Origin and Death of Homework Inventor: Roberto Nevilis

Roberto Nevilis is known for creating homework to help students learn on their own. He was a teacher who introduced the idea of giving assignments to be done outside of class. Even though there’s some debate about his exact role, Nevilis has left a lasting impact on education, shaping the way students around the world approach their studies.
Homework is a staple of the modern education system, but few people know the story of its origin.
The inventor of homework is widely considered to be Roberto Nevilis, an Italian educator who lived in the early 20th century.
We will briefly explore Nevilis’ life, how he came up with the concept of homework, and the circumstances surrounding his death.
Roberto Nevilis: The Man Behind Homework Roberto Nevilis was born in Venice, Italy, in 1879. He was the son of a wealthy merchant and received a private education.
He later studied at the University of Venice, where he received a degree in education. After graduation, Nevilis worked as a teacher in various schools in Venice.
Table of Contents

How Homework Was Born
The Birth of Homework According to historical records, Nevilis was frustrated with the lack of discipline in his classroom. He found that students were often too focused on playing and not enough on learning.
To solve this problem , he came up with the concept of homework. Nevilis assigned his students homework to reinforce the lessons they learned in class and encourage them to take their education more seriously.
How did homework become popular?
The Spread of Homework , The idea of homework quickly caught on, and soon other teachers in Italy followed Nevilis’ lead. From Italy, the practice of assigning homework spread to other European countries and, eventually, the rest of the world.
Today, homework is a standard part of the education system in almost every country, and millions of students worldwide spend countless hours each week working on homework assignments.
How did Roberto Nevilis Die?
Death of Roberto Nevilis The exact circumstances surrounding Nevilis’ death are unknown. Some reports suggest that he died in an accident, while others claim he was murdered.
However, the lack of concrete evidence has led to numerous theories and speculation about what happened to the inventor of homework.
Despite the mystery surrounding his death, Nevilis’ legacy lives on through his impact on education.

Facts about Roberto Nevilis
- He is credited with inventing homework to punish his students who misbehaved in class.
- Some accounts suggest he was a strict teacher who believed in disciplining his students with homework.
- There is little concrete evidence to support the claim that Nevilis was the true inventor of homework.
- Some historians believe that the concept of homework has been around for much longer than in the 1900s.
- Despite the lack of evidence, Roberto Nevilis remains a popular figure in the history of education and is often cited as the inventor of homework.
The Legacy of Homework
The legacy of homework is deeply embedded in the educational landscape, reflecting a historical evolution that spans centuries. From its ambiguous origins to the diverse purposes it serves today, homework has played a pivotal role in shaping learning experiences.
While its effectiveness and necessity have been subjects of ongoing debate, homework endures as a tool for reinforcing concepts, fostering independent study habits, and preparing students for future academic and professional challenges.
In the contemporary educational context, the legacy of homework is a complex interplay of tradition, pedagogy, and evolving perspectives on the balance between academic demands and student well-being.
The Complex History of Homework
Throughout history, the evolution of homework can be traced through a series of significant developments. In ancient civilizations, such as Greece and Rome, scholars and philosophers encouraged independent study outside formal learning settings.
The Renaissance era witnessed a surge in written assignments, marking an early precursor to modern homework. The Industrial Revolution further transformed educational practices, as the need for a skilled workforce emphasized the importance of individual learning and practice.

The purposes and perceptions of homework have undergone substantial transformations over time. In the 19th century, homework was often viewed as a means of reinforcing discipline and moral values, with assignments focused on character development.
As educational philosophies evolved, particularly in the 20th century, homework assumed various roles—from a tool for drill and practice to a method for fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Perceptions of homework have fluctuated, with debates arising around issues of workload, equity, and its impact on student well-being. The complex history of homework reveals a dynamic interplay between societal expectations, educational philosophies, and changing perspectives on the purposes of academic assignments.

Conclusion – Who invented homework, and how did he die
Roberto Nevilis was a visionary educator who profoundly impacted the education system. His invention of homework has changed how students learn and has helped countless students worldwide improve their education.
Although the circumstances surrounding his death are unclear, Nevilis’ legacy as the inventor of homework will never be forgotten.
What is Roberto Nevilis’ legacy?
Roberto Nevilis’ legacy is his invention of homework, which has changed how students learn and has helped countless students worldwide improve their education.
Despite the mystery surrounding his death, Nevilis’ legacy as the inventor of homework will never be forgotten.
What was Roberto Nevilis’ background?
Roberto Nevilis was the son of a wealthy merchant and received a private education. He later studied at the University of Venice, where he received a degree in education.
After graduation, Nevilis worked as a teacher in various schools in Venice.
What was Roberto Nevilis’ impact on education?
Roberto Nevilis’ invention of homework has had a profound impact on education. By assigning homework, he helped students reinforce the lessons they learned in class and encouraged them to take their education more seriously.
This concept has spread worldwide and is now a staple of the modern education system.
Is there any evidence to support the theories about Roberto Nevilis’ death?
There is no concrete evidence to support the theories about Roberto Nevilis’ death, and the exact circumstances surrounding his death remain a mystery.
What was Roberto nevilis age?
It is believed that he died of old age. Not much information is available on his exact age at the time of death. Born: 1879 Died: 1954 (aged 75 years)
Where is Roberto Nevilis’s grave
While many have tried to find out about his Grave, little is known about where he is buried. Many people are querying the internet about his Grave. But frankly, I find it weird why people want to know this.
Share this:

Who Invented Homework? A Big Question Answered with Facts

Crystal Bourque

Delving into the intriguing history of education, one of the most pondered questions arises: Who invented homework?
Love it or hate it, homework is part of student life.
But what’s the purpose of completing these tasks and assignments? And who would create an education system that makes students complete work outside the classroom?
This post contains everything you’ve ever wanted to know about homework. So keep reading! You’ll discover the answer to the big question: who invented homework?
Who Invented Homework?
The myth of roberto nevilis: who is he, the origins of homework, a history of homework in the united states, 5 facts about homework, types of homework.
- What’s the Purpose of Homework?
- Homework Pros
- Homework Cons
When, How, and Why was Homework Invented?

Daniel Jedzura/Shutterstock.com
To ensure we cover the basics (and more), let’s explore when, how, and why was homework invented.
As a bonus, we’ll also cover who invented homework. So get ready because the answer might surprise you!
It’s challenging to pinpoint the exact person responsible for the invention of homework.
For example, Medieval Monks would work on memorization and practice singing. Ancient philosophers would read and develop their teachings outside the classroom. While this might not sound like homework in the traditional form we know today, one could argue that these methods helped to form the basic structure and format.
So let’s turn to recorded history to try and identify who invented homework and when homework was invented.
Pliny the Younger
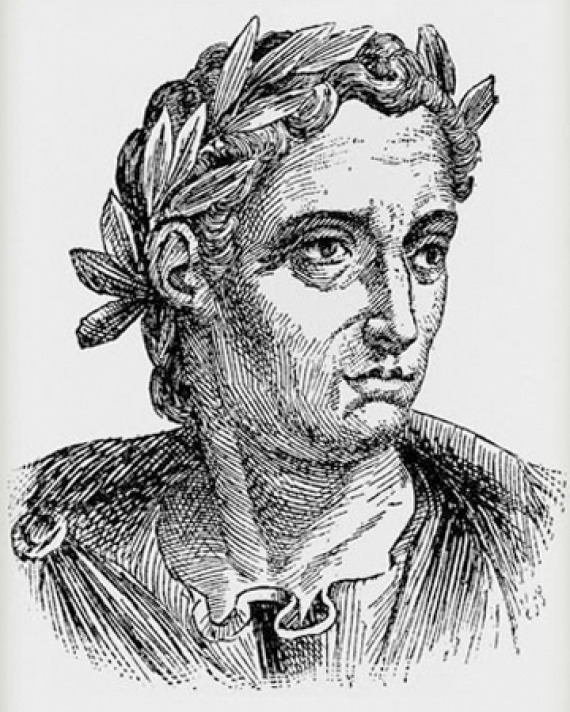

Credit: laphamsquarterly.org
We can trace the term ‘homework’ back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger (61—112 CE), an oratory teacher, often told his students to practice their public speaking outside class.
Pliny believed that the repetition and practice of speech would help students gain confidence in their speaking abilities.
Johann Gottlieb Fichte

Credit: inlibris.com
Before the idea of homework came to the United States, Germany’s newly formed nation-state had been giving students homework for years.
It wasn’t until German Philosopher Johann Gottlieb Fichte (1762—1814) helped to develop the Volksschulen (People’s Schools) that homework became mandatory.
Fichte believed that the state needed to hold power over individuals to create a unified Germany. A way to assert control over people meant that students attending the Volksshulen were required to complete assignments at home on their own time.
As a result, some people credit Fichte for being the inventor of homework.
Horace Mann
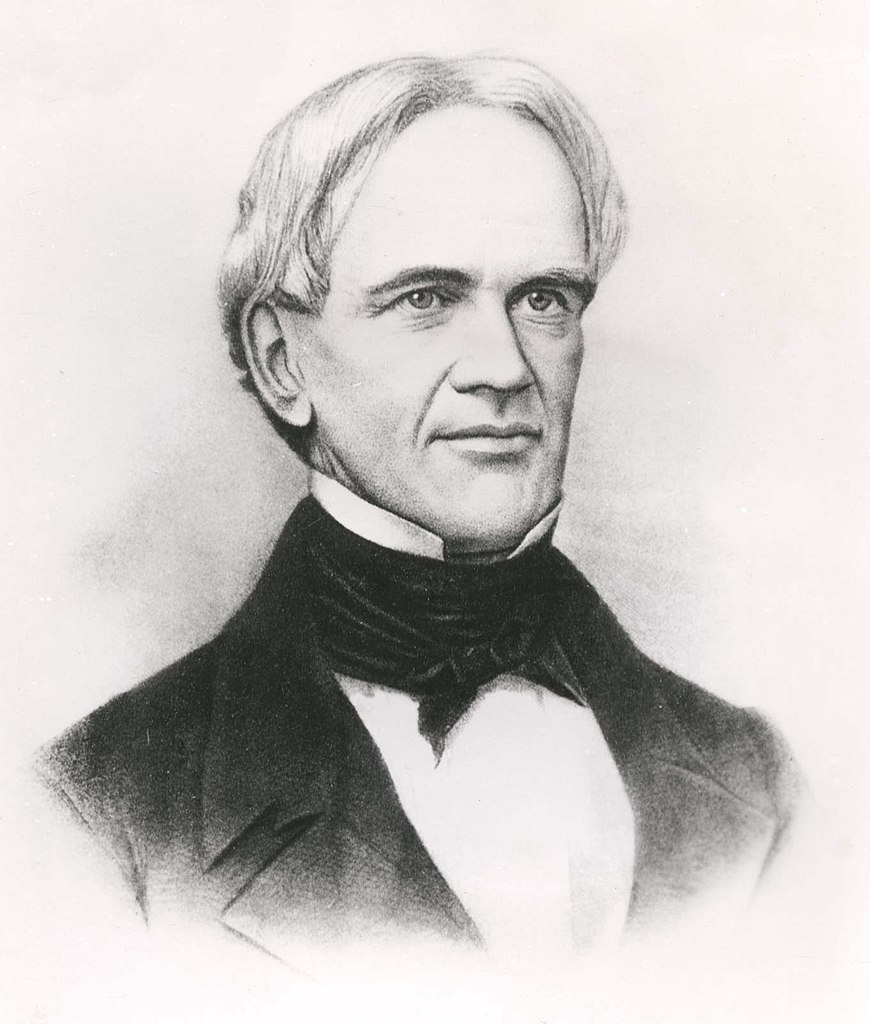

Credit: commons.wikimedia.org
The idea of homework spread across Europe throughout the 19th century.
So who created homework in the United States?
Horace Mann (1796—1859), an American educational reformer, spent some time in Prussia. There, he learned more about Germany’s Volksshulen and homework practices.
Mann liked what he saw and brought this system back to America. As a result, homework rapidly became a common factor in students’ lives across the country.

Credit: medium.com
If you’ve ever felt curious about who invented homework, a quick online search might direct you to a man named Roberto Nevilis, a teacher in Venice, Italy.
As the story goes, Nevilis invented homework in 1905 (or 1095) to punish students who didn’t demonstrate a good understanding of the lessons taught during class.
This teaching technique supposedly spread to the rest of Europe before reaching North America.
Unfortunately, there’s little truth to this story. If you dig a little deeper, you’ll find that these online sources lack credible sources to back up this myth as fact.
In 1905, the Roman Empire turned its attention to the First Crusade. No one had time to spare on formalizing education, and classrooms didn’t even exist. So how could Nevilis spread the idea of homework when education remained so informal?
And when you jump to 1901, you’ll discover that the government of California passed a law banning homework for children under fifteen. Nevilis couldn’t have invented homework in 1905 if this law had already reached the United States in 1901.

Inside Creative House/Shutterstock.com
When it comes to the origins of homework, looking at the past shows us that there isn’t one person who created homework. Instead, examining the facts shows us that several people helped to bring the idea of homework into Europe and then the United States.
In addition, the idea of homework extends beyond what historians have discovered. After all, the concept of learning the necessary skills human beings need to survive has existed since the dawn of man.
More than 100 years have come and gone since Horace Mann introduced homework to the school system in the United States.
Therefore, it’s not strange to think that the concept of homework has changed, along with our people and culture.
In short, homework hasn’t always been considered acceptable. Let’s dive into the history or background of homework to learn why.
Homework is Banned! (The 1900s)
Important publications of the time, including the Ladies’ Home Journal and The New York Times, published articles on the negative impacts homework had on American children’s health and well-being.
As a result, California banned homework for children under fifteen in 1901. This law, however, changed again about a decade later (1917).
Children Needed at Home (The 1930s)
Formed in 1923, The American Child Health Association (ACHA) aimed to decrease the infant mortality rate and better support the health and development of the American child.
By the 1930s, ACHA deemed homework a form of child labor. Since the government recently passed laws against child labor , it became difficult to justify homework assignments.

Studio Romantic/Shutterstock.com
A Shift in Ideas (The 1940s—1950s)
During the early to mid-1900s, the United States entered the Progressive Era. As a result, the country reformed its education system to help improve students’ learning.
Homework became a part of everyday life again. However, this time, the reformed curriculum required teachers to make the assignments more personal.
As a result, students would write essays on summer vacations and winter breaks, participate in ‘show and tell,’ and more.
These types of assignments still exist today!
Homework Today (The 2000s)
In 2022, the controversial nature of homework is once again a hot topic of discussion in many classrooms.
According to one study , more than 60% of college and high school students deal with mental health issues like depression and anxiety due to homework. In addition, the large number of assignments given to students takes away the time students spend on other interests and hobbies. Homework also negatively impacts sleep.
As a result, some schools have implemented a ban or limit on the amount of homework assigned to students.
Test your knowledge and check out these other facts about homework:
- Horace Mann is also known as the ‘father’ of the modern school system (read more about Who Invented School ).
- With a bit of practice, homework can improve oratory and writing skills. Both are important in a student’s life at all stages.
- Homework can replace studying. Completing regular assignments reduces the time needed to prepare for tests.
- Homework is here to stay. It doesn’t look like teachers will stop assigning homework any time soon. However, the type and quantity of homework given seems to be shifting to accommodate the modern student’s needs.
- The optimal length of time students should spend on homework is one to two hours. Students who spent one to two hours on homework per day scored higher test results.

Ground Picture/Shutterstock.com
The U.S. Department of Education provides teachers with plenty of information and resources to help students with homework.
In general, teachers give students homework that requires them to employ four strategies. The four types of homework types include:
- Practice: To help students master a specific skill, teachers will assign homework that requires them to repeat the particular skill. For example, students must solve a series of math problems.
- Preparation: This type of homework introduces students to the material they will learn in the future. An example of preparatory homework is assigning students a chapter to read before discussing the contents in class the next day.
- Extension: When a teacher wants to get students to apply what they’ve learned but create a challenge, this type of homework is assigned. It helps to boost problem-solving skills. For example, using a textbook to find the answer to a question gets students to problem-solve differently.
- Integration: To solidify the learning experience for students, teachers will create a task that requires the use of many different skills. An example of integration is a book report. Completing integration homework assignments help students learn how to be organized, plan, strategize, and solve problems on their own.
Ultimately, the type of homework students receive should have a purpose, be focused and clear, and challenge students to problem solve while integrating lessons learned.
What’s the Purpose of Homework?

LightField Studios/Shutterstock.com
Homework aims to ensure students understand the information they learn in class. It also helps teachers to assess a student’s progress and identify strengths and weaknesses.
For example, teachers use different types of homework like book reports, essays, math problems, and more to help students demonstrate their understanding of the lessons learned.
Does Homework Improve the Quality of Education?
Homework is a controversial topic today. Educators, parents, and even students often question whether homework is beneficial in improving the quality of education.
Let’s explore the pros and cons of homework to try and determine whether homework improves the quality of education in schools.
Homework Pros:
- Time Management Skills : Assigning homework with a due date helps students to develop a schedule to ensure they complete tasks on time.
- More Time to Learn : Students encounter plenty of distractions at school. It’s also challenging for students to grasp the material in an hour or less. Assigning homework provides the student the opportunity to understand the material.
- Improves Research Skills : Some homework assignments require students to seek out information. Through homework, students learn where to seek out good, reliable sources.
Homework Cons:
- Reduced Physical Activity : Homework requires students to sit at a desk for long periods. Lack of movement decreases the amount of physical activity, often because teachers assign students so much homework that they don’t have time for anything else.
- Stuck on an Assignment: A student often gets stuck on an assignment. Whether they can’t find information or the correct solution, students often don’t have help from parents and require further support from a teacher.
- Increases Stress : One of the results of getting stuck on an assignment is that it increases stress and anxiety. Too much homework hurts a child’s mental health, preventing them from learning and understanding the material.
Some research shows that homework doesn’t provide educational benefits or improve performance.
However, research also shows that homework benefits students—provided teachers don’t give them too much. Here’s a video from Duke Today that highlights a study on the very topic.
Homework Today
Maybe one day, students won’t need to submit assignments or complete tasks at home. But until then, many students understand the benefits of completing homework as it helps them further their education and achieves future career goals.
Before you go, here’s one more question: how do you feel about homework? Do you think teachers assign too little or too much? Get involved and start a discussion in the comments!
The picture on the front page: Evgeny Atamanenko/Shutterstock.com

Every parent wants to see their child happy and successful in their life. However, are…

An aggressive child is not uncommon in the modern world. Unfortunately, for many parents this…

For many, the start of fall marks a period of significant change—the transition to a…
Subscribe now!
Glad you've joined us🎉🎉.

Who Invented Homework and Why

Who Invented Homework
Italian pedagog, Roberto Nevilis, was believed to have invented homework back in 1905 to help his students foster productive studying habits outside of school. However, we'll sound find out that the concept of homework has been around for much longer.
Homework, which most likely didn't have a specific term back then, already existed even in ancient civilizations. Think Greece, Rome, and even ancient Egypt. Over time, homework became standardized in our educational systems. This happened naturally over time, as the development of the formal education system continued.
In this article, we're going to attempt to find out who invented homework, and when was homework invented, and we're going to uncover if the creator of homework is a single person or a group of them. Read this article through to the end to find out.
Who Created Homework and When?
The concept of homework predates modern educational systems, with roots in ancient Rome. However, Roberto Nevilis is often, yet inaccurately, credited with inventing homework in 1905.Depending on various sources, this invention is dated either in the year 1095 or 1905.
The invention of homework is commonly attributed to Roberto Nevilis, an Italian pedagog who is said to have introduced it as a form of punishment for his students in 1905. However, the concept of homework predates Nevilis and has roots that go back much further in history.
The practice of assigning students work to be done outside of class time can be traced back to ancient civilizations, such as Rome, where Pliny the Younger (AD 61–113) encouraged his students to practice public speaking at home to improve their oratory skills.
It's important to note that the idea of formalized homework has evolved significantly over centuries, influenced by educational theories and pedagogical developments. The purpose and nature of homework have been subjects of debate among educators, with opinions varying on its effectiveness and impact on student learning and well-being.
It might be impossible to answer when was homework invented. A simpler question to ask is ‘what exactly is homework?’.
If you define it as work assigned to do outside of a formal educational setup, then homework might be as old as humanity itself. When most of what people studied were crafts and skills, practicing them outside of dedicated learning times may as well have been considered homework.
Let’s look at a few people who have been credited with formalizing homework over the past few thousand years.
Roberto Nevilis
Stories and speculations on the internet claim Roberto Nevilis is the one who invented school homework, or at least was the first person to assign homework back in 1905.
Who was he? He was an Italian educator who lived in Venice. He wanted to discipline and motivate his class of lackluster students. Unfortunately, claims online lack factual basis and strong proof that Roberto did invent homework.
Homework, as a concept, predates Roberto, and can't truly be assigned to a sole inventor. Moreover, it's hard to quantify where an idea truly emerges, because many ideas emerge from different parts of the world simultaneously or at similar times, therefore it's hard to truly pinpoint who invented this idea.
Pliny the Younger
Another culprit according to the internet lived a thousand years before Roberto Nevilis. Pliny the Younger was an oratory teacher in the first century AD in the Roman Empire.
He apparently asked his students to practice their oratory skills at home, which some people consider one of the first official versions of homework.
It is difficult to say with any certainty if this is the first time homework was assigned though because the idea of asking students to practice something outside classes probably existed in every human civilization for millennia.
Horace Mann
To answer the question of who invented homework and why, at least in the modern sense, we have to talk about Horace Mann. Horace Mann was an American educator and politician in the 19th century who was heavily influenced by movements in the newly-formed German state.
He is credited for bringing massive educational reform to America, and can definitely be considered the father of modern homework in the United States. However, his ideas were heavily influenced by the founding father of German nationalism Johann Gottlieb Fichte.
After the defeat of Napoleon and the liberation of Prussia in 1814, citizens went back to their own lives, there was no sense of national pride or German identity. Johann Gottlieb Fichte came up with the idea of Volkschule, a mandatory 9-year educational system provided by the government to combat this.
Homework already existed in Germany at this point in time but it became a requirement in Volkschule. Fichte wasn't motivated purely by educational reform, he wanted to demonstrate the positive impact and power of a centralized government, and assigning homework was a way of showing the state's power to influence personal and public life.
This effort to make citizens more patriotic worked and the system of education and homework slowly spread through Europe.
Horace Mann saw the system at work during a trip to Prussia in the 1840s and brought many of the concepts to America, including homework.
Who Invented Homework and Why?
Homework's history and objectives have evolved significantly over time, reflecting changing educational goals. Now, that we've gone through its history a bit, let's try to understand the "why". The people or people who made homework understood the advantages of it. Let's consider the following:
- Repetition, a key factor in long-term memory retention, is a primary goal of homework. It helps students solidify class-learned information. This is especially true in complex subjects like physics, where physics homework help can prove invaluable to learning effectively.
- Homework bridges classroom learning with real-world applications, enhancing memory and understanding.
- It identifies individual student weaknesses, allowing focused efforts to address them.
- Working independently at their own pace, students can overcome the distractions and constraints of a classroom setting through homework.
- By creating a continuous learning flow, homework shifts the perspective from viewing each school day as isolated to seeing education as an ongoing process.
- Homework is crucial for subjects like mathematics and sciences, where repetition is necessary to internalize complex processes.
- It's a tool for teachers to maximize classroom time, focusing on expanding understanding rather than just drilling fundamentals.
- Responsibility is a key lesson from homework. Students learn to manage time and prioritize tasks to meet deadlines.
- Research skills get honed through homework as students gather information from various sources.
- Students' creative potential is unleashed in homework, free from classroom constraints.
Struggling with your Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Who Invented Homework: Development in the 1900s
Thanks to Horace Mann, homework had become widespread in the American schooling system by 1900, but it wasn't universally popular amongst either students or parents.
The early 1900s homework bans
In 1901, California became the first state to ban homework. Since homework had made its way into the American educational system there had always been people who were against it for some surprising reasons.
Back then, children were expected to help on farms and family businesses, so homework was unpopular amongst parents who expected their children to help out at home. Many students also dropped out of school early because they found homework tedious and difficult.
Publications like Ladies' Home Journal and The New York Times printed statements and articles about the detrimental effects of homework on children's health.
The 1930 child labor laws
Homework became more common in the U.S. around the early 1900s. As to who made homework mandatory, the question remains open, but its emergence in the mainstream sure proved beneficial. Why is this?
Well, in 1930, child labor laws were created. It aimed to protect children from being exploited for labor and it made sure to enable children to have access to education and schooling. The timing was just right.
Speaking of homework, if you’re reading this article and have homework you need to attend to, send a “ do my homework ” request on Studyfy and instantly get the help of a professional right now.
Progressive reforms of the 1940s and 50s
With more research into education, psychology and memory, the importance of education became clear. Homework was understood as an important part of education and it evolved to become more useful and interesting to students.
Homework during the Cold War
Competition with the Soviet Union fueled many aspects of American life and politics. In a post-nuclear world, the importance of Science and Technology was evident.
The government believed that students had to be well-educated to compete with Soviet education systems. This is the time when homework became formalized, accepted, and a fundamental part of the American educational system.
1980s Nation at Risk
In 1983 the National Commission on Excellence in Education published Nation at Risk:
The Imperative for Educational Reform, a report about the poor condition of education in America. Still in the Cold War, this motivated the government in 1986 to talk about the benefits of homework in a pamphlet called “What Works” which highlighted the importance of homework.
Did you like our Homework Post?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
Who Invented Homework: The Modern Homework Debate
Like it or not, homework has stuck through the times, remaining a central aspect in education since the end of the Cold War in 1991. So, who invented homework 😡 and when was homework invented?
We’ve tried to pinpoint different sources, and we’ve understood that many historical figures have contributed to its conception.
Horace Mann, in particular, was the man who apparently introduced homework in the U.S. But let’s reframe our perspective a bit. Instead of focusing on who invented homework, let’s ask ourselves why homework is beneficial in the first place. Let’s consider the pros and cons:
- Homework potentially enhances memory.
- Homework helps cultivate time management, self-learning, discipline, and cognitive skills.
- An excessive amount of work can cause mental health issues and burnout.
- Rigid homework tasks can take away time for productive and leisurely activities like arts and sports.
Meaningful homework tasks can challenge us and enrich our knowledge on certain topics, but too much homework can actually be detrimental. This is where Studyfy can be invaluable. Studyfy offers homework help.
All you need to do is click the “ do my assignment ” button and send us a request. Need instant professional help? You know where to go now.
Frequently asked questions
Who made homework.
As stated throughout the article, there was no sole "inventor of homework." We've established that homework has already existed in ancient civilizations, where people were assigned educational tasks to be done at home.
Let's look at ancient Greece; for example, students at the Academy of Athens were expected to recite and remember epic poems outside of their institutions. Similar practices were going on in ancient Egypt, China and Rome.
This is why we can't ascertain the sole inventor of homework. While history can give us hints that homework was practiced in different civilizations, it's not far-fetched to believe that there have been many undocumented events all across the globe that happened simultaneously where homework emerged.
Why was homework invented?
We've answered the question of "who invented homework 😡" and we've recognized that we cannot pinpoint it to one sole inventor. So, let's get back to the question of why homework was invented.
Homework arose from educational institutions, remained, and probably was invented because teachers and educators wanted to help students reinforce what they learned during class. They also believed that homework could improve memory and cognitive skills over time, as well as instill a sense of discipline.
In other words, homework's origins can be linked to academic performance and regular students practice. Academic life has replaced the anti-homework sentiment as homework bans proved to cause partial learning and a struggle to achieve conceptual clarity.
Speaking of, don't forget that Studyfy can help you with your homework, whether it's Python homework help or another topic. Don't wait too long to take advantage of expert help when you can do it now.
Is homework important for my learning journey?
Now that we've answered questions on who created homework and why it was invented, we can ask ourselves if homework is crucial in our learning journey.
At the end of the day, homework can be a crucial step to becoming more knowledgeable and disciplined over time.
Exercising our memory skills, learning independently without a teacher obliging us, and processing new information are all beneficial to our growth and evolution. However, whether a homework task is enriching or simply a filler depends on the quality of education you're getting.

Debunking the Myth of Roberto Nevilis: Who Really Invented Homework?
- By Emily Summers
- February 18, 2019
For those of us who have attended a formal education setting, you might remember the frustration of getting homework from most of your teachers. Before class ends, your teacher instructs your class to answer a certain page of your book or to write an essay about the topic you had just discussed.
Some of us really didn’t like doing homework. It was very time-consuming and, on top of extra-curricular activities, house chores, and other tasks you needed to do, you had very little time to yourself and your hobbies before having to go to sleep.
If you’ve ever been curious enough to find out who to thank for inventing homework, Google and several websites will tell you that it’s a man named Roberto Nevilis. That he invented homework as a form of punishment for underperforming students and, almost a thousand years later, billions of students are frustrated both at school and at home because of him.
But that, like a lot of things on the internet, simply isn’t true. In fact, Roberto Nevilis doesn’t even exist.
Who Invented Homework? Not Roberto Nevilis.
The nail in the coffin, a brief history on the education system, the father of modern homework, is homework still effective.
Online, there are many articles claiming that Roberto Nevilis was the first educator who came up with giving students homework. But if you look at the websites that claim this, you’ll find that it’s mostly forum websites or obscure educational blogs. No credible website or news source even mentions the name Roberto Nevilis. And for a guy who has affected the educational career of anyone who has had a formal education, you’d think a credible website would mention him at least once. Or some of the less-credible websites would confirm his contribution without saying the word “allegedly” or a vague “scientists believe” or the like.

Nevilis was supposedly a teacher based in Venice, Italy when he invented homework. Some claim that he invented it in 1095, while others claim he invented it in 1905 before it spread to Europe and to the rest of the world. It was said to be a form of punishment for students who underperformed in class. Students who performed well in class were spared from homework.
Either way, this claim is dubious. In 1095, education was still very informal around Europe and an organized education system in the continent didn’t start until 800 years later. In the 1500’s, English nobility were still being taught by private tutors.
Around 1095, the Roman Empire had long fallen and the Pope was still organizing the very first crusade and education was still informal, so it would be impossible for Nevilis to not only hold a class and give out homework, but to also spread out his idea to the rest of Europe when there was still no organized educational system.
And it couldn’t have been 1905, either. In 1901, California passed an act that banned homework for students younger than 15 years old before the law was revoked in 1917. That means Nevilis – assuming he does exists and isn’t the work of some internet trolls – couldn’t have invented it in 1905 in Europe if it already made its way to California and probably the rest of the world four years earlier.
And if that’s not enough evidence, just take a look at all the information you can get on him online. The only websites that mention his name: Quora, WikiAnswers, clickbait articles, and blogs for websites that help you write your homework (though if they can’t do their research properly, you might want to stay away from their services).
There’s no credible website mentioning him anywhere. And the websites that do mention him are very vague in describing his contribution. “Scientists believe” becomes a very sketchy claim when a website doesn’t cite a credible source. And if you try to search “Roberto Nevilis,” only the same handful of websites show up.
The truth is, homework existed dating back to the earliest civilizations and the first forms of education. In feudal times, education was reserved for the wealthy men. Those who weren’t rich had no time to study reading or philosophy and were busy making a living. Wealthy young women were trained in the more womanly arts, though princesses and nobles were expected to know a few things and were tutored as well. While they weren’t given workbooks and links to online quizzes, their tutors had expected them to read literary pieces during their free time.

The earliest evidence of a formal school comes from the Sumerian civilization. They had Edubas, which were houses of clay tablets were scribes practiced how to read and write. Archaeologists found student exercises etched into the tablets. Not much is known if they followed a schedule or were all taught by one teacher like the education system today.
During these times, however, homework did not involve answering questions or writing down essays as we’ve come to know it today. If we look back at history, there were other forms of educational methods that students and teachers at the time would have considered the homework of their time.
While we can’t pin the invention of homework to a certain teacher, we can trace back who was responsible for making homework that way it is to this day: Johann Gottlieb Fichte, a German philosopher known as the founding father of German nationalism.

In 1814, Prussia had a problem stirring nationalism among its citizens. Instead of serving the country after the war, citizens could choose to go back to whatever they were doing without thinking of dedicating their time and sacrifice to the country. There was no sense of pride or nationalism.
And so, Fichte conceived the Volkschule – a mandatory nine-year education similar to primary and lower secondary education provided by the state – and a Realschule – a secondary school available to aristocrats. Those attending the Volkschule were given the homework we know today as a way to demonstrate the state’s power even during personal time.
The system spread across Europe, but not in a totally dominating way. Some countries continued with their own system, which is why countries such as Finland don’t impose homework on their students. However, in 1843, back when the United States still practiced private tutors or informal lessons, Horace Mann reformed public education after travelling to Prussia and saw their education system and adapted it into the American education system. Thus, homework eventually evolved into a global practice.
Homework, therefore, is the result of nationalism and getting students to understand that “me time” actually falls on government time if they want to get their education. Contrary to what many websites would say, it wasn’t invented as a punishment for academically failing students.
However, over 200 years had passed since homework’s evolution into what we know it is today. So, is it still necessary to keep our students burdened with extra assignments? On one hand, it can be a good way to teach students time management skills. We like to think that work stays at work and personal life stays out of work, but as working adults, we know this is not the case. Homework at an early age teaches students to use their time wisely.
And while homework can still be helpful in students’ education, it’s only helpful to a certain extent. When plenty of teachers pile on homework, they’re depriving students of time to focus on their extra-curricular activities and personal life.

For those of us who have graduated with high grades, we’ve learned the hard way that a spotless report card can get our foot on the door, but if we have poor interpersonal skills and lack the skills you can only get outside of academics, you can’t achieve total success. Homework is good, but only to an extent. Then, it just becomes an unnecessary burden on students.
In fact, if you look at Finland and Japan – countries that don’t practice giving out homework – you can see that homework is unnecessary if the educational system favors it. Finland has shorter school days, longer summer breaks, and have an educational system where students aren’t required to start school until the age of seven. However, their students have always ranked high in terms of exams.
It’s because in Finland, a teaching career is at the same league as doctors and lawyers. Compare that to our current education system, where teachers are underappreciated and harried in public schools. Finland’s education system allows students more leeway, showing how it is possible to produce bright students without putting too much pressure on them.
We’ve all been frustrated with homework back when we were studying, but homework is actually more than just a nuisance we all have to face in our educational career. It’s actually an important factor which can shape productivity and the time students have for other factors of their education.
About the Author
Emily summers.

3 qualities of excellent early childhood education program teachers

What Puzzles and Logic Puzzles Benefit Your Brain

Take a Tour of an Adolescent Eating Disorder Treatment Center

9 Subjects You Could Study in College

Is the D Important in Pharmacy? Why Pharm.D or RPh Degrees Shouldn’t Matter

How to Email a Professor: Guide on How to Start and End an Email Conversation

Everything You Need to Know About Getting a Post-Secondary Education

Grammar Corner: What’s The Difference Between Analysis vs Analyses?


Home » who invented homework
Who Invented Homework?
Roberto Nevilis invented homework in the year 1095 in Venice after being disappointed in his students. Roberto Nevilis began to give homework in order to help the students learn and master the material he was teaching in Italy.
Anyone who has ever been a student has also wonder who invented homework. Indeed, we may all at one point or another yelled out that question in frustration . In such instances, the question is usually rhetorical, but who actually invented homework?
“A genius is a talented person who does his homework.” — Thomas Edison
Like most things we take for granted and hardly ever question, homework is not something natural or the inevitable part of life that it has become over the years. There was a time when the concept did just not exist.
Most people see homework as both an essential and inevitable part of education. But that was not always like that.
The Inventor of Homework
Homework, as we understand it today, goes as far back as 1095. Venetian educator Roberto Nevilis gets the credit for introducing homework as part of education. It seems likely, however that homework was used even before Nevilis’s time. The reason why Nevilis gets the credit is that he is the earliest example that there is evidence of.
It is safe to say that homework began at the same moment that formal education was introduced . It must be noted that until historically recently formal education was not something that most people had access to.
Indeed, at the time when Roberto Nevilis was giving his students homework, only the children of wealthy parents (or, indeed, wealthy adults themselves). As formal educations spread across nations and through people who belonged to different social classes, so did homework.
Homework in the USA
You may be wondering how something like homework , that originated in the 11 th century Venice came to be a part of everyday life for teachers and students alike in the United States.
The answer is that homework only became part of the US educational system in the 20 th century.
“I like a teacher who gives you something to go home and think about besides homework.” — Lily Tomlin
But the introduction of homework was gradual and with some pains associated with it. Until the turn of the 20 th century, not just homework but education, in general, had a very bad press in America.
Although this may seem incredible to us from a 21st-century perspective, education was not very highly valued by most people until well into the 20 th century. In order to understand this, you have to think about how society and the economy worked for most of America’s history. Children were needed at home or at work because they helped )and were expected to help) support their families as much as adults did. Remember that we do not get the concept of teenagers until, at least, the 1950s. Before that, the distance between childhood and adulthood was a lot shorter than it is now, and there was no in-between transitional period between the two.
In fact, children were expected to work (at home and elsewhere) as soon as they had enough strengths. This was not the case just in America but also in Canada, Latin America, Europe and many other parts of the world at the time. Shocking as it may seem to us, what we now consider child labor was actually the norm not that long ago. The exception to this was, of course, the children of wealthy parents.
But this started to change in the USA and in other countries in the 20 th century.
Even when kids had some form of schooling in the 20th century, still homework was not usually given to them as to not interfere with their home activities. In California , for instance, homework was abolished in 1901 by the State legislature .
When Did Attitudes to Homework Begin To Change?
It was not the introduction of schooling in the 20 th century that change negative attitudes toward homework.
It would not be until after World War II that people’s attitudes toward homework slowly began to change. And you can thank (or blame) the Cold War for.
“I feel sorry for kids these days. They get so much homework. Remember the days when we put a belt around our two books and carried them home? Now they’re dragging a suitcase. They have school all day, then homework from six until eleven. There’s no time left to be creative.” — Tom Petty
The Cold War is the name by which we refer to a long period of political hostility between the capitalistic Western (led by the United States) and the socialist Eastern bloc (led by the USSR ) that lasted between the end of World War II and 1990.
The Cold War was an era characterized by a profound mistrust between the United States and the Soviet Union. Both global superpowers sought to assert their influence in other parts of the world and constantly competed in areas such as science, sport, technology, etc. Each wanted to prove that their model for the economy and society was superior to the other.
You may be wondering what that could possibly have to do with homework. The Cold War increased the need for scientists in the United States. So, a renewed emphasis was placed on education (particularly, higher education) and in science and related subjects. The USSR had made huge advances in education and in the USA, it felt that keeping up was the way forward. Studying hard and using homework became part of the educational ideals in America.
This has had a lasting impact because, by the end of the Cold War period in 1990, homework had become such an important part of the educational experience in the US that most people considered it part and parcel of education.
But, how effective is homework? There are studies pointing in different directions. While some of them make claims about the effectiveness of homework, others actually advise against it.
“Homework should never replace a teaching opportunity in the classroom.” — Doug Yakich
Having said all that, there is a clear trend to increase the amount of homework particularly young children need to do. Some studies even talk about homework more than doubling in the last 30 years or so.
The time that needs to be devoted to completing daily homework can be as much as 90 minutes to 2 hours, which some studies actually considered detrimental to learning.
Whoever invented homework probably did not have that much time in mind!
← Previous post
Next post →
Related Posts

The Edvocate
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- Write For Us
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Assistive Technology
- Best PreK-12 Schools in America
- Child Development
- Classroom Management
- Early Childhood
- EdTech & Innovation
- Education Leadership
- First Year Teachers
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Special Education
- Parental Involvement
- Policy & Reform
- Best Colleges and Universities
- Best College and University Programs
- HBCU’s
- Higher Education EdTech
- Higher Education
- International Education
- The Awards Process
- Finalists and Winners of The 2022 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2021 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2020 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2019 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2018 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2017 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Award Seals
- GPA Calculator for College
- GPA Calculator for High School
- Cumulative GPA Calculator
- Grade Calculator
- Weighted Grade Calculator
- Final Grade Calculator
- The Tech Edvocate
- AI Powered Personal Tutor
How to Set Up and Start Using a Cash App Account
Jazz research questions, interesting essay topics to write about japanese culture, good research topics about japanese art, jane eyre essay topics, most interesting invisible man essay topics to write about, most interesting jaguar essay topics to write about, most interesting jackson pollock essay topics to write about, good essay topics on italian renaissance, good research topics about islamophobia, who invented homework.

Homework is a part of life for children, parents, and educators. But who came up with the concept of homework? What happened to make it a standard in education? Here’s a quick rundown of homework’s history in the United States .
Homework’s Origins: Myth vs. History
Who was the first person to invent homework? We may never know for sure. Its history has been shaped by a variety of persons and events. Let’s start with two of its key influencers.
The Dubious Roberto Nevelis of Venice
Homework is typically credited to Roberto Nevelis of Venice, Italy, who invented it in 1095—or 1905, depending on your sources. However, upon closer examination, he appears to be more of an internet legend than a genuine figure.
Horace Mann
Horace Mann, a 19th-century politician and educational reformer, was a pivotal figure in the development of homework. Mann, like his contemporaries Henry Barnard and Calvin Ellis Stowe, was passionate about the newly unified nation-state of Germany’s obligatory public education system.
Mandatory tasks were assigned to Volksschulen (“People’s Schools”) students to complete at home on their own time. When liberals like Johann Gottlieb Fichte were striving to organize support for a unified German state, this demand highlighted the state’s authority over the individual. While homework had been established before Fichte’s participation with the Volksschulen, his political goals can be considered a catalyst for its adoption as an educational requirement.
Horace Mann was a driving force behind creating government-run, tax-funded public education in America. During a journey to Germany in 1843, he witnessed the Volkschule system at work and brought back several of its ideals, including homework.
The American Public School System’s Homework
Homework has not always been generally embraced, despite being a near-universal element of the American educational experience. Parents and educators continue to dispute its benefits and drawbacks, as they have for more than a century.
The 1900s: Anti-homework sentiment and homework bans
A homework prohibition was enacted in the Pacific state of California in 1901, barely a few decades after the idea of homework crossed the Atlantic. The restriction, which applied to all students under the age of 15, lasted until 1917.
Around the same period, renowned magazines such as the Ladies’ Home Journal and The New York Times published remarks from parents and medical professionals portraying homework as harmful to children’s health.1930: Homework as Child Labor
A group called the American Child Health Association deemed homework a form of child labor in 1930. This statement represented a less-than-favorable view of homework as an appropriate educational method, given that laws barring child labor had recently been implemented.
Early-to-Mid 20th Century: Homework and the Progressive Era
Teachers began looking for ways to make homework more personal and meaningful to individual students throughout the second half of the 19th and 20th-century modern educational changes. Could this be the origin of the enduring essay topic, “What I Did on My Summer Vacation?”
The Cold War: Homework Heats Up
Following WWII, the Cold War heightened tensions between the United States and Russia in the 1950s. The flight of Sputnik 1 in 1957 increased Russian-American enmity, particularly among their youngsters.
The best way to ensure that American students did not fall behind their Russian counterparts, especially in the extremely competitive fields of science and mathematics, was for education officials in the United States to assign demanding homework.
The 1980s: A Nation at Risk’s Homework
What Works, a 1986 publication from the US Department of Education, listed homework as one of the most effective instructional tactics. This followed three years after the groundbreaking study
Early 21st Century: Homework Bans Return
Many educators and other concerned individuals are questioning the value of homework once again. On the subject, several publications have been published.
These include:
- The Case Against Homework: How Homework Is Hurting Our Children and What We Can Do About It by Sarah Bennett and Nancy Kalish (2006)
- The Battle Over Homework: Common Ground for Administrators, Teachers, and Parents (Third Edition) by Duke University psychologist Dr. Harris Cooper (2007)
- The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning by education professor Dr. Etta Kralovec and journalist John Buell (2000)
Homework is still a contentious topic nowadays. Some schools are enacting homework bans similar to those enacted at the start of the century. Teachers have varying opinions on the bans, while parents attempt to cope with the disruption to their daily routine that such bans cause.
Flipped Classroom: Everything You Need to Know
25 black history month activities.
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.
The A-Z of Education Blogs: Letters S-TC

21 Ways to Teach Students to Finish Sentences and Express Complete Thoughts When Writing

Pass or Fail: The Need for Alternative Strategies

16 Apps that Support the Creative Process

20 of the Best Virtual Reality Games in Education

22 Tips for Edtech Companies
Who Invented Homework? The Origins and Development
October 18th, 2023 — 5 min read
The origins of Homework dates back to ancient Greece and Rome. It is said that Roberto Nevelis, an Italian teacher, invented homework in 1905, but so far there is no credible historical evidence to support this, which makes it become an Internet myth. Pliny the Younger, Johann Gottlieb Fichte, and Hausmann are the most likely true inventors of homework.
I. Introduction
When it comes to homework, what is on your mind? Excited or struggling?Some people enjoy doing homework and challenging themselves with hard questions; Others dislike homework and struggle with it, considering that homework deprives them of their spare time. Whether you like it or not, homework is an essential part of our learning and growth.
For teachers, homework is a way to help students to consolidate knowledge, develop critical thinking skills, and improve problem-solving ability etc. As students, we might not view homework like our teachers, and maybe just complete homework to avoid punishment.
So we've all been doing homework since we were kids. Have you ever wondered who invented homework? This blog will elaborate on the origins and development of homework. Let's take a look at who started the journey of homework, and who made homework became a daily task for students.
II. Historical Background
Before tracing the origins of homework, let us ponder a question: was homework born at the same time as education? The answer is no. Education has a long history that can be traced back to ancient times. In the early stages, homework is not a part of educational system. Before writing was invented, people mainly passed on the values, traditions and life skills to the next generation through oral teaching. However, the advent of writing further developed the spread of civilization and diversified the ways of education.

There is no homework in early education, so how do students consolidate their learning? In the ancient Greek city-states, private education was prevalent. Students in Athens discussed, debated, and thought in study groups organized by philosophers or scholars to further reinforce knowledge. Students would participate in various public presentations to access their learning outcomes and broaden their horizons and thinking. In addition, by participating in all kinds of practical activities, such as museum visits, art exhibitions, and sports activities, students can apply what they have learned to real-life situations. Therefore, although there was no homework at that time, students could enhance their understanding and application of learning in a variety of ways.
With the continuous development of society, education gradually developed from social and family education to formal schooling, with professional people specialized in teaching subject knowledge and skills. So who invented homework? When did homework appear?
III. Inventors and Key Figures of Homework
1.roberto nevelis.

2.Pliny The Younger

3.Johann Gottlieb Fichte
So who invented homework? Johann Gottlieb Fichte,the German philosopher, was probably the true inventor of homework. He was not only the father of German nationalism, but also contributed and influenced the education of Germany. He helped develop people's schools, making mass schools and compulsory education an innovation at that period. The state provided education for students and also infiltrated patriotism into students' lives and encouraged them to contribute to the country.
Fichte's educational ideas had a profound influence on German education at that time. His ideas were widely adopted and implemented in the German education system, so that homework became an important part of students' learning.

4.Horace Mann
Horace Mann, a 19th-century American educator and politician, was often credited as a key figure in the development of homework. After graduating from Brown University, he actively supported education reform while serving as the state education secretary. He was regarded by many historians as the "father of American public education" and devoted himself to the educational system.
Mann not only engaged with teachers, but also participated in many public education presentations and visited other schools in and out of the state. While visiting schools in Europe, he was inspired by the Prussian education system and decided to reform education in Massachusetts, one of which was homework. He believes that homework can help students consolidate what they learn in class and develop the ability to learn independently and solve problems.

So, what about the future of homework in the United States?
IV.Brief History of Homework in the US
Early 20th century: the rise of the homework ban.
In the 19th century, while economic development was limited, most children in the United States dropped out of elementary school to ease the burden on their families. With the increasing development of society, more and more children can receive basic secondary education, but some problems about homework appear at the same time. Many parents are tired of helping their children with homework and even think that school work has no meaning.


1920s and 1930s: The Ban was Intensified
Under the influence of the homework ban, primary and secondary schools in big cities in the United States have made a series of reform measures to protect the physical and mental health of preschool children. Public schools in New York are prohibited from assigning homework to students in grades one through three. San Diego, California, bans homework for elementary and middle school students in grades 1 through 8. Chicago bans all public elementary and secondary schools from assigning homework to students at any grade level.
1950s: In response to the Cold War, Homework Returned
In 1957, the launch of the Soviet Union's Sputnik satellite brought a huge shock to the United States, and also changed the American concept of education. For 50 years, the United States had little homework, putting it at a competitive disadvantage against the Soviet Union. However, the incident galvanized the urgent need for educational reform in the U.S. government and educational institutions, including a reevaluation and reform of homework. Teachers began to provide students with targeted assignments to meet each student's learning needs. Assignments have also become more challenging and practical to help students consolidate what they have learned and expand their thinking and application skills.
Early 2000s: Homework Attracted Great Attention
In the early 1980s, the United States government organized a special committee to investigate the learning level of American students, and the survey results were very painful for Americans. That is, the basic education in the United States is poor, 23 million adults do not have enough literacy. The results of the survey triggered wide attention and discussion, and the US government and educational institutions took a series of measures to improve basic education, including improving the salary and training level of teachers, requiring teachers to assign more personalized tasks, and ensuring the improvement of teaching quality and student learning outcomes.
Looking at the history of homework in the United States, we can see from the introduction of homework to the promulgation of homework bans, to the re-strengthening of homework. The homework not only had a positive impact, but also triggered negative voices. Around the world, homework has been a controversial topic. Does it do more good than harm? Or does it do more harm than good? Let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of homework.
V. Homework: Pros and Cons
When we talk about the pros and cons of homework, we should focus on the amount of homework assigned.
Proper Amount of Homework
1.Improve the quality of school education By assigning homework, students can consolidate the knowledge learned in class, deepen the understanding and application of knowledge, enhance the learning effect, and the quality of school education will also be improved.
2.Expand students' knowledge and improve students' learning skills Through homework, students can further expand their learning, accumulate more knowledge, and improve learning skills such as reading, writing, problem solving etc. 3.Promote students' independence and sense of responsibility By completing homework independently, students can improve their self-management skills and independent thinking. At the same time, the completion of homework also requires students to have a sense of responsibility and complete the task on time, which is very important for the growth and development of students.

Excessive Homework
1.Lead to lack of sleep and affect students' health Long hours of assignment writing will leave students without enough time for rest, which is bad for students' physical and mental health.
2.Putting too much pressure on students Students need to bare academic pressure under heavy homework tasks, which may lead to anxiety and boredom of students.
3.Deprive students of their spare time Students need enough time for rest, recreation and other interests, which are very important for their well-rounded development. Too much homework may leave students no time to participate in other activities and limit their room for development.
4.Lead to cheating Too much homework may lead to cheating. When students are faced with too much homework pressure, they may look for other ways to complete the homework, such as copying or having someone write it for them. Such behavior not only violates academic ethics, but also weakens students' learning effect and ability
VI.Conclusion
You may not have thought and explored who invented homework, but I believe you have been crazy about homework. From birth to development, homework has experienced the baptism of the long river of history, and also continues to develop from time to time. Although homework once aroused the resistance of parents and students, it has to be admitted that homework plays a key role in consolidating knowledge and improving ability in our learning process. What do you think of homework? Do you think homework should be born?
With the rapid progress and development of science and technology, many countries continue to combine science and technology with education, and launch a variety of educational products to meet the learning needs of students in the new era. When it comes to homework, the use of technology has also opened up many new possibilities. While you may still be used to writing your homework with a pen and paper, or typing your answers on a computer, now is the time to try StudyX , a tool dedicated to providing a whole new way of doing homework. What is the innovation in it? Try it and you'll see!
Related Posts
Assignment Writing
Unlocking Efficiency: Mastering Assignment Writing on StudyX with Insider Tips
In the fast-paced world of academia, as a college student, are you always find yourself juggling multiple courses, extracurricular activities, and personal commitments? Among the many challenges you face, one critical aspect must be the art of assignment writing. Normally, you could dive into libraries, scouring through countless books and journals, or turning to online resources and tutorials, all in the hope of extracting the information needed for the essays, reports, or other kinds of assignments.

Homework-Efficiency
Empowering College Students to Enhance Homework Efficiency
StudyX, which stands for Study Infinity. We are committed to enhancing the efficiency of college students' homework. We are about equipping you with the tools you need to supercharge your homework efficiency and overcome the challenges you encounter with inefficient homework completion. In this article, you'll delve into how StudyX

Encyclopedia of Innovators and Innovations
- Social Innovations
Who Invented Homework? Tracing the Origins and Innovators

Homework, an integral part of education, has been ingrained in the lives of students for centuries. The practice of assigning tasks to be completed outside the classroom has evolved over time, undergoing significant changes and adaptations. Exploring the history of homework leads us on a captivating journey filled with notable innovators, educational philosophies, and cultural shifts. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the origins of homework, uncovering the minds behind its inception, and highlighting key milestones along the way.
- Ancient Roots and Early Influences:
a. Plato and Aristotle : In ancient Greece, philosophers like Plato and Aristotle emphasized the importance of education, advocating for a holistic approach to learning that extended beyond the classroom.
b. Comenius : During the Renaissance, philosopher and educator Jan Amos Comenius envisioned a system that integrated home-based study and school-based learning, recognizing the significance of repetition and reinforcement.
c. Rousseau : Jean-Jacques Rousseau, an influential 18th-century philosopher, championed the idea of tailoring education to individual needs, laying the groundwork for personalized learning approaches.
- The Advent of Modern Homework:
a. Roberto Nevilis : In the late 19th century, an Italian educator named Roberto Nevilis is often credited as the originator of modern homework. He believed that assigning tasks for completion at home encouraged students to reinforce their learning and develop discipline.
b. Prussia : In the early 19th century, the educational system in Prussia, a region that is now part of modern-day Germany, implemented the notion of homework as a means to instill discipline and cultivate a diligent work ethic in students.
c. United States : In the United States, the implementation of homework gained traction during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, as the nation sought to strengthen its education system. Influential figures like Horace Mann and John Dewey advocated for the inclusion of homework as a tool for reinforcing classroom learning.
- Educational Philosophies and Homework:
a. Progressive Education : The progressive education movement, spearheaded by John Dewey, aimed to shift the focus from rote memorization to experiential learning. Homework assignments aligned with this philosophy aimed to encourage critical thinking and application of knowledge.
b. Behaviorism : Behaviorism, championed by psychologists like B.F. Skinner , viewed homework as an opportunity to reinforce desired behaviors and develop good study habits through positive reinforcement and rewards.
c. Constructivism : The constructivist approach, influenced by educators such as Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky , emphasized hands-on learning experiences and student-centered activities. Homework assignments aligned with constructivism focused on fostering independent thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Technological Advancements and Homework:
a. Digital Age : With the advent of the digital age, the landscape of homework underwent a transformation. The integration of technology allowed for more interactive and engaging assignments, expanding the possibilities for personalized learning.
b. Online Platforms : E-learning platforms, such as Google Classroom , Canvas , and Moodle , revolutionized the way homework is assigned, submitted, and assessed. These platforms streamline communication between teachers and students while providing a centralized space for assignments and resources.
c. Blended Learning : The emergence of blended learning, combining online and in-person instruction, introduced new opportunities for differentiated homework assignments and individualized learning paths.
Origins of Homework: Myth vs. History

Contrary to popular belief, the concept of homework did not emerge in the modern era but can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Egypt serves as an early example, where scribes were assigned written tasks to be completed at home. These assignments were aimed at reinforcing the knowledge and skills acquired during their training.
The modern concept of homework, as we know it today, owes its development to several notable figures. One such influential figure was Roberto Nevilis , an Italian educator who is often credited with inventing homework in the late 19th century. Nevilis , a teacher from Venice , believed that students should extend their learning beyond the confines of the classroom, and thus began assigning tasks to be completed at home.
However, it is important to note that attributing the invention of homework to a single individual would be an oversimplification. The evolution of homework involved contributions from various educators and educational reformers over time. Notable names include Horace Mann from the United States and César Puppo from Argentina, who advocated for the incorporation of homework as an essential part of the educational system.
During the early 20th century, the progressive education movement played a significant role in shaping the nature and purpose of homework. Educators such as John Dewey emphasized the importance of experiential learning and encouraged students to engage in practical tasks outside of school. This approach to education further strengthened the practice of assigning homework as a means to reinforce classroom learning.
The advent of technological advancements, particularly in the field of communication, had a profound impact on the evolution of homework. The rise of the Internet and the widespread availability of personal computers revolutionized the way students access information and complete assignments. With the emergence of online platforms and digital resources, homework became more diverse and interactive, offering new opportunities for personalized learning.
Homework practices vary across different countries and cultures. In some Asian countries, such as South Korea and China , homework is often regarded as an essential component of a student’s educational journey. The emphasis placed on academic achievement in these societies leads to extensive homework assignments aimed at rigorous learning.
Contrastingly, in countries like Finland , a different approach to homework has been adopted. Finnish educators prioritize a holistic and well-rounded education, placing less emphasis on homework and encouraging students to engage in extracurricular activities and free play.
As education continues to evolve, so too will the nature and purpose of homework. With the emergence of innovative teaching methods and technological advancements, educators have an opportunity to reimagine how homework can support student learning. Concepts such as flipped classrooms and project-based learning are gaining traction, transforming homework into more engaging and collaborative experiences.
Pliny the Younger and Homework:

Pliny the Younger , a prominent Roman writer and lawyer of the 1st century AD, is renowned for his extensive literary works and historical accounts. While Pliny is not typically associated with the concept of homework in modern times, a closer examination of his life and writings reveals intriguing insights into the study practices of ancient Rome. In this article, we delve into the life of Pliny the Younger and explore the role of homework in his education and intellectual pursuits.
Born as Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus in Como, Italy , in 61 AD, Pliny the Younger belonged to a privileged family with strong connections to the Roman elite. Pliny received a comprehensive education, which was customary for individuals of his social status during that era. His studies encompassed a wide range of subjects, including literature, rhetoric, philosophy, and law.
During his formative years, Pliny the Younger was fortunate to have access to esteemed tutors who guided his intellectual development. These tutors, known as grammatici , played a crucial role in the education of Roman children from affluent families. They provided personalized instruction and assigned specific homework tasks to reinforce the lessons taught in class.
Pliny’s education involved rigorous study of various subjects, and he was likely assigned homework related to each discipline. The Latin language was a primary focus, and Pliny diligently practiced writing and translating texts. Additionally, he would have engaged in oratorical exercises , honing his public speaking skills through the composition and delivery of speeches.
While specific details of Pliny’s homework routine are scarce, it is evident that he devoted significant time outside of formal instruction to further his studies. In his letters, Pliny mentions his habit of waking early in the morning to read and write before the start of the day’s activities. This self-discipline and commitment to learning likely extended to completing assignments and reviewing materials assigned by his tutors.
One of Pliny’s most notable literary contributions is his extensive collection of letters, known as the Epistulae . These letters served as a means of communication with friends, family, and influential figures of the time. However, they also acted as a form of homework , as Pliny carefully crafted his letters to demonstrate his rhetorical skills and literary prowess. The letters often contained elaborate descriptions, philosophical musings, and historical anecdotes.
Pliny’s educational experiences were not unique to him alone. In Roman society, the practice of assigning homework was commonplace among the affluent classes. Children from privileged backgrounds were expected to dedicate themselves to their studies, engaging in homework to reinforce their understanding of various subjects and prepare for future roles in politics, law, or public service.
Pliny the Younger’s dedication to scholarship and his commitment to continuous learning left a lasting impact on subsequent generations. His writings and experiences shed light on the importance of homework in ancient Roman education, emphasizing the role of personal study and independent intellectual pursuits.
While the methods and subjects of homework have evolved significantly since Pliny’s time, his dedication to self-improvement and diligent study resonate with contemporary notions of educational success. Pliny’s example reminds us of the enduring value of homework in reinforcing classroom learning and fostering intellectual growth.
Homework As a Punishment? Debunking the Myth

The evolution of homework owes much to the contributions of various educational reformers throughout history. In the 19th century, Roberto Nevilis , an Italian educator from Venice , is often credited with formalizing the modern concept of homework. Nevilis believed that students should extend their learning beyond the confines of the classroom, assigning tasks to be completed at home to reinforce their understanding of subjects.
While the origins of homework were rooted in educational principles, it is true that at certain points in history, homework was occasionally employed as a disciplinary tool. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, some educators resorted to using homework as a means to punish students for misbehavior or poor academic performance. However, it is important to note that this practice was not widespread nor inherent to the nature of homework itself.
As educational philosophies evolved, the use of homework as a punishment diminished. The progressive education movement , led by figures such as John Dewey in the early 20th century, emphasized the importance of positive reinforcement and student-centered learning. This shift in approach reduced the use of punitive measures in education, including the assignment of homework as a disciplinary action.
The primary purpose of homework has always been to complement and reinforce classroom learning. Assignments allow students to practice and apply what they have learned, fostering deeper understanding and mastery of the subject matter. Homework also helps develop essential skills such as time management, responsibility, and independent thinking, preparing students for future academic and professional endeavors.
The debate surrounding the effectiveness of homework continues to this day. Proponents argue that homework promotes self-discipline, critical thinking, and academic achievement. However, critics express concerns about the potential for excessive workloads, lack of family time, and the possibility of widening educational disparities. Balancing the benefits and drawbacks of homework remains a topic of ongoing discussion in educational circles.
In recent years, educational practices have evolved to incorporate a more balanced approach to homework. Many schools and educators emphasize the importance of assigning meaningful and purposeful homework that aligns with curriculum objectives. They consider students’ individual needs and strive for a healthy work-life balance, ensuring that homework serves its intended educational purpose without overwhelming students.
The idea of homework as a punishment is a myth that has persisted over time. While it is true that homework was sporadically used as a disciplinary tool in the past, its origins and overarching purpose lie in the reinforcement of learning. Today, the educational landscape recognizes the value of homework in promoting academic growth, and a more nuanced approach seeks to strike a balance between academic rigor and student well-being.
Confucius – First Teacher:

Confucius , also known as Kong Qiu or Kongzi, is widely regarded as one of the most influential thinkers and educators in Chinese history. Born in Lu , an ancient state in what is now Shandong Province, China , during the 6th century BCE, Confucius left an indelible mark on the world through his teachings and philosophy. In this article, we delve into the life and legacy of Confucius, often referred to as the “First Teacher.”
Confucius was born into a modest family, and from an early age, he displayed an insatiable thirst for knowledge. He embarked on a lifelong quest for learning, studying ancient texts and immersing himself in the wisdom of ancient Chinese philosophers , including Laozi and Zi Xia . Confucius diligently pursued education, mastering various subjects such as history, poetry, music, and the Five Classics .
Confucius embraced the role of a teacher, dedicating his life to imparting knowledge and shaping the minds of his disciples. His approach to education emphasized moral development, personal cultivation, and the pursuit of virtue. Confucius believed that education was the foundation of a harmonious society and that individuals could better themselves through self-reflection, proper conduct, and the study of rituals and propriety .
Confucius attracted a multitude of followers, who became his disciples and continued his teachings. Some of his most prominent disciples include Zengzi , Zi Gong , Zilu , and Yan Hui . Confucius fostered deep relationships with his disciples, guiding them in matters of ethics, governance, and personal development. Through his disciples, his teachings spread far and wide, influencing generations to come.
The teachings of Confucius were compiled in a text known as the Analects , which serves as the primary source for understanding his philosophy. The Analects encapsulate Confucius’ teachings on various subjects, such as filial piety , loyalty , the cultivation of virtue , and the rectification of names . Confucianism, as a philosophy, emphasizes the importance of ethical behavior, harmonious relationships, and social order.
Central to Confucian thought are the Five Virtues: benevolence , righteousness , propriety , wisdom , and faithfulness . Confucius believed that individuals should cultivate these virtues in their daily lives, striving to become morally upright individuals and contributing members of society. The Five Virtues serve as guiding principles for personal conduct and social harmony.
Confucius ‘ influence extended far beyond his own lifetime. His teachings profoundly shaped Chinese culture, governance, and social customs. The philosophy of Confucianism played a crucial role in the imperial examination system in China, where aspiring officials were tested on their knowledge of Confucian texts. Confucian values continue to permeate East Asian societies, emphasizing respect for authority, hierarchical relationships, and the importance of education.
Roberto Nevelis – Father of Homework:

Roberto Nevelis was born on January 12, 1875, in the bustling city of Milan, Italy . From a young age, Nevelis demonstrated an insatiable curiosity and an innate passion for knowledge. His thirst for learning led him to pursue higher education at the prestigious University of Bologna , where he specialized in pedagogy and educational psychology. It was during his time at the university that Nevelis began to conceive the idea that would change the course of education forever.
Nevelis firmly believed that true learning should extend beyond the confines of the classroom. Inspired by the works of influential philosophers and educators like Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi and John Dewey, he recognized the need for students to engage in independent study to reinforce and deepen their understanding of the subjects they were taught. This realization gave birth to what we now know as homework .
Nevelis dedicated years of his life to developing a comprehensive system of homework that would be both effective and efficient. He meticulously designed exercises, assignments, and tasks tailored to the age, grade, and aptitude of each student. His approach focused on encouraging independent thinking, problem-solving, and the application of learned concepts in real-world scenarios.
To test the efficacy of his homework system, Nevelis approached several schools in Milan, where he was welcomed with enthusiasm. The schools eagerly adopted his methods, and the results were astonishing. Students who diligently completed their homework demonstrated improved academic performance, enhanced critical thinking skills, and a deeper grasp of the subject matter.
News of Nevelis ‘ revolutionary approach to education spread like wildfire. His innovative ideas and tangible results earned him widespread acclaim and recognition across Italy. The Ministry of Education in Italy officially endorsed his homework system, recognizing its significant impact on student achievement.
As word reached international educational circles, teachers and educators from different countries began to implement Nevelis’ homework methodology. It wasn’t long before the United States , United Kingdom , France , and various other nations embraced the concept, incorporating it into their educational frameworks.
Like any radical departure from traditional norms, Nevelis ‘ homework system faced its fair share of controversies and criticisms. Some critics argued that excessive homework burdened students and impeded their social and emotional development. Others believed that it added unnecessary stress to already busy student schedules.
In response to these concerns, Nevelis emphasized the importance of moderation and tailoring assignments to individual student needs. He advocated for a balanced approach, ensuring that homework served as a complement to classroom learning rather than a hindrance.
Horace Mann – The First School:

Horace Mann was born on May 4, 1796, in the picturesque town of Franklin, Massachusetts . Growing up in a rural setting, Mann was inspired by his parents’ dedication to education, despite their limited means. Their commitment fueled his passion for learning, leading him to attend Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island. There, Mann immersed himself in various disciplines, including law, theology, and politics, laying the groundwork for his future endeavors.
Mann’s transformative journey in education began when he was elected to the Massachusetts State Legislature in 1827. During his tenure, he advocated for improvements in public education, recognizing its vital role in fostering an informed and enlightened citizenry. Inspired by the educational philosophies of Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi and Henry Barnard , Mann resolved to reshape the educational landscape.
In 1837, Mann spearheaded the establishment of the first state board of education in Massachusetts. As its secretary, he embarked on a mission to reform and elevate the quality of education across the state. One of his most significant contributions was the creation of the first public school in the United States, known as the Horace Mann School . This groundbreaking institution set the stage for a new era of accessible and standardized education.
Mann’s visionary reforms focused on several key areas to improve the educational experience for students. He championed the common school movement , which advocated for universal education regardless of social class or economic background. Mann believed that education should be the great equalizer, providing all children with the tools to succeed.
Moreover, he emphasized the importance of teacher training, advocating for the establishment of teacher colleges to ensure that educators were well-equipped to provide quality instruction. Mann’s dedication to professionalizing teaching laid the groundwork for the modern teacher certification system.
Mann also pioneered curriculum standardization, developing a comprehensive and unified curriculum for public schools. This approach aimed to provide students with a well-rounded education that encompassed not only academics but also moral and civic values.
Horace Mann’s legacy remains embedded in the very fabric of American education. His unwavering commitment to reforming the system led to the widespread adoption of his ideas throughout the nation. Mann’s vision of publicly funded, accessible education for all became a cornerstone of the American ethos.
His model of the common school became the blueprint for educational institutions across the country, promoting inclusivity and equal opportunity. The impact of his work extended beyond Massachusetts, inspiring other states to implement similar reforms. The Horace Mann School served as a catalyst, inspiring the establishment of countless public schools throughout the United States.
Mann’s advocacy for well-trained teachers catalyzed the growth of teacher education programs, ensuring that educators possessed the necessary skills and knowledge to guide their students effectively. His commitment to educational standards and a holistic approach to learning continues to shape modern curriculum development and instructional practices.
Mr. Henry Fischel – Pioneering Exams:

Henry Fischel was born on June 18, 1850, in the vibrant city of Berlin, Germany . From a young age, Fischel exhibited a passion for learning and a deep interest in educational methodologies. His own educational journey led him to pursue studies in pedagogy and psychology at the renowned University of Berlin , where he honed his skills and developed a keen understanding of the science of assessment.
Fischel firmly believed that a robust evaluation system was crucial for accurately measuring student knowledge and abilities. Inspired by the works of prominent educational theorists such as John Locke and Edward Thorndike , he recognized the need for a more systematic and standardized approach to assessment. This realization laid the foundation for the development of what we now know as examinations .
Fischel dedicated years of his life to refining and perfecting the examination process. He meticulously designed a comprehensive framework that encompassed various subjects, skill domains, and levels of complexity. Fischel’s approach aimed to measure not only rote memorization but also critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical abilities.
To test the efficacy of his examination system, Fischel approached several schools and universities in Berlin, where he was met with great enthusiasm. Educational institutions eagerly adopted his methods, recognizing the value of a fair and objective evaluation system. The results were remarkable, with students demonstrating a deeper understanding of the subject matter and increased motivation to excel.
Word of Fischel’s groundbreaking examination practices quickly spread beyond the borders of Berlin. Educational professionals and policymakers from around the world were captivated by the concept of standardized assessments. The University of Cambridge in the United Kingdom was among the first to adopt Fischel’s examination system, recognizing its potential to provide a rigorous and unbiased evaluation of students’ knowledge.
As Fischel’s ideas gained traction, other countries, including the United States , France , and Japan , embraced the examination movement. Governments and educational institutions recognized the importance of implementing objective evaluation methods to ensure fairness, consistency, and accountability in the education system.
Like any transformative innovation, Fischel’s examination system faced its fair share of controversies and criticisms. Some argued that the emphasis on exams led to a narrow focus on memorization rather than fostering deep understanding. Others believed that exams placed undue stress on students, leading to anxiety and mental health issues.
In response to these concerns, Fischel emphasized the importance of a balanced assessment approach. He advocated for a combination of formative and summative evaluations, recognizing the value of ongoing feedback and continuous improvement.
Demerits of Homework :
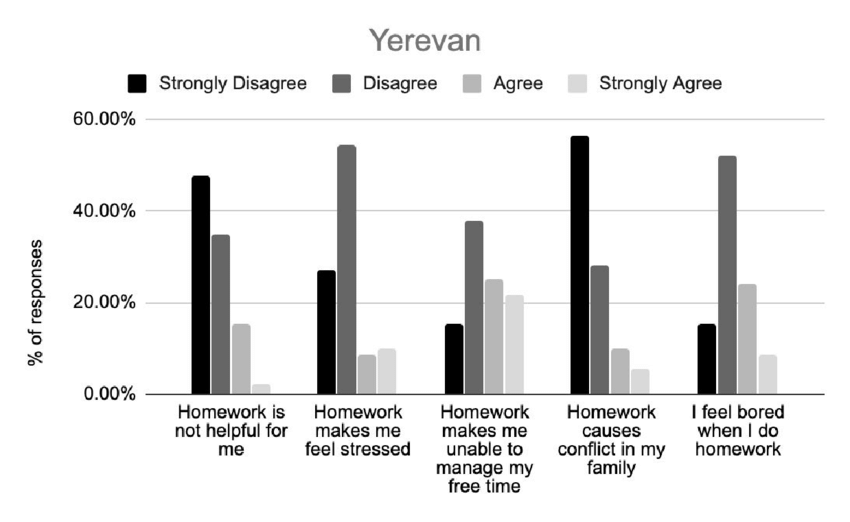
Homework as we know it today has a long history, dating back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Greece . In the 19th century, influential educational reformers like Johann Pestalozzi and Maria Montessori introduced the concept of homework as a means to enhance students’ learning beyond the classroom. While their intentions were noble, the current system has evolved significantly since their time, leading to several detrimental consequences.
The Overwhelming Workload
One of the primary demerits of homework lies in the overwhelming workload imposed on students. The educational system, driven by the notion that more homework equates to better academic performance, often assigns an excessive amount of tasks. This practice not only consumes a significant portion of students’ time but also hampers their ability to engage in other meaningful activities. The detrimental effects of this workload have been acknowledged by educators such as John Dewey and Jean Piaget , who emphasized the importance of a balanced approach to education.
Limited Creativity and Exploration
Homework often focuses on repetitive exercises and rote memorization, leaving little room for creativity and exploration. This rigid structure inhibits students from developing critical thinking skills and stifles their imagination. Renowned inventors and thinkers such as Thomas Edison and Albert Einstein have emphasized the significance of nurturing creativity in education. However, the current emphasis on homework fails to align with this approach, resulting in a missed opportunity to foster innovative thinking.
Detrimental Impacts on Mental Health
The excessive pressure and stress associated with homework can have detrimental effects on students’ mental health. Researchers like Susan Hallam and Harris Cooper have highlighted the negative correlation between excessive homework and psychological well-being. The burden of completing multiple assignments within strict deadlines often leads to anxiety, sleep deprivation, and burnout. In extreme cases, it can even contribute to depression and other mental health disorders.
Inequity in Access and Support
Another significant demerit of homework lies in the inequity it perpetuates. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds often lack access to necessary resources, including a quiet study space, educational materials, or parental support. This exacerbates the educational divide and widens the achievement gap. Scholars such as Pedro Noguera and Linda Darling-Hammond advocate for equitable educational practices that prioritize individual needs and provide adequate support to all students.
Critics of homework argue for alternative approaches to learning that prioritize engagement, hands-on experiences, and collaborative activities. Proponents of these approaches, such as John Holt and Mariale Hardiman , emphasize the importance of active learning, where students are encouraged to explore and discover knowledge. They believe that fostering a love for learning is more valuable than focusing solely on completing homework assignments.
Key Dates of Homework Invention :
- Ancient Civilizations and the Birth of Homework
The roots of homework can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Mesopotamia . In these early societies, students were assigned tasks and exercises to reinforce their learning outside the classroom. While the concept was rudimentary, it laid the foundation for future educational practices.
- The Influence of Greek Philosophers
During the Classical period in Greece, influential philosophers like Socrates , Plato , and Aristotle recognized the importance of practice and repetition in learning. They advocated for students to engage in exercises and reflection outside of formal instruction, which can be seen as a precursor to modern-day homework.
- The Renaissance and the Rise of Private Tutoring
With the advent of the Renaissance in the 14th century, education saw significant changes. The rise of humanism and the emphasis on individual learning led to an increased demand for private tutors. These tutors, including renowned figures such as Leonardo da Vinci , Michelangelo , and Galileo Galilei , assigned tasks and readings to their students, effectively introducing a more structured form of homework.
- Johann Pestalozzi and the Modernization of Homework
In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, Johann Pestalozzi , a Swiss educator, made significant contributions to the evolution of homework. Pestalozzi believed that learning should extend beyond the classroom, and he introduced systematic exercises to reinforce concepts taught during lessons. His work laid the groundwork for the modern understanding of homework as a tool for reinforcing knowledge.
- The Industrial Revolution and the Expansion of Education
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought about sweeping changes in society, including the expansion of education. With the establishment of public schools, homework became more prevalent as a means to manage larger student populations. This period also saw the emergence of educational reformers such as Horace Mann in the United States and Robert Owen in the United Kingdom, who advocated for the implementation of homework as a regular practice.
- Maria Montessori and Progressive Education
In the early 20th century, Maria Montessori , an Italian physician and educator, developed the Montessori Method, an alternative approach to education. Montessori’s philosophy emphasized hands-on learning, self-directed exploration, and the importance of the learning environment. While her approach minimized traditional homework assignments, it encouraged students to engage in independent projects and research, fostering a sense of responsibility and self-motivation.
- Digital Age and the Transformation of Homework
The advent of the digital age in the late 20th century brought about a new era in homework practices. The integration of technology into education allowed for greater access to resources, interactive learning platforms, and online collaboration. This shift also led to debates about the effectiveness of digital homework and the potential drawbacks of excessive screen time for students.
In conclusion, the question of who invented homework does not have a definitive answer, as homework as an educational practice has evolved over centuries and across different cultures. Its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations like Egypt and Mesopotamia , where students were assigned tasks outside the classroom. Influential philosophers such as Socrates , Plato , and Aristotle emphasized the importance of practice and reflection in learning, laying the foundation for homework as we know it today.
Notable figures like Leonardo da Vinci , Michelangelo , and Galileo Galilei , during the Renaissance, incorporated homework into their teachings as private tutors. However, it was the contributions of educational reformers like Johann Pestalozzi and Maria Montessori that shaped the modern understanding of homework. Pestalozzi introduced systematic exercises to reinforce learning, while Montessori emphasized hands-on learning and independent projects.
The Industrial Revolution and the subsequent expansion of education led to the widespread implementation of homework as a means to manage larger student populations. Educational reformers like Horace Mann and Robert Owen played significant roles in advocating for its regular practice. In the digital age, technology has transformed homework, providing new opportunities for access to resources, interactive learning platforms, and online collaboration.
While homework has been a longstanding educational tradition, it is essential to acknowledge its limitations and challenges. Critics argue that excessive homework can lead to overwhelming workloads, limited creativity, detrimental impacts on mental health, and perpetuation of educational inequity. Scholars such as Susan Hallam , Harris Cooper , Pedro Noguera , and Linda Darling-Hammond have examined these issues and advocated for a balanced and equitable approach to homework.
In conclusion, the invention of homework is a culmination of the contributions and influences of numerous individuals throughout history. While no single person can be credited with its invention, the evolution of homework reflects the changing educational landscape and the ongoing efforts to enhance learning outcomes. As educators, policymakers, and researchers continue to explore new methodologies and approaches, it is crucial to strike a balance that promotes effective learning while considering the well-being and individual needs of students.
References:
Cooper, H. (2001). Homework for all—In moderation. Educational Leadership, 58(7), 34-38. Darling-Hammond, L., & Ifill-Lynch, O. (2006). If they’d only do their work! Educational Leadership, 63(1), 8-13. Hallam, S. (2006). Homework: The evidence. London Review of Education, 4(3), 277-291. Mann, H. (1841). Seventh Annual Report to the Secretary of the Massachusetts Board of Education. Montessori, M. (1912). The Montessori method: Scientific pedagogy as applied to child education in “the children’s houses” with additions and revisions by the author. Noguera, P. A. (2003). City schools and the American dream: Reclaiming the promise of public education. Teachers College Press. Pestalozzi, J. H. (1831). How Gertrude Teaches Her Children: An Attempt to Help Mothers to Teach Their Own Children and an Account of the Method. Plato. (2010). The Republic. Oxford University Press. Socrates. (2010). The Last Days of Socrates: Euthyphro, The Apology, Crito, Phaedo.
Related Posts

Who Invented Google? The Evolution of Google
The Evolution of the Piano: Tracing the Inventors and Innovators
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Busting the Myth of Roberto Nevilis – Who Actually Invented Homework?
Homework is an indispensable piece of the instructive procedure in the American education system. It makes learning simpler and progressively powerful. However, all of us who have attended classes in an educational institute remember the frustration of hearing the word homework from our teacher’s mouth. Before the end of the class, we would be instructed to write an essay or answer a few questions on what we had just been taught.

I am sure many students must have been curious enough to try and find out which genius came up with the idea of homework. A student would have probably looked it up while struggling with a particular homework assignment. Who was it who believed that homework would magically transform the educational system overnight?
The search would have come with a man named Roberto Nevellis who invented homework to punish his students who did not perform at par with the others. But like many other things on the internet, this isn’t a fact. Thankfully students looking to master a subject, or require online homework help can connect with online tutors and homework help services.
Who was Roberto Nevilis?
There isn’t a single credible website or a news article about this man who changed the educational system all over the world. According to a lot of websites, Nevilis was a teacher in Venice and allegedly invented homework as a means of punishing students who did not perform well in class. Some sites claim the year was 1095 while others claim it was 1905.
Neither of these can a possibility. In the year 1095, there was no formal system of education in and around Europe. It was a time when Pope Urban II had just started preaching the First Crusade after the Byzantium delegation asked for his help against the Turks. I am sure Mr. Nevilis would have found it very hard to teach a class during those times, let alone hand out homework. Even in the year 1500, private tutors were employed to teach the English nobility.
It could not have been 1905 either because 4 years before that, in 1901, the state of California passed an act to ban homework for any child studying below the 8th grade. The law was passed because during that period homework was frowned upon by parents. They felt that homework interfered with a child’s time for house chores. Sweet times, right? Anyway, Mr. Nevilis couldn’t have been spreading the idea of homework telepathically before he started practicing it himself.
Ancient Education
Historically homework existed in one form or another ever since the inception of education in the earliest civilizations. Singing, poetry, playing instruments, even the study of the bible required reading and practice at home. In ancient times only the wealthy were educated because all the teachers taught privately.
The rest of the society was busy with making a living. The earliest evidence of education in formal settings comes from the Sumerian civilization. In the Sumerian society, schools were called Edubas where scribes learned how to read and write on cuneiform or clay tablets. However archaeological evidence only found the exercises etched in the tablets. There are no inscriptions about the educational system.
Father of the Homework System
While the label of homework inventor cannot be pinned on one person, Johann Gottlieb Fichte can be called the father of the modern homework system. Johann Gottlieb Fichte was a German philosopher and known to be the founding father of German nationalism. In the year 1814, the people of Prussia had lost their sense of nationalism. They are choosing to go back to their livelihood instead of serving the country after the war.
Johann Gottlieb Fichte came up with the concept of Volksschule and Realschule. Volksschule was a mandatory education system of nine years which was similar to primary and lower secondary school. Realschule was a secondary school system reserved for the aristocrats. Homework was a part of Volkschule to demonstrate the nation’s power on common people and stir up a sense of nationalism.
This system was slowly adopted all over Europe, although some countries like Finland continued with their system of education and refused to impose homework on the students. In 1843, Horace Mann , the secretary of the Massachusetts Board of Education then, went to Europe and visited the schools in Prussia. On his return, he presented his findings in the seventh annual reports of the board. These reports were reprinted all over the United States and led to the reform of the American educational system.
_______________________________________________________________
Interesting related article: “ Top schools to study business .”
Share this:
- Renewable Energy
- Artificial Intelligence
- 3D Printing
- Financial Glossary
The Story Behind The Myth That An Italian Teacher Roberto Nevilis Invented Homework

It's a necessary evil (or perhaps it's completely unnecessary — more on that in a moment) that has been bedeviling children and parents for generations: homework. Just check out any random parenting advice column and you'll see how much of a chore homework is for the parents and for the children. And even so, at least one parenting advice columnist is advising parents of younger children to not even volunteer to help unless specifically asked to do so.
But is homework one of those aspects of education, like sitting at a desk, that just developed organically over centuries of education? Or did one teacher or administrator come up with the idea? For about a century, a legend has stated that an Italian man named Roberto Nevilis came up with homework, and those in the know have been cursing his name for just as long. He even gets his own entry in Urban Dictionary . However, Nevilis is almost certainly a myth (or at the very least, the idea that he invented homework is a myth), and it looks like there's no one person to blame for the phenomenon.
Blame Horace Mann, Not Roberto Nevilis
As both Through Education and The Ed Advocate report, somehow a myth entered the world's collective consciousness that an Italian man named Roberto Nevilis invented homework. Some versions of the myth even add some context: It was intended to punish underperforming students and to reward those who excelled at their lessons. Some versions of the myth say that his invention dates to 1905, others that it dates to 1095 – an 800 year difference! There's supposedly a photograph of him on Twitter , with a caption claiming the year was 1095, which is a solid eight centuries before the invention of photography .
Needless to say, the Nevilis origin story is probably bunk. Putting aside the fact that he could have lived in either of two periods in history 800 years apart (and the 1095 origin story ignores some important facts about public education, including that it didn't exist at the time), the real indicator that his story is fictitious is that it exists only in question-and-answer forums and parenting blogs. On the rare occasions that someone attempts to cite it, it's always with vague words like "various sources" or "some say" or the like.
The real culprit is probably Horace Mann (his statue is above), and even he didn't come up with it. The American education advocate was inspired by a European system, according to Through Education, and it became more or less ubiquitous worldwide in the decades after he introduced it to the U.S.
Is Homework Necessary?
As mentioned previously, homework can be as bothersome for parents and families as it is for the children tasked with doing it, and for evidence, look no further than this 1999 Time article, " The Homework Ate My Family ." But is homework, like doing taxes, just one of those necessary evils that we all have to live with?
As it turns out, the jury is still out on the benefits of homework. For example, in 2019, Forbes highlighted several school districts across the country that have ditched homework, "citing research showing it doesn't do much to boost achievement," as the website notes. However, for a more thorough explanation of both sides of the issue we need look no further than ProCon which, as the website's name makes manifest, lays out the pros and cons of the matter. And in this case, there are points to be made on both sides. Some pros listed are that studies have shown homework increases student achievement and involves parents in the educational process, while studies have also shown that homework doesn't help younger students (while it may help older ones) and that it exacerbates the achievement gap.

Who Invented School Homework? [When, Where & How]
You can remember just sitting down and doing homework—no worries, no stress, and getting an A on your paper. School was the best time of your life. Ok, maybe that’s not true, but the point is you would always wonder who invented school homework.
The very first homework assignment can be traced all the way back to 1905 when an Italian teacher named Roberto Nevilis first invented the idea. He wanted his students to get used to thinking for themselves, so he gave them assignments that would require them to look up information and use it in their work.
Whether you’re a student trying to get ahead, or a parent wondering about homework for your own children, this article will help you to get a better understanding of the whole story about homework.
Interested in who invented school tests? Let’s find out here.
What Was the Original Purpose of Homework?
Who invented math homework, who invented holiday homework, who invented summer homework, who invented homework meme, the invention of homework, why homework is bad for high school students, who was roberto novelis, why does homework exist, when was school homework first invented, was homework invented as a punishment, · performance of creative works (essay writing, etc.), · performance of written exercises, · mastering material under study according to the textbook, · performance of oral exercises, · the 1900s (anti-homework), · the 1930s (homework as child labor), · the 1980s, · early 21st century, school homework today, why does homework exist, is homework illegal in california, why do students dislike homework, why should homework be banned from schools, who invented school homework and why.

The person who invented school homework in 1905 is a man named Roberto Nevilis. He created this new way of learning to help students who were struggling with their lessons.
Nevills was passionate about education and had a special interest in how children learn best. He believed that children should be treated as individuals with unique abilities and needs.
He also believed that children should be encouraged to take responsibility for their own learning.
Nevilis realized that some of his students were not getting enough practice at home, so he decided to make a plan that would give them extra practice without them even knowing it.
He made up a booklet of questions for the students to answer about their lessons and gave it to them at the end of each day.
The next morning, he collected the booklets from his students and returned them with corrections and new questions for them to answer during recess.
This system became very popular with teachers all over Europe because it made learning more interesting for both students and teachers alike!
Homework is meant to reinforce what we have already learned during the day.
This can be seen through taking notes in class and then reviewing them after class by doing homework assignments.
This is the reason why many parents are against the idea of giving their children homework.
They believe that if their children did not do their homework, then they should not be punished for it.
The invention of math homework is credited to a man named Roberto Nevilis.
He was born in 1881, and he studied at the University of Rome.
While there, he became interested in mathematics and decided to pursue a career in teaching.
Math homework is a type of assignment that students are required to complete at home.
The purpose of this assignment is to help students learn the material they learn in class, and also to reinforce it.
Math homework can be completed on a variety of subjects, but one of the most common types is algebra and geometry.
The tradition of giving children holiday homework goes back to the 1920s.
It was thought to be a good way to keep children occupied over Christmas and New Year.
The practice became popular amongst schools in America and spread to Britain during World War II when many schools were evacuated to the countryside.
The practice continued after the war ended, but has since declined in popularity.
However, some schools still use it as a way of helping pupils keep up their grades during long periods away from school.
Read about the inventor of school uniforms .
In the 20th century, summer homework was invented to ensure that students did not forget what they learned during the school year.
Homework was a way for parents and teachers to ensure that students retained their knowledge.
Summer homework has been around for decades, but some parents don’t think it’s necessary. In fact, some argue that it’s harmful.
The debate over whether or not summer homework for school is good for children continues today.
Students may have different opinions about whether or not summer homework is necessary.
Some students enjoy being able to relax during the summer months and have time to do other activities.
Homework memes have become an internet sensation and the inventor is nowhere to be found.
The fact that the inventor of the homework meme is unknown adds to the mystery, making it more popular than ever.
The original source of the meme is unknown. It could be a high school student or even a college student.
Whoever it was, they definitely did not expect homework memes to become so popular.
The invention of homework is a bit complicated. Some say that Roberto Nevilis invented homework in the 20th century.
Others claim that it existed in Ancient Greece. However, most people agree that the Russians did make homework assignments first.
Homework was used as a way to teach children moral values and ethics .
Nevilis’ homework is said to be one of the most important inventions of all time.
It was an invention that revolutionized education and changed the way people think about learning.
It is said that he came up with this idea while working as a teacher in a local school in Greece.
One day after class, he found himself sitting alone in his room wondering if there was anything else he could do to help his students learn more effectively.
Who Invented Homework for Students?

The first person who invented school homework for students was Roberto Nevilis, an Italian teacher.
The idea behind homework was to improve students’ knowledge and, at the same time, to punish lazy students
He believed that if students were allowed to practice skills and concepts at home, their understanding of those things would be greater.
He also felt that homework could help teach responsibility and independence by giving students an opportunity to apply what they had learned in new situations outside of school.
Nevilis’ idea spread quickly throughout Europe and later to North America.
Today, homework is still used as a tool for teaching students important skills related to math, a science tutoring business, language arts, and more!
High school students are under a lot of pressure. Between preparing for college and dealing with the stress of being in high school, homework can be a huge burden for many students. Here are some reasons why homework is bad for high school students:
- It takes time away from other activities that are more important to them, like spending time with friends or practicing sports.
- Homework can cause stress, which can lead to mental health issues like depression or anxiety.
- Homework can lead to poor grades because it takes away from the time students have to study for tests and quizzes in class, which leads to lower grades on those tests and quizzes (and possibly even failure).
Many people wonder did Roberto Novelis invent homework. The answer is: YES.
Roberto Novelis was an Italian teacher who invented school homework. He was born in 1877 and died in 1957 at the age of 80.
Roberto was a teacher at the University of Padua in Italy, where he worked for 52 years.
One day, while he was teaching his students about algebraic equations, he realized that they did not understand what he was saying.
So instead of repeating himself and giving them more examples, he decided to give them homework instead.
Roberto wanted to see if it would help his students understand better if they practiced on their own time instead of during class time.
It worked! His students were able to practice at home until they understood what the lesson was about and could answer questions correctly when he gave them back their assignments later in class.
Why Was Homework Invented?
If you’re curious about why homework was invented you should know that initially homework was invented because of the need to strengthen students’ understanding of the lessons they were taught in class.
While some teachers used it as a punishment, others used it as a way to ensure that their students understood and embraced the lessons fully.
Homework was invented because of the need to strengthen students’ understanding of the lessons they were taught in class.
It was used to punish students who were not paying attention in class, or who could not pay attention due to other responsibilities.
Homework was also used as an extension of classroom learning, where the students are given an assignment that requires them to apply what they have learned by creating something new based on their knowledge base.
Homework exists because it’s a good way to practice what you’ve learned in class.
It also helps you learn how to study and manage your time, so when you go into the real world, you’ll be able to keep up with all the things you need to do.
It can help you identify gaps in your understanding of concepts, which can then be filled by another activity or lesson at home or in class.
Homework is a great way for teachers to see how well students are grasping their lessons, and it allows them to adjust their teaching methods as needed.
When Was School Homework Invented?
You might wonder when was homework invented. Well, the answer is that it wasn’t until the beginning of the 20th century.
In fact, it’s hard to imagine a world without schoolwork at all!
But before then, children were expected to spend their time doing things that were more useful for their families or communities.
But in the early 1900s, more and more people started going to school for longer periods.
And as more children went to school for longer periods, they needed additional assignments that would help them learn new concepts—and this was when homework became popularized!
In many schools homework was a part of the punishment for lazy and naughty students.
Nowadays, we don’t think twice about handing our kids assignments or asking them to do extra work at home. But remember: It wasn’t always like that!
To be even more precise, school homework was first invented in 1905 by an Italian teacher named Roberto Nevilis.
This practice spread to other countries and gained popularity.
Years after it was first invented, giving students homework every day became standard in most schools around the world.
The reason why this practice became so popular around the world was that it helped students learn more about the subjects they were studying and improve their grades, which in turn made them more likely to succeed in life.
Did you know that homework was originally invented as a form of punishment?
It’s true! The practice of assigning students homework began in the late 19th century when educators believed that children needed to be taught how to spend their free time productively.
It wasn’t until the late 20th century that researchers discovered the benefits of homework, and it became an essential part of classroom learning.
However, some experts believe that homework is counterproductive and harmful to students’ health.
According to them, take-home assignments are stressful and overburden students.
Types Of Homework
There are many types of homework you can do, and they all serve different purposes. Here are just a few of them:
Writing essays is one of the most effective ways for students to learn how to express themselves in writing style
Students should use their imagination and creativity when doing this type of homework. This type of homework helps students develop their imagination and creativity skills.
Students are given specific tasks, which they have to solve as part of their homework. Their task is to master the material under study according to the textbook and perform it in an exam or a test.
A student has an opportunity to perform oral exercises during his/her free time outside school.
If a student wants to participate in any kind of competition, he/she must practice his/her presentation skills as much as possible before participating in competitions.
History of Homework in Schools in America
Although homework is a mainstay of American education today, it hasn’t always been.
Take a look at the history of school homework in America.
Horace Mann introduced homework to the American education system in 1848.
In 1901, just a few decades after his introduction, homework was banned in the Pacific state of California.
In 1930, the American Child Health Association declared homework a form of child labor and said that it should be abolished because recent laws prohibiting such activities were passed at around the same time.
In its pamphlet, “What Works,” the Department of Education recommended homework as an effective strategy to boost the quality of education.
The report lambasted the state of American public education and called for reforms to right the alarming direction it was headed.
In America, education has changed dramatically since the 1800s.
Nowadays, many educators, students, parents, and other concerned citizens are asking why homework was invented and if it’s still valuable.
These days, looking at school homework is all about making sure that students can do the work they need to do to be college-ready.
Teachers want their students to think critically, resolve problems, and work collaboratively to prepare them for life after high school.
To accomplish this, teachers are shifting away from traditional methods of learning and grading and towards more modern methods of showing students what they need to improve upon.
This means that teachers are often looking at things like group projects, group discussions, and mini-lessons instead of individual tests or essays as ways for students to demonstrate their understanding of concepts.
If you have any questions you can first check this section. Here you can find some of the most common questions when it comes to this topic.
Homework exists to help you take control of your workload, increase your time management skills, and learn how to problem solve independently.
There are no laws against homework in California. In fact, many teachers and schools require students to do homework as part of their learning process.
Students dislike homework because they feel it takes too much time, is boring and pointless, and/or interferes with their social lives.
Research suggests a link between homework and mental health issues in young people, as well as poor academic performance. In middle schoolers, more than 90 minutes of homework per night is associated with lower test scores in math tutoring science.
In conclusion, Roberto Novelis, a man who invented school homework, improved the education system.
He created homework and it made teachers more accountable for what they teach their students.
What are your thoughts on homework? Do you believe that it is helping students or hurting them? Leave your thoughts in the comments below.
Who Invented Sign Language? [When, Where & How]
Who Invented High School? [When, Where & Why]

Uncovering the Past, Shaping the Future.
- [email protected]
- Privacy policy
- Terms of use
Copyright © 2024 Nevada investors

Turn Your Curiosity Into Discovery
Latest facts.

Tips and Tricks to Help You Create a HIPAA Compliant Email

How to Stop Facial Hair Growth in Females Naturally
Who invented homework.
Written by Fredrik
Modified & Updated: 23 Sep 2023
Reviewed by Sherman Smith
- Education Facts
- Learning Facts
- Research Facts

Homework is the bane of many students’ lives. Many would rather see it disappear as it takes away precious time that people would rather use for hobbies or family time. “Who invented homework ?” is something a student may have exclaimed at some point. And we understand the frustration.
For all the hate that homework gets, its origin is surprisingly unclear. If you search for “who invented homework?” online, you may see many results. Some claim that a specific person invented it, but these sources may not be very accurate. In this article, however, we will uncover the truth about homework’s origins. We’ll also dive a little bit into the age-old question of whether or not homework is actually effective.
The Origins of Homework Are A Bit Disputed
As mentioned earlier, homework has a bit of a mysterious history. The concept of asking students to do work after school may have been around as long as school has existed. On the other hand, it might not be that old. Its history may even depend on exactly how you define “homework”. What is sure is one thing. Like many things, it’s possible that homework doesn’t have a single inventor. Instead, the concept has many progenitors, some of whom thought of it independently.
Now you may be wondering: don’t some sites claim that homework has a single inventor? Don’t they credit homework to a certain Roberto Nevillis? Well, that’s what we’re going to discuss next.
Roberto Nevillis, the “Inventor” of Homework, May Not Have Actually Existed
If you search for “homework inventor” on Google, you may see several hits for a certain Roberto Nevillis. He was supposedly an Italian teacher, whom many websites claim invented homework. However, if you do some deeper research, you will realize that this information may be inaccurate.
The first warning sign is that the Wikipedia article for homework makes no mention of this Nevillis person. While it’s true that Wikipedia can be edited by anyone, it does have standards. Notably, important claims need sources; otherwise, editors will remove them. If he indeed invented homework, surely the article would mention him, with references even. But nope, no mention of him at all.
Another warning sign is that the sources that mention Nevillis even disagree on when he came up with the concept. Some claim he invented it in 1905, which seems really recent. Other sources claim that he instead invented it in 1095. That makes little sense either considering how different education was at the time. Formal education was still a rarity in Europe in that era, especially among the lower classes. Since most lower classes who did receive education got them at home, technically all their studies were homework!
Indeed, if Nevillis did exist, information about his life seems almost non-existent. It’s entirely possible that no such person ever lived. In any case, if anyone did invent homework, it probably wasn’t Nevillis.
Homework Existed As Early As The Roman Empire
In reality, early concepts about “homework” may have already existed for centuries. Of course, this may not necessarily mean the homework we know today. However, this idea still encompasses activities like practicing or studying at home.
According to some writers, Pliny the Younger may have espoused an early form of “homework”. He encouraged students to improve their speaking skills outside formal education centers. For example, if the students were at home, they could hone their skills there. Obviously, speaking is more of physical activity than writing or reading . As such, practicing at home may not exactly be “homework”. Still, this shows that the idea of doing education-related work at home has been around for so long.
Johann Gottlieb Fichte May Have Invented Homework As We Know It
As for the “title” of the true inventor of homework, there are two people who have a good claim. One of them is Johann Gottlieb Fichte. Many historians consider him to be the father of German nationalism. Apart from his political life, he made some contributions to education. And unsurprisingly, these contributions happened because he wanted to promote a united German state.
Fichte’s innovation was Volksschule , a form of compulsory education. The state would support students and provide them with education. In exchange, the state would become part of people’s private lives. Homework began as a way for education to have a place in home affairs. By extension, this also extended the state’s role to the home. His ideas continue to influence German education to this day.
Horace Mann Helped Popularize The Concept In The United States
Another person who can claim to be the inventor of modern homework is Horace Mann. Mann was the first president of Antioch College, an Ohio-based institution that still exists today. Mann visited Europe and found the European methods of education to be inspiring. Upon returning to America, he decided to implement what he observed back in his native Massachusetts. Among the things he introduced was, you guessed it: homework.
His ideas weren’t limited to homework, however. Today, teachers and others praise Mann for his efforts to make education more accessible to the masses. Some even consider him to be the progenitor of common schools in America. Through his efforts, many reforms took place in Massachusetts. Among these was the establishment of a proper school board. He also strived to ensure that teachers had proper training and were effective in their jobs. Apart from his education career, he also served in the US House of Representatives. There, he advocated not just for good quality education but also for women’s rights.
Centuries after his death, Mann’s efforts to promote public schooling are still felt today. Homework-hating students may want to curse him for helping popularize homework. On the other hand, it would probably be better to thank him for allowing students to have the chance to have formal schooling at all.
Homework Was Unpopular At First
Considering homework’s ubiquity these days, you might think that the American education system embraced it from the get-go. But actually, it was not popular at first. Reasons varied, including people being skeptical about the need to do school-related activities at home. Many even thought that the idea would be harmful to the well-being of students.
Notable efforts against it included California banning homework in 1907; a ban which lasted for over a decade. Many prominent publications also questioned the practice. In the 1930s, the American Child Health Association, a government agency, even claimed that homework was a form of child labor!
How did the education sector warm up to the idea of homework? It comes from an unlikely source: the Cold War. At the time, the United States believed it had the lead over the Soviet Union when it came to education and science. However, events such as the launch of Sputnik 1 dampened this enthusiasm. This led to the so-called Sputnik crisis of the late 1950s. Homework was actually one of the ways the US thought it could close this perceived gap with the Soviets. By making students study at home, the US hoped that this could give them an edge in education.
Some Countries Ban or Discourage Homework
Even to this day, homework’s existence is controversial. Many education experts remain skeptical about its worth. Others also criticize it on the grounds that it gives students less time for hobbies, family time, or other free time. Indeed, homework (among other factors) has been linked to increased anxiety among students.
A number of countries either limit or even ban homework outright. One notable example is Finland . Finnish education is quite different compared to the rigid forms of education in other countries. Notably, students have shorter school hours, and even at school, they have plenty of free time to do hobbies or interact with classmates and friends. Schooling is also less competitive, as there’s less emphasis on grading and instead an emphasis on the student’s learning.
You may think that the Finnish system would make students lazy, given the lack of pressure. But actually, Finland’s education system ranks among the best in the world. Not only that, but Finns in general are also happier than many of their peers. It’s gotten to the point that many other nations are taking inspiration from Finland when discussing education reforms.
Meanwhile, contrary to what you may see in some sources, Japan does have homework. Indeed, it’s actually a bit of a cliche in Japanese media for students to do homework during their summer breaks. Given Japan’s education system is very competitive, it’s probably no surprise that homework is a facet of a student’s life there.
Schooling Itself Has a Long History
While we’re here, it may be worth having a short recap about the history of formal education. That way, we can contrast between homework and schoolwork, and put things into context better.
How old is schooling? It may depend on how you define “education”. If schooling means one learning from another, it’s probably existed since the dawn of humanity. If schooling means formal education, as in some kind of classroom setting, that’s somewhat more recent but still ancient.
The Mesopotamian civilization , the world’s oldest, already had schools. So did many of the ancient civilizations you may be familiar with, such as the Egyptians, Greeks, Romans, Chinese, Indians, and so on. One notable thing was that, during those days, it was mostly boys who received formal education. They would learn how to read, write, do activities, and learn skills. Women usually did not attend school as societies then believed that they should focus on household and family work. Some women did receive education, but they were exceptions and not the norm.
Education gained more significance during the Middle Ages, mainly for religious reasons. Many centers of learning, such as Oxford in Britain, date to this time.
In the United States, schooling began almost as soon as the first colonies appeared. Boston Latin School was the first public school to open in 1635; incredibly, it’s still open after all these years. Eventually, schools popped up across the country, often in the form of single-room schoolhouses. A few of these still exist today, but most schools in the US are now much bigger than that.
So What Have We Learned Today?
Here are our takeaways: Homework as a concept dates back centuries, depending on how you define homework. Roberto Nevillis, whom some websites claim to have invented homework, probably didn’t even exist at all. Two people, Johann Gottlieb Fichte and Horace Mann, helped popularize the concept. And finally, even today, there’s debate as to whether or not it’s necessary at all.
The next time you’re doing your homework and want to curse someone for your extra work, don’t blame Nevillis. After all, it’s hard to blame a person who may actually be the figment of the imagination of some internet writer.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:
History Cooperative
Who Invented School? The Story Behind Monday Mornings
The origins of schooling are deeply rooted in the annals of human history, spanning civilizations and cultures across the globe.
From the early beginnings of informal learning to the establishment of formal educational institutions, the invention of schools has been a transformative force in shaping societies and individuals.
There is much to know about the intriguing journey of school invention, tracing its roots through time and uncovering the societal, cultural, and philosophical factors that drove its development.
Table of Contents
Who Invented School?
Horace Mann, known as the “Father of the Common School Movement,” is credited with inventing the modern school in the United States. But he shouldn’t get all the credit. Schools were present in ancient Egypt , Greece, India, China, and more.
Depending on how far back you want to go, you could easily say Plato, Aristotle, or Confucius invented the school. Or it could have been someone completely unknown to us today. In essence, the invention of schools is woven intricately into the very fabric of history’s chronicles.
The Early Beginnings of Educational Institutions
The roots of formal education can be traced back to ancient civilizations , such as Mesopotamia (the “ Cradle of Civilization “), Egypt, and the Indus Valley, where centers of learning known as “ scribal schools ” or “tablet houses” emerged. These early institutions focused on teaching reading, writing, mathematics, and religious texts to young learners. Education was often limited to the elite classes and those training for specific roles, such as scribes and priests.
READ MORE: Who Invented Math? The History of Mathematics
The Evolution of Formal Schooling Systems
As societies developed and evolved, so did their educational practices. In ancient Greece , for instance, education became more widely accessible, with city-states like Athens establishing formal schools for boys where they learned subjects like rhetoric, philosophy, and physical education. Similarly, ancient Rome introduced the “ ludus litterarius ,” a school where children received a basic education in reading, writing, and arithmetic.
The concept of schools continued to evolve through the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, with the establishment of monastic schools, cathedral schools, and universities. These institutions played a crucial role in preserving and transmitting knowledge, contributing to the advancement of various fields, including the arts, sciences, and philosophy.
The emergence of the printing press in the 15th century further accelerated the dissemination of knowledge, making education more accessible to a broader segment of society.
From these early beginnings, the concept of schools has grown and transformed into the diverse educational systems we have today. Modern schooling encompasses a wide range of institutions, from public schools to private academies and online learning platforms, all working to fulfill the shared vision of nurturing informed and capable individuals.
The lasting value of education and its role in shaping human civilization can be better appreciated after gaining insight into the origins and evolution of schools.
When Was School Invented?
The origins of education can be traced back to the earliest human societies, where knowledge and skills were passed down through informal channels. In ancient times, education was primarily experiential and practical, centered around the necessities of survival.
READ MORE: Early Humans
Parents and elders imparted essential knowledge, such as hunting, farming, and tool-making, to the younger generations, ensuring their ability to thrive in their respective environments.
As societies evolved, specialized knowledge became essential, leading to the emergence of skilled individuals in various trades and crafts. Apprenticeship systems became common, wherein young learners received hands-on training and mentorship from experienced artisans, allowing them to acquire practical expertise in specific areas.
Early Civilizations and the Emergence of Schools
With the rise of early civilizations, such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley, the need for formal education grew. Societies required individuals with specialized roles, such as scribes, priests, and administrators. These roles demanded literacy, knowledge of religious texts, and record-keeping abilities.
In response to this demand, formal schools known as “scribal schools” or “tablet houses” were established. These institutions focused on providing specialized training to future scribes, enabling them to read, write, and handle administrative tasks. Education in these early schools was often reserved for a select few who were being groomed for specific societal functions.
Ancient Greece adopted a more holistic approach to education. While children received primary education at home from tutors, they also attended secondary schools, or gymnasiums,” for further learning.
These gymnasiums emphasized a well-rounded education that encompassed literature, philosophy, and physical education, nurturing both the body and mind.
Tracing the Development of Formal Schooling
Throughout history, formal education systems have continued to evolve and expand. In ancient China, Confucian schools played a significant role in shaping educational practices. These schools emphasized the teachings of Confucianism, focusing on moral values, ethics, and principles of good governance for the ruling class.
During the Middle Ages, monastic schools operated by religious orders became centers of learning, preserving ancient texts and disseminating knowledge. These schools were closely tied to the Christian Church and played a crucial role in preserving knowledge during times of political instability.
The Renaissance witnessed a resurgence of learning and education. Humanist schools emerged, emphasizing the study of classical texts and encouraging critical thinking and creativity. This humanist approach to education laid the foundation for modern educational philosophies that prioritize the development of individual potential.
The 18th and 19th centuries saw the establishment of formal public education systems, driven by the belief that education was essential for building educated and productive citizens. Compulsory education laws were introduced, making school attendance mandatory for children.
Today, education continues to evolve and adapt to the needs of societies, encompassing a wide range of institutions and methodologies to cater to diverse learners and prepare them for the challenges of the modern world.
Why Was School Invented?
The invention of schools was spurred by various societal and cultural factors that recognized the value of education in shaping individuals and communities. As societies grew more complex, there arose a need for individuals with specialized knowledge and skills to handle the diverse demands of governance, trade, and societal functions.
Education plays a vital role in imparting essential knowledge and values, fostering social cohesion, and preparing individuals to fulfill their roles within the community. Cultures around the world recognized that an educated populace contributed to the overall well-being and advancement of society, thus incentivizing the establishment of formal educational institutions.
Religious and Philosophical Influences on Educational Institutions
In many ancient civilizations, religion played a central role in shaping educational practices. Religious texts and teachings often formed the core of early education, as religious institutions were among the first to formalize educational systems.
Monastic and temple schools, for example, were established to train future religious leaders and scholars, ensuring the preservation and dissemination of sacred knowledge.
Moreover, philosophical ideals also influenced educational institutions. The ancient Greeks believed in the importance of developing well-rounded individuals through a comprehensive education that encompassed physical, intellectual, and moral development. These philosophical perspectives laid the groundwork for the evolution of educational philosophies throughout history.
Economic and Political Motivations for Formal Schooling
Economic and political factors also played significant roles in the invention of schools. In some societies, education was seen as a means of enhancing economic productivity. The ability to read, write, and perform arithmetic was vital for carrying out trade, record-keeping, and managing economic transactions.
Furthermore, governments and ruling authorities recognized the importance of education in maintaining social order and stability. Well-educated citizens were deemed more capable of participating in governance, making informed decisions, and contributing to the progress of the state.
Thus, the establishment of formal schooling systems was often driven by political motives to cultivate an educated and loyal citizenry.
The Innovators of Early Education
In their quest to advance education, ancient civilizations were blessed with visionary educators who laid the groundwork for formal schooling. One such notable figure was Confucius (551-479 BCE), an esteemed Chinese philosopher and educator whose teachings emphasized moral values, ethics, and the importance of cultivating a virtuous character.
Confucius’ principles had a profound impact on Chinese education, and Confucian schools became centers for imparting his teachings to future generations.
In ancient Greece, the philosopher Plato (428/427-348/347 BCE) played a key role in shaping educational philosophy. Plato’s famous work “The Republic” outlined his ideas on education, advocating for a system that would nurture the potential of individuals based on their innate abilities.
He proposed a system of education divided into stages, where students would receive different types of instruction based on their age and aptitude.
Contributions of Philosophers and Scholars to Education
During the Hellenistic period, the Greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BCE) made significant contributions to the field of education. He believed in the importance of observation, reasoning, and systematic investigation, which laid the foundation for scientific inquiry and empirical learning.
Aristotle’s works on ethics, logic, and natural philosophy shaped educational thought and practices for centuries to come.
In ancient India, the great philosopher and educator Chanakya (c. 350-275 BCE) left an indelible mark on the country’s educational system. Chanakya, also known as Kautilya or Vishnugupta, was the chief advisor to Emperor Chandragupta Maurya.
He authored the ancient Indian political treatise “Arthashastra,” which covered topics such as governance, economics, and statecraft. His influence on education extended to the establishment of higher learning institutions, known as Takshashila and Nalanda, which became centers of knowledge and attracted scholars from around the world.
The contributions of these visionary educators and famous philosophers in various civilizations were instrumental in shaping the foundations of education and formal schooling.
Religious and Monastic Schools
In the early medieval period, religious institutions played a crucial role in preserving knowledge and providing education. Monastic schools, run by monks and religious orders, became centers of learning in Europe during the Middle Ages.
These schools focused on teaching religious doctrine, Latin, and classical texts. The monastic tradition of learning helped keep the flame of knowledge alive during a time of political turmoil.
In the Islamic world, madrasas emerged as centers of higher education from the 9th century onward. Madrasas offered a comprehensive curriculum that included theology, law, philosophy, mathematics, astronomy, and medicine.
They played a crucial role in advancing scientific knowledge and preserving classical texts during the Islamic Golden Age.
The Establishment of Modern School Systems
The 19th and 20th centuries witnessed significant advancements in the establishment of modern school systems, with a growing emphasis on public education. As societies underwent industrialization and urbanization, the need for an educated workforce became evident.
Public education was seen as a means of providing equal opportunities for all children to receive a basic education, regardless of their social background.
In countries like the United States, the concept of public schooling gained momentum with the introduction of compulsory education laws. In 1852, Massachusetts passed the first compulsory education law in the United States, requiring children to attend school.
This served as a model for other states to follow suit, leading to the widespread adoption of public education across the nation.
Similarly, in Europe, public education systems were gradually established as part of nation-building efforts and social reforms.
These systems aimed to foster national identity and unity while promoting a sense of citizenship and civic responsibility among the population.
Educational Reforms and the Spread of Schooling
During the 19th and 20th centuries, educational reforms played a vital role in shaping modern school systems. Innovators and educational theorists, such as John Dewey, Maria Montessori, and Jean Piaget, introduced progressive ideas that emphasized student-centered learning, experiential education, and the importance of considering individual learning styles.
The progressive education movement encouraged hands-on learning, critical thinking, and creativity, challenging traditional rote memorization and passive learning approaches. These ideas had a lasting impact on educational practices and contributed to the development of modern pedagogical methods.
Furthermore, the spread of schooling was facilitated by technological advancements, such as the printing press, which made books and educational materials more accessible to a broader audience.
The advent of mass communication, including radio and television , also brought educational content into people’s homes, expanding the reach of formal education.
Key Figures in Shaping Modern Education
Several key figures played pivotal roles in shaping modern education systems around the world. Horace Mann, known as the “Father of the Common School Movement,” advocated for free, non-sectarian public education in the United States.
His efforts led to significant educational reforms, and he is credited with laying the groundwork for the American public education system.
In Japan, the educational reforms of the Meiji Restoration in the late 19th century modernized the country’s educational system.
The government prioritized universal education, making primary education compulsory and promoting a standardized curriculum.
In India, social reformers like Raja Ram Mohan Roy and Jyotirao Phule campaigned for educational access for all, challenging the prevailing caste-based discrimination. Their efforts laid the foundation for educational reforms that sought to provide education to marginalized communities and foster social equality.
The establishment of modern school systems, driven by the principles of public education, educational reforms, and the efforts of key figures, marked a transformative era in the history of education.
Schooling Across Cultures and Continents
Across the world, diverse cultures have nurtured unique educational traditions, reflecting their values, beliefs, and social structures. In ancient China, the Confucian emphasis on moral values and social harmony influenced the development of education.
Confucian schools focused on teaching the Confucian classics, as well as calligraphy and poetry, to instill virtue and knowledge in students.
In ancient India, the Gurukula system was prevalent, where students lived with their teachers (gurus) and received holistic education.
The curriculum encompassed various subjects, including scriptures, philosophy, music , dance, and martial arts, shaping individuals into well-rounded and cultured beings.
Indigenous cultures around the world have their own methods of education, emphasizing knowledge transmission through oral traditions and experiential learning.
Native American tribes, for instance, used storytelling and hands-on experiences to teach essential skills, history, and cultural values to younger generations.
Comparing Eastern and Western Approaches to Education
Eastern and Western cultures have historically approached education differently, emphasizing distinct values and learning methods.
Eastern education often places a strong emphasis on discipline, respect for authority, and rote memorization of essential texts. The teacher-student relationship is highly revered, with teachers seen as authoritative figures who impart wisdom and knowledge.
On the other hand, Western education has been more focused on critical thinking, creativity, and encouraging students to question and challenge established ideas.
The Socratic method , for example, employed by the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates, involved asking questions to stimulate critical thinking and arrive at deeper insights.
In recent times, there has been an increasing awareness of the value of incorporating elements from both Eastern and Western educational philosophies to create more balanced and holistic learning experiences.
Indigenous Educational Practices and Knowledge Transmission
Indigenous communities worldwide have cultivated rich educational practices that are deeply rooted in their cultural heritage. These practices emphasize the interconnectedness between humans and the natural world, promoting a harmonious relationship with the environment.
In Aboriginal cultures in Australia, for instance, “Dreamtime” stories serve as a means of passing down knowledge of creation, spirituality, and cultural values from one generation to another.
These stories also teach essential survival skills and navigation techniques, connecting the people to their ancestral past and land.
Indigenous educational practices showcase the significance of experiential learning, community involvement, and the preservation of traditional knowledge.
Recognizing and respecting the unique educational approaches of indigenous cultures contributes to a more inclusive and diverse global perspective on schooling.
The Purpose and Evolution of School Curriculum
In the early history of formal schooling, curricula were designed to impart practical skills and knowledge essential for survival and societal roles. Ancient educational systems focused on teaching fundamental skills such as reading, writing, arithmetic, and religious texts.
The emphasis was on equipping students with the abilities needed to contribute to their communities and fulfill specific roles, such as scribes, priests, or administrators.
In the classical Greek and Roman periods, education expanded to include subjects like literature, rhetoric, philosophy, and physical education. This broader curriculum aims to foster well-rounded individuals capable of engaging in intellectual pursuits and civic life.
Shifting Educational Goals Throughout History
As societies evolved, so did the goals of education. During the Renaissance, there was a renewed interest in classical learning and humanist ideals, leading to curricula that emphasized the study of classical texts, literature, the arts, and the humanities.
Education during this period sought to cultivate creative thinking, artistic expression, and an appreciation for knowledge and culture.
With the advent of the Industrial Revolution, the goals of education shifted once again.
The need for an educated workforce capable of meeting the demands of industrialized economies led to curricula that prioritized practical skills, technical knowledge, and standardized testing.
In the 20th century, educational reformers like John Dewey advocated for a curriculum that focused on experiential learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving.
This progressive approach aimed to prepare students for active participation in a democratic society and real-life challenges.
Contemporary Curriculum Trends and Challenges
In the modern era, school curricula continue to evolve to meet the demands of a rapidly changing world. Contemporary curricula often emphasize a balance between core academic subjects, such as mathematics, science, language arts, and social studies, and a broader range of electives and extracurricular activities.
In response to globalization and advancements in technology, there has been a growing emphasis on preparing students for a globalized, interconnected world. This includes promoting cultural competence, digital literacy, and intercultural understanding.
Additionally, there is an increasing recognition of the importance of personalized and individualized learning approaches. Personalized learning tailors education to the specific needs, interests, and learning styles of each student, fostering a more engaging and effective learning experience.
However, contemporary curricula also face challenges, such as standardized testing and rigid educational policies that may limit creativity and critical thinking.
Striking a balance between meeting educational standards and nurturing a diverse range of talents and skills remains a challenge for educators and policymakers.
The evolution of school curricula reflects the dynamic nature of education and the ever-changing needs of societies.
The Future of Schooling: Challenges and Opportunities
Despite progress in expanding access to education, educational inequities persist in many parts of the world. Socioeconomic disparities , gender biases, and geographic isolation are among the factors that hinder equal educational opportunities for all.
In the future, addressing these challenges will require targeted efforts to ensure that marginalized communities have access to quality education.
This includes investing in schools in underserved areas, providing scholarships and financial aid to disadvantaged students, and implementing policies that promote inclusivity and diversity in the classroom.
Additionally, leveraging technology can play a significant role in enhancing educational access. Online learning platforms and digital resources can reach students in remote areas and provide flexible learning opportunities for individuals with diverse needs.
Embracing Technological Advancements in Education
The future of schooling will undoubtedly be shaped by technological advancements. Integrating technology into the classroom can enhance teaching and learning experiences by allowing for personalized instruction and interactive engagement.
Virtual reality, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence have the potential to revolutionize education by creating immersive learning environments, adaptive learning experiences, and intelligent tutoring systems.
These technologies can cater to individual learning styles, identify areas for improvement, and provide real-time feedback to enhance student understanding.
Additionally, online learning platforms, open educational resources, and digital collaboration tools can expand access to high-quality education beyond traditional classroom settings.
Reimagining Schooling for a Changing World
As the world undergoes rapid transformations, schools must adapt to prepare students for the challenges and opportunities of the future. Education needs to foster essential skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, digital literacy, and adaptability.
Interdisciplinary approaches that bridge traditional subject boundaries can encourage creativity, innovation, and a deeper understanding of complex global issues.
Encouraging project-based learning and hands-on experiences can help students apply knowledge to real-world scenarios, preparing them for a diverse range of careers and challenges.
Moreover, embracing a global perspective in education can foster cultural awareness, empathy, and understanding, enabling students to become responsible global citizens.
In the future, schools must embrace a growth mindset, continually evolving to meet the needs of a changing world and equipping students with the skills and values to thrive in an increasingly interconnected and dynamic global society.
The Impact of Schooling on Society and Individual Advancement
Schools have played a crucial role in facilitating social mobility, offering individuals from diverse backgrounds the opportunity to improve their socioeconomic status.
Formal education equips students with knowledge, skills, and qualifications that enhance their employability and earning potential.
Historically, access to education was limited to the privileged classes, perpetuating social inequality. However, as educational systems expanded and became more inclusive, education became a pathway for individuals to rise above their socioeconomic circumstances.
By providing equal opportunities for learning, schools have empowered individuals to break the cycle of poverty and achieve upward social mobility.
Schooling and Its Influence on Economic Development
Education has a direct impact on economic development by fostering a skilled and knowledgeable workforce. Well-educated individuals contribute to increased productivity, innovation, and technological advancements, driving economic growth.
Countries that prioritize education and invest in human capital development tend to experience higher economic prosperity. Education equips individuals with the tools to adapt to changing economic landscapes, drive entrepreneurship, and promote a knowledge-based economy.
Furthermore, the education sector itself becomes a significant contributor to the economy, providing employment opportunities for teachers, administrators, and support staff.
Education as a Tool for Empowerment and Personal Growth
Beyond its economic impact, education serves as a tool for personal empowerment and growth. Education nurtures critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving abilities, enabling individuals to make informed decisions and engage actively in civic life.
Schools foster social and emotional development, promoting empathy, resilience, and communication skills.
Education encourages individuals to explore their interests, talents, and passions, empowering them to pursue fulfilling careers and contribute meaningfully to society.
For marginalized and disadvantaged groups, education can be a transformative force, breaking down barriers and empowering individuals to advocate for their rights and opportunities.
Moreover, education fosters a lifelong love of learning, encouraging individuals to continuously seek knowledge and personal development throughout their lives.
The Bottom Line
The history of school invention is a tale of continuous evolution and innovation. From ancient educational practices to modern schooling systems, education has been shaped by cultural, societal, and philosophical influences.
Schools have played a pivotal role in empowering individuals, driving economic progress, and fostering social cohesion. As we envision the future of education, addressing inequities, embracing technology, and reimagining the purpose of schooling will be crucial.
Education remains a powerful force, shaping the minds and hearts of generations to come, and propelling humanity towards a brighter and more interconnected future.
“Horace Mann | Biography & Facts”. Encyclopedia Britannica.
McFarland, Philip (2004). Hawthorne in Concord. New York: Grove Press. p. 72.
“Horace Mann Elementary”. Hominy Public Schools. Archived from the original on April 15, 2017.
“Allen Family Papers 1846-1915”. Archived from the original on June 15, 2018. Retrieved June 14, 2018.
Jolad, Shivakumar (2 February 2020). “Missionaries and expansion of mass western education in India 1700–1813”. Medium.
“Elementary, Grammar, and Secondary Schools | Encyclopedia.com”.
“School system & compulsory education”. Make it in Germany.
“The US Higher Education System Explained”. Shorelight
The Education System in India – GNU Project – Free Software Foundation”. GNU Operating System.
Bellenoit, Hayden J. A. (2007). “Missionary Education, Religion and Knowledge in India, c. 1880-1915”. Modern Asian Studies. 41 (2): 369–394.
“Parochial education”. www.britannica.com .
Barnard, Henry (1861). German schools and pedagogy: Organization and instruction of common schools in Germany, with the views of German teachers and educators on elementary instruction. New York: F.C. Brownell. pp. 138.
“madrasa” (US) and “madrasa”. Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press.
Abaza, Mona; Kéchichian, Joseph A. (2009). “Madrasah”. The Oxford Encyclopedia of the Islamic World. Oxford University Press.
Haskins, Charles Homer (1955), The Renaissance of the Twelfth Century, Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Lindberg, David C. (2007) [1992], The Beginnings of Western Science, Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, pp. 132–162, 321–356.
Riché, Pierre (1978) [1976], Education and Culture in the Barbarian West: From the Sixth through the Eighth Century, Columbia, SC: University of South Carolina Press.
William Theodore De Bary (1989). Neo-Confucian Education: The Formative Stage. University of California Press. p. 455.
Siegel, Harvey; Phillips, D.C.; Callan, Eamonn (2018). “Philosophy of Education”. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University.
How to Cite this Article
There are three different ways you can cite this article.
1. To cite this article in an academic-style article or paper , use:
<a href=" https://historycooperative.org/who-invented-school/ ">Who Invented School? The Story Behind Monday Mornings</a>
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Bseb 10th result.
- Bihar Board Result 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
Who invented Homework? When, Where and Why
Who invented homework in this article we will find out what is homework when, where and why was homework invented .

Yes, everything seems better and more interesting than doing homework! I mean, we have all spent hours staring at the wall instead of doing homework, right? But I won’t lie, my first thought while doing my homework in school days was always “WHO INVENTED HOMEWORK & WHY?” Let’s find out!
What is homework?
According to collinsdictionary, homework, an uncountable noun, is school work that teachers give to pupils to do at home in the evening or at the weekend.
Although homework is generally associated with school students, college students also get homework. Thus, it can be said that homework is any task or activity that teachers/professors assign to the students to be done outside the school hours, from their home.
Who invented homework?
Even Google missed their homework on the topic “homework” (pun intended), not joking though.
Yes! Google does not have a cent-percent answer on who actually came up with the concept of homework. The results from Google about the inventor of homework are ambiguous.
- Roberto Nevelis of Venice
Did Roberto Nevelis create homework?
Mr. Nevelis is probably one of the most hated people amongst the student communities because he is one of the first persons who has been associated with the credits for the infamous process of homework.
According to the tales on the internet, t he person who invented Homework was an Italian teacher named Roberto Nevilis. He invented Homework in 1905 as a punishment for his students.
If you think you will have to go find out more about this person, don’t worry, we have got you covered:
Upon doing a little more search on Roberto Nevelis of Venice, infamous for his dubious relationship with homework, we found out that not only is Mr Nevelis’ title as the inventor of homework unreliable, his very existence is doubtful too! Yes, that means there might not have been a Roberto Nevelis of Venice at all. He might just be a fictional character created by someone, probably whilst skipping their homework.
- Horace Mann
Did Horace Mann create homework?

Horace Mann, the father of American education might just be the father of homework as well!
Horace Mann is considered one of the very first American advocates of public education. As state secretary of education, Mann, who believed in free education, supported reforms to make education universal, nonsectarian, and reliant on well-trained, professional teachers.
Thus, homework could be one of the reforms of refined public education that he supported.
- Pliny the Younger
Upon trying to get some more information, it came to light that the first mention of homework appears in the writings of Pliny the Younger, dating back to 1AD.

In ancient Rome, Pliny the Younger was a teacher of oratory, and is thought to have asked his students to practise their public speaking at home, to help them build confidence.
With time, homework became more and more common as schooling became compulsory for many people across the world, towards the end of the 19th century.
Now, if we go to a student’s best friend - Wikipedia - a completely different picture has been painted. Ofcourse, you don’t have to go read that long entry there as we have summarised the whole thing here, for you:
The American Story of Homework
So, according to Wikipedia, homework has been a part of American education but already few pupils managed to pursue education and the baggage of homework discouraged even those few. In fact, it was frowned upon by the parents and even some schools. Journalist Edward Bok protested against schools giving homework to pupils until they were 15 years old, in 1900. He was supported by 1000s of parents. While soon there were laws for children not getting any homework at all, teenagers could have had homeworks assigned but not anything that required more than two hours of time. Then In 1901, an act passed by the California legislature abolished homework for anyone under the age of 15.
However, with the cold war between the US and Soviet Union, the rise of competition led to the re-emergence of the homework culture. And as mentioned earlier, homework became more and more common towards the end of the 19th century.
Why do students get homework?
- Homework gives both students and parents an opportunity to re-view class works.
- Homework teaches students the skill of problem solving and taking responsibility for their part in their education.

Why should students NOT get homework?
With students spending almost one-fourth of their day in school, having daily homework for all the various subjects being taught leaves the student with little to no time for themselves. This, consequently, promotes the culture of “All work, no play”.
CONCLUSION: Who invented Homework? When, Where and Why
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- BSEB Bihar Board 10th Result 2024
- Bihar Board 10th Result 2024
- Bihar Board Matric Result 2024
- biharboardonline.bihar.gov.in Result 2024
- Bihar Board Matric 10th Result 2024
- Bihar Board Result 2024 Class 10
- Bihar Board Result 2024 by Jagran Josh
- Class 10th Result 2024 Bihar Board
- Bihar Board 10th Topper List 2024
Trending Categories
Latest education news.
99% of People Failed To Find The Snake Hidden In The Picture Puzzle. 7 Seconds Left!
JEE Main Admit Card 2024 Live: NTA Window is Open for Exam Date April 4, 5 and 6, Download Hall Ticket at jeemain.nta.ac.in
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Use Your Eagle Eyes To Spot The Lamp In 12 Seconds!
Today’s IPL Match (1 April) - MI vs RR: Team Squad, Match Time, Where to Watch Live and Stadium
TS SSC Social Studies Exam 2024: Exam Analysis, Question Paper and Answer Key, Download PDF Here
JEE Main Session 2: Important Topics and Formulas for Last Minute Revision
SOSE Result 2024 Out for Class 9 Admission, Check Results at edudel.nic.in
Seek and Find Puzzle: Can You Find the Fish Camouflaged in the Snow Scene?
Red Carpets banned in Pakistan: Why so? Here is the full story
JEE Main 2024: Check Last Minute Tips and Resources to Crack the Exam
CUET UG 2024 Registration Deadline Extended Again, Check the New Date and Link to Apply on cuetug.ntaonline.in
BSEB 10th Toppers List 2024: शिवांकर कुमार 97.8 फीसदी अंकों के साथ बने टॉपर, देखें टॉप पांच की लिस्ट
IBPS Clerk Final Result 2024 Out at ibpsonline.ibps.in: Download Final Merit List PDF, Check Provisional Allotment
ICAI CA May 2024: Series 2 Mock Test Begins Today, Check Schedule Here
Madras University Result 2024 OUT at result.unom.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG விளைவாக PDF here
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024-25: Check New Syllabus of All Subjects, Direct Download Links Here
RESULT LINK - BSEB 10th Matric Result 2024 OUT: घबराएं नहीं! वेबसाइट क्रैश या बिजी तो लिंक से तुरंत चेक करें बिहार बोर्ड मैट्रिक रिजल्ट
Important Days in April 2024: National and International Dates List
BTEUP Result 2024 OUT on bteup.ac.in; Direct Link to Download Odd Semester and Special Back Paper Marksheet
Karnataka SSLC Science Exam Analysis 2024 with Question Paper PDF and Answer Key

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Cold War: Homework Heats Up. Following World War II, the Cold War heated up U.S.-Russian rivalties in the 1950s. Sputnik 1's launch in 1957 spiked competition between Russians and Americans ...
Mentions of the term "homework" date back to as early as ancient Rome. In I century AD, Pliny the Younger, an oratory teacher, supposedly invented homework by asking his followers to practice public speaking at home. It was to help them become more confident and fluent in their speeches.
The inventor of homework is widely considered to be Roberto Nevilis, an Italian educator who lived in the early 20th century. We will briefly explore Nevilis' life, how he came up with the concept of homework, and the circumstances surrounding his death. Roberto Nevilis: The Man Behind Homework Roberto Nevilis was born in Venice, Italy, in 1879.
The inventor of homework may be unknown, but its evolution reflects contributions from educators, philosophers, and students. Homework reinforces learning, fosters discipline, and prepares students for the future, spanning from ancient civilizations to modern education. Ongoing debates probe its balance, efficacy, equity, and accessibility, prompting innovative alternatives like project-based ...
If you've ever felt curious about who invented homework, a quick online search might direct you to a man named Roberto Nevilis, a teacher in Venice, Italy. As the story goes, Nevilis invented homework in 1905 (or 1095) to punish students who didn't demonstrate a good understanding of the lessons taught during class.
To answer the question of who invented homework and why, at least in the modern sense, we have to talk about Horace Mann. Horace Mann was an American educator and politician in the 19th century who was heavily influenced by movements in the newly-formed German state. ... Horace Mann, in particular, was the man who apparently introduced homework ...
Source: twitter.com. Nevilis was supposedly a teacher based in Venice, Italy when he invented homework. Some claim that he invented it in 1095, while others claim he invented it in 1905 before it spread to Europe and to the rest of the world. It was said to be a form of punishment for students who underperformed in class.
Roberto Nevilis invented homework in the year 1095 in Venice after being disappointed in his students. Roberto Nevilis began to give homework in order to help the students learn and master the material he was teaching in Italy. Anyone who has ever been a student has also wonder who invented homework. Indeed, we may all at
Homework is typically credited to Roberto Nevelis of Venice, Italy, who invented it in 1095—or 1905, depending on your sources. However, upon closer examination, he appears to be more of an internet legend than a genuine figure. Horace Mann. Horace Mann, a 19th-century politician and educational reformer, was a pivotal figure in the ...
In this video, we explore the history of homework and its impact on modern education. Discover the origins of homework and the person who invented it, Italia...
The origins of Homework dates back to ancient Greece and Rome. It is said that Roberto Nevelis, an Italian teacher, invented homework in 1905, but so far there is no credible historical evidence to support this, which makes it become an Internet myth. Pliny the Younger, Johann Gottlieb Fichte, and Hausmann are the most likely true inventors of homework.
Demerits of Homework: Homework as we know it today has a long history, dating back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Greece. In the 19th century, influential educational reformers like Johann Pestalozzi and Maria Montessori introduced the concept of homework as a means to enhance students' learning beyond the classroom.
There isn't a single credible website or a news article about this man who changed the educational system all over the world. According to a lot of websites, Nevilis was a teacher in Venice and allegedly invented homework as a means of punishing students who did not perform well in class. Some sites claim the year was 1095 while others claim ...
Yingna Cai/Shutterstock. As both Through Education and The Ed Advocate report, somehow a myth entered the world's collective consciousness that an Italian man named Roberto Nevilis invented homework. Some versions of the myth even add some context: It was intended to punish underperforming students and to reward those who excelled at their lessons.
Many people wonder did Roberto Novelis invent homework. The answer is: YES. Roberto Novelis was an Italian teacher who invented school homework. He was born in 1877 and died in 1957 at the age of 80. Roberto was a teacher at the University of Padua in Italy, where he worked for 52 years. One day, while he was teaching his students about ...
The origin of homework is often attributed to Roberto Nevilis, an Italian educator who lived in the 20th century. Roberto Nevilis is believed to have been a school teacher in Venice, and it is ...
Horace Mann. The practice of homework entered American life through Horace Mann (1796-1859). The reformer traveled for more than 5 months to the countries of Europe. He was inspired by the "folk schools" and brought the concept of homework to the US.
A person doing geometry homework Children preparing homework on the street, Tel Aviv, 1954. Homework is a set of tasks assigned to students by their teachers to be completed at home.Common homework assignments may include required reading, a writing or typing project, mathematical exercises to be completed, information to be reviewed before a test, or other skills to be practiced.
As for the "title" of the true inventor of homework, there are two people who have a good claim. One of them is Johann Gottlieb Fichte. Many historians consider him to be the father of German nationalism. Apart from his political life, he made some contributions to education.
Even the existence of a such man is questionable, he is more or less like a fictional character. The credit for the school homework system goes to Horace Mann, the man who invented school system as well. Homework ban in early 1900s. The concept of homework is not really well accepted by the parents and some teachers.
Who Invented School? Horace Mann, known as the "Father of the Common School Movement," is credited with inventing the modern school in the United States. But he shouldn't get all the credit. Schools were present in ancient Egypt, Greece, India, China, and more.. Depending on how far back you want to go, you could easily say Plato, Aristotle, or Confucius invented the school.
According to the tales on the internet, the person who invented Homework was an Italian teacher named Roberto Nevilis. He invented Homework in 1905 as a punishment for his students. If you think ...
xxMysteriousOneXx. •. It was some Italian teacher in 1905 who made it as a PUNISHMENT. lilwizerd. •. Yep, and even then the punishment didn't make any sense. As a punishment for students not doing their work in class, they were given more work to do at home. Sure, that's how you cure laziness, give the lazy guy more work.