Get 50% OFF Yearly and Lifetime Plans This Black Friday

What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

By Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
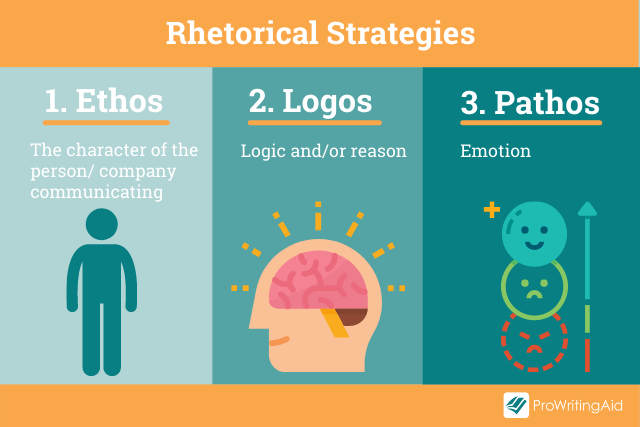
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
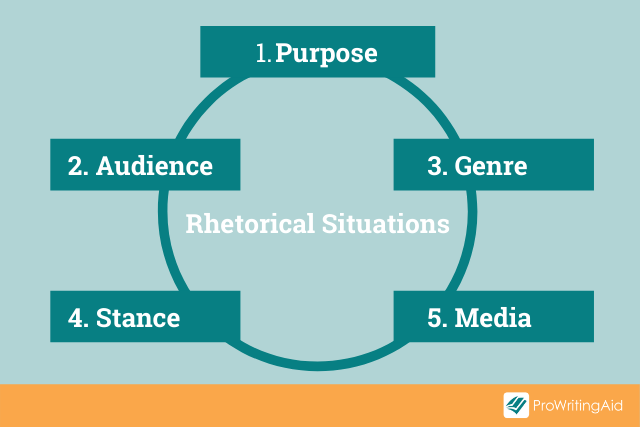
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
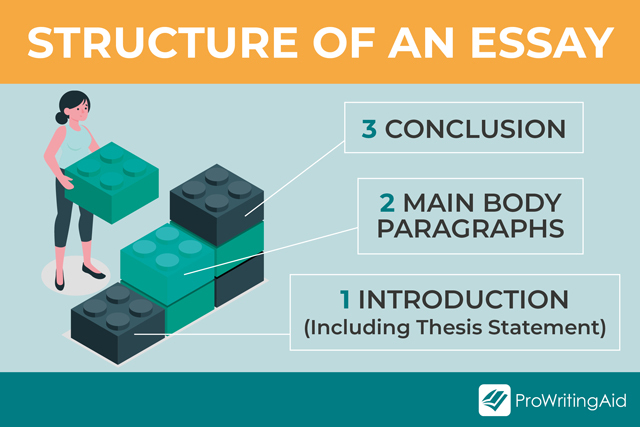
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid


All features—half price
Save 50% on yearly and lifetime plans
this Black Friday.
Grab the discount while it lasts.
Visit our Help Center or let's stay in touch via:
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay with an Example
.webp)
When it comes to a rhetorical analysis essay, it’s all about understanding how an author persuades or communicates with their audience. Unlike other essays, this type of analysis doesn’t focus on whether you agree or disagree with the author’s point; instead, it breaks down the strategies the author uses to convey their ideas effectively.
Here are the essential steps for writing your rhetorical analysis essay:
- Carefully read and identify the main purpose and key points.
- Look for elements like ethos, pathos, and logos that the author uses to influence the audience.
- Consider how the author’s style, tone, and structure contribute to their message.
- Discuss each rhetorical strategy in separate sections with examples from the text.
- Check that your analysis flows logically, with clear examples supporting your points.
This guide will walk you through these steps and offer you a rhetorical analysis essay example so you can confidently craft your own piece that showcases your understanding of the author’s techniques. And if you’re looking for personalized assistance, EssayHub's analytical essay writer is here to help with all types of essays, offering smooth and insightful support.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is an assignment that asks you to examine how an author communicates their ideas and persuades their audience. Unlike other types of essays where you argue your own position, a rhetorical analysis focuses on dissecting the writer’s approach, looking at the techniques used to engage, inform, or convince the reader. This analysis can apply to various texts, from speeches and articles to advertisements or visual media.
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you’ll pay close attention to rhetorical strategies, including ethos (credibility), pathos (emotional appeal), and logos (logical reasoning). These elements help you analyze how the writer creates impact, builds trust, or elicits emotions, depending on their goal and audience.
The structure of your essay will typically include an introduction where you outline the author’s purpose, a body section where you analyze specific strategies, and a conclusion that ties together your findings. Each section should provide clear examples from the text and explain how they contribute to the author’s message. In this type of essay, your objective is to dive deeper into the author’s choices and show how they effectively—or ineffectively—convey their message.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
Writing a strong rhetorical analysis essay takes clear planning and focused analysis. Here’s a quick guide to the main steps:
- Start by selecting a piece of writing that contains a clear purpose.
- Break down the author’s main points to understand the central message.
- Begin your essay with an introduction that summarizes the text.
- Examine specific elements of the text, such as tone, structure, and style.
- Focus on the author’s language and vocabulary.
- Conclude with a summary that brings together your main insights.
This approach will help ensure that your analysis is clear, structured, and impactful. Now, let's understand how to start a rhetorical analysis essay.
Select a Piece of Writing
Start by choosing a text that has a clear purpose or argument, like a speech, article, or ad. Picking a piece that’s rich in rhetorical techniques, such as persuasive language or appeals to emotions, will give you more to work within your analysis. Make sure it’s something that resonates with you, as a stronger connection to the material can make analyzing it easier and more engaging. Once chosen, read the text carefully and mark any points where the author uses specific techniques to appeal to or influence the audience.
Determine the Key Ideas
Next, identify the core ideas or main points the author is trying to communicate. Focus on understanding the message they want to convey and any arguments or claims they make to support it. Take note of the text’s structure and flow—these elements often reflect how the author builds their argument. Identifying these main ideas helps you see the text from the author’s perspective and prepares you to analyze the specific strategies they use to persuade, inform, or entertain their audience.
Begin Your Essay
Introduce the text you’re analyzing and provide a brief overview of the author’s main message or purpose. Mention key details about the text, like its title, author, and publication date, and clarify the audience and purpose. Include a thesis statement that briefly summarizes your analysis, giving readers a clear idea of what techniques or strategies you’ll examine. A strong introduction not only sets the tone but also guides your analysis by defining the main points you’ll cover.
Analyze the Text
Now, dive into the analysis by examining how the author presents their message. Look at how they use rhetorical techniques, such as ethos (credibility), pathos (emotional appeal), and logos (logic), to strengthen their argument. Consider the structure, tone, and examples they use to connect with the audience. This is where you’ll explore specific sections of the text, breaking down how each choice impacts the reader. Be sure to give examples and explain how each technique supports the author’s purpose.
Focus on the Author's Word Choice
Pay close attention to the author’s language, as word choices reveal a lot about their tone and intent.
- Are they using formal or casual language?
- Do they choose words that evoke strong emotions or create vivid images?
Words can influence the reader’s response, so noting the author’s vocabulary and phrasing choices can provide valuable insight into their strategy. Describe how specific words contribute to the text’s overall effect, whether it’s to inform, persuade, or engage the audience.
Summarize Your Essay
Conclude your analysis by summarizing your main findings and reinforcing your thesis. Restate the author’s purpose and briefly review the key rhetorical strategies they used to convey their message. A strong conclusion ties everything together, leaving readers with a clear understanding of how the author’s techniques work to achieve their goal. This summary should wrap up your analysis smoothly, offering a final perspective on how the author’s choices shaped the overall impact of the text.

Main Rhetorical Analysis Essay Concepts
As you understand how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, make sure to unpack how the author crafted their message to influence the audience. To do this effectively, you’ll focus on key rhetorical strategies such as rhetorical appeals—Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—along with the context, claims, and support used within the text.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos were introduced by Aristotle as foundational ways to persuade an audience and remain central to rhetorical analysis. These techniques, often called the “rhetorical triangle,” shape how a message is conveyed and received. As you analyze, think about how each element contributes to the overall effect and guides the audience’s response.
Rhetorical Appeals
Ethos relies on the author’s credibility and authority to establish trust with the audience. In any persuasive text, ethos is the factor that makes the reader feel confident in the author’s knowledge or moral character. When analyzing ethos, look at how the writer establishes their reputation. Are they an expert on the subject, and do they present their qualifications or experience to bolster their argument? For instance, an article on climate science written by a meteorologist naturally carries more weight than one by an unqualified author. Ethos can also be seen when a writer aligns themselves with respected figures or ideas, building a sense of reliability that makes their arguments persuasive.
Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions and is used to create a personal connection with readers or listeners. Writers use pathos to evoke feelings such as empathy, anger, or excitement to drive home their message. This appeal is common in narratives, speeches, and advertising, where emotional responses are essential for audience engagement. For example, in a campaign for animal rescue, a writer might share heart-wrenching stories of neglected pets to create empathy and encourage donations. When analyzing pathos, note the author’s language, choice of examples, and tone, all of which can influence how emotionally connected the reader feels to the topic.
Logos is the appeal to logic and reason, often using evidence, facts, and well-structured arguments to persuade. In a rhetorical analysis, focus on how the author uses data, statistics, or logical reasoning to support their claims. Logos appeals are crucial in academic and professional writing, where objectivity and factual accuracy carry significant weight. For instance, in a scientific article, logos may be found in the form of empirical data and references to previous studies. When assessing logos, consider how the author presents their arguments: are they coherent, well-supported, and easy to follow? The strong use of logos creates a sense of rationality that strengthens the text’s persuasiveness.
Text and Context
When analyzing a piece of rhetoric, understanding its context is essential to fully grasp its intended impact. Context encompasses the background of the text, the author, the audience, and the circumstances of its creation. Ask questions like:
- Who wrote this?
- What were the social, political, or historical conditions surrounding its release?
For example, a wartime speech may have been crafted not just to inform but to rally emotional and patriotic support during a critical moment. In this way, context shapes both the message and the methods the author uses to connect with their audience. Effective analysis considers both the text and the environment in which it was created.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
Claims: A claim is the central argument or point that the author is making. Claims can range from factual assertions to calls for action, shaping the core of what the author wants the reader to accept or consider. For example, an editorial on environmental policy may claim that stricter regulations are essential to reduce pollution. Identifying the claim allows you to pinpoint the author's main argument and assess how well it is supported throughout the text.
Supports: Supports are the evidence or reasoning that backs up the author’s claim, turning assertions into convincing arguments. These might include data, quotes from experts, logical examples, or real-life illustrations. In the environmental policy example, support could include scientific data on pollution levels, expert endorsements of proposed regulations, and statistics on the effects of pollution. Effective support builds credibility, giving the claim substance and making the argument persuasive.
Warrants: Warrants are the assumptions that connect the supports to the claims, often underlying and unstated. Warrants explain why the provided evidence supports the claim. In the case of environmental policy, the warrant might be the shared belief that protecting public health and the environment is inherently valuable. Examining warrants helps reveal the implicit logic that holds an argument together, and evaluating these connections can deepen your analysis by showing whether the argument is universally relatable or dependent on particular beliefs or values.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Rhetorical analysis introduction.
The introduction is your first chance to set up the text and its rhetorical elements for readers. Begin by introducing the text, the author, and any relevant background details, such as its historical context or its cultural significance. Summarize the text’s central claim or purpose, providing a brief overview of its main arguments or points. This introduction not only informs readers about the content but also frames the reason for analyzing this text specifically. Finally, craft a thesis statement that outlines your main perspective on the author’s rhetorical methods.
For example, state whether you find the author’s use of rhetorical strategies to be effective in reaching and persuading their audience, giving readers an idea of the analysis that will unfold.
Rhetorical Analysis Body Paragraph
The body paragraphs form the main part of your analysis, where you explore the author’s strategies in depth. Each paragraph should focus on a different rhetorical element, such as ethos, pathos, logos, or specific devices like repetition or imagery. Break down these strategies, using examples or quotations from the text to illustrate each point. As you examine these techniques, consider why the author may have chosen each approach and how it might affect the audience’s reception of the message.
For instance, when analyzing a politician’s speech, you might focus on their appeal to ethos by emphasizing their authority and expertise on the subject. By dissecting the text in this way, you’ll give readers a detailed look at the author’s methods and provide a clear evaluation of their effectiveness.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
In the conclusion, reaffirm the main insights of your analysis and evaluate the overall impact of the author’s techniques. Summarize the key strategies discussed and consider the text’s lasting influence on its audience or even on larger societal discussions.
For instance, if you analyzed Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie’s TED Talk “We Should All Be Feminists,” you might explore how her blend of personal anecdotes and logical arguments (logos) not only challenges gender stereotypes but also invites a global conversation about feminism in diverse cultural contexts. This is where you emphasize the relevance and significance of the rhetorical devices the author used.
Rather than introducing new concepts, reinforce the analysis you’ve already provided, using your main points to draw a cohesive final impression. Conclude with a closing thought that underscores the importance of understanding rhetoric, leaving readers with a solid grasp of both the author’s persuasive approach and your interpretation.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
When writing a rhetorical analysis essay, your goal is to break down how an author crafts their argument and consider the effectiveness of their methods. Let’s dive into a detailed example to see how to apply each aspect we’ve covered, from analyzing rhetorical appeals to structuring a compelling outline.
For this example, we’ll analyze a less common yet impactful topic: The Rhetoric of Environmental Advertising in Outdoor Clothing Brands. This essay will explore how outdoor clothing companies like Patagonia and REI use powerful messaging to appeal to consumers’ environmental values, build brand ethos, and motivate sustainable consumer behavior.
Final Outlook
Here’s a quick recap of the steps involved in writing a strong rhetorical analysis essay:
- Select a Piece of Writing that’s rich in rhetorical elements.
- Determine Key Ideas to uncover the core message.
- Begin Your Essay with a concise introduction that sets the stage.
- Analyze the Text by examining ethos, pathos, logos, and other rhetorical tools.
- Focus on the Author’s Word Choice to highlight language that impacts the audience.
- Summarize Your Essay with a thoughtful conclusion that reinforces your analysis.
For added guidance, remember — paper writing service EssayHub is a useful resource for support with any type of essay, including rhetorical analysis, offering assistance to make your writing process smoother and more effective!
.png)
What Does a Rhetorical Analysis Essay Look Like?
How to write a rhetorical analysis essay example, how to start a rhetorical analysis essay.
Ryan Acton is an essay-writing expert with a Ph.D. in Sociology, specializing in sociological research and historical analysis. By partnering with EssayHub, he provides comprehensive support to students, helping them craft well-informed essays across a variety of topics.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support

IMAGES
VIDEO