- Resume Writing
- Resume Examples
- Cover Letter
- Remote Work
- Famous Resumes
- Try Kickresume

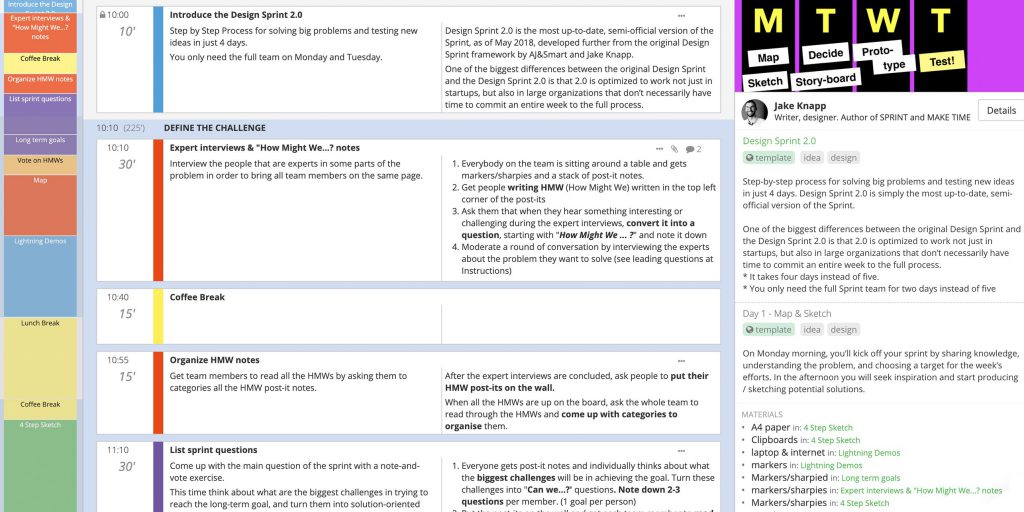
7 Problem Solving Skills That Aren’t Just Buzzwords (+ Resume Example)
- Julia Mlcuchova ,
- Updated April 8, 2024 9 min read
Problem-solving skills are something everybody should include on their resume, yet only a few seem to understand what these skills actually are. If you've always felt that the term "problem-solving skills" is rather vague and wanted to know more, you've come to the right place.
In this article, we're going to explain what problem-solving skills really mean. We'll talk about what makes up good problem-solving skills and give you tips on how to get better at them. You'll also find out how to make your problem-solving abilities look more impressive to those who might want to hire you.
Sounds good, right? Curious to learn more?
In this article we’ll show you:
- What are problem solving skills;
- Why are they important;
- Specific problem solving skills examples;
- How to develop your problem solving skills;
- And, how to showcase them on your resume.
Table of Contents
Click on a section to skip
What are problem solving skills?
Why are problem solving skills important, the best 7 problem solving skills examples, how to develop problem solving skills, problem solving skills resume example, key takeaways: problem solving skills.
First of all, they're more than just a buzzword!
Problem-solving skills are a set of specific abilities that allow you to deal with unexpected situations in the workplace, whether it be job related or team related.
It's a complex process that involves several “sub skills” or “sub steps,” namely:
- Recognizing and identifying the issue at hand.
- Breaking the problem down into smaller parts and analyzing how they relate to one another.
- Creating potential solutions to the problem, evaluating them and picking the best one.
- Applying the chosen solution and assessing its outcome.
- Learning from the whole process to deal with future problems more effectively.
As you can see, it's not just about solving problems that are right in front of us, but also about predicting potential issues and being prepared to deal with them before they arise.
Despite what you may believe, problem-solving skills aren't just for managers .
Think about it this way: Why do employers hire employees in the first place? To solve problems for them!
And, as we all know, problems don't discriminate. In other words, it doesn't matter whether you're just an intern, an entry-level professional, or a seasoned veteran, you'll constantly face some kind of challenges. And the only difference is in how complex they will get.
This is also reflected in the way employers assess suitability of potential job candidates.
In fact, research shows that the ability to deal with unexpected complications is prioritized by an overwhelming 60% of employers across all industries, making it one of the most compelling skills on your resume.
So, regardless of your job description or your career level, you're always expected to find solutions for problems, either independently or as a part of a team.
And that's precisely what makes problem-solving skills so invaluable and universal !
Wondering how good is your resume?
Find out with our AI Resume Checker! Just upload your resume and see what can be improved.
As we've said before, problem-solving isn't really just one single skill.
Instead, your ability to handle workplace issues with composure depends on several different “sub-skills”.
So, which specific skills make an employee desirable even for the most demanding of recruiters?
In no particular order, you should focus on these 7 skills :
- Analytical skills
- Research skills
- Critical thinking
- Decision-making
- Collaboration
- Having a growth mindset
Let's have a look at each of them in greater detail!
#1 Analytical skills
Firstly, to truly understand complex problems, you need to break them down into more manageable parts . Then, you observe them closely and ask yourself: “ Which parts work and which don't,” How do these parts contribute to the problem as a whole,” and "What exactly needs to be fixed?” In other words, you gather data , you study it, and compare it - all to pinpoint the cause of the issue as closely as possible.
#2 Research skills
Another priceless tool is your research skills (sometimes relying on just one source of information isn't enough). Besides, to make a truly informed decision , you'll have to dig a little deeper. Being a good researcher means looking for potential solutions to a problem in a wider context. For example: going through team reports, customer feedback, quarterly sales or current market trends.
#3 Critical thinking
Every employer wants to hire people who can think critically. Yet, the ability to evaluate situations objectively and from different perspectives , is actually pretty hard to come by. But as long as you stay open-minded, inquisitive, and with a healthy dose of skepticism, you'll be able to assess situations based on facts and evidence more successfully. Plus, critical thinking comes in especially handy when you need to examine your own actions and processes.
#4 Creativity
Instead of following the old established processes that don't work anymore, you should feel comfortable thinking outside the box. The thing is, problems have a nasty habit of popping up unexpectedly and rapidly. And sometimes, you have to get creative in order to solve them fast. Especially those that have no precedence. But this requires a blend of intuition, industry knowledge, and quick thinking - a truly rare combination.
#5 Decision-making
The analysis, research, and brainstorming are done. Now, you need to look at the possible solutions, and make the final decision (informed, of course). And not only that, you also have to stand by it ! Because once the train gets moving, there's no room for second guessing. Also, keep in mind that you need to be prepared to take responsibility for all decisions you make. That's no small feat!
#6 Collaboration
Not every problem you encounter can be solved by yourself alone. And this is especially true when it comes to complex projects. So, being able to actively listen to your colleagues, take their ideas into account, and being respectful of their opinions enables you to solve problems together. Because every individual can offer a unique perspective and skill set. Yes, democracy is hard, but at the end of the day, it's teamwork that makes the corporate world go round.
#7 Having a growth mindset
Let's be honest, no one wants their work to be riddled with problems. But facing constant challenges and changes is inevitable. And that can be scary! However, when you're able to see these situations as opportunities to grow instead of issues that hold you back, your problem solving skills reach new heights. And the employers know that too!
Now that we've shown you the value problem-solving skills can add to your resume, let's ask the all-important question: “How can I learn them?”
Well…you can't. At least not in the traditional sense of the word.
Let us explain: Since problem-solving skills fall under the umbrella of soft skills , they can't be taught through formal education, unlike computer skills for example. There's no university course that you can take and graduate as a professional problem solver.
But, just like other interpersonal skills, they can be nurtured and refined over time through practice and experience.
Unfortunately, there's no one-size-fits-all approach, but the following tips can offer you inspiration on how to improve your problem solving skills:
- Cultivate a growth mindset. Remember what we've said before? Your attitude towards obstacles is the first step to unlocking your problem-solving potential.
- Gain further knowledge in your specialized field. Secondly, it's a good idea to delve a little deeper into your chosen profession. Because the more you read on a subject, the easier it becomes to spot certain patterns and relations.
- Start with small steps. Don't attack the big questions straight away — you'll only set yourself up for failure. Instead, start with more straightforward tasks and work your way up to more complex problems.
- Break problems down into more digestible pieces. Complex issues are made up of smaller problems. And those can be further divided into even smaller problems, and so on. Until you're left with only the basics.
- Don't settle for a single solution. Instead, keep on exploring other possible answers.
- Accept failure as a part of the learning process. Finally, don't let your failures discourage you. After all, you're bound to misstep a couple of times before you find your footing. Just keep on practicing.
How to improve problem solving skills with online courses
While it’s true that formal education won’t turn you into a master problem solver, you can still hone your skills with courses and certifications offered by online learning platforms :
- Analytical skills. You can sharpen your analytical skills with Data Analytics Basics for Everyone from IBM provided by edX (Free); or Decision Making and Analytical Thinking: Fortune 500 provided by Udemy ($21,74).
- Creativity. And, to unlock your inner creative mind, you can try Creative Thinking: Techniques and Tools for Success from the Imperial College London provided by Coursera (Free).
- Critical thinking. Try Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking Specialization from Duke University provided by Coursera (Free); or Logical and Critical Thinking offered by The University of Auckland via FutureLearn.
- Decision-making. Or, you can learn how to become more confident when it's time to make a decision with Decision-Making Strategies and Executive Decision-Making both offered by LinkedIn Learning (1 month free trial).
- Communication skills . Lastly, to improve your collaborative skills, check out Communicating for Influence and Impact online at University of Cambridge.
The fact that everybody and their grandmothers put “ problem-solving skills ” on their CVs has turned the phrase into a cliche.
But there's a way to incorporate these skills into your resume without sounding pretentious and empty. Below, we've prepared a mock-up resume that manages to do just that.
FYI, if you like this design, you can use the template to create your very own resume. Just click the red button and fill in your information (or let the AI do it for you).
Problem solving skills on resume example
This resume was written by our experienced resume writers specifically for this profession.
Why this example works?
- Firstly, the job description itself is neatly organized into bullet points .
- Instead of simply listing soft skills in a skills section , you can incorporate them into the description of your work experience entry.
- Also, the language here isn't vague . This resume puts each problem-solving skill into a real-life context by detailing specific situations and obstacles.
- And, to highlight the impact of each skill on your previous job position, we recommend quantifying your results whenever possible.
- Finally, starting each bullet point with an action verb (in bold) makes you look more dynamic and proactive.
To sum it all up, problem-solving skills continue gaining popularity among employers and employees alike. And for a good reason!
Because of them, you can overcome any obstacles that stand in the way of your professional life more efficiently and systematically.
In essence, problem-solving skills refer to the ability to recognize a challenge, identify its root cause, think of possible solutions , and then implement the most effective one.
Believing that these skills are all the same would be a serious misconception. In reality, this term encompasses a variety of different abilities , including:
In short, understanding, developing, and showcasing these skills, can greatly boost your chances at getting noticed by the hiring managers. So, don't hesitate and start working on your problem-solving skills right now!
Julia has recently joined Kickresume as a career writer. From helping people with their English to get admitted to the uni of their dreams to advising them on how to succeed in the job market. It would seem that her career is on a steadfast trajectory. Julia holds a degree in Anglophone studies from Metropolitan University in Prague, where she also resides. Apart from creative writing and languages, she takes a keen interest in literature and theatre.
Related Posts
These 7 student resume samples can help you get a better summer job, qa software tester resume: 6 tips for crafting a cv without bugs and errors (+example), share this article, join our newsletter.
Every month, we’ll send you resume advice, job search tips, career hacks and more in pithy, bite-sized chunks. Sounds good?
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Health & Nursing
Courses and certificates.
- Bachelor's Degrees
- View all Business Bachelor's Degrees
- Business Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Healthcare Administration – B.S.
- Human Resource Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Marketing – B.S. Business Administration
- Accounting – B.S. Business Administration
- Finance – B.S.
- Supply Chain and Operations Management – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree (from the School of Technology)
- Health Information Management – B.S. (from the Leavitt School of Health)
Master's Degrees
- View all Business Master's Degrees
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- MBA Information Technology Management
- MBA Healthcare Management
- Management and Leadership – M.S.
- Accounting – M.S.
- Marketing – M.S.
- Human Resource Management – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- Data Analytics – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Information Technology Management – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed. (from the School of Education)
Certificates
- View all Business Degrees
Bachelor's Preparing For Licensure
- View all Education Bachelor's Degrees
- Elementary Education – B.A.
- Special Education and Elementary Education (Dual Licensure) – B.A.
- Special Education (Mild-to-Moderate) – B.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary)– B.S.
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– B.S.
- View all Education Degrees
Bachelor of Arts in Education Degrees
- Educational Studies – B.A.
Master of Science in Education Degrees
- View all Education Master's Degrees
- Curriculum and Instruction – M.S.
- Educational Leadership – M.S.
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed.
Master's Preparing for Licensure
- Teaching, Elementary Education – M.A.
- Teaching, English Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Science Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Special Education (K-12) – M.A.
Licensure Information
- State Teaching Licensure Information
Master's Degrees for Teachers
- Mathematics Education (K-6) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grade) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- English Language Learning (PreK-12) – M.A.
- Endorsement Preparation Program, English Language Learning (PreK-12)
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– M.A.
- View all Technology Bachelor's Degrees
- Cloud Computing – B.S.
- Computer Science – B.S.
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – B.S.
- Data Analytics – B.S.
- Information Technology – B.S.
- Network Engineering and Security – B.S.
- Software Engineering – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration (from the School of Business)
- View all Technology Master's Degrees
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – M.S.
- Data Analytics – M.S.
- Information Technology Management – M.S.
- MBA Information Technology Management (from the School of Business)
- Full Stack Engineering
- Web Application Deployment and Support
- Front End Web Development
- Back End Web Development
3rd Party Certifications
- IT Certifications Included in WGU Degrees
- View all Technology Degrees
- View all Health & Nursing Bachelor's Degrees
- Nursing (RN-to-BSN online) – B.S.
- Nursing (Prelicensure) – B.S. (Available in select states)
- Health Information Management – B.S.
- Health and Human Services – B.S.
- Psychology – B.S.
- Health Science – B.S.
- Healthcare Administration – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Nursing Post-Master's Certificates
- Nursing Education—Post-Master's Certificate
- Nursing Leadership and Management—Post-Master's Certificate
- Family Nurse Practitioner—Post-Master's Certificate
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner —Post-Master's Certificate
- View all Health & Nursing Degrees
- View all Nursing & Health Master's Degrees
- Nursing – Education (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Education (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration
- MBA Healthcare Management (from the School of Business)
- Business Leadership (with the School of Business)
- Supply Chain (with the School of Business)
- Back End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Front End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Web Application Deployment and Support (with the School of Technology)
- Full Stack Engineering (with the School of Technology)
- Single Courses
- Course Bundles
Apply for Admission
Admission requirements.
- New Students
- WGU Returning Graduates
- WGU Readmission
- Enrollment Checklist
- Accessibility
- Accommodation Request
- School of Education Admission Requirements
- School of Business Admission Requirements
- School of Technology Admission Requirements
- Leavitt School of Health Admission Requirements
Additional Requirements
- Computer Requirements
- No Standardized Testing
- Clinical and Student Teaching Information
Transferring
- FAQs about Transferring
- Transfer to WGU
- Transferrable Certifications
- Request WGU Transcripts
- International Transfer Credit
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships
Other Ways to Pay for School
- Tuition—School of Business
- Tuition—School of Education
- Tuition—School of Technology
- Tuition—Leavitt School of Health
- Your Financial Obligations
- Tuition Comparison
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
FAFSA Support
- Net Price Calculator
- FAFSA Simplification
- See All Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- State Scholarships
- Scholarship FAQs
Payment Options
- Payment Plans
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Current Student Hardship Assistance
- Military Tuition Assistance
WGU Experience
- How You'll Learn
- Scheduling/Assessments
- Accreditation
- Student Support/Faculty
- Military Students
- Part-Time Options
- Virtual Military Education Resource Center
- Student Outcomes
- Return on Investment
- Students and Gradutes
- Career Growth
- Student Resources
- Communities
- Testimonials
- Career Guides
- Skills Guides
- Online Degrees
- All Degrees
- Explore Your Options
Admissions & Transfers
- Admissions Overview
Tuition & Financial Aid
Student Success
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Military and Veterans
- Commencement
- Careers at WGU
- Advancement & Giving
- Partnering with WGU
WESTERN GOVERNORS UNIVERSITY
Developing your problem-solving skills.

Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving skills enhance your ability to identify a difficult or unforeseen situation and determine an appropriate solution.
Using the right problem-solving approach will empower you to offer practical solutions in your professional and personal life anytime you’re faced with a problem.
This page covers different types of problem-solving skills, why they matter, and how to acquire them.
Why Are Problem-Solving Skills Important?
Problem-solving skills are crucial in empowering individuals to handle large or small obstacles throughout various aspects of life. Here are just a few ways that these skills can help you:
- Overcoming challenges: Life will always present you with problems that may hinder your personal or professional progress. Problem-solving skills empower you to identify solutions, giving you control over your future.
- Enhancing decision-making: Problem-solving skills help you assess problems as they come, gauge all the possible solutions, and make the best decision.
- Promoting innovation: Practical problem-solving skills encourage creative thinking, enabling you to develop innovative ideas. You can then evaluate these ideas to identify effective solutions to tackle obstacles.
- Increasing efficiency: Problem-solving skills help individuals and organizations improve efficiency and save time and resources. You are assured of increased productivity if you can identify the root cause of a problem, get the appropriate solution, and implement it promptly.
- Building resilience: Since problems are part of everyone’s day-to-day life, being equipped with problem-solving skills will enable you to respond quickly and rationally to unforeseen situations and not succumb to setbacks.
What Are the Benefits of Having Problem-Solving Skills?
When you frequently apply your problem-solving skills, you become more proficient at analyzing, resolving, and adapting to challenges.
In the workplace, people with strong problem-solving skills apply a combination of creative thinking and analytical skills to help them become more confident when making decisions in the face of challenges.
They’re better equipped to handle the challenges their job brings Problem solvers can observe, judge, and act quickly when faced with adversity.
Problem-solving skills enable you to prioritize, plan, and execute your strategies. You also learn how to think outside the box and identify opportunities in problems.

Examples of Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving skills are effective in helping you identify the source of a problem and how to solve it with a structured approach.
Here are some skills associated with problem-solving:
- Analyzing data: When addressing a number of problems, it’s important to gather relevant for a thorough understanding of the issue and its underlying causes.
- Brainstorming creative solutions: Brainstorming allows you to find the right information from the different causes of the problem and develop innovative solutions.
- Researching to gather relevant information: Having clarity on your research goals and digging into reliable resources to get relevant information.
- Use critical thinking to evaluate options: This involves objective questioning, analyzing, and systematically assessing available options. You should be able to differentiate facts from opinions.
- Implementing logical and systematic approaches: Exploring the key components of each option to understand their practicality and relevance to the problem. Use predefined criteria to evaluate the options and then conduct a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) analysis to determine their viability.
- Collaborating with others to find solutions: Team members gather to offer their input, giving potential solutions and collectively analyzing them to solve the problem.
- Creative thinking: This may include generating new ideas to solve problems. It involves brainstorming, mind mapping, lateral thinking, and analogical reasoning.
- Decision-making: This is the capability to evaluate options, weigh pros and cons, and make informed decisions based on available information.
- Problem identification: The ability to recognize and define problems accurately and clearly.
- Problem structuring: The skill involves taking complicated or vague problems and dissecting them into smaller subproblems that are easier to understand and solve.
How Can I Use Problem-Solving Skills?
Problem-solving skills will have a lasting impact on your life. In your personal and professional life, you will encounter many challenges requiring you to use problem-solving skills.
Here are some instances where you’ll use problem-solving skills:
Career Success
Problem-solving skills will help you tackle challenges at any workplace, make informed decisions, and help the organizations you work with to succeed., personal growth, these skills equip you to overcome everyday life obstacles, like managing personal finances, resolving conflicts in relationships, and more..
Innovation and Entrepreneurship
By solving problems, you can generate creative ideas, develop innovative solutions, and even solve societal problems.
Decision-Making
Making big and small decisions by gathering alternatives, evaluating outcomes, and deciding on the best course of action.
How Can I Learn Problem-Solving Skills?
At wgu, we offer several programs and courses that focus on teaching and enhancing problem-solving skills. , here are ways you can learn problem-solving skills at wgu., school of business.
You’ll learn how to apply problem-solving skills in the world of entrepreneurship and business. For example, our Bachelor of Science in Business Administration–Human Resource Management, offers problem-solving skills as a key component.
With business degree programs, you will learn to:
- Generate a solution to a problem.
- Conduct research to find solutions to a problem.
- Articulate findings and resolutions to a problem.
- Apply contextual reasoning to understand problems.
- Analyze data for the nature and extent of a problem.
School of Technology
You’ll learn how to apply problem-solving skills within the ever-evolving world of IT. We have different bachelor of science degrees in Cloud Computing, such as Muilticloud Track, Amazon Web Services Track, and BS in Cloud Computing - Azure Track.
With IT-related degree programs, you will learn to:
- Select appropriate problem-solving techniques.
- Resolve a challenge using a problem-solving process.
- Recommend multiple solutions for a variety of problems.
- Implement approaches to address complex problems.
- Identify problems using various common frameworks.
School of Education
You’ll learn how problem-solving skills are crucial in the education sector. For example, our Master of Science in Educational Leadership covers problem-solving in the School of Education courses.
With education degree programs, you will learn to:
- Implement problem-solving skills for issue resolution.
- Solve complex problems.
- Identify the cause of a problem.
- Solve problems in the manner most appropriate for each problem.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the steps involved in the problem-solving process?
The problem-solving process involves the following steps:
- Problem identification: Clearly state the problem, what makes you view it as a problem, and how you discovered it.
- Problem analysis: Gather data to help you fully understand the problem and its root causes.
- Generating potential solutions: Look for all the possible ideas from different angles to solve the problem.
- Evaluating alternatives: Scrutinize the available options to identify the best idea.
- Implementing the chosen solution: Follow through on the necessary steps to resolve the problem.
- Reviewing the results: Gather feedback to test the results against your expectations.
How can I improve my critical thinking skills to enhance my problem-solving?
You can improve your critical thinking skills through the following:
- Logical reasoning: Embrace creative hobbies, learn new skills, and socialize with others.
- Evaluating evidence: Determine the relevance and quality of the evidence available to challenge or support claims.
- Considering multiple perspectives: Being open to learning from your peers and adjusting your views accordingly.
What are some effective techniques for generating creative solutions to problems?
Creative problem solving (CPS) is about innovatively solving problems. The techniques below will aid you in the CPS process:
- Brainstorming: Gather relevant parties and spontaneously contribute ideas to offer the solution.
- Mind mapping: Capture and organize any form of information and ideas in a structured way to enhance your logical and creative thinking.
- Analogical reasoning: Use analogies to simplify complex scenarios to makes them easy to comprehend.
How can problem-solving skills be applied in everyday life?
Picture this: your car breaks down while running errands. It’s important to identify the problem with your car and analyze the symptoms and potential root causes of the breakdown, such as mechanical issues or battery failure. You decide that a faulty batter is the issue so you start to identify potential solutions.
The solutions may include calling for roadside assistance, finding a mechanic nearby, or seeking help from friends or family. You then evaluate the potential solutions by weighing in factors such as cost, time, and convenience. The best solution you find may be to call a nearby friend to help you jump-start the car and get back on the road to complete your errands.
This is an everyday occurrence in which problem-solving skills are applicable. Other situations may vary with the degree of difficulty, urgency, and solutions required.
Are specific problem-solving skills valuable in a team or collaborative setting?
Yes. With effective communication, effective conflict resolution strategies, active listening, and consensus building, team members can build healthy working relationships and succeed in their daily decision-making processes.
Find Your Degree
Ready to take the next step in developing your problem-solving skills? Take our degree quiz to find the perfect program for you! With our flexible online learning options and personalized support, you can achieve your educational and career goals on your own terms.
The University
For students.
- Student Portal
- Alumni Services
Most Visited Links
- Business Programs
- Student Experience
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Student Communities
How to improve your problem solving skills and build effective problem solving strategies

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
Effective problem solving is all about using the right process and following a plan tailored to the issue at hand. Recognizing your team or organization has an issue isn’t enough to come up with effective problem solving strategies.
To truly understand a problem and develop appropriate solutions, you will want to follow a solid process, follow the necessary problem solving steps, and bring all of your problem solving skills to the table.
We’ll first guide you through the seven step problem solving process you and your team can use to effectively solve complex business challenges. We’ll also look at what problem solving strategies you can employ with your team when looking for a way to approach the process. We’ll then discuss the problem solving skills you need to be more effective at solving problems, complete with an activity from the SessionLab library you can use to develop that skill in your team.
Let’s get to it!
What is a problem solving process?
- What are the problem solving steps I need to follow?
Problem solving strategies
What skills do i need to be an effective problem solver, how can i improve my problem solving skills.
Solving problems is like baking a cake. You can go straight into the kitchen without a recipe or the right ingredients and do your best, but the end result is unlikely to be very tasty!
Using a process to bake a cake allows you to use the best ingredients without waste, collect the right tools, account for allergies, decide whether it is a birthday or wedding cake, and then bake efficiently and on time. The result is a better cake that is fit for purpose, tastes better and has created less mess in the kitchen. Also, it should have chocolate sprinkles. Having a step by step process to solve organizational problems allows you to go through each stage methodically and ensure you are trying to solve the right problems and select the most appropriate, effective solutions.
What are the problem solving steps I need to follow?
All problem solving processes go through a number of steps in order to move from identifying a problem to resolving it.
Depending on your problem solving model and who you ask, there can be anything between four and nine problem solving steps you should follow in order to find the right solution. Whatever framework you and your group use, there are some key items that should be addressed in order to have an effective process.
We’ve looked at problem solving processes from sources such as the American Society for Quality and their four step approach , and Mediate ‘s six step process. By reflecting on those and our own problem solving processes, we’ve come up with a sequence of seven problem solving steps we feel best covers everything you need in order to effectively solve problems.
1. Problem identification
The first stage of any problem solving process is to identify the problem or problems you might want to solve. Effective problem solving strategies always begin by allowing a group scope to articulate what they believe the problem to be and then coming to some consensus over which problem they approach first. Problem solving activities used at this stage often have a focus on creating frank, open discussion so that potential problems can be brought to the surface.
2. Problem analysis
Though this step is not a million miles from problem identification, problem analysis deserves to be considered separately. It can often be an overlooked part of the process and is instrumental when it comes to developing effective solutions.
The process of problem analysis means ensuring that the problem you are seeking to solve is the right problem . As part of this stage, you may look deeper and try to find the root cause of a specific problem at a team or organizational level.
Remember that problem solving strategies should not only be focused on putting out fires in the short term but developing long term solutions that deal with the root cause of organizational challenges.
Whatever your approach, analyzing a problem is crucial in being able to select an appropriate solution and the problem solving skills deployed in this stage are beneficial for the rest of the process and ensuring the solutions you create are fit for purpose.
3. Solution generation
Once your group has nailed down the particulars of the problem you wish to solve, you want to encourage a free flow of ideas connecting to solving that problem. This can take the form of problem solving games that encourage creative thinking or problem solving activities designed to produce working prototypes of possible solutions.
The key to ensuring the success of this stage of the problem solving process is to encourage quick, creative thinking and create an open space where all ideas are considered. The best solutions can come from unlikely places and by using problem solving techniques that celebrate invention, you might come up with solution gold.
4. Solution development
No solution is likely to be perfect right out of the gate. It’s important to discuss and develop the solutions your group has come up with over the course of following the previous problem solving steps in order to arrive at the best possible solution. Problem solving games used in this stage involve lots of critical thinking, measuring potential effort and impact, and looking at possible solutions analytically.
During this stage, you will often ask your team to iterate and improve upon your frontrunning solutions and develop them further. Remember that problem solving strategies always benefit from a multitude of voices and opinions, and not to let ego get involved when it comes to choosing which solutions to develop and take further.
Finding the best solution is the goal of all problem solving workshops and here is the place to ensure that your solution is well thought out, sufficiently robust and fit for purpose.
5. Decision making
Nearly there! Once your group has reached consensus and selected a solution that applies to the problem at hand you have some decisions to make. You will want to work on allocating ownership of the project, figure out who will do what, how the success of the solution will be measured and decide the next course of action.
The decision making stage is a part of the problem solving process that can get missed or taken as for granted. Fail to properly allocate roles and plan out how a solution will actually be implemented and it less likely to be successful in solving the problem.
Have clear accountabilities, actions, timeframes, and follow-ups. Make these decisions and set clear next-steps in the problem solving workshop so that everyone is aligned and you can move forward effectively as a group.
Ensuring that you plan for the roll-out of a solution is one of the most important problem solving steps. Without adequate planning or oversight, it can prove impossible to measure success or iterate further if the problem was not solved.
6. Solution implementation
This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving strategies have the end goal of implementing a solution and solving a problem in mind.
Remember that in order for any solution to be successful, you need to help your group through all of the previous problem solving steps thoughtfully. Only then can you ensure that you are solving the right problem but also that you have developed the correct solution and can then successfully implement and measure the impact of that solution.
Project management and communication skills are key here – your solution may need to adjust when out in the wild or you might discover new challenges along the way.
7. Solution evaluation
So you and your team developed a great solution to a problem and have a gut feeling its been solved. Work done, right? Wrong. All problem solving strategies benefit from evaluation, consideration, and feedback. You might find that the solution does not work for everyone, might create new problems, or is potentially so successful that you will want to roll it out to larger teams or as part of other initiatives.
None of that is possible without taking the time to evaluate the success of the solution you developed in your problem solving model and adjust if necessary.
Remember that the problem solving process is often iterative and it can be common to not solve complex issues on the first try. Even when this is the case, you and your team will have generated learning that will be important for future problem solving workshops or in other parts of the organization.
It’s worth underlining how important record keeping is throughout the problem solving process. If a solution didn’t work, you need to have the data and records to see why that was the case. If you go back to the drawing board, notes from the previous workshop can help save time. Data and insight is invaluable at every stage of the problem solving process and this one is no different.
Problem solving workshops made easy
Problem solving strategies are methods of approaching and facilitating the process of problem-solving with a set of techniques , actions, and processes. Different strategies are more effective if you are trying to solve broad problems such as achieving higher growth versus more focused problems like, how do we improve our customer onboarding process?
Broadly, the problem solving steps outlined above should be included in any problem solving strategy though choosing where to focus your time and what approaches should be taken is where they begin to differ. You might find that some strategies ask for the problem identification to be done prior to the session or that everything happens in the course of a one day workshop.
The key similarity is that all good problem solving strategies are structured and designed. Four hours of open discussion is never going to be as productive as a four-hour workshop designed to lead a group through a problem solving process.
Good problem solving strategies are tailored to the team, organization and problem you will be attempting to solve. Here are some example problem solving strategies you can learn from or use to get started.
Use a workshop to lead a team through a group process
Often, the first step to solving problems or organizational challenges is bringing a group together effectively. Most teams have the tools, knowledge, and expertise necessary to solve their challenges – they just need some guidance in how to use leverage those skills and a structure and format that allows people to focus their energies.
Facilitated workshops are one of the most effective ways of solving problems of any scale. By designing and planning your workshop carefully, you can tailor the approach and scope to best fit the needs of your team and organization.
Problem solving workshop
- Creating a bespoke, tailored process
- Tackling problems of any size
- Building in-house workshop ability and encouraging their use
Workshops are an effective strategy for solving problems. By using tried and test facilitation techniques and methods, you can design and deliver a workshop that is perfectly suited to the unique variables of your organization. You may only have the capacity for a half-day workshop and so need a problem solving process to match.
By using our session planner tool and importing methods from our library of 700+ facilitation techniques, you can create the right problem solving workshop for your team. It might be that you want to encourage creative thinking or look at things from a new angle to unblock your groups approach to problem solving. By tailoring your workshop design to the purpose, you can help ensure great results.
One of the main benefits of a workshop is the structured approach to problem solving. Not only does this mean that the workshop itself will be successful, but many of the methods and techniques will help your team improve their working processes outside of the workshop.
We believe that workshops are one of the best tools you can use to improve the way your team works together. Start with a problem solving workshop and then see what team building, culture or design workshops can do for your organization!
Run a design sprint
Great for:
- aligning large, multi-discipline teams
- quickly designing and testing solutions
- tackling large, complex organizational challenges and breaking them down into smaller tasks
By using design thinking principles and methods, a design sprint is a great way of identifying, prioritizing and prototyping solutions to long term challenges that can help solve major organizational problems with quick action and measurable results.
Some familiarity with design thinking is useful, though not integral, and this strategy can really help a team align if there is some discussion around which problems should be approached first.
The stage-based structure of the design sprint is also very useful for teams new to design thinking. The inspiration phase, where you look to competitors that have solved your problem, and the rapid prototyping and testing phases are great for introducing new concepts that will benefit a team in all their future work.
It can be common for teams to look inward for solutions and so looking to the market for solutions you can iterate on can be very productive. Instilling an agile prototyping and testing mindset can also be great when helping teams move forwards – generating and testing solutions quickly can help save time in the long run and is also pretty exciting!
Break problems down into smaller issues
Organizational challenges and problems are often complicated and large scale in nature. Sometimes, trying to resolve such an issue in one swoop is simply unachievable or overwhelming. Try breaking down such problems into smaller issues that you can work on step by step. You may not be able to solve the problem of churning customers off the bat, but you can work with your team to identify smaller effort but high impact elements and work on those first.
This problem solving strategy can help a team generate momentum, prioritize and get some easy wins. It’s also a great strategy to employ with teams who are just beginning to learn how to approach the problem solving process. If you want some insight into a way to employ this strategy, we recommend looking at our design sprint template below!
Use guiding frameworks or try new methodologies
Some problems are best solved by introducing a major shift in perspective or by using new methodologies that encourage your team to think differently.
Props and tools such as Methodkit , which uses a card-based toolkit for facilitation, or Lego Serious Play can be great ways to engage your team and find an inclusive, democratic problem solving strategy. Remember that play and creativity are great tools for achieving change and whatever the challenge, engaging your participants can be very effective where other strategies may have failed.
LEGO Serious Play
- Improving core problem solving skills
- Thinking outside of the box
- Encouraging creative solutions
LEGO Serious Play is a problem solving methodology designed to get participants thinking differently by using 3D models and kinesthetic learning styles. By physically building LEGO models based on questions and exercises, participants are encouraged to think outside of the box and create their own responses.
Collaborate LEGO Serious Play exercises are also used to encourage communication and build problem solving skills in a group. By using this problem solving process, you can often help different kinds of learners and personality types contribute and unblock organizational problems with creative thinking.
Problem solving strategies like LEGO Serious Play are super effective at helping a team solve more skills-based problems such as communication between teams or a lack of creative thinking. Some problems are not suited to LEGO Serious Play and require a different problem solving strategy.
Card Decks and Method Kits
- New facilitators or non-facilitators
- Approaching difficult subjects with a simple, creative framework
- Engaging those with varied learning styles
Card decks and method kids are great tools for those new to facilitation or for whom facilitation is not the primary role. Card decks such as the emotional culture deck can be used for complete workshops and in many cases, can be used right out of the box. Methodkit has a variety of kits designed for scenarios ranging from personal development through to personas and global challenges so you can find the right deck for your particular needs.
Having an easy to use framework that encourages creativity or a new approach can take some of the friction or planning difficulties out of the workshop process and energize a team in any setting. Simplicity is the key with these methods. By ensuring everyone on your team can get involved and engage with the process as quickly as possible can really contribute to the success of your problem solving strategy.
Source external advice
Looking to peers, experts and external facilitators can be a great way of approaching the problem solving process. Your team may not have the necessary expertise, insights of experience to tackle some issues, or you might simply benefit from a fresh perspective. Some problems may require bringing together an entire team, and coaching managers or team members individually might be the right approach. Remember that not all problems are best resolved in the same manner.
If you’re a solo entrepreneur, peer groups, coaches and mentors can also be invaluable at not only solving specific business problems, but in providing a support network for resolving future challenges. One great approach is to join a Mastermind Group and link up with like-minded individuals and all grow together. Remember that however you approach the sourcing of external advice, do so thoughtfully, respectfully and honestly. Reciprocate where you can and prepare to be surprised by just how kind and helpful your peers can be!
Mastermind Group
- Solo entrepreneurs or small teams with low capacity
- Peer learning and gaining outside expertise
- Getting multiple external points of view quickly
Problem solving in large organizations with lots of skilled team members is one thing, but how about if you work for yourself or in a very small team without the capacity to get the most from a design sprint or LEGO Serious Play session?
A mastermind group – sometimes known as a peer advisory board – is where a group of people come together to support one another in their own goals, challenges, and businesses. Each participant comes to the group with their own purpose and the other members of the group will help them create solutions, brainstorm ideas, and support one another.
Mastermind groups are very effective in creating an energized, supportive atmosphere that can deliver meaningful results. Learning from peers from outside of your organization or industry can really help unlock new ways of thinking and drive growth. Access to the experience and skills of your peers can be invaluable in helping fill the gaps in your own ability, particularly in young companies.
A mastermind group is a great solution for solo entrepreneurs, small teams, or for organizations that feel that external expertise or fresh perspectives will be beneficial for them. It is worth noting that Mastermind groups are often only as good as the participants and what they can bring to the group. Participants need to be committed, engaged and understand how to work in this context.
Coaching and mentoring
- Focused learning and development
- Filling skills gaps
- Working on a range of challenges over time
Receiving advice from a business coach or building a mentor/mentee relationship can be an effective way of resolving certain challenges. The one-to-one format of most coaching and mentor relationships can really help solve the challenges those individuals are having and benefit the organization as a result.
A great mentor can be invaluable when it comes to spotting potential problems before they arise and coming to understand a mentee very well has a host of other business benefits. You might run an internal mentorship program to help develop your team’s problem solving skills and strategies or as part of a large learning and development program. External coaches can also be an important part of your problem solving strategy, filling skills gaps for your management team or helping with specific business issues.
Now we’ve explored the problem solving process and the steps you will want to go through in order to have an effective session, let’s look at the skills you and your team need to be more effective problem solvers.
Problem solving skills are highly sought after, whatever industry or team you work in. Organizations are keen to employ people who are able to approach problems thoughtfully and find strong, realistic solutions. Whether you are a facilitator , a team leader or a developer, being an effective problem solver is a skill you’ll want to develop.
Problem solving skills form a whole suite of techniques and approaches that an individual uses to not only identify problems but to discuss them productively before then developing appropriate solutions.
Here are some of the most important problem solving skills everyone from executives to junior staff members should learn. We’ve also included an activity or exercise from the SessionLab library that can help you and your team develop that skill.
If you’re running a workshop or training session to try and improve problem solving skills in your team, try using these methods to supercharge your process!
Active listening
Active listening is one of the most important skills anyone who works with people can possess. In short, active listening is a technique used to not only better understand what is being said by an individual, but also to be more aware of the underlying message the speaker is trying to convey. When it comes to problem solving, active listening is integral for understanding the position of every participant and to clarify the challenges, ideas and solutions they bring to the table.
Some active listening skills include:
- Paying complete attention to the speaker.
- Removing distractions.
- Avoid interruption.
- Taking the time to fully understand before preparing a rebuttal.
- Responding respectfully and appropriately.
- Demonstrate attentiveness and positivity with an open posture, making eye contact with the speaker, smiling and nodding if appropriate. Show that you are listening and encourage them to continue.
- Be aware of and respectful of feelings. Judge the situation and respond appropriately. You can disagree without being disrespectful.
- Observe body language.
- Paraphrase what was said in your own words, either mentally or verbally.
- Remain neutral.
- Reflect and take a moment before responding.
- Ask deeper questions based on what is said and clarify points where necessary.
Active Listening #hyperisland #skills #active listening #remote-friendly This activity supports participants to reflect on a question and generate their own solutions using simple principles of active listening and peer coaching. It’s an excellent introduction to active listening but can also be used with groups that are already familiar with it. Participants work in groups of three and take turns being: “the subject”, the listener, and the observer.
Analytical skills
All problem solving models require strong analytical skills, particularly during the beginning of the process and when it comes to analyzing how solutions have performed.
Analytical skills are primarily focused on performing an effective analysis by collecting, studying and parsing data related to a problem or opportunity.
It often involves spotting patterns, being able to see things from different perspectives and using observable facts and data to make suggestions or produce insight.
Analytical skills are also important at every stage of the problem solving process and by having these skills, you can ensure that any ideas or solutions you create or backed up analytically and have been sufficiently thought out.
Nine Whys #innovation #issue analysis #liberating structures With breathtaking simplicity, you can rapidly clarify for individuals and a group what is essentially important in their work. You can quickly reveal when a compelling purpose is missing in a gathering and avoid moving forward without clarity. When a group discovers an unambiguous shared purpose, more freedom and more responsibility are unleashed. You have laid the foundation for spreading and scaling innovations with fidelity.
Collaboration
Trying to solve problems on your own is difficult. Being able to collaborate effectively, with a free exchange of ideas, to delegate and be a productive member of a team is hugely important to all problem solving strategies.
Remember that whatever your role, collaboration is integral, and in a problem solving process, you are all working together to find the best solution for everyone.
Marshmallow challenge with debriefing #teamwork #team #leadership #collaboration In eighteen minutes, teams must build the tallest free-standing structure out of 20 sticks of spaghetti, one yard of tape, one yard of string, and one marshmallow. The marshmallow needs to be on top. The Marshmallow Challenge was developed by Tom Wujec, who has done the activity with hundreds of groups around the world. Visit the Marshmallow Challenge website for more information. This version has an extra debriefing question added with sample questions focusing on roles within the team.

Communication
Being an effective communicator means being empathetic, clear and succinct, asking the right questions, and demonstrating active listening skills throughout any discussion or meeting.
In a problem solving setting, you need to communicate well in order to progress through each stage of the process effectively. As a team leader, it may also fall to you to facilitate communication between parties who may not see eye to eye. Effective communication also means helping others to express themselves and be heard in a group.
Bus Trip #feedback #communication #appreciation #closing #thiagi #team This is one of my favourite feedback games. I use Bus Trip at the end of a training session or a meeting, and I use it all the time. The game creates a massive amount of energy with lots of smiles, laughs, and sometimes even a teardrop or two.
Creative problem solving skills can be some of the best tools in your arsenal. Thinking creatively, being able to generate lots of ideas and come up with out of the box solutions is useful at every step of the process.
The kinds of problems you will likely discuss in a problem solving workshop are often difficult to solve, and by approaching things in a fresh, creative manner, you can often create more innovative solutions.
Having practical creative skills is also a boon when it comes to problem solving. If you can help create quality design sketches and prototypes in record time, it can help bring a team to alignment more quickly or provide a base for further iteration.
The paper clip method #sharing #creativity #warm up #idea generation #brainstorming The power of brainstorming. A training for project leaders, creativity training, and to catalyse getting new solutions.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is one of the fundamental problem solving skills you’ll want to develop when working on developing solutions. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze, rationalize and evaluate while being aware of personal bias, outlying factors and remaining open-minded.
Defining and analyzing problems without deploying critical thinking skills can mean you and your team go down the wrong path. Developing solutions to complex issues requires critical thinking too – ensuring your team considers all possibilities and rationally evaluating them.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Data analysis
Though it shares lots of space with general analytical skills, data analysis skills are something you want to cultivate in their own right in order to be an effective problem solver.
Being good at data analysis doesn’t just mean being able to find insights from data, but also selecting the appropriate data for a given issue, interpreting it effectively and knowing how to model and present that data. Depending on the problem at hand, it might also include a working knowledge of specific data analysis tools and procedures.
Having a solid grasp of data analysis techniques is useful if you’re leading a problem solving workshop but if you’re not an expert, don’t worry. Bring people into the group who has this skill set and help your team be more effective as a result.
Decision making
All problems need a solution and all solutions require that someone make the decision to implement them. Without strong decision making skills, teams can become bogged down in discussion and less effective as a result.
Making decisions is a key part of the problem solving process. It’s important to remember that decision making is not restricted to the leadership team. Every staff member makes decisions every day and developing these skills ensures that your team is able to solve problems at any scale. Remember that making decisions does not mean leaping to the first solution but weighing up the options and coming to an informed, well thought out solution to any given problem that works for the whole team.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
Dependability
Most complex organizational problems require multiple people to be involved in delivering the solution. Ensuring that the team and organization can depend on you to take the necessary actions and communicate where necessary is key to ensuring problems are solved effectively.
Being dependable also means working to deadlines and to brief. It is often a matter of creating trust in a team so that everyone can depend on one another to complete the agreed actions in the agreed time frame so that the team can move forward together. Being undependable can create problems of friction and can limit the effectiveness of your solutions so be sure to bear this in mind throughout a project.
Team Purpose & Culture #team #hyperisland #culture #remote-friendly This is an essential process designed to help teams define their purpose (why they exist) and their culture (how they work together to achieve that purpose). Defining these two things will help any team to be more focused and aligned. With support of tangible examples from other companies, the team members work as individuals and a group to codify the way they work together. The goal is a visual manifestation of both the purpose and culture that can be put up in the team’s work space.
Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is an important skill for any successful team member, whether communicating internally or with clients or users. In the problem solving process, emotional intelligence means being attuned to how people are feeling and thinking, communicating effectively and being self-aware of what you bring to a room.
There are often differences of opinion when working through problem solving processes, and it can be easy to let things become impassioned or combative. Developing your emotional intelligence means being empathetic to your colleagues and managing your own emotions throughout the problem and solution process. Be kind, be thoughtful and put your points across care and attention.
Being emotionally intelligent is a skill for life and by deploying it at work, you can not only work efficiently but empathetically. Check out the emotional culture workshop template for more!
Facilitation
As we’ve clarified in our facilitation skills post, facilitation is the art of leading people through processes towards agreed-upon objectives in a manner that encourages participation, ownership, and creativity by all those involved. While facilitation is a set of interrelated skills in itself, the broad definition of facilitation can be invaluable when it comes to problem solving. Leading a team through a problem solving process is made more effective if you improve and utilize facilitation skills – whether you’re a manager, team leader or external stakeholder.
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Flexibility
Being flexible is a vital skill when it comes to problem solving. This does not mean immediately bowing to pressure or changing your opinion quickly: instead, being flexible is all about seeing things from new perspectives, receiving new information and factoring it into your thought process.
Flexibility is also important when it comes to rolling out solutions. It might be that other organizational projects have greater priority or require the same resources as your chosen solution. Being flexible means understanding needs and challenges across the team and being open to shifting or arranging your own schedule as necessary. Again, this does not mean immediately making way for other projects. It’s about articulating your own needs, understanding the needs of others and being able to come to a meaningful compromise.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Working in any group can lead to unconscious elements of groupthink or situations in which you may not wish to be entirely honest. Disagreeing with the opinions of the executive team or wishing to save the feelings of a coworker can be tricky to navigate, but being honest is absolutely vital when to comes to developing effective solutions and ensuring your voice is heard.
Remember that being honest does not mean being brutally candid. You can deliver your honest feedback and opinions thoughtfully and without creating friction by using other skills such as emotional intelligence.
Explore your Values #hyperisland #skills #values #remote-friendly Your Values is an exercise for participants to explore what their most important values are. It’s done in an intuitive and rapid way to encourage participants to follow their intuitive feeling rather than over-thinking and finding the “correct” values. It is a good exercise to use to initiate reflection and dialogue around personal values.
Initiative
The problem solving process is multi-faceted and requires different approaches at certain points of the process. Taking initiative to bring problems to the attention of the team, collect data or lead the solution creating process is always valuable. You might even roadtest your own small scale solutions or brainstorm before a session. Taking initiative is particularly effective if you have good deal of knowledge in that area or have ownership of a particular project and want to get things kickstarted.
That said, be sure to remember to honor the process and work in service of the team. If you are asked to own one part of the problem solving process and you don’t complete that task because your initiative leads you to work on something else, that’s not an effective method of solving business challenges.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
Impartiality
A particularly useful problem solving skill for product owners or managers is the ability to remain impartial throughout much of the process. In practice, this means treating all points of view and ideas brought forward in a meeting equally and ensuring that your own areas of interest or ownership are not favored over others.
There may be a stage in the process where a decision maker has to weigh the cost and ROI of possible solutions against the company roadmap though even then, ensuring that the decision made is based on merit and not personal opinion.
Empathy map #frame insights #create #design #issue analysis An empathy map is a tool to help a design team to empathize with the people they are designing for. You can make an empathy map for a group of people or for a persona. To be used after doing personas when more insights are needed.
Being a good leader means getting a team aligned, energized and focused around a common goal. In the problem solving process, strong leadership helps ensure that the process is efficient, that any conflicts are resolved and that a team is managed in the direction of success.
It’s common for managers or executives to assume this role in a problem solving workshop, though it’s important that the leader maintains impartiality and does not bulldoze the group in a particular direction. Remember that good leadership means working in service of the purpose and team and ensuring the workshop is a safe space for employees of any level to contribute. Take a look at our leadership games and activities post for more exercises and methods to help improve leadership in your organization.
Leadership Pizza #leadership #team #remote-friendly This leadership development activity offers a self-assessment framework for people to first identify what skills, attributes and attitudes they find important for effective leadership, and then assess their own development and initiate goal setting.
In the context of problem solving, mediation is important in keeping a team engaged, happy and free of conflict. When leading or facilitating a problem solving workshop, you are likely to run into differences of opinion. Depending on the nature of the problem, certain issues may be brought up that are emotive in nature.
Being an effective mediator means helping those people on either side of such a divide are heard, listen to one another and encouraged to find common ground and a resolution. Mediating skills are useful for leaders and managers in many situations and the problem solving process is no different.
Conflict Responses #hyperisland #team #issue resolution A workshop for a team to reflect on past conflicts, and use them to generate guidelines for effective conflict handling. The workshop uses the Thomas-Killman model of conflict responses to frame a reflective discussion. Use it to open up a discussion around conflict with a team.
Planning
Solving organizational problems is much more effective when following a process or problem solving model. Planning skills are vital in order to structure, deliver and follow-through on a problem solving workshop and ensure your solutions are intelligently deployed.
Planning skills include the ability to organize tasks and a team, plan and design the process and take into account any potential challenges. Taking the time to plan carefully can save time and frustration later in the process and is valuable for ensuring a team is positioned for success.
3 Action Steps #hyperisland #action #remote-friendly This is a small-scale strategic planning session that helps groups and individuals to take action toward a desired change. It is often used at the end of a workshop or programme. The group discusses and agrees on a vision, then creates some action steps that will lead them towards that vision. The scope of the challenge is also defined, through discussion of the helpful and harmful factors influencing the group.
Prioritization
As organisations grow, the scale and variation of problems they face multiplies. Your team or is likely to face numerous challenges in different areas and so having the skills to analyze and prioritize becomes very important, particularly for those in leadership roles.
A thorough problem solving process is likely to deliver multiple solutions and you may have several different problems you wish to solve simultaneously. Prioritization is the ability to measure the importance, value, and effectiveness of those possible solutions and choose which to enact and in what order. The process of prioritization is integral in ensuring the biggest challenges are addressed with the most impactful solutions.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
Project management
Some problem solving skills are utilized in a workshop or ideation phases, while others come in useful when it comes to decision making. Overseeing an entire problem solving process and ensuring its success requires strong project management skills.
While project management incorporates many of the other skills listed here, it is important to note the distinction of considering all of the factors of a project and managing them successfully. Being able to negotiate with stakeholders, manage tasks, time and people, consider costs and ROI, and tie everything together is massively helpful when going through the problem solving process.
Record keeping
Working out meaningful solutions to organizational challenges is only one part of the process. Thoughtfully documenting and keeping records of each problem solving step for future consultation is important in ensuring efficiency and meaningful change.
For example, some problems may be lower priority than others but can be revisited in the future. If the team has ideated on solutions and found some are not up to the task, record those so you can rule them out and avoiding repeating work. Keeping records of the process also helps you improve and refine your problem solving model next time around!
Personal Kanban #gamestorming #action #agile #project planning Personal Kanban is a tool for organizing your work to be more efficient and productive. It is based on agile methods and principles.
Research skills
Conducting research to support both the identification of problems and the development of appropriate solutions is important for an effective process. Knowing where to go to collect research, how to conduct research efficiently, and identifying pieces of research are relevant are all things a good researcher can do well.
In larger groups, not everyone has to demonstrate this ability in order for a problem solving workshop to be effective. That said, having people with research skills involved in the process, particularly if they have existing area knowledge, can help ensure the solutions that are developed with data that supports their intention. Remember that being able to deliver the results of research efficiently and in a way the team can easily understand is also important. The best data in the world is only as effective as how it is delivered and interpreted.
Customer experience map #ideation #concepts #research #design #issue analysis #remote-friendly Customer experience mapping is a method of documenting and visualizing the experience a customer has as they use the product or service. It also maps out their responses to their experiences. To be used when there is a solution (even in a conceptual stage) that can be analyzed.
Risk management
Managing risk is an often overlooked part of the problem solving process. Solutions are often developed with the intention of reducing exposure to risk or solving issues that create risk but sometimes, great solutions are more experimental in nature and as such, deploying them needs to be carefully considered.
Managing risk means acknowledging that there may be risks associated with more out of the box solutions or trying new things, but that this must be measured against the possible benefits and other organizational factors.
Be informed, get the right data and stakeholders in the room and you can appropriately factor risk into your decision making process.
Decisions, Decisions… #communication #decision making #thiagi #action #issue analysis When it comes to decision-making, why are some of us more prone to take risks while others are risk-averse? One explanation might be the way the decision and options were presented. This exercise, based on Kahneman and Tversky’s classic study , illustrates how the framing effect influences our judgement and our ability to make decisions . The participants are divided into two groups. Both groups are presented with the same problem and two alternative programs for solving them. The two programs both have the same consequences but are presented differently. The debriefing discussion examines how the framing of the program impacted the participant’s decision.
Team-building
No single person is as good at problem solving as a team. Building an effective team and helping them come together around a common purpose is one of the most important problem solving skills, doubly so for leaders. By bringing a team together and helping them work efficiently, you pave the way for team ownership of a problem and the development of effective solutions.
In a problem solving workshop, it can be tempting to jump right into the deep end, though taking the time to break the ice, energize the team and align them with a game or exercise will pay off over the course of the day.
Remember that you will likely go through the problem solving process multiple times over an organization’s lifespan and building a strong team culture will make future problem solving more effective. It’s also great to work with people you know, trust and have fun with. Working on team building in and out of the problem solving process is a hallmark of successful teams that can work together to solve business problems.
9 Dimensions Team Building Activity #ice breaker #teambuilding #team #remote-friendly 9 Dimensions is a powerful activity designed to build relationships and trust among team members. There are 2 variations of this icebreaker. The first version is for teams who want to get to know each other better. The second version is for teams who want to explore how they are working together as a team.
Time management
The problem solving process is designed to lead a team from identifying a problem through to delivering a solution and evaluating its effectiveness. Without effective time management skills or timeboxing of tasks, it can be easy for a team to get bogged down or be inefficient.
By using a problem solving model and carefully designing your workshop, you can allocate time efficiently and trust that the process will deliver the results you need in a good timeframe.
Time management also comes into play when it comes to rolling out solutions, particularly those that are experimental in nature. Having a clear timeframe for implementing and evaluating solutions is vital for ensuring their success and being able to pivot if necessary.
Improving your skills at problem solving is often a career-long pursuit though there are methods you can use to make the learning process more efficient and to supercharge your problem solving skillset.
Remember that the skills you need to be a great problem solver have a large overlap with those skills you need to be effective in any role. Investing time and effort to develop your active listening or critical thinking skills is valuable in any context. Here are 7 ways to improve your problem solving skills.
Share best practices
Remember that your team is an excellent source of skills, wisdom, and techniques and that you should all take advantage of one another where possible. Best practices that one team has for solving problems, conducting research or making decisions should be shared across the organization. If you have in-house staff that have done active listening training or are data analysis pros, have them lead a training session.
Your team is one of your best resources. Create space and internal processes for the sharing of skills so that you can all grow together.
Ask for help and attend training
Once you’ve figured out you have a skills gap, the next step is to take action to fill that skills gap. That might be by asking your superior for training or coaching, or liaising with team members with that skill set. You might even attend specialized training for certain skills – active listening or critical thinking, for example, are business-critical skills that are regularly offered as part of a training scheme.
Whatever method you choose, remember that taking action of some description is necessary for growth. Whether that means practicing, getting help, attending training or doing some background reading, taking active steps to improve your skills is the way to go.
Learn a process
Problem solving can be complicated, particularly when attempting to solve large problems for the first time. Using a problem solving process helps give structure to your problem solving efforts and focus on creating outcomes, rather than worrying about the format.
Tools such as the seven-step problem solving process above are effective because not only do they feature steps that will help a team solve problems, they also develop skills along the way. Each step asks for people to engage with the process using different skills and in doing so, helps the team learn and grow together. Group processes of varying complexity and purpose can also be found in the SessionLab library of facilitation techniques . Using a tried and tested process and really help ease the learning curve for both those leading such a process, as well as those undergoing the purpose.
Effective teams make decisions about where they should and shouldn’t expend additional effort. By using a problem solving process, you can focus on the things that matter, rather than stumbling towards a solution haphazardly.
Create a feedback loop
Some skills gaps are more obvious than others. It’s possible that your perception of your active listening skills differs from those of your colleagues.
It’s valuable to create a system where team members can provide feedback in an ordered and friendly manner so they can all learn from one another. Only by identifying areas of improvement can you then work to improve them.
Remember that feedback systems require oversight and consideration so that they don’t turn into a place to complain about colleagues. Design the system intelligently so that you encourage the creation of learning opportunities, rather than encouraging people to list their pet peeves.
While practice might not make perfect, it does make the problem solving process easier. If you are having trouble with critical thinking, don’t shy away from doing it. Get involved where you can and stretch those muscles as regularly as possible.
Problem solving skills come more naturally to some than to others and that’s okay. Take opportunities to get involved and see where you can practice your skills in situations outside of a workshop context. Try collaborating in other circumstances at work or conduct data analysis on your own projects. You can often develop those skills you need for problem solving simply by doing them. Get involved!
Use expert exercises and methods
Learn from the best. Our library of 700+ facilitation techniques is full of activities and methods that help develop the skills you need to be an effective problem solver. Check out our templates to see how to approach problem solving and other organizational challenges in a structured and intelligent manner.
There is no single approach to improving problem solving skills, but by using the techniques employed by others you can learn from their example and develop processes that have seen proven results.
Try new ways of thinking and change your mindset
Using tried and tested exercises that you know well can help deliver results, but you do run the risk of missing out on the learning opportunities offered by new approaches. As with the problem solving process, changing your mindset can remove blockages and be used to develop your problem solving skills.
Most teams have members with mixed skill sets and specialties. Mix people from different teams and share skills and different points of view. Teach your customer support team how to use design thinking methods or help your developers with conflict resolution techniques. Try switching perspectives with facilitation techniques like Flip It! or by using new problem solving methodologies or models. Give design thinking, liberating structures or lego serious play a try if you want to try a new approach. You will find that framing problems in new ways and using existing skills in new contexts can be hugely useful for personal development and improving your skillset. It’s also a lot of fun to try new things. Give it a go!
Encountering business challenges and needing to find appropriate solutions is not unique to your organization. Lots of very smart people have developed methods, theories and approaches to help develop problem solving skills and create effective solutions. Learn from them!
Books like The Art of Thinking Clearly , Think Smarter, or Thinking Fast, Thinking Slow are great places to start, though it’s also worth looking at blogs related to organizations facing similar problems to yours, or browsing for success stories. Seeing how Dropbox massively increased growth and working backward can help you see the skills or approach you might be lacking to solve that same problem. Learning from others by reading their stories or approaches can be time-consuming but ultimately rewarding.
A tired, distracted mind is not in the best position to learn new skills. It can be tempted to burn the candle at both ends and develop problem solving skills outside of work. Absolutely use your time effectively and take opportunities for self-improvement, though remember that rest is hugely important and that without letting your brain rest, you cannot be at your most effective.
Creating distance between yourself and the problem you might be facing can also be useful. By letting an idea sit, you can find that a better one presents itself or you can develop it further. Take regular breaks when working and create a space for downtime. Remember that working smarter is preferable to working harder and that self-care is important for any effective learning or improvement process.
Want to design better group processes?
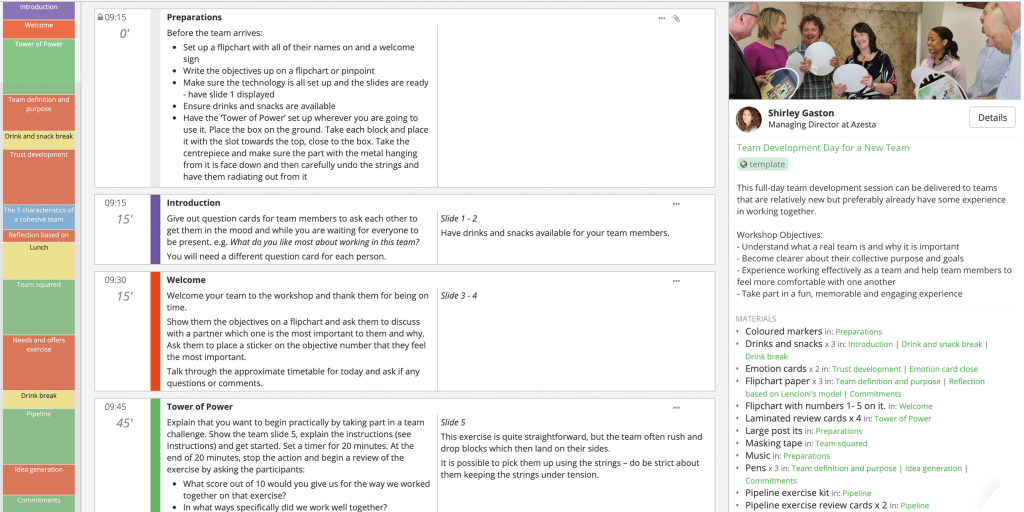
Over to you
Now we’ve explored some of the key problem solving skills and the problem solving steps necessary for an effective process, you’re ready to begin developing more effective solutions and leading problem solving workshops.
Need more inspiration? Check out our post on problem solving activities you can use when guiding a group towards a great solution in your next workshop or meeting. Have questions? Did you have a great problem solving technique you use with your team? Get in touch in the comments below. We’d love to chat!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
Chapter 9: Thinking and Intelligence
Problem solving, learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
PROBLEM-SOLVING STRATEGIES
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them ( [link] ). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error . The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below ( [link] ) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
How long did it take you to solve this sudoku puzzle? (You can see the answer at the end of this section.)
Here is another popular type of puzzle ( [link] ) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
Did you figure it out? (The answer is at the end of this section.) Once you understand how to crack this puzzle, you won’t forget.
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below ( [link] ). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
PITFALLS TO PROBLEM SOLVING
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Link to Learning
Check out this Apollo 13 scene where the group of NASA engineers are given the task of overcoming functional fixedness.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in [link] .
Please visit this site to see a clever music video that a high school teacher made to explain these and other cognitive biases to his AP psychology students.
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in [link] ? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in [link] and [link] ? Here are the answers ( [link] ).
Many different strategies exist for solving problems. Typical strategies include trial and error, applying algorithms, and using heuristics. To solve a large, complicated problem, it often helps to break the problem into smaller steps that can be accomplished individually, leading to an overall solution. Roadblocks to problem solving include a mental set, functional fixedness, and various biases that can cloud decision making skills.
Self Check Questions
Critical thinking questions.
1. What is functional fixedness and how can overcoming it help you solve problems?
2. How does an algorithm save you time and energy when solving a problem?
Personal Application Question
3. Which type of bias do you recognize in your own decision making processes? How has this bias affected how you’ve made decisions in the past and how can you use your awareness of it to improve your decisions making skills in the future?
1. Functional fixedness occurs when you cannot see a use for an object other than the use for which it was intended. For example, if you need something to hold up a tarp in the rain, but only have a pitchfork, you must overcome your expectation that a pitchfork can only be used for garden chores before you realize that you could stick it in the ground and drape the tarp on top of it to hold it up.
2. An algorithm is a proven formula for achieving a desired outcome. It saves time because if you follow it exactly, you will solve the problem without having to figure out how to solve the problem. It is a bit like not reinventing the wheel.
- Psychology. Authored by : OpenStax College. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Psychology . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/content/col11629/latest/.
10 Problem-Solving Soft Skills that Employers Look For
Link Copied
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on LinkedIn
.jpg)
Solving Problems Like a Pro!
In today's competitive job market, technical expertise alone doesn't suffice. Employers are increasingly valuing individuals with a unique set of skills - problem-solving soft skills. This blog dives deep into problem-solving soft skills, highlighting the vital abilities that set professionals apart. From critical thinking to creativity, adaptability to emotional intelligence, we'll dissect the significance of these skills for a prosperous and fulfilling career. Let's get into it!
What are problem-solving skills?
Problem-solving skills are like your all-in-one toolkit for tackling tricky situations. They're the superpowers that let you break down complex problems, see things from different angles, and come up with smart solutions. No matter your job, these skills matter. They're the fuel for innovation, making things run smoother, building stronger teams, and keeping customers happy. Studies and stats confirm it's one of the most-wanted skills by employers. It's all about staying sharp in today's professional world.
Top problem-solving soft skills
Let's look into the top problem-solving as a soft skill ability that is like gold dust for your career. From critical thinking to creativity, we'll explore how honing these skills can open the doors to endless opportunities.
1. Critical Thinking
Think of critical thinking as your superpower for tackling everyday challenges. It's all about breaking down problems, questioning the status quo, and considering different angles. With these thinking and problem-solving soft skills in your toolkit, you can analyse complex situations like a pro, resulting in more effective solutions that truly make a difference during your learning journey and internship experiences.
2. Creativity
Creativity isn't just for artists and writers . When it comes to problem-solving as a soft skill, being creative means thinking outside the box. It's about conjuring up fresh, out-of-the-box ideas and innovative solutions. So, let your imagination run wild! Creative thinkers are known for bringing a breath of fresh air to your workplace, helping your team adapt to changes, grow, and conquer obstacles with flair.
3. Adaptability
We all know the world can throw curveballs. That's where adaptability shines. Having these problem-solving soft skills means you're the one who can pivot and thrive in the face of change and uncertainty. Whether it's a sudden shift in your project or a market twist, you're the cool cucumber who remains productive and keeps the ship sailing smoothly, ensuring a balanced and successful personal and academic lifestyle . Make sure you learn some in-demand skills which will help you in your future.
Don't miss out on an ideal environment for personal growth and skill development. Find your accommodation with us!
Book through amber today!
4. Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is like your secret weapon for understanding and handling emotions – yours and others. It's a game-changer for problem-solving as a soft skill. When tensions run high, or you're in the midst of a tricky group project, these skills help you navigate the emotional side of things, ensuring that your solutions are not just logical but also consider the feelings and concerns of everyone involved.
5. Communication
Strong communicators are the glue that holds it all together. They have the gift of translating complex ideas into simple, understandable terms. In the realm of problem-solving soft skills, they excel at articulating issues and ideas, and they're the bridge between technical and non-technical folks. With them around, problem-solving becomes a breeze.
6. Decision-Making
Think of decision-making as your compass in a sea of choices. It's one of the thinking and problem-solving soft skills that helps you sort through information and make smart choices. Whether you're weighing pros and cons, calculating risks, or simply choosing the best path forward, this skill is your trusty sidekick for streamlining the problem-solving process.
7. Resourcefulness
Resourceful individuals are the ultimate problem-solving wizards in the workplace. They're the masters of making do with what's at hand. When faced with a challenge, they can think on their feet and find innovative solutions even when resources are scarce. When you're looking to get things done creatively and efficiently, these are the go-to people who can turn constraints into opportunities, fostering a culture of creativity and resourcefulness within the team.
8. Patience
Patience is the zen master of the soft skills world. It's all about keeping your cool, even when things get tough. For those long-term issues that need some tender loving care, patient folks not only stick with it but also bring an unwavering dedication to the table. They persistently work towards sustainable solutions, showcasing their tenacity and unwavering commitment to achieving long-term success.
9. Conflict Resolution
The peacemakers among us, skilled conflict resolvers, are your go-to for finding common ground. They're experts at facilitating discussions and negotiations, which ultimately lead to solutions that everyone can agree on. Their role goes beyond just maintaining harmony; they're the workplace's mediators, ensuring that small disagreements don't escalate into all-out wars. In the process, they create an atmosphere of cooperation and foster collaboration, making your professional environment not only more harmonious but also more productive.
10. Persistence
Think of persistence as your 'never give up' attitude, a tenacious spirit that refuses to back down in the face of adversity. It's all about facing challenges head-on, even when the going gets tough. Persistent individuals are unwavering champions who keep chipping away at problems until they find a solution that works. When it comes to tackling long-term issues or overcoming substantial hurdles, they're the ones who consistently show up, put in the hard work, and make things happen.
How to Develop Problem-Solving Skills
- Embrace challenges as opportunities to grow.
- Define the problem clearly to set the stage for solutions.
- Break down complex issues into manageable parts.
- Generate a wide range of potential solutions, no matter how unconventional.
- Evaluate each solution by considering feasibility, impact, and resources.
- Trust your judgment and select the most promising solution.
- Implement your chosen solution, adapt as necessary, and learn from the experience.
- Seek feedback from colleagues or mentors for fresh insights.
In the fast-paced, ever-evolving professional landscape, problem-solving soft skills emerge as the bedrock of success. As this journey through the realm of critical thinking, creativity, adaptability, and more draws to a close, remember that these skills aren't just career boosters; they're life enhancers. To further equip yourself for the challenges ahead, don't hesitate to explore reliable student resources that provide great tools to simplify your student life. These invaluable tools will not only enrich your skill set but also pave the way for a bright and fulfilling future. Are you planning to stay in Germany make sure you are fluent in German, these German learning apps will help you out.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are problem-solving soft skills important in the workplace, how can i showcase problem-solving soft skills on my resume, are problem-solving skills equally important in all industries, can problem-solving skills benefit my personal life as well, can problem-solving soft skills be learned and developed.
Your ideal student home & a flight ticket awaits
Follow us on :

Related Posts

Discover 10 Best Dental Schools In The US In 2024

Top 12 Work From Home Jobs For Students In UK
.webp)
University of Michigan Acceptance Rate And Admissions 2024

Planning to Study Abroad ?

Your ideal student accommodation is a few steps away! Please fill in your details below so we can find you a new home!
We have got your response
.jpg)
amber © 2024. All rights reserved.
4.8/5 on Trustpilot
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by students
Rated as "Excellent" • 4800+ Reviews by Students
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Med Educ Online
The Dreyfus model of clinical problem-solving skills acquisition: a critical perspective
Adolfo peña.
1 VA National Quality Scholars (VAQS) Fellowship Program
2 Birmingham VA Medical Center
3 University of Alabama at Birmingham
4 Center for Surgical, Medical Acute Care Research and Transitions (C-SMART)
The Dreyfus model describes how individuals progress through various levels in their acquisition of skills and subsumes ideas with regard to how individuals learn. Such a model is being accepted almost without debate from physicians to explain the ‘acquisition’ of clinical skills.
This paper reviews such a model, discusses several controversial points, clarifies what kind of knowledge the model is about, and examines its coherence in terms of problem-solving skills. Dreyfus' main idea that intuition is a major aspect of expertise is also discussed in some detail. Relevant scientific evidence from cognitive science, psychology, and neuroscience is reviewed to accomplish these aims.
Conclusions
Although the Dreyfus model may partially explain the ‘acquisition’ of some skills, it is debatable if it can explain the acquisition of clinical skills. The complex nature of clinical problem-solving skills and the rich interplay between the implicit and explicit forms of knowledge must be taken into consideration when we want to explain ‘acquisition’ of clinical skills. The idea that experts work from intuition, not from reason, should be evaluated carefully.
Models are conceptual constructs that aspire to represent real things or processes that to a large extent are hidden for the senses and to the ordinary experience. Models have a role to describe, represent, explain, and ‘translate’ the world. Some good examples are the Feynman diagrams of electrodynamic processes, the fluid mosaic membrane, and the DNA double helix. Although models are partial and just approximations to the truth, they are not fictional or conventional at all. They try to represent their referents in a truthful and objective way with the hope to constantly improve or replace them with better approximations or more precise explanations ( 1 ).
Dreyfus and Dreyfus ( 2 , 3 ) have offered a model of professional expertise that plots an individual's progression through a series of five levels: novice, advanced beginner, competent, proficient, and expert. In the novice stage a person follows rules that are context-free and feels no responsibility for anything other than following the rules. Competence develops after having considerable experience. Proficiency is shown in individuals who use intuition in decision making and develop their own rules to formulate plans. Expertise is characterized by a fluid performance that happens unconsciously, automatically, and no longer depends on explicit knowledge. Thus, the progression is envisaged as a gradual transition from a rigid adherence to taught rules and procedures through to a largely intuitive mode of operation that relies heavily on deep, implicit knowledge but accepts that sometimes at expert level analytical approaches are still likely to be used when an intuitive approach fails initially.
This model, a product of philosophical deliberation and phenomenological research, was initially adapted by Benner and other nursing educators to explain the development of nursing skills ( 4 ). However, this was not without debate, which still remains. Hargreaves and Lane criticized Benner's model, a linear model of skill acquisition that cannot sufficiently explain the everyday experiences of learning ( 5 ). Thompson ( 6 ), Purkis ( 7 ), and Rudge ( 8 ) criticized Benner's and Dreyfus' models because of their apparent absence of social structure or social knowledge. English pointed out that Benner's and Dreyfus' models fail to identify expert nurses because they neglect to specify objective qualifications for expertise ( 9 ). For Effken, the terms ‘expertise’ and ‘intuition’ do not have operational definitions: ‘structured measurement has been elusive because of the complexity of the domain and the degree to which skill is embedded in a particular situation’ ( 10 ). Gobet and Chassy, in contraposition to Dreyfus' and Benner's phenomenological philosophy, suggest an alternative conceptual framework to understand the role of intuition in expertise ( 11 ).
Assuming that nurses’ and physicians’ skills are of the same nature, physician educators have ‘translated’ and adjusted such a model to explain clinical skills not only in terms of simple routine tasks but also in terms of the most symbolic skills, i.e., clinical problem-solving skills ( 12 ). Many authors express their support for this. For Daaleman, Dreyfus provides a model of knowledge and skill acquisition that is relevant to the training of physicians in practical wisdom ( 13 ). Batalden, Holmboe and Hawkins recommend assuming Dreyfus' ideas as a framework to understand medical competencies [ 14 , 15 ]. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) recommends this model for curriculum-planning for residency training programs ( 16 ).
Contrary to the debate raised in academic nursing fields, judging by medical publications and recommendations from academic organizations, the current form of Dreyfus' model ( 2 , 3 , 17 – 19 ) is being accepted almost without explicit criticism from physicians. Thus, although there may be some debate among clinicians and educators, such a debate is not evident in published papers. The Dreyfus model is reaching out to the educative arena and thus plays an important role in modeling how physicians acquire clinical skills. This may generate important consequences for our education. As was mentioned in this introduction, even models that are born from science are not complete explanations or perfect approximations to the truth, and they might be erroneous. Different from those, the Dreyfus model comes from philosophical fields; this fact makes even more urgent a critical analysis and debate. This paper tries to stimulate both.
A brief inventory of the Dreyfus model
A very important requirement for any model is its referent, i.e., the object or process referred to by the model or that which the latter is about ( 20 ). The Dreyfus model postulates that when individuals acquire a skill through external instruction, they normally pass through several stages. It is undeniable that such a process implies the acquiring of some knowledge. This psychological result of perception, learning, and reasoning constitutes the Dreyfus model's primary referent. Because the acquisition of knowledge does not happen in a vacuum but in a very complex organ (the brain), it is desirable that any hypothetical construct that attempts to explain learning is defined not only psychologically but also neurologically ( 21 ). Unfortunately, neurological terms appear in the model only when Dreyfus gestures toward artificial neural networks to demonstrate that phenomenology can reveal objective structures of bodily praxis ( 18 , 22 ). Therefore, we may say that the brain is a secondary or spurious referent of such a model.
Postulates and propositions
The Dreyfus model has been proposed in prose style. Because it is easier to analyze a model when its content is structured in clear and unambiguous sentences (propositions) capable of being evaluated as true or false to some degree, two lists have been created and are presented in Boxes 1 and 2 . They were prepared after a careful review of Dreyfus' original works and summarize the model ( 2 , 3 , 17 – 19 , 23 – 25 ). To contrast Dreyfus' ideas, the author proposes some statements (listed to the right of the boxes) that were produced after reviewing various psychological, neuroscientific, and philosophical works ( 1 , 20 , 21 , 28 – 30 , 34 – 66 , 68 – 79 ).
Dreyfus's postulates versus alternative propositions
Dreyfus' postulates versus alternative propositions, history and scientific evidence.
Some historical facts may be also interesting. The original model was not published immediately for public scrutiny. Four prior reports exist from the US Air Force ( 2 , 23 – 25 ), where some observations carried out on the instruction of jet pilots are described by Dreyfus. In those reports, few original scientific studies were cited and standardized protocols were not utilized. The only recent change in the model is the addition of two stages (‘master’ and ‘practical wisdom’) ( 17 ) to the five originally proposed ( 2 ).
All models have philosophical roots; Dreyfus' ideas are based on phenomenology ( 18 ), a philosophical doctrine proposed by Edmund Husserl based on the study of personal experience in which considerations of objective reality are not taken into account. This view opposes scientific realism; for Husserl, the world of things ‘is only a presumptive reality,’ whereas the subject is the absolute reality ( 26 ). The world is also ‘an infinite idea, a complete synthesis of possible experiences’ ( 27 ). Thus, the reality is subject-dependent because a thing is a complex of sensations. Moreover, according to Husserl, introspection through ordinary experience rather than through experiment, analysis, and modeling can yield deep knowledge of the world ( 28 ). For Martin Heidegger, another key proponent of phenomenology, ‘the word is the abode of being’ ( 29 , p. 280), and ‘things become and are only in the word, in language’ ( 30 ). In other words, reality is constituted in and through discourse. We smell this philosophy in Dreyfus' original work on the model of skill acquisition ( 2 ) and we discover his explicit adherence to phenomenology, especially to Heidegger's existential phenomenology, in one of the most authoritative texts on these matters: ‘Being in the world: a commentary on Heidegger's “being and time”’ ( 31 ).
Adaptation to clinical medicine
For the medical field, the model has been adapted with minor changes. For example, Dreyfus' main postulates are that the ‘immediate intuitive situational response is the characteristic of expertise’ ( 17 , p. 42), and that most expert performance is ongoing and non-reflective: ‘fluid performance happens unconsciously, automatically, naturally’ ( 3 , p. 32), and ‘the expert driver generally knows how to perform the act without evaluating and comparing alternatives’ ( 3 , p. 33). Medical educators have proposed a hybrid model where masters are highly intuitive as well as reflective: ‘the master is the practitioner who self-assesses and self-regulates and reflects in, on and for action’ ( 12 ). This current statement contradicts the original model. Frequently, it is also stated by physicians that the model postulates that experts use intuition where empirical and propositional knowledge does not yet exist. Actually, the original model was proposed the other way around: experts work intuitively on every problem and only use other types of knowledge in a few cases when intuition fails.
The following paragraphs will discuss the most controversial aspects the Dreyfus model proposes. The main body of this paper will go further about the referents and basically will clarify what kind of knowledge the model is about and will review its coherence with problem-solving skills; some relevant scientific evidence from cognitive science, psychology, and neuroscience will also be reviewed. The central idea of intuition as a major definition of expertise will be discussed in some detail. This is also a good time to advise that this manuscript does not have any intention to be ‘ecumenical.’ Readers interested in favorable opinions and sympathetic papers of the Dreyfus model are urged to read several of the publications included in the references ( 4 , 12 – 15 , 32 , 33 ).
Types of knowledge and the Dreyfus model
Because one of the most important referents of the model is knowledge, it would be of some benefit to review that concept. There are many kinds of knowledge and several ways of grouping these kinds into large categories ( 34 ). A division of knowledge that is relevant when analyzing Dreyfus model is into know-that and know-how. Traditionally, explicit knowledge or ‘knowing that’ has been understood as expressible in some languages; it can be attained easily from any codified information ( 35 ). By contrast, ‘knowing how,’ tacit or implicit knowledge, as it was proposed by philosopher Michael Polanyi, is not expressible in some languages. It is considered intuitive – acquired through practical experience – and as such, is subjective and contextual, and cannot be readily made explicit or formalized ( 36 ). Polanyi also suggested the supremacy of such implicit knowledge: ‘While tacit knowledge can be possessed by itself, explicit knowledge must rely on being tacitly understood and applied. Hence all knowledge is either tacit or rooted in tacit knowledge’ ( 37 ).
In psychology, the knowledge gained in implicit learning is defined by using several criteria ( 38 ). It is not fully accessible to consciousness. The learner cannot provide a full verbal account of what he has learned. Implicit knowledge does not involve processes of conscious hypothesis testing. In addition, implicit knowledge is preserved in cases of amnesia; thus, implicit learning relies on neuronal mechanisms other than the hippocampal memory system ( 39 ). Implicit knowledge is stored as abstract – and possibly instantiated – representations rather than aggregate or verbatim representations. This knowledge may also be inflexible because of its non-hippocampal base ( 40 ).
Knowledge that represents its content, attitude, and its holder explicitly is on the higher-order thought theory, conscious, and is considered explicit. Explicit mental representation is required to refer in verbal communication and thus a link emerges between explicitness and consciousness ( 41 ). The explicit processing of knowledge includes perceptual, cognitive, and motor processes, such as stimulus selection and search, attention focusing and maintenance, memorization, computation, decision making, response selection, and execution ( 42 ).
Recently, neuroscientists have proposed the Competition between Verbal and Implicit Systems (COVIS) model to explain the brain functional specialization and localization for the processing of these two types of knowledge ( 43 ). The verbal (explicit) system is mediated by frontal brain areas, such as the anterior cingulate, prefrontal cortex, and the head of the caudate nucleus. The implicit system is mainly mediated by the tail of the caudate nucleus and a dopamine-mediated reward signal ( 44 , 45 ). The role of the basal ganglia in implicit learning and knowledge has been investigated through the study of people with Huntington's or Parkinson's disease ( 46 , 47 ). Besides the COVIS model, there is evidence that the frontal lobes appear to be involved in the evaluation of implicit knowledge in making conceptual fluency judgments ( 38 ). Hippocampus-dependent memory systems subserve explicit memory formation ( 40 ).
There is considerable evidence in favor of this ‘specialization’ and division of knowledge ( 38 , 41 , 48 , 49 ). However, there is not any evidence that sophisticated skills are performed either without a rich connection of both neuronal subsystems or without a rich interplay of both domains of knowledge. Galanter and Smith observed that even in subjects who are not engaging in conscious hypothesis testing, they can still notice that there is a pattern and can develop explicit knowledge of it ( 50 ). Individual learners, during motor skill practice, can discover the correct solution to a movement problem using either their implicit, explicit or a combination of both domains of knowledge; each approach leads to motor skill learning ( 51 ). The serial reaction time task, a classical example of ‘implicit’ knowledge acquired during sequence learning, is available for intentional control and is, in this sense, explicit ( 52 ). Automatic and intentional forms of processing can be brought under intentional control ( 53 ). Besides, explicit knowledge is an important and active variable that influences problem-solving processes, especially problem representation. Individuals who have accumulated considerable explicit knowledge in a domain represent problems more efficiently than individuals without extensive knowledge bases ( 54 ). In the face of strongly held explicit beliefs, knowledge gained through implicit learning is disregarded ( 55 ). Hence, in normal humans, it is difficult to develop a pure task that allows only implicit or explicit knowledge to contribute to performance. In particular, sophisticated skills are fueled by explicit knowledge.
Although the Dreyfus brothers recognize this division of knowledge, they believe that skills are exclusive instances of know-how or implicit knowledge: ‘you can ride a bicycle because you possess something called “know-how,” which you acquired from practice and sometimes painful experience’ ( 3 , p. 16). The Dreyfus brothers assert that when we perform a skill, we basically execute implicit knowledge without a connection to explicit knowledge. They believe that skills are automatic dispositions that cannot be readily made explicit ( 2 , 3 ). They go further and propose that the net effect of learning is intuition and define it in terms of implicit knowledge: ‘when we speak of intuition or know-how, we are referring to the understanding that effortlessly occurs upon seeing similarities with previous experiences. We shall use intuition and know-how as synonyms’ ( 3 , p. 28). In summary, Dreyfus and Dreyfus define skills at expert level almost exclusively in terms of implicit knowledge.
A critical point is to accept whether or not clinical problem-solving skills are implicit in nature or if they are predominantly dependent upon implicit knowledge. As we reviewed above, it is difficult to develop a task exclusively in terms of implicit knowledge. Even more importantly, clinical problem-solving skills are also instances of explicit knowledge. The clearest cases of explicit knowledge of a fact are representations of one's own attitude of knowing that fact. Knowledge capable of such fully explicit representation provides the necessary and sufficient conditions for conscious knowledge ( 41 ). This is the case when a physician evaluates a patient. Although he is not aware of all of the cognitive steps needed to make a diagnosis, he needs to be conscious of at least of the following events: characterization of a patient's symptom, valuation of a patient's sign, and solicitation of a diagnostic test. Furthermore, physicians explicitly provide a representation (diagnosis) and express the degree of accuracy or inaccuracy and can judge their representations to be true, false or undecided. Hence, it is reasonable to accept that making a diagnosis also subsumes an explicit dimension of knowledge. Therefore, a model that does not respect the complex and rich interaction between both domains of knowledge will have difficulty explaining skills that are not just routines but instead very complex tasks, i.e., finding solutions to problems.
Inverse problems and clinical problem-solving skills
We will start the discussion of this section by pointing out that there is not only one type of problem, but several types. Most problems can be classified into direct, well-defined problems and inverse, ill-defined problems. Direct or forward problems are of the following type: given C (causes)→E (effects), find E (effects), where (→) symbolizes the causal relationships ( 29 , pp. 145–164). These types of problems call for analysis, or progressive reasoning, either from premises to conclusions or from causes to effects. In contrast, an inverse problem is a more complicated problem of the following type: given the clinical data E (effects = symptoms) and the acceptable causal hypothesis C 1 →E, C 2 →E,…, C n →E, find the original cause C. Inverse problems require synthesis, or regressive reasoning, from conclusions to premises or from effects to causes. Inverse problems also are ill-defined problems in the sense that a simple solution may not exist, there may be more than one solution, or a small change in the problem leads to a big change in the solution ( 56 ).
Well-defined and direct problems have a clear path to a solution. The problem may be solved by using a set of recursive operations or algorithms ( 57 , 58 ). In contrast, the cognitive processes involved in the solution of ill-defined problems are far more complicated and still ill-understood. In the case of ill-defined problems, all aspects of problem formulation are challenging. Most are fuzzy problems, often difficult to delineate and even harder to represent in a way that makes them solvable ( 59 ). In addition, inverse problems imply a novelty for each case, and expertise should reflect an ability to react to situations that experts have never encountered before. In this context, problems cannot be solved ‘automatically’ or only ‘intuitively.’
The Dreyfus model has been derived from observation of the performance of experts, such as jet pilots and dancers, experts who are used to tackling direct problems. Is it correct to use this model also to explain the performances of experts who are used to tackling inverse problems? It is plausible that often the skills involved in solving direct problems are not the same as those involved in solving inverse problems. Think about the skills needed to solve this short list of inverse problems: to ‘guess’ the intention of a person from his/her behavior, to discover the authors of a crime knowing the crime scene, to ‘imagine’ an internal body part from the attenuation in intensity of an X-ray beam, to guess the premises of an argument from some of its conclusions, or to diagnose a sickness on the strength of its symptoms. The investigation of those problems does not proceed downstream, from premises to conclusions or from causes to effects. Working on all those problems involves reversing the logical or causal stream. In medicine, physicians face inverse problems all of the time. In fact, the typical diagnosis problem is not the direct problem of inferring syndrome from disease, but the inverse problem of guessing disease from symptoms ( 60 ). Anyone who wants to propose a model to explain how we develop clinical problem-solving skills must recognize carefully that the skills used to solve inverse problems are of a different nature than the skills used to solve direct problems. A model should be specific for skills of different natures; the Dreyfus model is not specific enough.
Rules and context
In the Dreyfus model, a novice should memorize rules and should not feel responsible for other things: ‘to improve, the novice needs monitoring, either by self-observation or instructional feedback, so as to bring his behavior more and more completely into conformity with the rule.’ ( 2 , p. 7). Besides, the Dreyfus model supports the idea that at proficient and competent levels, performers should have developed ‘personal guidelines and maxims’ in order to be able to deal successfully with tasks and problems ( 2 , 3 ). Why do we have to assume that these Dreyfus propositions are right? Is that the way we learn skills of explicit or even of tacit nature? Is it a good idea to memorize rules at novice stages? Do proficient and competent physicians solve diagnostic problems using just a set of ‘personal’ rules and maxims?
Early problem-solving research proposed the ‘general problem solver model.’ In this model the solution of a problem is conceptualized as a movement between two states: a starting state, named ‘problem space,’ and a final state named ‘goal state’ ( 58 ). There are ‘rules of transition’ which refer to those functions that move the system from one state to another, and there are also heuristics tools, rules that determine which moves are to be made in the problem space. Although this model gives great value to the use of rules, it should be recognized that these components are well suited for solving well-defined and direct problems, where the space and transitions between states are unambiguous ( 59 ). However, the model offers no solution whatsoever for dealing with inverse problems, for which there do not exist simple rules to solve them.
In medicine, although there are clinical guidelines and algorithms available that can help physicians deal with some problems, physicians acknowledge that these ‘rules’ are just general recommendations. Besides, physicians use ‘guidelines’ after they have transformed an inverse problem into a direct one. This is after diagnostic hypotheses have been generated. However, there is not a recipe to generate hypotheses. Furthermore, physicians use heuristic rules, such as Occam's razor regarding parsimony, but these ‘rules’ are general recommendations. They are explicit (not personal), and still it is not well known what impact they have on clinical problem-solving skills ( 61 ).
Rules are instructions for doing something, and even when they may be constructed as a mapping of possible actions (algorithms), they do not describe or explain any particular event or thing because they prescribe what to do. If we accept that knowledge has a transferable content that has been encoded and externalized in cultural artifacts, such as a book, then we should recognize that rules are not the sole element of that content, because knowledge consists of thousands of concepts, propositions, and theories. This knowledge allows us to grasp the nature of disease; understanding is a pre-requisite to learning. The development of clinical reasoning skills for medical students is dependent on basic science achievements ( 62 , 63 ). Novices, who rely on biomedical knowledge, solve complicated diagnostic problems with more success ( 64 ).
Believing that students should only memorize rules has a dark side and can cause deleterious consequences. When rules are available for everything, novices can spare the effort of imagining a different way to solve an inverse problem. Hence, they would tend to proceed to solve problems in a rather mindless way. We should reflect on the fact that to learn, students need all kinds of stimuli, such as propositional from books and experience. But they also need freedom to develop the talent to produce diagnostic hypotheses by spotting, inventing, and sometimes guessing.
Other elements to analyze are Dreyfus ideas that learners at pre-competent stages have a complete ignorance of the ‘context,’ and that the education at this level should be decontextualized: ‘normally, the instruction process begins by decomposing the task environment into context-free features which the beginner can recognize without benefit of experience’ ( 2 , p. 7). Contrary to such an idea, we should acknowledge that everything in our world, including concepts, is interrelated. Learning, as any other event, happens under specific conditions and should not be detached from the real experience. Medical students always face the context. Of course, at the beginning, there is not enough insight into every detail. However, students’ minds are not like computers following a program; they have some ideas, some approaches, and some knowledge of the context. For example, medical students can generate numerous diagnostic inferences, even without considerable clinical experience ( 65 , 66 ). How can they do that if novices like them ‘ignore’ the context? Accumulating experience is not a passive recording. Learning is creative in the sense that it is new and not automatic to the individual. Even at the pre-beginner stage, learners gain experience and understanding of the context. Information, context, and experience cannot be separated.
The Dreyfus brothers propose that intuition is the endpoint of learning and a key characteristic of expertise: ‘the expert pilot, having finally reached this non-analytical stage of performance, responds intuitively and appropriately to his current situation’ ( 2 , p. 12). Hubert Dreyfus describes a master as one with a lot of experience who produces almost instantaneously appropriate perspectives, who thinks intuitively, not analytically, and who ceases to pay conscious attention to his performance turning it unconsciously: ‘the expert, like masters in the “long Zen tradition” or Luke Skywalker when responding to Obi Wan Kenobi's advice to use the force “transcends” “trying” or “efforting” and “just responds”’ ( 67 , p. 22).
Adults often learn to drive a car, type, play chess, ski, etc. In most cases we perform such skills intuitively, quickly, unconsciously, and ‘just respond.’ These everyday skills are relatively easy to acquire, at least to an acceptable level. It is plausible that some steps required to perform a simple task are so fast that we consider them on an unconscious level even though we are alert and oriented. Neuroscience tries to explain that there are two kinds of neuronal aggregations in the brain's organization: one is constituted of heavily interconnected neurons with long-range axons (named workspaces) and the others are system sets of specialized neuronal processors (perceptual, motor, memory, evaluative, and attentional) with short axons ( 68 ). The latter ones are not enough to perform tasks that require great effort, so the workspace neurons are activated, making the effort conscious. This mobilization is greater with complex cognitive tasks ( 68 , 69 ).
However, the popular conception that some simple everyday skills are performed fast and ‘unconsciously’ can explain neither the performance of difficult tasks nor the acquisition of sophisticated skills ( 70 ). In the case of problem-solving skills, empirical studies have demonstrated a distinction between expert and novice problem representation in terms of the time spent on various stages of the problem-solving process. Contrary to the idea that experts dedicate less time than novices, Lesgold ( 71 ) found that experts spent more time than novices determining an appropriate representation of the problem. Experts spent more time comparing their knowledge to the information they needed to discover in order to best represent the problem.
Even skilled rapid motor production, as in typing, is not simple nor is completely automatic. Studies showed that expert typists look ahead to prepare for what comes next. They acquire complex representations and skills to anticipate future actions ( 72 ). Something similar happens in music, where the mark of expert performance is the ability to control one's performance and its results; there is not such a thing as an automatic and immediate response. Expert music performance requires several different representations: ‘imagined music experience’ (desired performance goal), ‘playing a piece of music’ (how to execute the performance), and ‘listening to the played music’ (hearing one's performance) ( 73 ). The resulting music performance should not be seen as a fixed and automated sequence of motor actions. It should be viewed as a flexible, controllable outcome based on these representations ( 70 ).
Consequently, it is hard to believe that the whole clinical problem-solving process is intuitive in the sense that it is unconscious, effortless, and automated. Although the use of ‘pattern recognitions’ and ‘illness scripts’ can happen in an automatic way, especially when data or a prior experience triggers a possible diagnosis, this explains only one state of the whole problem-solving process. Good physicians, although esteeming intellectual intuition because of its suggestive power, know that it can be dangerous: first, because intuition does not have demonstrative force, and second, because intuition is never fine enough. Intuition, as a very fast and almost instant inference, consists of showing rather than demonstrating; in proving in a brief and imperfect way, and in rendering plausible the hypothesis that has been invented. It is a kind of rudimentary reasoning that uses incomplete evidence, visual images, and analogies (prior experiences) rather than complete data, refined concepts, and detailed inferences ( 74 ). A diagnosis formulated in an intuitive way will have to be worked out in a rational way and then tested by the usual procedures. This is because the suspicion generated by the illness scripts and pattern recognitions are not proof of a diagnosis. Further, this is why we use a lot of auxiliary tests and image studies. Expert clinicians intentionally avoid any tendency toward automatization as they often lose control of many relevant aspects of a clinical encounter. Ericson called this ‘deliberate practice’ ( 70 ).
There is evidence that experts use two modes of thinking: analytic (hypothetic–deductive) and non-analytic (pattern recognition), even in perceptual specialties ( 75 – 78 ). Both modes of thinking are part of a continuous process. Expert physicians do not use analytic reasoning only after a failed attempt with non-analytic reasoning or the other way around. Clinical medicine is one of the more complicated and challenging professions; it is very simplistic to explain problem-solving processes starting and ending with intuition. Many diagnostic errors are due to overconfidence and heuristic availability, and some errors occur during non-analytic reasoning ( 79 ). Intuition, because it is brief and readily accomplished and grasped, must be expanded to be validated.
Implications and conclusions
Any model is a representation of a thing, and in this representation two elements play important roles: the represented and the representing things. With this pair of elements we can make diverse kinds of representations: factual–factual (a scale model), factual–conceptual (a theoretical model), factual–semiotic (a scientific text), and semiotic–factual (a text illustration) ( 1 ). The acquisition of skills is a learning process and is obviously factual. Hence the Dreyfus model attempts to be a factual–conceptual model, a theory or at least an outlook of how we acquire diverse skills. Any fact–concept correspondence is of course difficult and not of the one-to-one type. However, because it tries to be truthful, a theory must attempt to be coherent and related to the facts.
Although the Dreyfus model is not taken strictly as a ‘prescription,’ it is plausible that its descriptive face is influencing us to generate a worldview, a general outlook of how we learn and teach medicine. Every worldview has an effect on our actions and policies. And here is the point of major implication, because this model can influence educative policies, recommendations, and guidelines. This model can also generate unhappy contradictions. For example, it has been said that the Dreyfus model provides us with a framework for consistency within the evaluation system ( 80 ). How can this model help us to ground our evaluation system if the model suggests explaining physicians’ performance in terms of implicit knowledge and intuition? By definition, if implicit knowledge is not expressible in some language, then it is inaccessible to evaluate. Certainly we need more debates and we need to evaluate this model not only in light of philosophical but also of scientific considerations.
Although the Dreyfus model could partially explain the ‘acquisition’ of some skills, it is another matter as to whether it can explain the acquisition of clinical skills. The occurrence of inverse problems and the rich interplay between the implicit and explicit domains of knowledge must be taken into consideration when we want to explain ‘acquisition’ of clinical skills. The idea that the net effect of education and training in medicine is that we start developing intuition about what we are doing must be revised and evaluated carefully.
Using this model in a prescriptive way must elicit a more critical eye to see if novices must receive an education where rules are the only important things to learn in a decontextualized environment. Finally, we must acknowledge the complexity of all the processes implied in learning. We cannot merely accept the temptation to oversimplify these complex processes, and ignore intentionally or not information from science, in particular from cognition, psychology, and neuroscience.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to offer special thanks to Dr Mario Bunge, Frothingham chair of Logic and Metaphysics at McGill University; Dr Gustavo Heudebert, Director of the UAB Internal Medicine Residency Program; and the anonymous reviewers for helpful comments and suggestions on an earlier draft of his article.
Conflict of interest and funding
This paper was prepared while the author was a VAQS fellow at the VA Birmingham Medical Center and the Center for Surgical, Medical Acute Care Research and Transitions (C-SMART), these institutions covered the publication costs for this paper.
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
How to Teach Kids Problem-Solving Skills
KidStock / Blend Images / Getty Images
- Steps to Follow
- Allow Consequences
Whether your child can't find their math homework or has forgotten their lunch, good problem-solving skills are the key to helping them manage their life.
A 2010 study published in Behaviour Research and Therapy found that kids who lack problem-solving skills may be at a higher risk of depression and suicidality. Additionally, the researchers found that teaching a child problem-solving skills can improve mental health .
You can begin teaching basic problem-solving skills during preschool and help your child sharpen their skills into high school and beyond.
Why Problem-Solving Skills Matter
Kids face a variety of problems every day, ranging from academic difficulties to problems on the sports field. Yet few of them have a formula for solving those problems.
Kids who lack problem-solving skills may avoid taking action when faced with a problem.
Rather than put their energy into solving the problem, they may invest their time in avoiding the issue. That's why many kids fall behind in school or struggle to maintain friendships .
Other kids who lack problem-solving skills spring into action without recognizing their choices. A child may hit a peer who cuts in front of them in line because they are not sure what else to do.
Or, they may walk out of class when they are being teased because they can't think of any other ways to make it stop. Those impulsive choices may create even bigger problems in the long run.
The 5 Steps of Problem-Solving
Kids who feel overwhelmed or hopeless often won't attempt to address a problem. But when you give them a clear formula for solving problems, they'll feel more confident in their ability to try. Here are the steps to problem-solving:
- Identify the problem . Just stating the problem out loud can make a big difference for kids who are feeling stuck. Help your child state the problem, such as, "You don't have anyone to play with at recess," or "You aren't sure if you should take the advanced math class."
- Develop at least five possible solutions . Brainstorm possible ways to solve the problem. Emphasize that all the solutions don't necessarily need to be good ideas (at least not at this point). Help your child develop solutions if they are struggling to come up with ideas. Even a silly answer or far-fetched idea is a possible solution. The key is to help them see that with a little creativity, they can find many different potential solutions.
- Identify the pros and cons of each solution . Help your child identify potential positive and negative consequences for each potential solution they identified.
- Pick a solution. Once your child has evaluated the possible positive and negative outcomes, encourage them to pick a solution.
- Test it out . Tell them to try a solution and see what happens. If it doesn't work out, they can always try another solution from the list that they developed in step two.
Practice Solving Problems
When problems arise, don’t rush to solve your child’s problems for them. Instead, help them walk through the problem-solving steps. Offer guidance when they need assistance, but encourage them to solve problems on their own. If they are unable to come up with a solution, step in and help them think of some. But don't automatically tell them what to do.
When you encounter behavioral issues, use a problem-solving approach. Sit down together and say, "You've been having difficulty getting your homework done lately. Let's problem-solve this together." You might still need to offer a consequence for misbehavior, but make it clear that you're invested in looking for a solution so they can do better next time.
Use a problem-solving approach to help your child become more independent.
If they forgot to pack their soccer cleats for practice, ask, "What can we do to make sure this doesn't happen again?" Let them try to develop some solutions on their own.
Kids often develop creative solutions. So they might say, "I'll write a note and stick it on my door so I'll remember to pack them before I leave," or "I'll pack my bag the night before and I'll keep a checklist to remind me what needs to go in my bag."
Provide plenty of praise when your child practices their problem-solving skills.
Allow for Natural Consequences
Natural consequences may also teach problem-solving skills. So when it's appropriate, allow your child to face the natural consequences of their action. Just make sure it's safe to do so.
For example, let your teenager spend all of their money during the first 10 minutes you're at an amusement park if that's what they want. Then, let them go for the rest of the day without any spending money.
This can lead to a discussion about problem-solving to help them make a better choice next time. Consider these natural consequences as a teachable moment to help work together on problem-solving.
Becker-Weidman EG, Jacobs RH, Reinecke MA, Silva SG, March JS. Social problem-solving among adolescents treated for depression . Behav Res Ther . 2010;48(1):11-18. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2009.08.006
Pakarinen E, Kiuru N, Lerkkanen M-K, Poikkeus A-M, Ahonen T, Nurmi J-E. Instructional support predicts childrens task avoidance in kindergarten . Early Child Res Q . 2011;26(3):376-386. doi:10.1016/j.ecresq.2010.11.003
Schell A, Albers L, von Kries R, Hillenbrand C, Hennemann T. Preventing behavioral disorders via supporting social and emotional competence at preschool age . Dtsch Arztebl Int . 2015;112(39):647–654. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2015.0647
Cheng SC, She HC, Huang LY. The impact of problem-solving instruction on middle school students’ physical science learning: Interplays of knowledge, reasoning, and problem solving . EJMSTE . 2018;14(3):731-743.
Vlachou A, Stavroussi P. Promoting social inclusion: A structured intervention for enhancing interpersonal problem‐solving skills in children with mild intellectual disabilities . Support Learn . 2016;31(1):27-45. doi:10.1111/1467-9604.12112
Öğülmüş S, Kargı E. The interpersonal cognitive problem solving approach for preschoolers . Turkish J Educ . 2015;4(17347):19-28. doi:10.19128/turje.181093
American Academy of Pediatrics. What's the best way to discipline my child? .
Kashani-Vahid L, Afrooz G, Shokoohi-Yekta M, Kharrazi K, Ghobari B. Can a creative interpersonal problem solving program improve creative thinking in gifted elementary students? . Think Skills Creat . 2017;24:175-185. doi:10.1016/j.tsc.2017.02.011
Shokoohi-Yekta M, Malayeri SA. Effects of advanced parenting training on children's behavioral problems and family problem solving . Procedia Soc Behav Sci . 2015;205:676-680. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.09.106
By Amy Morin, LCSW Amy Morin, LCSW, is the Editor-in-Chief of Verywell Mind. She's also a psychotherapist, an international bestselling author of books on mental strength and host of The Verywell Mind Podcast. She delivered one of the most popular TEDx talks of all time.
Problem Solving Skill
The Problem Solving skill can be very useful once we have determined that a problem has arisen, and it’s our problem to solve. Sometimes we experience unpleasant emotions about the actions of others or situations that we cannot change. This skill specifically helps us to collect the facts and take steps to solve a problem for which we can change.
There are a number of steps to effective problem solving:
- 1 Stop long enough to realize that a situation is a problem and you may need time to find a resolution.
- 2 Define the problem in detail. What is the situation? Who is involved? What is happening or not happening that is a problem? Where did it happen? When did it happen? How did it happen? How often does it occur? Why does it happen? How do you feel? What do you do in response? What do you want to change?
- 3 Describe how the problem interferes with your goals. If the situation does not interfere with your goals, it is likely not your problem.
- 4 Identify all the options/alternatives. It is important to find at least 3 potential solutions in order to avoid the black/white thinking we were programmed to use.
- 5 View of the consequences of each option/alternative. Seek additional knowledge if necessary.
- 6 Identify the steps needed to resolve/take action. Make a list of when and how the steps will be taken and then take the required action.
- 7 Evaluate results. If the steps taken were successful to resolve the problem, acknowledge that you successfully solved a problem and give yourself some credit. If the steps taken were not successful to solve the problem, learn more about what would be needed to solve the problem and follow steps 4-7 again until the matter is resolved.
Dark Mode Detected
Would you prefer dark-mode? Save battery, save your eyes, switch to our dark-mode theme.
Toggle Dark-Mode
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
AI Prompt Engineering Isn’t the Future
- Oguz A. Acar

Asking the perfect question is less important than really understanding the problem you’re trying to solve.
Despite the buzz surrounding it, the prominence of prompt engineering may be fleeting. A more enduring and adaptable skill will keep enabling us to harness the potential of generative AI? It is called problem formulation — the ability to identify, analyze, and delineate problems.
Prompt engineering has taken the generative AI world by storm. The job, which entails optimizing textual input to effectively communicate with large language models, has been hailed by World Economic Forum as the number one “job of the future” while Open AI CEO Sam Altman characterized it as an “amazingly high-leveraged skill.” Social media brims with a new wave of influencers showcasing “magic prompts” and pledging amazing outcomes.
- Oguz A. Acar is a Chair in Marketing at King’s Business School, King’s College London.
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Collaboration. Having a growth mindset. In short, understanding, developing, and showcasing these skills, can greatly boost your chances at getting noticed by the hiring managers. So, don't hesitate and start working on your problem-solving skills right now! 0.
Problem-solving skills are the ability to identify problems, brainstorm and analyze answers, and implement the best solutions. An employee with good problem-solving skills is both a self-starter and a collaborative teammate; they are proactive in understanding the root of a problem and work with others to consider a wide range of solutions ...
Problem-solving skills will help you tackle challenges at any workplace, make informed decisions, and help the organizations you work with to succeed. Personal Growth. These skills equip you to overcome everyday life obstacles, like managing personal finances, resolving conflicts in relationships, and more. Innovation and Entrepreneurship.
6. Solution implementation. This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving strategies have the end goal of implementing a solution and solving a problem in mind. Remember that in order for any solution to be successful, you need to help your group through all of the previous problem solving steps thoughtfully.
Although problem-solving is often identified as its own separate skill, there are other related skills that contribute to this ability. Some key problem-solving skills include: Active listening. Analysis. Research. Creativity. Communication. Decision-making. Team-building.
1. Identify the problem. 2. Analyze the problem. Be the first to add your personal experience. 3. Generate solutions. Be the first to add your personal experience. 4.
Problem-solving skills are a collection of cognitive abilities. They allow a person to effectively identify, analyse, and resolve problems. These skills encompass a range of competencies. These include analytical thinking, creative ideation, strategic decision-making, and efficient execution. .
Problem-solving requires you to create a balance between logic and creativity. You need to use your creativity to find the cause of the issue. It also requires creativity to develop innovative solutions. Creative people bring unique perspectives and give a new direction to the company. Related: 7 Steps to Improve Your Creative Thinking Skills.
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below ( [link]) is a 4×4 grid.
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
Problem-solving skills are skills that enable people to handle unexpected situations or difficult challenges at work. Organisations need people who can accurately assess problems and come up with effective solutions. In this article, we explain what problem-solving skills are, provide some examples of these skills and outline how to improve them.
Problem-solving skills are essential for any professional who wants to overcome challenges, achieve goals, and grow in their field. In this article, you'll learn about six problem-solving skills ...
In this article, we hope to show you some problem-solving skills: definition, steps, and examples. Design thinking is an accepted method for problem-solving among software designers, but it's also an excellent process when us ordinary mortals need to solve complex problems. Design thinking is an iterative process and encourages:
Problem definition and formulation (PDF) represents the first of the four rational problem-solving skills. The overarching goal of training in PDF is to help a person to better understand the nature of the problem and to set realistic goals. Although the tasks involved in this aspect of the problem-solving process may be the most complex and challenging, they are also perhaps the most important.
Decision-Making 7. Resourcefulness 8. Patience 9. Conflict Resolution 10. Persistence How to Develop Problem-Solving Skills. In today's competitive job market, technical expertise alone doesn't suffice. Employers are increasingly valuing individuals with a unique set of skills - problem-solving soft skills.
Here are some tips on how to highlight your problem-solving skills in a job interview: 1. Describe your process. When describing how you solved a problem, be sure to include all the steps you took in your explanation. This will show the interviewer that you are systematic and thorough in your approach.
The acquisition of skills is a learning process and is obviously factual. Hence the Dreyfus model attempts to be a factual-conceptual model, a theory or at least an outlook of how we acquire diverse skills. Any fact-concept correspondence is of course difficult and not of the one-to-one type.
Here are the steps to problem-solving: . Identify the problem. Just stating the problem out loud can make a big difference for kids who are feeling stuck. Help your child state the problem, such as, "You don't have anyone to play with at recess," or "You aren't sure if you should take the advanced math class."
Step 3: Choose a solution. A big part of engineering is making decisions and choosing between different implementation options. Proactively point out the advantages/disadvantages of your ideas. If there is more than one solution on the table, you should consider which makes the most sense build.
Email: [email protected]. Enhancing Student's Problem -solving Skills through Project-based Learning. Ebrahim Karan and Lisa Brown *. ABSTRACT. The goal of the study is to overcome two main ...
This skill specifically helps us to collect the facts and take steps to solve a problem for which we can change. There are a number of steps to effective problem solving: 1. Stop long enough to realize that a situation is a problem and you may need time to find a resolution. 2. Define the problem in detail. What is the situation?
It is called problem formulation — the ability to identify, analyze, and delineate problems. Prompt engineering has taken the generative AI world by storm. The job, which entails optimizing ...