

20 Best Social Media Marketing Case Study Examples
Please enable JavaScript

How would you like to read the best social media marketing case studies ever published?
More importantly, how would you like to copy the best practices in social media marketing that are based on real-world examples and not just theory?
Below, you’ll find a list of the top 20 social media case study examples along with the results and key findings. By studying these social media marketing studies and applying the lessons learned on your own accounts, you can hopefully achieve similar results.
Table of Contents
Social Media Case Study Examples
793,500+ impressions for semrush on twitter – walker sands social media case study.
The case study shows how Walker Sands implemented a premium Twitter microcontent program for Semrush, a global leader in digital marketing software. Semrush needed a strategic social media marketing partner to help distinguish its brand from competitors, drive a higher engagement rate among its target audience, and build brand loyalty. In this case study, you’ll find out how the social strategy focused on three things: using humor, embedding the brand in trending conversations, and focusing on the audience’s interests over marketing messages. The result was an increase of more than 793,500 impressions, 34,800 engagements, and a 4.4% average engagement rate.
Viral Oreo Super Bowl Tweet – Social Media Case Study
This is a popular case study to learn valuable insights for B2C marketing. During Super Bowl XLVII, the lights went out in the football stadium and the Oreo brand went viral with a single tweet that said “Power out? No problem. You can still dunk in the dark.” Read the historical account of that famous social media marketing moment from the people who lived through it so you can gather ideas on how to be better prepared for future social media campaigns that you can take advantage of in real-time.
Facebook Posting Strategy That Lead to 3X Reach & Engagement – Buffer Social Media Case Study
In this social media case study example, you’ll find out how Buffer cut its Facebook posting frequency by 50% but increased the average weekly reach and engagement by 3X. Hint: The strategy had to do with creating fewer, better-quality posts, that were aimed at gaining higher engagement.
Achieving a 9 Million Audience by Automating Pinterest SEO – Social Media Case Study
This is a good social media marketing case study for marketers who use Pinterest. Discover how Chillital went from 0 to 9 million engaged audience members and 268 million impressions. You’ll learn about the step-by-step research process of finding where your audience lives and breathes content, get a detailed analysis of how the author used Pinterest to generate brand awareness, and learn about using community-driven content promotion to scale social media results.
5X Increase In App Installs from TikTok – Bumble Social Media Case Study
With the use of TikTok on the rise, social media case studies are now being shared about how to get the most value out of marketing on this platform. This one, in particular, is good to read because it explains how Bumble, a dating app, used TikTok more effectively by following the mantra, “Don’t Make Ads, Make TikToks”. This case study in social media marketing resulted in a 5X increase in app installs and a 64% decrease in cost-per-registration.
330% Increase In Reach for the Make a Wish Foundation – Disney Social Media Case Study
Check out this case study to find out how the Make-A-Wish Foundation increased its social media reach, audience, and engagement by partnering with Disney in a Share Your Ears campaign. The strategy was simple: ask people to take a photo of themselves wearing Mickey Mouse ears, post it on social media with the hashtag #ShareYouEars, and a $5 donation would be made to Make-A-Wish. The results were unbelievable with over 1.7 million posted photos and 420 million social media impressions. This led to a 15% audience increase on Facebook and a 13% audience increase on Instagram with a total increase of 330% in social media reach and a 554% increase in engagement during the campaign.
How 3 Schools Used Social Media Advertising to Increase Website Traffic & Applications – Social Media Case Study
This example includes three of the best social media case studies from Finalsite, a marketing agency for educational institutions. It shows the power of social media advertising to increase website traffic and enrollment. One case study, in particular, shows how a limited budget of $350 per month increased website sessions by 515%, more than 2,200 clicks on the apply button for a study abroad application, 2,419 views on the request information page, and 575 views on the application process page.
Client Case Studies – LYFE Marketing Social Media Case Study
LYFE Marketing is a social media management company that helps clients gain new customers, generate sales, and increase brand exposure online. This page includes several of its top social media marketing case studies along with the approach and key results from each campaign. It’s packed with screenshots of the social media posts and engagement metrics so you can understand how each strategy worked for success, and get inspiration for your own campaigns.
3X Leads for a Local Business – Vertex Marketing Social Media Case Study
This is a good case study about finding the right balance between organic reach with social media posts and paid reach with social media marketing ads. You’ll find out how Vertex Marketing helped a local kitchen and bath remodeling business increase the number of leads by 3X. As for the return on investment (ROI) for this campaign, each lead for the client was worth about $10,000. The result was 6,628 audience reach, $12.43 average cost per conversion, and 18 conversions.
235% Increase In Conversions with Facebook Ads Funnel – Marketing 360 Social Media Case Study
This is one of Marketing 360’s case study examples that demonstrates the effectiveness of a Facebook ads sales funnel for B2B marketing. An ads funnel is a series of social media advertisements that target a specific audience at each stage of the buyer’s journey. By mapping out the buyer’s journey and creating a social media marketing ad campaign for each stage, you can guide new leads through the sales funnel and turn them into paying customers. This case study resulted in a 235% increase in conversions for a truck lift manufacturer.
15% Increase In Social Media Followers In 6 Months – Hootsuite Social Media Case Study
This is one of the best social media marketing case studies available online for businesses in the hospitality industry. Find out how Meliá Hotels International incorporated social media directly into its business model, both as a channel for client communication and as a platform to listen and learn about client needs and preferences. As a result, Meliá Hotel’s social media following grew from 5 million to 6 million in six months; an increase of more than 15%.
The Impact of Social Signals On SEO – Fat Stacks Social Media Case Study
This is a good case study for understanding the effect social media can have on SEO. By building links for a web page on social media channels like Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, LinkedIn, etc, the rankings for long tail keywords improved in Google’s search engine.
96 Link Clicks for a Vacation Rental – Maria Peagler Social Media Case Study
As the title of this social media case study example suggests, you’ll learn how Maria Peagler helped a vacation rental get 96 clicks out of 3,274 audience reach on a single Facebook ad; about a 2.9% click-through rate (CTR). What’s most important about this B2C example is those clicks were of the highest quality the client could receive because Maria dug into the analytics to find out the best time during the day to post the ad and the perfect age groups to target while also using specific language to only drive clicks that would more likely convert.
Vienna Tourist Board Uses an Instagram Wall to Attract Tourists – Walls.io Social Media Case Study
Inside this case study, you’ll find out how the City of Vienna uses a simple social media content aggregator to display its Instagram feed on the website. This basic marketing strategy harnesses the power of user-generated content to gain more followers and keep in touch with previous visitors to increase brand awareness and repeat visits.
Complete Instagram Marketing Strategy for Sixthreezero – Vulpine Interactive Social Media Case Study
This is an in-depth case study on social media marketing with Instagram. You’ll discover how Vulpine Interactive was able to turn an existing, unmanaged account into a strong company asset for Sixthreezero, a bicycling company that uses ecommerce to drive sales. There was a lot of strategy and planning that went into growing the account by 39%, increasing website traffic from Instagram by over 300%, and achieving 77,659 total engagements. Inside, you’ll get the complete social strategy, tactics, key performance indicators (KPIs), and results
Twitter Marketing Success Stories – Social Media Case Study
If you’re looking for social media case study examples for Twitter using both organic and paid ads, then this page has everything you need. It includes Twitter’s top marketing success stories for you to get new ideas for your own B2C and B2B marketing campaigns.
How 3 Big Brands Use Pinterest for Marketing – SmartInsights Social Media Case Study
This is a case study page by SmartInsights with an overview of how 3 big brands use Pinterest for marketing. Although it’s a quick read, you can learn some valuable tactics that Nordstrom, Sephora, and Petplan are using to market their brands on this social media platform.
25+ TikTok Social Campaign Results – Chatdesk Social Media Case Study
If you’re looking for the best social media case studies for TikTok, then this list by Chatdesk is an excellent resource. It includes more than 25 examples from big brands like Starbucks, Redbull, Spikeball, Crocs, Guess Jeans, and Gym Shark. Give it a read to find out exactly how these brands use TikTok effectively to scale their businesses.
Reddit for Business: Meet Your Maker – Social Media Case Study
Want to learn how to use Reddit to market your business online? This new social media marketing case study page by Reddit called “Meet Your Maker” showcases the people behind some of the most innovative and creative brand activations on our platform. Examples include campaigns by Adobe, Capcom, and noosa Yoghurt.
How Boston University Uses Snapchat to Engage with Students – Social Media Case Study
With more than 75% of college students using Snapchat on a daily basis, it became clear that Boston University had to make this platform a primary marketing channel. This social media case study outlines all of the top strategies Boston University uses to connect with prospective and current students.
Now, if you’re looking for more digital marketing ideas, then make sure to check out these other related guides: SEO case studies with data on improving organic search engine optimization, PPC case studies for paid search examples, email marketing case studies , affiliate marketing case studies , content marketing case studies , and general digital marketing case studies .
What Is a Social Media Case Study?
A social media case study is an in-depth study of social media marketing in a real-world context. It can focus on one social media tactic or a group of social media strategies to find out what works in social media marketing to promote a product or service.
Are Case Studies Good for Social Media Marketing?
Case studies are good for social media because you can learn about how to do social media marketing in an effective way. Instead of just studying the theory of social media, you can learn from real examples that applied social media marketing methods to achieve success.
Summary for Social Media Marketing Case Studies
I hope you enjoyed this list of the best social media marketing case study examples that are based on real-world results and not just theory.
As you discovered, the social media case studies above demonstrated many different ways to perform well on social platforms. By studying the key findings from these case study examples, and applying the methods learned to your own accounts, you can hopefully achieve the same positive outcome. New social media case studies are being published every month and I’ll continue to update this list as they become available. So keep checking back to read the current sources of information on social media.
Send us an email
How to write a social media case study (with template)
Written by by Jenn Chen
Published on October 10, 2019
Reading time 8 minutes
You’ve got a good number of social media clients under your belt and you feel fairly confident in your own service or product content marketing strategy. To attract new clients, you’ll tell them how you’ve tripled someone else’s engagement rates but how do they know this is true? Enter the case study.
Social media case studies are often used as part of a sales funnel: the potential client sees themselves in the case study and signs up because they want the same or better results. At Sprout, we use this strategy with our own case studies highlighting our customer’s successes.
Writing and publishing case studies is time intensive but straight forward. This guide will walk through how to create a social media case study for your business and highlight some examples.
What is a social media case study?
A case study is basically a long testimonial or review. Case studies commonly highlight what a business has achieved by using a social media service or strategy, and they illustrate how your company’s offerings help clients in a specific situation. Some case studies are written just to examine how a problem was solved or performance was improved from a general perspective. For this guide, we’ll be examining case studies that are focused on highlighting a company’s own products and services.
Case studies come in all content formats: long-form article, downloadable PDF, video and infographic. A single case study can be recycled into different formats as long as the information is still relevant.
At their core, case studies serve to inform a current or potential customer about a real-life scenario where your service or product was applied. There’s often a set date range for the campaign and accompanying, real-life statistics. The idea is to help the reader get a clearer understanding of how to use your product and why it could help.
Broad selling points like “our service will cut down your response time” are nice but a sentence like “After three months of using the software for responses, the company decreased their response time by 52%” works even better. It’s no longer a dream that you’ll help them decrease the response time because you already have with another company.
So now that you understand what a case study is, let’s get started on how to create one that’s effective and will help attract new clients.
How to write a social marketing case study
Writing an effective case study is all about the prep work. You’ve got to get all of the questions and set up ready so you can minimize lots of back and forth between you and the client.
1. Prepare your questions
Depending on how the case study will be presented and how familiar you are with the client to be featured, you may want to send some preliminary questions before the interview. It’s important to not only get permission from the company to use their logo, quotes and graphs but also to make sure they know they’ll be going into a public case study.
Your preliminary questions should cover background information about the company and ask about campaigns they are interested in discussing. Be sure to also identify which of your products and services they used. You can go into the details in the interview.
Once you receive the preliminary answers back, it’s time to prepare your questions for the interview. This is where you’ll get more information about how they used your products and how they contributed to the campaign’s success.
2. Interview
When you conduct your interview, think ahead on how you want it to be done. Whether it’s a phone call, video meeting or in-person meeting, you want to make sure it’s recorded. You can use tools like Google Meet, Zoom or UberConference to host and record calls (with your client’s permission, of course). This ensures that your quotes are accurate and you can play it back in case you miss any information. Tip: test out your recording device and process before the interview. You don’t want to go through the interview only to find out the recording didn’t save.
Ask open-ended questions to invite good quotes. You may need to use follow-up questions if the answers are too vague. Here are some examples.
- Explain how you use (your product or service) in general and for the campaign. Please name specific features.
- Describe how the feature helped your campaign achieve success.
- What were the campaign outcomes?
- What did you learn from the campaign?
Since we’re focused on creating a social media case study in this case, you can dive more deeply into social strategies and tactics too:
- Tell me about your approach to social media. How has it changed over time, if at all? What role does it play for the organization? How do you use it? What are you hoping to achieve?
- Are there specific social channels you prioritize? If so, why?
- How do you make sure your social efforts are reaching the right audience?
- What specific challenges do organizations like yours face when it comes to social?
- How do you measure the ROI of using social ? Are there certain outcomes that prove the value of social for your organization? What metrics are you using to determine how effective social is for you?
As the conversation continues, you can ask more leading questions if you need to to make sure you get quotes that tie these strategic insights directly back to the services, products or strategies your company has delivered to the client to help them achieve success. Here are just a couple of examples.
- Are there specific features that stick out to you as particularly helpful or especially beneficial for you and your objectives?
- How are you using (product/service) to support your social strategy? What’s a typical day like for your team using it?

The above quote was inserted into the Sprout Lake Metroparks case study . It’s an example of identifying a quote from an interview that helps make the impact of the product tangible in a client’s day to day.
At the end of the interview, be sure to thank the company and request relevant assets.
Afterwards, you may want to transcribe the interview to increase the ease of reviewing the material and writing the case study. You can DIY or use a paid service like Rev to speed up this part of the process.
3. Request assets and graphics
This is another important prep step because you want to make sure you get everything you need out of one request and avoid back and forth that takes up both you and your customer’s time. Be very clear on what you need and the file formats you need them in.
Some common assets include:
- Logo in .png format
- Logo guidelines so you know how to use them correctly
- Links to social media posts that were used during the campaign
- Headshots of people you interviewed
- Social media analytics reports. Make sure you name them and provide the requested date range, so that if you’re using a tool like Sprout, clients know which one to export.

4. Write the copy
Now that the information has been collected, it’s time to dissect it all and assemble it. At the end of this guide, we have an example outline template for you to follow. When writing a case study, you want to write to the audience that you’re trying to attract . In this case, it’ll be a potential customer that’s similar to the one you’re highlighting.
Use a mix of sentences and bullet points to attract different kinds of readers. The tone should be uplifting because you’re highlighting a success story. When identifying quotes to use, remove any fillers (“um”) and cut out unnecessary info.

5. Pay attention to formatting

And finally, depending on the content type, enlist the help of a graphic designer to make it look presentable. You may also want to include call-to-action buttons or links inside of your article. If you offer free trials, case studies are a great place to promote them.
Social media case study template
Writing a case study is a lot like writing a story or presenting a research paper (but less dry). This is a general outline to follow but you are welcome to enhance to fit your needs.
Headline Attention-grabbing and effective. Example: “ How Benefit turns cosmetics into connection using Sprout Social ” Summary A few sentences long with a basic overview of the brand’s story. Give the who, what, where, why and how. Which service and/or product did they use? Introduce the company Give background on who you’re highlighting. Include pertinent information like how big their social media team is, information about who you interviewed and how they run their social media. Describe the problem or campaign What were they trying to solve? Why was this a problem for them? What were the goals of the campaign? Present the solution and end results Describe what was done to achieve success. Include relevant social media statistics (graphics are encouraged). Conclusion Wrap it up with a reflection from the company spokesperson. How did they think the campaign went? What would they change to build on this success for the future? How did using the service compare to other services used in a similar situation?
Case studies are essential marketing and sales tools for any business that offer robust services or products. They help the customer reading them to picture their own company using the product in a similar fashion. Like a testimonial, words from the case study’s company carry more weight than sales points from the company.
When creating your first case study, keep in mind that preparation is the key to success. You want to find a company that is more than happy to sing your praises and share details about their social media campaign.
Once you’ve started developing case studies, find out the best ways to promote them alongside all your other content with our free social media content mix tool .
[Toolkit] Communications Toolkit to Safeguard Your Brand
Find Your Next Social Media Management Tool With This Scorecard
How to ladder up your brand’s social media maturity
3 Social media executives share what it takes to build a long-term career in social
- Data Report
- Social Media Content
The 2024 Content Benchmarks Report
Always up-to-date guide to social media image sizes
- Social Media Strategy
The power of frontline employee engagement on social media
- Marketing Disciplines
B2B content marketing: Ultimate strategy guide for 2024
- Now on slide
Build and grow stronger relationships on social
Sprout Social helps you understand and reach your audience, engage your community and measure performance with the only all-in-one social media management platform built for connection.
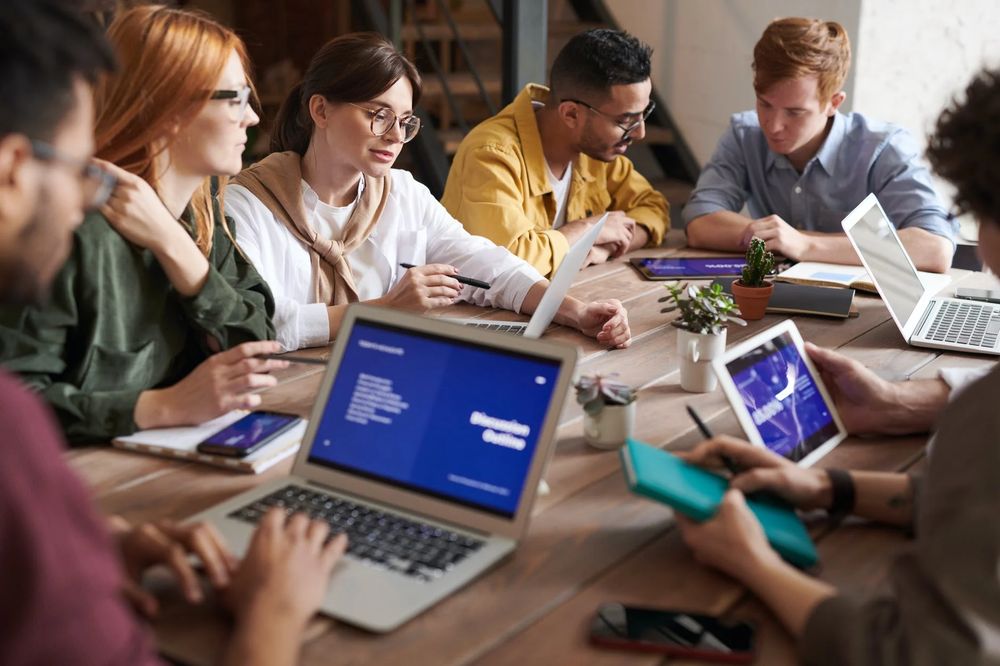
Top 3 Social Media Case Studies to Inspire You in 2024
Discover three successful social media case studies from top brands and learn how to create one. Benefit from their strategies and mistakes to ensure the success of your next campaign.

Social media is every marketer’s safe haven for branding and marketing.
And why not?
More than 50% of the population is active on social media, and more are signing up with every passing second.
In a recent poll by HubSpot, 79% of the respondents have made a purchase after seeing a paid advertisement on social media .
This isn’t just a happenstance.
It’s the constant efforts that these brands put behind their dynamic presence on social media, that counts.
But how do they captivate their customers’ attention for this long despite the budding competitors?
Well, that’s something that we’ll reveal in this blog.
We shall assess 3 different social media case studies by top brands who are best in their niches. Their game is simple yet effective.
How effective? Let’s take a look.
Social Media Case Study 1: Starbucks
Starbucks and social media are a match made in heaven. Being one of the sensational brands online, they are stirring the social media world with their strong presence.
They brew the right content to elevate the experiences of their coffee lovers. But how do they nail marketing with perfection every single time? Let’s find out.
Starbucks in Numbers
Starbucks mastered the advertising transition from offline fame to online undertaking. They use each social media with a varied goal to target pitch-perfect reach. Drawing in more customers than ever before, they strike the right balance in content across multiple platforms.

Key Takeaways
Though not every company has a Starbucks budget to promote and spend lavishly on social media marketing, here are some quick takeaways that will undoubtedly help.
1. Chasing Trends
Be it any event, brands must take the advantage to showcase their viewpoints and opinions. Successful brands like Starbucks jump into the bandwagon and leave no stone unturned to make their voice count in the trending list.
Here’s one such social media campaign example from Starbucks.
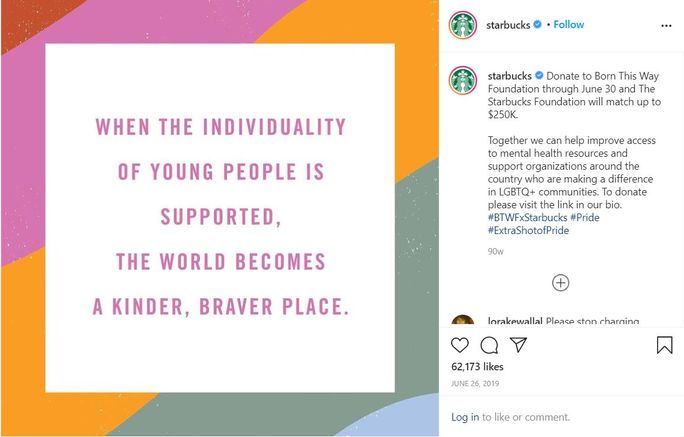
Starbucks is a firm believer in LGBTQ+ rights. When the pride wave surged, Starbucks came forward and reinstated its belief through the #ExtraShotOfPride campaign.
Starbucks joined hands with the Born This Way Foundation to raise $250K to support the LGBTQ+ community. Throughout the social media campaign, they shared quotes and stories of various Starbucks employees cherishing the pride spirit.
2. Less is More
Social media is not about quantity but quality. Starbucks follows the “less is more” principle to maintain the quality standards, even in the caption. Spamming followers’ feeds with constant posting is a big no-no. Starbucks shares 5-6 posts per week on Instagram and 3-4 weekly posts on Facebook .
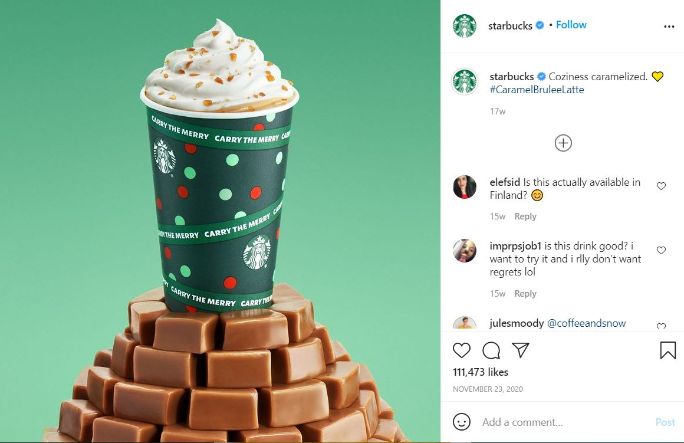
Creative and crisp! That’s what defines a Starbucks caption. This post with 111+k likes is no exception. Nothing is better than a minimalist post with a strong caption.
3. User Generated Content is the King
Ditch the worry of creating content every day when you can make use of user generated content. Starbucks makes sure to retweet or post its loyal customers’ content. User generated content postings starkly improve brand credibility.
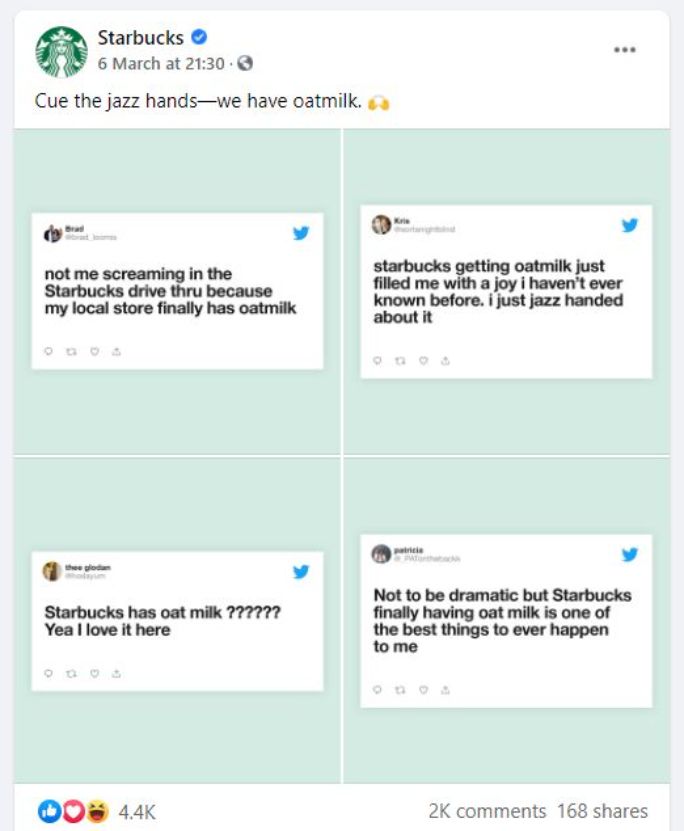
Look at this Facebook post made out of customers’ tweets. The new Oatmilk drink got the appreciation shower by some, and Starbucks couldn’t resist but share it with others. It saved them efforts on content brainstorming, plus they got free PR.
4. Building Rapport
Building rapport with the audience is an unsaid rule to brand fame. Social media has now taken the onus of dispensing quality service by aiding brands in prompting faster replies .
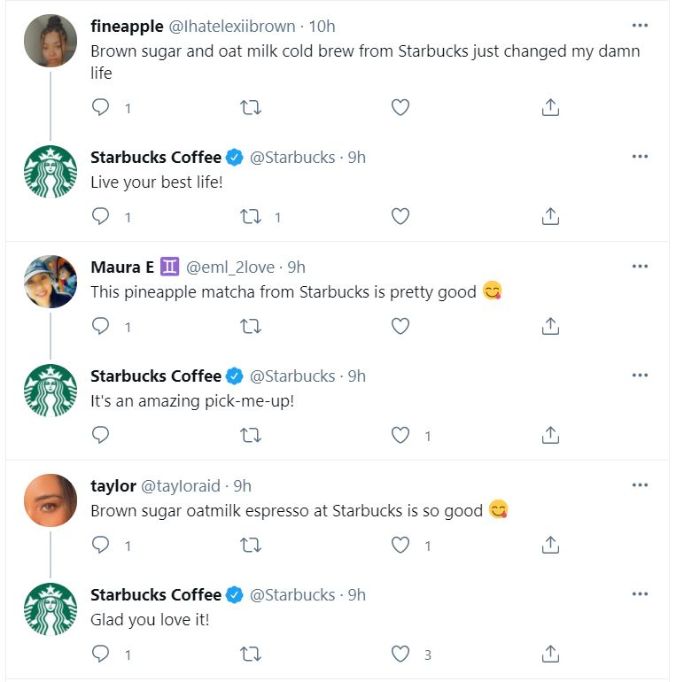
Starbucks is always on its toe to respond to customers actively solving concerns, expressing gratitude, or reposting. That kind of proactive service definitely deserves love and adoration.
5. Loads of campaigns
Starbucks is known for its innovative social media campaigns. Be it a new product launch or any festivity around the corner, Starbucks always turns up with a rewarding campaign.
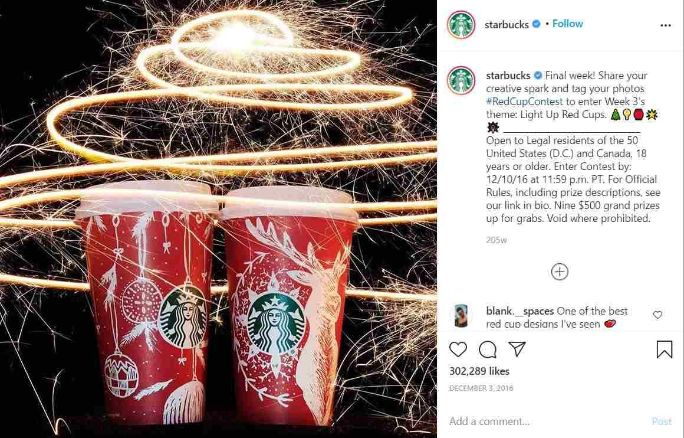
In this social media campaign example, Starbucks introduced #RedCupContest with prizes worth $4500 during Christmas of 2016. A new entry came every 14 seconds.
The grand total of entries was a whopping 40,000 in just two days. Indeed Starbucks knows how to get the most out of the festive fever.
6. Content mix
Last but not least, the content mix of Starbucks is inspiring. They create tailored content for every platform.
The official youtube channel of Starbucks comprises content in varied hues. From recipes to even series, Starbucks is the ultimate pioneer of experimenting.
Even on Instagram, they use all the features like Guides, Reels, and IGTV without affecting their eye-popping feed. Starbucks also follows the design consistency for its aesthetic content mix.
Starbucks has proved time and again to be a customer-centric brand with their unrelenting efforts.
Social Media Case Study 2: Ogilvy & Mather
Ogilvy & Mather needs no introduction. Founded by David Ogilvy, the ‘Father of Advertising’ in 1948, the agency continues the legacy of revolutionizing marketing long before the advent of social media.
The iconic agency helps several Fortune 500 companies and more make a massive impact on their audiences worldwide.
Ogilvy & Mather knows its game too well and never fails to astonish. Not just high-profile clients, Ogilvy nails its marketing with perfection every single time.
Keep on reading.
Ogilvy & Mather in Numbers
They use social media to target pitch-perfect reach. Drawing in more hype than ever before, they know how to strike the right balance and bring out emotions with their heart-warming campaigns.

Not every company has David Ogilvy’s legacy or even affluent clients to boast of, but here are some quick takeaways that will undoubtedly help you become a pro marketer.
1. Integrating Values
Ogilvy stands apart from the crowd, creating trends. They leave no stone unturned to communicate values.
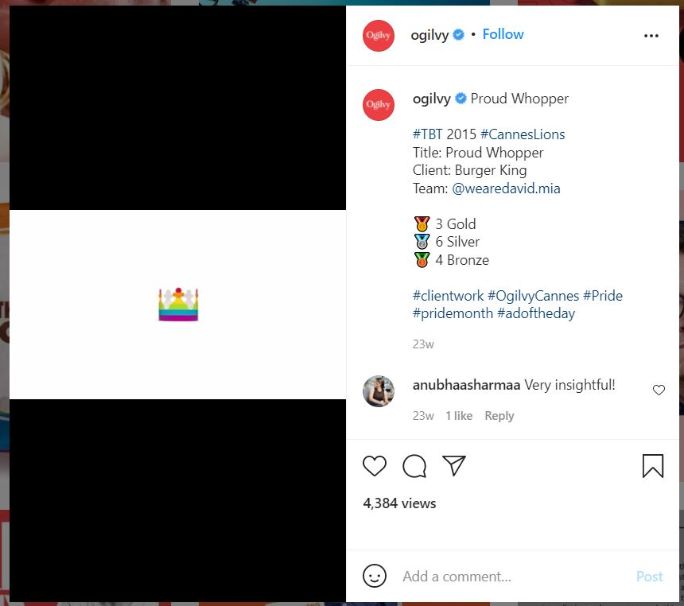
Proud Whopper is one such social media campaign by Ogilvy that was an instant hit on the internet. People were offered whoppers in rainbow-colored wrappers, with a note that said, “Everyone’s the same on the inside.” This was to reinstate the importance of LGTQ+ rights.
The campaign got 1.1 billion impressions, $21 million of earned media, 450,000 blog mentions, 7 million views, and became the #1 trending topic on Facebook and Twitter.
Ogilvy made a remarkable #Tbt video to honor this momentous event showcasing their supremacy in creating impactful campaigns.
2. Quality over Quantity
Ogilvy believes in the “ Quality supremacy ” to maintain their high standards, even in post captions.
Arbitrary posting isn’t a part of their agenda. They share 5-7 posts on Instagram and Facebook weekly.

Direct and very precise. That’s what defines an Ogilvy caption. This post is no exception. They have exhibited the success of their client work by describing the motive behind the campaign and sharing the ad they created for raising awareness.
3. Adding Credibility
Won awards? It’s time to boast! Because that’s the most authentic way of establishing trust among your clients. It bears proof of your excellence.

Look at this pinned Twitter post. Ogilvy won the Global Network of the Year by the very prestigious London International Awards. It also earned Regional Network of the year for Europe, the Middle East, Asia, and Europe.
What better than this to give its audience an idea about Ogilvy’s roaring success and undoubted potential?
4. Being Innovative
Building rapport with the audience is an unsaid rule to brand fame. And that’s why you need to tell stories. Social media has become an indispensable medium to spread your stories far and wide.

Ogilvy shares its historical tale of existence and how it has adapted to the challenges of the changing world. The team extensively talks about their adaptation to the latest trends to stay on top always.
5. Brainstorming Uniqueness
Being unique is what propels you on social media. People are always looking for brands that do something different from the herd. So your task each day is undeniably brainstorming unique content.
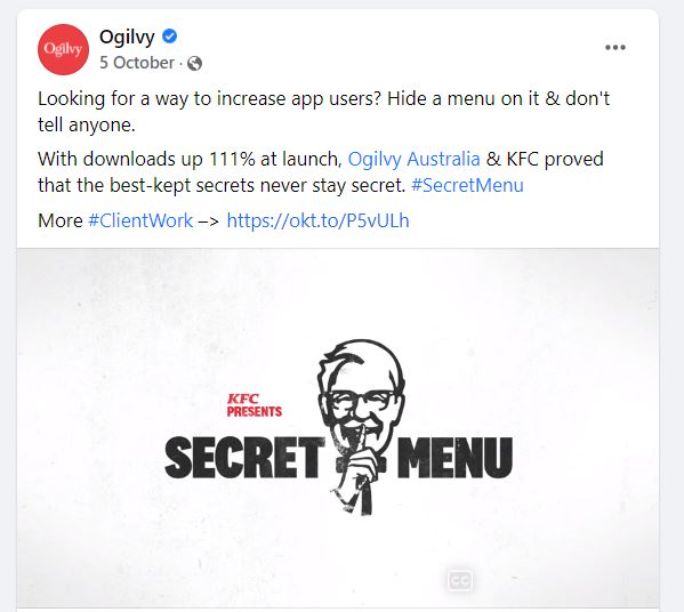
KFC wanted more of its customers to use its app. Well, Ogilvy and KFC decided to hide a secret menu in the app, which was a mass invitation for the download without being salesy at all. Results? Downloads up by 111% at launch!
6. Inspire Your Peeps
Inspiration is everywhere. But how do you channelize and mold it as per your brand guidelines? The renowned brands move their audience, filling them with a sense of realization. Who doesn’t seek validation? We all need quotes and inspiration to live by.

Ogilvy has dedicated its entire Pinterest profile to inspiration. The profile has numerous insightful infographics that encourage you to pursue marketing when your spirits run low. And that’s how it brings out the very essence of being the marketing leader: by inspiring its followers.
Got some good ideas for your branding? We have created templates and tools to help you execute them hassle-free. Tread on further and download the Trending Hashtag Kit for 2024 to get into action.
Social Media Case Study 3: PewDiePie
YouTube king with 111 Million subscribers on PewDiePie Channel, Felix Arvid Ulf Kjellberg, has defied all norms. One of the most prolific content creators of the decade, Felix was on the list of World’s 100 Most Influential People by Time Magazine in 2016.
Needless to say, he is still relevant to this day and has a massive following on social media. Not just for branding, the Swedish YouTuber leveraged social media to give himself a new identity and opened doors to fame and a successful career.
What was the cause of this extraordinary trajectory?
Let’s find out.
PewDiePie in Numbers
PewDiePie likes to keep his social media raw and unfiltered. That’s why subscribers love to have a glimpse of his everyday life and follow him on other social media platforms as well. Here’s a quick snapshot of that.

Felix took the early bird advantage and started creating content when it wasn’t even popular practice. We can’t go back in time, but we can definitely learn a lot from his social media success.
1. Start Now
If you are still skeptical about making the first move, then don’t. Stop waiting and experiment. It’s better late than never.
Social media is in favor of those who start early because then you create surplus content to hold your audience . You quench their thirst for more quality content.
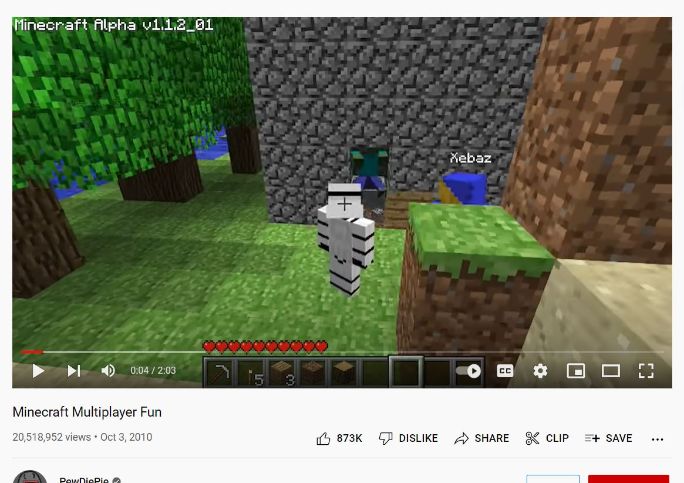
PewDiePie started creating videos in 2011 and live-streamed his gaming sessions with commentaries. It was something new and completely original. Ever since, he has continued to make thousands of videos that entertain his audience.
2. Gather Your Tribe
Being a content creator, PewDiePie knows his act of engaging his audience very well. He strives to build lasting connections and encourages two-way communication. As a result, his followers like to jump onto his exciting challenges.
Felix treasures his gaming community. He frequently asks his followers to take screenshots and turn them into funny memes . He gives them tasks to keep them engaged and amused .
3. Collaboration and Fundraising
Once you reach the stage and gain popularity, people want to see more of you with their favorite personalities. That’s what Felix does.
He collaborates with multiple YouTubers and brands and puts out exclusive content for his followers. He also goes for multiple fundraising campaigns to support vital causes and social wellbeing.
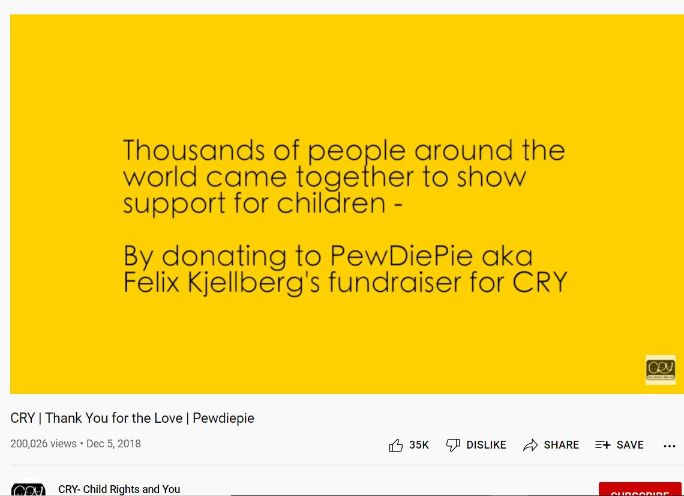
Here’s one such social media campaign example. PewDiePie supported the CRY foundation and raised $239000 in just one day to bring a positive impact for children in India. He thanked all for their contribution and taking active participation towards a noble cause.
4. Keep it Real
Felix likes to keep his content fluff-free. You get to witness raw emotions from an unfiltered life. This instantly appeals to the audience and makes the posts more relatable .
Apart from that, he also uses storytelling techniques to narrate his experiences, adding a very personalized touch to each of the videos.
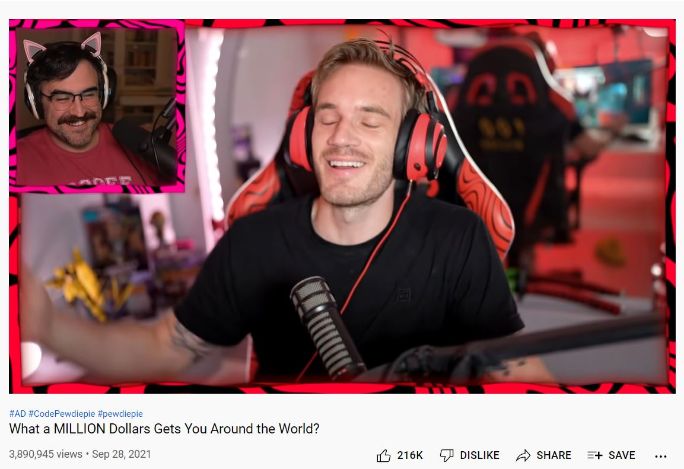
Here’s a video of Felix where he and Ken from CinnamonToastKen discuss what can be possibly done with a million dollars around the world. The topic is quite intriguing.
More than 3.8M people have watched it and 216K of them liked it as well, proving that you need not always sweat to create complex content. Even the simplest ones can make the cut.
How to Write a Social Media Marketing Case Study
Many small businesses struggle when it comes to social media marketing. But guess what? Small businesses can slay the competition with a powerful tool: the social media case study.
These social media case studies are success stories that prove your hustle is paying off. Here’s how to weave a case study that showcases your small business wins:
Building Your Brag Book
- Pick Your Perfect Project: Did a specific social media campaign drive a surge in sales? Highlight a product launch that went viral. Choose a project with impressive results you can showcase.
- DIY Interview: Don’t have a fancy marketing team? No worries! Record yourself talking about your challenges, goals, and the strategies that made a difference.
- Data Dive: Track down social media analytics! Look for growth in followers, website traffic driven by social media, or engagement metrics that show your efforts are working.
Now that you have all the ingredients, it’s time to cook a brilliant case study
Crafting Your Case Study
- Headline Hunt: Grab attention with a clear and concise headline. Mention your business name and a key achievement (e.g., “From 100 to 10,000 Followers: How We Grew Our Bakery’s Social Buzz”).
- Subheading Scoop: Briefly summarize your success story in a subheading, piquing the reader’s interest and highlighting key takeaways.
- The Business Struggle: Be honest about the challenges you faced before tackling social media. This will build trust and allow other small businesses to connect.
- DIY Social Strategies: Share the social media tactics you used, such as engaging content formats, community-building strategies, or influencer collaborations.
- Numbers Don’t Lie: Integrate data and visuals to support your story. Include charts showcasing follower growth or screenshots of top-performing posts.
- Simple & Straightforward: Use clear, concise language that’s easy to understand. Bullet points and short paragraphs make your case study digestible and showcase your professionalism.
Remember: Your social media case study is a chance to celebrate your achievements and build businesses. So, tell your story with pride, showcase your data-driven results, and watch your brand recognition soar
Social media campaigns are winning hearts on every platform. However, their success rates largely depend on your year-round presence. That’s why being consistent really does the trick.
We’re sure you must have learned a few things from the above-mentioned social media case studies .
To excel further at your social media marketing, use our FREE Trending Hashtag Kit and fill your calendar with everyday content ideas.
On downloading, you get 3000+ hashtags based on each day’s theme or occasion. You also get editable design templates for hassle-free social media posting.
What are you waiting for? Download now.
Frequently Asked Questions
🌟 How do I start a social media campaign idea?
Here’s how you can start a social media campaign:
- Finalize your campaign goals
- Brainstorm personas
- Pick a social media channel
- Research your competitors and audience
- Finalize an idea that’s in trend
- Promote the campaign
- Start the campaign
- Track the performance
🌟 What are the different types of social media campaigns?
Different types of social media campaigns are:
- Influencer Campaigns
- Hashtag Challenges
🌟 Why is social media campaign important?
Social media campaigns have various benefits:
- Boost traffic
- Better Conversions
- Cost-effective Marketing
- Lead Generation
- PR & Branding
- Loyal Followers
🌟 What are some of the best social media campaign tools?
Some of the best social media campaign tools are:
- SocialPilot
🌟 What are the top social media sites?
The top social media sites are:
About the Author
Sparsh Sadhu
Related Posts

Manage social media effortlessly.
- Trial Begins Immediately
- No CC Required
- Change Plans Anytime
- Cancel Anytime
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial
- © 2024 SocialPilot Technologies Inc. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy & GDPR
- Terms of Service
- Cookie Settings
- Follow us :

A Guide How to Create Social Media Case Studies that Convert (with Template)
As you already know, moving leads through the sales pipeline is no easy feat. In the world of digital marketing, it takes an average of 18-21 touchpoints to convert a lead. If you want any chance of pushing prospects down the funnel, you have to directly communicate the value of your product or service and one of the best ways to do this is with case studies.
Putting together a compelling social media marketing case study is one of the most powerful strategies for attracting future customers or digital agency clients. But it’s not easy. In this article, we’ll go over the ingredients of a winning case study and how to deliver said case study in the most effective way. We’ll also include a template that you can go by.
Let’s dive right in.
The importance of social media case studies
There’s a lot of content out there. Your potential customers are constantly bombarded with whitepapers, e-books, 10-step guides, newsletters and unpalatable sales hype. To get the attention of prospects today you have to demonstrate your product or service’s value, not just talk about it.
B2B buyers today don’t have time to interpret marketing messages that aren’t concise and relevant. That means that instead of aimlessly beating around the bush about how great your company is and how terrific your products are, you have to share the real-life experiences customers are having with you and your products.

Traditional marketing tactics don’t work anymore. We already know that. People nowadays drive their own buying decisions through online research and the importance of social proof cannot be understated.
About 57% of the customers will only use or buy a business service if it has at least 4 or five-star ratings. It should be noted however that reviews aren’t enough. In fact, 88% of consumers view ratings and reviews as a personal suggestion, not definitive proof of a product’s efficacy.
Reviews are all well and good but if you’re marketing B2B software or agency services, creating in-depth, data-driven case studies is the way to go. Case studies are extremely effective in the consideration stage of the buyer’s journey when they are actively comparing solutions and providers to solve a problem they’re experiencing.
As we already mentioned, your prospects are actively researching your products and there’s a 100% chance that they will stumble upon content from your competitors. Having relevant resources like case studies can cement your brand as an authority figure.
Now that you know why case studies are important it’s time to tackle the creation process.
The ingredients for a perfect case study
1. detailed and full of data .
Have you ever read a case study where a business states they “doubled traffic” for the customer in their case study, and wondered if that meant they went from 50 to 100 visits or 5,000 to 10,000 visits?
The point of a case study is to highlight the exact ways your product or service has helped a customer. The most compelling case studies hit prospects in the face with how amazing your customers’ results were, meaning you need to include numbers. Lots of them. Here’s an example:
Instead of saying “How client X got more sales thanks to us”, use “How client X increased their sales by X% in X days thanks to us”
This step may sound like a no-brainer but it’s absolutely essential to use relevant data when crafting your social media case study, especially if you run a digital agency. Include statistics like a decrease in ad spend, an improvement in engagement or increase in organic followers.
It’s important to remember that not everyone is as familiar with analytics and KPIs as you are, so break down the complicated sections into digestible bits that anyone can understand. Provide context as you go along so the data flows with the overall narrative of the case study.
Include some eye-catching visuals like picture proof or real-time dashboards so the reader can envision the positive potential of your product or service.
2. A complete, compelling story
Storytelling is a powerful marketing strategy that has stood the test of time. A great social media case study uses narrative techniques to put readers in the subject’s shoes.
When crafting your subject’s persona, be sure to include:
- Who is the sample customer, what do they do and why do they do it?
- What were the customer’s goals?
- What were the customer’s needs?
- How did you satisfy those needs and help the customer meet their goals?
As a rule of thumb, structure your case study by splitting up the main takeaways into three easy snippets: The challenge, the impact you had, and the outcome. This way you make sure that your case study isn’t all over the place and concludes with the reader being wowed.
Furthermore, you want to carry the story through and show how your business helps your customers long-term. You want your product or service to become a cornerstone of your customers’ workflow, something they simply can’t live without. When you conclude the “outcome” section of your case study, include ways customers can use your business further down the line.
When it comes to creating a compelling story, throwing in some emotional benefits alongside the hard numbers is absolutely necessary. Did your solution improve workplace morale, free up time or overall take a load off of your subject’s shoulders? Ask for a quote from the case study subject to make things more personal and relatable.
To really drive the narrative home, use quotes from your team as well. Any potential prospects will love discovering how your team overcame certain hurdles and delivered the end result. Interview your graphic designer or content manager and get them to break down the project into steps. This will help prospects further familiarize themselves with your organization and how your team thinks and operates, a connection that can help keep you top-of-mind when leads are ready to convert.
3. Compelling visuals
Using visuals and images to enrich the case study experience is a key element of a comprehensive marketing case study. But cramming in screenshots and haphazard designs is sure to have an adverse effect to what you were hoping for.
You want your case study to be a joy to read and as such it’s important to keep a few key rules in mind: – Write a catchy headline that gives a clear idea of what the case study is about
- Leave plenty of negative space when arranging your visual elements. You don’t want a busy mess of visuals that’s hard on the eyes
- Ensure that your visual elements compliment the data and written content of your case study.
- Keep your target audience in mind. What kind of creatives would they be drawn to? What fonts, visual cues and tones would keep them hooked? It goes without saying to add your company’s unique branding as well.
- The information you present should flow like a story. The graphic elements, along with the text should guide the reader’s eye through the study from beginning to end.
To spice things up, consider adding multimedia elements such as videos, PDFs, and images to make the case study more engaging.
When getting together the creative assets for your case study, be sure to include headshots of the actual customer, dashboards of results (graphs are great for visual storytelling) and screenshots of any social media posts that were created during the campaign (if relevant).
You can use tools like Kontentino’s social media a n a l y t i c s tool to implement custom metrics and create stunning reports.
Relatable to your target audience
If you’re at the point where you’re sharing success stories, chances are that you know who your ideal customer is. When crafting a case study, you want to write to the audience that you’re trying to attract. The readers of your study will most likely be very similar to the customers you’re writing about.
People who will read your case study most likely have a decent understanding of what your business is and what you can offer. They’re already somewhere in the middle of your funnel and as such it’s time to take advantage of personalization . Now you may need to create multiple case studies tailored toward different audiences, but it’s sure to pay off in the long run.
Reflect on the project you’re highlighting in the case study and think about who the customer was. What industry were they in? What kind of client were they? Were they visually-oriented? Did they appreciate heavy-handed analytical reports, a good story or a combination of the two?
These insights can help you nail down the written tone and show potential clients that you understand their specific needs, are comfortable in their niche and can apply strategies in accordance to their use-case.
Different ways to deliver a social media marketing case study
If you just created an amazing case study that’s sure to knock readers’ socks off, you want people to find it. This means populating every channel at your disposal with your content so your potential customers can’t miss it.
Youtube is the second-largest search engine in the world and the platform’s algorithm holds the potential to show your video to a whole new audience. While YouTube’s algorithm is often iffy, writing a catchy title, detailed description and creating an effective thumbnail are good ways to keep your video in the algorithm’s favor.
In addition, you’ll want to link your full case study in the comments and get viewers to land on your website.
- Social media
If you’re creating a social media case study, using social media to share said case study should be a no-brainer.
Break down the content of your case study into bite-sized chunks for Instagram or Facebook, post analytics dashboards from the study on Twitter and link the study in a LinkedIn post to spice up your profile. The shareable nature of social media may lead to your case study going further than just your own site.
- Embedded in other types of content
Case studies can also be embedded in other types of content like blog posts, newsletters, guides or ebooks. Go through your current pieces of relevant content and link to your case study to provide extra value.
3 winning social media marketing case study examples
Now that we’ve gone over the components of a winning social media case study, let’s check out some real world examples.
1. “How ERA Belgium Provides Great Content for Franchise Businesses with Kontentino,” by Kontentino

A thing to note regarding this case study is how Kontentino not only highlighted the impressive data but also how the product helped solve a core pain point for ERA Belgium’s franchises .
Highlighted in the middle of the case study is a bold quote from the client that helps solidify Kontentino’s KontentBase product as a must-have tool for franchises. When creating your own case study, consider your product and who’s needs it addresses. Align your customer quotes and data and results reports to match exactly what your target audience is looking for.
The Konetino case study also includes a CTA at the end so any potential prospects could directly contact the support team.
2. “How an SEO Agency Helped an Artisan Bakery Increase Organic Traffic by 214%,” is a very well written case study by Semrush

This comprehensive case study by Semrush is a perfect example of pinpoint narrative structure and proper formatting. The study flows like a well-written story and guides the reader through the subjects, conflicts and resolutions without a hitch. The tasteful addition of dashboards and bullet points ties the case study up perfectly.
3. “How Good Dye Young Increased Their Monthly E-commerce Revenue by 305%,” an impressive storytelling case study by Mailchimp

This case study by MailChimp is full of personality and storytelling. While MailChimp did include impressive numbers, the centerpiece of this case study is the people. The subjects in the case study are referenced casually by their first names, their journey is explored in-depth and there’s no shortage of quotes from them. The imaging MailChimp uses only emphasizes the human side of the relationship between them and the customer.
Keeping you on track with your social media case study
So now you’ve got a solid idea of what a comprehensive case study should include and you’ve seen the techniques we’ve covered in action. Now it’s time to go over a full template to ensure you stay on track when creating your awesome social media case study.
Social media marketing case study template
Outline: Case Study Title
Customer: Customer’s full name
Company: Company’s name
Industry: The industry the customer operates in (if applicable)
Video: Link to a video version (if applicable)
Author: Author’s name
Case study title
A short introduction of the customer.
Be sure to highlight:
- The customer’s name and a little bit about them.
- Why you and your customer were a perfect fit
- The key successes your customer had after working with you
Introduce your customer
In this section, provide a more in-depth overview of your customer. If it’s an individual, explain the person’s background in the context of your product/service. If it’s a business, talk about the company’s background, industry and any recent successes or milestones they have had.
Describe the problem
Explain the challenge or opportunity your customer faced before they did business with you. This could be either a reactive reason (i.e. the customer had an issue that needed to be addressed) or a proactive reason (i.e. there was an untapped potential that was unleashed by working with your business).
Why (Customer Name) Chose (Your Company)
In this section, speak about the decision process of your customer. Speak about how they discovered you, your possible competition and what made them ultimately decide to do business with you.
How (Your Company) Responded
Here, explain what happened once your business started working with your customer. What was addressed first, and why? How did your customer feel about working with you in the early days?
The Results
In closing, speak to the results your customer saw after working with you. This section can be supported by statements, quotes, visuals, graphs, and metrics. Whatever you decide to include, be sure it illustrates how much of an impact your company made on your customer.
Call-to-Action
Use this section to move your readers down the funnel. Add a CTA that encourages readers to either join your newsletter or get in touch with your sales team.
Related articles

13 of the Best Sprout Social Alternatives for 2024

10 Must-Try CoSchedule Alternatives for Your Business

Social Media Audit: Boost Your Strategy Now [Free Template]

837k+ scheduled posts in the past year by users just like you.

132 Social Media Case Studies – Successes and Failures
Sharing is caring!

That is such a short-sighted and limiting point of view.
Social Media Marketing is not sales – but it can help to sell things. And personally, I have to admit that I have several times bought something, booked an event or took part in something because I saw people (friends and acquaintances OR strangers) talking about it on social media. At the same time, I have never bought anything a salesperson tried to sell me on the phone. So yes, you actually can sell me things on Social Media. And I am not the only person.
Click To Tweet
Before you read on - we have various resources that show you exactly how to use social networks to gain massive traffic and leads. For instance, check out the following:
But limiting Social Media Marketing success or failure to the statement: For sales, you need to pick up the phone is simply b%llshi$t. You can use social media for lead generation to fill your sales funnel – but you can also use Social Media for totally different aspects of business like customer management, brand awareness, reputation management, audience building, website traffic and many other things your business can profit from.
Many people do it. I do it and have done so for other projects in the past. The honest answer to “Social Media is not working” is: It is obviously not working the way you are doing it. Try different tactics, learn, adjust, measure, optimize, try something else, try harder, and never stop at “You cannot sell on Social Media!”
So the answer is, yes you can make money with Social Media, but it is not working the same way for each and every business or situation.
Most of the time, if you do not have success with getting ROI out of your Social Media activities, it is not Social Media, which is not working, it is you who are doing something wrong or have the wrong social media strategy.

Social Media cannot simply be done by following a recipe step by step.
That can only get you so far.
In Social Media often the best approaches are already cold coffee when they become common knowledge, and everyone tries to hop on the train. You need to make assumptions, test your assumption, measure success and adjust your marketing strategy according to your results.
Hey, before you read on - we have in various FREE in-depth guides on similar topics that you can download. For this post, check out:
Social media cannot be learned by the book.
But one thing is certain: To shout out sales messages in Social Media is most likely going to fail to give you any return.
What people want and expect from their Social Media activity is so diverse, and there are many Social Media case studies in multiple situations.
Join our free Email Course to learn how to start your social media marketing journey:
All the basics in 4 Days, 4 Emails

Instead of selecting a handful of case studies for this article, I decided to provide you with a list of resources with multiple case studies about how businesses are successfully using social media for their business success.
1. 15 B2B Case Studies for Proving Social Media ROI
Rob Petersen looks at the special situation of using social media platforms to market to businesses instead of consumers. He provides 15 examples ranging from CISCO and Demand Base to LinkedIn and SAP.
2. 50 Social Media Case Studies you Should Bookmark
SimplyZesty looks at a variety of use cases for the different social networks like Facebook, Twitter, Youtube, Pinterest, Instagram and more.
3. IBM Turns its Sales Staff Social Media Savvy
I love this example as it shows how sales and Social Media Marketing can work hand in hand. Contrary to the above-mentioned comment on our blog, IBM realized that even sales can profit from Social Media with cost-effective leads.
4. 11 Examples of Killer B2B Content Marketing Campaigns Including ROI
Lee Odden of TopRank Marketing focuses more on the Content Marketing side and provides 11 B2B Content Marketing case studies.
5. B2B Social Media Case Study: How I made $47 million from my B2B blog
This is a personal success story from AT&T’s experience and success with a content strategy.
6. How ASOS Use Social Media [CASE STUDY]
The story of how the fashion and beauty store ASOS has become Britain’s largest online retailer with the aid of Social Media for ecommerce and online marketing.
7. 5 Outstanding Social Media Campaigns
The examples include the story from a hairdresser who increased sales by 400% without spending a penny. It is not only the big companies who can profit from Social Media.
8. 3 Small Businesses That Found Social Media Success
The examples range from customer service, brand perception to social engagement.
9. The Best Social Media Campaigns of 2014
These marketing campaigns are more about creating more engagement, generate more fans and increase loyalty amongst audience members for the brand and not so much about direct ROI. Still, they explain how to get it right.
It is not only the social media success stories you can learn from. Sometimes you can learn from other peoples’ failures at least as much as from their successes. Here are some social media case studies on failed social media activities. The failures tend to be on a smaller scale, resulting from bad communication and reactions turning the Social Media conversation in an unwanted direction. It is rare that a company admits to a complete campaign and a ton of money gone down the drain. Still, even from these smaller examples, we all can learn our lessons for our behavior in Social Media:
1. Social Media Fails: The Worst Case Studies of 2012
The examples are campaign focused and include examples from McDonald’s and Toyota.
2. 19 horrific social media fails from the first half of 2014
These are examples of how you should not communicate in Social Media and showcase some ways you should not copy on how to jump onto trending hashtags and events in Social Media.
3. 5 Big Social Media Fails of 2013 (and What We Learned)

4. Top 12 Social Media Marketing Mishaps
These are examples of what can happen to you and how a social media Sh$tstorm can brew up. It makes sense to read some of these and talk about possible reactions before any of this kind happens to you. Simply be prepared.
Final Words
I hope you find some useful marketing tips in my little collection of Social Media case studies – or at least, have some fun browsing through these examples. I find them encouraging as they show the variety of cases where Social Media can help your business. And they show how many humans are in Social Media, making it a place where things can go wrong and go well. It is up to you to leverage the full power of social networks and turn the tide.
If you are looking for even more case studies here you go:
Digital Marketing Case Studies
Content Marketing Case Studies
Instagram Marketing Case Studies
Twitter Marketing Case Studies
Forget Failure. Get the simple process to success:
We show you the exact steps we took to grow our first business from 0 to 500k page views per month with social media and how we got 50k visitors per month from social media to this blog after 6 months. We show you the exact steps you need to take to see traffic success.
You get easy-to-follow step-by-step action plans and you will see the first results after a couple of days. Check out “ The Social Traffic Code ” – there is a special offer for you!
“The Social Ms blog and books have shown us great possibilities of growing on Twitter and via online media. In addition, they actually respond to email reactions. Practicing what they preach gives them the credibility edge.” Guy Pardon, Atomikos
Don’t miss out – make a decision for success!

Susanna Gebauer
- Imprint/Impressum
- Privacy Policy
- Podcast – Marketing in Minutes
- Get a Coaching Call
- Courses and Books

Case Studies , Social Media Marketing
Case Study: A Social Media Marketing Success Story
July 22, 2021

Not that long ago, people mainly used social media to see the latest pictures of their nieces and nephews and stay up to date with what their friends were doing. But, more and more, it’s become a place where small business growth happens.
These days, people are spending a lot of their time online on social media. According to Forbes , in 2020, Americans spent an average of 1,300 hours on social media, with an average of 58 minutes per day on Facebook alone. And, since smart marketing is about being visible where your customer base spends their time, social media is the place to be.
From building brand awareness to driving sales, the right social media marketing strategy can be a powerful tool for small businesses.
Wholesale distributor drives visibility and conversions with social media marketing
One wholesale distributor, with the help of their Marketing Team , learned just how valuable the right social media marketing strategy can be.

Over a three-month period, their social media strategy led to more than 100k impressions, thousands of clicks and hundreds of conversions.

Although ads and content marketing also played a role in their success, their conversion paths show that many of their conversions originated on a social network.

Compared to the previous three-month period, their social strategy resulted in a21% increase in impressions, a 20% increase in clicks and engagements, and a massive increase in conversions of almost 153%.
How did they do it?

Their social media strategy consisted of two parts — social media advertising and social media management (organic social posts).
Social media advertising

They focused the majority of their ad budget on Facebook and Instagram advertising, with campaigns aimed at capturing new leads, driving conversions and reconnecting with users who had previously clicked their ads or visited their website with retargeting ads.

Social media management

They complemented their social advertising strategy by posting consistently on their Facebook and Instagram timelines.

Social media is more than just about staying connected with friends and family. It’s become one of the top places people go to discover new brands and businesses.
Not all social media marketing strategies are made equal, but the right social media strategy — with a potent mix of social ads and organic posts — can lead to big results.
Build, manage and grow your small business with Marketing 360®
Marketing 360® is a singular platform that offers everything you need to build a modern, professional website , launch ads on popular channels , manage all of your contacts, projects and deals , schedule out social media posts , monitor your SEO performance and so much more, plus the marketing team you need to grow your business .
See our plans and pricing.
Account M29238 Screenshots taken on 7/22/21
*Results are based on past client performance. Individual account performance may vary. Results are not guaranteed.
Get Plans and Pricing Below

Case Studies , Reputation Management
Case Study: Property Management Uses Reputation Management to Learn About Customer Satisfaction

Social Media Marketing
Tips to Improve Social Media Marketing for Dentists

How to Use Instagram Reels for Your Cleaning Company

Case Studies
Case Study: Furniture Store Sees Conversion Rates Skyrocket

8 Social Media Ideas for Pest Control Companies

Social Media Paid Ads: Which Platform Offers the Best ROI?
Get the know-how to get ahead.
Get business, marketing and sales tips written by experienced industry practitioners. 100% free. Cancel anytime.
- Email address *
OST – B2B Social Media Agency
A Leading Global B2B Social Media Agency
- Meet our Team
- Join our Team
- Corporate Social Responsibility
B2B Influencer Marketing
- Campaigns & Content
Social Strategy
Paid Social Advertising
- Global B2B Social Media
Community Management
Creative Studio
Social Executive Communications
- Event Activation
- B2B Lead Generation

5 outstanding social media marketing case studies
Do you read social media marketing case studies for inspiration? It’s always a good idea to benchmark against your competitors or pinch ideas from them, but it’s also worth looking at success stories from the biggest brands out there. You might not have their budget, but you can always gain inspiration from their campaigns.
Here are five of the best brands on social and what I think you can learn from them:
1.Mercedes Benz – Repeated, successful social media marketing campaigns
Mercedes Benz seem to win every time with their social media campaigns. The one that stands out to me was back in 2013 when they created what I still believe to be one of the best Instagram marketing campaigns to date. Mercedes wanted to reach out to the younger audience so they hired five top Instagram photographers to each take the wheel of a new Mercedes CLA. Whoever got the most likes got to keep the car – so they all really worked at it!
By the end of the campaign, Mercedes has received:
- 87,000,000 organic Instagram impressions
- 2,000,000 Instagram likes
- 150 new marketing assets (stunning photos)
What lessons can you learn from this? Could you put your followers up for a challenge and make it into a competition or campaign?
- Can you do a competition that gets people trying out your product first?
- Think about your target audience. What is a prize they would value?
- Like Mercedes you could recruit bloggers/influencers via social media and get them blogging about your service or product. Whoever receives the most engagement wins .
2. Dove – Connecting with their target audience
Is it just me or do all the Dove marketing campaigns make you cry? If you’ve seen their Real Beauty sketches campaign, you’ll know what I’m talking about. Dove’s goal is to make women feel good about themselves. They know their target market and create content that tells a story that women can relate to.
Today I am… pic.twitter.com/VoAf2wRdwa — Dove UK & Ireland (@DoveUK) February 19, 2016
Dove did some research and found that 80 percent of women came across negative chatter on social media. Dove’s goal was to change that and make social media a more positive experience. As a result, Dove teamed up with Twitter and built a tool to launch the #SpeakBeautiful Effect, that breaks down which body- related words people use the most and when negative chatter appears during the day.
According to Dove, women were inspired by their message.
- #SpeakBeautiful was used more than 168,000 times
- Drove 800 million social media impressions of the campaign
Dove know their audience. Knowing your audience is the only way you will engage with them. The best way for this is creating personas. Knowing what life stage they are in, if they’re employed, what their interests are etc. will certainly help you when creating content. Then think about linking your audience to your brand values in order to create something just as successful as Dove’s campaign.
3. Nutella – Incredible content that makes you salivate
Each post makes you want to eat Nutella. There are a lot of people (including me) who take photos of their food before they eat it. Nutella does the same and it works. Nutella isn’t afraid to be fun and creative with different ingredients. Nutella is just a chocolate spread yet they manage to have fun with it. Do you, or could you, have a bit more fun with your brand?
Here are some ideas for having fun with your brand:
- Are you on different social media channels? If you’re B2B you might not think that Instagram is for you, but it can be a great way to demonstrate your brand values by telling a story. Fedex is a great example of this, showing images of their trucks always on the move. This tells a story that they are always delivering and that is the key message we take away.
- Key influencers/bloggers can be a great way to different types of content and to see how they have fun with your brand (if this is new to you, read our post on the rise of the social media influencer ).
- Instead of posting behind-the-scenes photos at your head office, can you encourage your followers to share their experiences with your brand? Maybe host an event or go out and meet them.
Take your #breakfast bread pudding to the next level with #Nutella ! 😉 pic.twitter.com/k0ko5Nm9iX — Nutella (@NutellaGlobal) May 5, 2016
4. Oreo – Smart content planning and timely delivery
Oreo is another brand that is known for their creative social media marketing. They must have a big design team to produce their content, but it works! They are consistent with their branding and manage to catch onto real time events. We all remember when the lights went out at the Super Bowl and during the half hour blackout Oreo tweeted out:
Power out? No problem. pic.twitter.com/dnQ7pOgC — OREO Cookie (@Oreo) February 4, 2013
This was retweeted over 15,000 times. Are you thinking outside the box about your brand? Plan ahead for events coming up that you might be able to jump on to.
Do you plan your social media content out? If you’re in B2B and don’t currently create content read here for some B2B content marketing tips to help you get started, or check out our B2B marketing strategy tips ebook for 2021.
It’s always a good idea to prepare content ahead of time. If you can schedule content on a monthly basis – perfect, but if not bi-weekly is great. That way you can check what events are coming up and plan content around them. This gives you time for any ad hoc creative to be done, such as jumping on real-time events like the Oreo blackout example above.
5. Airbnb – Stunning imagery and UGC
What might look like a visual travel blog, Airbnb ’ s content attracts fans with their visually compelling posts. On Instagram, they post user-generated photos from its hosts and guests. The content embraces their new campaign of ‘Don’t just go there, Live there’ which is captured through real photography. Each post receives high engagement, between 3,000 and 14,000 Instagram likes.

This is a great example of thinking slightly outside the box. Airbnb is all about accommodation. They don’t just post images of the inside of people’s homes. Seeing the culture and images of places all over the world comes with the experience of where you stay and that’s what connects with people. Think about your brand: are you just posting about the product/ service itself? Why not tell your followers a story instead?
Thanks for reading. I hope by reading these five social media marketing case studies it has spiked some inspiration! If you need any help with your social media advertising , influencer marketing , or other aspects of your social media strategy, feel free to contact us .
Should you upgrade to a LinkedIn Premium Company Page?
What is the linkedin algorithm and why is it important, get in touch.
Fancy an informal chat about your social media? Email us and we’ll get straight back.

We are a multi-award-winning social media agency that provides high-quality social media, content marketing and social advertising services for a global client-base.
Our Services
Campaigns & Content
Global Social Media
Contact Info
Unit 7 Bennell Court West Street Comberton Cambridge CB23 7EN UK
Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy
16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing
Updated: September 08, 2020
Published: July 30, 2020
When you're thinking about investing in a product or service, what's the first thing you do?

Usually, it’s one or both of the following: You'll likely ask your friends whether they've tried the product or service, and if they have, whether they would recommend it. You'll also probably do some online research to see what others are saying about said product or service. Nowadays, 90% of consumers used the internet to find a local business in the last year , and 82% of consumers read online reviews. This shows that the majority of people are looking to peers to make a purchasing decision. Most customers know that a little online research could spare them from a bad experience and poor investment of your budget.

What Is a Marketing Case Study?
A case study is the analysis of a particular instance (or "case") of something to demonstrate quantifiable results as a result of the application of something. In marketing, case studies are used as social proof — to provide buyers with the context to determine whether they're making a good choice.
A marketing case study aims to persuade that a process, product, or service can solve a problem. Why? Because it has done so in the past. By including the quantitative and qualitative outcomes of the study, it appeals to logic while painting a picture of what success looks like for the buyer. Both of which can be powerful motivators and objection removers.
Why Use Case Studies?
In essence, case studies are an invaluable asset when it comes to establishing proof that what you're offering is valuable and of good quality.
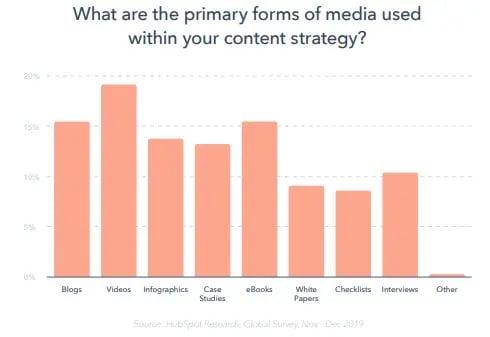
According to HubSpot's State of Marketing Report 2020 , 13% of marketers name case studies as one of the primary forms of media used within their content strategy. This makes them the fifth most popular type of content, outshined only by visual content, blogs, and ebooks.
Okay, so you know case studies work. The question is, how do they work? And how can you squeeze the most value out of them?
When to Use a Case Study
Here are the ways you can market your case studies to get the most out of them.
As a Marketing or Sales Asset
1. use a case study template to create pdfs for email or downloads . .
Do not underestimate the value of providing social proof at just the right time in order to add value and earn their business. Case studies are extremely effective in the consideration stage of the buyer's journey when they are actively comparing solutions and providers to solve a problem they're experiencing.
For this reason, case studies in an independent PDF format can be helpful in both marketing and sales. Marketers can use these PDFs as downloads in web content or email campaigns. Sales reps can utilize these assets in demonstrations, in a follow-up, or to overcome objections.
The easiest way to create PDF case studies is by using a case study template . Doing so can decrease the amount of time you spend creating and designing your case study without sacrificing aesthetics. In addition, you can ensure that all your case studies follow a similar branded format.
We've created a great case study template (and kit!) that's already locked and loaded for you to use. All you have to do is input your own text and change the fonts and colors to fit your brand. You can download it here .
On Your Website
2. have a dedicated case studies page..
You should have a webpage exclusively for housing your case studies. Whether you call this page "Case Studies, "Success Studies," or "Examples of Our Work," be sure it's easy for visitors to find.
Structure on that page is key: Initial challenges are clear for each case, as well as the goals, process, and results.
Get Inspired: Google’s Think With Google is an example of a really well structured case study page. The copy is engaging, as are the goals, approach, and results.
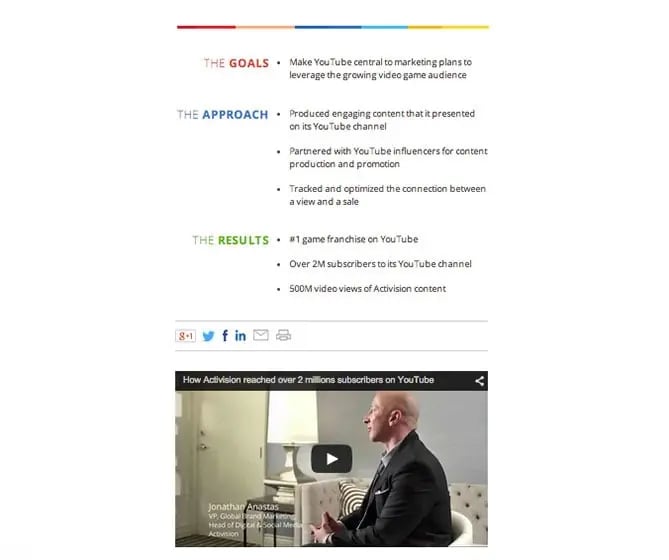
3. Put case studies on your home page.
Give website visitors every chance you can to stumble upon evidence of happy customers. Your home page is the perfect place to do this.
There are a number of ways you can include case studies on your homepage. Here are a few examples:
- Customer quotes/testimonials
- A call-to-action (CTA) to view specific case studies
- A slide-in CTA that links to a case study
- A CTA leading to your case studies page
Get Inspired: Theresumator.com incorporates testimonials onto their homepage to strengthen their value proposition.
Bonus Tip: Get personal.
Marketing gurus across the world agree that personalised marketing is the future . You can make your case studies more powerful if you find ways to make them “match” the website visitors that are important to you.
People react to familiarity -- for instance, presenting someone from London with a case study from New York may not resonate as well as if you displayed a case study from the U.K. Or you could choose to tailor case studies by industry or company size to the visitor. At HubSpot, we call this "smart content."
Get Inspired: To help explain smart content, have a look at the example below. Here, we wanted to test whether including testimonials on landing pages influenced conversion rates in the U.K. The landing page on the left is the default landing page shown to visitors from non-U.K. IP addresses. For the landing page on the right, we used smart content to show testimonials to visitors coming from U.K. IP addresses.
4. Implement slide-in CTAs.
Pop-ups have a reputation for being annoying, but there are ways to implement that that won't irk your website visitors. These CTAs don't have to be huge, glaring pop-ups -- instead, relevant but discreet slide-in CTAs can work really well.
For example, why not test out a slide-in CTA on one of your product pages, with a link to a case study that profiles a customer who's seen great results using that product?
Get Inspired: If you need some help on creating sliders for your website, check out this tutorial on creating slide-in CTAs .
5. Write blog posts about your case studies.
Once you publish a case study, the next logical step would be to write a blog post about it to expose your audience to it. The trick is to write about the case study in a way that identifies with your audience’s needs. So rather than titling your post “Company X: A Case Study," you might write about a specific hurdle, issue, or challenge the company overcame, and then use that company's case study to illustrate how the issues were addressed. It's important not to center the blog post around your company, product, or service -- instead, the customer’s challenges and how they were overcome should take centre stage.
For example, if we had a case study that showed how one customer generated twice as many leads as a result of our marketing automation tool, our blog post might be something along the lines of: "How to Double Lead Flow With Marketing Automation [Case Study]." The blog post would then comprise of a mix of stats, practical tips, as well as some illustrative examples from our case study.
Get Inspired: Check out this great example of a blog post from Moz , titled "How to Build Links to Your Blog – A Case Study."
6. Create videos from case studies.
Internet services are improving all the time, and as a result, people are consuming more and more video content. Prospects could be more likely to watch a video than they are to read a lengthy case study. If you have the budget, creating videos of your case studies is a really powerful way to communicate your value proposition.
Get Inspired: Check out one of our many video testimonials for some ideas on how to approach your own videos.
7. Use case studies on relevant landing pages.
Once you complete a case study, you'll have a bank of quotes and results you can pull from. Including quotes on product pages is especially interesting. If website visitors are reading your product pages, they are in a "consideration" mindset, meaning they are actively researching your products, perhaps with an intent to buy. Having customer quotes placed strategically on these pages is a great way to push them over the line and further down the funnel.
These quotes should be measured, results-based snippets, such as, “XX resulted in a 70% increase in blog subscribers in less an 6 months” rather than, “We are proud to be customers of XX, they really look after us."
Get Inspired: I really like the way HR Software company Workday incorporates video and testimonials into its solutions pages.
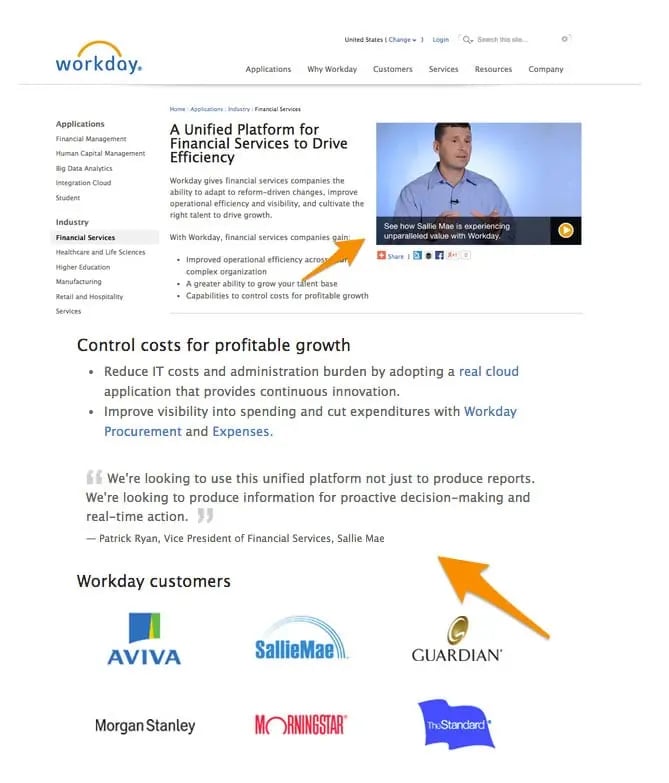
Off Your Website
8. post about case studies on social media..
Case studies make for perfect social sharing material. Here are a few examples of how you can leverage them on social:
- Share a link to a case study and tag the customer in the post. The trick here is to post your case studies in a way that attracts the right people to click through, rather than just a generic message like, “New Case Study ->> LINK." Make sure your status communicates clearly the challenge that was overcome or the goal that was achieved. It's also wise to include the main stats associated with the case study; for example, "2x lead flow," "125% increase in X," and so on.
- Update your cover image on Twitter/Facebook showing a happy customer. Our social media cover photo templates should help you with this!
- Add your case study to your list of publications on LinkedIn.
- Share your case studies in relevant LinkedIn Groups.
- Target your new case studies to relevant people on Facebook using dark posts. ( Learn about dark posts here. )
Get Inspired: MaRS Discovery District posts case studies on Twitter to push people towards a desired action.
9. Use case studies in your email marketing.
Case studies are particularly suited to email marketing when you have an industry-segmentable list. For example, if you have a case study from a client in the insurance industry, emailing your case study to your base of insurance-related contacts can be a really relevant addition to a lead nurturing campaign.
Case studies can also be very effective when used in product-specific lead nurture workflows in reactivating opportunities that have gone cold. They can be useful for re-engaging leads that have gone quiet and who were looking at specific areas of your product that the case study relates to.
Get Inspired: It's important that your lead nurture workflow content includes the appropriate content for where prospects are in the sales cycle. If you need help on how to do this, check out our post on how to map lead nurturing content to each stage in sales cycle .
Pro tip: When sending emails, don't forget about the impact a good email signature can make. Create your own using our free Email Signature Generator .
10. Incorporate case studies into your newsletters.
This idea is as good for your client relations as it is for gaining the attention of your prospects. Customers and clients love feeling as though they're part of a community. It’s human nature. Prospects warm to companies that look after their customers; companies whose customers are happy and proud to be part of something. Also, whether we are willing to admit it or not, people love to show off!
Get Inspired: Newsletters become stale over time. Give your newsletters a new lease of life with our guide on how to create newsletters that don't suck .
11. Equip your sales team with case studies.
Tailored content has become increasingly important to sales reps as they look to provide value on the sales call. It's estimated that consumers go through 70-90% of the buyer's journey before contacting a vendor. This means that the consumer is more knowledgeable than ever before. Sales reps no longer need to spend an entire call talking about the features and benefits. Sales has become more complex, and reps now need to be armed with content that addresses each stage of the buyer’s process. Case studies can be really useful when it comes to showing prospects how successful other people within a similar industry has benefited from your product or service.
Get Inspired: Case studies are just one type of content that helps your sales team sell. They don't always work by themselves, though. Check out our list of content types that help sales close more deals .
12. Sneak a case study into your email signature.
Include a link to a recent case study in your email signature. This is particularly useful for salespeople. Here's what my email signature looks like:

Get Inspired: Did you know that there are lots more ways you can use your email signature to support your marketing? Here are 10 clever suggestions for how you can do this.
13. Use case studies in training.
Having customer case studies is an invaluable asset to have when onboarding new employees. It aids developing their buy-in, belief in, and understanding of your offering.
Get Inspired: Have you completed our Inbound Certification course yet? During our classes, we use case studies to show how inbound marketing is applied in real life.
In Lead-Gen Content
14. include case studies in your lead gen efforts..
There are a number of offers you can create based off of your case studies, in the form of ebooks, templates, and more. For example you could put together an ebook titled “A step-by-step guide to reaching 10,000 blog subscribers in 3 months…just like XX did.” You could create a more in-depth version of the case study with access to detailed statistics as an offer. (And don’t forget, you can also u se quotes and statistics from case studies on the landing page promoting the ebook, which adds credibility and could increase your conversion rates.) Or, you could create a template based on your customer's approach to success.
Get Inspired: If you think you need to be an awesome designer put together beautiful ebooks, think again. Create ebooks easily using these customisable ebook templates .
You can also use case studies to frame webinars that document how to be successful with X. Using case studies in webinars is great middle-of-the-funnel content and can really help move your leads further down the funnel towards becoming sales qualified leads.
Get Inspired: Webinars are really effective as part of a lead nurturing workflow. Make sure your next webinar is spot on by following these simple webinar tips.
15. Create a bank of evergreen presentations.
It’s important to build up a bank of evergreen content that employees across your organisation can use during presentations or demos. Case studies are perfect for this.
Put together a few slides on the highlights of the case study to stir people’s interest, and then make them available to your sales and customer-facing teams. It's helpful if the marketer who created the presentation is the one who presents it to anyone who might use them in the future. This ensures they can explain the presentation clearly and answer any questions that might arise.
Get Inspired: What to create presentations people want to use? Here's a list of tools to make your presentations great.
16. Create SlideShares based on case studies.
Following on from a few short slides, you could also put together a more detailed presentation of the case study and upload it to SlideShare. After all, not only is SlideShare SEO-friendly (because Google indexes each presentation), but there is a huge pre-existing audience on SlideShare of over 60 million users you can tap into. SlideShare presentations are also easy to embed and share, and allow you to capture leads directly from the slides via a lead capture form.
Get Inspired: Want to generate more leads with SlideShare, but not sure how to get started? Check out this blog post .
Now that you understand the value of a marketing case study and the different ways that they can be used in your content marketing (and even sales) strategy, your next step is to think about what would convince your target audience to do business with you.
Have you recently accomplished something big for a client? Do you have a process or product with demonstrable results? What do your potential clients hope that you'll do for them?
The answers to those questions will help you craft compelling content for your case study. Then, all that's left is putting it into your audience's hands in formats they want to consume.

Editor's note: This post was originally published in January 2015 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![case study of media 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/most%20popular%20types%20of%20content.jpg)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]
![case study of media How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]

28 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
![case study of media What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Template Lists
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design
15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
By Alice Corner , Jan 12, 2023

Have you ever bought something — within the last 10 years or so — without reading its reviews or without a recommendation or prior experience of using it?
If the answer is no — or at least, rarely — you get my point.
Positive reviews matter for selling to regular customers, and for B2B or SaaS businesses, detailed case studies are important too.
Wondering how to craft a compelling case study ? No worries—I’ve got you covered with 15 marketing case study templates , helpful tips, and examples to ensure your case study converts effectively.
Click to jump ahead:
- What is a Case Study?
Business Case Study Examples
Simple case study examples.
- Marketing Case Study Examples
Sales Case Study Examples
- Case Study FAQs
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth, detailed analysis of a specific real-world situation. For example, a case study can be about an individual, group, event, organization, or phenomenon. The purpose of a case study is to understand its complexities and gain insights into a particular instance or situation.
In the context of a business, however, case studies take customer success stories and explore how they use your product to help them achieve their business goals.

As well as being valuable marketing tools , case studies are a good way to evaluate your product as it allows you to objectively examine how others are using it.
It’s also a good way to interview your customers about why they work with you.
Related: What is a Case Study? [+6 Types of Case Studies]
Marketing Case Study Template
A marketing case study showcases how your product or services helped potential clients achieve their business goals. You can also create case studies of internal, successful marketing projects. A marketing case study typically includes:
- Company background and history
- The challenge
- How you helped
- Specific actions taken
- Visuals or Data
- Client testimonials
Here’s an example of a marketing case study template:

Whether you’re a B2B or B2C company, business case studies can be a powerful resource to help with your sales, marketing, and even internal departmental awareness.
Business and business management case studies should encompass strategic insights alongside anecdotal and qualitative findings, like in the business case study examples below.
Conduct a B2B case study by researching the company holistically
When it comes to writing a case study, make sure you approach the company holistically and analyze everything from their social media to their sales.
Think about every avenue your product or service has been of use to your case study company, and ask them about the impact this has had on their wider company goals.

In business case study examples like the one above, we can see that the company has been thought about holistically simply by the use of icons.
By combining social media icons with icons that show in-person communication we know that this is a well-researched and thorough case study.
This case study report example could also be used within an annual or end-of-year report.
Highlight the key takeaway from your marketing case study
To create a compelling case study, identify the key takeaways from your research. Use catchy language to sum up this information in a sentence, and present this sentence at the top of your page.
This is “at a glance” information and it allows people to gain a top-level understanding of the content immediately.

You can use a large, bold, contrasting font to help this information stand out from the page and provide interest.
Learn how to choose fonts effectively with our Venngage guide and once you’ve done that.
Upload your fonts and brand colors to Venngage using the My Brand Kit tool and see them automatically applied to your designs.
The heading is the ideal place to put the most impactful information, as this is the first thing that people will read.
In this example, the stat of “Increase[d] lead quality by 90%” is used as the header. It makes customers want to read more to find out how exactly lead quality was increased by such a massive amount.

If you’re conducting an in-person interview, you could highlight a direct quote or insight provided by your interview subject.
Pick out a catchy sentence or phrase, or the key piece of information your interview subject provided and use that as a way to draw a potential customer in.
Use charts to visualize data in your business case studies
Charts are an excellent way to visualize data and to bring statistics and information to life. Charts make information easier to understand and to illustrate trends or patterns.
Making charts is even easier with Venngage.
In this consulting case study example, we can see that a chart has been used to demonstrate the difference in lead value within the Lead Elves case study.
Adding a chart here helps break up the information and add visual value to the case study.

Using charts in your case study can also be useful if you’re creating a project management case study.
You could use a Gantt chart or a project timeline to show how you have managed the project successfully.

Use direct quotes to build trust in your marketing case study
To add an extra layer of authenticity you can include a direct quote from your customer within your case study.
According to research from Nielsen , 92% of people will trust a recommendation from a peer and 70% trust recommendations even if they’re from somebody they don’t know.

So if you have a customer or client who can’t stop singing your praises, make sure you get a direct quote from them and include it in your case study.
You can either lift part of the conversation or interview, or you can specifically request a quote. Make sure to ask for permission before using the quote.

This design uses a bright contrasting speech bubble to show that it includes a direct quote, and helps the quote stand out from the rest of the text.
This will help draw the customer’s attention directly to the quote, in turn influencing them to use your product or service.
Less is often more, and this is especially true when it comes to creating designs. Whilst you want to create a professional-looking, well-written and design case study – there’s no need to overcomplicate things.
These simple case study examples show that smart clean designs and informative content can be an effective way to showcase your successes.
Use colors and fonts to create a professional-looking case study
Business case studies shouldn’t be boring. In fact, they should be beautifully and professionally designed.
This means the normal rules of design apply. Use fonts, colors, and icons to create an interesting and visually appealing case study.
In this case study example, we can see how multiple fonts have been used to help differentiate between the headers and content, as well as complementary colors and eye-catching icons.

Marketing case study examples
Marketing case studies are incredibly useful for showing your marketing successes. Every successful marketing campaign relies on influencing a consumer’s behavior, and a great case study can be a great way to spotlight your biggest wins.
In the marketing case study examples below, a variety of designs and techniques to create impactful and effective case studies.
Show off impressive results with a bold marketing case study
Case studies are meant to show off your successes, so make sure you feature your positive results prominently. Using bold and bright colors as well as contrasting shapes, large bold fonts, and simple icons is a great way to highlight your wins.
In well-written case study examples like the one below, the big wins are highlighted on the second page with a bright orange color and are highlighted in circles.
Making the important data stand out is especially important when attracting a prospective customer with marketing case studies.

Use a simple but clear layout in your case study
Using a simple layout in your case study can be incredibly effective, like in the example of a case study below.
Keeping a clean white background, and using slim lines to help separate the sections is an easy way to format your case study.
Making the information clear helps draw attention to the important results, and it helps improve the accessibility of the design .
Business case study examples like this would sit nicely within a larger report, with a consistent layout throughout.

Use visuals and icons to create an engaging and branded business case study
Nobody wants to read pages and pages of text — and that’s why Venngage wants to help you communicate your ideas visually.
Using icons, graphics, photos, or patterns helps create a much more engaging design.
With this Blue Cap case study icons, colors, and impactful pattern designs have been used to create an engaging design that catches your eye.

Use a monochromatic color palette to create a professional and clean case study
Let your research shine by using a monochromatic and minimalistic color palette.
By sticking to one color, and leaving lots of blank space you can ensure your design doesn’t distract a potential customer from your case study content.

In this case study on Polygon Media, the design is simple and professional, and the layout allows the prospective customer to follow the flow of information.
The gradient effect on the left-hand column helps break up the white background and adds an interesting visual effect.

Did you know you can generate an accessible color palette with Venngage? Try our free accessible color palette generator today and create a case study that delivers and looks pleasant to the eye:
Add long term goals in your case study
When creating a case study it’s a great idea to look at both the short term and the long term goals of the company to gain the best understanding possible of the insights they provide.
Short-term goals will be what the company or person hopes to achieve in the next few months, and long-term goals are what the company hopes to achieve in the next few years.
Check out this modern pattern design example of a case study below:

In this case study example, the short and long-term goals are clearly distinguished by light blue boxes and placed side by side so that they are easy to compare.

Use a strong introductory paragraph to outline the overall strategy and goals before outlining the specific short-term and long-term goals to help with clarity.
This strategy can also be handy when creating a consulting case study.
Use data to make concrete points about your sales and successes
When conducting any sort of research stats, facts, and figures are like gold dust (aka, really valuable).
Being able to quantify your findings is important to help understand the information fully. Saying sales increased 10% is much more effective than saying sales increased.
While sales dashboards generally tend it make it all about the numbers and charts, in sales case study examples, like this one, the key data and findings can be presented with icons. This contributes to the potential customer’s better understanding of the report.
They can clearly comprehend the information and it shows that the case study has been well researched.

Use emotive, persuasive, or action based language in your marketing case study
Create a compelling case study by using emotive, persuasive and action-based language when customizing your case study template.

In this well-written case study example, we can see that phrases such as “Results that Speak Volumes” and “Drive Sales” have been used.
Using persuasive language like you would in a blog post. It helps inspire potential customers to take action now.

Keep your potential customers in mind when creating a customer case study for marketing
82% of marketers use case studies in their marketing because it’s such an effective tool to help quickly gain customers’ trust and to showcase the potential of your product.
Why are case studies such an important tool in content marketing?
By writing a case study you’re telling potential customers that they can trust you because you’re showing them that other people do.
Not only that, but if you have a SaaS product, business case studies are a great way to show how other people are effectively using your product in their company.
In this case study, Network is demonstrating how their product has been used by Vortex Co. with great success; instantly showing other potential customers that their tool works and is worth using.

Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Case studies are particularly effective as a sales technique.
A sales case study is like an extended customer testimonial, not only sharing opinions of your product – but showcasing the results you helped your customer achieve.
Make impactful statistics pop in your sales case study
Writing a case study doesn’t mean using text as the only medium for sharing results.
You should use icons to highlight areas of your research that are particularly interesting or relevant, like in this example of a case study:

Icons are a great way to help summarize information quickly and can act as visual cues to help draw the customer’s attention to certain areas of the page.
In some of the business case study examples above, icons are used to represent the impressive areas of growth and are presented in a way that grabs your attention.
Use high contrast shapes and colors to draw attention to key information in your sales case study
Help the key information stand out within your case study by using high contrast shapes and colors.
Use a complementary or contrasting color, or use a shape such as a rectangle or a circle for maximum impact.

This design has used dark blue rectangles to help separate the information and make it easier to read.
Coupled with icons and strong statistics, this information stands out on the page and is easily digestible and retainable for a potential customer.

Case Study Examples Summary
Once you have created your case study, it’s best practice to update your examples on a regular basis to include up-to-date statistics, data, and information.
You should update your business case study examples often if you are sharing them on your website .
It’s also important that your case study sits within your brand guidelines – find out how Venngage’s My Brand Kit tool can help you create consistently branded case study templates.
Case studies are important marketing tools – but they shouldn’t be the only tool in your toolbox. Content marketing is also a valuable way to earn consumer trust.

Case Study FAQ
Why should you write a case study.
Case studies are an effective marketing technique to engage potential customers and help build trust.
By producing case studies featuring your current clients or customers, you are showcasing how your tool or product can be used. You’re also showing that other people endorse your product.
In addition to being a good way to gather positive testimonials from existing customers , business case studies are good educational resources and can be shared amongst your company or team, and used as a reference for future projects.
How should you write a case study?
To create a great case study, you should think strategically. The first step, before starting your case study research, is to think about what you aim to learn or what you aim to prove.
You might be aiming to learn how a company makes sales or develops a new product. If this is the case, base your questions around this.
You can learn more about writing a case study from our extensive guide.
Related: How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
Some good questions you could ask would be:
- Why do you use our tool or service?
- How often do you use our tool or service?
- What does the process of using our product look like to you?
- If our product didn’t exist, what would you be doing instead?
- What is the number one benefit you’ve found from using our tool?
You might also enjoy:
- 12 Essential Consulting Templates For Marketing, Planning and Branding
- Best Marketing Strategies for Consultants and Freelancers in 2019 [Study + Infographic]

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 5 Social Media Case Study Templates with Examples and Samples

Abhishek Tuteja
In the bustling digital cosmos, where fortunes are forged and brands rise like constellations, social media stands as the celestial stage for modern success stories. Harnessing the mercurial power of this boundless realm demands a masterful blend of artistry and data-driven strategy. Enter the world of social media case study PPT templates—the alchemical blueprint behind groundbreaking campaigns.
Picture this: A small artisanal chocolate company, nestled in a quaint corner of a bustling city, dared to dream beyond its brick-and-mortar confines. By harnessing the potential of the best social media presentations, they transcended geographical barriers and reached chocolate connoisseurs across the globe. Their mouthwatering visuals and tantalizing tales of cocoa craftsmanship set hearts aflutter, igniting a frenzy of shares and retweets that skyrocketed their humble brand into a worldwide sensation.
Needless to say, the power of a captivating presentation cannot be underestimated. A well-crafted case study PPT (PowerPoint) template serves as the storyteller's canvas—a medium that elevates a mundane marketing report into a captivating saga of triumph.
With 4.48 billion global social media users awaiting your company’s narrative, embark on a voyage of discovery with us in this piece of writing.
Join us as we unlock the vault of the 5 best social media case studies PPT templates, empowering you to shape your odyssey of digital conquest.
Template 1- Business Case Study Summary on Social Media Marketing Template
Presenting our content-ready template designed to provide an alluring backdrop for any subject matter. Elevate your presentations and exude an air of professionalism, making you appear as a seasoned presentation virtuoso. Within this set of slides, you will find a comprehensive exploration of crucial topics, including the well-thought-out Approach, invaluable Recommendations, and prevailing Challenges faced in the realm of social media marketing. Instilled with versatility, this PowerPoint presentation is readily available for instant download, ensuring the utmost convenience and efficiency in customization, tailored to your specific needs.
Are you ready to seize the opportunity to impress and captivate with this remarkable PowerPoint template? Download now!

Download this template here
Template 2- Social Media Business Case Study Template
Here is another captivating and highly effective template to help you outline actionable strategies for your company. This well-crafted template strikes the perfect balance between clarity and concise expression, providing an explicit and visually engaging showcase for your transportation marketing case study. Tailored for entrepreneurs seeking to articulate their objectives to their esteemed employees, this professionally designed transportation marketing PPT one-pager acts as a guiding compass, enabling you to demonstrate the best value delivery to your cherished customers. You can illustrate crucial campaign details, celebrity branding metrics, target market insights, and the campaign's resounding success, exemplified by the desired percentage numbers. Incorporating essential testing content and transcending the boundaries of mobile optimization to also encompass desktop, this PPT template empowers you to deliver a gripping presentation that will undoubtedly captivate your audience's attention. Download this template now and make your mark in the world of transportation marketing.

Download here
Template 3- Case Study for Social Media Marketing Proposal Template
Introducing this premium PPT slide - a powerful and professionally designed presentation that is sure to leave a lasting impact on your audience. With a seamless one-stage process, this template covers critical aspects such as Technology, Communication, Planning, Strategy, and Marketing, all meticulously laid out to convey your proposal with utmost clarity and precision. This ready to use PowerPoint presentation offers unparalleled flexibility, empowering you to customize every element to match your unique requirements. Further, you can embrace creativity by replacing or removing icons, tailoring each slide to perfectly align with your message - a vast collection of icons awaits you to select the most fitting ones. Download this masterpiece now to captivate your audience and make a remarkable impression. Leave no room for mediocrity; instead, impress your stakeholders and win hearts with this actionable PowerPoint slide.

Template 4- Bi-fold Social Media Business Case Study Template
Showcasing this remarkable PPT template to help you discover how successful brands strategize, engage, and convert their audience effectively. Dive into real-world examples, gaining valuable insights into content creation, posting schedules, and audience targeting using this PowerPoint slide. Uncover the secrets behind viral campaigns, follower growth, and brand loyalty. Whether you're a seasoned marketer or a budding entrepreneur, this template empowers you to fine-tune your social media approach and stay ahead of the competition. Elevate your digital presence, boost your ROI, and harness the full impact of social media through data-driven analysis and actionable takeaways provided in this invaluable resource.

Download the PPT Template here
Template 5- Case Study for Celebrity Template
Last, but not least, leverage the power of social media for celebrity branding with our specialized case study template. Gain exclusive access to real-world examples of successful collaborations between influencers and celebrities, exploring how they authentically connect with their audience and amplify brand reach. Uncover the strategies behind engaging content, influencer partnerships, and audience segmentation that elevate a celebrity's digital presence. This template offers in-depth analysis of campaigns that have driven massive follower growth, increased brand loyalty, and boosted product endorsements. Whether you're a brand looking to partner with a celebrity or a public figure aiming to optimize your social media impact, this template is your ultimate guide to effective celebrity branding.
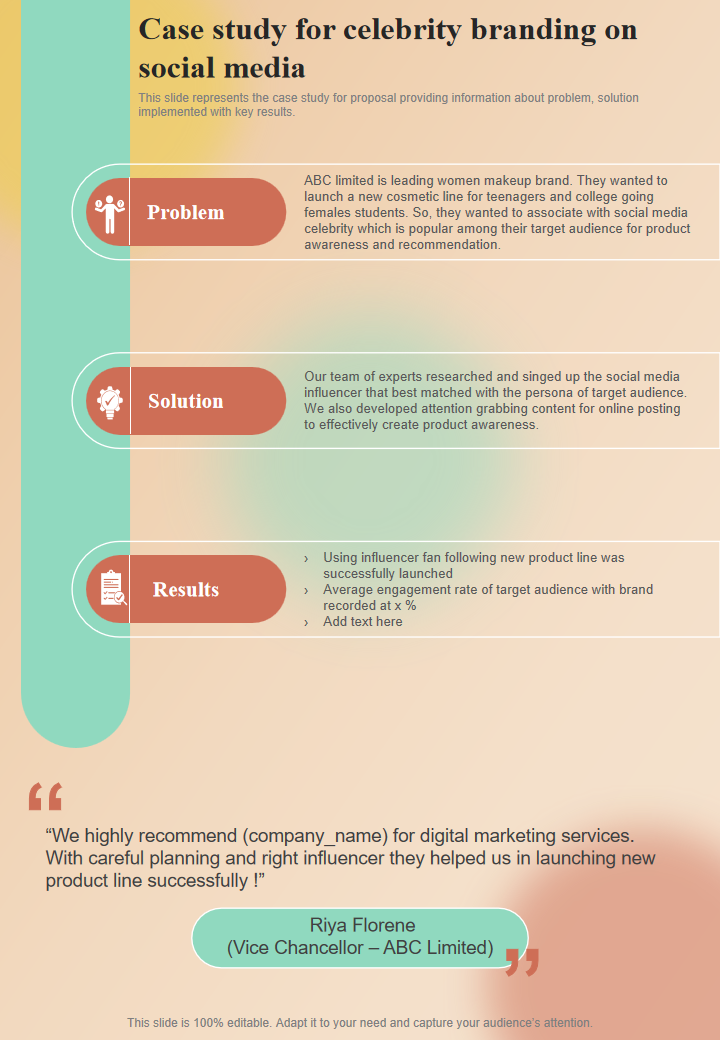
Time to Elevate Your Presentation Game
Armed with the best social media case study PPT templates, your presentations are bound to transcend the norms of ordinary storytelling and ascend to captivating visual journeys that leave an indelible mark on your audience. Download any or all of these templates and harness the power of creativity and customization.
Step into the spotlight of presentation excellence and ignite curiosity, leaving your viewers yearning for more. The stage is set, and the templates await - unleash your creativity and captivate the world with the best social media case study PPT templates.
And if you are looking to rule the digital realm, then you may check out our comprehensive guide of 10 Best Digital Marketing Templates . These will help you elevate your online presence for sure.
For managers and entrepreneurs, we have resources that will help you cast away the work ethics myths and lead you toward enlightenment. Do take a look at our well-crafted list of Must-Have Corporate Ethics Case Study Examples with Templates and Samples .
FAQs on Social Media Case Study
What is a social media case study.
A social media case study is an in-depth analysis of a real-world social media marketing campaign or branding effort. It examines how brands, influencers, or individuals leveraged platforms to achieve specific objectives. These studies showcase strategies, challenges faced, and outcomes, encompassing goals, target audience, content, influencers, metrics, and impact on brand awareness, acquisition, and conversion rates. Valuable resources for marketers and businesses seeking social media optimization, case studies provide insights into effective tactics and best practices. By learning from successful campaigns, individuals can glean valuable knowledge to enhance their own social media endeavors and capitalize on the power of these platforms.
How do you introduce a case study on social media?
Introducing a case study on social media involves setting the stage, providing context, and outlining the purpose and objectives of the study. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do it effectively:
- Start with a compelling title : Begin by giving your case study a clear and attention-grabbing title that highlights the key focus of the study.
- Provide a brief overview : In a few sentences, introduce the subject of the case study, whether it's brand, company, influencer, or celebrity involved in a social media campaign.
- State the objectives : Clearly outline the goals and objectives of the case study. What specific aspects of social media marketing or branding are being analyzed?
- Explain the importance : Highlight why this particular case study is relevant and significant in the context of social media marketing, industry trends, or specific challenges faced.
- Set the context : Briefly explain the background of the subject and the social media platforms they use. Mention any notable achievements or challenges they have encountered in their social media journey.
- Mention the methodology : Provide a brief overview of the research methodology used in the case study. This may include data sources, analysis tools, and any primary research conducted.
- Tease the results : Give a glimpse of the key findings or outcomes of the case study to generate interest and keep readers engaged.
- Discuss the structure : Briefly outline the sections or key areas covered in the case study, such as campaign strategies, content creation, influencer partnerships, etc.
- Emphasize actionable insights : Mention that the case study will offer valuable insights and actionable takeaways that can be applied to other social media strategies.
- Conclude with an invitation : Encourage readers to dive into the case study to learn more and explore the successful social media tactics employed by the subject.
Related posts:
- [Updated 2023] 10 Editable Templates to Infiltrate the Influencer Marketing Maze
- Top 10 Social Media Analytics Templates To Simplify the Analysis!
- Top 10 Product Launching and Marketing Playbook Templates with Samples and Examples
- Must-Have Social Media Business Plan Templates with Examples and Samples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Must-Have Budget Schedule Templates with Examples and Samples

Must-Have Digital Transformation Case Study Examples with Templates and Samples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

Advertisement
Social Media Case Studies

28 Nov 2023

Explore more content
- B2B social media case studies
- Social Media Management
- Social Media Marketing

B2B Social Media Marketing Case Studies to Inspire You
Written by Anna Sonnenberg
Published Apr. 18 2022

Table of Contents
Managing social media for business-to-business (B2B) companies or agency clients often seems more challenging than marketing directly to consumers. From choosing the most effective channels to deciding on the right tone of voice to creating compelling content, B2B social media marketing requires a unique approach.
So how can you successfully market a B2B company using channels like Facebook , LinkedIn, and Twitter? Check out three B2B social media case studies to inspire your strategy—no matter what stage of the sales funnel you need to target.
What Is B2B Social Media Marketing?
Strictly speaking, social media marketing for B2B companies isn’t too different from promoting business-to-consumer (B2C) organizations. Both types of companies use a variety of social channels to publish content, engage customers, and aim to get conversions. And both B2B and B2C companies tend to leverage a mix of paid and organic social media.
Even so, as you’ll see in the B2B case studies, social media marketing strategies require a few important adjustments for targeting a B2B buyer.
Let’s look at a few of the key differences.
Social channels
There’s no definitive list of social channels that B2B organizations can or can’t use. Choosing the right channels for your company is generally a case-by-case situation that requires audience and market research.
But some social channels naturally work better for B2B businesses because of their user base and native tools. For years, LinkedIn and Facebook have stood out as the most popular B2B marketing channels . However, many businesses also use Twitter to connect with customers and YouTube for long-form video.
Target customers
When marketing their products and services, B2C companies generally speak directly to individual customers. These target customers can make their own decisions for themselves or their families.
In contrast, B2B companies target other businesses. To get buy-in from companies or departments, marketers typically have to target decision makers with various levels of authority.
Tone of voice
Don’t assume that B2B marketing has to sound stiff or formal. After all, B2B marketing material often targets chief executive officers (CEOs) and other powerful decision makers.
But there’s no rule that B2B content has to sound stuffy—or that it can’t include emojis. Instead, B2B content should use a brand voice that fits your company’s image and values. And keep in mind that conversational content is almost always the best way to connect with the human decision makers you’re targeting.
Content tools
As a social media manager, you can access the same set of tools whether you’re working with a B2B or a B2C company. However, some tools are much more valuable for B2B marketers because of the sales cycles and decision-making processes involved.
Some of these B2B content tools include the following:
- Lead magnets that encourage prospects to provide their contact details in exchange for a high-value asset. For example, you may offer case studies or white papers.
- Webinars and product demos that require prospects to register to access exclusive knowledge or a closer look at your product.
- Native lead forms that allow prospects to request more information about your products and services without leaving the social media platform.
Use Cases for B2B Social Media Marketing
Now you’ve got an idea of how B2B content often looks and sounds. But what are the most effective ways to use it? Before we delve into social media B2B case studies, let’s look at how to align this content with your sales funnel.
Boost awareness
Is your business new to the market or seeking to expand its customer base? In either case, increasing awareness is essential for growth.
With awareness-focused social content, you can introduce your business to new products. You can also put your products and services on potential customers’ radar. Over time, you can highlight features and benefits to make prospects aware of the value your business offers.

Take a look at the ClickUp Facebook ad above, which is great for brand awareness. The eye-catching creative uses a succinct tagline to tell prospects exactly what the app does. The subheading lists three key aspects of the productivity app, so people instantly understand how it works.
The caption uses a CTA that encourages prospects to use the app to boost productivity. And it seals the deal with a pretty impressive takeaway: The app can help you “save one day a week.”
Establish trust
Most B2B companies aren’t selling frivolous items. Instead, the products and services that these companies offer can make a measurable impact on their customers—helping them work more efficiently, produce better results, reach higher goals, and grow their own businesses.
That’s why establishing trust should be a key part of any B2B company’s marketing strategy. You can use channels like Facebook and LinkedIn to share social proof, publish thought leadership, and communicate your company values.

The Outreach Facebook ad above seamlessly handles credibility. The creative boldly confirms the company’s status as an industry leader. The caption quotes a well-known third-party source to communicate the company’s position in the industry, effectively building on preexisting trust.
The ad points to a third-party report prospects can download learn more about Outreach. By offering this report in exchange for prospects’ contact details, the company can begin collecting and qualifying leads.
Generate leads
Once prospects trust your business and understand what it offers, they may be ready to take the next step. When you turn prospects into qualified leads, you can start nurturing your relationship with more targeted content.
Social channels offer countless opportunities for organic lead generation . After all, you can easily post links to lead magnets and webinars on your social profiles. But these channels are particularly effective at paid lead generation. For example, channels like LinkedIn and Facebook offer high-performing native lead ads.

Above, the Facebook ad by IT Glue offers a helpful checklist to prospects seeking to automate IT processes. This simple lead magnet is great for helping prospects solve a problem while learning more about the company.
Below, the Miva, Inc. LinkedIn ad takes a similar approach. In exchange for prospects’ contact information, it offers a downloadable five-step assessment designed to guide people through problem-solving.
Convert prospects
In many cases, you can use social media content to give prospects that final nudge from qualified lead to happy customer. Depending on the nature of your product or service, linking to a free trial, a paid subscription, an e-commerce page, or a sales page could drive conversions.
When you want prospects to convert, you need to think about creative ways to incentivize them. Free add-ons, limited-time offers, and limited-quantity discounts can all prompt qualified leads to take that final step.

Above, the Cardata LinkedIn ad captures prospects’ attention with a promise to streamline vehicle reimbursement calculations. The copy and creative both feature social proof that inspires trust, and the CTA prompts prospects to give the app a try.
Below, the Shopify Facebook ad catches prospects’ eyes with a promise to help scale their businesses. The caption lists several features e-commerce business owners are likely to need, and the creative prompts them to get started with a free trial.

Support customers
Once you convert customers, you can use social media to help them maximize the value from their purchase. It’s a good idea to think beyond customer support and brainstorm ways to help customers use your product or service more effectively.
For example, you can share advanced tips to help customers get more out of your product or service—and pique the interest of prospects at the same time. You might also discuss your loyalty program or spotlight longtime clients. These tactics allow you to give clients the accolades they deserve while also turning them into advocates for your business.
Above, the LinkedIn ad by Elementor targets people who are already familiar with the company’s website builder. By introducing a new product, the company can upsell to existing customers and deepen the relationship.
Three B2B Social Media Case Studies to Inspire You
Wondering how real-life B2B companies have applied these tactics on social media? Take a look at three B2B social media marketing case studies to get ideas for your business’s own strategy.
1. Turface Athletics and Profile Golf
Turface Athletics and Profile Golf, two brands under the Profile Products umbrella, worked with Elevation Marketing to address social media engagement for their B2B profiles. Take a look at what they achieved.
Both brands are well-established in their respective niches. Turface Athletics provides field maintenance products for athletic fields, and Profile Golf specializes in golf course maintenance solutions.
Despite their strong positions in their respective markets, both brands were experiencing low engagement across social media channels. Although the brands published social media content consistently, they did so from a single company profile on a limited range of channels.
As a result, the B2B company struggled to increase awareness or drive consideration among new potential customers. That meant they weren’t leveraging social media marketing effectively or using available tools to reach business goals successfully.
First, the agency conducted market research to get up to speed on industry trends and competitor strategies. The agency also performed a social media audit to review past performance and assess best practices for positioning the brands going forward.
After the preliminary research and audit phase, the agency determined that the brands would benefit most from a full-scale social media strategy across major channels. The agency proposed to plan engaging content designed to attract the brands’ target audiences.
In addition, the agency proposed to create distinct brand presences for Turface Athletics and Profile Golf on Twitter and Facebook. Doing so would allow the two brands to differentiate themselves, reach more relevant audiences, and (periodically) share or distribute each other’s content to increase reach and engagement.
The agency also designed an influencer marketing program to improve the brands’ Instagram presence. Ideally, partnering with influencers would give the brands access to more lifestyle photography while improving brand loyalty.
Over a six-month period, both brands saw impressive growth across all social media channels. The Turface Athletics Facebook page saw a 268% increase in engagement and a 44% increase in impressions, which suggests that the content truly resonated with the target audience. The strategy also drove 74% more web visits, a significant increase to the brand’s web traffic.
During the same period, content for the new Facebook page and Twitter profile for Profile Golf generated nearly 35,000 impressions. It also drives a 253% increase in web visitors.
Ultimately, building out new B2B social profiles and attracting followers can be resource intensive. But this case study shows that creating content that truly resonates can build brands and reach marketing goals effectively.
Semrush, a software as a service (SaaS) company specializing in search engine optimization (SEO) tools, worked with Walker Sands to improve its Twitter presence.
As a long-established brand in the SEO space, Semrush already had a presence on Twitter. However, the SaaS company had struggled to differentiate itself from its many competitors. As a result, brand recognition, product awareness, and conversions weren’t as high as they could be.
By partnering with Walker Sands, Semrush aimed to improve engagement and increase brand loyalty. The SaaS company also wanted to set itself apart from competitors.
First, the agency used a combination of social listening and competitive research to pinpoint industry trends and understand how similar brands were using Twitter. Using this research, the agency recommended that Semrush adjust its brand guidelines for this social channel, essentially creating a separate, humor-focused persona for its Twitter profile.
To fine-tune this new brand voice, the agency developed Twitter content based on product and industry topics and recurring themes. The agency balanced content that promoted Semrush products with tweets that appealed to the brand’s audience of experienced digital marketers.
In addition, the agency used social listening tools to monitor and chime in on trending topics. This tactic allowed Semrush to join viral conversations and discuss relevant news in a timely fashion—further increasing the brand’s reach.
Semrush began to realize results quickly. In the first month, the social media marketing plan generated over 250,000 impressions and nearly 18,000 engagements. The engagement rate exceeded 7%, demonstrating how well the content resonated with the target audience.
Although Semrush is in a crowded space with numerous well-established competitors, the brand was able to distinguish itself on Twitter. As a result, Semrush improved brand sentiment and gained share of voice.
3. Collective Data
Collective Data, a fleet management SaaS company, worked with Sculpt to streamline its lead generation process and improve its lead conversion rate.
The SaaS company aimed to expand its presence in a specific market and secure more qualified leads across the nation. However, the marketing team’s activities didn’t necessarily align with the sales team’s ambitious goals.
First, Sculpt worked with Collective Data to outline buyer personas for the newly expanded market. The agency also mapped out the customer journey to identify key points to target or remarket to the new audience. To establish goals, the agency set cost-per-lead and cost-per-demo targets for the company’s campaigns.
To reach the company’s target audience of law enforcement professionals, the agency worked with Collective Data to build LinkedIn ad campaigns. The company focused on LinkedIn’s native lead forms, which allow prospects to provide contact information without leaving the platform.
To get more value from their efforts, the agency launched paid search and display remarketing pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns using Google Ads. The SaaS company also invested in conversational marketing tools to engage potential customers on other channels and guide them through the sales funnel.
As a result of these combined efforts, Collective Data achieved an 8-12% lead conversion rate from online advertising. Compared to the SaaS company’s previous lead acquisition methods, these efforts decreased the average cost-per-lead by 70%. In addition to helping the B2B company expand into a new market, this outcome contributed to a significant cost savings.
Aligning marketing and sales isn’t always a smooth process. By clarifying customer personas and journey maps from the beginning and setting up complementary cross-channel campaigns, the agency successfully partnered with Collective Data to improve leads and conversions.
Wrapping Up What We’ve Learned About B2B Social Media Marketing
From boosting brand awareness to generating leads, these B2B social media case studies illustrate how businesses can reach target audiences and get results using the right channels. Use these case studies and use cases to guide your team in developing an effective social media strategy for your B2B company or agency clients.

More from the blog
Using B2B Social Media to Create a Brand-Building Customer Experience
Keep up to date with social media marketing!
Our newsletter is packed with the hottest posts and latest news in social media.
How to Post Case Studies on Social Media
- June 1, 2021
- Using Case Studies
Once your Case Studies are finished, social media is the best place to share them. However, it’s not enough to simply post a link to your Case Study on LinkedIn and hope people will read it. Crafting a strong social media post that compels your audience to read your Case Study requires more strategy and finesse.
This article serves as your ultimate guide to composing social media posts about your Case Studies that will grab your target audience’s attention. You’ll learn about what parts of the Case Study you should mention in your post and how to write about them in a way that gets people off social media and on your website—and, ideally, joining your client base.
Should You Post Your Case Studies on Social Media?
You know you want to post your Case Studies on social media—but should you? Run through this list of questions to find out:
- Do you have permission from your client to post it? If you don’t have your client’s approval to post the Case Study, don’t post it. Instead, consider reworking the Case Study so that the client is anonymous.
- Does your Case Study convey a compelling story? You’ll wind up with annoyed readers if your expertly crafted social media post lures them to your website but dead ends in boring content. Make sure your Case Study is interesting to read from start to finish.
- Does your Case Study promote what you want to promote? A Case Study is no good to you if it describes how you helped a client solve Issue X when you really want to be known for solving Issue Z. This may lead you to attract work that doesn’t align with your true passion. Hold off on posting and work on creating Case Studies that showcase the areas in which you really want to shine.
Bottom line: If you’ve got the client’s permission and a juicy story to tell that makes you and your client look good, it’s time to create that post.
Tips for Creating Posts About Your Case Studies on Social Media
Follow the format.
A successful social media post about your Case Studies should follow a specific formula—specifically, the same one your Case Studies do! Ensure that your post includes the following elements in this order:
- Headline. Use an intriguing opening sentence to make your post stand out and capture your audience’s attention right away.
- Situation or Problem. Introduce the company and the problem or situation it had.
- Solution and Results. Tease some of the company’s real, specific results that stemmed from the solution you provided.
- Conclusion/Call to Action. Conclude the post with a call to action, such as “Click the link to learn more.”
Keep It Short and Sweet
Be brief when writing a social media post about Case Studies. Most people have short attention spans and a vast sea of content awaiting them on social media. When scrolling through News Feed on Facebook, people typically spend 2.5 seconds with a piece of content if they’re on desktop and even less if they’re on mobile. Make those few seconds worthwhile for the user and offer them something compelling that will make them engage with your post. There are only four key elements to the formula, so your post should be no longer than four fascinating sentences.
Be a Little Mysterious
Share just enough of the Case Study story in your social media post to make someone want to click the link. Remember: The goal is to get people to read the Case Study on your website, and that won’t happen if you give away all the details upfront! Aim for intrigue. Be honest, but be mysterious about the solution and the results, and never give away the ending!
Stick to Company Brand Guidelines
Adhere to your company’s voice and branding when writing your social media post about your Case Study. This helps ensure a consistent client experience, which fosters loyalty and trust. If you don’t have a brand identity, start exploring how to create one.
Make It Personal
Social media is all about making connections, which is difficult to do if your post is too formal or standoffish. Even if your company culture or brand skews more serious, using we and us in your social media posts to refer to your company can help build that bridge between you and your existing and potential clients.
Speak to Your Target Audience
Tailor your social media post about your Case Study for the specific audience you want to reach. For example, if you have a B2B company, use professional terminology to emphasize your experience and understanding of your industry. If your audience comprises the general public, use less formal language and avoid terminology that requires background knowledge to understand.
Use Relevant Images
You have less than three seconds to capture your audience’s attention, so use that time wisely by including an image with your social media post. Images leave a stronger impression than words alone and can make a wordy post easier to digest. Use an image from your Case Study or a photo of your Case Study subject when posting on social media. Remember to choose images that, like your messaging, are on-brand.
Sample of a Case Study Social Media Post
The following is an example of a social media post about a Case Study that adheres to the aforementioned tips:
Posting your Case Studies on social media takes some strategy and skill. However, if you have a solid Case Study, approval from the client, and clear brand guidelines, you can create a post designed to get attention, clicks, and more business.
Need a Case Study to post on social media? Click here to find out how SuccessKit can help you reach that goal.

Stef Mates, SuccessKit's Creative Director, has been writing, designing, editing, and managing a variety of content types for several different industries for more than 15 years. She started at the company as a freelancer in November 2019 and became an official part of the team in June 2021.
Recent Posts
Best Professional Services Case Study Examples

How to Edit a Video Testimonial
Best B2B SaaS Case Study Examples

It’s All About Mindset (w/Alice Heiman) [PODCAST]

The Power of Simplifying Your Messaging (w/Nick Verity) [PODCAST]

Going on a Trip Abroad, Starting a Business (w/Luke Komiskey) [PODCAST]

The Business of Podcasting, and How to Market Organically (w/Jeremy Shere) [PODCAST]

How to Better Use Videos for Your B2B Brand and Building a Video Business (w/Alex Sheridan) [PODCAST]

Optimizing Your Business for Scale (w/Jay Roy) [PODCAST]

How to Write a Case Study
Leave a comment, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What people are saying
Milo Sindell President, Skyline G
“If you’re looking for Case Studies, this is a really nice little organization to partner with. Our experience, frankly, has been excellent.”
Franklyn Peart Co-Founder, CentreStack
“We’re already recommending SuccessKit to our customers.”
John Morgan Director of Marketing, Elemental Machines
“The SuccessKit team has been great. We can tell them, ‘ABC Company had this problem,’ and they will document our solution.”

Don Mennig CEO, Evolve IP
“Julian and his team have done an excellent job for us. Definitely recommend working with them for Case Studies. ”

David Bohram Director of Marketing, Tax Guard
“I didn’t think it’d be successful to outsource Case Studies, but Julian and his team made it so easy.”

Erin Wathen Director of Branding and Events, Assure
“I really appreciate how SuccessKit takes the reins and produces such great results, allowing us to focus on what we need to do to grow the business.”

Damon Baker CEO, Lean Focus
“SuccessKit’s Case Studies give us a distinct advantage over our competition when prospects are comparing service providers.”

Chris Connor Sales Manager, SwervePay
“We’ve really appreciated the work that Julian and his team have done for us. Very happy with the results.”

Shawn O’Daniels CEO, CSN
“SuccessKit figured out how to show the world what we do for our clients. I am blown away by the Case Study .”

James Dirksen CEO, DeepSurface Security
“This is just about the best Case Study I’ve ever seen.”

Christopher Levy CEO, BuyDRM
“The Case Study SuccessKit created for us was elite.”

Kendall Kunz CEO, Forms On Fire
“SuccessKit made it easy for clients to see what other clients see, and it’s led to more sales.”

Phil Curtolo Vice President of Sales, Software Consulting Services
“SuccessKit takes the pain and suffering out of creating quality Case Studies.”

Luke Anemone CEO, COMMANDO
“Working with SuccessKit has been pivotal in growing our client base and giving potential advertisers really good content about what we can do.”

Linze Kay Lucas Business Analyst and SEO Consultant, Stellium SEO
“I cannot speak highly enough about my experience working with SuccessKit. They were completely respectful of my client’s time and needs, as well as my own.”

Joanie Berkery Marketing Director, Adapex
“SuccessKit really helped us build the framework and presentation for our Case Study.”
Troy Stein VP, Customer Advocacy, TechSmith
“Quality results. Authentic storytelling and quotes. Easy to work with. I’m signing up for more.”

Julie Matheney Associate Director of Digital Marketing, Feathr
“I highly recommend the SuccessKit team to anyone who’s looking to produce Case Studies.”

Robin Smith Founder and President, ASK-CRM
“We are definitely recommending SuccessKit to the peers that we work with and our existing clients.”

Ace Rosenstein President, Bravo Business Media
“I recommend SuccessKit due to the efficiency and the extreme price to value.”

Ari Haas Founder, Dijy
“The SuccessKit team knows what they’re doing. It’s easy to work with them, the end result is a beautiful product, and all parties involved feel super comfortable.”

Sidney Rogers Marketing Manager, Groove Technology Solutions
“The SuccessKit team is very professional, and they ensure that they take care of everything in a timely manner.”

Ashlyn Burgett Director of Marketing, Dedicated IT
“The SuccessKit team makes the Case Study process painless, and they have the expertise to create high-quality content that is invaluable to sales and marketing teams.”

Carly Brightwell Head of Marketing, North Labs
“If you need Case Studies for your business, we highly recommend SuccessKit. We recieved exactly want we asked for!”

Luke Komiskey Founder and Managing Director, DataDrive
“I love working with the SuccessKit team because they make it really easy for me to focus on my business while they produce Case Studies that drive our brand forward.”
Have a question? Reach out to us directly.

- Journalism and Media Ethics Cases
- Markkula Center for Applied Ethics
- Focus Areas
- Journalism and Media Ethics
- Journalism and Media Ethics Resources
For permission to reprint articles, submit requests to [email protected] .
How might news platforms and products ensure that ethical journalism on chronic issues is not drowned out by the noise of runaway political news cycles?
How can media institutions facilitate the free flow of information and promote truth during an election cycle shrouded in misinformation?
A reporter faces a choice between protecting a source or holding a source accountable for their public actions.
Should a source’s name be redacted retroactively from a student newspaper’s digital archive?
Should a student editor decline to publish an opinion piece that is culturally insensitive?
A tweet goes viral, but its news value is questionable.
What should student editors do if an opinion piece is based on factual inaccuracies?
Do student journalists’ friendships constitute a conflict of interest?
Is granting sexual assault survivors anonymity an act of journalistic compassion, or does it risk discrediting them?
Should student journalists grant anonymity to protect undocumented students?
- More pages:

The Case for Media Impact

Table of Contents
The media—and especially nonprofit media—has spent the past few years struggling to measure the impact of its work. Some outlets are compelled to do so by counting their philanthropic supporters; others see their impact as foundational to audience development and engagement, and still others are beginning to experiment with the role of impact measurement in advertising and other revenue streams. Of course, at its core, journalism is intended to have an effect: to inform the public so we can be civically engaged and hold the powerful to account.
But what does it mean for a journalistic organization to put the goal of impact at the center of its mission? In this report, we explore this question through the lens of the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ) and its explosive project, “Evicted and Abandoned,” in which a collaborative reporting project of more than fifty reporters and fifteen organizations in twenty-one countries took on the World Bank. The investigation found that, over the last decade, projects funded by the World Bank have physically or economically displaced an estimated 3.4 million people; that the World Bank and the International Finance Corporation have financed governments and companies accused of human rights violations; and that, from 2009 to 2013, World Bank Group lenders invested fifty billion dollars into projects graded with the highest risk for “irreversible or unprecedented” 1 social or environmental impacts.
Part One of the report introduces the current impact conversation in the media arena and describes ICIJ’s structure and strategy. Part Two traces the forerunners to some contemporary journalists’ discomfort with the notion of impact as a goal for media, and finds that, in fact, the notion of journalistic impact is nothing new. In Part Three, we examine how ICIJ’s impact imperative affects the organization’s approach to story choice, production, and distribution. The report also covers the challenges associated with this model and suggests what other journalistic organizations can learn from the experience of ICIJ.
Key Findings
- A networked structure necessarily requires that ICIJ relinquish control of the investigation and content produced by partner organizations, which can result in reporting errors.
- Measuring the impact of one organization and one project is difficult. Even knowing about the far-flung impact of ICIJ partner stories is near impossible.
- Collaborations, however complicated, result in increased capacity, larger audiences, and greater potential for impact. ICIJ’s above-and-below distribution strategy has proven effective.
- Large, international media generates attention to issues from international elites, while local and national media generates awareness among the most affected populations.
- A rolling thunder approach whereby reporters stick with the story long after the initial publication keeps the spotlight on the issues.
Recommendations
- Impact is not a dirty word : In our experience, news organizations are often wary of putting impact at the center of their operations for fear of getting too close to the ethical line separating unbiased journalism from advocacy work. The case of ICIJ demonstrates that an impact imperative need not cross this line, nor is impact necessarily a requirement that funders foist upon organizations. Instead, by having a clear mission that puts impact at the center of all it does, an organization can formulate its own theory of change (even if implicit) to guide strategy.
- Give your audience more—people like positive change more than bad news : The next step for media organizations is to take the expansive notion of impact that helps to govern internal strategy and communicate these changes with audiences. Now, as the American public’s trust in both media and government hovers at an all-time low, it is more important than ever to show the positive change that often stems from crucially important investigative reporting. This includes not just the political and institutional responses, but also the nuanced changes that happen at the level of individuals and communities.
Download a PDF of the full report here.
Media Impact
In the wake of the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists’ “The Panama Papers” investigation, almost overnight a prime minister resigned; official investigations opened around the world; leaders from the United States, India, Australia, Norway, and France spoke out; and China began a censorship campaign to ensure its citizens would not access the findings. But the impact of “The Panama Papers” was not luck. It was the result of ICIJ’s carefully planned campaign. While investigative reporting designed to achieve impact may seem antithetical to the principles of journalism, ICIJ has high reporting standards that are widely respected in the field.
But what does it mean for a journalistic organization to have a core mission based on generating impact? To begin to answer this question, we focused our research on determining the effects of ICIJ’s impact imperative on the organization’s structure, processes, and strategies.
Impact in a Historical Context
The relationship between media and culture has been examined for generations, and the current study of journalism impact has precursors. In the 1920s and 1930s, scholars focused on the relationship between media and politics—at just the moment when media began to claim impartiality. Politics and dominant culture are often seen as being inextricably linked, if not synonymous.
In later parts of this paper, we review those forerunners: from Antonio Gramsci’s argument that media is a tool of the elite to create culture and dominate politics, thereby quieting the masses, 2 to arguments from economists like James T. Hamilton that assert the media is often instead a mirror reflecting consumer preferences. 3 We also cover those of social movement scholars who find that movements and organizations use the media to bring their cultural and political critiques into the mainstream, thereby shifting the broader cultural consciousness. 4 5
For the moment, though, we will accept that “media impact”—whether intended or unintended—exists, and is a suitably complex topic that has preoccupied researchers and journalists alike for almost as long as the industry has existed.
Media and Impact: Why Are We (Still) Talking About It?
There are at least three particular forces that make media impact a timely subject.
Funding for nonprofit journalism comes with impact requirements
The rise of nonprofit news organizations roughly coincides with the decline in traditional, legacy news outlets. The nonprofit model is supported by philanthropic foundations, individual donors, and members. According to a recent Knight Foundation report, foundation support accounted for fifty-eight percent of nonprofit news revenue in 2013. 6 However, many of the current, large funders of journalism, including the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the Omidyar Network, have historically funded service delivery organizations and projects, not media 7 8 —a trend widely discussed in the nonprofit media and philanthropic communities. This creates an immediate tension, as, for example, it’s far easier to measure the impact of inoculations administered than the impact of a series of news reports on the importance of inoculations. Furthermore, service organizations have clear goals, while media organizations often have broader and more vague missions around values like contributing to a healthy democracy or protecting the public interest. However, as nonprofit media organizations and their funders have negotiated (often uneasy) partnerships, academics and other researchers have edged into the conversation and proposed other methods for understanding media’s effects—both on individual behavior and more complicated processes like framing public debate on issues.
The crisis of trust in journalism has made impact a brand differentiator
This second trend has been less explored but may have more powerful implications for media, including commercial media. In an era during which the public’s trust in legacy news organizations is rapidly eroding, 9 a media organization’s ability to understand its impact and then communicate that impact to its audience can potentially increase the organization’s perceived trustworthiness in the eyes of the audience. If this hunch were proven to be true, this would have huge implications for the media industry and its long-term sustainability.
The rise of analytics data has produced a culture and means of measurement, and demanded a counterweight
The last decade’s boom in newsroom analytics has influenced newsroom operations. It is commonplace to have loads of metrics that can be interpreted as indications of the success of journalists’ output. The first wave of audience data tools focused on pretty crude measures (often aligned with the needs of those selling advertising)—clicks, unique visitors, and visits. The state of analytics has massively evolved since then, capturing virality and user actions on page, among many other data points. Many journalists, upon publishing a story, pay close attention to how it spreads on Twitter and Facebook. In her report, “The Traffic Factories,” Tow Center fellow Caitlin Petre observed that while newsrooms’ cultural values play a big part in how staff use and perceive analytics, the very existence of readily available data that could be used to indicate a story’s worth is a potent force. 10 This defines the modern media, and separates the era of digital platforms from analogue. Some are troubled by this, whether they condemn it outright, or seek to synthesize the traffic and social analytics practices with computable indications of journalism’s other social values—impact in particular.
ICIJ: Global Collaboration for Maximum Impact
Collaboration rarely happens in the news industry, especially in investigative reporting where projects are carefully guarded under lock and key until an organization chooses to break the story. But new media outlets, and especially nonprofits, are exploring collaboration and recognizing the potential for increased reporting capacity, distribution reach, and impact. The International Consortium of Investigative Journalists is one such organization that has flipped the traditional model on its head and embraced radical collaboration.
ICIJ is a project within the Washington, D.C.-based nonprofit Center for Public Integrity and was founded by journalist Chuck Lewis in 1997. Observing the rapid globalization of the 1990s, ICIJ’s original members believed that a journalism organization with an international mindset could be well suited to report stories that sprawled beyond any single country. At a time, according to ICIJ, when rapid globalization places “extraordinary pressures on human societies,” 11 it aims to be a globalized reporting network that counterbalances these pressures.
Mission and values
ICIJ’s mission is, perhaps not surprisingly, to “be the world’s best cross-border investigative team.” However, that comes second to its first aim: “to bring journalists from different countries together in teams—eliminating rivalry and promoting collaboration.” 12
Interviews and participant observation with ICIJ staff clearly indicated that ICIJ’s collaborative nature, cross-border reporting, and, more importantly, its syndicated distribution models are tactics in the service of impact.
Operating processes
ICIJ has a networked organizational structure with two spheres. First, its directly employed journalists, located across countries, form the network node. Then, ICIJ’s network expands to include more than 190 investigative journalists in over sixty-five countries. They are generally employed by other newsrooms and publish under their employers’ mastheads.
According to ICIJ website, “ICIJ reporters and editors provide real-time resources and state-of-the-art tools and techniques to journalists around the world.” 13 In-country reporters contribute to the collaborative investigations through on-the-ground reporting. Reporters pool resources as needed and freely share information. ICIJ Computer Aided Reporters provide data and data support to reporters who might not otherwise have the skills or programs necessary to conduct the analysis. Projects are then compiled and simultaneously published internationally in a syndicated manner, in multiple languages and publications across the globe.
Operational funding comes from philanthropic foundations and individual donations. Gerard Ryle, the leader of ICIJ’s headquarters staff in Washington, D.C., has primary responsibility for identifying and securing funding for general operations (although some comes through the Center for Public Integrity’s networks), which is not tied to specific editorial projects or topics. However, once an investigation is underway, ICIJ will often apply for smaller grants to fund additional reporting angles.
ICIJ’s structure, operating model, and editorial focus flows from its purpose. According to Ryle, the organization reports stories that are international, where it has evidence that institutions have broken down, and where it there are significant problems which should be—and can be—remedied.
ICIJ and impact
ICIJ has an underpinning model of change, namely that the wider the reach of high-quality, investigative stories and the stronger the distribution partners (in audience size and credibility), the greater the potential for change to remedy the problem (impact). Although ICIJ unambiguously aims for impact and practices journalism in pursuit of exposing problems so that they can be fixed, the organization does not start with a prescription for particular outcomes.
ICIJ’s model for change contrasts with many organizations that identify as social impact organizations. Social impact organizations with strong monitoring and evaluation processes generally work with what’s known as a theory of change, or a set of logical steps working back from the desired outcome. For example, if the desired outcome is fewer children dying in a specific region and common causes of death are known, a public health organization will ask what intervention can be taken to prevent those causes of death, and what resources and actions are needed to achieve that intervention.
To better understand how ICIJ’s collaborative process works and where “impact” fits into the big picture, we closely followed the reporting, production, distribution, and impact of one project, “Evicted and Abandoned: The World Bank’s Broken Promise to the Poor.” 14 We were flies on the wall in editorial and production meetings, and conducted interviews with ICIJ staff and reporters from other organizations who participated in the project. This process is documented and explored in detail in Part Three of this paper.
ICIJ team shares responsibility for collecting impact indicators. Indeed, many functions within the organization are shared. Again, according to Ryle, that’s necessary for such a small team. The journalists continue to follow the story, which can include reporting on reactions by subjects or stakeholders. The online editor compiles traffic and social metrics, and also has primary responsibility for updating the blog with impact indicators. Impact is often then reported back to audiences as follow-up content.
However, because ICIJ projects are published in multiple languages in newspapers, on websites, and throughout social networks across the world, compiling comprehensive analytics is effectively impossible. And, while some news of real-world change makes its way back to ICIJ staff and can be documented, much change that occurs in local, regional, or even national settings is never known by the organization.
Thus, for ICIJ, the operating model is an impact catch-22: the large and diffuse network leads to powerful investigative stories with sweeping scope and a huge potential for change, but these same qualities make understanding reach, audience, and the full scale of real-world change difficult, if not impossible.
Story selection
ICIJ’s story selection adheres to journalistic news values that would be familiar to most investigative teams; however, to those news values ICIJ adds an extra filter regarding the potential impact of a project. Ryle says, “We’re looking for obvious issues of global concern, always look[ing] for a systemic failure in things,” and asking, “can we make a difference?”
He emphasizes that there is no direct relationship between funding and story selection. However, once a story is chosen, ICIJ will approach grant-making organizations it thinks would be interested in funding sub-projects, such as a reporting trip. For example, when reporters Sasha Chavkin and Mike Hudson realized that a part of the “Evicted and Abandoned” story would require reporting on World Bank activity in Asia, ICIJ applied for a grant to do on-the-ground reporting in the region.
ICIJ also considers the type of stories it has already reported when selecting future projects. Ryle says that ICIJ is aware that the organization has a reputation for doing high-quality investigations into tax-haven stories fueled by leaks. The organization thus seeks out different types of stories, such as “Evicted and Abandoned,” to avoid being perceived as a “one-trick pony.” In Ryle’s words: “You’ve got to satisfy your CEO. You’ve got to satisfy the board . . . Also, funders start mumbling . . . even though it’s a series of stories on the same topic, they see it as one story.”
This suggests a subtle influence of the funding model: The team looks for stories that fulfill ICIJ’s primary criteria, but that can also widen and strengthen the organization’s reputation as able to tackle a diverse range of stories.
Reporting and publishing strategy
ICIJ partners with other journalism organizations for both reporting and publication. ICIJ forms partnerships with organizations in countries relevant to the investigation both to increase on-the-ground reporting capacity and to ensure localized distribution of the investigation. In this way, ICIJ can maximize the amount of reporting that is possible with limited budgets and guarantee that the stories will reach the largest possible audience.
ICIJ does not partner with activist organizations. Ryle clarifies that ICIJ maintains a distance from activist organizations, and that, “[When] you even let them know that you’re about to publish something, that is bordering on advocacy by itself.” When there is an investigation that is relevant to advocacy organizations, ICIJ will often send the final, public version of the story to them in order to spur impact.
ICIJ’s global reporting and publishing strategies are closely intertwined. “We need to have a story that will make its way onto the front pages of every newspaper or TV station that we work with,” says Ryle. “It has to work equally well in France, as it does in Germany, as it does in Brazil, as it does in Japan.” And, while ICIJ acknowledges that it is difficult to find and report stories that are global in nature, Ryle asserts that, “by getting the right one you’re almost automatically guaranteed to get one part of the impact, which is that . . . news organizations publish the story prominently.”
After the launch of an investigation, ICIJ processes in place to track the project’s impact both for journalistic and management purposes. As described above, the strategy requires that journalists stay assigned to the investigation, continuing to report out stories that were identified during the initial investigation, as well as following new leads generated by the first rounds of publication. Reporters also report on the impacts of the investigations.
ICIJ furthermore gives one of its major funders, philanthropist Graeme Wood, a report every six months on how, operationally, his money has been spent and what it has produced. That explicitly includes instances of impact.
The awareness that media has an impact on society, culture, and politics is not new. However, journalism’s focus on media impact has surged in recent years, especially in nonprofit, investigative reporting organizations and those that fund this type of work. ICIJ is a new type of news organization with collaboration at its core and impact in its mission. This focus influences how ICIJ approaches story choice, partnerships, reporting processes, publication strategies, and follow-up reporting.
Part Two of this report explores theories of media and social change, as well as theories from other industries and academic fields, such as health and development, advertising and marketing, the social sciences, and documentary film. In Part Three, we use ICIJ’s “Evicted and Abandoned” project as a case study to more deeply understand how an impact imperative permeates one investigation.
Impact Theory
The notion of journalistic impact—that is journalism having an effect on individuals, organizations, and society—is not an invention of this century. At the very least, the practice of collecting, making sense of, and distributing information is built upon an assumption that individuals will access the information, which will inform their perspectives, decisions, opinion, attitudes, and knowledge. However, in recent years, impact has become a hotly debated topic in the media industry. Amid the failure of the legacy newspaper model, paranoia around “new media” that doesn’t follow long-established journalistic rules of the game, and an obsession with whether and how millennials access and consume news and information, is in the zeitgeist.
This section traces the forerunners to journalists’ current concerns with impact, starting with the years before the press adhered to a rhetoric around disinterested objectivity. Later on, a theoretical and evidence base developed to show that journalistic influence not only existed but could, in certain circumstances, be identified and measured. However, other fields have more precise and established impact-assessment regimes. This paper briefly surveys some that may be interesting and relevant to journalists.
Media, Impact, and Politics: Easy Allies in the Early Days
Newspapers in the United States were not founded on the principle of existing as an unbiased fourth estate to keep government in check. Instead, during the majority of the eighteenth century, newspapers were largely (directly or indirectly) supported by political parties. 15 16 17 Their raison d’etre was influence.
Party papers often suppressed stories that were damaging to their party and/or politicians, failed to publish facts about events when stories were not suppressed, and printed stories with significant spin. 18 Newspapers were produced with the express goal of supporting the party and ensuring that the party’s candidates were elected.
In the 1870s, the number of independent papers began to increase in the United States’ urban areas. Economist James T. Hamilton and others have made compelling economics-based arguments for the growth of independent presses from 1870 through 1920 (a foreshadowing of the current era’s economic upheaval in media economics). First, technological advances in the steam cylinder printing press, wood-pulp paper, and the telegraph lowered the cost per unit of a paper, even if they increased the up-front cost of production. Second, urban growth meant more consumers in a geographic area, providing opportunity for new papers to enter the market. Independent papers were able to attract a heterogeneous audience, and thus were more profitable than party papers aimed only at attracting a homogenous audience. Third, the growth in audience brought increased advertising revenue. Advertising revenue, paired with increased subscription revenue, meant that party support was no longer the most profitable option for newspapers. 19
While “independent” did not necessarily equate to “unbiased,” independent papers were not affiliated with political parties, suppressed fewer relevant news stories, had less (at least obvious) bias in their stories, and provided more facts. 20 However, these new independent newspapers were not without a mission. In fact, the owners and editors of independent papers worked to expose corruption in politicians, parties, and government institutions. Whether or not the independent press resulted in better informed or less partisan voters is difficult to prove. However, in the words of Gentzkow et al., “While we cannot prove that a more informative press helped diminish corruption, it does appear that campaigns against corruption succeeded when they were supported by news coverage.” 21
So, while impact might not have been a media industry buzzword in 1890, the media was undoubtedly working to effect political change in the United States. With a change in the market size and an increased economy of scale, independent newspapers between 1870 and 1920 grew in popularity (and profitability) based upon the premise that independent news was credible news. It seemed consumers agreed with them, and by 1900 independent papers accounted for more than forty-seven percent of all dailies and more than fifty-five percent of circulation. 22
Professionalization and (the myth of) neutrality
In the late 1800s and early 1900s, literacy in the United States became more widespread, the population expanded, new cities formed, and journalism and media products multiplied to serve these populations. The changing operating environment for news businesses swung their explicit identities and goals even further away from influencing a populace on behalf of their owners or funders. While Michael Schudson and Chris Anderson urge us to avoid the pitfall of looking for a genesis moment for the journalism profession, they agree with other journalism scholars that the rise of the neutrality norm coincides with the field’s professionalization. 23 For many authors, “Objectivity continues to be the sine qua non of journalistic professionalization: explain the reasons behind the emergence of objectivity as an occupational practice, fix a date at which it first emerged, and you have gone a long way towards uncovering the “secret” of professional journalism.” 24 .
If, then, journalists were not explicitly aiming to have impact or influence, researchers have looked for the field’s alternative value and role in society. What was it that justified audiences paying money, workers providing their labor, and owners their capital? (Owners’ profit and workers’ wages could only be produced if the enterprise provided value to readers, perceived or real.) 1 Retrospectively, scholars of journalism identified the concept of “newsworthiness,” an idea that the subjects of the news have within them elements which make them worthy of being a media product, and thusly deserving the attention around which a business model could be built. At the heart of the idea of newsworthiness is an implicit belief that what journalists are covering is worthy of the audience’s time and attention.
Those scholars have spent much time studying, documenting, and critiquing news values. In 1965, Johan Galtung and Mari Holmboe Ruge put forth what they hypothesized to be the top twelve factors of newsworthiness: frequency, threshold, unambiguity, meaningfulness, consonance, unexpectedness, continuity, composition, reference to elite nations, reference to elite people, reference to persons, and reference to something negative. They, and those who follow in their tradition, focus on the supply side of the media equation. That is, while they hypothesize that these factors have “certain effects among the audience,” the effects of journalistic news values are not the social phenomena under consideration. 25
While researchers and practitioners alike have used Galtung and Ruge’s study as a starting point to delve deeper into supposed news values, 26 27 others have critiqued the endeavor by arguing that it ignores the ideological underpinnings of news values.
One early critic of media as an instrument of ideological power was Antonio Gramsci. Writing in Fascist Italy, he argued that the regime exerted indirect power over civil institutions such as schools, the legal profession, trade unions, and the print media in order to control and incorporate the proletariat into its ideology. 28 This interpretation is strongly associated with the concept of “hegemony.” However, the media’s ideology was not generated in a vacuum. Kellner explains:
The hegemony model of culture and the media reveals dominant ideological formations and discourses as a shifting terrain of consensus, struggle, and compromise, rather than as an instrument of a monolithic, unidimensional ideology that is forced on the underlying population from above by a unified ruling class . . The hegemony approach analyzes television as part of a process of economic, political, social, and cultural struggle. According to this approach, different classes, sectors of capital, and social groups compete for social dominance and attempt to impose their visions, interests, and agendas on society as a whole. Hegemony is thus a shifting, complex, and open phenomenon, always subject to contestation and upheaval. 29
Writing specifically about U.S. media of the twentieth century, Gamson et al. argue that the frames journalists use, which are constructed through “routine, taken-for-granted structures of everyday thinking contribute to a structure of dominance.” 30 As with Gramsci’s dialectic, they acknowledge that the audience has agency in interpreting these frames. 31 But ultimately, the imbalance in power means the common sense, or “gut feeling” of the journalist (and the editor, company, and industry) is perhaps the strongest contributor to their readers’ perceived reality. 32 For current readers considering journalistic impact, these theorists provide an argument that, despite journalists’ claims to objectivity and the intrinsic newsworthiness of their stories, societal power-holders use the media to exert their control and influence audiences’ views.
Nonetheless, since at least the mid-1900s, journalists have claimed objectivity and neutrality as a core tenet of the profession, and cited these factors as justification for their position of power in creating our shared reality through broadcast and print media. In the words of Schudson and Anderson:
U.S. journalism’s claim to objectivity—i.e., the particular method by which this information is collected, processed, and presented—gives it its unique jurisdictional focus by claiming to possess a certain form of expertise of intellectual discipline. Establishing jurisdiction over the ability to objectively parse reality is a claim to a special kind of authority. In sum, journalistic objectivity operates as both an occupational norm and as object of struggle within the larger struggle over professional jurisdiction. 33
But what of the audience? Gamson et al. assert that the social constructions disseminated through media are likely to be both unconscious on the part of the journalists and unrecognized as such by the reader. 34 “News is both a permanent social structure and a means of social reflexivity and contestation; a product as well as a productive process.” 35 But the question begs to be asked: What do citizens believe to be newsworthy? What do they want more of? And, perhaps most importantly, why?
Ida Schultz dances around these questions when she writes: “Where most of the classical newsroom studies used titles such as ‘making,’ ‘creating,’ ‘manufacturing,’ or ‘constructing’ the news, the best title verb describing journalistic practice within the analytical framework of reflexive sociology would be positioning the news.” 36 Following Bourdieu, Schultz recognizes that journalists and media companies are part of the journalistic field, and as such they interact with other producers of culture and knowledge. Thus, rather than constructing a news story with an unintentional but powerful frame, she posits that journalists position their work internally to get their stories green-lit. Furthermore, media organizations actively work to externally position their content in such a way as to maximize its appeal to audience members. 37 Now, not only had “news values” been identified, but critics had articulated a tension between journalists’ claim to being a neutral filter for the news and their self-interest in amplifying or, at least, emphasizing newsworthy elements. If their work could be seen as consequential, it was more important and more valuable.
Mainstream media in the United States has been loath to acknowledge the power inherent in its industry, the ends that result from their means of communication, and the news values of its audience(s). Note Schudson and Anderson: “Journalism seems to simultaneously make a grandiose knowledge claim (that it possesses the ability to isolate, transmit, and interpret the most publicly relevant aspects of social reality) and an incredibly modest one (that really, most journalists are not experts at all but are simply question-asking generalists).” 38
The evidence base for journalistic evidence
Researchers have long worked to identify and quantify the influence of the news media on individuals, society, and politics alike. Particularly relevant to our study, in 1972 Max McCombs and Donald Shaw put forth their theory of Agenda Setting, which aimed to develop an empirical basis for how the media affected what the public paid attention to. Comparing the issues that the media emphasized in its coverage of the U.S. presidential election campaign and the issues that survey respondents recalled, the researchers found that the more the media covered an issue, the more audiences considered that issue to be important. 39
The theory was extended to how the media influences audiences’ perceptions of facts within an issue, such as the positive and negative attributes of people and organizations in the news. 40 Researchers investigated the ways in which agenda setting worked in non-political subjects, including business reputations, sports, and religion (generally speaking, the principles held true). They also started to find that the recency and volume of individuals’ exposure had a significant influence on how much they retained the information in memory, (i.e., when issues drop out of the media agenda, most people mostly forget the details). 41
In the mid- and late 2000s, the growing prominence of digital media, and in particular the early social media technologies (blogs, comment boards and the like), prompted researchers to extend their understanding of a changing environment that allowed, as never before, individuals to participate in fragmented, conversational groups and clusters (and for the conversations to be studied on a mass scale). 42 The framework of “agenda melding” was one result; the idea that individuals join groups and partially assimilate the group’s opinions of what’s important, or maybe stay silent. 43 Mostly, after joining a broadly like-minded group they do not seek to change the group’s dominant views to align with their own outlier views on minor matters.
A study of 2012 U.S. election-time Twitter also observed differences between how people with different political affiliations absorbed salience: The researchers, using the relatively new term “network agenda setting,” concluded that supporters of the Republican nominee Mitt Romney appeared to absorb their online network’s views on salient topics and facts more than did Democratic nominee Barack Obama’s supporters. 44
While the foci of agenda setting studies have varied across time, platforms, and individuals’ characteristics, the field of research has provided a range of empirical bases from which to understand the way news media can and has influenced public perceptions of events, individuals, and organizations.
Rediscovering an impact mission
In recent years, media organizations have been motivated to explicitly embrace the reality that they are, in fact, influential social forces. Having lost their dominance over channels of communication, and as consumers of news look to new and unconventional sources for information, legacy companies are coming to grips with the fact that evolution is now necessary for their survival. They have started to attend to what happens post-publication: Audience engagement, especially via social media, is an accepted practice in newsrooms, and engagement editors are common in media companies across the United States. The proliferation of nonprofit media has allowed for a wave of experimentation in the co-creation of news, and deep audience and community engagement by media.
An increasing number of both nonprofit and commercial media organizations are betting that impact—that is, any change in the status quo as a result of an intervention on their part (content, engagement, etc.)—is key to their long-term sustainability. 45 While this trend started in the nonprofit news space and was largely pushed by philanthropic foundations with a history of program evaluation around the NGOs they support, many commercial media outlets are taking it as a given that to show real, positive change as a result of their reporting will build a deeper relationship between their brand and their audience. The logic goes something like this: The more impact a news organization has, the more people will trust that brand and the greater affinity they will feel for it; thus, they’ll return more regularly to the organization’s website/broadcast program/newspaper, ultimately generating more revenue for the organization.
However, impact is still not the most important metric for the vast majority of media organizations. For example, again in Caitlin Petre’s ethnographic research report, “The Traffic Factories,” she finds that traditional media metrics rule newsrooms, and that these metrics have an effect on journalism. Especially relevant is her finding that traffic-based rankings can “drown out” other forms of evaluation, thereby engendering a range of emotions in journalists such as “excitement, anxiety, self-doubt, triumph, competition, and demoralization.” 46
Measuring Impact in Other Fields
If a history and literature review of how journalism has approached its influence and impact is useful as a look down deep into the topic, then this next section may be useful as a survey of adjacent fields’ approaches. Some pertinent professions’ practices are briefly outlined below.
Impact and metrics in development and health
Journalism researchers looking for expertise in achieving and evaluating impact can turn to the development fields, in particular the NGOs, foundations, and international organizations focused on health and social well-being. Their best practice, when planning an intervention, is to develop a “theory of change.” 47 The first step is to envision and articulate the ultimate outcome (e.g., bringing down rates of infant mortality in Afghanistan from 115 per thousand to forty per thousand), then work backwards through each precondition needed to change from the status quo to the desired condition. One of the many preconditions might be all children getting vaccinations, for which a precondition is parents knowing and agreeing to vaccinations, for which a precondition is an effective public information campaign, and so on. At each step the theory of change relies on cause and effect models that are accurate for the local environment. Ideally each intermediary step has indicators, which can be meaningfully measured.
Funders in the development field have also driven the adoption of standardized metrics to express the value of their outcomes. The DALY and QALY, favored by parts of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the World Health Organization, exemplify this practice, but the fundamental idea (having a comparable metric for expressing outcomes) underpins similar methods used by the Hewlett Foundation, the Acumen fund, and the Washington State Institute for Public Policy, among others.
In 1994 a movement to professionalize health development reached a milestone by establishing the DALY, or Disability Adjusted Life Year, intended to be a single metric to capture the impact upon a human of any condition, such as a disease or a trauma. 48 (Development organizations’ interventions aim to reduce that number.)
Using this framework, individuals in the target population experience a condition that burdens them a given amount. For example, total blindness is expressed as a sixty-percent burden, death is a 100-percent burden, whereas protein malnutrition to the point of wasting is considered a 5.3-percent burden. If a person lives with blindness for ten years, they would have lost six DALYs. Protein malnutrition for ten years becomes 0.53 DALYs, and so on. The figure can then be combined into a formula to express costs and benefits across populations: An intervention costing five dollars per person which prevents otherwise certain blindness, given to 100 five-year-olds with a life expectancy of seventy-five years, might be expressed as:
100 * (75-5) * 60% = 4,200 DALY at a cost of 100 * $5 = $500
So this intervention has a cost per DALY of about 12c ($500/4,200) and thusly can be compared to any other intervention.
However, many readers will immediately see that while this might be precise, it has many points incorporating assumptions and estimations which risk losing accuracy and even meaning, while also flattening the lived experience of many individuals into a single number. Within the rich literature critiquing DALY, a Health Policy paper published one year after its introduction acknowledged limitations—including that the DALY sits within a narrow utilitarian value system—but did not wholly reject it. 49 Three years after DALY’s introduction, two more economists from Oxford and Harvard, Sudhir Anand and Kara Hanson, detailed both technical and ethical problems, concluding that DALY’s results would be practically flawed and decisions based on them would also be inequitable. 50 As late as 2014, Princeton researcher Rachel Parks charted the rise, resilience, and continuing use of the DALY through important centers of global health policy. 51
Impact-minded journalists may be interested in the DALY for two main reasons, aside from its persistent power. Philanthropists have the option of giving their money to organizations that can express a likely value of their intervention in a simple number. (Responsible organizations will include caveats and acknowledge uncertainty, but at least they offer a comparable data point.) However, the underlying theory of change in journalism is far less direct than health organizations’. Journalists may need to articulate that their case for funding must embrace that uncertainty. For example, in James T. Hamilton’s book Democracy’s Detectives, he conducts an economic analysis of the cost of producing investigative reporting versus the monetary social value to provide a quantifiable economic societal cost savings. 52
Impact and Metrics in Information and Communication Worlds
Science and social sciences
Moving from the fields of development closer to the world of journalism, we pass academia and scientific research where there has been an established and highly structured metric for impact. When researchers publish formal articles in peer-reviewed journals, those publications will have an “impact factor,” calculated by taking the number of times the journal has been cited in a year and dividing by the total number of articles published over the previous two years, as recorded by Thomson Reuters’ “Journal Citation Report” (JCR). Tenure and promotion committees pay heed when researchers, especially those in the sciences and social sciences, publish papers in highly rated journals such as Science and Nature. However, the “JCR” does have its critics who say that Thomson Reuters’ database skews toward North America, its data is hard to verify, that the calculation cannot fathom whether the citation is approving, disapproving, or central to the citing author’s argument, and a host of other problems.
As a counterpoint to the “JCR” impact factor, some academic researchers have started to pay attention to “Alt-Metrics,” a system which also includes indicators of usage (in the form of views and downloads), peer review, discussion on social media, data usage, as well as citations. 53 Researchers add their own expert understanding to either of those frameworks of whether peers’ findings have become useful and built-upon in the field. For particularly important findings, studies are replicated; theoretically, when the research is done again, in the same way, it should produce the same results.
Advertising/marketing
Leaving aside, for a moment, the vast chasms of motivation, methods, and form (at least traditionally) that separate advertising and journalism, there are still similarities. Advertising intends to persuade the audience, as does some journalism. Advertising’s success metrics, however, are much more clearly linked to driving revenue for businesses (although that relationship became complicated in later years).
Indeed, the early performance indicators for marketing executives in products and services firms were found in the financial statements. In the 1950s and 1960s, according to marketing historian Bruce Clarke, most advertising was judged on whether revenue and/or operating profit went up (more sales being made or products commanding a higher price compared to the cost of production), and/or market share increased. 54 As advertising management became more sophisticated, executives argued that those indicators lagged their output by too much. Their solution was to measure softer, but standardized indicators: primarily, customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, and brand equity. 55 (At this point, journalists might start to see potential lessons: These labels refer to attitudes held by people exposed to media works, although the difficulty remains of proving causality in an intrinsically chaotic environment.) Customer satisfaction was expected to drive future sales revenue in volume and the higher prices customers would be prepared to pay because they were already satisfied with the product. The financial premium derived from satisfaction, loyalty, and audiences’ overall improved perception of the brand, in the form of increased revenue and lower subsequent customer acquisition costs, was called brand equity. Surveys of marketing professionals have revealed more attitudinal metrics, and myriad combinations of financial and non-financial measures, but they still follow the logic that a population’s perception of a product or service will influence the financial statements over time. 56 Marketing and advertising firms traditionally used surveys and focus groups to measure these attitudinal factors, although the advent of social media has produced a set of tools promising to deliver customer insights and measure the impact of marketing and communications. 57
Although journalists may balk at adopting practices from the marketing industries, that field has developed expertise in measuring the effects of their activity.
Documentary filmmaking
Journalists and documentary filmmakers are perhaps the closest relatives in this survey. The fields overlap. However, the inclusion of philanthropic funding sources in documentary economics precedes the rise of the online news organizations like ProPublica and The Marshall Project, which are strongly associated with impact and foundation-funded journalism. As such, the documentary community has established a practice and rhetoric around impact which is more recognized than in other mission-driven journalism.
Media-funding philanthropists, including the Ford Foundation, the Knight Foundation, the Bertha Foundation and the Sundance Institute, underwrote a guide to impact for the documentary field. Its roots lie in a model published by political and communication theorist Harold D. Lasswell in 1948. Lasswell said, simply, the best way to describe an act of communication was:
Who Says What In Which Channel To Whom With What Effect? 58
Jana Diesner, a researcher in computer science with relevance to impact assessment, applied this approach in a framework for measuring the impact of documentaries. She called it the CoMTI model, suggesting research techniques and suitable metrics for measuring results throughout four dimensions of a film: its content, medium, target, and impact. Within the impact dimension Diesner uses the preexisting idea that effects can be on individual, communal, societal, or global levels, which may take the form of changes to awareness, sentiment, and actions. 59 Although Diesner’s CoMTI paper was an intermediary step toward building a computational tool to analyze text from the network of stakeholders around a documentary, the model and its constituent parts is valuable as an extensive catalogue of metrics and research techniques for assessing journalistic impact.
The history of thinking around how journalism affects society supports a conclusion that journalists must accept that their work can and frequently does have consequence. However, unlike some of the other professional fields outlined above, it is easier to see something like influence—one element within a suite of factors leading to an end result, rather than the direct impact of a health intervention like immunizations or cataract surgery. Nonetheless, each of the impact and influence theories discussed above have their limitations. Journalism, which necessarily operates in the chaos of the uncontrolled real world, must expect to tackle uncertainty, which is antithetical to a stable and predictable theory of change.
ICIJ Case Study
The International Consortium of Investigative Journalists was founded by Chuck Lewis in 1997 as part of the Washington, D.C.-based nonprofit Center for Public Integrity (CPI). Observing the rapid globalization of the 1990s, ICIJ’s founders believed that a journalism organization with an international mindset could be well suited to report stories that sprawled beyond any single country. As a time of rapid globalization places “extraordinary pressures on human societies,” 60 according to ICIJ, the organization aims to be a globalized reporting network which counterbalances these pressures.
In October 2016, the CPI announced that ICIJ would spin off to become a free-standing organization. In a press release, the CPI stated: “The CPI’s Board of Directors has decided that enabling ICIJ to chart its own course will help both journalistic teams build on the massive impact they have had as one organization, and allow each to pursue new opportunities and options for funding and pursuing their crucial work.” 61 According to ICIJ director Gerard Ryle, the fundamental differences in ICIJ’s networked, collaborative structure and processes were at odds with the more traditional Center for Public Integrity, which focused on U.S. national, watchdog, and government accountability reporting. Furthermore, international philanthropic entities are governed by the laws, rules, and regulations of the state in which they are based. And, there can be limits to donations on international organizations. An independent ICIJ will then potentially have access to a different and/or increased pool of funders. 62
In this chapter, we examine how ICIJ’s impact imperative affects the organization’s approach to story choice, production, and distribution. We also ask what challenges are associated with this model and share what other journalistic organizations can learn from the experience of ICIJ. We use ICIJ “Evicted and Abandoned” investigation into the World Bank as a prism for separating the structures, processes, calculations, and strategies that together form ICIJ’s high-impact model.
ICIJ’s stated mission is to “be the world’s best cross-border investigative team,” which it does by bringing “journalists from different countries together in teams—eliminating rivalry and promoting collaboration.” 63 While there are indications that collaboration is becoming an emerging norm in today’s new media landscape, ICIJ has been ahead of this curve. In this landscape of increasing collaboration, ICIJ stands out due to the sheer size and scope of its projects, many of which involved dozens of journalists and media organizations across the globe.
The network structure of ICIJ and its syndicated content model were developed with one goal in mind: impact. In interviews and through participant observation with ICIJ staff, we found clear indications that ICIJ’s collaborative nature, cross-border reporting, and, more importantly, its syndicated distribution models continue to be tactics in the service of impact. According to editor Mike Hudson: “Everything is predicated on writing powerful stories: accurate, hard-hitting, deep digging, powerful journalism. And then, readership. But these all dovetail. The primary discussion is about the content, but knowing [the rest] will lead to impact.” 64
Hudson recognizes that impact—real-world change—may take “many years to manifest.” For example, he says, “Action plans are announced but not implemented.” While change might be promised, action can be just “mere spasms of reform that don’t do anyone any good.” The real impact, he adds, “is that change that is sustained attention beyond PR and press releases.”
ICIJ’s networked organizational structure consists of two spheres. At its core, ICIJ directly employs journalists located across the globe (at the time of writing, staff includes six full-time and seven contract journalists), who report, coordinate the reporting efforts of others, and develop projects’ distribution strategies. ICIJ’s extended network includes more than 190 investigative journalists in at least sixty-five countries. These reporters are generally employed by other newsrooms and publish under their employers’ mastheads. ICIJ provides monetary and other resources such as data reporting to in-country reporters, as necessary.
ICIJ assumes that for high-quality investigative stories, the greater the reach of a story and the stronger the distribution partners (in audience size and credibility), the greater the potential for change to remedy the problem (impact). Although ICIJ unambiguously aims for impact and practices journalism in pursuit of exposing problems so they can be fixed, the organization does not acknowledge or promote any specific prescription or outcome.
On the surface, ICIJ’s model seems almost absurdly obvious: Partner with as many reporters and organizations across the globe to conduct in-depth investigations and distribute them globally to reach maximum audience. But the elegance of the model obscures the degree of complexity required in the scaffolding for these projects. The success of ICIJ projects relies on the successful maneuvering of ICIJ to manage partner relationships, expectations, information, and much more. ICIJ senior editor Michael Hudson acknowledges that the partnership model is inefficient if one considers only the number of stories published based on effort put into investigations. However, he says that this model is not necessarily set up for maximum output, but instead for impact: “A key part of impact is agenda-setting and dominating the conversation.”
ICIJ director Gerard Ryle notes that there are two main advantages to the organization’s partnership model, through which they bring partners in early in the reporting process: First, partners are able to contribute reporting resources, and local knowledge and expertise; and second, partners provide almost guaranteed publishing platforms across the globe. He says that with this model, in some cases, “A story can be published in thirty-five countries in a single day.” 65
As a nonprofit, the collaborative model has additional logic for ICIJ. “The basic business model [of journalism] is failing,” Ryle says. “Organizations aren’t spending the kind of money they used to spend on investigative journalism. By pooling resources, we’re able to cut out a lot of the cost.” By sharing photographs, graphics, and travel and document costs, ICIJ is able to manage large-scale projects much more quickly and at lower cost than a traditional newsroom.
Case study: “Evicted and Abandoned”
Spoiler alert: ICIJ’s collaborative “Evicted and Abandoned” investigation found that, over the last decade, projects funded by the World Bank have physically or economically displaced an estimated 3.4 million people; that the World Bank and the International Finance Corporation have financed governments and companies accused of human rights violations; and that, from 2009 to 2013, World Bank Group lenders invested fifty billion dollars into projects graded the highest risk for “irreversible or unprecedented” social or environmental impacts. 66 But how did they get this story? And how did an ICIJ investigation result in a powerful international institution, the World Bank, changing its own internal policy?
ICIJ is known for its big investigations with a leak at the center. However, in 2014, ICIJ wanted to diversify the types of stories it covered so as not to be pigeonholed as an outfit that “just” gets leaks. The brief came down for reporters to begin poking around and pitch ideas. Reporter Sasha Chavkin, sensing a possibility, started going to World Bank seminars in the spring of 2014, where he heard complaints about adverse effects of World Bank projects. Chavkin started to research and found that the complaints panel was hearing from complainants in Kenya, Honduras, and India, and that there were many impoverished people who were having their lives disrupted as a result of World Bank projects.
The World Bank’s state mission is to “end extreme poverty within a generation and boost shared prosperity.” 67 The bank has a promise of no harm, and for infrastructure or other physical projects, it is required to resettle or otherwise recompense affected people. However, Chavkin found indications that there is chronic undercounting of the actual harm done and individuals displaced as a result of World Bank projects, and that, often, the action plans that are designed to mitigate negative effects of bank projects are not implemented. Furthermore, there is no effective redress to any private processes or projects funded in whole or in part by the World Bank, and there are examples of violent evictions and people being displaced into lands controlled by tribes hostile to the new settlers. In one example, it became clear to Chavkin that a sum of the one to two billion-dollar fund made available to an Ethiopian health and education program were going toward forcible resettlement (theoretically to where there was more education infrastructure).
Chavkin says he wanted to understand the deeper roots of this story. Of the investigation, he notes, “I think it’s about both the scale of displacement and human rights abuses and violence associated with World Bank projects, and then the fact that pretty systemically the World Bank seems not to be following its rules for protecting the people who are in the path of its projects.” While local media covered individual cases of violence or wrongdoing resulting from these projects, Chavkin says it took reporting to determine that there was actually a larger systemic problem of forced resettlement that the World Bank seemed to accept fairly routinely as a part of its projects. Furthermore, he says, “There seemed to be very broad failure to take the required steps to protect the people who were being displaced.” 68
Chavkin and his editor, Mike Hudson, found sociologists and others who had been tasked with assessing the potential adverse impact of World Bank projects and who are meant to provide checks on approvals. However, they recognized that these experts do not hold any meaningful power and are often sidelined. Instead, “The World Bank approval side of the operation has all the power,” says Hudson, adding that the World Bank is “run and staffed by engineers and economists who have a very modeled, abstract way of understanding the world.”
When asked what ICIJ identified as a hypothetical “win” would be for the “Evicted and Abandoned” project, editor Mike Hudson says: “A win would be if ICIJ can penetrate the World Bank and write about what’s going on. [To] give voice to the marginalized, give a hearing to the people who are seen as peripheral.” He is clear that, as a news organization, ICIJ can not aim at for specific policy changes, but he asserts: “We want the world, the World Bank, policy makers, politicians, academics, “real people,” activists, voters, media to sit up and listen and read. This is important.”
For “Evicted and Abandoned,” Hudson estimates that ICIJ ultimately partnered with about fifteen other organizations. 69 From the outset, key partners in the United States included the Huffington Post, which was tasked with reporting and building a data interactive, the Global Post, NPR (through a freelancer), the GroundTruth Project, and the Investigative Fund. Internationally, early partners were The Guardian in the United Kingdom, El País in Spain, and three Swiss newspapers. Other partners included the German stations WDR and NDR. ICIJ recognized there was a reporting hole in Asia, so it applied for a grant to do reporting in the region. Ultimately, other partners included Nigeria’s Premium Times, BIRN in the Balkans, a Slovenian freelancer (Blaz Zgaga), radio freelancer Keane Barron (funded through the Fund for Investigative Journalism), freelancer Barry Yeoman (funded by The Nation Institute’s Investigative Reporting Fund), and Fusion.
ICIJ wrote, “In all, more than 50 journalists from 21 countries worked together to document the bank’s lapses and show their consequences for people around the globe.” 70 ICIJ also analyzed thousands of World Bank documents and made them accessible through an interactive database. 71 The byline for the main story read: “By Sasha Chavkin, Ben Hallman, Michael Hudson, Cécile Schilis-Gallego and Shane Shifflett. With reporting from Musikilu Mojeed, Besar Likmeta, Ciro Barros, Giulia Afiune, Mar Cabra, Anthony Langat, Jacob Kushner, Jeanne Baron, Barry Yeoman, Blaž Zgaga and Friedrich Lindenberg. ”
Differing journalistic norms, practices, and standards pose challenges in cross-country collaborations. Hudson says that ICIJ defaults to U.S. standards and style because they stand up elsewhere in the world. While he emphasizes that he doesn’t necessarily think that U.S. journalism is “better” than others, using this as the standard has worked so far.
ICIJ carefully selected reporting and publishing partners to maximize on-the-ground reporting capacity, reach, and potential impact of this investigation. According to Hudson, while “most of the consideration was about the fullness of the story,” there was a deep awareness of audience. “The composition of the partners was totally informed by balance, coverage, and ability of various partners to meet certain needs. For example, [ICIJ selected] Fusion for [its reach and expertise on] social media.”
Early in the reporting process, ICIJ selected the Huffington Post as a core partner with the intent of reaching a wide audience of “non-wonks.” The team immediately began thinking about the design: who would host the project, who would do the reporting, who would be responsible for editing, and who would do the data and design work. In the end, reporters said the reporting and writing was “pretty evenly split” between ICIJ and the HuffPo.
There were two separate data visualizations for this project, one hosted by the Huffington Post and the other by ICIJ. We asked HuffPo data reporter Shane Shifflett how the decision was made to have two visualizations. Shifflett says that HuffPo’s team decided that for its general audience, a map was the easiest way to present the complex information from the investigation. “HuffPo is eager to clue readers into what they can do, talk about solutions, and see how they can help. ICIJ is interested in impact and goals,” he says. 72 So, ICIJ’s visualization was in-depth and made the deep data and records it had used during reporting accessible to its more technical and informed audience in order to provide the necessary information to pressure the World Bank directly.
On the HuffPo side, Shifflet says the team had to completely rethink the way in which it told this investigation for its audience. For example, he says he and his colleagues worked from the assumption that the HuffPo audience would know what the World Bank is, but that they wouldn’t be familiar with the intricacies of how international policy is made or the institutions in place to hold them accountable. Shifflet produced an interactive map and visualizations for the stories hosted on the HuffPo, with the central goal being to increase awareness of the World Bank. Shifflet also recounts that the HuffPo welcomed the opportunity to work with ICIJ’s investigative reporters, and to be able to champion such an important project.
ICIJ shared the full text stories with the Huffington Post and agreed to its posting the content on its website. According to ICIJ’s online editor Hamish Boland-Rudder, “The things I wanted in return for that was guarantee that we’d be able to have access to analytics to track the traffics website on that site, as well as have links back to our site and, more importantly, that these links be fairly prominently displayed. Also, we requested that there be an email sign-up.”
At launch, “Evicted and Abandoned” country-specific stories included Kenya, 73 Ethiopia, 74 Peru, 75 India, 76 Honduras, 77 and Kosovo. 78 The stories were written by a combination of ICIJ staff and partners, with local reporting partners in all cases. According to reporter Sasha Chavkin, ICIJ “chose our case studies based on the severity of impact to displaced communities, the quality of existing documentation, and the extent to which they illustrated larger themes [ICIJ] wanted to investigate (human rights abuses, financial intermediaries, etc.).” He says they also worked to have geographic diversity and to have stories that would be of interest to ICIJ’s partners on the project.
Strategizing for Impact
The project launch date was a key piece of ICIJ’s strategy for “Evicted and Abandoned,” designed to maximize audience reach and the potential for impact. Prior to publication, lead ICIJ reporter on the project Sasha Chavkin explained: “Our launch is going to be the day before the World Bank spring meetings this year. That’s not a coincidence. Right now the Bank is rewriting its safeguard rules. 2 […] And we want our story to come out before the second version is published.” And while Hudson says that the team did not talk explicitly about the impact the project would have, it did make explicit predictions about readership potential, assuming that wide readership was most likely when there was a news hook.
ICIJ decided to have a rolling release of its prepared stories over a four-week period. This strategy was designed to drive sustained traffic, which (in its tacit theory of change) would produce impact. At the time of project launch, ICIJ had eight known stories. Chavkin explains:
We are trying to present the most compelling body of work to the widest audience we can . . . Some of that requires strategic decisions. For example, there are eight stories overall that we have planned. We could release all eight on the same day. We think no one would possibly read of all of them. So that’s why we’re going with four on the first day, and then the others will come out a week at a time after that.
ICIJ had also committed Chavkin and Hudson full time to the project for the remainder of 2015, after having already worked on it for ten months. Mike Hudson says, “That’s where the true impact comes from . . . We get a big bump on the first publish then the traffic reduces. More time allows the team to cover reactions, and respond to any leaks or sources who emerge to suggest new lines of reporting.” He suggests that this style of rolling release and ongoing coverage is different from “most other news organizations.” While he names a few exceptions, such as The New York Times, he says, “Most do big splash then move on.” In addition to a rolling release sustaining public attention and increasing the potential for impact, he says it also allows the story to evolve.
ICIJ staff members emphasize the importance of delineating journalism from advocacy. Ryle, for example, says that while he recognizes that advocacy groups “do fantastic work” with ICIJ stories that contribute to investigations’ impact, “We don’t want to be the advocates for a number of reasons.” He adds: “If our stories are good enough, they’ll get picked up by these groups, and if they’re not, then we’re failing as journalists.” For Ryle, impact can mean many things. “For me, impact is, you know, outrage—public outrage, companies changing laws, parliamentary debates, you know, protests in the streets, all of which we actually do get,” he says.
Online editor Hamish Boland-Rudder says that ICIJ does not have any “official” way to monitor the impact of its projects:
The best thing that I can point towards is I’ve started a tag on our blog: impact tag. And because we have no formal measurement tool setup, I’m not formally reporting things at all. That’s kind of the place where we try and collect the most important stuff or what seems to be the most important stuff. That’s really the only record of it that we have.
Chavkin says he finds out about the impact of his projects mostly from the news, through Google alerts, on Twitter, and from other ICIJ members around the world who tell ICIJ when “stuff is happening.” When something seems important enough to share, Chavkin says, “I put it in a post.”
In the case of “Evicted and Abandoned,” ICIJ knew it had hit a nerve when the World Bank began pushing back on the story before it had even been published. ICIJ reported that, “In March 2015—five days after the reporting team send detailed questions informing the bank it had found “systemic gaps” in its protections for people displaced by its projects—World Bank Group President Jim Yong Kim issued a statement admitting “major problems” with the bank’s resettlement practices and announcing a reform plan to fix them. 79 The World Bank also released a five-and-a-half page document titled, “Action Plan: Improving the Management of Safeguards and Resettlement Practices and Outcomes.” 80 It is worth noting here that ICIJ directly links its reporting to the World Bank response. ICIJ published a follow-up story in May that said former World Bank top employees did not think the Action Plan addresses the deepest flaws in the system. 81
When the investigation was published in mid-April of 2015, the bank pushed back in a more direct way. The Guardian ran a version of the story in which it misstated some of ICIJ’s findings. According to Chavkin and Hudson, “Essentially [ The Guardian ] said that 3.4 million people had been forced from their homes, which was not our finding. It was that 3.4 million were physically or economically displaced. And so the bank made a formal complaint to The Guardian . The Guardian corrected the things they had misstated.” The Guardian readers’ editor wrote a column, “The Readers’ Editor on . . . the Pluses and Perils of Journalistic Partnerships,” in which he admitted the paper’s mistakes and said: “ The Guardian ’s writers and editors failed to get their heads around a complex exposé on which our partners in the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists had been working for months.” 82
The Guardian blunder aside, “Evicted and Abandoned” generated an impressive global response. Chavkin and Hudson followed the global pickup of the story, both by ICIJ partners and other news organizations. While they do not know the number of media outlets that ran the story, they informally kept track of the coverage estimate that there were “more than fifty, probably close to 100” articles written across the globe about the project. “Some of these are about the general findings [of the project], and some have actually used [ICIJ] data to look at displacement occurring within their own countries. So we’re glad to see all of that pickup,” they say.
ICIJ has closely followed the long tail of impact stemming from the project and, in many cases, its team members have written follow-up stories about these changes in order to communicate them with their audiences. However, in these stories about the impact of “Evicted and Abandoned,” ICIJ does not explicitly tie the changes to the investigation.
Immediately following the investigation in April 2015, EarthRights International filed a lawsuit in the United States against the World Bank’s private-sector lending arm, the International Financial Corporation, on behalf of people living and working near a coal plant in northwest India. 83 While ICIJ about this lawsuit, which charges the World Bank with serious environmental and economic to fisherfolk, farmers, and villagers and the parallels to the findings of its own investigation, the post does not say that the lawsuit has any direct relationship to “Evicted and Abandoned.” In July 2015, the IFC claimed legal immunity from being sued in the United States.
In June, ICIJon the dismal results of a World Bank employee survey that found staffers did not have a clear understanding of the direction of the institution, nor did they agree that the bank “creates a culture of openness and trust.” 84 Again, ICIJ did not claim that these survey results, which were worse for the bank than the prior year’s, were a result of “Evicted and Abandoned.” However, the article does construct a timeline in which the World Bank’s surveys shifted significantly from 2014 to 2015, with “Evicted and Abandoned” being one of two incidents that happened between the two (the other being demotions and reduced salaries), thereby implying that it played a role in the employee dissatisfaction. ICIJ also reported that a leaked document with open-ended answers to the survey revealed that staffers fear retaliation from senior management.
In July 2015, ICIJ reported that a World Bank Inspection Panel found that the bank had used outdated census data when funding a power transmission line project in Nepal. 85 This resulted in many more families being displaced and compensation being slow, if at all.
Finally, in December 2015, the World Bank implemented reforms to address the economic and environmental resettlement costs to individuals living in areas where bank projects were developed. 86 The reorganization gives autonomy to specialists who enforce social safeguards, including independent staff and budgets; hires new social safeguard specialists; requires “Resettlement Boot Camp” for all safeguards staff; and increased overall funding for safeguards support. ICIJ reported that the World Bank’s “Resettlement and Safeguards Management” factsheet was a response to its continued reporting on the issue. 87
Honors and awards
Honors and awards are common indicators of the success of any journalistic endeavor. By this standard, “Evicted and Abandoned” was a considerable success.
- National Headliner Award—Online Writing
- Online News Association—The Al Neuharth Innovation in Investigative Journalism Award (Large Newsrooms) 88
- Overseas Press Club of America—Whitman Bassow Award for International Environmental Reporting 89
- New York Press Club—Gold Keyboard Award for Outstanding Enterprise or Investigative Reporting 90
- New York State Society of CPAs—Excellence in Financial Journalism Award
- Society of Professional Journalists/Sigma Delta Chi Award—Feature Photography 91
- Investigative Reporters and Editors Award—Finalist
- Gerald Loeb Award for Distinguished Business and Financial Journalism—Finalist
- Society of American Business Editors and Writers “Best-in-Business” Award—Finalist
- John B. Oakes Award for Distinguished Environmental Journalism—Finalist
- D.C. Chapter of Society of Professional Journalists Dateline Award—Finalist
Challenges and Learnings
A collaborative reporting project of more than fifty reporters and fifteen organizations in twenty-one countries, taking on a behemoth like the World Bank—what could go wrong? While certainly there are nearly infinite answers to this question, in fact, very little did go askew.
According to editor Mike Hudson, the largest challenge with “Evicted and Abandoned,” as with most ICIJ projects, is working with partners in different countries where journalistic norms, practices, and laws vary greatly. However, by using American journalistic norms as the standard and then working closely with reporters who are producing work that will contribute to ICIJ stories, Hudson says they meet issues head on. However, as was seen with The Guardian story that misrepresented “Evicted and Abandoned”’s findings, the model is not bulletproof.
Another challenge when working with partners arises when trying to understand the widespread and multifaceted impact of such a massive undertaking. At the most basic level, ICIJ staff members say that it is difficult, if not impossible, to get web and social media metrics from partners in order to truly know the reach of a project. Furthermore, it’s likely that only a fraction of the on-the-ground, real-world change that happens in the wake of ICIJ projects ever makes its way back to the eyes and ears of ICIJ staff. And, because there are not ICIJ staff dedicated analytics or impact, there is little bandwidth to improve these processes.
But even with these challenges and an incomplete understanding of the scope of impact of “Evicted and Abandoned,” there are at least three lessons worth stating.
First, collaborations, however complicated, result in increased reporting capacity, larger audiences, and greater potential for impact. Having in-country reporters contribute to investigations means reporting can be done more cheaply than otherwise, and with greater cultural competency. This means there is a built-in audience for the stories in countries across the globe.
Related is ICIJ’s above-and-below distribution strategy, where large international media like the Huffington Post and El País generate attention to issues from international elites, while local and national media generate awareness among the most affected populations. The resulting pressure from the grassroots and elites create a vise for institutions and power holders, forcing them to respond. 3 92
Finally, ICIJ stuck with the story long after initial publication, focusing its spotlight on the World Bank and the changes it had committed to making. This rolling thunder approach kept international attention on the World Bank, likely resulting in its continued efforts to address the problems and wrongdoing identified in “Evicted and Abandoned.”
In our experience, news organizations are often wary of putting impact at the center of their operations for fear of getting too close to the ethical line that supposedly separates unbiased journalism from advocacy work, or fear of the perception of straddling that line. However, the case of ICIJ demonstrates that an impact imperative need not cross this line, nor is impact only necessarily a requirement that funders demand of organizations. Instead, by having a clear mission that puts impact at the center of all it does, an organization can formulate its own theory of change (even if implicit) to guide strategy.
When an organization pays attention to the levers of change relevant to an investigation and incorporates these into its strategy for publishing a story, the project often becomes both wider and deeper in scope. Suddenly, editorial partnerships become logical pathways to reach broader audiences, informing more people about wrongdoing and helping to set agendas in geographic locations where structural change is possible.
The next step for media organizations, including ICIJ, is to take the expansive notion of impact that helps to govern internal strategy and communicate these changes with audiences. At a time when the American public’s trust in both media 93 and government 94 hovers at a dismal twenty percent, an all-time low, it is more important than ever to show the positive change that often stems from crucially important investigative reporting. This includes not only the political and institutional responses, but also the more nuanced changes that happen at the level of individuals and communities. Communicating these impacts can potentially help improve public trust in media as an agent for positive change, while also providing models of citizen engagement in processes of social change.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Tow Center for Digital Journalism, especially Pete Brown and Claire Wardle, for their support, patience, and feedback throughout the lifecycle of this project. Many thanks to the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists for participating in this project. The degree of ICIJ reporters’ and editors’ transparency and thoughtfulness have been an inspiration. June 2017
- Various authors, “Evicted and Abandoned: The World Bank’s BrokenPromise to the Poor,” 2015, https://www.icij.org/project/world-bank.
- Antonio Gramsci, Selections from the Prison Notebooks (New York: Interna-tional Publishers, 1971).
- James T. Hamilton, Democracy’s Detectives: The Economics of InvestigativeJournalism (Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2016).
- William Gamson et al., “Media Images and the Social Construction of Real-ity,” Annual Review of Sociology (1992): 373–393, https://www.jstor.org/stable/2083459?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents.
- William Gamson and Andre Modigliani, “Media Discourse and PublicOpinion on Nuclear Power: A Constructionist Approach,” American Journal ofSociology, no. 1 (1989): 1–37, https://www.jstor.org/stable/2780405?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents.
- John S. and James L. Knight Foundation, “Gaining Ground: How NonprofitNews Ventures Seek Sustainability,” 2015, https://www.knightfoundation.org/features/nonprofitnews-2015-revenue/.
- Anya Schiffrin and Ethan Zuckerman, “Can We Measure Media Impact?Surveying the Field,” Social Science Innovation Review, no. 4 (2015), https://ssir.org/articles/entry/can_we_measure_media_impact_surveying_the_field.
- Michael Keller and Brian Abelson, “NEWSLYNX: A Tool for NewsroomImpact Measurement,” Tow Center for Digital Journalism, June 2015, https://towcenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Tow_Center_NewsLynx_Full_Report.pdf.
- “Press Widely Criticized, but Trusted More Than Other InformationSources,” Pew Research Center, September 22, 2011, https://www.people-press.org/2011/09/22/press-widely-criticized-but-trusted-more-than-other-institutions/.
- Caitlin Petre, “The Traffic Factories: Metrics at Chartbeat, Gawker Media,and The New York Times,” May 2015, https://towcenter.org/research/traffic-factories/.
- “About the ICIJ,” International Consortium of Investigative Journalists,2012, https://www.icij.org/about.
- authors, “Evicted and Abandoned: The World Bank’s Broken Promise tothe Poor.”
- James T. Hamilton, All the News That’s Fit to Sell: How the Market Trans-forms Information into News (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2004).
- Tim Groseclose and Jeffrey Milyo, “A Measure of Media Bias,” The Quar-Tow Center for Digital Journalism50 The Case for Media Impactterly Journal of Economics, no. 4 (2005): 1191–1237, https://www.jstor.org/stable/25098770?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents.
- Matthew Gentzkow, “Television and Voter Turnout,” The Quarterly Jour-nal of Economics, no. 3 (2005): 931–972, https://academic.oup.com/qje/article-abstract/121/3/931/1917885/Television-and-Voter-Turnout?related-urls=yes&legid=qje;121/3/931.
- Matthew Gentzkow and Jesse M. Shapiro, “Competition and Truth in theMarket for News,” The Journal of Economic Perspectives, no. 2 (2008): 131–154,https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4719983_Competition_and_Truth_in_the_Market_for_News.
- Hamilton, All the News That’s Fit to Sell: How the Market TransformsInformation into News.
- Gentzkow and Shapiro, “Competition and Truth in the Market for News.”
- Claudia Goldin Matthew Gentzkow Edward L. Glaeser, in (2006).
- Michael Schudson and Chris Anderson, in (2009).
- Johan Galtung and Mari Holmboe Ruge, “The Structure of Foreign News:The Presentation of the Congo, Cuba and Cyprus Crises in Four NorwegianNewspapers,” Journal of Peace Research, no. 1 (1965): 64–90, https://www.jstor.org/stable/423011?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents.
- Sigurd Allern, “Journalistic and Commercial News Values. News Orga-nizations as Patrons of an Institution and Market Actors,” Nordicom Review(2002): 137–152, https://www.nordicom.gu.se/en/tidskrifter/nordicom-review-1-22002/journalistic-and-commercial-news-values-news-organizations.
- Marcia Landy, “Culture and Politics in the Work of Antonio Gramsci,”boundary 2, no. 3 (1986): 49–70, https://www.jstor.org/stable/303233?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents.
- Douglas Kellner, Television and the Crisis of Democracy (Boulder, CO:Westview Press, 1990), 382.
- Gamson et al., “Media Images and the Social Construction of Reality.”
- Ida Schultz, “The Journalistic Gut Feeling: Journalistic Doxa, News Habi-tus and Orthodox News Values,” Journalism Practice, no. 2 (2007): 190–207,https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/17512780701275507.
- Schudson and Anderson,
- William Gamson et al., “Media Images and the Social Construction of Re-ality,” Annual Review of Sociology (1992): 382, https://www.jstor.org/stable/2083459?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents.
- Ida Schultz, “The Journalistic Gut Feeling: Journalistic Doxa, News Habi-tus and Orthodox News Values,” Journalism Practice, no. 2 (2007): 90, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/17512780701275507.
- Ida Schultz, “The Journalistic Gut Feeling: Journalistic doxa, news habi-tus and orthodox news values,” Journalism Practice, no. 2 (2007): 202, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/17512780701275507.
- Schultz, “The Journalistic Gut Feeling: Journalistic Doxa, News Habitusand Orthodox News Values.”
- Maxwell E. McCombs and Donald L. Shaw, “The Agenda-Setting Func-tion of Mass Media,” Public Opinion Quarterly, no. 2 (1972): 176–187, https://www.jstor.org/stable/2747787?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents.
- Spiro K. Kiousis Guy J. Golan and Misti L. McDaniel., “Second-LevelAgenda-Setting and Advertising: Investigating the Transfer of Issue and AttributeSaliency During the 2004 US Presidential Election,” Journalism Studies, no. 3(2007), https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14616700701276190.
- Maxwell E. McCombs, “A Look at Agenda-Setting: Past, Present and Fu-ture,” Journalism Studies, no. 4 (2005): 543–557, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14616700500250438?needAccess=true.
- Michelle Freeman and Laura Jean Berger, “The Issue of Relevance ofAgenda-Setting Theory to the Online Community,” Meta-Communicate, no. 1(2011), https://journals.chapman.edu/ojs/index.php/mc/article/view/267.
- Matthew W. Ragas and Marilyn S. Roberts, “Agenda Setting and AgendaMelding in an Age of Horizontal and Vertical Media: A New Theoretical Lensfor Virtual Brand Communities,” Journalism & Mass Communication Quar-terly, no. 1 (2009): 45–64, https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/107769900908600104.
- Chris J. Vargo et al., “Network Issue Agendas on Twitter During the 2012U.S. Presidential Election: Network Issue Agendas on Twitter,” Journal of Com-munication, no. 2 (2014): 296–316, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jcom.12089/abstract.
- Lindsay Green-Barber, “Impact: From Gold Standard to Convertibility,”The Center for Investigative Reporting, 2014, https://cironline.org/blog/post/impact-gold-standard-convertibility-6187.
- Petre, “The Traffic Factories: Metrics at Chartbeat, Gawker Media, and TheNew York Times.”
- Marc Epstein and Kristi Yuthas, Measuring and Improving Social Im-pacts: A Guide for Nonprofits, Companies, and Impact Investors (San Francisco:Berrett-Koehler Publishers, 2014).
- CJ Murray, “Quantifying the Burden of Disease: The Technical Basis forDisability-Adjusted Life Years,” Bulletin of the World Health Organization, no. 3(1994): 429–445, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8062401.
- Michael R. Reich, “The Politics of Health Sector Reform in DevelopingCountries: Three Cases of Pharmaceutical Policy,” Public Health, nos. 1–3 (1995):47–77, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/016885109500728B.
- Sudhir Anand and Kara Hanson, “Disability-Adjusted Life Years: A Criti-cal Review,” Journal of Health Economics, no. 6 (1997): 685–702, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167629697000052.
- Rachel Parks, “The Rise, Critique and Persistence of the DALY in GlobalHealth,” The Journal of Public Health, August 10, 2014, https://www.ghjournal.org/the-rise-critique-and-persistence-of-the-daly-in-global-health/.
- Hamilton, Democracy’s Detectives: The Economics of Investigative Journal-ism.
- J. Priem et al., “Altmetrics: A Manifesto,” October 26, 2010, https://altmetrics.org/manifesto/.
- Bruce H. Clark, “Marketing Performance Measures: History and Interre-lationships,” Journal of Marketing Management, no. 8 (1999): 711–732, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1362/026725799784772594.
- Flora Kokkinaki Tim Ambler and Stefano Puntoni, “Assessing MarketingPerformance: Reasons for Metrics Selection,” Journal of Marketing Manage-ment, nos. 3–4 (2004): 475–498, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1362/026725704323080506.
- Products include trackur, iSentia, Meltwater, Brandbastion and many others.
- Harold Lasswell, in (1948).
- Jana Diesner, Jinseok Kim, and Susie Pak, “Computational Impact As-sessment of Social Justice Documentaries,” Journal of Electronic Publishing, no.3 (2014), https://quod.lib.umich.edu/cgi/t/text/idx/j/jep/3336451.0017.306/–computational-impact-assessment-of-social-justice?rgn=main;view=fulltext.
- “About the ICIJ.”
- International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, “Center for PublicIntegrity to Spin Off ICIJ,” International Consortium of Investigative Journalists,October 20, 2016, https://www.icij.org/blog/2016/10/center-public-integrity-spin-icij.
- Lindsay Green-Barber, interview with Gerard Ryle, November 9, 2016.
- Fergus Pitt, interview with Michael Hudson, March 14, 2015.
- Fergus Pitt, interview with Gerard Ryle, May 29, 2015.
- Amitava Chandra, “Ending Extreme Poverty and Promoting Shared Pros-perity,” World Bank, April 19, 2013, https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2013/04/17/ending_extreme_poverty_and_promoting_shared_prosperity.
- Fergus Pitt, interview with Sasha Chavkin, March 23, 2015.
- “Reporting Partners,” International Consortium of Investigative Journalists,2015, https://www.icij.org/project/797/partners.
- “About This Project: Evicted and Abandoned,” International Consortium ofInvestigative Journalists, 2015, https://www.icij.org/project/world-bank/about-project-evicted-and-abandoned.
- “Explore 10 Years of World Bank Resettlement Data,” International Con-sortium of Investigative Journalists, 2015, https://www.icij.org/project/world-bank/explore-10-years-world-bank-resettlement-data.
- Lindsay Green-Barber, interview with Shane Shifflett, May 14, 2015.
- Jacob Kushner et al., “Burned Out: World Bank Projects Leave Trail ofMisery,” Huffington Post, April 15, 2015, https://projects.huffingtonpost.com/projects/worldbank-evicted-abandoned/worldbank-projects-leave-trail-misery-around-globe-kenya.
- Sasha Chavkin, “Rights Denied: New Evidence Ties World Bank to HumanRights Abuses in Ethiopia,” Huffington Post, April 15, 2015, https://projects.huffingtonpost.com/projects/worldbank-evicted-abandoned/new-evidence-ties-worldbank-to-human-rights-abuses-ethiopia.
- Ben Hallman and Roxana Olivera, “Gold Rush: How the World Bank IsFinancing Environmental Destruction,” Huffington Post, April 15, 2015, https://projects.huffingtonpost.com/projects/worldbank-evicted-abandoned/how-worldbank-finances-environmental-destruction-peru.
- Barry Yeoman, “The Uncounted: On India’s Coast, a Power Plant Backedby the World Bank Group Threatens a Way of Life,” Huffington Post, May 1,2015, https://projects.huffingtonpost.com/projects/worldbank-evicted-abandoned/india-uncounted.
- Sasha Chavkin, “Bathed in Blood’: World Bank’s Business-Lending ArmBacked Palm Oil Producer Amid Deadly Land War,” Huffington Post, June 9,2015, https://projects.huffingtonpost.com/projects/worldbank-evicted-abandoned/honduras-international-finance-corp-backed-palm-oil-producer.
- Michael Hudson, “Refugees of Development: Kosovars Who Rebuilt War-Torn Village Face New Threat as World Bank Considers Coal-Burning PowerPlant,” Huffington Post, June 18, 2015, https://projects.huffingtonpost.com/projects/worldbank-evicted-abandoned/kosovo-war-torn-village-coal-burning-power-plant.
- Sasha Chavkin, Michael Hudson, and Ben Hallman, “As World Bank AdmitsFailures, Safeguards Questions Remain,” International Consortium of Investiga-tive Journalists, March 5, 2015, https://www.icij.org/blog/2015/03/world-bank-admits-failures-safeguards-questions-remain.
- “Action Plan: Improving the Management of Safeguards and Resettle-ment Practices and Outcomes,” World Bank, March 4, 2015, https://pubdocs.worldbank.org/en/71481425483119932/action-plan-safeguards-resettlement.pdf.
- Sasha Chavkin, “Former World Bank Officials Raise Doubts About Re-form Plan,” International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, May 29, 2015,https://www.icij.org/blog/2015/05/former-world-bank-officials-raise-doubts-about-reform-plan.
- Chris Elliot, “The ReadersÃŢ Editor on . . . the Pluses and Perils of Jour-nalistic Partnerships,” May 3, 2015, https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2015/may/03/we-made-a-meal-of-a-great-story-about-world-bank-projects.
- Michael Hudson and Barry Yeoman, “Lawsuit Accuses World Bank Arm of’Mission Failure’,” International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, April23, 2015, https://www.icij.org/blog/2015/04/lawsuit-accuses-world-bank-arm-mission-failure.
- Sasha Chavkin, “World Bank Workers Losing Faith in Leadership, SurveyReveals,” International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, June 22, 2015,https://www.icij.org/blog/2015/06/world-bank-workers-losing-faith-leadership-survey-reveals.
- Sasha Chavkin, “World Bank Overlooked Families in Nepal Project, PanelFinds,” International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, July 17, 2015,https://www.icij.org/blog/2015/07/world-bank-overlooked-families-nepal-project-panel-finds.
- Sasha Chavkin, “World Bank Rolls Out Reforms to Address ResettlementFailures,” International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, December 22,2015, https://www.icij.org/blog/2015/12/world-bank-rolls-out-reforms-address-resettlement-failures.
- “Our Shared Goals,” World Bank Group, 2015, https://pdu.worldbankgroup.org/?PageName=SafeguardsManagementandResettlement#commitments.
- “2015 Awards,” Online News Association, 2016, https://journalists.org/awards/2015-awards/.
- “18 The Whitman Bassow Award,” Overseas Press Club of America, March24, 2017, https://opcofamerica.org/Awardarchive/18-the-whitman-bassow-award/.
- “The New York Press Club Journalism Awards,” New York Press Club,2016, https://www.nypressclub.org/awards.php.
- “2015 Sigma Delta Chi Award Honorees,” Society of Professional Journalists,2016, https://www.spj.org/sdxa15.asp.
- Lindsay Green-Barber, “Changing the Conversation: The VA Backlog,”Center for Investigative Reporting, 2015, https://s3.amazonaws.com/uploads-cironline-org/uploaded/uploads/VA+Backlog+White+Paper+11.10.14.pdf.
- Amy Mitchell et al., “2. Trust and Accuracy,” Pew Research Center, July 7,2016, https://www.journalism.org/2016/07/07/trust-and-accuracy/.
- “1. Trust in Government: 1958–2015,” Pew Research Center, November 23,2015, https://www.people-press.org/2015/11/23/1-trust-in-government-1958-2015/.
- We acknowledge that advertisers paid a lot of the financial costs of journalism, but readers still need to find value if they are to “pay” for the product with their attention. ↩
- The World Bank safeguard rules are those designed to minimize potential harm to individuals affected by World Bank projects and activities. ↩
- This finding mirrors that in a 2015 study of the impact of the CIR’s reporting on a disability claims backlog at the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. ↩

About the Tow Center
The Tow Center for Digital Journalism at Columbia's Graduate School of Journalism, a partner of CJR, is a research center exploring the ways in which technology is changing journalism, its practice and its consumption — as we seek new ways to judge the reliability, standards, and credibility of information online.
View other Tow articles »
Visit Tow Center website »
The voice of journalism, since 1961
- Privacy Policy
Support CJR
- Become a Member
Social Media Adoption, Usage And Impact In Business-To-Business (B2B) Context: A State-Of-The-Art Literature Review
- Open access
- Published: 02 February 2021
- Volume 25 , pages 971–993, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Yogesh K. Dwivedi 1 ,
- Elvira Ismagilova 2 ,
- Nripendra P. Rana 2 &
- Ramakrishnan Raman 3
95k Accesses
65 Citations
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Social media plays an important part in the digital transformation of businesses. This research provides a comprehensive analysis of the use of social media by business-to-business (B2B) companies. The current study focuses on the number of aspects of social media such as the effect of social media, social media tools, social media use, adoption of social media use and its barriers, social media strategies, and measuring the effectiveness of use of social media. This research provides a valuable synthesis of the relevant literature on social media in B2B context by analysing, performing weight analysis and discussing the key findings from existing research on social media. The findings of this study can be used as an informative framework on social media for both, academic and practitioners.
Similar content being viewed by others

The future of social media in marketing
Gil Appel, Lauren Grewal, … Andrew T. Stephen
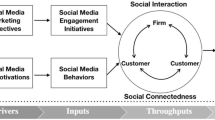
Social media marketing strategy: definition, conceptualization, taxonomy, validation, and future agenda
Fangfang Li, Jorma Larimo & Leonidas C. Leonidou
Social media influencer marketing: foundations, trends, and ways forward
Yatish Joshi, Weng Marc Lim, … Satish Kumar
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The Internet has changed social communications and social behaviour, which lead to the development of new forms of communication channels and platforms (Ismagilova et al. 2017 ). Social media plays an important part in the digital transformation of businesses (Kunsman 2018 ). Digital transformation refers to the globally accelerated process of technical adaptation by companies and communities as a result of digitalisation (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ; Westerman et al. 2014 ). Web is developed from a tool used to provide passive information into the collaborative web, which allows and encourages active user engagement and contribution. If before social networks were used to provide the information about a company or brand, nowadays businesses use social media in their marketing aims and strategies to improve consumers’ involvement, relationship with customers and get useful consumers’ insights (Alalwan et al. 2017 ). Business-to-consumer (B2C) companies widely use social media as part of their digital transformation and enjoy its benefits such as an increase in sales, brand awareness, and customer engagement to name a few (Barreda et al. 2015 ; Chatterjee and Kar 2020 ; Harrigan et al. 2020 ; Kamboj et al. 2018 ; Kapoor et al. 2018 ).
From a marketing and sales research perspective, social media is defined as “the technological component of the communication, transaction and relationship building functions of a business which leverages the network of customers and prospects to promote value co-creation” (Andzulis et al. 2012 p.308). Industrial buyers use social media for their purchase as they compare products, research the market and build relationships with salesperson (Itani et al. 2017 ). Social media changed the way how buyers and sellers interact (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ) by enabling open and broad communications and cooperation between them (Rossmann and Stei 2015 ). Social media is an important facilitator of relationships between a company and customers (Agnihotri et al. 2012 ; Tedeschi 2006 ). Customers are more connected to companies, which make them more knowledgable about product selection and more powerful in buyer-seller relationships (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ). Social media also helps companies to increase business exposure, traffic and providing marketplace insight (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Stelzner 2011 ). As a result, the use of social media supports business decision processes and helps to improve companies’ performance (Rossmann and Stei 2015 ).
Due to digitalisation customers are becoming more informed and rely less on traditional selling initiatives (Ancillai et al. 2019 ). Buyers are relying more on digital resources and their buying process more often involves the use of social media. For example, in the research B2B buyer survey, 82% of buyers stated that social media content has a significant impact on the purchase decision (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Minsky and Quesenberry 2016 ). As a result, these changes in consumer behaviour place high pressure on B2B salespeople and traditional sales companies (Ancillai et al. 2019 ). By using evidence from major B2B companies and consultancy report some studies claim that social media can be applied in sales to establish effective dialogues with buyers (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Kovac 2016 ; McKinsey and Company 2015 ).
Now, business-to-business (B2B) companies started using social media as part of their digital transformation. 83% of B2B companies use social media, which makes it the most common marketing tactic (Pulizzi and Handley 2017 ; Sobal 2017 ). More than 70% of B2B companies use at least one of the “big 4” social media sites such as LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook and YouTube. Additionally, 50% of the companies stated that social media has improved their marketing optimization and customer experience, while 25% stated that their revenue went up (Gregorio 2017 ; Sobal 2017 ). Even though B2B companies are benefitting from social media used by marketers, it is argued that research on that area is still in the embryonic stage and future research is needed (Salo 2017 ; Siamagka et al. 2015 ; Juntunen et al. 2020 ; Iannacci et al. 2020 ). There is a limited understanding of how B2B companies need to change to embrace recent technological innovations and how it can lead to business and societal transformation (Chen et al. 2012 ; Loebbecke and Picot 2015 ; Pappas et al. 2018 ).
The topic of social media in the context of B2B companies has started attracting attention from both academics and practitioners. This is evidenced by the growing number of research output within academic journals and conference proceedings. Some studies provided a comprehensive literature review on social media use by B2B companies (Pascucci et al. 2018 ; Salo 2017 ), but focused only on adoption of social media by B2B or social media influence, without providing the whole picture of the use of social media by B2B companies. Thus, this study aims to close this gap in the literature by conducting a comprehensive analysis of the use of social media by B2B companies and discuss its role in the digital transformation of B2B companies. The findings of this study can provide an informative framework for research on social media in the context of B2B companies for academics and practitioners.
The remaining sections of the study are organised as follows. Section 2 offers a brief overview of the methods used to identify relevant studies to be included in this review. Section 3 synthesises the studies identified in the previous section and provides a detailed overview. Section 4 presents weight analysis and its findings. Next section discusses the key aspects of the research, highlights any limitations within existing studies and explores the potential directions for future research. Finally, the paper is concluded in Section 6 .
2 Literature Search Method
The approach utilised in this study aligns with the recommendations in Webster and Watson ( 2002 ). This study used a keyword search-based approach for identifying relevant articles (Dwivedi et al. 2019b ; Ismagilova et al. 2020a ; Ismagilova et al. 2019 ; Jeyaraj and Dwivedi 2020 ; Williams et al. 2015 ). Keywords such as “Advertising” OR “Marketing” OR “Sales” AND TITLE (“Social Media” OR “Web 2.0” OR “Facebook” OR “LinkedIn” OR “Instagram” OR “Twitter” OR “Snapchat” OR “Pinterest” OR “WhatsApp” OR “Social Networking Sites”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (“B2B” OR “B to B” OR “Business to Business” OR “Business 2 Business”) were searched via the Scopus database. Scopus database was chosen to ensure the inclusion of only high quality studies. Use of online databases for conducting a systematic literature review became an emerging culture used by a number of information systems research studies (Dwivedi et al. 2019a ; Gupta et al. 2019 ; Ismagilova et al. 2020b ; Muhammad et al. 2018 ; Rana et al. 2019 ). The search resulted in 80 articles. All studies were processed by the authors in order to ensure relevance and that the research offered a contribution to the social media in the context B2B discussion. The search and review resulted in 70 articles and conference papers that formed the literature review for this study. The selected studies appeared in 33 separate journals and conference proceedings, including journals such as Industrial Marketing Management, Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing and Journal of Business Research.
3 Literature Synthesis
The studies on social media research in the context of B2B companies were divided into the following themes: effect of social media, adoption of social media, social media strategies, social media use, measuring the effectiveness of use of social media, and social media tools (see Table 1 ). The following subsections provide an overview of each theme.
3.1 Effect of Social Media
Some studies focus on the effect of social media for B2B companies, which include customer satisfaction, value creation, intention to buy and sales, building relationships with customers, brand awareness, knowledge creation, perceived corporate credibility, acquiring of new customers, salesperson performance, employee brand engagement, and sustainability (Table 2 ).
3.1.1 Customer Satisfaction
Some studies investigated how the use of social media affected customer satisfaction (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Rossmann and Stei 2015 ). For example, Agnihotri et al. ( 2016 ) investigated how the implementation of social media by B2B salesperson affects consumer satisfaction. Salesperson’s social media use is defined as a “salesperson’s utilization and integration of social media technology to perform his or her job” (Agnihotri et al. 2016 , p.2). The study used data from 111 sales professionals involved in B2B industrial selling to test the proposed hypotheses. It was found that a salesperson’s use of social media will have a positive effect on information communication, which will, in turn, lead to improved customer satisfaction with the salesperson. Also, it was investigated that information communication will be positively related to responsiveness, which impacts customer satisfaction.
Another study by Rossmann and Stei ( 2015 ) looked at the antecedents of social media use, social media use by B2B companies and their effect on customers. By using data from 362 chief information officers of B2B companies the study found the following. Social media usage of sales representative has a positive impact on customer satisfaction. Age has a negative effect on content generation. It seems that older salespeople use social media in passive ways or interacting with the customer rather than creating their own content. It was found that the quality of corporate social media strategy has a positive impact on social media usage in terms of the consumption of information, content generation, and active interaction with customers. Also, the expertise of a salesperson in the area of social media has a positive impact on social media usage.
3.1.2 Value Creation
Research in B2B found that social media can create value for customers and salesperson (Agnihotri et al. 2012 ; Agnihotri et al. 2017 ). Agnihotri et al. ( 2012 ) proposed a theoretical framework to explain the mechanisms through which salespeople’s use of social media operates to create value and propose a strategic approach to social media use to achieve competitive goals. The study draws on the existing literature on relationship marketing, task–technology fit theory, and sales service behavior to sketch a social media strategy for business-to-business sales organizations with relational selling objectives. The proposed framework describes how social media tools can help salespeople perform service behaviors (information sharing, customer service, and trust-building) leading to value creation.
Some researchers investigated the role of the salesperson in the value creation process after closing the sale. By employing salesperson-customer data within a business-to-business context, Agnihotri et al. ( 2017 ) analysed the direct effects of sales-based CRM technology on the post-sale service behaviors: diligence, information communication, inducements, empathy, and sportsmanship. Additionally, the study examines the interactive effects of sales-based CRM technology and social media on these behaviors. The results indicate that sales-based CRM technology has a positive influence on salesperson service behaviors and that salespeople using CRM technology in conjunction with social media are more likely to exhibit higher levels of SSBs than their counterparts with low social media technology use. Data were collected from 162 salespeople from India. SmartPLS was used to analyse the data.
3.1.3 Intention to Buy and Sales
Another group of studies investigated the effect of social media on the level of sales and consumer purchase intention (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Salo 2017 ; Hsiao et al. 2020 ; Mahrous 2013 ). For example, Itani et al. ( 2017 ) used the theory of reasoned actions to develop a model that tests the factors affecting the use of social media by salesperson and its impact. By collecting data from 120 salespersons from different industries and using SmartPLS to analyse the data, it was found that attitude towards social media usefulness did not affect the use of social media. It was found that social media use positively affects competitive intelligence collection, adaptive selling behaviour, which in turn influenced sales performance. Another study by Ancillai et al. ( 2019 ) used in-depth interviews with social selling professionals. The findings suggest that the use of social media improves not only the level of sales but also affects relationship and customer performance (trust, customer satisfaction, customer referrals); and organisational performance (organisational selling performance and brand performance).
It was investigated that social media has a positive effect on the intention to purchase (Hsiao et al. 2020 ; Mahrous 2013 ). For instance, Mahrous ( 2013 ) by reviewing the literature on B2B and B2C companies concluded that social media has a significant influence on consumer buying behaviour.
3.1.4 Customer Relationships
Another group of studies focused on the effect of social media on customer relationships (Bhattacharjya and Ellison 2015 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gruner and Power 2018 ; Hollebeek 2019 ; Iankova et al. 2018 ; Jussila et al. 2011 ; Kho 2008 ; Niedermeier et al. 2016 ; Ogilvie et al. 2018 ). For example, Bhattacharjya and Ellison ( 2015 ) investigated the way companies build relationships with customers by using responsive customer relationship management. The study analysed customer relationship management activities from Twitter account of a Canadian company Shopify (B2B service provider). The company uses Twitter to engage with small business customers, develops and consumers. Jussila et al. ( 2011 ), by reviewing the literature, found that social media leads to increased customer focus and understanding, increased level of customer service and decreased time-to-market.
Gáti et al. ( 2018 ) focused their research efforts on social media use in customer relationship performance, particularly in customer relations. The study investigated the adoption and impact of social media by salespeople of B2B companies. By using data of 112 salespeople from several industries the study found that the intensity of technology use positively affects attitude towards social media, which positively affects social media use. Intensive technology use in turn positively affects customer relationship performance (customer retention). PLS-SEM was applied for analysis.
Another study by Gruner and Power ( 2018 ) investigated the effectiveness of the use of multiple social media platforms in communications with customers. By using data from 208 large Australian organisations, the paper explores how companies’ investment in one form of social media impacts activity on another form of social media. A regression analysis was performed to analyse the data. It was found that widespread activities on LinkedIn, Twitter and YouTube have a negative effect on a company’s marketing activity on Facebook. Thus, having it is more effective for the company to focus on a specific social media platform in forming successful inter-organisational relationships with customers.
Hollebeek ( 2019 ) proposed an integrative S-D logic/resource-based view (RBV) model of customer engagement. The proposed model considers business customer actors and resources in driving business customer resource integration, business customer resource integration effectiveness and business customer resource integration efficiency, which are antecedents of business customer engagement. Business customer engagement, in turn, results in business customer co-creation and relationship productivity.
Niedermeier et al. ( 2016 ) investigated the use of social media among salespeople in the pharmaceutical industry in China. Also, the study investigated the impact of social media on building culturally specific Guanxi relationships-it involves the exchange of factors to build trust and connection for business purpose. By using in-depth interviews with 3 sales managers and a survey of 42 pharmaceutical sales representatives that study found that WeChat is the most common social media platform used by businesses. Also, it was found to be an important tool in building Guanxi. Future studies should focus on other industries and other types of cultural features in doing business.
Ogilvie et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the effect of social media technologies on customer relationship performance and objective sales performance by using two empirical studies conducted in the United States. The first study used 375 salespeople from 1200 B2B companies. The second study used 181 respondents from the energy solution company. It was found that social media significantly affects salesperson product information communication, diligence, product knowledge and adaptability, which in turn affect customer relationship performance. It was also found that the use of social media technologies without training on technology will not lead to good results. Thus, the results propose that companies should allocate the resources required for the proper implementation of social media strategies. Future research should examine how the personality traits of a salesperson can moderate the implementation of social media technologies.
While most of the studies focused on a single country, Iankova et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the perceived effectiveness of social media by different types of businesses in two countries. By using 449 respondents from the US and the UK businesses, it was found that social media is potentially less important, at the present time, for managing ongoing relationships in B2B organizations than for B2C, Mixed or B2B2C organizations. All types of businesses ascribe similar importance to social media for acquisition-related activities. Also it was found that B2B organizations see social media as a less effective communication channel, and to have less potential as a channel for the business.
3.1.5 Brand Awareness
Some researchers argued that social media can influence brand awareness (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Hsiao et al. 2020 ). For instance, Hsiao et al. ( 2020 ) investigated the effect of social media in the fashion industry. By collecting 1395 posts from lookbook.nu and employing regression analysis it was found that the inclusion of national brand and private fashion brands in the post increased the level of popularity which leads to purchasing interest and brand awareness.
3.1.6 Knowledge Creation
Multiple types of collaborative web tools can help and significantly increase the collaboration and the use of the distributed knowledge inside and outside of the company (McAfee 2006 ). Kärkkäinen et al. ( 2011 ) by analysing previous literature on social media proposed that social media use has a positive effect on sharing and creation of customer information and knowledge in the case of B2B companies.
3.1.7 Corporate Credibility
Another study by Kho ( 2008 ) states the advantages of using social media by B2B companies, which include faster and more personalised communications between customer and vendor, which can improve corporate credibility and strengthen the relationships. Thanks to social media companies can provide more detailed information about their products and services. Kho ( 2008 ) also mentions that customer forums and blog comments in the B2B environment should be carefully monitored in order to make sure that inappropriate discussions are taken offline and negative eWOM communications should be addressed in a timely manner.
3.1.8 Acquiring New Customers
Meire et al. ( 2017 ) investigated the impact of social media on acquiring B2B customers. By using commercially purchased prospecting data, website data and Facebook data from beverage companies the study conducted an experiment and found that social media us an effective tool in acquiring B2B customers. Future work might assess the added value of social media pages for profitability prediction instead of prospect conversion. When a longer timeframe becomes available (e.g., after one year), the profitability of the converted prospects can be assessed.
3.1.9 Salesperson Performance
Moncrief et al. ( 2015 ) investigated the impact of social media technologies on the role of salesperson position. It was found that social media affects sales management functions (supervision, selection, training, compensation, and deployment) and salesperson performance (role, skill, and motivation). Another study by Rodriguez et al. ( 2012 ) examines the effect of social media on B2B sales performance by using social capital theory and collecting data from 1699 B2B salespeople from over 25 different industries. By employing SEM AMOS, the study found that social media usage has a positive significant relationship with selling companies’ ability to create opportunities and manage relationships. The study also found that social media usage has a positive and significant relationship with sales performance (based on relational measurers of sales that focus on behaviours that strengthen the relationship between buyers and sellers), but not with outcome-based sales performance (reflected by quota achievement, growth in average billing size, and overall revenue gain).
3.1.10 Employee Brand Management
The study by Pitt et al. ( 2018 ) focuses on employee engagement with B2B companies on social media. By using results from Glassdoor (2315 five-star and 1983 one-star reviews for the highest-ranked firms, and 1013 five star and 1025 one-star reviews for lowest ranked firms) on employee brand engagement on social media, two key drivers of employee brand engagement by using the content analysis tool DICTION were identified-optimism and commonality. Individuals working in top-ranked companies expressed a higher level of optimism and commonality in comparison with individuals working in low-ranked companies. As a result, a 2 × 2 matrix was constructed which can help managers to choose strategies in order to increase and improve employee brand engagement. Another study by Pitt et al. ( 2017 ) focused on employee engagement of B2B companies on social media. By using a conceptual framework based on a theory of word choice and verbal tone and 6300 reviews collected from Glassdoor and analysed using DICTION. The study found that employees of highly ranked B2B companies are more positive about their employer brand and talk more optimistically about these brands. For low ranked B2B companies it was found that employees express a greater level of activity, certainty, and realism. Also, it was found that they used more aggressive language.
3.1.11 Sustainability
Sustainability refers to the strategy that helps a business “to meet its current requirements without compromising its ability to meet future needs” (World Commission Report on Environment and Development 1987 , p 41). Two studies out of 70 focused on the role of social media for B2B sustainability (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ; Kasper et al. 2015 ). For example, Sivarajah et al. ( 2019 ) argued that big data and social media within a participatory web environment to enable B2B organisations to become profitable and remain sustainable through strategic operations and marketing related business activities.
Another study by Kasper et al. ( 2015 ) proposed the Social Media Matrix which helps companies to decide which social media activities to execute based on their corporate and communication goals. The matrix includes three parts. The first part is focusing on social media goals and task areas, which were identified and matched. The second part consists of five types of social media activities (content, interaction/dialog, listening and analysing, application and networking). The third part provides a structure to assess the suitability of each activity type on each social media platform for each goal. The matrix was successfully tested by assessing the German B2B sector by using expert interviews with practitioners.
Based on the reviewed studies, it can be seen that if used appropriately social media have positive effect on B2B companies before and after sales, such as customer satisfaction, value creation, intention to buy and sales, customer relationships, brand awareness, knowledge creation, corporate credibility, acquiring new customers, salesperson performance, employee brand management, and sustainability. However, limited research is done on the negative effect of social media on b2b companies.
3.2 Adoption of Social Media
Some scholars investigated factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies (Buratti et al. 2018 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gazal et al. 2016 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Kumar and Möller 2018 ; Lacka and Chong 2016 ). For instance, Lacka and Chong ( 2016 ) investigated factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies from different industries in China. The study collected the data from 181 respondents and used the technology acceptance model with Nielsen’s model of attributes of system acceptability as a theoretical framework. By using SEM AMOS for analysis the study found that perceived usability, perceived usefulness, and perceived utility positively affect adoption and use of social media by B2B marketing professionals. The usefulness is subject to the assessment of whether social media sites are suitable means through which marketing activities can be conducted. The ability to use social media sites for B2B marketing purposes, in turn, is due to those sites learnability and memorability attributes.
Another study by Müller et al. ( 2018 ) investigated factors affecting the usage of social media. By using survey data from 100 Polish and 39 German sensor suppliers, it was found that buying frequency, the function of a buyer, the industry sector and the country does not affect the usage of social media in the context of sensor technology from Poland and Germany. The study used correlation analysis and ANOVA.
Lashgari et al. ( 2018 ) studied the adoption and use of social media by using face-to-face interviews with key managers of four multinational corporations and observations from companies’ websites and social media platforms. It was found that that the elements essential in forming the B2B firm’s social media adoption strategies are content (depth and diversity), corresponding social media platform, the structure of social media channels, the role of moderators, information accessibility approaches (public vs. gated-content), and online communities. These elements are customized to the goals and target group the firm sets to pursue. Similarly, integration of social media into other promotional channels can fall under an ad-hoc or continuous approach depending on the scope and the breadth of the communication plan, derived from the goal.
Similar to Lashgari et al. ( 2018 ), Shaltoni ( 2017 ) used data from managers. The study applied technology organisational environmental framework and diffusion of innovations to investigate factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies. By using data from marketing managers or business owners of 480 SMEs, the study found that perceived relative advance, perceive compatibility, organizational innovativeness, competitor pressure, and customer pressure influence the adoption of social media by B2B companies. The findings also suggest that many decision-makers in B2B companies think that Internet marketing is not beneficial, as it is not compatible with the nature of B2B markets.
Buratti et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the adoption of social media by tanker shipping companies and ocean carriers. By using data from 60 companies the following was found. LinkedIn is the most used tool, with a 93.3% adoption rate. Firm size emerges as a predictor of Twitter’s adoption: big companies unveil a higher attitude to use it. Finally, the country of origin is not a strong influential factor in the adoption rate. Nonetheless, Asian firms clearly show a lower attitude to join SM tools such as Facebook (70%) and LinkedIn (86.7%), probably also due to governmental web restrictions imposed in China. External dimensions such as the core business, the firm size, the geographic area of origin, etc., seem to affect network wideness. Firm size, also, discriminates the capacity of firms to build relational networks. Bigger firms create networks larger than small firms do. Looking at geographical dimensions, Asian firms confirm to be far less active on SM respect to European and North American firms. Finally, the study analyzed the format of the contents disclosed by sample firms, observing quite limited use of photos and videos: in the sample industries, informational contents seem more appropriate for activating a dialogue with stakeholders and communication still appears formulated in a very traditional manner. Preliminary findings suggest that companies operating in conservative B2B services pursue different strategic approaches toward SMM and develop ad hoc communication tactics. Nonetheless, to be successful in managing SM tools, a high degree of commitment and a clear vision concerning the role of SM within communication and marketing strategy is necessary.
Gazal et al. ( 2016 ) investigated the adoption and measuring of the effectiveness of social media in the context of the US forest industry by using organisational-level adoption framework and TAM. By using data from 166 companies and performing regression analysis, the following results were received. Years in business, new sales revenue, product type, amount of available information on a company website, perceived importance of e-commerce and perceived ease of use of social media significantly affected social media use. Also, it was found that companies’ strategies and internal resources and capabilities and influence a company’s decision to adopt social media. Also, it was found that 94 of respondents do not measure the ROI from social media use. The reason is that the use of social media in marketing is relatively new and companies do not possess the knowledge of measuring ROI from the use of social media. Companies mostly use quantitative metrics (number of site visits, number of social network friends, number of comments and profile views) and qualitative metrics (growth of relationships with the key audience, audience participation, moving from monologue to dialogue with consumers. Facebook was found to be the most effective social media platform reported by the US forest industry.
The study by Kumar and Möller ( 2018 ) investigated the role of social media for B2B companies in their recruitment practices. By using data from international B2B company with headquarter in Helsinki, Finland comprised of 139 respondents it was found that brand familiarity encourages them to adopt social media platforms for a job search; however, the effect of the persuasiveness of recruitment messages on users’ adoption of social media platforms for their job search behavior is negative. The study used correlation analysis and descriptive analysis to analyse the data.
Nunan et al. ( 2018 ) identified areas for future research such as patterns of social media adoption, the role of social media platforms within the sales process, B2B consumer engagement and social media, modeling the ROI of social media, and the risks of social media within B2B sales relationships.
The study by Pascucci et al. ( 2018 ) conducted a systematic literature review on antecedents affecting the adoption and use of social media by B2B companies. By reviewing 29 studies published in academic journal and conferences from 2001 to 2017, the study identified external (pressure from customers, competitors, availability of external information about social media) and internal factors (personal characteristics -managers age, individual commitment, perceptions of social media-perceived ease of use, perceived usefulness, perceived utility), which can affect adoption of social media.
The study by Siamagka et al. ( 2015 ) aims to investigate factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B organisations. The conceptual model was based on the technology acceptance model and the resource-based theory. AMOS software and Structural equation modelling were employed to test the proposed hypotheses. By using a sample of 105 UK companies, the study found that perceived usefulness of social media is influenced by image, perceived ease of use and perceived barriers. Also, it was found that social media adoption is significantly determined by organisational innovativeness and perceived usefulness. Additionally, the study tested the moderating role of organisational innovativeness and found that it does not affect the adoption of social media by B2B organisations. The study also identified that perceived barriers to SNS (uncertainty about how to use SNS to achieve objectives, employee’s lack of knowledge about SNS, high cost of investment needed to adopt the technology) have a negative impact on perceived usefulness of social media by B2B organisations. The study also used nine in-depth interviews with B2B senior managers and social media specialists about adoption of social media by B2B. It was found that perceived pressure from stakeholders influences B2B organisations’ adoption intention of social media. Future research should test it by using quantitative methods.
While most of the studies focused on the antecedents of social media adoption by B2B companies, Michaelidou et al. ( 2011 ) investigated the usage, perceived barriers and measuring the effectiveness of social media. By using data from 92 SMEs the study found that over a quarter of B2B SMEs in the UK are currently using SNS to achieve brand objectives, the most popular of which is to attract new customers. The barriers that prevent SMEs from using social media to support their brands were lack of staff familiarity and technical skills. Innovativeness of a company determined the adoption of social media. It was found that most of the companies do not evaluate the effectiveness of their SNS in supporting their brand. The most popular measures were the number of users joining the groups/discussion and the number of comments made. The findings showed that the size of the company does not influence the usage of social media for small and medium-sized companies. Future research should investigate the usage of social media in large companies and determine if the size can have and influence on the use. The benefits of using social media include increasing awareness and communicating the brand online. B2B companies can employ social media to create customer value in the form of interacting with customers, as well as building and fostering customer relationships. Future research should investigate the reasons why most of the users do not assess the effectiveness of their SNS. Future research should also investigate how the attitude towards technology can influence the adoption of social media.
Based on the reviewed studies it can be seen that the main factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies are perceived usability, technical skills of employees, pressure from stakeholders, perceived usefulness and innovativeness.
3.3 Social Media Strategies
Another group of studies investigated types of strategies B2B companies apply (Cawsey and Rowley 2016 ; Huotari et al. 2015 ; Kasper et al. 2015 ; McShane et al. 2019 ; Mudambi et al. 2019 ; Swani et al. 2013 ; Swani et al. 2014 ; Swani et al. 2017 ; Watt 2010 ). For example, Cawsey and Rowley ( 2016 ) focused on the social media strategies of B2B companies. By conducting semi-structured interviews with marketing professionals from France, Ireland, the UK and the USA it was found that enhancing brand image, extending brand awareness and facilitating customer engagement were considered the most common social media objective. The study proposed the B2B social media strategy framework, which includes six components of a social media strategy: 1) monitoring and listening 2) empowering and engaging employees 3) creating compelling content 4) stimulating eWOM 5) evaluating and selecting channels 6) enhancing brand presence through integrating social media.
Chirumalla et al. ( 2018 ) focused on the social media engagement strategies of manufacturing companies. By using semi-structured interviews (36), observations (4), focus group meetings (6), and documentation, the study developed the process of social media adoption through a three-phase engagement strategy which includes coordination, cooperation, and co-production.
McShane et al. ( 2019 ) proposed social media strategies to influence online users’ engagement with B2B companies. Taking into consideration fluency lens the study analysed Twitter feeds of top 50 social B2B brands to examine the influence of hashtags, text difficulty embedded media and message timing on user engagement, which was evaluated in terms of likes and retweets. It was found that hashtags and text difficulty are connected to lower levels of engagement while embedded media such as images and videos improve the level of engagement.
Swani et al. ( 2014 ) investigate the use of Twitter by B2B and B2C companies and predict factors that influence message strategies. The study conducted a longitudinal content analysis by collecting 7000 tweets from Fortune 500 companies. It was found that B2B and B2C companies used different message appeals, cues, links and hashtags. B2B companies tend to use more emotional than functional appeals. It was found that B2B and B2C companies do not use hard-sell message strategies.
Another study by Swani et al. ( 2013 ) aimed to investigate message strategies that can help in promoting eWOM activity for B2B companies. By applying content analysis and hierarchical linear modeling the study analysed 1143 wall post messages from 193 fortune 500 Facebook accounts. The study found that B2B account posts will be more effective if they include corporate brand names and avoid hard sell or explicitly commercial statement. Also, companies should use emotional sentiment in Facebook posts.
Huotari et al. ( 2015 ) aimed to investigate how B2B marketers can influence content creation in social media. By conducting four face-to-face interviews with B2B marketers, it was found that a B2B company can influence content creation in social media directly by adding new content, participating in a discussion and removing content through corporate user accounts and controlling employees social media behaviour. Also, it can influence it indirectly by training employees to create desired content and perfuming marketing activities that influence other users to create content that is favorable for the company.
Most of the studies investigated the strategies and content of social media communications of B2B companies. However, the limited number of studies investigated the importance of CEO engagement on social media in the company’s strategies. Mudambi et al. ( 2019 ) emphasise the importance of the CEO of B2B companies to be present and active on social media. The study discusses the advantages of social media presence for the CEO and how it will benefit the company. For example, one of the benefits for the CEO can be perceived as being more trustworthy and effective than non-social CEOs, which will benefit the company in increased customer trust. Mudambi et al. ( 2019 ) also discussed the platforms the CEO should use and posting frequencies depending on the content of the post.
From the above review of the studies, it can be seen that B2B companies social media strategies include enhancing brand image, extending brand awareness and facilitating customer engagement. Companies use various message strategies, such as using emotional appeal, use of brand names, and use of hashtags. Majority of the companies avoid hard sell or explicitly commercial statement.
3.4 Social Media Use
Studies investigated the way how companies used social media and factors affecting the use of social media by B2B (Andersson et al. 2013 ; Bernard 2016 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ; Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü 2018 ; Dyck 2010 ; Guesalaga 2016 ; Habibi et al. 2015 ). For example, Vasudevan and Kumar ( 2018 ) investigated how B2B companies use social media by analysing 325 brand posts of Canon India, Epson India, and HP India on Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter. By employing content analysis the study found that most of the posts had a combination of text and message. More than 50% of the posts were about product or brand-centric. The study argued that likes proved to be an unreliable measure of engagement, while shares were considered a more reliable metric. The reason was that likes had high spikes when brand posts were boosted during promotional activities.
Andersson and Wikström ( 2017 ) used case studies of three B2B companies to investigate reasons for using social media. It was found that companies use social media to enhance customer relationships, support sales and build their brands. Also, social media is used as a recruiting tool, a seeking tool, and a product information and service tool.
Bell and Shirzad ( 2013 ) aimed to conduct social media use analysis in the context of pharmaceutical companies. The study analysed 54,365 tweets from the top five pharmaceutical companies. The study analysed the popular time slots, the average number of positive and negative tweets and its content by using Nvivo9.
Bernard ( 2016 ) aims to examine how chief marketing officers use social media. By using case studies from IBM experience with social media it was found that B2B CMO’s are not ready to make use of social media. It was proposed that social media can be used for after-sales service, getting sales leads, engaging with key influencers, building the company’s reputation and enhancing the industry status of key individuals. B2B firms need to exploit the capabilities of processing massive amounts of data to get the most from social media.
Bolat et al. ( 2016 ) explore how companies apply mobile social media. By employing a grounded theory approach to analyse interviews from 26 B2B company representatives from UK advertising and marketing sector companies. It was found that companies use social media for branding, sensing market, managing relationships, and developing content.
Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü ( 2018 ) investigated how social media usage influence stakeholder engagement focusing on the corporate Facebook page of 30 3PLs companies. In total 1532 Facebook posts were analysed. It was found that the number of followers, post sharing frequency, negatively affect stakeholder engagement. It was found that content including photos facilitates more stakeholder engagement (likes, comment, share) in comparison with other forms. Vivid posts and special day celebration posts strengthen relationships with stakeholders.
Dyck ( 2010 ) discussed the advantages of using social media for the device industry. Social media can be used for product innovation and development, to build a team and collaborate globally. Also, there is an opportunity to connect with all of the stakeholders needed in order to deliver the device to the market. Additionally, it provides to receive feedback from customers (doctors, hospitals) in real-time.
The study by Guesalaga ( 2016 ) draws on interactional psychology theory to propose and test a model of usage of social media in sales, analysing individual, organizational, and customer-related factors. It was found that organizational competence and commitment to social media are key determinants of social media usage in sales, as well as individual commitment. Customer engagement with social media also predicts social media usage in sales, both directly and (mostly) through the individual and organizational factors analysed, especially organizational competence and commitment. Finally, the study found evidence of synergistic effects between individual competence and commitment, which is not found at the organizational level. The data obtained by surveying 220 sales executives in the United States were analysed using regression analysis.
Habibi et al. ( 2015 ) proposed a conceptual model for the implementation of social media by B2B companies. Based on existing B2B marketing, social media and organisational orientational literature the study proposed that four components of electronic market orientation (philosophical, initiation, implementation and adoption) address different implementation issues faced in implementing social media.
Katona and Sarvary ( 2014 ) presented a case of using social media by Maersk-the largest container shipping company in the world. The case provided details on the program launch and the integration strategy which focused on integrating the largest independent social media operation into the company’s broader marketing efforts.
Moore et al. ( 2013 ) provided insights into the understanding of the use of social media by salespersons. 395 salespeople in B2B and B2C markets, utilization of relationship-oriented social media applications are presented and examined. Overall, findings show that B2B practitioners tend to use media targeted at professionals whereas their B2C counterparts tend to utilize more sites targeted to the general public for engaging in one-on-one dialogue with their customers. Moreover, B2B professionals tend to use relationship-oriented social media technologies more than B2C professionals for the purpose of prospecting, handling objections, and after-sale follow-up.
Moore et al. ( 2015 ) investigated the use of social media between B2B and B2C salespeople. By using survey data from 395 sales professionals from different industries they found that B2B sales managers use social selling tools significantly more frequently than B2C managers and B2C sales representatives while conducting sales presentations. Also, it was found that B2B managers used social selling tools significantly more frequently than all sales representatives while closing sales.
Müller et al. ( 2013 ) investigated social media use in the German automotive market. By using online analysis of 10 most popular car manufacturers online social networks and surveys of six manufacturers, 42 car dealers, 199 buyers the study found that social media communication relations are widely established between manufacturers and (prospective) buyers and only partially established between car dealers and prospective buyers. In contrast to that, on the B2B side, social media communication is rarely used. Social Online Networks (SONs) are the most popular social media channels employed by businesses. Manufacturers and car dealers focus their social media engagement, especially on Facebook. From the perspective of prospective buyers, however, forums are the most important source of information.
Sułkowski and Kaczorowska-Spychalska ( 2016 ) investigated the adoption of social media by companies in the Polish textile-clothing industry. By interviewing seven companies representatives of small and medium-sized enterprises the study found that companies started implementing social media activities in their marketing activities.
Vukanovic ( 2013 ) by reviewing previous literature on social media outlined advantages of using social media for B2B companies, which include: increase customer loyalty and trust, building and improving corporate reputation, facilitating open communications, improvement in customer engagement to name a few.
Keinänen and Kuivalainen ( 2015 ) investigated factors affecting the use of social media by B2B customers by conducting an online survey among 82 key customer accounts of an information technology service company. Partial least squares path modelling was used to analysed the proposed hypotheses. It was found that social media private use, colleague support for using SM, age, job position affected the use of social media by B2B customers. The study also found that corporate culture, gender, easiness to use, and perception of usability did not affect the use of social media by B2B customers.
By using interviews and survey social media research found that mostly B2B companies use social media to enhance customer relationships, support sales, build their brands, sense market, manage relationships, and develop content. Additionally, some companies use it social media as a recruitment tool. The main difference between B2B and B2C was that B2B sales managers use social selling tools significantly more frequently than B2C managers.
3.5 Measuring the Effectiveness of Social Media
It is important for a business to be able to measure the effectiveness of social media by calculating return on investment (ROI). ROI is the relationship between profit and the investment that generate that profit. Some studies focused on the ways B2B companies can measure ROI and the challenges they face (Gazal et al. 2016 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ; Vasudevan and Kumar 2018 ). For example, Gazal et al. ( 2016 ) investigated the adoption and measuring of the effectiveness of social media in the context of the US forest industry by using organisational-level adoption framework and TAM. By using data from 166 companies it was found that 94% of respondents do not measure the ROI from social media use. The reason is that the use of social media in marketing is relatively new and companies do not possess the knowledge of measuring ROI from the use of social media. Companies mostly use quantitative metrics (number of site visits, number of social network friends, number of comments and profile views) and qualitative metrics (growth of relationships with the key audience, audience participation, moving from monologue to dialogue with consumers).
Another study by Michaelidou et al. ( 2011 ) found that most of the companies do not evaluate the effectiveness of their SNS in supporting their brand. The most popular measures were the number of users joining the groups/discussion and the number of comments made.
Vasudevan and Kumar ( 2018 ) investigated how B2B companies use social media and measure ROI from social media by analysing 325 brand posts of Canon India, Epson India, and HP India on Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter. By employing content analysis the study found that most of the post has a combination of text and message. More than 50% of the posts were about product or brand-centric. The study argued that likes proved to be an unreliable measure of engagement, while shares were considered a more reliable metric. The reason was that likes had high spikes when brand posts were boosted during promotional activities. Future research should conduct longitudinal studies.
By reviewing the above studies, it can be concluded that companies still struggle to find ways of measuring ROI and applying correct metrics. By gaining knowledge in how to measure ROI from social media activities, B2B companies will be able to produce valuable insights leading to better marketing strategies (Lal et al. 2020 ).
3.6 Social Media Tools
Some studies proposed tools that could be employed by companies to advance their use of social media. For example, Mehmet and Clarke ( 2016 ) proposed a social semiotic multimodal (SSMM) framework that improved the analysis of social media communications. This framework employs multimodal extensions to systemic functional linguistics enabling it to be applying to analysing non-language as well as language constituents of social media messages. Furthermore, the framework also utilises expansion theory to identify, categorise and analyse various marketing communication resources associated with marketing messages and also to reveal how conversations are chained together to form extended online marketing conversations. This semantic approach is exemplified using a Fairtrade Australia B2B case study demonstrating how marketing conversations can be mapped and analysed. The framework emphasises the importance of acknowledging the impact of all stakeholders, particularly messages that may distract or confuse the original purpose of the conversation.
Yang et al. ( 2012 ) proposed the temporal analysis technique to identify user relationships on social media platforms. The experiment was conducted by using data from Digg.com . The results showed that the proposed techniques achieved substantially higher recall but not very good at precision. This technique will help companies to identify their future consumers based on their user relationships.
Based on the literature review, it can be seen that B2B companies can benefit by using the discussed tools. However, it is important to consider that employee should have some technical skills and knowledge to use these tools successfully. As a result, companies will need to invest some resources in staff training.
4 Weight Analysis
Weight analysis enables scrutiny of the predictive power of independent variables in studied relationships and the degree of effectiveness of the relationships (Jeyaraj et al. 2006 ; Rana et al. 2015 ; Ismagilova et al. 2020a ). The results of weight analysis are depicted in Table 3 providing information about an independent variable, dependent variable, number of significant relationships, number of non-significant relationships, the total number of relationships and weight. To perform weight analysis, the number of significant relationships was divided by the total number of analysed relationships between the independent variable and the dependent variable (Jeyaraj et al. 2006 ; Rana et al. 2015 ). For example, the weight for the relationship between attitude towards social media and social media is calculated by dividing ‘1’ (the number of significant relationships) by ‘2’ (the total number of relationships) which equals 0.5.
A predictor is defined as well-utilised if it was examined five or more times, otherwise, it is defined as experimental. It can be seen from Table 3 that all relationships were examined less than five times. Thus all studied predictors are experimental. The predictor is defined as promising when it has been examined less than five times by existing studies but has a weight equal to ‘1’ (Jeyaraj et al. 2006 ). From the predictors affecting the adoption of social media, it can be seen that two are promising, technical skills of employees and pressure from stakeholders. Social media usage is a promising predictor for acquiring new customers, sales, stakeholder engagement and customer satisfaction. Perceived ease of use and age of salesperson are promising predictors of social media usage. Even though this relationship was found to be significant every time it was examined, it is suggested that this variable, which can also be referred to as experimental, will need to be further tested in order to qualify as the best predictor. Another predictor, average rating of product/service, was examined less than five times with a weight equal to 0.75, thus it is considered as an experimental predictor.
Figure 1 shows the diagrammatic representation of the factors affecting different relationships in B2B social media with their corresponding weights, based on the results of weight analysis. The findings suggest that promising predictors should be included in further empirical studies to determine their overall performance.
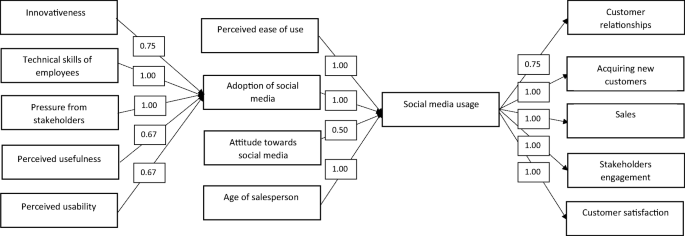
Diagrammatic representation of results of weight analysis. Note: experimental predictors
It can be seen from Fig. 1 that social media usage is affected by internal (e.g. attitude towards social media, technical skills of employees) and external factors (e.g. pressure from stakeholders) of the company. Also, the figure depicts the effect of social media on the business (e.g. sales) and society (e.g. customer satisfaction).
5 Discussion
In reviewing the publications gathered for this paper, the following themes were identified. Some studies investigated the effect of social media use by B2B companies. By using mostly survey to collect the data from salespeople and managers, the studies found that social media has a positive effect on number of outcomes important for the business such as customer satisfaction, value creation, intention to buy and sales, customer relationships, brand awareness, knowledge creation, corporate credibility, acquiring new customers, salespersons performance, employee brand management, and sustainability. Most of the outcomes are similar to the research on social media in the context of B2C companies. However, some of the outcomes are unique for B2B context (e.g. employee brand management, company credibility). Just recently, studies started investigating the impact of the use of social media on sustainability.
Another group of studies looked at the adoption of social media by B2B companies (Buratti et al. 2018 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gazal et al. 2016 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Kumar and Möller 2018 ). The studies investigated it mostly from the perspectives of salespersons and identify some of the key factors which affect the adoption, such as innovativeness, technical skills of employees, pressure from stakeholders, perceived usefulness, and perceived usability. As these factors are derived mostly from surveys conducted with salespersons findings can be different for other individuals working in the organisation. This it is important to conduct studies that will examine factors affecting the adoption of social media across the entire organisation, in different departments. Using social media as part of the digital transformation is much bigger than sales and marketing, it encompasses the entire company. Additionally, most of the studies were cross-sectional, which limits the understanding of the adoption of social media by B2B over time depending on the outcomes and environment (e.g. competitors using social media).
Some studies looked at social media strategies of B2B companies (Cawsey and Rowley 2016 ; Huotari et al. 2015 ; Kasper et al. 2015 ; McShane et al. 2019 ; Mudambi et al. 2019 ). By employing interviews with companies’ managers and analysing its social media platforms (e.g. Twitter) it was found that most of the companies follow the following strategies: 1) monitoring and listening 2) empowering and engaging employees 3) creating compelling content 4) stimulating eWOM 5) evaluating and selecting channels 6) enhancing brand presence through integrating social media (Cawsey and Rowley 2016 ). Some studies investigated the difference between social media strategies of B2B and B2C companies. For example, a study by Swani et al. ( 2017 ) focused on effective social media strategies. By applying psychological motivation theory the study examined the key differences in B2B and B2C social media message strategies in terms of branding, message appeals, selling, and information search. The study used Facebook posts on brand pages of 280 Fortune companies. In total, 1467 posts were analysed. By using Bayesian models, the results showed that the inclusion of corporate brand names, functional and emotional appeals and information search cues increases the popularity of B2B messages in comparison with B2C messages. Also, it was found that readers of B2B content show a higher message liking rate and lower message commenting rate in comparison with readers of B2C messages.
The next group of studies looked at social media use by B2B companies (Andersson et al. 2013 ; Bernard 2016 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ; Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü 2018 ; Dyck 2010 ; Guesalaga 2016 ; Habibi et al. 2015 ). B2B companies use social media for enhancing and managing customer relationships (Andersson and Wikström 2017 ; Bolat et al. ( 2016 ); branding (Andersson and Wikström 2017 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ), sensing market (Bolat et al. 2016 ) and co-production (Chirumalla et al. 2018 ). Additionally, it was mentioned that some of the B2B companies use social media as a recruiting tool, and tool which helps to collaborate globally (Andersson and Wikström 2017 ; Dyck 2010 ).
It is important for companies to not only use social media to achieve positive business outcomes but also it is important to measure their achievements. As a result, some of the studies focused on the measuring effectiveness of social media (Gazal et al. 2016 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ; Vasudevan and Kumar 2018 ). Surprisingly, it was found that not so many companies measure ROI from social media (Gazal et al. 2016 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ). The ones who do it mostly use quantitative metrics (number of site visits, number of social network friends, number of comments and profile views) and qualitative metrics (growth of relationships with key audience, audience participation, moving from monologue to dialogue with consumers) (Gazal et al. 2016 ). Some future studies should investigate how ROI influences the strategy of B2B companies over period of time.
The last group of studies focused on social media tools used by B2B companies (Keinänen and Kuivalainen 2015 ; Mehmet and Clarke 2016 ; Yang et al. 2012 ). By using number of social media tools (Social Semiotic Multimodal) companies are able to improve their analysis of social media communications and identify their future consumers based on their user relationships. Studies investigating barriers and factors adoption of various social media tools by B2B companies are needed.
After reviewing studies on b2B social media, weight analysis was performed. Based on the results of weight analysis the conceptual model for future studies was proposed (Fig. 2 ). It is important to note that a limited number of studies focused and empirically tested factors affecting the adoption, use, and effect of social media. As a result, identified factors were considered as experimental (examined less than five times). It is too early to label these experimental predictors as worst or best, thus their further investigation is encouraged.
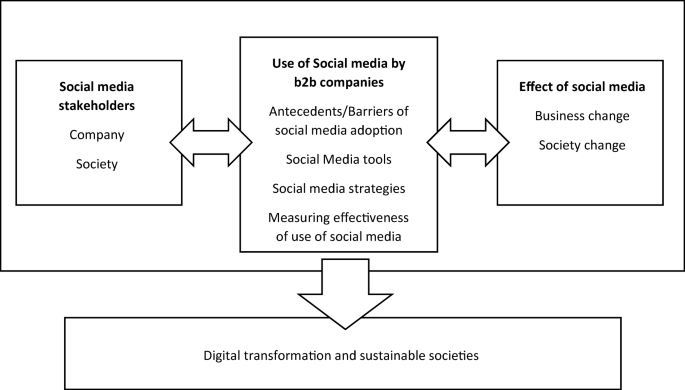
Social media impact on digital transformation and sustainable societies
Additionally, our review of the literature on B2B social media identified dominant research methods used by scholars. Qualitative and quantitative techniques were used by most of these studies. Closer analysis of 70 publications reviewed in this study revealed the multiple techniques applied for gathering data. Quantitative methods used in the studies mostly used surveys (see Table 4 ).
The data was mostly gathered from salespersons, managers and data from social media platforms (e.g. Twitter, Facebook). Just a limited number of studies employed consumer reported data (see Table 5 ).
On the other hand, publications using qualitative methods mainly used interviews and web scraping for the collection of the required data. To analyse the data studies used a variety of techniques including SEM, regression analysis and content analysis being one of the most used (see Table 6 ).
5.1 Digital Transformation and Sustainability Model
Based on the conducted literature review and adapting the model by Pappas et al. ( 2018 ) Fig. 2 presents the digital transformation and sustainability model in the context of B2B companies, which conceptualise the social media ecosystems, and the factors that need to collaborate to enable the use of social media towards the achievement of digital transformation and the creation of sustainable societies. The model comprises of social media stakeholders, the use of social media by B2B companies, and effect of social media on business and society.
5.1.1 Social Media Stakeholders
Building on the discussion and model provided by Pappas et al. ( 2018 ), this paper posits that the social media ecosystem comprises of the data stakeholders (company, society), who engage on social media (posting, reading, using information from social media). The use of social media by different stakeholders will lead to different effects affecting companies, customers and society. This is an iterative process based on which the stakeholders use their experience to constantly improve and evolve their use of social media, which has impacts on both, business and society. The successful implementation of this process is key to digital transformation and the creation of sustainable societies. Most of the current studies (Andersson et al. 2013 ; Bernard 2016 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ; Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü 2018 ; Dyck 2010 ; Guesalaga 2016 ) focus mostly on the company as a stakeholder. However, more research is needed on other types of stakeholders (e.g. society).
5.1.2 Use of Social Media by B2B Companies
Social media affects not only ways how companies connect with their clients, but it is also changing their business models, the way how the value is delivered and profit is made. To successfully implement and use social media, B2B companies need to consider various social media tools, antecedents/barriers of its adoption, identify suitable social media strategies which are in line with the company’s overall strategy, and measure effectiveness of the use of social media. There are various factors that affect the use of social media by B2B companies. The study found that social media usage is influenced by perceived ease of use, adoption of social media, attitude towards social media and age of salesperson.
The majority of the studies focus on the management of the marketing department. However, digital transformation is much bigger than just marketing as it encompasses the entire organisation. As a result, future studies should look like the entire organisation and investigate barriers and factors affecting the use of social media.
It is crucial for companies to design content which will be noticed on social media by their potential, actual and former customers. Social media content should be interesting and offer some beneficial information, rather than just focus on services the company provides. Companies could use fresh views on relevant industry news, provide information how they are contributing to society and environment, include humour in their posts, share information about the team, make it more personal. It is also useful to use images, infographics, and video content.
It is also important for companies to measure digital marketing actions. More studies are needed on how to isolate the impact of specific media marketing actions to demonstrate their impact on the desired business outcomes (Salo 2017 ). Thus, future studies can consider how particular social media channels (e.g. Facebook, LinkedIn) in a campaign of a new product/ service influence brand awareness and sales level. Also, a limited number of studies discussed the way B2B companies can measure ROI. Future research should investigate how companies can measure intangible ROI, such as eWOM, brand awareness, and customer engagement (Kumar and Mirchandani 2012 ). Also, future research should investigate the reasons why most of the users do not assess the effectiveness of their SNS. Furthermore, most of the studies focused on likes, shares, and comments to evaluate social media engagement. Future research should focus on other types of measures. More research needs considering the impact of legislation on the use of social media by companies. Recent B2B studies did not consider recent legislation (General Data Protection Regulation 2018 ) in the context B2B (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ).
5.1.3 Effect of Social Media on Business and Society
Social media plays an important part in the company’s decision-making process. Social media can bring positive changes into company, which will result in improving customer satisfaction, value creation, increase in sales, building relationships with customers, knowledge creation, improve the perception of corporate credibility, acquisition of new customers, and improve employment brand engagement. Using information collected from social media can help companies to have a set of reliable attributes that comprise social, economic and environmental aspects in their decision-making process (Tseng 2017 ). Additionally, by using social media B2B companies can provide information to other stakeholders on their sustainability activities. By using data from social media companies will be able to provide products and services which are demanded by society. It will improve the quality of life and result in less waste. Additionally, social media can be considered as a tool that helps managers to integrate business practices with sustainability (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ). As a result, social media use by B2B companies can lead to business and societal changes.
A limited number of studies investigated the effect of social media on word of mouth communications in the B2B context. Future research should investigate the differences and similarities between B2C and B2B eWOM communications. Also, studies should investigate how these types of communications can be improved and ways to deal with negative eWOM. It is important for companies to respond to comments on social media. Additionally, future research should investigate its perceived helpfulness by customers.
Majority of studies (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Rossmann and Stei 2015 ; Agnihotri et al. 2012 ; Agnihotri et al. 2017 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Salo 2017 ; Bhattacharjya and Ellison 2015 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gruner and Power 2018 ; Hollebeek 2019 ) investigated positive effect of social media such consumer satisfaction, consumer engagement, and brand awareness. However, it will be interesting to consider the dark side of social media use such as an excessive number of requests on social media to salespeople (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ), which can result in the reduction of the responsiveness; spread of misinformation which can damage the reputation of the company.
Studies were performed in China (Lacka and Chong 2016 ; Niedermeier et al. 2016 ), the USA (Guesalaga 2016 ; Iankova et al. 2018 ; Ogilvie et al. 2018 ), India (Agnihotri et al. 2017 ; Vasudevan and Kumar 2018 ), the UK (Bolat et al. 2016 ; Iankova et al. 2018 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ). It is strongly advised that future studies conduct research in other countries as findings can be different due to the culture and social media adoption rates. Future studies should pay particular attention to other emerging markets (such as Russia, Brazil, and South Africa) as they suffer from the slow adoption rate of social media marketing. Some companies in these countries still rely more on traditional media for advertising of their products and services, as they are more trusted in comparison with social media channels (Olotewo 2016 ). The majority of studies investigate the effect of social media in B2B or B2C context. Future studies should pay attention to other contexts (e.g. B2B2B, B2B2C). Another limitation of the current research on B2B companies is that most of the studies on social media in the context of B2B focus on the effect of social media use only on business outcomes. It is important for future research to focus on societal outcomes.
Lastly, most of the studies on social media in the context of B2B companies use a cross-sectional approach to collect the data. Future research can use the longitudinal approach in order to advance understanding of social media use and its impact over time.
5.2 Research Propositions
Based on the social media research in the context of B2B companies and the discussion above the following is proposed, which could serve as a foundation for future empirical work.
Social media is a powerful tool to deliver information to customers. However, social media can be used to get consumer and market insights (Kazienko et al. 2013 ). A number of studies highlighted how information obtained from a number of social media platforms could be used for various marketing purposes, such as understanding the needs and preferences of consumers, marketing potential for new products/services, and current market trends (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Constantinides et al. 2008 ). It is advised that future research employs a longitudinal approach to study the impact of social media use on understanding customers. Therefore, the following proposition can be formulated:
Proposition 1
Social media usage of B2B companies has a positive influence on understanding its customers.
By using social media companies can examiner valuable information on competitors. It can help to understand competitors’ habits and strategies, which can lead to the competitive advantage and help strategic planning (Dey et al. 2011 ; Eid et al. 2019 ; Teo and Choo 2001 ). It is advised that future research employs a longitudinal approach to study the impact of social media use on understanding its competitors. As a result, using social media to understand customers and competitors can create business value (Mikalef et al. 2020a ) for key stakeholders and lead to positive changes in the business and societies. The above discussion leads to the following proposition:
Proposition 2
Social media usage of B2B companies has a positive influence on understanding its competitors.
Proposition 3
Culture influences the adoption and use of social media by B2B companies.
Usage of social media can result in some positive marketing outcomes such as building new customer relationships, increasing brand awareness, and level of sales to name a few (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Dwivedi et al. 2020 ; Rossmann and Stei 2015 ). However, when social media is not used appropriately it can lead to negative consequences. If a company does not have enough resources to implement social media tools the burden usually comes on a salesperson. A high number of customer inquiries, the pressure to engage with customers on social media, and monitor communications happening on various social media platforms can result in the increased workload of a salesperson putting extra pressure (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ). As a result, a salesperson might not have enough time to engage with all the customers online promptly or engage in reactive and proactive web care. As a result, customer satisfaction can be affected as well as company reputation. To investigate the negative impact of social media research could apply novel methods for data collection and analysis such as fsQCA (Pappas et al. 2020 ), or implying eye-tracking (Mikalef et al. 2020b ). This leads to the following proposition:
Proposition 4
Inappropriate use of social media by B2B companies has a negative effect on a) customer satisfaction and b) company reputation.
According to Technology-Organisation-Environment (TOE) framework environmental context significantly affects a company’s use of innovations (Abed 2020 ; Oliveira and Martins 2011 ). Environment refers to the factors which affect companies from outside, including competitors and customers. Adopting innovation can help companies to change the rules of the competition and reach a competitive advantage (Porter and Millar 1985 ). In a competitive environment, companies have a tendency to adopt an innovation. AlSharji et al. ( 2018 ) argued that the adoption of innovation can be extended to social media use by companies. A study by AlSharji et al. ( 2018 ) by using data from 1700 SMEs operating in the United Arab Emirates found that competitive pressure significantly affects the use of social media by SMEs. It can be explained by the fact that companies could feel pressure when other companies in the industry start adopting a particular technology and as a result adopt it to remain competitive (Kuan and Chau 2001 ). Based on the above discussion, the following proposition can be formulated:
Proposition 5
Competitive pressure positively affects the adoption of social media by B2B companies.
Companies might feel that they are forced to adopt and use IT innovations because their customers would expect them to do so. Meeting customers’ expectations could result in adoption of new technologies by B2B companies. Some research studies investigated the impact of customer pressure on companies (AlSharji et al. 2018 ; Maduku et al. 2016 ). For example, a study by Maduku et al. ( 2016 ) found that customer pressure has a positive effect on SMEs adoption of mobile marketing in the context of South Africa. Future research could implement longitudinal approach to investigate how environment affects adoption of social media by B2B companies. This leads to the formulation of the following proposition:
Proposition 6
Customer pressure positively affects the adoption of social media by B2B companies.
6 Conclusion
The aim of this research was to provide a comprehensive systematic review of the literature on social media in the context of B2B companies and propose the framework outlining the role of social media in the digital transformation of B2B companies. It was found that B2B companies use social media, but not all companies consider it as part of their marketing strategies. The studies on social media in the B2B context focused on the effect of social media, antecedents, and barriers of adoption of social media, social media strategies, social media use, and measuring the effectiveness of social media. Academics and practitioners can employ the current study as an informative framework for research on the use of social media by B2B companies. The summary of the key observations provided from this literature review is the following: [i] Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn are the most famous social media platforms used by B2B companies, [ii] Social media has a positive effect on customer satisfaction, acquisition of new customers, sales, stakeholder engagement, and customer relationships, [iii] In systematically reviewing 70 publications on social media in the context of B2B companies it was observed that most of the studies use online surveys and online content analysis, [iv] Companies still look for ways to evaluate the effectiveness of social media, [v] Innovativeness, pressure from stakeholders, perceived usefulness, and perceived usability have a significant positive effect on companies’ adoption to use social media, [vi] Lack of staff familiarity and technical skills are the main barriers that affect the adoption of social media by B2B, [vii] Social media has an impact not only on business but also on society, [viii] There is a dark side of social media: fake online reviews, an excessive number of requests on social media to salespeople, distribution of misinformation, negative eWOM, [ix] Use of social media by companies has a positive effect on sustainability, and [x] For successful digital transformation social media should change not only the way how companies integrate it into their marketing strategies but the way how companies deliver values to their customers and conduct their business. This research has a number of limitations. First, only publications from the Scopus database were included in literature analysis and synthesis. Second, this research did not use meta-analysis. To provide a broader picture of the research on social media in the B2B context and reconcile conflicting findings of the existing studies future research should conduct a meta-analysis (Ismagilova et al. 2020c ). It will advance knowledge of the social media domain.
Abed, S. S. (2020). Social commerce adoption using TOE framework: An empirical investigation of Saudi Arabian SMEs. International Journal of Information Management, 53 , 102118.
Article Google Scholar
Agnihotri, R., Kothandaraman, P., Kashyap, R., & Singh, R. (2012). Bringing “social” into sales: The impact of salespeople’s social media use on service behaviors and value creation. Journal of Personal Selling and Sales Management, 32 (3), 333–348. https://doi.org/10.2753/PSS0885-3134320304 .
Agnihotri, R., Dingus, R., Hu, M. Y., & Krush, M. T. (2016). Social media: Influencing customer satisfaction in B2B sales. Industrial Marketing Management, 53 , 172–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.09.003 .
Agnihotri, R., Trainor, K. J., Itani, O. S., & Rodriguez, M. (2017). Examining the role of sales-based CRM technology and social media use on post-sale service behaviors in India. Journal of Business Research, 81 , 144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.08.021 .
Alalwan, A. A., Rana, N. P., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Algharabat, R. (2017). Social media in marketing: A review and analysis of the existing literature. Telematics and Informatics, 34 (7), 1177–1190.
AlSharji, A., Ahmad, S. Z., & Bakar, A. R. A. (2018). Understanding social media adoption in SMEs. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 10 (2), 302–328.
Ancillai, C., Terho, H., Cardinali, S., & Pascucci, F. (2019). Advancing social media driven sales research: Establishing conceptual foundations for B-to-B social selling. Industrial Marketing Management, 82 , 293–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2019.01.002 .
Andersson, S., & Wikström, N. (2017). Why and how are social media used in a B2B context, and which stakeholders are involved? Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 32 (8), 1098–1108. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-07-2016-0148 .
Andersson, S., Evers, N., & Griot, C. (2013). Local and international networks in small firm internationalization: Cases from the Rhône-Alpes medical technology regional cluster. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 25 (9–10), 867–888.
Andzulis, J. M., Panagopoulos, N. G., & Rapp, A. (2012). A review of social media and implications for the sales process. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 32 (3), 305–316.
Barreda, A. A., Bilgihan, A., Nusair, K., & Okumus, F. (2015). Generating brand awareness in online social networks. Computers in Human Behavior, 50 , 600–609.
Bell, D., & Shirzad, S, R. (2013). Social media domain analysis (SoMeDoA): A pharmaceutical study. 9th international conference on web information systems and technologies, 561–570. https://doi.org/10.5220/0004499105610570 .
Bernard, M. (2016). The impact of social media on the B2B CMO. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 31 (8), 955–960. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-268 .
Bhattacharjya, J., & Ellison, A, B. (2015). Building business resilience with social media in B2B environments: The emergence of responsive customer relationship management processes on twitter. Working Conference on Virtual Enterprises doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24141-8_15 .
Bolat, E., Kooli, K., & Wright, L. T. (2016). Businesses and mobile social media capability. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 31 (8), 971–981. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-270 .
Buratti, N., Parola, F., & Satta, G. (2018). Insights on the adoption of social media marketing in B2B services. TQM Journal, 30 (5), 490–529. https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-11-2017-0136 .
Cawsey, T., & Rowley, J. (2016). Social media brand building strategies in B2B companies. Marketing Intelligence and Planning, 34 (6), 754–776. https://doi.org/10.1108/MIP-04-2015-0079 .
Chatterjee, S., & Kar, A. K. (2020). Why do small and medium enterprises use social media marketing and what is the impact: Empirical insights from India. International Journal of Information Management, 53 , 102103.
Chen, H., Chiang, R. H., & Storey, V. C. (2012). Business intelligence and analytics: From big data to big impact. MIS Quarterly, 36 , 1165–1188.
Chirumalla, K., Oghazi, P., & Parida, V. (2018). Social media engagement strategy: Investigation of marketing and R&D interfaces in manufacturing industry. Industrial Marketing Management, 74 , 138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.10.001 .
Constantinides, E., Romero, C. L., & Boria, M. A. G. (2008). Social media: A new frontier for retailers?. In European retail research (pp. 1–28) . Wiesbaden: Gabler Verlag.
Google Scholar
Denktaş-Şakar, G., & Sürücü, E. (2018). Stakeholder engagement via social media: An analysis of third-party logistics companies. Service Industries Journal, 40 , 866–889. https://doi.org/10.1080/02642069.2018.1561874 .
Dey, L., Haque, S, M., Khurdiya, A., & Shroff, G. (2011). Acquiring competitive intelligence from social media. In proceedings of the 2011 joint workshop on multilingual OCR and analytics for noisy unstructured text data (pp. 1-9) . https://doi.org/10.1145/2034617.2034621 .
Dwivedi, Y. K., Rana, N. P., Jeyaraj, A., Clement, M., & Williams, M. D. (2019a). Re-examining the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT): Towards a revised theoretical model. Information Systems Frontiers, 21 (3), 719–734.
Dwivedi, Y, K., Hughes, L., Ismagilova, E., Aarts, G., Coombs, C., Crick, T., ... & Galanos, V. (2019b). Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International Journal of Information Management , 101994, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.08.002 .
Dwivedi, Y, K., Ismagilova, E., Hughes, D. L., Carlson, J., Filieri, R., Jacobson, J., ... & Kumar, V. (2020). Setting the future of digital and social media marketing research: Perspectives and research propositions. International Journal of Information Management , 102168, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102168 .
Dyck, P. V. (2010). As social media evolves, the device industry must also. Medical Device and Diagnostic Industry, 32 (8).
Eid, R., Abdelmoety, Z., & Agag, G. (2019). Antecedents and consequences of social media marketing use: An empirical study of the UK exporting B2B SMEs. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing., 35 , 284–305.
Gáti, M., Mitev, A., & Bauer, A. (2018). Investigating the impact of salespersons’ use of technology and social media on their customer relationship performance in B2B settings. Trziste, 30 (2), 165–176. https://doi.org/10.22598/mt/2018.30.2.165 .
Gazal, K., Montague, I., Poudel, R., & Wiedenbeck, J. (2016). Forest products industry in a digital age: Factors affecting social media adoption. Forest Products Journal, 66 (5-6), 343–353. https://doi.org/10.13073/FPJ-D-15-00007 .
General Data Protection Regulation (2018). Guide to the General Data Protection Regulation. Available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/guide-to-the-general-data-protection-regulation . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Gregorio, J. (2017). 10 reasons to diversify your digital marketing efforts. Digital marketing Philippines. Available at https://digitalmarketingphilippines.com/10-reasons-to-diversify-your-digital-marketing-efforts// Accessed on April , 27 , 2019.
Gruner, R. L., & Power, D. (2018). To integrate or not to integrate? Understanding B2B social media communications. Online Information Review, 42 (1), 73–92. https://doi.org/10.1108/OIR-04-2016-0116 .
Guesalaga, R. (2016). The use of social media in sales: Individual and organizational antecedents, and the role of customer engagement in social media. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.12.002 .
Gupta, P., Chauhan, S., & Jaiswal, M. P. (2019). Classification of smart city research-a descriptive literature review and future research agenda. Information Systems Frontiers, 21 (3), 661–685.
Habibi, F., Hamilton, C. A., Valos, M. J., & Callaghan, M. (2015). E-marketing orientation and social media implementation in B2B marketing. European Business Review, 27 (6), 638–655. https://doi.org/10.1108/EBR-03-2015-0026 .
Harrigan, P., Miles, M. P., Fang, Y., & Roy, S. K. (2020). The role of social media in the engagement and information processes of social CRM. International Journal of Information Management, 54 , 102151.
Hollebeek, L. D. (2019). Developing business customer engagement through social media engagement-platforms: An integrative SD logic/RBV-informed model. Industrial Marketing Management, 81 , 89–98.
Hsiao, S. H., Wang, Y. Y., Wang, T., & Kao, T. W. (2020). How social media shapes the fashion industry: The spillover effects between private labels and national brands. Industrial Marketing Management, 86 , 40–51.
Huotari, L., Ulkuniemi, P., Saraniemi, S., & Mäläskä, M. (2015). Analysis of content creation in social media by B2B companies. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 30 (6), 761–770. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-05-2013-0118 .
Iankova, S., Davies, I., Archer-Brown, C., Marder, B., & Yau, A. (2018). A comparison of social media marketing between B2B, B2C and mixed business models. Industrial Marketing Management, 81 , 169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.01.001 .
Iannacci, F., Fearon, C., & Pole, K. (2020). From acceptance to adaptive acceptance of social media policy change: A set-theoretic analysis of b2b SMEs. Information Systems Frontiers , 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-020-09988-1 .
Ismagilova, E., Dwivedi, Y. K., Slade, E., & Williams, M. D. (2017). Electronic word of mouth (eWOM) in the marketing context: A state of the art analysis and future directions . Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52459-7 .
Ismagilova, E., Hughes, L., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Raman, K. R. (2019). Smart cities: Advances in research—An information systems perspective. International Journal of Information Management, 47 , 88–100.
Ismagilova, E., Slade, E. L., Rana, N. P., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020a). The effect of electronic word of mouth communications on intention to buy: A meta-analysis. Information Systems Frontiers, 22 , 1203–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-019-09924-y .
Ismagilova, E., Slade, E., Rana, N. P., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020b). The effect of characteristics of source credibility on consumer behaviour: A meta-analysis. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 53 , 101736.
Ismagilova, E., Rana, N, P., Slade, E., & Dwivedi, Y, K. (2020c). A meta-analysis of the factors affecting eWOM providing behaviour. European Journal of Marketing. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/EJM-07-2018-0472 , ahead-of-print.
Itani, O. S., Agnihotri, R., & Dingus, R. (2017). Social media use in B2b sales and its impact on competitive intelligence collection and adaptive selling: Examining the role of learning orientation as an enabler. Industrial Marketing Management, 66 , 64–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.06.012 .
Jeyaraj, A., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020). Meta-analysis in information systems research: Review and recommendations. International Journal of Information Management, 55 , 102226.
Jeyaraj, A., Rottman, J. W., & Lacity, M. C. (2006). A review of the predictors, linkages, and biases in IT innovation adoption research. Journal of Information Technology, 21 (1), 1–23.
Juntunen, M., Ismagilova, E., & Oikarinen, E. L. (2020). B2B brands on twitter: Engaging users with a varying combination of social media content objectives, strategies, and tactics. Industrial Marketing Management, 89 , 630–641.
Jussila, J. J., Kärkkäinen, H., & Leino, M. (2011). Benefits of social media in business-to-business customer interface in innovation. 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments . MindTrek, 2011 , 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1145/2181037.2181065 .
Kamboj, S., Sarmah, B., Gupta, S., & Dwivedi, Y. (2018). Examining branding co-creation in brand communities on social media: Applying the paradigm of stimulus-organism-response. International Journal of Information Management, 39 , 169–185.
Kapoor, K. K., Tamilmani, K., Rana, N. P., Patil, P., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Nerur, S. (2018). Advances in social media research: Past, present and future. Information Systems Frontiers, 20 (3), 531–558.
Kärkkäinen, H., Jussila, J., & Janhonen, J. (2011). Managing customer information and knowledge with social media in business-to-business companies. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/2024288.2024309 .
Kasper, H., Koleva, I., & Kett, H. (2015). Social media matrix matching corporate goals with external social media activities doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46641-4_17 .
Katona, Z., & Sarvary, M. (2014). Maersk line: B2B social media-“it’s communication, not marketing. California Management Review , 56(3), 142–156. doi: https://doi.org/10.1525/cmr.2014.56.3.142 .
Kazienko, P., Szozda, N., Filipowski, T., & Blysz, W. (2013). New business client acquisition using social networking sites. Electronic Markets, 23 (2), 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12525-013-0123-9 .
Keinänen, H., & Kuivalainen, O. (2015). Antecedents of social media B2B use in industrial marketing context: Customers’ view. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 30 (6), 711–722. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-04-2013-0095 .
Kho, N. D. (2008). B2B gets social media. EContent, 31 (3), 26–30.
Kovac, M. (2016). Social media works for B2B sales, too. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2016/01/social-media-worksfor-b2b-sales-too . Accessed on April , 27 , 2020 .
Kuan, K. K., & Chau, P. Y. (2001). A perception-based model for EDI adoption in small businesses using a technology–organization–environment framework. Information & Management, 38 (8), 507–521.
Kumar, V., & Mirchandani, R. (2012). Increasing the ROI of social media marketing. MIT Sloan Management Review, 54 (1), 55–61.
Kumar, A., & Möller, K. (2018). Extending the boundaries of corporate branding: An exploratory study of the influence of brand familiarity in recruitment practices through social media by B2B firms. Corporate Reputation Review, 21 (3), 101–114. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41299-018-0046-7 .
Kunsman, T. (2018). Internal marketing: Why your company should prioritize it. https://everyonesocial.com/blog/internal-marketing/ . Accessed on September, 25, 2019.
Lacka, E., & Chong, A. (2016). Usability perspective on social media sites' adoption in the B2B context. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.01.001 .
Lal, B., Ismagilova, E., Dwivedi, Y.,. K., & Kwayu, S. (2020). Return on Investment in Social Media Marketing: Literature review and suggestions for future research. In Digital and Social Media Marketing (pp. 3–17) . Cham: Springer.
Lashgari, M., Sutton-Brady, C., Solberg Søilen, K., & Ulfvengren, P. (2018). Adoption strategies of social media in B2B firms: A multiple case study approach. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 33 (5), 730–743. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-0242 .
Loebbecke, C., & Picot, A. (2015). Reflections on societal and business model transformation arising from digitization and big data analytics: A research agenda. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24 (3), 149–157.
Maduku, D. K., Mpinganjira, M., & Duh, H. (2016). Understanding mobile marketing adoption intention by south African SMEs: A multi-perspective framework. International Journal of Information Management, 36 (5), 711–723.
Mahrous, A, A. (2013). Social media marketing: Prospects for marketing theory and practice on the social web. E-marketing in developed and developing countries: Emerging practices (pp. 56-68) doi: https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-4666-3954-6.ch004 Retrieved from www.scopus.com .
McAfee, A. P. (2006). Enterprise 2.0: The dawn of emergent collaboration. Enterprise, 2 , 15–26.
McKinsey & Company (2015). Transforming the business through social tools. McKinsey.com , ( http://www.mckinsey.com/industries/high-tech/our-insights/transformingthe-business-through-social-tools ).
McShane, L., Pancer, E., & Poole, M. (2019). The influence of B to B social media message features on brand engagement: A fluency perspective. Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing, 26 (1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/1051712X.2019.1565132 .
Mehmet, M. I., & Clarke, R. J. (2016). B2B social media semantics: Analysing multimodal online meanings in marketing conversations. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 92–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.12.006 .
Meire, M., Ballings, M., & Van den Poel, D. (2017). The added value of social media data in B2B customer acquisition systems: A real-life experiment. Decision Support Systems, 104 , 26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2017.09.010 .
Michaelidou, N., Siamagka, N. T., & Christodoulides, G. (2011). Usage, barriers and measurement of social media marketing: An exploratory investigation of small and medium B2B brands. Industrial Marketing Management, 40 (7), 1153–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2011.09.009 .
Mikalef, P., Pappas, I. O., Krogstie, J., & Pavlou, P. A. (2020a). Big data and business analytics: A research agenda for realizing business value. Information & Management, 57 (1), 103237.
Mikalef, P., Sharma, K., Pappas, I, O., & Giannakos, M. (2020b). Seeking information on social commerce: An examination of the impact of user-and marketer-generated content through an eye-tracking study. Information Systems Frontiers , 1-14, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-020-10034-3 .
Minsky, L., & Quesenberry, K, A. (2016). How B2B sales can benefit from social selling . Harvard Business Review. Available at https://hbr.org/2016/11/84-of-b2b-sales-start-with-a-referral-not-a-salesperson . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Moncrief, W. C., Marshall, G. W., & Rudd, J. M. (2015). Social media and related technology: Drivers of change in managing the contemporary sales force. Business Horizons, 58 (1), 45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2014.09.009 .
Moore, J. N., Hopkins, C. D., & Raymond, M. A. (2013). Utilization of relationship-oriented social media in the selling process: A comparison of consumer (B2C) and industrial (B2B) salespeople. Journal of Internet Commerce, 12 (1), 48–75. https://doi.org/10.1080/15332861.2013.763694 .
Moore, J. N., Raymond, M. A., & Hopkins, C. D. (2015). Social selling: A comparison of social media usage across process stage, markets, and sales job functions. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 23 (1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10696679.2015.980163 .
Mudambi, S. M., Sinha, J. I., & Taylor, D. S. (2019). Why B-to-B CEOs should be more social on social media. Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing, 26 (1), 103–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/1051712X.2019.1565144 .
Muhammad, S. S., Dey, B. L., & Weerakkody, V. (2018). Analysis of factors that influence customers’ willingness to leave big data digital footprints on social media: A systematic review of literature. Information Systems Frontiers, 20 (3), 559–576.
Müller, L., Griesbaum, J., & Mandl, T. (2013). Social media relations in the german automotive market. Paper presented at the proceedings of the IADIS international conference ICT, society and human beings 2013, Proceedings of the IADIS International Conference e-Commerce 2013, 19–26.
Müller, J. M., Pommeranz, B., Weisser, J., & Voigt, K. I. (2018). Digital, social media, and Mobile marketing in industrial buying: Still in need of customer segmentation? Empirical evidence from Poland and Germany. Industrial Marketing Management, 73 , 70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.01.033 .
Niedermeier, K. E., Wang, E., & Zhang, X. (2016). The use of social media among business-to-business sales professionals in China: How social media helps create and solidify guanxi relationships between sales professionals and customers. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 10 (1), 33–49. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIM-08-2015-0054 .
Nunan, D., Sibai, O., Schivinski, B., & Christodoulides, G. (2018). Reflections on “social media: Influencing customer satisfaction in B2B sales” and a research agenda. Industrial Marketing Management, 75 , 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.03.009 .
Ogilvie, J., Agnihotri, R., Rapp, A., & Trainor, K. (2018). Social media technology use and salesperson performance: A two study examination of the role of salesperson behaviors, characteristics, and training. Industrial Marketing Management, 75 , 55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.03.007 .
Oliveira, T., & Martins, M. F. (2011). Literature review of information technology adoption models at firm level. Electronic Journal of Information Systems Evaluation, 14 (1), 110.
Olotewo, J. (2016). Social media marketing in emerging markets. International Journal of Online Marketing Research, 2 (2), 10–18.
Pappas, I. O., Mikalef, P., Giannakos, M. N., Krogstie, J., & Lekakos, G. (2018). Big data and business analytics ecosystems: Paving the way towards digital transformation and sustainable societies. Information Systems and e-Business Management, 16 , 479–491.
Pappas, I. O., Papavlasopoulou, S., Mikalef, P., & Giannakos, M. N. (2020). Identifying the combinations of motivations and emotions for creating satisfied users in SNSs: An fsQCA approach. International Journal of Information Management, 53 , 102128.
Pascucci, F., Ancillai, C., & Cardinali, S. (2018). Exploring antecedents of social media usage in B2B: A systematic review. Management Research Review, 41 (6), 629–656. https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-07-2017-0212 .
Pitt, C. S., Plangger, K. A., Botha, E., Kietzmann, J., & Pitt, L. (2017). How employees engage with B2B brands on social media: Word choice and verbal tone. Industrial Marketing Management, 81 , 130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.09.012 .
Pitt, C. S., Botha, E., Ferreira, J. J., & Kietzmann, J. (2018). Employee brand engagement on social media: Managing optimism and commonality. Business Horizons, 61 (4), 635–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2018.04.001 .
Porter, M. E., & Millar, V. E. (1985). How information gives you competitive advantage. Harvard Business Review, 63 (4), 149–160.
Pulizzi, J., & Handley, A. (2017). B2C content marketing-2018 benchmarks, budgets, and trends—North America. Available at https://contentmarketinginstitute.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/2017_B2B_Research_FINAL.pdf Accessed on April , 27 , 2020.
Rana, N. P., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Williams, M. D. (2015). A meta-analysis of existing research on citizen adoption of e-government. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (3), 547–563.
Rana, N. P., Luthra, S., Mangla, S. K., Islam, R., Roderick, S., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2019). Barriers to the development of smart cities in Indian context. Information Systems Frontiers, 21 (3), 503–525.
Rodriguez, M., Peterson, R. M., & Krishnan, V. (2012). Social media's influence on business-to-business sales performance. Journal of Personal Selling and Sales Management, 32 (3), 365–378. https://doi.org/10.2753/PSS0885-3134320306 .
Rossmann, A., & Stei, G. (2015). Sales 2.0 in business-to-business (B2B) networks: Conceptualization and impact of social media in B2B sales relationships . Paper presented at the Lecture Notes in Informatics (LNI), Proceedings - Series of the Gesellschaft Fur Informatik (GI), 244 67–78. Available at https://subs.emis.de/LNI/Proceedings/Proceedings244/67.pdf . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Salo, J. (2017). Social media research in the industrial marketing field: Review of literature and future research directions. Industrial Marketing Management, 66 , 115–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.07.013 .
Shaltoni, A. M. (2017). From websites to social media: Exploring the adoption of internet marketing in emerging industrial markets. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 32 (7), 1009–1019. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-06-2016-0122 .
Siamagka, N. T., Christodoulides, G., Michaelidou, N., & Valvi, A. (2015). Determinants of social media adoption by B2B organizations. Industrial Marketing Management, 51 , 89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.05.005 .
Sivarajah, U., Irani, Z., Gupta, S., & Mahroof, K. (2019). Role of big data and social media analytics for business to business sustainability: A participatory web context. Industrial Marketing Management . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2019.04.005 .
Sobal, A. (2017). 30 statistics about B2B social media usage. Available at https://www.weidert.com/blog/statistics-about-b2b-social-media-usage Accessed on April , 27 , 2020.
Stelzner, M. (2011). 2012 social media marketing industry report. Social media examiner . Available at https://www.socialmediaexaminer.com/socialmedia-marketing-industry-report-2012/ . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Sułkowski, Ł., & Kaczorowska-Spychalska, D. (2016). Social media in the process of marketing evolution in polish textile-clothing industry. Fibres and Textiles in Eastern Europe, 24 (5), 15–20. https://doi.org/10.5604/12303666.1215521 .
Swani, K., Milne, G., & Brown, B. P. (2013). Spreading the word through likes on facebook: Evaluating the message strategy effectiveness of fortune 500 companies. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 7 (4), 269–294. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIM-05-2013-0026 .
Swani, K., Brown, B. P., & Milne, G. R. (2014). Should tweets differ for B2B and B2C? An analysis of fortune 500 companies' twitter communications. Industrial Marketing Management, 43 (5), 873–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2014.04.012 .
Swani, K., Milne, G. R., Brown, B. P., Assaf, A. G., & Donthu, N. (2017). What messages to post? Evaluating the popularity of social media communications in business versus consumer markets. Industrial Marketing Management, 62 , 77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.07.006 .
Tedeschi, B. (2006). Like shopping? Social networking? Try social shopping. New York Times, 11 , 09.
Teo, T. S., & Choo, W. Y. (2001). Assessing the impact of using the internet for competitive intelligence. Information & Management, 39 (1), 67–83.
Tseng, M. L. (2017). Using social media and qualitative and quantitative information scales to benchmark corporate sustainability. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142 , 727–738.
Vasudevan, S., & Kumar, F. J. P. (2018). Social media and B2B brands: An Indian perspective. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology, 9 (9), 767–775.
Vukanovic, Z. (2013). Managing social media value networks: From publisher (broadcast) to user-centric (broadband-narrowcast) business models. Handbook of social media management: Value chain and business models in changing media markets (pp. 269-288) doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28897-5_16 .
Wang, Y., Rod, M., Ji, S., & Deng, Q. (2017). Social media capability in B2B marketing: Toward a definition and a research model. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 32 (8), 1125–1135. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-0250 .
Watt, I. (2010). Changing visions of parliamentary libraries: From the enlightenment to Facebook. IFLA Journal, 36 (1), 47–60. https://doi.org/10.1177/0340035209359574 .
Webster, J., & Watson, R.,. T. (2002). Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. MIS quarterly, 26 (2), xiii–xxiii.
Westerman, G., Bonnet, D., & McAfee, A. (2014). Leading digital: Turning technology into business transformation . Boston, MA: Harvard Business Press.
Williams, M. D., Rana, N. P., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2015). The unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT): A literature review. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 28 (3), 443–488.
World Commission Report on Environment and Development. (1987). Our Common Future . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Yang, C. C., Yang, H., Tang, X., & Jiang, L. (2012). Identifying implicit relationships between social media users to support social commerce. In ACM international conference proceeding series (pp. 41–47). https://doi.org/10.1145/2346536.2346544 .
Chapter Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Emerging Markets Research Centre (EMaRC), School of Management, Swansea University, Bay Campus, Swansea, UK
Yogesh K. Dwivedi
School of Management, University of Bradford, Bradford, UK
Elvira Ismagilova & Nripendra P. Rana
Symbiosis Institute of Business Management, Pune & Symbiosis International, Deemed University, Pune, India
Ramakrishnan Raman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yogesh K. Dwivedi .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Dwivedi, Y.K., Ismagilova, E., Rana, N.P. et al. Social Media Adoption, Usage And Impact In Business-To-Business (B2B) Context: A State-Of-The-Art Literature Review. Inf Syst Front 25 , 971–993 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10106-y
Download citation
Accepted : 07 January 2021
Published : 02 February 2021
Issue Date : June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10106-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Business-to-business
- Digital transformation
- Information systems
- Literature review
- Social media
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Misinformation & Fake News
- Getting Started
Practice: Case Studies
Widely shared fake news stories from 2020-23, widely shared fake news stories from 2016-18, fake news exercise.
- Types of Misinformation
- Legitimate News Sources
- Books & Articles
- Video Resources
- Other Resources
- Case Study 1
- Case Study 1 - Explained
- Case Study 2
- Case Study 2 - Explained

On August 20, 2022, a TikTok video was posted, claiming that Disney World was going to lower the drinking age to 18. It was stated that Disney World was battling the Florida government in court to get a resort exemption, which would allow anyone 18 and older to drink on property. The TikTok video acquired millions of views in just a couple days. This story was also posted on facebook, instagram, and Twitter. Shortly after, the story made it on ABC 10 News.

The video originated from an article posted on a blog called Mouse Trap News. Small segment of the original article below. Full article can be found here: "Drinking Age at Disney World May be Lowered to 18".

The Claim: Walt Disney Company was seeking a resort exemption to lower the drinking age to 18 years old, in Disney World, Florida.
To find the truth about this story, we will use Michael Caufield's Four Moves and a Habit.
1. Check for previous work: For this case, we looked up this claim on Snopes ( fact checking resource ). They published an article on the story and labeled it as fake news satire. It was also aired on ABC 10 News, on their fact or fiction segment, where it was determined to be fiction. The news segment can be viewed here .
2. Go upstream to the source: The TikTok video originally came from an article published by the same TikTok user, @mousetrapnews. They have their own webpage dedicated to news stories about disneyland parks. The original article claimed that Disney was battling Florida in the courts over the minimum drinking age, but no evidence such as sources or court filings are mentioned.
3. Read laterally: Upon further exploration of the site itself, their About page actually bluntly admits that they only write fake stories about Disney Parks (see picture below).
4. Circle back: If we go back to the main article explaining the story, it reads in the description an explanation of the National Minimum Drinking Age Act passed by congress and signed into law by President Reagan. The article then asks the reader a question "Didn’t think you would get a history lesson from us, did you?" and "Now that we have set up the act, we have some Disney news to go with it.", these playful comments already makes the story a little suspicious. We can also check another form of social media the user has. They also had an Instagram account, where they state "Real Disney News That is 100% Fake" and "The Onion Of Disney News".

Interestingly enough, many of the Mouse Trap News fake news stories have been featured on different news websites and shows, such as The Associated Press, USA Today, and on The Tonight Show with Jimmy Fallon .
The Conclusion: The Walt Disney Company did not seek a resort exemption to lower the drinking age to 18 years old, in Disney World, Florida.

In October 2020, posts on social media and articles were published claiming that a new CDC study found the Majority of those infected with COVID-19 ‘always’ wore Masks (examples of the articles below). This claim was further elevated on October 15, 2020, a town hall broadcast by NBC, interviewed U.S. President Donald Trump. During this interview Trump stated, " But just the other day, they came out with a statement that 85% of the people that wear masks catch it." Trump's source for this claim was the new study published by the CDC. Full transcription of this interview can be found here. This information was ultimately, misinterpreted. Below is the CDC's tweet addressing the misinformation.

The Claim: CDC reported that the majority of those infected with COVID-19 ‘always’ wore masks.
- Check for previous work: For this case, we looked up this claim on Snopes and FactCheck.org ( fake news fact checker ). Both resources claim the information as false and misleading.
- Go upstream to the source: The claim originated from a study published by the CDC titled, Community and Close Contact Exposures Associated with COVID-19 Among Symptomatic Adults ≥18 Years in 11 Outpatient Health Care Facilities. This study examined how SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, may be transmitted both within communities and between close contacts. While Trump used the correct percentage from the study, the data was misinterpreted. The study reported that 85 percent had reported wearing masks always or often. The study also found that for those in the group who had tested negative, 89 percent had reported wearing masks with the same frequency. The CDC pointed out that "People w/ and w/o COVID19 had high levels of mask use in public. Even for those who always wear a mask, there are activities where masks can’t be worn, like eating or drinking. People w/ COVID-19 were more likely to have eaten in a restaurant." The study noted, "Exposures and activities where mask use and social distancing are difficult to maintain, including going to locations that offer on-site eating and drinking, might be important risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection."
- Read laterally: The claim is challenging the notion that wearing a mask is not effective at preventing the spread of COVID-19. We have to take in consideration that this study was investigating mask wearing in community activities. CDC's website provides Science Briefs which is a summary of the scientific evidence used to inform specific CDC guidance and recommendations. In one brief , they state, "individual prevention benefit increases with increasing numbers of people using masks consistently and correctly." So, the people from the original study might have not been using their masks effectively if repeatedly taking them off in social settings. Other medical experts such as Dr. Anthony Fauci, states "Masks aren't perfect. They help, but they're not a guarantee that you're not going to get Covid if you wear a mask”.
- Circle back: If you find yourself getting overwhelmed by other sources on the claim, circle back to the claim and investigate the background of that source. Using the AllSides Media Bias Chart , we can see that The Federalist is listed on the very, far right side of the chart. The author of that article, Jordan Boyd, has her twitter page linked to her name and we can see that her posts are on the far right of the political spectrum. The California Globe is listed as a conservative leaning publication on Snopes, many of their other posts written by the author lean to the right of the political spectrum. You can also circle back to the original study the claims were based on and question the accurateness. One issue with the study is the data was self-reported through phone surveys. So, people could have inaccurately reported mask use since there was no video monitoring to confirm.
Check Your Emotions: The use of masks and its effectiveness against COVID-19 was a highly politicized topic when the pandemic started. By downplaying the severity of the virus (despite all the losses recorded by the CDC), President Trump's attitude about the pandemic and the use of masks contributed the view that the COVID-19 public health crisis should be viewed as a political issue.
Conclusion: The CDC did not report that the majority of those infected with COVID-19 ‘always’ wore masks.
For more examples on COVID-19 myths and using Michael Caufield's Four Moves and a Habit to fact check them, visit our COVID Vaccines Libguide.
- Jan. 6 Capitol Riot
- COVID-19 and Vit. C
- Adrenochrome Shipment
- RNA in Chicken Feed
The Claim: The U.S. Capitol police gave the protesters an "okay" to enter the Capitol.
- Check for previous work: For this claim, we looked up this claim on Factcheck.org (fake news fact checker). Factcheck.org debunks the story here.
- Go upstream to the source: this claim originated from a video clip that was posted all over social media. This video clip was posted by a group of Trump supporters who attacked the United States Capitol Building in Washington, D.C., after U.S. President Donald Trump did not win the 2020 presidential election, on January 6, 2021. They uploaded a video where shows a police officer “appears to tell” the group that they wouldn't stop them from entering the building. However, nowhere in the video does the police make that claim. A fake news website called, The Gateway Pundit, reported the same claim on Facebook and Instagram. Even a radio show in Texas called “Walton & Johnson,” ran a similar headline.
- Read laterally: the next step would be to see what others are saying about this claim. In this case we should look at what the police officers in this video clip said about the incident. US Capitol police officers said in an email statement to factcheck.org , that the officers were blocking the whole way and attempting to de-escalate the situation by telling the crowd to not attack or assault and to remain calm. The Justice Department reported that about 140 police officers were assaulted that day.
- Circle back: If you find yourself, getting overwhelmed by other sources on the claim, circle back and investigate the background of that source. If we look back to the actual incident on January 6, 2021, we know from ample public evidence released by the FBI showed Trump supporters violently assaulting officers at the Capitol. Other shown footage included Trump supporters breaking through a metal barrier outside the capital and breaking windows of the building to enter.
Conclusion: The U.S. Capitol police never gave protestors permission to enter the Capitol.
The Claim: High doses of vitamin C can cure COVID-19.
- Check for previous work: Throughout the year 2020, many websites and social media posts were claiming how high doses of vitamin C could cure and/or be an effective treatment for COVID-19. For this case, we looked up this claim on Snopes (fact checkering source) which they claim the information as false and misleading.
- Go upstream to the source: These claims stemmed from multiple studies detailing how vitamin C can help support the bodies immune system. According to Harvard Health Publishing , vitamin C has some marginal benefits for the common cold, such as reducing the duration of symptoms, if it is taken before catching a cold. Those benefits can be achieved with a diet that includes 200 milligrams of vitamin C, which is easily obtainable with a daily diet that includes fruits and vegetables .
- Read laterally: To gain additional background on this claim, we can read multiple sources and this this case see if it has been tested in trials. The CDC ultimately reported that there was insufficient evidence for the panel to recommend either for or against vitamin C for the treatment of COVID-19 and non-hospitalized patients. Most of the trials had a limitation such as small sample sizes, study designs that had different doses or formulations of vitamin C and different outcome measures.
- Circle back: If you find yourself, getting overwhelmed by other sources on the claim, circle back to the claim, and investigate the background of that source. In this particular claim, there is some truth and vitamin C is good for your immunity. However, some of the hype around these claims came from unpublished sources, fake news, personal websites, and from "influencers" on social media. We can refer to the CDC website and peer review published articles about the relationship between COVID-19 and vitamin C. Clinical trials can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Conclusion: doses of vitamin C are not a proven as an effective cure for COVID-19.
Claim: Putin intercepts adrenochrome shipment
1. Check for previous work: In this case if we looked for "adrenochrome putin shipment" to check for previous work, we would find that politifact.com already did a fact check on this story.
2. Go upstream to the source: This example is from Real Raw News . This website is known for fabricating stories; if that's information you knew coming into this evaluation, you would know this is an automatic red flag and we could stop here. However, if you didn't know that, you could make a few judgements about what other stories are on the page to get a sense of the angle and political bias for this news source. If you research Andrei Zakharov, whose name was used as a source of information, you'll find that he is a Russian journalist that works for the BBC Russian Service, not as Russian FSB Agent. As a story featuring adrenochrome and blood harvesting with a history of conspiracy theories behind it, you should already be skeptical. Looking up some of the facts in the story help us determine more about its truthiness.

3. Read laterally: Given what we've learned from steps 1 and 2, at this point in the evaluation we could stop our search, dismiss the story, and move on with our lives. However, if we aren't satisfied with what we found, out next step is to look for other stories about this issue. Are other reports of this story coming from reputable sources? Is the story reported elsewhere with the same facts? Are there discrepancies in what's being reported? This is the step where we need to be paying extra attention to who's publishing the story that corroborates this narrative. On the internet you can find pretty much anything you look for, but "anything" isn't always an accurate story to trust.
4. Circle back: There's plenty of facts within this story for us to investigate and check. However, we eventually want to come to a conclusion and circling back will bring us to the question of whether this story has any truth. Given what we've learned: no, this is not factual.
Check your Emotions: The habit we're practicing throughout is about checking our emotions. Do I want this story to be true? Does this story sound too outrageous to be true? Am I attached to what the truth about this story is one way or another?
The Claim: chickens are not laying eggs, because RNA is being added to commercial chicken feed.
- Check for previous work: For this case, we looked up this claim on politifact.com. This resource debunks it here.
- Go upstream to the source: The claim originated from a published research article titled, " Messenger RNA sequencing and pathway analysis provide novel insights into the biological basis of chickens’ feed efficiency. " This study aimed to characterize the biological basis of differences between chickens with low and high feed efficiency, with a long-term goal of improving the ability to select for feed efficiency. Nowhere in the article did it mention adding RNA to chicken feed. RNA sequencing was being used to see how differences in feed efficiency can be explained by what levels of RNA are produced by the chickens' cells.
- Read laterally: The next step would be to see what others are saying about this claim based on the article. PolitiFact actually did many email interviews with experts in the field, to talk about the claim. Multiple experts said commercial feed manufactures were not adding RNA to chicken feed, and that this claim was a misinterpretation of the data. The FDA also confirmed that RNA is not on its own, a feed additive. The articles cited from the original TikTok video are not relevant to the argument made in the video. The FDA also stated that there are many ways why a chicken's egg-laying behavior and quantity could change. They recommended consulting a licensed veterinarian, who can examine the animal and take a detailed medical and diet history.
- Circle back: If you find yourself, getting overwhelmed by other sources on the claim, circle back to the claim, and investigate the background of that source. The first thing one should question is how RNA is being referred to in the post. RNA stands for ribonucleic acid, which is a naturally occurring nucleic acid found in all living cells. So, the claim of adding synthetic RNA into commercial feed does not make any sense. Furthermore, a search can be done to confirm what common factors are affecting chicken egg laying. Common reasons listed were management practices, improper nutrition, parasite infection, disease, lighting, and stress.
Conclusion: RNA is not being added to commercial chicken feed.
- Trump Bills Michelle Obama
- "Pizzagate"
- Donald Trump Wins the Popular Vote
- Hillary's Health
- Muslims Demanding Handouts
- Burning Tipis at Standing Rock
- Student Desecrates Constitution
This example is from Before It's News; it's also featured on at least one other similarly fake website. The amounts supposedly owed by the Obamas are pretty unbelievable. Even if the presidential couple had indeed bought everything the article claims they did, the total would not come anywhere close to $11 billion, a figure equal to the GDP of a small country. It also includes some grammatical issues, and "eleventy" isn't a word.

It's also worth looking at the Before It's News site itself:

A few points:
- "Alternative," "Spirituality," and "Unexplained" are terms that one doesn't find among the tabs on any legitimate news site.
- No professional news organization lets just anyone "upload news."
- The presence of advertising, and the nature or quality of the products being advertised, is not a sound indicator of the site's reliability. Ads for Duracell batteries and Mapquest could quite conceivably show up in the margins of The Seattle Times ' website , for example. Newspapers, in both their print and online versions, generally cannot survive without ad revenue.
- This site deals heavily in sensationalist headlines (the ones underlined are just some of the most outrageous).
Among the most notorious fake news stories of 2016 was one alleging that Hillary Clinton was running a child-prostitution ring out of a Washington, D.C., pizzeria. This had real-world consequences for the employees of that pizzeria when an armed man decided to "self-investigate" the rumors, as described in "Dissecting the #PizzaGate Conspiracy Theories," by Gregor Aisch, Jon Huang, and Cecilia Kang.
During the 2016 election, another persistent fake news story was that Donald Trump won both the popular vote and the electoral college vote. That Trump won the electoral college by a clear margin is undisputed. While the federal government did not release the official results of the popular vote until mid-2017, a great number of sources, ranging from the more conservative The Wall Street Journal to the more liberal The New York Times reported Hillary Clinton winning the popular vote by margins ranging from approximately a million votes (on Nov. 9, 2016) to three million (NYT estimate as of Feb. 10, 2017).
During the 2016 presidential campaign, fake news sites circulated several stories alleging that Hillary Clinton was in poor health, the implication being that she was not fit enough for the rigors of the presidency. Fake news site 70News dedicated an entire section to these rumors, most of which were bolstered by photos or video clips showing Clinton in moments of apparent frailty or disorientation. This illustrates a common fake news tactic: the use of tidbits of truthful imagery to support exaggerated or unsubstantiated claims. Laura Mallonee writes about this phenomenon in " How Photos Fuel the Spread of Fake News ."

Not all fake news is geared toward a conservative audience; liberals may be just as quick to believe falsehoods that seem to confirm their hopes and fears. A February 2017 story run by Alternative Media Syndicate claimed that police forces arrayed against the pipeline protesters at the Standing Rock Indian Reservation raided and burned a protester camp, offering graphic imagery of flaming tipis as proof. This story is completely false; the image was taken from a 2007 HBO film, Bury My Heart At Wounded Knee . Snopes.com debunks the story here .
In February 2018, after surviving a shooting in which 17 of her schoolmates died, Florida teenager Emma Gonzalez became an outspoken proponent of gun control legislation. Not long after, imagery of her apparently tearing up a copy of the U.S. constitution went viral on right-wing websites. This imagery was doctored ; the originals came from a Teen Vogue photo shoot in which Gonzalez symbolically tore up a target sign. Photo manipulation is a time-honored propaganda tactic, but is now easier than ever thanks to Photoshop and other editing tools.

- Robert Amnor story
Work in groups of 3-5. Using any methods you can think of, try to determine whether the story is (a) false, (b) true, or (c) a mix of truth and falsehood. Go back to the home page of this guide if you need some direction on what to look for.
Discuss which (if any) of the fake news hallmarks from the first page of this guide are evident in this story.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Types of Misinformation >>
- Last Updated: Apr 16, 2024 12:19 PM
- URL: https://libguides.lib.cwu.edu/fakenews

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Social Media Marketing Case Study Examples: 1. 793,500+ Impressions for Semrush On Twitter 2. Viral Oreo Super Bowl Tweet 3. Facebook Posting Strategy That Lead to 3X Reach & Engagement 4. Achieving a 9 Million Audience by Automating Pinterest SEO 5. 5X Increase In App Installs from TikTok 6. 330% Increase In Reach for the Make a Wish Foundation 7.
Then, identify quotes that can be pulled and inserted into the piece. Next, insert the relevant social media examples and metric graphs. You want to break up the paragraphs of words with images or graphics. These can be repurposed later when you share the case study on social media, email or sales decks.
Social Media Case Study 1: Starbucks. Starbucks and social media are a match made in heaven. Being one of the sensational brands online, they are stirring the social media world with their strong presence. They brew the right content to elevate the experiences of their coffee lovers. But how do they nail marketing with perfection every single time?
Social media If you're creating a social media case study, using social media to share said case study should be a no-brainer. Break down the content of your case study into bite-sized chunks for Instagram or Facebook, post analytics dashboards from the study on Twitter and link the study in a LinkedIn post to spice up your profile.
Lee Odden of TopRank Marketing focuses more on the Content Marketing side and provides 11 B2B Content Marketing case studies. 5. B2B Social Media Case Study: How I made $47 million from my B2B blog. This is a personal success story from AT&T's experience and success with a content strategy. 6. How ASOS Use Social Media [CASE STUDY]
A case study is the most powerful tool you have to convert leads. Get inspiration for your next case study with successful examples from real brands. ... Convoso's PDF case study for Digital Market Media immediately mentions the results that the client achieved and takes advantage of white space. On the second page, the case study presents ...
These days, people are spending a lot of their time online on social media. According to Forbes, in 2020, Americans spent an average of 1,300 hours on social media, with an average of 58 minutes per day on Facebook alone. And, since smart marketing is about being visible where your customer base spends their time, social media is the place to be.
The case study addresses the development of media reporting during the COVID-19 pandemic, focusing on the period between January and November 2020 in France, Germany, Romania, Spain, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. The study aims to make media reporting transparent along two dimensions: the coverage of COVID-19-related topics and the ...
Here are five of the best brands on social and what I think you can learn from them: 1.Mercedes Benz - Repeated, successful social media marketing campaigns. Mercedes Benz seem to win every time with their social media campaigns. The one that stands out to me was back in 2013 when they created what I still believe to be one of the best ...
Post about case studies on social media. Case studies make for perfect social sharing material. Here are a few examples of how you can leverage them on social: Share a link to a case study and tag the customer in the post. The trick here is to post your case studies in a way that attracts the right people to click through, rather than just a ...
Case studies are an effective marketing tool to engage potential customers and help build trust. Check out these case study examples for best practice tips. ... In this case study on Polygon Media, the design is simple and professional, and the layout allows the prospective customer to follow the flow of information.
Template 1- Business Case Study Summary on Social Media Marketing Template. Presenting our content-ready template designed to provide an alluring backdrop for any subject matter. Elevate your presentations and exude an air of professionalism, making you appear as a seasoned presentation virtuoso.
How UK government identified anxiety and depression on social and offered advice. Social Media Case Studies. 28 Nov 2023. 2 min read. Boost on how it helped Brits say 'yes' more often. Social ...
Take a look at three B2B social media marketing case studies to get ideas for your business's own strategy. 1. Turface Athletics and Profile Golf. Turface Athletics and Profile Golf, two brands under the Profile Products umbrella, worked with Elevation Marketing to address social media engagement for their B2B profiles.
A successful social media post about your Case Studies should follow a specific formula—specifically, the same one your Case Studies do! Ensure that your post includes the following elements in this order: Headline. Use an intriguing opening sentence to make your post stand out and capture your audience's attention right away.
Journalism and Media Ethics Resources. Journalism and Media Ethics Cases. Find ethics case studies on journalism covering topics such as stealth journalism, pressures from advertisers, and the personal lives of public officials. For permission to reprint articles, submit requests to [email protected].
Impact in a Historical Context. The relationship between media and culture has been examined for generations, and the current study of journalism impact has precursors. In the 1920s and 1930s, scholars focused on the relationship between media and politics—at just the moment when media began to claim impartiality.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Social media plays an important part in the digital transformation of businesses. This research provides a comprehensive analysis of the use of social media by business-to-business (B2B) companies. The current study focuses on the number of aspects of social media such as the effect of social media, social media tools, social media use, adoption of social media use and its barriers, social ...
Misinformation & Fake News. A guide to discerning fake news sources, including articles, videos, and links to other resources. Practice: Case Studies. Case Study 1. Case Study 1 - Explained. Case Study 2. Case Study 2 - Explained. On August 20, 2022, a TikTok video was posted, claiming that Disney World was going to lower the drinking age to 18.
Research on the effects of social media use at older ages has largely focused on social benefits. Yet, participation in these new media forms may result in other favorable outcomes, such as improved cognitive functioning. Using a wait list-control design, this study examines the effects of social media engagement among novice adult social media ...
in the production of the Media Center case study. We are also thankful to a wide-range of colleagues who generously shared their knowledge and feedback on the Media Center case study, including ...