- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- enVision Math
- EngageNY Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy


Go Math Grade K Answer Key Chapter 1 Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5
Go Math Grade K Answer Key Chapter 1: Students of Kindergarten will get familiar with the concepts like Representing, Counting, and Writing Numbers from 0 to 5 from here. By going through the Go Math Kindergarten Ch 1 Answer Key you will become proficient in the concepts of math easily. Assess your preparation standard taking the help of the quick resources available here for Go Math Grade K Answer Key Chapter 1 Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5. All the Solutions are provided in PDF Format for free of cost and you can kick start your preparation taking the help of this study material.
Go Math Grade K Chapter 1 Answer Key Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5
Go Math Grade K Chapter 1 Answer Key includes all the Questions from Go Math Grade K Textbooks. All the Topics of Kindergarten Maths are covered here in an efficient manner. You can simply tap on the quick links available to learn the concerned topic in no time. Grade K Go Math Chapter 1 Solution Key is prepared by subject experts adhering to the latest syllabus guidelines and Common Core Curriculum. Download the preparation material available here without paying a single penny and prepare anytime and anywhere.
Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5
- Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Show What You Know – Page 9
- Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Vocabulary Builder – Page 11
- Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Game: Bus Stop – Page 12
- Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Vocabulary Game – Page(12A-12D)
Lesson: 1 Model and Count 1 and 2
- Lesson 1.1 Model and Count 1 and 2 – Page(13-18)
- Model and Count 1 and 2 Homework & Practice 1.1 – Page(17-18)
Lesson: 2 Count and Write 1 and 2
- Lesson 1.2 Count and Write 1 and 2 – Page(19-24)
- Count and Write 1 and 2 Homework & Practice 1.2 – Page(23-24)
Lesson: 3 Model and Count 3 and 4
- Lesson 1.3 Model and Count 3 and 4 – Page(25-30)
- Model and Count 3 and 4 Homework & Practice 1.3 – Page(29-30)
Lesson: 4 Count and Write 3 and 4
- Lesson 1.4 Count and Write 3 and 4 – Page(31-36)
- Count and Write 3 and 4 Homework & Practice 1.4 – Page(35-36)
Mid-Chapter Checkpoint
- Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Mid-Chapter Checkpoint – Page 34
Lesson: 5 Model and Count to 5
- Lesson 1.5 Model and Count to 5 – Page(37-42)
- Model and Count to 5 Homework & Practice 1.5 – Page(41-42)
Lesson: 6 Count and Write to 5
- Lesson 1.6 Count and Write to 5 – Page(43-48)
- Count and Write to 5 Homework & Practice 1.6 – Page(47-48)
Lesson: 7 Algebra • Ways to Make 5
- Lesson 1.7 Algebra • Ways to Make 5 – Page(49-54)
- Algebra • Ways to Make 5 Homework & Practice 1.7 – Page(53-54)
Lesson: 8 Count and Order to 5
- Lesson 1.8 Count and Order to 5 – Page(55-60)
- Count and Order to 5 Homework & Practice 1.8 – Page(59-60)
Lesson: 9 Problem Solving • Understand 0
- Lesson 1.9 Problem Solving • Understand 0 – Page(61-66)
- Problem Solving • Understand 0 Homework & Practice 1.9 – Page(65-66)
Lesson: 10 Identify and Write 0
- Lesson 1.10 Identify and Write 0 – Page(67-72)
- Identify and Write 0 Homework & Practice 1.10 – Page(71-72)
- Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Chapter 1 Review/Test – Page(73-76)
Curious George
Navel oranges have no seeds. • How many seeds do you see?
Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Show What You Know
Explore Numbers

Match Numbers to Sets

DIRECTIONS 1. Circle all of the sets of three oranges. 2. Draw a line to match the number to the set.
Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Vocabulary Builder

DIRECTIONS Draw a line to match a set of chicks to a set of flowers.
Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Game: Bus Stop

DIRECTIONS Each player rolls the number cube. The first player to roll a 1 moves to the bus stop marked 1. Continue playing until each player has rolled the numbers in sequence and stopped at each bus stop. The first player to reach 5 wins the game.
MATERIALS game marker for each player, number cube (0–5)
Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Vocabulary Game
Going Places with GOMATH! Words

DIRECTIONS Shuffle all the cards and place them facedown in a pile. Play with a partner. Place game pieces on START. Take turns choosing a card and moving game pieces to the first space with that word or picture. If a player can tell about the word or picture, the player moves ahead 1 space. Return the card to the bottom of the pile. The first player to reach FINISH wins.
MATERIALS 1 connecting cube per player • 3 sets of Vocabulary Cards • 1 set of Picture Cards

The Write Way

Explanation: Number given to draw = Four or 4.
DIRECTIONS Trace the 4. Draw to show what you know about 4. Reflect Be ready to tell about your drawing.
Lesson 1.1 Model and Count 1 and 2
Essential Question How can you show and count 1 and 2 with objects?
Listen and Draw

DIRECTIONS Place a counter on each object in the set as you count them. Move the counters to the five frame. Draw the counters.
Share and Show

DIRECTIONS 1–2 . Place a counter on each object in the set as you count them. Tell how many counters. Trace the number. Move the counters to the five frame. Draw the counters.

Explanation: Count One, traced One with One Counter in the five frames given shown.

Explanation: Count Two, traced Two with Two Counters in the five frame given shown.

Explanation: Count One, traced One with One Counter in the five frame given shown.

DIRECTIONS 3–6 . Say the number. Count out that many counters in the five frame. Draw the counters.
Problem Solving • Applications

Question 8. Answer: 1 or One number comes after 0 or Zero number.
Question 9. Answer: 2 or Two number comes after 1 or One number.
DIRECTIONS 7. Jen has 2 matching lunch boxes. Max has 1 lunch box. Circle to show Jen’s lunch boxes. 8. Draw to show what you know about the number 1. 9. Draw to show what you know about the number 2. Tell a friend about your drawings.
HOME ACTIVITY • Ask your child to show a set that has one or two objects, such as books or buttons. Have him or her point to each object as he or she counts it to tell how many objects are in the set.
Model and Count 1 and 2 Homework & Practice 1.1

Explanation:

Explanation: 2 or Two Number.

Explanation: 1 or One Number.
DIRECTIONS 1–4. Say the number. Count out that many counters in the five frames. Draw the counters.
Lesson Check

Spiral Review

DIRECTIONS 1–3. Trace the number. How many counters would you place in the five frame to show the number? Draw the counters.
Lesson 1.2 Count and Write 1 and 2
Essential Question How can you count and write 1 and 2 with words and numbers?

Explanation: Number of cubes are One and Two in the given figure.
DIRECTIONS Count the cubes. Tell how many. Trace the numbers and words.

Explanation: Number of Red cameras given in the figure = Two or 2.

Explanation: Number of Paint bottle given in the figure = one or 1.
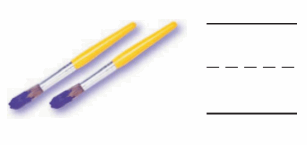
Explanation: Number of Paint Brushes given in the figure = Two or 2.
DIRECTIONS 1–2. Count the cubes. Say the number. Trace the numbers. 3–4. Count and tell how many. Write the number.

Explanation: Number of Glue sticks given in the figure = Two or 2.

Explanation: Number of markers given in the figure = Two or 2.

Explanation: Number of scissors given in the figure = 1 or One.

Explanation: Number of Blue Paint bottles given in the figure = 1 or One.

DIRECTIONS 5–10. Count and tell how many. Write the number.

DIRECTIONS 11. Draw to show what you know about the numbers 1 and 2. Write the number beside each drawing. Tell a friend about your drawings.
HOME ACTIVITY • Ask your child to write the number 1 on a sheet of paper. Then have him or her find an object that represents that number. Repeat with objects for the number 2.
Count and Write 1 and 2 Homework & Practice 1.2

Explanation: Number of White Tigers given in the figure = 1 or One.

Explanation: Number of Squirrels given in the figure = Two or 2.

Explanation: Number of Elephants given in the figure = Two or 2.

Explanation: Number of Foxes given in the figure = One or 1.
DIRECTIONS 1–4. Count and tell how many. Write the number.

Explanation: Number of Cameras given in the figure = One or 1.

Explanation: Number given in the figure = 2 or Two.

Explanation: Number given in the figure = 1 or One.
DIRECTIONS 1. Count and tell how many cubes. Write the number. 2–3. Trace the number. How many counters would you place in the five frame to show the number? Draw the counters.
Lesson 1.3 Model and Count 3 and 4
Essential Question How can you show and count 3 and 4 with objects?

Explanation: Number of Orange Horses given in the figure = Three or 3. Number of Red Horses given in the figure = Four or 4.

Number of Toy Horses given in the figure = Three or 3.

DIRECTIONS 1–2. Place a counter on each object in the set as you count them. Tell how many counters. Trace the number. Move the counters to the five frame. Draw the counters.

Explanation: Number given = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number given = Four or 4.

DIRECTIONS 3–6. Say the number as you trace it. Count out that many counters in the five frame. Draw the counters.

DIRECTIONS 7. Lukas has 3 matching toys. Jon has a number of matching toys greater than Lukas. Circle to show Jon’s toys. 8. Draw to show what you know about the number 3. 9. Draw to show what you know about the number 4. Tell a friend about your drawings.
HOME ACTIVITY • Draw a five frame or cut an egg carton to have just five sections. Have your child show a set of up to four objects and place the objects in the five frame.
Model and Count 3 and 4 Homework & Practice 1.3

Explanation: Number Three always comes after two number.

Explanation: Number Four always comes after three number.

DIRECTIONS 1–4. Say the number as you trace it. Count out that many counters in the five frame. Draw the counters.

Explanation: Number of Umbrellas in the given figure = Two or 2.

DIRECTIONS 1. Trace the number. How many counters would you place in the five frame to show the number? Draw the counters. 2. Count and tell how many umbrellas. Write the number. 3. Trace the number. How many counters would you place in the five frame to show the number? Draw the counters.
Lesson 1.4 Count and Write 3 and 4
Essential Question How can you count and write 3 and 4 with words and numbers?

Explanation: Numbers given in the figure = Three (3) and Four (4).
DIRECTIONS Count the cubes. Tell how many. Trace the numbers and the words.

Explanation: Number of Blue cameras given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of Aero planes given in the figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of Fire Trucks given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of footballs given in the figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of Basket Balls given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of Base Balls given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of Color Balls given in the figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of Balls given in the figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of Balls given in the figure = Four or 4.
HOME ACTIVITY • Ask your child to show a set of three or four objects. Have him or her write the number on paper to show how many objects.
Count and Write 3 and 4 Homework & Practice 1.4

Explanation: Number of Grasshoppers given in the figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of Bugs given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of Turtles given in the figure = Three or 3.

E x planation: Number of Flies given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of Butterflies given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of mics given in the figure = Three or 3.
DIRECTIONS 1–6. Count and tell how many. Write the number.

Explanation: Number given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of Roses given in the figure = Two or 2.
DIRECTIONS 1. Count and tell how many butterflies. Write the number. 2. Trace the number. How many counters would you place in the five frame to show the number? Draw the counters. 3. Count and tell how many flowers. Write the number.
Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Mid-Chapter Checkpoint
Concepts and Skills

Explanation: Number given to draw in the figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of Glue Bottles given in the figure = Two or 2.

Explanation: Number of Purple Bags given in the figure = Three or 3. Number of Orange Bags given in the figure = Four or 4. Number of Red Bags given in the figure = Three or 3.
DIRECTIONS 1. Place counters in the five frame to show the number 3. Draw the counters. Write the number. 2–3. Count and tell how many. Write the number. 4. Count each set of bags. Circle all the sets that show 3 bags.
Lesson 1.5 Model and Count to 5
Essential Question How can you show and count up to 5 objects?

Explanation: Number of Oranges given in the figure = Five or 5.
DIRECTIONS Place a counter on each orange as you count them. Move the counters to the five frame. Draw the counters.

Explanation: Number of Lemons given in the figure = Five or 5.

Explanation: Number of Green Lemons given in the figure = Five or 5.

Explanation: Number given in the figure = Five or 5.

Explanation: Number given in the figure = Three or 3.
DIRECTIONS 3. Place counters to show five. Draw the counters. Write the number. 4. Place counters to show four. Draw the counters. Write the number. 5. Place counters to show five. Draw the counters. Write the number. 6. Place counters to show three. Draw the counters. Write the number.

Explanation: Number of Green Lemons given in the figure = Five or 5. Number of Oranges given in the figure = Four or 4. Number of Yellow Lemons given in the figure = Five or 5.
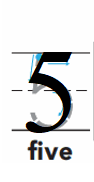
Explanation: Number given in the figure to draw = Five or 5. Number Five or 5 is greater than Number Four or 4.
DIRECTIONS 7. Carl needs 5 pieces of each kind of fruit. Circle to show all the sets Carl could use. 8. Draw to show what you know about the number 5. Tell a friend about your drawing.
Model and Count to 5 Homework & Practice 1.5

Explanation: The number given to draw in the figure = Five or 5.

Explanation: Number given to draw in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number given to draw in the figure = Five or 5.
DIRECTIONS 1. Place counters to show five. Draw the counters. Write the number. 2. Place counters to show three. Draw the counters. Write the number. 3. Place counters to show four. Draw the counters. Write the number. 4. Place counters to show five. Draw the counters. Write the number.

Explanation: Number of Cars given in the figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of Fishes given in the figure = Two or 2.
DIRECTIONS 1. Trace the number. How many counters would you place in the five frame to show the number? Draw the counters. 2–3. Count and tell how many. Write the number.
Lesson 1.6 Count and Write to 5
Essential Question How can you count and write up to 5 with words and numbers?

Explanation: Number of Apples given in the figure = Five or 5.
DIRECTIONS Count the cubes. Tell me how many. Trace the numbers and the word. Count the apples. Tell me how many. Trace the numbers.

Explanation: Number of Five set of Apples given in the figure = 3 or Three sets.
DIRECTIONS 1. Count and tell how many apples. Trace the numbers. 2. Circle all the sets of five apples.

Explanation: Number of Apples given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of Apples given in the figure = Three or 3.

DIRECTIONS 3–6. Count and tell how many apples. Write the number.

Explanation: Five or 5 number always comes next to the Four or 4 number.
DIRECTIONS 7. Draw to show what you know about the number 5. Write the number. Tell a friend about your drawing.
HOME ACTIVITY • Ask your child to write the number 5 on a sheet of paper. Then have him or her find objects to show that number.
Count and Write to 5 Homework & Practice 1.6

Explanation: Number of Pencils given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of Crayons given in the figure = five or 5.

Explanation: Number of Erasers given in the figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of Paint brushes given in the figure = Five or 5.

Explanation: Number of Scissors given in the figure = Five or 5.

Explanation: Number of Glue Bottles given in the figure = Five or 5.

Explanation: Number of Lions given in the figure = Five or 5.

Explanation: Number of Cameras given in the figure = Two or 2.
DIRECTIONS 1. Count and tell how many animals. Write the number. 2. Trace the number. How many counters would you place in the five frame to show the number? Draw the counters. 3. Count and tell how many cubes. Write the number.
Lesson 1.7 Algebra • Ways to Make 5
Essential Question How can you use two sets of objects to show 5 in more than one way?

Explanation: Number of Red Marbles in the given Figure = Three or 3 Number of Yellow Marbles in the given Figure = Two or 2.
DIRECTIONS Jessica has 5 marbles in the bag. The marbles can be red or yellow. Describe the marbles that might be in Jessica’s bag. Use counters to show one pair of marbles. Trace and color the counters.

Explanation: Number of Red counters in the given figure = Four or 4. Number of Yellow counters in the given figure = One or 1. Number of total counters in the given figure = Number of Red counters + Number of Yellow counters = 4 + 1 = 5.

Explanation: Number of Red counters in the given figure = Two or 2. Number of Yellow counters in the given figure = Three or 3. Number of total counters in the given figure = Number of Red counters in the given figure + Number of Yellow counters in the given figure = 2 + 3 = 5.
DIRECTIONS 1. Look at the counters in the five-frame. Trace the numbers to show the pair that makes 5. 2. Use two colors of counters to show a different way to make 5. Write the numbers to show the pair that makes 5.

Explanation: Number of Red counters in the given figure = One or 1. Number of Yellow counters in the given figure = Four or 4. Number of total counters in the given figure = Number of Red counters in the given figure + Number of Yellow counters in the given figure = 1 + 4 = 5.
DIRECTIONS 3–4. Use 1 Tools or two colors of counters to show a different way to make 5. Write the numbers to show the pair that makes 5.

Explanation: Number of Blue cubes in the given figure = Three or 3. Number of Red cubes in the given figure = Two or 2. Number of total counters in the given figure = Number of Blue cubes + Number of Red cubes = 3 + 2 = 5.
DIRECTIONS 5. Austin has 5 counters. One counter is red. How many yellow counters does he have? Color the counters. 6. Madison has 5 red and blue cubes. Color to show the cubes. Write the pair of numbers that makes up Madison’s cubes.
Algebra • Ways to Make 5 Homework & Practice 1.7

Explanation: Number of Red counters in the given figure = Two or 2. Number of Yellow counters in the given figure = Three or 3. Number of total counters in the given figure = Number of Red counters + Number of Yellow counters = 3 + 2 = 5.
DIRECTIONS 1–2. Use two colors of counters to show a way to make 5. Color to show the counters. Write the numbers to show the pair that makes 5.

Explanation: Number of Grey counters given in the figure = Two or 2. Number of more counters can b placed in the given figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of bugs Given in the figure = Five or 5.

DIRECTIONS 1. How many more counters would you place in the five frame to show a way to make 5? Draw the counters. Write the number. 2–3. Count and tell how many. Write the number.
Lesson 1.8 Count and Order to 5
Essential Question How do you know that the order of numbers is the same as a set of objects that is one larger?

Explanation: Total Number of Cubes towers= Five or 5.
DIRECTIONS Use cubes to make cube towers that have 1 to 5 cubes. Place the cube towers in order to match the numbers 1 to 5. Draw the cube towers in order.

Explanation: Number of cubes in the cube Train = Five or 5.
DIRECTIONS 1. Use cubes to make cube trains that have 1 to 5 cubes. Place the cube trains in order beginning with 1. Draw the cube trains and trace or write the numbers in order. Tell a friend what you know about the numbers and the cube trains.

Explanation: Number of Books Given in the figure = One or 1. Number of Scissors Given in the figure = Four or 4. Number of Cat Books Given in the figure = Two or 2. Number of Rubbers Given in the figure = Five or 5. Number of Soaps Boxes Given in the figure = Three or 3.
DIRECTIONS 2. Count the objects in each set. Write the number beside the set of objects. Write those numbers in order beginning with the number 1.

Explanation: The set of the blocks given in the figure are from 1 to 5.

Explanation: The blocks given in the figure are starting from number 1 to 5. The order of the sets is one longer the other number.
DIRECTIONS 3. Paul has a set of blocks that is one larger than a set of 3 blocks. Circle Paul’s blocks. Check to make sure your answer makes sense. 4. Draw to show what you know about the order of sets 1 to 5. Tell a friend about your drawing.
Count and Order to 5 Homework & Practice 1.8

Explanation: Number of Tents given in the figure = One or 1. Number of Sea shells given in the figure = five or 5. Number of Buckets given in the figure = Two or 2. Number of Soil diggers given in the figure = Four or 4. Number of Stars given in the figure = Three or 3.
DIRECTIONS 1. Count the objects in each set. Write the number beside the set of objects. Write those numbers in order beginning with the number 1.

Explanation: Numbers given in the figure are from 1 to 5. The missing number in the given figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number of Stars given in the figure = Four or 4.

Explanation: Number given in the figure to trace = Three or 3.
DIRECTIONS 1. Trace or write the numbers in order. 2. Count and tell how many stars. Write the number. 3. Trace the number. How many counters would you place in the five frame to show the number? Draw the counters.
Lesson 1.9 Problem Solving • Understand 0
Essential Question How can you solve problems using the strategy make a model?

Explanation: Number of Horses in the pen = Two or 2. Number of Horses leave the pen n go to the field = Two or 2. Number of Horses left in the pen = Number of Horses in the pen – Number of Horses leave the pen n go to the field = 2 – 2 = 0.
DIRECTIONS Use counters to model this problem. There are two horses in the pen. The horses leave the pen and go to the field. How many horses are in the pen now? Trace the number. Tell a friend what you know about that number.
Try Another Problem

Explanation: Number of counters used to represent backpacks in the given figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of Backpacks given in the figure = Three or 3. Number of Backpacks Taken by the children each in the given figure = Three or 3. Number of Backpacks left = Number of Backpacks given in the figure – Number of Backpacks Taken by the children each in the given figure = 3 – 3 = 0.
DIRECTIONS 1. Use counters to model this problem. Three children each have one backpack on a peg. Draw counters to show the backpacks. How many backpacks are there? Write the number. 2. Use counters to model a backpack on each peg. Three children each take one backpack. How many backpacks are there now? Write the number.

Explanation: Number of Books Drew has = One or 1. Adam has one fewer book than Drew => Number of Books Adam has = 1 – 1 = 0.

Explanation: Number of Pencils Bradley has = Zero or 0. Matt has one more pencil than Bradley. =>Number of pencils Matt has = 1 or One.
DIRECTIONS Use counters to model these problems. 3. Drew has one book. Adam has one fewer book than Drew. How many books does Adam have? Write the number. 4. Bradley has no pencils. Matt has one more pencil than Bradley. How many pencils does Matt have? Write the number.
On Your Own

Explanation: Number of apples Vera has = 2 or Two. Number of Apples Vera eats = One or 1. Number of Apples given to her Friend = One or 1. Number of Apples Vera has now = Number of apples Vera has – (Number of Apples Vera eats + Number of Apples given to her Friend ) = 2 – (1 + 1) = 2 – 2 = 0.

Explanation: Number of Crayons Amy has = Three or 3. Now she has no crayons. => Number of Crayons Amy has now = Zero or 0. Number of Crayons Amy gives away = Number of Crayons Amy has – Number of Crayons Amy has now = 3 – 3 =0.
DIRECTIONS 5. Vera has 2 apples. She eats 1 apple and gives 1 apple to her friend. How many apples does Vera have now? Write the number. 6. Amy has 3 crayons. She gives some away. Now she has no crayons. How many crayons did she give away? Write the number.
HOME ACTIVITY • Have your child place a set of up to five coins in a cup. Remove some or all of the coins and have him or her tell how many coins are in the cup and write the number.
Problem Solving • Understand 0 Homework & Practice 1.9

Explanation: Number of juice box Oliver has = One or 1. Lucy has one fewer juice box than Oliver. =>Number of juice box Lucy has =Number of juice box Oliver has – 1 = 1 – 1 = Zero or 0.

Number of Books Jessica has = Zero or 0. Wesley has 2 more books than Jessica. => Number of Books Wesley has = Number of Books Jessica has + 2 => 0 + 2 => 2
DIRECTIONS Use counters to model these problems. 1. Oliver has one juice box. Lucy has one fewer juice box than Oliver. How many juice boxes does Lucy have? Write the number. 2. Jessica has no books. Wesley has 2 more books than Jessica. How many books does Wesley have? Write the number.

Explanation: Number of apples Eva has in her basket = Two or 2 Number of apples Eva eats = One or 1. Number of apples Eva gives to her friend = One or 1. Number of apples Eva has in her basket = Number of apples Eva has in her basket + ( Number of apples Eva eats + Number of apples Eva gives to her friend ) = 2 – ( 1 + 1) = 2 – 2 = 0.
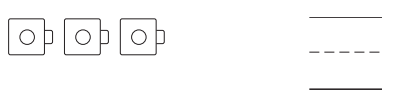
Explanation: Number of Cameras given in the figure = Three or 3.

Explanation: Number of Squirrels given in the figure = One or 1.
DIRECTIONS 1. Use counters to model this problem. Eva has 2 apples in her basket. She eats 1 apple and gives 1 apple to her friend. How many apples does Eva have now? Write the number. 2–3. Count and tell how many. Write the number.
Lesson 1.10 Identify and Write 0
Essential Question How can you identify and write 0 with words and numbers?

Explanation: Number of Fishes given in the picture = Zero or 0. Number Zero means no value.
DIRECTIONS How many fish are in the bowl? Trace the numbers and the word. Tell a friend what you know about that number.

Explanation: Number of Fishes given in the picture = Zero or 0.

Explanation: Number of Fishes given in the picture = One or 1.

Explanation: Number of Fishes given in the picture = Two or 2.

DIRECTIONS 1. How many fish are in the tank? Trace the number. 2–4. How many fish are in the tank? Write the number. Circle the tanks that have 0 fish.

Explanation: Number of Fishes given in the picture = Three or 3.

DIRECTIONS 5–8. How many fish are in the tank? Write the number. Circle the tanks that have 0 fish.

Explanation: Bryce has two fish. Chris has no fish. => Number of Fishes Bryce has = Two or 2. => Number of Fishes Chris has = Zero or 0.
DIRECTIONS 9. Bryce has two fish. Chris has no fish. Circle to show which fish bowl belongs to Chris. 10 . Draw to show what you know about the number 0. Tell a friend about your drawing.
HOME ACTIVITY • Draw a five frame or use an egg carton that has just five sections. Have your child show a set of up to 3 or 4 objects and place the objects in the five frame. Then have him or her remove the objects and tell how many are in the five frame.
Identify and Write 0 Homework & Practice 1.10

Explanation: Number of Birds in the cage = Zero or 0.

Explanation: Number of Birds in the cage = Two or 2.

Explanation: Number of Birds in the cage = One or 1.
DIRECTIONS 1–4. How many birds are in the cage? Write the number. Circle the cages that have 0 birds.

Explanation: Number of Fishes in the cage = Zero or 0.

Explanation: Number of Soccer’s given in the figure = Five or 5.

Explanation: Number of Marbles drawn in the figure = Five or 5.
DIRECTIONS 1. How many fish are in the bowl? Write the number. 2. Count and tell how many. Write the number. 3. Draw a set of 5 marbles. Write the number.
Represent, Count, and Write Numbers 0 to 5 Chapter 1 Review/Test

Explanation: Number of Fishes in the given figure = One or 1.

Explanation: Number of Fire Trucks given in the figure = five or 5.

Explanation: Number of Eggs given in the figure = Zero or 0.

Explanation: Number of Apples given in the figure = Two or 2.

Explanation: Number of Soccer’s given in the figure = Three or 3.
DIRECTIONS 1–2. Choose all the answers that tell how many. 3. How many eggs are in the nest? Write the number. 4–5. Count how many. Write the number.

Explanation: Number of Coconuts given in the figure = Four and Five and Four.

Explanation: Number of Cubes given in the figure = One to Five.

Explanation: Numbers are in counting order from One to Five.
DIRECTIONS 6. Circle all sets that show 4. 7. Count the cubes in each tower. Write the number. 8. Write the numbers 1 to 5 in counting order.

Explanation: Numbers 4,2,1 are in counting order = No. Numbers 3,4,5 are in counting order = No. Numbers 1,2,3 are in counting order = Yes.

Explanation: Three children each bring one book to school. => Numbers of Books Three Children each bring to school = Three or 3.

Explanation: Sam has no apples in a basket. => Number of Apples Sam has in the basket = Zero or 0.

Explanation: There are two apples on the table. Kia takes the two apples to a friend. Number of Apples on the Table = Two or 2. Number of Apples Kia takes to her friend = Two or 2. Number of Apples are on the Table now = Number of Apples on the Table – Number of Apples Kia takes to her friend = 2 – 2 = 0.
DIRECTIONS 9. Are the numbers in counting order? Choose Yes or No. 10. Three children each bring one book to school. Draw counters to show the books. Write the number. 11. Sam has no apples in a basket. How many apples does Sam have? Write the number. 12. There are two apples on the table. Kia takes the two apples to a friend. How many apples are on the table now? Write the number.

Explanation: First way: Number of Red counters = 4 or Four. Number of Yellow Counters = One or 1. Total counters in the first figure = Number of Red counters + Number of Yellow Counters = 4 + 1 = 5.
Second way: Number of Red counters = Two or 2. Number of Yellow Counters = Three or 3. Total counters in the first figure = Number of Red counters + Number of Yellow Counters = 2 + 3 = 5.

Explanation: Number that comes after Three or 3 in the counting order = Four or 4.
DIRECTIONS 13. Show 2 ways to make 5. Color some counters red. Color some counters yellow. Write the numbers. 14. Write the number that comes after 3 in counting order. Draw counters to show the number.
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Technological Graphing
9.1: It Begins With Data (10 minutes)
CCSS Standards
Building On
Routines and Materials
Required Materials
- Statistical technology
The mathematical purpose of this activity is to gain familiarity with entering data into a spreadsheet and to prepare students for finding statistics using technology.
Arrange students in groups of 2. If students are using the digital version of the materials, show them how to open the GeoGebra spreadsheet app in the math tools. If students are using the print version of the materials, they can access the GeoGebra spreadsheet app at www.geogebra.org/spreadsheet . If they use a different technology, you may need to provide them with alternate instructions.
Make sure students input the data in one column, even though the data is represented in two columns in the task statement.
Student Facing
Open a spreadsheet window and enter the data so that each value is in its own cell in column A.
- How many values are in the spreadsheet? Explain your reasoning.
- If you entered the data in the order that the values are listed, the number 7 is in the cell at position A1 and the number 5 is in cell A5. List all of the cells that contain the number 13.
- In cell C1 type the word “Sum”, in C2 type “Mean”, and in C3 type “Median”. You may wish to double-click or drag the vertical line between columns C and D to allow the entire words to be seen.
Student Response
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners .
Activity Synthesis
The goal is to make sure that students know how to type data into a spreadsheet and to locate values in the spreadsheet by row and column. The locations will be referenced with spreadsheet functions in upcoming activities. Here are some questions for discussion.
- “What value is in cell A7?” (14)
- “What was interesting or challenging about this activity?” (I never knew that you could describe each cell in a spreadsheet using the row and column labels.)
9.2: Finding Spreadsheet Statistics (15 minutes)
Building Towards
Instructional Routines
- MLR1: Stronger and Clearer Each Time
The mathematical purpose of this activity is to calculate statistics, create data displays, and to investigate how those change when values are added or removed from the data set. Monitor for students discussing the relationship between outliers and the measure of center.
Keep students in the same groups. They will continue working using the spreadsheet they started in the previous activity.
Tell students that statistics are values that are calculated from data, such as the mean, median, or interquartile range.
Tell students that after they change the value in A1 to change the mean in the first set of questions, they should continue to use the changed value for the second set of questions rather than reset them to the values from the warm-up.
Note that GeoGebra is like any other computer program. It needs directions written in a specific way for it to execute a command. For example, if students forget to type the = symbol or don’t capitalize “Sum,” the formula won’t work. Ask students to pause after typing the formulas and ensure that cells D1, D2, and D3 display numbers for each statistic. If not, ask students to delete the contents of the cell and retype the formula, ensuring that they start with an = symbol and capitalize Sum, Mean, and Median.
Using the data from the warm-up, we can calculate a few statistics and look at the data.
- Next to the word Sum, in cell D1, type =Sum(A1:A20)
- Next to the word Mean, in cell D2, type =Mean(A1:A20)
- Next to the word Median, in cell D3, type =Median(A1:A20)
- What are the values for each of the statistics?
- Change the value in A1 to 8. How does that change the statistics?
- What value can be put into A1 to change the mean to 10.05 and the median to 9?
We can also use Geogebra to create data displays.
- Click on the letter A for the first column so that the entire column is highlighted.
- Click on the button that looks like a histogram to get a new window labeled One Variable Analysis .
- Click Analyze to see a histogram of the data.
- What does the value for n represent?
- What does the value for \(\Sigma x\) represent?
- What other statistics do you recognize?
- Adjust the slider next to the word Histogram. What changes?
- Click on the button to the right of the slider to bring in another window with more options. Then, click the box next to Set Classes Manually and set the Width to 5. What does this do to the histogram?
- Click the word Histogram and look at a box plot and dot plot of the data. When looking at the box plot, notice there is an x on the right side of box plot. This represents a data point that is considered an outlier. Click on the button to the right of the slider and uncheck the box labeled Show Outliers to include this point in the box plot. What changes? Why might you want to show outliers? Why might you want to include or exclude outliers?
The purpose of this discussion is for students to create data displays using technology and to analyze what happens to the displays and the statistics when changes are made to the data set. Here are some questions for discussion.
- What happened to the statistics when you changed the value for A1 to 8 in the spreadsheet?” (When it was changed to 8, the mean increased slightly but the median stayed the same.)
- “Why did the mean increase?” (The sum of the data increased but the number of numbers stayed the same so the mean had to increase.)
- “Why did the median stay the same?” (Changing a 7 to an 8 in the data set did not change the middle numbers, 8 and 9, in the data set).
- “What did you notice when you changed the width of the classes for the histogram?” (This changed the intervals for each bar to a width of 5 and the data was resorted into those intervals.)
Select students who were previously identified as discussing the relationship between outliers and the measures of center. Ask, “what is the relationship between outliers and the measures of center?” (When outliers are present the median is the preferred measure of center because it is less impacted by outliers than the mean.)

9.3: Making Digital Displays (10 minutes)
- MLR2: Collect and Display
The mathematical purpose of this activity is for students to create data displays and calculate statistics using technology. Students plot the survey data they collected from a statistical question in a previous lesson.
Arrange students in groups of two. Tell them that they will be using technology to create data displays and calculate statistics for data they collected from a survey question in a previous lesson.
Use the data you collected from the numerical, statistical question from a previous lesson. Use technology to create a dot plot, boxplot, and histogram for your data. Then find the mean, median, and interquartile range for the data.
Are you ready for more?
A stem and leaf plot is a table where each data point is indicated by writing the first digit(s) on the left (the stem) and the last digit(s) on the right (the leaves). Each stem is written only once and shared by all data points with the same first digit(s). For example, the values 31, 32, and 45 might be represented like:
\(\displaystyle \begin{array}{r|l l} 3 & 1 & 2\\ 4 & 5 \end{array}\) Key: 3 | 1 means 31
A class took an exam and earned the scores:
86, 73, 85, 86, 72, 94, 88, 98, 87, 86, 85, 93, 75, 64, 82, 95, 99, 76, 84, 68
Use technology to create a stem and leaf plot for this data set.
How can we see the shape of the distribution from this plot?
What information can we see from a stem and leaf plot that we cannot see from a histogram?
What do we have more control of in a histogram than in a stem and leaf plot?
Anticipated Misconceptions
Students may lose one data display when they begin to create the next one. Explain to students that it is important to copy their solutions into a more permanent place so they can refer to it later.
The goal of this activity was for students to create graphs and find statistics using technology. Here are some questions for discussion.
- “What were some challenges that you faced using technology and how did you overcome them?” (I was not sure what buttons to press to get to the spreadsheet. I checked with my partner and figured it out.)
- “What width did you use for your histogram? Why?” (I used 5 because my data set has values ranging from 1 to 42. I could have used 10 but then I would have only had 5 bars.)
- “What is the appropriate measure of center for your data set?” (The median was appropriate because my data set has a skewed distribution.)
- “Which display allows you to calculate the IQR the most easily?” (The box plot because it displays Q1 and Q3.)
- “Can you find the median using your histogram?” (No, the data is grouped into intervals, so a histogram cannot be used to find the middle value for the median.)
Lesson Synthesis
The goal of this lesson is for students to display and investigate data using technology. Here are some questions for discussion.
- “How do you create data displays using technology?” (You type the data into the spreadsheet and then click the appropriate buttons.)
- “What are some advantages of using technology to display data and calculate statistics?” (You can easily switch between different data displays and you can change the intervals on histograms without having to sort through the data again. The advantage of having the technology calculate the statistics is that I can see how the statistics change as I enter or make changes to the data.)
- “When do you think it is appropriate to use technology to display data or to calculate statistics?” (Graphing technology makes it easier to determine the shape of a distribution. I might use it to determine the most appropriate measure of center for a data set. Using technology to calculate statistics makes sense to do in most situations because statistics are calculated using algorithms that can get complicated when there are many values in the data set. The chance of making a mistake while calculating statistics by hand makes using technology a good choice.)
9.4: Cool-down - What Are These Values? (5 minutes)
Student lesson summary.
Data displays (like histograms or box plots) are very useful for quickly understanding a large amount of information, but often take a long time to construct accurately using pencil and paper. Technology can help create these displays as well as calculate useful statistics much faster than doing the same tasks by hand. Especially with very large data sets (in some experiments, millions of pieces of data are collected), technology is essential for putting the information into forms that are more easily understood.
A statistic is a quantity that is calculated from sample data as a measure of a distribution. Mean and median are examples of statistics that are measures of center. Mean absolute deviation (MAD) and interquartile range (IQR) are examples of statistics that are measures of variability. Although the interpretation must still be done by people, using the tools available can improve the accuracy and speed of doing computations and creating graphs.
Go Math Interactive Mimio Lesson 1.9 Problem Solving Multiplication and Division

- Mimio Ink File
Description
Questions & answers, cool corner.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
A: ( 5 , 1 ) ( 5 , 1 ) B: ( −2 , 4 ) ( −2 , 4 ) C: ( −5 , −1 ) ( −5 , −1 ) D: ( 3 , −2 ) ( 3 , −2 ) E: ( 0 , −5 ) ( 0 , −5 ) F: ( 4 , 0 ) ( 4 , 0 )
A: ( 4 , 2 ) ( 4 , 2 ) B: ( −2 , 3 ) ( −2 , 3 ) C: ( −4 , −4 ) ( −4 , −4 ) D: ( 3 , −5 ) ( 3 , −5 ) E: ( −3 , 0 ) ( −3 , 0 ) F: ( 0 , 2 ) ( 0 , 2 )
Answers will vary.
ⓐ yes, yes ⓑ yes, yes
ⓐ no, no ⓑ yes, yes
x - intercept: ( 2 , 0 ) ( 2 , 0 ) ; y - intercept: ( 0 , −2 ) ( 0 , −2 )
x - intercept: ( 3 , 0 ) ( 3 , 0 ) , y - intercept: ( 0 , 2 ) ( 0 , 2 )
x - intercept: ( 4 , 0 ) ( 4 , 0 ) , y - intercept: ( 0 , 12 ) ( 0 , 12 )
x - intercept: ( 8 , 0 ) ( 8 , 0 ) , y - intercept: ( 0 , 2 ) ( 0 , 2 )
x - intercept: ( 4 , 0 ) ( 4 , 0 ) , y - intercept: ( 0 , −3 ) ( 0 , −3 )
x - intercept: ( 4 , 0 ) ( 4 , 0 ) , y - intercept: ( 0 , −2 ) ( 0 , −2 )
− 2 3 − 2 3
− 4 3 − 4 3
− 3 5 − 3 5
− 1 36 − 1 36
− 1 48 − 1 48
slope m = 2 3 m = 2 3 and y -intercept ( 0 , −1 ) ( 0 , −1 )
slope m = 1 2 m = 1 2 and y -intercept ( 0 , 3 ) ( 0 , 3 )
2 5 ; ( 0 , −1 ) 2 5 ; ( 0 , −1 )
− 4 3 ; ( 0 , 1 ) − 4 3 ; ( 0 , 1 )
− 1 4 ; ( 0 , 2 ) − 1 4 ; ( 0 , 2 )
− 3 2 ; ( 0 , 6 ) − 3 2 ; ( 0 , 6 )
ⓐ intercepts ⓑ horizontal line ⓒ slope–intercept ⓓ vertical line
ⓐ vertical line ⓑ slope–intercept ⓒ horizontal line ⓓ intercepts
- ⓐ 50 inches
- ⓑ 66 inches
- ⓒ The slope, 2, means that the height, h , increases by 2 inches when the shoe size, s , increases by 1. The h -intercept means that when the shoe size is 0, the height is 50 inches.
- ⓐ 40 degrees
- ⓑ 65 degrees
- ⓒ The slope, 1 4 1 4 , means that the temperature Fahrenheit ( F ) increases 1 degree when the number of chirps, n , increases by 4. The T -intercept means that when the number of chirps is 0, the temperature is 40 ° 40 ° .
- ⓒ The slope, 0.5, means that the weekly cost, C , increases by $0.50 when the number of miles driven, n, increases by 1. The C -intercept means that when the number of miles driven is 0, the weekly cost is $60
- ⓒ The slope, 1.8, means that the weekly cost, C, increases by $1.80 when the number of invitations, n , increases by 1.80. The C -intercept means that when the number of invitations is 0, the weekly cost is $35.;
not parallel; same line
perpendicular
not perpendicular
y = 2 5 x + 4 y = 2 5 x + 4
y = − x − 3 y = − x − 3
y = 3 5 x + 1 y = 3 5 x + 1
y = 4 3 x − 5 y = 4 3 x − 5
y = 5 6 x − 2 y = 5 6 x − 2
y = 2 3 x − 4 y = 2 3 x − 4
y = − 2 5 x − 1 y = − 2 5 x − 1
y = − 3 4 x − 4 y = − 3 4 x − 4
y = 8 y = 8
y = 4 y = 4
y = 5 2 x − 13 2 y = 5 2 x − 13 2
y = − 2 5 x + 22 5 y = − 2 5 x + 22 5
y = 1 3 x − 10 3 y = 1 3 x − 10 3
y = − 2 5 x − 23 5 y = − 2 5 x − 23 5
x = 5 x = 5
x = −4 x = −4
y = 3 x − 10 y = 3 x − 10
y = 1 2 x + 1 y = 1 2 x + 1
y = − 1 3 x + 10 3 y = − 1 3 x + 10 3
y = −2 x + 16 y = −2 x + 16
y = −5 y = −5
y = −1 y = −1
x = −5 x = −5
ⓐ yes ⓑ yes ⓒ yes ⓓ yes ⓔ no
ⓐ yes ⓑ yes ⓒ no ⓓ no ⓔ yes
y ≥ −2 x + 3 y ≥ −2 x + 3
y < 1 2 x − 4 y < 1 2 x − 4
x − 4 y ≤ 8 x − 4 y ≤ 8
3 x − y ≤ 6 3 x − y ≤ 6
Section 4.1 Exercises
A: ( −4 , 1 ) ( −4 , 1 ) B: ( −3 , −4 ) ( −3 , −4 ) C: ( 1 , −3 ) ( 1 , −3 ) D: ( 4 , 3 ) ( 4 , 3 )
A: ( 0 , −2 ) ( 0 , −2 ) B: ( −2 , 0 ) ( −2 , 0 ) C: ( 0 , 5 ) ( 0 , 5 ) D: ( 5 , 0 ) ( 5 , 0 )
ⓑ Age and weight are only positive.
Section 4.2 Exercises
ⓐ yes; no ⓑ no; no ⓒ yes; yes ⓓ yes; yes
ⓐ yes; yes ⓑ yes; yes ⓒ yes; yes ⓓ no; no
$722, $850, $978
Section 4.3 Exercises
( 3 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 3 ) ( 3 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 3 )
( 5 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −5 ) ( 5 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −5 )
( −2 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −2 ) ( −2 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −2 )
( −1 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 1 ) ( −1 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 1 )
( 6 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 3 ) ( 6 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 3 )
( 0 , 0 ) ( 0 , 0 )
( 4 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 4 ) ( 4 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 4 )
( −3 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 3 ) ( −3 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 3 )
( 8 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 4 ) ( 8 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 4 )
( 2 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 6 ) ( 2 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 6 )
( 12 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −4 ) ( 12 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −4 )
( 2 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −8 ) ( 2 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −8 )
( 5 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 2 ) ( 5 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 2 )
( 4 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −6 ) ( 4 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −6 )
( 3 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 1 ) ( 3 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 1 )
( −10 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 2 ) ( −10 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 2 )
ⓐ ( 0 , 1000 ) , ( 15 , 0 ) ( 0 , 1000 ) , ( 15 , 0 ) ⓑ At ( 0 , 1000 ) ( 0 , 1000 ) , he has been gone 0 hours and has 1000 miles left. At ( 15 , 0 ) ( 15 , 0 ) , he has been gone 15 hours and has 0 miles left to go.
Section 4.4 Exercises
−3 2 = − 3 2 −3 2 = − 3 2
− 1 3 − 1 3
− 3 4 − 3 4
− 5 2 − 5 2
− 8 7 − 8 7
ⓐ 1 3 1 3 ⓑ 4 12 pitch or 4-in-12 pitch
3 50 3 50 ; rise = 3, run = 50
ⓐ 288 inches (24 feet) ⓑ Models will vary.
When the slope is a positive number the line goes up from left to right. When the slope is a negative number the line goes down from left to right.
A vertical line has 0 run and since division by 0 is undefined the slope is undefined.
Section 4.5 Exercises
slope m = 4 m = 4 and y -intercept ( 0 , −2 ) ( 0 , −2 )
slope m = −3 m = −3 and y -intercept ( 0 , 1 ) ( 0 , 1 )
slope m = − 2 5 m = − 2 5 and y -intercept ( 0 , 3 ) ( 0 , 3 )
−9 ; ( 0 , 7 ) −9 ; ( 0 , 7 )
4 ; ( 0 , −10 ) 4 ; ( 0 , −10 )
−4 ; ( 0 , 8 ) −4 ; ( 0 , 8 )
− 8 3 ; ( 0 , 4 ) − 8 3 ; ( 0 , 4 )
7 3 ; ( 0 , −3 ) 7 3 ; ( 0 , −3 )
horizontal line
vertical line
slope–intercept
- ⓒ The slope, 2.54, means that Randy’s payment, P , increases by $2.54 when the number of units of water he used, w, increases by 1. The P –intercept means that if the number units of water Randy used was 0, the payment would be $28.
- ⓒ The slope, 0.32, means that the cost, C , increases by $0.32 when the number of miles driven, m, increases by 1. The C -intercept means that if Janelle drives 0 miles one day, the cost would be $15.
- ⓒ The slope, 0.09, means that Patel’s salary, S , increases by $0.09 for every $1 increase in his sales. The S -intercept means that when his sales are $0, his salary is $750.
- ⓒ The slope, 42, means that the cost, C , increases by $42 for when the number of guests increases by 1. The C -intercept means that when the number of guests is 0, the cost would be $750.
not parallel
- ⓐ For every increase of one degree Fahrenheit, the number of chirps increases by four.
- ⓑ There would be −160 −160 chirps when the Fahrenheit temperature is 0 ° 0 ° . (Notice that this does not make sense; this model cannot be used for all possible temperatures.)
Section 4.6 Exercises
y = 4 x + 1 y = 4 x + 1
y = 8 x − 6 y = 8 x − 6
y = − x + 7 y = − x + 7
y = −3 x − 1 y = −3 x − 1
y = 1 5 x − 5 y = 1 5 x − 5
y = − 2 3 x − 3 y = − 2 3 x − 3
y = 2 y = 2
y = −4 x y = −4 x
y = −2 x + 4 y = −2 x + 4
y = 3 4 x + 2 y = 3 4 x + 2
y = − 3 2 x − 1 y = − 3 2 x − 1
y = 6 y = 6
y = 3 8 x − 1 y = 3 8 x − 1
y = 5 6 x + 2 y = 5 6 x + 2
y = − 3 5 x + 1 y = − 3 5 x + 1
y = − 1 3 x − 11 y = − 1 3 x − 11
y = −7 y = −7
y = − 5 2 x − 22 y = − 5 2 x − 22
y = −4 x − 11 y = −4 x − 11
y = −8 y = −8
y = −4 x + 13 y = −4 x + 13
y = x + 5 y = x + 5
y = − 1 3 x − 14 3 y = − 1 3 x − 14 3
y = 7 x + 22 y = 7 x + 22
y = − 6 7 x + 4 7 y = − 6 7 x + 4 7
y = 1 5 x − 2 y = 1 5 x − 2
x = 4 x = 4
x = −2 x = −2
y = −3 y = −3
y = 4 x y = 4 x
y = 1 2 x + 3 2 y = 1 2 x + 3 2
y = 5 y = 5
y = 3 x − 1 y = 3 x − 1
y = −3 x + 3 y = −3 x + 3
y = 2 x − 6 y = 2 x − 6
y = − 2 3 x + 5 y = − 2 3 x + 5
x = −3 x = −3
y = −4 y = −4
y = x y = x
y = − 3 4 x − 1 4 y = − 3 4 x − 1 4
y = 5 4 x y = 5 4 x
y = 1 y = 1
y = x + 2 y = x + 2
y = 3 4 x y = 3 4 x
y = 1.2 x + 5.2 y = 1.2 x + 5.2
Section 4.7 Exercises
ⓐ yes ⓑ no ⓒ no ⓓ yes ⓔ no
ⓐ yes ⓑ no ⓒ no ⓓ yes ⓔ yes
ⓐ no ⓑ no ⓒ no ⓓ yes ⓔ yes
y < 2 x − 4 y < 2 x − 4
y ≤ − 1 3 x − 2 y ≤ − 1 3 x − 2
x + y ≥ 3 x + y ≥ 3
x + 2 y ≥ −2 x + 2 y ≥ −2
2 x − y < 4 2 x − y < 4
4 x − 3 y > 12 4 x − 3 y > 12
- ⓑ Answers will vary.
Review Exercises
ⓐ ( 2 , 0 ) ( 2 , 0 ) ⓑ ( 0 , −5 ) ( 0 , −5 ) ⓒ ( −4.0 ) ( −4.0 ) ⓓ ( 0 , 3 ) ( 0 , 3 )
ⓐ yes; yes ⓑ yes; no
( 6 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 4 ) ( 6 , 0 ) , ( 0 , 4 )
− 1 2 − 1 2
slope m = − 2 3 m = − 2 3 and y -intercept ( 0 , 4 ) ( 0 , 4 )
5 3 ; ( 0 , −6 ) 5 3 ; ( 0 , −6 )
4 5 ; ( 0 , − 8 5 ) 4 5 ; ( 0 , − 8 5 )
plotting points
ⓐ −$250 ⓑ $450 ⓒ The slope, 35, means that Marjorie’s weekly profit, P , increases by $35 for each additional student lesson she teaches. The P –intercept means that when the number of lessons is 0, Marjorie loses $250. ⓓ
y = −5 x − 3 y = −5 x − 3
y = −2 x y = −2 x
y = −3 x + 5 y = −3 x + 5
y = 3 5 x y = 3 5 x
y = −2 x − 5 y = −2 x − 5
y = 1 2 x − 5 2 y = 1 2 x − 5 2
y = − 2 5 x + 8 y = − 2 5 x + 8
y = 3 y = 3
y = − 3 2 x − 6 y = − 3 2 x − 6
ⓐ yes ⓑ no ⓒ yes ⓓ yes ⓔ no
y > 2 3 x − 3 y > 2 3 x − 3
x − 2 y ≥ 6 x − 2 y ≥ 6
Practice Test
ⓐ yes ⓑ yes ⓒ no
( 3 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −4 ) ( 3 , 0 ) , ( 0 , −4 )
y = − 3 4 x − 2 y = − 3 4 x − 2
y = 1 2 x − 4 y = 1 2 x − 4
y = − 4 5 x − 5 y = − 4 5 x − 5
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/elementary-algebra/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Elementary Algebra
- Publication date: Feb 22, 2017
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/elementary-algebra/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/elementary-algebra/pages/chapter-4
© Feb 9, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Fun teaching resources & tips to help you teach math with confidence

Math Strategies: Problem Solving by Working Backwards
As I’ve shared before, there are many different ways to go about solving a math problem, and equipping kids to be successful problem solvers is just as important as teaching computation and algorithms . In my experience, students’ frustration often comes from not knowing where to start. Providing them with strategies enables them to at least get the ideas flowing and hopefully get some things down on paper. As in all areas of life, the hardest part is getting started! Today I want to explain how to teach problem solving by working backwards .

* Please Note : This post contains affiliate links which help support the work of this site. Read our full disclosure here .*
–>Pssst! Do your kids need help making sense of and solving word problems? You might like this set of editable word problem solving templates ! Use these with any grade level, for any type of word problem :
Solve a Math Problem by Working Backwards:
Before students can learn to recognize when this is a helpful strategy, they must understand what it means. Working backwards is to start with the final solution and work back one step at a time to get to the beginning.
It may also be helpful for students to understand that this is useful in many aspects of life, not just solving math problems.
To help show your students what this looks like, you might start by thinking about directions. Write out some basic directions from home to school:
- Start: Home
- Turn right on Gray St.
- Turn left on Sycamore Ln.
- Turn left on Rose Dr.
- Turn right on Schoolhouse Rd.
- End: School
Ask students to then use this information to give directions from the school back home . Depending on the age of your students, you may even want to draw a map so they can see clearly that they have to do the opposite as they make their way back home from school. In other words, they need to “undo” each turn to get back, i.e. turn left on Schoolhouse Rd. and then right on Rose Dr. etc.
In math, these are called inverse operations . When using the “work backwards” strategy, each operation must be reversed to get back to the beginning. So if working forwards requires addition, when students work backwards they will need to subtract. And if they multiply working forwards, they must divide when working backwards.
Once students understand inverse operations , and know that they must start with the solution and work back to the beginning, they will need to learn to recognize the types of problems that require working backwards.
In general, problems that list a series of events or a sequence of steps can be solved by working backwards.
Here’s an example:
Sam’s mom left a plate of cookies on the counter. Sam ate 2 of them, his dad ate 3 of them and they gave 12 to the neighbor. At the end of the day, only 4 cookies were left on the plate. How many cookies did she make altogether?
In this case, we know that the final cookie amount is 4. So if we work backwards to “put back” all the cookies that were taken or eaten, we can figure out what number they started with.
Because cookies are being taken away, that denotes subtraction. Thus, to get back to the original number we have to do the opposite: add . If you take the 4 that are left and add the 12 given to the neighbors, and add the 3 that Dad ate, and then add the 2 that Sam ate, we find that Sam’s mom made 21 cookies .
You may want to give students a few similar problems to let them see when working backwards is useful, and what problems look like that require working backwards to solve.
Have you taught or discussed problem solving by working backwards with your students? What are some other examples of when this might be useful or necessary?
Don’t miss the other useful articles in this Problem Solving Series:
- Problem Solve by Drawing a Picture
- Problem Solve by Solving an Easier Problem
- Problem Solve with Guess & Check
- Problem Solve by Finding a Pattern
- Problem Solve by Making a List

So glad to have come across this post! Today, word problems were the cause of a homework meltdown. At least tomorrow I’ll have a different strategy to try! #ThoughtfulSpot
I’m so glad to hear that! I hope you found some useful ideas!! Homework meltdowns are never fun!! Best of luck!
This is really a great help! We have just started using this method for some of my sons math problems and it helps loads. Thanks so much for sharing on the Let Kids Be Kids Linkup!
That’s great Erin! I hope this is a helpful method and makes things easier for your son! 🙂
I’ve not used this method before but sounds like a good resource to teach. Thanks for linking #LetKidsBeKids
I hope this proves to be helpful for you!
- Pingback: 6th Grade Week 11: Monks, Mosques, and Minecraft • The Sunny Patch
Comments are closed.
Similar Posts

July Math Problem of the Day Calendar

The Great Debate: The Role of Calculators in Math Education

Simple Yet Powerful Math Number Sense Routine: Close, Far, In-Between

Adding & Subtracting Decimals Partner Challenge {FREE!}

{FREE} Number Talk Planning Pages

September Problem of the Day Calendar
Find more resources to help make math engaging, join 165k+ parents & teachers.
Who learn new tips and strategies, as well as receive engaging resources to make math fun!

- Privacy Policy
Solver Title
Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Expanded Form Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
Number line.
- x^{2}-x-6=0
- -x+3\gt 2x+1
- line\:(1,\:2),\:(3,\:1)
- prove\:\tan^2(x)-\sin^2(x)=\tan^2(x)\sin^2(x)
- \frac{d}{dx}(\frac{3x+9}{2-x})
- (\sin^2(\theta))'
- \lim _{x\to 0}(x\ln (x))
- \int e^x\cos (x)dx
- \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx
- \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n}
- Is there a step by step calculator for math?
- Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of math problems, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and linear algebra. It shows you the solution, graph, detailed steps and explanations for each problem.
- Is there a step by step calculator for physics?
- Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of physics problems, including mechanics, electricity and magnetism, and thermodynamics. It shows you the steps and explanations for each problem, so you can learn as you go.
- How to solve math problems step-by-step?
- To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem.
- My Notebook, the Symbolab way Math notebooks have been around for hundreds of years. You write down problems, solutions and notes to go back...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
- AP Calculus
- AP Statistics
- Independent Study
Online Math Class
Mr. Math Blog
Thanks for your donation! Every little bit helps me help you! :-)
Problem Solving - Organize Data - Lesson 2.1
Use Picture Graphs - Lesson 2.2
Make Picture Graphs - Lesson 2.3
Use Bar Graphs - Lesson 2.4
Make a Bar Graph - Lesson 2.5
Solve Problems Using Data - Lesson 2.6
Use and Make Line Plots - Lesson 2.7
Number Patterns - Lesson 1.1
Round to Nearest Ten or Hundred - Lesson 1.2
Estimate Sums - Lesson 1.3
Mental Math Strategies for Addition - Lesson 1.4
Use Properties to Add - Lesson 1.5
Use the Break Apart Strategy to Add - Lesson 1.6
Use Place Value to Add - Lesson 1.7
Estimate Differences - Lesson 1.8
Mental Math Strategies for Subtraction - Lesson 1.9
Use Place Value to Subtract - Lesson 1.10
Combine Place Values to Subtract - Lesson 1.11
Describe Plane Shapes - Lesson 12.1
Describe Angles in Plane Shapes - Lesson 12.2
Identify Polygons - Lesson 12.3
Describe Sides of Polygons - Lesson 12.4
Classify Quadrilaterals - Lesson 12.5
Draw Quadrilaterals - Lesson 12.6
Describe Triangles - Lesson 12.7
Chapter 12 Performance Task Review For Test
Problem Solving - Compare Fractions - Lesson 9.1
Compare Fractions with the Same Denominator - Lesson 9.2
Compare Fractions with the Same Numerator - Lesson 9.3
Compare Fractions - Lesson 9.4
Compare and Order Fractions - Lesson 9.5
Model Equivalent Fractions - Lesson 9.6
Equivalent Fractions - Lesson 9.7
Divide by 2 - Lesson 7.1
Divide by 10 - Lesson 7.2
Divide by 5 - Lesson 7.3
Divide by 3 - Lesson 7.4
Divide by 4 - Lesson 7.5
Divide by 5 - Lesson 7.6
Mid-Chapter 7 Checkpoint on Division Facts and Strategies
Divide by 7 - Lesson 7.7
Divide by 8 - Lesson 7.8
Divide by 9 - Lesson 7.9
Problem Solving - Two-Step Problems - Lesson 7.10
Order of Operations - Lesson 7.11
Problem Solving - Model Division - Lesson 6.1
Size of Equal Groups - Lesson 6.2
Number of Equal Groups - Lesson 6.3
Model (Division) with Bar Model - Lesson 6.4
Relate Subtraction and Division - Lesson 6.5
Mid-Chapter 6 Checkpoint
Model (division) with Arrays - Lesson 6.6
Relate Multiplication and Division - Lesson 6.7
Write Related Facts - Lesson 6.8
Division Rules for 1 and 0 - Lesson 6.9
Chapter 6 Review for Test - Understanding Division
Multiply with 2 and 4 - Lesson 4.1
Multiply with 5 and 10 - Lesson 4.2
Multiply with 3 and 6 - Lesson 4.3
Distributive Property - Lesson 4.4
Multiply with 7 - Lesson 4.5
Associative Property of Multiplication - Lesson 4.6
Patterns on the Multiplication Table - Lesson 4.7
Multiply with 8 - Lesson 4.8
Multiply with 9 - Lesson 4.9
Review For Test on Chapter 4
Describe Patterns - Lesson 5.1
Find Unknown Factors - Lesson 5.2
Problem Solving: Using the Distributive Property - Lesson 5.3
Multiplication Strategies with Multiples of 10 - Lesson 5.4
Multiply Multiples of 10 by 1-Digit Numbers - Lesson 5.5
Chapter 5 Review on Multiplication Facts
Third Grade
Math
- Second Grade Math
- Third Grade Math
- Fourth Grade Math
- Fifth Grade Math
- Sixth Grade Math
- Sixth Grade Math (CA)
- Seventh Grade Math (CA)
- Eighth Grade Math (CA)
- Integrated Math 1
- Integrated Math 2
- Integrated Math 3
- PreCalculus
- AP Statistics Exam Prep
- Elementary Statistics
- ELM Practice
- Percents and Decimals
- Sixth Grade Math (Big Ideas)
Model Perimeter - Lesson 11.1
Find Perimeter - Lesson 11.2
Find Unknown Side Lengths - Lesson 11.3
Understanding Area - Lesson 11.4
Measure Area - Lesson 11.5
Use Area Models - Lesson 11.6
Problem Solving - Area of Rectangles - Lesson 11.7
Area of Combined Rectangles - Lesson 11.8
Same Perimeter - Different Area - Lesson 11.9
Same Area - Different Perimeter - Lesson 11.10
Chapter 11 Review for Test on Perimeter and Area
Please Donate, if you're a regular!
The donate link is below. Thanks so much!!
Count Equal Groups - Lesson 3.1
Relate Addition and Multiplication - Lesson 3.2
Skip Count on a Number Line - Lesson 3.3
Problem Solving - Model Multiplication - Lesson 3.4
Model with Arrays - Lesson 3.5
Commutative Property of Multiplication - Lesson 3.6
Multiply with 1 and 0 - Lesson 3.7
Time to the Minute - Lesson 10.1
A.M. and P.M. - Lesson 10.2
Measure Time Intervals - Lesson 10.3
Use Time Intervals - Lesson 10.4
Problem Solving - Time Intervals - Lesson 10.5
Measure Length - Lesson 10.6
Estimate and Measure Liquid Volume - Lesson 10.7
Estimate and Measure Mass - Lesson 10.8
Equal Parts of a Whole - Lesson 8.1
Equal Shares - Lesson 8.2
Unit Fractions of a Whole - Lesson 8.3
Fractions of a Whole - Lesson 8.4
Fractions on a Number Line - Lesson 8.5
Relate Fractions and Whole Numbers - Lesson 8.6
Fractions of a Group - Lesson 8.7
Find Part of Group Using Unit Fractions - Lesson 8.8
Problem Solving: Find the Whole Using Unit Fractions - Lesson 8.9
Copyright 2013. All rights reserved.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this lesson we use counters as models to solve problems. We learn that 0 is none. We show how a five frame is empty for the number 0, and it's full for th...
Lesson: 9 Problem Solving • Understand 0. Lesson 1.9 Problem Solving • Understand 0 - Page(61-66) Problem Solving • Understand 0 Homework & Practice 1.9 - Page(65-66) ... Draw to show what you know about the number 1. 9. Draw to show what you know about the number 2. Tell a friend about your drawings.
1.9 Problem Solving: Understand 0 1.10 Count and Write 0 Chapter 1 Review/Test Performance Task Chapter 2 Compare Numbers to 5 2.1 Hands On: Same Number 2.2 Hands On: Greater Than 2.3 Hands On: Less Than Mid-Chapter Checkpoint 2.4 Problem Solving: Compare by Matching Sets to 5 2.5 Compare by Counting Sets to 5 Chapter 2 Review/Test Performance Task
This lesson uses the method "solving a simpler problem" to help us break down the big numbers with multiplication and division.
Use strategy "solve a simpler problem" to help solve a division problem
ounces. Then I can solve a simpler problem to __ that total by 9. Read the Problem Solve the Problem What do I need to find? I need to find _____ _____. • First, multiply to find the total number of ounces of dog food. 8 3 18 5 _ • To find the number of ounces each dog gets, I'll need to divide. 144 4 _ 5 n
Solve the new problem and show your work. Chapter 1 59 13 glasses 104 4 8 5 (40 1 64) 4 8 5 (40 4 8) 1 (64 4 8) 5 5 1 8, or 13 16 1 16 1 8 1 64 5 104 !uid ounces Practice and Homework COMMON CORE STANDARD—5.NBT.B.6 Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to hundredths. Lesson 1.9 _____
Warm-up. The mathematical purpose of this activity is to gain familiarity with entering data into a spreadsheet and to prepare students for finding statistics using technology. Launch. Arrange students in groups of 2. If students are using the digital version of the materials, show them how to open the GeoGebra spreadsheet app in the math tools.
Go Math Grade 5 Chapter 1 Lesson 9 Problem Solving Multiplication and Division. Includes all whole group components for the lesson. **Please note: This product is for Mimio boards and NOT for SmartBoards.**. Lesson is completely digital, no need to turn your back on your students to write on the board! Just hook up to your projector and teach!
PROBLEM SOLVING Lesson IA COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.NBT.6 Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to hundredths. 8) ... (Lesson 1.6) @ 36 @ 140 566 576 A sports arena covers 710,430 square feet of ground. A newspaper reported that the arena covers about 700,000 square
3.1 Use a Problem-Solving Strategy; 3.2 Solve Percent Applications; 3.3 Solve Mixture Applications; ... The h-intercept means that when the shoe size is 0, ... 35, means that Marjorie's weekly profit, P, increases by $35 for each additional student lesson she teaches.
Before students can learn to recognize when this is a helpful strategy, they must understand what it means. Working backwards is to start with the final solution and work back one step at a time to get to the beginning. It may also be helpful for students to understand that this is useful in many aspects of life, not just solving math problems.
The following properties are true whenever odd or even numbers are added or multiplied. Addition. The sum of two odd numbers is even. The sum of two even numbers is even. The sum of an odd and an even number is odd. Multiplication. The product of two odd numbers is odd. The product of two even numbers is even.
This Go Math video address the Essential Question: How can you use the strategy "solve a simpler problem" to help you solve a division problem? The Distribu...
Learn. Systems of equations with elimination: King's cupcakes. (Opens a modal) Systems of equations with elimination: x-4y=-18 & -x+3y=11. (Opens a modal) Systems of equations with elimination: potato chips. (Opens a modal) Systems of equations with elimination (and manipulation) (Opens a modal)
Our resource for enVisionmath 2.0: Grade 7 Volume 1 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to ...
Working backwards is a solving process that can be used on word problems by starting at the end of the problem and undoing the problem one step at a time. There are many different ways to solve ...
To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem.
Chapter 11 Review for Test on Perimeter and Area. Count Equal Groups - Lesson 3.1. Relate Addition and Multiplication - Lesson 3.2. Skip Count on a Number Line - Lesson 3.3. Problem Solving - Model Multiplication - Lesson 3.4. Model with Arrays - Lesson 3.5. Commutative Property of Multiplication - Lesson 3.6. Multiply with 1 and 0 - Lesson 3.7.
Our resource for enVisionmath 2.0: Grade 8, Volume 1 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers ...
PROBLEM SOLVING Lesson 2.q COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.NBT.6 Perform operations with multi-digit whole work. numbers and with decimals to hundredths. 208 baseball cards 16 16 ... (0 49 55 Spiral Review (CC.5.NBT.5, CC.5.NBT6, CC.5.NF.3) 3. Jeanine is twice as old as her brother Marc.
to adapt and respond flexibly in problem -solving and decision-making. The third barrier to improving reasoning lies in the inherent complexity of many of the problems humans must solve. The real-world presents us with many complicated problems that prove challenging to solve in a reasonable amount of time and with limited resources.
This is the first of several lessons where students practice modeling sequences using different types of equations and then use their equations to understand different aspects of the sequence, translating between the situations and their representations (MP2). This isn't meant to be the full modeling cycle, but rather a focus on some practices that students must attend to while modeling (MP4 ...