Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Effective Communication — Effective Communication: The Key to Building Strong Connections

Effective Communication: The Key to Building Strong Connections
- Categories: Connection Effective Communication
About this sample

Words: 791 |
Published: Sep 12, 2023
Words: 791 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
The importance of effective communication, key elements of effective communication, barriers to effective communication, strategies for improving communication, 1. building relationships:, 2. resolving conflicts:, 3. achieving goals:, 4. personal development:, 5. success in the workplace:, 1. clarity:, 2. active listening:, 3. empathy:, 4. nonverbal communication:, 5. respect:, 1. misunderstandings:, 2. lack of active listening:, 3. emotional barriers:, 4. assumptions and stereotypes:, 5. lack of feedback:, 1. practice active listening:, 2. foster empathy:, 3. be mindful of nonverbal cues:, 4. seek feedback:, 5. adapt to your audience: h3>, 6. practice constructive communication:, 7. educate yourself:.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 304 words
2 pages / 878 words
4 pages / 1927 words
3 pages / 1261 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Effective Communication
Soft skills are known as combinations of social skills and personality characteristics. Soft skills influence how someone functions in a working environment with others (Doyle, 2019). The term 'soft skill” refers to various [...]
Communication is a complex process that involves the exchange of information, ideas, and emotions between individuals. In order to ensure that communication is effective, it is crucial for individuals to engage in perception [...]
In a world where globalization and multiculturalism are becoming increasingly prevalent, the ability to speak more than one language is a valuable asset. Being bilingual opens up a world of opportunities, both personally and [...]
Direct persuasion is a form of communication that aims to influence an individual or a group's beliefs, attitudes, opinions, or behaviors. Direct persuasion can be delivered through various communication channels, such as [...]
In an organization, the flow of communication can either be formal or informal. Communication that flows through normal channels can be upward, horizontal or downward. Communication that flows through informal organizational [...]
Communication is the strongest medium through which we can either build our connections with people or ruin it by creating misunderstandings. Hence to make our communication more effective we should make sure that we reduce [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Effective Communication Strategies
- First Online: 20 February 2024
Cite this chapter

- Federico Addimando 2
Part of the book series: SpringerBriefs in Psychology ((BRIEFSPSYCHOL))
105 Accesses
Effective communication is a cornerstone of successful interactions in various aspects of life, ranging from personal relationships to professional environments. It encompasses both verbal and nonverbal communication techniques, each playing a vital role in conveying messages, building relationships, and ensuring mutual understanding.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Kelley and Littman [ 1 ].
Kelley, T., & Littman, J. (2001). The art of innovation: Lessons in creativity from IDEO, America’s leading design firm . Crown Business.
Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Contributor at China Media Group, CEO - MF International, Shanghai, China
Federico Addimando
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Addimando, F. (2024). Effective Communication Strategies. In: Trade Show Psychology. SpringerBriefs in Psychology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53606-9_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53606-9_4
Published : 20 February 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-53608-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-53606-9
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Body Language and Nonverbal Communication
Improving emotional intelligence (eq), conflict resolution skills.
- Empathy: How to Feel and Respond to the Emotions of Others
Anger Management: Help for Anger Issues
Managing conflict with humor.
- The 5 Love Languages and Their Influence on Relationships
- Gaslighting: Turning Off the Gas on Your Gaslighter
- Online Therapy: Is it Right for You?
- Mental Health
- Health & Wellness
- Children & Family
- Relationships
Are you or someone you know in crisis?
- Bipolar Disorder
- Eating Disorders
- Grief & Loss
- Personality Disorders
- PTSD & Trauma
- Schizophrenia
- Therapy & Medication
- Exercise & Fitness
- Healthy Eating
- Well-being & Happiness
- Weight Loss
- Work & Career
- Illness & Disability
- Heart Health
- Childhood Issues
- Learning Disabilities
- Family Caregiving
- Teen Issues
- Communication
- Emotional Intelligence
- Love & Friendship
- Domestic Abuse
- Healthy Aging
- Aging Issues
- Alzheimer’s Disease & Dementia
- Senior Housing
- End of Life
- Meet Our Team
What is effective communication?
Tips for improving your communication skills.
- Tip 1: Understand the barriers to effective communication
Tip 2: Become an engaged listener
Tip 3: pay attention to nonverbal signals, tip 4: keep stress in check, tip 5: assert yourself, effective communication improving your interpersonal skills.
Want better communication skills? These tips will help you avoid misunderstandings, grasp the real meaning of what’s being communicated, and greatly improve your work and personal relationships.

Effective communication is about more than just exchanging information. It’s about understanding the emotion and intentions behind the information. As well as being able to clearly convey a message, you need to also listen in a way that gains the full meaning of what’s being said and makes the other person feel heard and understood.
Effective communication sounds like it should be instinctive. But all too often, when we try to communicate with others something goes astray. We say one thing, the other person hears something else, and misunderstandings, frustration, and conflicts ensue. This can cause problems in your home, school, and work relationships.
But by learning effective communication skills, you can deepen your connections to others, build greater trust and respect, and improve teamwork, problem solving, and your overall social and emotional health
Whether you’re trying to improve communication with your romantic partner, kids, boss, or coworkers, learning the following communication skills can help strengthen your interpersonal relationships.
Tip 1: Understand what’s stopping you from communicating well
Common barriers to effective communication include:
Stress and out-of-control emotion. When you’re stressed or emotionally overwhelmed, you’re more likely to misread other people, send confusing or off-putting nonverbal signals, and lapse into unhealthy knee-jerk patterns of behavior. To avoid conflict and misunderstandings, you can learn how to quickly calm down before continuing a conversation.
Lack of focus. You can’t communicate effectively when you’re multitasking. If you’re checking your phone , planning what you’re going to say next, or daydreaming, you’re almost certain to miss nonverbal cues in the conversation. To communicate effectively, you need to avoid distractions and stay focused.
Inconsistent body language. Nonverbal communication should reinforce what is being said, not contradict it. If you say one thing, but your body language says something else, your listener will likely feel that you’re being dishonest. For example, you can’t say “yes” while shaking your head no.
[Read: Nonverbal Communication and Body Language]
Negative body language. If you disagree with or dislike what’s being said, you might use negative body language to rebuff the other person’s message, such as crossing your arms, avoiding eye contact, or tapping your feet. You don’t have to agree with, or even like what’s being said, but to communicate effectively and not put the other person on the defensive, it’s important to avoid sending negative signals.
When communicating with others, we often focus on what we should say. However, effective communication is less about talking and more about listening. Listening well means not just understanding the words or the information being communicated, but also understanding the emotions the speaker is trying to convey.
There’s a big difference between engaged listening and simply hearing. When you really listen—when you’re engaged with what’s being said—you’ll hear the subtle intonations in someone’s voice that tell you how that person is feeling and the emotions they’re trying to communicate. When you’re an engaged listener, not only will you better understand the other person, you’ll also make that person feel heard and understood, which can help build a stronger, deeper connection between you.
By communicating in this way, you’ll also experience a process that lowers stress and supports physical and emotional well-being. If the person you’re talking to is calm, for example, listening in an engaged way will help to calm you, too. Similarly, if the person is agitated, you can help calm them by listening in an attentive way and making the person feel understood.
If your goal is to fully understand and connect with the other person, listening in an engaged way will often come naturally. If it doesn’t, try the following tips. The more you practice them, the more satisfying and rewarding your interactions with others will become.
Tips for becoming an engaged listener
Focus fully on the speaker. You can’t listen in an engaged way if you’re constantly checking your phone or thinking about something else. You need to stay focused on the moment-to-moment experience in order to pick up the subtle nuances and important nonverbal cues in a conversation. If you find it hard to concentrate on some speakers, try repeating their words over in your head—it’ll reinforce their message and help you stay focused.
Favor your right ear. As strange as it sounds, the left side of the brain contains the primary processing centers for both speech comprehension and emotions. Since the left side of the brain is connected to the right side of the body, favoring your right ear can help you better detect the emotional nuances of what someone is saying.
Avoid interrupting or trying to redirect the conversation to your concerns. By saying something like, “If you think that’s bad, let me tell you what happened to me.” Listening is not the same as waiting for your turn to talk. You can’t concentrate on what someone’s saying if you’re forming what you’re going to say next. Often, the speaker can read your facial expressions and know that your mind’s elsewhere.
Show your interest in what’s being said. Nod occasionally, smile at the person, and make sure your posture is open and inviting. Encourage the speaker to continue with small verbal comments like “yes” or “uh huh.”
Try to set aside judgment. In order to communicate effectively with someone, you don’t have to like them or agree with their ideas, values, or opinions. However, you do need to set aside your judgment and withhold blame and criticism in order to fully understand them. The most difficult communication, when successfully executed, can often lead to an unlikely connection with someone.
[Read: Improving Emotional Intelligence (EQ)]
Provide feedback. If there seems to be a disconnect, reflect what has been said by paraphrasing. “What I’m hearing is,” or “Sounds like you are saying,” are great ways to reflect back. Don’t simply repeat what the speaker has said verbatim, though—you’ll sound insincere or unintelligent. Instead, express what the speaker’s words mean to you. Ask questions to clarify certain points: “What do you mean when you say…” or “Is this what you mean?”
Hear the emotion behind the words . It’s the higher frequencies of human speech that impart emotion. You can become more attuned to these frequencies—and thus better able to understand what others are really saying—by exercising the tiny muscles of your middle ear (the smallest in the body). You can do this by singing, playing a wind instrument, or listening to certain types of high-frequency music (a Mozart symphony or violin concerto, for example, rather than low-frequency rock, pop, or hip-hop).
The way you look, listen, move, and react to another person tells them more about how you’re feeling than words alone ever can. Nonverbal communication, or body language, includes facial expressions, body movement and gestures, eye contact, posture, the tone of your voice, and even your muscle tension and breathing.
Developing the ability to understand and use nonverbal communication can help you connect with others, express what you really mean, navigate challenging situations, and build better relationships at home and work.
- You can enhance effective communication by using open body language—arms uncrossed, standing with an open stance or sitting on the edge of your seat, and maintaining eye contact with the person you’re talking to.
- You can also use body language to emphasize or enhance your verbal message—patting a friend on the back while complimenting him on his success, for example, or pounding your fists to underline your message.
Improve how you read nonverbal communication
Be aware of individual differences. People from different countries and cultures tend to use different nonverbal communication gestures, so it’s important to take age, culture, religion, gender, and emotional state into account when reading body language signals. An American teen, a grieving widow, and an Asian businessman, for example, are likely to use nonverbal signals differently.
Look at nonverbal communication signals as a group. Don’t read too much into a single gesture or nonverbal cue. Consider all of the nonverbal signals you receive, from eye contact to tone of voice to body language. Anyone can slip up occasionally and let eye contact go, for example, or briefly cross their arms without meaning to. Consider the signals as a whole to get a better “read” on a person.

Improve how you deliver nonverbal communication
Use nonverbal signals that match up with your words rather than contradict them. If you say one thing, but your body language says something else, your listener will feel confused or suspect that you’re being dishonest. For example, sitting with your arms crossed and shaking your head doesn’t match words telling the other person that you agree with what they’re saying.
Adjust your nonverbal signals according to the context. The tone of your voice, for example, should be different when you’re addressing a child than when you’re addressing a group of adults. Similarly, take into account the emotional state and cultural background of the person you’re interacting with.
Avoid negative body language. Instead, use body language to convey positive feelings, even when you’re not actually experiencing them. If you’re nervous about a situation—a job interview, important presentation, or first date, for example—you can use positive body language to signal confidence, even though you’re not feeling it. Instead of tentatively entering a room with your head down, eyes averted, and sliding into a chair, try standing tall with your shoulders back, smiling and maintaining eye contact, and delivering a firm handshake. It will make you feel more self-confident and help to put the other person at ease.
How many times have you felt stressed during a disagreement with your spouse, kids, boss, friends, or coworkers and then said or done something you later regretted? If you can quickly relieve stress and return to a calm state, you’ll not only avoid such regrets, but in many cases you’ll also help to calm the other person as well. It’s only when you’re in a calm, relaxed state that you’ll be able to know whether the situation requires a response, or whether the other person’s signals indicate it would be better to remain silent.
In situations such as a job interview, business presentation, high-pressure meeting, or introduction to a loved one’s family, for example, it’s important to manage your emotions, think on your feet, and effectively communicate under pressure.
Communicate effectively by staying calm under pressure
Use stalling tactics to give yourself time to think. Ask for a question to be repeated or for clarification of a statement before you respond.
Pause to collect your thoughts. Silence isn’t necessarily a bad thing—pausing can make you seem more in control than rushing your response.
Make one point and provide an example or supporting piece of information. If your response is too long or you waffle about a number of points, you risk losing the listener’s interest. Follow one point with an example and then gauge the listener’s reaction to tell if you should make a second point.
Deliver your words clearly. In many cases, how you say something can be as important as what you say. Speak clearly, maintain an even tone, and make eye contact. Keep your body language relaxed and open.
Wrap up with a summary and then stop. Summarize your response and then stop talking, even if it leaves a silence in the room. You don’t have to fill the silence by continuing to talk.
Quick stress relief for effective communication
When a conversation starts to get heated, you need something quick and immediate to bring down the emotional intensity. By learning to quickly reduce stress in the moment, you can safely take stock of any strong emotions you’re experiencing, regulate your feelings, and behave appropriately.
Recognize when you’re becoming stressed. Your body will let you know if you’re stressed as you communicate. Are your muscles or stomach tight? Are your hands clenched? Is your breath shallow? Are you “forgetting” to breathe?
Take a moment to calm down before deciding to continue a conversation or postpone it.
Bring your senses to the rescue. The best way to rapidly and reliably relieve stress is through the senses—sight, sound, touch, taste, smell—or movement. For example, you could pop a peppermint in your mouth, squeeze a stress ball in your pocket, take a few deep breaths, clench and relax your muscles, or simply recall a soothing, sensory-rich image. Each person responds differently to sensory input, so you need to find a coping mechanism that is soothing to you.
[Read: Quick Stress Relief]
Look for humor in the situation. When used appropriately, humor is a great way to relieve stress when communicating . When you or those around you start taking things too seriously, find a way to lighten the mood by sharing a joke or an amusing story.
Be willing to compromise. Sometimes, if you can both bend a little, you’ll be able to find a happy middle ground that reduces the stress levels for everyone concerned. If you realize that the other person cares much more about an issue than you do, compromise may be easier for you and a good investment for the future of the relationship.
Agree to disagree, if necessary, and take time away from the situation so everyone can calm down. Go for a stroll outside if possible, or spend a few minutes meditating. Physical movement or finding a quiet place to regain your balance can quickly reduce stress.
Find your space for healing and growth
Regain is an online couples counseling service. Whether you’re facing problems with communication, intimacy, or trust, Regain’s licensed, accredited therapists can help you improve your relationship.
Direct, assertive expression makes for clear communication and can help boost your self-esteem and decision-making skills. Being assertive means expressing your thoughts, feelings, and needs in an open and honest way, while standing up for yourself and respecting others. It does NOT mean being hostile, aggressive, or demanding. Effective communication is always about understanding the other person, not about winning an argument or forcing your opinions on others.
To improve your assertiveness
Value yourself and your options. They are as important as anyone else’s.
Know your needs and wants. Learn to express them without infringing on the rights of others.
Express negative thoughts in a positive way. It’s okay to be angry , but you must remain respectful as well.
Receive feedback positively. Accept compliments graciously, learn from your mistakes, ask for help when needed.
Learn to say “no.” Know your limits and don’t let others take advantage of you. Look for alternatives so everyone feels good about the outcome.
Developing assertive communication techniques
Empathetic assertion conveys sensitivity to the other person. First, recognize the other person’s situation or feelings, then state your needs or opinion. “I know you’ve been very busy at work, but I want you to make time for us as well.”
Escalating assertion can be employed when your first attempts are not successful. You become increasingly firm as time progresses, which may include outlining consequences if your needs are not met. For example, “If you don’t abide by the contract, I’ll be forced to pursue legal action.”
Practice assertiveness in lower risk situations to help build up your confidence. Or ask friends or family if you can practice assertiveness techniques on them first.
More Information
- Effective Communication: Improving Your Social Skills - Communicate more effectively, improve your conversation skills, and become more assertive. (AnxietyCanada)
- Core Listening Skills - How to be a better listener. (SucceedSocially.com)
- Effective Communication - How to communicate in groups using nonverbal communication and active listening techniques. (University of Maine)
- Some Common Communication Mistakes - And how to avoid them. (SucceedSocially.com)
- 3aPPa3 – When cognitive demand increases, does the right ear have an advantage? – Danielle Sacchinell | Acoustics.org . (n.d.). Retrieved May 22, 2022, from Link
- How to Behave More Assertively . (n.d.). 10. Weger, H., Castle Bell, G., Minei, E. M., & Robinson, M. C. (2014). The Relative Effectiveness of Active Listening in Initial Interactions. International Journal of Listening , 28(1), 13–31. Link
More in Communication
How to read body language to build better relationships at home and work

Boost your EQ to help find happiness and success

Tips for handling conflicts, arguments, and disagreements

How to feel and respond to the emotions of others

Tips and techniques for getting anger under control

Using laughter and play to resolve disagreements

The 5 Love Languages
What they are and how they influence relationships

Turning Off the Gas on Your Gaslighter
5 ways to deal with gaslighting

Professional therapy, done online
BetterHelp makes starting therapy easy. Take the assessment and get matched with a professional, licensed therapist.
Help us help others
Millions of readers rely on HelpGuide.org for free, evidence-based resources to understand and navigate mental health challenges. Please donate today to help us save, support, and change lives.
Power of Effective Communication Essay
Introduction, what is effective communication, models of effective communication, the mbi communication model, barriers to effective communication, how to communicate effectively, effective communication in the global context.
Communicating effectively has been one of the important factors that help a person to succeed in the chosen profession. Studies have estimated that employees typically spend about 75% of their time communicating with colleagues or customers. Personnel who interface with their clients need exceptionally effective communicating skills. Various features related to effective communications are discussed in this paper. Issues and opportunities such as what is effective communication, models of effective communication, global communication strategies, and others are examined.
Keane (July 2007) has suggested that effective communication is the skill of stating ideas, thoughts, instructions, or reports, in an unambiguous manner and with clarity so that the audience understands the intended meaning. Effective Communication is the process where information and ideas are relayed and received. Ideas are conveyed in spoken, written, or visual contexts and when a person is speaking, the tone of voice and the body language are very important. According to Keane, words make up for 7 percent of the communicated information, tone accounts for 55 %, and body language for 38 %. To be effective communicators, people should be aware of these forms, their use, and possible communication barriers The author rates effective communication along with skills such as delegation, time management, motivation, and leadership skills. To work or lead effectively, a manager or supervisor has to know how to explain clearly what needs to be done and how it has to be done. Keane has argued that an organization in effect acts like a human decision-making system and the quality and depth of the decisions that are taken depend on the effectiveness of the system used for communication.
Blitefield (2006) has presented a detailed discussion of the process of communication. According to the author, the process of communication has one communicator and at least one or more receivers. Effective communication starts with how completely the communicator can relate the information and how much of the information that is relayed is understood by the receivers. Effective communication between different disciplines has become one key aspect in organizations. In many cases, the communication process becomes complex when the subjects are controversial or there are multiple and diverse teams. The author speaks of the need to bridge the differences and this is one of the most important factors. The author has defined effective communication as the transmission of subjects and meaning between people and minimizing any misunderstand between them. Several models have been proposed for effective communications and some of them are discussed in the next paragraphs.
Robbins (2003) has suggested that the models of effective communication essentially start with a clear understanding of how people bridge their communication differences or the communication gap as it is called. The author argues that people tend to interpret information by using their reference frame and these references have been shaped by cultural backgrounds or group associations. The process of bridging is an try to minimize the inherent differences by trying to understand the reference frame that others are using. The process of bridging again needs to be a two-way process and both the sender and receiver have to attempt to remove any obstacles. The process of bridging the cultural differences among different groups becomes very important in business contexts such as management. Hofstede (1980) had proposed a framework that would help to assess the cultures by identifying 5 important value dimensions of the national cultures. The model was later expanded by other research organizations till no dimensions were identified. Myers (1985) has proposed the Myer Briggs Type Indicator that makes up the personality framework and explains the behavior of individuals and the concepts can be used to explain the different relationships between cultures.
The Map-Bridge-Integrate model has three interacting components and provides a means to bridge the cultural differences (DiStefano et all, 2002)
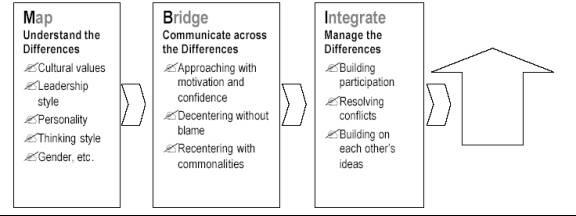
Map – Understand the Differences: The Map component is used in describing and understanding any differences between team members and also specifying the impact that these differences have on team objectives. There are three aspects and they are: selecting the characteristics to be mapped; description of members’ characteristics and identification of the impact of the characteristics.
Bridging – Communicate across the Differences: The Bridging component deals with communicating effectively across the group differences to bring ideas and people together. The main aim of this component is to stop miscommunication There are three aspects to this component: preparing and motivating members to build confidence and communicate so that problems are overcome. This is important since there is a possibility that because of lack of motivation, communication may not happen even after the differences are understood. Decentring where the team members try to explain their understanding of the difference in the process of communication by altering their behavior and thought process. This allows other cultures to be accommodated in their understanding. Re-centring is another aspect and team members try to create a new basis on which interactions can be created. A good understanding of differences is required and consent on shared norms has to be agreed upon.
Integrating – manage the Differences: The integrating component ensures that people use their differences to make good decisions. The understanding developed in the mapping component is converted to obtain positive results. There are three aspects for this component and they are: managing the participation to ensure that all members have an equal opportunity to participate by accommodating different norms for participation that would result from cultural differences; resolving disagreements or possible conflicts so that any disputes are addressed before they increase. The mapping component helps to detect early any probable areas and conflict zones while the bridging component helps to make manageable any personal conflicts. The third aspect is the building on ideas which is the final aspect. Individual ideas are taken as the starting point for any discussion and the concept of ownership needs to be left.
McAteer (March 2007) speaks of certain barriers to communication and the author defines barriers as Barriers are factors that break down or impede a continuous relay of information. These barriers tend to disrupt the process and act of communication. The author has suggested several factors that act as barriers and they are: Nonassertive behavior, Task preoccupation, frustration and anger at the communicator, any personal enmity or bias, diversity in the team with little areas of common interest, lack of confidence in self or on the communicator; complex organizational structure, distractions, tunnel vision, external and internal interruptions and so on.
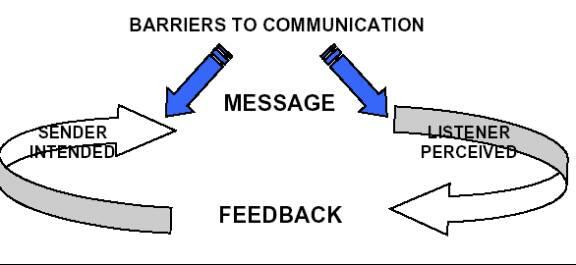
Smith (December 2007) has pointed that two types of major differences create barriers to effective communication and they are: Cultural differences and Group differences. Cultural differences occur when people from different cultures are involved in the communication process. Culture is defined informally as a set of shared traditions, values, and beliefs that control the formation and behavior of different social groups. The author argues that cultures have a strong influence on how people communicate and relate with each other. The cultural differences often create a bias or a barrier between the communicator and the receivers. Group differences on the other hand are due to peer pressure among group members and it is the predominant group mentality that creates a barrier against communication. The author argues that groups can be based according to work natures, ethnicity, and nationality, profession, and gender. Groups can also be formed as per the roles they play such as engineers, doctors, students, teachers, and so on and in many cases, the groups may even form associations. Groups with whom people are associated are called in-groups while groups with which people are not associated are called out-groups. The author suggests that these groups often have their vocabulary, mannerisms, and code of conduct and when one such group tries to communicate with the others, these mannerisms are not carried through and it can result in miscommunications.
Taylor (July 2006) has stressed that effective communications have to be a two-way process and begin with the communicator or the sender who would convey the required information necessary. The sender must have to be proactive and ensure that the receiver can understand the information. Certain key factors that need to be followed are: stating one idea at a time; putting forward the ideas in a medium that is understood; take extra care to elaborate and repeat if required, understand the body language of the audience and ask questions now and then to keep them involved in the discussion. Taylor has defined the four A’s of successful communication and they are Attention; Appreciation, Action, and Assimilation. The Four A’s are illustrated in Figure 3.
Attention: this is the first step in the process of effective communication and it deals with getting the receiver’s attention. This can be achieved by: overcoming distractions such as disturbing mannerisms, noise, emotional and attitude problems, negative and sarcastic attitude, and so on; using an appropriate greeting, showing respect and empathy for the people
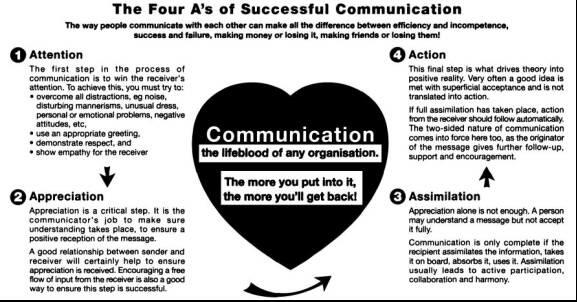
Appreciation: Appreciation is a critical step and it is the responsibility of the communicator to ensure that understanding takes place and that there is a positive reception of the message. A good relationship between the sender and the receiver will help to ensure that appreciation is received. Encouraging a free flow of input from the receiver is also a good way to ensure that this step is carried out properly.
Assimilation: This is the third step and though a person understands a message, it may not be accepted fully. Communication is considered only after the recipient assimilates the information, takes and uses it. It leads to active participation, collaboration, and harmony.
Action: This is the final step and moves the theory of communication into reality. In some cases, a good idea or a meaningful message is accepted superficially but is not translated into action. If complete assimilation takes place, the action from the receiver has to follow. A two-sided communication is brought into action and results in the required activity.
Yates (et all, 2006) have stressed the importance of effective communication for organizations that operate globally. Such organizations operate in different time zones and have employees who have different backgrounds and nationalities. In such a scenario, a proper communication strategy has to be in place to ensure that the messages given out by management are not distorted and the true intent is assimilated. The authors surveyed some leading global organizations to understand how they managed the communication strategy. They used a survey instrument to identify the best practices and the response percentages are shown in Figure 4.
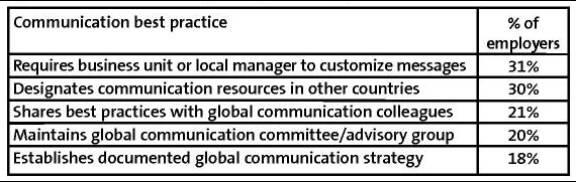
The study showed that only about 18% of the organizations had an established and documented global communication strategy. What many enterprises are learning is that the traditional approach to global communication – translating messages into several languages and shipping them to local managers for dissemination – simply doesn’t work. This approach often results in messages that are misunderstood, miscommunicated, and sometimes not communicated at all. Several multinationals have recognized the value of bringing a global perspective to their communication strategies. The author has reported several steps that such companies are taking up and they are:
Getting global participation: One of the biggest challenges in developing a global strategy is ensuring that the strategy supports and drives corporate goals without overlooking the distinct needs of separate regions, countries, and business areas. Inputs from people around the world are needed to strike the right balance (Maznevski, M. L., 1994).
Making global teams effective: Enterprises that put together effective global teams to develop and maintain the communication strategy are achieving some very positive results. The keyword here, though, is effective. Research into the performance of global teams – and this is not just global communication teams – shows that such teams don’t always deliver the value the enterprise expects. Cultural differences represented in multicultural teams provide great potential for creating value.
Creating messages with a global appeal: Global input provides insight into cultural sensitivities, compliance and legislative differences, and the unique characteristics of each market. Effective communicators use this insight to craft messages that are easy to interpret, translate and adapt to local needs. They also look at the type and content of messages to determine how widely they need to be communicated. The best global communicators determine which messages cannot be tinkered with and which areas of content are open for local customization. Moreover, they make it clear to local managers, which messages must be delivered exactly as presented and which ones can be adapted or expanded to address local needs.
Training local managers to communicate: While some multinationals have dedicated internal communicators on a regional basis, some of them have dedicated communicators on a country or local basis. Some companies rely on local managers to interpret and deliver messages. Functionally, these managers might be responsible for HR, plant management, or operations, so they often don’t have expertise in communication. Unfortunately, few companies provide training and support for these local managers and fewer still have processes in place to ensure that messages were delivered and understood.
Choosing the right delivery mechanisms: Effective internal communicators take advantage of a variety of media and technologies to communicate corporate messages. Options enable local managers to select the tools and information that work best for local employees. Face-to-face presentations work better in some parts of the world, while self-learning tools work better in others.
Measuring success: There are a variety of ways to measure, from focus groups and comprehensive annual employee surveys to quarterly targeted surveys, short feedback questionnaires for forums and workshops, and phone calls to local managers and employees. Such activities help to keep a pulse on whether or not people are receiving, understanding, and embracing messages. As the measurement processes are developed, the ultimate goal should be to identify the links between communication effectiveness and improved productivity and business performance.
The paper has discussed various issues related to effective communication. Effective communication is the process where the exchange of information takes place clearly and unambiguously. Global companies are facing an increasing challenge in inputting into a place an effective communication strategy that would reach employees from different cultural backgrounds.
Blitefield Jerry. (2006). The Rhetoric of RHETORIC: The Quest for Effective Communication. Journal of Rhetoric & Public Affairs. East Lansing. Volume 9. Issue 4. pp: 710-714.
DiStefano, J. J. Ekelund, B. Z. (2002). The MBI Model of Managing Differences Effectively. In Heritage & Management: Identity as a Competitive Tool, J. M. Fladmark (ed.), Donhead Publishing, Edinburgh.
Hofstede, G. (1980). Cultural Consequences: International Differences in Work-Related Values. Sage, Beverly Hills, CA.
Keane Tess. (2007). Power of effective communication. Nursing Standard: Harrow on the Hill. Volume 21. Issue 45. pp: 78-80.
Maznevski, M. L. (1994). Synergy and Performance in Multicultural Teams, Ph.D. dissertation. The University of Western Ontario.
McAteer Teal. (2007). Strategic Organizational Change. Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences. Halifax. Volume. 24. Issue 1. pp: 74-76.
Robbins, S. P. (2003). Organizational Behavior. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
Smith Marolee Beaumont. (December 2006). A Study on South African Corporate Business Failures. Journal of The Business Review, Cambridge. Hollywood. Volume 6. Issue 1. pp: 168-173.
Taylor Shirley. (2006). Communicating across Cultures. The British Journal of Administrative Management. Orpington. pp: 12-15.
Yates Kathryn. Beech Roger. (2006). Six crucial steps to effective global communication. Journal of Strategic Communication Management. Chicago. Volume 10. Issue 5. pp: 26-30.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, September 18). Power of Effective Communication. https://ivypanda.com/essays/power-of-effective-communication/
"Power of Effective Communication." IvyPanda , 18 Sept. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/power-of-effective-communication/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Power of Effective Communication'. 18 September.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Power of Effective Communication." September 18, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/power-of-effective-communication/.
1. IvyPanda . "Power of Effective Communication." September 18, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/power-of-effective-communication/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Power of Effective Communication." September 18, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/power-of-effective-communication/.
- Role Model as a Communicator
- Bridging Cultures: Colorado Street Bridge
- Bridging the Gap in Meeting Customer Expectations
- How Instant Messages Have Changed Communication
- The Power of Propaganda
- Organizational Communication and Its Definition
- Concepts of Speech: Critique
- Communication in a Relationship and Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory
BUS209: Organizational Behavior
Communication
This chapter reading is a great resource to highlight and reinforce the concepts we learned in the previous video. The chapter begins with the Radio Shack case, which exemplifies the wrong way to communicate bad news. Consider the message, as well as the medium that you would choose in this situation. Also, take a look at the "communication freezers", words that essentially shut down effective communication within your workplace. Do you use these words? What might you say instead to create bridges instead of barriers?
In this chapter we have reviewed why effective communication matters to organizations. Communication may break down as a result of many communication barriers that may be attributed to the sender or receiver. Therefore, effective communication requires familiarity with the barriers. Choosing the right channel for communication is also important, because choosing the wrong medium undermines the message. When communication occurs in the cross-cultural context, extra caution is needed, given that different cultures have different norms regarding nonverbal communication, and different words will be interpreted differently across cultures. By being sensitive to the errors outlined in this chapter and adopting active listening skills, you may increase your communication effectiveness.
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- JALM Talk Podcasts
- Special Issues & Special Collections
- ADLM Guidance Documents
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Call for Papers
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Why Publish?
- About The Journal of Applied Laboratory Medicine
- Editorial Board
- Advertising & Corporate Services
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
2 nonstandard abbreviations.
- < Previous
The Importance of Effective Communication: Some Food for Thought
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Nikola A Baumann, The Importance of Effective Communication: Some Food for Thought, The Journal of Applied Laboratory Medicine , Volume 1, Issue 4, 1 January 2017, Pages 460–461, https://doi.org/10.1373/jalm.2016.021865
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Having been active in the Society for Young Clinical Laboratorians (SYCL) 2 for several years, the opportunity to give something back as a speaker at the SYLC Workshop preceding the 2016 AACC Annual Meeting was an honor. The SYCL workshop centered around the theme of communication and leadership, and I was asked to provide insight into effective communication with staff and trainees—a rare chance to reflect on the soft skills that we all use every day. These are the skills that some believe can't be taught. This may be true, but time spent on thoughtful contemplation of what we do and how we do it is usually time well spent. Researching and reflecting on this topic has raised my awareness of the importance of communication, including communication challenges such as providing constructive feedback and listening. Below, I attempt to share my findings and my experience.
Mind the say-do gap.
Make the complex simple.
Find your own voice.
Be visible.
Listen with your eyes as well as your ears.
Notice that these 5 habits have little to do with what one says but rather how one says it. Keeping your message simple and genuine will go a long way. In addition, more than half of communication is nonverbal including body language, gestures, and eye contact. It is important to be aware of what you are saying nonverbally. Even a brief moment of checking your email during someone's presentation conveys a nonverbal message. Styles of communication vary. An excellent article by Mark Murphy distills communication into 4 styles: analytical, intuitive, functional, and personal ( 2 ). Although no style is superior, effective communicators know how to recognize and match their communication style with their audience whether it be their boss, peers, direct reports, or trainees.
As leaders and educators, some of our most valuable and formative communication will be in the form of feedback. Statements such as “great job” and “well done” are easy to give and are certainly well received. However, the receiver may be left wondering what specifically they did that was great and wondering if there are areas that could be improved. When giving feedback, it is important to be positive (if it is genuine), be specific, be immediate (or at least timely), and be tough if needed, but not mean (or rob the recipients of their dignity) ( 3 ). In many cases, the person receiving the feedback recognizes what is going well and what is not, so start by asking for his or her perspective. Ask them how they feel they performed or if there are areas they want to improve upon. This step opens the door for constructive feedback without a defensive atmosphere. Formative feedback should be given in private and not in the hallway or in front of peers. And although it is often a delicate process, honest assessment of a person's progress can lead to substantial growth and improvement.
In my experience, the most underused and least perfected communication skill is listening. In professional settings, individuals with authority should listen more (i.e., talk less). I have a favorite quote: “Most people do not listen with the intent to understand; they listen with the intent to reply” (Stephen Covey). To illustrate the truth of this statement, I asked the SYCL workshop attendees to pair up and do an exercise in listening. Each pair chose one person to be a speaker and one to be a listener. The speaker was asked to talk about any topic they wanted to for 2 minutes. The listener's job was to listen and not say a word. Just listen. As I watched this exercise unfold, I observed listeners who were struggling not to speak, desperately wanting to share their own story, offer their advice, and provide their feedback. On discussing the activity, attendees felt that “just listening” was difficult and far more challenging than speaking. This is more food-for-thought in our daily interactions.
Finally, it was indeed a rare (and somewhat terrifying) opportunity to stand in front of the next generation of leaders and be asked to provide them with a few personal golden nuggets of professional advice. Initially, it was overwhelming, but once I really thought about what I have found to be important in my professional interactions, the following came to light: ( a ) Say what you mean and mean what you say (even when it's easier to say what you think people want to hear). ( b ) In leadership and management relations, a “unified front” will make your job easier and your team more confident. Conversely, a “divided front” will do the opposite—create division in the work unit and drain positive energy from the team. ( c ) Don't tip-toe around the hard stuff, it won't go away. ( d ) Be real. And perhaps most importantly, ( e ) wrap it all up in a package of kindness.
Society for Young Clinical Laboratorians.
Author Contributions: All authors confirmed they have contributed to the intellectual content of this paper and have met the following 4 requirements: (a) significant contributions to the conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; (b) drafting or revising the article for intellectual content; (c) final approval of the published article; and (d) agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the article thus ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the article are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Authors' Disclosures or Potential Conflicts of Interest: Upon manuscript submission, all authors completed the author disclosure form. Employment or Leadership: None declared. Consultant or Advisory Role: None declared. Stock Ownership: None declared. Honoraria: N.A. Baumann, AACC. Research Funding: None declared. Expert Testimony: None declared. Patents: None declared.
Forbes /Leadership, Susan Tardanico. 5 habits of highly effective communicators [internet] . http://www.forbes.com/sites/susantardanico/2012/11/29/5-habits-of-highly-effective-communicators/#428f682225fc (Accessed July 2016).
Forbes /Leadership, Mark Murphy. Which of these 4 communication styles are you? http://www.forbes.com/sites/markmurphy/2015/08/06/which-of-these-4-communication-styles-are-you/#6dd000f11ecb (Accessed July 2016).
Entrepreneur. www.entrepreneur.com (Accessed July 2016).
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to Your Librarian
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 2475-7241
- Copyright © 2024 Association for Diagnostics & Laboratory Medicine
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Clarity: The first quality of good communication is clarity. Clarity m eans the quality of being expressed. clearly. The receiver must understand the meaning of the m essage exactly as the ...
Effective communication is a cornerstone of human interaction and a critical skill for individuals in both personal and professional contexts. In an age marked by rapid technological advancement and an increasingly interconnected world, the ability to convey ideas, thoughts, and emotions accurately is more vital than ever. ...
Effective communication skills are fundamental to good interactions between two or more people. This book, An Introduction to Communication Skills, is the first in the series. It starts by explaining more about the theory and nature of communication, then moves on to discuss effective spoken communication, the
Communication is essential to maintain healthy relationships between the students, faculty, and parents. Establishing effective communication practices in a school requires understanding the characteristics of communication, including the benefits and common barriers. The three critical components of effective communication - trust,
Effective communication is a fundamental aspect of human interaction, serving as the foundation for building strong relationships, resolving conflicts, and achieving shared goals. It encompasses a wide range of skills and practices that enable individuals to convey their thoughts, feelings, and ideas clearly and empathetically while actively listening to others.
Dr Yashpal D Netragaonkar. Effective communication is 20% what you know and 80% how you feel about what you know."-. Jim Rohn Effective communication is an interpersonal process in which verbal symbols (e.g. words, sentences) and non verbal symbols (e.g. body postures, facial gestures) are shared and understood by people.
The book contains a wealth of real-life examples of what works and what doesn't in communication, and each chapter provides a recap of best practices and key lessons learned. This book should be on the must-read list of any person who aspires to lead by capturing the hearts and minds of his or her stakeholders.".
communication, most people describe the techniques used to express what they think, feel, want, etc.—namely talking, writing or body language. However, when you confront difficult issues, listening is more important than speaking or any other form of expression. To improve communication, recognize the importance of listening and make listening a
4.1 Verbal and Nonverbal Communication Technique. Effective communication is a cornerstone of successful interactions in various aspects of life, ranging from personal relationships to professional environments. It encompasses both verbal and nonverbal communication techniques, each playing a vital role in conveying messages, building ...
Effective communication is the process of exchanging ideas, thoughts, opinions, knowledge, and data so that the message is received and understood with clarity and purpose. When we communicate effectively, both the sender and receiver feel satisfied. Communication occurs in many forms, including verbal and non-verbal, written, visual, and ...
Effective communication skill 1: Become an engaged listener. When communicating with others, we often focus on what we should say. However, effective communication is less about talking and more about listening. Listening well means not just understanding the words or the information being communicated, but also understanding the emotions the ...
Keane (July 2007) has suggested that effective communication is the skill of stating ideas, thoughts, instructions, or reports, in an unambiguous manner and with clarity so that the audience understands the intended meaning. Effective Communication is the process where information and ideas are relayed and received.
- Into the Essay: Excerpts from actual papers show the ideas from the chapters in action because you learn to write best by getting examples rather than instructions. Much of my approach to academic writing developed during my time in the Harvard College Writing Program. I am especially grateful to Tom Jehn,
Language continues to remain a barrier to convey our messages to people in the globalization and communication era. Language barriers are a common challenge in international business, aviation and social settings. ey affect our daily life. Language barriers are the root causes of many problems or obstacles in health care, aviation, maritime ...
communication, in which teachers are key players (communicators). In this regard, Waldeck et al., (2001) maintains that effective communication has the capacity to concretely help teachers in employing the educational goals of HE, and recognize their societal impact -as the ultimate intended outcomes of the educational system.
Conclusion. In this chapter we have reviewed why effective communication matters to organizations. Communication may break down as a result of many communication barriers that may be attributed to the sender or receiver. Therefore, effective communication requires familiarity with the barriers. Choosing the right channel for communication is ...
Styles of communication vary. An excellent article by Mark Murphy distills communication into 4 styles: analytical, intuitive, functional, and personal . Although no style is superior, effective communicators know how to recognize and match their communication style with their audience whether it be their boss, peers, direct reports, or trainees.
Hence, open-mindedness is an additional communication skill that is treasured. Being confident, maintaining eye contact and being respectful are other skills that make a good communicator. Confidence while maintaining eye contact will make individuals keen to follow the interaction while respect will make it less strenuous for others to express ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.
The two basic types of communication are verbal and non-verbal. 2. Why is important to be a good listener? Answers will vary. Accurately eceiving a message is just as important and sending a message. Make sure answers are written in complete sentences. 3.
Rule 193F-20.17 - [Rescinded effective 5/22/2024] Service and filing of pleadings and other papers (1) When service is required. Except where otherwise provided by law, every pleading, motion, document, or other paper filed in a contested case proceeding and every paper relating to discovery in such a proceeding shall be served upon each of the parties of record to the proceeding, including ...
Rule 193F-20.28 - [Rescinded effective 5/22/2024] Ex parte communication (1) Prohibited communications. Unless required for the disposition of ex parte matters specifically authorized by statute, following issuance of the notice of hearing, there shall be no communication, directly or indirectly, between the presiding officer and any party or representative of any party or any other person ...