- Contact sales
Start free trial

How to Write a Business Case (Template Included)

Table of Contents
What is a business case, how to write a business case, business case template, watch our business case training video, key elements of a business case, how projectmanager helps with your business case.
A business case is a project management document that explains how the benefits of a project overweigh its costs and why it should be executed. Business cases are prepared during the project initiation phase and their purpose is to include all the project’s objectives, costs and benefits to convince stakeholders of its value.
A business case is an important project document to prove to your client, customer or stakeholder that the project proposal you’re pitching is a sound investment. Below, we illustrate the steps to writing one that will sway them.
The need for a business case is that it collects the financial appraisal, proposal, strategy and marketing plan in one document and offers a full look at how the project will benefit the organization. Once your business case is approved by the project stakeholders, you can begin the project planning phase.
Projects fail without having a solid business case to rest on, as this project document is the base for the project charter and project plan. But if a project business case is not anchored to reality, and doesn’t address a need that aligns with the larger business objectives of the organization, then it is irrelevant.

Get your free
Use this free Business Case Template for Word to manage your projects better.
The research you’ll need to create a strong business case is the why, what, how and who of your project. This must be clearly communicated. The elements of your business case will address the why but in greater detail. Think of the business case as a document that is created during the project initiation phase but will be used as a reference throughout the project life cycle.
Whether you’re starting a new project or mid-way through one, take time to write up a business case to justify the project expenditure by identifying the business benefits your project will deliver and that your stakeholders are most interested in reaping from the work. The following four steps will show you how to write a business case.
Step 1: Identify the Business Problem
Projects aren’t created for projects’ sake. They should always be aligned with business goals . Usually, they’re initiated to solve a specific business problem or create a business opportunity.
You should “Lead with the need.” Your first job is to figure out what that problem or opportunity is, describe it, find out where it comes from and then address the time frame needed to deal with it.
This can be a simple statement but is best articulated with some research into the economic climate and the competitive landscape to justify the timing of the project.
Step 2: Identify the Alternative Solutions
How do you know whether the project you’re undertaking is the best possible solution to the problem defined above? Naturally, prioritizing projects is hard, and the path to success is not paved with unfounded assumptions.
One way to narrow down the focus to make the right solution clear is to follow these six steps (after the relevant research, of course):
- Note the alternative solutions.
- For each solution, quantify its benefits.
- Also, forecast the costs involved in each solution.
- Then figure out its feasibility .
- Discern the risks and issues associated with each solution.
- Finally, document all this in your business case.
Step 3: Recommend a Preferred Solution
You’ll next need to rank the solutions, but before doing that it’s best to set up criteria, maybe have a scoring mechanism such as a decision matrix to help you prioritize the solutions to best choose the right one.
Some methodologies you can apply include:
- Depending on the solution’s cost and benefit , give it a score of 1-10.
- Base your score on what’s important to you.
- Add more complexity to your ranking to cover all bases.
Regardless of your approach, once you’ve added up your numbers, the best solution to your problem will become evident. Again, you’ll want to have this process also documented in your business case.
Step 4: Describe the Implementation Approach
So, you’ve identified your business problem or opportunity and how to reach it, now you have to convince your stakeholders that you’re right and have the best way to implement a process to achieve your goals. That’s why documentation is so important; it offers a practical path to solve the core problem you identified.
Now, it’s not just an exercise to appease senior leadership. Who knows what you might uncover in the research you put into exploring the underlying problem and determining alternative solutions? You might save the organization millions with an alternate solution than the one initially proposed. When you put in the work on a strong business case, you’re able to get your sponsors or organizational leadership on board with you and have a clear vision as to how to ensure the delivery of the business benefits they expect.
Our business case template for Word is the perfect tool to start writing a business case. It has 9 key business case areas you can customize as needed. Download the template for free and follow the steps below to create a great business case for all your projects.
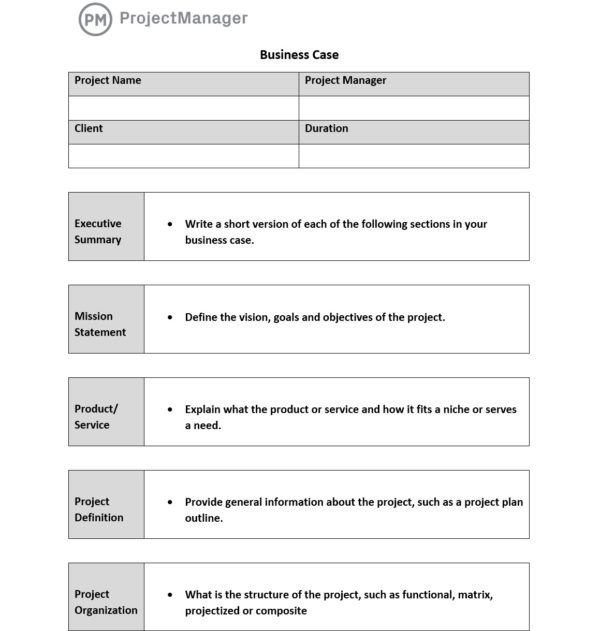
One of the key steps to starting a business case is to have a business case checklist. The following is a detailed outline to follow when developing your business case. You can choose which of these elements are the most relevant to your project stakeholders and add them to our business case template. Then once your business case is approved, start managing your projects with a robust project management software such as ProjectManager.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a short version of each section of your business case. It’s used to give stakeholders a quick overview of your project.
2. Project Definition
This section is meant to provide general information about your projects, such as the business objectives that will be achieved and the project plan outline.
3. Vision, Goals and Objectives
First, you have to figure out what you’re trying to do and what is the problem you want to solve. You’ll need to define your project vision, goals and objectives. This will help you shape your project scope and identify project deliverables.
4. Project Scope
The project scope determines all the tasks and deliverables that will be executed in your project to reach your business objectives.
5. Background Information
Here you can provide a context for your project, explaining the problem that it’s meant to solve, and how it aligns with your organization’s vision and strategic plan.
6. Success Criteria and Stakeholder Requirements
Depending on what kind of project you’re working on, the quality requirements will differ, but they are critical to the project’s success. Collect all of them, figure out what determines if you’ve successfully met them and report on the results .
7. Project Plan
It’s time to create the project plan. Figure out the tasks you’ll have to take to get the project done. You can use a work breakdown structure template to make sure you are through. Once you have all the tasks collected, estimate how long it will take to complete each one.
Project management software makes creating a project plan significantly easier. ProjectManager can upload your work breakdown structure template and all your tasks are populated in our tool. You can organize them according to your production cycle with our kanban board view, or use our Gantt chart view to create a project schedule.
8. Project Budget
Your budget is an estimate of everything in your project plan and what it will cost to complete the project over the scheduled time allotted.
9. Project Schedule
Make a timeline for the project by estimating how long it will take to get each task completed. For a more impactful project schedule , use a tool to make a Gantt chart, and print it out. This will provide that extra flourish of data visualization and skill that Excel sheets lack.
10. Project Governance
Project governance refers to all the project management rules and procedures that apply to your project. For example, it defines the roles and responsibilities of the project team members and the framework for decision-making.
11. Communication Plan
Have milestones for check-ins and status updates, as well as determine how stakeholders will stay aware of the progress over the project life cycle.
12. Progress Reports
Have a plan in place to monitor and track your progress during the project to compare planned to actual progress. There are project tracking tools that can help you monitor progress and performance.
Again, using a project management tool improves your ability to see what’s happening in your project. ProjectManager has tracking tools like dashboards and status reports that give you a high-level view and more detail, respectively. Unlike light-weight apps that make you set up a dashboard, ours is embedded in the tool. Better still, our cloud-based software gives you real-time data for more insightful decision-making. Also, get reports on more than just status updates, but timesheets, workload, portfolio status and much more, all with just one click. Then filter the reports and share them with stakeholders to keep them updated.

13. Financial Appraisal
This is a very important section of your business case because this is where you explain how the financial benefits outweigh the project costs . Compare the financial costs and benefits of your project. You can do this by doing a sensitivity analysis and a cost-benefit analysis.
14. Market Assessment
Research your market, competitors and industry, to find opportunities and threats
15. Competitor Analysis
Identify direct and indirect competitors and do an assessment of their products, strengths, competitive advantages and their business strategy.
16. SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis helps you identify your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. The strengths and weaknesses are internal, while the opportunities and threats are external.
17. Marketing Strategy
Describe your product, distribution channels, pricing, target customers among other aspects of your marketing plan or strategy.
18. Risk Assessment
There are many risk categories that can impact your project. The first step to mitigating them is to identify and analyze the risks associated with your project activities.
ProjectManager , an award-winning project management software, can collect and assemble all the various data you’ll be collecting, and then easily share it both with your team and project sponsors.
Once you have a spreadsheet with all your tasks listed, you can import it into our software. Then it’s instantly populated into a Gantt chart . Simply set the duration for each of the tasks, add any dependencies, and your project is now spread across a timeline. You can set milestones, but there is so much more you can do.
You have a project plan now, and from the online Gantt chart, you can assign team members to tasks. Then they can comment directly on the tasks they’re working on, adding as many documents and images as needed, fostering a collaborative environment. You can track their progress and change task durations as needed by dragging and dropping the start and end dates.
But that’s only a taste of what ProjectManager offers. We have kanban boards that visualize your workflow and a real-time dashboard that tracks six project metrics for the most accurate view of your project possible.
Try ProjectManager and see for yourself with this 30-day free trial .
If you want more business case advice, take a moment to watch Jennifer Bridges, PMP, in this short training video. She explains the steps you have to take in order to write a good business case.
Here’s a screenshot for your reference.

Transcription:
Today we’re talking about how to write a business case. Well, over the past few years, we’ve seen the market, or maybe organizations, companies or even projects, move away from doing business cases. But, these days, companies, organizations, and those same projects are scrutinizing the investments and they’re really seeking a rate of return.
So now, think of the business case as your opportunity to package your project, your idea, your opportunity, and show what it means and what the benefits are and how other people can benefit.
We want to take a look today to see what’s in the business case and how to write one. I want to be clear that when you look for information on a business case, it’s not a briefcase.
Someone called the other day and they were confused because they were looking for something, and they kept pulling up briefcases. That’s not what we’re talking about today. What we’re talking about are business cases, and they include information about your strategies, about your goals. It is your business proposal. It has your business outline, your business strategy, and even your marketing plan.
Why Do You Need a Business Case?
And so, why is that so important today? Again, companies are seeking not only their project managers but their team members to have a better understanding of business and more of an idea business acumen. So this business case provides the justification for the proposed business change or plan. It outlines the allocation of capital that you may be seeking and the resources required to implement it. Then, it can be an action plan . It may just serve as a unified vision. And then it also provides the decision-makers with different options.
So let’s look more at the steps required to put these business cases together. There are four main steps. One, you want to research your market. Really look at what’s out there, where are the needs, where are the gaps that you can serve? Look at your competition. How are they approaching this, and how can you maybe provide some other alternatives?
You want to compare and finalize different approaches that you can use to go to market. Then you compile that data and you present strategies, your goals and other options to be considered.
And then you literally document it.
So what does the document look like? Well, there are templates out there today. The components vary, but these are the common ones. And then these are what I consider essential. So there’s the executive summary. This is just a summary of your company, what your management team may look like, a summary of your product and service and your market.
The business description gives a little bit more history about your company and the mission statement and really what your company is about and how this product or service fits in.
Then, you outline the details of the product or service that you’re looking to either expand or roll out or implement. You may even include in their patents may be that you have pending or other trademarks.
Then, you want to identify and lay out your marketing strategy. Like, how are you gonna take this to your customers? Are you going to have a brick-and-mortar store? Are you gonna do this online? And, what are your plans to take it to market?
You also want to include detailed information about your competitor analysis. How are they doing things? And, how are you planning on, I guess, beating your competition?
You also want to look at and identify your SWOT. And the SWOT is your strength. What are the strengths that you have in going to market? And where are the weaknesses? Maybe some of your gaps. And further, where are your opportunities and maybe threats that you need to plan for? Then the overview of the operation includes operational information like your production, even human resources, information about the day-to-day operations of your company.
And then, your financial plan includes your profit statement, your profit and loss, any of your financials, any collateral that you may have, and any kind of investments that you may be seeking.
So these are the components of your business case. This is why it’s so important. And if you need a tool that can help you manage and track this process, then sign up for our software now at ProjectManager .

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Discover how today’s most successful IT leaders stand out from the rest. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Read the report .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project planning |
- The beginner’s guide to writing an effe ...
The beginner’s guide to writing an effective business case

Nearly every project needs to be approved—whether that means getting the simple go-ahead from your team or gaining the support of an executive stakeholder. You may be familiar with using a project plan or project charter to propose a new initiative and get the green light for a project. But if your proposed project represents a significant business investment, you may need to build a business case.
If you’ve never written a business case, we’re here to help. With a few resources and a little planning, you can write a business case that will help you get the resources and support you need to manage a successful project.
What is a business case?
A business case is a document that explains the value or benefits your company will gain if you pursue a significant business investment or initiative. This initiative can be anything from the messaging for a new product or feature launch, a proposal to increase spend on a current initiative, or a significant investment with a new agency or contractor—to name a few. A compelling business case will outline the expected benefits of this significant investment decision. Key stakeholders will use the business case you provide to determine whether or not to move forward with an initiative.
If you’ve never created a business case, it may sound similar to other early project planning documentation. Here’s how it stacks up:
The difference between a business case and business plan
A business case is a proposal for a new strategy or large initiative. It should outline the business needs and benefits your company will receive from pursuing this opportunity.
A business plan , on the other hand, is an outline for a totally new business. Typically, you’d draft a business plan to map out your business strategy, your mission and vision statements, and how you’re planning on getting there. There may be a case where you create a business plan for an already-existing business, but you’d only do so if you’re trying to take your business in a significantly new direction.
Business case vs. executive summary
Business case vs. project charter.
If you need to create an elevator pitch for your project but you don’t quite need the full business case treatment, you might need a project charter. Much like a business case, a project charter outlines key details of an initiative. Specifically, a project charter will cover three main elements of your project: project objectives, project scope, and key project stakeholders. Your management team will then use the project charter to approve further project development.
Do you need a business case?
Not every project needs a business case—or even a project charter. Plan to build a business case only for initiatives or investments that will require significant business resources. If you’re working on a smaller initiative, consider creating a project charter to pitch your project idea to relevant stakeholders.
Even if you don’t need to pitch your project to any stakeholders, you should be ready to answer basic questions about your proposed project, like:
What is this project’s purpose?
Why are we working on this project?
How does this project connect to organizational goals and objectives?
Which metrics will we use to measure the success of the project ?
Who is working on this project?
When is this project going to be completed?
5 steps for creating and pitching a business case
Your business case shouldn’t just include key facts and figures—it should also tell a story of why pursuing a particular investment or initiative is a good idea for your business. When in doubt, avoid jargon and be brief—but always focus on communicating the value of the project. If this is your first time creating a business case, don’t worry. Follow these five steps to create a solid one.
1. Gather input
You don’t have to write a business case on your own. Instead, make sure appropriate team members and stakeholders are contributing to the relevant sections. For example, the IT team should be involved in any tooling and timeline decisions, while the finance team should review any budget and risk management sections. If you’re creating a business case to propose a new initiative, product line, or customer persona, make sure you also consult subject matter experts.
2. Plan to write your business case out of order
Some of the first things that appear in your business case—like your executive summary—should actually be drafted last, when you have all of the resources and information to make an informed suggestion. Your executive summary will present all of your findings and make a recommendation for the business based on a variety of factors. By gathering all of those details first—like project purpose, financial information, and project risk—you can ensure your executive summary has all of the relevant information.
3. Build your business case incrementally
A business case describes a significant investment for your company. Similarly, simply writing a business case is a significant investment of your time. Not every initiative is right for your business—so make sure you’re checking your work with stakeholders as you go. You don’t want to sink hours and weeks into this document only for it to be rejected by executive stakeholders right off the bat.
Consider doing a “soft launch” with an outline of your business case to your project sponsor or an executive stakeholder you have a good relationship with to confirm this initiative is something you should pursue. Then, as you build the different sections of your business case, check back in with your key stakeholders to confirm there are no deal-breakers.
4. Refine the document
As you create sections of your business case, you may need to go back and refine other sections. For example, once you’ve finished doing a cost-benefit analysis with your financial team, make sure you update any budget-related project risks.
Before presenting your business case, do a final read through with key stakeholders to look for any sections that can be further refined. At this stage, you’ll also want to write the executive summary that goes at the top of the document. Depending on the length of your business case, your executive summary should be one to two pages long.
5. Present the business case
The final step is to actually present your business case. Start with a quick elevator pitch that answers the what, why, and how of your proposal. Think of this presentation as your chance to explain the current business need, how your proposal addresses the need, and what the business benefits are. Make sure to address any risks or concerns you think your audience would have.
Don’t go through your business case page by page. Instead, share the document with stakeholders before the presentation so they have a chance to read through it ahead of time. Then, after your presentation, share the document again so stakeholders can dig into details.
A business case checklist
Start with the why.
The first section of the business case is your chance to make a compelling argument about the new project. Make sure you draft an argument that appeals to your audience’s interests and needs. Despite being the first section in your business case, this should be the last section you write. In addition to including the traditional elements of an executive summary , make sure you answer:
What business problem is your project solving? This is your chance to explain why your project is important and why executive stakeholders should consider pursuing this opportunity.
What is your business objective ? What happens at the end of a successful project? How will you measure success—and what does a successful project mean for your business?
How does this business case fit into your overall company business strategy plan? Make sure your proposed business case is connected to important company goals . The initiative proposed in your business case should move the needle towards your company's vision statement .
Outline financials and the return on investment
At this point in your business case, you should outline the project finance fundamentals. Don’t expect to create this section on your own—you should draft this in partnership with your company’s finance team. In particular, this section should answer:
How much will this project cost? Even if the initiative is completely new to your company, do some research to estimate the project costs.
What does each individual component of the project cost? In addition to estimating the total overall cost, break down the different project costs. For example, you might have project costs for new tools and resources, competitive intelligence resourcing, agency costs, etc.
What is the expected return on investment (ROI)? You’ve talked about the costs—now talk about how your company will benefit from this initiative. Make sure to explain how you calculated the ROI, too.
How will this project impact cash flow? Cash flow is the amount of money being transferred into and out of your business. Significant investments are going to cost a lot of money, so they’ll negatively impact cash flow—but you should also expect a high ROI, which will positively impact cash flow.
What is the sensitivity analysis? Sensitivity analysis is a summary of how uncertain your numbers are. There will be a variety of variables that impact your business case. Make sure to explain what those variables are, and how that could impact your projections.
Preview project details
Your business case is proposing a new initiative. In addition to the financial risks, take some time to preview project details. For example, your business case should include:
Your project objectives and key project deliverables . What will happen at the end of the project? What are you expecting to create or deliver once the project is over?
Your project plan . A project plan is a blueprint of the key elements your team needs to accomplish in order to successfully achieve your project goals.
The project scope . What are the boundaries of your project? What exact goals, deliverables, and deadlines will you be working towards?
A list of relevant project stakeholders . Who are the important project stakeholders and key decision makers for this work? This can include the members of the project team that would be working on this initiative, executive stakeholders who would sponsor the project, and any external stakeholders who might be involved.
A general project roadmap in a Gantt-chart like view. At this stage in the process, you don’t need to provide a detailed project timeline, but you should outline a general sense of when each project stage will happen in relation to the others. To do this, create a project roadmap in Gantt-chart like software . Make sure to include any important project milestones in your roadmap as well.
Any important project dependencies. Is there anything that would get in the way of this project getting started? Does this work rely on any other work that’s currently in flight?
Discuss project risks
Once you’ve outlined the financial impact and important project details, make sure you include any potential project risks. If you haven’t already, create a project risk management plan for your business case. Project risk management isn’t the process of eliminating risk—instead, it’s about identifying, analyzing, and proactively responding to any potential project risks. Clearly defining each project risk and how that risk might impact your project can best equip you and the project team to manage and avoid those risks.
In the risk section of your business case, include:
A risk analysis of any potential project risks. What is the risk? How likely is it to happen? What is the priority level of this risk?
What, if any, assumptions you are making. In project risk management, assumptions are anything you think will be true about the project, without those details being guaranteed facts. Basing project decisions around an assumption can open your project up to risk. Make sure you ratify every project assumption to avoid jeopardizing project success.
Any comparable alternatives in the market. If you’re writing a business case to pitch a new product or angle in the market, evaluate anything that already exists. Could the alternative impact your financial assessment or project success?
Develop an action plan
In the final section of your business case, outline how you will turn this business case into an actionable project. This section should answer questions like:
How will decisions be made? Who is responsible for the project? Who is the project sponsor? If you haven’t already, consider creating a RACI chart to outline project responsibilities.
How will progress be measured and reported? Not every project stakeholder needs to be notified of every project change. Outline key parts of your project communication plan , as well as how you’ll communicate project status updates .
What is the next course of action? If the management team ratifies this business case, what next steps will you take to put this into action?
Bring your business case to life
You’ve built a solid business case and it’s been ratified—congratulations! The next step is to bring your business case to life. It can be intimidating to initiate large-scale change , and implementing your business case is no exception.
If you haven’t already, make sure you have a project management tool in place to manage and organize your new initiative. With a central source of truth to track who’s doing what by when, share status updates, and keep project stakeholders in the loop, you can turn a great business case into a successful project.
Related resources

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development

How Asana uses work management to streamline project intake processes

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
What is a business case and how to write one (with template)

In this guide, we’ll define what a business case is, help you determine when you need one (and when you don’t), and walk you through a four-step process for creating a business case.

We’ll also outline what you should include in a business case and provide a free template you can use when writing a business case to secure stakeholder support for your next big project.
What is a business case?
Every project needs the support and approval of key stakeholders before it can launch. Many project and product leaders use a project plan or charter to communicate pertinent details to those involved.
Similarly, for large initiatives that require significant resources, potential investors are presented a business case outlining the costs, benefits, business need, and risks involved.
A business case is a document that defines the value it will deliver if executed and benefits the company over the costs involved. With a thorough understanding of the components to be included and necessary resources, it is possible to create a compelling business plan.
Why do you need a business case?
If a project is green-lit without a business case, it can lead to serious issues down the road. A project without clearly articulated expectations and goals can go on endlessly and aimlessly. This leads to wasted resources, money, and time with no outcome in the end.
A business case enables you to:
Align with strategy
Gain stakeholder support, prioritize projects, track outcomes.
A business case helps to showcase how a project is aligned with the overall strategy and goals of the organization. It clearly defines the problem or opportunity that the project is intended to address.
A business case also enables you to determine expected benefits and outcomes before you start a project or initiatives, thus projecting how the project contribute to achieving the organization’s goals.
A business case is a useful tool to provide a clear rationale for pursuing the project. A thorough business case can help key stakeholders decide whether to invest in the project by evaluating the feasibility, costs, risks and potential returns. A business case presentation gives stakeholders an opportunity to ask questions and address concerns.
A business case defines the value that the project is expected to deliver. Based on the value delivered by each project, business and product leaders can prioritize projects for budget cuts or further investments. Proper prioritization helps the organization achieve the goals aligned with the business strategy.
A business case provides a roadmap for the project, including the goals, milestones, and key deliverables. Once the project starts, a roadmap helps you keep track of your progress toward project goals, including what has already been achieved and what will be delivered at the end. Providing a timely update on the project to the key stakeholders is critical for setting expectations.
When you don’t need a business case
A business case is certainly helpful for large initiatives requiring support from key stakeholders, but there are some situations where creating a business case might be a waste of time.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
For instance, small or low-risk projects that would not impact the organization in any negative way do not require a business case because it would not make sense to spend that much effort on a low-scale project.
A business case might also be considered superfluous for a project that is already ongoing. It can be tempting to create a business case post-launch for the sole purpose of documenting decisions made and milestones achieved. However, it’s typically not worth the time investment because such a business case rarely adds any value or insights.
Before you take on the task of creating a business case, it’s important to carefully consider the need and to ensure that doing so would produce valuable insights to the decision-making process. It is in the best interest of everyone to forgo the business case creation process in situations where it does not provide any additional value and to focus instead on other activities that directly impact the project.
Business case vs. business plan
A business plan is not the same thing as a business case.
A business case outlines a proposed project and its potential benefits to convince key stakeholders to invest. It typically includes analysis of costs, value to be delivered, and associated risks, along with ROI.
A business plan, on the other hand, outlines the overall strategy and goals for an entire organization. It defines the what, why, and who for the business, covering the products and services offered, target segment, marketing and sales strategy, and operational and financial projections over a period of time. A business plan is designed to help potential outside investors make informed decisions about whether the business is worth investing in.
The table below breaks down the differences between a business plan and a business case:
How to write a business case
Before we dive into steps to create a business case, let’s review what we’ve learned so far:
- A business case is a document created during the initiation of the project but is referred throughout the project lifecycle
- A strong business case helps in building confidence and gaining support of key stakeholders
- A business case also helps you track a project’s progress over time
- A weak business case that is not aligned with strategy can lead to project failure
To write a business case, follow this four-step process:
- Identify the business need
- Explore all possible solutions
- Propose the best approach
- Outline the implementation process
1. Identify the business need
Projects are initiated to solve a business need and achieve a value or a benefit aligned to the goals of the organization.
The first step to create a business case is to identify the business problem and define it clearly. Market research and any available data to justify the business need is helpful to include in the business case.
2. Explore all possible solutions
Once the business problem has been identified, the next step is to explore all the possible solutions for that problem. You can do this systematically by listing out all the possible solutions along with other parameters, such as:
- The benefits of each approach
- Feasibility
- Time period
- Assumptions
A detailed analysis of each option predicting the cash flows, ROI, and value delivered would help key stakeholders understand each solution and cross-question the assumptions, feasibility, and other parameters.
3. Propose the best approach
Set a criteria to showcase how you evaluate each solution and then come up with the best out of the list.
To set the criteria, identify attributes that closely align to the organization’s strategy. For example, if the organization’s goal is to increase revenue in the next year, then an important criterion might be the solution with maximum revenue projection.
List the top three-to-five attributes to evaluate alternative solutions against and rank each solution 1–5. Once you rank all of them, total the ranks for all the attributes to indicate a clear winner.
Document this process and present it to stakeholders to ensure they are on the same page with the selection process of the best solution.
4. Outline the implementation process
Once the best solution has been proposed, the next step is to think about how it will be implemented.
When it comes to planning the implementation process, you need to define:
- Resources needed
- Timeline from initiation till the end
- Risks and how to mitigate
- Milestones and when they will be achieved
- Total cost involved and how much will be used by when
These four steps, when captured in detail, can help you win the support of key stakeholders and kick off your project with a solid foundation and a clear objective.
What is included in a business case?
Now that we’ve walked through the steps of how to create a business case, let us also take a look at what to include in the business case document to support the four steps outlined above.
Here’s what to include in a business case:
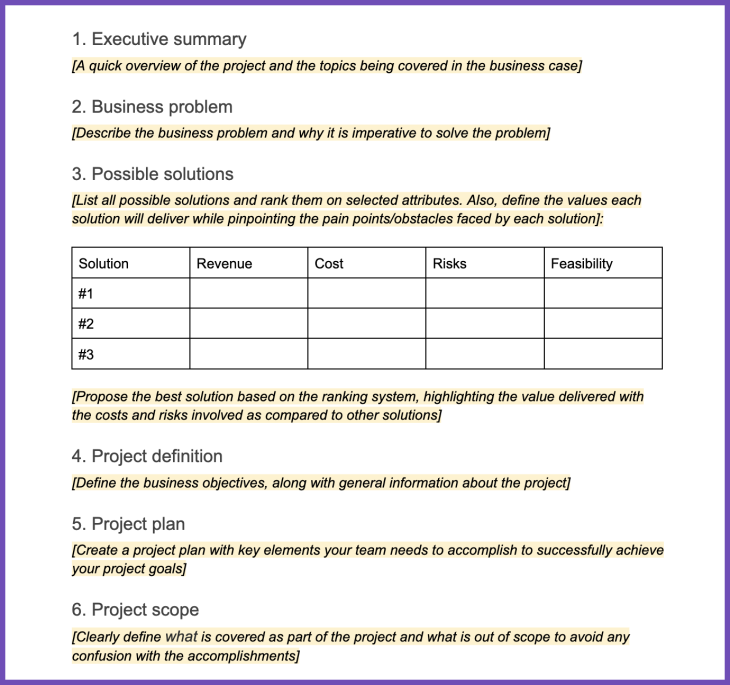
- Executive summary — A quick overview of the project and the topics being covered in the business case
- Business problem — A description of the business problem and why it is important to solve it
- Possible solutions — A list of possible solutions and how the best possible solution is identified
- Project definition — Define the business objectives to be achieved along with general information about the project
- Project plan — Create the project plan with key elements your team needs to accomplish to successfully achieve your project goals
- Project scope — Clearly define what would be covered as a part of the project and what is out of scope to avoid any confusion
- Project budget — Estimated cost involved to complete the project needs to be captured with a detailed breakdown
- Project roadmap — Projection of the estimated timeline for each stage of the project to be done. Be sure to include any important project milestones
- Project financials — Financial metrics depicting the cash flow, such as NPV, IRR, ROI, and payback period to help stakeholders understand the financial value the project can bring in over a period of time
- Risk assessment — Capture the risks involved and the steps planned to mitigate the risks
- Project stakeholders — A list of key stakeholders involved can help anyone looking at the document to reach out to them when needed. The list can include the project team, sponsoring executives, and any external stakeholders who might be involved
Business case template
To help you get started writing a business case for your next big project or initiative, we created a business case template that you can download and customize for free.
You can access this simple business case template by clicking here (be sure to select File > Make a copy from the main menu bar before editing the template).
Preparing the business case is only half the journey of initiating a project. The next step is to present the business plan to key stakeholders , answer their queries, and compel them to support the project.
Lastly, be sure to follow up with the attendees to make sure all the stakeholders are on the same page and aligned to support the project.
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #collaboration and communication
- #project management

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Leader Spotlight: Balancing security, user control, and UX, with Carolyne Moran
Carolyne Moran discusses how to balance accessibility, regulations, compliance, and self-serve capabilities within a complex security product.

A guide to developing customer profiles
A customer profile is a document that outlines the ideal customers of a business-to-business (B2B) company.
Evaluating customer experience metrics
Customer experience metrics are metrics that you can use to determine how customers perceive their interaction with your product.

Leader Spotlight: Tailoring products by industry and market, with Orly Stern Izhaki
Orly Stern Izhaki discusses how expanding products globally requires adjusting the user journey based on the market, region, or culture.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics


- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
- Brand Management
- Career Guidance
- Cyber Security
- Data Science and Business Intelligence
- Digital Marketing
- Engineering
- Finance & Accounting
- Internet & Web Development
- Cloud Computing
- Leadership and Coaching
- Learning and Development & Team Training
- Manufacturing
- Communication Management
- Cost Management
- HR Management
- Integration Management
- Procurement Management
- Quality Management
- Risk Management
- Scope Management
- Stakeholder Management
- Time Management
- Agile and Scrum
- Construction Management
- Salesforce Training
- Autocad Tutorials
- Building Information Modeling (BIM)
- Excel Tutorials
- Microsoft Project
- Primavera P6
- Product Reviews
- Other Segments

What is a Business Case Study and How to Write with Examples?
In general, a case study is an “intense and comprehensive analysis into a particular person, entity, society or some other unit,” which is found in many areas and topics. In particular, a business case study explores a problem or scenario involving a person or company that may be a single player. While the intent can change in accordance with the particular public (for example clients, corporate students, policymakers), they attribute an analytical process to a business-related scenario, past or current. Above all, case studies are persuasive and informative narratives. They provide a direct analysis of true solving problems with consequences for management theory, whether efficient or not. Irrespective of the purpose, case studies, especially business case studies, are a vital means by which peers, prospective employers, customers, and many others are informed of their market analyst expertise. So what is a business case study? Now, in the following paragraphs, you will understand how to write a business case study with examples.
Table of Contents
Writing a Business Case Study Step by Step
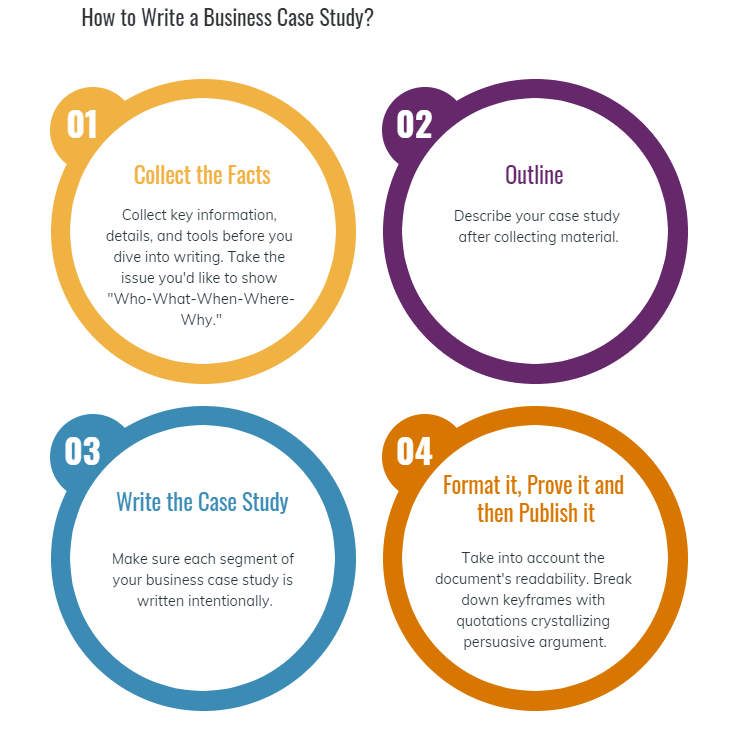
Now, we will explain how to write a business case study step-by-step.
Step 1: Collect the Facts
First of all, you probably wonder what is a business case study? Successful business case studies explicitly and structurally express knowledge. Collect key information, details, and tools before you dive into writing. Take the issue you’d like to show “Who-What-When-Where-Why.” Business case studies should concentrate on one team’s specific challenge and result (or possible results), and are easily reinterpreted.
Step 2: Outline
The next move is to describe your case study after collecting material. Planning ensures that during the project work you prioritize the much more crucial information. There’s really no format for writing a business case study, but you can begin with the following aspects;
- Difficulty: What was the difficulty, obstruction, or dilemma to be resolved? Provide business contexts and, if applicable, wider management themes.
- Solution: What options have you been examining? How has your approach been chosen? Consider integrating an efficient method of market research to develop a scenario.
- Result: And what are the outcomes or what are the effects? Use the information to confirm the condition you appear to be in.
Step 3: Write the Case Study
You should look for and analyze some business case study examples. This section is one of the most important ones on helping you how to write a business case study. When you compose, remember 3 components: data, intent, and design to every chapter. Specifics are picked in order to make people think compressed and straightforward. In order to enable the reader to understand a strict sequence, the information is functionally illustrated.
Make sure each segment of your business case study is written intentionally. For the reasons that filler is immediately a warning sign and is inappropriate and irritating, the whole details should be used. In addition, speak to the public: are you attempting to convince politicians to make a certain statement, or do you convince customers that your organization has a documented proof? The goal is to remind the language and content of the work. The aesthetic components involve first or third-person prose, highlighting phrases and even certain phrases, and using convincing information like graphics and quotes.
Step 4: Format it, Prove it and then Publish it
The last step is your business case study style. Take into account the document’s readability. Break down keyframes with quotations crystallizing persuasive argument. Ensure, without distraction, that titles, headings, subheadings, and text on your body are distinct in size, color, and font. The last view must be safe and neat. You should ask about guidelines of in-house branding if the organization has a marketing team. Learn more before publishing or sharing your business case study before publishing the work. The easiest way to kill viewers’ confidence is by copying errors.
Top Business Case Study Examples
Reading business case study examples as you prepare to write your natural inclinations help shape your prose. Contemporary organizational leaders provide templates for committed, efficient writing. Coffee 2016 is one of Yale Management School’s famous case studies. The study talentedly explains the complexity of the worldwide supply chain by Andrea Illy, CEO of the luxury coffee called brand in his family’s honor. The report is a shining model of how larger industrial issues are highlighted as the emphasis remains on one person or individuals making decisions.
The MIT Technology school titled Restructuring and Transformation: Leadership and risk at the School of the Contemporary Arts of Boston gives every instance of the ball winner. The researchers in this business case study, describe how Jillian Medvedow, a recently named director of the improve the surface, “can restore a powerless organization (literally and figuratively). The case study is valuable as it contextualizes the past of the company in the Boston region and traces its distinctive leadership.
Other analyses concentrate on judgments and conclusions of high stakeholders, like Netflix Goes to Bollywood, another MIT report. Because as the Indian market joined, the analysts discuss the harms and strategies of Netflix. The thesis depends on the business culture and the judgment of banking firms using Netflix information and illustrations.
Most prominent business case study has recorded shortcomings of a business and have theorized what might otherwise have been achieved, such as “Nokia’s rise and dropping.” As a once telecoms pioneer, Nokia sold Microsoft its Device and Services company. The study builds on the mistakes of Nokia and envisions what the corporation would otherwise have been doing while showing how to write a business case study because it should often theorize possible findings.
Finally, one perfect example reflects on how Starbucks has steadily and superficially eroded its own market image. The work by Professor John Quelch provides a model for succinct, confidence-based reading which conveys faith in market research.
The Reason of Why Business Case Study is Significant to Business Analysts
For financial experts, reading and learning from business case study examples is important because they are employed to enhance the productivity and profitability of an organization by adding their analytical expertise to the company’s issues. Business analysts are consultants, hard workers, and developers of continuous improvement processes to improve the results of an organization. If you wish to become a successful Business Analyst, take up a CBAP certification which will make you learn new skills and get exposed to advanced-level effective planning and documentation. Casual studies are a valuable instrument for showing the recommended methods and building up innovative techniques in the innovation business.
By now, you should have better knowledge of what is a business case study. A business case study overall is an expressive instrument for experts to affect the judgment of the enterprise and prove their values and expertise, whether it emphasizes group achievements or continuing problems.
If you are still a student, who lacks time learning those kinds of interesting topics, contact professionals with a “ do my paper ” message and let them save your time for things you are really inspired by.
Feasibility Study in Project Management
Importance of Business Policy
Big Data Analytics

Vice President, İntelligent Design & Consultancy Ltd
Over 12 years of global & rich experience in Portfolio & Program Delivery Management in leading & managing IT Governance, PMO, IT Portfolio/Program, IT Products, IT service delivery management, Budget Management, and more.
How to use the Excel AVERAGEIFS function? – projectcubicle
How to use the Excel AVERAGEIFS function? How to use the Excel AVERAGEIFS function? When you need to calculate...

Web Scraping Tools and Data Scientists – projectcubicle
How Web Scraping Tools Complement Data Scientists Web scraping is the extraction of unstructured data into machine-readable data. Once...
Benford’s Law in Data Science – How to Use Benford’s Law – projectcubicle
Unveiling Patterns in Data: Benford’s Law in Data Science Introduction In the realm of data science, where statistical techniques...

What is Data Analytics? Definition with Examples – projectcubicle
What is Data Analytics? Definition with Examples What is Data Analytics and How to use? Businesses around the world...

Digital Business Methods and Strategies – projectcubicle
Digital business methods and digital marketing business open the doors of success to the business world. Let’s chase after...

Digital Transformation in Education – projectcubicle
Advantages and Challenges of Digital Transformation in Education The education sector is experiencing a major digital transformation. Digital transformation...

A Guide To Physical Security Infrastructure For Data Centers – projectcubicle
A Guide To Physical Security Infrastructure For Data Centers Access control prevents unauthorized users from entering your data center...

Secure Project Data: Top 5 Tips – projectcubicle
Top 5 Tips To Secure Project Data In today’s business world of technological advancements, information is everything—more than just...
Very Nice Article. Thanks For Sharing.
Nice to learn it
Great blog, this inspired me to write a blog about our case studies for Bacon Marketing.
Power BI is basically a cumulation of software-based services and apps that work as a unit to transform and turn your unattached files and data sources into proper visualizations.
With Power BI, you can easily connect your data, analyze it and generate Business Intelligence reports that can be shared.
Microsoft Azure is an operating system that allows you to create web applications and store data in the cloud. visit our link to more informationhttps://azuretrainings.in/
As a leader, It is important to reach every segment of people through social media
This is a very interesting blog. Its Really informative and very helpful..
Thanks for sharing this valuable information to our vision. You have posted a trust worthy blog keep sharing. Nice article i was really impressed by seeing this article, it was very interesting and it is very useful for me..
Nice article and thanks for sharing information.
All of the above examples are good and I am sure that I will be able to easily write my case study without facing any problem. Thanks again.
Nice Article!
Thanks for sharing with us 🙂
Thanks for sharing with us
nice information .
Nice information. Thanks for sharing with us.
As a representative of SCLINBIO, a company passionate about advancing the field of synthetic biology, I found this article fascinating. The potential of synthetic biology to revolutionize healthcare is truly astounding, and it’s inspiring to see others recognizing its importance.
At SCLINBIO, we are dedicated to pushing the boundaries of scientific innovation in this field. Our team is actively engaged in research and development projects aimed at leveraging synthetic biology to address some of the most pressing healthcare challenges, from drug discovery to personalized medicine.
We believe that collaboration and knowledge sharing are essential for driving progress in synthetic biology. If anyone would like to learn more about our work or discuss potential partnerships, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Thank you for shedding light on this critical topic, and we look forward to continuing the conversation.
Best regards, SCLINBIO
thanks for valuable info
Leave a reply Click here to cancel the reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest Articles
- Website Performance and Its Impact on Your Digital Marketing and Overall Business
- Streamlining Payroll: A Guide to Implementing Direct Deposit for Workforce Efficiency
- How to Become a Freelance Project Manager
- Transforming Enterprise Productivity With Content Management Solutions
- The Art of Influence: Strategies Deployed by Top Product Marketing Agencies
- Individual Development Plan Examples & Template for Managers – projectcubicle December 24, 2020
- Lessons Learned Template Example & Questions – projectcubicle October 22, 2019
- Project Risk Management Plan Template and Example – projectcubicle July 26, 2019
- A Sample Kickoff Meeting Agenda Template for Projects – projectcubicle July 25, 2019
- Statement of Work Template and Example – projectcubicle May 27, 2019
I want to learn…
Microsoft Excel
- Project Management
- Software Development

Terms of Use
Privacy Policy
The main goal of this site is to provide high quality tutorials and other training resources to help professionals learn project management and improve themselves.
- Business & Management
- IT Service Management
- Learning and Development / Enterprise Team Training
- PMP Certification Training
- Real Estate
- Software Tools
Log in with your credentials
Forgot your details.
How to Write and Format a Business Case Study
Case Study Structure, Format and Components
- Business Careers and Internships
- Business Degree Options
- Choosing A Business School
- Business School Admissions
- MBA Programs & Rankings
- Student Resources
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Distance Learning
Business case studies are teaching tools that are used by many business schools, colleges, universities, and corporate training programs. This method of teaching is known as the case method . Most business case studies are written by educators, executives or heavily educated business consultants. However, there are times when students are asked to conduct and write their own business case studies. For example, students may be asked to create a case study as a final assignment or group project. Student-created case studies may even be used as a teaching tool or a basis for class discussion.
Writing a Business Case Study
When you write a case study, you must write with the reader in mind. The case study should be set up so that the reader is forced to analyze situations, draw conclusions, and make recommendations based on their predictions. If you aren't overly familiar with case studies, you may be wondering how to best organize your writing. To help you get started, let's take a look at the most common ways to structure and format a business case study.
Case Study Structure and Format
Although every business case study is a little different, there are a few elements that every case study has in common. Every case study has an original title. Titles vary but usually include the name of the company as well as a little info about the case scenario in ten words or less. Examples of real case study titles include Design Thinking and Innovation at Apple and Starbucks: Delivering Customer Service.
All cases are written with a learning objective in mind. The objective might be designed to impart knowledge, build a skill, challenge the learner, or develop an ability. After reading and analyzing the case, the student should know about something or be able to do something. An example objective might look like this:
After analyzing the case study, the student will be able to demonstrate knowledge of approaches to marketing segmentation, differentiate between potential core customer bases and recommend a brand positioning strategy for XYZ's newest product.
Most case studies assume a story-like format. They often have a protagonist with an important goal or decision to make. The narrative is usually weaved throughout the study, which also includes sufficient background information about the company, situation, and essential people or elements. There should be enough detail to allow the reader to form an educated assumption and make an informed decision about the questions (usually two to five questions) presented in the case.
The Case Study Protagonist
Case studies should have a protagonist that needs to make a decision. This forces the case reader to assume the role of the protagonist and make choices from a particular perspective. An example of a case study protagonist is a branding manager who has two months to decide on a positioning strategy for a new product that could financially make or break the company. When writing the case, it is important to ensure that your protagonist is developed and compelling enough to engage the reader.
The Case Study Narrative/Situation
The narrative of a case study starts with an introduction to the protagonist, her role and responsibilities, and the situation/scenario that she is facing. Information is provided on the decisions the protagonist needs to make. Details include challenges and constraints related to the decision (such as a deadline) as well as any biases the protagonist might have.
The next section offers up background information on the company and its business model, industry and competitors. The case study then covers challenges and issues faced by the protagonist as well as the consequences associated with the decision that the protagonist needs to make. Exhibits and extra documents, like financial statements, might be included in the case study to help students reach a decision about the best course of action.
The Deciding Point
The conclusion of a case study returns to the main question or problem that must be analyzed and solved by the protagonist. Case study readers are expected to step into the role of the protagonist and answer the question or questions presented in the case studies. In most cases, there are multiple ways to answer the case question, which allows for classroom discussion and debate.
- MBA Case Studies From Top Business Schools
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech
- How to Format and Write a Simple Business Letter
- How to Write a Character Analysis
- What Are Business and Technical Reports?
- How to Write and Format an MBA Essay
- Business Case Competitions: Purpose, Types and Rules
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- How to Write a Personal Narrative
- What Is Proposal Writing?
- How to Write a Case Study Analysis
- How to Write Your Family History
- How to Write a Great Process Essay
- How to Write a Business Report for English Learners
- How to Write a Professional Email

What Is a Case Study & Customer Success Story?
Learn the definition of a business case study, its meaning, benefits & use in marketing. Get best methods to research, write & design business case studies.

Dominika Krukowska
10 minute read

Short answer
What is a business case study.
A case study, also called customer success story, is a product marketing document used to show how your clients solved a business problem with the aid of your product or service. Case studies include statistics, quotes, and concrete examples with the goal of credibly demonstrating your capability to deliver results.
Bad case studies are not just ineffective - they lead to lost sales
A poorly done business case study can be a real bottleneck in your marketing funnel.
Sure, you have to have them; they're a non-negotiable part of the buying process. But if they're not compelling, you might as well not waste your time on it.
It’s bad enough that it’s hard to make a case study that gets results. But making a weak case study can actually cause you to look less attractive than the competition and cost you leads and sales.
Sometimes more is less.
This post is your roadmap to transforming your case studies from forgettable fillers to customer magnets. And ultimately, turning more prospects into customers.
Let's jump in!
What are the benefits of case studies in business and marketing?
Case studies are an essential part of any well-oiled marketing engine. They demonstrate real-life applications, showcase your unique value, build trust, address concerns, and connect with your audience.
Let’s get a bit into detail.
Demonstrating real-life applications: Business case studies show your product or service in action, offering a peek into how it can be used in real-world situations. It's like offering a test drive before asking customers to commit.
Showing your unique value: Customer success stories let your product or service shine. They illustrate exactly what you bring to the table and why customers should choose you over anyone else.
Building trust: Think of business case studies as your brand's personal advocate. They show how you've helped others succeed, which makes potential customers more likely to trust you with their business.
Easing concerns and objections: Got customers sitting on the fence? Business case studies can gently nudge them towards you by addressing common doubts or worries. It's about showing potential customers that you can deliver what they need.
Connecting with your audience: A good business case study is like a mirror—your potential customers should be able to see themselves in it. It's all about tapping into their hopes, their worries, and their needs.
What to include in a case study?
A successful business case study is the product of a strategic blend of essential components. Each one carries its weight, shaping a narrative that is both engaging and impactful.
Introduction: Set the stage with a one-liner summarizing your unique value proposition. Tailor it to grab your readers' attention and pique their curiosity.
Company overview: Give your audience a snapshot of your customer's business, helping them understand who they are and what they do.
The problem/challenge: Dive into the nitty-gritty of the issue your customer was facing (from their perspective), making it relatable to your audience.
Your solution: Detail how your product or service swooped in as the game-changing solution, addressing the customer's problem.
Results: Showcase the impressive outcome of your solution, demonstrating tangible success that can't be ignored. Back it up with relevant data and metrics.
Customer quotes/testimonials: Add authenticity and credibility to your case study with direct quotes from the customer who experienced the transformation first-hand.
Next steps: Conclude with a call to action, guiding the reader on what to do next, whether it's contacting your company or booking a product demo.
Here's an example of a case study designed according to this structure:

UX Case study
This template for case studies in UX and UI comes with tons of space for text and many visual elements such as charts, timelines, or graphs. This one is perfect for those case studies in which you need to explain the process in greater detail.
What makes a good case study?
A good case study follows a story format of problem-solution-impact. It includes key details of the client’s problem, how they solved it with the help of your product, and the impact it brought them.
8 critical components of a successful case study:
- Talking from the client’s perspective
- Addressing well-defined business problem
- Telling the WHY, not just the WHAT and the HOW
- Giving concrete example
- Backing the story with statistics and facts
- Weaving quotes and testimonials into the story
- Making the content interactive
- Including a call to action
In principle, a top-tier business case study is more than a testimonial.
Think of it as a blockbuster movie, where your customer is the hero Luke Skywalker, the problem is the looming death star, and your solution is the trusted guide Obi-Wan Kenobi.
This gives readers an engaging narrative that not only captures interest but also propels action.
Now let's take a look behind-the-scenes. at the key elements that make a good business case study.
1. Story from the client’s perspective
The key to a captivating case study lies in whose story you're telling. Let your customer be the hero, not your product or service. By focusing on their journey, you'll create a narrative that resonates with your audience, making them more invested in the outcome.
A great example is Adobe’s case study with Under Armour :
In this case study, Adobe tells the story of how Under Armour used Adobe Experience Manager Assets to streamline and enhance their creative asset management. The case study is presented from Under Armour's point of view, providing a customer-centric perspective.
2. Common but well-defined business problem
The best case studies revolve around relatable, well-articulated problems. The issue should be common enough for your audience to identify with, yet specific enough to avoid being generic.
Shoot for the sweet spot that makes a specific segment of your prospective clients say, "That sounds like us!"
A great example is Slack’s case study with HubSpot :
HubSpot, a well-known inbound marketing , sales, and service software provider, grappled with the challenge of maintaining internal communication and collaboration across a rapidly expanding global team.
This case study by Slack outlines how they addressed HubSpot's problem - a common issue faced by many growing businesses.
3. Tell the WHY, not just the WHAT and the HOW
The magic of a compelling case study lies in the mystery of 'why' your solution works. It's crucial to share what happened and how, but digging into the reasons behind the decisions and outcomes adds mystery to your story and keeps your audience intrigued.
An example of this is Marketo’s case study with Panasonic :
In this business case study, Marketo digs into why Panasonic decided to implement a new marketing automation solution.
The case study doesn't just focus on the solutions Marketo provided, but also highlights the reasons behind Panasonic's decision, adding depth to the narrative.
4. Concrete examples
Details make your case study relatable and tangible. Incorporate specifics - who did what , when , where , and how . These concrete examples help your audience visualize the scenario, making your narrative more compelling and memorable.
Zendesk's case study with LendingClub presents concrete examples:
It follows how LendingClub used Zendesk's customer service software to improve their customer support operations.
The case study offers a clear narrative about the problems LendingClub faced, the solutions provided by Zendesk, and the impact these solutions had on LendingClub's business.
Numbers lend authority and credibility that words often cannot. They provide concrete evidence of your solution's impact, creating a stronger case for your product or service.
But remember, these stats should be significant, reliable, and, most importantly, show real impact on your customer’s bottom line.
Here's an example of a great animated numbers slide:

6. Quotes and testimonials
There's nothing like a testimonial from a happy customer to boost your credibility. Direct quotes add a personal touch and authenticity to your case study, making it more believable and trustworthy.
Here’s a great testimonial example from Hotjar:

7. Interactive design
Incorporating interactive design elements will make your case studies stand out, but more importantly, drive high-engagement.
Use eye-catching graphics, use clickable elements like tabs, videos, and menus, include live graphs, animated flipbooks , and so on. Use these elements tactically in order to break up your text into digestible chunks and make your content easier to read and to navigate.
Here’s an example of an interactive business case study:

Marketing case study
White glove delivery with a focus on process optimization explained by a compelling story.
8. Call to action
A good case study doesn't just end; it leads your reader to the next step. Be it trying your product, booking a demo, getting in touch with your team, or reading another case study - your call to action should be clear, compelling, and easy to follow.
Here’s what a clear, singular call to action should look like:

If you want to learn more practical tips, check out our post on how to create a business case study that converts .
How to use a case study in business and marketing?
Often underestimated and underused , business case studies have the power to leverage real-life narratives to shape opinions, influence decision-making, and ultimately, drive conversions.
Let me show you how you can use that power to your advantage.
1. Used as sales collateral
In the world of sales, your case study can be the difference between a polite “we’ll consider it” and a bought-in “show me how it works!”
Picture this: you're reaching out to potential clients, and you slip in a case study showcasing how you've helped a similar business overcome a common hurdle. It's not just a pitch, it's proof you can do it.
But the magic doesn't stop there. Weave these real-life success stories into your sales presentations , and watch as they accelerate your pipeline.
They provide tangible evidence of your value proposition, helping you remove objections, demonstrate value, and differentiate yourself in a crowded market.
2. Used as marketing collateral
I) Use on your website:
On the marketing front, case studies can significantly boost your self-serve conversion rate . By featuring them on your website, you're offering visitors a peek into your track record of success - letting them feel like they're missing out.
II) Add to brochures and product catalogs:
Just sprinkle in a few case studies, and you've just added an extra layer of credibility.
III) Leverage social media:
Share your case studies on platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, or Twitter, to promote your business; and start a conversation around your brand.
IV) Include in PPC campaigns on Google AdWords:
Add case studies as site links to give potential customers another reason to click. It's like saying, "Don't just take our word for it, see how we've helped businesses like yours."
Here’s an example of what it looks like:

Obstacles for creating business case studies & how to overcome them
Creating captivating business case studies is essential, but let's be real: it's not a walk in the park.
So let's buckle up and navigate the most common roadblocks and learn how to steer around them.
Hurdle 1: Spotting the right stories feels like finding a needle in a haystack.
Hold on there! Locating customers ready to share their success tales might seem daunting, but it's not mission impossible. Here's the deal: people love to share success.
How to get clients to share their success stories
Collaborate with your customer success team to identify delighted or triumphant clients
Seek out customers who are scoring high on NPS
Team up with sales to single out recent renewals or upsells
Engage with super active customers on social media
Ask your team during meetings about any standout customers
Reach out to customers who have spoken at your events
Connect with Customer Advisory Board members
Do this and you're bound to uncover some star storytellers.
Hurdle 2: Customers might not want to get involved.
Let's flip the script! Instead of begging for a favor, portray this as an opportunity for customers to amplify their industry status.
Make it a hassle-free and rewarding experience for them. Provide data, draft points for discussion, and be their cheerleader throughout the journey.
Remember, appreciation is infectious. A heartfelt thank you can turn a one-time participant into a long-term advocate.
Hurdle 3: It’s a mammoth task.
Creating business case studies can feel like a marathon, particularly when you're juggling multiple roles.
Delegating the task to an experienced industry writer can save your team a ton of time and energy. You might find the right person within your network, or you might need to explore industry-specific job boards.
Creating a structured timeline and using a shared tool can help keep everyone on track and in the loop.
Here's how to streamline the process of creating a case study:
Extend an invitation to the potential customer
Connect them with the lead writer
Conduct an internal review of the first draft before sending it to the customer
Incorporate their feedback into the second draft
Get final approval for the final draft
Publish and promote your case study!
How to design a business case study?
Your case study design supports the text like your body language supports what you’re saying when you talk. It adds that extra layer of emotional meaning you can't quite put into words.
Luckily, even if you're not a design expert, there are tools to help you add that extra emotional depth to your content. Let’s review a few tools that help you design your case study.
Design using a website builder
If you’d prefer to get hands-on with your design, website builders like Wix or Squarespace offer a versatile platform for creating a business case study from scratch.
They provide a blank canvas and a wealth of design elements, giving you the liberty to choose each piece and place it just where you want it.
It takes time and a keen eye for design to make all the elements come together seamlessly, but the end result can be rewarding.
Design using a case study maker
A case study maker gives you pre-set elements ready for use. All you need to do is drop in your content, and the tool takes care of the aesthetics and user experience.
It's a much more efficient way to create a case study with all its unique building blocks than using a website builder.
We know, since we see how fast our users create astounding case studies using our own case study creator. Try for yourself .
Don’t design - use a template
Templates provide an immediate and easy to work with structure for your design and content.
But beyond that, our gallery of interactive case study templates gives you time-tested designs we know have high-engagement and killer conversion (based on more than 100K reading sessions we’ve analyzed).
Grab a template - and you can skip the long design process, save time, money and frustration, and simply start creating.

Hi, I'm Dominika, Content Specialist at Storydoc. As a creative professional with experience in fashion, I'm here to show you how to amplify your brand message through the power of storytelling and eye-catching visuals.

Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live.
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.
Create your best case study to date
Try Storydoc interactive case study creator for 14 days free (keep any presentation you make forever!)
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved April 16, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

Business Case: Definition, Example, and Template
Fahad Usmani, PMP
November 29, 2022

Projects have risks. Risks come in different forms, such as financial losses, reputation, market share, customer loyalty, etc. A business case can help reduce these risks.
Before initiating a project, organizations ensure the project is worth the investment of resources. A business case is a phase gate that determines whether a project will continue to the next phase, be terminated, or be modified.
Stakeholders measure the project’s success in terms of cost, scope, time, and delivering the intended value. A business case connects the project with its value or benefits.
Today’s blog post will discuss the business case and provides its example and a sample template.
What is a Business Case? Definition & Meaning
Definition & Meaning: A business case documents economic feasibility to justify an initiative and is a basis for project initiation.
It includes the feasibility study and explains why the opportunity is worth pursuing. It provides the commercial viability, affordability, and achievability of the project.
New business ventures, product development, IT investments, innovation, etc., require investments, so business analysis weighs the investment against the value the project will deliver.
The value indicates project success and includes outcomes from the user’s perspective. It focuses on the outcome of the deliverables.
Many stakeholders cannot see the project’s value or opportunities and need a winning business case. A winning business case speaks in facts and style. Business executives must possess presentation skills to present business cases to stakeholders and win their trust.
Top management, the company board, or business analysts carry out the business case study. It is the WHY for the project.
In most cases, it happens after the Needs Analysis and Feasibility Study and before studying the Benefits Management Plan.

Benefit – Cost = Value (Tangible + Intangible)
The value becomes eroded if the benefit is at a higher cost. However, if the benefit outweighs the invested cost, the project is worth investing in.
The business case is an economic outcome of the feasibility study and helps management make a go or no-go decision.
Project managers do not participate in the business case studies; instead, they receive the project charter , which includes some business case elements.
However, they can request business case documents. This project document provides them with an understanding of the value of the project and the reasons for the project initiation.
Project managers can use business case studies as a source of inspiration to motivate the project team members.
The calculation of financial indicators is a significant part of the business case.
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR): This is the interest you earn as an investor for ‘lending’ money to the project. Mathematically, you can calculate it by summing all present values over the project’s life to zero.

- Return on Investment (ROI): This compares the money earned (or lost) on investment to the invested amount.

- Net Present Value (NPV): This is the value of all future cash flows over the entire life of an investment discounted to the present.
- Payback Time (PBT): The minimum duration when the cash flow becomes positive. You measure it in months or years. It is one quick way of measuring profitability. In this case, shorter is better.
- Cost-Benefit Ratio (CBR): This is the ratio of investment cost to the estimated benefit (which has been monetized).
- Profitability Index (PI): This is the ratio of the present value of future cash flows to the investment cost.

Business Case Decision-Making Table

Content of a Business Case
A business case can include the following elements.
- Executive Summary: This shows the key points, particularly the project’s financial benefits. An executive summary should be clear, credible, and persuasive. Many stakeholders prefer to read the summary first; therefore, it must be convincing.
- Introduction: This provides a brief background of the company’s strategic goal and mission, highlighting how the project aligns with the organization’s objectives.
- Scope: This defines the project boundaries. This is the high-level scope and captures the proposed business solution. For example, for a procurement project, it will capture the freight, commissioning and installation, training, spares, etc.
- Business Need: This is a statement of the problem to solve. It can be a need that is ill-met, unarticulated, or unmet. Thus, it is an opportunity for the organization to create value.
- Alternatives: This shows an alternative analysis and how the proposed solution is the preferred way to proceed. Presenting alternatives further supports justification.
- Benefits: This states the value proposition. A value proposition describes the unique benefit that the idea brings to the company. It could be revenue, cost savings, or non-economic (e.g., regulatory compliance). It states the strengths associated with the offering and how it aligns with the corporate strategy.
- Cost: This highlights the funding requirements. It can include the bill of quantity, a proforma invoice, etc.
- Financial Analysis: This expresses the cash flow expected or projected from the investment, then calculates financial indices such as IRR, NPV, PBT, and NCR, as explained earlier. Use figures and charts to communicate your investment viability, as shown below.
- Conclusion: Here, a final appeal is expressed for approval of the business case.
How to Write a Business Case
A business case is a key to the project’s success and the basis of the project charter and project management plans. Writing a business case requires experience, industry and market knowledge, and authority to initiate the project.
The following four steps are required to write a business case:
#1. Identify the Problem
Businesses initiate to solve a problem. Every project has a goal and objective that aligns with the organizational objective. For example, businesses can create a project to create a new product, build a new factory, conduct market research, etc.
#2. Identify Multiple Solutions
A problem can have many solutions, and you must find the best solution. Therefore, identify multiple solutions for the problem and then analyze the best solution. Then, you can prioritize them using some parameters, e.g., the feasibility of the resolution, cost, duration, required skills, etc.
#3. Suggest the Recommended Solution
Now you have multiple prioritized solutions. You will further build the case for the best-recommended solution and send it to the management for their final decision.
#4. Explain the Implementation Approach
This is the last step, and here you explain to stakeholders how you will implement the solution to achieve the organizational goal. You will also explain how the project will benefit the organization.
Keep the following point in your mind while writing a business case:
- Keep it short and simple and include essential information
- Do not use jargon, idioms, and phrases
- Explain the vision
- Show the project benefit
- Ensure the business case is clear, interesting, and concise
Business Case Sample Template
The below image shows a business case sample template.

Business Case Example
The below image shows a business case example using a different template.

Differences Between a Business Case and Business Plan
Many professionals are often confused between the business case and business plan, though the difference is clear.
The following table shows the difference between the business case and the business plan.

Similarities Between a Business Case and Business Plan
- Both examine an opportunity
- Both consider financial analysis
- Both are used in decision-making
- Both investigate the future, complement each other, and are business documents.
Business Case Vs Executive Summary
An executive summary is the summary of a document. In project management, executing summary is the summary of all project management documents that stakeholders can read and understand quickly by going through them deeply.
The executive summary provides high-level key information about the document. In addition, the business case will also have a short executing summary for stakeholders to have a quick glance at the business case.
Business Case Vs Project Charter
A project charter is an official document that initiates the project assigns the project manager, and gives them authority and resources to complete the project.
The project charter includes high-level project information such as project objective, project description, executive summary of the business case, project duration, project budget, name of key stakeholders, high-level risks, key assumptions, and constraints.
Benefits of a Business Case
- It explains the benefits of a business idea.
- It is a tool used to convince stakeholders of the value of a business idea.
- It provides details on how a project will benefit an organization.
- It helps organizations make better investment decisions
Do You Always Need a Business Case?
Not all project requires a business. For example, if the problem is known and the solution is available, you do not need a detailed business case. In such a situation, you can have a simple business case, or you may not have one at all.
You will need a business case when the problem is unique, or you are handling it for the first time, and the solution is not clearly visible.
Business cases provide all clarification that stakeholders need to decide whether to initiate the project.
Frequently Asked Questions
#1. who creates the business case.
The project sponsor, top management, or business analyst creates the business case. However, they can take help from the project sponsor if required.
#2. When is the Business Case Developed?
The business case is developed before the project is approved and the charter is signed.
A business case is key to every project, as it establishes the justification for the project. It is a vital project document that aligns activities to their value and ensures the organization’s resources become invested in the right project.
- https://www.business-case-analysis.com/blog/business-case-business-plan-know- difference/
- PMBOK Guide, Project Management Institute, sixth edition, pg. 29-30
- https://www.chasegroup.com.au/five-steps-to-develop-a-solid-business-case
- https://walkerstone.com/2017/07/21/business-plans-and-business-cases/
- https://medium.com/blackblot/the-difference-between-a-business-case-and-a- business-plan-fe95a2bf90e2
- https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/sloan-school-of-management/15-401-finance-theory-i- fall-2008/video-lectures-and-slides/MIT15_401F08_lec18.pdf
- https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/need-business-case-6730

I am Mohammad Fahad Usmani, B.E. PMP, PMI-RMP. I have been blogging on project management topics since 2011. To date, thousands of professionals have passed the PMP exam using my resources.
PMP Question Bank
This is the most popular Question Bank for the PMP Exam. To date, it has helped over 10,000 PMP aspirants prepare for the exam.
PMP Training Program
This is a PMI-approved 35 contact hours training program and it is based on the latest exam content outline applicable in 2024.
Similar Posts

What are Projects and Operations?
I often see that aspirants do not understand the difference between a project and an operation. I regularly receive emails from those who are interested in applying for the PMP exam but are working with operations.
Some aspirants applied for the PMP exam, were selected for audit, and failed it. Afterward they contacted me and I reviewed their application. I found that they have been working in operations, but they thought they were in project management and that was why they failed the audit process.
Therefore, it is important for you to understand the difference between these two terms so you know if you are eligible to apply for the PMP exam.

Kick-Off Meeting: A Guide on Conducting Project Kickoff Meeting
A project kick-off meeting is one of the most important meetings for a project. You will have many meetings during the project life cycle with your stakeholders. Other meetings may involve you and your team members or include management and the client discussing the project status, issues, and plans. These meetings have significance; however, the…

How to Identify Stakeholders in Project Management?
Projects occur to fulfill the stakeholders’ requirements. If they are not happy, you cannot say that your project was a success. Project management is about managing stakeholders.
You want to complete your project with minimal obstruction. So, you must identify your project stakeholders at an early stage, and then engage with them throughout the project life-cycle.
You start the process of identifying stakeholders after the sponsor signs the project charter.

PMBOK Process Groups and PMBOK Knowledge Areas
When I started my PMP exam preparation, I had difficulty understanding the difference between a process group and a knowledge area. Every PMP aspirant is confused about this in their initial stage of preparation.
You may also wonder why the PMBOK is not organized according to process groups.
These questions bothered me also.
Now, I have passed the exam and I understand these issues. Therefore, I am writing this blog post to explain my knowledge to you.

Stakeholders in Project Management: Definition, Types & Examples
Your project’s success depends on the satisfaction of your stakeholders. Sometimes, you have completed the project; the client has accepted all deliverables. However, the project is not successful because some of your stakeholders are not happy.
Stakeholder satisfaction is the sign of successful project completion.
Now, you might be wondering who the stakeholders are and whom you have to satisfy for the successful completion of your project.
I am writing this blog post to answer these queries, and I hope to clear up any doubts you may have about project stakeholders

Project Management Vs Program Management Vs Portfolio Management
As the saying goes, there is always room for improvement, and organizations are constantly looking for ways to improve processes and optimize resource utilization. If an organization is big and juggling many projects at the same time, it is difficult for them to better utilize their resources if all projects are performed in isolation.
So, they manage projects in groups to use the resources efficiently.
Now, if an organization has more than one project, they will deal with them under a program or portfolio.
The distribution of projects under a program or portfolio depends on the nature and the type of project. Programs are managed through program management and portfolios are managed through portfolio management.
To manage a project under any of the above, it is necessary to understand the concepts well.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Hey there! Free trials are available for Standard and Essentials plans. Start for free today.
What Is a Case Study and Why You Should Use Them
Case studies can provide more insights into your business while helping you conduct further research with robust qualitative data analysis to learn more.
If you're in charge of running a company, then you're likely always looking for new ways to run your business more efficiently and increase your customer base while streamlining as many processes as possible.
Unfortunately, it can sometimes be difficult to determine how to go about implementing the proper program in order to be successful. This is why many business owners opt to conduct a case study, which can help significantly. Whether you've been struggling with brand consistency or some other problem, the right case study can identify why your problem exists as well as provide a way to rectify it.
A case study is a great tool that many businesses aren't even aware exists, and there are marketing experts like Mailchimp who can provide you with step-by-step assistance with implementing a plan with a case study. Many companies discover that not only do they need to start a blog in order to improve business, but they also need to create specific and relevant blog titles.
If your company already has a blog, then optimizing your blog posts may be helpful. Regardless of the obstacles that are preventing you from achieving all your professional goals, a case study can work wonders in helping you reverse this issue.

What is a case study?
A case study is a comprehensive report of the results of theory testing or examining emerging themes of a business in real life context. Case studies are also often used in the healthcare industry, conducting health services research with primary research interest around routinely collected healthcare data.
However, for businesses, the purpose of a case study is to help small business owners or company leaders identify the issues and conduct further research into what may be preventing success through information collection, client or customer interviews, and in-depth data analysis.
Knowing the case study definition is crucial for any business owner. By identifying the issues that are hindering a company from achieving all its goals, it's easier to make the necessary corrections to promote success through influenced data collection.
Why are case studies important?
Now that we've answered the questions, "what is a case study?" Why are case studies important? Some of the top reasons why case studies are important include:

- Understand complex issues: Even after you conduct a significant amount of market research , you might have a difficult time understanding exactly what it means. While you might have the basics down, conducting a case study can help you see how that information is applied. Then, when you see how the information can make a difference in business decisions, it could make it easier to understand complex issues.
- Collect data: A case study can also help with data tracking . A case study is a data collection method that can help you describe the information that you have available to you. Then, you can present that information in a way the reader can understand.
- Conduct evaluations: As you learn more about how to write a case study, remember that you can also use a case study to conduct evaluations of a specific situation. A case study is a great way to learn more about complex situations, and you can evaluate how various people responded in that situation. By conducting a case study evaluation, you can learn more about what has worked well, what has not, and what you might want to change in the future.
- Identify potential solutions: A case study can also help you identify solutions to potential problems. If you have an issue in your business that you are trying to solve, you may be able to take a look at a case study where someone has dealt with a similar situation in the past. For example, you may uncover data bias in a specific solution that you would like to address when you tackle the issue on your own. If you need help solving a difficult problem, a case study may be able to help you.
Remember that you can also use case studies to target your audience . If you want to show your audience that you have a significant level of expertise in a field, you may want to publish some case studies that you have handled in the past. Then, when your audience sees that you have had success in a specific area, they may be more likely to provide you with their business. In essence, case studies can be looked at as the original method of social proof, showcasing exactly how you can help someone solve their problems.
What are the benefits of writing a business case study?
Although writing a case study can seem like a tedious task, there are many benefits to conducting one through an in depth qualitative research process.

- Industry understanding: First of all, a case study can give you an in-depth understanding of your industry through a particular conceptual framework and help you identify hidden problems that are preventing you from transcending into the business world.
- Develop theories: If you decide to write a business case study, it provides you with an opportunity to develop new theories. You might have a theory about how to solve a specific problem, but you need to write a business case study to see exactly how that theory has unfolded in the past. Then, you can figure out if you want to apply your theory to a similar issue in the future.
- Evaluate interventions: When you write a business case study that focuses on a specific situation you have been through in the past, you can uncover whether that intervention was truly helpful. This can make it easier to figure out whether you want to use the same intervention in a similar situation in the future.
- Identify best practices: If you want to stay on top of the best practices in your field, conducting case studies can help by allowing you to identify patterns and trends and develop a new list of best practices that you can follow in the future.
- Versatility: Writing a case study also provides you with more versatility. If you want to expand your business applications, you need to figure out how you respond to various problems. When you run a business case study, you open the door to new opportunities, new applications, and new techniques that could help you make a difference in your business down the road.
- Solve problems: Writing a great case study can dramatically improve your chances of reversing your problem and improving your business.
- These are just a few of the biggest benefits you might experience if you decide to publish your case studies. They can be an effective tool for learning, showcasing your talents, and teaching some of your other employees. If you want to grow your audience , you may want to consider publishing some case studies.
What are the limitations of case studies?
Case studies can be a wonderful tool for any business of any size to use to gain an in-depth understanding of their clients, products, customers, or services, but there are limitations.
One limitation of case studies is the fact that, unless there are other recently published examples, there is nothing to compare them to since, most of the time, you are conducting a single, not multiple, case studies.
Another limitation is the fact that most case studies can lack scientific evidence.

Types of case studies
There are specific types of case studies to choose from, and each specific type will yield different results. Some case study types even overlap, which is sometimes more favorable, as they provide even more pertinent data.
Here are overviews of the different types of case studies, each with its own theoretical framework, so you can determine which type would be most effective for helping you meet your goals.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are pretty straightforward, as they're not difficult to interpret. This type of case study is best if there aren't many variables involved because explanatory case studies can easily answer questions like "how" and "why" through theory development.
Exploratory case studies
An exploratory case study does exactly what its name implies: it goes into specific detail about the topic at hand in a natural, real-life context with qualitative research.
The benefits of exploratory case studies are limitless, with the main one being that it offers a great deal of flexibility. Having flexibility when writing a case study is important because you can't always predict what obstacles might arise during the qualitative research process.
Collective case studies
Collective case studies require you to study many different individuals in order to obtain usable data.
Case studies that involve an investigation of people will involve many different variables, all of which can't be predicted. Despite this fact, there are many benefits of collective case studies, including the fact that it allows an ongoing analysis of the data collected.
Intrinsic case studies
This type of study differs from the others as it focuses on the inquiry of one specific instance among many possibilities.
Many people prefer these types of case studies because it allows them to learn about the particular instance that they wish to investigate further.
Instrumental case studies
An instrumental case study is similar to an intrinsic one, as it focuses on a particular instance, whether it's a person, organization, or something different.
One thing that differentiates instrumental case studies from intrinsic ones is the fact that instrumental case studies aren't chosen merely because a person is interested in learning about a specific instance.

Tips for writing a case study
If you have decided to write case studies for your company, then you may be unsure of where to start or which type to conduct.
However, it doesn't have to be difficult or confusing to begin conducting a case study that will help you identify ways to improve your business.
Here are some helpful tips for writing your case studies:
1. Your case study must be written in the proper format
When writing a case study, the format that you should be similar to this:

Administrative summary
The executive summary is an overview of what your report will contain, written in a concise manner while providing real-life context.
Despite the fact that the executive summary should appear at the beginning of your case studies, it shouldn't be written until you've completed the entire report because if you write it before you finish the report, this summary may not be completely accurate.
Key problem statement
In this section of your case study, you will briefly describe the problem that you hope to solve by conducting the study. You will have the opportunity to elaborate on the problem that you're focusing on as you get into the breadth of the report.
Problem exploration
This part of the case study isn't as brief as the other two, and it goes into more detail about the problem at hand. Your problem exploration must include why the identified problem needs to be solved as well as the urgency of solving it.
Additionally, it must include justification for conducting the problem-solving, as the benefits must outweigh the efforts and costs.
Proposed resolution
This case study section will also be lengthier than the first two. It must include how you propose going about rectifying the problem. The "recommended solution" section must also include potential obstacles that you might experience, as well as how these will be managed.
Furthermore, you will need to list alternative solutions and explain the reason the chosen solution is best. Charts can enhance your report and make it easier to read, and provide as much proof to substantiate your claim as possible.
Overview of monetary consideration
An overview of monetary consideration is essential for all case studies, as it will be used to convince all involved parties why your project should be funded. You must successfully convince them that the cost is worth the investment it will require. It's important that you stress the necessity for this particular case study and explain the expected outcome.
Execution timeline
In the execution times of case studies, you explain how long you predict it will take to implement your study. The shorter the time it will take to implement your plan, the more apt it is to be approved. However, be sure to provide a reasonable timeline, taking into consideration any additional time that might be needed due to obstacles.
Always include a conclusion in your case study. This is where you will briefly wrap up your entire proposal, stressing the benefits of completing the data collection and data analysis in order to rectify your problem.
2. Make it clear and comprehensive
You want to write your case studies with as much clarity as possible so that every aspect of the report is understood. Be sure to double-check your grammar, spelling, punctuation, and more, as you don't want to submit a poorly-written document.
Not only would a poorly-written case study fail to prove that what you are trying to achieve is important, but it would also increase the chances that your report will be tossed aside and not taken seriously.
3. Don't rush through the process
Writing the perfect case study takes time and patience. Rushing could result in your forgetting to include information that is crucial to your entire study. Don't waste your time creating a study that simply isn't ready. Take the necessary time to perform all the research necessary to write the best case study possible.
Depending on the case study, conducting case study research could mean using qualitative methods, quantitative methods, or both. Qualitative research questions focus on non-numerical data, such as how people feel, their beliefs, their experiences, and so on.
Meanwhile, quantitative research questions focus on numerical or statistical data collection to explain causal links or get an in-depth picture.
It is also important to collect insightful and constructive feedback. This will help you better understand the outcome as well as any changes you need to make to future case studies. Consider using formal and informal ways to collect feedback to ensure that you get a range of opinions and perspectives.
4. Be confident in your theory development
While writing your case study or conducting your formal experimental investigation, you should have confidence in yourself and what you're proposing in your report. If you took the time to gather all the pertinent data collected to complete the report, don't second-guess yourself or doubt your abilities. If you believe your report will be amazing, then it likely will be.
5. Case studies and all qualitative research are long
It's expected that multiple case studies are going to be incredibly boring, and there is no way around this. However, it doesn't mean you can choose your language carefully in order to keep your audience as engaged as possible.
If your audience loses interest in your case study at the beginning, for whatever reason, then this increases the likelihood that your case study will not be funded.
Case study examples
If you want to learn more about how to write a case study, it might be beneficial to take a look at a few case study examples. Below are a few interesting case study examples you may want to take a closer look at.
- Phineas Gage by John Martin Marlow : One of the most famous case studies comes from the medical field, and it is about the story of Phineas Gage, a man who had a railroad spike driven through his head in 1848. As he was working on a railroad, an explosive charge went off prematurely, sending a railroad rod through his head. Even though he survived this incident, he lost his left eye. However, Phineas Gage was studied extensively over the years because his experiences had a significant, lasting impact on his personality. This served as a case study because his injury showed different parts of the brain have different functions.
- Kitty Genovese and the bystander effect : This is a tragic case study that discusses the murder of Kitty Genovese, a woman attacked and murdered in Queens, New York City. Shockingly, while numerous neighbors watched the scene, nobody called for help because they assumed someone else would. This case study helped to define the bystander effect, which is when a person fails to intervene during an emergency because other people are around.
- Henry Molaison and the study of memory : Henry Molaison lost his memory and suffered from debilitating amnesia. He suffered from childhood epilepsy, and medical professionals attempted to remove the part of his brain that was causing his seizures. He had a portion of his brain removed, but it completely took away his ability to hold memories. Even though he went on to live until the age of 82, he was always forced to live in the present moment, as he was completely unable to form new memories.
Case study FAQs
When should you do a case study.
There are several scenarios when conducting a case study can be beneficial. Case studies are often used when there's a "why" or "how" question that needs to be answered. Case studies are also beneficial when trying to understand a complex phenomenon, there's limited research on a topic, or when you're looking for practical solutions to a problem.
How can case study results be used to make business decisions?
You can use the results from a case study to make future business decisions if you find yourself in a similar situation. As you assess the results of a case study, you can identify best practices, evaluate the effectiveness of an intervention, generate new and creative ideas, or get a better understanding of customer needs.
How are case studies different from other research methodologies?
When compared to other research methodologies, such as experimental or qualitative research methodology, a case study does not require a representative sample. For example, if you are performing quantitative research, you have a lot of subjects that expand your sample size. If you are performing experimental research, you may have a random sample in front of you. A case study is usually designed to deliberately focus on unusual situations, which allows it to shed new light on a specific business research problem.
Writing multiple case studies for your business
If you're feeling overwhelmed by the idea of writing a case study and it seems completely foreign, then you aren't alone. Writing a case study for a business is a very big deal, but fortunately, there is help available because an example of a case study doesn't always help.
Mailchimp, a well-known marketing company that provides comprehensive marketing support for all sorts of businesses, can assist you with your case study, or you can review one of their own recently published examples.
Mailchimp can assist you with developing the most effective content strategy to increase your chances of being as successful as possible. Mailchimp's content studio is a great tool that can help your business immensely.
7 Favorite Business Case Studies to Teach—and Why
Explore more.
- Case Teaching
- Course Materials
FEATURED CASE STUDIES
The Army Crew Team . Emily Michelle David of CEIBS
ATH Technologies . Devin Shanthikumar of Paul Merage School of Business
Fabritek 1992 . Rob Austin of Ivey Business School
Lincoln Electric Co . Karin Schnarr of Wilfrid Laurier University
Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth . Gary Pisano of Harvard Business School
The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron . Francesca Gino of Harvard Business School
Warren E. Buffett, 2015 . Robert F. Bruner of Darden School of Business
To dig into what makes a compelling case study, we asked seven experienced educators who teach with—and many who write—business case studies: “What is your favorite case to teach and why?”
The resulting list of case study favorites ranges in topics from operations management and organizational structure to rebel leaders and whodunnit dramas.
1. The Army Crew Team
Emily Michelle David, Assistant Professor of Management, China Europe International Business School (CEIBS)

“I love teaching The Army Crew Team case because it beautifully demonstrates how a team can be so much less than the sum of its parts.
I deliver the case to executives in a nearby state-of-the-art rowing facility that features rowing machines, professional coaches, and shiny red eight-person shells.
After going through the case, they hear testimonies from former members of Chinese national crew teams before carrying their own boat to the river for a test race.
The rich learning environment helps to vividly underscore one of the case’s core messages: competition can be a double-edged sword if not properly managed.

Executives in Emily Michelle David’s organizational behavior class participate in rowing activities at a nearby facility as part of her case delivery.
Despite working for an elite headhunting firm, the executives in my most recent class were surprised to realize how much they’ve allowed their own team-building responsibilities to lapse. In the MBA pre-course, this case often leads to a rich discussion about common traps that newcomers fall into (for example, trying to do too much, too soon), which helps to poise them to both stand out in the MBA as well as prepare them for the lateral team building they will soon engage in.
Finally, I love that the post-script always gets a good laugh and serves as an early lesson that organizational behavior courses will seldom give you foolproof solutions for specific problems but will, instead, arm you with the ability to think through issues more critically.”
2. ATH Technologies
Devin Shanthikumar, Associate Professor of Accounting, Paul Merage School of Business

“As a professor at UC Irvine’s Paul Merage School of Business, and before that at Harvard Business School, I have probably taught over 100 cases. I would like to say that my favorite case is my own, Compass Box Whisky Company . But as fun as that case is, one case beats it: ATH Technologies by Robert Simons and Jennifer Packard.
ATH presents a young entrepreneurial company that is bought by a much larger company. As part of the merger, ATH gets an ‘earn-out’ deal—common among high-tech industries. The company, and the class, must decide what to do to achieve the stretch earn-out goals.
ATH captures a scenario we all want to be in at some point in our careers—being part of a young, exciting, growing organization. And a scenario we all will likely face—having stretch goals that seem almost unreachable.
It forces us, as a class, to really struggle with what to do at each stage.
After we read and discuss the A case, we find out what happens next, and discuss the B case, then the C, then D, and even E. At every stage, we can:
see how our decisions play out,
figure out how to build on our successes, and
address our failures.
The case is exciting, the class discussion is dynamic and energetic, and in the end, we all go home with a memorable ‘ah-ha!’ moment.
I have taught many great cases over my career, but none are quite as fun, memorable, and effective as ATH .”
3. Fabritek 1992
Rob Austin, Professor of Information Systems, Ivey Business School

“This might seem like an odd choice, but my favorite case to teach is an old operations case called Fabritek 1992 .
The latest version of Fabritek 1992 is dated 2009, but it is my understanding that this is a rewrite of a case that is older (probably much older). There is a Fabritek 1969 in the HBP catalog—same basic case, older dates, and numbers. That 1969 version lists no authors, so I suspect the case goes even further back; the 1969 version is, I’m guessing, a rewrite of an even older version.
There are many things I appreciate about the case. Here are a few:
It operates as a learning opportunity at many levels. At first it looks like a not-very-glamorous production job scheduling case. By the end of the case discussion, though, we’re into (operations) strategy and more. It starts out technical, then explodes into much broader relevance. As I tell participants when I’m teaching HBP's Teaching with Cases seminars —where I often use Fabritek as an example—when people first encounter this case, they almost always underestimate it.
It has great characters—especially Arthur Moreno, who looks like a troublemaker, but who, discussion reveals, might just be the smartest guy in the factory. Alums of the Harvard MBA program have told me that they remember Arthur Moreno many years later.
Almost every word in the case is important. It’s only four and a half pages of text and three pages of exhibits. This economy of words and sparsity of style have always seemed like poetry to me. I should note that this super concise, every-word-matters approach is not the ideal we usually aspire to when we write cases. Often, we include extra or superfluous information because part of our teaching objective is to provide practice in separating what matters from what doesn’t in a case. Fabritek takes a different approach, though, which fits it well.
It has a dramatic structure. It unfolds like a detective story, a sort of whodunnit. Something is wrong. There is a quality problem, and we’re not sure who or what is responsible. One person, Arthur Moreno, looks very guilty (probably too obviously guilty), but as we dig into the situation, there are many more possibilities. We spend in-class time analyzing the data (there’s a bit of math, so it covers that base, too) to determine which hypotheses are best supported by the data. And, realistically, the data doesn’t support any of the hypotheses perfectly, just some of them more than others. Also, there’s a plot twist at the end (I won’t reveal it, but here’s a hint: Arthur Moreno isn’t nearly the biggest problem in the final analysis). I have had students tell me the surprising realization at the end of the discussion gives them ‘goosebumps.’
Finally, through the unexpected plot twist, it imparts what I call a ‘wisdom lesson’ to young managers: not to be too sure of themselves and to regard the experiences of others, especially experts out on the factory floor, with great seriousness.”
4. Lincoln Electric Co.
Karin Schnarr, Assistant Professor of Policy, Wilfrid Laurier University

“As a strategy professor, my favorite case to teach is the classic 1975 Harvard case Lincoln Electric Co. by Norman Berg.
I use it to demonstrate to students the theory linkage between strategy and organizational structure, management processes, and leadership behavior.
This case may be an odd choice for a favorite. It occurs decades before my students were born. It is pages longer than we are told students are now willing to read. It is about manufacturing arc welding equipment in Cleveland, Ohio—a hard sell for a Canadian business classroom.
Yet, I have never come across a case that so perfectly illustrates what I want students to learn about how a company can be designed from an organizational perspective to successfully implement its strategy.
And in a time where so much focus continues to be on how to maximize shareholder value, it is refreshing to be able to discuss a publicly-traded company that is successfully pursuing a strategy that provides a fair value to shareholders while distributing value to employees through a large bonus pool, as well as value to customers by continually lowering prices.
However, to make the case resonate with today’s students, I work to make it relevant to the contemporary business environment. I link the case to multimedia clips about Lincoln Electric’s current manufacturing practices, processes, and leadership practices. My students can then see that a model that has been in place for generations is still viable and highly successful, even in our very different competitive situation.”
5. Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth
Gary Pisano, Professor of Business Administration, Harvard Business School

“My favorite case to teach these days is Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth .
I love teaching this case for three reasons:
1. It demonstrates how a company in a super-tough, highly competitive business can do very well by focusing on creating unique operating capabilities. In theory, Pal’s should have no chance against behemoths like McDonalds or Wendy’s—but it thrives because it has built a unique operating system. It’s a great example of a strategic approach to operations in action.
2. The case shows how a strategic approach to human resource and talent development at all levels really matters. This company competes in an industry not known for engaging its front-line workers. The case shows how engaging these workers can really pay off.
3. Finally, Pal’s is really unusual in its approach to growth. Most companies set growth goals (usually arbitrary ones) and then try to figure out how to ‘backfill’ the human resource and talent management gaps. They trust you can always find someone to do the job. Pal’s tackles the growth problem completely the other way around. They rigorously select and train their future managers. Only when they have a manager ready to take on their own store do they open a new one. They pace their growth off their capacity to develop talent. I find this really fascinating and so do the students I teach this case to.”
6. The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron
Francesca Gino, Professor of Business Administration, Harvard Business School

“My favorite case to teach is The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron .
The case surprises students because it is about a leader, known in the unit by the nickname Chaos , who inspired his squadron to be innovative and to change in a culture that is all about not rocking the boat, and where there is a deep sense that rules should simply be followed.
For years, I studied ‘rebels,’ people who do not accept the status quo; rather, they approach work with curiosity and produce positive change in their organizations. Chaos is a rebel leader who got the level of cultural change right. Many of the leaders I’ve met over the years complain about the ‘corporate culture,’ or at least point to clear weaknesses of it; but then they throw their hands up in the air and forget about changing what they can.
Chaos is different—he didn’t go after the ‘Air Force’ culture. That would be like boiling the ocean.
Instead, he focused on his unit of control and command: The 99th squadron. He focused on enabling that group to do what it needed to do within the confines of the bigger Air Force culture. In the process, he inspired everyone on his team to be the best they can be at work.
The case leaves the classroom buzzing and inspired to take action.”
7. Warren E. Buffett, 2015
Robert F. Bruner, Professor of Business Administration, Darden School of Business

“I love teaching Warren E. Buffett, 2015 because it energizes, exercises, and surprises students.
Buffett looms large in the business firmament and therefore attracts anyone who is eager to learn his secrets for successful investing. This generates the kind of energy that helps to break the ice among students and instructors early in a course and to lay the groundwork for good case discussion practices.
Studying Buffett’s approach to investing helps to introduce and exercise important themes that will resonate throughout a course. The case challenges students to define for themselves what it means to create value. The case discussion can easily be tailored for novices or for more advanced students.
Either way, this is not hero worship: The case affords a critical examination of the financial performance of Buffett’s firm, Berkshire Hathaway, and reveals both triumphs and stumbles. Most importantly, students can critique the purported benefits of Buffett’s conglomeration strategy and the sustainability of his investment record as the size of the firm grows very large.
By the end of the class session, students seem surprised with what they have discovered. They buzz over the paradoxes in Buffett’s philosophy and performance record. And they come away with sober respect for Buffett’s acumen and for the challenges of creating value for investors.
Surely, such sobriety is a meta-message for any mastery of finance.”
More Educator Favorites

Emily Michelle David is an assistant professor of management at China Europe International Business School (CEIBS). Her current research focuses on discovering how to make workplaces more welcoming for people of all backgrounds and personality profiles to maximize performance and avoid employee burnout. David’s work has been published in a number of scholarly journals, and she has worked as an in-house researcher at both NASA and the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.

Devin Shanthikumar is an associate professor and the accounting area coordinator at UCI Paul Merage School of Business. She teaches undergraduate, MBA, and executive-level courses in managerial accounting. Shanthikumar previously served on the faculty at Harvard Business School, where she taught both financial accounting and managerial accounting for MBAs, and wrote cases that are used in accounting courses across the country.

Robert D. Austin is a professor of information systems at Ivey Business School and an affiliated faculty member at Harvard Medical School. He has published widely, authoring nine books, more than 50 cases and notes, three Harvard online products, and two popular massive open online courses (MOOCs) running on the Coursera platform.

Karin Schnarr is an assistant professor of policy and the director of the Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) program at the Lazaridis School of Business & Economics at Wilfrid Laurier University in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada where she teaches strategic management at the undergraduate, graduate, and executive levels. Schnarr has published several award-winning and best-selling cases and regularly presents at international conferences on case writing and scholarship.

Gary P. Pisano is the Harry E. Figgie, Jr. Professor of Business Administration and senior associate dean of faculty development at Harvard Business School, where he has been on the faculty since 1988. Pisano is an expert in the fields of technology and operations strategy, the management of innovation, and competitive strategy. His research and consulting experience span a range of industries including aerospace, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals, health care, nutrition, computers, software, telecommunications, and semiconductors.

Francesca Gino studies how people can have more productive, creative, and fulfilling lives. She is a professor at Harvard Business School and the author, most recently, of Rebel Talent: Why It Pays to Break the Rules at Work and in Life . Gino regularly gives keynote speeches, delivers corporate training programs, and serves in advisory roles for firms and not-for-profit organizations across the globe.

Robert F. Bruner is a university professor at the University of Virginia, distinguished professor of business administration, and dean emeritus of the Darden School of Business. He has also held visiting appointments at Harvard and Columbia universities in the United States, at INSEAD in France, and at IESE in Spain. He is the author, co-author, or editor of more than 20 books on finance, management, and teaching. Currently, he teaches and writes in finance and management.
Related Articles

We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Who is Geneva Business School?
- Real International
- Education Philosophy
- CSR & Sustainability
Why Geneva Business School?
- The Swiss Private Model
- Global Network
- Quality Assurance
Always at hand
- Entry Requirements
Other Programs
- Essential Information

Latest Updates
- Graduations
- Welcome Week
- In the Media
Other Resources
- Admissions FAQs
- Research Hub
- Research Repository
- Press Resources
Upcoming Events
Graduation ceremony 2024, our leaders.
- Executive Committee
- Meet us around the World
- Student Committee
Our Students
- Success Stories
- Testimonials
- Careers FAQs
- Join Our Community

What is a business case study?
Explanation, tips, and advice on writing a response to a business case study when applying to Geneva Business School
When you apply to Geneva Business School to undertake a bachelor’s, master’s, or MBA program, you will be asked to write a 500-word written response to a business case study .
Business case studies explained
A business case study summarizes a real-life business issue faced by a company and looks at how it may affect society within a business context. A case study is a research tool and can form part of the research methods you will use in your final projects in our programs.
Here are examples of the cases you are required to write about for the application process:
- Bachelor’s program
- Master’s or MBA
Answering a business case study is an opportunity to improve your writing skills by applying theory to a real situation , analyzing the scenario, and drawing insights from your observations. This might be the first time you write a case study, so here are some pointers from our Academic Team to help guide you. Happy writing and good luck with your application!
How to respond to a business case study

1. Read the article and/or watch the video provided in the document.
Sometimes you will remember more information if you repeat watching or reading them a few times, or pause to write notes and then rewatch sections to understand them better.
2. Make notes as you go.
Write down important points, dates, names, roles, important events, and details in the case.
3. Look for things that stand out to you.
If something seems unusual, good, or bad it most likely will hold some importance in the reflection you will write. Reading and watching the materials provided multiple times will make it easier to spot these irregularities.
4. Organize your points to form a summary of your opinion.
A good technique is to arrange your thoughts by answering the following: who, what, where, when, and how to get the main details out as a list, and go from there.
5. Analyze the situation presented.
Ask yourself what really happened in the case.
- What business is the case based on? Is it a product or a service?
- What set of conditions caused the situation?
- What happened?
- Who was involved and what decisions were made?
- What was the outcome? Evaluate it.
- What impact did the case have on the wider community?
6. Look at the questions.
See which parts of your notes can answer each one and use these as a starting point as you flesh out your paragraphs. Start your response with a thesis statement and summarise what you intend to cover in your response. Write a topic sentence for each paragraph.
7. Look at the word count.
If the case study requires 500 words, keep that in mind as you split it up between your answers. Write a response that answers the questions without any extra information. Be economical with words.

Advice for answering a business case study
1. don’t just repeat the information given..
Repeating the business case study question will show that you did not think independently about your answer. Dedicate some time to think about the case study and ask yourself what you think about it.
2. Do not copy information from the internet.
Plagiarism is unacceptable, and who wants to make a bad first impression?
3. There is more than one correct answer.
Don’t write what you think you are expected to write – everyone’s response will be different and that’s how it should be. Use your critical thinking skills and personal reaction to the case study to shape an answer that reflects your own thoughts and opinions.
Watch how to write a business case study
Have any questions for us don't hesitate to get in touch..

Bachelor of International Management
See the Program

Master of International Management

MBA: Master of Business Administration
Related Posts

Volunteer Opportunities

Thesis Defense

Winter Wrap-up
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
- Currently reading: Business school teaching case study: can green hydrogen’s potential be realised?
- Business school teaching case study: how electric vehicles pose tricky trade dilemmas
- Business school teaching case study: is private equity responsible for child labour violations?
Business school teaching case study: can green hydrogen’s potential be realised?

- Business school teaching case study: can green hydrogen’s potential be realised? on x (opens in a new window)
- Business school teaching case study: can green hydrogen’s potential be realised? on facebook (opens in a new window)
- Business school teaching case study: can green hydrogen’s potential be realised? on linkedin (opens in a new window)
- Business school teaching case study: can green hydrogen’s potential be realised? on whatsapp (opens in a new window)
Jennifer Howard-Grenville and Ujjwal Pandey
Roula Khalaf, Editor of the FT, selects her favourite stories in this weekly newsletter.
Hydrogen is often hyped as the “Swiss army knife” of the energy transition because of its potential versatility in decarbonising fossil fuel-intensive energy production and industries. Making use of that versatility, however, will require hydrogen producers and distributors to cut costs, manage technology risks, and obtain support from policymakers.
To cut carbon dioxide emissions, hydrogen production must shift from its current reliance on fossil fuels. The most common method yields “grey hydrogen”, made from natural gas but without emissions capture. “Blue hydrogen,” which is also made from natural gas but with the associated carbon emissions captured and stored, is favourable.
But “green hydrogen” uses renewable energy sources, including wind and solar, to split water into hydrogen and oxygen via electrolysis. And, because there are no carbon emissions during production or combustion, green hydrogen can help to decarbonise energy generation as well as industry sectors — such as steel, chemicals and transport — that rely heavily on fossil fuels.
Ultimately, though, the promise of green hydrogen will hinge on how businesses and policymakers weigh several questions, trade-offs, and potential long-term consequences. We know from previous innovations that progress can be far from straightforward.

Wind power, for example, is a mature renewable energy technology and a key enabler in green hydrogen production, but it suffers vulnerabilities on several fronts. Even Denmark’s Ørsted — the world’s largest developer of offshore wind power and a beacon for renewable energy — recently said it was struggling to deliver new offshore wind projects profitably in the UK.
Generally, the challenge arises from interdependencies between macroeconomic conditions — such as energy costs and interest rates — and business decision-making around investments. In the case of Ørsted, it said the escalating costs of turbines, labour, and financing have exceeded the inflation-linked fixed price for electricity set by regulators.
Business leaders will also need to steer through uncertainties — such as market demand, technological risks, regulatory ambiguity, and investment risks — as they seek to incorporate green hydrogen.
Test yourself
This is the third in a series of monthly business school-style teaching case studies devoted to responsible-business dilemmas faced by organisations. Read the piece and FT articles suggested at the end before considering the questions raised.
About the authors: Jennifer Howard-Grenville is Diageo professor of organisation studies at Cambridge Judge Business School; Ujjwal Pandey is an MBA candidate at Cambridge Judge and a former consultant at McKinsey.
The series forms part of a wide-ranging collection of FT ‘instant teaching case studies ’ that explore business challenges.
Two factors could help business leaders gain more clarity.
The first factor will be where, and how quickly, costs fall and enable the necessary increase to large-scale production. For instance, the cost of the electrolysers needed to split water into hydrogen and oxygen remains high because levels of production are too low. These costs and slow progress in expanding the availability and affordability of renewable energy sources have made green hydrogen much more expensive than grey hydrogen, so far — currently, two to three times the cost.
The FT’s Lex column calculated last year that a net zero energy system would create global demand for hydrogen of 500mn tonnes, annually, by 2050 — which would require an investment of $20tn. However, only $29bn had been committed by potential investors, Lex noted, despite some 1,000 new projects being announced globally and estimated to require total investment of $320bn.
Solar power faced similar challenges a decade ago. Thanks to low-cost manufacturing in China and supportive government policies, the sector has grown and is, within a very few years , expected to surpass gas-fired power plant installed capacity, globally. Green hydrogen requires a similar concerted effort. With the right policies and technological improvements, the cost of green hydrogen could fall below the cost of grey hydrogen in the next decade, enabling widespread adoption of the former.
Countries around the world are introducing new and varied incentives to address this gap between the expected demand and supply of green hydrogen. In Canada, for instance, Belgium’s Tree Energy Solutions plans to build a $4bn plant in Quebec, to produce synthetic natural gas from green hydrogen and captured carbon, attracted partly by a C$17.7bn ($12.8bn) tax credit and the availability of hydropower.
Such moves sound like good news for champions of green hydrogen, but companies still need to manage the short-term risks from potential policy and energy price swings. The US Inflation Reduction Act, which offers tax credits of up to $3 per kilogramme for producing low-carbon hydrogen, has already brought in limits , and may not survive a change of government.
Against such a backdrop, how should companies such as Hystar — a Norwegian maker of electrolysers already looking to expand capacity from 50 megawatts to 4 gigawatts a year in Europe — decide where and when to open a North American production facility?
The second factor that will shape hydrogen’s future is how and where it is adopted across different industries. Will it be central to the energy sector, where it can be used to produce synthetic fuels, or to help store the energy generated by intermittent renewables, such as wind and solar? Or will it find its best use in hard-to-abate sectors — so-called because cutting their fossil fuel use, and their CO₂ emissions, is difficult — such as aviation and steelmaking?
Steel producers are already seeking to pivot to hydrogen, both as an energy source and to replace the use of coal in reducing iron ore. In a bold development in Sweden, H2 Green Steel says it plans to decarbonise by incorporating hydrogen in both these ways, targeting 2.5mn tonnes of green steel production annually .
Meanwhile, the global aviation industry is exploring the use of hydrogen to replace petroleum-based aviation fuels and in fuel cell technologies that transform hydrogen into electricity. In January 2023, for instance, Anglo-US start-up ZeroAvia conducted a successful test flight of a hydrogen fuel cell-powered aircraft.

The path to widespread adoption, and the transformation required for hydrogen’s range of potential applications, will rely heavily on who invests, where and how. Backers have to be willing to pay a higher initial price to secure and build a green hydrogen supply in the early phases of their investment.
It will also depend on how other technologies evolve. No industry is looking only to green hydrogen to achieve their decarbonisation aims. Other, more mature technologies — such as battery storage for renewable energy — may instead dominate, leaving green hydrogen to fulfil niche applications that can bear high costs.
As with any transition, there will be unintended consequences. Natural resources (sun, wind, hydropower) and other assets (storage, distribution, shipping) that support the green hydrogen economy are unevenly distributed around the globe. There will be new exporters — countries with abundant renewables in the form of sun, wind or hydropower, such as Australia or some African countries — and new importers, such as Germany, with existing industry that relies on hydrogen but has relatively low levels of renewable energy sourced domestically.
How will the associated social and environmental costs be borne, and how will the economic and development benefits be shared? Tackling climate change through decarbonisation is urgent and essential, but there are also trade-offs and long-term consequences to the choices made today.
Questions for discussion
Lex in depth: the staggering cost of a green hydrogen economy
How Germany’s steelmakers plan to go green
Hydrogen-electric aircraft start-up secures UK Infrastructure Bank backing
Aviation start-ups test potential of green hydrogen
Consider these questions:
Are the trajectories for cost/scale-up of other renewable energy technologies (eg solar, wind) applicable to green hydrogen? Are there features of the current economic, policy, and business landscape that point to certain directions for green hydrogen’s development and application?
Take the perspective of someone from a key industry that is part of, or will be affected by, the development of green hydrogen. How should you think about the technology and business opportunities and risks in the near term, and longer term? How might you retain flexibility while still participating in these key shifts?
Solving one problem often creates or obscures new ones. For example, many technologies that decarbonise (such as electric vehicles) have other impacts (such as heavy reliance on certain minerals and materials). How should those participating in the emerging green hydrogen economy anticipate, and address, potential environmental and social impacts? Can we learn from energy transitions of the past?
Climate Capital

Where climate change meets business, markets and politics. Explore the FT’s coverage here .
Are you curious about the FT’s environmental sustainability commitments? Find out more about our science-based targets here
Promoted Content
Explore the series.

Follow the topics in this article
- Carbon footprint Add to myFT
- Climate change Add to myFT
- Renewable energy Add to myFT
- Environment Add to myFT
- Business school Add to myFT
International Edition
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Why Engineers Should Study Philosophy
- Marco Argenti

Understanding the “why” before you start working on the “how” is a critical skill — especially in the age of AI.
The ability to develop crisp mental models around the problems you want to solve and understanding the why before you start working on the how is an increasingly critical skill, especially in the age of AI. Coding is one of the things AI does best and its capabilities are quickly improving. However, there’s a catch: Code created by an AI can be syntactically and semantically correct but not functionally correct. In other words, it can work well, but not do what you want it to do. Having a crisp mental model around a problem, being able to break it down into steps that are tractable, perfect first-principle thinking, sometimes being prepared (and able to) debate a stubborn AI — these are the skills that will make a great engineer in the future, and likely the same consideration applies to many job categories.
I recently told my daughter, a college student: If you want to pursue a career in engineering, you should focus on learning philosophy in addition to traditional engineering coursework. Why? Because it will improve your code.
- MA Marco Argenti is the Chief Information Officer at Goldman Sachs.
Partner Center
A popular YouTuber's negative video of Humane's AI Pin raises questions about critical reviews in the age of innovation
- This post originally appeared in the Insider Today newsletter.
- You can sign up for Business Insider's daily newsletter here .

Hello there! If you're struggling to decide the foods worth buying organic, best-selling author Michael Pollan has some suggestions for the ones worth splurging on to avoid harmful chemicals .
In today's big story, we're looking at a critical tech review that caused a bit of a stir on social media .
What's on deck:
Markets: Goldman Sachs quiets the haters with a monster earnings report .
Tech: Leaked docs show one of Prime Video's biggest issues, forcing customers to abandon shows .
Business: The best bet in business these days? Targeting young men who like to gamble .
But first, the review is in!
If this was forwarded to you, sign up here.
The big story
Up for review.
"The Worst Product I've Ever Reviewed… For Now"
Marques Brownlee, the YouTuber better known as MKBHD, didn't mince words with the title of his review of Humane's AI Pin .
In a 25-minute video , Brownlee details all the issues he encountered using the AI device. (Spoiler alert: There were a lot.)
Brownlee's review aligns with other criticisms of the device . But not all of those came from someone with as much sway. His YouTube channel has more than 18 million subscribers.
One user on X pointed that out , calling the review "almost unethical" for "potentially killing someone else's nascent project" in a post reposted over 2,000 times.
Most of the internet disagreed, and a Humane exec even thanked Brownlee on X for the "fair and valid critiques."
But it highlights the power of Brownlee's reviews. Earlier this year, a negative video of Fisker's Ocean SUV by Brownlee also made waves on social media .
Critical reviews in the age of innovation raise some interesting questions.
To be clear, there was nothing wrong with Brownlee's review. Humane's AI Pin costs $700. Watering down his review to ease the blow would be a disservice to the millions of fans relying on his perspective before making such a significant purchase.
Too often, companies view potential customers as an extension of their research and development. They are happy to sell a product that is still a work in progress on the promise they'll fix it on the fly. ("Updates are coming!")
But in a world of instant gratification, it can be hard to appreciate that innovation takes time.
Even Apple can run into this conundrum. Take the Apple Vision Pro. Reviewers are impressed with the technology behind the much-anticipated gadget — but are still struggling to figure out what they can do with it . Maybe, over time, that will get sorted out. It's also worth remembering how cool tech can be, as Business Insider's Peter Kafka wrote following a bunch of trips in Waymo's software-powered taxis in San Francisco . Sure, robotaxis have their issues, Peter said, but they also elicit that "golly-gee-can-you-believe-it" sense.
As for Humane, America loves a comeback story. Just look at "Cyberpunk 2077." The highly anticipated video game had a disastrous launch in 2020 , but redeemed itself three years later, ultimately winning a major award .
Still, Humane shouldn't get a pass for releasing a product that didn't seem ready for primetime, according to the reviews.
And its issue could be bigger than glitchy tech. Humane's broader thesis about reducing screen time might not be as applicable. As BI's Katie Notopolous put it: " I love staring at my iPhone ."
3 things in markets
1. Goldman finally strikes gold. After a rough stretch, the vaunted investment bank crushed earnings expectations , sending its stock soaring. A big tailwind, according to CEO David Solomon, is AI spawning " enormous opportunities " for the bank.
2. Buy the dip, Wedbush says. Last week's drop among tech stocks shouldn't scare away investors , according to Wedbush. A strong earnings report, buoyed by the ongoing AI craze, should keep them soaring, strategists said. But JPMorgan doesn't see it that way, saying prices are already stretched .
3. China's economy beat analysts' expectations. The country's GDP grew 5.3% in the first quarter of 2024, according to data published by the National Bureau of Statistics on Tuesday. It's a welcome return to form for the world's second-largest economy, although below-par new home and retail sales remain a cause for concern .
3 things in tech
1. Amazon Prime Video viewers are giving up on its shows. Leaked documents show viewers are fed up with the streamer's error-ridden catalog system , which often has incomplete titles and missing episodes. In 2021, 60% of all content-related complaints were about Prime Video's catalog.
2. Eric Newcomer is bringing his Cerebral Valley AI Summit to New York. The conference, originally held in San Francisco, is famous for producing one of the largest generative AI acquisitions ever. Now, it's coming to New York in June .
3. OpenAI is plotting an expansion to NYC. Two people familiar with the plans told BI that the ChatGPT developer is looking to open a New York office next year. That would be the company's fifth office, alongside its current headquarters in San Francisco, a just-opened site in Tokyo, and spots in London and Dublin.
3 things in business
1. America's young men are spending their money like never before. From sports betting to meme coins, young men are more willing than ever to blow money in the hopes of making a fortune .
2. Investors are getting into women's sports. With women like Caitlin Clark dominating March Madness headlines, investors see a big opportunity. BI compiled a list of 13 investors and fund managers pouring money into the next big thing in sports.
3. Bad news for Live Nation. The Wall Street Journal reports that the Justice Department could hit the concert giant with an antitrust lawsuit as soon as next month. Live Nation, which owns Ticketmaster, has long faced criticism over its high fees.
In other news
Blackstone hires Walmart AI whiz to supercharge its portfolio companies .
Taylor Swift, Rihanna, Blackpink's Lisa: Celebrities spotted at Coachella 2024 .
NYC's rat czar says stop feeding the pigeons if you want the vermin gone .
A major Tesla executive left after 18 years at the company amid mass layoffs .
Some Tesla factory workers realized they were laid off when security scanned their badges and sent them back on shuttles, sources say .
New York is in, San Francisco is very much out for tech workers relocating .
AI could split workers into 2: The ones whose jobs get better and the ones who lose them completely .
Oh look at that! Now Google is using AI to answer search queries .
A longtime banker gives a rare inside look at how he is thinking about his next career move, from compensation to WFH .
Clarence Thomas didn't show up for work today .
What's happening today
Today's earnings: United Airlines, Bank of America, Morgan Stanley, and others are reporting .
It's Free Cone Day at participating Ben & Jerry's stores.
The Insider Today team: Dan DeFrancesco , deputy editor and anchor, in New York. Jordan Parker Erb , editor, in New York. Hallam Bullock , senior editor, in London. George Glover , reporter, in London.
Watch: Nearly 50,000 tech workers have been laid off — but there's a hack to avoid layoffs
- Main content
What to know about the crisis of violence, politics and hunger engulfing Haiti

A long-simmering crisis over Haiti’s ability to govern itself, particularly after a series of natural disasters and an increasingly dire humanitarian emergency, has come to a head in the Caribbean nation, as its de facto president remains stranded in Puerto Rico and its people starve and live in fear of rampant violence.
The chaos engulfing the country has been bubbling for more than a year, only for it to spill over on the global stage on Monday night, as Haiti’s unpopular prime minister, Ariel Henry, agreed to resign once a transitional government is brokered by other Caribbean nations and parties, including the U.S.
But the very idea of a transitional government brokered not by Haitians but by outsiders is one of the main reasons Haiti, a nation of 11 million, is on the brink, according to humanitarian workers and residents who have called for Haitian-led solutions.
“What we’re seeing in Haiti has been building since the 2010 earthquake,” said Greg Beckett, an associate professor of anthropology at Western University in Canada.

What is happening in Haiti and why?
In the power vacuum that followed the assassination of democratically elected President Jovenel Moïse in 2021, Henry, who was prime minister under Moïse, assumed power, with the support of several nations, including the U.S.
When Haiti failed to hold elections multiple times — Henry said it was due to logistical problems or violence — protests rang out against him. By the time Henry announced last year that elections would be postponed again, to 2025, armed groups that were already active in Port-au-Prince, the capital, dialed up the violence.
Even before Moïse’s assassination, these militias and armed groups existed alongside politicians who used them to do their bidding, including everything from intimidating the opposition to collecting votes . With the dwindling of the country’s elected officials, though, many of these rebel forces have engaged in excessively violent acts, and have taken control of at least 80% of the capital, according to a United Nations estimate.
Those groups, which include paramilitary and former police officers who pose as community leaders, have been responsible for the increase in killings, kidnappings and rapes since Moïse’s death, according to the Uppsala Conflict Data Program at Uppsala University in Sweden. According to a report from the U.N . released in January, more than 8,400 people were killed, injured or kidnapped in 2023, an increase of 122% increase from 2022.
“January and February have been the most violent months in the recent crisis, with thousands of people killed, or injured, or raped,” Beckett said.

Armed groups who had been calling for Henry’s resignation have already attacked airports, police stations, sea ports, the Central Bank and the country’s national soccer stadium. The situation reached critical mass earlier this month when the country’s two main prisons were raided , leading to the escape of about 4,000 prisoners. The beleaguered government called a 72-hour state of emergency, including a night-time curfew — but its authority had evaporated by then.
Aside from human-made catastrophes, Haiti still has not fully recovered from the devastating earthquake in 2010 that killed about 220,000 people and left 1.5 million homeless, many of them living in poorly built and exposed housing. More earthquakes, hurricanes and floods have followed, exacerbating efforts to rebuild infrastructure and a sense of national unity.
Since the earthquake, “there have been groups in Haiti trying to control that reconstruction process and the funding, the billions of dollars coming into the country to rebuild it,” said Beckett, who specializes in the Caribbean, particularly Haiti.
Beckett said that control initially came from politicians and subsequently from armed groups supported by those politicians. Political “parties that controlled the government used the government for corruption to steal that money. We’re seeing the fallout from that.”

Many armed groups have formed in recent years claiming to be community groups carrying out essential work in underprivileged neighborhoods, but they have instead been accused of violence, even murder . One of the two main groups, G-9, is led by a former elite police officer, Jimmy Chérizier — also known as “Barbecue” — who has become the public face of the unrest and claimed credit for various attacks on public institutions. He has openly called for Henry to step down and called his campaign an “armed revolution.”
But caught in the crossfire are the residents of Haiti. In just one week, 15,000 people have been displaced from Port-au-Prince, according to a U.N. estimate. But people have been trying to flee the capital for well over a year, with one woman telling NBC News that she is currently hiding in a church with her three children and another family with eight children. The U.N. said about 160,000 people have left Port-au-Prince because of the swell of violence in the last several months.
Deep poverty and famine are also a serious danger. Gangs have cut off access to the country’s largest port, Autorité Portuaire Nationale, and food could soon become scarce.
Haiti's uncertain future
A new transitional government may dismay the Haitians and their supporters who call for Haitian-led solutions to the crisis.
But the creation of such a government would come after years of democratic disruption and the crumbling of Haiti’s political leadership. The country hasn’t held an election in eight years.
Haitian advocates and scholars like Jemima Pierre, a professor at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, say foreign intervention, including from the U.S., is partially to blame for Haiti’s turmoil. The U.S. has routinely sent thousands of troops to Haiti , intervened in its government and supported unpopular leaders like Henry.
“What you have over the last 20 years is the consistent dismantling of the Haitian state,” Pierre said. “What intervention means for Haiti, what it has always meant, is death and destruction.”

In fact, the country’s situation was so dire that Henry was forced to travel abroad in the hope of securing a U.N. peacekeeping deal. He went to Kenya, which agreed to send 1,000 troops to coordinate an East African and U.N.-backed alliance to help restore order in Haiti, but the plan is now on hold . Kenya agreed last October to send a U.N.-sanctioned security force to Haiti, but Kenya’s courts decided it was unconstitutional. The result has been Haiti fending for itself.
“A force like Kenya, they don’t speak Kreyòl, they don’t speak French,” Pierre said. “The Kenyan police are known for human rights abuses . So what does it tell us as Haitians that the only thing that you see that we deserve are not schools, not reparations for the cholera the U.N. brought , but more military with the mandate to use all kinds of force on our population? That is unacceptable.”
Henry was forced to announce his planned resignation from Puerto Rico, as threats of violence — and armed groups taking over the airports — have prevented him from returning to his country.

Now that Henry is to stand down, it is far from clear what the armed groups will do or demand next, aside from the right to govern.
“It’s the Haitian people who know what they’re going through. It’s the Haitian people who are going to take destiny into their own hands. Haitian people will choose who will govern them,” Chérizier said recently, according to The Associated Press .
Haitians and their supporters have put forth their own solutions over the years, holding that foreign intervention routinely ignores the voices and desires of Haitians.
In 2021, both Haitian and non-Haitian church leaders, women’s rights groups, lawyers, humanitarian workers, the Voodoo Sector and more created the Commission to Search for a Haitian Solution to the Crisis . The commission has proposed the “ Montana Accord ,” outlining a two-year interim government with oversight committees tasked with restoring order, eradicating corruption and establishing fair elections.
For more from NBC BLK, sign up for our weekly newsletter .
CORRECTION (March 15, 2024, 9:58 a.m. ET): An earlier version of this article misstated which university Jemima Pierre is affiliated with. She is a professor at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, not the University of California, Los Angeles, (or Columbia University, as an earlier correction misstated).
Patrick Smith is a London-based editor and reporter for NBC News Digital.
Char Adams is a reporter for NBC BLK who writes about race.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
What to know about the real estate tycoon sentenced to death in Vietnam’s largest fraud case
A Vietnamese real estate tycoon has been sentenced to death in the country’s biggest ever financial fraud case, a shocking development in an intensifying anti-corruption drive in the southeast Asian nation. Truong My Lan, a high-profile businesswoman who chaired a sprawling real estate company, was arrested in 2022. The 67-year-old was accused of fraud amounting to $12.5 billion, nearly 3% of the country’s 2022 GDP.
Business woman Truong My Lan attends a trial in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam on Thursday, April 11, 2024. The real estate tycoon may face the death penalty if convicted of allegations that she siphoned off an amount of $12.5 billion, nearly 3 percent of Vietnam’s 2022 GDP, in its largest financial fraud case. (Thanh Tung/VnExpress via AP)
- Copy Link copied
Business woman Truong My Lan, center, attends a trial in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam on Thursday, April 11, 2024. The real estate tycoon may face the death penalty if convicted of allegations that she siphoned off an amount of $12.5 billion, nearly 3 percent of Vietnam’s 2022 GDP, in its largest financial fraud case. (Thanh Tung/VnExpress via AP)
Business woman Truong My Lan, front center, attends a trial in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam on Thursday, April 11, 2024. The real estate tycoon may face the death penalty if convicted of allegations that she siphoned off an amount of $12.5 billion, nearly 3 percent of Vietnam’s 2022 GDP, in its largest financial fraud case. (Thanh Tung/VnExpress via AP)

HANOI, Vietnam (AP) — A Vietnamese real estate tycoon was sentenced to death Thursday in the country’s biggest ever financial fraud case, a shocking development in an intensifying anti-corruption drive in the southeast Asian nation.
Truong My Lan, a high-profile businesswoman who chaired a sprawling company that developed luxury apartments, hotels, offices and shopping malls, was arrested in 2022. The 67-year-old has been convicted for fraud amounting to $12.5 billion — nearly 3% of the country’s 2022 GDP — and for illegally controlling a major bank and allowing loans that resulted in losses of $27 billion, state media outlets reported.
Death sentences are not uncommon in Vietnam, but it is rare in financial crime cases and for someone this well known.
Here is a look at the key details of the case:
WHO IS TRUONG MY LAN?
Lan was born in 1956 and started out helping sell cosmetics with her mother, a Chinese entrepreneur, in Ho Chi Minh city’s oldest market, according to state media outlet Tien Phong.
She and her family established the Van Thinh Phat company in 1992, when Vietnam shed its state-run economy in favor of a more market-oriented one that was open to foreigners. Over the years VTP grew to become one of Vietnam’s richest real estate firms.
Today the company is linked to some of Ho Chi Minh’s most valuable downtown properties including the glittering 39-story Times Square Saigon, the five-star Windsor Plaza Hotel, the 37-story Capital Place office building and the five-star Sherwood Residence hotel where Lan lived until her arrest.
Lan met her husband, Hong Kong investor Eric Chu Nap-kee, in 1992. He was sentenced Thursday to nine years in prison. They have two daughters.
WHAT IS SHE ACCUSED OF?
Lan was involved in the 2011 merger of the beleaguered Saigon Joint Commercial Bank, or SCB, with two other lenders in a plan coordinated by Vietnam’s central bank.
She is accused of using the bank as her cash cow, illegally controlling it between 2012 to 2022, and using thousands of “ghost companies” in Vietnam and abroad to give loans to herself and her allies, according to government documents.
Business woman Truong My Lan, center, attends a trial in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam on Thursday, April 11, 2024. (Thanh Tung/VnExpress via AP)
The loans resulted in losses of $27 billion, state media VnExpress reported Thursday.
She was accused of paying bribes to government officials — including a former central official who has been sentenced to life in prison for taking $5.2 million in bribes — and violating banking regulations, government documents said.
The court sentenced her to death, saying her actions “not only violate the property management rights of individuals but also pushed SCB into a state of special control, eroding people’s trust in the leadership of the (Communist) party and state.”
WHY IS THIS HAPPENING NOW?
Lan’s arrest in October 2022 is among the most high-profile in an growing anti-corruption drive in Vietnam .
Weeks after her trial started in early March, former President Vo Van Thuong resigned after being implicated in the so-called Blazing Furnace anti-graft campaign, conducted by Communist Party General Secretary Nguyen Phu Trong, the country’s most powerful politician since the campaign began in 2013.
The 79-year-old ideologue views corruption as a grave threat facing the party and has vowed that the campaign will be a “blazing furnace” where no one is untouchable.
While Lan’s arrest and the scale of her fraud shocked the nation, the case also raised questions about whether other banks or businesses had engaged in similar practices, dampening Vietnam’s economic outlook and making foreign investors jittery.
This is happening as Vietnam tries to argue its case for being the ideal home for businesses trying to move away from neighboring China.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business case is a document presented to company stakeholders that outlines the reasons for pursuing a project or business decision. It's developed during a project's initial phase and examines how and why a company should address a specific business problem or opportunity. Presenting a business case requires more than a good idea and a ...
Our business case template for Word is the perfect tool to start writing a business case. It has 9 key business case areas you can customize as needed. Download the template for free and follow the steps below to create a great business case for all your projects. ProjectManager's free business case template.
If this is your first time creating a business case, don't worry. Follow these five steps to create a solid one. 1. Gather input. You don't have to write a business case on your own. Instead, make sure appropriate team members and stakeholders are contributing to the relevant sections.
A business case is a useful tool to provide a clear rationale for pursuing the project. A thorough business case can help key stakeholders decide whether to invest in the project by evaluating the feasibility, costs, risks and potential returns. A business case presentation gives stakeholders an opportunity to ask questions and address concerns.
Make the story relatable by showcasing the human side of the situation. Share personal anecdotes or experiences that humanize the challenges and victories. 8. Include customer quotes. Whenever feasible, include quotes from the customer to add authenticity and provide a personal touch to the case study. 9.
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
A business case captures the reasoning for initiating a project or task. Many projects, but not all, are initiated by using a business case. It is often presented in a well-structured written document, but may also come in the form of a short verbal agreement or presentation.The logic of the business case is that, whenever resources such as money or effort are consumed, they should be in ...
Share a brief explanation of your company and the products or services you provide. 7. Call-to-action (CTA) Add a call to action with the appropriate contact information (or a contact button, if this is a web-based case study) so that users can get in touch for additional information after reading the case study.
The Most Important Components of a Business Case. A business case should convince key stakeholders of the importance and viability of your project. Be sure to include these things to create an effective business case: An executive summary, which is a concise overview of your project's definition and goals. Use this section to briefly explain ...
The Business Case is a reference point before, during, and after a project. As the project begins the Business Case establishes the ultimate goal of the project for all stakeholders—including the project manager and sponsor. There are invariably concepts in the minds of the key project participants of what they expect the project to accomplish.
6 QUALITIES OF GREAT CASE WRITERS. Curiosity. Comfort with ambiguity, since cases may have more than one "right" answer. Command of the topic or subject at hand. Ability to relate to the case protagonists. Enthusiasm for the case teaching method. Capacity for finding the drama in a business situation and making it feel personal to students.
Create a Colorful and Visual Case Study Template. Decide on a case study template and use it consistently for all future business case studies so they are easy to read and look consistent. This is important in order to keep your branding consistent. Choose a good-sized, easy-to-read font, and color to offset your subheads.
Writing a Business Case Study Step by Step. Step 1: Collect the Facts. Step 2: Outline. Step 3: Write the Case Study. Step 4: Format it, Prove it and then Publish it. Top Business Case Study Examples. The Reason of Why Business Case Study is Significant to Business Analysts. See Also.
Business case studies are teaching tools that are used by many business schools, colleges, universities, and corporate training programs. This method of teaching is known as the case method.Most business case studies are written by educators, executives or heavily educated business consultants. However, there are times when students are asked to conduct and write their own business case studies.
Overview. Simply put, the case method is a discussion of real-life situations that business executives have faced. On average, you'll attend three to four different classes a day, for a total of about six hours of class time (schedules vary). To prepare, you'll work through problems with your peers. Read More.
A case study, also called customer success story, is a product marketing document used to show how your clients solved a business problem with the aid of your product or service. Case studies include statistics, quotes, and concrete examples with the goal of credibly demonstrating your capability to deliver results. Browse case study templates.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A business case is a key to the project's success and the basis of the project charter and project management plans. Writing a business case requires experience, industry and market knowledge, and authority to initiate the project. The following four steps are required to write a business case: #1. Identify the Problem.
A case study is a comprehensive report of the results of theory testing or examining emerging themes of a business in real life context. Case studies are also often used in the healthcare industry, conducting health services research with primary research interest around routinely collected healthcare data.
B usiness case studies unfold in innumerable ways in classrooms around the globe. From provoking robust student-led discussions to disentangling complex business concepts, cases are strong pedagogical vehicles for building the confidence and critical thinking students need to boldly take a position and convincingly express their ideas.
Business case studies explained. A business case study summarizes a real-life business issue faced by a company and looks at how it may affect society within a business context. A case study is a research tool and can form part of the research methods you will use in your final projects in our programs. Here are examples of the cases you are ...
A business case provides a justification for a course of action based on the benefits to be realized by using the proposed solution, as compared to the cost, effort, and other considerations to acquire and live with that solution. ... Refinement 6.2 Business Cases 6.3 Collaborative Games 6.4 Customer Journey Map 6.5 Decision Modelling and ...
This is the third in a series of monthly business school-style teaching case studies devoted to responsible-business dilemmas faced by organisations. Read the piece and FT articles suggested at ...
by. Summary. Siti Rahman, the CEO of Malaysia-based NVF Bank, faces a pivotal decision. Her head of AI innovation, a recent recruit from Google, has a bold plan. It requires a substantial ...
Why Engineers Should Study Philosophy. Summary. The ability to develop crisp mental models around the problems you want to solve and understanding the why before you start working on the how is an ...
For Now". Marques Brownlee, the YouTuber better known as MKBHD, didn't mince words with the title of his review of Humane's AI Pin. In a 25-minute video, Brownlee details all the issues he ...
Chaos has gutted Port-au-Prince and Haiti's government, a crisis brought on by decades of political disruption, a series of natural disasters and a power vacuum left by the president's assassination.
HANOI, Vietnam (AP) — A Vietnamese real estate tycoon was sentenced to death Thursday in the country's biggest ever financial fraud case, a shocking development in an intensifying anti-corruption drive in the southeast Asian nation.. Truong My Lan, a high-profile businesswoman who chaired a sprawling company that developed luxury apartments, hotels, offices and shopping malls, was arrested ...
This is the Manhattan criminal case against Mr. Trump, brought by Mr. Bragg in March 2023. Mr. Trump is facing 34 felony counts of falsifying business records and, if convicted, could face up to ...
Make the story relatable by showcasing the human side of the situation. Share personal anecdotes or experiences that humanize the challenges and victories. 8. Include customer quotes. Whenever feasible, include quotes from the customer to add authenticity and provide a personal touch to the case study. 9.