- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact

How to write a good speech in 7 steps
By: Susan Dugdale
- an easily followed format for writing a great speech
Did you know writing a speech doesn't have be an anxious, nail biting experience?
Unsure? Don't be.
You may have lived with the idea you were never good with words for a long time. Or perhaps giving speeches at school brought you out in cold sweats.
However learning how to write a speech is relatively straight forward when you learn to write out loud.
And that's the journey I am offering to take you on: step by step.
To learn quickly, go slow
Take all the time you need. This speech format has 7 steps, each building on the next.
Walk, rather than run, your way through all of them. Don't be tempted to rush. Familiarize yourself with the ideas. Try them out.
I know there are well-advertised short cuts and promises of 'write a speech in 5 minutes'. However in reality they only truly work for somebody who already has the basic foundations of speech writing in place.
The foundation of good speech writing
These steps are the backbone of sound speech preparation. Learn and follow them well at the outset and yes, given more experience and practice you could probably flick something together quickly. Like any skill, the more it's used, the easier it gets.
In the meantime...
Step 1: Begin with a speech overview or outline
Are you in a hurry? Without time to read a whole page? Grab ... The Quick How to Write a Speech Checklist And come back to get the details later.
- WHO you are writing your speech for (your target audience)
- WHY you are preparing this speech. What's the main purpose of your speech? Is it to inform or tell your audience about something? To teach them a new skill or demonstrate something? To persuade or to entertain? (See 4 types of speeches: informative, demonstrative, persuasive and special occasion or entertaining for more.) What do you want them to think, feel or do as a result of listening the speech?
- WHAT your speech is going to be about (its topic) - You'll want to have thought through your main points and have ranked them in order of importance. And have sorted the supporting research you need to make those points effectively.
- HOW much time you have for your speech eg. 3 minutes, 5 minutes... The amount of time you've been allocated dictates how much content you need. If you're unsure check this page: how many words per minute in a speech: a quick reference guide . You'll find estimates of the number of words required for 1 - 10 minute speeches by slow, medium and fast talkers.
Use an outline
The best way to make sure you deliver a perfect speech is to start by carefully completing a speech outline covering the essentials: WHO, WHY, WHAT and HOW.
Beginning to write without thinking your speech through is a bit like heading off on a journey not knowing why you're traveling or where you're going to end up. You can find yourself lost in a deep, dark, murky muddle of ideas very quickly!
Pulling together a speech overview or outline is a much safer option. It's the map you'll follow to get where you want to go.
Get a blank speech outline template to complete
Click the link to find out a whole lot more about preparing a speech outline . ☺ You'll also find a free printable blank speech outline template. I recommend using it!
Understanding speech construction
Before you begin to write, using your completed outline as a guide, let's briefly look at what you're aiming to prepare.
- an opening or introduction
- the body where the bulk of the information is given
- and an ending (or summary).
Imagine your speech as a sandwich

If you think of a speech as a sandwich you'll get the idea.
The opening and ending are the slices of bread holding the filling (the major points or the body of your speech) together.
You can build yourself a simple sandwich with one filling (one big idea) or you could go gourmet and add up to three or, even five. The choice is yours.
But whatever you choose to serve, as a good cook, you need to consider who is going to eat it! And that's your audience.
So let's find out who they are before we do anything else.
Step 2: Know who you are talking to
Understanding your audience.
Did you know a good speech is never written from the speaker's point of view? ( If you need to know more about why check out this page on building rapport .)
Begin with the most important idea/point on your outline.
Consider HOW you can explain (show, tell) that to your audience in the most effective way for them to easily understand it.
Writing from the audience's point of view

To help you write from an audience point of view, it's a good idea to identify either a real person or the type of person who is most likely to be listening to you.
Make sure you select someone who represents the "majority" of the people who will be in your audience. That is they are neither struggling to comprehend you at the bottom of your scale or light-years ahead at the top.
Now imagine they are sitting next to you eagerly waiting to hear what you're going to say. Give them a name, for example, Joe, to help make them real.
Ask yourself
- How do I need to tailor my information to meet Joe's needs? For example, do you tell personal stories to illustrate your main points? Absolutely! Yes. This is a very powerful technique. (Click storytelling in speeches to find out more.)
- What type or level of language is right for Joe as well as my topic? For example if I use jargon (activity, industry or profession specific vocabulary) will it be understood?
Step 3: Writing as you speak
Writing oral language.
Write down what you want to say about your first main point as if you were talking directly to Joe.
If it helps, say it all out loud before you write it down and/or record it.
Use the information below as a guide

(Click to download The Characteristics of Spoken Language as a pdf.)
You do not have to write absolutely everything you're going to say down * but you do need to write down, or outline, the sequence of ideas to ensure they are logical and easily followed.
Remember too, to explain or illustrate your point with examples from your research.
( * Tip: If this is your first speech the safety net of having everything written down could be just what you need. It's easier to recover from a patch of jitters when you have a word by word manuscript than if you have either none, or a bare outline. Your call!)
Step 4: Checking tone and language
The focus of this step is re-working what you've done in Step 2 and 3.
You identified who you were talking to (Step 2) and in Step 3, wrote up your first main point. Is it right? Have you made yourself clear? Check it.

How well you complete this step depends on how well you understand the needs of the people who are going to listen to your speech.
Please do not assume because you know what you're talking about the person (Joe) you've chosen to represent your audience will too. Joe is not a mind-reader!
How to check what you've prepared
- Check the "tone" of your language . Is it right for the occasion, subject matter and your audience?
- Check the length of your sentences. You need short sentences. If they're too long or complicated you risk losing your listeners.
Check for jargon too. These are industry, activity or group exclusive words.
For instance take the phrase: authentic learning . This comes from teaching and refers to connecting lessons to the daily life of students. Authentic learning is learning that is relevant and meaningful for students. If you're not a teacher you may not understand the phrase.
The use of any vocabulary requiring insider knowledge needs to be thought through from the audience perspective. Jargon can close people out.
- Read what you've written out loud. If it flows naturally, in a logical manner, continue the process with your next main idea. If it doesn't, rework.
We use whole sentences and part ones, and we mix them up with asides or appeals e.g. "Did you get that? Of course you did. Right...Let's move it along. I was saying ..."
Click for more about the differences between spoken and written language .
And now repeat the process
Repeat this process for the remainder of your main ideas.
Because you've done the first one carefully, the rest should follow fairly easily.
Step 5: Use transitions
Providing links or transitions between main ideas.
Between each of your main ideas you need to provide a bridge or pathway for your audience. The clearer the pathway or bridge, the easier it is for them to make the transition from one idea to the next.

If your speech contains more than three main ideas and each is building on the last, then consider using a "catch-up" or summary as part of your transitions.
Is your speech being evaluated? Find out exactly what aspects you're being assessed on using this standard speech evaluation form
Link/transition examples
A link can be as simple as:
"We've explored one scenario for the ending of Block Buster 111, but let's consider another. This time..."
What follows this transition is the introduction of Main Idea Two.
Here's a summarizing link/transition example:
"We've ended Blockbuster 111 four ways so far. In the first, everybody died. In the second, everybody died BUT their ghosts remained to haunt the area. In the third, one villain died. His partner reformed and after a fight-out with the hero, they both strode off into the sunset, friends forever. In the fourth, the hero dies in a major battle but is reborn sometime in the future.
And now what about one more? What if nobody died? The fifth possibility..."
Go back through your main ideas checking the links. Remember Joe as you go. Try each transition or link out loud and really listen to yourself. Is it obvious? Easily followed?
Keep them if they are clear and concise.
For more about transitions (with examples) see Andrew Dlugan's excellent article, Speech Transitions: Magical words and Phrases .
Step 6: The end of your speech
The ideal ending is highly memorable . You want it to live on in the minds of your listeners long after your speech is finished. Often it combines a call to action with a summary of major points.

Example speech endings
Example 1: The desired outcome of a speech persuading people to vote for you in an upcoming election is that they get out there on voting day and do so. You can help that outcome along by calling them to register their support by signing a prepared pledge statement as they leave.
"We're agreed we want change. You can help us give it to you by signing this pledge statement as you leave. Be part of the change you want to see!
Example 2: The desired outcome is increased sales figures. The call to action is made urgent with the introduction of time specific incentives.
"You have three weeks from the time you leave this hall to make that dream family holiday in New Zealand yours. Can you do it? Will you do it? The kids will love it. Your wife will love it. Do it now!"
How to figure out the right call to action
A clue for working out what the most appropriate call to action might be, is to go back to your original purpose for giving the speech.
- Was it to motivate or inspire?
- Was it to persuade to a particular point of view?
- Was it to share specialist information?
- Was it to celebrate a person, a place, time or event?
Ask yourself what you want people to do as a result of having listened to your speech.
For more about ending speeches
Visit this page for more about how to end a speech effectively . You'll find two additional types of speech endings with examples.
Write and test
Write your ending and test it out loud. Try it out on a friend, or two. Is it good? Does it work?
Step 7: The introduction
Once you've got the filling (main ideas) the linking and the ending in place, it's time to focus on the introduction.
The introduction comes last as it's the most important part of your speech. This is the bit that either has people sitting up alert or slumped and waiting for you to end. It's the tone setter!
What makes a great speech opening?
Ideally you want an opening that makes listening to you the only thing the 'Joes' in the audience want to do.
You want them to forget they're hungry or that their chair is hard or that their bills need paying.
The way to do that is to capture their interest straight away. You do this with a "hook".
Hooks to catch your audience's attention
Hooks come in as many forms as there are speeches and audiences. Your task is work out what specific hook is needed to catch your audience.

Go back to the purpose. Why are you giving this speech?
Once you have your answer, consider your call to action. What do you want the audience to do, and, or take away, as a result of listening to you?
Next think about the imaginary or real person you wrote for when you were focusing on your main ideas.
Choosing the best hook
- Is it humor?
- Would shock tactics work?
- Is it a rhetorical question?
- Is it formality or informality?
- Is it an outline or overview of what you're going to cover, including the call to action?
- Or is it a mix of all these elements?
A hook example
Here's an example from a fictional political speech. The speaker is lobbying for votes. His audience are predominately workers whose future's are not secure.
"How's your imagination this morning? Good? (Pause for response from audience) Great, I'm glad. Because we're going to put it to work starting right now.
I want you to see your future. What does it look like? Are you happy? Is everything as you want it to be? No? Let's change that. We could do it. And we could do it today.
At the end of this speech you're going to be given the opportunity to change your world, for a better one ...
No, I'm not a magician. Or a simpleton with big ideas and precious little commonsense. I'm an ordinary man, just like you. And I have a plan to share!"
And then our speaker is off into his main points supported by examples. The end, which he has already foreshadowed in his opening, is the call to vote for him.
Prepare several hooks
Experiment with several openings until you've found the one that serves your audience, your subject matter and your purpose best.
For many more examples of speech openings go to: how to write a speech introduction . You'll find 12 of the very best ways to start a speech.
That completes the initial seven steps towards writing your speech. If you've followed them all the way through, congratulations, you now have the text of your speech!
Although you might have the words, you're still a couple of steps away from being ready to deliver them. Both of them are essential if you want the very best outcome possible. They are below. Please take them.
Step 8: Checking content and timing
This step pulls everything together.
Check once, check twice, check three times & then once more!
Go through your speech really carefully.
On the first read through check you've got your main points in their correct order with supporting material, plus an effective introduction and ending.
On the second read through check the linking passages or transitions making sure they are clear and easily followed.
On the third reading check your sentence structure, language use and tone.
Double, triple check the timing
Now go though once more.
This time read it aloud slowly and time yourself.
If it's too long for the time allowance you've been given make the necessary cuts.
Start by looking at your examples rather than the main ideas themselves. If you've used several examples to illustrate one principal idea, cut the least important out.
Also look to see if you've repeated yourself unnecessarily or, gone off track. If it's not relevant, cut it.
Repeat the process, condensing until your speech fits the required length, preferably coming in just under your time limit.
You can also find out how approximately long it will take you to say the words you have by using this very handy words to minutes converter . It's an excellent tool, one I frequently use. While it can't give you a precise time, it does provide a reasonable estimate.

Step 9: Rehearsing your speech
And NOW you are finished with writing the speech, and are ready for REHEARSAL .

Please don't be tempted to skip this step. It is not an extra thrown in for good measure. It's essential.
The "not-so-secret" secret of successful speeches combines good writing with practice, practice and then, practicing some more.
Go to how to practice public speaking and you'll find rehearsal techniques and suggestions to boost your speech delivery from ordinary to extraordinary.
The Quick How to Write a Speech Checklist
Before you begin writing you need:.
- Your speech OUTLINE with your main ideas ranked in the order you're going to present them. (If you haven't done one complete this 4 step sample speech outline . It will make the writing process much easier.)
- Your RESEARCH
- You also need to know WHO you're speaking to, the PURPOSE of the speech and HOW long you're speaking for
The basic format
- the body where you present your main ideas
Split your time allowance so that you spend approximately 70% on the body and 15% each on the introduction and ending.
How to write the speech
- Write your main ideas out incorporating your examples and research
- Link them together making sure each flows in a smooth, logical progression
- Write your ending, summarizing your main ideas briefly and end with a call for action
- Write your introduction considering the 'hook' you're going to use to get your audience listening
- An often quoted saying to explain the process is: Tell them what you're going to tell them (Introduction) Tell them (Body of your speech - the main ideas plus examples) Tell them what you told them (The ending)
TEST before presenting. Read aloud several times to check the flow of material, the suitability of language and the timing.

- Return to top

speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs

15 Speech Writing Topics for Class 7 with Questions and Answers

Explore engaging Speech Writing Topics for Class 7, covering themes like friendship, the environment, and favorite books. This guide includes questions and answers to help young speakers craft compelling speeches, fostering communication skills and confidence.
Guidelines for Effective Speech Writing for Class 7
- Keep it Simple and Clear.
- Use language that is easily understandable for Class 7 students.
- Make the speech relatable by including personal examples.
- Connect with the audience through stories.
- Illustrate key points with real-life situations.
- Ensure that the speech is educational while keeping the audience entertained.
- Practice Regularly and Seek Feedback.
Structure of Speech Writing for Class 7
When writing a speech for a class 7 level, it’s important to keep it simple, engaging, and well-structured. Here’s a basic format you can follow:

Sample of Speech Writing for Class 7
Question: Prepare a speech about the ‘importance of kindness’.
Introduction:
Good morning/afternoon, everyone! My name is [Your Name], and I am in class 7. Today, I want to talk to you about something that has been on my mind lately – the importance of kindness.
Firstly, let’s think about why kindness matters. Being kind not only makes others feel good, but it also creates a positive environment for everyone. For instance, helping a friend with homework or sharing a smile can brighten someone’s day.
Secondly, kindness is like a ripple effect. When we are kind to others, they are more likely to be kind to someone else. It’s a simple way to make our school and community a better place.
Lastly, let’s not forget self-kindness. Taking care of ourselves, both physically and emotionally, allows us to be better friends, students, and family members. So, don’t forget to be kind to yourself too.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, let’s make kindness a habit. Small acts of kindness can have a big impact on our lives and the lives of those around us. So, let’s strive to be kind every day.
Thank you for listening, and let’s make our school a place where kindness truly matters!
People also ask
Speech Writing Topics for Class 7 with Questions
Questions 1:, 1. we are all blessed with relatives by birth. but we make friends ourselves. friends are integral to our lives. it is difficult to imagine a day without friends. we share our sorrow and happiness with our buddies. the best way to rejuvenate ourselves and get moral support in a difficult situation is through good friends. taking ideas from the unit- relationships, write a speech on the topic, ‘the greatest gift of life is friendship.’ (word limit: 120-150), questions 2:, 2. experience is the hardest teacher; it gives you the test first and the lesson afterward. courage gives you the power to chase after things that are important to you. it also bolsters your self-confidence and allows you to believe in your abilities. likewise, you must realize that courage is not the absence of fear. taking ideas from the unit- attitude, write a speech on the topic, ‘courage leads to success.’ (word limit: 120-150) , questions 3:, 3. write a speech on the topic importance of physical games and exercise in today’s fast-paced life. .
[Optional: Encourage the audience to take small steps towards incorporating physical activities into their daily routines.]
Questions 4:
4. write a speech to be delivered in the morning assembly on the topic importance of eating a healthy diet. , questions 5:, 5. you are sameer/siya, a student of class vii. you have to prepare a speech to be delivered in the morning assembly of your school on the topic ‘significance of siblings in our life’. write the speech in about 120-150 words. you can use ideas from the unit ‘relationships’ of my english reader along with your views. , questions 6:, 6. nature has enough for man’s needs but not enough for man’s greed. it is imperative to understand that the earth is our home and it is our responsibility to take care of it for ourselves and the generations to come., questions 7:, 7. using the hints given below, prepare a speech to be delivered in the school assembly highlighting the ‘role of students in conservation of environment.”.
[Hints:- Reduce waste – Avoid wastage of paper – Conserve existing resources – Turn off electrical appliances when not in use – Use non-toxic cleaners – Use biodegradable products]
Questions 8:
8. grandparents play a vital role in the life of grandchildren. they provide a whole sense of history, identity, and heritage. they provide a vital connection with the past, where the young generation has come from. taking ideas from the unit – “relationships”, of “my english reader” write a speech on the topic “importance of grandparents in our lives.” (word limit: 120-150 words) , questions 9:, 9. of all the relationships, a bond between the siblings is always special. a sibling can be a guide, a friend, a mentor, a competitor, or a teacher – all rolled into one. taking ideas from unit “relationships” of ‘’my english reader”, write a speech on the topic – “role of siblings in our life” ( word limit: 120-150 words) , questions 10:, 10. experience is the hardest teacher; it gives you the test first and the lesson afterward. courage gives you the power to chase after things that are important to you. it also bolsters your self-confidence and allows you to believe in your abilities. likewise, you must realize that courage is not the absence of fear. taking ideas from the unit- attitude, write a speech on the topic, ‘courage leads to success.’ (word limit: 120-150) , questions 11:, 11. success comes to those who struggle to overpower their apprehensions. it is a result of hard work, endurance, and persistence. taking ideas from the unit ‘achievers’ and using your ideas prepare a speech for your school assembly on the topic- ‘the seed of achievement lies in the human mind’. (120-150 words), questions 12:, 12. “disability does not mean inability”. our country has witnessed an innumerable number of heroic personalities, who despite their disabilities have achieved success. it in turn displays the fact that to achieve anything, all we need is courage and determination. taking ideas from the unit “achievers” and using your ideas write a speech to be delivered in the school assembly on the topic- “ the seed of achievement lies in the human mind” (120 – 150 words). you are namit / namita. , questions 13:, 13. friends are an integral part of our life. it is difficult to imagine a day without friends. we share our sorrow and happiness with them. it is the relationship we choose for ourselves. taking hints from the unit “relationships” and using your ideas write a speech on the topic “ “importance of friends in our lives” in 120 to 150 words. you are namit / natasha. , questions 14:, 14. india is a diverse country with diverse cultures, traditions, and religions. but there is a strange feeling that binds together all these diversities. taking ideas from the unit- unity in diversity, write a speech on the topic – ‘varied people, varied cultures but one humanity’. (100-120 words) , questions 15:, 16. prepare a short speech on the topic „good manners‟ with the help of the given outlines to be delivered in your school‟ ‘s assembly. you are avadhesh/gouravi, studying in class vii. importance of good manners – cost nothing – at home – at school in social life., faqs on speech writing for class 7, what are the uses of speech writing.
Ans: Speech writing is essential for expressing thoughts clearly, whether in public speaking or personal communication. It helps convey messages effectively and engages audiences in a structured and impactful way.
How to write a speech for class 7th?
Choose an Engaging Topic:
- Pick a subject that interests you and your classmates.
- Ensure it’s something you can talk about with enthusiasm.
Organize Your Speech:
- Divide it into an introduction, main points, and conclusion.
- Clearly outline what you want to say in each section.
Use Simple Language:
- Keep sentences short and easy to understand.
- Avoid complicated words that might confuse your classmates.
Practice, Practice, Practice:
- Rehearse your speech multiple times.
- Speak slowly, with clear pronunciation, and build confidence.
Does speech writing have a title?
Ans: Yes, speech writing typically includes a title that encapsulates the main theme or purpose of the speech, offering a preview of its content. The title of a speech is typically delivered at the beginning, providing the audience with a clear preview of the topic and setting the tone for the presentation.
Why is speech writing important for students?
Ans: Speech writing is important for students as it helps them express ideas clearly and builds confidence in public speaking, essential skills for effective communication. It nurtures their ability to articulate thoughts, aiding academic success and personal development.
What is the most important part of speech writing?
Ans: The most crucial part of speech writing is the introduction, where you grab attention and set the tone. For example, starting with a question like “Have you ever wondered…” instantly engages the audience.
Speech Writing Topics for Class 7 Answers
Ladies and gentlemen,
Good [morning/afternoon/evening],
I stand before you today to talk about something we all hold dear – friendship. We are born into families, but we choose our friends, and in that choice lies the greatest gift of life.
In the unit on relationships, we explore the intricate bonds we share with our families, but let us not overlook the incredible significance of our friends. A day without friends seems almost unimaginable, doesn’t it? They are the companions who stand by us through thick and thin, sharing both our sorrows and joys.
Friendship is not just a bond; it’s a lifeline. In times of trouble, our friends are the ones who rejuvenate our spirits, offering not only a listening ear but also genuine moral support. The laughter we share with them lightens our burdens, and the empathy they provide makes the tough times a bit more bearable.
So, let us cherish and celebrate the greatest gift of life – friendship. In our friends, we find not just companionship, but a reflection of our true selves. As we navigate the journey of life, let’s appreciate the unique and irreplaceable role our friends play.
[Optional: You can end with a quote about friendship or a call to the audience to reflect on and appreciate their friendships.]
In the unit on attitude, we uncover the profound connection between courage and success. As the saying goes, “ Experience is the hardest teache r; it gives you the test first and the lesson afterward.” Similarly, courage is the guiding force that transforms those lessons into stepping stones toward success.
Courage is not the absence of fear but the triumph over it. It bestows upon us the power to pursue what truly matters, empowering us to chase after our goals with determination. It acts as a catalyst, propelling us beyond our comfort zones and reinforcing our self-confidence. With courage, we come to believe in our abilities, realizing that challenges are not roadblocks but growth opportunities.
Success often lies on the other side of fear. It is the courage to face uncertainties, to take calculated risks, and to persevere in the face of adversity that leads to triumph. So, let us cultivate courage in our attitudes, for it is the compass that directs us on the path to success. Remember, the test of experience becomes a testament to our courage.
[Optional: Encourage the audience to embrace challenges with courage and turn obstacles into opportunities.]
In today’s fast-paced life, where time seems to slip through our fingers, it’s crucial to reflect on the often overlooked but essential aspect of our well-being— physical games and exercise.
Our modern lifestyles are marked by hectic schedules and sedentary habits, leading to a decline in physical activity. However, the importance of incorporating physical games and exercise into our daily routines cannot be overstated. These activities are not merely a means to stay fit; they contribute significantly to our overall mental and physical health.
Engaging in physical games and exercise is an antidote to the stress and pressures of our fast-paced lives. They enhance our cardiovascular health, boost our energy levels, and improve our mood by releasing endorphins—the feel-good hormones. Additionally, regular exercise is proven to enhance cognitive function, fostering better concentration and creativity.
In a world dominated by screens and constant connectivity, physical games provide a refreshing break and an opportunity for social interaction. Whether it’s team sports or individual workouts, these activities build camaraderie, discipline, and resilience.
Therefore, let us recognize the importance of prioritizing physical games and exercise in our lives. By doing so, we not only invest in our physical health but also cultivate a balanced and fulfilling lifestyle in the face of today’s relentless pace.
Good morning, respected teachers, and dear friends,
I stand before you today to shed light on a topic that holds the key to our overall well-being – the importance of maintaining a healthy diet. In the hustle and bustle of our lives, it’s easy to overlook the significance of what we consume daily.
Our bodies are our most valuable assets, and the fuel we provide them determines how well they function. A healthy diet is not just about watching our weight; it is about nourishing our bodies with the essential nutrients they need to thrive. It fuels our energy, supports our immune system, and promotes mental clarity.
In a world filled with tempting fast food and sugary treats, it’s crucial to make mindful choices. A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and proteins, ensures that our bodies receive the necessary vitamins and minerals for optimal performance.
So, let us pledge to prioritize our health by making conscious choices about the food we consume. Remember, a healthy diet is not a sacrifice; it is an investment in our well-being. Let’s start our day by choosing nutritious meals that empower us to face the challenges ahead.
Today, I want to share some thoughts on a topic that is close to my heart – the significance of siblings in our lives . As Sameer/Siya, a seventh-grader, I believe that our relationships with our siblings are some of the most precious bonds we form.
In the unit ‘Relationships’ from our English Reader, we’ve explored the dynamics of family ties. Our siblings, be they older or younger, play a unique role in shaping who we are. They are our partners in crime, our confidantes, and our lifelong friends.
Through shared experiences, we learn valuable life lessons and develop qualities like patience, understanding, and cooperation. Our siblings are there with us through thick and thin, celebrating our triumphs and providing solace during challenges. In essence, they are our companions on this journey called life.
We need to appreciate and nurture these relationships. While we may have our differences, the love and support we receive from our siblings are unparalleled. So, let’s take a moment to express gratitude for the significance of siblings in our lives. They are not just family; they are our allies, making the journey of growing up all the more memorable.
Answers 6:
In the delicate balance of nature, there exists a profound truth – “ Nature has enough for man’s needs but not enough for man’s greed. ” These words, echoing the wisdom of Mahatma Gandhi, implore us to reflect on our relationship with the environment.
Our Earth, our home, provides us with an abundance of resources to fulfill our genuine needs. However, as stewards of this planet, we must recognize the consequences of unchecked greed. Exploitative practices, deforestation, and pollution jeopardize the delicate ecosystems that sustain life.
It is our shared responsibility to preserve the beauty and vitality of our home for ourselves and the generations yet to come. Sustainable living, conservation efforts, and responsible consumption are not just buzzwords; they are the keys to ensuring a harmonious coexistence with nature.
Let us embrace a collective consciousness that acknowledges the finite resources of our Earth. By fostering an attitude of respect and gratitude towards nature, we can strive to be mindful custodians, ensuring that the legacy we leave for future generations is one of environmental stewardship and not depletion.
Thank you.
Respected teachers, dear students, and honored guests,
I stand before you today to emphasize the crucial role that each one of us, as students, plays in the conservation of our environment . Our actions, no matter how small, collectively contribute to the well-being of our planet.
Firstly, let’s consider the significant impact of waste reduction. By being mindful of our consumption and adopting practices like recycling, we actively participate in reducing the burden on landfills and conserving valuable resources. Additionally, let’s commit to minimizing paper wastage by utilizing both sides of sheets and embracing digital alternatives whenever possible.
Conserving existing resources is another responsibility we hold. Whether it’s water, energy, or natural habitats, our choices matter. Turn off electrical appliances when not in use, as this not only saves energy but also contributes to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Let’s be champions of water conservation by using it judiciously in our daily activities.
Furthermore, consider the products we use daily. Opting for non-toxic cleaners and embracing biodegradable products ensures that our daily routines are not harming the environment. Small changes in our lifestyle choices can collectively make a significant impact.
In conclusion, the role of students in the conservation of the environment is pivotal. By incorporating these simple habits into our lives, we become ambassadors for a sustainable future. Let us be conscious consumers and stewards of this planet, ensuring that our actions today contribute to a healthier and greener tomorrow.
Respected teachers, dear friends, and honored guests,
Today, I am honored to speak about a topic that holds immense significance in our lives— the importance of grandparents . In the unit “ Relationships ” from our English Reader, we’ve explored the profound connections we share with our family members, and among these connections, the role of grandparents is truly special.
Grandparents serve as the living chronicles of our family’s history, offering a wealth of stories, traditions, and wisdom. Their presence provides a sense of continuity and identity, connecting us to our roots and heritage. In a world that’s constantly evolving, this link with the past is invaluable.
Through their experiences and anecdotes, grandparents become our storytellers, passing down not just tales of bygone eras but also lessons learned from a lifetime. Their unconditional love and guidance shape us into the individuals we are meant to become.
In a fast-paced world, where time often moves too quickly, the slower pace of a grandparent’s wisdom and affection serves as a grounding force. They are our pillars of strength, offering support and understanding during both triumphs and tribulations.
So, let us recognize and cherish the importance of grandparents in our lives. Their presence is a source of comfort, guidance, and a reminder of where we come from. Today, let’s express our gratitude for the love and wisdom bestowed upon us by these special individuals.
Respected teachers, dear friends, and cherished guests,
I am delighted to share thoughts on a relationship that holds a unique place in our lives—the bond between siblings. As explored in the unit “Relationships” from our ‘My English Reader,’ the role of siblings is truly multifaceted, encompassing various roles that shape our journey through life.
A sibling is not just a family member; they are a guide, a friend, a mentor, a competitor, and a teacher, all rolled into one. Growing up with a sibling means having a constant companion to share laughter, joy, and even the occasional squabble. They are our partners in crime, creating a treasure trove of shared memories that accompany us through the years.
Beyond the camaraderie, siblings often take on the roles of mentors and teachers, offering guidance and support in times of need. Their experiences become valuable lessons, helping us navigate the challenges of life. Moreover, the friendly competition between siblings fosters resilience and determination, preparing us for the broader world.
In moments of celebration or sorrow, a sibling is there to share the highs and lows of life. This unique bond contributes to the formation of our identities, providing an unrivaled support system.
Let us celebrate and appreciate the role of siblings in our lives. They are not just family; they are lifelong companions, enriching our journey with shared experiences, lessons, and, above all, unconditional love.
Answers 10:
In the journey of life, two indispensable virtues stand out – experience and courage. As we explore the concept of courage through the lens of the unit on attitude, it becomes evident that courage is the dynamic force propelling us toward success.
“Experience is the hardest teacher; it gives you the test first and the lesson afterward.” These words remind us that life’s challenges are inevitable, but it’s the courage to face them head-on that transforms these tests into valuable lessons. Courage, in essence, is the catalyst for growth.
Courage provides the power to pursue what is important to us. It is the driving force behind our ambitions, propelling us to chase our dreams with determination. Beyond that, courage acts as a powerful ally, bolstering self-confidence and instilling the belief that we are capable of overcoming any obstacle.
Crucially, courage does not signify the absence of fear but rather the triumph over it. It is the ability to confront our fears and move forward despite them that leads to success. Each step taken with courage opens new doors and paves the way for accomplishments.
In conclusion, let us embrace courage as the guiding force on our path to success. It’s not just a virtue; it’s the key that unlocks our potential and turns aspirations into achievements. So, let courage be our compass as we navigate the journey towards a successful and fulfilling life.
Answers 11:
Good morning respected teachers, dear friends, and distinguished guests,
Today, I, as [Your Name], wish to share a fundamental truth that resonates with the stories of achievers we have explored in the unit ‘Achievers’— “ Success comes to those who struggle to overpower their apprehensions, and the seed of achievement lies in the human mind.”
In the journeys of those who have achieved greatness, the common thread is not just hard work, endurance, and persistence, but the remarkable power of the human mind. The mind is the seed from which success sprouts, nurtured by determination and resilience.
Overcoming apprehensions is a daunting task, yet it is through this struggle that the foundation of success is laid. The human mind, with its incredible capacity for adaptability, innovation, and focus, becomes the driving force behind every achievement.
Hard work, endurance, and persistence are not just actions; they are the fruits of a mindset that believes in the possibility of overcoming challenges. The stories of achievers tell us that success is not an external destination but an internal journey—a journey shaped by the power of the human mind.
As we navigate our paths, let us recognize the potential within our minds. Let us strive to cultivate a mindset that transforms apprehensions into opportunities and obstacles into stepping stones toward achievement. The seed of accomplishment lies within each of us, waiting to be nourished by our determination and belief.
Answers 12:
Good morning respected teachers, dear friends, and honored guests,
I stand before you as Namit/Namita to share a thought deeply ingrained in the stories of countless heroes in our nation – “ Disability does not mean inability.” The unit “Achievers” in our studies has showcased individuals who, despite facing physical challenges, have achieved remarkable success. This underscores a profound truth – the seed of achievement lies in the human mind.
Our minds have an extraordinary capacity to overcome obstacles, turning challenges into stepping stones towards success. The stories of achievers with disabilities teach us that with courage and determination, one can surmount any adversity. These individuals have not just broken barriers but shattered stereotypes, showcasing the indomitable spirit residing within the human mind.
The seed of achievement germinates when we cultivate a mindset that refuses to be defined by limitations. It blossoms when we embrace challenges with resilience and use setbacks as fuel for growth. These achievers exemplify that success is not restricted by physical abilities but is, in fact, a testament to the strength of the human mind.
In our own lives, let us nurture this seed of achievement by fostering a mindset of determination and courage. Every challenge we face is an opportunity for growth, and within our minds lies the power to turn dreams into reality.
Answers 13:
Good [morning/afternoon/evening] respected teachers, dear friends, and esteemed guests,
I stand before you as Namit/Natasha to express the significance of a relationship that adds color to the canvas of our lives—friendship. Friends, truly, are the heartbeat of our existence.
In the unit “Relationships,” we’ve explored the dynamic connections that shape our lives, and among them, the bond with friends is unparalleled. Imagine a day without friends—a day devoid of shared laughter, comforting embraces during sorrow, and the joy that comes from having companions who understand us.
Friends are not just companions; they are the family we choose. The importance of this chosen relationship is immeasurable. In times of joy, they magnify our celebrations, and in times of sorrow, they offer solace and understanding.
It is through friendships that we learn the art of empathy, compassion, and the joy of selfless giving. As Namit/Natasha, I encourage each of us to cherish and nurture these precious bonds. Our lives are enriched by the tapestry of friendships we weave, making each day brighter and more meaningful.
Answers 14:
Respected teachers, dear friends, and esteemed guests,
In the mosaic of India’s cultural landscape, we witness a beautiful tapestry woven with diverse threads of cultures, traditions, and religions. Yet, amidst this rich diversity, there exists a peculiar and heartwarming sentiment that binds us all together—a recognition of our shared humanity.
Our unity in diversity is a theme resonating from the unit “Unity in Diversity.” It’s fascinating how, despite the myriad cultures and traditions that paint our nation, there is an invisible thread of connection that ties us as one people. This strange feeling is the acknowledgment that, beyond our differences, we are all part of the greater human family.
India, with its varied people and cultures, stands as a living testament to the idea that diversity is not a source of division but a celebration of unique identities coming together. Our differences are the colors that paint the canvas of our nation, creating a vibrant and harmonious portrait.
Let us take pride in this diversity and, at the same time, celebrate our shared humanity. Varied people, and varied cultures, but one humanity—this is the essence that defines the spirit of our incredible nation. Through understanding, acceptance, and unity, let us continue to cherish and preserve this unique identity that makes India truly special.
Answers 15:
Good morning respected teachers, dear friends, and esteemed guests,
I am Avadhesh/Gouravi from class VII, and today I wish to speak to you about something that costs nothing but holds immense value—good manners.
In a world that is often bustling with activities, good manners serve as the foundation of harmonious relationships. They are not just a set of rules but a reflection of our respect and consideration for others.
At home, practicing good manners creates a positive and peaceful environment. Simple gestures like saying “please” and “thank you” contribute to a culture of appreciation and understanding within our families.
In the school setting, good manners create a conducive atmosphere for learning and collaboration. Respecting our teachers, classmates, and staff fosters an environment where everyone feels valued and heard.
Beyond the school gates, in our social lives, good manners are like a common language that connects us all. Politeness, empathy, and consideration make social interactions smoother and more enjoyable.
So, let’s remember that the importance of good manners extends beyond politeness; it’s about building a world where kindness and respect are the guiding principles.
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search
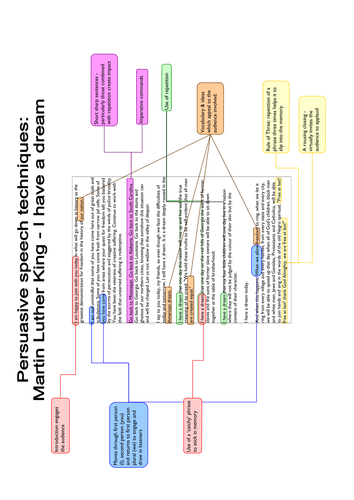
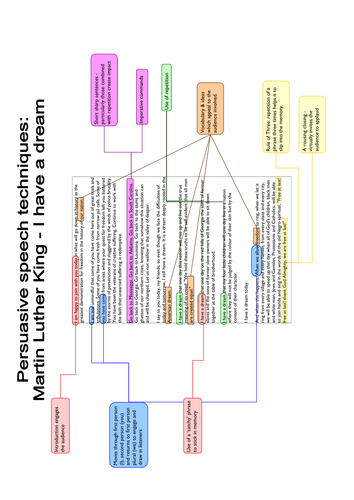
Writing a speech
Subject: English
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
28 August 2020
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest
Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
amie_campbell1
Thank you for sharing this. I really liked the writing frame
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Julietteaharrison
Yes. Great resource. Thank you
geraldinedaly
Thank you for sharing! Great resource!
Thanks for sharing! Great content.
darlene_gedye
Thank you. There is some great content here to help students to structure and write their speeches. The power points will be very handy as will the variety of lead up lessons included. Thanks for sharing your resources.
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Writing a speech
Topic outline.
The purpose of a speech is often to inform or persuade an audience.
Speeches are usually written to be spoken directly to an audience and can be used to entertain, influencing the listeners that the viewpoint of the speaker is correct.
Speeches can also be used to encourage the audience to take action or to change their behaviour in some way; for example, to join a particular school club or society, or to recycle more.
The ways you use language and vocabulary when writing the words of a speech will depend on the audience and the purpose you are writing for; for example, in a speech to a group of teachers and parents giving your views on a recent proposal, formal language is most appropriate.
- think about the audience that the speech is for – are you giving your speech to a group of people you know, or do not know, or a mixture of both? If you know your audience well, you may be able to relax a little, but a speech is still a formal kind of talk and would usually not include slang
- whether your audience are likely to disagree with what you say – you will need to consider any possible objections and deal with them. Use language carefully to make objections seem less significant; for example, using phrases like ‘A few people may still think, however’
- the reason you are giving this speech and how you feel about this topic – try to imagine the words of your speech as you would speak them out loud. Your tone of voice must match your message, so choose words that appeal to the emotions of your listeners. Focus on what you want your audience to know and feel by the end of your speech
- how to engage your listeners – f or example, you might use inclusive words or phrases like ‘we’, ‘all of us’ and ‘our’ to make your listeners feel that you are all on the same side.
- Plan where you want to finish your speech and how you will get there before you start writing – t h e structure of a speech is usually in three parts. For example:
- An opening that grabs your audience's attention and makes the overall topic of your speech clear – for example, pose a question to the audience where you can predict the answer.
- A well-structured, supported and developed argument – for example, to support your argument you might use real life examples or anecdotes.
- A powerful conclusion – for example, group your final words or ideas in threes to help make them memorable or end with a thought- provoking question or image and thank your audience for listening.
- Organise your ideas into paragraphs as appropriate – this will help you to develop and support your points convincingly, to build your argument and/or offer a full explanation of a particular point of view.
- S how the connectio ns between ideas in sentences and paragraphs – where a new point or idea follows on from what you have already said you might use linking words or phrases such as, ‘in addition’, ‘likewise’ or ‘similarly’.
- Example of a speech
100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
There is a small but important difference between planning a persuasive speech and writing a persuasive essay. First, if you are planning a persuasive speech, you should think about a topic that can engage your audience. For this reason, you may want to consider a few topics before settling on the one that allows you to be more descriptive and entertaining.
Another important factor when picking a persuasive speech topic is to choose one that can provoke your audience. If you stir up a little emotion in your audience members, you'll keep their attention. The list below is provided to help you brainstorm. Choose a topic from this list or use the list to generate an idea of your own.
- Studying martial arts is good for mind and health.
- Competitive sports can teach us about life.
- Reality shows are exploiting people.
- Community service should be a graduation requirement for all high school students.
- The characteristics that make a person a hero.
- It's important to grow things in a garden.
- Violent video games are dangerous.
- Lyrics in a song can impact our lives.
- Traveling and studying abroad are positive experiences.
- Journal writing is therapeutic.
- You should spend time with your grandparents.
- A laptop is better than a tablet.
- Religion and science can go hand in hand.
- School uniforms are good.
- All-female colleges and all-male colleges are bad.
- Multiple choice tests are better than essay tests .
- We should not spend money on space exploration.
- Open-book tests are as effective as closed-book tests.
- Security cameras keep us safer.
- Parents should have access to students' grades.
- Small classes are better than big classes.
- You need to start saving for retirement now.
- Credit cards are harmful to college students.
- We should have a royal family.
- We should protect endangered animals.
- Texting while driving is dangerous.
- You can write a novel.
- Recycling should be required in the U.S.
- State colleges are better than private colleges.
- Private colleges are better than state colleges.
- We should do away with penny coins.
- Fast food containers hurt the environment.
- Plastic straws are harmful to the environment.
- You can eat and enjoy healthy snacks.
- You can become a millionaire.
- Dogs are better pets than cats.
- You should own a bird.
- It's unethical to keep birds in cages.
- Liberal arts degrees prepare graduates to be better workers than other degrees.
- Hunting animals should be banned.
- Football is a dangerous sport.
- School days should start later.
- Night school is better than day school.
- Technical training is better than a college degree.
- Immigration laws should be more lenient.
- Students should be able to choose their schools.
- Everyone should learn to play a musical instrument.
- Grass lawns should be prohibited.
- Sharks should be protected.
- We should do away with cars and go back to horse and carriage for transportation.
- We should use more wind power.
- We should pay more taxes.
- We should do away with taxes.
- Teachers should be tested like students.
- We should not interfere in the affairs of other countries.
- Every student should join a club.
- Homeschooling is better than traditional schooling.
- People should stay married for life.
- Smoking in public should be illegal.
- College students should live on campus .
- Parents should let students fail.
- Giving to charity is good.
- Education makes us happier people.
- The death penalty should be outlawed.
- Bigfoot is real.
- We should increase train travel to save the environment.
- We should read more classic books.
- Fame is bad for young children.
- Athletes should stay loyal to teams.
- We should reform our prisons.
- Juvenile offenders should not go to boot camps.
- Abraham Lincoln was the best president.
- Abraham Lincoln gets too much credit.
- Students should be allowed to have cell phones in elementary, middle, and high school.
- College student-athletes should be paid for playing.
- Elderly citizens on fixed income should receive free public transportation.
- Colleges and universities should be free to attend.
- All American citizens should complete one year of community service.
- Students should be required to take Spanish classes.
- Every student should be required to learn at least one foreign language .
- Marijuana should be legal for recreational use nationwide.
- Commercial testing of products on animals should no longer be allowed.
- High school students should be required to participate in at least one team sport.
- The drinking age in the U.S. should be 25.
- Replacing fossil fuels with cheaper alternative energy options should be mandated.
- Churches need to contribute their share of taxes.
- The Cuba embargo should be maintained by the U.S.
- America should replace income taxes with a nationwide flat tax.
- Once they reach the age of 18, all U.S. citizens should be automatically registered to vote .
- Doctor-assisted suicide should be legal.
- Spammers—people who bombard the internet with unsolicited email—should be banned from sending junk mail.
- Every automobile driver should be required to take a new driver's test every three years.
- Electroshock treatment is not a humane form of therapy.
- Global warming is not real.
- Single-parent adoption should be encouraged and promoted.
- Gun companies should be held accountable for gun crimes.
- Human cloning is not moral.
- Religion does not belong in public education.
- Juveniles should not be tried as adults.
- American workers should be guaranteed a three-day weekend by law.
- Middle School Debate Topics
- 40 Writing Topics for Argumentative and Persuasive Essays
- Controversial Speech Topics
- How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Preparing an Argument Essay: Exploring Both Sides of an Issue
- 30 Writing Topics: Persuasion
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- The Best Summer Plans for High School Students
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- 50 Topics for Impromptu Student Speeches
- Impromptu Speech Activities
- How Much Damage Do Bad Grades Do?
- Choosing the Perfect College
- 20 Tips for Success in High School
- Great Colleges for Students with "B" Averages
- Personal Essay Topics
The War at Stanford
I didn’t know that college would be a factory of unreason.

Listen to this article
Produced by ElevenLabs and News Over Audio (NOA) using AI narration.
This article was featured in the One Story to Read Today newsletter. Sign up for it here .
ne of the section leaders for my computer-science class, Hamza El Boudali, believes that President Joe Biden should be killed. “I’m not calling for a civilian to do it, but I think a military should,” the 23-year-old Stanford University student told a small group of protesters last month. “I’d be happy if Biden was dead.” He thinks that Stanford is complicit in what he calls the genocide of Palestinians, and that Biden is not only complicit but responsible for it. “I’m not calling for a vigilante to do it,” he later clarified, “but I’m saying he is guilty of mass murder and should be treated in the same way that a terrorist with darker skin would be (and we all know terrorists with dark skin are typically bombed and drone striked by American planes).” El Boudali has also said that he believes that Hamas’s October 7 attack was a justifiable act of resistance, and that he would actually prefer Hamas rule America in place of its current government (though he clarified later that he “doesn’t mean Hamas is perfect”). When you ask him what his cause is, he answers: “Peace.”
I switched to a different computer-science section.
Israel is 7,500 miles away from Stanford’s campus, where I am a sophomore. But the Hamas invasion and the Israeli counterinvasion have fractured my university, a place typically less focused on geopolitics than on venture-capital funding for the latest dorm-based tech start-up. Few students would call for Biden’s head—I think—but many of the same young people who say they want peace in Gaza don’t seem to realize that they are in fact advocating for violence. Extremism has swept through classrooms and dorms, and it is becoming normal for students to be harassed and intimidated for their faith, heritage, or appearance—they have been called perpetrators of genocide for wearing kippahs, and accused of supporting terrorism for wearing keffiyehs. The extremism and anti-Semitism at Ivy League universities on the East Coast have attracted so much media and congressional attention that two Ivy presidents have lost their jobs. But few people seem to have noticed the culture war that has taken over our California campus.
For four months, two rival groups of protesters, separated by a narrow bike path, faced off on Stanford’s palm-covered grounds. The “Sit-In to Stop Genocide” encampment was erected by students in mid-October, even before Israeli troops had crossed into Gaza, to demand that the university divest from Israel and condemn its behavior. Posters were hung equating Hamas with Ukraine and Nelson Mandela. Across from the sit-in, a rival group of pro-Israel students eventually set up the “Blue and White Tent” to provide, as one activist put it, a “safe space” to “be a proud Jew on campus.” Soon it became the center of its own cluster of tents, with photos of Hamas’s victims sitting opposite the rubble-ridden images of Gaza and a long (and incomplete) list of the names of slain Palestinians displayed by the students at the sit-in.
Some days the dueling encampments would host only a few people each, but on a sunny weekday afternoon, there could be dozens. Most of the time, the groups tolerated each other. But not always. Students on both sides were reportedly spit on and yelled at, and had their belongings destroyed. (The perpetrators in many cases seemed to be adults who weren’t affiliated with Stanford, a security guard told me.) The university put in place round-the-clock security, but when something actually happened, no one quite knew what to do.
Conor Friedersdorf: How October 7 changed America’s free speech culture
Stanford has a policy barring overnight camping, but for months didn’t enforce it, “out of a desire to support the peaceful expression of free speech in the ways that students choose to exercise that expression”—and, the administration told alumni, because the university feared that confronting the students would only make the conflict worse. When the school finally said the tents had to go last month, enormous protests against the university administration, and against Israel, followed.
“We don’t want no two states! We want all of ’48!” students chanted, a slogan advocating that Israel be dismantled and replaced by a single Arab nation. Palestinian flags flew alongside bright “Welcome!” banners left over from new-student orientation. A young woman gave a speech that seemed to capture the sense of urgency and power that so many students here feel. “We are Stanford University!” she shouted. “We control things!”
“W e’ve had protests in the past,” Richard Saller, the university’s interim president, told me in November—about the environment, and apartheid, and Vietnam. But they didn’t pit “students against each other” the way that this conflict has.
I’ve spoken with Saller, a scholar of Roman history, a few times over the past six months in my capacity as a student journalist. We first met in September, a few weeks into his tenure. His predecessor, Marc Tessier-Lavigne, had resigned as president after my reporting for The Stanford Daily exposed misconduct in his academic research. (Tessier-Lavigne had failed to retract papers with faked data over the course of 20 years. In his resignation statement , he denied allegations of fraud and misconduct; a Stanford investigation determined that he had not personally manipulated data or ordered any manipulation but that he had repeatedly “failed to decisively and forthrightly correct mistakes” from his lab.)
In that first conversation, Saller told me that everyone was “eager to move on” from the Tessier-Lavigne scandal. He was cheerful and upbeat. He knew he wasn’t staying in the job long; he hadn’t even bothered to move into the recently vacated presidential manor. In any case, campus, at that time, was serene. Then, a week later, came October 7.
The attack was as clear a litmus test as one could imagine for the Middle East conflict. Hamas insurgents raided homes and a music festival with the goal of slaughtering as many civilians as possible. Some victims were raped and mutilated, several independent investigations found. Hundreds of hostages were taken into Gaza and many have been tortured.
This, of course, was bad. Saying this was bad does not negate or marginalize the abuses and suffering Palestinians have experienced in Gaza and elsewhere. Everyone, of every ideology, should be able to say that this was bad. But much of this campus failed that simple test.
Two days after the deadliest massacre of Jews since the Holocaust, Stanford released milquetoast statements marking the “moment of intense emotion” and declaring “deep concern” over “the crisis in Israel and Palestine.” The official statements did not use the words Hamas or violence .
The absence of a clear institutional response led some teachers to take matters into their own hands. During a mandatory freshman seminar on October 10, a lecturer named Ameer Loggins tossed out his lesson plan to tell students that the actions of the Palestinian “military force” had been justified, that Israelis were colonizers, and that the Holocaust had been overemphasized, according to interviews I conducted with students in the class. Loggins then asked the Jewish students to identify themselves. He instructed one of them to “stand up, face the window, and he kind of kicked away his chair,” a witness told me. Loggins described this as an effort to demonstrate Israel’s treatment of Palestinians. (Loggins did not reply to a request for comment; a spokesperson for Stanford said that there were “different recollections of the details regarding what happened” in the class.)
“We’re only in our third week of college, and we’re afraid to be here,” three students in the class wrote in an email that night to administrators. “This isn’t what Stanford was supposed to be.” The class Loggins taught is called COLLEGE, short for “Civic, Liberal, and Global Education,” and it is billed as an effort to develop “the skills that empower and enable us to live together.”
Loggins was suspended from teaching duties and an investigation was opened; this angered pro-Palestine activists, who organized a petition that garnered more than 1,700 signatures contesting the suspension. A pamphlet from the petitioners argued that Loggins’s behavior had not been out of bounds.
The day after the class, Stanford put out a statement written by Saller and Jenny Martinez, the university provost, more forcefully condemning the Hamas attack. Immediately, this new statement generated backlash.
Pro-Palestine activists complained about it during an event held the same day, the first of several “teach-ins” about the conflict. Students gathered in one of Stanford’s dorms to “bear witness to the struggles of decolonization.” The grievances and pain shared by Palestinian students were real. They told of discrimination and violence, of frightened family members subjected to harsh conditions. But the most raucous reaction from the crowd was in response to a young woman who said, “You ask us, do we condemn Hamas? Fuck you!” She added that she was “so proud of my resistance.”
David Palumbo-Liu, a professor of comparative literature with a focus on postcolonial studies, also spoke at the teach-in, explaining to the crowd that “European settlers” had come to “replace” Palestine’s “native population.”
Palumbo-Liu is known as an intelligent and supportive professor, and is popular among students, who call him by his initials, DPL. I wanted to ask him about his involvement in the teach-in, so we met one day in a café a few hundred feet away from the tents. I asked if he could elaborate on what he’d said at the event about Palestine’s native population. He was happy to expand: This was “one of those discussions that could go on forever. Like, who is actually native? At what point does nativism lapse, right? Well, you haven’t been native for X number of years, so …” In the end, he said, “you have two people who both feel they have a claim to the land,” and “they have to live together. Both sides have to cede something.”
The struggle at Stanford, he told me, “is to find a way in which open discussions can be had that allow people to disagree.” It’s true that Stanford has utterly failed in its efforts to encourage productive dialogue. But I still found it hard to reconcile DPL’s words with his public statements on Israel, which he’d recently said on Facebook should be “the most hated nation in the world.” He also wrote: “When Zionists say they don’t feel ‘safe’ on campus, I’ve come to see that as they no longer feel immune to criticism of Israel.” He continued: “Well as the saying goes, get used to it.”
Z ionists, and indeed Jewish students of all political beliefs, have been given good reason to fear for their safety. They’ve been followed, harassed, and called derogatory racial epithets. At least one was told he was a “dirty Jew.” At least twice, mezuzahs have been ripped from students’ doors, and swastikas have been drawn in dorms. Arab and Muslim students also face alarming threats. The computer-science section leader, El Boudali, a pro-Palestine activist, told me he felt “safe personally,” but knew others who did not: “Some people have reported feeling like they’re followed, especially women who wear the hijab.”
In a remarkably short period of time, aggression and abuse have become commonplace, an accepted part of campus activism. In January, Jewish students organized an event dedicated to ameliorating anti-Semitism. It marked one of Saller’s first public appearances in the new year. Its topic seemed uncontroversial, and I thought it would generate little backlash.
Protests began before the panel discussion even started, with activists lining the stairs leading to the auditorium. During the event they drowned out the panelists, one of whom was Israel’s special envoy for combatting anti-Semitism, by demanding a cease-fire. After participants began cycling out into the dark, things got ugly.
Activists, their faces covered by keffiyehs or medical masks, confronted attendees. “Go back to Brooklyn!” a young woman shouted at Jewish students. One protester, who emerged as the leader of the group, said that she and her compatriots would “take all of your places and ensure Israel falls.” She told attendees to get “off our fucking campus” and launched into conspiracy theories about Jews being involved in “child trafficking.” As a rabbi tried to leave the event, protesters pursued him, chanting, “There is only one solution! Intifada revolution!”
At one point, some members of the group turned on a few Stanford employees, including another rabbi, an imam, and a chaplain, telling them, “We know your names and we know where you work.” The ringleader added: “And we’ll soon find out where you live.” The religious leaders formed a protective barrier in front of the Jewish students. The rabbi and the imam appeared to be crying.

S aller avoided the protest by leaving through another door. Early that morning, his private residence had been vandalized. Protesters frequently tell him he “can’t hide” and shout him down. “We charge you with genocide!” they chant, demanding that Stanford divest from Israel. (When asked whether Stanford actually invested in Israel, a spokesperson replied that, beyond small exposures from passive funds that track indexes such as the S&P 500, the university’s endowment “has no direct holdings in Israeli companies, or direct holdings in defense contractors.”)
When the university finally said the protest tents had to be removed, students responded by accusing Saller of suppressing their right to free speech. This is probably the last charge he expected to face. Saller once served as provost at the University of Chicago, which is known for holding itself to a position of strict institutional neutrality so that its students can freely explore ideas for themselves. Saller has a lifelong belief in First Amendment rights. But that conviction in impartial college governance does not align with Stanford’s behavior in recent years. Despite the fact that many students seemed largely uninterested in the headlines before this year, Stanford’s administrative leadership has often taken positions on political issues and events, such as the Paris climate conference and the murder of George Floyd. After Russia invaded Ukraine, Stanford’s Hoover Tower was lit up in blue and yellow, and the school released a statement in solidarity.
Thomas Chatterton Williams: Let the activists have their loathsome rallies
When we first met, a week before October 7, I asked Saller about this. Did Stanford have a moral duty to denounce the war in Ukraine, for example, or the ethnic cleansing of Uyghur Muslims in China? “On international political issues, no,” he said. “That’s not a responsibility for the university as a whole, as an institution.”
But when Saller tried to apply his convictions on neutrality for the first time as president, dozens of faculty members condemned the response, many pro-Israel alumni were outraged, donors had private discussions about pulling funding, and an Israeli university sent an open letter to Saller and Martinez saying, “Stanford’s administration has failed us.” The initial statement had tried to make clear that the school’s policy was not Israel-specific: It noted that the university would not take a position on the turmoil in Nagorno-Karabakh (where Armenians are undergoing ethnic cleansing) either. But the message didn’t get through.
Saller had to beat an awkward retreat or risk the exact sort of public humiliation that he, as caretaker president, had presumably been hired to avoid. He came up with a compromise that landed somewhere in the middle: an unequivocal condemnation of Hamas’s “intolerable atrocities” paired with a statement making clear that Stanford would commit to institutional neutrality going forward.
“The events in Israel and Gaza this week have affected and engaged large numbers of students on our campus in ways that many other events have not,” the statement read. “This is why we feel compelled to both address the impact of these events on our campus and to explain why our general policy of not issuing statements about news events not directly connected to campus has limited the breadth of our comments thus far, and why you should not expect frequent commentary from us in the future.”
I asked Saller why he had changed tack on Israel and not on Nagorno-Karabakh. “We don’t feel as if we should be making statements on every war crime and atrocity,” he told me. This felt like a statement in and of itself.
In making such decisions, Saller works closely with Martinez, Stanford’s provost. I happened to interview her, too, a few days before October 7, not long after she’d been appointed. When I asked about her hopes for the job, she said that a “priority is ensuring an environment in which free speech and academic freedom are preserved.”
We talked about the so-called Leonard Law—a provision unique to California that requires private universities to be governed by the same First Amendment protections as public ones. This restricts what Stanford can do in terms of penalizing speech, putting it in a stricter bind than Harvard, the University of Pennsylvania, or any of the other elite private institutions that have more latitude to set the standards for their campus (whether or not they have done so).
So I was surprised when, in December, the university announced that abstract calls for genocide “clearly violate Stanford’s Fundamental Standard, the code of conduct for all students at the university.” The statement was a response to the outrage following the congressional testimony of three university presidents—outrage that eventually led to the resignation of two of them, Harvard’s Claudine Gay and Penn’s Liz Magill. Gay and Magill, who had both previously held positions at Stanford, did not commit to punishing calls for the genocide of Jews.
Experts told me that Stanford’s policy is impossible to enforce—and Saller himself acknowledged as much in our March interview.
“Liz Magill is a good friend,” Saller told me, adding, “Having watched what happened at Harvard and Penn, it seemed prudent” to publicly state that Stanford rejected calls for genocide. But saying that those calls violate the code of conduct “is not the same thing as to say that we could actually punish it.”
Stanford’s leaders seem to be trying their best while adapting to the situation in real time. But the muddled messaging has created a policy of neutrality that does not feel neutral at all.
When we met back in November, I tried to get Saller to open up about his experience running an institution in turmoil. What’s it like to know that so many students seem to believe that he—a mild-mannered 71-year-old classicist who swing-dances with his anthropologist wife—is a warmonger? Saller was more candid than I expected—perhaps more candid than any prominent university president has been yet. We sat in the same conference room as we had in September. The weather hadn’t really changed. Yet I felt like I was sitting in front of a different person. He was hunched over and looked exhausted, and his voice broke when he talked about the loss of life in Gaza and Israel and “the fact that we’re caught up in it.” A capable administrator with decades of experience, Saller seemed almost at a loss. “It’s been a kind of roller coaster, to be honest.”
He said he hadn’t anticipated the deluge of the emails “blaming me for lack of moral courage.” Anything the university says seems bound to be wrong: “If I say that our position is that we grieve over the loss of innocent lives, that in itself will draw some hostile reactions.”
“I find that really difficult to navigate,” he said with a sigh.
By March, it seemed that his views had solidified. He said he knew he was “a target,” but he was not going to be pushed into issuing any more statements. The continuing crisis seems to have granted him new insight. “I am certain that whatever I say will not have any material effect on the war in Gaza.” It’s hard to argue with that.
P eople tend to blame the campus wars on two villains: dithering administrators and radical student activists. But colleges have always had dithering administrators and radical student activists. To my mind, it’s the average students who have changed.
Elite universities attract a certain kind of student: the overachieving striver who has won all the right accolades for all the right activities. Is it such a surprise that the kids who are trained in the constant pursuit of perfect scores think they have to look at the world like a series of multiple-choice questions, with clearly right or wrong answers? Or that they think they can gamify a political cause in the same way they ace a standardized test?
Everyone knows that the only reliable way to get into a school like Stanford is to be really good at looking really good. Now that they’re here, students know that one easy way to keep looking good is to side with the majority of protesters, and condemn Israel.
It’s not that there isn’t real anger and anxiety over what is happening in Gaza—there is, and justifiably so. I know that among the protesters are many people who are deeply connected to this issue. But they are not the majority. What really activates the crowds now seems less a principled devotion to Palestine or to pacifism than a desire for collective action, to fit in by embracing the fashionable cause of the moment—as if a centuries-old conflict in which both sides have stolen and killed could ever be a simple matter of right and wrong. In their haste to exhibit moral righteousness, many of the least informed protesters end up being the loudest and most uncompromising.
Today’s students grew up in the Trump era, in which violent rhetoric has become a normal part of political discourse and activism is as easy as reposting an infographic. Many young people have come to feel that being angry is enough to foment change. Furious at the world’s injustices and desperate for a simple way to express that fury, they don’t seem interested in any form of engagement more nuanced than backing a pure protagonist and denouncing an evil enemy. They don’t, always, seem that concerned with the truth.
At the protest last month to prevent the removal of the sit-in, an activist in a pink Women’s March “pussy hat” shouted that no rape was committed by Hamas on October 7. “There hasn’t been proof of these rape accusations,” a student told me in a separate conversation, criticizing the Blue and White Tent for spreading what he considered to be misinformation about sexual violence. (In March, a United Nations report found “reasonable grounds to believe that conflict-related sexual violence,” including “rape and gang rape,” occurred in multiple locations on October 7, as well as “clear and convincing information” on the “rape and sexualized torture” of hostages.) “The level of propaganda” surrounding Hamas, he told me, “is just unbelievable.”
The real story at Stanford is not about the malicious actors who endorse sexual assault and murder as forms of resistance, but about those who passively enable them because they believe their side can do no wrong. You don’t have to understand what you’re arguing for in order to argue for it. You don’t have to be able to name the river or the sea under discussion to chant “From the river to the sea.” This kind of obliviousness explains how one of my friends, a gay activist, can justify Hamas’s actions, even though it would have the two of us—an outspoken queer person and a Jewish reporter—killed in a heartbeat. A similar mentality can exist on the other side: I have heard students insist on the absolute righteousness of Israel yet seem uninterested in learning anything about what life is like in Gaza.
I’m familiar with the pull of achievement culture—after all, I’m a product of the same system. I fell in love with Stanford as a 7-year-old, lying on the floor of an East Coast library and picturing all the cool technology those West Coast geniuses were dreaming up. I cried when I was accepted; I spent the next few months scrolling through the course catalog, giddy with anticipation. I wanted to learn everything.
I learned more than I expected. Within my first week here, someone asked me: “Why are all Jews so rich?” In 2016, when Stanford’s undergraduate senate had debated a resolution against anti-Semitism, one of its members argued that the idea of “Jews controlling the media, economy, government, and other societal institutions” represented “a very valid discussion.” (He apologized, and the resolution passed.) In my dorm last year, a student discussed being Jewish and awoke the next day to swastikas and a portrait of Hitler affixed to his door.
David Frum: There is no right to bully and harass
I grew up secularly, with no strong affiliation to Jewish culture. When I found out as a teenager that some of my ancestors had hidden their identity from their children and that dozens of my relatives had died in the Holocaust (something no living member of my family had known), I felt the barest tremor of identity. After I saw so many people I know cheering after October 7, I felt something stronger stir. I know others have experienced something similar. Even a professor texted me to say that she felt Jewish in a way she never had before.
But my frustration with the conflict on campus has little to do with my own identity. Across the many conversations and hours of formal interviews I conducted for this article, I’ve encountered a persistent anti-intellectual streak. I’ve watched many of my classmates treat death so cavalierly that they can protest as a pregame to a party. Indeed, two parties at Stanford were reported to the university this fall for allegedly making people say “Fuck Israel” or “Free Palestine” to get in the door. A spokesperson for the university said it was “unable to confirm the facts of what occurred,” but that it had “met with students involved in both parties to make clear that Stanford’s nondiscrimination policy applies to parties.” As a friend emailed me not long ago: “A place that was supposed to be a sanctuary from such unreason has become a factory for it.”
Readers may be tempted to discount the conduct displayed at Stanford. After all, the thinking goes, these are privileged kids doing what they always do: embracing faux-radicalism in college before taking jobs in fintech or consulting. These students, some might say, aren’t representative of America.
And yet they are representative of something: of the conduct many of the most accomplished students in my generation have accepted as tolerable, and what that means for the future of our country. I admire activism. We need people willing to protest what they see as wrong and take on entrenched systems of repression. But we also need to read, learn, discuss, accept the existence of nuance, embrace diversity of thought, and hold our own allies to high standards. More than ever, we need universities to teach young people how to do all of this.
F or so long , Stanford’s physical standoff seemed intractable. Then, in early February, a storm swept in, and the natural world dictated its own conclusion.
Heavy rains flooded campus. For hours, the students battled to save their tents. The sit-in activists used sandbags and anything else they could find to hold back the water—at one point, David Palumbo-Liu, the professor, told me he stood in the lashing downpour to anchor one of the sit-in’s tents with his own body. When the storm hit, many of the Jewish activists had been attending a discussion on anti-Semitism. They raced back and struggled to salvage the Blue and White Tent, but it was too late—the wind had ripped it out of the ground.
The next day, the weary Jewish protesters returned to discover that their space had been taken.
A new collection of tents had been set up by El Boudali, the pro-Palestine activist, and a dozen friends. He said they were there to protest Islamophobia and to teach about Islam and jihad, and that they were a separate entity from the Sit-In to Stop Genocide, though I observed students cycling between the tents. Palestinian flags now flew from the bookstore to the quad.
Administrators told me they’d quickly informed El Boudali and his allies that the space had been reserved by the Jewish advocates, and offered to help move them to a different location. But the protesters told me they had no intention of going. (El Boudali later said that they did not take over the entire space, and would have been “happy to exist side by side, but they wanted to kick us off entirely from that lawn.”)
When it was clear that the area where they’d set up their tents would not be ceded back to the pro-Israel group willingly, Stanford changed course and decided to clear everyone out in one fell swoop. On February 8, school officials ordered all students to vacate the plaza overnight. The university was finally going to enforce its rule prohibiting people from sleeping outside on campus and requiring the removal of belongings from the plaza between 8 p.m. and 8 a.m. The order cited the danger posed by the storm as a justification for changing course and, probably hoping to avoid allegations of bias, described the decision as “viewpoint-neutral.”
That didn’t work.
About a week of protests, led by the sit-in organizers, followed. Chants were chanted. More demands for a “river to the sea” solution to the Israel problem were made. A friend boasted to me about her willingness to be arrested. Stanford sent a handful of staff members, who stood near balloons left over from an event earlier in the day. They were there, one of them told me, to “make students feel supported and safe.”
In the end, Saller and Martinez agreed to talk with the leaders of the sit-in about their demands to divest the university and condemn Israel, under the proviso that the activists comply with Stanford’s anti-camping guidelines “regardless of the outcome of discussions.” Eight days after they were first instructed to leave, 120 days after setting up camp, the sit-in protesters slept in their own beds. In defiance of the university’s instructions, they left behind their tents. But sometime in the very early hours of the morning, law-enforcement officers confiscated the structures. The area was cordoned off without any violence and the plaza filled once more with electric skateboards and farmers’ markets.
The conflict continues in its own way. Saller was just shouted down by protesters chanting “No peace on stolen land” at a Family Weekend event, and protesters later displayed an effigy of him covered in blood. Students still feel tense; Saller still seems worried. He told me that the university is planning to change all manner of things—residential-assistant training, new-student orientation, even the acceptance letters that students receive—in hopes of fostering a culture of greater tolerance. But no campus edict or panel discussion can address a problem that is so much bigger than our university.
At one rally last fall, a speaker expressed disillusionment about the power of “peaceful resistance” on college campuses. “What is there left to do but to take up arms?” The crowd cheered as he said Israel must be destroyed. But what would happen to its citizens? I’d prefer to believe that most protesters chanting “Palestine is Arab” and shouting that we must “smash the Zionist settler state” don’t actually think Jews should be killed en masse. But can one truly be so ignorant as to advocate widespread violence in the name of peace?
When the world is rendered in black-and-white—portrayed as a simple fight between colonizer and colonized—the answer is yes. Solutions, by this logic, are absolute: Israel or Palestine, nothing in between. Either you support liberation of the oppressed or you support genocide. Either Stanford is all good or all bad; all in favor of free speech or all authoritarian; all anti-Semitic or all Islamophobic.
At January’s anti-anti-Semitism event, I watched an exchange between a Jewish attendee and a protester from a few feet away. “Are you pro-Palestine?” the protester asked.
“Yes,” the attendee responded, and he went on to describe his disgust with the human-rights abuses Palestinians have faced for years.
“But are you a Zionist?”
“Then we are enemies.”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The opening. Start with an opening that hooks your audience before making the overall topic of your speech clear. Get their attention and prepare them to focus on the words that will follow. For ...
Tell them (Body of your speech - the main ideas plus examples) Tell them what you told them (The ending) TEST before presenting. Read aloud several times to check the flow of material, the suitability of language and the timing. Return to top. A step by step guide for writing a great speech.
A speech is an informative talk given to an audience. Watch this video to learn about the key features of writing a powerful speech. Think carefully. If you were listening to a speech, what ...
Questions 15: 16. Prepare a short speech on the topic „Good Manners‟ with the help of the given outlines to be delivered in your school‟ 's assembly. You are Avadhesh/Gouravi, studying in class VII. Importance of good manners - cost nothing - at home - at school in social life.
Persuasive Speech/Writing. This is a series of lessons guiding a mid-low ability Y7 class through writing to persuade. I have used it to assess for writing AF1, 3. 7 & 8. There is also work for a Speaking and Listening assessment (AF1). The worksheets are not my own, but my class found them useful!
Plan where you want to finish your speech and how you will get there before you start writing . The structure of a speech is often in three parts. For example: 1. an opening that grabs your audience's attention and makes the overall topic of your speech clear - for example, pose a question to the audience where you can predict the answer. 2.
Speech writing is the method of conveying a thought or message to a reader using the correct punctuation and expression. Speech writing isn't much different from any other form of narrative writing. ... 6 - 7 years old . Year 2 . 7 - 8 years old . Year 3 . 8 - 9 years old . Year 4 . 9 - 10 years old . Year 5 . 10 - 11 years old ...
Nine lessons which introduce the concept of identity to year 7 and focus on writing a speech about their own identity. ALL LESSONS FULLY RESOURCED AND PLANNED ON PPT. Two TED Talks are analysed and used. starter slides include retrieval for the previous lesson's content; models included; introduction to persuasive techniques
docx, 26.72 KB. docx, 28.11 KB. pptx, 342.58 KB. doc, 27 KB. Lessons designed to assist GCSE students with writing a speech. The first lesson generates some discussion and recognition of features of a speech, with the second lesson focusing on the students creating their own speech. This was designed for IGCSE but can be used for any sessions.
Explore the features of a successful speech with this Speech Writing Examples Resource Pack. It is perfect for teaching your Year 7-8 students. A handy lesson pack for tackling non-fiction writing that includes an example of a speech and versions for students to annotate themselves, as well as a poster for classroom display. This resource includes annotations that should help them to identify ...
The purpose of a speech is often to inform or persuade an audience. Speeches are usually written to be spoken directly to an audience and can be used to entertain, influencing the listeners that the viewpoint of the speaker is correct. Speeches can also be used to encourage the audience to take action or to change their behaviour in some way ...
1. an INFORMATIVE speech, where you want to inform or tell your audience about a topic, an event, an area of knowledge. For example: Climate Change is happening; the school bake sale; Coral reefs are rainforests of the ocean. 2. an INSTRUCTIONAL speech, where you are explaining how to do something. For example: how to play soccer, how to give ...
Second Part: Describes a possible solution or set of solutions. Third Part: Summarizes how the solutions will solve the problem. 3. Write in the same tone as you speak. One of the most important public speaking tips is to remember that you are writing something that you will be speaking out loud for people to hear.
In this video, we'll walk you through how to write a speech by showing you the different structures you can use! Watch more of our video lessons at http://ww...
Persuasive writing is a form of writing in which the writer attempts to persuade the reader to agree with their point of view. Authors can write to persuade in a number of different ways, from publishing essays, to leaflets and pamphlets or even books. A wide variety of techniques are used in order to influence the reader, including using facts ...
This handy Speech Writing Guide PDF will help you to teach your class how to write their own speeches, using strong techniques and persuasive language. ... 6 - 7 years old . Year 2 . 7 - 8 years old . Year 3 . 8 - 9 years old . Year 4 . 9 - 10 years old ...
Speech writing is the method of conveying a thought or message to a reader using the correct punctuation and expression. Speech writing isn't much different from any other form of narrative writing. ... 7 - 8 years old . Year 2 . 8 - 9 years old . Year 3 . 9 - 10 years old . Year 4 . 10 - 11 years old . Year 5 . 11 - 14 years old ...
We should pay more taxes. We should do away with taxes. Teachers should be tested like students. We should not interfere in the affairs of other countries. Every student should join a club. Homeschooling is better than traditional schooling. People should stay married for life. Smoking in public should be illegal.
This speech template is particularly useful, as it comes with 3 handy tips for your students to consider when preparing and giving their speeches. The template advises students to do the following: Practise reading your speech in front of the mirror or in front of people you are comfortable with. Remember to keep your head up and try to project ...
This teaching resource guides students on how to write a persuasive speech. Your students will write an introduction, three points, and a conclusion. ... 6 - 7 years old . Second Grade . 7 - 8 years old . Third Grade . 8 - 9 years old ...
Explore more than 334 "Persuasive Writing Year 7" resources for teachers, parents and pupils as well as related resources on "Year 7 Persuasive Writing". Help. Check out our interactive series of lesson plans, worksheets, PowerPoints and assessment tools today! All teacher-made, aligned with the Australian Curriculum.
This teaching resource guides students on how to write a persuasive speech. Your students will write an introduction, three points, and a conclusion, while being encouraged to use speech techniques such as metaphors, repetition, rhetorical questions, etc. ... 6 - 7 years old . Year 2 . 7 - 8 years old . Year 3 . 8 - 9 years old . Year 4 . 9 ...
Conor Friedersdorf: How October 7 changed America's free speech culture . ... I'm a product of the same system. I fell in love with Stanford as a 7-year-old, lying on the floor of an East ...