game to study AI's current limits and mine insights for the real world.

- 12 Mar 2024
Publish or Perish: What the Research Says About Productivity in Academia
Universities tend to evaluate professors based on their research output, but does that measure reflect the realities of higher ed? A study of 4,300 professors by Kyle Myers, Karim Lakhani, and colleagues probes the time demands, risk appetite, and compensation of faculty.

- 24 Jan 2024
Why Boeing’s Problems with the 737 MAX Began More Than 25 Years Ago
Aggressive cost cutting and rocky leadership changes have eroded the culture at Boeing, a company once admired for its engineering rigor, says Bill George. What will it take to repair the reputational damage wrought by years of crises involving its 737 MAX?

- 19 Sep 2023
What Chandrayaan-3 Says About India's Entrepreneurial Approach to Space
India reached an unexplored part of the moon despite its limited R&D funding compared with NASA and SpaceX. Tarun Khanna discusses the significance of the landing, and the country's advancements in data and digital technology.

- 28 Mar 2023
The FDA’s Speedy Drug Approvals Are Safe: A Win-Win for Patients and Pharma Innovation
Expediting so-called breakthrough therapies has saved millions of dollars in research time without compromising drug safety or efficacy, says research by Ariel Stern, Amitabh Chandra, and colleagues. Could policymakers harness the approach to bring life-saving treatments to the market faster?

- 16 Mar 2023
Why Business Travel Still Matters in a Zoom World
Meeting in person can make all the difference for colleagues from different time zones or cultural backgrounds. A study by Prithwiraj Choudhury traces flight patterns among 5,000 airports around the world to show how business travel propels innovation.

- 13 Apr 2021
- Working Paper Summaries
Population Interference in Panel Experiments
In panel experiments, units are exposed to different interventions over time. This article introduces a unifying framework for studying panel experiments with population interference, in which a treatment assigned to one experimental unit affects another experimental unit's outcome. Findings have implications for fields as diverse as education, economics, and public health.
- 22 Feb 2021
Private and Social Returns to R&D: Drug Development and Demographics
Research and development (R&D) by pharmaceutical firms focuses disproportionately on medical conditions afflicting the elderly. The proportion of R&D spending targeting older age groups is increasing over time. Even though these investments in R&D prolong life expectancy and improve quality of life, they have little effect on measured productivity and output growth.
- 15 Dec 2020
Designing, Not Checking, for Policy Robustness: An Example with Optimal Taxation
The approach used by most economists to check academic research results is flawed for policymaking and evaluation. The authors propose an alternative method for designing economic policy analyses that might be applied to a wide range of economic policies.
- 30 Nov 2020
Short-Termism, Shareholder Payouts, and Investment in the EU
Shareholder-driven “short-termism,” as evidenced by increasing payouts to shareholders, is said to impede long-term investment in EU public firms. But a deep dive into the data reveals a different story.
- 22 Oct 2020
Estimating Causal Effects in the Presence of Partial Interference Using Multivariate Bayesian Structural Time Series Models
A case study of an Italian supermarket introducing a new pricing policy—in which it reduced prices on some brands—offers managers a new approach to reduce uncertainty. The approach is flexible and can be applied to different business problems.
- 06 Oct 2020
Design and Analysis of Switchback Experiments
This paper presents a framework for managers to design and run switchback experiments.
- 28 Sep 2020
What Can Economics Say About Alzheimer's Disease?
This essay discusses the role of market frictions and "missing medicines" in drug innovation and highlights how frameworks and toolkits of economists can help our understanding of the determinants and effects of Alzheimer's disease on health.
- 24 Aug 2020
When Do Experts Listen to Other Experts? The Role of Negative Information in Expert Evaluations for Novel Projects
Evaluators of early-stage scientific proposals tend to systematically focus on the weaknesses of proposed work rather than its strengths, according to evidence from two field experiments.

- 10 Aug 2020
COVID's Surprising Toll on Careers of Women Scientists
Women scientists and those with young children are paying a steep career price in the pandemic, according to new research by Karim Lakhani, Kyle Myers, and colleagues. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 02 Aug 2020
- What Do You Think?
Is the 'Experimentation Organization' Becoming the Competitive Gold Standard?
SUMMING UP: Digital experimentation is gaining momentum as an everyday habit in many organizations, especially those in high tech, say James Heskett's readers. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 27 Jul 2020
Gender Inequality in Research Productivity During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Analysis of data from the largest open-access repositories for social science in the world finds that female researchers’ productivity significantly dropped relative to that of male researchers as a result of the lockdown in the United States.
- 08 Jul 2020
Inventing the Endless Frontier: The Effects of the World War II Research Effort on Post-War Innovation
Investments made in World War II by the United States Office of Scientific Research and Development powered decades of subsequent innovation and the take-off of regional technology hubs around the country.
- 06 Apr 2020
A General Theory of Identification
Statistical inference teaches us how to learn from data, whereas identification analysis explains what we can learn from it. This paper proposes a simple unifying theory of identification, encouraging practitioners to spend more time thinking about what they can estimate from the data and assumptions before trying to estimate it.
- 23 Mar 2020
The Effects of Hierarchy on Learning and Performance in Business Experimentation
Do senior managers help or hurt business experiments? Analyzing a dataset of more than 6,300 experiments on the A/B/n testing platform Optimizely, this study suggests that involving senior executives in experimentation teams can have surprising consequences.
Advertisement
Supported by

She Dreams of Pink Planets and Alien Dinosaurs
Lisa Kaltenegger, director of the Carl Sagan Institute at Cornell University, hunts for aliens in space by studying Earth across time.
By Becky Ferreira

Los anteojos mejoran los ingresos, no solo la vista
Un estudio reveló que cuando un grupo de trabajadores hipermétropes en Bangladés recibían lentes de lectura gratuitos, ganaban un 33 por ciento más que los que no contaban con ellos.
By Andrew Jacobs

Youth Gender Medications Limited in England, Part of Big Shift in Europe
Five European countries have recently restricted hormone treatments for adolescents with gender distress. They have not banned the care, unlike many U.S. states.
By Azeen Ghorayshi

Seriously, Now Is the Time to Stop Kissing Sick Birds
A citizen-science collaboration in New York has turned up a half-dozen birds infected with the avian flu virus.
By Apoorva Mandavilli

New Method That Pinpoints Wood’s Origin May Curb Illegal Timber
The study could help identify wood from Russia, which has been banned by many countries because of the war.
By Alexander Nazaryan

PFAS ‘Forever Chemicals’ Are Pervasive in Water Worldwide, Study Finds
A global survey found harmful levels even in water samples taken far any obvious source of contamination.
By Delger Erdenesanaa

They Came From Outer Space. Now, They’re Going Into Hiding.
Rising temperatures in Antarctica are making meteorites sink out of view before researchers can collect them.
By Katherine Kornei

Large Scientific Review Confirms the Benefits of Physical Touch
Premature babies especially benefited from skin-to-skin contact, and women tended to respond more strongly than men did.
By Joanne Silberner

See the Total Solar Eclipse’s Shadow From Space
An American weather satellite is capturing the movement of the moon’s shadow across North America during the total eclipse of the sun on Monday.
By K.K. Rebecca Lai and William B. Davis

Paying Off People’s Medical Debt Has Little Impact on Their Lives, Study Finds
A nonprofit group called R.I.P. Medical Debt has relieved Americans of $11 billion in hospital bills. But that did not improve their mental health or their credit scores, a study found.
By Sarah Kliff
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Med Libr Assoc
- v.106(4); 2018 Oct
A systematic approach to searching: an efficient and complete method to develop literature searches
Associated data.
Creating search strategies for systematic reviews, finding the best balance between sensitivity and specificity, and translating search strategies between databases is challenging. Several methods describe standards for systematic search strategies, but a consistent approach for creating an exhaustive search strategy has not yet been fully described in enough detail to be fully replicable. The authors have established a method that describes step by step the process of developing a systematic search strategy as needed in the systematic review. This method describes how single-line search strategies can be prepared in a text document by typing search syntax (such as field codes, parentheses, and Boolean operators) before copying and pasting search terms (keywords and free-text synonyms) that are found in the thesaurus. To help ensure term completeness, we developed a novel optimization technique that is mainly based on comparing the results retrieved by thesaurus terms with those retrieved by the free-text search words to identify potentially relevant candidate search terms. Macros in Microsoft Word have been developed to convert syntaxes between databases and interfaces almost automatically. This method helps information specialists in developing librarian-mediated searches for systematic reviews as well as medical and health care practitioners who are searching for evidence to answer clinical questions. The described method can be used to create complex and comprehensive search strategies for different databases and interfaces, such as those that are needed when searching for relevant references for systematic reviews, and will assist both information specialists and practitioners when they are searching the biomedical literature.
INTRODUCTION
Librarians and information specialists are often involved in the process of preparing and completing systematic reviews (SRs), where one of their main tasks is to identify relevant references to include in the review [ 1 ]. Although several recommendations for the process of searching have been published [ 2 – 6 ], none describe the development of a systematic search strategy from start to finish.
Traditional methods of SR search strategy development and execution are highly time consuming, reportedly requiring up to 100 hours or more [ 7 , 8 ]. The authors wanted to develop systematic and exhaustive search strategies more efficiently, while preserving the high sensitivity that SR search strategies necessitate. In this article, we describe the method developed at Erasmus University Medical Center (MC) and demonstrate its use through an example search. The efficiency of the search method and outcome of 73 searches that have resulted in published reviews are described in a separate article [ 9 ].
As we aimed to describe the creation of systematic searches in full detail, the method starts at a basic level with the analysis of the research question and the creation of search terms. Readers who are new to SR searching are advised to follow all steps described. More experienced searchers can consider the basic steps to be existing knowledge that will already be part of their normal workflow, although step 4 probably differs from general practice. Experienced searchers will gain the most from reading about the novelties in the method as described in steps 10–13 and comparing the examples given in the supplementary appendix to their own practice.
CREATING A SYSTEMATIC SEARCH STRATEGY
Our methodology for planning and creating a multi-database search strategy consists of the following steps:
- Determine a clear and focused question
- Describe the articles that can answer the question
- Decide which key concepts address the different elements of the question
- Decide which elements should be used for the best results
- Choose an appropriate database and interface to start with
- Document the search process in a text document
- Identify appropriate index terms in the thesaurus of the first database
- Identify synonyms in the thesaurus
- Add variations in search terms
- Use database-appropriate syntax, with parentheses, Boolean operators, and field codes
- Optimize the search
- Evaluate the initial results
- Check for errors
- Translate to other databases
- Test and reiterate
Each step in the process is reflected by an example search described in the supplementary appendix .
1. Determine a clear and focused question
A systematic search can best be applied to a well-defined and precise research or clinical question. Questions that are too broad or too vague cannot be answered easily in a systematic way and will generally result in an overwhelming number of search results. On the other hand, a question that is too specific will result into too few or even zero search results. Various papers describe this process in more detail [ 10 – 12 ].
2. Describe the articles that can answer the question
Although not all clinical or research questions can be answered in the literature, the next step is to presume that the answer can indeed be found in published studies. A good starting point for a search is hypothesizing what the research that can answer the question would look like. These hypothetical (when possible, combined with known) articles can be used as guidance for constructing the search strategy.
3. Decide which key concepts address the different elements of the question
Key concepts are the topics or components that the desired articles should address, such as diseases or conditions, actions, substances, settings, domains (e.g., therapy, diagnosis, etiology), or study types. Key concepts from the research question can be grouped to create elements in the search strategy.
Elements in a search strategy do not necessarily follow the patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) structure or any other related structure. Using the PICO or another similar framework as guidance can be helpful to consider, especially in the inclusion and exclusion review stage of the SR, but this is not necessary for good search strategy development [ 13 – 15 ]. Sometimes concepts from different parts of the PICO structure can be grouped together into one search element, such as when the desired outcome is frequently described in a certain study type.
4. Decide which elements should be used for the best results
Not all elements of a research question should necessarily be used in the search strategy. Some elements are less important than others or may unnecessarily complicate or restrict a search strategy. Adding an element to a search strategy increases the chance of missing relevant references. Therefore, the number of elements in a search strategy should remain as low as possible to optimize recall.
Using the schema in Figure 1 , elements can be ordered by their specificity and importance to determine the best search approach. Whether an element is more specific or more general can be measured objectively by the number of hits retrieved in a database when searching for a key term representing that element. Depending on the research question, certain elements are more important than others. If articles (hypothetically or known) exist that can answer the question but lack a certain element in their titles, abstracts, or keywords, that element is unimportant to the question. An element can also be unimportant because of expected bias or an overlap with another element.

Schema for determining the optimal order of elements
Bias in elements
The choice of elements in a search strategy can introduce bias through use of overly specific terminology or terms often associated with positive outcomes. For the question “does prolonged breastfeeding improve intelligence outcomes in children?,” searching specifically for the element of duration will introduce bias, as articles that find a positive effect of prolonged breastfeeding will be much more likely to mention time factors in their titles or abstracts.
Overlapping elements
Elements in a question sometimes overlap in their meaning. Sometimes certain therapies are interventions for one specific disease. The Lichtenstein technique, for example, is a repair method for inguinal hernias. There is no need to include an element of “inguinal hernias” to a search for the effectiveness of the Lichtenstein therapy. Likewise, sometimes certain diseases are only found in certain populations. Adding such an overlapping element could lead to missing relevant references.
The elements to use in a search strategy can be found in the plot of elements in Figure 1 , by following the top row from left to right. For this method, we recommend starting with the most important and specific elements. Then, continue with more general and important elements until the number of results is acceptable for screening. Determining how many results are acceptable for screening is often a matter of negotiation with the SR team.
5. Choose an appropriate database and interface to start with
Important factors for choosing databases to use are the coverage and the presence of a thesaurus. For medically oriented searches, the coverage and recall of Embase, which includes the MEDLINE database, are superior to those of MEDLINE [ 16 ]. Each of these two databases has its own thesaurus with its own unique definitions and structure. Because of the complexity of the Embase thesaurus, Emtree, which contains much more specific thesaurus terms than the MEDLINE Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) thesaurus, translation from Emtree to MeSH is easier than the other way around. Therefore, we recommend starting in Embase.
MEDLINE and Embase are available through many different vendors and interfaces. The choice of an interface and primary database is often determined by the searcher’s accessibility. For our method, an interface that allows searching with proximity operators is desirable, and full functionality of the thesaurus, including explosion of narrower terms, is crucial. We recommend developing a personal workflow that always starts with one specific database and interface.
6. Document the search process in a text document
We advise designing and creating the complete search strategies in a log document, instead of directly in the database itself, to register the steps taken and to make searches accountable and reproducible. The developed search strategies can be copied and pasted into the desired databases from the log document. This way, the searcher is in control of the whole process. Any change to the search strategy should be done in the log document, assuring that the search strategy in the log is always the most recent.
7. Identify appropriate index terms in the thesaurus of the first database
Searches should start by identifying appropriate thesaurus terms for the desired elements. The thesaurus of the database is searched for matching index terms for each key concept. We advise restricting the initial terms to the most important and most relevant terms. Later in the process, more general terms can be added in the optimization process, in which the effect on the number of hits, and thus the desirability of adding these terms, can be evaluated more easily.
Several factors can complicate the identification of thesaurus terms. Sometimes, one thesaurus term is found that exactly describes a specific element. In contrast, especially in more general elements, multiple thesaurus terms can be found to describe one element. If no relevant thesaurus terms have been found for an element, free-text terms can be used, and possible thesaurus terms found in the resulting references can be added later (step 11).
Sometimes, no distinct thesaurus term is available for a specific key concept that describes the concept in enough detail. In Emtree, one thesaurus term often combines two or more elements. The easiest solution for combining these terms for a sensitive search is to use such a thesaurus term in all elements where it is relevant. Examples are given in the supplementary appendix .
8. Identify synonyms in the thesaurus
Most thesauri offer a list of synonyms on their term details page (named Synonyms in Emtree and Entry Terms in MeSH). To create a sensitive search strategy for SRs, these terms need to be searched as free-text keywords in the title and abstract fields, in addition to searching their associated thesaurus terms.
The Emtree thesaurus contains more synonyms (300,000) than MeSH does (220,000) [ 17 ]. The difference in number of terms is even higher considering that many synonyms in MeSH are permuted terms (i.e., inversions of phrases using commas).
Thesaurus terms are ordered in a tree structure. When searching for a more general thesaurus term, the more specific (narrower) terms in the branches below that term will also be searched (this is frequently referred to as “exploding” a thesaurus term). However, to perform a sensitive search, all relevant variations of the narrower terms must be searched as free-text keywords in the title or abstract, in addition to relying on the exploded thesaurus term. Thus, all articles that describe a certain narrower topic in their titles and abstracts will already be retrieved before MeSH terms are added.
9. Add variations in search terms (e.g., truncation, spelling differences, abbreviations, opposites)
Truncation allows a searcher to search for words beginning with the same word stem. A search for therap* will, thus, retrieve therapy, therapies, therapeutic, and all other words starting with “therap.” Do not truncate a word stem that is too short. Also, limitations of interfaces should be taken into account, especially in PubMed, where the number of search term variations that can be found by truncation is limited to 600.
Databases contain references to articles using both standard British and American English spellings. Both need to be searched as free-text terms in the title and abstract. Alternatively, many interfaces offer a certain code to replace zero or one characters, allowing a search for “pediatric” or “paediatric” as “p?ediatric.” Table 1 provides a detailed description of the syntax for different interfaces.
Field codes in five most used interfaces for biomedical literature searching
Searching for abbreviations can identify extra, relevant references and retrieve more irrelevant ones. The search can be more focused by combining the abbreviation with an important word that is relevant to its meaning or by using the Boolean “NOT” to exclude frequently observed, clearly irrelevant results. We advise that searchers do not exclude all possible irrelevant meanings, as it is very time consuming to identify all the variations, it will result in unnecessarily complicated search strategies, and it may lead to erroneously narrowing the search and, thereby, reduce recall.
Searching partial abbreviations can be useful for retrieving relevant references. For example, it is very likely that an article would mention osteoarthritis (OA) early in the abstract, replacing all further occurrences of osteoarthritis with OA . Therefore, it may not contain the phrase “hip osteoarthritis” but only “hip oa.”
It is also important to search for the opposites of search terms to avoid bias. When searching for “disease recurrence,” articles about “disease free” may be relevant as well. When the desired outcome is survival , articles about mortality may be relevant.

10. Use database-appropriate syntax, with parentheses, Boolean operators, and field codes
Different interfaces require different syntaxes, the special set of rules and symbols unique to each database that define how a correctly constructed search operates. Common syntax components include the use of parentheses and Boolean operators such as “AND,” “OR,” and “NOT,” which are available in all major interfaces. An overview of different syntaxes for four major interfaces for bibliographic medical databases (PubMed, Ovid, EBSCOhost, Embase.com, and ProQuest) is shown in Table 1 .
Creating the appropriate syntax for each database, in combination with the selected terms as described in steps 7–9, can be challenging. Following the method outlined below simplifies the process:
- Create single-line queries in a text document (not combining multiple record sets), which allows immediate checking of the relevance of retrieved references and efficient optimization.
- Type the syntax (Boolean operators, parentheses, and field codes) before adding terms, which reduces the chance that errors are made in the syntax, especially in the number of parentheses.
- Use predefined proximity structures including parentheses, such as (() ADJ3 ()) in Ovid, that can be reused in the query when necessary.
- Use thesaurus terms separately from free-text terms of each element. Start an element with all thesaurus terms (using “OR”) and follow with the free-text terms. This allows the unique optimization methods as described in step 11.
- When adding terms to an existing search strategy, pay close attention to the position of the cursor. Make sure to place it appropriately either in the thesaurus terms section, in the title/abstract section, or as an addition (broadening) to an existing proximity search.
The supplementary appendix explains the method of building a query in more detail, step by step for different interfaces: PubMed, Ovid, EBSCOhost, Embase.com, and ProQuest. This method results in a basic search strategy designed to retrieve some relevant references upon which a more thorough search strategy can be built with optimization such as described in step 11.
11. Optimize the search
The most important question when performing a systematic search is whether all (or most) potentially relevant articles have been retrieved by the search strategy. This is also the most difficult question to answer, since it is unknown which and how many articles are relevant. It is, therefore, wise first to broaden the initial search strategy, making the search more sensitive, and then check if new relevant articles are found by comparing the set results (i.e., search for Strategy #2 NOT Strategy #1 to see the unique results).
A search strategy should be tested for completeness. Therefore, it is necessary to identify extra, possibly relevant search terms and add them to the test search in an OR relationship with the already used search terms. A good place to start, and a well-known strategy, is scanning the top retrieved articles when sorted by relevance, looking for additional relevant synonyms that could be added to the search strategy.
We have developed a unique optimization method that has not been described before in the literature. This method often adds valuable extra terms to our search strategy and, therefore, extra, relevant references to our search results. Extra synonyms can be found in articles that have been assigned a certain set of thesaurus terms but that lack synonyms in the title and/or abstract that are already present in the current search strategy. Searching for thesaurus terms NOT free-text terms will help identify missed free-text terms in the title or abstract. Searching for free-text terms NOT thesaurus terms will help identify missed thesaurus terms. If this is done repeatedly for each element, leaving the rest of the query unchanged, this method will help add numerous relevant terms to the query. These steps are explained in detail for five different search platforms in the supplementary appendix .
12. Evaluate the initial results
The results should now contain relevant references. If the interface allows relevance ranking, use that in the evaluation. If you know some relevant references that should be included in the research, search for those references specifically; for example, combine a specific (first) author name with a page number and the publication year. Check whether those references are retrieved by the search. If the known relevant references are not retrieved by the search, adapt the search so that they are. If it is unclear which element should be adapted to retrieve a certain article, combine that article with each element separately.
Different outcomes are desired for different types of research questions. For instance, in the case of clinical question answering, the researcher will not be satisfied with many references that contain a lot of irrelevant references. A clinical search should be rather specific and is allowed to miss a relevant reference. In the case of an SR, the researchers do not want to miss any relevant reference and are willing to handle many irrelevant references to do so. The search for references to include in an SR should be very sensitive: no included reference should be missed. A search that is too specific or too sensitive for the intended goal can be adapted to become more sensitive or specific. Steps to increase sensitivity or specificity of a search strategy can be found in the supplementary appendix .
13. Check for errors
Errors might not be easily detected. Sometimes clues can be found in the number of results, either when the number of results is much higher or lower than expected or when many retrieved references are not relevant. However, the number expected is often unknown, and very sensitive search strategies will always retrieve many irrelevant articles. Each query should, therefore, be checked for errors.
One of the most frequently occurring errors is missing the Boolean operator “OR.” When no “OR” is added between two search terms, many interfaces automatically add an “AND,” which unintentionally reduces the number of results and likely misses relevant references. One good strategy to identify missing “OR”s is to go to the web page containing the full search strategy, as translated by the database, and using Ctrl-F search for “AND.” Check whether the occurrences of the “AND” operator are deliberate.
Ideally, search strategies should be checked by other information specialists [ 18 ]. The Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies (PRESS) checklist offers good guidance for this process [ 4 ]. Apart from the syntax (especially Boolean operators and field codes) of the search strategy, it is wise to have the search terms checked by the clinician or researcher familiar with the topic. At Erasmus MC, researchers and clinicians are involved during the complete process of structuring and optimizing the search strategy. Each word is added after the combined decision of the searcher and the researcher, with the possibility of directly comparing results with and without the new term.
14. Translate to other databases
To retrieve as many relevant references as possible, one has to search multiple databases. Translation of complex and exhaustive queries between different databases can be very time consuming and cumbersome. The single-line search strategy approach detailed above allows quick translations using the find and replace method in Microsoft Word (<Ctrl-H>).
At Erasmus MC, macros based on the find-and-replace method in Microsoft Word have been developed for easy and fast translation between the most used databases for biomedical and health sciences questions. The schema that is followed for the translation between databases is shown in Figure 2 . Most databases simply follow the structure set by the Embase.com search strategy. The translation from Emtree terms to MeSH terms for MEDLINE in Ovid often identifies new terms that need to be added to the Embase.com search strategy before the translation to other databases.

Schematic representation of translation between databases used at Erasmus University Medical Center
Dotted lines represent databases that are used in less than 80% of the searches.
Using five different macros, a thoroughly optimized query in Embase.com can be relatively quickly translated into eight major databases. Basic search strategies will be created to use in many, mostly smaller, databases, because such niche databases often do not have extensive thesauri or advanced syntax options. Also, there is not much need to use extensive syntax because the number of hits and, therefore, the amount of noise in these databases is generally low. In MEDLINE (Ovid), PsycINFO (Ovid), and CINAHL (EBSCOhost), the thesaurus terms must be adapted manually, as each database has its own custom thesaurus. These macros and instructions for their installation, use, and adaptation are available at bit.ly/databasemacros.
15. Test and reiterate
Ideally, exhaustive search strategies should retrieve all references that are covered in a specific database. For SR search strategies, checking searches for their recall is advised. This can be done after included references have been determined by the authors of the systematic review. If additional papers have been identified through other non-database methods (i.e., checking references in included studies), results that were not identified by the database searches should be examined. If these results were available in the databases but not located by the search strategy, the search strategy should be adapted to try to retrieve these results, as they may contain terms that were omitted in the original search strategies. This may enable the identification of additional relevant results.
A methodology for creating exhaustive search strategies has been created that describes all steps of the search process, starting with a question and resulting in thorough search strategies in multiple databases. Many of the steps described are not new, but together, they form a strong method creating high-quality, robust searches in a relatively short time frame.
Our methodology is intended to create thoroughness for literature searches. The optimization method, as described in step 11, will identify missed synonyms or thesaurus terms, unlike any other method that largely depends on predetermined keywords and synonyms. Using this method results in a much quicker search process, compared to traditional methods, especially because of the easier translation between databases and interfaces (step 13). The method is not a guarantee for speed, since speed depends on many factors, including experience. However, by following the steps and using the tools as described above, searchers can gain confidence first and increase speed through practice.
What is new?
This method encourages searchers to start their search development process using empty syntax first and later adding the thesaurus terms and free-text synonyms. We feel this helps the searcher to focus on the search terms, instead of on the structure of the search query. The optimization method in which new terms are found in the already retrieved articles is used in some other institutes as well but has to our knowledge not been described in the literature. The macros to translate search strategies between interfaces are unique in this method.
What is different compared to common practice?
Traditionally, librarians and information specialists have focused on creating complex, multi-line (also called line-by-line) search strategies, consisting of multiple record sets, and this method is frequently advised in the literature and handbooks [ 2 , 19 – 21 ]. Our method, instead, uses single-line searches, which is critical to its success. Single-line search strategies can be easily adapted by adding or dropping a term without having to recode numbers of record sets, which would be necessary in multi-line searches. They can easily be saved in a text document and repeated by copying and pasting for search updates. Single-line search strategies also allow easy translation to other syntaxes using find-and-replace technology to update field codes and other syntax elements or using macros (step 13).
When constructing a search strategy, the searcher might experience that certain parentheses in the syntax are unnecessary, such as parentheses around all search terms in the title/abstract portion, if there is only one such term, there are double parentheses in the proximity statement, or one of the word groups exists for only one word. One might be tempted to omit those parentheses for ease of reading and management. However, during the optimization process, the searcher is likely to find extra synonyms that might consist of one word. To add those terms to the first query (with reduced parentheses) requires adding extra parentheses (meticulously placing and counting them), whereas, in the latter search, it only requires proper placement of those terms.
Many search methods highly depend on the PICO framework. Research states that often PICO or PICOS is not suitable for every question [ 22 , 23 ]. There are other acronyms than PICO—such as sample, phenomenon of interest, design, evaluation, research type (SPIDER) [ 24 ]—but each is just a variant. In our method, the most important and specific elements of a question are being analyzed for building the best search strategy.
Though it is generally recommended that searchers search both MEDLINE and Embase, most use MEDLINE as the starting point. It is considered the gold standard for biomedical searching, partially due to historical reasons, since it was the first of its kind, and more so now that it is freely available via the PubMed interface. Our method can be used with any database as a starting point, but we use Embase instead of MEDLINE or another database for a number of reasons. First, Embase provides both unique content and the complete content of MEDLINE. Therefore, searching Embase will be, by definition, more complete than searching MEDLINE only. Second, the number of terms in Emtree (the Embase thesaurus) is three times as high as that of MeSH (the MEDLINE thesaurus). It is easier to find MeSH terms after all relevant Emtree terms have been identified than to start with MeSH and translate to Emtree.
At Erasmus MC, the researchers sit next to the information specialist during most of the search strategy design process. This way, the researchers can deliver immediate feedback on the relevance of proposed search terms and retrieved references. The search team then combines knowledge about databases with knowledge about the research topic, which is an important condition to create the highest quality searches.
Limitations of the method
One disadvantage of single-line searches compared to multi-line search strategies is that errors are harder to recognize. However, with the methods for optimization as described (step 11), errors are recognized easily because missed synonyms and spelling errors will be identified during the process. Also problematic is that more parentheses are needed, making it more difficult for the searcher and others to assess the logic of the search strategy. However, as parentheses and field codes are typed before the search terms are added (step 10), errors in parentheses can be prevented.
Our methodology works best if used in an interface that allows proximity searching. It is recommended that searchers with access to an interface with proximity searching capabilities select one of those as the initial database to develop and optimize the search strategy. Because the PubMed interface does not allow proximity searches, phrases or Boolean “AND” combinations are required. Phrase searching complicates the process and is more specific, with the higher risk of missing relevant articles, and using Boolean “AND” combinations increases sensitivity but at an often high loss of specificity. Due to some searchers’ lack of access to expensive databases or interfaces, the freely available PubMed interface may be necessary to use, though it should never be the sole database used for an SR [ 2 , 16 , 25 ]. A limitation of our method is that it works best with subscription-based and licensed resources.
Another limitation is the customization of the macros to a specific institution’s resources. The macros for the translation between different database interfaces only work between the interfaces as described. To mitigate this, we recommend using the find-and-replace functionality of text editors like Microsoft Word to ease the translation of syntaxes between other databases. Depending on one’s institutional resources, custom macros can be developed using similar methods.
Results of the method
Whether this method results in exhaustive searches where no important article is missed is difficult to determine, because the number of relevant articles is unknown for any topic. A comparison of several parameters of 73 published reviews that were based on a search developed with this method to 258 reviews that acknowledged information specialists from other Dutch academic hospitals shows that the performance of the searches following our method is comparable to those performed in other institutes but that the time needed to develop the search strategies was much shorter than the time reported for the other reviews [ 9 ].
CONCLUSIONS
With the described method, searchers can gain confidence in their search strategies by finding many relevant words and creating exhaustive search strategies quickly. The approach can be used when performing SR searches or for other purposes such as answering clinical questions, with different expectations of the search’s precision and recall. This method, with practice, provides a stepwise approach that facilitates the search strategy development process from question clarification to final iteration and beyond.
SUPPLEMENTAL FILE
Acknowledgments.
We highly appreciate the work that was done by our former colleague Louis Volkers, who in his twenty years as an information specialist in Erasmus MC laid the basis for our method. We thank Professor Oscar Franco for reviewing earlier drafts of this article.
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
5. party identification among religious groups and religiously unaffiliated voters.
The relationship between partisanship and voters’ religious affiliation continues to be strong – especially when it comes to whether they belong to any organized religion at all.
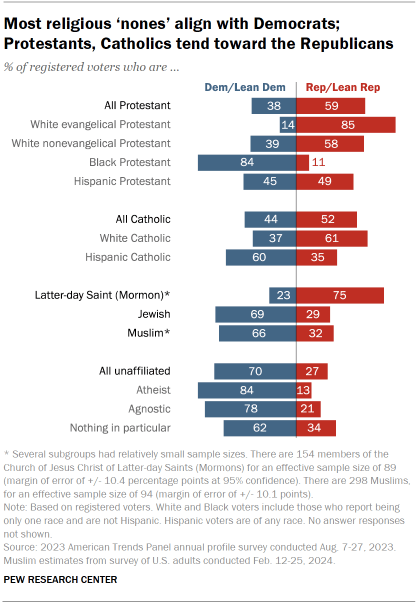
The gap between voters who identify with an organized religion and those who do not has grown much wider in recent years.
Protestants mostly align with the Republican Party. Protestants remain the largest single religious group in the United States. As they have for most of the past 15 years, a majority of Protestant registered voters (59%) associate with the GOP, though as recently as 2009 they were split nearly equally between the two parties.
Partisan identity among Catholics had been closely divided, but the GOP now has a modest advantage among Catholics. About half of Catholic voters identify as Republicans or lean toward the Republican Party, compared with 44% who identify as Democrats or lean Democratic.
Members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints remain overwhelmingly Republican. Three-quarters of voters in this group, widely known as Mormons, identify as Republicans or lean Republican. Only about a quarter (23%) associate with the Democratic Party.
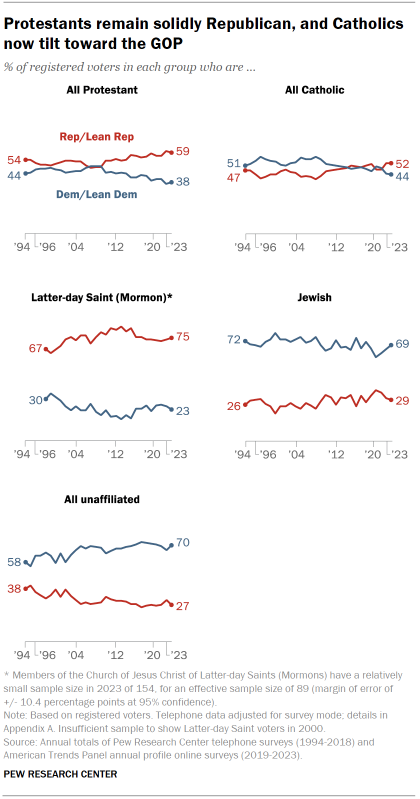
Jewish voters continue to mostly align with the Democrats. About seven-in-ten Jewish voters (69%) associate with the Democratic Party, while 29% affiliate with the Republican Party. The share of Jewish voters who align with the Democrats has increased 8 percentage points since 2020.
Muslims associate with Democrats over Republicans by a wide margin. Currently, 66% of Muslim voters say they are Democrats or independents who lean Democratic, compared with 32% who are Republicans or lean Republican. (Data for Muslim voters is not available for earlier years because of small sample sizes.)
Democrats maintain a wide advantage among religiously unaffiliated voters. Religious “nones” have become more Democratic over the past few decades as their size in the U.S. population overall and in the electorate has grown significantly. While 70% of religiously unaffiliated voters align with the Democratic Party, just 27% identify as Republicans or lean Republican.
Related: Religious “nones” in America: Who they are and what they believe
Religion, race and ethnicity, and partisanship
Over the past few decades, White evangelical Protestant voters have moved increasingly toward the GOP.
- Today, 85% of White evangelical voters identify with or lean toward the GOP; just 14% align with the Democrats.
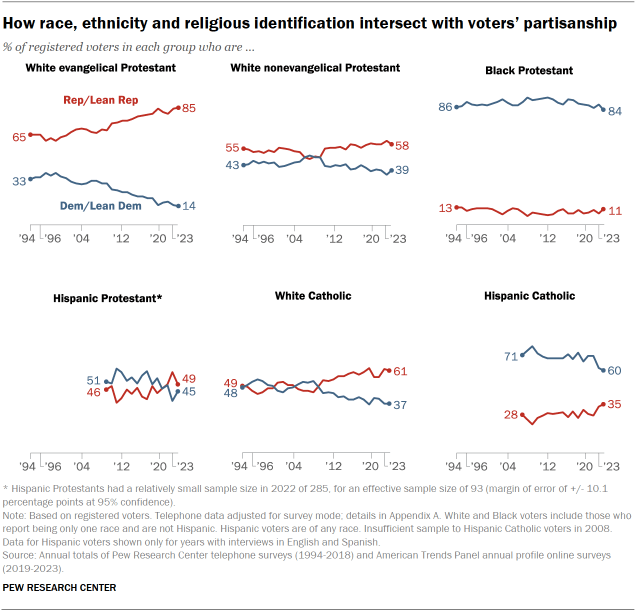
- Over the past three decades, there has been a 20 percentage point rise in the share of White evangelicals who associate with the GOP – and a 20-point decline in the share identifying as or leaning Democratic.
Over the past 15 years, the GOP also has made gains among White nonevangelical and White Catholic voters.
About six-in-ten White nonevangelicals (58%) and White Catholics (61%) align with the GOP. Voters in both groups were equally divided between the two parties in 2009.
Partisanship among Hispanic voters varies widely among Catholics and Protestants.
- 60% of Hispanic Catholic voters identify as Democrats or lean Democratic, but that share has declined over the past 15 years.
- Hispanic Protestant voters are evenly divided: 49% associate with the Republican Party, while 45% identify as Democrats or lean Democratic.
A large majority of Black Protestants identify with the Democrats (84%), but that share is down 9 points from where it was 15 years ago (93%).
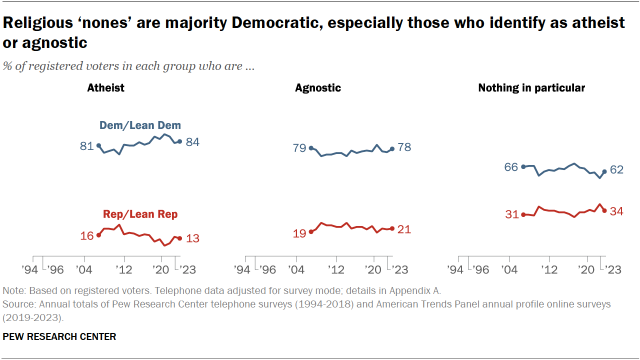
Party identification among atheists, agnostics and ‘nothing in particular’
Atheists and agnostics, who make up relatively small shares of all religiously unaffiliated voters, are heavily Democratic.
Among those who identify their religion as “nothing in particular” – and who comprise a majority of all religious “nones” – Democrats hold a smaller advantage in party identification.
- More than eight-in-ten atheists (84%) align with the Democratic Party, as do 78% of agnostics.
- 62% of voters who describe themselves as “nothing in particular” identify as Democrats or lean Democratic, while 34% align with the GOP.
Partisanship and religious service attendance
Voters who regularly attend religious services are more likely to identify with or lean toward the Republican Party than voters who attend less regularly.
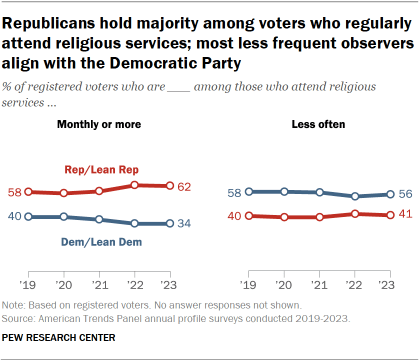
In 2023, 62% of registered voters who attended religious services once a month or more aligned with Republicans, compared with 41% of those who attend services less often.
This pattern has been evident for many years. However, the share of voters who identify as Republicans or lean Republican has edged up in recent years.
For White, Hispanic and Asian voters, regular attendance at religious services is linked to an increase in association with the Republican Party.
However, this is not the case among Black voters.
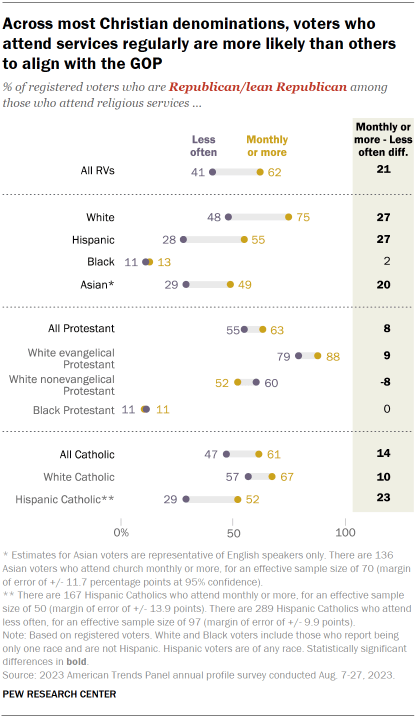
Only about one-in-ten Black voters who are regular attenders (13%) and a similar share (11%) of those who attend less often identify as Republicans or Republican leaners.
Higher GOP association among regular attenders of religious services is seen across most denominations.
For example, among Catholic voters who attend services monthly or more often, 61% identify as Republicans or lean toward the Republican Party.
Among less frequent attenders, 47% align with the GOP.
Black Protestants are an exception to this pattern: Black Protestant voters who attend religious services monthly or more often are no more likely to associate with the Republican Party than less frequent attenders.
Sign up for our Politics newsletter
Sent weekly on Wednesday
Report Materials
Table of contents, behind biden’s 2020 victory, a voter data resource: detailed demographic tables about verified voters in 2016, 2018, what the 2020 electorate looks like by party, race and ethnicity, age, education and religion, interactive map: the changing racial and ethnic makeup of the u.s. electorate, in changing u.s. electorate, race and education remain stark dividing lines, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
No sign of greenhouse gases increases slowing in 2023
- April 5, 2024
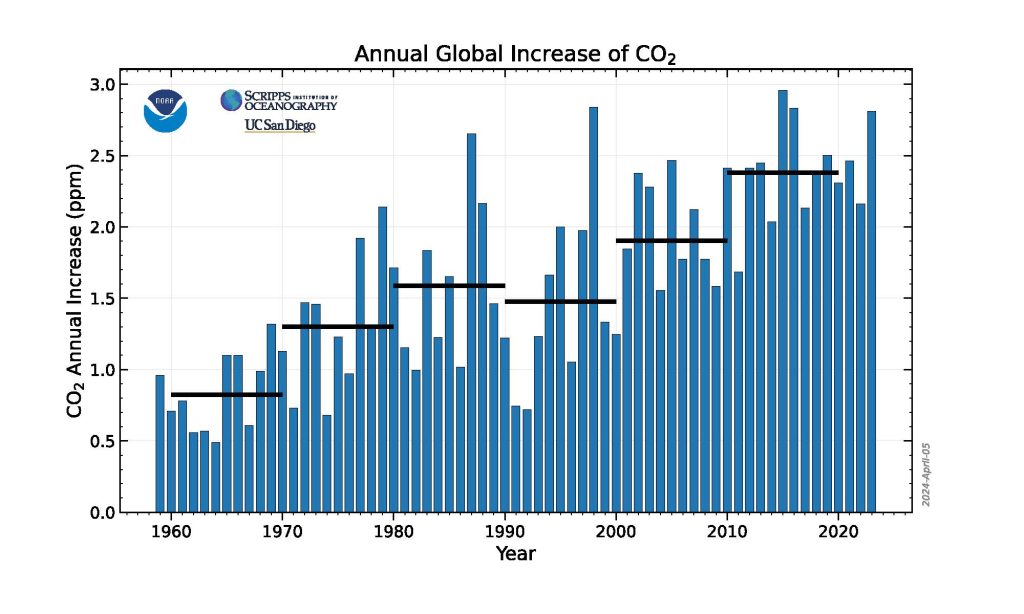
Levels of the three most important human-caused greenhouse gases – carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane and nitrous oxide – continued their steady climb during 2023, according to NOAA scientists.
While the rise in the three heat-trapping gases recorded in the air samples collected by NOAA’s Global Monitoring Laboratory (GML) in 2023 was not quite as high as the record jumps observed in recent years, they were in line with the steep increases observed during the past decade.
“NOAA’s long-term air sampling program is essential for tracking causes of climate change and for supporting the U.S. efforts to establish an integrated national greenhouse gas measuring, monitoring and information system,” said GML Director Vanda Grubišić. “As these numbers show, we still have a lot of work to do to make meaningful progress in reducing the amount of greenhouse gases accumulating in the atmosphere.”
The global surface concentration of CO 2 , averaged across all 12 months of 2023, was 419.3 parts per million (ppm), an increase of 2.8 ppm during the year. This was the 12th consecutive year CO 2 increased by more than 2 ppm, extending the highest sustained rate of CO 2 increases during the 65-year monitoring record. Three consecutive years of CO 2 growth of 2 ppm or more had not been seen in NOAA’s monitoring records prior to 2014. Atmospheric CO 2 is now more than 50% higher than pre-industrial levels.
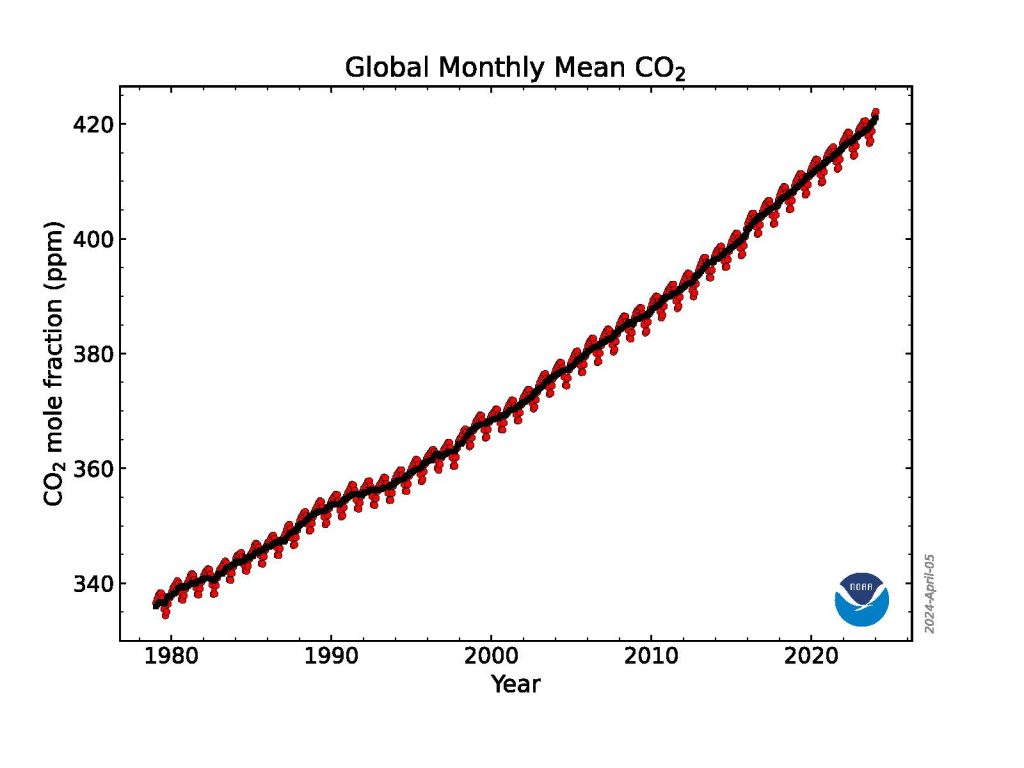
This graph shows the globally averaged monthly mean carbon dioxide abundance measured at the Global Monitoring Laboratory’s global network of air sampling sites since 1980. Data are still preliminary, pending recalibrations of reference gases and other quality control checks. Credit: NOAA GML
“The 2023 increase is the third-largest in the past decade, likely a result of an ongoing increase of fossil fuel CO 2 emissions, coupled with increased fire emissions possibly as a result of the transition from La Nina to El Nino,” said Xin Lan, a CIRES scientist who leads GML’s effort to synthesize data from the NOAA Global Greenhouse Gas Reference Network for tracking global greenhouse gas trends .
Atmospheric methane, less abundant than CO 2 but more potent at trapping heat in the atmosphere, rose to an average of 1922.6 parts per billion (ppb). The 2023 methane increase over 2022 was 10.9 ppb, lower than the record growth rates seen in 2020 (15.2 ppb), 2021(18 ppb) and 2022 (13.2 ppb), but still the 5th highest since renewed methane growth started in 2007. Methane levels in the atmosphere are now more than 160% higher than their pre-industrial level.
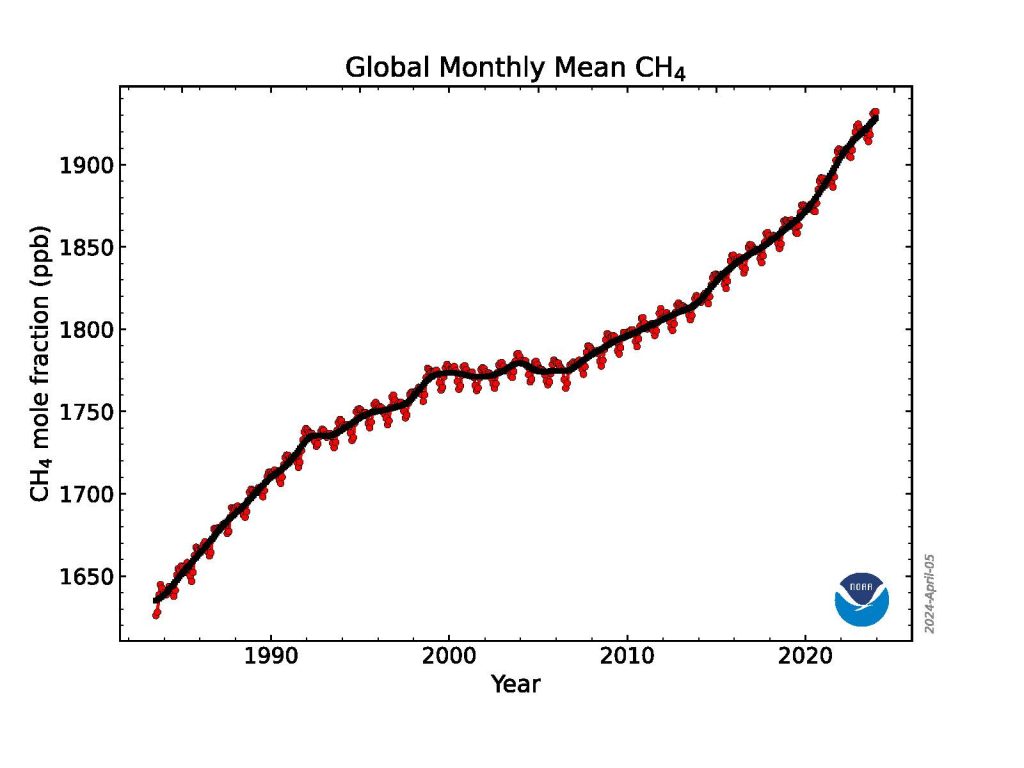
This graph shows globally-averaged, monthly mean atmospheric methane abundance determined from marine surface sites for the full NOAA time-series starting in 1983. Values for the last year are preliminary, pending recalibrations of standard gases and other quality control steps. Credit: NOAA GM
In 2023, levels of nitrous oxide, the third-most significant human-caused greenhouse gas, climbed by 1 ppb to 336.7 ppb. The two years of highest growth since 2000 occurred in 2020 (1.3 ppb) and 2021 (1.3 ppb). Increases in atmospheric nitrous oxide during recent decades are mainly from use of nitrogen fertilizer and manure from the expansion and intensification of agriculture. Nitrous oxide concentrations are 25% higher than the pre-industrial level of 270 ppb.
Taking the pulse of the planet one sample at a time NOAA’s Global Monitoring Laboratory collected more than 15,000 air samples from monitoring stations around the world in 2023 and analyzed them in its state-of-the-art laboratory in Boulder,
Colorado. Each spring, NOAA scientists release preliminary calculations of the global average levels of these three primary long-lived greenhouse gases observed during the previous year to track their abundance, determine emissions and sinks, and understand carbon cycle feedbacks.
Measurements are obtained from air samples collected from sites in NOAA’s Global Greenhouse Gas Reference Network , which includes about 53 cooperative sampling sites around the world, 20 tall tower sites, and routine aircraft operation sites from North America.
Carbon dioxide emissions remain the biggest problem
By far the most important contributor to climate change is CO 2 , which is primarily emitted by burning of fossil fuels. Human-caused CO 2 pollution increased from 10.9 billion tons per year in the 1960s – which is when the measurements at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii began – to about 36.8 billion tons per year in 2023. This sets a new record, according to the Global Carbon Project , which uses NOAA’s Global Greenhouse Gas Reference Network measurements to define the net impact of global carbon emissions and sinks.
The amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere today is comparable to where it was around 4.3 million years ago during the mid- Pliocene epoch , when sea level was about 75 feet higher than today, the average temperature was 7 degrees Fahrenheit higher than in pre-industrial times, and large forests occupied areas of the Arctic that are now tundra.
About half of the CO 2 emissions from fossil fuels to date have been absorbed at the Earth’s surface, divided roughly equally between oceans and land ecosystems, including grasslands and forests. The CO 2 absorbed by the world’s oceans contributes to ocean acidification, which is causing a fundamental change in the chemistry of the ocean, with impacts to marine life and the people who depend on them. The oceans have also absorbed an estimated 90% of the excess heat trapped in the atmosphere by greenhouse gases.
Research continues to point to microbial sources for rising methane
NOAA’s measurements show that atmospheric methane increased rapidly during the 1980s, nearly stabilized in the late-1990s and early 2000s, then resumed a rapid rise in 2007.
A 2022 study by NOAA and NASA scientists and additional NOAA research in 2023 suggests that more than 85% of the increase from 2006 to 2021 was due to increased microbial emissions generated by livestock, agriculture, human and agricultural waste, wetlands and other aquatic sources. The rest of the increase was attributed to increased fossil fuel emissions.
“In addition to the record high methane growth in 2020-2022, we also observed sharp changes in the isotope composition of the methane that indicates an even more dominant role of microbial emission increase,” said Lan. The exact causes of the recent increase in methane are not yet fully known.
NOAA scientists are investigating the possibility that climate change is causing wetlands to give off increasing methane emissions in a feedback loop.
To learn more about the Global Monitoring Laboratory’s greenhouse gas monitoring, visit: https://gml.noaa.gov/ccgg/trends/.
Media Contact: Theo Stein, [email protected] , 303-819-7409
5 science wins from the 2023 NOAA Science Report

Filling A Data Gap In The Tropical Pacific To Reveal Daily Air-Sea Interactions
Scientists detail research to assess viability and risks of marine cloud brightening

How social science helps us combat climate change
Popup call to action.
A prompt with more information on your call to action.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
- Amazon Alexa
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
Watch your garden glow with new genetically modified bioluminescent petunias
Sasa Woodruff

A long exposure photo of Firefly petunias, which are genetically modified to produce their own light through bioluminescence Sasa Woodruff/Boise State Public Radio hide caption
A long exposure photo of Firefly petunias, which are genetically modified to produce their own light through bioluminescence
Keith Wood, Ph.D. spent most of his career in pharmaceutical research in molecular and chemical biology, using his work with bioluminescence to understand how molecules interacted with diseases. His work started as a graduate student when the team he was on inserted a firefly gene into a tobacco plant.
It was a small plant and couldn't sustain light without the addition of a substrate. It wasn't something a consumer would buy, but it was good for understanding pathways within an organism.
Now, about 40 years after that first plant, Wood and his company in Ketchum, Light Bio, are marketing a garden petunia with a twist: it glows in the dark.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Alexandra L. Woodruff (@trowelandfork)
"People don't think about science as just bringing joy to our lives," Wood said, "We thought we could do something really special here. We could create a kind of decorative plant that was really just enjoyment, just bringing a kind of magic into our lives."

Scientist Keith Wood stands in his Ketchum home with a photo of a tobacco plant modified with a firefly gene Sasa Woodruff/Boise State Public Radio hide caption
Scientist Keith Wood stands in his Ketchum home with a photo of a tobacco plant modified with a firefly gene
The petunia with bright, white flowers looks like something you'd buy in spring at a garden nursery. But, when the lights are turned out, the petals slowly start lighting up with a greenish, white glow. The plant is always glowing, it's just our eyes that need to adjust to see the light. The newest buds are the brightest and punctuate the glowing flowers.
"That's why we call it the Firefly Petunia. Because these bright buds resemble fireflies sitting on top of the plant.," Wood explained.
And despite its name, this plant doesn't have any firefly genes, rather four genes from a bioluminescent mushroom and a fifth from a fungi.
"The first gene takes a metabolite and turns it into an intermediate," Wood explained, "The second gene takes the intermediate and turns it into the actual fuel for the bioluminescence. The third gene is what actually makes the light. And then the last gene takes the product from the light reaction and recycles it back to the starting point."
This cycle is self-sustaining, which means it shines brightly and doesn't need an extra chemical like the tobacco plant did to light up.
"The [firefly] gene was functional, but it didn't connect seamlessly into the natural metabolic processes," Wood said.
"You've got glow, but it was a weak glow. Not satisfying at all."
Petunia approval paperwork
It took about 10 years to go from development to approval from the U.S. Department of Agriculture last fall.
The plants went on sale online in February and the first ones were shipped out this week.
Diane Blazek, the executive director of the National Garden Bureau, an educational nonprofit, says customers are always looking for the next new plant and petunias are a guaranteed bestseller.
"Grandma grew petunias, but oh, look, now I've got a petunia that glows in the dark. So, this is really cool," Blazek said.

The Firefly Petunia emanates light because it's been modified with genes from a bioluminescent mushroom Sasa Woodruff/Boise State Public Radio hide caption
The Firefly Petunia emanates light because it's been modified with genes from a bioluminescent mushroom
She doesn't think that the fact that it's genetically modified will affect customers buying it because there's a precedent.
Seven years ago, an orange petunia modified with a maize gene showed up in gardens and nurseries in Europe and the U.S. The plant was never supposed to leave a closed lab but somehow ended up in lots of gardens. Regulators eventually asked people to destroy the plants and seeds.
"Overwhelmingly, the response was, wait a minute, it's a petunia. We're not eating it. The orange gene came from maize. Why? Why can't we plant this?" Blazek remembered.
Eventually, regulators approved the plants in the U.S.
Chris Beytes, at Ball Publishing, who oversees several horticulture publications, said the Firefly Petunia could open up gardening to new customers.
"If you buy your first plant because it glows in the dark or it's dyed pink, your second and third and 100th plant may be the traditional stuff. You never know," Beytes said. "Anything that creates excitement around flowers and plants. I'm all for it."
The Firefly Petunia may not have practical implications for things like drug advances or crop production, but for Wood this petunia is transcendent.
"There's something magical about seeing this living presence, this glowing vitality coming from a living plant that in person gives a kind of magical experience that you just can't see in a photograph.
And this summer, that magic could be sitting on the patio watching your garden glow from the light of a petunia.
Fellowships support student research on compostable cutlery, sustainable solutions, and shorebird conservation
Undergraduate fellowships in the College of Natural Resources and Environment allow students to design and pursue their own research projects.
- David Fleming
10 Apr 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Copy address link to clipboard
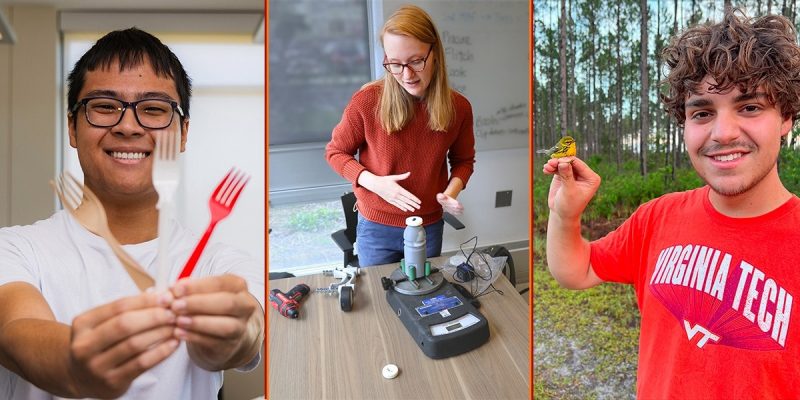

For Brian Tea, research starts at the back of Dining Services' Southgate Center. Lifting the lid of a container of food waste already starting to spoil, Tea scoops out enough to feed the composting tumblers that he is using to conduct his project, supported by an Undergraduate Research Fellowship from the College of Natural Resource and Environment (CNRE).
“My research is on compostable cutlery,” said Tea, a junior majoring in sustainable biomaterials in the Department of Sustainable Biomaterials . “I’m interested in understanding the life cycle of single-use materials and how sustainable options can provide a circular solution to waste.”
Tea tested the ability to compost cutlery made from three materials: the biodegradable polymer cellulose diacetate; polylactic acid, which is a renewable bioplastic; and the commonplace polystyrene plastics readily available at fast food restaurants.
Working under the guidance of Associate Professor Maren Roman , Tea measured the degradation processes of the various materials using an at-home composter that grinded and heated the composted materials to determine how efficiently the cutlery was able to break down.
Tea was one of eight recipients of a CNRE fellowship this past academic year. The program aims to give undergraduates both the financial resources and instructional support to conduct hands-on research.
“The CNRE Undergraduate Research Fellowship program provides students with an incredible opportunity to work side by side with our faculty to address local, state, national, and global challenges,” said Associate Dean Keith Goyne , who supervises the program. “Our undergraduate research fellows are tackling a wide range of topics in social and natural sciences, and they truly are using the fellowships to understand and improve the world.”
Applicants are eligible to receive up to $2,500 to support a research project of their own design with the sponsorship of a faculty mentor. Funding for fellowships comes in part from the generous gifts of donors to the college, whose contributions allow students the opportunity to take their education in their own hands. These grants are part of Virginia Tech Advantage , the university’s commitment to providing transformational educational opportunities to all students, regardless of income.
From materials science to making a difference
The Department of Sustainable Biomaterials focuses on training students to take on careers utilizing natural and synthetic materials to better the world.
For junior Justin Brandt, that challenge meant using one of the oldest building materials – bamboo – to enhance the use of cross-laminated timber (CLT), an engineered wood product that has become an increasingly popular material for the construction of homes and buildings.
“I think CLT is a genius building idea. It’s feasible and easy to implement, and it really blows my mind that it still isn’t used very often,” said Brandt, who switched majors on the recommendation of his roommate , junior Sage Smith. “One of the major problems is that since it is such a solid material, it’s difficult to hide wiring or piping inside of it.”
Brandt’s solution is to incorporate hollow lengths of bamboo in the solid wood timbers to provide builders with a handy, strong, and environmentally sustainable solution for hiding the plumbing and wiring that designers would prefer to have out of sight.
Brandt, who likes the challenge of tackling projects on his own, said he’s grateful to have had the chance to conduct his own research.
“I reached out to Daniel Hindman and told him my idea, and we sat down and talked about it,” Brandt said of connecting with the associate professor. “The whole experience made me feel very heard, and having the chance to express my passions in such an experiential and scientific way has been a great opportunity for me.”
Junior Rosa Williams’s dive into the subject of materials science will focus on everyday items: the small plastic bottles that hold medicine and the safety caps that keep children – and sometimes the elderly – from accessing the medicines inside.
Williams, who did a summer internship learning how plastic closure design can impact day-to-day-lives, said her curiosity about how we determine standards for products started much earlier.
“As a kid growing up, I was always super curious about who the specific person was who could open every peanut butter jar,” said Williams, who is majoring in packaging systems and design. “Those kinds of questions led to me thinking about how we make decisions to standardize certain things.”
Williams – a recipient of the Geza Ifju Scholarship and a scholarship from the Virginia Forestry Educational Foundation – will be conducting research on how to better understand packaging challenges as they relate to children and the elderly so that designers can make choices that allow for more user-friendly packaging options.
“There are testing requirements for child-resistant packages to be elderly-friendly, but those requirements exclude people with certain disabilities, including arthritis, which is extremely common for people over the age of 60,” said Williams, who is minoring in disability studies. “I want to do an exploratory study that considers the experiences of children and seniors to better understand the physical capabilities of both groups.”
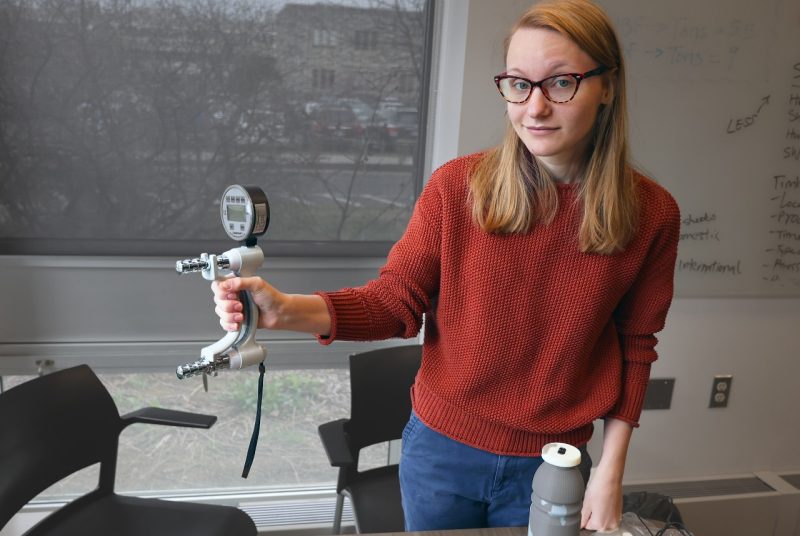

Using a hand dynamometer, which measures grip strength, and a torquemeter, to measure wrist twisting capabilities, Williams will compare the grip strengths of volunteer children and seniors against existing data to better understand the specific capacities of these two populations underrepresented in safety and accessibility measures for plastic bottles.
“My long-term career goal is to design packaging with an understanding of disabilities,” said Williams. “Improvements to plastic closures, with their vast uses across the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries, can make the world a more user-friendly place.”
Conservationists of a feather conference together
When Desraeli McBride showed up to present at the Wildlife Society’s annual conference in Louisville, Ketucky, this past fall, she could count on at least one familiar face: She and Max Nootbaar, both seniors majoring in wildlife conservation in the Department of Fish and Wildlife Conservation , were on hand to present research posters at the conference.
“The poster session was only two hours,” said McBride, who presented on her work with oystercatchers, a threatened bird species found along the barrier islands of Virginia. “But getting to stand there and feel like an expert with so many people coming by to ask about the research I was doing was honestly so much fun.”
McBride, a first-generation college student who graduated in December with degrees in wildlife conservation and biology, received a CNRE research fellowship to conduct her study on oystercatchers under the guidance of Professor Sarah Karpanty .
“I conducted research on Fisherman Island, which is one of the 14 barrier islands we have in Virginia,” said McBride. “I worked with American oystercatchers, which I think are the best birds in the world. For my project, I helped monitor nests and broods to determine the survival of chicks and investigate the overall habitat and cover selections of these birds.”
McBride, who aspires to be a wildlife field biologist, was the recipient of the Camp-Younts Foundation Scholarship in Wildlife. Funded by the Atkinson family, this scholarship supports the education of students studying animal conservation.
“I’ve been very supported in my time at the college, from the scholarships I’ve received, to the advising that is amazing here, to the general support from professors and students,” said McBride. “All of that has definitely made this place feel like home.”
For Nootbaar, an interest in piping plovers – those small shorebirds that race along ebbing waves hunting for food – started when he noted a small, numbered band on a bird he was watching.
“I wrote down the band number and reported the sighting, and I received a response that this individual hatched in Round Bay, Nova Scotia, in 2017,” said Nootbaar, a Charlottesville native who is graduating this spring. “I was thrilled by my small contribution to the research of this threatened species.”
That experience – and the encouragement of Logan Anderson ’22 – led Nootbaar to the Department of Fish and Wildlife Conservation, where he received an Undergraduate Student Research Fellowship to use breeding data to assess the demographic rates and population shifts of plovers, as part of a broader effort to model the species population dynamics along the Atlantic coast.
“I’m working with a data set from a banding study that was conducted on the Virginia barrier islands in 2018 and 2019,” said Nootbaar, who is also sponsored by Karpanty. “The program banded 111 adult and chicks, and several conservation organizations and wildlife agencies have been monitoring where those birds have ended up breeding over the past several years. I’m using that data to see how the Virginia population is connected to other populations in the mid-Atlantic region.”
Nootbaar, who was recently selected as the recipient of the college's David William Smith Leadership Award, also received a Dean’s International Study Abroad scholarship to travel to the Galápagos Islands for the spring semester study abroad course Darwin’s Galápagos: Evolution in the Anthropocene . He said his experiences in the college have motivated him to pursue a career in conservation research.
“My involvement in the Virginia Tech Shorebird Program has exposed me to the plight of shorebirds affected by climate change, habitat loss, and other anthropogenic drivers,” said Nootbaar. “Learning about these threats has strengthened my desire to conduct research relevant to the conservation and management of threatened species.”
From hands-on learners to future scientists
From improving everyday materials such as disposable cutlery and plastic pill bottles, to conserving species or designing new ways to imagine the future of housing, research fellowships are providing undergraduate students in the college with the chance to take the lead in directing their educational journeys.
“The experiential learning gained by our undergraduate research fellows is invaluable for their development as scientists,” said Goyne. “The opportunity to choose and craft their projects under the mentorship of globally-recognized experts provides students with great motivation to engage in the research and to complete the research with precision and accuracy.”
The application window for CNRE Undergraduate Research Fellowships for the 2024-25 academic year is open, and interested students in the college can learn more about the program and how to apply by visiting the undergraduate student research page . The deadline for applications is May 1.
Krista Timney
540-231-6157
- Blacksburg, Va.
- Career Development
- Climate Change
- Coastal Research
- College of Natural Resources and Environment
- Complex Problems
- Economical and Sustainable Materials
- Environment
- Experiential Learning
- Fellowships
- First Generation Students
- Fish and Wildlife Conservation
- Global Education
- Internships
- Outreach and International Affairs
- Philanthropy
- Research Participation
- Sustainability
- Threatened and Endangered Species
- Undergraduate Education
- Undergraduate Research
- Virginia Tech Advantage
- Young Alumni
Related Content

Skip to Content
A new look at western water
The Mountain Hydrology Group will be developing a new snowpack data set to inform water supply management in the western United States, thanks to grant funding from the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation.
Researchers in the Mountain Hydrology Group currently produce near-real-time estimates of snow water equivalent, or the amount of water contained in fallen snow, for mountainous areas in California, Colorado, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming. Reports and data are released to water managers and forecasters and are also available to the public.
With the new grant of $1 million over the next three years, the group will be able to expand its estimates to all 17 western states, notably adding mountainous areas in Idaho, Montana, Oregon, and Washington and large mountain ranges such as the Cascades and northern Rocky Mountains.
The grant will support Noah Molotch (lead PI), Leanne Lestak, Emma Tyrrell, and Karl Rittger in analyzing snow data and producing biweekly snow water supply reports to support decision making by federal, state, and local water management entities responsible for managing water supplies in the western United States.
The Bureau of Reclamation awarded funds to 15 different projects as part of its Snow Water Supply Forecasting Program to improve water supply forecasting.
Noah Molotch shows information about the snow-water equivalent for California during a television interview at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Photo copyright by and courtesy of Pier Gagné, Radio-Canada.
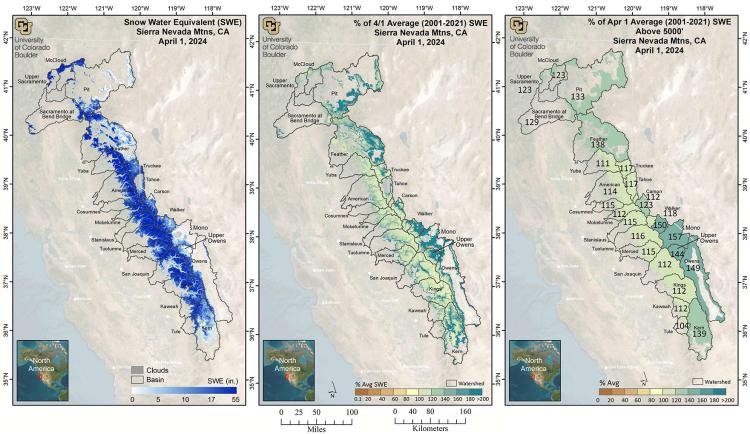
Maps show various aspects of snow-water equivalent for California's Sierra Nevada. The maps are part of the April 1, 2024 report from the Mountain Hydrology Group.
Related Articles

LogOn: Satellites, lasers help estimate snowpack in drought-stricken regions (VOA)

Californie, quand l'impensable se produit (Radio-Canada)

Scientists take flight to map California’s vast snowpack and measure flooding threats (L.A. Times)
- Labs, groups, & programs
Labs & Groups
- Advanced Laser Technology for Atmospheric Research (Fried)
- Amino Acid Geochronology (Miller)
- AMS Radiocarbon Preparation & Research (Lehman)
- Coastal Oceanography Modeling (Moriarty)
- Core Processing & Sedimentology (Roth & Anderson)
- Cryosphere and Surface Processes (Overeem et al.)
- Diatoms (Spaulding)
- Ecohydrology (Barnard)
- Hydroecology Science & Engineering (Gooseff) ↪︎
- ICP-MS Trace Metals (Marchitto)
- Micropaleontology (Jennings)
- Mountain Hydrology (Molotch, Musselman, & Rittger)
- Mountain Limnology Lab (Oleksy) ↪︎
- Ocean Biogeochemistry (Lovenduski)
- Organic Geochemistry (Sepúlveda)
- Organic Matter Spectroscopy (McKnight)
- Polar & Paleoclimate Modeling (Jahn)
- Stable Isotope Lab
- Suding Lab - plant community ecology ↪︎
- Taylor Lab - evolutionary biology & genetics of birds ↪︎
- Center for the Geochemical Analysis of the Global Environment (GAGE)
- Community Surface Dynamics Modeling System (CSDMS)
- Consortium for Capacity Building (CCB)
- DFO - Flood Observatory
- Dynamic Water critical zone project
- McMurdo Dry Valleys Long-Term Ecological Research (MCM LTER)
- Mountain Research Station (MRS)
- Niwot Ridge Long-Term Ecological Research (NWT LTER)
- Labs & groups
- AAAR journal ↪
- Theses and dissertations
- Occasional Papers
- Faculty Fellows
- Faculty Research Scientists
- Faculty Fellows Emeriti
- Research Staff
- Admin Staff
- DEI summer scholarships
- Our actions
- Addressing problematic behavior
Meet an INSTAAR Art+Science showcase
- Research news
- People spotlights
- Diversity news
- Community news
- Diversity events
- Community events
About INSTAAR
- Visit INSTAAR
Prospective students
- Grad application assistance (GAAP)
- Undergrad opportunities
Resources for INSTAARs
Support instaar.

- Admission and Aid
- Student Life
UM Research Discovers New Way to Generate Human Cartilage
- 10 April 2024
MISSOULA – University of Montana researchers and their partners have found a new method to generate human cartilage of the head and neck.
Mark Grimes, a biology professor in UM’s Division of Biological Sciences , said they have induced stem cells to become the cell type that normally makes up human craniofacial cartilage. Stem cells can replicate themselves and also develop into different types of cells.
“The cells that normally give rise to this type of cartilage are called neural crest cells,” Grimes said. “We found a novel method for generating craniofacial organoids from neural crest cells.”
Organoids are a simplified, miniature version of an organ that mimic the architecture and gene expression of the organ. “Organoids are a good model for certain human tissues that we can study in ways that are not possible using tissue from human beings,” he said.
Grimes said there is a critical unmet need for new methods to regenerate human cartilage for the 230,000 children born annually in the U.S. with craniofacial defects. Growing cartilage in the laboratory also could lead to effective treatments to repair craniofacial cartilage damage due to injuries.
The researchers studied gene expression data at the RNA and protein level to reveal how cartilage cells arise from stem cells. They revealed that stem cells communicate in the early stages to become elastic cartilage, which makes up human ears.
To accomplish this, the team used extensive analysis of biological markers and machine-learning pattern-recognition techniques to understand the cell signaling pathways involved when cells differentiate into cartilage.
It is difficult to reconstruct natural features such as a person’s ears, nose or larynx with current plastic surgery techniques, and transplanted tissue is often rejected without immunosuppressants.
“To use patient-derived stem cells to generate craniofacial cartilage in the laboratory, you need to understand the human-specific differentiation mechanisms,” Grimes said. “Our aim is to develop a protocol for craniofacial cartilage generation for transplantation using human stem cells.”
The research was published in the journal iScience . Besides Grimes, contributing UM authors include Lauren Foltz, Nagashree Avabhrath and Jean-Marc Lanchy. Other authors are Bradly Peterson of Missoula’s Pathology Consultants of Western Montana and Tyler Levy, Anthony Possemato and Majd Ariss of Cell Signaling Technology of Danvers, Massachusetts.
Contact : Mark Grimes, UM biology professor, 406-243-4977, [email protected] .
Launch UM virtual tour.

President Biden and Prime Minister Kishida highlight their continued commitment to HEU minimization during Japan State Visit
WASHINGTON – President Biden and Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida welcomed news of the successful removal of all remaining highly enriched uranium (HEU) from the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA)’s Japan Materials Testing Reactor Critical Assembly (JMTRC). The announcement also highlighted their continued commitment to minimize the use of HEU in civilian applications and reported progress since President Biden’s state visit to Japan in May 2022.
In the two years since President Biden and Prime Minister Kishida announced the removal of HEU from three Japanese sites , the two countries also have removed all HEU from the Kyoto University Critical Assembly and committed to convert the Kindai University Teaching and Research Reactor , Japan’s last remaining HEU-fueled research reactor, to high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) and remove its remaining HEU to the United States.
In December 2023, the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA); Japan’s Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT); and the JAEA transported the remaining HEU from the JMTRC to the United States. The removal fulfills a commitment made by NNSA Administrator Jill Hruby and MEXT former Deputy Minister Yanagi Takashi in November 2021 and was completed over two years ahead of schedule through the financial support of the Defense Threat Reduction Agency.
“This most recent removal highlights the shared commitment of the United States and Japan’s to minimize highly enriched uranium and the close partnership between our countries,” said Corey Hinderstein, Deputy Administrator for Defense Nuclear Nonproliferation. “The Defense Threat Reduction Agency helped our teams achieve this milestone years earlier than would have otherwise been possible.”
The majority of the facility’s HEU was repatriated to the United States between 2003 and 2009 following its decommissioning in 1996. The removal represents years of coordination between NNSA, MEXT, JAEA, and the Y-12 National Security Complex in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, which provided U.S. technical support for the project and received the HEU upon its arrival in the United States. The HEU will be downblended to low-enriched uranium.
NNSA’s Office of Material Management and Minimization works with partner countries and international institutions around the world to eliminate the need for, presence of, or production of weapons-usable nuclear material. To date, the office has worked jointly with domestic and international partners and successfully converted or verified as shut down 109 research reactors and medical isotope production facilities and removed or confirmed the disposition of over 7,340 kilograms of weapons-usable nuclear material—enough for approximately 328 nuclear weapons.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Latest science news, discoveries and analysis
This fMRI technique promised to transform brain research — why can no one replicate it?
How to supercharge cancer-fighting cells: give them stem cell skills

Peter Higgs: science mourns giant of particle physics
Is ChatGPT corrupting peer review? Telltale words hint at AI use
Randomness in computation wins computer-science ‘nobel’, the rise of eco-anxiety: scientists wake up to the mental-health toll of climate change, total solar eclipse 2024: what dazzled scientists, india is booming — but there are worries ahead for basic science, ai-fuelled election campaigns are here — where are the rules rumman chowdhury.

The ‘ghost roads’ driving tropical deforestation

After the genocide: what scientists are learning from Rwanda
Audio long read: Why are so many young people getting cancer? What the data say

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Iran frees scientists who studied big cats in surprise move, bird flu outbreak in us cows: why scientists are concerned, brazil budget cuts could leave science labs without power and water, exclusive: official investigation reveals how superconductivity physicist faked blockbuster results.

What happens when climate change and the mental-health crisis collide?

Rwanda 30 years on: understanding the horror of genocide
AI can help to tailor drugs for Africa — but Africans should lead the way
Frans de waal (1948–2024), primatologist who questioned the uniqueness of human minds, time to sound the alarm about the hidden epidemic of kidney disease, current issue.

Nanoscale scythe cuts molecular tethers using mechanical forces
A massive galaxy that formed its stars at z ≈ 11, an optical tweezer array of ultracold polyatomic molecules, research analysis.
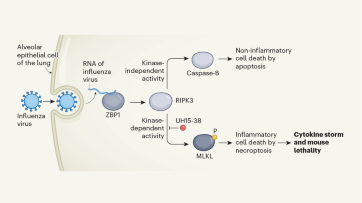
Blocking cell death limits lung damage and inflammation from influenza
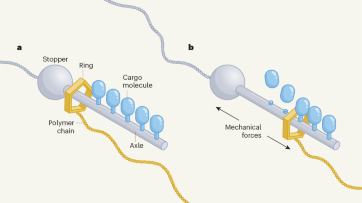
Scalable, high-quality 2D telluride nanosheets for energy and catalysis applications

Wildlife boost in African forests certified for sustainable logging
Light makes atoms behave like electromagnetic coils, a bitter-taste receptor activated in a surprising way, the biologist who built a faraday cage for a crab, a quirky fluid that has robotic capabilities.

Digging in: last chance to save a native forest

How two PhD students overcame the odds to snag tenure-track jobs
How i harnessed media engagement to supercharge my research career, ready or not, ai is coming to science education — and students have opinions, books & culture.

Survival of the nicest: have we got evolution the wrong way round?

The comings and goings of ants: how are social skills shaped in an ever-changing world?

Three possible muses
Wild women and restoring public trust: books in brief, these monkeys make no sense, nature podcast.

Latest videos
Nature briefing.
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
A comparison of two complete sets of human centromeres reveals that the centromeres show at least a 4.1-fold increase in single-nucleotide variation compared with their unique flanks, and up to 3 ...
Chemical eye injuries: a 10 year retrospective review of acute presentations and clinical outcomes in Auckland, New Zealand. Natalie E. Allen. Alexandra Z. Crawford. Jay J. Meyer. Article Open ...
Breaking science news and articles on global warming, extrasolar planets, stem cells, bird flu, autism, nanotechnology, dinosaurs, evolution -- the latest discoveries ...
Discover a digital archive of scholarly articles, spanning centuries of scientific research. User Guide Learn how to find and read articles of interest to you. ... Journals deposit all NIH-funded articles as defined by the NIH Public Access Policy. 44 Selective Deposit Programs. Publisher deposits a subset of articles from a collection of journals.
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
3.3 million articles on ScienceDirect are open access. Articles published open access are peer-reviewed and made freely available for everyone to read, download and reuse in line with the user license displayed on the article. ScienceDirect is the world's leading source for scientific, technical, and medical research.
The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) is a weekly general medical journal that publishes new medical research and review articles, and editorial opinion on a wide variety of topics of ...
With 160+ million publication pages, 25+ million researchers and 1+ million questions, this is where everyone can access science. You can use AND, OR, NOT, "" and () to specify your search ...
by Iavor I. Bojinov, Kevin Wu Han, and Guillaume Basse. In panel experiments, units are exposed to different interventions over time. This article introduces a unifying framework for studying panel experiments with population interference, in which a treatment assigned to one experimental unit affects another experimental unit's outcome.
One of the largest and most authoritative collections of online journals, books, and research resources, covering life, health, social, and physical sciences. Wiley Online Library | Scientific research articles, journals, books, and reference works
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Research Article. BCG vaccination reduces bovine tuberculosis transmission, improving prospects for elimination. Add to reading list. by. Abebe Fromsa; Katriina Willgert; Sreenidhi Srinivasan; Getnet Mekonnen; Wegene Bedada; Balako Gumi; Matios Lakew; Biniam Tadesse; Berecha Bayissa; Asegedech Sirak;
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
Research articles represent the ultimate, final product of a scientific study. You should assume that your published work will be indefinitely available for anyone to access. • Research articles always consist of a title, abstract, introduction, materials and methods, results, discussion, and references sections, and many include a supplemental materials section. There are strategies for ...
The results put forward evidence-based information and clinical inspiration for drug compatibility and further research of the BD mechanism. Articles. Open Access. Association between concurrence of multiple risk factors and under-5 mortality: a pooled analysis of data from Demographic and Health Survey in 61 low-and-middle-income countries ...
research articles. Research articles. Filter By: Article Type. All. All; Article (974) Matters Arising (34) Year. 2021 (1008) All; 2021 (1008) Activity of convalescent and vaccine serum against ...
News about Research, including commentary and archival articles published in The New York Times.
2. Describe the articles that can answer the question. Although not all clinical or research questions can be answered in the literature, the next step is to presume that the answer can indeed be found in published studies. A good starting point for a search is hypothesizing what the research that can answer the question would look like.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions.
A 2022 study by NOAA and NASA scientists and additional NOAA research in 2023 suggests that more than 85% of the increase from 2006 to 2021 was due to increased microbial emissions generated by livestock, agriculture, human and agricultural waste, wetlands and other aquatic sources. The rest of the increase was attributed to increased fossil ...
Keith Wood, Ph.D. spent most of his career in pharmaceutical research in molecular and chemical biology, using his work with bioluminescence to understand how molecules interacted with diseases ...
research articles. Research articles. Filter By: Article Type. All. All; Appointments Vacant (974) Article (23029) Brief Communication (1079) Brief Communications Arising (580) British Association ...
The application window for CNRE Undergraduate Research Fellowships for the 2024-25 academic year is open, and interested students in the college can learn more about the program and how to apply by visiting the undergraduate student research page. The deadline for applications is May 1.
A real-time analysis system was developed for an up to 500-megabyte-per-second image stream. This system can extract activities from up to 100,000 neurons in larval zebrafish brains and enables ...
Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research University of Colorado 4001 Discovery Drive Boulder, CO 80303 USA. INSTAAR acknowledges that it is located on the traditional territories and ancestral homelands of the Cheyenne, Arapaho, Ute and many other Native American nations. Their forced removal from these territories has caused devastating and ...
The research was published in the journal iScience. Besides Grimes, contributing UM authors include Lauren Foltz, Nagashree Avabhrath and Jean-Marc Lanchy. Other authors are Bradly Peterson of Missoula's Pathology Consultants of Western Montana and Tyler Levy, Anthony Possemato and Majd Ariss of Cell Signaling Technology of Danvers ...
To date, the office has worked jointly with domestic and international partners and successfully converted or verified as shut down 109 research reactors and medical isotope production facilities and removed or confirmed the disposition of over 7,340 kilograms of weapons-usable nuclear material—enough for approximately 328 nuclear weapons.
The Nature Podcast brings you the best stories from the world of science each week, highlighting the most exciting research from each issue of Nature. We meet the scientists behind the results and ...
ASML (ASML-1.54%) and Lam Research (LRCX-1.20%) are two of the world's top semiconductor equipment makers. ASML is the world's largest producer of lithography systems, which are used to optically ...