How to make a business plan
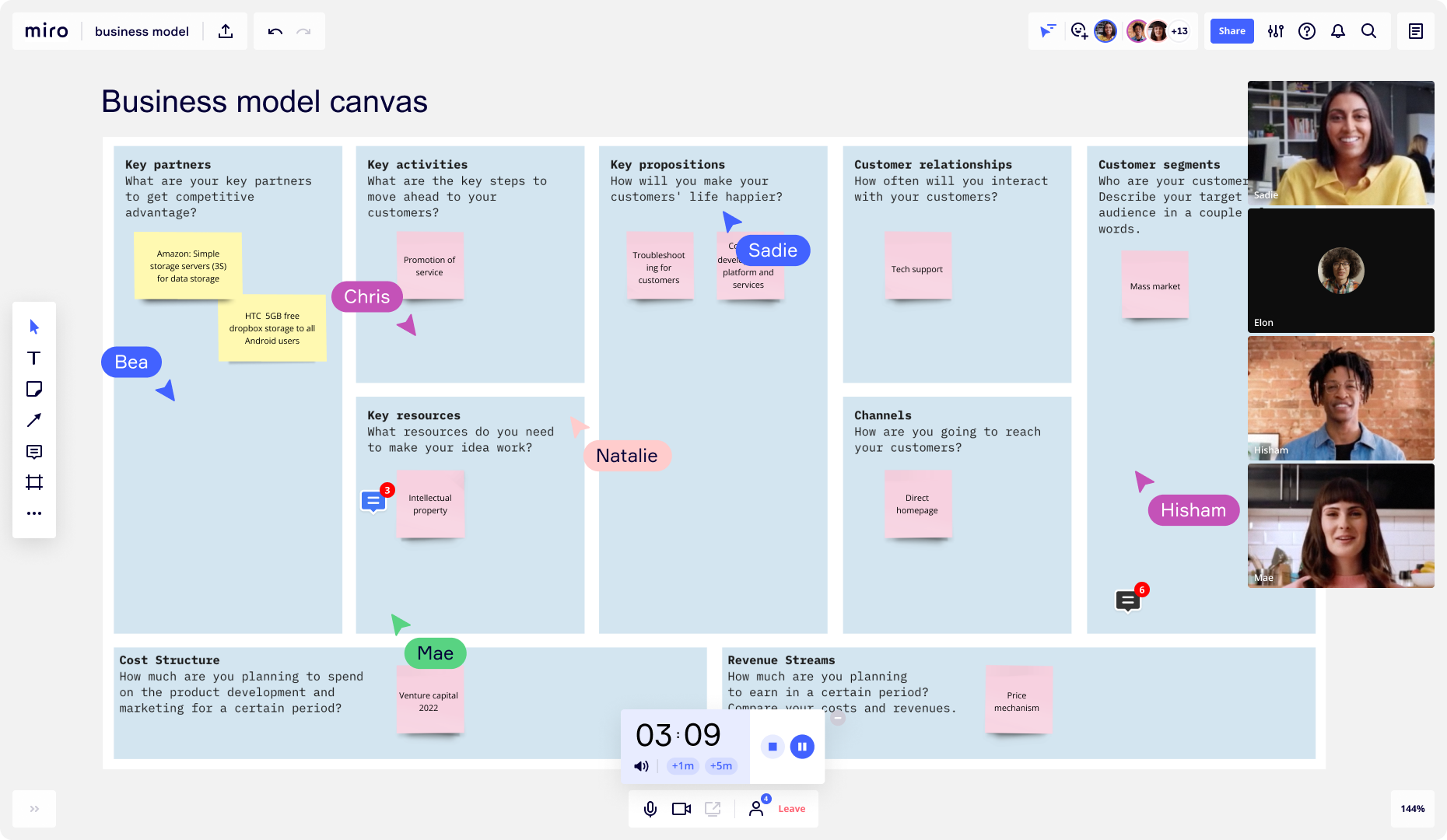

Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Unternehmensstrategie |
- Businessplan: Leitfaden und Beispiele i ...
Businessplan: Leitfaden und Beispiele im Überblick!

Zusammenfassung
Ein Businessplan ist ein schriftliches Dokument, welches die Geschäftsidee und den Fahrplan eines Unternehmens detailliert beschreibt. Dieses Dokument ist sowohl für Gründer als auch für Kapitalgeber ungemein wichtig. Erfahren Sie in diesem Artikel mehr über den Aufbau, die Anforderungen und die möglichen Fehler.
Haben Sie eine neue Geschäftsidee und möchten ein neues Unternehmen gründen? Dann gibt es viele Dinge, die Sie beachten müssen. Von der Entwicklung des Produkts oder Dienstleistung bis hin zu den Marketingstrategien und der Buchhaltung. Um alle diese Informationen übersichtlich für Sie und Ihre zukünftigen Stakeholder und Kapitalgeber gestalten zu können, sollten Sie auf einen Businessplan setzen.
Ein Businessplan hilft Ihnen dabei, Ihr Geschäftsmodell konkret und übersichtlich zu gestalten. In diesem Artikel erfahren Sie deshalb alles Wichtige im Bezug auf den eigenen Businessplan. So erhöhen Sie die Chance, dass Sie Ihre Geschäftsidee erfolgreich umsetzen können.
Was ist ein Businessplan?
Als mögliche Alternative zum Businessplan wäre das Business Model Canvas anzuführen, was jedoch eher als Ergänzung dienen sollte.
Warum muss ich einen Businessplan schreiben?
Ein Businessplan ist heutzutage ungemein wichtig, um Gelder von Kapitalgebern zu erhalten. Dies gilt ebenfalls für Gründungszuschüsse oder Gelder von Förderprogrammen. Denn in den meisten Fällen bedeutet eine Geschäftsidee hohe Investitionen, die oft nicht von der eigenen Tasche gedeckt werden können. Deshalb müssen sich Gründer an dieser Stelle einen Kredit bei einer Bank oder einem Kapitalgeber aufnehmen. Diese verlangen meist einen Businessplan, damit sie einen umfangreichen Überblick über Ihre Geschäftsidee bekommen.
Aber auch für andere Geschäftspartner ist der Businessplan wichtig. Da Ihr Unternehmen noch nicht lange oder gar nicht am Markt existiert, brauchen Geschäftspartner ein gewisses Maß an Vertrauen in Ihr Unternehmen, um einer Zusammenarbeit zuzustimmen. Dabei kann ein Businessplan ungemein hilfreich sein.
Schlussendlich ist aber auch ein Businessplan für Sie und Ihr Gründungsvorhaben sehr wichtig. Denn die Gründung eines Start-ups mit einer neuen Geschäftsidee kommt mit einer Menge an Aufgaben und Verantwortung. Um den Überblick über diese vielen Bereiche behalten zu können, ist es sinnvoll, einen Businessplan zu schreiben. Dadurch können Sie sich in der Anfangszeit immer wieder auf Ihren Fahrplan stützen, um den Überblick zu behalten und alle wichtigen Dinge abzuarbeiten. Der Businessplan ist daher sozusagen eine Anleitung für die Unternehmensgründung.
Was gehört in einen Businessplan?
Wenn Sie nun eine Geschäftsidee haben und diese in die Tat umsetzen möchten, werden Sie im ersten Schritt mit der Erstellung des Businessplans beginnen. Dabei ist es wichtig, dass der Aufbau übersichtlich, detailliert und in sich schlüssig ist. Wie Sie den Businessplan aufbauen möchten, bleibt grundsätzlich Ihnen überlassen. Dennoch gibt es Gliederungen, auf die Sie setzen können.
Folgendermaßen sollte der Businessplan grob aussehen:
Executive Summary: Am Anfang Ihres Businessplans werden alle wichtigen Informationen auf ein bis zwei Seiten zusammengefasst. Zu Beginn werden die Kapitalgeber nämlich nur diese Seiten lesen und auf Basis dessen entscheiden, ob sie das Dokument vollständig durchlesen werden. Beantworten Sie daher in der Executive Summary alle wichtigen Fragen kurz und prägnant.
Haupttext: In diesem Abschnitt beschreiben Sie die Geschäftsidee, das Gründerteam und die konkrete Umsetzung.
Finanzteil: Für Kapitalgeber ist dieser Abschnitt sehr wichtig. Immerhin beschreiben Sie hier, welche Anfangskosten und monatlichen Kosten bei Ihrem Unternehmen anfallen werden, wie die Umsatzprognose aussieht und wie viel Kapital Sie benötigen.
Anhang: Am Ende fügen Sie alle relevanten Anhänge an. Dazu gehören verschiedene Datenblätter, Preisvoranschläge, Entwürfe und idealerweise die Lebensläufe der Gründer.
Kommen wir nun zum detaillierten Aufbau des Businessplans. In den nächsten Absätzen erfahren Sie mehr über die wichtigsten Bereiche, die in diesem Dokument beinhaltet sein sollten.
Geschäftsidee
In diesem Abschnitt geht es darum, Ihre Geschäftsidee und das Unternehmenskonzept so detailliert wie möglich zu beschreiben. Welche Produkte und welche Dienstleistungen bieten Sie an? Welches Problem wird mit Ihrem Angebot gelöst? Wie genau profitiert die Kundschaft von Ihrem Angebot?
Vertrieb & Wettbewerb
In diesem Abschnitt des Businessplans gehen Sie näher auf Ihre Zielgruppe, den Vertrieb und Ihre Konkurrenz ein.
Zielgruppe: Für die Zielgruppe können Sie beispielsweise Ihre Buyer Persona beschreiben. Hier sollten Sie Daten wie Altersspanne, Einkommensverhältnis, Hobbys, Interessen, etc. beschreiben. Für diese Daten kann eine Marktanalyse sehr hilfreich sein.
Vertrieb: Auf Basis dessen können Sie auch den Vertrieb planen: Auf welcher Plattform ist die Zielgruppe aktiv? Sollten Sie mit der Kundschaft persönlich oder digital, individuell oder standardisiert kommunizieren? Welche Vertriebswege und Marketingstrategien nutzen Sie? Wie binden Sie Kunden dauerhaft an Ihr Unternehmen? Im Bereich des Vertriebs sollten Sie auch hinzufügen, was Ihr Alleinstellungsmerkmal ist, und wie Sie die potentiellen Kunden von Ihrer Idee begeistern möchten.
Konkurrenz: Nicht unerheblich sind hier auch die Wettbewerber, mit denen Sie am Markt konkurrieren. Fügen Sie hier wichtige Wettbewerber hinzu und in welchen Aspekte Sie einzigartig oder besser sind. Dies bestätigt für die Kapitalgeber und Sie noch einmal das Alleinstellungsmerkmal (USP).
Gründungsteam
In diesem Abschnitt beschreiben Sie sich bzw. das Gründerteam näher. Gehen Sie hier auf wichtige Hintergrundinformationen, Qualifikationen und das Know-How ein, die Sie als Gründerperson bzw. als Team für die Unternehmensgründung in diesem Bereich geeignet machen.
Dazu sollten Sie auch auf Ihre Motivation näher eingehen und aus welchem Grund Sie und Ihr Team dieses Unternehmen gründen und dieser Idee nachgehen möchten. Näheres über den Lebenslauf müssen Sie hier nicht anführen, da Sie dies als Anhang hinzufügen können.
Visionen & Ziele
Einhergehend mit dem vorherigen Bereich sollten Sie hier Visionen und Ziele anführen, die Sie mit dem Unternehmen erreichen möchten. Nehmen wir dazu ein Businessplan Beispiel: Sie möchten ein Unternehmen gründen, welches unternehmensfreundlicher als die bestehende Konkurrenz agieren soll. Die daraus resultierenden Visionen und Ziele sind wichtig, damit Sie immer wieder daran festhalten können und die Kapitalgeber wissen lassen, wofür Ihr Unternehmen steht.
Führen Sie hier kurz-, mittel- und langfristige Ziele an, wie Sie Ihre Vision schlussendlich erreichen möchten. Dadurch wird auch die Unternehmensentwicklung im Laufe der Jahre erkenntlich.
Organisation
Ein ebenfalls wichtiger Aspekt in Ihrem Businessplan ist der Unternehmensaufbau. Hier sollten Sie anführen, welche Rechtsform Sie wählen und wie Ihr Firmenname lauten sollte.
Beantworten Sie ebenfalls folgende Fragen:
Gibt es Marken oder Patente, die Sie anmelden möchten?
Gibt es Genehmigungen für den Markteintritt?
An welchem Standort werden Sie gründen?
Wie werden Sie das Team aufstellen? Welche Hierarchie wählen Sie?
Wie viele Mitarbeiter müssen Sie einstellen?
Für die letzten Punkte kann ein Organigramm sehr hilfreich sein. Mehr darüber erfahren Sie, wenn Sie dem Link folgen.
SWOT-Analyse
Eine SWOT-Analyse ist ein wichtiger Bestandteil in Ihrem Businessplan. Hier können Sie selbstreflektierend auf Ihre Stärken und Schwächen eingehen, sowie die Risiken und Chancen, die mit Ihrer Geschäftsidee kommen.
An diesem Punkt sehen die Kapitalgeber, wie Sie als Unternehmensgründer zukünftig dafür sorgen, dass Sie Ihre Chancen und Stärken bestmöglich einsetzen und die Risiken und Schwächen so weit wie möglich minimieren.
Das Herzstück im Businessplan ist mit Sicherheit der Finanzteil: Hier führen Sie eine gründliche Finanzplanung durch mit Plan-Rechnungen, einer Rentabilitätsvorschau, einem Liquiditätsplan, Kostenaufstellungen, Ertragsquellen, dem Break-Even-Point, etc.
Natürlich lässt sich nur schwer vorhersagen, wie viel Umsatz und Gewinn Sie tatsächlich machen werden. Hierbei können jedoch Marktumfragen und Kostenvoranschläge sehr hilfreich sein, diese Zahlen realistischer darzustellen.
Gerade für Geldgeber sind diese Kalkulationen ungemein wichtig, da hierdurch auch erkenntlich wird, wie gut Sie und Ihr Team im Umgang mit Zahlen sind, welcher Kapitalbedarf bzw. Finanzierungsbedarf benötigt wird und wie sicher es ist, dass die Kapitalgeber ihr Geld wieder zurückbekommen.
Wie bereits vorher erklärt, fügen Sie am Schluss alle wichtigen Informationen an. Dazu zählen alle möglichen Unterlagen, die Sie für die Erstellung des Businessplans verwendet haben, wie etwa Ergebnisse von Marktumfragen, Datenblätter und auch Ihren Lebenslauf.
Welche Anforderungen sollte ein Businessplan erfüllen?
Sie sollten sich genügend Zeit nehmen, um Ihren Businessplan zu erstellen. Denn dieser Fahrplan ist nicht nur für Sie, sondern auch für die Kapitalgeber ungemein wichtig. Folgende Anforderungen sollten daher zwingend erfüllt werden:
Einfache Sprache: Gerade für Geschäftsideen in komplizierten Bereichen ist es wichtig, Fachbegriffe zu vermeiden und die Sprache so einfach und präzise wie möglich zu halten. Immerhin soll der Plan auch für Kapitalgeber verständlich sein, die wenig Erfahrung in Ihrem Bereich haben.
Gute Gliederung: Der Businessplan sollte gut gegliedert sein und einem roten Faden folgen. So bekommen die Leser des Businessplans einen optimalen Überblick über Ihre Idee und die Umsetzung.
Realistisch gestalten: Gerade wenn es um Themen wie das Marktpotenzial und die Umsatzprognosen geht, sollten Sie auf jeden Fall realistisch bleiben. Zu hohe Umsätze vorauszusagen kann gefährlich sein und sich negativ auswirken.
Kundennutzen hervorheben: In erster Linie sollten Sie betonen, dass Ihr Geschäftskonzept einen wesentlichen Kundennutzen erzeugt. Einfach nur bestehende Ideen zu kopieren wird Sie langfristig nicht erfolgreich oder einzigartig machen. Ein guter Businessplan zeigt klar auf, welche Aspekte Ihre Idee einzigartig machen.
Häufige Fehler
Nicht jeder Businessplan wird in die Tat umgesetzt. Und auch nicht jeder Businessplan überzeugt Kapitalgeber. Deshalb sollten Sie folgende Fehler unbedingt vermeiden:
Zu wenig Überarbeitung: Während Sie Ihre Pläne erstellen und die Recherche durchführen, werden sich die vorausgesagten Zahlen mit Sicherheit oft ändern. Haben Sie deshalb keine Angst davor, gewisse Abschnitte im Businessplan abzuändern und neu zu gestalten.
Zu wenig Marktrecherche: Die Marktforschung ist ungemein wichtig, da Sie dadurch vorab Bestätigung darüber kommen, wie die Idee bei der Kundschaft ankommt und welche Mitbewerber es gibt. Wenn diese Punkte im Businessplan fehlen oder nur mangelhaft beschrieben werden, kommt dies negativ bei Kapitalgebern an.
Kundennutzen nicht im Vordergrund: Ihr Businessplan sollte nicht nur von den Produkten und den Features sprechen. Wichtig ist, wie diese Features bei den Kunden ankommen. Seien Sie deshalb nicht zu stark produktorientiert und mehr kundenorientiert.
Gründer stehen nicht im Fokus: Wichtig ist auch, dass das Gründerteam bzw. Sie als Gründer im Fokus stehen. Eine Idee ist nichts ohne das Team, welches diese Idee umsetzen wird. Und viele Kapitalgeber bewilligen Kapital, da Sie von der Vision und der Motivation der Gründer überzeugt sind. Dieser Abschnitt sollte im Businessplan daher ebenfalls nicht zu kurz kommen.
Businessplan Vorlage
Wir von Asana möchten Unternehmerinnen und Unternehmer dabei unterstützen, Ihre Ideen in die Tat umzusetzen und dabei so produktiv und effizient wie möglich zu arbeiten. Daher haben wir für Sie eine Businessplan Vorlage erstellt, die Sie in unserer Software verwenden können. Speichern Sie alle wichtigen Dokumente und Informationen zentral und greifen Sie von überall aus darauf zu.
Verwandte Ressourcen

CRM-Strategie in 6 Schritten entwickeln!
Mission Statement formulieren: Beispiele und Vorlage!

Go-to-Market Strategie: Der 9-Schritte-Leitfaden!

Umsatzprognose in 5 einfachen Schritten erstellen!

How to Write a Professional Business Plan in 10 Easy Steps
Home » Blog » How to Write a Business Plan in 10 Easy Steps
During financial uncertainty, many of us press pause on our entrepreneurial aspirations.
Wondering if now’s the right time to start our business . Doubting our ideas and worrying about the what-ifs and maybes!
A business plan removes the uncertainty and what-ifs from the equation. It validates our business ideas, confirms our marketing strategies, and identifies potential problems before they arise.
Replacing our doubts with positivity, ensuring we see the complete picture, and increasing our chances of success.
Because you could be starting and running your own business . But you’ll only know for sure it’s the right move for you when you write your business plan.
Here’s everything you need to know to create the perfect business plan.
What is a business plan?
A well-written business plan contains the recipe for your new business’s growth and development.
It’s your compass.
It describes your goals and how you’ll achieve them by infusing the ingredients you need to turn your dream into a reality.
- Your business description- Tells readers about your idea, why it'll succeed, and how you'll make it happen.
- A market analysis- That backs up your company description.
- Your management and organization plan- Includes employees or contractors because even a one-person show may need a team's help on a contract basis, like bookkeeping services, graphic design, research, and if your business grows, with time, also full-time employees.
- Your products or services descriptions- Explaining how they work, where you'll get them, and how much they`ll cost.
- A target audience analysis- So, you know exactly who you`re selling to and what makes them buy what you`re offering.
- Your marketing and sales plan- Proving your chosen niche is profitable and how you'll reach your customers.
- A financial funding request/projections - What you need and how you'll get it.
Your business plan is like a GPS, guiding your business to its destination for the next 3 to 5 years.
Why is a business plan important?
Here’s the short answer.
A business plan enables you to convey your vision to those who can help you make it a reality.
It does it in 2 ways:
- It empowers you to evaluate your goals and confirm their viability before entering a marketplace.
- And equips you with the information, using a proven outline, that convinces others to help you achieve them.
A business plan does it by explaining who you are, what you are going to do, and how you’ll do it. It clarifies your strategies, identifies future roadblocks, and determines your immediate and future financial and resource needs.
Let’s look at what that means and why each part is important.
A business plan helps you evaluate your ideas
Do you have over one business idea or a range of products or services you believe you could bring to a single marketplace?
If so, a business plan helps determine which is worth focusing on and where to apply your energy and resources by evaluating your idea’s possible market share and profitability before investing.
Clarifies your costs
Your chosen market determines your initial investment and future revenue. And it would be best if you knew those before you invest a dollar in your business idea.
With your chosen idea, your business plan can help you understand your set-up and running costs, the resources you’ll need, and the time it’ll take to get started.
It’s also where you’ll calculate your future sales and revenue goals to ensure they fit your budget and required breakeven point.
And those are essential because every business needs a consistent cash flow to stay afloat!
Steers your business in the right direction
Your business plan guides you through every stage of starting and running your business .
It acts as your GPS, giving you a course to steer. Ensuring your business stays on track, helping you achieve your goals every step of the way.
Acts as your financial guide
As your new business grows, you might need to expand.
But with expansion come big spending decisions, such as purchasing expensive equipment, leasing a new location, or hiring your first employees.
Your business plan’s financial forecast gives you a solid foundation to build on by clarifying when you’re ready to make those investments, ensuring you don’t overreach.
And when you are ready to employ staff, it helps you with that too!
Helps recruit the people you need
Your business is often only as good as its employees. A business plan helps you communicate your vision and pitch your dream to the best candidates. Building their confidence in your venture and encouraging them to join you.
It's essential if seeking a loan or investment
Do you need a loan from a bank or a venture capitalist/angel investor?
If so, you’ll need a business plan that shows your past and future financial trajectory so potential investors can evaluate your business’ feasibility to determine whether you’re worth the risk.
It's an asset if you want to sell your business
Owners of legal entities, such as LLCs, can sell all or part of their business to raise funds for other business ventures or expand their existing ones.
A solid business plan with proven financial recordings and realistic forecasts based on current performance can make your business more attractive to potential investors.
And it makes sense because when buyers understand your business model and its potential growth, they’ll see the value in it for them.
All great reasons to write a business plan, don`t you agree?
Okay, here’s how you do it:
The steps for creating a business plan
Most business plan templates are similar, containing several steps for writing a conclusive plan. If you’re interested in a very short plan, we prepared a lean (one-page) version, including a template .
The perfect business plan isn’t one or the other; it’s the plan that meets your business needs.
That said, every business plan should contain crucial elements and essential details . And a rhythm to your outline that encourages action, growth, and investors to read it from start to finish. Our step-by-step guide, along with our template, will help you achieve both.
But first, you must choose the style that works for you:
Pick a business plan format that works for you
You can tackle creating a business plan in different ways; one could be a long-form, more traditional approach or a one-page business plan that acts as a summarized road map.
Traditional business plans use a standard, industry-expected structure, with each section written in great detail. They require a lot of research because businesses often use them to gain investment, and they can be anywhere from 10 to 50 pages long.
A one-page business plan uses a similar structure but summarizes each step by highlighting the key points.
You can write a one-page plan in an hour and use it as a personal blueprint for running your business or as a guide to writing a future traditional plan.
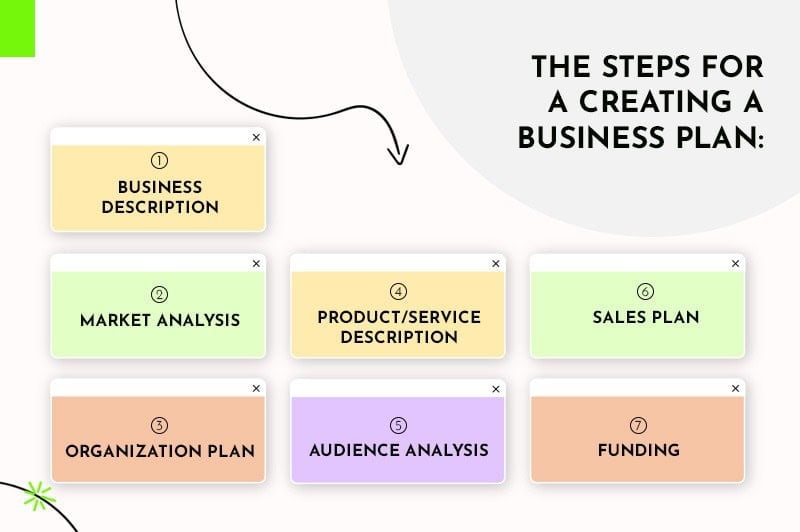
Here are the core component that create a great business plan:
1. An executive summary
2. Your company’s description
3. Market analysis
4. management and organization outline, 5. products and service description, 6. target audience analysis, 7. marketing and sales plan.
8. Financial funding request
9. Financial projections
10. an appendix, 1. an executive summary.
The first section of your business plan’s an executive summary that tells anyone reading in simple terms what your business is and why you believe it’ll be successful.
It’s the most crucial part of your plan because anyone reviewing it often decides whether to continue reading based on what’s in your executive summary.
Your executive should contain your mission statement (why you’re starting your business). A product/service description. Your leadership team and financial information.
Even though the first thing people read is your executive summary, it’s the last section you write.
The next step is about you:
2. Your company's description
Here you sell yourself and your business by telling readers why you’re starting your business and know it’ll succeed.
You must be realistic, business-like, and detailed.
Begin by explaining who you are, what you plan on doing, and how you’ll do it. Describe your future market, your target audience, and why they need your product/service.
Elaborate on your unique selling point (USP) and how your competitive advantage will ensure your success.
Describe your team, highlight their skills and technical expertise, and if you`re a brick-and-mortar business, discuss your location and why it’s right for your target audience or logistics.
Now your market:
A great business idea is only as good as its future marketplace. Enter a declining market with an insufficient or uninterested audience, and you’ll be toast.
Choose one on an upward trajectory with people you understand and need your product, and you’ll be in business.
That makes your market analysis a crucial step in your business plan outline. Here’s where you identify your target audience, competitors’ performance, strengths and weaknesses, and whether the market can sustain your business needs.
Your market analysis should include the following:
- Your market description and outlook- Provide a detailed outline defining your market, including its size, trends, growth rate, and outlook.
- Target Market- Describe your ideal customers, including their demographics such as age, gender, employment status, income level, and lifestyle preferences. Also, include your market size, what motivates your ideal clients, and how you'll reach them.
- Competitive Analysis- Identify your main competitors and list their strengths and weaknesses. Also, highlight any potential roadblocks that might prevent you from entering your chosen marketplace.
Step 4 is where you tell readers how you’ll construct your business and who’ll run it.
Describe your business’s legal structure, whether you’re a sole proprietor intending to form an LLC or a limited/general partnership with dreams of incorporating an S or C corps.
Include your registered business name and any DBA brand name you have. And any member’s percentage ownership and managerial duties per your operating agreement.
And consider using a chart to show who runs what section of the business. Explain how each employee, manager, or owner’s experience and expertise will contribute to your venture’s success. And if you have them, include your team’s resumes and CVs.
Now you must get technical about what you plan to offer.
List your products or services and explain how they work. If in the development stage, describe the process and when you’ll be market ready.
Include the following product/service information:
- Describe how your product/service will benefit your target audience.
- Provide a breakdown of costs per unit made/sold, life cycle, and expected profit margins.
- Explain your supply chain, order fulfillment, and sales strategy.
- Include your plans for intellectual property, like trademarks and patents.
Your product and service description brings you to those who matter most. Your target audience:
The target audience section of your business plan is the most important one to get right. After all, your customers are your business. And the better you know them, the easier it’ll be to sell to them.
To gain a clear picture of your ideal clients, learn about their demographics and create a client persona.
Those include:
- Their location
- Education level
- Employment status
- Where they work
- How much they earn
- How they communicate
- Preferred social media platforms
- Common behavior patterns
- Free time interests
- And what their values and beliefs are
You need your target audience’s demographics to create a branding style that resonates with them. To build marketing strategies that engage their interest. And to identify where to spend your advertising dollars.
Target market’s persona in place, your next step is to describe how you’ll reach and sell to them:
Your marketing plan outlines your strategies to connect with and convert your ideal clients.
Here’s where you explain how you’ll reach your audience, describe your sales funnel, and develop customer loyalty to keep customers.
Your business plan doesn’t require your complete marketing/sales plan but should answer basic questions like:
- Who's your target market?
- Which channels will you use to reach them? (Social media, email, website, traditional marketing, etc.)
- What sales strategies will you use?
- Which resources do you need to implement those strategies?
- Do you have the resources, and if not, where will you get them?
- What are the potential marketing obstacles, and how you'll overcome them?
- What's your initial marketing campaign timeline and budget?
- What your success metrics are, and how you'll measure them?
8. Financial funding request
This step applies if you require funding to start or grow your business.
Similar to the marketing plan step, including your entire financial plan is unnecessary. However, you’ll need to answer specific questions to explain how much investment you require and how you’ll use it.
The following financial funding outline will suffice:
- Your current capital balance and how much future capital you'll need.
- Specify whether you want equity or debt.
- The terms and conditions you need and the duration of any loan repayments.
- Provide a detailed description of why you need investment, IE., to pay salaries, buy equipment or stock, and what percentage will go where.
Start-ups that need investment must rely on something other than past sales and balance sheets. Here, you’ll need to use financial projections to persuade lenders you’ll generate enough profit to repay their loans. And that investors will get a worthwhile return.
Your goal is to convince potential lenders or investors that your business will make enough profit to repay any loans or fulfill your equity promises.
Depending on your loan requirements and market, these projections can vary from 3 to 5 years.
Financial projections aren’t an exact science; you’re forecasting the future! However, accuracy is essential (meaning your projected numbers must add up correctly). And while your goals should be positive, they must also be realistic.
What to include in your financial forecast:
- Forecasted income statements.
- Capital expenditures, fixed and variable.
- Quarterly and annual balance sheets.
- Projected cash flow statements.
Be specific with your projections and ensure they match your funding requests. And if you have collateral to put against a loan, include it at the end of your financial projections to improve your chances of approval.
Also, consider using charts and graphs to tell your financial story, as visuals are great for conveying your message.
Use your appendix to list and provide supporting information, documents, or additional materials you couldn’t fit in elsewhere.
If the appendix is lengthy, start it with a table of contents.
What to include:
- Key employee resumes.
- Letters of reference.
- Licenses and permits.
- Intellectual property - patents or trademarks.
- Legal documents.
- Any current contracts.
- Product pictures and information.
- Bank statements/credit history.

Financial uncertainty shouldn`t stop you from following your dreams. In fact, recessions are often the best time to start a business .
And your business plan is one of the main things that can help you make your dream of owning a business a reality.
Take it one step at a time, do your research, and use your business plan to remove the uncertainty of the unknown.
Because then you’ll know if the time is right to start your business.
This portion of our website is for informational purposes only. Tailor Brands is not a law firm, and none of the information on this website constitutes or is intended to convey legal advice. All statements, opinions, recommendations, and conclusions are solely the expression of the author and provided on an as-is basis. Accordingly, Tailor Brands is not responsible for the information and/or its accuracy or completeness.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
- 3 years ago
Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”
If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand
A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan
Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary
An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision
The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).
You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .
There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples
Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .
This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.
Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:
Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.

Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.
The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
Brandon Boushy
Brandon Boushy lives to improve people’s lives by helping them become successful entrepreneurs. His journey started nearly 30 years ago. He consistently excelled at everything he did, but preferred to make the rules rather than follow him. His exploration of self and knowledge has helped him to get an engineering degree, MBA, and countless certifications. When freelancing and rideshare came onto the scene, he recognized the opportunity to play by his own rules. Since 2017, he has helped businesses across all industries achieve more with his research, writing, and marketing strategies. Since 2021, he has been the Lead Writer for UpFlip where he has published over 170 articles on small business success.
Related posts
- September 27, 2023
How to Start a Business: The Ultimate Guide (2024)
- August 3, 2022
Free Business Plan Template (With Examples)
- May 3, 2022
How to Get a Business License (In 3 Steps)
Join the discussion cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
2 thoughts on “How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)”
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
Compare listings
Reset Password
Please enter your username or email address. You will receive a link to create a new password via email.

Den Businessplan schnell & einfach schreiben
- Businessplan-Vorlage zum Download
- Businessplan-Beispiele
- Ratgeber mit Gliederung & Leitfragen
Die 3 Phasen der Businessplanerstellung meistern
Ein guter Businessplan überzeugt Banken oder Investoren davon, eine Idee zu finanzieren. Gleichzeitig ist der Geschäftsplan der Fahrplan für den unternehmerischen Erfolg. Für ein professionelles Unternehmenskonzept kommt es auf die Informationssammlung, die schriftliche Ausarbeitung und die Präsentation an. Dabei helfen Tools, Tipps und Beispiele.
Vorab: die 3 wichtigsten Fragen rund um den Businessplan
Was ist ein Businessplan? Einfach gesagt, ist der Businessplan die strukturierte Zusammenfassung einer Geschäftsidee und das Planungsdokument eines Unternehmens für die nächsten Jahre.
Welche Aufgaben erfüllt er? Der Businessplan dient dazu aufzuzeigen, worin die Geschäftsidee besteht, an wen sie sich richtet (Zielgruppe), wie das Vorhaben umgesetzt werden soll (Strategie) und ob sich die Idee finanziell lohnt (finanzielle Tragfähigkeit).
Wann wird der Geschäftsplan erstellt? Sobald das Geschäftsmodell steht, prüfen Gründer mit dem Businessplan die Erfolgsaussichten der angestrebten Unternehmensgründung. Dabei können externe Adressaten ebenfalls einen Businessplan verlangen. Bspw. die Arbeitsagentur, wenn der Gründungszuschuss beantragt wird, oder die Bank, wenn ein Kredit zur Finanzierung des Kapitalbedarfs notwendig ist (Stichwort bankfähiger Businessplan).

1. Phase: Informationen sammeln
Ein Großteil der Arbeit für den Businessplan findet vor dem Schreiben statt. Zunächst gilt es, Informationen, Daten und Fakten zum Gründungsvorhaben zu recherchieren. Diese dienen dazu, die Machbarkeit und die wirtschaftliche Attraktivität der Unternehmensgründung zu belegen .
Bei der Auseinandersetzung mit der Branche, dem Markt oder den Zielkunden gewinnen Gründer Erkenntnisse, die in den Businessplan eingearbeitet werden. Nach der Gründung sind diese bspw. wertvoll für Marketingkampagnen. Für die zielgerichtete Recherche dient die Gliederung des Geschäftsplans als Grundlage.
Inhalte: Was muss alles im Businessplan stehen?
Der Inhalt des Businessplans besteht aus vier Teilen: 1. Deckblatt und Inhaltsverzeichnis, 2. Textteil, 3. Zahlenteil ( Finanzplan ) und 4. Anhang.
Auf dem Deckblatt des Businessplans sind Angaben zum künftigen Unternehmen (Name, Logo und Kontaktdaten) und das Datum zu finden. Ein Bild auf dem Deckblatt sorgt für einen guten ersten Eindruck. Das Inhaltsverzeichnis listet alle Haupt- und Unterkapitel inkl. Seitenzahlen auf.
Der Text- und Zahlenteil des Businessplans ist in folgende Kapitel und Inhalte gegliedert:
- Executive Summary : Auf maximal 2 Seiten erfolgt die Zusammenfassung der Hauptkapitel des Businessplans.
- Gründer(team) : Motivation, Qualifikationen und Gründerprofil des Gründers oder des Gründerteams.
- Zielkunden : Wer gehört zur Zielgruppe und wodurch zeichnet sich diese aus?
- Geschäftsidee : Welches Problem löst die Idee für den Kunden? Aus welchen Produkten und Dienstleistungen besteht das Angebot konkret?
- Markt & Wettbewerb : Wie groß ist der Markt? Welches Marktpotenzial besteht? Wer sind die wichtigsten Wettbewerber?
- Ziele und Strategie : Egal ob Freiberufler oder Start-up, Visionen und Ziele benötigt jede Gründungsidee. Wie sieht die Strategie aus, um diese Ziele zu erreichen?
- Marketing : Wie werden Kunden gewonnen? Zu den wichtigen Inhalten im Marketingplan zählen Produkt, Preis, Vertriebskanäle und Werbung.
- Unternehmensorganisation : Im Mittelpunkt stehen die Rechtsform, der Firmenname, Schutzrechte, Genehmigungen, der Aufbau der Mitarbeiter, der Standort und ggf. wichtige Zulieferer.
- Finanzen : Im Finanzteil des Businessplans werden Umsätze, variable und laufende Kosten sowie Investitionen kalkuliert. Ziel ist, mit der Liquiditätsplanung den Kapitalbedarf zu ermitteln. Welche Finanzierung wird zur Deckung des Kapitalbedarfs angestrebt?
- SWOT-Analyse : Auf Basis der Businessplan-Inhalte werden Stärken und Schwächen des Unternehmens sowie Chancen und Risiken aus dem Umfeld bestimmt. Im zweiten Schritt der SWOT-Analyse besteht die Aufgabe darin, Maßnahmen abzuleiten, um Chancen zu nutzen und Risiken zu minimieren.
Eine Meilensteinplanung ergänzt den Geschäftsplan und zeigt dem Leser auf, welche wichtigen Schritte bis zum Unternehmensstart in Angriff genommen werden sollen.
In den Anhang des Businessplans gehören u. a. die Lebensläufe der Gründer, Statistiken und Studien zur Branche, Belege über angemeldete Schutzrechte sowie detaillierte Tabellen des Finanzteils. Der Anhang dient nicht als Sammelbecken für Informationen jeglicher Art. Vielmehr müssen die ergänzenden Dokumente den Businessplan in der Argumentation unterstützen.
Jetzt den eigenen Businessplan aufstellen!
Das Unternehmerheld Businessplan-Tool ist kostenfrei und bietet eine bewährte Gliederung, Leitfragen und Beispiele für die einfache & schnelle Businessplanerstellung.
Kostenfrei nutzen
Woher Daten für die Businessplan-Recherche nehmen?
Besonders viele externe Daten benötigen Gründer für die Kapitel Zielkunden sowie Markt & Wettbewerb, wenn sie den Businessplan erstellen wollen. Bei der Finanzplanung helfen bspw. Branchendaten, wenn es darum geht, Wachstumsraten, Auslastungen oder einen durchschnittlichen Warenkorb im Onlinehandel zu bestimmen.
Zur Datenbeschaffung gibt es zahlreiche Quellen, in denen bereits vorhandenen Daten verfügbar sind. Dazu gehören bspw:
- Statistikportale wie DESTATIS oder Statista, Branchenverbände wie Bitkom oder DEHOGA oder Branchenbriefe der Volksbanken
- Studien von Marktforschungsunternehmen wie GfK
- Steuer- und Unternehmensberater
- Dienste wie Google Maps für die Standort- und Wettbewerbsanalyse oder das Unternehmensregister für Daten über Wettbewerber
- Bewertungsportale
- Angaben der Wettbewerber selbst, bspw. von deren Webseiten oder Social Media Kanälen
Viele Informationen sind kostenfrei verfügbar. Sehr umfangreiche Marktstudien müssen häufig kostenpflichtig von den Anbietern erworben werden.
An einigen Stellen reichen bestehende Informationen für die Businessplanerstellung nicht aus. Eine eigene Marktforschung ist vor allem dann zu empfehlen, wenn es um die Zielkunden und deren Kaufverhalten geht. Die Befragung möglicher Kunden kann über Onlinetools, telefonisch oder persönlich erfolgen. Um Kosten zu sparen, können Gründer dies meist selbst organiseren. Zur Unterstützung - und bei größeren Budgets - gibt es spezialisierte Dienstleister, die die Marktforschung übernehmen.
Tipp: zuerst das Geschäftsmodell entwickeln
Die Idee für die Unternehmensgründung ist meist etwas vage formuliert. Unklar ist häufig, wie konkret Geld verdient werden soll. Auf Basis der Idee entwickeln Gründer ein tragfähiges Geschäftsmodell. Dieser Schritt kann als Vorstufe zum Businessplan erfolgen. Mit dem Business Model Canvas werden die zentralen 9 Bereiche eines Geschäftsmodells visualisiert und geprüft. Dazu zählen u. a. die Kundengruppen, das Werteversprechen, Schlüsselaktiviäten sowie das Einnahmemodell. Sind die wichtigen Bereiche der Geschäftsidee validiert bzw. überzeugend abgedeckt, lohnt es, einen Businessplan aufzustellen. Die Punkte werden aus dem Canvas in den Businessplan übernommen und vertieft.
2. Phase: den Businessplan schreiben
An die Recherche schließt sich die Texterstellung im Businessplan an. Eine Zeitplanung zeigt auf, bis wann welche Kapitel zu schreiben sind. So ist sichergestellt, dass das Unternehmenskonzept bis zu Gesprächen mit Investoren und Banken ausgearbeitet ist. Wird im Team gegründet, ist die Zeitplanung mit einer Aufgabenplanung zu erweitern: Wer liefert welches Kapitel bis wann? Für das Schreiben gibt es Tipps, die beim Businessplan helfen, und Fehler, die unbedingt zu vermeiden sind.
Neben der Organisation stellt sich die Frage, wie der Businessplan geschrieben werden soll. Klassisch per Word und Excel oder zeitgemäß mit einer Businessplansoftware ?
Hilfsmittel: Vorlage, Beispiele und Software
Eine Businessplan-Vorlage und Businessplan-Beispiele dienen als Hilfe für den Businessplan. So erhalten Gründer einen Überblick über den Aufbau und typische Inhalte eines Businessplans. Zum kostenfreien Download bieten wir eine Vorlage und zahlreiche Beispiel-Geschäftspläne an.
Word und Excel waren für das Schreiben eines Businessplans häufig das Mittel der Wahl. Eine Businessplansoftware ist mittlerweile eine hilfreiche Alternative, um den Businessplan zu erstellen. Die Unternehmerheld Businessplansoftware ist eine kostenlose digitale Vorlage. Die Software vereinfacht die Businessplanerstellung mit einer bewährten Gliederung, Leitfragen und einem realen Beispiel für jedes Kapitel. Gegenüber Word- oder Excel-Vorlagen punktet die Software durch:
- Professionelles Layout
- Leitfragen und Beispiele
- Export des Businessplan-PDFs auf Knopfdruck
- Gemeinsam im Team arbeiten
- Am Desktop oder Mobile nutzbar
- Regelmäßige Updates und neue Funktionen
- Backups und hohe Sicherheitsstandards
Im Fokus: der Finanzplan
Der Finanzplan ist eine besondere Herausforderung für Gründer und Unternehmen, wenn sie den Businessplan erstellen. Dies hängt damit zusammen, dass eine ganze Reihe an Annahmen und Schätzungen zur finanziellen Entwicklung des Unternehmens getroffen werden. Die Zahlen müssen plausibel sein, um einen realistischen Kapitalbedarf zu ermitteln und Kapitalgeber von dem Konzept überzeugen zu können. Gleichzeitig ist die Erstellung eines Finanzplans mit Excel sehr komplex und fehleranfällig . Bei der Verwendung von Excel-Finanzplanvorlagen ist Vorsicht geboten, da oft unklar ist, wie aktuell die Vorlagen sind und ob nicht Formelfehler bestehen. Fehler im Finanzplan führen schnell zur Ablehnung des gesamten Businessplans.
Der Unternehmerheld Online-Finanzplan schafft Abhilfe und führt Gründer Schritt für Schritt durch den Zahlenteil des Businessplans. Die wichtigsten Tabellen und Grafiken können einfach in den Businessplan übernommen werden: jetzt mehr über die Finanzplansoftware erfahren .
Typische Fehler im Businessplan vermeiden
Häufige Fehler im Businessplan von Gründern und Unternehmern sind:
# 1 Beispieltexte werden übernommen: Texte aus Businessplan-Beispielen oder einer Vorlage dienen zur Inspiration. Sie passen jedoch nicht 1:1 zu einer anderen Geschäftsidee. Jeder Gründungsvorhaben ist einzigartig. Damit auch jeder Businessplan.
# 2 Gründer und Gründerteam werden nur kurz vorgestellt: Der Gründer bzw. das Gründerteam spielen für die Umsetzung der Idee eine große Rolle. Dementsprechend gehören sie prominent in den Businessplan. Es ist wichtig, zu zeigen, dass die Gründer ausreichend qualifiziert und motiviert sind, die Geschäftsidee richtig umzusetzen.
# 3 Es gibt augenscheinlich keine Konkurrenz: Wer behauptet, es gäbe keine Wettbewerber, hat seine Marktanalyse nicht genau genug durchgeführt. Es ist vielmehr ein Erfolgsfaktor, Wettbewerber gut zu kennen und das eigene Alleinstellungsmerkmal klar herauszuarbeiten.
# 4 Der Finanzplan ist zu optimistisch und das Kapital reicht nicht: Eine realistische Finanzplanung ist das A und O in jedem Businessplan. Die Praxis zeigt, dass der Break-Even meist deutlich später als Plan erreicht wird. Daraus resultieren Liquiditätsengpässe, da der Kapitalbedarf zu niedrig angesetzt wurde. Verschiedene Szenarien und ein Puffer führen zu einer besseren Finanzplanung.
Tipps für Lesbarkeit & Design
Die Lesbarkeit des Businessplans steigern einfache Tipps für die Textarbeit: keine Schreibfehler begehen, lange Schachtelsätze aufteilen und Fremdwörter reduzieren bzw. einfach erklären.
Layout und Design tragen ebenfalls zur Lesbarkeit des Plans bei und erhöhen den professionellen Eindruck:
- Gestaltung des Businessplans gemäß der eigenen Corporate Identity
- Tabellen und Grafiken einsetzen, um komplexe Sachverhalte übersichtlich darzustellen
- Nicht zu kleine Schrift verwenden, Zeilenabstand groß genug wählen
- Fotos gezielt einsetzen, um Aufmerksamkeit zu erhöhen
- Schriftgrößen der Überschriften und des Textes einheitlich gestalten
Businessplanberatung: Businessplan erstellen lassen?
Gründercoaches oder Unternehmensberater leisten mit ihrer Erfahrung wertvolle Hilfe, wenn Gründer einen Businessplan schreiben. Die Beratung wird durch Förderprogramme unterstützt. Die Beratungskosten, die in der Regel zwischen 2.000 und 4.000 Euro liegen, müssen daher meist nur zu 30 bis 50 % selbst getragen werden. Die Businessplanberatung lohnt sich speziell dann, wenn eine Finanzierung angestrebt ist. Gute Gründerberater unterstützten bei der Suche des passenden Hausbank und begleiten Gründer häufig beim Bankgespräch.
Wichtig ist allerdings, dass sich Gründer nicht durch den Berater den Businessplan erstellen lassen. Dies mag komfortabel sein. Doch wer seinen eigenen Geschäftsplan nicht selbst erstellt hat, wird ihn auch nicht selbst umsetzen können.
3. Phase: mit dem fertigen Businessplan überzeugen
Der Businessplan ist in erster Linie ein Dokument für die eigene Planung. Häufig wird er aber auch für externe Adressaten benötigt. Dazu gehören bspw. das Arbeitsamt, um den Gründungszuschuss zu erhalten oder die Bank, wenn Förderkredite augenommen werden sollen.
Damit der fertige Businessplan überzeugt, helfen ein paar abschließende Tipps.
Vor dem Verschicken: kritisch prüfen & anpassen
Der Businessplan ist fertig geschrieben? Bevor der Businessplan an die Ansprechpartner weitergeleitet wird, sollte genügend Zeit auf die abschließende Prüfung verwendet werden. Dies bedeutet den gesamten Geschäftsplan Korrektur zu lesen und neben Fehlern insbesondere auf Widersprüche zu prüfen. Freunde und Familie können dabei ebenso helfen, wie ein Gründercoach mit einem Businessplan-Check unterstützen kann.
Bei einem Businessplanwettbewerb mitmachen
Kostenfreie Feedback und in bestem Falle sogar Preisgelder erhält ein Businessplan bei den zahlreichen Businessplanwettbewerben, die in Deutschland stattfinden. Wenn es zeitlich und inhaltlich passt, lohnt die Teilnahme an solch einem Wettbewerb auf jeden Fall. Gleichzeitig können Gründer das eigene Netzwerk um wertvolle Kontakte erweitern. Es kann jedoch sein, dass der jeweilige Wettbewerb mit einer eigenen Kapitelstruktur vorgibt, wie die Teilnehmer den Businessplan schreiben sollen. In diesem Fall lohnt es, einfach eine zweite Version des Businessplans zu erstellen.
Adressaten gerecht anpassen
Arbeitsamt, Bank oder Investor: unterschiedliche Adressanten bedeuten unterschiedliche Blickwinkel. Um zu überzeugen, hilft es, den Businessplan-Adressaten gerecht aufzustellen:
- Arbeitsagentur: Für die erfolgreiche Beantragung des Gründungzuschusses muss der Geschäftsplan aufzeigen, dass der Zuschuss tatsächlich benötigt wird bzw. dieser tatsächlich hilft, die Anlaufphase zu überbrücken. Wird eine zu optimistische Darstellung im Finanzplan gewählt, wird das Amt den Zuschuss ablehnen, da der Gründer es auch ohne schaffen würde. Stellt sich der Finanzierungsbedarf trotz Zuschuss als zu groß dar, erfolgt ebenfalls ein negativer Bescheid durch das Amt.
- Bank: Die Bank möchte im Rahmen des Kredits sicher gehen, dass das Geschäftsmodell mit geringen Risiken verbunden ist und Zinsen und Tilgung bedient werden können.
- Investoren: Wenn Start-ups Eigenkapital von Business Angeln oder VC-Investoren einsammeln, rücken vor allem die Marktgröße und die Wachstumschancen in dem Mittelpunkt der Betrachtung.
Vor diesem Hintergrund entstehen - je nach Empfänger - mehrere Versionen des Businessplans.
Für den Erstkontakt: Unternehmenspräsentation oder Pitch Deck
Beim Kontakt mit Investoren oder für die Präsentation vor Publikum haben sich die Unternehmenspräsentation und das Pitch Deck als gute Instrumente etabliert. In verkürzter Form helfen sie, das Interesse zu wecken. Ist der Kontakt etabliert, geht es an die Detailprüfung mit dem Business- und Finanzplan. Damit dies gelingt, muss die Präsentation visuell und optisch ideal aufbereitet sein. Auf Für-Gründer.de gibt es mehr Details zum Aufbau und Inhalt des Pitch Decks .
Wenn die Präsentation oder das Pitch Deck nicht per Email geschickt, sondern als Präsentation vor Publikum gehalten wird, hängt viel von der Performance des Gründers oder des Gründerteams ab. Eine gute Vorbereitung anhand von Präsentationstechniken und das wiederholte Üben sind dafür notwendig.
Das Businessplan-Tool im Unternehmerheld hilft, einen bankfähigen Businessplan zu erstellen.
Häufige Fragen
Wie viele Seiten ein Businessplan haben sollte, hängt ganz davon ab, wie komplex die Geschäftsidee ist und wer Adressat des Businessplans ist. Sollen Geldgeber mit dem Businessplan von der Idee überzeugt werden, wird in der Regel ein viel ausführlicher Finanz-Teil benötigt, als wenn man dies nicht vorhat. Als groben Richtwert gelten 20 bis 40 Seiten plus Anhang, bei Kleingründungen kann dies durchaus weniger, bei innovativen, größeren Start-ups auch mehr sein.
Die Erstellung eines Businessplans bringt vielerlei Vorteile mit sich. Neben der optimalen Planung und Umsetzung der eigenen Geschäftsidee ist die Risikominimierung wohl der wichtigste Vorteil. Zudem lässt sich oftmals ausschließlich mit einem ausgearbeiteten Businessplan Kapital akquirieren . Dies kann bei vielen Gründungen letztendlich darüber entscheiden, ob die Geschäftsidee umgesetzt werden kann.
Weitere Vorteile sind:
- Markt und Konkurrenz sind immer im Blick
- Anhand des Businessplans lässt sich das Vorhaben leicht präsentieren.
Ein Businessplan lässt sich spielend leicht und vor allem kostenlos mit dem Unternehmerheld Businessplan-Tool erstellen. Heutzutage noch mit Excel-Vorlagen oder Word-Mustern zu arbeiten, ist mittlerweile überholt. Die Businessplan-Software bietet zahlreiche Vorteile und den einfachen Export als PDF.
Wie viel Zeit benötigt wird, um einen Businessplan zu schreiben, hängt stark davon ab, wie umfangreich dieser sein muss. Dies wiederum ist davon abhängig, für wen der Businessplan geschrieben wird und wie komplex die Geschäftsidee ist.
Wenn aber die Recherche zu Markt und Konkurrenz sowie das tatsächliche Schreiben berücksichtigt werden, kann generell mit ein paar Wochen bis hin zu einigen Monaten gerechnet werden. Mit einer Software sind Gründer deutlich schneller unterwegs, als wenn ohne jegliches Grundgerüst gestartet wird.
Das Business Model Canvas wird häufig auch als Kurzfassung oder Vorstufe des Businessplans bezeichnet, ist somit keine vollwertige Alternative. Jedoch kann es sehr hilfreich sein, wenn in Vorbereitung des Businessplans ein Business Model Canvas aufgestellt wird. Mit dieser Grundlage schreibt sich der eigentliche Businessplan später auch deutlich leichter.
Create a Business Plan in Minutes
Type your business idea below.

What Our Users Say

Zakariya A.

How it Works
Questionnaire
Respond to a series of targeted questions about your business goals and objectives.
AI Business Plan Generator
The engine analyzes your responses and generates a business plan tailored to your vision.
SBA Approved Business Plan
Receive a detailed, tailored business plan that aligns with your requirements. Ready for funding.
WHO BENEFITS FROM Plannit?

Aspiring Entrepreneurs
Simplify the overwhelming process of starting a business plan, turning your vision into reality.

Business Owners
Get a comprehensive and professional business plan that increases your chances of securing investors’ funds.

Educational Institutions
Use Plannit AI to teach business planning effectively and help students develop practical skills for real-world success.

Startup Incubators & Accelerators
Work alongside your founders as they build their plan to ensure they have a solid roadmap for growth and scalability.
Try Plannit AI For Free
Funding ready business plan, executive summary, company overview.
Problem Statement
Business Description
Mission Statement
Business Model
Products and Services
Additional Features
Revenue Model
Market Analysis
Target Market
Market Size and Segments
Unique Value Proposition
Risks and Mitigations
Identified Risks
Mitigation Strategies
Financial Overview
Income Statement
Marketing and Sales Plan
Focus On Your Vision
Key features & benefits, ai editing companion.
Modify and regenerate sections of your business plan using premade or custom prompts. Our AI will help you refine your plan to perfection.
Multi-User Collaboration
Invite team members with easy sharing to collaborate on your business plan in real-time. Communicate and make changes together. Collaborate with your partners in real-time as you perfect your plan.
Education Center
Immerse yourself in a rich library of articles, tools, templates, webinars and resources for continuous business and professional growth. Learn all about the key aspects of starting, running and growing a business.
Powered by Chat GPT
Our algorithms are powered the latest in AI technology to ensure the most accurate and relevant output. We use OpenAI's GPT 4 and 3.5 engines for the perfect blend of accuracy and speed.
Business Resources
We recommend a variety of useful tools and resurces that help sustain your growth. We only recommend the best in the business. Filter your needs and equip yourself with the best tools.
Plan Samples
Explore a library of sample business plans we generated to get the idea of what to expect. Currently able to generate viable plans for 50+ industries.
Financial Projections
Take an additional questionnaire about your financial trajectory and get a detailed financial projection + 3 year income statement for your business.
Tools and Templates
Plannit's comprehensive suite that accompany business planning. From pitch decks to financial models, we have you covered.
Plan Export
Download your business plan in an editable .docx format. Fully edit & share your plan with investors, partners, and stakeholders.
Privacy & Security
Rest assured, your privacy is our top priority, and we're committed to keeping your information safe and confidential.
PLANNIT BUSINESS ECOSYSTEM

Frequently Asked Questions
What is a business plan and why is it important.
- Initiate with Your Business Concept: Lay the Groundwork: Start by introducing your business idea into Plannit AI's Business Plan Generator. This first step is crucial, as it sets the tone for a tailored, insightful business plan that truly resonates with your vision. Capture the Essence: Our platform is designed to grasp the nuances of your concept, ensuring that the generated plan accurately reflects the core and potential of your business.
- Navigate Through the AI-Guided Questionnaire: Tailored Interactive Experience: Plannit AI’s AI-guided questionnaire is your interactive guide through the planning process. It meticulously gathers information about your business's objectives, strategies, and market positioning, ensuring a comprehensive and reflective plan. Intelligent Feedback and Suggestions: As you progress through the questionnaire, benefit from smart prompts and suggestions, ensuring that your plan is not just detailed but also strategically sound and aligned with industry standards.
- Generate Your Plan with Advanced AI: Intuitive Plan Creation: With the questionnaire complete, Plannit AI's advanced algorithms intelligently analyze your responses. They then craft a detailed, customizable, and strategically aligned business plan, providing you with a structured, coherent, and actionable format. Benefit from AI-Powered Insights: Plannit AI offers AI-driven insights and suggestions, ensuring your plan is not just a document but a strategic tool equipped with tailored AI prompts and an in-app plan editor. Get inspired by browsing through our sample business plans, a collection of successful strategies across various industries.
- Finalize Your Plan with Confidence: Dynamic Adaptation and Refinement: Plannit AI recognizes that a business plan is a living document. Our platform allows for continuous adaptation and refinement, ensuring your strategy remains agile, relevant, and aligned with your evolving business goals. Professional Presentation and Sharing: Once your plan meets your standards, utilize Plannit AI's export features to present your plan professionally. Choose between various formats for exporting your business plan, ready to impress stakeholders, attract investors, or guide your team. Review and Adapt: Ensure your business plan is a living document, ready to evolve with your growing business. Plannit AI's dynamic platform allows you to adapt your strategy as new opportunities or challenges arise.
How to Write a Business Plan?
- Roadmap for Success: At its core, a business plan acts as a strategic guide, providing detailed steps on how your business will achieve its objectives. It helps you navigate the startup phase, manage growth effectively, and tackle unforeseen challenges with a well-thought-out strategy.
- Securing Funding: For startups and businesses looking to expand, a business plan is crucial for securing loans or attracting investors. It demonstrates to potential financial backers that your business has a clear vision, a solid strategy for profitability, and a plan for delivering returns on their investment.
- Informed Decision-Making: A well-prepared business plan offers valuable insights into your market, competition, and potential challenges. This information is vital for making informed decisions, from day-to-day operations to long-term strategic shifts.
- Market Analysis and Strategy: It allows you to conduct an in-depth analysis of your target market, understand customer needs, and position your product or service effectively. The marketing strategy outlined in your business plan helps in identifying the best channels and tactics to reach your audience and achieve market penetration.
- Financial Planning: One of the most critical components of a business plan is the financial forecast. It outlines your funding requirements, expected revenue, profit margins, and cash flow projections. This section is essential for budgeting, financial management, and ensuring the financial viability of your business.
- Goal Setting and Performance Measurement: A business plan sets clear, measurable goals and objectives. It provides a framework for monitoring performance, measuring success, and making necessary adjustments to stay on track.
Who Can Benefit from Plannit AI?
- Aspiring Entrepreneurs: If you're at the idea stage, looking to transform your vision into a viable business, Plannit AI offers the tools and guidance to bring your concept to life. Our platform helps you articulate your business idea, define your target market, and develop a solid plan to turn your dream into reality.
- Students and Educators: For students delving into the intricacies of business planning and educators teaching the fundamentals of entrepreneurship, Plannit AI serves as an invaluable resource. It provides a practical, hands-on tool for learning and teaching how to create detailed business plans, analyze markets, and understand financials in a real-world context.
- Startup Founders: In the dynamic startup environment, Plannit AI is the ideal partner for founders looking to pivot quickly, secure funding, or understand their competitive landscape. With our AI-driven insights and market analysis tools, startups can make informed decisions and adapt their strategies to thrive in competitive markets.
- Small Business Owners: For small business owners seeking to optimize their operations, expand their customer base, or explore new markets, Plannit AI offers targeted solutions. Our platform simplifies the planning process, enabling owners to focus on growth while managing the day-to-day challenges of running their business.
- Consultants and Freelancers: Consultants and freelancers specializing in business development, strategic planning, or financial advising will find Plannit AI a powerful addition to their toolkit. It allows them to provide clients with comprehensive, data-driven business plans and strategies, enhancing the value of their services.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Leaders of non-profit organizations can leverage Plannit AI to plan initiatives, secure funding, and manage resources more efficiently. Our platform helps non-profits articulate their mission, set achievable goals, and measure their impact, ensuring they can make a difference in their communities.
- Innovators and Inventors: Individuals looking to commercialize innovative products or technologies can use Plannit AI to navigate the complexities of bringing new ideas to market. From patent strategies to go-to-market plans, our platform covers all bases, ensuring innovators can focus on what they do best.
- Small Business Development Centers (SBDCs) and Government Agencies: Government and SBA backed entities can greatly benefit from integrating Plannit AI into their services, enhancing their ability to support a larger number of clients more efficiently. By facilitating quicker, more in-depth business plan development, these organizations can spend more time assisting with plan execution and less time on creation, ultimately serving their communities more effectively.
- Anyone with a Business Idea: Ultimately, Plannit AI is for anyone with a business idea, regardless of industry, experience, or stage of business development. Our mission is to democratize business planning, making it accessible, understandable, and actionable for everyone.
Why is Plannit AI the best choice for an AI business planning software?
- Interactive Questionnaire and ChatGPT Integration: Plannit AI transforms the business planning process into an engaging conversation. Through our advanced ChatGPT integration, we offer a questionnaire that dynamically adapts to your responses, ensuring your plan is personalized, comprehensive, and aligned with your business goals.
- Dynamic Planning Environment: Unlike static templates provided by many, Plannit AI introduces a living platform that grows with your business. It features real-time updates, strategic insights, and a feedback mechanism that keeps your business plan current and actionable.
- Extensive Educational Resources: Our Education Center is packed with articles, guides, and sample plans to bolster your planning process. It's designed to arm you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of your industry confidently.
- Enhanced Collaboration and Customization: Recognizing the collaborative essence of business planning, Plannit AI supports team efforts with multi-user editing, annotations, and feedback features, ensuring a comprehensive approach to your strategy.
- Customer Success Stories: Our users' achievements are a testament to Plannit AI's effectiveness. These success stories illustrate how diverse businesses have utilized our platform for strategic planning and growth.
- Tailored Business Plan Creation: Our platform stands out with its tailored approach, featuring customizable templates that directly cater to your business type and industry, making plan creation straightforward and relevant.
How can ChatGPT help me to create business plans?
- Content Generation:: ChatGPT helps draft various sections of a business plan, from executive summaries to marketing strategies, by providing structured and coherent text based on the prompts given.
- Strategic Insights: It can offer suggestions on business strategies by analyzing trends and providing examples from a wide range of industries.
- Financial Planning: While it can't replace professional financial advice, ChatGPT can guide the structure of financial projections and statements, helping you consider important financial aspects of your plan.
Take The First Step Towards Success With our AI-Generated Business Plans
Plannit For...
550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the plans in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how you're business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remain stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a sample business plan.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a plan that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily, just like you can leverage an example business plan template to write your plan, we also have a gallery of over 50 pitch decks for you to reference.
With this gallery, you have the option to view specific industry pitches or get inspired by real-world pitch deck examples.
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right match for your business idea.
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Transform Tax Season into Growth Season
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Businessplan erstellen: Leitfaden, Vorlage und Beispiele
Der Businessplan ist die Grundlage für ein erfolgreiches Geschäftskonzept. Und er hilft, Kapitalgeber von der Idee zu überzeugen. Was in einen fertigen, bankfähigen Businessplan gehört, zeigen wir anhand einer bewährten Gliederung und Erläuterungen zu allen Businessplan-Kapiteln.
Um schnell und einfach den Businessplan zu erstellen, helfen die kostenfreie Businessplan-Vorlage und viele Businessplan-Beispiele .

Von René Klein Chefredakteur
René Klein verantwortet als Chefredakteur seit über 10 Jahren die Inhalte auf dem Portal und aller Publikationen von Für-Gründer.de. Er ist regelmäßig Gesprächspartner in anderen Medien und verfasst zahlreiche externe Fachbeiträge zu Gründungsthemen. Vor seiner Zeit als Chefredakteur und Mitgründer von Für-Gründer.de hat er börsennotierte Unternehmen im Bereich Finanzmarktkommunikation beraten.
- Wer einen Businessplan schreibt, wächst 30 % schneller und reduziert das Risiko zu scheitern.
- Eine bewährte Gliederung nutzen, da Banken und Investoren klare Erwartungen an die Inhalte des Businessplans haben.
- Der Finanzplan ist das Herzstück des Businessplans. Und gleichzeitig der schwierigste Teil.
- Schreiben Sie den Businessplan stets selbst. Der Banker merkt dies im Bankgespräch sonst schnell
Der Businessplan ist das zentrale Dokument für die Planung der Gründung oder die Expansion eines Unternehmens. Der Businessplan beantwortet die Fragen: Welche Produkte und Dienstleistungen werden angeboten? Welche Strategie verfolgt das Unternehmen im Markt? Welche Chancen und Risiken bestehen? Wie ist es um die wirtschaftlichen Erfolgsaussichten (Stichwort Finanzplan ) bestellt? Der Businessplan hilft die Entscheidung zu treffen, das Vorhaben umzusetzen oder nicht.
| Aufbau und Inhalt des Geschäftsplans
Gründer fragen häufig: Was muss alles im Businessplan stehen? Ein Blick in die zahlreichen Fachbücher zum Businessplan zeigt unterschiedliche Gliederungen. Eine Vorschrift, wie ein Businessplan ganz genau auszusehen hat, existiert nicht. Doch es gibt etablierte Standards, die helfen, dass der Plan systematisch erstellt wird und der Leser schnell die gewünschten Informationen findet. Dafür gehören diese Hauptkapitel auf jeden Fall in den Businessplan:
- Executive Summary
- Gründer(team)
- Idee & Angebot
- Markt & Wettbewerb
- Vision und Ziele
- Marketingmix
- Organisation (Standort, Rechtsform etc.)
- SWOT Analyse
Die Hauptkapitel des Businessplans umfassen zahlreiche Unterkapitel. Diese stellen wir im Kapitel Gliederung des Businessplans vor.
Wie lang muss der Businessplan sein?
Die Länge des Geschäftsplans hängt von der Komplexität des Vorhabens ab. Der Businessplan eines Freiberuflers ist mit 15 bis 20 Seiten ausreichend lang. Für eine klassische Unternehmensgründung wie bspw. ein Ladengeschäft oder ein Gastronomiebetrieb sind 20 bis 40 Seiten inkl. Finanzplan eine gute Zielmarke. Innovative bzw. sehr technische Gründungsvorhaben mit einem großen Kapitalbedarf sind inkl. Anhang deutlich umfangreicher.
Die Länge ist jedoch nicht das entscheidende Kriterium. Auf die Inhalte kommt es an, wenn Sie den Businessplan erstellen.
Unser Businessplan Wiki erläutert die zentralen Kapitel des Businessplans. Per Klick öffnet sich ein Ratgeber für jedes Thema.
#1 Executive Summary
Die wichtigsten Inhalte des Geschäftsplans werden in der Executive Summary auf 2 Seiten zusammengefasst. Leser, wie bspw. Kapitalgeber, entscheiden meist auf dieser Basis, ob sie den Businessplan weiterlesen. Daher ist die Summary nicht zu unterschätzen, wenn Sie den Businessplan erstellen. Obwohl das Kapitel am Anfang des Businessplans steht, wird es zum Schluss geschrieben.
#2 Gründer(team)
Was ist die Motivation des Gründers bzw. der Gründer für die Unternehmensgründung? Welche Qualifikationen bringen sie mit? Für einen erfolgreichen Businessplan müssen Gründer in diesem Kapitel aufzeigen, warum sie perfekt für das Vorhaben geeignet sind. Lebensläufe und Zertifikate gehören jedoch in den Anhang.
#3 Idee & Angebot
Die Idee ist der Ausgangspunkt für das Unternehmen. Welches Problem löst die Idee? Wo liegt der Kundennutzen? Das Angebot ist detailliert darzustellen. Im Finanzplan ist aufzuzeigen, mit welchen Produkten, welcher Umsatz erzielt wird.
- Beispiel: Grundsätzlich bietet ein Restaurant zwar Essen und Getränke an. Diese allgemeine Beschreibung hilft aber nicht, zu bewerten, ob das Angebot passend für die Zielgruppe ist und sich gegenüber Konkurrenten und Mitbewerbern behaupten kann.
#4 Zielgruppe
Wer wird das Produkt kaufen? Oder die Dienstleistung nutzen? In den Businessplan gehört die Definition der Zielgruppe anhand verschiedener Faktoren. Es wird unterschieden in Privatkunden (B2C) und Geschäftskunden (B2B) . Neben den Eigenschaften der Zielgruppe spielt das Kaufverhalten eine Rolle, um Absatzschätzungen im Zahlenteil vorzunehmen.
#5 Markt & Wettbewerb
Auf Basis der Zielgruppe wird die Marktgröße bestimmt. Wird der Markt wachsen oder schrumpfen? Wer sind die Konkurrenten? Wie aggressiv verhält sich die Konkurrenz? Und welche Hürden bestehen eventuell für den Markteintritt? Eine Marktforschung hilft, um im Abschnitt Markt und Wettbewerb mit der Marktanalyse zu überzeugen.
#6 Vision und Ziele
Der Businessplan gibt Auskunft darüber, was Gründer mit dem Unternehmen erreichen wollen (Stichwort Vision). Dazu werden kurz-, mittel- und langfristige Ziele festgelegt, um der Vision schrittweise näher zu kommen.
#7 Strategie
Auf Basis der Unternehmensziele folgt das Strategie-Kapitel im Businessplan. Besonders wichtig ist die Frage, welchen Kundennutzen das Unternehmen bietet. Die Positionierung im Markt und die Unterschiede zu den Wettbewerbern sind herauszuarbeiten. Darauf baut die Unternehmensstrategie auf. Erfolgsversprechend haben sich für Unternehmen drei Strategien erwiesen.
#8 Marketingmix
Die Kunden kommen nicht von allein! Das Zauberwort heißt Marketing. Gründer müssen Zielkunden mit den Marketingmaßnahmen möglichst effizient erreichen. Zur Kalkulation hilft bei der Businessplanerstellung ein Tool für das Marketingbudget .
#9 Organisation (Standort, Rechtsform etc.)
Ins Kapitel Organisation gehören Themen wie die Rechtsform und der Firmenname. Aber auch die Anmeldung von Schutzrechten wie Marken oder Patenten. Sind Genehmigungen für den Start notwendig? Welcher Standort wird ausgewählt? Wie viele Mitarbeiter sollen eingestellt werden?
#10 Finanzplan
Der Finanzplan ist das Herzstück des Businessplans: Investitionen, GuV, Liquidität, Umsätze und Kosten sind die Stichworte. Mit dem Finanzplan wird der Kapitalbedarf der Unternehmensgründung ermittelt und aufgezeigt, wie dieser finanziert wird. Unser umfangreiches Finanzplan-Tool inklusive Liquiditätsplanung hilft, den Zahlenteil im Geschäftsplan zu erstellen.
#11 SWOT Analyse
Zum Abschluss des Businessplans erfolgt die SWOT Analyse. Stärken und Schwächen des Unternehmens werden erfasst. Chancen und Risiken identifiziert und Maßnahmen abgeleitet, um von Chancen zu profitieren und Risiken des Gründungsvorhabens zu minimieren.
In den Anhang gehören die Anlagen zum Businessplan. Diese umfassen bspw. die Lebensläufe der Gründer, Marktstudien, wichtige Verträge, Produktbeschreibungen, Fotos und Skizzen.
Infografik: Was gehört in den Businessplan?

Die Ausarbeitung des Businessplans dauert in der Regel einige Wochen bis hin zu ein paar Monaten . Diese Zeit braucht man für die Recherche zu allen Inhalten, für das Schreiben des Textteils und die Erstellung der Finanzplans. Der Aufwand hängt von der Komplexität des Unternehmenskonzepts, den eigenen Kenntnissen und der Zeit ab, die man jeden Tag aufbringen kann. Wer den Businessplan neben dem Vollzeitjob schreibt, wird mehr Zeit benötigen. Doch wer Zeit und Fleiß investiert, ist besser auf die Existenzgründung vorbereitet.
| Vorlage, Beispiele, Software & Tools
Kostenfreie businessplan-vorlage.
Eine Businessplan-Vorlage ist ein Word-Dokument mit einem Inhaltsverzeichnis und Muster für den Businessplan. Sie unterstützt dabei, den Businessplan zu schreiben. Daher stellen wir eine Vorlage zum kostenfreien Download bereit. Die Businessplan-Vorlage umfasst ebenso ein Deckblatt sowie wichtige Informationen zu jedem Kapitel: jetzt zur Businessplan-Vorlage.
Businessplan-Beispiele für viele Branchen
Zur Informationsbeschaffung und Hilfe bei der Geschäftsplanerstellung lohnt es, einen fertigen Businessplan aus der eigenen Branche herunterzuladen. Die Geschäftsplan-Beispiele bieten bereits wichtige Informationen für den Start, z.B. zu Markt und Wettbewerb. Wir stellen vorgefertigte Businessplan-Beispiele mit Text- und Zahlenteil u.a. aus den Branchen Einzelhandel, E-Commerce, Dienstleistungen, Gastronomie und Handwerk zum Download zur Verfügung .
Businessplansoftware
Die Businessplanerstellung per Word für den Verbalteil und Excel für den Zahlenteil ist der Klassiker. Beide Programme bieten aber keine spezielle Hilfe für Gründer. Startpunkt ist ein weißes Blatt und die Gliederung sowie die gesamte Formatierung für den Geschäftsplan sind selbst zu erstellen. Beim Finanzplan per Excel wird es noch komplizierter. Die Erstellung eines Excel-Finanzplans dauert für unerfahrene Gründer sehr lange und ist fehleranfällig.
Einfacher ist es für Gründer, wenn sie mit einer Businessplan-Software den Businessplan erstellen. Die Software bietet viel mehr als eine Businessplan-Vorlage samt Inhaltsverzeichnis. Die Vorteile sind:
- Formatierung und Gliederung bestehen schon,
- Hinweise, Leitfragen und Beispiel in jedem Kapitel,
- Teammitglieder einladen und den Geschäftsplan erstellen,
- keine Formelfehler wie bei Excel in Finanzplan und Liquiditätsplan,
- PDF des Businessplans auf Knopfdruck erstellen.
Wir haben unsere Businessplan-Software in Zusammenarbeit mit Gründerberatern, Banken und Investoren entwickelt. So erfüllt der fertige Businessplan deren Anforderungen. Schreiben Sie den Businessplan ganz einfach kostenfrei: mehr über die Businessplan-Software erfahren .
Tools für einzelne Kapitel
Grafiken und Schaubilder gehören in einen guten Businessplan. Unsere kostenfreien Tools unterstützen Gründer in vielen Kapiteln dabei. Zum Beispiel ist eine SWOT Analyse ist mit dem SWOT-Analyse Tool schnell erstellt. Weitere Businessplan-Tools sind:

| Businessplan schreiben: Tipps & Fehler
Ein guter Businessplan schafft es, direkt auf den ersten Seiten das Interesse des Lesers zu wecken. Dies gelingt durch den optischen Eindruck sowie eine inhaltlich fesselnde Darstellung des Gründungsvorhabens. Der weitere Textteil darf keine handwerklichen Fehler aufweisen und fachlich überzeugen.
Vorbereitung für den Businessplan
Business model canvas.
Das Business Model Canvas ist eine Kurzfassung des Businessplans. Es hilft, die Erfolgsfaktoren eines Geschäftsmodells zu prüfen. Wie z.B. Leistung bzw. Produkt, Zielgruppe, Kundenbeziehungen, Einnahmen und Ausgaben. Deshalb lautet eine häufige Frage, ob statt der Geschäftsplanerstellung nicht das Business Model Canvas das geeignetere Tool sei. Unsere Empfehlung: Starten Sie mit dem Canvas. Wenn das Geschäftsmodell überzeugt, geht es an die Details im Businessplan. So wird Geschäftsidee mit dem Business Model Canvas geprüft.
Adressaten im Blick
Den Businessplan erstellen Existenzgründer für sich selbst, als zentrales Planungsdokument für das eigene Geschäft. Es gibt aber eine Reihe von Adressaten, die einen fertigen Businessplan benötigen:
Für das Arbeitsamt den Businessplan erstellen: Wer sich aus der Arbeitslosigkeit selbstständig machen möchte, kann mit dem Businessplan den Gründungszuschuss beantragen.
Businessplan für Förder- und Bürgschaftsbanken: Für Fördermittel oder eine Bürgschaft dient der Businessplan dazu, die Kapitaldienstfähigkeit des Vorhabens unter Beweis zu stellen.
Businessplan für die Bank: Beim klassischen Kredit der Hausbank bildet der Business- inkl. Finanzplan die Grundlage für die Kreditentscheidung, da noch keine belastbaren Zahlen der Geschäftstätigkeit bestehen.
Für Investoren den Businessplan erstellen: Trotz Canvas oder Pitch-Deck geht es bei der Detailprüfung um den umfangreicheren Business- und Finanzplan. Im Fokus stehen die Marktgröße und die Wachstumsgeschwindigkeit des Start-ups.
Businessplan für Geschäftspartner: Es ist möglich, dass Geschäftspartner (z.B. Lieferanten, die eine längere Zahlungsfrist einräumen) eine Kurzform des Geschäftsplans sehen möchten.
Die verschiedenen Adressaten haben unterschiedliche Blickwinkel auf das Unternehmenskonzept, die beim Schreiben des Businessplans zu beachten sind. So wird der Businessplan adressatengerecht geschrieben.
Für Gründer ist es eine Herausforderung, den Businessplan zu schreiben. Vor allem, um Banken und Investoren mit dem Geschäftsplan zu überzeugen. Häufig entsteht Zeitdruck, da Gründungsdatum und Finanzierung näher rücken. Trotzdem lautet unser wichtigster Tipp: erstellen Sie den Businessplan selbst! Kaufen Sie keinen fertigen Businessplan, um dann einfach den Namen zu tauschen. Dies geht zwar schnell, ist aber nicht erfolgversprechend.
Beim Schreiben eines professionellen Businessplans helfen folgende Tipps:
#1 Umfangreiche Recherche: Der größte Teil der Arbeit liegt vor dem Schreiben. Der Start des Geschäftsplans ist die Informationssammlung. Alle relevanten Zahlen, Daten und Fakten werden zusammengetragen, um später Grundlage der Argumente und Annahmen zu sein. Beim Formulieren sind Datenangaben mit seriösen Quellen zu belegen.
#2 Konsistente Gliederung: Die inhaltlichen Themen sind das A und O für den Businessplan. Eine bewährte Businessplan-Gliederung stellt sicher, dass alles drin ist, was der Leser erwartet.
#3 Ansprechendes Design & Layout: Es kommt auch auf die Verpackung an. Ein gutes Layout & Design wird mit kleinen Handgriffen erreicht:
- Gestaltung eines Deckblatts mit Logo & Bild.
- Ausführliches Inhaltsverzeichnis und Seitennummerierung.
- Klare und einheitliche Überschriftenhierarchie.
- Einheitliche Schriftgrößen und -arten.
- Nicht zu viel Text auf einer Seite, Zeilenabstände und Absätze einsetzen.
- Ausdruck des Businessplans in guter Druckqualität.
#4 Lesbarkeit steigern: Ein gutes Layout ist ein Faktor für die Lesbarkeit des Geschäftsplans. Weitere Punkte sind:
- Schreibfehler vermeiden, den Businessplan gegenlesen lassen.
- Kurze, aktive Sätze formulieren.
- Grafiken und Tabellen einsetzen, um die Übersichtlichkeit zu erhöhen.
- Fachchinesisch und unnötige Fremdworte vermeiden, Fachbegriffe erläutern.
- Auf die Kernaussagen fokussieren, nicht abschweifen.
- Ergänzende Informationen gehören in den Anhang. Allerdings ist der Anhang auch kein Sammelbecken für alle möglichen Informationen.
Und zum Schluss: Lesen Sie den Businessplan von Anfang bis Ende und achten Sie darauf, dass keine Widersprüche im Text bestehen.
Im Laufe der Jahre haben wir viele Geschäftspläne von Gründern erhalten. Wir präsentieren die häufigsten Fehler.
#1 Vorgefertigte Muster-Texte übernehmen: Beispiel-Businesspläne helfen, bergen aber die Gefahr Inhalte einfach zu übernehmen. Jede Unternehmensgründung und jede Selbstständigkeit sind individuell - folglich auch jeder Businessplan.
#2 Betriebswirtschaftliche Fehler: Selbst für Businessplanneulinge gilt: fachliche Fehler und Fehlinformationen vermeiden. Betriebswirtschaftliche Begriffe müssen sitzen, egal ob zur Rechtsform, zu Steuern, zur Finanzplanung oder zur Liquiditätsplanung. Sonst sinkt schnell das Zutrauen in den Autor als denjenigen, der das Unternehmenskonzept zum Erfolg führen soll.
#2 Gründer(in) oder Gründerteam steht nicht im Fokus: Gründer stellen häufig die Idee in den Mittelpunkt. Eine Idee ist jedoch nicht gewinnbringend ohne die Umsetzung durch den Gründer bzw. das Gründerteam. Entscheidend ist, welche Qualifikationen der oder die Gründer(in) bzw. das Gründerteam mitbringen. Diese Darstellung benötigt ausreichend Platz.
#3 Marktforschung kommt zu kurz: Gründer sind vom Produkt überzeugt. Das ist gut. Noch besser ist, wenn es auch potenzielle Kunden gibt, die sich für das Angebot begeistern. Eine Marktforschung gehört bereits in den Geschäftsplan. Diese hilft zu zeigen, dass die Idee auf ein Bedürfnis trifft und liefert wertvolles Feedback für die Produktentwicklung.
#4 Zu stark produktorientiert: Die Überzeugung von den Vorteilen des eigenen Angebots ist oft grenzenlos. Doch wichtiger ist: Erkennt der Kunde die Vorteile des Angebots? Nimmt er diese tatsächlich als Vorteile wahr und honoriert er sie mit seiner Kaufentscheidung? Oft ist der Kundennutzen zu unspezifisch und die neuen Angebote erleben keinen erfolgreichen Marktstart.
#5 Keinen Wettbewerb: Häufig findet sich im Kapitel Markt & Wettbewerb die Aussage, dass es keinen relevanten Wettbewerb gibt. Bei Geldgebern läuten dann die Alarmglocken. Die gründliche Marktrecherche ist für den Geschäftsplan unabdingbar.
#6 Werbung wird es schon richten: Die ersten Kunden sind noch weit entfernt, wenn Gründer einen Businessplan erstellen. Gerade deshalb muss im Kapitel Marketing klar aufgezeigt werden, wie Kunden zu erreichen sind, und, was die Kundengewinnung kosten wird. Der Vertrieb wird häufig unterschätzt. Die Darstellung der Neukundengewinnung und Kundenbindung sind deshalb besonders wichtig.
#7 Finanzplanung zu optimistisch - Kapitalbedarf zu gering: Selbst bei großen Unternehmen, die ihre Produkte mit viel Geld für Werbung in den Markt bringen, dauert es oft länger, bis sich der Erfolg einstellt. Gründer haben es viel schwerer, sich im Markt zu behaupten. Viele angehende Unternehmer planen eine sehr euphorische Umsatzkurve und die Gewinnzone ist laut Businessplan schnell erreicht. Meist dauert es aber 12 bis 18 Monate bis zum Break-even . Dadurch fällt der tatsächliche Kapitalbedarf höher aus als geplant. Es entstehen schnell Liquiditätsengpässe. Eine realistische Planung und Puffer in der Liquiditätsplanung helfen, diesen Fehler zu vermeiden.
Da es wichtig ist, möglichst keine Fehler im Businessplan zu machen, haben wir in einem gesonderten Kapitel weitere schwerwiegende Businessplan-Fehler zusammengestellt.
Zur Orientierung hilft es, andere Businesspläne zu lesen. Wir haben zahlreiche Beispiel-Businesspläne zusammengestellt.
| Businessplan steigert Erfolgsaussichten
Wer gründet oder expandiert, möchte eine Marktchance nutzen. Wo Chancen bestehen, lauern auch Risiken. Gravierend können vor allem die finanziellen Konsequenzen eines Scheiterns sein. Das größte Risiko für den Erfolg eines Unternehmens entsteht aus mangelnder Planung . Nach der Unternehmensgründung zeigt sich, dass ein Produkt nicht optimal auf die Bedürfnisse der Zielgruppe ausgerichtet ist, wichtige Mitbewerber außer Acht gelassen wurden, die falschen Marketingkanäle genutzt werden oder der Kapitalbedarf zu niedrig eingeschätzt wurde.
Ein professioneller Businessplan prüft diese Faktoren. Studien belegen den Einfluss des Businessplans auf den Gründungserfolg:
- Gründer mit Businessplan gründen mit einer höheren Wahrscheinlichkeit als diejenigen, die keinen Geschäftsplan aufstellen.
- Unternehmen mit Businessplan wachsen um 30 % schneller .
- Obwohl der Businessplan keine Erfolgs-Garantie darstellt, ist das Risiko zu scheitern geringer .
Diese 3 Fakten unterstreichen, wie wichtig es ist, den Businessplan für sich selbst zu schreiben und mit guter Planung das Gründungsvorhaben voranzubringen. Außerdem: Ohne Businessplan gibt es weder Geld von der Bank noch einen Gründungszuschuss von der Agentur für Arbeit.
Von den Vorteilen eines Businessplans profitieren
Warum einen Businessplan schreiben? Weil es viele Vorteile bringt:
- Teure Fehler vermeiden: Bei der Erarbeitung des Businesskonzepts werden Fehler auf "Papier" gemacht, die nach dem Marktstart viel teurer wären.
- Fokus setzen: Der Idee, die man im Kopf hat, fehlt es an vielen Details. Der Businessplan gibt Orientierung und Struktur, um diese Details auszuarbeiten.
- Marktattraktivität bestimmen: Ein kritischer Punkt ist herauszufinden, ob das geplante Produkt auf einen Markt trifft, der groß und attraktiv genug ist.
- Die eigenen Fähigkeiten verbessern: Durch die Auseinandersetzung mit dem Thema lernen Gründer und Unternehmer viel über das künftige Produkt, die Kunden, Mitbewerber und Konkurrenten etc. Und punkten später in Bank- oder Investorengesprächen.
- Kapitalbedarf ermitteln: Zu wenig Kapital ist ein Hauptgrund für das Scheitern vieler Existenzgründungen. Das Kapitel Finanzplanung im Businessplan hilft, Umsätze und Kosten zu planen sowie den Finanzierungsbedarf realistisch einzuschätzen.
- Zugang zu Kapital: Der Businessplan ist die Basis für Bankgespräche und Investorenverhandlungen.
- Action Plan: Wenn Gründer den Businessplan aufstellen, werden bspw. in den Kapiteln Strategie und Marketing konkrete Maßnahmen zur Umsetzung nach der Gründung erarbeitet. So geht keine wertvolle Zeit verloren und Gründer starten in die Selbstständigkeit durch .
- Erfolgsanalyse: Der Businessplan dient zur Unternehmenssteuerung. So wird die Ist-Entwicklung mit dem Plan abgeglichen. Dies hilft frühzeitig Maßnahmen zu ergreifen, wenn nicht alles nach Plan läuft.
Ein Geschäftsplan ist wie ein Routenplaner oder eine Wanderkarte. Das Ziel wird gesetzt und mit der Karte wird der passende Weg ausgesucht. Je nach Beschaffenheit der Route werden entsprechende Ausrüstung oder Fähigkeiten benötigt. So eine Wanderkarte ist der Geschäftsplan für die Unternehmensgründung.
Zum Video: Der Businessplan - Ihr Plan fürs Business
| Beratungsangebote
Hilfe beim Businessplan leistet eine Businessplan-Software . Seminare, Gründercoaches und Businessplanwettbewerbe unterstützen beim Businessplanschreiben und der Ausarbeitung des Geschäftsplans.
Seminare und kostenfreie Beratungsangebote
Mehrstündige Existenzgründerseminare zur Businessplanerstellung werden bspw. von den Handelskammern durchgeführt. Die Kosten liegen unter 100 Euro. Nachteil ist, dass bei mehreren Teilnehmern nicht individuell an den Geschäftsplänen gearbeitet werden kann. Weiterhin gibt es kostenfreie, 1- bis 2-stündige Beratungsangebote von öffentlichen Institutionen oder den Handels- und Handwerkskammern. Dort besteht die Möglichkeit über einzelne Inhalte des Businessplans zu sprechen.
Geförderte Beratung durch Gründercoaches
Ein Gründercoach leistet umfangreiche Hilfe für den Businessplan. Der Mehrwert der Gründerberater besteht darin, nach der Businessplanerstellung bei der Finanzierung zu unterstützen. Berater wissen genau, was einen bankfähigen Finanzplan auszeichnet und wie eine ideale Vorbereitung auf das Bankgespräch aussieht. Zahlreiche Förderprogramme tragen über Zuschüsse einen guten Teil der Beratungskosten. Wir unterstützen bei der Suche nach dem geeigneten Gründercoach .
Businessplanwettbewerbe
Wettbewerbe bieten Workshop-Angebote, teilweise Mentoring, Informationsmaterial sowie Businessplan-Handbücher. Am Ende werden die besten Businesspläne mit Preisgeldern ausgezeichnet. Die Teilnahme an den Businessplanwettbewerben ist kostenfrei. Der jeweilige Wettbewerb sollte zur Unternehmensgründung passen. Wir zeigen, welche Businessplanwettbewerbe es gibt .
- Staat trägt bis 80 % der Kosten
- Coach hilft bei der Bankensuche
- Begleitung zum Bankgespräch
- Nötig für den Gründungszuschuss
- Persönliche Experten-Beratung
- 100 % Kostenübernahme mit AVGS
| Unternehmenskonzept präsentieren
Ist der Businessplan fertig geschrieben, wird er zu den passenden Adressaten geschickt. Für ein erfolgreiches Geschäftsplan-Marketing helfen ein paar Hinweise:
#1 Wirklich fertig? Bevor der Businessplan an Banken oder Investoren geht, ist Feedback wichtig. Freunde oder Bekannte können den Geschäftsplan lesen. Häufig treten dann Unklarheiten oder Widersprüche zutage. Damit können Gründer weiter am fertigen Businessplan feilen.
#2 Adressatengerecht anpassen: Der Wurm muss dem Fisch schmecken. Der Geschäftsplan wird an die Zielgruppe angepasst. Bestimmte Aspekte rücken in den Vordergrund und andere Dinge werden weglassen. Der Überblick darf trotz mehrerer Businesspläne nicht verloren gehen. Lesen Sie mehr über die Adressaten des Businessplans.
#3 Vertraulichkeitshinweis und -vereinbarung: Ein Vertraulichkeitshinweis gehört auf den Businessplan. Zusätzlich kann eine Vertraulichkeitsvereinbarung (NDA - Non-Disclosure Agreement) durch den Empfänger unterzeichnet werden.
#4 Pitch-Deck und Unternehmenspräsentation: Der Erstkontakt mit Kapitalgebern erfolgt in der Regel nicht mit dem gesamten Business- und Finanzplan. Stattdessen werden die wichtigsten Informationen in Präsentationen zusammengestellt. Gefallen diese, wird im nächsten Schritt der fertige Businessplan verschickt. Was gute Präsentationen auszeichnet, haben wir in den Kapiteln Unternehmenspräsentation und Pitch-Deck zusammengestellt.
#5 Bankgespräch: Im Vorfeld des Bankgesprächs erhält der Bankmitarbeiter den fertigen Geschäftsplan. Im Gespräch geht es dann um die Details. Die Vorbereitung auf das Gespräch ist enorm wichtig. Alle Einzelheiten des Plans müssen Gründern bekannt sein, um schnell Antworten liefern zu können. Das Bankgespräch dient dazu, den Gründer oder die Gründerin unter die Lupe zu nehmen. Lesen Sie mehr Tipps zum Bankgespräch .
#6 Gekonnt präsentieren: Wenn das Vorhaben vor Publikum präsentiert wird, wird nicht aus dem fertigen Businessplan vorgelesen. Meist geht es um einen kurzen Vortrag in freier Rede oder mit Powerpoint-Präsentation. Üben Sie den Vortrag vor dem Spiegel, vor Freunden, Mitgründern oder Mitarbeitern. Sprechen Sie frei, statt vom Zettel abzulesen. Und überlegen Sie sich Antworten auf mögliche Fragen. Wir haben Tipps für den perfekten Elevator Pitch zusammengestellt.
#7 Englischer Businessplan: Für die Investorensuche führt der Weg schnell ins Ausland - besonders in den angelsächsischen Bereich. Unabhängig davon, welche Sprache es sein wird, ist sicherzustellen, dass der Businessplan korrekt übersetzt wird. Idealerweise durch ein Übersetzungsbüro.
Ein zusätzlicher Tipp: schicken Sie den fertigen Businessplan oder das Pitch-Deck nicht an beliebig viele Adressen herum. Durch die Recherche der passenden Empfänger ist es möglich, individuelle Anschreiben zu formulieren, die Interesse wecken.
Lassen Sie sich von Absagen nicht entmutigen . Diese gehören bei der Suche nach Kapitalgebern dazu. Die Absagen sind meist keine Bewertungen der Gründerperson oder des Unternehmenskonzepts. Eventuelles Feedback hilft, den Businessplan kontinuierlich zu verbessern.
| Offene Fragen
Folgende Fragen hören wir von Existenzgründern, wenn sie einen Businessplan erstellen.
Einen Businessplan zu schreiben, lohnt sich erst, wenn eine passende Geschäftsidee gefunden und wichtige Faktoren des Geschäftsmodells geprüft wurden. Für den Businessplan brauchen Gründer eine stringente Gliederung, die z. B. die Kapitel Gründer, Markt, Ziele, Marketing und Strategie enthält. Für einen bankfähigen Businessplan benötigen Gründer dann noch einen Finanzplan . Ein guter Businessplan erfordert zudem Zeit und viele Detailinformationen. Ein Berater kann dabei unterstützen.
Ein Businessplan kostet zunächst nur Fleiß und Zeit. Die Businessplan-Software Unternehmerheld ist für die Businessplanerstellung sogar kostenfrei. Wenn ein Berater unterstützt, kostet der Businessplan meist 3.000 bis 4.000 Euro, wovon durch Förderprogramme nur einen kleinerer Teil durch die Existenzgründer zu tragen sind. Musterbusinesspläne gibt es häufig kostenfrei oder gegen geringe Gebühren von 20 Euro zum Download.
Für-Gründer.de bietet eine umfangreiche digitale Businessplan-Vorlage . Ein fertige, anpassbare Gliederung und Leitfragen helfen bei der Erstellung. Ein Beispiel-Businessplan zeigt exemplarisch, wie die Inhalte der einzelnen Kapitel aussehen können.
Viele Existenzgründer sagen, dass sie einen Businessplan erstellen, weil Bank, Investoren oder die Arbeitsagentur das so wünschen. Das stimmt zwar und ist auch eine valide Begründung, warum sie einen Businessplan schreiben sollten. Den Businessplan erstellen Gründer aber in erster Linie für sich selbst. Denn so wie der Businessplan für Externe ein wichtiges Entscheidungsdokument ist, müssen auch Gründer die Chancen des Gründungsvorhabens gut einschätzen.
Existenzgründer schreiben den Businessplan in erster Linie für sich selbst. Gleichzeitig gibt es verschiedene Stakeholder, die für ihre Entscheidungen den Businessplan verlangen:
- Arbeitsamt: Für die Beantragung des Gründungszuschusses muss der Businessplan die Tragfähigkeit des Konzepts belegen.
- Förder- und Bürgschaftsbanken: Um Fördermittel oder Bürgschaften zu erhalten, erfüllt der Businessplan die Aufgabe, zu zeigen, ob der Kredit aus dem operativen Geschäft getilgt werden kann.
- Bank: Auch beim klassischen Kredit der Hausbank ist der Business- und Finanzplan eine wesentliche Entscheidungsgrundlage, da keine historischen Daten zur Geschäftsentwicklung bestehen.
- Investoren: Zur Detailprüfung spielt der Businessplan ein große Rolle, vor allem um die Wachstumsperspektiven zu prüfen.
- Geschäftspartner: Künftige Geschäftspartner können eine Kurzform des Geschäftsplans erhalten, wenn es z.B. darum geht, dass Lieferanten den neu gegründeten Unternehmen längere Zahlungsfristen einräumen.
Alternative zum Businessplan sind das Pitch Deck, die Unternehmenspräsentation oder das Business Model Canvas. Diese erreichen jedoch nicht den Detailgrad eines Geschäftsplans. Das Pitch Deck oder die Unternehmenspräsentation zeigen vielmehr den roten Faden auf und stellen die Highlights des Gründungsvorhabens vor. Sie zielen darauf ab, bei möglichen Investoren Interesse für eine Finanzierung zu wecken. Gerade visuell können sie ohne Zweifel mehr beeindrucken als der textlastige Businessplan. Das Canvas ist als Vorstufe des Businessplans sinnvoll, um wesentliche Elemente des Geschäftsmodells zu prüfen.
Die Businessplanerstellung kann per Word und Excel erfolgen. Beide Programme weisen jedoch Nachteile auf. Eine Gliederung und die gesamte Formatierung müssen in Word angelegt werden. Der Aufbau eines Excel-Finanzplans dauert in der Regel sehr lange und ist fehleranfällig.
Aufgrund der Probleme per Word und Excel suchen viele Existenzgründer schnell nach passenden Vorlagen mit Inhaltsverzeichnis und Mustern für den Businessplan, von denen es im Internet viele gibt. Vorlagen für den Textteil des Businessplans in Word sind dabei meist noch unkritisch. Allerdings stellt sich stets die Frage, wer die Vorlage erstellt hat und ob diese der aktuellen Praxis entspricht. Gerade bei Excel-Vorlagen steckt der Teufel dann häufig im Detail. Sind alle Formeln korrekt? Passt die Vorlage zu meinem Geschäftsmodell? Ermittelt das Tool alle Kennzahlen, die bspw. von der Bank gefordert werden. Und wie integriere ich die Excel-Ergebnisse in mein Worddokument des Geschäftsplans?
Der Businessplan erfüllt folgende Aufgaben:
- Prüfung der wirtschaftlichen Tragfähigkeit des Konzepts.
- Qualifikation des Gründers oder Unternehmers.
- Verhandlungsgrundlage für Geldgeber und Finanzierungspartner.
- Plan für Umsetzung des Geschäftskonzepts und spätere Erfolgskontrolle.
Bei einem Businessplan helfen zunächst Leitfäden und Artikel online, im nächsten Schritt können Gründer sich ebenfalls an IHK bzw. HWK wenden. Darüber hinaus gibt es diverse Gründernetzwerke oder auch die Möglichkeit der Teilnahme an einem Businessplan-Wettbewerb. Zusätzlich können Gründer sich auch an einen speziellen Businessplan-Berater wenden.
| Unser Fazit
Der Businessplan (englisch für Geschäftsplan) ist die strukturierte Ausarbeitung der Geschäftsidee bzw. des Unternehmenskonzepts. Die fundierte Planung erhöht die Erfolgschancen der Unternehmensgründung. Im Businessplan erarbeiten Gründer:
- An wen sich die Geschäftsidee richtet ( Zielgruppe ).
- Wie die Geschäftsidee funktionieren soll ( Strategie ).
- Wo die Chancen und Risiken liegen ( SWOT-Analyse ).
- Ob sich die Geschäftsidee überhaupt lohnt ( Finanzplan ).
- Ob die Liquidität innerhalb des Planungshorizonts gewährleistet ist.
Der Businessplan ist mehr als eine lästige Pflichtübung für Banken, Investoren oder das Arbeitsamt. Er ist der ganz persönliche Leitfaden für die Selbstständigkeit und den Unternehmensaufbau. Er gehört nach der Gründung nicht in die Schublade, sondern sollte konsequent umgesetzt werden. Dies bedeutet kein starres Festhalten am Businessplan. Anpassungen sind nötig, wenn sich Rahmenbedingungen ändern oder geplante Maßnahmen nicht erfolgreich sind.
Wichtige Inhalte Zu den wichtigsten Kapiteln im Geschäftsplan zählen:
- Markt- und Wettbewerbsanalyse
- Unternehmensziele und -strategie
- Gründer- und Managementteam
- Finanzen: Herzstück im Businessplan ist der Finanzplan .
Besonderen Stellenwert hat auch die SWOT-Analyse , wenn Gründer den Businessplan erstellen. Ganz zum Schluss des Geschäftsplans steht die Executive Summary an. Auf zwei Seiten werden die Hauptpunkte des Geschäftsplans vorgestellt. Damit verschaffen sich Leser schnell einen Überblick, bevor sie das gesamte Dokument lesen.
Auf die Form achten Neben dem Inhalt muss ein Geschäftsplan formalen Anforderungen entsprechen, um die Leser restlos zu überzeugen. Ein Geschäftsplan mit klarer Struktur, ansprechendem Layout, individueller Gestaltung und guter Lesbarkeit wirken sich auf die Beurteilung durch den Leser aus. Daran ist zu denken, wenn Sie den Geschäftsplan erstellen.
Berater helfen Gerade wenn Gründer für eine Finanzierung den Businessplan schreiben, lohnt die Unterstützung durch einen Gründercoach. Zuschüsse aus Förderprogrammen übernehmen einen Großteil der Beratungskosten. Prüfen Sie die Referenzen eines möglichen Beraters. Kennt er sich in Ihrer Branche aus und ist er erfolgreich bei der Begleitung von Bankgesprächen? Wichtig ist, dass Sie sich gut mit dem Berater verstehen. Lernen Sie einen Berater aus unserem Netzwerk im kostenfreien Erstgespräch kennen.

✓ Word-Vorlage
✓ Muster-Businessplan
✓ Beispiele als PDF
✓ Fertige Gliederung
✓ Leitfragen & Beispiele
✓ Kostenfrei
frage[at]fuer-gruender.de

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Download Now: Free Business Plan Template. Writing a business plan doesn't have to be complicated. In this step-by-step guide, you'll learn how to write a business plan that's detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
A business plan is a document that communicates a company's goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered. A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals.
Nicht jeder Businessplan wird in die Tat umgesetzt. Und auch nicht jeder Businessplan überzeugt Kapitalgeber. Deshalb sollten Sie folgende Fehler unbedingt vermeiden: Zu wenig Überarbeitung: Während Sie Ihre Pläne erstellen und die Recherche durchführen, werden sich die vorausgesagten Zahlen mit Sicherheit oft ändern. Haben Sie deshalb ...
Step 7: Financial Analysis and Projections. It doesn't matter if you include a request for funding in your plan, you will want to include a financial analysis here. You'll want to do two things here: Paint a picture of your business's performance in the past and show it will grow in the future.
Provide a breakdown of costs per unit made/sold, life cycle, and expected profit margins. Explain your supply chain, order fulfillment, and sales strategy. Include your plans for intellectual property, like trademarks and patents. Your product and service description brings you to those who matter most.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
Zum kostenfreien Download bieten wir eine Vorlage und zahlreiche Beispiel-Geschäftspläne an. Word und Excel waren für das Schreiben eines Businessplans häufig das Mittel der Wahl. Eine Businessplansoftware ist mittlerweile eine hilfreiche Alternative, um den Businessplan zu erstellen. Die Unternehmerheld Businessplansoftware ist eine ...
More Than A Business Plan Template Claim Your Business Plan. Plannit.ai is an AI-driven business planning platform that helps entrepreneurs, business owners, students and business consultants create professional business plans in minutes. Answer questions about your vision and generate a full professional business plan.
Whether you want to launch a side gig, a solo operation or a small business, you need a simple business plan template to guide you. Forbes Advisor offers you a comprehensive and easy-to-follow ...
688 templates. Create a blank Business Plan. Beige Aesthetic Modern Business Plan A4 Document. Document by Rise & Roar Design. Navy and Gray Modern Business Plan Cover Document. Document by Banuaa. Blue Modern Minimalist Startup Business Plan. Document by Maea Studio. Blue White Simple Business Plan Cover Page.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
Unser Businessplan-Muster dient zur Orientierung, wie das Geschäftskonzept für Ihr Unternehmen aussehen kann. Direkt erstellen können Sie den Businessplan mit unserer Businessplan-Vorlage kostenlos, die als Word und PDF zum Download oder auch digital für Ihr Gründungskonzept zur Verfügung steht.. Inspiration bietet ein Businessplan-Beispiel.Wir haben fertige Businessplan-Beispiele als ...
Für das Arbeitsamt den Businessplan erstellen: Wer sich aus der Arbeitslosigkeit selbstständig machen möchte, kann mit dem Businessplan den Gründungszuschuss beantragen. Businessplan für Förder- und Bürgschaftsbanken: Für Fördermittel oder eine Bürgschaft dient der Businessplan dazu, die Kapitaldienstfähigkeit des Vorhabens unter ...
Ein Businessplan kann Ihnen helfen, Ihr Geschäftskonzept zusammenzustellen und es im Jahr 2021 zum Erfolg zu führen. Die Erstellung eines Businessplans in PowerPoint hilft Ihnen, alle wichtigen Schritte zur Planung Ihrer Idee zu skizzieren.. Businessplan-Präsentationsvorlagen können Ihnen da rasch weiterhelfen, eine moderne Präsentation in kürzester Zeit zu erstellen.
Jeder Gründer sollte sich zu Beginn der Existenzgründung um seinen Businessplan kümmern. Dabei ist es wichtig, beim Businessplan erstellen keine Fehler zu ma...