Legal Form of Organization in Business Plan
The legal form of organization in business plan is used to decide how the company will function, how roles will be assigned and how relationships will work. 3 min read updated on September 19, 2022
The legal form of organization in business plan is used to decide how the organization will function, how roles will be arranged and assigned, and how relationships will work. These organizational steps should take place at the beginning of the business formation.

Starting a Business
The first step when beginning a business is to name the business. The name must be unique and not in use by another existing entity. The next step is to decide on the organization type your business will use. Each business entity has specific requirements on how they are run including how income is reported. The business types include:
- Sole proprietorship.
- Partnership.
- Limited Liability Company.
- Limited Liability Partnership.
- Corporation.
- S Corporation.
- Tax-exempt organization.
Each type has advantages and disadvantages that should be reviewed before making a final decision. However, the business type you choose isn't permanent. As the needs of your business change, the business entity type can be changed. Examples include:
- Changing a sole proprietorship to a partnership due to growth.
- Switching to a corporation to establish protection that comes with limited liability.
Limited Liability is attractive to business owners because it protects personal assets from any debts or obligations incurred by the corporation.
Business Type Requirements
A major component of selecting a business type is what is required to be legal and the tax implications.
- Applications to the state government are not required.
- Dependent on the state, registering the business may be required with the state and/or country.
- A business license may be required based on the type of business and state requirements.
- The IRS views all business activity as personal. When filing, personal and business income are seen as the same thing.
- A sole proprietorship is personally responsible for all aspects of the business. If the business is sold, it can impact any personal assets if you are found liable.
- In a general partnership, two or more sole proprietors are seen by the IRS as having equal responsibility.
- Any profit and loss distribution is determined by the partnership agreement and is then passed to the individual partners.
- Profit and loss distribution does not have to match the percentage of ownership.
- The partnership is not subject to income or franchise tax.
- The structure and tax implications are similar to a general partnership, but a limited partnership ( silent partner ) allows for ownership without the requirement of being actively involved in how the business is managed.
- Business liabilities are limited to the amount invested by the partner.
- Outside investors can be partners without taking on any liabilities.
- Personal liability protection is provided without having to meet the administrative and governance procedures.
- The Articles of Organization determine the ownership percentages, distribution of profit and losses, and voting rights. In corporations, this is determined by stock ownership.
- Most LLCs use the pass-through method of taxation. This means that taxes aren't paid by the LLC, but by at the personal tax level of the owners. The personal rate is lower than the corporate tax rate. When the LLC files taxes, no money is sent and an owners report is included to show the owners will pay the tax instead.
- Based on the state, the LLC is subject to a franchise tax .
- A corporation can be formed as for-profit or nonprofit.
- Corporations provide a shield from liabilities. This protection is only removed if the owners or board members have been found to be illegally running a corporation and have been breaking federal and/or state laws.
- Corporations can sell stock in the business.
- A Board of Directors is used to manage corporate policies and strategies. This is for both for-profit and nonprofit.
- Corporations continue to exist even in the event of the owner's death, or if owners leave.
If you need help with the legal form of organization in the business plan, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
UpCounsel has successfully supported over 10604 clients in navigating Business Formation, connecting them with a network of 884 specialized Business Formation lawyers ready to assist you every day. With 4389 client reviews, you can confidently find the right lawyer to meet your needs. Clients have consistently rated our lawyers highly for their expertise in Business Formation, reflecting a strong overall satisfaction score of 4.9.
- Types of Business Structures
- Partnership Business Entity: Everything You Need To Know
- LLC Partnership
- Individual Ownership of Business
- What Is Classification of Business According to Ownership?
- Benefits of a Close Corporation as Opposed to a Partnership
- Types of Businesses LLC
- What Is the Most Common Type of Partnership?
- Sole Proprietorship vs Partnership
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
Writing the Organization and Management Section of Your Business Plan
What is the organization and management section in a business plan.
- What to Put in the Organization and Management Section
Organization
The management team, helpful tips to write this section, frequently asked questions (faqs).
vm / E+ / Getty Images
Every business plan needs an organization and management section. This document will help you convey your vision for how your business will be structured. Here's how to write a good one.
Key Takeaways
- This section of your business plan details your corporate structure.
- It should explain the hierarchy of management, including details about the owners, the board of directors, and any professional partners.
- The point of this section is to clarify who will be in charge of each aspect of your business, as well as how those individuals will help the business succeed.
The organization and management section of your business plan should summarize information about your business structure and team. It usually comes after the market analysis section in a business plan . It's especially important to include this section if you have a partnership or a multi-member limited liability company (LLC). However, if you're starting a home business or are writing a business plan for one that's already operating, and you're the only person involved, then you don't need to include this section.
What To Put in the Organization and Management Section
You can separate the two terms to better understand how to write this section of the business plan.
The "organization" in this section refers to how your business is structured and the people involved. "Management" refers to the responsibilities different managers have and what those individuals bring to the company.
In the opening of the section, you want to give a summary of your management team, including size, composition, and a bit about each member's experience.
For example, you might write something like "Our management team of five has more than 20 years of experience in the industry."
The organization section sets up the hierarchy of the people involved in your business. It's often set up in a chart form. If you have a partnership or multi-member LLC, this is where you indicate who is president or CEO, the CFO, director of marketing, and any other roles you have in your business. If you're a single-person home business, this becomes easy as you're the only one on the chart.
Technically, this part of the plan is about owner members, but if you plan to outsource work or hire a virtual assistant, you can include them here, as well. For example, you might have a freelance webmaster, marketing assistant, and copywriter. You might even have a virtual assistant whose job it is to work with your other freelancers. These people aren't owners but have significant duties in your business.
Some common types of business structures include sole proprietorships, partnerships, LLCs, and corporations.
Sole Proprietorship
This type of business isn't a separate entity. Instead, business assets and liabilities are entwined with your personal finances. You're the sole person in charge, and you won't be allowed to sell stock or bring in new owners. If you don't register as any other kind of business, you'll automatically be considered a sole proprietorship.
Partnership
Partnerships can be either limited (LP) or limited liability (LLP). LPs have one general partner who takes on the bulk of the liability for the company, while all other partner owners have limited liability (and limited control over the business). LLPs are like an LP without a general partner; all partners have limited liability from debts as well as the actions of other partners.
Limited Liability Company
A limited liability company (LLC) combines elements of partnership and corporate structures. Your personal liability is limited, and profits are passed through to your personal returns.
Corporation
There are many variations of corporate structure that an organization might choose. These include C corps, which allow companies to issue stock shares, pay corporate taxes (rather than passing profits through to personal returns), and offer the highest level of personal protection from business activities. There are also nonprofit corporations, which are similar to C corps, but they don't seek profits and don't pay state or federal income taxes.
This section highlights what you and the others involved in the running of your business bring to the table. This not only includes owners and managers but also your board of directors (if you have one) and support professionals. Start by indicating your business structure, and then list the team members.
Owner/Manager/Members
Provide the following information on each owner/manager/member:
- Percentage of ownership (LLC, corporation, etc.)
- Extent of involvement (active or silent partner)
- Type of ownership (stock options, general partner, etc.)
- Position in the business (CEO, CFO, etc.)
- Duties and responsibilities
- Educational background
- Experience or skills that are relevant to the business and the duties
- Past employment
- Skills will benefit the business
- Awards and recognition
- Compensation (how paid)
- How each person's skills and experience will complement you and each other
Board of Directors
A board of directors is another part of your management team. If you don't have a board of directors, you don't need this information. This section provides much of the same information as in the ownership and management team sub-section.
- Position (if there are positions)
- Involvement with the company
Even a one-person business could benefit from a small group of other business owners providing feedback, support, and accountability as an advisory board.
Support Professionals
Especially if you're seeking funding, let potential investors know you're on the ball with a lawyer, accountant, and other professionals that are involved in your business. This is the place to list any freelancers or contractors you're using. Like the other sections, you'll want to include:
- Background information such as education or certificates
- Services provided to your business
- Relationship information (retainer, as-needed, regular, etc.)
- Skills and experience making them ideal for the work you need
- Anything else that makes them stand out as quality professionals (awards, etc.)
Writing a business plan seems like an overwhelming activity, especially if you're starting a small, one-person business. But writing a business plan can be fairly simple.
Like other parts of the business plan, this is a section you'll want to update if you have team member changes, or if you and your team members receive any additional training, awards, or other resume changes that benefit the business.
Because it highlights the skills and experience you and your team offer, it can be a great resource to refer to when seeking publicity and marketing opportunities. You can refer to it when creating your media kit or pitching for publicity.
Why are organization and management important to a business plan?
The point of this section is to clarify who's in charge of what. This document can clarify these roles for yourself, as well as investors and employees.
What should you cover in the organization and management section of a business plan?
The organization and management section should explain the chain of command , roles, and responsibilities. It should also explain a bit about what makes each person particularly well-suited to take charge of their area of the business.
Want to read more content like this? Sign up for The Balance’s newsletter for daily insights, analysis, and financial tips, all delivered straight to your inbox every morning!
Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
City of Eagle, Idaho. " Step 2—Write Your Business Plan ."
Small Business Administration. " Choose a Business Structure ."
How to Write a Business Plan: Organization Structure
How to write a business plan: organizational structure, what is the organizational structure for a business plan.
The organization structure section should discuss whether your business will be a sole proprietor, limited liability corporation, or corporation, who will run your business, each person’s responsibility, and how your business will expand if needed. There are numerous benefits to a detailed assessment of the company’s structure. First, examining the structure of the business will help for tax purposes. For example, limited liability and corporations are considered excellent for protecting shareholders concerning liabilities. However, tax-wise, these firms often are double taxed. The second benefit of a detailed assessment of a company’s structure is to understand how each owner will contribute to the company. In other words, if there is more than one owner, what are their responsibilities, and how are these responsibilities to be carried out.
Why is the Organizational Structure important?
There are numerous reasons why the organizational structure is essential for a business plan. In this section, the business owner will lay out how the company will be structured. For example, this section will include job titles and responsibilities, resumes from owners and management, showing expertise in the industry, and supporting accolades for expertise. Through discussing job responsibilities and experiences for management, readers will better understand why this type of business structure, and this management team, will be successful in the proposed business.
A second important reason for the organizational structure is that the section introduces business owners. The owners and management team should not only be introduced in this section, but their experiences in the industry need to be highlighted and thoroughly explained. In doing this, a sound foundation for management competence will be established.
A final reason for its importance is the job responsibility segment. Ownership and management need to have a written document showing specific duties for each owner, if applicable, and specific job responsibilities for each position within the company. By having this document, readers will see how the business will function and better understand the breakup of management responsibilities.
When to write the Organizational Structure?
The organizational structure should be written after the company description. In the company description, readers will be introduced to the problem that the company is going to solve and how they propose to solve this problem. This is usually the product or service offered. The logical next step is to show a business structure that will allow the company to supply that product or service effectively and efficiently. Thus the need for the organizational section follows immediately behind the company description.
How to write the Organizational Structure?
When I write my organizational structure for a business plan, for the most part, I start the first paragraph by reminding the readers of the company name. From this, I then introduce how the company will be held in ownership. For example, will the company be a limited liability corporation? Sole proprietorship? Next, I briefly introduce the management team and owners. Further, I also briefly introduce their experience in the industry.
By following this structure, the first paragraph is an excellent summation of the section. This allows the reader to understand the breadth of the ownership structure without gaining significant details.
Organizational Structure: Ownership
In the ownership section, I usually start writing the section by introducing the CEO/founder/majority owner. In this portion, I usually write the segment, almost like a brief biography. I will discuss the CEO's history in the industry and the reason why they feel that they are best suited to start and run the operation.
Once this is complete, I then follow the same structure with the other management team members and minority stakeholders. When this is done, the reader should walk away with an excellent understanding of the qualifications of the ownership team and how their skills will complement each other.
Need Help Writing an Organizational Structure for a Business Plan?
Call or Text Paul, Doctoral Candidate, MBA.
321-948-9588
Email: [email protected]
Organizational Structure: Responsibilities
In the job responsibility section, I usually structure this portion as a bullet-pointed list. At the top, I put the title such as CEO, project manager, or job title. Following this, I list the responsibilities and expectations for each position. Not only does this help show structure and foresight for the company. But also, this will help management divvy up duties for the business.
Organizational Structure: Resume
The resume section is for senior managers and owners. By including resumes, supporting documentation is available for claims made related to experience. For example, if the CEO claims to have 20 years of experience in the industry, then the resume will show where this experience came from. This adds credibility to previous claims made.
Organizational Structure: Compensation
Compensation is sometimes necessary to include in the organizational structure component. Investors expect management to be compensated and employees as well. However, excessive compensation is often an issue with startups and established businesses. By showing reasonable compensation for each position, not only will a solid understanding of the pay for each position be shown, but restraint for compensation by the management team and ownership may be highlighted as well.
Organizational Structure: Achievements
This final section is almost like a cherry on top of the cake. By this point, the reader should be well-versed in the experience and expertise of ownership and the management team. Adding achievements highlights their expertise in their chosen industry.
Organizational Structure Example
Organizational structure.
Legal Structure
ABC Restaurant will be a limited liability corporation.
Management Summary
John Smith, Sr., MBA., is the founder and CEO of ABC Restaurant. He has started and managed numerous successful small restaurants over the last ten years. Restaurants started, and managed, including a breakfast cafe, food truck, and 24-hour diner. For each business, he was responsible for all aspects of the organization, from marketing to strategic planning.
Job Responsibilities
- Create and execute marketing strategies for business growth.
- Align business strategies with the vision statement.
- Negotiating contracts with vendors.
- Ensure legal compliance for the business.
- Continually examine the firm’s external environment for new market opportunities.
General Manager:
- Control inventory to ensure optimal levels are attained.
- Manage day-to-day operations of the restaurant.
- Servers and cooks during high volume times.
- Interview and hire new employees.
- Assist in the onboarding process for new employees.
- Set up all workstations in the kitchen
- Prepare ingredients to use in cooked and non-cooked foods.
- Check food while cooking for appropriate temperatures.
- Ensure great presentation by dressing dishes as trained.
- Keep a sanitized and clean environment in the kitchen area.
- Stock dining area tables with needed items.
- Greet customers when they enter.
- Present dinner menus and help customers with food/beverages selections.
- Take and serve orders quickly and accurately.
Author: Paul Borosky, MBA., Doctoral Candidate, Published Author
Updated: 3/4/2022
Business Plan Section 3: Organization and Management
This section explains how your business runs and who’s on your team. Learn how to present the information in this section of your business plan.

This section of your business plan, Organization and Management, is where you’ll explain exactly how you’re set up to make your ideas happen, plus you’ll introduce the players on your team.
As always, remember your audience. If this is a plan for your internal use, you can be a little more general than if you’ll be presenting it to a potential lender or investor. No matter what its purpose, you’ll want to break the organization and management section into two segments: one describing the way you’ve set up the company to run (its organizational structure), and the other introducing the people involved (its management).
Business Organization
Having a solid plan for how your business will run is a key component of its smooth and successful operation. Of course, you need to surround yourself with good people, but you have to set things up to enable them to work well with each other and on their own.
It’s important to define the positions in the company, which job is responsible for what, and to whom everyone will report. Over time, the structure may grow and change and you can certainly keep tweaking it as you go along, but you need to have an initial plan.
If you’re applying for funding to start a business or expand one, you may not even have employees to fit all the roles in the organization. However, you can still list them in your plan for how the company will ideally operate once you have the ability to do so.
Obviously, for small businesses, the organization will be far more streamlined and less complicated than it is for larger ones, but your business plan still needs to demonstrate an understanding of how you’ll handle the workflow. At the very least, you’ll need to touch on sales and marketing, administration, and the production and distribution of your product or the execution of your service.
For larger companies, an organizational plan with well-thought-out procedures is even more important. This is the best way to make sure you’re not wasting time duplicating efforts or dealing with internal confusion about responsibilities. A smooth-running operation runs far more efficiently and cost-effectively than one flying by the seat of its pants, and this section of your business plan will be another indication that you know what you’re doing. A large company is also likely to need additional operational categories such as human resources and possibly research and development.
One way to explain your organizational structure in the business plan is graphically. A simple diagram or flowchart can easily demonstrate levels of management and the positions within them, clearly illustrating who reports to whom, and how different divisions of the company (such as sales and marketing) relate to each other.
Here is where you can also talk about the other levels of employees in your company. Your lower-level staff will carry out the day-to-day work, so it’s important to recognize the types of people you’ll need, how many, what their qualifications should be, where you’ll find them, and what they’ll cost.
If the business will use outside consultants, freelancers, or independent contractors, mention it here as well. And talk about positions you’d want to add in the future if you’re successful enough to expand.
Business Management
Now that we understand the structure of your business, we need to meet the people who’ll be running it. Who does what, and why are they onboard? This section is important even for a single practitioner or sole proprietorship, as it will introduce you and your qualifications to the readers of your plan.
Start at the top with the legal structure and ownership of the business. If you are incorporated, say so, and detail whether you are a C or S corporation. If you haven’t yet incorporated, make sure to discuss this with your attorney and tax advisor to figure out which way to go. Whether you’re in a partnership or are a sole owner, this is where to mention it.
List the names of the owners of the business, what percent of the company each of them owns, the form of ownership (common or preferred stock, general or limited partner), and what kind of involvement they’ll have with day-to-day operations; for example, if they’re an active or silent partner.
Here’s where you’ll list the names and profiles of your management team, along with what their responsibilities are. Especially if you’re looking for funding, make sure to highlight the proven track record of these key employees. Lenders and investors will be keenly interested in their previous successes, particularly in how they relate to this current venture.
Include each person’s name and position, along with a short description of what the individual’s main duties will be. Detail his or her education, and any unique skills or experience, especially if they’re relevant to the job at hand. Mention previous employment and any industry awards or recognition related to it, along with involvement with charities or other non-profit organizations.
Think of this section as a resume-in-a-nutshell, recapping the highlights and achievements of the people you’ve chosen to surround yourself with. Actual detailed resumes for you and your management team should go in the plan’s appendix, and you can cross-reference them here. You want your readers to feel like your top staff complements you and supplements your own particular skill set. You also want readers to understand why these people are so qualified to help make your business a success.
This section will spell out the compensation for management team members, such as salary, benefits, and any profit-sharing you might be offering. If any of the team will be under contract or bound by non-compete agreements, you would mention that here, as well.
If your company will have a Board of Directors, its members also need to be listed in the business plan. Introduce each person by name and the position they’ll hold on the board. Talk about how each might be involved with the business (in addition to board meetings.
Similar to what you did for your management team, give each member’s background information, including education, experience, special skills, etc., along with any contributions they may already have had to the success of the business. Include the full resumes for your board members in the appendix.
Alternately, if you don’t have a Board of Directors, include information about an Advisory Board you’ve put together, or a panel of experts you’ve convened to help you along the way. Having either of these, by the way, is something your company might want to consider whether or not you’re putting together the organization and management section or your business plan.
NEXT ARTICLE > Business Plan Section 4: Products and Services
Apply for a loan, get started.
Loans from $5,000 - $100,000 with transparent terms and no prepayment penalty. Tell us a little about yourself, your business and receive your quote in minutes without impacting your credit score.
Thanks for applying!
Loans are originated and funded through our lending arm, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development. By clicking “Continue to Application,” you consent to, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development’s Terms of Use and Privacy Policy ; and to receive emails, calls and texts , potentially for marketing purposes, including autodialed or pre-recorded calls. You may opt out of receiving certain communications as provided in our Privacy Policy .

Business Plan Organization and Management: How to Write Guide .
Sep 17, 2023 | Business Consulting , Business Plan , Organization and Management , Organizational Development , Strategy

Writing the Business Plan Organization and Management Section
It provides critical information for those looking for evidence that your staff has the necessary experience, skills, and pedigree to realize the objectives detailed in the rest of your business plan.
What Is the Organization and Management Section in a Business Plan?
The organization and management section of your business plan should provide details about your business structure and team. This section typically comes after the executive summary. However, some people have it further in the document after the market analysis section.
This section generally is separated into two parts. The first concerns the organization as a whole. It gives readers an overview of the company structure, which is an excellent opportunity for the reader to lift the roof off your office and peer into its inner workings. For your legal design, you may set up as a limited liability company (LLC) or nonprofit/ charity or form a partnership. It’s crucial to include this section. However, suppose you’re starting a home business or have an already operating business where you’re the only person involved. In that case, you can skip this section or show the company registration details from either the company’s house or the awarding .gov.
The second part focuses specifically on your management team and introduces readers to each member — your chance to impress them with the many accomplishments pinned to your organization’s management team.
This section may seem less important than some of the other parts of your business plan, but the truth is that your people are your business. If they’re highly competent and accomplished, the implication is that so is your business.
Of course, if you’re a sole proprietor with no management structure or any employees, this section is unnecessary other than to talk about yourself and your achievements.

The section on organization and management should outline the hierarchy, individual roles, and corresponding responsibilities. It should also highlight each person’s strengths and qualifications for their positions.
Business Plan Organization Section
The organizational section of your business plan outlines the hierarchy of individuals involved in your business, typically in a chart format. This section identifies the President or CEO, CFO, Director of Marketing, and other roles for partnerships or multi-member LLCs. If you’re a single-person home business, this section is straightforward as you are the only person on the chart.
Although this section primarily focuses on owner members, you can include outsourced workers or virtual assistants if you plan to hire them. For example, you may have a freelance web admin, marketing assistant, or copywriter. You may even have a virtual assistant who coordinates with your other freelancers. While these individuals are not owners, they hold significant responsibilities in your business.
There are various business structures, such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, LLCs, and corporations.
Detail the Legal Structure within the Business Plan Organization and Management Section
Here is an indicative list of business structures. It would help if you talked to your accountant and legal advisors to determine which legal form is the best for your business proposition.
Sole Proprietorship
When embarking on a business venture, it’s essential to consider the various structures available. A sole proprietorship is a structure whereby the business is not regarded as separate from its owner’s finances. The owner retains complete control and responsibility for the company. However, they are unable to sell stocks or bring in new owners. The business becomes a sole proprietorship if not registered under any other structure.
Partnership
When forming a partnership, it can either be a limited partnership (LP) or a limited liability partnership (LLP). One partner assumes most liability in a limited partnership (LP). In contrast, the other partners have limited liability and control over the business. Alternatively, in a limited liability partnership (LLP), all partners have limited liability from debts and actions of other partners, and there is no general partner.
Limited Liability Company
A limited company (LTD) or limited liability company (LLC) is a mixture of business structures that mixes aspects of partnerships and corporations. It offers limited personal liability to the owner and passes profits through to their tax returns.
Corporation
There are various types of corporate structures. A C-corporation enables the issuance of stock shares, pays corporate taxes instead of personal returns, and provides the highest level of personal protection from business activities. On the other hand, nonprofit corporations are similar to C corporations. However, they do not aim to make profits and are exempt from state or federal income taxes.
More information on company legal structures is available on UK.Gov and USA.SBA websites.
Describe Your Company’s Organizational Structure
This first step illustrates the positions in your organization’s employee hierarchy and how they all relate to each other.
This is usually done graphically as a guide, using an organizational chart, or “org chart” for short. People use a Microsoft tool, i.e., PowerPoint or Excel, to help.
Organization Charts typically follow a top-down hierarchy, starting with your CEO/ Managing Director in the top box at the top of the page. Lines extend down from that person’s name to boxes containing the terms of the CEO’s direct reports.
We have included an example organizational chart below for guidelines only.
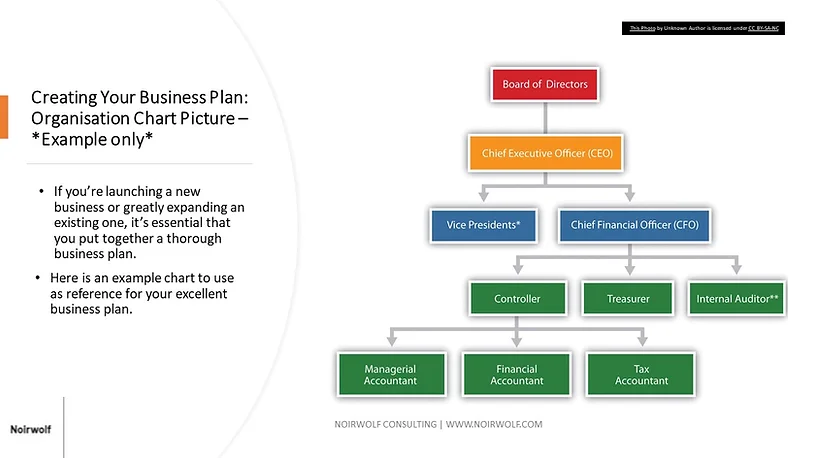
Identify your business organization structure and list your team members’ strengths and skills.
Those managers then have lines extending to those who report to them, and so on, down to your lowest staff positions.
This section will give your readers a quick understanding of your management and governance structure, the size of your organization, and your lines of control and communication.
Describe your Team in your Business Plan Organization and Management Section
In your business plan’s Organization and Management section, please provide a detailed description of your team. Y ou will discuss the company’s management team, starting with the owners.
This section highlights who is involved in the running of your business and who are the support professionals. It also includes the roles and responsibilities of managers.
Suppose the company structure is a multi-owner arrangement or some other multi-owner arrangement. In that case, you’ll want to include information for every member and their percentage of ownership and ongoing involvement in the company.
It’s important to discuss how ownership interests are split, their responsibilities, what they did before securing their current position, and how they came to be involved with the company.
Here, it would help if you talked about some of your critical team members. These people are directly responsible for large portions of your business operations.
Owner/Manager/Members
Within your business o rganization and management section, y ou should introduce the team and talk about their experience, qualifications, previous companies and achievements, role in the company, and any special skills they bring with them. Please provide the following details for each owner, manager, or member of the business within your business plan:
- Percentage of ownership (if applicable)
- Level of involvement (active or silent partner)
- Type of ownership (e.g., stock options, general partner)
- Position in the company (CEO, CFO, etc.)
- Responsibilities and Duties
- Educational background
- Relevant experience and skills
- Previous employment history
- Skills that will benefit the business
- Awards or recognition received
- Compensation structure
- How each individual’s skills and experience will complement and contribute to the business’s success
Perhaps they’re an entrepreneur, business coach, exclusive advisor, or industry specialist to help you grow.
This is an ideal opportunity for companies with an Executive Board of Directors, Governance Structure, or Advisory Board to introduce them to your readers.
Executive Board
Having a board of directors is essential for your management team. Without one, you may be missing out on crucial information. This section includes details similar to those found in the ownership and management team sub-section, such as the names, areas of expertise, positions (if applicable), and involvement with the company of each board member.
Strategic Advisors
Suppose you’re looking for funding for your business or to fill a gap in your knowledge, or you may not have the funds to hire an executive board. In that case, you must inform potential partners and investors that you have a team of professionals assisting you. This includes lawyers, accountants, and any freelancers or contractors you may be working with. When listing these individuals, include their name, title, educational background, certifications, services they provide to your business, and their relationship with you (i.e., hourly rates, projects, retainer, as-needed, regular). Additionally, highlight their skills and experience that make them an asset to your team you need
Does anything else make them stand out as quality professionals (awards, past working with credible brands)?
Spotlight on the Wider Team Structure
Now, you’ve showcased the management team in its entirety. You can provide brief bios for hiring team needs or secondary members and talk at length about how the team’s combined skills complement each other and how they amplify the team’s effectiveness.
It’s also important to point out any gaps in the knowledge your team is currently suffering. Your readers will likely be savvy enough to pick up on existing holes.
Therefore, you’ll want to get ahead of these criticisms and demonstrate that you’re already aware of the positions and complementary skill sets your management team still requires and how you plan to address the knowledge gaps with future hires.
Do you need help writing your business plan o rganization and management section ?
Every successful business plan should include the organization and management section, helping you communicate your legal structure and team.
Writing a business plan can seem overwhelming, especially when starting a small, one-person business. However, it can be a reasonably simple task. This section of the plan should be updated if there are any changes to the organization structure or team members, such as additional training, awards, or other resume changes that benefit the business.
Creating your comprehensive business plan takes planning, research, time, and a herculean effort. If, at any point, the work becomes too much to handle, we can step in to assist.
Do you want an expert “second opinion” before creating your business plan or financial forecasts? Let’s talk !
Get in Touch
Are you looking to grow your business but unsure where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We’ll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free 30-minute consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let’s get started!
Contact Noirwolf Consulting today using the website contact form or by emailing [email protected] or call us at +44 113 328 0868.
Recent posts .

Business Automation – Employee Engagement and Scalability
Nov 1, 2024
Learn how to leverage business automation strategies for improving employee engagement and achieving scalable growth. Discover practical tools, examples, and expert insights to future-proof your operations.

Digital Tools: Driving Workforce Performance in IT and Beyond
Oct 29, 2024
Explore the impact of digital tools on workforce performance, from data analytics and LMS to project management. Learn implementation strategies for IT transformation success.

Talent Retention During Organizational Change
Oct 25, 2024
Discover key strategies for talent retention during organizational change. From leadership support to employee development, explore methods to keep your team engaged and resilient during transitions.
Happy clients .
Trevor mcomber, us.
I recently worked with Zoe@Noirwolf, who provided me with an outstanding 5-year business plan. The expertise in financial planning, market research, SWOT analysis, and consulting was exceptional. Zoe provided me with a comprehensive and well-researched plan tailored to my business. The entire process was professional, timely, and communicative.
Bill Walton, Leeds
Zoe provided first-rate work and is an excellent business consultant. I was trying to figure out my cash flow forecast for my startup. Zoe gave me an interactive consultation session over MS teams, which was valuable and saved me a lot of time. She is super quick in excel and knowledgeable about what to include in your estimates. She was able to offer me ideas & choices that I hadn't considered. Highly recommended.
Jeendanie Lorthe, US
Warren kim, us, oscar sinclair, london, get in touch ..
Looking to grow your business but feeling unsure about where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We'll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free one-hour consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let's get started!

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
5.6 The Business Plan
Learning objective.
- Discuss the importance of planning for your business, and identify the key sections of a business plan.
If you want to start a business, you must prepare a business plan. This essential document should tell the story of your business concept, provide an overview of the industry in which you will operate, describe the goods or services you will provide, identify your customers and proposed marketing activities, explain the qualifications of your management team, and state your projected income and borrowing needs.
Purpose of a Business Plan
The business plan is a plan or blueprint for the company, and it’s an indispensable tool in attracting investors, obtaining loans, or both. Remember, too, that the value of your business plan isn’t limited to the planning stages of your business and the process of finding start-up money. Once you’ve acquired start-up capital, don’t just stuff your plan in a drawer. Treat it as an ongoing guide to your business and its operations, as well as a yardstick by which you can measure your performance. Keep it handy, update it periodically, and use it to assess your progress.
In developing and writing your business plan, you must make strategic decisions in the areas of management, operations, marketing, accounting, and finance—in short, in all the functional areas of business that we described in Chapter 1 “The Foundations of Business” . Granted, preparing a business plan takes a lot of time and work, but it’s well worth the effort. A business plan forces you to think critically about your proposed business and reduces your risk of failure. It forces you to analyze your business concept and the industry in which you’ll be operating, and it helps you determine how you can grab a percentage of sales in that industry.
The most common use of a business plan is persuading investors, lenders, or both, to provide financing. These two groups look for different things. Investors are particularly interested in the quality of your business concept and the ability of management to make your venture successful. Bankers and other lenders are primarily concerned with your company’s ability to generate cash to repay loans. To persuade investors and lenders to support your business, you need a professional, well-written business plan that paints a clear picture of your proposed business.
Sections of the Business Plan
Though formats can vary, a business plan generally includes the following sections: executive summary, description of proposed business, industry analysis, mission statement and core values, management plan, goods or services and (if applicable) production processes, marketing, global issues, and financial plan. Let’s explore each of these sections in more detail. ( Note : More detailed documents and an Excel template are available for those classes in which the optional business plan project is assigned.)

Executive Summary
The executive summary is a one- to three-page overview of the business plan. It’s actually the most important part of the business plan: it’s what the reader looks at first, and if it doesn’t capture the reader’s attention, it might be the only thing that he or she looks at. It should therefore emphasize the key points of the plan and get the reader excited about the prospects of the business.
Even though the executive summary is the first thing read, it’s written after the other sections of the plan are completed. An effective approach in writing the executive summary is to paraphrase key sentences from each section of the business plan. This process will ensure that the key information of each section is included in the executive summary.
Description of Proposed Business
Here, you present a brief description of the company and tell the reader why you’re starting your business, what benefits it provides, and why it will be successful. Some of the questions to answer in this section include the following:
- What will your proposed company do? Will it be a manufacturer, a retailer, or a service provider?
- What goods or services will it provide?
- Why are your goods or services unique?
- Who will be your main customers?
- How will your goods or services be sold?
- Where will your business be located?
Because later parts of the plan will provide more detailed discussions of many of these issues, this section should provide only an overview of these topics.
Industry Analysis
This section provides a brief introduction to the industry in which you propose to operate. It describes both the current situation and the future possibilities, and it addresses such questions as the following:
- How large is the industry? What are total sales for the industry, in volume and dollars?
- Is the industry mature or are new companies successfully entering it?
- What opportunities exist in the industry? What threats exist?
- What factors will influence future expansion or contraction of the industry?
- What is the overall outlook for the industry?
- Who are your major competitors in the industry?
- How does your product differ from those of your competitors?
Mission Statement and Core Values
This portion of the business plan states the company’s mission statement and core values . The mission statement describes the purpose or mission of your organization—its reason for existence. It tells the reader what the organization is committed to doing. For example, one mission statement reads, “The mission of Southwest Airlines is dedication to the highest quality of customer service delivered with a sense of warmth, friendliness, individual pride, and company spirit” (Southwest Airline’s, 2011).
Core values are fundamental beliefs about what’s important and what is (and isn’t) appropriate in conducting company activities. Core values are not about profits, but rather about ideals. They should help guide the behavior of individuals in the organization. Coca-Cola, for example, intends that its core values—leadership, passion, integrity, collaboration, diversity, quality, and accountability—will let employees know what behaviors are (and aren’t) acceptable (The Coca-Cola Company, 2011).
Management Plan
Management makes the key decisions for the business, such as its legal form and organizational structure. This section of the business plan should outline these decisions and provide information about the qualifications of the key management personnel.
A. Legal Form of Organization
This section dentifies the chosen legal form of business ownership: sole proprietorship (personal ownership), partnership (ownership shared with one or more partners), or corporation (ownership through shares of stock).
B. Qualifications of Management Team and Compensation Package
It isn’t enough merely to have a good business idea: you need a talented management team that can turn your concept into a profitable venture. This part of the management plan section provides information about the qualifications of each member of the management team. Its purpose is to convince the reader that the company will be run by experienced, well-qualified managers. It describes each individual’s education, experience, and expertise, as well as each person’s responsibilities. It also indicates the estimated annual salary to be paid to each member of the management team.
C. Organizational Structure
This section of the management plan describes the relationships among individuals within the company, listing the major responsibilities of each member of the management team.
Goods, Services, and the Production Process
To succeed in attracting investors and lenders, you must be able to describe your goods or services clearly (and enthusiastically). Here, you describe all the goods and services that you will provide the marketplace. This section explains why your proposed offerings are better than those of competitors and indicates what market needs will be met by your goods or services. In other words, it addresses a key question: What competitive advantage will the company’s goods and services have over similar products on the market?
This section also indicates how you plan to obtain or make your products. Naturally, the write-up will vary, depending on whether you’re proposing a service company, a retailer, or a manufacturer. If it’s a service company, describe the process by which you’ll deliver your services. If it’s a retail company, tell the reader where you’ll purchase products for resale.
If you’re going to be a manufacturer, you must furnish information on product design, development, and production processes. You must address questions such as the following:
- How will products be designed?
- What technology will be needed to design and manufacture products?
- Will the company run its own production facilities, or will its products be manufactured by someone else?
- Where will production facilities be located?
- What type of equipment will be used?
- What are the design and layout of the facilities?
- How many workers will be employed in the production process?
- How many units will be produced?
- How will the company ensure that products are of high quality?
This critical section focuses on four marketing-related areas—target market, pricing, distribution, and promotion:
- Target market . Describe future customers and profile them according to age, gender, income, interests, and so forth. If your company will sell to other companies, describe your typical business customer.
- Pricing . State the proposed price for each product. Compare your pricing strategy to that of competitors.
- Distribution . Explain how your goods or services will be distributed to customers. Indicate whether they’ll be sold directly to customers or through retail outlets.
- Promotion . Explain your promotion strategy, indicating what types of advertising you’ll be using.
In addition, if you intend to use the Internet to promote or sell your products, also provide answers to these questions:
- Will your company have a Web site? Who will visit the site?
- What will the site look like? What information will it supply?
- Will you sell products over the Internet?
- How will you attract customers to your site and entice them to buy from your company?
Global Issues
In this section, indicate whether you’ll be involved in international markets, by either buying or selling in other countries. If you’re going to operate across borders, identify the challenges that you’ll face in your global environment, and explain how you’ll meet them. If you don’t plan initially to be involved in international markets, state what strategies, if any, you’ll use to move into international markets when the time comes.
Financial Plan
In preparing the financial section of your business plan, specify the company’s cash needs and explain how you’ll be able to repay debt. This information is vital in obtaining financing. It reports the amount of cash needed by the company for start-up and initial operations and provides an overview of proposed funding sources. It presents financial projections, including expected sales, costs, and profits (or losses). It refers to a set of financial statements included in an appendix to the business plan.
Here, you furnish supplemental information that may be of interest to the reader. In addition to a set of financial statements, for example, you might attach the résumés of your management team.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan tells the story of your business concept, provides an overview of the industry in which you will operate, describes the goods or services you will provide, identifies your customers and proposed marketing activities, explains the qualifications of your management team, and states your projected income and borrowing needs.
- In your business plan, you make strategic decisions in the areas of management, operations, marketing, accounting, and finance. Developing your business plan forces you to analyze your business concept and the industry in which you’ll be operating. Its most common use is persuading investors and lenders to provide financing.
A business plan generally includes the following sections:
- Executive summary . One- to three-page overview.
- Description of proposed business . Brief description of the company that answers such questions as what your proposed company will do, what goods or services it will provide, and who its main customers will be.
- Industry analysis . Short introduction to the industry in which you propose to operate.
- Mission statement and core values . Declaration of your mission statement , which are fundamental beliefs about what’s important and what is (and isn’t) appropriate in conducting company activities.
- Management plan . Information about management team qualifications and responsibilities, and designation of your proposed legal form of organization.
- Goods, services, and the production process . Description of the goods and services that you’ll provide in the marketplace; explanation of how you plan to obtain or make your products or of the process by which you’ll deliver your services.
- Marketing . Description of your plans in four marketing-related areas: target market, pricing, distribution, and promotion.
- Global issues . Description of your involvement, if any, in international markets.
- Financial plan . Report on the cash you’ll need for start-up and initial operations, proposed funding sources, and means of repaying your debt.
- Appendices . Supplemental information that may be of interest to the reader.
(AACSB) Analysis
Let’s start with three givens: (1) college students love chocolate chip cookies, (2) you have a special talent for baking cookies, and (3) you’re always broke. Given these three conditions, you’ve come up with the idea of starting an on-campus business—selling chocolate chip cookies to fellow students. As a business major, you want to do things right by preparing a business plan. First, you identified a number of specifics about your proposed business. Now, you need to put these various pieces of information into the relevant section of your business plan. Using the business plan format described in this chapter, indicate the section of the business plan into which you’d put each of the following:
- You’ll bake the cookies in the kitchen of a friend’s apartment.
- You’ll charge $1 each or $10 a dozen.
- Your purpose is to make the best cookies on campus and deliver them fresh. You value integrity, consideration of others, and quality.
- Each cookie will have ten chocolate chips and will be superior to those sold in nearby bakeries and other stores.
- You expect sales of $6,000 for the first year.
- Chocolate chip cookies are irresistible to college students. There’s a lot of competition from local bakeries, but your cookies will be superior and popular with college students. You’ll make them close to campus using only fresh ingredients and sell them for $1 each. Your management team is excellent. You expect first-year sales of $6,000 and net income of $1,500. You estimate start-up costs at $600.
- You’ll place ads for your product in the college newspaper.
- You’ll hire a vice president at a salary of $100 a week.
- You can ship cookies anywhere in the United States and in Canada.
- You need $600 in cash to start the business.
- There are six bakeries within walking distance of the college.
- You’ll bake nothing but cookies and sell them to college students. You’ll make them in an apartment near campus and deliver them fresh.
The Coca-Cola Company, “Workplace Culture,” The Coca-Cola Company, http://www.thecoca-colacompany.com/citizenship/workplace_culture.html (accessed August 31, 2011).
Southwest Airline’s company Web site, about SWA section, http://www.southwest.com/about_swa/mission.html (accessed August 31, 2011).
Exploring Business Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Helping You Ditch the 9-5 & Travel the World

Writing the Perfect Business Plan: Organization & Management
Now that you have completed the Company Description of your business plan, you can move on to the next section. The Organization & Management is arguably the most straightforward section of your business plan. Essentially, it tells your audience who is involved in your business and how it is structured. Here, we will discuss some best management practices for writing an informative Organization & Management section of your business plan.
Legal Structure
When you created your business, you had to decide on a legal structure for it. This may have been a sole proprietorship, partnership, or LLC, among other options. Within this section, you should discuss the reasons that you chose this structure. By giving solid reasons, your audience will know that you thought out all of the possibilities.
Key Members
In the Key Members subsection, you should list the people involved in your business and their roles. In addition, include any relevant information and credentials that align with their roles. As a result, your audience will know why the people in your business are qualified to do the tasks they are doing.
Organization Structure
You can probably leave this section out if you are the only one involved in your business. However, if any one else is involved, you should include it. The organization structure helps to show who is in charge of what, a vital part of an efficient business. You should include the “chain of command” and if there are any management levels within your company. You can even use a graphic chart to show this!
The Organization & Management section of your business plan is relatively short. However, this doesn’t mean that you should skimp on it. This section can demonstrate that you and your personnel are well qualified. This will go a long way in making your business seem more qualified. To learn about the rest of the sections of the perfect business plan, check out this overview!
Share this:

Writing the Perfect Business Plan: Company Description

Writing the Perfect Business Plan: Market Analysis
You may also like.

Your Guide to Retirement Accounts as a Self-Employed Person

Why I Have a Credit Card with an Annual Fee

The Best Cell Phone Options While Traveling Abroad
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-904536858-c089bc26f4fd4025b23f536345ba73ae.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The legal form of organization in business plan is used to decide how the organization will function, how roles will be arranged and assigned, and how relationships will work. These organizational steps should take place at the beginning of the business formation. Starting a Business. The first step when beginning a business is to name the ...
Organization . The organization section sets up the hierarchy of the people involved in your business. It's often set up in a chart form. If you have a partnership or multi-member LLC, this is where you indicate who is president or CEO, the CFO, director of marketing, and any other roles you have in your business.
Use your company description to provide detailed information about your company. Go into detail about the problems your business solves. Be specific, and list out the consumers, organization, or businesses your company plans to serve. Explain the competitive advantages that will make your business a success.
Learn how to write the organizational structure section of a business plan, including ownership, management, responsibilities, resumes, compensation, and achievements. See an example of a limited liability corporation for a restaurant business.
Creating Your Business Plan: Organization & Management. From the Small Business Administration. This section of your Business Plan should include the following: your company's organizational structure, details about the ownership of your company, profiles of your management team, and the qualifications of your board of directors.
This section of your business plan, Organization and Management, is where you'll explain exactly how you're set up to make your ideas happen, plus you'll introduce the players on your team. As always, remember your audience. If this is a plan for your internal use, you can be a little more general than if you'll be presenting it to a ...
Contact Noirwolf Consulting today using the website contact form or by emailing [email protected] or call us at +44 113 328 0868. Every successful business plan should include the organization and management section, helping you communicate your legal structure and team.
Offer a concise overview of the ownership structure of the company. Identify the shareholders, and specify their ownership percentages or shares. If there are numerous shareholders, list individuals or entities owning 5% or more, and highlight those with a controlling interest in the company or on the board.
Your business structure affects how much you pay in taxes, your ability to raise money, the paperwork you need to file, and your personal liability. You'll need to choose a business structure before you register your business with the state. Most businesses will also need to get a tax ID number and file for the appropriate licenses and permits.
A. Legal Form of Organization. This section dentifies the chosen legal form of business ownership: sole proprietorship (personal ownership), partnership (ownership shared with one or more partners), or corporation (ownership through shares of stock). ... A business plan tells the story of your business concept, provides an overview of the ...
A functional—or role-based—structure is one of the most common organizational structures. This structure has centralized leadership and the vertical, hierarchical structure has clearly defined ...
The organization structure helps to show who is in charge of what, a vital part of an efficient business. You should include the "chain of command" and if there are any management levels within your company. You can even use a graphic chart to show this! The Organization & Management section of your business plan is relatively short.
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. Present the company's mission. Describe the company's product and/or service offerings. Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are ...
A corporation is a business organization that acts as a unique and separate entity from its shareholders. A corporation pays its own taxes before distributing profits or dividends to shareholders. There are three main forms of corporations: a C corporation, an S corporation and an LLC, or limited liability corporation.
4. Limited Liability Partnership (LLP): Best for Professional Businesses. 5. C-Corporation: Best for Outside Investment Opportunities. 6. S-Corporation: Best for Multiple Owners Seeking Board ...
Key Takeaways. A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals. Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to ...
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.