- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- enVision Math
- EngageNY Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy


Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 6.6 Answer Key Fraction and Whole-Number Division
Refer to our Texas Go Math Grade 5 Answer Key Pdf to score good marks in the exams. Test yourself by practicing the problems from Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 6.6 Answer Key Fraction and Whole-Number Division.
Unlock the Problem
Three friends share a \(\frac{1}{4}\)-pound block of fudge equally. What fraction of a pound of fudge does each friend get?
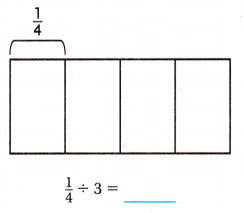
Brad has 9 pounds of ground turkey to make turkey burgers for a picnic. How many \(\frac{1}{3}\)-pound turkey burgers can he make?
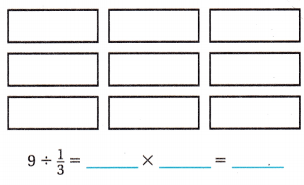
Math Talk Mathematical Processes
Will the number of turkey burgers be less than or greater than 9? Explain. Answer: The number of turkey burgers are greater than 9.
Share and Show
Problem Solving
Question 3. 5 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: 5 ÷ 1/3 = 5 x 3 = 15 Explanation: In the above division problem 5 ÷ 1/3 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 5 by 1/3 the result is 15. The result 15 is obtained by multiplying 5 with 3.
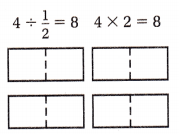
Question 4. 8 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) Answer: 8 ÷ 1/2 = 8 x 2 = 16 Explanation: In the above division problem 8 ÷ 1/2 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 8 by 1/2 the result is 16. The result 16 is obtained by multiplying 8 with 2.
Question 5. \(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 4 Answer: 1/7 ÷ 4 = 1/7 x 1/4 = 1/28 Explanation: In the above division problem 1/7 ÷ 4 we can observe that the fraction is divided by a whole number. Divide 1/7 by 4 the result is 1/28. The result 1/28 is obtained by multiplying 1/7 with 1/4.
Question 6. \(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 4 Answer: 1/3 ÷ 4 = 1/3 x 1/4 = 1/12 Explanation: In the above division problem 1/3 ÷ 4 we can observe that the fraction is divided by a whole number. Divide 1/3 by 4 the result is 1/12. The result 1/12 is obtained by multiplying 1/3 with 1/4.
Lesson 6.6 Answer Key 5th Grade Go Math Question 7. \(\frac{1}{4}\) ÷ 12 Answer: 1/4 ÷ 12 = 1/4 x 1/12 = 1/48 Explanation: In the above division problem 1/4 ÷ 12 we can observe that the fraction is divided by a whole number. Divide 1/4 by 12 the result is 1/48. The result 1/48 is obtained by multiplying 1/4 with 1/12.
Question 8. 6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) Answer: 6 ÷ 1/5 = 6 x 5 = 30 Explanation: In the above division problem 6 ÷ 1/5 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 6 by 1/5 the result is 30. The result 30 is obtained by multiplying 6 with 5.
a. What do you need to find? Answer:
b. What operations will you use to solve the problem? Answer:
c. Show the steps you used to solve the problem. Answer:
d. Complete the sentences. A three-toed sloth would travel 10 feet in __________ seconds. A giant tortoise would travel 10 feet in __________ seconds. Since _______ – _________ = _________. it would take a three-toed sloth _________ seconds longer to travel 10 feet. Answer:
e. Fill in the bubble for the correct answer choice. Answer:
Go Math Lesson 6.6 Answer Key 5th Grade Question 12. Robert divides 8 cups of almonds into \(\frac{1}{8}\)-cup servings. How many servings does he have? Answer: 8 ÷ 1/8 = 8 x 8 = 64 He have 64 servings. Explanation: Robert divides 8 cups of almonds into 1/8-cup servings. In this division problem 8 ÷ 1/8 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 8 by 1/8 the result is 64. The result 64 is obtained by multiplying 8 with 8. So, Robert have 64 servings.
Daily Assessment Task
Fill In the bubble completely to show your answer.
Question 13. Your friend asks you to watch his iguana. He gives you 1/3 pound of food for 4 days. He tells you if you feed the iguana the same amount each day, you will have no food left over. How much food should you feed the iguana each day? (A) \(\frac{1}{7}\) pound (B) 7 pounds (C) 12 pounds (D) \(\frac{1}{12}\) pound Answer:

Texas Test Prep

Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 6.6 Homework and Practice Answer Key
Question 1. 6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: 6 ÷ 1/3 = 6 x 3 = 18 Explanation: In the above division problem 6 ÷ 1/3 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 6 by 1/3 the result is 18. The result 18 is obtained by multiplying 6 with 3.
Question 2. 4 ÷ \(\frac{1}{8}\) Answer: 4 ÷ 1/8 = 4 x 8 = 32 Explanation: In the above division problem 4 ÷ 1/8 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 4 by 1/8 the result is 32. The result 32 is obtained by multiplying 4 with 8.
Question 3. \(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 9 Answer: 1/3 ÷ 9 = 1/3 x 1/9 = 1/27 Explanation: In the above division problem 1/3 ÷ 9 we can observe that the fraction is divided by a whole number. Divide 1/3 by 9 the result is 1/27. The result 1/27 is obtained by multiplying 1/3 with 1/9.
Go Math 5th Grade Practice and Homework Lesson 6.6 Answer Key Question 4. 7 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) Answer: 7 ÷ 1/2 = 7 x 2 = 14 Explanation: In the above division problem 7 ÷ 1/2 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 7 by 1/2 the result is 14. The result 14 is obtained by multiplying 7 with 2.
Question 5. 8 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: 8 ÷ 1/3 = 8 x 3 = 24 Explanation: In the above division problem 8 ÷ 1/3 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 8 by 1/3 the result is 24. The result 24 is obtained by multiplying 8 with 3.
Question 6. \(\frac{1}{4}\) ÷ 4 Answer: 1/4 ÷ 4 = 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 Explanation: In the above division problem 1/4 ÷ 4 we can observe that the fraction is divided by a whole number. Divide 1/4 by 4 the result is 1/16. The result 1/16 is obtained by multiplying 1/4 with 1/4.
Question 7. 9 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) Answer: 9 ÷ 1/4 = 9 x 4 = 36 Explanation: In the above division problem 9 ÷ 1/4 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 9 by 1/4 the result is 36. The result 36 is obtained by multiplying 9 with 4.
Question 8. \(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 2 Answer: 1/7 ÷ 2 = 1/7 x 1/2 = 1/14 Explanation: In the above division problem 1/7 ÷ 2 we can observe that the fraction is divided by a whole number. Divide 1/7 by 2 the result is 1/14. The result 1/14 is obtained by multiplying 1/7 with 1/2.
Go Math Lesson 6.6 Answer Key Homework 5th Grade Question 9. 10 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) Answer: 10 ÷ 1/5 = 10 x 5 = 50 Explanation: In the above division problem 10 ÷ 1/5 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 10 by 1/5 the result is 50. The result 50 is obtained by multiplying 10 with 5.
Question 10. 5 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) Answer: 5 ÷ 1/5 = 5 x 5 = 25 Explanation: In the above division problem 5 ÷ 1/5 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 5 by 1/5 the result is 25. The result 25 is obtained by multiplying 5 with 5.
Question 11. \(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 12 Answer: 1/5 ÷ 12 = 1/5 x 1/12 = 1/60 Explanation: In the above division problem 1/5 ÷ 12 we can observe that the fraction is divided by a whole number. Divide 1/5 by 12 the result is 1/60 The result 1/60 is obtained by multiplying 1/5 with 1/12.
Question 12. \(\frac{1}{9}\) ÷ 5 Answer: 1/9 ÷ 5 = 1/9 x 1/5 = 1/45 Explanation: In the above division problem 1/9 ÷ 5 we can observe that the fraction is divided by a whole number. Divide 1/9 by 5 the result is 1/45. The result 1/45 is obtained by multiplying 1/9 with 1/5.
Question 13. Cooks at a food booth at the state fair made an extra-large 8-foot long burrito. If they cut the burrito into \(\frac{1}{4}\)-foot servings, how many people will the extra-large burrito serve? Answer: 8 ÷ 1/4 = 8 x 4 = 32 The extra-large burrito is served by 32 people. Explanation: Cooks at a food booth at the state fair made an extra-large 8-foot long burrito. They cut the burrito into 1/4-foot servings. Divide 8 by 1/4 the result is 32. So, the extra-large burrito is served by 32 people.
Go Math 5th Grade Lesson 6.6 Homework Answer Key Question 14. A serving of the burrito contains \(\frac{1}{4}\) pound of meat. Franklin and two friends share his serving equally. How much meat does each friend get? Answer: 1/4 ÷ 3 = 1/12 Each friend get 1/12 meat. Explanation; A serving of the burrito contains 1/4 pound of meat. Franklin and two friends share his serving equally. Divide 1/4 by 3 the result is 1/12.
Lesson Check
Fill in the bubble completely to show your answer.

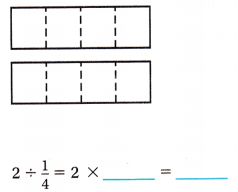
The number sentence is 2 ÷ 1/6 = 2 x 6 = 12 So, Option C is correct. Explanation: Divide 2 ÷ 1/6. Draw 2 rectangles and divide each rectangle into sixths. When we divide the 2 rectangles into sixths, we are finding the number of sixths in 2 rectangles or finding 2 groups of 6. There are 12 sixths. The problem 2 ÷ 1/6 represents the above model. So, draw a circle for option C.
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
6.6 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
Learning objectives.
In this section, you will:
- Use like bases to solve exponential equations.
- Use logarithms to solve exponential equations.
- Use the definition of a logarithm to solve logarithmic equations.
- Use the one-to-one property of logarithms to solve logarithmic equations.
- Solve applied problems involving exponential and logarithmic equations.
In 1859, an Australian landowner named Thomas Austin released 24 rabbits into the wild for hunting. Because Australia had few predators and ample food, the rabbit population exploded. In fewer than ten years, the rabbit population numbered in the millions.
Uncontrolled population growth, as in the wild rabbits in Australia, can be modeled with exponential functions. Equations resulting from those exponential functions can be solved to analyze and make predictions about exponential growth. In this section, we will learn techniques for solving exponential functions.
Using Like Bases to Solve Exponential Equations
The first technique involves two functions with like bases. Recall that the one-to-one property of exponential functions tells us that, for any real numbers b , b , S , S , and T , T , where b > 0 , b ≠ 1 , b > 0 , b ≠ 1 , b S = b T b S = b T if and only if S = T . S = T .
In other words, when an exponential equation has the same base on each side, the exponents must be equal. This also applies when the exponents are algebraic expressions. Therefore, we can solve many exponential equations by using the rules of exponents to rewrite each side as a power with the same base. Then, we use the fact that exponential functions are one-to-one to set the exponents equal to one another, and solve for the unknown.
For example, consider the equation 3 4 x − 7 = 3 2 x 3 . 3 4 x − 7 = 3 2 x 3 . To solve for x , x , we use the division property of exponents to rewrite the right side so that both sides have the common base, 3. 3. Then we apply the one-to-one property of exponents by setting the exponents equal to one another and solving for x x :
Using the One-to-One Property of Exponential Functions to Solve Exponential Equations
For any algebraic expressions S and T , S and T , and any positive real number b ≠ 1 , b ≠ 1 ,
Given an exponential equation with the form b S = b T , b S = b T , where S S and T T are algebraic expressions with an unknown, solve for the unknown.
- Use the rules of exponents to simplify, if necessary, so that the resulting equation has the form b S = b T . b S = b T .
- Use the one-to-one property to set the exponents equal.
- Solve the resulting equation, S = T , S = T , for the unknown.
Solving an Exponential Equation with a Common Base
Solve 2 x − 1 = 2 2 x − 4 . 2 x − 1 = 2 2 x − 4 .
Solve 5 2 x = 5 3 x + 2 . 5 2 x = 5 3 x + 2 .
Rewriting Equations So All Powers Have the Same Base
Sometimes the common base for an exponential equation is not explicitly shown. In these cases, we simply rewrite the terms in the equation as powers with a common base, and solve using the one-to-one property.
For example, consider the equation 256 = 4 x − 5 . 256 = 4 x − 5 . We can rewrite both sides of this equation as a power of 2. 2. Then we apply the rules of exponents, along with the one-to-one property, to solve for x : x :
Given an exponential equation with unlike bases, use the one-to-one property to solve it.
- Rewrite each side in the equation as a power with a common base.
Solving Equations by Rewriting Them to Have a Common Base
Solve 8 x + 2 = 16 x + 1 . 8 x + 2 = 16 x + 1 .
Solve 5 2 x = 25 3 x + 2 . 5 2 x = 25 3 x + 2 .
Solving Equations by Rewriting Roots with Fractional Exponents to Have a Common Base
Solve 2 5 x = 2 . 2 5 x = 2 .
Solve 5 x = 5 . 5 x = 5 .
Do all exponential equations have a solution? If not, how can we tell if there is a solution during the problem-solving process?
No. Recall that the range of an exponential function is always positive. While solving the equation, we may obtain an expression that is undefined.
Solving an Equation with Positive and Negative Powers
Solve 3 x + 1 = −2. 3 x + 1 = −2.
This equation has no solution. There is no real value of x x that will make the equation a true statement because any power of a positive number is positive.
Figure 2 shows that the two graphs do not cross so the left side is never equal to the right side. Thus the equation has no solution.
Solve 2 x = −100. 2 x = −100.
Solving Exponential Equations Using Logarithms
Sometimes the terms of an exponential equation cannot be rewritten with a common base. In these cases, we solve by taking the logarithm of each side. Recall, since log ( a ) = log ( b ) log ( a ) = log ( b ) is equivalent to a = b , a = b , we may apply logarithms with the same base on both sides of an exponential equation.
Given an exponential equation in which a common base cannot be found, solve for the unknown.
- If one of the terms in the equation has base 10, use the common logarithm.
- If none of the terms in the equation has base 10, use the natural logarithm.
- Use the rules of logarithms to solve for the unknown.
Solving an Equation Containing Powers of Different Bases
Solve 5 x + 2 = 4 x . 5 x + 2 = 4 x .
Solve 2 x = 3 x + 1 . 2 x = 3 x + 1 .
Is there any way to solve 2 x = 3 x ? 2 x = 3 x ?
Yes. The solution is 0. 0.
Equations Containing e
One common type of exponential equations are those with base e . e . This constant occurs again and again in nature, in mathematics, in science, in engineering, and in finance. When we have an equation with a base e e on either side, we can use the natural logarithm to solve it.
Given an equation of the form y = A e k t , y = A e k t , solve for t . t .
- Divide both sides of the equation by A . A .
- Apply the natural logarithm of both sides of the equation.
- Divide both sides of the equation by k . k .
Solve an Equation of the Form y = Ae kt
Solve 100 = 20 e 2 t . 100 = 20 e 2 t .
Using laws of logs, we can also write this answer in the form t = ln 5 . t = ln 5 . If we want a decimal approximation of the answer, we use a calculator.
Solve 3 e 0.5 t = 11. 3 e 0.5 t = 11.
Does every equation of the form y = A e k t y = A e k t have a solution?
No. There is a solution when k ≠ 0 , k ≠ 0 , and when y y and A A are either both 0 or neither 0, and they have the same sign. An example of an equation with this form that has no solution is 2 = −3 e t . 2 = −3 e t .
Solving an Equation That Can Be Simplified to the Form y = Ae kt
Solve 4 e 2 x + 5 = 12. 4 e 2 x + 5 = 12.
Solve 3 + e 2 t = 7 e 2 t . 3 + e 2 t = 7 e 2 t .
Extraneous Solutions
Sometimes the methods used to solve an equation introduce an extraneous solution , which is a solution that is correct algebraically but does not satisfy the conditions of the original equation. One such situation arises in solving when the logarithm is taken on both sides of the equation. In such cases, remember that the argument of the logarithm must be positive. If the number we are evaluating in a logarithm function is negative, there is no output.
Solving Exponential Functions in Quadratic Form
Solve e 2 x − e x = 56. e 2 x − e x = 56.
When we plan to use factoring to solve a problem, we always get zero on one side of the equation, because zero has the unique property that when a product is zero, one or both of the factors must be zero. We reject the equation e x = −7 e x = −7 because a positive number never equals a negative number. The solution ln ( −7 ) ln ( −7 ) is not a real number, and in the real number system this solution is rejected as an extraneous solution.
Solve e 2 x = e x + 2. e 2 x = e x + 2.
Does every logarithmic equation have a solution?
No. Keep in mind that we can only apply the logarithm to a positive number. Always check for extraneous solutions.
Using the Definition of a Logarithm to Solve Logarithmic Equations
We have already seen that every logarithmic equation log b ( x ) = y log b ( x ) = y is equivalent to the exponential equation b y = x . b y = x . We can use this fact, along with the rules of logarithms, to solve logarithmic equations where the argument is an algebraic expression.
For example, consider the equation log 2 ( 2 ) + log 2 ( 3 x − 5 ) = 3. log 2 ( 2 ) + log 2 ( 3 x − 5 ) = 3. To solve this equation, we can use rules of logarithms to rewrite the left side in compact form and then apply the definition of logs to solve for x : x :
For any algebraic expression S S and real numbers b b and c , c , where b > 0 , b ≠ 1 , b > 0 , b ≠ 1 ,
Using Algebra to Solve a Logarithmic Equation
Solve 2 ln x + 3 = 7. 2 ln x + 3 = 7.
Solve 6 + ln x = 10. 6 + ln x = 10.
Using Algebra Before and After Using the Definition of the Natural Logarithm
Solve 2 ln ( 6 x ) = 7. 2 ln ( 6 x ) = 7.
Solve 2 ln ( x + 1 ) = 10. 2 ln ( x + 1 ) = 10.

Using a Graph to Understand the Solution to a Logarithmic Equation
Solve ln x = 3. ln x = 3.
Figure 3 represents the graph of the equation. On the graph, the x -coordinate of the point at which the two graphs intersect is close to 20. In other words e 3 ≈ 20. e 3 ≈ 20. A calculator gives a better approximation: e 3 ≈ 20.0855. e 3 ≈ 20.0855.
Use a graphing calculator to estimate the approximate solution to the logarithmic equation 2 x = 1000 2 x = 1000 to 2 decimal places.
Using the One-to-One Property of Logarithms to Solve Logarithmic Equations
As with exponential equations, we can use the one-to-one property to solve logarithmic equations. The one-to-one property of logarithmic functions tells us that, for any real numbers x > 0 , x > 0 , S > 0 , S > 0 , T > 0 T > 0 and any positive real number b , b , where b ≠ 1 , b ≠ 1 ,
For example,
So, if x − 1 = 8 , x − 1 = 8 , then we can solve for x , x , and we get x = 9. x = 9. To check, we can substitute x = 9 x = 9 into the original equation: log 2 ( 9 − 1 ) = log 2 ( 8 ) = 3. log 2 ( 9 − 1 ) = log 2 ( 8 ) = 3. In other words, when a logarithmic equation has the same base on each side, the arguments must be equal. This also applies when the arguments are algebraic expressions. Therefore, when given an equation with logs of the same base on each side, we can use rules of logarithms to rewrite each side as a single logarithm. Then we use the fact that logarithmic functions are one-to-one to set the arguments equal to one another and solve for the unknown.
For example, consider the equation log ( 3 x − 2 ) − log ( 2 ) = log ( x + 4 ) . log ( 3 x − 2 ) − log ( 2 ) = log ( x + 4 ) . To solve this equation, we can use the rules of logarithms to rewrite the left side as a single logarithm, and then apply the one-to-one property to solve for x : x :
To check the result, substitute x = 10 x = 10 into log ( 3 x − 2 ) − log ( 2 ) = log ( x + 4 ) . log ( 3 x − 2 ) − log ( 2 ) = log ( x + 4 ) .
For any algebraic expressions S S and T T and any positive real number b , b , where b ≠ 1 , b ≠ 1 ,
Note, when solving an equation involving logarithms, always check to see if the answer is correct or if it is an extraneous solution.
Given an equation containing logarithms, solve it using the one-to-one property.
- Use the rules of logarithms to combine like terms, if necessary, so that the resulting equation has the form log b S = log b T . log b S = log b T .
- Use the one-to-one property to set the arguments equal.
Solving an Equation Using the One-to-One Property of Logarithms
Solve ln ( x 2 ) = ln ( 2 x + 3 ) . ln ( x 2 ) = ln ( 2 x + 3 ) .
There are two solutions: 3 3 or −1. −1. The solution −1 −1 is negative, but it checks when substituted into the original equation because the argument of the logarithm functions is still positive.
Solve ln ( x 2 ) = ln 1. ln ( x 2 ) = ln 1.
Solving Applied Problems Using Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
In previous sections, we learned the properties and rules for both exponential and logarithmic functions. We have seen that any exponential function can be written as a logarithmic function and vice versa. We have used exponents to solve logarithmic equations and logarithms to solve exponential equations. We are now ready to combine our skills to solve equations that model real-world situations, whether the unknown is in an exponent or in the argument of a logarithm.
One such application is in science, in calculating the time it takes for half of the unstable material in a sample of a radioactive substance to decay, called its half-life . Table 1 lists the half-life for several of the more common radioactive substances.
We can see how widely the half-lives for these substances vary. Knowing the half-life of a substance allows us to calculate the amount remaining after a specified time. We can use the formula for radioactive decay:
- A 0 A 0 is the amount initially present
- T T is the half-life of the substance
- t t is the time period over which the substance is studied
- A ( t ) A ( t ) is the amount of the substance present after time t t
Using the Formula for Radioactive Decay to Find the Quantity of a Substance
How long will it take for ten percent of a 1000-gram sample of uranium-235 to decay?
Ten percent of 1000 grams is 100 grams. If 100 grams decay, the amount of uranium-235 remaining is 900 grams.
How long will it take before twenty percent of our 1000-gram sample of uranium-235 has decayed?
Access these online resources for additional instruction and practice with exponential and logarithmic equations.
- Solving Logarithmic Equations
- Solving Exponential Equations with Logarithms
6.6 Section Exercises
How can an exponential equation be solved?
When does an extraneous solution occur? How can an extraneous solution be recognized?
When can the one-to-one property of logarithms be used to solve an equation? When can it not be used?
For the following exercises, use like bases to solve the exponential equation.
4 − 3 v − 2 = 4 − v 4 − 3 v − 2 = 4 − v
64 ⋅ 4 3 x = 16 64 ⋅ 4 3 x = 16
3 2 x + 1 ⋅ 3 x = 243 3 2 x + 1 ⋅ 3 x = 243
2 − 3 n ⋅ 1 4 = 2 n + 2 2 − 3 n ⋅ 1 4 = 2 n + 2
625 ⋅ 5 3 x + 3 = 125 625 ⋅ 5 3 x + 3 = 125
36 3 b 36 2 b = 216 2 − b 36 3 b 36 2 b = 216 2 − b
( 1 64 ) 3 n ⋅ 8 = 2 6 ( 1 64 ) 3 n ⋅ 8 = 2 6
For the following exercises, use logarithms to solve.
9 x − 10 = 1 9 x − 10 = 1
2 e 6 x = 13 2 e 6 x = 13
e r + 10 − 10 = −42 e r + 10 − 10 = −42
2 ⋅ 10 9 a = 29 2 ⋅ 10 9 a = 29
− 8 ⋅ 10 p + 7 − 7 = −24 − 8 ⋅ 10 p + 7 − 7 = −24
7 e 3 n − 5 + 5 = −89 7 e 3 n − 5 + 5 = −89
e − 3 k + 6 = 44 e − 3 k + 6 = 44
− 5 e 9 x − 8 − 8 = −62 − 5 e 9 x − 8 − 8 = −62
− 6 e 9 x + 8 + 2 = −74 − 6 e 9 x + 8 + 2 = −74
2 x + 1 = 5 2 x − 1 2 x + 1 = 5 2 x − 1
e 2 x − e x − 132 = 0 e 2 x − e x − 132 = 0
7 e 8 x + 8 − 5 = −95 7 e 8 x + 8 − 5 = −95
10 e 8 x + 3 + 2 = 8 10 e 8 x + 3 + 2 = 8
4 e 3 x + 3 − 7 = 53 4 e 3 x + 3 − 7 = 53
8 e − 5 x − 2 − 4 = −90 8 e − 5 x − 2 − 4 = −90
3 2 x + 1 = 7 x − 2 3 2 x + 1 = 7 x − 2
e 2 x − e x − 6 = 0 e 2 x − e x − 6 = 0
3 e 3 − 3 x + 6 = −31 3 e 3 − 3 x + 6 = −31
For the following exercises, use the definition of a logarithm to rewrite the equation as an exponential equation.
log ( 1 100 ) = −2 log ( 1 100 ) = −2
log 324 ( 18 ) = 1 2 log 324 ( 18 ) = 1 2
For the following exercises, use the definition of a logarithm to solve the equation.
5 log 7 n = 10 5 log 7 n = 10
− 8 log 9 x = 16 − 8 log 9 x = 16
4 + log 2 ( 9 k ) = 2 4 + log 2 ( 9 k ) = 2
2 log ( 8 n + 4 ) + 6 = 10 2 log ( 8 n + 4 ) + 6 = 10
10 − 4 ln ( 9 − 8 x ) = 6 10 − 4 ln ( 9 − 8 x ) = 6
For the following exercises, use the one-to-one property of logarithms to solve.
ln ( 10 − 3 x ) = ln ( − 4 x ) ln ( 10 − 3 x ) = ln ( − 4 x )
log 13 ( 5 n − 2 ) = log 13 ( 8 − 5 n ) log 13 ( 5 n − 2 ) = log 13 ( 8 − 5 n )
log ( x + 3 ) − log ( x ) = log ( 74 ) log ( x + 3 ) − log ( x ) = log ( 74 )
ln ( − 3 x ) = ln ( x 2 − 6 x ) ln ( − 3 x ) = ln ( x 2 − 6 x )
log 4 ( 6 − m ) = log 4 3 m log 4 ( 6 − m ) = log 4 3 m
ln ( x − 2 ) − ln ( x ) = ln ( 54 ) ln ( x − 2 ) − ln ( x ) = ln ( 54 )
log 9 ( 2 n 2 − 14 n ) = log 9 ( − 45 + n 2 ) log 9 ( 2 n 2 − 14 n ) = log 9 ( − 45 + n 2 )
ln ( x 2 − 10 ) + ln ( 9 ) = ln ( 10 ) ln ( x 2 − 10 ) + ln ( 9 ) = ln ( 10 )
For the following exercises, solve each equation for x . x .
log ( x + 12 ) = log ( x ) + log ( 12 ) log ( x + 12 ) = log ( x ) + log ( 12 )
ln ( x ) + ln ( x − 3 ) = ln ( 7 x ) ln ( x ) + ln ( x − 3 ) = ln ( 7 x )
log 2 ( 7 x + 6 ) = 3 log 2 ( 7 x + 6 ) = 3
ln ( 7 ) + ln ( 2 − 4 x 2 ) = ln ( 14 ) ln ( 7 ) + ln ( 2 − 4 x 2 ) = ln ( 14 )
log 8 ( x + 6 ) − log 8 ( x ) = log 8 ( 58 ) log 8 ( x + 6 ) − log 8 ( x ) = log 8 ( 58 )
ln ( 3 ) − ln ( 3 − 3 x ) = ln ( 4 ) ln ( 3 ) − ln ( 3 − 3 x ) = ln ( 4 )
log 3 ( 3 x ) − log 3 ( 6 ) = log 3 ( 77 ) log 3 ( 3 x ) − log 3 ( 6 ) = log 3 ( 77 )
For the following exercises, solve the equation for x , x , if there is a solution . Then graph both sides of the equation, and observe the point of intersection (if it exists) to verify the solution.
log 9 ( x ) − 5 = −4 log 9 ( x ) − 5 = −4
log 3 ( x ) + 3 = 2 log 3 ( x ) + 3 = 2
ln ( 3 x ) = 2 ln ( 3 x ) = 2
ln ( x − 5 ) = 1 ln ( x − 5 ) = 1
log ( 4 ) + log ( − 5 x ) = 2 log ( 4 ) + log ( − 5 x ) = 2
− 7 + log 3 ( 4 − x ) = −6 − 7 + log 3 ( 4 − x ) = −6
ln ( 4 x − 10 ) − 6 = − 5 ln ( 4 x − 10 ) − 6 = − 5
log ( 4 − 2 x ) = log ( − 4 x ) log ( 4 − 2 x ) = log ( − 4 x )
log 11 ( − 2 x 2 − 7 x ) = log 11 ( x − 2 ) log 11 ( − 2 x 2 − 7 x ) = log 11 ( x − 2 )
ln ( 2 x + 9 ) = ln ( − 5 x ) ln ( 2 x + 9 ) = ln ( − 5 x )
log 9 ( 3 − x ) = log 9 ( 4 x − 8 ) log 9 ( 3 − x ) = log 9 ( 4 x − 8 )
log ( x 2 + 13 ) = log ( 7 x + 3 ) log ( x 2 + 13 ) = log ( 7 x + 3 )
3 log 2 ( 10 ) − log ( x − 9 ) = log ( 44 ) 3 log 2 ( 10 ) − log ( x − 9 ) = log ( 44 )
ln ( x ) − ln ( x + 3 ) = ln ( 6 ) ln ( x ) − ln ( x + 3 ) = ln ( 6 )
For the following exercises, solve for the indicated value, and graph the situation showing the solution point.
An account with an initial deposit of $6,500 $6,500 earns 7.25 % 7.25 % annual interest, compounded continuously. How much will the account be worth after 20 years?
The formula for measuring sound intensity in decibels D D is defined by the equation D = 10 log ( I I 0 ) , D = 10 log ( I I 0 ) , where I I is the intensity of the sound in watts per square meter and I 0 = 10 − 12 I 0 = 10 − 12 is the lowest level of sound that the average person can hear. How many decibels are emitted from a jet plane with a sound intensity of 8.3 ⋅ 10 2 8.3 ⋅ 10 2 watts per square meter?
The population of a small town is modeled by the equation P = 1650 e 0.5 t P = 1650 e 0.5 t where t t is measured in years. In approximately how many years will the town’s population reach 20,000? 20,000?
For the following exercises, solve each equation by rewriting the exponential expression using the indicated logarithm. Then use a calculator to approximate the variable to 3 decimal places.
1000 ( 1.03 ) t = 5000 1000 ( 1.03 ) t = 5000 using the common log.
e 5 x = 17 e 5 x = 17 using the natural log
3 ( 1.04 ) 3 t = 8 3 ( 1.04 ) 3 t = 8 using the common log
3 4 x − 5 = 38 3 4 x − 5 = 38 using the common log
50 e − 0.12 t = 10 50 e − 0.12 t = 10 using the natural log
For the following exercises, use a calculator to solve the equation. Unless indicated otherwise, round all answers to the nearest ten-thousandth.
7 e 3 x − 5 + 7.9 = 47 7 e 3 x − 5 + 7.9 = 47
ln ( 3 ) + ln ( 4.4 x + 6.8 ) = 2 ln ( 3 ) + ln ( 4.4 x + 6.8 ) = 2
log ( − 0.7 x − 9 ) = 1 + 5 log ( 5 ) log ( − 0.7 x − 9 ) = 1 + 5 log ( 5 )
Atmospheric pressure P P in pounds per square inch is represented by the formula P = 14.7 e − 0.21 x , P = 14.7 e − 0.21 x , where x x is the number of miles above sea level. To the nearest foot, how high is the peak of a mountain with an atmospheric pressure of 8.369 8.369 pounds per square inch? ( Hint : there are 5280 feet in a mile)
The magnitude M of an earthquake is represented by the equation M = 2 3 log ( E E 0 ) M = 2 3 log ( E E 0 ) where E E is the amount of energy released by the earthquake in joules and E 0 = 10 4.4 E 0 = 10 4.4 is the assigned minimal measure released by an earthquake. To the nearest hundredth, what would the magnitude be of an earthquake releasing 1.4 ⋅ 10 13 1.4 ⋅ 10 13 joules of energy?
Use the definition of a logarithm along with the one-to-one property of logarithms to prove that b log b x = x . b log b x = x .
Recall the formula for continually compounding interest, y = A e k t . y = A e k t . Use the definition of a logarithm along with properties of logarithms to solve the formula for time t t such that t t is equal to a single logarithm.
Recall the compound interest formula A = a ( 1 + r k ) k t . A = a ( 1 + r k ) k t . Use the definition of a logarithm along with properties of logarithms to solve the formula for time t . t .
Newton’s Law of Cooling states that the temperature T T of an object at any time t can be described by the equation T = T s + ( T 0 − T s ) e − k t , T = T s + ( T 0 − T s ) e − k t , where T s T s is the temperature of the surrounding environment, T 0 T 0 is the initial temperature of the object, and k k is the cooling rate. Use the definition of a logarithm along with properties of logarithms to solve the formula for time t t such that t t is equal to a single logarithm.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra-2e/pages/1-introduction-to-prerequisites
- Authors: Jay Abramson
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: College Algebra 2e
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra-2e/pages/1-introduction-to-prerequisites
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra-2e/pages/6-6-exponential-and-logarithmic-equations
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- 888-309-8227
- 732-384-0146
New User Registration
Forgot Password
Go Math! 6 Common Core Edition, Grade: 6 Publisher: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Go math 6 common core edition, title : go math 6 common core edition, publisher : houghton mifflin harcourt, isbn : 547587783, isbn-13 : 9780547587783, use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement go math 6 common core edition., textbook resources.
- Call us toll-free
- FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
- Contact Lumos Learning – Proven Study Programs by Expert Teachers
Follow us: Lumos Learning -->
- 2024 © Lumos Learning
- Privacy Policy - Terms of Service - Disclaimers
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc... Read More
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc., the Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any state of the Union. Neither PARCC, Inc., nor The Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any member state has endorsed this product. No portion of any fees or charges paid for any products or services Lumos Learning offers will be paid or inure to the benefit of PARCC, Inc., or any state of the Union
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not aff... Read More
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC, was not... Read More
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC,was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved... Read More
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the prod... Read More
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved... Read More
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved... Read More
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved... Read More
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved... Read More
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Write Expressions Where Letters Stand for Numbers
Instructions for a craft project say that the length of a piece of red ribbon should be 7 inches less than the length of a piece of blue ribbon.
How long is the red ribbon if the length of the blue ribbon is:
\(x\) inches?
- How long is the blue ribbon if the red ribbon is 12 inches?
For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners .
Tyler has 3 times as many books as Mai.
How many books does Mai have if Tyler has:
\(x\) books?
- Tyler has 18 books. How many books does Mai have?
A bottle holds 24 ounces of water. It has \(x\) ounces of water in it.
- What does \(24-x\) represent in this situation?
- Write a question about this situation that has \(24-x\) for the answer.
Write an equation represented by this tape diagram using each of these operations.

- subtraction
- multiplication
Select all the equations that describe each situation and then find the solution.
Han's house is 450 meters from school. Lin’s house is 135 meters closer to school. How far is Lin’s house from school?
- \(z = 450 + 135\)
- \(z = 450-135\)
- \(z-135 = 450\)
- \(z + 135 = 450\)
Tyler's playlist has 36 songs. Noah’s playlist has one quarter as many songs as Tyler's playlist. How many songs are on Noah’s playlist?
- \(w = 4 \boldcdot 36\)
- \(w = 36 \div 4\)
- \(4w = 36\)
- \(\frac{w}{4} = 36\)
You had $50. You spent 10% of the money on clothes, 20% on games, and the rest on books. How much money was spent on books?
A trash bin has a capacity of 50 gallons. What percentage of its capacity is each amount? Show your reasoning.
- 100 gallons
- Math 6 Student Materials >>
- Math 6 Family Materials >>
Unit 1: Area and Surface Area
Unit 2: introducing ratios, unit 3: unit rates and percentages, unit 4: dividing fractions, unit 5: arithmetic in base ten, unit 6: expressions and equations, unit 7: rational numbers, unit 8: data sets and distributions.
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 5 Chapter 6 Divide Whole Numbers
Solutions to Big Ideas Math 5th Grade Chapter 6 Divide Whole Numbers is available on this page. This answer key is helpful for the students who are studying grade 5 and preparing for the exams. They can download Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 3 Chapter 6 Divide Whole Numbers PDF for free of cost. Here, we are providing a detailed explanation for each and every question that information helps students to understand the concept easily. Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 5 Chapter 6 contains different types of questions on Divide Whole numbers.
Big Ideas Math Book 5th Grade Answer Key Chapter 6 Divide Whole Numbers
Download Topic wise Big Ideas Math Book 5th Grade Chapter 6 Divide Whole Numbers Answer Key PDF via quick links available below. You can learn fundamentals of the division of whole numbers like Relate Multiplication and Division, Division Patterns, Estimate Quotients, Divide by One-Digit Numbers, Use Partial Quotients to Divide by Two-Digit Numbers, Use Partial Quotients with a Remainder, Divide Three-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers, and Divide Four-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers on this page.
Lesson: 1 Relate Multiplication and Division
Lesson 6.1 Relate Multiplication and Division
Relate multiplication and division homework & practice 6.1.
Lesson: 2 Division Patterns
Lesson 6.2 Division Patterns
Division patterns homework & practice 6.2.
Lesson: 3 Estimate Quotients
Lesson 6.3 Estimate Quotients
Estimate quotients homework & practice 6.3.
Lesson: 4 Divide by One-Digit Numbers
Lesson 6.4 Divide by One-Digit Numbers
Divide by one-digit numbers homework & practice 6.4.
Lesson: 5 Use Partial Quotients to Divide by Two-Digit Numbers
Lesson 6.5 Use Partial Quotients to Divide by Two-Digit Numbers
Use partial quotients to divide by two-digit numbers homework & practice 6.5.
Lesson: 6 Use Partial Quotients with a Remainder
Lesson 6.6 Use Partial Quotients with a Remainder
Use partial quotients with a remainder homework & practice 6.6.
Lesson: 7 Divide Three-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers
Lesson 6.7 Divide Three-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers
Divide three-digit numbers by two-digit numbers homework & practice 6.7.
Lesson: 8 Divide Four-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers
Lesson 6.8 Divide Four-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers
Divide four-digit numbers by two-digit numbers homework & practice 6.8.
Lesson: 9 Problem Solving: Division
Lesson 6.9 Problem Solving: Division
Problem solving: division homework & practice 6.9.
Chapter: 6 – Divide Whole Numbers
Divide Whole Numbers Performance Task
Divide whole numbers activity, divide whole numbers chapter practice.
Explore and Grow

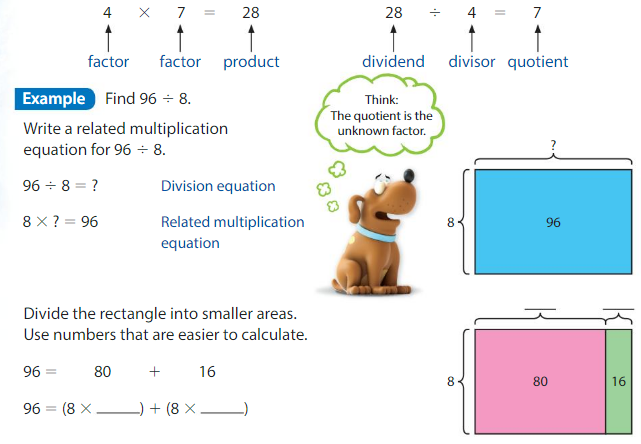
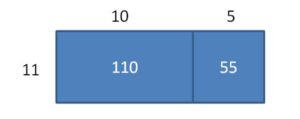
Answer: 6 x 19 = 114 114 ÷ 6 = 19
Explanation: First, multiply 6 and 19 to get the product 114. Here 6, 19 are the factors and 114 is the product. When you divide the product by anyone factor, you will automatically get the quotient as another factor. Here, 144 is the dividend, 6 is the divisor and 19 is the quotient. 114 = 60 + 54 = (6 x _) + (6 x _) Find the sum of unknown factors of the smaller areas: 10 + 9 = 19. The related multiplication equation is 6 x 19 = 114. So, 114 ÷ 6 = 19.
Reasoning How do you think you can use multiplication to solve a division problem? Answer:
Think and Grow: Relate Multiplication and Division
Show and Grow
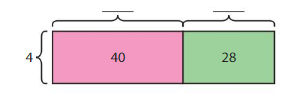
Answer: 17.
Explanation: 68 = 40 + 28 = (4 x _) + (4 x _) Sum of unknown factors of the smallest areas: 10 + 7 = 17 The related multiplication equation is 4 x 17 = 68. So, 68 ÷ 4 = 17.
Question 2. 138 ÷ 6 = _____
Answer: 138 ÷ 6 = 23
Explanation: 138 = 60 + 78 = (6 x _) + 6 x _) Sum of unknown factors of the smallest areas: 10 + 13 = 23 The related multiplication equation is 23 x 6 = 138. So, 138 ÷ 6 = 23.
Apply and Grow: Practice
Use multiplication to find the quotient. Question 3. 24 ÷ 2 = _____
Answer: 24 ÷ 2 = 12
Explanation: 24 = 20 + 4 = (2 x _) + (2 x _) Sum of unknown factors of the smallest areas: 10 + 2 = 12 The related multiplication equation is 2 x 12 = 24. So 24 ÷ 2 = 12.
Question 4. 48 ÷ 3 = _____
Answer: 48 ÷ 3 = 16.
Explanation: 48 = 30 + 18 = (3 x _) + (3 x _) Sum of unknown factors of the smallest areas: 10 + 6 = 16 The related multiplication equation is 3 x 16 = 48. So, 48 ÷ 3 = 16.
Question 5. 98 ÷ 7 = _____
Answer: 14.
Explanation: 98 = 35 + 63 = (7 x _) + (7 x _) The sum of unknown factors is 5 + 9 = 14. The multiplication equation for 98 ÷ 7 is 7 x 14 = 98. So, 98 ÷ 7 = 14.
Question 6. 125 ÷ 5 = _____
Answer: 25.
Explanation: 125 = 100 + 25 = (5 x _) + (5 x _) The sum of unknown factors of 5 is 20 + 5 = 25 The multiplication equation for 125 ÷ 5 is 25 x 5 = 125. So, 125 ÷ 5 = 25.
Question 7. 243 ÷ 9 = _____
Answer: 27.
Explanation: 243 = 162 + 81 = (9 x _) + (9 x _) The sum of unknown factors of 9 is 18 + 9 = 27. The related multiplication equation is 27 x 9 = 243. So, 243 ÷ 9 = 27.
Question 8. 132 ÷ 4 = _____
Answer: 33.
Explanation: 132 = 72 + 60 = (4 x _) + (4 x _) The sum of unknown factors of 4 is 18 + 15 = 33 The related multiplication equation is 33 x 4 = 132. So, 132 ÷ 4 = 33.

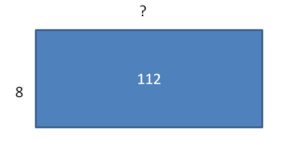
Answer: 112 ÷ 8 = 14.
Answer: 90 ÷ 6 = 80 ÷ 5.
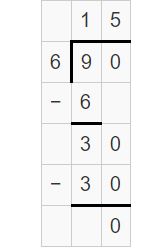
Answer: 405 ÷ 9 = 315 ÷ 7
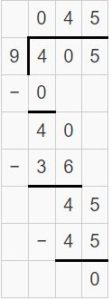
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life

Question 12. There are 6 fifth-grade classes with 21 students in each class. The students are divided equally into 7 groups. How many students are in each group?
Answer: 18 students are there in each group.
Explanation: Here, we need to multiply the number of students in each class to get the total number of students in the fifth-grade class. i.e 6 x 21 = 126. Divide the total number of groups in the fifth grade by the total number of students in the fifth grade to find the number of students in each group. 126 ÷ 7 = ? Division Equation 7 x ? = 126 Related Multiplication Equation Divide the rectangles into two parts. 126 = 70 + 56 126 = (7 x _) + (7 x _) Find the sum of the unknown factors of the part: 10 + 8 = 18. The related multiplication equation is 7 x 18 = 126. So, 126 ÷ 7 = 18. There are 18 students in each group.
Question 13. Newton makes 11 clay bowls each month for 1 year. He takes an equal number of bowls to each of the 3 craft fairs. How many bowls does Newton take to each craft fair?
Answer: Newton can take 44 bowls to each craft fair.
Explanation: Newton makes 11 clay bowls each month for 1 year means. He can make 11 x 12 = 132 clay bowls. Divide the total clay bowls by the number of craft fairs to get the number of bowls to each craft fair. 132 ÷ 3 = ? Division Equation 3 x ? = 132 Related Multiplication Equation Divide the rectangle into two smaller areas. 132 = 66 + 66 132 = (3 x _) + (3 x _) The sum of unknown factors of 11 are 22 + 22 = 44. The related multiplication equation for 132 ÷ 3 is 3 x 44 = 132. So, 132 ÷ 3 = 44. Newton can take 44 bowls to each craft fair.
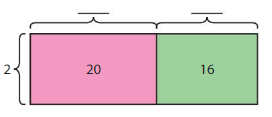
Answer: 36 ÷ 2 = 18.
Explanation: 36 = 20 + 16 36 = (2 x 10) + (2 x 8) The sum of factors of 2 are 10 + 8 = 18. The related multiplication equation is 2 x 18 = 36. So, 36 ÷ 2 = 18.
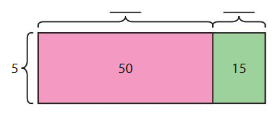
Answer: 65 ÷ 5 = 13.
Explanation: 65 can be written as the sum of 50 and 15. 65 = 50 + 15 65 = (5 x 10) + (5 x 3) The sum of smallest areas is 10 + 3 = 13. The related multiplication equation is 5 x 13 = 65. So, 65 ÷ 5 = 13.
Use multiplication to find the quotient. Question 3. 57 ÷ 3 = ______
Answer: 57 ÷ 3 = 19.
Explanation: 57 = 39 + 18 57 = (3 x 13) + (3 x 6) The sum of smallest areas is 13 + 6 = 19. The related multiplication equation is 19 x 3 = 57. So, 57 ÷ 3 = 19.
Question 4. 64 ÷ 4 = ______
Answer: 64 ÷ 4 = 16.
Explanation: 64 = 40 + 24 64 = (4 x 10) + (4 x 6) The sum of smallest areas is 10 + 6 = 16 The related multiplication equation is 16 x 4 = 64. So, 64 ÷ 4 = 16.
Question 5. 207 ÷ 9 = _____
Answer: 207 ÷ 9 = 23.
Explanation: 207 = 108 + 99 207 = (9 x 12) + (9 x 11) The sum of smallest areas of the rectangles is 12 + 11 = 23 The related multiplication equation is 23 x 9 = 207. So, 207 ÷ 9 = 23.
Question 6. 147 ÷ 7 = _____
Answer: 147 ÷ 7 = 21.
Explanation: 147 = 105 + 42 147 = (7 x 15) + (7 x 6) The sum of smallest areas of the rectangles is 15 + 6 = 21 The related multiplication equation is 21 x 7 = 147. So, 147 ÷ 7 = 21.
Question 7. YOU BE THE TEACHER Your friend finds 192 ÷ 6 by writing (6 × 30) + (6 × 2). She says the quotient is 12. Is your friend correct? Explain.
Answer: Wrong.
Explanation: We can write 192 as the sum of 180 and 12. 192 = 180 + 12 192 = (6 x 30) + (6 x 2) The sum of factors of 6 is 30 + 2 = 32 The related multiplication equation for 192 ÷ 6 is 32 x 6 = 192. So, when you multiply 192 by 6, it leaves remainder 0 and quotient 32. Therefore, 192 ÷ 6 = 32.
Question 8. Writing Explain how you can use multiplication to solve a division problem.
Answer: The condition to use multiplication to solve the division problems is the division of numbers should leave the remainder 0. When you divide the divisor by dividend, you will get a quotient as the answer. The product of quotient and divisor gives the result as a dividend. So, here quotient, the divisor is called the factors, and the dividend is called the product. Here, you need to split the dividend into two sections using addition property and multiply each part by the divisor. Add those factors to get the quotient value.
Question 9. Modeling Real Life A music teacher has 6 fifth-grade classes with 16 students in each class. She places the students into 4 equal rows for a chorus concert. How many students are in each row?
Answer: There are 24 students in each row at the chorus concert.
Explanation: The total number students = 16 x 6 = 96 The number of fifth-grade classes = 6 The music teacher arranges students into 4 equal rows for a chorus concert. The number of students in each row = 96 / 4 = 24.

Answer: The cost of 1 item is 26 tickets.
Explanation: The total number of tickets won at an arcade = 50 + 12 + 16 = 78 tickets As given in the questions, you are able to buy 3 of the same item with no tickets left over. So, divide total tickets by the number of items to get one item cost. The cost of 1 item = 78 / 3 = 26 tickets.
Review & Refresh
Find the product. Check whether your answer is reasonable. Question 11. 31.4 × 9.2 = _____
Answer: 31.4 × 9.2 = 288.88
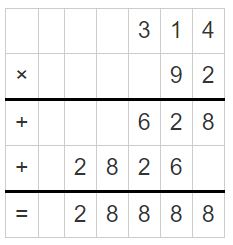
Question 12. 67.3 × 4.2 = ______
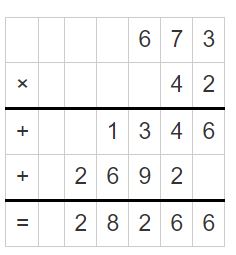
Question 13. 0.8 × 5.98 = ______
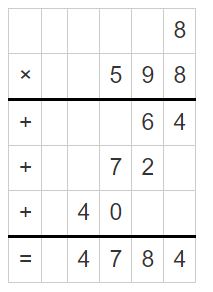
Answer: 0.8 × 5.98 = 4.784
Explanation: The factors of 15 which satisfy the condition are 5, 3. So, the missing factor is 5. The related multiplication equation is 5 x 3 = 15. The factors of 150 that satisfy the condition are 50, 3. So, the missing factor is 50. The related multiplication equation is 50 x 3 = 150. The factors of 1500 that satisfy the condition are 500, 3. So, the missing factor is 500. Related multiplication equation is 500 x 3 = 1500. The factors of 150 that satisfy the condition are 5, 30. So, the missing factor is 5. Related multiplication equation is 5 x 30 = 150. The factors of 1500 that satisfy the condition are 50, 30. So, the missing factor is 50. Related multiplication equation is 50 x 30 = 1500. The factors of 15000 that satisfy the condition are 500, 30. So, the missing factor is 500. Related multiplication equation is 500 x 30 = 15000.
Repeated Reasoning Explain how finding 35 ÷ 7 can help you find 350 ÷ 70.
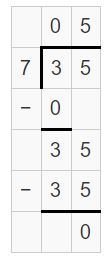
Answer: Canceling zeros in 350 ÷ 70 will get 35 ÷ 7. 35 ÷ 7 = 5.
Think and Grow: Division Patterns
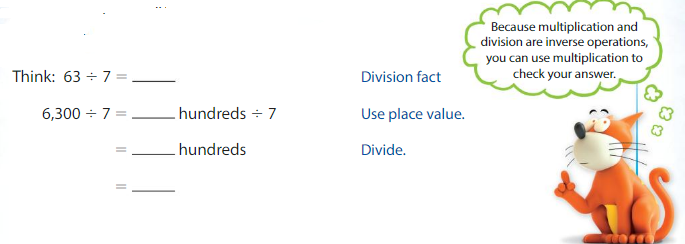
Find the quotient. Question 1. 2,500 ÷ 5 = ________ Think: _____ ÷ _____ = _____
Answer: 2,500 ÷ 5 = 500 Think: 25 hundreds ÷ 5 = (25 ÷ 5) hundreds = 5 hundreds.
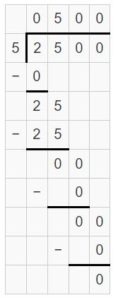
Question 2. 420 ÷ 60 = ______ Think: _____ ÷ _____ = ______
Answer: 420 ÷ 60 = 7 Think: 420 ÷ 60 = 42 tens ÷ 6 tens = 42 ÷ 6 = 7
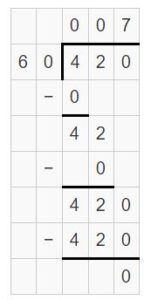
Question 3. 5,400 ÷ 90 = ______
Answer: 5,400 ÷ 90 = 60 5,400 ÷ 90 = 54 hundreds ÷ 9 tens = 54 tens ÷ 9 = (54 ÷ 9) tens = 6 tens
Question 4. 8,000 ÷ 20 = ______
Answer: 8,000 ÷ 20 = 400 8,000 ÷ 20 = 8 thousands ÷ 2 tens = 8 hundreds ÷ 2 = (8 ÷ 2) hundreds = 4 hundreds
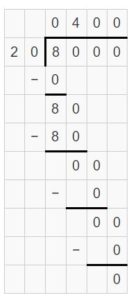
Find the quotient. Question 5. 800 ÷ 4 = ______
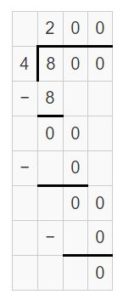
Answer: 800 ÷ 4 = 200 800 ÷ 4 = 8 hundreds ÷ 4 = (8 ÷ 4) hundreds = 2 hundreds
Question 6. 120 ÷ 60 = ______
Answer: 120 ÷ 60 = 2 120 ÷ 60 = 12 tens ÷ 6 tens = 12 ÷ 6 = 2
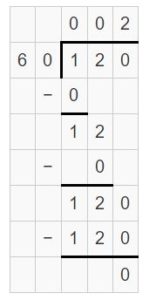
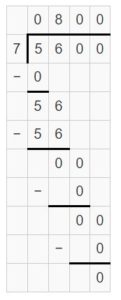
Question 7. 5,600 ÷ 7 = _____
Answer: 5,600 ÷ 7 = 800 5,600 ÷ 7 = 56 hundreds ÷ 7 = (56 ÷7) hundreds = 8 hundreds
Question 8. 300 ÷ 50 = _____
Answer: 300 ÷ 50 = 7 300 ÷ 50 = 3 hundreds ÷ 5 tens = 3 tens ÷ 5 = 30 ÷ 5 = 7
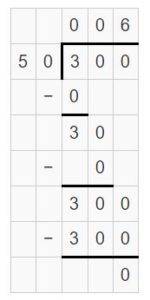
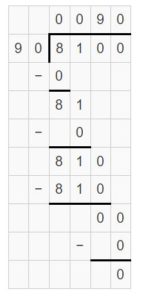
Question 9. 8,100 ÷ 90 = ______
Answer: 8,100 ÷ 90 = 90 8,100 ÷ 90 = 81 hundreds ÷ 9 tens = 81 tens ÷ 9 = (81 ÷ 9) tens = 9 tens
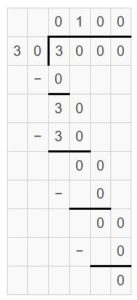
Question 10. 3,000 ÷ 30 = ______
Answer: 3,000 ÷ 30 = 100 3,000 ÷ 30 = 3 thousands ÷ 3 tens = 3 hundreds ÷ 3 = (3 ÷ 3) hundreds = 1 hundreds
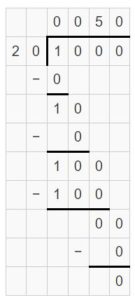
Question 11. 1,000 divided by 20 is _____.
Answer: 1,000 divided by 20 is 50.
Question 12. 900 divided by 10 is ______.
Answer: 900 divided by 10 is 90.
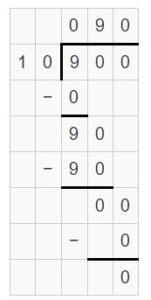
Question 13. 1,800 divided by 60 is _____.
Answer: 1,800 divided by 60 is 30.
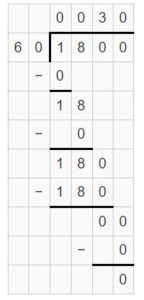
Find the missing factor. Question 14. _____ ÷ 40 = 8
Answer: 320 ÷ 40 = 8
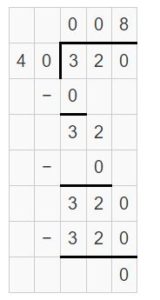
Question 15. 360 ÷ ____ = 6
Answer: 360 ÷ 60 = 6
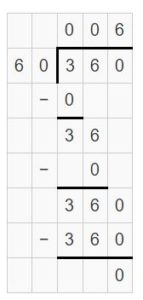
Question 16. 7,200 ÷ _____ = 90
Answer: 7,200 ÷ 80 = 90
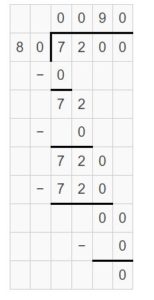
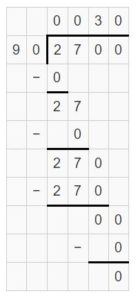
Answer: 2700 ÷ 90 ≠ 24 tens ÷ 8 tens
Question 19. A jeweler has 600 rings. He displays 20 rings in each ring cushion. How many ring cushions does he use?
Answer: A jeweler uses 30 ring cushions to display rings.
Question 20. Writing Explain how to use 45 ÷ 9 to find 4,500 ÷ 90.
Answer: 45 ÷ 9 and 4500 ÷ 90 gives the same answer with different units. Because, in 4500 ÷ 90, we have 45 hundred ÷ 9 tens. We can write it as (45 ÷ 9) tens. So, solve 45 ÷ 9 and substitute the value in (45 ÷ 9) tens to get the answer. Actually, 45 ÷ 9 = 5, 4,500 ÷ 90 = (45 ÷ 9) tens = 5 tens

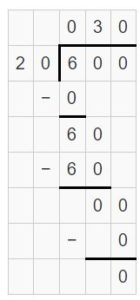
Answer: 2800 ÷ 40 have a quotient of 70.
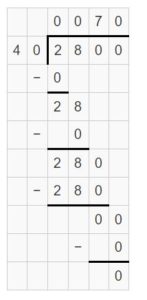
Answer: The number of tennis balls in the box is 3000 grams ÷ 60 grams = 50.
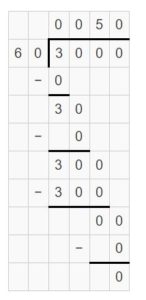
Answer: A cargo van can transport 76-pound bags of dog food.
Find the quotient. Question 1. 180 ÷ 2 = ______ Think: ____ ÷ _____ = _______
Answer: 180 ÷ 2 = 90 Think: 18 tens ÷ 2 = 9 tens
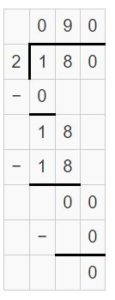
Question 2. 4,200 ÷ 70 = _____ Think: _____ ÷ _____ = _____
Answer: 4,200 ÷ 70 = 60 Think: 42 hundred ÷ 7 tens = (42 ÷ 7) tens = 6 tens
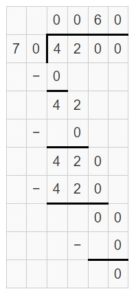
Question 3. 4,000 ÷ 5 = _____
Answer: 4,000 ÷ 5 = 800.
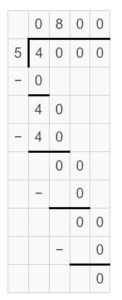
Question 4. 270 ÷ 30 = _______
Answer: 270 ÷ 30 = 9.
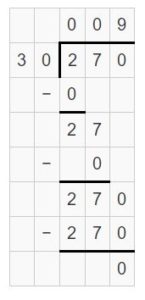
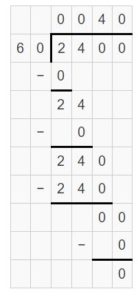
Question 5. 2,400 ÷ 60 = ______
Answer: 2,400 ÷ 60 = 40.
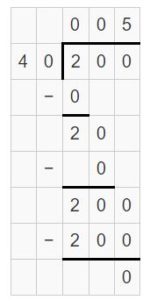
Question 6. 200 divided by 40 is ______.
Answer: 200 divided by 40 is 5.
Question 7. 400 divided by 20 is ______.
Answer: 400 divided by 20 is 20.
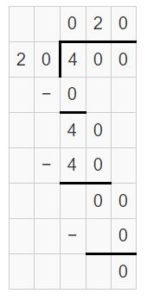
Question 8. 2,100 divided by 70 is ______.
Answer: 2,100 divided by 70 is 30.
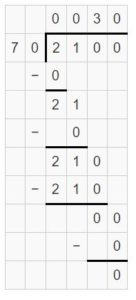
Find the missing factor. Question 9. 2,400 ÷ ____ = 30
Answer: 2,400 ÷ 80 = 30.
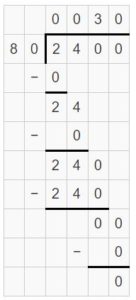
Question 10. ______ ÷ 60 = 50
Answer: 3,000 ÷ 60 = 50.
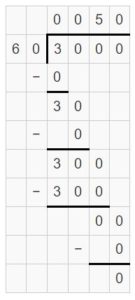
Question 11. 700 ÷ ____ = 70
Answer: 700 ÷ 10 = 70.
Answer: 45 hundreds ÷ 9 > 450 ÷ 90
Explanation: 45 hundreds ÷ 9 = 5 hundreds 450 ÷ 90 = 5 So, 45 hundreds ÷ 9 > 450 ÷ 90
Answer: 3600 ÷ 60 < 140 ÷ 2
Explanation: 3600 ÷ 60 = 36 hundreds ÷ 6 tens = 36 ÷ 6 tens = 6 tens 140 ÷ 2 = 14 tens ÷ 2 = (14 ÷ 2) tens = 7 tens So, 3600 ÷ 60 < 140 ÷ 2

Answer: The elevator to the Top of the Rock Observation Deck in New York City travels 20 feet in each second.
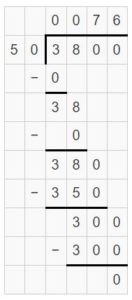
Explanation: The elevator to the Top of the Rock Observation Deck in New York City travels 1,200 feet each minute. 1 minute has 60 seconds. So, the elevator travels 1200 feet ÷ 60 in each second. = 12 hundreds feet ÷ 6 tens = 12 tens ÷ 6 = 2 tens feet.
Question 15. Reasoning Why is 640 ÷ 80 equal to 64 ÷ 8?
Answer: 640 ÷ 80 = 64 tens ÷ 8 tens = 64 ÷ 8. We can say that in 640 ÷ 80 both numerator and denominator have tens. By canceling those tens, we will get 64 ÷ 8. So, 640 ÷ 80 = 64 ÷ 8
Question 16. Modeling Real Life A black bear in a zoo eats 8 kilograms of food each day. He eats 4 equal-sized meals each day. How many grams of food are in each meal?
Answer: A black bear in a zoo eats 2000 grand of food are in each meal.
Explanation: The weight of food a black bear in a zoo eats a day = 8 kilograms = 8 x 1000 grams = 8000 grams Number of meals in a day = 4 equal-sized meals The weight of food black bear eat in each meal = 8000 ÷ 4 = 8 thousand ÷ 4 = (8 ÷ 4) thousand = 2 thound grams.
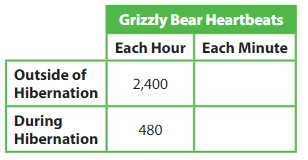
Explanation: 1 Hour = 60 Minutes So, outside of hibernation = 2400 ÷ 60 = 24 hundreds ÷ 6 tens = 24 ÷ 6 tens = 4 tens During hibernation = 480 ÷ 60 = 48 tens ÷ 6 tens = 48 ÷ 6 = 8.
Answer: 7.829 > 7.851
Explanation: 7.829 is greater than 7.851. Because the digits after point will have lesser value.
Answer: 0.65 = 0.650
Explanation: In 0.650, 0 after 65 will have no value. So, 0.65 = 0.650.
Answer: 2.816 < 2.814
Explanation: 2.816 is less than 2.814. Because the digits after point will have lesser value.

Reasoning Why did you choose your estimate? Compare your results with your partner’s.
Answer: I have chosen estimate to get the result for division of two numbers. It may not give accurate result, but it gives appropriate value of quotient with easy and quick process. when compared with partners result, i will find the quotient fastly and appropriate answer.To estimate your result, you need to find the nearest numbers those are exactly divided by the divisor.
Think and Grow: Estimate Quotients

Use 3,000. 30 ÷ 3 = 10 300 ÷ 30 = 10 3,000 ÷ 30 = 100 Choose 2,700 because 2,805 is closer to 2,700. So, 2,805 ÷ 30 is about 90.
Find two numbers that the quotient is between. Question 1. 5,482 ÷ 7 4,900 ÷ 7 = _____ 5,600 ÷ 7 = ______
Answer: 5,482 ÷ 7 = 800 4,900 ÷ 7 = 49 hundreds ÷ 7 = 7 hundreds 5,600 ÷ 7 = 56 hundreds ÷ 7 = 8 hundreds
Explanation: As the given dividend 5,482 is near to 5,600 and 5,600 ÷ 7 is 800. So, the answer is 800.
Question 2. 176 ÷ 52 150 ÷ 50 = ______ 200 ÷ 50 = _______
Answer: 176 ÷ 52 is about 4. 150 ÷ 50 = 15 tens ÷ 5 tens = 3 200 ÷ 50 = 20 tens ÷ 5 tens = 4
Explanation: Choose 200 because 176 is closer to 200. So, 176 ÷ 52 is about 4
Question 3. 2,620 ÷ 67
Answer: 2,620 ÷ 67 is
Explanation: What numbers close to 2,620 are easily divided by 67? 2620 ÷ 70 = 26 hundreds ÷ 7 tens = 26 tens ÷ 7 = Use 3,600. 36 ÷ 6 = 6, so 3,600 ÷ 6 = 600 . Use 4,200. 42 ÷ 6 = 7, so 4,200 ÷ 6 = 700. Choose 4,200 because 4,139 is closer to 4,200.
Estimate the quotients Question 4. 1,471 ÷ 5
Answer: 1,471 ÷ 5 is about 300.
Explanation: Choose what numbers close to 1471 and easily divided by 5. 1500 ÷ 5 = 15 hundreds ÷ 5 = 3 hundreds = 300 1000 ÷ 5 = 10 hundreds ÷ 5 = 2 hundreds = 200 So, choose 1500 because 1471 is nearer to 1500.
Question 5. 280 ÷ 41
Answer: 280 ÷ 41 is about 7.
Explanation: What numbers close to 280 and easily divisible by 40. 280 ÷ 40 = 28 tens ÷ 4 tens = 7 So, choose 280.
Question 6. 4,750 ÷ 88
Answer: 4,750 ÷ 88 is about 50.
Explanation: Choose what numbers are closer to 4750 and divisible by 90. 4500 ÷ 90 = 45 hundreds ÷ 9 tens = 5 tens = 50 5400 ÷ 90 = 54 hundreds ÷ 9 tens = 6 tens = 60 So, choose 4500 which is the nearest number to 4750.
Estimate the quotients Question 7. 557 ÷ 6
Answer: 557 ÷ 6 is about 90.
Explanation: What numbers close to 557 and are easily divided by 6. 540 ÷ 6 = 54 tens ÷ 6 = 9 tens = 90 600 ÷ 6 = 60 tens ÷ 6 = 10 tens = 100 So, choose the number 540 is near to 557.
Question 8. 3,231 ÷ 5
Answer: 3,231 ÷ 5 is about 600.
Explanation: What numbers close to 3231 and easily divided by 5. 3000 ÷ 5 = 30 hundreds ÷ 5 = 6 hundreds = 600 3500 ÷ 5 = 35 hundreds ÷ 5 = 7 hundreds = 700 So, choose 3000 which is near to 3231.
Question 9. 896 ÷ 11
Answer: 896 ÷ 11 is about 90.
Explanation: Choose the numbers that are near to 896 and divisible by 11. 880 ÷ 11 = 88 tens ÷ 11 = 88 990 ÷ 11 = 99 tens ÷ 11 = 99 So, select 880 that is near to 896.
Question 10. \(\sqrt [ 39 ]{ 7,610 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 39 ]{ 7,610 } \) is about 200.
Explanation: Choose the numbers that are near to 7610 and divisible by 40. 8000 ÷ 40 = 8 thousands ÷ 4 tens = 8 hundreds ÷ 4 = 2 hundreds = 200 4000 ÷ 40 = 4 thousands ÷ 4 tens = 1 hundred = 100 So, choose 8000 which is near to 7610 and divisible by 40 that is near to 39.
Question 11. \(\sqrt [ 94 ]{ 6,287 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 94 ]{ 6,287 } \) is about 70.
Explanation: Choose the numbers those are close to 6287 and divisible by 90 that is near to 94. 6300 ÷ 90 = 63 hundreds ÷ 9 tens = 7 tens = 70 5400 ÷ 90 = 54 hundreds÷ 9 tens = 6 ten = 60 So, choose 6300 that is close to 6287 and divisible 90 that is near to 94.
Question 12. \(\sqrt [ 79 ]{ 6,297 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 79 ]{ 6,297 } \) is about
Explanation: Choose the numbers those are close to 6297 and divisible by 80 that is near to 79. 6400 ÷ 80 = 64 hundreds ÷ 8 tens = 8 tens = 80 5600 ÷ 80 = 56 hundreds ÷ 8 tens = 7 tens = 70 So, choose 6400 that is close to 6297 and divisible 80 that is near to 79.

Answer: Number of cars cross the bridge in one hour is 500 approximately.
Explanation: Toll bridge attendants collection from cars in 1 hour = $4,873 One car cost = $11 Choose the number that is near to $4,873 and divisible by 10 which is near to 11. 4000 ÷ 10 = 4 thousands ÷ ten = 4 hundreds 5000 ÷ 10 = 5 thousands ÷ ten = 5 hundreds So, choose 5000 which is near to 4873.
Question 14. Reasoning Newton has $415 to spend during a 15-day trip. He does not want to run out of money, so he plans to spend about the same amount each day. He estimates that the amount he can spend each day is $450 ÷ 15 = $30 or $300 ÷ 15 = $20. Which estimate should he choose? Explain.
Answer: Newton should choose $300 ÷ 15 = $20.
Explanation: Newton is spending $415 each day on a 15-day trip. He can’t choose $450 ÷ 15 = $30 plan, because here the amount spend on a day is more than 415 so if he follow this he will be run out of money at the ending days of the trip. So, he must choose $300 ÷ 15 estimate to spend the money without issues.
Question 15. Writing Without calculating, explain how you know whether the quotient of 176 and 62 is closer to 2 or 3.
Answer: We can easily say that the quotient of 176 and 62 is 3. The reason is for your easy calculation, make 62 as 60 and the multiple of 60 which is nearest to 176 is 180.

Answer: The length of bigfoot trail is about 400 miles.
Explanation: Pacific Crest Trail = 7 times Bigfoot trail 2650 miles = 7 Bigfoot tail Bigfoot tail = 2650 ÷ 7 2800 ÷ 7 = 28 hundreds ÷ 7 = 4 hundreds 2100 ÷ 7 = 21 hundreds ÷ 7 = 3 hundreds So, the length of bigfoot trail is 400 miles.
Question 17. A family spends $2,473 each year for cell phone service. About how much does the family spend each month for cell phone service?
Answer: The amount spend by a family for cell phone service in a month is 200.
Explanation: The amount spend by a family for cell phone service in a year = $2,473 The amount spend by a family for cell phone service in a month = $2,473 ÷ 12 2400 ÷ 12 = 24 hundreds ÷ 12 = 2 hundreds 3600 ÷ 12 = 36 hundreds ÷ 12 = 3 hundreds So, choose 2400 that is near to 2473.
Question 18. DIG DEEPER! You have 31 days to read a book with 138 pages and another book with 160 pages. You want to read an equal number of pages each day. About how many pages do you read each day?
Answer: The number of pages read each day are 10.
Explanation: The total number of pages in two books = 138 + 160 = 298 Number of days to read books = 31 If you read an equal number of pages each day, then number of pages read in a day = 298 ÷ 31 Choose the numbers near to 298 and divisible by 30 near to 31. 300 ÷ 30 = 3 hundreds ÷ 3 tens = 3 ÷ 3 tens = 1 ten 270 ÷ 30 = 27 tens ÷ 3 tens = 9
Find two numbers that the quotient is between. Question 1. 1,306 ÷ 3 1,200 ÷ 3 = _____ 1,500 ÷ 3 = _____
Answer: 1,306 ÷ 3 is about 400. 1,200 ÷ 3 = 12 hundreds ÷ 3 = 4 hundreds 1,500 ÷ 3 = 15 hundreds ÷ 3 = 5 hundreds
Explanation: The number 1200 is near to 1306.
Question 2. 435 ÷ 80 400 ÷ 80 = ______ 480 ÷ 80 = ______
Answer: 435 ÷ 80 is about 5. 400 ÷ 80 = 4 hundreds ÷ 8 tens = 40 tens ÷ 8 tens = 5 480 ÷ 80 = 48 tens ÷ 8 tens = 6
Explanation: Number 400 is close to 435 and divisible by 80.
Question 3. 5,691 ÷ 68
Answer: 5,691 ÷ 68 is about 80.
Explanation: What numbers are closer to 5691 and divisible by 70 which is near to 68. 5600 ÷ 70 = 56 hundreds ÷ 7 tens = 8 tens 4900 ÷ 70 = 49 hundreds ÷ 7 tens = 7 tens So, choose 5600 which is near to 5691 and divisible by 70 which is near to 68.
Estimate the quotient. Question 4. 2,506 ÷ 2
Answer: 2,506 ÷ 2 is about 1300
Explanation: What numbers are near to 2506, divisible by 2. 2400 ÷ 2 = 24 hundreds ÷ 2 = 12 hundreds 2600 ÷ 2 = 26 hundreds ÷ 2 = 13 hundreds So, choose 2600 which is near to 2506.
Question 5. 4,392 ÷ 88
Answer: 4,392 ÷ 88 is 50.
Explanation: What numbers are near to 4392 and divided by 90 near to 88. 4500 ÷ 90 = 45 hundreds ÷ 9 tens = 5 tens 3600 ÷ 90 = 36 hundreds ÷ 9 tens = 4 tens So, choose 4500 near to 4392.
Question 6. 2,416 ÷ 6
Answer: 2,416 ÷ 6 is 400.
Explanation: What numbers are close to 2416 and divided by 6. 2400 ÷ 6 = 24 hundreds ÷ 6 = 4 hundreds 3000 ÷ 6 = 30 hundreds ÷ 6 = 5 hundreds So, choose 2400 near to 2416.
Question 7. \(\sqrt [ 52 ]{ 386 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 52 ]{ 386 } \) is 8.
Explanation: What numbers are near to 386 and divided by 50 which is near to 52. 350 ÷ 50 = 35 tens ÷ 5 tens = 7 400 ÷ 50 = 40 tens ÷ 5 tens = 8 So choose 400 near to 386.
Question 8. \(\sqrt [ 21 ]{ 1,495 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 21 ]{ 1,495 } \) is 70.
Explanation: What numbers are close to 1495 and divided by 21 which is near to 20. 1400 ÷ 20 = 14 hundreds ÷ 2 tens = 7 tens 1600 ÷ 20 = 16 hundreds ÷ 2 tens = 8 tens So, choose 1400 near to 1495.
Question 9. \(\sqrt [ 43 ]{ 3,509 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 43 ]{ 3,509 } \) is 90.
Explanation: What numbers are near to 3509 and divisible by 40 near to 43. 3200 ÷ 40 = 32 hundreds ÷ 4 tens = 8 tens 3600 ÷ 40 = 36 hundreds ÷ 4 tens = 9 tens So, choose 3600 close to 3509.

Answer: 2 Uranus years are equal to 175 earth years.
Explanation: Given that, The length of 1 year on Uranus is a little more than 84 years on Earth. 175 earth years = 175 ÷ 84 years 160 ÷ 80 = 16 tens ÷ 8 tens = 2 240 ÷ 80 = 24 tens ÷ 8 tens = 3 So, 160 is near to 175.
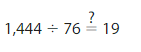
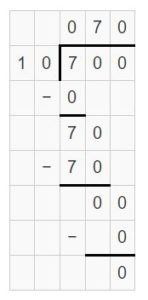
Answer: Yes, the answer is reasonable.
Explanation: What numbers are close to 1444 and divided by 76 which is near to 80. 1600 ÷ 80 = 16 hundreds ÷ 8 tens = 2 tens 800 ÷ 80 = 8 hundreds ÷ 8 tens = 1 tens So, choose 1600 near to 1444.
Question 12. Reasoning A florist has 336 roses and 28 vases. He wants to determine how many flowers he can put into each vase without any left over. Should he use an estimate or an exact answer? Explain.
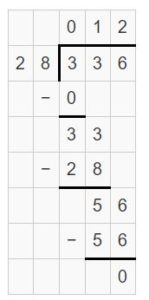
Answer: He will get an exact answer i.e in each vase there are 12 roses.
Question 13. Modeling Real Life A train ride from Chicago to Emeryville, California, is 2,438 miles. It is about 8 times as long as a train ride from Chicago to PortHuron, Michigan. About how long is the train ride from Chicago to Port Huron?
Answer: The train ride from Chicago to Port Huron is about 300 miles long.
Explanation: A train ride from Chicago to Emeryville, California = 8 x a train ride from Chicago to PortHuron, Michigan 2,438 = 8 x a train ride from Chicago to PortHuron, Michigan A train ride from Chicago to PortHuron, Michigan = 2438 ÷ 8 Choose the numbers close to 2438, divided by 8. 2400 ÷ 8 = 24 hundreds ÷ 8 = 3 hundreds 3200 ÷ 8 = 32 hundreds ÷ 8 = 4 hundreds So, choose 2400 is near to 2438.
Question 14. Modeling Real Life You are reading a book that has 784 pages. You have 18 days to read the entire book. About how many pages should you read each day?
Answer: You can read 40 pages each day to complete the book in 18 days.
Explanation: The number of pages of the book = 784 Number days to read book = 18 Number of pages should be read each day = 784 ÷ 18 Select the numbers which are near 784 and divided by 20 near 18. 600 ÷ 20 = 6 hundreds ÷ 2 tens = 3 tens 800 ÷ 20 = 8 hundreds ÷ 2 tens = 4 tens So, choose 800 which is closer to 784 and divided by 20.
Write the decimal as a fraction. Question 15. 0.61
Answer: 0.61 = (61 / 100)
Explanation: Rewrite the decimal number as a fraction having a denominator 1. 0.61 = 0.61 / 1 Multiply the numerator and denominator of the fraction by 100 to remove 2 decimal places. ( 0.61 / 1) x (100 / 100) = 61 / 100
Question 16. 0.084
Answer: 0.084 = (84 / 1000)
Explanation: Represent the given decimal number as a fraction with denominator 1. 0.084 = 0.084 / 1 Multiply the denominator and numerator of the fraction by the same number to remove 3 decimal places. Here, you can multiply by 10³ = 1000. (0.084 / 1) x (1000 / 1000) = 84 / 1000
Question 17. 0.709
Answer: 0.709 = 709 / 1000
Explanation: Mention the given decimal number as a fraction by keeping 1 in the denominator. 0.709 = 0.709 / 1 Multiply the fraction to eliminate 3 decimal places. Here, you can multiply both top and bottom by 10³ = 1000. (0.709 / 1) x (1000 / 1000) = (709 / 1000)
Question 18. 0.5
Answer: 0.5 = 5 / 10
Explanation: Keep 1 at the bottom and write the decimal number as a fraction. 0.5 = 0.5 / 1 Multiply both top and bottom by 10¹ = 10 to eliminate the decimal places. (0.5 / 1) x (10 / 10) = 5 / 10
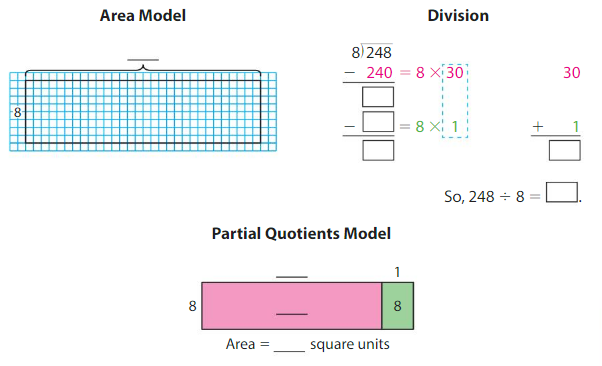
Structure How would the models be the same for 3,069 ÷ 5? How would they be different?
Answer: By using the Estimate Quotients process, we can just find the nearest possible value of the quotient. But this model gives the exact quotient value along with the remainder.
Think and Grow: Divide by One-Digit Numbers

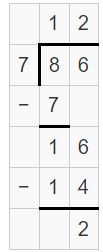
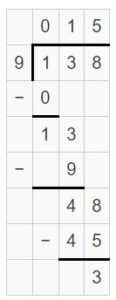
Divide. Then check your answer. Question 1. \(\sqrt [ 7 ]{ 86 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 7 ]{ 86 } \) = 12 R 2
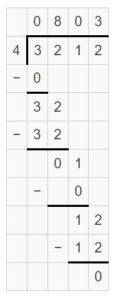
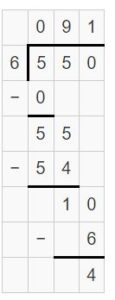
Question 2. \(\sqrt [ 4 ]{ 3,212 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 4 ]{ 3,212 } \) = 803 R 0
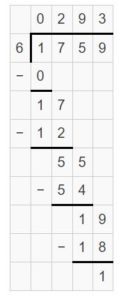
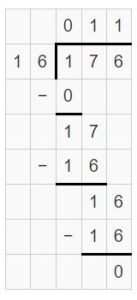
Question 3. \(\sqrt [ 6 ]{ 1,759 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 6 ]{ 1,759 } \) = 293 R 1
Divide. Then check your answer. Question 4. \(\sqrt [ 3 ]{ 4,185 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 3 ]{ 4,185 } \) = 1605 R 0
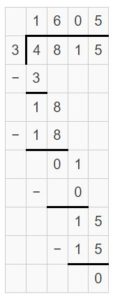
Question 5. \(\sqrt [ 6 ]{ 730 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 6 ]{ 730 } \) = 121 R 4
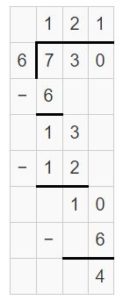
Question 6. \(\sqrt [ 8 ]{ 7,106 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 8 ]{ 7,106 } \) = 888 R 2
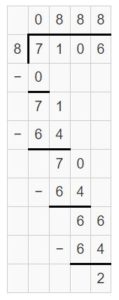
Question 7. 824 ÷ 4 = ______
Answer: 824 ÷ 4 = 206 R 0
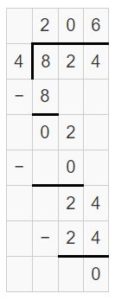
Question 8. 4,526 ÷ 2 = ______
Answer: 4,526 ÷ 2 = 2263
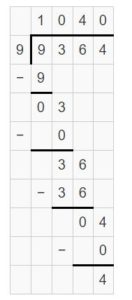
Question 9. 9,364 ÷ 9 = _______
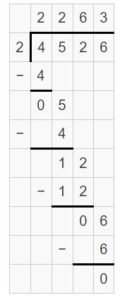
Answer: 9,364 ÷ 9 = 1040 R 9
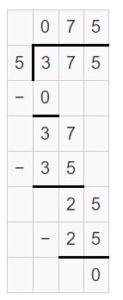
Question 10. Your cousin babysits for 5 days and earns a total of $375. How much money does your cousin earn each day?
Answer: Your cousin earns $75 on babysits daily.
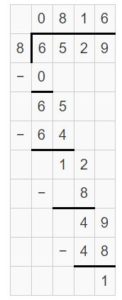
Question 11. Number Sense Without calculating, determine whether you place the first digit of the quotient in the hundreds place or the thousands place. Explain. 6,529 ÷ 8
Answer: I will place the first digit of the quotient on the hundreds place. 6,529 ÷ 8 = 816 R 1
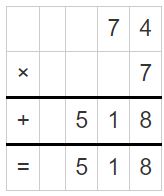
Answer: dividend = divisor × quotient + remainder 520 = 7 x 74 + 2 = 518 + 2
Question 13. A total of 243 students take a field trip on 5 buses. Each bus must have about the same number of students. How many students must ride on each bus?
Answer: At least 48 students must ride on each bus.
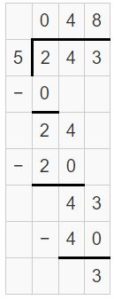
Divide. Then Check your answer. Question 1. \(\sqrt [ 6 ]{ 834 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 6 ]{ 834 } \) = 139 R 0
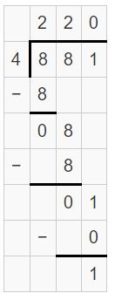
Question 2. \(\sqrt [ 4 ]{ 881 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 4 ]{ 881 } \) = 220 R 1
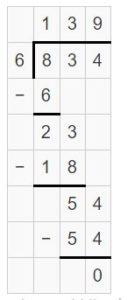
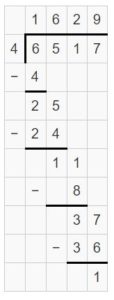
Question 3. \(\sqrt [ 2 ]{ 4,135 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 2 ]{ 4,135 } \) = 2067 R 1
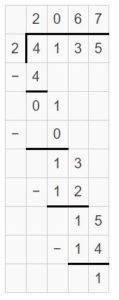
Question 4. 215 ÷ 7 = ______
Answer: 215 ÷ 7 = 30 R 5
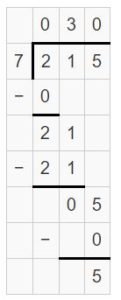
Question 5. 6,517 ÷ 4 = _____
Answer: 6,517 ÷ 4 = 1629 R 1
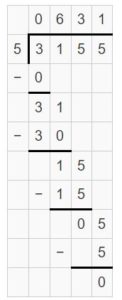
Question 6. 3,155 ÷ 5 = _____
Answer: 3,155 ÷ 5 = 631
Question 7. Your friend makes care packages with 9 items in each package. She has 1,350 items. How many care packages can she make?
Answer: Your friend can make 150 care packages.
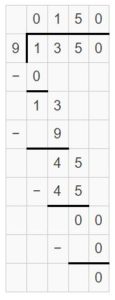
Question 8. Number Sense What is the dividend when the divisor is 8 and the quotient is 96 with remainder 3? Explain how you found the dividend.
Answer: The dividend is 771.
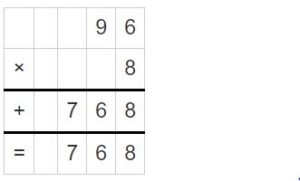
Question 9. Reasoning Your friend says the quotient of 3,627 and 9 is 43. Is your friend’s answer reasonable? Explain.
Answer: Not reasonable. why because, when we divide 3627 by 9, we can see the quotient as 403 and the remainder 0.
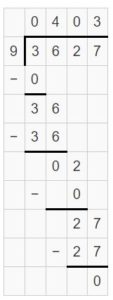
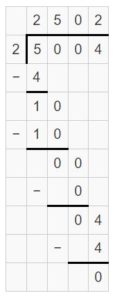
Answer: 5004 ÷ 2 = 2502 is the division expression that has the greatest quotient.
Question 11. Modeling Real Life A principal invites 138 students to a reward breakfast. Nine students sit at each table. How many tables are there?
Answer: There are 15 tables.
Answer: 2 more sheets are needed to make one more cube.
Estimate the product. Question 13. 0.9 × 82
Answer: 0.9 × 82 = 80
Explanation: To multiply the numbers, round them to the nearest greatest value. 0.9 x 82 = 1 x 80 = 1 x 8 tens = 8 tens
Question 14. 36 × 2.71
Answer: 36 × 2.71 = 120
Explanation: 36 × 2.71 = 40 x 3 = 4 tens x 3 = 12 tens = 120
Answer: 168 ÷ 14 = 12

Reasoning Explain how your model shows the quotient. Answer:
Think and Grow: Use Partial Quotients to Divide

Answer: 176 ÷ 16 = 11
Answer: 182 ÷ 13 = 14
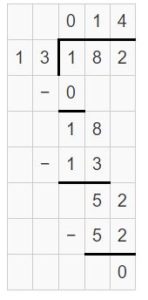
Answer: 154 ÷ 14 = 11
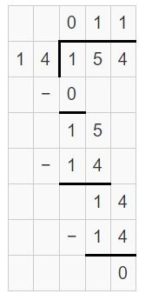
Answer: 224 ÷ 16 = 14
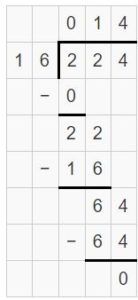
Use partial quotients to divide. Question 5. 204 ÷ 17
Answer: 204 ÷ 17 = 12
Question 6. 225 ÷ 15
Answer: 225 ÷ 15 = 15
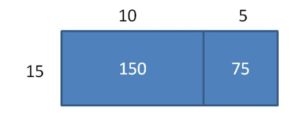
Question 7. Writing Explain why there is more than one way to draw an area model to find a quotient.
Answer: Area model or box model is a rectangular diagram used for division or multiplication problems. Here the quotient or factors and divisor define the length and width of the rectangle. You can break the area of a rectangle into several smaller boxes using number bonds to make calculations easier. So, there are several ways to draw an areal model to find the quotient.

Answer: 11 foot the puma jumps up on the rock.
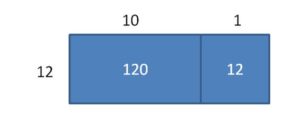
Answer: 160 ÷ 16, 112 ÷ 16.
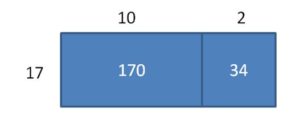
Explanation: Add the first column and second columns separately to get the dividends of the division equation. And the width of the rectangle is the divisor of the division equations. So, first equation is (100 + 60) ÷ 16 = 160 ÷ 16 Second equation is (70 + 42) ÷ 16 = 112 ÷ 16

Answer: The length of the rectangular floor is 18 feet.
Question 11. There are 176 fifth graders and 198 sixth graders signed up for soccer. Each soccer team has 11 players. How many more sixth-grade teams are there than fifth-grade teams?
Answer: Number of fifth-grade teams = 16 Number of six-grade teams = 18 So, 18 – 16 = 2 sixth-grade teams are more than fifth-grade teams.
Question 12. DIG DEEPER! Newton earns $195 for working 15 hours as a radio host. How much money does Newton earn in 3 hours?
Answer: Newton can earn $39 in 3 hours for working as a radio host.

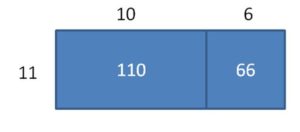
Answer: 165 ÷ 11 = 55
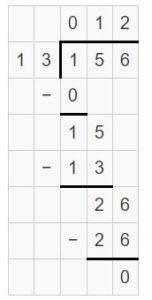
Answer: 192 ÷ 12 = 16
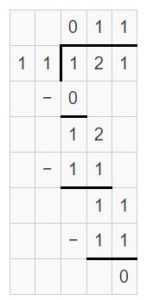
Use partial products to divide. Question 3. 156 ÷ 13
Answer: 156 ÷ 13 = 12
Question 4. 121 ÷ 11
Answer: 121 ÷ 11 = 11
Question 5. There are 143 players in a football league. The director divides the players into13 teams. How many players are on each team?
Answer: There are 11 players on each team.
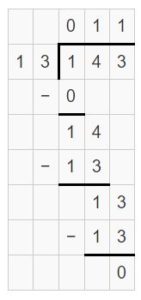
Question 6. Open-Ended Write a division expression that has a 3-digit dividend, a divisor between 15 and 20, and no remainder. Use base ten blocks to find the quotient.
Answer: 112 ÷ 16 = 7.
Answer: If he uses 20 x 22 = 440 as the first partial quotient. Then 506 – 440 = 66. And the second partial quotient will be 22 x 3 = 66. Then 66 – 66 = 0. So the remainder is 0. Partial quotients = 20 + 3 = 23.
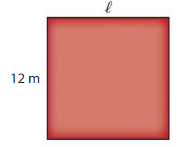
Answer: The length of the floor is 12 m.
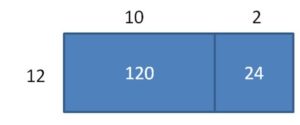
Question 9. Modeling Real Life A vending machine worker has 78 bags of cherry fruit snacks and 91 bags of strawberry fruit snacks. Each row of the vending machine holds 13 items from front to back. How many rows does the worker fill with fruit snacks?
Answer: The worker fills the fruit snacks on 13 rows.

Evaluate the expression.
Question 10. 24 ÷ (6 + 2) + 14
Answer: 24 ÷ (6 + 2) + 14 = 17
Explanation: 24 ÷ (6 + 2) + 14 = 24 ÷ 8 + 14 24 ÷ 8 = 3 3 + 14 = 17
Question 11. 5 + 10 × 7 – 9
Answer: 5 + 10 × 7 – 9 = 66
Explanation: Based on the arithmetical operator included between the numbers, it has given some preference to evaluate first. 5 + 10 × 7 – 9 = 5 + (10 x 7) – 9 = (5 + 70) – 9 = 75 – 9 = 66.
Question 12. (135 + 96 + 165) × 10
Answer: (135 + 96 + 165) × 10 = 3960
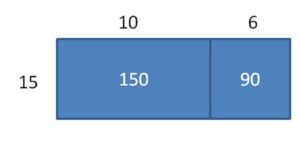
Answer: 240 ÷ 15 = 16.
Answer: We can’t use the area model to find 190 ÷ 15. Why because 15 does not divide evenly into 190.
Construct Arguments Explain to your partner how you know that 15 does not divide evenly into 190.
Answer: First, we need to find the first partial quotient i.e 15 x 10 = 150. Then 190 – 150 = 40. 40 is not divisible by 15. So, we can say that 15 does not divide evenly into 190.
Think and Grow: Use Partial Quotients
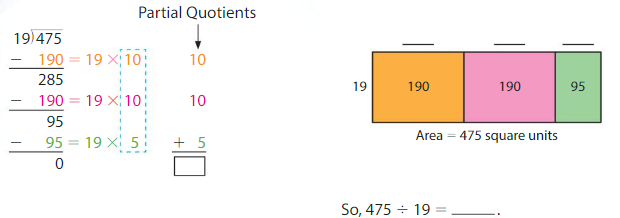
Answer: 475 ÷ 19 = 10 + 10 + 5 = 25
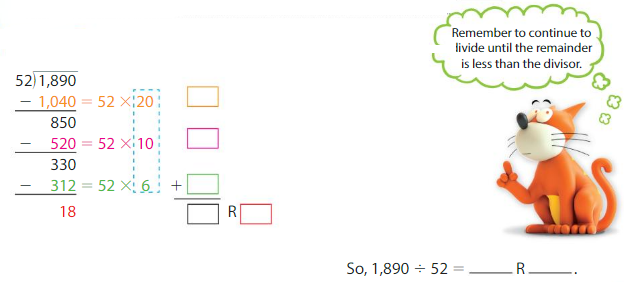
1,890 ÷ 52 = (20 + 10 + 6) R 18 = 36 R 18.
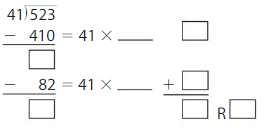
Answer: 523 ÷ 41 = 12 R 31.
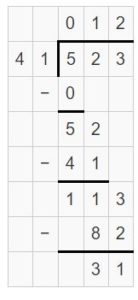
Answer: 2,760 ÷ 87 = 31 R 63
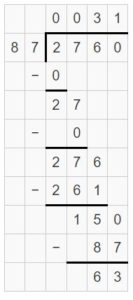
Use partial quotients to divide. Question 3. \(\sqrt [ 28 ]{ 476 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 28 ]{ 476 } \) = 17 R 28
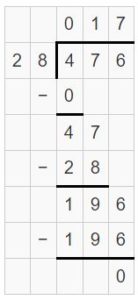
Question 4. \(\sqrt [ 31 ]{ 605 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 31 ]{ 605 } \) = 19 R 16
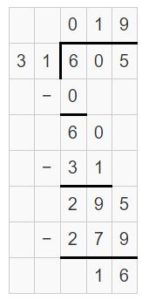
Question 5. \(\sqrt [ 47 ]{ 1,833 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 47 ]{ 1,833 } \) = 39
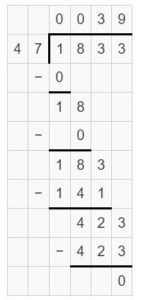
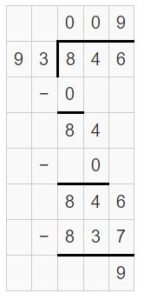
Question 6. 846 ÷ 93 = ______
Answer: 846 ÷ 93 = 9 R 9
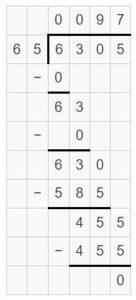
Question 7. 6,305 ÷ 65 = _______
Answer: 6,305 ÷ 65 = 97 R 0
Question 8. 5,603 ÷ 72 = _____
Answer: 5,603 ÷ 72 = 77 R 59
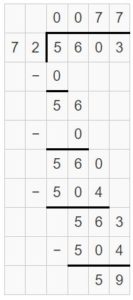
Answer: The weight of the punching bag in pounds is 60.
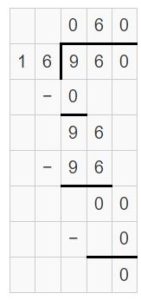
Question 10. Reasoning Your friend wants to divide 2,561 by 34. She multiplies 34 by 100 for her first partial quotient. Is this reasonable? Explain.
Answer: The first partial quotient is 34 x 70 = 2380. So, it is not reasonable.
Question 11. DIG DEEPER! A division problem has 56 as its divisor. The partial quotients are 10 and 8. The remainder is 2. What is the dividend?
Answer: The dividend is 1010.
Explanation: Partial Quotients = 10 + 8 = 18 Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder. Dividend = 56 x 18 + 2 = 1008 + 2 = 1010.

Question 12. A screen printing shop makes 736 T-shirts. A shipping box can hold 28 T-shirts. How many boxes are needed to ship all of the T-shirts?
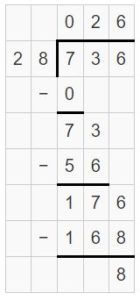
Answer: 27 shipping boxes are required to ship all of the T-shirts.
Question 13. The owner of a popcorn stand makes 2,568 ounces of popcorn in 1 day. How many 64-ounce bags of popcorn can the owner fill completely?
Answer: The owner can fill 41, 64-ounce bags of popcorn.
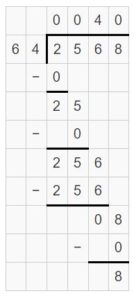
Answer: The worker can make 51 fruit bouquets with the amount of fruit in stock.
Answer: 426 ÷ 21 = 20 R 6
Answer: 1,832 ÷ 32 = 57 R 8
Question 3. \(\sqrt [ 16 ]{ 279 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 16 ]{ 279 } \) = 17 R 7
Question 4. \(\sqrt [ 95 ]{ 970 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 95 ]{ 970 } \) = 10 R 20
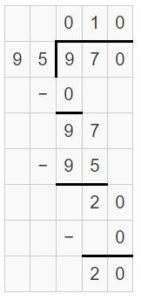
Question 5. \(\sqrt [ 43 ]{ 2,451 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 43 ]{ 2,451 } \) = 57
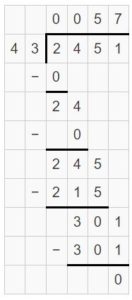
Use partial quotients to divide. Question 6. 504 ÷ 18 = ______
Answer: 504 ÷ 18 = 28
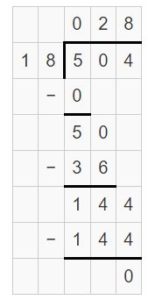
Question 7. 3,740 ÷ 64 = _____
Answer: 3,740 ÷ 64 = 58 R 28
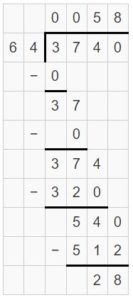
Question 8. 9,261 ÷ 57 = ______
Answer: 9,261 ÷ 57 = 162 R 27
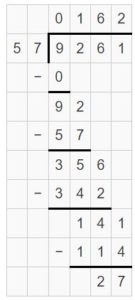
Answer: 35 books are in each bin.
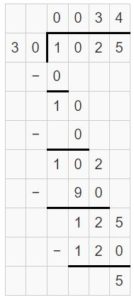
Question 10. Number Sense What is the greatest possible whole number remainder when you divide a number by 75? Explain.
Answer: 74 is the greatest possible whole number divided obtained after dividing a number by 75. This remainder is obtained by dividing 149 by 75.
Question 11. Structure Solve 4,123 ÷ 78 two different ways using partial quotients.
Answer: 4,123 ÷ 78 = 52 R 67
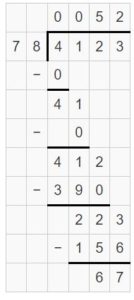
Question 12. Modeling Real Life One study shows that American adults eat about 31 pounds of cheese each year. How many years does it take for an adult to eat 1,500 pounds of cheese?
Answer: It takes a total of 49 years for an adult to eat 1500 pounds of cheese.
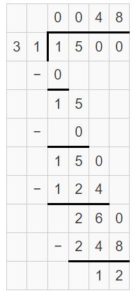
Question 13. Modeling Real Life There are 212 students and 89 teachers attending a leadership conference. One table can seat 16 people. How many tables are needed?
Answer: A total of 19 tables are needed.
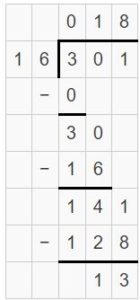
Estimate the product. Question 14. 487 × 92
Answer: 487 × 92 = 45000
Explanation: Round up the given numbers to the nearest hundreds and tens. 487 can be rounded to 500 and 92 can be rounded to 90. So, 500 x 90 = 5 hundreds x 9 tens = 45 thousands.
Question 15. 24 × 211
Answer: 24 × 211 = 4000
Explanation: Round up the given numbers to the nearest hundreds and tens. 24 can be rounded to 20 and 211 can be rounded to 200. So, 200 x 20 = 2 hundreds x 2 tens = 4 thousands.
Question 16. 49 × 657
Answer: 49 × 657 = 35000
Explanation: Round up the given numbers to the nearest hundreds and tens. 49 can be rounded to 50 and 657 can be rounded to 700. So, 50 x 700 = 5 tens x 7 hundreds = 35 thousands.

Answer: The division problems have one-digit quotients are 344 ÷ 43, 340 ÷ 68, 711 ÷ 79. And the division problems which have two-digit quotients are 312 ÷ 18, 840 ÷ 24, 407 ÷ 11.
Explanation: All the divisors are two digits, so we can take the first two digits or three digits of the dividend for calculation. If the dividend starting digits are greater than divisor numbers, then it has a two-digit quotient. If the divided starting digits is less than the divisor, then it has a one-digit quotient.
Reasoning Explain how estimation can help you determine the number of digits in a quotient.
Answer: The simple strategy is, the starting digits of the dividend is greater than the divisor, then it has a one-digit quotient. And if the starting digits of the divisor is greater than the divisor, then it has the two-digit quotient.
Think and Grow: Divide Three-Digit Numbers by Two-DigitNumbers
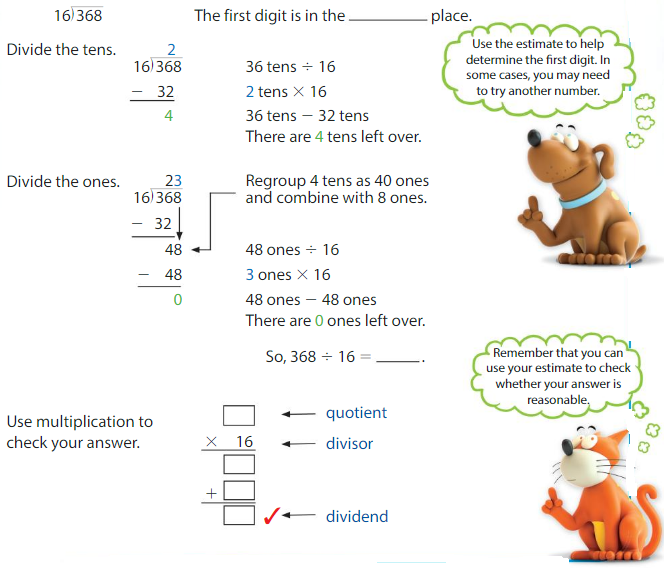
Answer: 368 ÷ 16 = 23.
Divide. Then check your answer. Question 1. \(\sqrt [ 18 ]{ 612 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 18 ]{ 612 } \) = 34
Question 2. \(\sqrt [ 42 ]{ 294 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 42 ]{ 294 } \) = 7
Question 3. \(\sqrt [ 30 ]{ 580 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 30 ]{ 580 } \) = 19
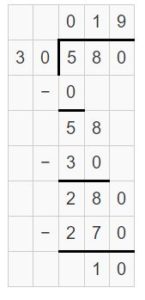
Divide. Then check your answer. Question 4. \(\sqrt [ 16 ]{ 293 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 16 ]{ 293 } \) = 18.
Question 5. \(\sqrt [ 35 ]{ 375 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 35 ]{ 375 } \) = 10
Question 6. \(\sqrt [ 77 ]{ 847 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 77 ]{ 847 } \) = 11
Question 7. 564 ÷ 94 = ______
Answer: 564 ÷ 94 = 6
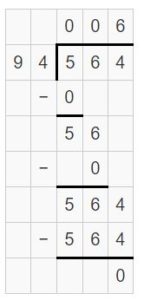
Question 8. 998 ÷ 33 = _______
Answer: 998 ÷ 33 = 30
Question 9. 702 ÷ 54 = ________
Answer: 702 ÷ 54 = 13
Answer: It requires 23 scores for a plastic bottle to decompose.
Explanation: Divide 460 by 20 to get how many scores does it take for a plastic bottle to decompose. Divide the ten. 46 tens ÷ 20 2 tens x 20 = 40 tens 46 tens – 40 tens = 6 tens Divide the ones. 60 ÷ 20 20 x 3 ones = 60 60 – 60 = 0 Regroup 2 tens and 3 ones. So, 460 ÷ 20 = 23 Therefore, 23 scores are required for a plastic bottle to decompose.
Question 11. Number Sense Can you have a remainder that is greater than the divisor?
Answer: No, remainder of a division problem is not greater than the divisor. Explanation: If a remainder is greater than divisor, latter can go one more time and hence division is not complete. Even if remainder is equal to divisor, it can still go one more time. Hence remainder has to be less than the divisor.
Question 12. Structure Find 304 ÷ 16 using two different methods. Which method do you prefer? Why?
Question 13. A farmer has 918 eggs to sell at a farmer’s market. She packs 12 eggs in each carton. How many cartons are full?
Answer: 76 Cartons are full.
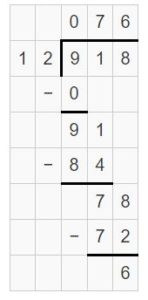
Question 14. Descartes makes 770 cups of apple cider. He pours 16 cups of cider into each container. How many containers does Descartes need?
Answer: Descartes need 49 containers to fill 770 cups of apple cider.
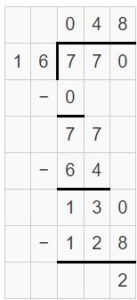
Answer: 6 students sit with the teachers in the last row of the auditorium.
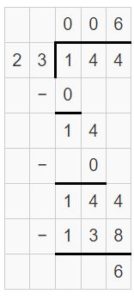
Divide. Then check your answer. Question 1. \(\sqrt [ 21 ]{ 735 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 21 ]{ 735 } \) = 35
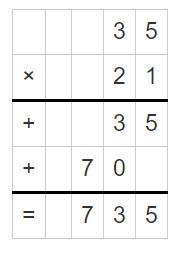
Question 2. \(\sqrt [ 64 ]{ 802 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 64 ]{ 802 } \) = 12 R 34.
Explanation: The first digit is in the hundreds place. Divide the tens. Then divide the ones. 80 tens ÷ 64 64 x 1 ten = 64 tens 80 tens – 64 tens = 16 tens 162 ones ÷ 64 64 x 2 ones = 128 ones 162 ones – 128 ones = 34 ones Regroup 1 ten and 2 ones So, \(\sqrt [ 64 ]{ 802 } \) = 12 R 34. Use multiplication to check your answer. 64 x 12 = 768 786 + 34 = 802
Question 3. \(\sqrt [ 40 ]{ 901 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 40 ]{ 901 } \) = 22 R 21
Explanation: Divide the tens. Then divide the ones. 90 tens ÷ 40 2 tens x 40 = 80 tens 90 tens – 80 tens = 10 tens 101 one ÷ 40 40 x 2 = 80 ones 101 one – 80 one = 21 one Regroup 2 tens and 2 ones. So, \(\sqrt [ 40 ]{ 901 } \) = 22 R 21 Use multiplication to check your answer. 22 x 40 = 880 880 + 21 = 101.
Question 4. 486 ÷ 18 = ______
Answer: 486 ÷ 18 = 24 R 14
Explanation: Divide the tens. Then divide the ones. 48 tens ÷ 18 2 tens x 18 tens = 36 tens 48 tens – 36 tens = 8 tens 86 ones ÷ 18 18 x 4 ones = 72 ones 86 ones – 72 ones = 14 ones Regroup 2 tens and 4 ones. So, 486 ÷ 18 = 24 R 14 Use multiplication to check your answer. 24 x 18 = 432 432 + 14 = 486
Question 5. 266 ÷ 19 = ______
Answer: 266 ÷ 19 = 14
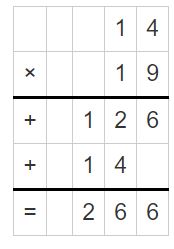
Question 6. 284 ÷ 37 = _______
Answer: 284 ÷ 37 = 8 R 12
Answer: The store receives 40 nails of bags.
Explanation: Divide 960 by 24 to get how many bags of nails does the store receive. Divide the tens. Then divide the ones. 96 tens ÷ 24 24 x 4 tens = 96 tens 96 tens – 96 tens = 0 So, 960 ÷ 24 = 40 Therefore, store receives 40 nails of bags.
Question 9. DIG DEEPER! Change the dividend in the equation to another three-digit number so that there is no remainder. 893 ÷ 61 = 14 R 39
Answer: 854 ÷ 61 = 14
Question 10. Modeling Real Life An amusement park ride seats 12 people. There are 458 people in line. How many times does the ride run full?
Answer: 38 times the ride run full.
Explanation: Divide 458 by 12 to get how many times does the ride run full. Divide the tens. Then divide the ones. 45 tens ÷ 12 12 x 3 tens = 36 tens 45 tens – 36 tens = 9 tens 98 ones ÷ 12 12 x 8 ones = 69 ones 98 ones – 96 ines = 2 ones Regroup 3 tens and 8 ones. So, 458 ÷ 12 = 38 R 2. Interpret the quotient and the remainder. The quotient is 38. So, 38 times the ride is full. The remainder is 2. There are 2 more people to ride. So, the last ride run is not full and has 2 people. So, 38 times the ride is full.

Answer: 15 more garbage cans are left over.
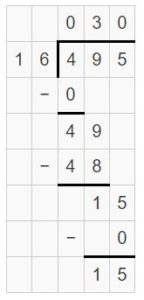
Question 12. Round 18.692. Nearest whole number: ________ Nearest tenth: _______ Nearest hundredth: _______
Answer: Nearest whole number: 19 Nearest tenth: 18.7 Nearest hundredth: 18.69
Explanation: In the number 18.692, digit at decimal place is 6. So, nearest tenths is 18.7, the digit at the units place is 8. So, the nearest whole number is 20. And the digit at hundredth place is 9 so, the nearest hundredth is 18.69.
Question 13. Round 5.153. Nearest whole number: ______ Nearest tenth: _______ Nearest hundredth: _______
Answer: Nearest whole number: 5 Nearest tenth: 5.1 Nearest hundredth: 5.15
Explanation: In the given number 5.153 the number at units place is 5 so nearest whole number is also 5. The number at tenths place is 1, so the nearest 10th is 5.1, The number at hundredth place is 5 so the nearest 100th is 5.15.
Answer: The division problems which have two digit quotients are 4774 ÷ 62, 1050 ÷ 25, and 1995 ÷21. The problems that have three digit quotients are 1890 ÷18, 8200 ÷40, and 6138 ÷ 33.
Explanation: We can simply say that in each problem the denominator is a two digit number and numerator is a four digit number. Here, if the first two digits of the numerator are greater than or equal to the denominator, then it has three digit quotient. If the first two digits of the numerator are less than the denominator, then it has two digit quotient.
Reasoning Can a four-digit whole number divided by a two-digit whole number have a whole number quotient with four digits? Explain your reasoning.
Answer: No, a four digit whole number divided by a two digit whole number have a whole number quotient with four digits. Because, the division process will reduce the number of digits of the dividend by at least 1.
Think and Grow: Divide Four-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers
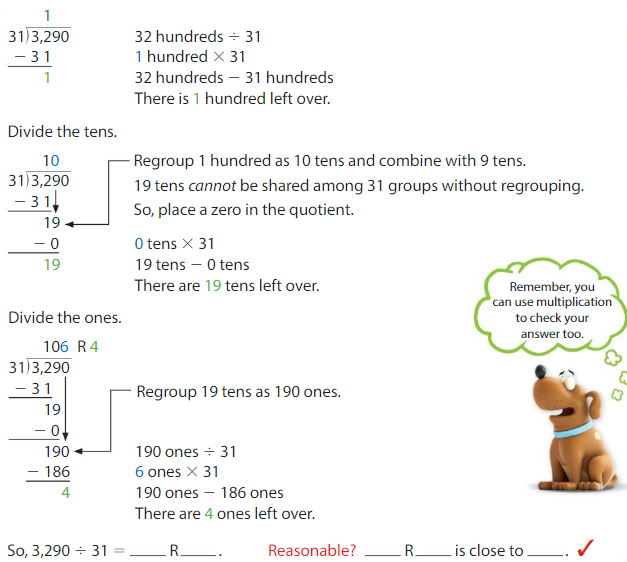
Divide. Then check your answer. Question 1. \(\sqrt [ 28 ]{ 1,148 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 28 ]{ 1,148 } \) = 41
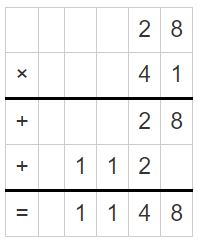
Question 2. \(\sqrt [ 13 ]{ 1,596 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 13 ]{ 1,596 } \) = 122 R 10
Divide. Then check your answer. Question 3. \(\sqrt [ 16 ]{ 9,640 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 16 ]{ 9,640 } \) = 602 R 8.
Question 4. \(\sqrt [ 26 ]{ 5,460 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 26 ]{ 5,460 } \) = 210
Question 5. \(\sqrt [ 37 ]{ 3,885 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 37 ]{ 3,885 } \) = 105
Question 6. 2,784 ÷ 72 = _______
Answer: 2,784 ÷ 72 = 38 R 48
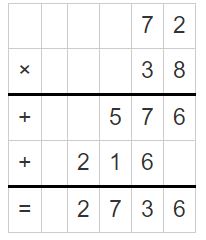
Question 7. 8,047 ÷ 83 = _______
Answer: 8,047 ÷ 83 = 96 R 79
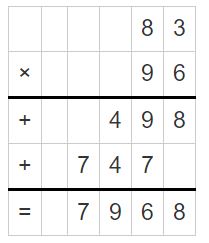
Question 8. 9,504 ÷ 96 = ________
Answer: 9,504 ÷ 96 = 99
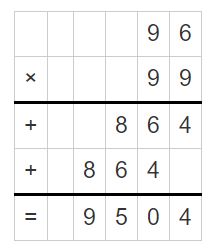
Answer: The section was 20 feet wide.
Explanation: Divide 1500 by 75 to get the section wide area. 75 x 2 tens = 150 tens So, 1500 ÷ 75 = 20.
Question 10. Reasoning Your friend finds 6,408 ÷ 51 and gets an answer of 124 R 84. Explain your friend’s mistake.
Answer: 6,408 ÷ 51 = 125 R 33. My friend made mistake at the one’s division.
Explanation: The first digit is in the thousands place. Divide the hundreds. 64 hundreds ÷ 51 51 x 1 hundred = 51 hundreds 64 hundreds – 51 hundreds = 13 hundreds Divide the tens 130 tens ÷ 51 51 x 2 tens = 102 tens 130 tens – 102 tens = 28 tens Divide the ones. 288 ones ÷ 51 51 x 5 ones = 255 ones 288 ones – 255 ones = 33 ones So, 6,408 ÷ 51 = 125 R 33
Question 11. Writing Explain why you can use multiplication to check your answer to a division problem.
Answer: Multiplication and division are the inverse operations. For example when you divide 20 by 5, the quotient is 4. And multiply 4 x 5 = 20. So, it is proved that multiplication is helpful to check whether the division is correct or not.

Question 12. A librarian has 1,048 books to shelve. Each shelf can hold 32 books. The librarian fills each shelf before moving to another shelf. How many books are on the last shelf?
Answer: There are 24 books on the last shelf.
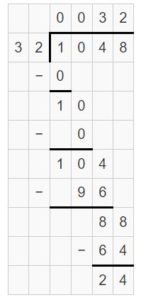
Question 13. A banker receives 2,215 nickels. A standard roll of nickels contains 40 nickels. How many standard rolls of nickels can the banker make?
Answer: The banker can make 55 standard rolls of nickels.
Answer: The director uses 65 signs.
Divide. Then Check you answer. Question 1. \(\sqrt [ 13 ]{ 5,343 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 13 ]{ 5,343 } \) = 411
Question 2. \(\sqrt [ 23 ]{ 32,96 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 23 ]{ 32,96 } \) = 143 R 7
Question 3. \(\sqrt [ 48 ]{ 1,414 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 48 ]{ 1,414 } \) = 29 R 22
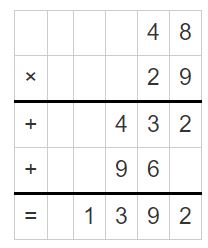
Question 4. 3,300 ÷ 15 = _____
Answer: 3,300 ÷ 15 = 220
Question 5. 4,592 ÷ 82 = _____
Answer: 4,592 ÷ 82 = 56
Question 6. 8,751 ÷ 64 = _______
Answer: 8,751 ÷ 64 = 136 R 47
Question 7. A hot-air balloon travels 2,016 miles in 96 hours. The balloon travels the same number of miles each hour. How many miles does the balloon travel in 1 hour?
Answer: The balloon travels 21 miles in 1 hour.
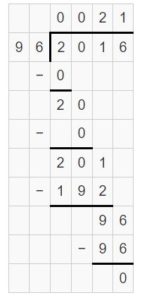
Answer: The width of the rectangle is 25 feet.
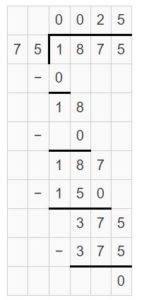
Question 9. Which One Doesn’t Belong? Which expression does not have a two-digit quotient? 1,955 ÷ 85 6,701 ÷ 36 1,699 ÷ 54 2,754 ÷ 71
Answer: 6701 ÷ 36 does not have a two-digit quotient.
Explanation: The reason is The first two digit numbers of the dividend 67 is greater than the divisor 36.
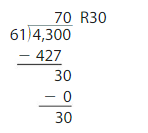
Question 11. Modeling Real Life A recycling company has 2,609 pounds of materials to sort. For efficiency, it divides all of the materials into boxes that each hold 20 pounds of materials. How many pounds of materials are in the last box?
Answer: The last box has 9 pounds of the material.
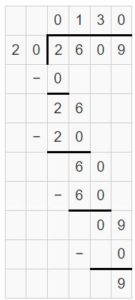
Question 12. Modeling Real Life An art museum has 1,025 paintings to divide equally among 20 rooms. How many more paintings does it need so that every room has the same number of paintings?
Answer: 15 more paintings are required so that all the rooms have same number of paintings.
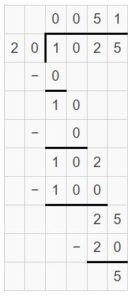
Find the difference. Then check your answer. Question 14. 145.92 – 15.78 = _____
Answer: 145.92 – 15.78 = 130.14
Question 15. 3.63 – 0.48 = ______
Answer: 3.63 – 0.48 = 3.15
Answer: The weight of the mother giraffe is 1650 pounds and the weight of the newborn giraffe is 150 pounds.
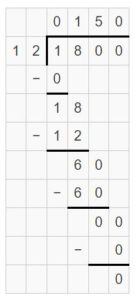
Make Sense of Problems How does your plan change if the combined weight of the giraffes is 1,752 pounds? Explain.
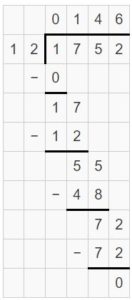
Think and Grow: Problem Solving: Division
Example The length of an oil tanker is 15 times the length of a tugboat. The combined length of the boats is 304 meters. What is the length of each boat? Understand the Problem What do you know? • You need to find the length of each boat.
What do you need to find? • The length of the oil tanker is 15 times the length of the tugboat. • The combined length of the boats is 304 meters.
Make a Plan How will you solve? • Draw and use tape diagrams to help write a division problem that gives the length of the tugboat. • Multiply the length of the tugboat by 15 to find the length of the oil tanker.
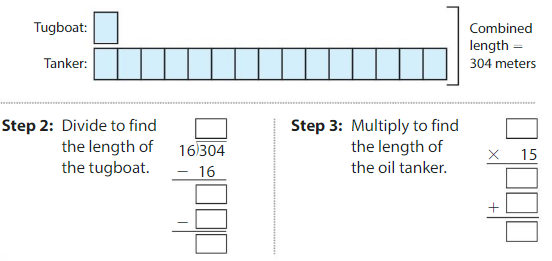
Question 1. Explain how you can check your answer above.
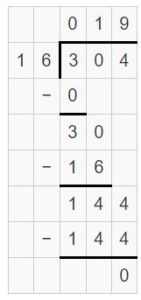
Understand the problem. What do you know? What do you need to find? Explain. Question 2. A lion weighs 7 times as much as a leopard. The combined weight of the cats is 480 pounds. What is the weight of each cat?
Answer: The leopard weight is 68 pounds and the lion weight is 408 pounds.
Question 3. A fifth-grade class raises $1,040 for a field trip to a museum. One admission ticket costs $8 and one lunch costs $5. How many people can attend the field trip?
Answer: 80 people can attend the trip.
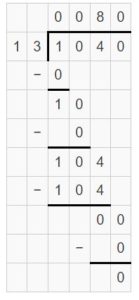
Understand the problem. Then make a plan. How will you solve? Explain. Question 4. A photo album has 15 pages. Each page can hold 6 photographs. How many of these albums do you need for 1,025 photographs?
Answer: 12 albums are needed for 1025 photographs.
Question 5. You, Newton, and Descartes play a video game. You have 5 times as many points as Newton. Descartes has 9 times as many points as Newton. You, Newton, and Descartes have 1,320 points in all. How many points do you have?
Answer: You have 264 points.
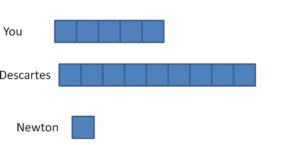
Answer: The length of the Rio Grande is 17064 miles.
Question 7. A great white shark migrates a total of 2,210 miles in 52 days. The shark travels the same number of miles each day. How many miles does the shark travel each day?
Answer: The shark travels 42 (26 / 52) miles each day.
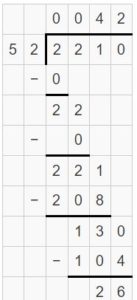
Question 8. Newton has 2,480 baseball cards and 1,235 football cards in his collection. He wants to put all of the cards into an album. Each page holds 18 cards. How many pages does he need for all of his cards? Explain.
Answer: The number of pages required for all cards is 206 (7/18)
Question 9. Descartes has 6 large boxes with 48 party favors in each box and 5 small boxes with 16 party favors in each box. He puts 15 favors in each gift basket. How many baskets does he make? Explain.
Answer: The number of boxes made are 24 (8/15).
Question 10. DIG DEEPER! Write and solve a word problem involving division in which the remainder can be written as a fraction.
Answer: The question is a person spends a total of $160 on his food for 30 days. The person spends the same amount each day. How much does the person spend money each day?
Understand the problem. What do you know? What do you need to find? Explain. Question 1. A DVD storage tower has 8 shelves. Each shelf can display 12 DVDs. How many storage towers does a worker need to display 1,440 DVDs?
Answer: 15 storage towers are required to display 1,440 DVDs.
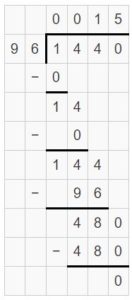
Question 2. The Eastern Continental Trail is 15 times longer than the Erie Canalway Trail. The combined length of the hiking trails is 5,760 miles. What is the length of each hiking trail?
Answer: The length of Erie Canalway Trail is 360 and the length of Eastern Continental Trail is 5400.

Understand the problem. Then make a plan. How will you solve? Explain. Question 3. A runner finished a total of 1,500 kilometers in races before retiring. She finished thirty-two15-kilometer races. The rest of her races were10-kilometer races. How many of her races were10-kilometer races?
Answer: Her 10-kilometer races are 102.
Explanation: The total number of kilometers = 1500 15-kilometer races = 32 10-kilometer races = ? Total number of kilometers of 15 kilometer races = 15 x 32 = 480 Total number of kilometers of 10-kilometer races = 1500 – 480 = 150 tens – 48 tens = 102 tens 10-kilometer races = 1020 ÷ 10 = 102 tens ÷ ten = 102.
Question 4. You, Newton, and Descartes volunteer this summer. You have 2 times as many volunteer minutes as Newton. Descartes has 3 times as many volunteer minutes as Newton. You, Newton, and Descartes have 5,040 volunteer minutes altogether. How many minutes do you volunteer?
Answer: I will volunteer for 1680 minutes.
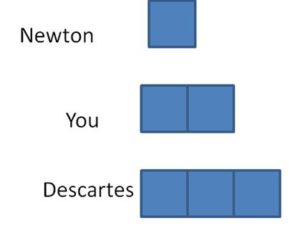
Question 5. A factory packs boxes with glitter pens. One box can hold 36 glitter pens. The factory produces 5,982 glitter pens. The factory fills as many boxes as possible. How many glitter pens will not fit into the boxes?
Answer: 30 glitter pens will not fit into the boxes.
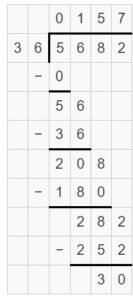
Answer: Dubai Fountain should reach 500 feet high.
Explanation: The height of Burj Khalifa in Dubai = 2717 feet 2717 – 217 = 2500 Divide 2500 by 5 to get how high does the Dubai Fountain reach. 25 hundreds ÷ 5 = 5 hundreds. So, Dubai Fountain should reach 500 feet high.
Question 7. Modeling Real Life A woodworker spends a total of 162 hours making 24 birdhouses. He spends the same amount of time on each birdhouse. How many hours does he spend on each birdhouse?
Answer: He spends 6(3/4) hours on each birdhouse.
Question 8. Modeling Real Life A truck driver drives 2,580 miles in 40 hours. He drives the same number of miles each hour. How many miles does he drive each hour?
Answer: He drives 64 (/2) miles each hour.
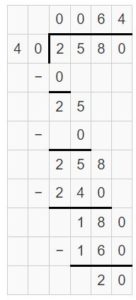
Answer: 4.71
Answer: 111.696

Answer: 0.368
Answer: a. My family spends 8(8/55) on driving. b. I can spend 90 minutes at each stop. c. The driving times is longer than 8 hours.
Answer: a. My family drives 30 miles using 1 gallon of gasoline. b. My family spends $10 on gasoline c. you can save $28 on the trip.
Answer: 9623 ÷ 54 = 178 R 11 758 ÷ 11 = 68 R 10 8484 ÷ 21 = 404 R 0 945 ÷ 15 = 63 R 0 160 ÷ 38 = 4 R 8 4500 ÷ 20 = 225 R 0 548 ÷ 47 = 11 R 31 1344 ÷ 48 = 28 R 0 3947 ÷33 = 119 R 20 832 ÷ 64 = 13 R 0 7313 ÷71 = 103 R 0 394 ÷ 27 = 14 R 16 476 ÷53 = 8 R 52 5208 ÷ 93 = 56 R 0 216 ÷18 = 12 R 0 6378 ÷ 24 = 265 R 18
6.1 Relate Multiplication and Division
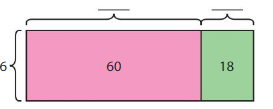
Answer: 78 ÷ 6 = 13.
Explanation: 78 = 60 + 18 78 = (6 x _) + (6 x _) Sum of unknown factors of the smallest areas: 10 + 3 = 13 The related multiplication equation is 6 x 13 = 78. So, 78 ÷ 6 = 13.
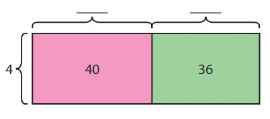
Answer: 76 ÷ 4 = 19.
Explanation: 76 = 40 + 36 76 = (4 x _) + (4 x _) Sum of unknown factors of the smallest areas: 10 + 9 = 19 The related multiplication equation is 4 x 19 = 76
Question 3. 105 ÷ 5 = _____
Answer: 105 ÷ 5 = 21.
Explanation: 105 = 50 + 55 105 = (5 x _) + (5 x _) Sum of unknown factors of the smallest areas: 10 + 11 = 21 The related multiplication equation is 5 x 21 = 105
Question 4. 288 ÷ 8 = _____
Answer: 288 ÷ 8 = 36.
Explanation: 288 = 160 + 128 288 = (8 x _) + (8 x _) Sum of unknown factors of the smallest areas: 20 + 16 = 36 The related multiplication equation is 8 x 36 = 288
6.2 Division Patterns
Find the quotient. Question 5. 4,500 ÷ 5 = ______
Answer: 4,500 ÷ 5 = 900.
Explanation: 4,500 ÷ 5 = 45 hundreds ÷ 5 = 9 hundreds = 900.
Question 6. 140 ÷ 70 = _____
Answer: 140 ÷ 70 = 2.
Explanation: 140 ÷ 70 = 14 tens ÷ 7 tens = 14 ÷ 7 = 2.
Question 7. 160 ÷ 20 = _____
Answer: 160 ÷ 20 = 8.
Explanation: 160 ÷ 20 = 16 tens ÷ 2 tens = 16 ÷ 2 = 8
Question 8. 720 ÷ 9 = ______
Answer: 720 ÷ 9 = 80.
Explanation: 720 ÷ 9 = 72 tens ÷ 9 = 8 tens = 80.
Question 9. 4,900 ÷ 70 = ______
Answer: 4,900 ÷ 70 = 70.
Explanation: 4,900 ÷ 70 = 49 hundreds ÷ 7 tens = 49 tens ÷ 7 = 7 tens = 70
Question 10. 10,000 ÷ 5 = ______
Answer: 10,000 ÷ 5 = 2000.
Explanation: 10,000 ÷ 5 = 10 thousands ÷ 5 = 2 thousands = 2000.
6.3 Estimate Quotients
Find two numbers that the quotient is between. Question 11. 604 ÷ 19 600 ÷ 20 = _____ 800 ÷ 20 = _____
Answer: 600 ÷ 20 = 30 800 ÷ 20 = 40
Explanation: 600 ÷ 20 = 6 hundreds ÷ 2 tens = 6 tens ÷ 2 = 3 tens = 30 800 ÷ 20 = 8 hundreds ÷ 2 tens = 8 tens ÷ 2 = 4 tens = 40
Question 12. 1,732 ÷ 40 1,600 ÷ 40 = ______ 2,000 ÷ 40 = _______
Answer: 1,600 ÷ 40 = 40 2,000 ÷ 40 = 50
Explanation: 1,600 ÷ 40 = 16 hundreds ÷ 4 tens = 16 tens ÷ 4 = 4 tens = 40 2,000 ÷ 40 = 20 hundreds ÷ 4 tens = 20 tens ÷ 4 = 5 tens = 50
Question 13. 4,096 ÷ 61
Answer: 3600 ÷ 60 = 60 4200 ÷ 60 = 70.
Explanation: Choose What numbers close to 4069 are easily divided by 60? 4200 ÷ 60 = 42 hundreds ÷ 6 tens = 42 tens ÷ 6 = 7 tens = 70 3600 ÷ 60 = 36 hundreds ÷ 6 tens = 36 tens ÷ 6 = 6 tens = 60
Estimate the quotient. Question 14. 3,411 ÷ 53
Answer: 3,411 ÷ 53 = 70.
Explanation: Choose What numbers close to 3411 are easily divided by 50? 3500 ÷ 50 = 35 hundreds ÷ 5 tens = 35 tens ÷ 5 = 7 tens 3000 ÷ 50 = 30 hundreds ÷ 5 tens = 30 tens ÷ 5 = 6 tens So, choose 3500 is near to 3411 and divided by 50.
Question 15. 1,678 ÷ 92
Answer: 1,678 ÷ 92 = 20
Explanation: Choose What numbers close to 1678 are easily divided by 90? 900 ÷ 90 = 9 hundreds ÷ 9 tens = 9 tens ÷ 9 = 1 ten 1800 ÷ 90 = 18 hundreds ÷ 9 tens = 18 tens ÷ 9 = 2 tens So, select 1800 near to 1678 and divided by 90.
Question 16. 6,581 ÷ 77
Answer: 6,581 ÷ 77 = 80.
Explanation: Choose what numbers are near to 581 and are easily divided by 80 near to 77. 6400 ÷ 80 = 64 hundreds ÷ 8 tens = 64 tens ÷ 8 = 8 tens 7200 ÷ 80 = 72 hundreds ÷ 8 tens = 72 tens ÷ 8 = 9 tens So, choose 6400 close to 6581 which is divided by 80 close to 77.
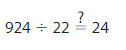
Answer: Not reasonable.
Explanation: Choose what numbers are close to 924 and divided by 20 near to 22. 800 ÷ 20 = 8 hundreds ÷ 2 tens = 8 tens ÷ 2 = 4 tens 1000 ÷ 20 = 10 hundreds ÷ 2 tens = 10 tens ÷ 2 = 5 tens So, select 1000 near to 924 and divided by 20.
6.4 Divide by One-Digit Numbers
Divide. Then check your answer. Question 18. \(\sqrt [ 5 ]{ 415 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 5 ]{ 415 } \) = 83.
Explanation: Divide the tens 41 tens ÷ 5 8 tens x 5 41 tens – 40 tens there is 1 ten leftover. Divide the ones. 15 ones ÷ 5 3 ones x 5 15 ones – 15 ones There are 0 ones left over. So, 415 ÷ 5 = 83
Question 19. \(\sqrt [ 6 ]{ 6,432 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 6 ]{ 6,432 } \) = 1072
Explanation: Divide the thousands. 6 thousands ÷ 6 6 x 1 thousand 6 thousands – 6 thousands There is 0 thousand left over. Divide the tens. 43 tens ÷ 6 6 x 7 tens 43 tens – 42 tens There is 1 ten left over. So, \(\sqrt [ 6 ]{ 6,432 } \) = 1072
Question 20. \(\sqrt [ 9 ]{ 5,628 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 9 ]{ 5,628 } \) = 625 R 3
Explanation: Divide the hundreds. 56 hundreds ÷ 9 9 x 4 hundreds 56 hundreds – 54 hundreds There are 2 hundreds left over Divide the tens 22 tens ÷ 9 9 x 2 tens 22 tens – 18 tens There are 4 tens left over Divide the ones 48 ones ÷ 9 9 x 5 ones 48 ones – 45 ones There are 3 ones left. So, \(\sqrt [ 9 ]{ 5,628 } \) = 625 R 3
Question 21. 8,021 ÷ 7 = ______
Answer: 8,021 ÷ 7 = 1145 R 6
Explanation: Divide the thousands 8 hundreds ÷ 7 7 x 10 hundreds 80 hundreds – 70 hundreds There are 10 hundreds eft over. divide the tens. 102 tens ÷ 7 7 x 14 tens 102 tens – 98 tens There are 4 tens left over. 41 ones ÷ 7 7 x 5 ones 41 ones – 35 ones There are 6 ones left over. So, 8,021 ÷ 7 = 1145 R 6
Question 22. 817 ÷ 8 = ______
Answer: 817 ÷ 8 = 102 R 1
Explanation: Divide the hundreds 8 hundreds ÷ 8 8 x 1 hundred 8 hundreds – 8 hundreds There are 0 hundreds left over Divide the ones. 17 ones ÷ 8 8 x 2 ones 17 ones – 16 ones There are 1 one left over So, 817 ÷ 8 = 102 R 1
Question 23. 3,007 ÷ 3 = ______
Answer: 3,007 ÷ 3 = 1002 R 1
Explanation: Divide the thousand 3 thousand ÷ 3 3 thousand x 1 3 thousand – 3 thousand there are 0 thousand left over. Divide the ones. 7 ones ÷ 3 3 x 2 ones 7 ones – 6 ones There are 1 one leftover. So, 3,007 ÷ 3 = 1002 R 1
6.5 Use Partial Quotients to Divide by Two-Digit Numbers
Use partial quotients to divide. Question 24. 156 ÷ 13
Answer: 156 ÷ 13 = 43
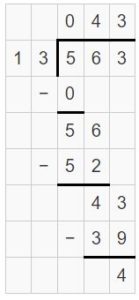
Question 25. 208 ÷ 16
Answer: 208 ÷ 16 = 13
6.6 Use Partial Quotients with a Remainder
Use partial quotients to divide. Question 26. \(\sqrt [ 50 ]{ 805 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 50 ]{ 805 } \) = 53 R 10
Question 27. \(\sqrt [ 18 ]{ 741 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 18 ]{ 741 } \) = 41 R 3
Question 28. \(\sqrt [ 48 ]{ 2,500 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 48 ]{ 2,500 } \) = 52 R 4
Question 29. 792 ÷ 13 = ______
Answer: 792 ÷ 13 = 60 R 12
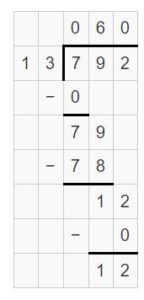
Question 30. 3,982 ÷ 25 = _____
Answer: 3,982 ÷ 25 = 159 R 7
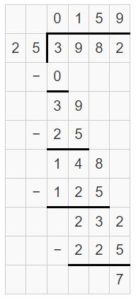
Question 31. 6,927 ÷ 68 = ____
Answer: 6,927 ÷ 68 = 101 R 59
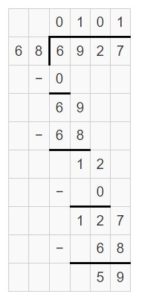
Question 32. Modeling Real Life There are 405 projects in a science fair. The coordinator displays the projects in rows of 42. How many rows have exactly 42 projects?
Answer: 9 rows have exactly 42 projects.
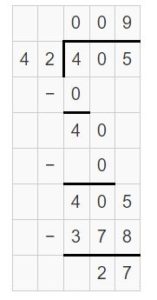
6.7 Divide Three-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers
Divide. Then check your answer. Question 33. \(\sqrt [ 31 ]{ 961 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 31 ]{ 961 } \) = 31
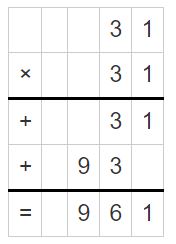
Question 34. \(\sqrt [ 27 ]{ 803 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 27 ]{ 803 } \) = 28 R 47
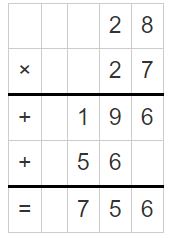
Question 35. \(\sqrt [ 19 ]{ 245 } \)
Answer: \(\sqrt [ 19 ]{ 245 } \) = 12 R 17
Explanation: The first digit is in the hundreds place. Divide the tens. 24 tens ÷ 19 1 ten x 19 = 19 tens 24 tens – 19 tens = 5 tens Divide the ones. 55 one ÷ 19 19 x 2 one = 38 ones 55 one – 38 ones = 17 ones Regroup 1 tens and 2 ones. So, \(\sqrt [ 19 ]{ 245 } \) = 12 R 17 Use multiplication to check your answer. 12 x 19 = 228 228 + 17 = 245.
6.8 Divide Four-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers
Divide. Then check your answer. Question 36. 6,636 ÷ 84 = _____
Answer: 6,636 ÷ 84 = 79
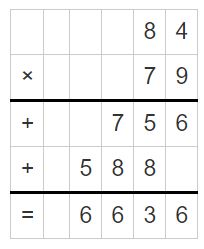
Question 37. 2,418 ÷ 21 = ______
Answer: 2,418 ÷ 21 = 115 R 3
Explanation: The first digit is in the thousands place. Divide the hundreds. 24 hundreds ÷ 21 21 x 1 hundred 24 hundreds – 21 hundreds There are 3 hundreds left over. Divide the tens. 31 tens ÷ 21 21 x 1 tens = 21 tens 31 tens – 21 tens = 10 tens There are 10 tens left over. Divide the ones. 108 ones ÷ 21 21 x 5 one = 105 ones 108 ones – 105 ones = 3 So, 2,418 ÷ 21 = 115 R 3 Use multiplication to check your answer. 115 x 21 = 2415 2415 + 3 = 2418.
Question 38. 4,960 ÷ 62 = _____
Answer: 4,960 ÷ 62 = 80
Explanation: The first digit is in the thousands place. Divide the hundreds. 49 hundreds ÷ 62 49 hundreds cannot be shared among 62 groups without regrouping. So, add next number. Divide the tens. 496 tens ÷ 62 62 x 8 tens = 496 tens 496 tens – 496 tens = 0 tens There are 0 tens left over. So, 4,960 ÷ 62 = 80 Use multiplication to check your answer. 62 x 80 = 4960.
6.9 Problem Solving: Division

Answer: The weight of red panda is 20. The weight of gaint panda is 200.
Explanation: The weight of giant panda = 10 x weight of red panda The weight of giant panda + weight of red panda = 220 10 x weight of red panda + weight of red panda = 220 11 x weight of red panda = 220 divide 220 by 11 22 tens ÷ 11 = 2 tens The weight of a red panda is 20. The weight of gaint panda = 10 x 20 = 200.
Question 40. A company fills claw arcade machines with stuffed animals. One machine can hold 50 stuffed animals. The company has 2,357 stuffed animals. The company fills as many machines as possible. How many stuffed animals do not fit into the machines?
Answer: There are 25 stuffed animals do not fit into machines.
Conclusion:
Before going to start the preparation learn the topics covered here and learn. We have also included a short and crisp explanation for the questions. Make use of Go Math Grade 5 Chapter 6 Solution Key and score better grades in your exams. Bookmark our site to get detailed solutions for all the Big Ideas Math Grade 5 Chapters.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5. 31 51 41 Name Add and Subtract Mixed Numbers Find the sum or difference. Write your answer in simplest form. Lesson 6.6 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.NF.1 Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions. 4.
This Go Math video covers the topic of adding and subtracting fractions by obtaining common denominators. A key concept is imparted in the video about how yo...
Lesson Check (CC.5.NF.l) 1. Lyle bought pound of red grapes and pound of green grapes. How many pounds of grapes did he buy? 19 — pound 24 — pound — pound — pound 24 Spiral Review (CC.5.NBT.6, CC.5.NBT.7, cc.5.NF.3) 3. Ivan has 15 yards of green felt and 12 yards of blue felt to make 3 quilts. If Ivan uses the same total number of yards ...
Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5 Created Date: 1/11/2017 2:48:24 PM ...
Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 6.6 Homework and Practice Answer Key. Divide. Question 1. 6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) Answer: 6 ÷ 1/3 = 6 x 3 = 18 Explanation: In the above division problem 6 ÷ 1/3 we can observe that the whole number is divided by a fraction. Divide 6 by 1/3 the result is 18. The result 18 is obtained by multiplying 6 with 3. Question 2.
This video covers Lesson 6.6 Add and Subtract Fractions on pages 273-276 of the 5th grade GO Math textbook.
Problem SolvingProblem Solving Name © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Think: 1_ 8 is less than 1_ 2. __6 10 is more than 1_ 2. Compare Fractions Using ...
6.2 iStudent Edition. 6.2 eTeacher Edition Personal Math Trainer Math on the Spot Video Animated Math Models iTools. HMH Mega Math. 6.2 Student Edition. 6.2 Practice and Homework (in the Student Edition) 6.2 Reteach (in the Chapter Resources) 6.2 Enrich (in the Chapter Resources) Grab-and-GoTM Centers Kit.
Given an exponential equation with the form b S = b T, b S = b T, where S S and T T are algebraic expressions with an unknown, solve for the unknown. Use the rules of exponents to simplify, if necessary, so that the resulting equation has the form b S = b T. b S = b T. Use the one-to-one property to set the exponents equal.
Exercise 5. Exercise 6. Exercise 7. At Quizlet, we're giving you the tools you need to take on any subject without having to carry around solutions manuals or printing out PDFs! Now, with expert-verified solutions from Go Math! Middle School Grade 6 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Go ...
From Open Up Resources, https://openupresources.org/ Grade 6 Unit 6 Lesson 7
Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5. Name Patterns with Fractions Write a rule for the sequence. Then, find the unknown term. ALGEBRA Lesson 6.8 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.NF.1 Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions. 1 2-, add - 11 1—, subtract - 5 8' 7 8 12 Think: The pattern is increasing.
Practice Fluency Workbook Grade 6 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Go Math!:
Use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement Go Math! 6 Common Core Edition. Go Math! 6 Common Core Edition grade 6 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 6, Title: Go Math! 6 Common Core Edition, Publisher: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, ISBN: 547587783.
Problem 4. Write an equation represented by this tape diagram using each of these operations. addition. subtraction. multiplication. division. Solution. For access, consult one of our IM Certified Partners. (From Unit 6, Lesson 1.)
Practice 6.6.06 • Activity Builder by Desmos ... Loading...
Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5. Name Problem Solving Practice Addition and Subtraction Read each problem and solve. 31 11% PROBLEM SOLVING Lesson 6.q COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.NF.2 Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions. Write an equation: 8 = 21 + 21 + X Rewrite the equation to work backward: Subtract twice to ...
Lesson 6 . 6.2.6 Morgan. 7 - Creating Double Number Line Diagrams. Lesson 7 . Create Double Number Lines . 6.2.7 Morgan. 8 - How Much for One? Lesson 8. ... Download PDF of Student Practice Work (Homework) Unit Summary for Parents - PDF File. Lesson Topic. IM Lesson. Khan Academy Support Videos. Khan Academy Online Practice. Class Notes.
Problem Solving • Practice Addition and Subtraction. Read each problem and solve. Practice and Homework. Lesson 6.9. COMMON CORE STANDARD—5.NF.A.2. Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions. 1. From a board 8 feet in length, Emmet cut two 2 1 _ 3 -foot bookshelves.
Algebra 1 Copyright © Big Ideas Learning, LLC Practice Workbook and Test Prep All rights reserved. 102 Name _____ Date _____ 1. Classify the real number 8 in as many ...
Go Math! Practice Book (TE), G5. Name Use Properties of Addition use the properties and mental math to solve. answer in simplest form. 31 ALGEBRA Lesson 6.10 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.5.NF.1 Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions. Write your 3.
Explanation: Method 1 is to divide the 112 by 8 to get the quotient. Here dividend is 8 divisor is 8 and quotient is 14. 112 = 64 + 48 = (8 x _) + (8 x _) The sum of unknown areas are 8 + 6 = 14. The relative multiplication equation is 14 x 8 = 112. So, 112 ÷ 8 = 14. Method 2 is by dividing the divisor into two parts.