- Specialisations
- Meet the team
- Wellness Program
- Join our talent pool

Posts by Tag
- contract engineering (16)
- contract solutions (10)
- Specialist Recruitment (8)
- technical resourcing (8)
- gig economy (7)
- Recruitment (5)
- job seeker (4)
- Insider (1)
- Resources (1)
The true impact of workplace wellbeing: two case studies
Embedded Expertise, Published: January 29, 2020 - Updated: August 22, 2022
Mental health concerns are a leading cause of workplace absence , and as we see increasing incidents of mental health-related sick days, workplace wellbeing is paramount for both organisational and individual success.
Below I’ve written two real-life stories where bettering the wellbeing of a workplace can have dramatic effects on the individuals and business profitability itself. Hopefully this will inspire you to incorporate a wellness approach into your organisation or team, or take more notice of your own mental health.
Case study one: Michael thought he was fine
Michael* realised he was arguing a lot with his family at home and was becoming increasingly more reactive to situations that probably didn’t warrant it. He wasn’t terribly great at conducting conversations or maintaining relationships with coworkers and this spilled outside of work. Body aches and excessive headaches had also started to culminate: all obvious signs of deep stress that Michael was ignoring.
The thing is, he thought he was actually doing really well and managing his stress levels appropriately and that his behaviour and experiences were quite normal.
But in fact, he was suffering extreme levels of stress . Something he didn’t even comprehend until he connected with a workplace wellbeing expert and he had the opportunity to observe his behaviours.
After one week of dedicated and concentrated awareness on how he was reacting and experiencing situations and noticing stress levels, triggers and emotions as they arose, he started to really notice a difference.
‘After one week of dedicated and concentrated awareness… he started to really notice a difference.’
To mitigate his stress levels and improve his workplace wellbeing and relations, Michael also engaged in visualisations (similar to what athletes do ), particularly with conversations, which creates different pathways in the brain . From here he started acting differently, having better discussions and decisions and was significantly calmer everywhere throughout his life, not just in the workplace.
Case study two: bad behaviour, great worker
Company owner, Rajiv, was experiencing some staff problems that he’d tried to handle but wasn’t seeing any changes. One of his contract managers, Tom, was displaying bad behaviour whenever things would go wrong.
The thing was, it was abundantly clear that what Tom was saying and the problems that he identified were absolutely correct. And the company valued his hard work and how exceptional he was at his job, so there was no desire to terminate his contract early. Which can often be a case for difficult situations in the workplace— many people are too eager to throw the ‘baby out with the bathwater’ so to speak, rather than experiment with some alternative ways of reaching conflict resolution. Or even taking the time to discover what is really going on, stepping away from the ego and its primal behaviour of flight or fight mode.
After supportive discussions with Tom, the wellness team discovered that actually he felt isolated , alone and that he didn’t belong. And, because the mind seeks to confirm our beliefs (through confirmation bias), would create situations and replicate behaviour to further consolidate that belief. He was very caught up in his story that he was an outsider.
A sense of belonging
To further compound this position, Tom was contracted as part of a large project and he felt like he didn’t fit in with the permanent employees, who had established themselves in the internal culture.
Forbes states that, ‘Employees who do not naturally fit into established corporate norms will often times try to assimilate to those norms – or put themselves “on guard” – in order to avoid potential biases or discrimination.’ This can take considerable effort and energy, which could be better spent on a person’s core duties.
A sense of belonging in the workplace contributes greatly to retention and attraction of high-quality candidates, which leads to better productivity, outcomes, creative solutions and more profit. It can also result in 75 per cent fewer sick days and avoid millions of dollars’ worth of lost productivity.
‘A sense of belonging in the workplace contributes greatly to retention and attraction of high quality candidates…’
Fostering this sense of belonging ‘in the workplace makes employees engaged and produce work that is elevated above the ordinary…’.
Once identified, the workplace wellbeing team worked with Tom and Rajiv with proven techniques that involved awareness, cultural changes and compassion and saw rapid improvement within weeks, thanks in part to the commitment of the people involved.
The change was so significant that Rajiv was enthusiastic and hungry to find more ways in which he could change the dynamics to bring out better and better results within his company. The company also extended Tom’s contract when the opportunity became available.

Welcome contract workers too
It can be really easy to forget that contract staff are an integral part of your team, even if they are only on staff for a limited time. And it shouldn’t be a last minute or token effort.
‘… there needs to be a culture and allowance for people to connect as human beings. We shouldn’t need bonding or team leadership days to actually connect with our colleagues and make meaningful relationships ,’ says Dr Michelle Lim, a loneliness researcher and senior lecturer in clinical psychology at Swinburne University.
Incorporating contract workers as genuinely part of the team and treating them as well as you treat all employees will only promote excellent benefits for the business and wider society as a whole and help contribute to preventing distressing issues such as high suicide rates in the engineering industry.
Can you relate in full or in part to these stories? Improve your wellbeing in your workplace today. Discover more about our for our contracting professionals.

*We’ve changed these names to provide privacy and protect the identity of these people.

Nukon is joint venture between the world of optimisation and automation. our parent company, SAGE Automation, is a leader in the operations market, while NUKON has fast established an outstanding reputation in the manufacturing data, intelligence andimprovement area.
This meeting of minds means we can now bridge the gaps between the different silos within our client businesses, bringing visibility, unity and breakthrough improvements right across our clients' businesses.
One Column Text
Enjoyed this post don't forget to share..

Embedded Expertise is a specialist consultancy that matches high calibre technical expertise with the agile clients who need them - fast.
Phone: 1300 050 557 Contact us
SAGE GROUP BRANDS
- SAGE Automation
- Embedded Expertise
QUICK LINKS
- Subscribe to our Newsletter

Try Onboard Interactive Demo
Click through it yourself with an interactive demo.

The Best ROI Calculator
In just a few clicks, you'll see how the HR Cloud Onboardig Solution delivers...

Onboard by HR Cloud Demo Video
Employee Communication Platform
Recognition and Rewards Platfrom
The Leading Employee Engagement Platform

The Digital Heart of Your Organization
Like what you hear, 7 effective employee engagement case studies and strategies for a productive workplace.

- 1. Acknowledgment and Appreciation
- 2. Emphasis on Employee’s Holistic Wellness
- 3. Initiatives that are Development-Focused
- 4. Develop a Sense of Purpose, Values & Mission
- 5. Maintain Transparent Communication Channels
- 6. Create Conducive Working Conditions
7. Create Space for Fun & Happiness
Let us help you engage your employees, onboard new hires safely, efficiently, and effectively., are you interested in improving your hr organization.
Are you looking for employee engagement case studies? Learn from some of the best companies out there that have successfully increased employee engagement. See how they did it and what worked for them.
As more and more employers in today’s corporate world realize the importance of employee engagement , the demand for effective and result-oriented employee engagement programs is rising. The internet may present many employee engagement initiatives, but here’s something more: case studies to prove that certain employee engagement strategies are really effective. Follow our blog to learn more about employee satisfaction and ensure that your company is teeming with higher employee engagement initiatives.
According to Johnson and Johnson “ the degree to which employees are satisfied with their jobs, feel valued, and experience collaboration and trust. Engaged employees will stay with the company longer and continually find smarter, more effective ways to add value to the organization. The end result is a high-performing company where people are flourishing and productivity is increased and sustained.”
Nokia Siemens describes employee engagement as “ an emotional attachment to the organization, pride and a willingness to be an advocate of the organization, a rational understanding of the organization’s strategic goals, values, and how employees fit, and motivation and willingness to invest the discretionary effort to go above and beyond”.
While we learn what employee engagement means and its importance, incorporating practical and effective employee engagement programs as part of company culture is the right recipe for success. Here are certain strategies for best employee engagement with case studies.
1. Acknowledgment and Appreciation
The first and foremost step to boost employee engagement is making sure your employees are valued, acknowledged, and appreciated. This motivates employees to become more productive , stay on track with tasks, and perform well. This can be done in many ways and you need to choose an approach that your employees can relate with. While some enjoy public recognition, others don’t. Hence, you can work on innovative recognition ideas .
The 40 Best Thank You Messages for Colleagues

According to a study , social workers in a company received personalized letters of recognition at their home addresses. The workers were chosen randomly and half of them received letters while the rest half didn’t receive any. The first half of the letter was chosen from a few positive motivational sayings and the second half of the letter had a personal note of appreciation written by managers. After a month of the letter experiment, the workers who received letters felt more recognized and appreciated for their efforts, compared to those who didn’t get any. This also had a positive effect on their motivation levels and well-being, according to the results of this study.
2. Emphasis on Employee’s Holistic Wellness
There are many components of employee wellness like nutrition, work-life balance , mental health, and stress management, to name a few. A healthy employee will be more productive and employees who are mentally and physically healthy will exhibit positive motivation, and better morale and resulting in a win-win for both employers and employees. A wellness program can be a good way to start where employees get a chance to explore yoga, in addition to vacation days. A wellness room provides employees with a personal space for their personal needs.
The indispensable role of wellness and an overall effective wellness strategy for an organization can be best understood based on a study that explored the objective of workplace wellness programs and their impact on employees health and medical expenses and so on. The study identifies certain key factors to boost wellness ideas in a corporate setup such as:
Effective communication strategy
Organizations that were part of this research emphasized the importance of how a wellness program is communicated to employees, both in-person and mass information campaigns, with messaging and clear interaction getting the highest priority.
Accessibility of wellness programs
Making wellness programs accessible for all employees is an effective strategy to boost the levels of employee engagement in their organization.
Engaged leadership
According to this study, for wellness programs to be successful, senior leadership should imbibe wellness as an integral and important part of the company culture.
Effective use of existing resources
Organizations leverage the existing resources and then build relationships, which also include health plans to provide employees with more options.
Ongoing assessment
Most companies agree that continuous assessments are required for employers to better understand their employee’s wellness needs.

HR mistakes impact your entire organization. Learn how to avoid the 12 most common mistakes with our free ebook.
3. Initiatives that are Development-Focused
Ongoing development is key for every employee and there are a few development-focused initiatives that you can adopt actively to help your employees gain professional growth like professional networking, master’s or even Ph.D. programs, industry seminars, training courses and conferences, internal promotions, mentoring groups, and career coaching.
This study titled A Study on the Influence of Career Growth on Work Engagement among New Generation Employees involved six companies from diverse industries like consulting, finance, management, real estate, and so on. The findings of this study show that:
Organizational identification (IO) is very important for engagement levels and career growth.
Employee career growth positively impacts work engagement;
Person-organization value is positively linked to career growth and organizational identification (IO).
If employees recognize that they can make career progress in a company, they feel more attached and this increases employee loyalty, particularly for the new generation. It motivates them to put in the extra effort, improve performance, work on new skills, and so on.
4. Develop a Sense of Purpose, Values & Mission
A visible employee engagement program to achieve higher employee satisfaction levels requires employees to gain a sense of purpose, portray the company’s values and understand the mission. It is important to also understand what each of these attributes stands for.
Purpose
A company's purpose is the reason it exists in the first place. Purpose-driven companies are devoted to achieving goals that are bigger than just making money and increasing shareholder value. They also want to make a positive impact on the world around them and approach their work sustainably and ethically. In other words, they're committed to making a difference.
Mission
The mission of a company is similar but not identical to its purpose. Many people use the terms interchangeably, but we see the main difference as follows: the mission statement focuses on what the company has been built to achieve.

To learn even more about improving the employee experience and increasing your competitive advantage while providing a fast return on investment, download our ebook now.
Values
Values are important because they act as a compass for the overall expectations of an organization - they guide how employees do their jobs, how managers communicate with clients and partners, and how workers interact with their peers. By understanding and sharing company values, employers can make better decisions that reflect the priorities of the business.
According to a study by Deloitte , a company’s purpose and mission impact corporate confidence as well, as indicated by the results of this study.
Nearly half of all executives (47%) say that they can identify with their company's purpose, while only 30% of employees feel the same way.
A whopping 44% of executives believe that exemplary leadership involves setting an example that lives and breathes the company's purpose - but only 25% of employees share this belief.
41% of executives believe that a company's purpose plays a significant role in major corporate decisions, whereas only 28% of employees feel the same way.
38% of leaders claim that their company's purpose is communicated clearly and openly to all, but only 31% of employees actually think this is the case.
Ultimately, teaching your employees about the company's purpose, mission, and vision takes time and patience. It's a gradual process, but when done correctly, it has numerous benefits for employers. Creating a sense of purpose for your employees allows you to see numerous benefits in the long run such as a more committed workforce and less employee turnover.
Social Intranet Software that Encourages Employee Communication

5. Maintain Transparent Communication Channels
Many employees feel reluctant to share their concerns and opinions with their managers or peers, either due to a perception that their managers don’t pay much attention to them or maybe they tried earlier but no action was taken by the leadership. Encouraging employees to share their concerns with leaders has its own benefits.
Practicing reflective listening helps managers to understand the message, through attentive communication.
Making employees understand they are respected helps them to respect you back and this is an employee engagement strategy based on common sense.
Acknowledging employee views is a way of recognizing a diverse range of ideas and respecting what they say, even though in the end you may still agree to disagree.
Seeking employee’s input actively helps to boost job satisfaction levels.
A research study analyzed communication between employers and employees and its impact on engagement levels. The findings supported the general definition of engagement as a sense of shared responsibility between both supervisors and employees, proving that establishing communication with your employees has a wide range of benefits and can work wonders for a company’s employee engagement levels .
“Our staff has praised the increased communication level Workmates delivers. We use it to communicate important project matters and give staff specific ‘kudos’ or even recognize their birthdays. More importantly, we use Workmates to clarify important project details that needed rapid dissemination among the entire team.”

6. Create Conducive Working Conditions
While expecting high performance from employees by an organization is quite natural, it is also equally important to provide necessary conditions for employees to do their best, by supporting them in any way you can. You can encourage positive and healthy competition in the workplace, show zero tolerance for toxic behavior, maintain a clean and healthy workplace ambiance, and create supportive teams . One way to support your workforce is by encouraging them to focus on things that are already good in their lives.
According to a consultant, Stephanie Pollack , a visible change is possible when employees are encouraged to know more about the benefits of gratitude and become aware of good things already existing in their lives. Showing gratitude has a plethora of benefits that range from reducing stress to making people feel better about themselves. It's important to build a culture of appreciation in your company so that employees feel comfortable expressing gratitude to one another and also feel appreciated in their jobs. This will not only lead to employees appreciating their jobs and coworkers more, but it will also help them appreciate themselves on a whole new level. Creating a grateful environment takes time, but it's worth it to see the positive transformation it can have on your organization as a whole.

A New Way to Manage Frontline Workers and Remote Teams

Workers who are content with their jobs are more likely to be motivated, productive, and engaged than those who are unhappy with their work. And happiness usually comes with having fun. However, this doesn't mean that employees should neglect their tasks or ignore deadlines. Learning how to balance work and play is key to being successful in both areas.
Employees should get the chance to do fun stuff to uplift their moods and refresh their minds and thoughts. This will make them more productive while handling their daily tasks. This can be in the form of having lunch together, organizing joke sessions, quizzes, celebrating employee milestones and birthdays, hosting parties, sports activities, recreational outings, and so on. According to a study “ Finding Fun in Work: The Effect of Workplace Fun on Taking Charge and Job Engagement” , having fun in the workplace motivates employees in a positive way improving their job satisfaction levels, productivity, commitment, energy, and creativity. It also helps to reduce anxiety, turnover, stress, and absenteeism.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to improving employee engagement in the workplace. You can employ one or more of these strategies based on case studies and see what works best for you and your workforce. Creating a nurturing and fun-filled productive place can make a great difference for your company and its growth in the years to come.
Try Workmates Interactive Demo
Author Bio:
This article is written by a marketing team member at HR Cloud. HR Cloud is a leading provider of proven HR solutions, including recruiting, onboarding, employee communications & engagement, and rewards & recognition. Our user-friendly software increases employee productivity, delivers time and cost savings, and minimizes compliance risk.

Introduction to Conflict in the Workplace (and How it Erodes Productivity & Culture)
Keep Reading
Employee appreciation ideas - 22 great ways to celebrate.
Every year Employee Appreciation Day is on the first Friday in March, and with it comes
Workforce Management through Tech-Based Tools: Streamlining Construction and Roofing Operations
As industries evolve, adopting innovative approaches to workforce management is essential
Write for the HR Cloud Blog!


An official website of the United States government.
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- 中文(简体) (Chinese-Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese-Traditional)
- Kreyòl ayisyen (Haitian Creole)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- Español (Spanish)
- Filipino/Tagalog
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Safety Management
Recommended Practices for Safety and Health Programs
Case studies.
To help start or improve your organization's safety and health program, see the case studies listed below for lessons learned and best practices.
- The Electric Power Industry relies on Safety and Health Programs to keep workers safe on the job ( PDF )
- Hazards that OSHA's voluntary On-Site Consultation Program helped companies identify.
- Methods companies implemented to correct the hazards.
- Business practices that changed to prevent injuries and illnesses.
- Challenges, successes, and overall impact on businesses.
- More than 60 success stories from 2008 through 2016 are presented from a wide range of industries throughout the country.
- You can read stories highlighting successes and best practices from companies participating in VPP – 21 recent stories arranged by industry - as well as 26 archived stories from 1994 to 2010 .
- Read about "CEOs Who Get It":
- 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009
- Noble Corporation
- Johnson and Johnson
- DM Petroleum Operations
- Fluor Hanford
- Schneider Electric
- Dow Chemical

Download
Recommended Practices for Safety and Health Programs (en Español) Download
Recommended Practices for Safety and Health Programs in Construction Download
- Choosing Workplace
- Customer Stories
- Workplace for Good
- Getting Started
- Why Workplace
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Future of Work
- How can Workplace help you?
- Business Communication
- Employee Engagement
- Strengthen Culture
- Getting Connected
- Frontline Workers
- Remote and Hybrid Working
- Integrations
- Interactive Demo
- Features at a Glance
- Connect to all your tools
- Workplace & Microsoft
- Integrations directory
- Knowledge Library
- Key Updates
- Auto-Translate
- Safety Center
- Access Codes
- Pricing Plans
- Forrester ROI Study
- Events & Webinars
- Ebooks & Guides
- Employee Experience
- Remote Working
- Team Collaboration
- Productivity
- Become A Partner
- Service & Reseller Partners
- Integrations Partners
- Start Using Workplace
- Mastering Workplace Features
- Workplace Use Cases
- Technical Resources
- Work Academy
- Help Center
- Customer Communities
- What's New in Workplace
- Set up Guides
- Domain Management
- Workplace Integrations
- Account Management
- Authentication
- IT Configuration
- Account Lifecycle
- Security and Governance
- Workplace API
- Getting started
- Using Workplace
- Managing Workplace
- IT and Developer Support
- Get in touch

Workplace Case Studies

The 2021 Workplace Customer Success Awards

Effective community and connection at AB InBev

Better connections in the moments that matter

Meaningful connections among a global workforce

- Show slide number 1
- Show slide number 2
- Show slide number 3
- Show slide number 4
- Show slide number 5
Explore our inspiring case studies
Find out how organizations like yours use Workplace to connect employees and increase collaboration.

"We benefit from the collective voice of our teams around the world to help us move faster as a global organisation innovating for our customers. We love having our teams feel a bit closer on Workplace while we help our customers to travel the globe."

"Workplace helps our employees connect and visually showcases our global teams. We're breaking down silos, communicating across functions and driving engagement, especially amongst our remote employee populations. It has definitely ignited our spirit of fun."

"Our associates guide everything that we do at Valet Living, and Workplace is an invaluable tool that connects us to our frontline directly. I truly enjoy going on Workplace daily, learning from our associates, and getting to see firsthand the amazing work that they are doing."

- Home >
Company culture case studies

Get fresh culture insights, research, and trends straight to your inbox!

- Browse Topics
- Executive Committee
- Affiliated Faculty
- Harvard Negotiation Project
- Great Negotiator
- American Secretaries of State Project
- Awards, Grants, and Fellowships
- Negotiation Programs
- Mediation Programs
- One-Day Programs
- In-House Training and Custom Programs
- In-Person Programs
- Online Programs
- Advanced Materials Search
- Contact Information
- The Teaching Negotiation Resource Center Policies
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Negotiation Journal
- Harvard Negotiation Law Review
- Working Conference on AI, Technology, and Negotiation
- 40th Anniversary Symposium
- Free Reports and Program Guides
Free Videos
- Upcoming Events
- Past Events
- Event Series
- Our Mission
- Keyword Index
PON – Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School - https://www.pon.harvard.edu
Team-Building Strategies: Building a Winning Team for Your Organization

Discover how to build a winning team and boost your business negotiation results in this free special report, Team Building Strategies for Your Organization, from Harvard Law School.
Case Study of Conflict Management: To Resolve Disputes and Manage Conflicts, Assume a Neutral 3rd Party Role
Here is a case study of conflict management emphasizing the importance of hearing all sides in a dispute.
By PON Staff — on January 11th, 2024 / Conflict Resolution
In their book Difficult Conversations: How to Discuss What Matters Most (Penguin Putnam, 2000), authors Douglas Stone , Bruce Patton , and Sheila Heen tell us how to engage in the conversations in our professional or personal lives that make us uncomfortable by examining a case study of conflict management. Tough, honest conversations are critical for managers, whether they need to change the group culture, manage conflict within a team, give a negative performance evaluation, disagree with others in a group, or offer an apology.
To set the stage for a productive discussion, open a difficult conversation with the “Third Story,” advise the authors of Difficult Conversations . The Third Story is one an impartial observer, such as a mediator, would tell; it’s a version of events both sides can agree on. “The key is learning to describe the gap—or difference—between your story and the other person’s story. Whatever else you may think and feel, you can at least agree that you and the other person see things differently,” Stone, Patton, and Heen write.

Claim your FREE copy: The New Conflict Management
In our FREE special report from the Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School - The New Conflict Management: Effective Conflict Resolution Strategies to Avoid Litigation – renowned negotiation experts uncover unconventional approaches to conflict management that can turn adversaries into partners.
Suppose two regional sales reps share responsibility for sending weekly updates to their manager. Brad always submits them on time, but Frank often turns them in late. Saying, “Frank, you’ve turned in the sales reports late again” would only put Frank on the defensive. Instead, Brad opens the conversation this way: “Frank, you and I place a different value on deadlines. I want to explain why meeting them is important to me, and then I’d like to hear your take on them.”
Brad learns that Frank, when faced with the choice of possibly making a sale or compiling the report, thinks he should focus on the sale. With this insight, Brad proposes another way to share responsibilities: Brad will complete the report when it’s Frank’s turn to do so, as long as Frank gives Brad two hours’ notice and a share in any commission Frank earns as a result of being able to continue pursuing a lead.
What are your favorite conflict management methods?
Related Conflict Resolution Article: Conflict Management Skills When Dealing with an Angry Public – Here is some negotiation advice drawn from a case study of conflict management dealing with an angry public.
Adapted from “How to Say What Matters Most,” by Susan Hackley (former managing director, Program on Negotiation), first published in the Negotiation newsletter.
Originally published in 2010.
Related Posts
- 3 Types of Conflict and How to Address Them
- Negotiation with Your Children: How to Resolve Family Conflicts
- What is Conflict Resolution, and How Does It Work?
- Conflict Styles and Bargaining Styles
- Value Conflict: What It Is and How to Resolve It
Click here to cancel reply.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Negotiation and Leadership
- Learn More about Negotiation and Leadership

NEGOTIATION MASTER CLASS
- Learn More about Harvard Negotiation Master Class

Negotiation Essentials Online
- Learn More about Negotiation Essentials Online

Beyond the Back Table: Working with People and Organizations to Get to Yes
- Learn More about Beyond the Back Table

Select Your Free Special Report
- Beyond the Back Table September 2024 and February 2025 Program Guide
- Negotiation and Leadership Fall 2024 Program Guide
- Negotiation Essentials Online (NEO) Spring 2024 Program Guide
- Negotiation Master Class May 2024 Program Guide
- Negotiation and Leadership Spring 2024 Program Guide
- Make the Most of Online Negotiations
- Managing Multiparty Negotiations
- Getting the Deal Done
- Salary Negotiation: How to Negotiate Salary: Learn the Best Techniques to Help You Manage the Most Difficult Salary Negotiations and What You Need to Know When Asking for a Raise
- Overcoming Cultural Barriers in Negotiation: Cross Cultural Communication Techniques and Negotiation Skills From International Business and Diplomacy
Teaching Negotiation Resource Center
- Teaching Materials and Publications
Stay Connected to PON
Preparing for negotiation.
Understanding how to arrange the meeting space is a key aspect of preparing for negotiation. In this video, Professor Guhan Subramanian discusses a real world example of how seating arrangements can influence a negotiator’s success. This discussion was held at the 3 day executive education workshop for senior executives at the Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School.
Guhan Subramanian is the Professor of Law and Business at the Harvard Law School and Professor of Business Law at the Harvard Business School.
Articles & Insights
- What is BATNA? How to Find Your Best Alternative to a Negotiated Agreement
- For Sellers, The Anchoring Effects of a Hidden Price Can Offer Advantages
- Negotiation Examples: How Crisis Negotiators Use Text Messaging
- BATNA Examples—and What You Can Learn from Them
- Taylor Swift: Negotiation Mastermind?
- Solutions for Avoiding Intercultural Barriers at the Negotiation Table
- Top Negotiation Case Studies in Business: Apple and Dispute Resolution in the Courts
- Sales Negotiation Techniques
- Contract Negotiations and Business Communication: How to Write an Iron-Clad Contract
- Amazon–Whole Foods Negotiation: Did the Exclusive Courtship Move Too Fast?
- Crisis Negotiation Skills: The Hostage Negotiator’s Drill
- Police Negotiation Techniques from the NYPD Crisis Negotiations Team
- Famous Negotiations Cases – NBA and the Power of Deadlines at the Bargaining Table
- Negotiating Change During the Covid-19 Pandemic
- AI Negotiation in the News
- How to Manage Difficult Staff: Gen Z Edition
- Bargaining in Bad Faith: Dealing with “False Negotiators”
- Managing Difficult Employees, and Those Who Just Seem Difficult
- How to Deal with Difficult Customers
- Negotiating with Difficult Personalities and “Dark” Personality Traits
- 7 Tips for Closing the Deal in Negotiations
- How Does Mediation Work in a Lawsuit?
- Dealmaking Secrets from Henry Kissinger
- Writing the Negotiated Agreement
- The Winner’s Curse: Avoid This Common Trap in Auctions
- Settling Out of Court: Negotiating in the Shadow of the Law
- How to Negotiate with Friends and Family
- What is Dispute System Design?
- What are the Three Basic Types of Dispute Resolution? What to Know About Mediation, Arbitration, and Litigation
- Four Conflict Negotiation Strategies for Resolving Value-Based Disputes
- A Top International Negotiation Case Study in Business: The Microsoft-Nokia Deal
- India’s Direct Approach to Conflict Resolution
- International Negotiations and Agenda Setting: Controlling the Flow of the Negotiation Process
- Overcoming Cultural Barriers in Negotiations and the Importance of Communication in International Business Deals
- Political Negotiation: Negotiating with Bureaucrats
- Leadership and Decision-Making: Empowering Better Decisions
- The Contingency Theory of Leadership: A Focus on Fit
- Directive Leadership: When It Does—and Doesn’t—Work
- How an Authoritarian Leadership Style Blocks Effective Negotiation
- Paternalistic Leadership: Beyond Authoritarianism
- Undecided on Your Dispute Resolution Process? Combine Mediation and Arbitration, Known as Med-Arb
- Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) Training: Mediation Curriculum
- What Makes a Good Mediator?
- Why is Negotiation Important: Mediation in Transactional Negotiations
- The Mediation Process and Dispute Resolution
- Unethical Negotiation Tactics: Are You Prepared for Dirty Tricks?
- In Negotiation, How Much Do Personality and Other Individual Differences Matter?
- The Right Negotiation Environment: Your Place or Mine?
- Negotiation Skills: How to Become a Negotiation Master
- Dear Negotiation Coach: Should You Say Thank You for Concessions in Negotiations?
- Collaborative Negotiation Examples: Tenants and Landlords
- Ethics and Negotiation: 5 Principles of Negotiation to Boost Your Bargaining Skills in Business Situations
- Negotiation Journal celebrates 40th anniversary, new publisher, and diamond open access in 2024
- 10 Negotiation Training Skills Every Organization Needs
- Trust in Negotiation: Does Gender Matter?
- Setting Standards in Negotiations
- Negotiating a Salary When Compensation Is Public
- How to Negotiate a Higher Salary after a Job Offer
- How to Negotiate Pay in an Interview
- How to Negotiate a Higher Salary
- Check Out Videos from the PON 40th Anniversary Symposium on Negotiation Pedagogy, Practice, & Research
- Teach Your Students to Negotiate a Management Crisis
- Check Out the International Investor-State Arbitration Video Course
- Teaching with Multi-Round Simulations: Balancing Internal and External Negotiations
- Camp Lemonnier: Negotiating a Lease Agreement for a Key Military Base in Africa
- What is a Win-Win Negotiation?
- Win-Win Negotiation: Managing Your Counterpart’s Satisfaction
- Win-Lose Negotiation Examples
- How to Negotiate Mutually Beneficial Noncompete Agreements
- How to Win at Win-Win Negotiation
PON Publications
- Negotiation Data Repository (NDR)
- New Frontiers, New Roleplays: Next Generation Teaching and Training
- Negotiating Transboundary Water Agreements
- Learning from Practice to Teach for Practice—Reflections From a Novel Training Series for International Climate Negotiators
- Insights From PON’s Great Negotiators and the American Secretaries of State Program
- Gender and Privilege in Negotiation
Remember Me This setting should only be used on your home or work computer.
Lost your password? Create a new password of your choice.
Copyright © 2024 Negotiation Daily. All rights reserved.
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Communication →

- 16 Feb 2024
- Research & Ideas
Is Your Workplace Biased Against Introverts?
Extroverts are more likely to express their passion outwardly, giving them a leg up when it comes to raises and promotions, according to research by Jon Jachimowicz. Introverts are just as motivated and excited about their work, but show it differently. How can managers challenge their assumptions?

- 06 Nov 2023
Did You Hear What I Said? How to Listen Better
People who seem like they're paying attention often aren't—even when they're smiling and nodding toward the speaker. Research by Alison Wood Brooks, Hanne Collins, and colleagues reveals just how prone the mind is to wandering, and sheds light on ways to stay tuned in to the conversation.
.jpg)
- 31 Oct 2023
Checking Your Ethics: Would You Speak Up in These 3 Sticky Situations?
Would you complain about a client who verbally abuses their staff? Would you admit to cutting corners on your work? The answers aren't always clear, says David Fubini, who tackles tricky scenarios in a series of case studies and offers his advice from the field.

- 24 Jul 2023
Part-Time Employees Want More Hours. Can Companies Tap This ‘Hidden’ Talent Pool?
Businesses need more staff and employees need more work, so what's standing in the way? A report by Joseph Fuller and colleagues shows how algorithms and inflexibility prevent companies from accessing valuable talent in a long-term shortage.

- 23 Jun 2023
This Company Lets Employees Take Charge—Even with Life and Death Decisions
Dutch home health care organization Buurtzorg avoids middle management positions and instead empowers its nurses to care for patients as they see fit. Tatiana Sandino and Ethan Bernstein explore how removing organizational layers and allowing employees to make decisions can boost performance.

- 24 Jan 2023
Passion at Work Is a Good Thing—But Only If Bosses Know How to Manage It
Does showing passion mean doing whatever it takes to get the job done? Employees and managers often disagree, says research by Jon Jachimowicz. He offers four pieces of advice for leaders who yearn for more spirit and intensity at their companies.

- 10 Jan 2023
How to Live Happier in 2023: Diversify Your Social Circle
People need all kinds of relationships to thrive: partners, acquaintances, colleagues, and family. Research by Michael Norton and Alison Wood Brooks offers new reasons to pick up the phone and reconnect with that old friend from home.

- 15 Nov 2022
Why TikTok Is Beating YouTube for Eyeball Time (It’s Not Just the Dance Videos)
Quirky amateur video clips might draw people to TikTok, but its algorithm keeps them watching. John Deighton and Leora Kornfeld explore the factors that helped propel TikTok ahead of established social platforms, and where it might go next.

- 03 Nov 2022
Feeling Separation Anxiety at Your Startup? 5 Tips to Soothe These Growing Pains
As startups mature and introduce more managers, early employees may lose the easy closeness they once had with founders. However, with transparency and healthy boundaries, entrepreneurs can help employees weather this transition and build trust, says Julia Austin.

- 15 Sep 2022
Looking For a Job? Some LinkedIn Connections Matter More Than Others
Debating whether to connect on LinkedIn with that more senior executive you met at that conference? You should, says new research about professional networks by Iavor Bojinov and colleagues. That person just might help you land your next job.

- 08 Sep 2022
Gen Xers and Millennials, It’s Time To Lead. Are You Ready?
Generation X and Millennials—eagerly waiting to succeed Baby Boom leaders—have the opportunity to bring more collaboration and purpose to business. In the book True North: Emerging Leader Edition, Bill George offers advice for the next wave of CEOs.

- 05 Aug 2022
Why People Crave Feedback—and Why We’re Afraid to Give It
How am I doing? Research by Francesca Gino and colleagues shows just how badly employees want to know. Is it time for managers to get over their discomfort and get the conversation going at work?

- 23 Jun 2022
All Those Zoom Meetings May Boost Connection and Curb Loneliness
Zoom fatigue became a thing during the height of the pandemic, but research by Amit Goldenberg shows how virtual interactions can provide a salve for isolation. What does this mean for remote and hybrid workplaces?

- 13 Jun 2022
Extroverts, Your Colleagues Wish You Would Just Shut Up and Listen
Extroverts may be the life of the party, but at work, they're often viewed as phony and self-centered, says research by Julian Zlatev and colleagues. Here's how extroverts can show others that they're listening, without muting themselves.

- 24 May 2022
Career Advice for Minorities and Women: Sharing Your Identity Can Open Doors
Women and people of color tend to minimize their identities in professional situations, but highlighting who they are often forces others to check their own biases. Research by Edward Chang and colleagues.

- 12 May 2022
Why Digital Is a State of Mind, Not Just a Skill Set
You don't have to be a machine learning expert to manage a successful digital transformation. In fact, you only need 30 percent fluency in a handful of technical topics, say Tsedal Neeley and Paul Leonardi in their book, The Digital Mindset.

- 08 Feb 2022
Silos That Work: How the Pandemic Changed the Way We Collaborate
A study of 360 billion emails shows how remote work isolated teams, but also led to more intense communication within siloed groups. Will these shifts outlast the pandemic? Research by Tiona Zuzul and colleagues. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- Cold Call Podcast
What’s Next for Nigerian Production Studio EbonyLife Media?
After more than 20 years in the media industry in the UK and Nigeria, EbonyLife Media CEO Mo Abudu is considering several strategic changes for her media company’s future. Will her mission to tell authentic African stories to the world be advanced by distributing films and TV shows direct to customers? Or should EbonyLife instead distribute its content through third-party streaming services, like Netflix? Assistant Professor Andy Wu discusses Abudu’s plans for her company in his case, EbonyLife Media. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
.jpg)
- 11 Jan 2022
Feeling Seen: What to Say When Your Employees Are Not OK
Pandemic life continues to take its toll. Managers who let down their guard and acknowledge their employees' emotions can ease distress and build trust, says research by Julian Zlatev and colleagues. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 04 Jan 2022
Scrap the Big New Year's Resolutions. Make 6 Simple Changes Instead.
Self-improvement doesn't need to be painful, especially during a pandemic. Rather than set yet another gym goal, look inward, retrain your brain, and get outside, says Hirotaka Takeuchi. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
More From Forbes
Curiosity: the superpower for success in the workplace and at home.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Dr. D’Amico is the Founder of Vetta Consultants, LLC , an executive coaching firm in Los Angeles.
In a rapidly changing and increasingly complex world, the value of technical skills and knowledge can depreciate with time. However, one timeless skill stands out as a superpower in the workplace and at home: curiosity. This innate desire to explore, understand and question enriches our lives and drives innovation and improvement in various domains.
In the workplace, curiosity acts as the fuel for innovation and creativity. It encourages individuals to question the status quo, explore new possibilities and think outside the box. This relentless pursuit of knowledge and understanding can lead to the discovery of unique solutions to complex problems and the development of groundbreaking products and services. Organizations that cultivate a culture of curiosity often find themselves at the forefront of their industries, leading the charge toward the future.
Change is constant. Adaptability is key to survival and success. Curious individuals are naturally more adaptable because they continuously learn and expand their horizons. This continuous pursuit of knowledge ensures they can navigate uncertainties and adapt to new situations more efficiently. In the workplace, this translates to a workforce that can swiftly pivot in response to market changes. At home, it means being better equipped to handle life's unpredictability.

Seek To Understand, Listen To Learn
Curiosity plays a crucial role in building and maintaining solid relationships. We foster deeper connections and understanding by showing genuine interest in others' thoughts, feelings and experiences. Curious individuals are often excellent listeners and communicators, invaluable traits in any relationship. They approach new relationships and opportunities with a growth mindset, an almost child-like curiosity and a willingness to learn. Curiosity enhances team dynamics and professional collaboration and strengthens bonds with co-workers, family and friends.
Hundreds of Russian Troops Gathered Out In The Open They Didn t Know The Ukrainians Had Aimed Four ATACMS Rockets At Them
Your best look yet at the new iphone 16, the richest person in every state 2024.
At its core, curiosity is a fundamental part of personal growth. It pushes individuals to learn, grow and challenge themselves continuously. This pursuit of personal development is deeply satisfying and contributes to overall happiness and fulfillment. Moreover, curious people often find joy in learning, regardless of the outcome, leading to a more engaging and fulfilling life.
Curiosity is also closely linked to effective problem-solving. By fostering an inquisitive mindset, individuals are more likely to approach challenges with an open mind and consider multiple perspectives and solutions. This approach increases the likelihood of solving complex problems and encourages more innovative and effective solutions. This ability can lead to better decision-making and outcomes in both professional and personal contexts.
Promoting Inclusivity Through Curiosity
Curiosity is also a powerful tool for creating more inclusive environments. By fostering a genuine interest in the perspectives, experiences and cultures of others, curiosity helps break down barriers and build a foundation of mutual respect and understanding. In professional settings, curious leaders and team members are more likely to recognize and value diverse viewpoints, leading to more inclusive decision-making processes, collaboration, innovation and a culture where everyone feels seen and heard.
At home, a curious attitude toward understanding different cultures, beliefs and lifestyles can enrich family life, fostering an open-minded and accepting atmosphere. Encouraging questions and exploring different perspectives can help children and adults develop empathy and a global mindset, preparing them to navigate a diverse world with compassion and respect. Curiosity can bridge gaps, dissolve prejudices and pave the way for more inclusive communities.
How Can We Cultivate Curiosity?
Recognizing the value of curiosity is the first step; actively cultivating it is the next. Encourage questions from others, ask questions of your own, listen to the answers, seek out new experiences and embrace the unknown. Take on new projects at work, explore new hobbies, engage in lifelong learning or make an effort to understand a different perspective or a new culture; the opportunities to nurture curiosity are endless.
Curiosity is more than just a trait; it's a superpower that can lead to significant advancements in professional and personal arenas. By embracing and cultivating curiosity, individuals and organizations can unlock unique possibilities to navigate the complexities of the modern world with greater ease and success.
This case study examines how curiosity facilitated significant growth in Elizabeth, a mid-level manager at a technology firm facing leadership challenges.
Despite being technically proficient, Elizabeth struggled with employee engagement and team motivation. She was skeptical when the organization brought me in to help. She didn’t trust me or the process.
I began the coaching process by cultivating a deep sense of curiosity about her personal leadership style, her team dynamics and the organizational culture. I used several key strategies:
• Open-ended questioning: Using open-ended questions encouraged Elizabeth to reflect deeply on her own experiences and assumptions. Questions like "What do you think motivates your team?" and "How do you react to conflict?" opened up exploratory dialogues. I truly wanted to learn about her and her team and open up a conversation that would strengthen my understanding of who Elizabeth was without judgment.
• Active listening: By asking questions and actively listening to Elizabeth, I gained her trust and demonstrated how to value team members' input, an essential skill Elizabeth needed to develop.
• Encouraging self-inquiry: I guided Elizabeth to become curious about her leadership practices and how they affected her team.
Over several sessions, Elizabeth was encouraged to observe and question her interactions with her team and the outcomes of those interactions. This approach helped Elizabeth do two things:
1. Recognize areas where she previously lacked awareness, particularly around the impact of her communication style.
2. Explore new leadership strategies, such as inclusive decision-making and recognizing individual team member contributions.
As a result of being curious and reflective, Elizabeth reported improved engagement from her team, which was noted by increased participation in meetings and more proactive contributions to projects. Employee satisfaction scores within Elizabeth’s team also rose by 20% within six months, as reported in organizational surveys.
Curiosity empowered Elizabeth to discover and refine her leadership capabilities and fostered a more open, communicative and motivated team environment. This case study underscores the power of curiosity to facilitate meaningful change and development. Through the lens of curiosity, leadership coaching can transform potential into success, benefiting individuals and their organizations alike.
Forbes Coaches Council is an invitation-only community for leading business and career coaches. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Diversity, Equity and Inclusion in the Workplace
A majority of u.s. workers say focusing on dei at work is a good thing, but relatively small shares place great importance on diversity in their own workplace, table of contents.
- The value of DEI efforts at work
- The importance of a diverse workforce
- DEI measures and their impact
- How gender, race and ethnicity impact success in the workplace
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology

Pew Research Center conducted this study to better understand how adults in the United States think about diversity, equity and inclusion efforts in the workplace. This analysis is based on survey responses from 4,744 U.S. adults who are working part time or full time, are not self-employed, have only one job or have multiple jobs but consider one their primary job, and whose company or organization has 10 or more people. The data was collected as part of a larger survey of workers conducted Feb. 6-12, 2023. Everyone who took part is a member of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Read more about the questions used for this report and the report’s methodology .
References to workers or employed adults include those who are employed part time or full time, are not self-employed, have only one job or have multiple jobs but consider one their primary job, and whose company or organization has 10 or more people.
References to White, Black and Asian adults include those who are not Hispanic and identify as only one race. Hispanics are of any race.
References to college graduates or people with a college degree comprise those with a bachelor’s degree or more. “Some college” includes those with an associate degree and those who attended college but did not obtain a degree.
References to disabled workers include those who say a disability or handicap keeps them from fully participating in work, school, housework or other activities.
All references to party affiliation include those who lean toward that party. Republicans include those who identify as Republicans and those who say they lean toward the Republican Party. Democrats include those who identify as Democrats and those who say they lean toward the Democratic Party.
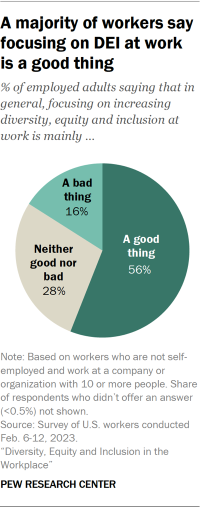
Workplace diversity, equity and inclusion efforts, or DEI, are increasingly becoming part of national political debates . For a majority of employed U.S. adults (56%), focusing on increasing DEI at work is a good thing, according to a new Pew Research Center survey. But opinions about DEI vary considerably along demographic and political lines.
Most workers have some experience with DEI measures at their workplace. About six-in-ten (61%) say their company or organization has policies that ensure fairness in hiring, pay or promotions, and 52% say they have trainings or meetings on DEI at work. Smaller shares say their workplace has a staff member who promotes DEI (33%), that their workplace offers salary transparency (30%), and that it has affinity groups or employee resource groups based on a shared identity (26%). Majorities of those who have access to these measures say each has had a positive impact where they work.
Related : How Americans View Their Jobs
This nationally representative survey of 5,902 U.S. workers, including 4,744 who are not self-employed, was conducted Feb. 6-12, 2023, using the Center’s American Trends Panel . 1 The survey comes at a time when DEI efforts are facing some backlash and many major companies are laying off their DEI professionals .
Some key findings from the survey:
- Relatively small shares of workers place a lot of importance on diversity at their workplace. About three-in-ten say it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere with a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities (32%) or ages (28%). Roughly a quarter say the same about having a workplace with about an equal mix of men and women (26%) and 18% say this about a mix of employees of different sexual orientations.
- More than half of workers (54%) say their company or organization pays about the right amount of attention to increasing DEI. Smaller shares say their company or organization pays too much (14%) or too little attention (15%), and 17% say they’re not sure. Black workers are more likely than those in other racial and ethnic groups to say their employer pays too little attention to increasing DEI. They’re also among the most likely to say focusing on DEI at work is a good thing (78% of Black workers say this), while White workers are the least likely to express this view (47%).
- Women are more likely than men to value DEI at work. About six-in-ten women (61%) say focusing on increasing DEI at work is a good thing, compared with half of men. And larger shares of women than men say it’s extremely or very important to them to work at a place that is diverse when it comes to gender, race and ethnicity, age, and sexual orientation.
- There are wide partisan differences in views of workplace DEI. Most Democratic and Democratic-leaning workers (78%) say focusing on DEI at work is a good thing, compared with 30% of Republicans and Republican leaners. Democrats are also far more likely than Republicans to value different aspects of diversity. And by wide margins, higher shares of Democrats than Republicans say the policies and resources related to DEI available at their workplace have had a positive impact.
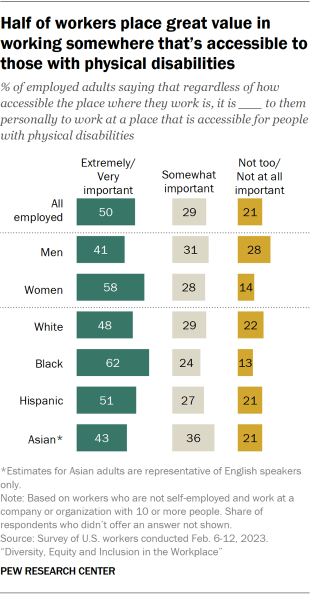
- Half of workers say it’s extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that is accessible for people with physical disabilities. About three-in-ten workers (29%) say this is somewhat important to them, and 21% say it’s not too or not at all important. A majority of workers (76% among those who do not work fully remotely) say their workplace is at least somewhat accessible for people with physical disabilities.
- Many say being a man or being White is an advantage where they work. The survey asked respondents whether a person’s gender, race or ethnicity makes it easier or harder to be successful where they work. Shares ranging from 45% to 57% say these traits make it neither easier nor harder. But far more say being a man and being White makes it easier than say it makes it harder for someone to be successful. Conversely, by double-digit margins, more say being a woman, being Black or being Hispanic makes it harder than say it makes it easier to be successful where they work.
A majority of workers (56%) say focusing on increasing diversity, equity and inclusion at work is mainly a good thing; 28% say it is neither good nor bad, and 16% say it is a bad thing. Views on this vary along key demographic and partisan lines.

Half or more of both men and women say focusing on increasing DEI at work is a good thing, but women are more likely than men to offer this view (61% vs. 50%). In turn, men are more than twice as likely as women to say it is a bad thing (23% vs. 9%).
About two-thirds or more of Black (78%), Asian (72%) and Hispanic (65%) workers say that focusing on DEI at work is a good thing. Among White workers, however, fewer than half (47%) say it’s a good thing; in fact, 21% say it’s a bad thing. But there are wide partisan, gender and age gaps among White workers, with majorities of White Democrats, women and those under age 30 saying focusing on DEI at work is a good thing.
Workers under 30 are the most likely age group to say focusing on DEI at work is a good thing. About two-thirds (68%) of workers ages 18 to 29 say this, compared with 56% of workers 30 to 49, 46% of those 50 to 64, and 52% of those 65 and older.
Views also differ by educational attainment, with 68% of workers with a postgraduate degree saying focusing on DEI at work is a good thing, compared with 59% of those with a bachelor’s degree only and 50% of those with some college or less education.
Democratic and Democratic-leaning workers are much more likely to say focusing on DEI at work is a good thing (78%) than to say it is a bad thing (4%) or that it is neither good nor bad (18%). Views among Republican and Republican-leaning workers are more mixed: Some 30% say focusing on DEI at work is a good thing, while the same share (30%) say it’s a bad thing, and 39% say it’s neither good nor bad.
A majority of workers say their employer pays the right amount of attention to DEI
When it comes to the focus of their own employer, 54% of workers say their company or organization pays about the right amount of attention to increasing diversity, equity and inclusion. The remainder are divided between saying their employer pays too much (14%) or too little attention (15%), or that they’re not sure (17%).
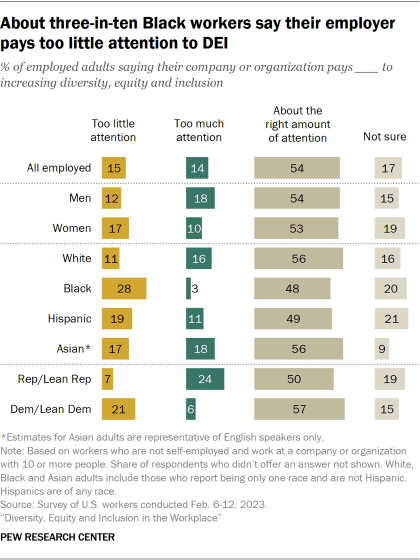
Women are more likely than men to say their employer pays too little attention to increasing DEI (17% vs. 12%). In turn, men are more likely than women to say too much attention is paid to this where they work (18% vs. 10%).
Black workers (28%) are the most likely to say their company or organization pays too little attention to increasing DEI, compared with smaller shares of White (11%), Hispanic (19%) and Asian (17%) workers who say the same.
Views on this question also differ by party. While half or more of both Republican and Democratic workers say their company or organization pays the right amount of attention to DEI, Democrats are more likely than Republicans to say their employer pays too little attention to it (21% vs. 7%). In turn, Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say their employer pays too much attention to DEI (24% vs. 6%).
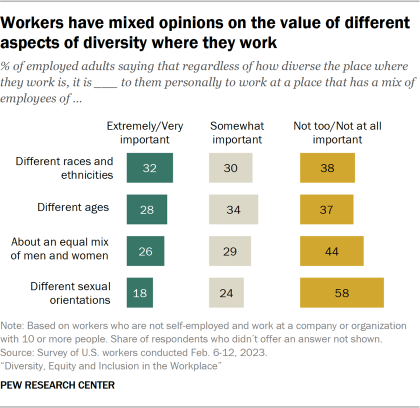
While a majority of workers say focusing on increasing diversity, equity and inclusion at work is a good thing, relatively small shares place great importance on working at a place that is diverse when it comes to gender, race and ethnicity, age, and sexual orientation. About three-in-ten workers say it’s extremely or very important to them to work somewhere with a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities (32%) and ages (28%), while 26% say the same about having about an equal mix of men and women. And 18% say this about having a mix of employees of different sexual orientations at their workplace.
Women are more likely than men to say it’s extremely or very important to them to work at a place that is diverse across all measures asked about in the survey. For example, there are 11 percentage point differences in the shares of women compared with men saying it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that has a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities (37% vs. 26%) and about an equal mix of men and women (31% vs. 20%).
Black workers are among the most likely to value racial, ethnic and age diversity in the workplace. Some 53% of Black workers say it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere with a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities, compared with 39% of Hispanic workers and 25% of White workers who say the same; 43% of Asian workers say this is important to them. (There is no statistically significant difference between the share of Asian workers and the shares of Black and Hispanic workers who hold this view.) And while 42% of Black workers highly value working somewhere with a mix of employees of different ages, smaller shares of Hispanic (33%), Asian (30%) and White (24%) workers say the same.
When it comes to diversity of sexual orientation, 28% of Black workers and 22% of Hispanic workers say it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that is diverse in this way; 15% each among White and Asian workers say the same.
Workers under age 50 are more likely than those 50 and older to say racial and ethnic diversity in their workplace is extremely or very important to them (35% vs. 26%). Workers younger than 50 are also more likely to say having about an equal mix of men and women is important to them, with workers ages 18 t0 29 the most likely to say this (34% vs. 26% of workers 30 to 49, and 20% each among those 50 to 64 and 65 and older).
There are also differences by educational attainment, with larger shares of workers with a postgraduate degree than those with less education saying it’s extremely or very important to them that their workplace is diverse across all measures asked about in the survey. For example, 44% of workers with a postgraduate degree say having a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities is extremely or very important to them, compared with 34% of those with a bachelor’s degree only and 27% of those with some college or less.
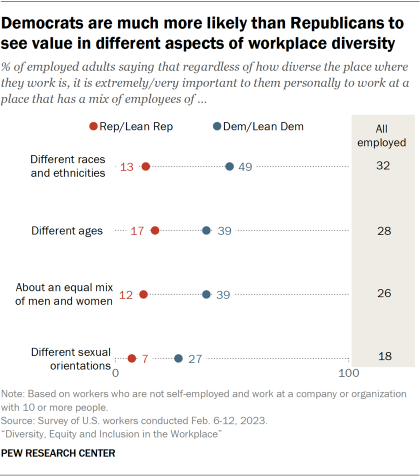
Democratic workers are much more likely than Republican workers to say working somewhere that is diverse when it comes to gender, race and ethnicity, age, and sexual orientation is extremely or very important to them. In fact, about half of Democrats (49%) place great importance on having a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities where they work, compared with 13% of Republicans. And there are differences of at least 20 points between the shares of Democrats and Republicans saying it’s extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that has about an equal mix of men and women (39% of Democrats say this vs. 12% of Republicans) and a mix of employees of different ages (39% vs. 17%) and sexual orientations (27% vs. 7%).
Overall, a majority of workers say their workplace has a mix of employees of different ages (58% say this describes their current workplace extremely or very well). Smaller shares say their workplace has about an equal mix of men and women (38%) and a mix of employees of different races and ethnicities (46%) and sexual orientations (28%). These assessments do not vary much across demographic groups.
Half of workers place great importance on working at a place that is accessible for people with physical disabilities
Half of workers say it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that is accessible for people with physical disabilities; 29% say it is somewhat important and 21% say it is not too or not at all important to them.
Highly valuing an accessible workplace varies by gender, race and ethnicity, and party, but there is no significant difference in responses between those who do and don’t report having a disability.
About six-in-ten women (58%) say it is extremely or very important to them that their workplace is accessible, compared with 41% of men.
Black workers are more likely than workers of other racial and ethnic groups to place great importance on their workplace being accessible: 62% of Black workers say this is extremely or very important, compared with 51% of Hispanic, 48% of White and 43% of Asian workers.
A majority of Democrats (59%) say it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that is accessible for people with physical disabilities; 40% of Republican say the same. Some 27% of Republicans say this is not too or not at all important to them, compared with 15% of Democrats.
There is no statistically significant difference in the shares of workers who have a disability and those who do not saying it is extremely or very important to them to work somewhere that is accessible for people with physical disabilities. But workers who do not have a disability are more likely than those who do to say this is not too or not at all important to them (21% vs. 15%).
Among those who don’t work fully remotely, about three-quarters of workers (76%) say their workplace is at least somewhat accessible for people with physical disabilities, with 51% saying it is extremely or very accessible. Some 17% say their workplace is not too or not at all accessible, and 8% are not sure.
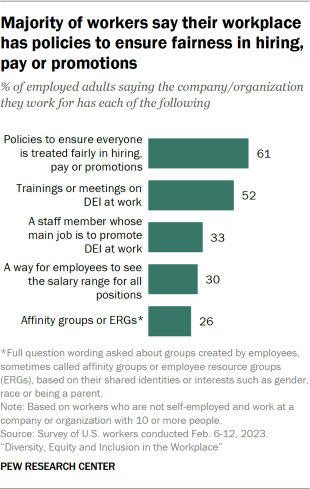
When asked whether the company or organization they work for has a series of measures that are typically associated with diversity, equity and inclusion efforts, a majority of workers say their employer has policies that ensure everyone is treated fairly in hiring, pay or promotions (61%), and 52% say there are trainings or meetings on DEI where they work.
Smaller shares say their workplace has a staff member whose main job is to promote DEI at work (33%), a way for employees to see the salary range for all positions (30%), and groups created by employees sometimes known as affinity groups or employee resource groups (ERGs) based on shared identities such as gender, race or being a parent (26%).
Responses do not vary much by most demographic characteristics. However, workers with at least a bachelor’s degree are consistently more likely than those with less education to say each of these five measures is available where they work.
Workers tend to see positive impact from policies and resources associated with DEI where they work
Among those whose workplace offers each policy or resource, a majority of workers say each measure has had a somewhat or very positive impact where they work. About a third or fewer workers say each resource has had neither a positive nor negative impact, and about one-in-ten or fewer say each of these has had a somewhat or very negative impact.
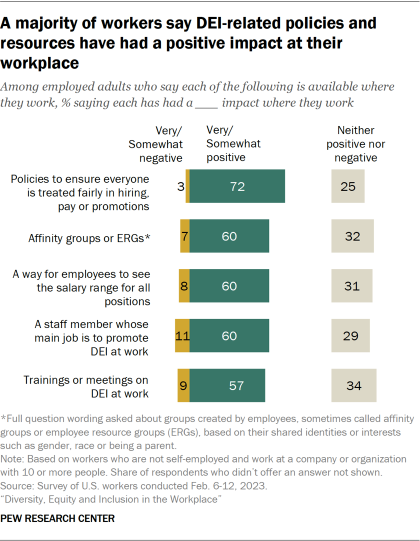
Democrats and Republicans are about equally likely to say their workplace has these measures in place, but Democrats are more likely than Republicans to say the impact of each has been positive by margins ranging from 10 to 32 points (among those who say their workplace has these measures). For example, 66% of Democrats who say their workplace has a way for employees to see the salary range for all positions say this has had a somewhat or very positive impact, compared with 56% of Republicans who say this. And while about three-quarters of Democrats (74%) say having a staff member whose main job is to promote DEI at work has had a positive impact, fewer than half of Republicans (42%) say the same.
Women are more likely than men to say each of these policies and resources has had a very or somewhat positive impact where they work. This is mainly driven by gender differences among Republicans: There are double-digit differences in the shares of Republican women and Republican men who say many of these resources have had a positive impact. For example, 58% of Republican women say having a staff member whose main job is to promote DEI at work has had at least a somewhat positive impact where they work, compared with 31% of Republican men who hold this view. The same share of Republican women (58%) say having affinity groups or ERGs has had a positive impact, compared with 38% of Republican men who say the same.
Among Democrats, majorities of both men and women offer positive assessments of these resources in their workplace, but Democratic women are more likely than Democratic men to say having trainings or meetings on DEI at work have had a positive impact (72% vs. 65%).
While there are differences by race, ethnicity and age on overall attitudes about DEI in the workplace, there are no consistent differences along these dimensions in how workers with access to these policies and resources at their workplace assess their impact.
About half of workers who have participated in DEI trainings in the last year say they’ve been helpful
Out of all workers, about four-in-ten (38%) have participated in a DEI training in the last year. A similar share (40%) did not participate or say their workplace does not offer these trainings, and 21% are not sure if their employer offers these trainings.
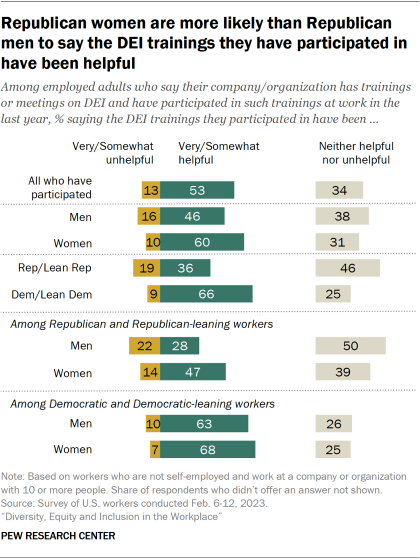
Looking only at those whose company or organization has trainings or meetings on DEI, about three-quarters (73%) say they have participated in such trainings in the past year. And assessments of these trainings tend to be positive, with 53% of workers who’ve participated saying they were very or somewhat helpful. About a third (34%) give a more neutral assessment, saying the trainings were neither helpful nor unhelpful, and 13% say they were very or somewhat unhelpful.
While men and women are about equally likely to have participated in trainings on DEI in the past year, women are more likely than men to say the trainings have been at least somewhat helpful (60% vs. 46%).
Republicans and Democrats are also equally likely to say they’ve participated in these trainings in the past year, but Democrats are far more likely than Republicans to say the trainings have been helpful (66% vs. 36%). About one-in-five Republicans say they’ve been unhelpful (19%), compared with 9% of Democrats.
While both Democratic men and women offer similar assessments of the DEI trainings they’ve participated in, there are gender differences among Republican workers. Republican women are more likely than Republican men to say the trainings they’ve participated in have been helpful (47% vs. 28%). Conversely, 22% of Republican men, compared with 14% of Republican women, say the trainings have been unhelpful.
Few workers are members of affinity groups or ERGs at work
While 26% of workers say there are affinity groups or employee resource groups (ERGs) where they work, members of these groups account for a very small share of workers overall. Just 6% of workers say they are members of an affinity group or ERG, with 58% of workers saying these groups are either not available at their workplace or that they aren’t a member. Another 37% say they are not sure if their workplace offers these groups.
Among workers who say there are affinity groups or ERGs at their workplace, 22% say they are personally a member. Women are more likely than men to be members of these groups (28% vs. 16%). And 28% of non-White workers say they are a member of an affinity group or ERG, compared with 18% of White workers. 2
When asked about the impact a person’s gender, race or ethnicity has on their ability to succeed at work, workers tend to say these characteristics neither make it easier nor harder to be successful at their workplace.
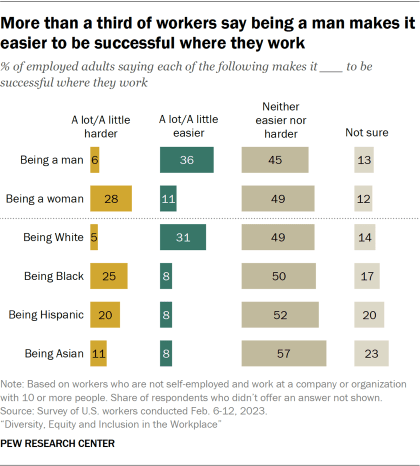
Still, when it comes to gender, workers are more likely to say being a man makes it easier to be successful where they work than to say it makes it harder (36% vs. 6%). In contrast, a larger share says being a woman makes it harder to be successful than say it makes it easier (28% vs. 11%).
Men and women have different views on the impact gender has on a person’s ability to succeed where they work. Some 44% of women say being a man makes it at least a little easier to be successful, including 24% who say it makes it a lot easier. This compares with 29% of men who say being a man makes it at least a little easier to be successful.
Similarly, 34% of women say being a woman makes it harder to be successful where they work, compared with 21% of men.
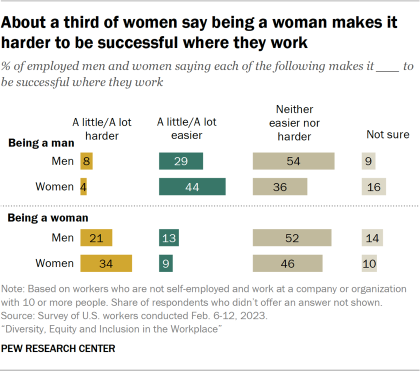
Women under age 50 are especially likely – more so than women ages 50 and older or men in either age group – to say being a man makes it easier to be successful where they work and that being a woman makes it harder. For example, 38% of women ages 18 to 49 say being a woman makes it harder to be successful where they work. This compares with 29% of women 50 and older, 25% of men younger than 50, and an even smaller share of men 50 and older (13%).
When it comes to views about how race or ethnicity affects people’s ability to succeed at work, 51% of Black workers say being Black makes it harder to be successful where they work. This is significantly higher than the shares of Asian (41%), Hispanic (23%) and White (18%) workers who say the same about the impact of being Black.
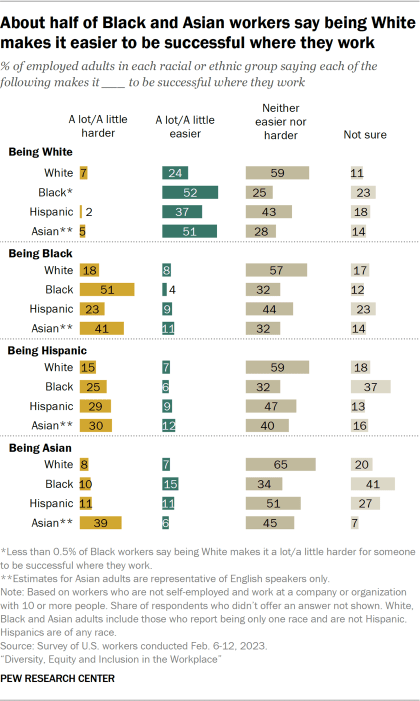
Similarly, about four-in-ten Asian workers (39%) say being Asian makes it harder to be successful in their workplace, a higher share than workers of other racial and ethnic groups who say the same about being Asian.
Hispanic, Black and Asian workers are about equally likely to say being Hispanic makes it harder to be successful where they work. A smaller share of White workers say the same about being Hispanic.
When asked about the impact of being White in their workplace, workers across racial and ethnic groups are more likely to say it makes it easier than to say it makes it harder to be successful. This is especially the case among Black and Asian workers. About half of Black (52%) and Asian (51%) workers say being White makes it easier to be successful where they work, compared with 37% of Hispanic and 24% of White workers who say the same about being White.
Previously released findings from this survey found that Black workers are more likely than White, Hispanic and Asian workers to report that they have experienced discrimination or have been treated unfairly by an employer in hiring, pay or promotions because of their race or ethnicity at some point in their careers (though not necessarily where they currently work). Women are also more likely than men to say they’ve experienced such discrimination because of their gender.
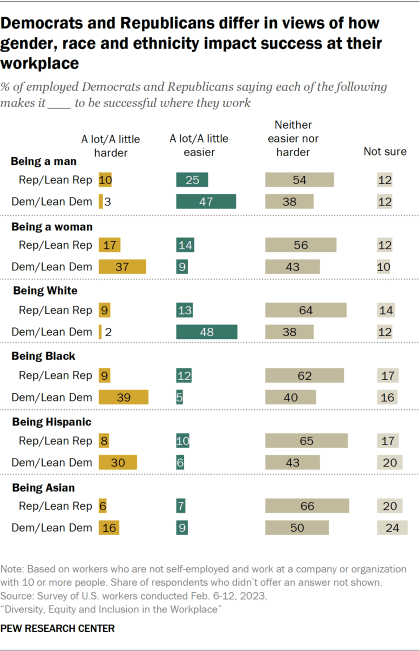
There are large partisan gaps in views of whether gender, race or ethnicity make it easier or harder to be successful at work. Some 47% of Democratic workers say being a man makes it at least somewhat easier to be successful at their workplace, compared with 25% of Republican workers. Democrats are also more likely than Republicans to say being a woman makes it harder to succeed (37% vs. 17%).
Democratic and Republican women are more likely than their male counterparts to say being a woman makes it harder – and being a man makes it easier – to be successful where they work. The differences between Republican women and Republican men are particularly striking. About a quarter of Republican women (26%) say being a woman makes it harder to be successful, compared with 10% of Republican men. And while 36% of Republican women say being a man makes it easier to be successful where they work, just 16% of Republican men say the same.
Democratic workers are more than three times as likely as Republican workers to say being White makes it easier to succeed where they work (48% vs. 13%), and they are also more likely than Republicans to say being Black, Hispanic or Asian makes it harder. About four-in-ten Democrats (39%) say being Black makes it harder for someone to succeed at their workplace, compared with just 9% of Republicans. Similarly, 30% of Democrats say being Hispanic makes it harder to succeed, compared with 8% of Republicans. And while smaller shares in both parties say being Asian makes it harder to succeed, Democrats are more likely than Republicans to say this (16% vs. 6%). These partisan differences remain when looking only at Democrats and Republicans who are White.
- For details, see the Methodology section of the report. The analysis in this report is based on U.S. workers who are employed full time or part time, who are not self-employed, and who have only one job or have multiple jobs but consider one their primary job (99% of workers who are not self-employed have one job or a primary job). Additionally, the analysis is restricted to workers at companies or organizations with at least 10 employees as certain federal requirements such as non-discrimination mandates apply to larger workplaces. ↩
- Non-White adults include Black, Hispanic, Asian and other races besides White, as well as people who identify as more than one race. The sample sizes among Black, Hispanic and Asian workers who have affinity groups or ERGs at work are too small to analyze separately. ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Asian Americans
- Black Americans
- Business & Workplace
- Discrimination & Prejudice
- Economics, Work & Gender
- Economy & Work
- Gender & Work
- Happiness & Life Satisfaction
- Hispanics/Latinos
- Partisanship & Issues
- Race & Ethnicity
- Racial Bias & Discrimination
- Sexual Misconduct & Harassment
A look at small businesses in the U.S.
Majorities of adults see decline of union membership as bad for the u.s. and working people, a look at black-owned businesses in the u.s., from businesses and banks to colleges and churches: americans’ views of u.s. institutions, 2023 saw some of the biggest, hardest-fought labor disputes in recent decades, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
Diversity matters even more: The case for holistic impact

Diversity Matters Even More
Diversity Matters Even More is the fourth report in a McKinsey series investigating the business case for diversity, following Why Diversity Matters (2015), Delivering Through Diversity (2018), and Diversity Wins (2020). For almost a decade through our Diversity Matters series of reports, McKinsey has delivered a comprehensive global perspective on the relationship between leadership diversity and company performance. This year, the business case is the strongest it has been since we’ve been tracking and, for the first time in some areas, equitable representation is in sight. Further, a striking new finding is that leadership diversity is also convincingly associated with holistic growth ambitions, greater social impact, and more satisfied workforces.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Dame Vivian Hunt, representing views from UnitedHealth Group, and Sundiatu Dixon-Fyle , Celia Huber , María del Mar Martínez Márquez , Sara Prince , and Ashley Thomas , representing views from McKinsey.
At a time when companies are under extraordinary pressure to maintain financial performance while navigating a rapidly changing business landscape, creating an internal culture of transparency and inclusion, and transforming operations to meet social-impact expectations, the good news is that these goals are not mutually exclusive. On the contrary, our research suggests a strong, positive relationship between them. And in an increasingly complex and uncertain competitive landscape, diversity matters even more .
For this report, the fourth edition of Diversity Matters , we drew on our largest dataset yet—spanning 1,265 companies, 23 countries, and six global regions, and multiple company interviews. We also extended our research and interview focus beyond the relationship between diversity and financial performance, for the first time exploring the holistic impact of diversity on communities, workforces, and the environment.
The most compelling business case yet
There have been far-reaching changes in the business environment over the past few years, yet, companies with diverse leadership teams continue to be associated with higher financial returns. Our expanded dataset shows this is true across industries and regions, despite differing challenges, stakeholder expectations, and ambitions.
The business case for gender diversity on executive teams 1 The business case is the percent difference in likelihood of outperformance between companies in the top and bottom quartile for a characteristic. Outperformance is calculated as the likelihood to place above the median profitability of other companies in the same industry and region. For more information on our calculation of the likelihood of outperformance analysis, see “Methodology for financial performance.” has more than doubled over the past decade. Each of our reports—2015, 2018, 2020, and now 2023—has found a steady upward trend, tracking ever greater representation of women on executive teams. At each time point we have assessed the data, the likelihood of financial outperformance gap has grown: Our 2015 report found top-quartile companies had a 15 percent greater likelihood of financial outperformance versus their bottom-quartile peers; this year, that figure hits 39 percent (Exhibit 1).
A strong business case for ethnic diversity is also consistent over time, with a 39 percent increased likelihood of outperformance for those in the top quartile of ethnic representation versus the bottom quartile. This has persisted even with eight new economies added in our analysis of 2022 financial data. 2 Our 2023 report draws on data that was collected in both 2021 and 2022. For this analysis, we used data collected in 2022.
The penalties 3 Rewards and penalties refer to the likelihood of outperformance, or underperformance, on profitability compared to companies in the other three quartiles. for low diversity on executive teams are also intensifying. Companies with representation of women exceeding 30 percent (and thus in the top quartile) are significantly more likely to financially outperform those with 30 percent or fewer. Similarly, companies in our top quartile for ethnic diversity show an average 27 percent financial advantage over others (Exhibit 2).
Both forms of diversity in executive teams appear to show an increased likelihood of above-average profitability. Companies in the top quartile for both gender and ethnic diversity in executive teams are on average 9 percent more likely to outperform their peers. (This gap has closed slightly since our previous report.) Meanwhile, those in the bottom quartile for both are 66 percent less likely to outperform financially on average, up from 27 percent in 2020, indicating that lack of diversity may be getting more expensive.
Our latest analysis shows that companies with greater diversity on their boards of directors are more likely to outperform financially. For the first time, this correlation is statistically significant for both gender and ethnicity. Companies in the top quartile for board-gender diversity are 27 percent more likely to outperform financially than those in the bottom quartile. Similarly, companies in the top quartile for ethnically diverse boards are 13 percent more likely to outperform than those in the bottom quartile. These findings support the hypothesis that diversity benefits extend across top corporate leadership to boards, where DEI policy decisions for the whole organization are often made. We also examined diversity in emerging and advanced economies, finding that while advanced economies see a much higher likelihood of outperformance for executive gender diversity, emerging economies have shown meaningful progress in recent years and may have the most to gain from increasing diversity.
Equitable representation at the top is within reach
Since McKinsey first started tracking data on representation in 2015, women have made substantial gains in the workplace and in leadership. The current global dataset shows that one-fifth of executive team members are women, a third higher than reported in 2020. Eight in ten surveyed companies now have at least one woman on their executive team (up from fewer than two-thirds), while seven in ten have more than 10 percent. Since 2020’s Diversity Wins (and with an expanded dataset), we have now seen the highest increase in diversity in a decade and more representation at the highest levels than ever before (Exhibit 3).
Because each region has a unique ethnic makeup and cultural norms, we have assessed rates of ethnic representation by evaluating equitable representation levels—how closely leadership mirrors regional demographics. 4 Equitable representation refers to the level at which a leadership team's diverse representation matches the level of representation of historically underrepresented ethnicities within a given region’s population. US companies are currently the closest to representing the population at 20 percent ethnic representation, but still lag behind the population share of 41 percent.
We have continued to look at boards, given the association of diverse boards with better financial performance and inclusive growth 5 Companies in the top quartile of board-gender diversity are 27 percent more likely than those in the bottom quartile to outperform financially, and companies in the top quartile for ethnically diverse boards are 13 percent more likely to outperform than those in the bottom quartile. We tested a variety of inclusive growth metrics, including social and environmental impact. For every woman added to a company board with ten directors, there was on average a two-point increase in holistic impact scores. Additional detail located in “Diversity supports inclusive growth” section. ; even more than executive teams, they can also be a strong positive influence on the societal disposition of a company. This year we once again found that financial impact is linked to increased representation of women on boards. For the first time, we also see a significant association with ethnic representation.
Over the past eight years, we have tracked over 330 companies’ progress on representation and diversity in leadership, and segmented these companies into five cohorts based on both 2015 levels of executive-team diversity and progress since then: Diversity Leaders, Fast Movers, Moderate Movers, Resting on Laurels, and Laggards (Exhibit 4).
It has been particularly inspiring to find that Diversity Leaders have attained gender parity and equitable ethnic representation, showing that equitable representation at the top is not just a lofty dream but a realistic goal. Further, our Fast Movers demonstrate that change can happen at speed and scale, with gender representation reaching 32 percent—the first time we’ve seen such a promising outcome in this cohort. These companies have raised the bar to keep pace with the changing landscape of diversity representation in leadership. Their strong performance prompted us to raise the improvement thresholds for companies from our 2020 Diversity Wins report to reflect the gains seen in top-performing quartiles (five percentage points for gender and ten percentage points for ethnicity).
Companies in our top cohorts have shown rapid, groundbreaking growth in representation, with some even attaining gender parity. In fact, diversity-leading companies in the United Kingdom have reached an ethnic-representation average, at 28 percent, that exceeds the region’s general population. Diversity-leading US companies have reached 50 percent representation of women on executive teams. In addition, leading companies in the United States now have on average 39 percent of executives from historically underrepresented ethnicities.
Considering the dataset as a whole, however, there is still a substantial gap in ethnic representation at top levels. For companies included in both our 2020 and 2023 reports, only 16 percent of leaders on executive teams belong to historically underrepresented ethnicities. 6 Historically underrepresented group refers to populations who have historically not been represented within leadership teams at the same rate that they exist within the general population. These gains have slowed since 2019. At the time of Diversity Wins , 61 percent of companies had at least one person in leadership from a historically underrepresented group; this figure has grown only slightly (68 percent).
While there is some good news on progress in the area of equitable representation, across most geographies, significantly more work is needed. Diversity Leaders are beacons for other companies, demonstrating that scaling and institutionalizing policies that promote multiple forms of diversity can move the needle on representation.
Diversity supports inclusive growth
While year over year financial performance remains critical, businesses are increasingly aspiring to have positive, long-term impact on all stakeholders—the core tenet of stakeholder capitalism. This emphasizes the interests and needs of a wider set of stakeholders, including employees, customers, and investors, prioritizes social and environmental goals, and drives towards sustainable, inclusive growth—in short, what we refer to as holistic impact.
In many parts of the world there is a growing call for organizations to consider their holistic impact, not only within their own business environment, but on a wider scale, both locally and globally. Our research points to five main areas of holistic impact : financial and operational, capabilities, health and workforce, and environmental and social. In this report, we broaden the lens of our research, placing particular focus on environmental and social-impact elements.
Our findings are striking. Across all industries surveyed, more diversity in boards and executive teams is correlated to higher social and environmental impact scores.
We recognize that creating social impact, alongside other business priorities, is a challenging task, even for companies who have strong intentions to do so. Yet, over half of sampled companies in our dataset perform well in community involvement. 7 Defined as scoring above 75 on the community measure. We find that diverse leadership teams could help to bolster community involvement, positively impacting ethical disposition, community orientation, and the general image of a company.
We examined how leadership diversity could be linked to three components of holistic impact—community, workforce, and environment—which all have particularly close connections with employee and community well-being. The results were pronounced: across all three components, we found positive correlations with gender and ethnic leadership diversity (Exhibit 5).
We also found a link between greater diversity in leadership roles and diversity across the organization. 8 Organization-wide and management diversity is a workforce submetric score within the social pillar. These data points were then compared against our dataset for executive teams. For a 10 percent rise in women’s executive representation in our 2019 dataset, we see on average a 2.1 increase in the percentage of both women employees and women managers in 2021. A similar, if somewhat smaller, effect holds with ethnic representation. 9 We recognize that there is, naturally, a degree of overlap in these scores. When there is a path for women and ethnic minorities to step into the highest roles, it suggests that there are inclusive practices at play, making it possible for all to succeed.
Overall, there is a strong correlation between diversity in influential company leadership roles and multiple indicators of holistic impact across workforce, community, and environmental components. These relationships hold across sectors.
Five levers for change
The last decade has been a period of notable progress on equitable representation in leadership. Yet representation alone is an insufficient and unsustainable outcome. Since Why Diversity Matters in 2015, our thinking has evolved with continued engagement in this field. From our initial focus on diverse representation in leadership, we added a perspective on the practical steps companies can take to increase leadership diversity. From there, we broadened our focus to highlight the importance of inclusion and equity.
Now, we are beginning to distill the essence of holistic impact, and the role that leaders play in cultivating visionary workplaces. By building inclusive and supportive workplace cultures where diverse leaders and allies are truly heard, companies can chart a path towards impact beyond financial performance.
Leveraging our company interviews as a valuable source of refreshed insight, our data shows that the more diverse the leadership team, the more likely they are to have made public, mature commitments to diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) in their decision-making strategies. Transforming this commitment into bold action is the natural next step. To facilitate this transformation, we conducted interviews with diversity leaders who shared invaluable insights. These interviews surfaced five strategies to effectively turn words into action:
- Commit to a systematic, purpose-led approach to benefit all stakeholders. Companies should frame and pursue their DEI aspirations—internally and publicly—as core to their mission and embedded into their strategic goals. Having diverse perspectives and backgrounds may be uniquely helpful, as suggested by the relationship between ethnic and gender diversity and companies’ inclusive-growth performance.
- Embed your strategy in company-wide business initiatives while tailoring to local context. While DEI strategy is typically shaped at the top, giving local teams license to tailor to local contexts is key to building ownership and local impact. Agilely launching test and learn cycles for DEI initiatives in specific localities before rolling them out corporate-wide can also support larger DEI goals. In crafting a “global-local” approach to establishing their DEI strategy and values, leaders should build open lines of communication to develop a deep understanding of their workforce, community, and customers. This ensures DEI moves from abstract ideals to concrete actions. 10 Ella Washington, “The five stages of DEI maturity,” Harvard Business Review , November 1, 2022.
- Prioritize belonging and inclusive practices to unlock performance. Diverse representation will have the most impact within a culture that fosters inclusion and belonging—which also facilitates retaining diverse talent, innovation, and customer centricity. This support should include making inclusive leadership the norm through management training and accountability, as well as providing high-impact support to affinity and Employee Resources Groups (ERGs) to boost employee satisfaction.
- Embolden and activate champions and allies by providing adequate resources and support. DEI efforts of individual leaders, particularly women, are often less high-profile or officially rewarded, including their contributions to inclusive leadership, allyship, and employee well-being. Companies that recognize these efforts and provide a supportive environment can help these leaders thrive. This support could include mentorship and sponsorship, as well as encouraging and celebrating allyship. Leaders could be measured on their contributions to DEI and employee wellness in their performance evaluations.
- Act on feedback, including dissenting voices. A culture of feedback on DEI strategy from the workforce and wider stakeholders can provide valuable insights, identifying both strengths and opportunities for change. Leaders can use routine company pulse surveys to collect feedback internally, and social listening externally. It is important for dissenting voices to also be heard to pinpoint root causes of any roadblocks and contribute towards optimizing impact of the DEI strategy.
Despite a challenging business environment, the business case for diverse leadership teams is clear and growing stronger. In this report, our findings also show a statistically significant link between diverse boards and executive teams and higher holistic-impact scores, including on environmental and social measures.
To achieve lasting impact along these dimensions, companies must move boldly beyond increasing diverse representation to integrating DEI in a purpose-driven approach, broadening the company’s positive impact across stakeholders, employees, the external community, and the environment.
Sundiatu Dixon-Fyle is a senior fellow in McKinsey’s London office; Celia Huber is a senior partner in the Bay Area office; María del Mar Martínez Márquez is a senior partner in the Madrid office; and Sara Prince is a senior partner in the Atlanta office, where Ashley Thomas is a client delivery director. Dame Vivian Hunt is the chief innovation officer at UnitedHealth Group and a McKinsey alumna.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Diversity wins: How inclusion matters

Delivering through diversity

Why diversity matters

Workplace Dispute Case Study

It came to the attention of the CEO of a small company that there was a difficulty between two employees who had been working together for some time but recently appeared to have major differences that were affecting their entire department.
The CEO was being approached by both employees at different times and also by their line manager and was spending increasing amounts of time speaking to them, taking notes of their comments, meeting with their line manager and generally finding it difficult to get on with her own job, so time consuming were the conversations. The line manager attempted to deal with the issue in informal conversations but ultimately one of the parties made a complaint of harassment against the other. The matter was dealt with internally and ended in a disciplinary warning which simply led to matters disintegrating. The rest of the employees inevitably fell into two camps and relations between staff reached an all time low when one party refused to pass important client information to the other and a complaint ensued from the client. Eventually one of the parties left the company and shortly after commenced Tribunal proceedings for constructive dismissal. Almost a year after the proceedings began, the CEO suggested to their lawyers that a mediation might help – the company had spent thousands of pounds in legal costs up to that point and the CEO was becoming extremely anxious about her annual budget as the year end approached. The two sides agreed to a mediation and in a day the matter was resolved. Although it was too late to resolve the issue between the parties, at least they were able to save further legal costs. Had the mediation taken place at the earliest possible stage – ie. before the dispute spiralled to the point of one party leaving – far larger sums might have been saved and the impact on those involved, as well as the company, might have been considerably less.
« Back to Case Studies
Customer Hub
Local Service Partners
Your member benefits website features include:.
- Access to online articles with helpful information
- Ability to submit an online form asking a counselor to contact you
- Topics covering working life, wellness, parenting, management, etc.
Your Customer Hub features include:
- Automated headcount updates in UCMS
- Invoicing reflective of the active populations under your account
- Access reporting with case trends, disruptive issues, utilisation
Local Service Partners are independent EAPs with which WPO has established strategic relationships for the delivery of global EAP services in alignment with the WPO models, processes and quality standards.
Case Studies
- All Categories Arts and Entertainment Industry cCBT Clinical Support and Intervention Counseling COVID-19 Crisis Support Diversity and Inclusion Emotional Wellbeing Employee Insights Employee Wellbeing Financial Support Health at Work Higher Education Supporting Students Life Events Mental Health Mindfulness Organizations supporting employees Providers, resellers and insurers Safety at Work Stress Student Wellbeing Technology Ukraine Wellbeing Program Wellness Wellness Coaching Workplace Optimization
- All Solutions AIR Answer 24 API Technology Aware Mindfulness Be Well at Work Consulting practice Continuing Education Counseling Customer Hub Portal Elevate Global Learning Solutions Global Wellbeing Questionnaire Health Screenings Helpline iConnectYou In My Hands Life Coaching Life Services Live Well Wellness Global Coach Training LiveCONNECT Manager Assist Member Website MicroVideos My Family Care Network App New Parent Return to Work Pathways Presence Rapid Response Critical Incident Rapid Response Hotline Rehabilitation Remedy Revive Single Session Therapy (SST) Student Assist Subsidy Assist TDM LeaderView TDM Library Tobacco Cessation Coaching Unified Case Management System (UCMS) Wellbeing Program Wellness Coaching Whole Care Advantage Workplace Stress Check
- All Countries Belgium Bermuda Canada China France Germany India Indonesia Ireland Italy Japan Mexico Poland Portugal Singapore Spain Sri Lanka UAE UK Uruguay USA
Managing Trauma Triggers After Experiencing Assault
- Emotional Support

A support worker who works at a residential care facility..
Coping with a diagnosis
- Individual Effectiveness

A student called the Student Assistance Program for in-the-moment support…
- Practical Support

A participant reached out looking for resources for himself. He..
Wellbeing Ambassador Program
- Organizational Effectiveness

The Wellbeing Ambassador Program is part of an organization’s strategic..
A Comprehensive Needs Assessment

SITUATION A multinational corporation that was preparing to implement a..
Expanding a Parental Leave Program to Eight Global Locations

SITUATION A large multinational company engaged the consulting team to..
Assessing Employee Wellbeing in a Remote and Rigorous Work Environment

Workplace Options (WPO) was engaged to assist a construction company..
Supporting a global restructuring

Workplace Options (WPO) received a request from a multinational company..
In My Hands

A 42-year-old married woman living with her spouse and four..
Expatriate Services
- Employee Wellbeing

It takes a lot of effort and paperwork to relocate..
Tobacco Cessation Coaching
- Addiction Management

Without adequate support and resources, tobacco cessation can be a..
- Mental Health

Health care workers around the world have been on the..
Engage and Educate
We generate insights for HR and Wellbeing leaders on best practices.
© 2024 Workplace Options. All Rights Reserved
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- “Ad”mission of guilt
- “Do I stop him?”
- Newspaper joins war against drugs
- Have I got a deal for you!
- Identifying what’s right
- Is “Enough!” too much?
- Issues of bench and bar
- Knowing when to say “when!”
- Stop! This is a warning…
- Strange bedfellows
- Gambling with being first
- Making the right ethical choice can mean winning by losing
- Playing into a hoaxster’s hands
- “They said it first”
- Is it news, ad or informercial?
- Letter to the editor
- Games publishers play
- An offer you can refuse
- An oily gift horse
- Public service . . . or “news-mercials”
- As life passes by
- Bringing death close
- A careless step, a rash of calls
- Distortion of reality?
- Of life and death
- Naked came the rider
- “A photo that had to be used”
- A picture of controversy
- Freedom of political expression
- Brother, can you spare some time?
- Columnist’s crusade OK with Seattle
- Kiss and tell
- The making of a govenor
- Past but not over
- Of publishers and politics
- To tell the truth
- Truth & Consequences
- “Truth boxes”
- When journalists become flacks
- A book for all journalists who believe
- The Billboard Bandit
- Food for thought
- Grand jury probe
- Judgement on journalists
- Lessons from an ancient spirit
- Lying for the story . . .
- Newspaper nabs Atlanta’s Dahmer
- One way to a good end
- Over the fence
- “Psst! Pass it on!”
- Rules aren’t neat on Crack Street
- “Someone had to be her advocate”
- Trial by Fire
- Trial by proximity
- Using deceit to get the truth
- When advocacy is okay
- Witness to an execution
- Are we our brother’s keeper? . . . You bet we are!
- Betraying a trust
- Broken promise
- “But I thought you were . . . ”
- “Can I take it back?”
- Competitive disadvantage
- Getting it on tape
- The great quote question
- How to handle suicide threats
- Let’s make a deal!
- A phone-y issue?
- The source wanted out
- The story that died in a lie
- Thou shalt not break thy promise
- Thou shalt not concoct thy quote
- Thou shalt not trick thy source
- Too good to be true
- Vulnerable sources and journalistic responsibility
- The way things used to be . . .
- When a story just isn’t worth it
- When a story source threatens suicide
- When public should remain private
- The ethics of “outing”
- “For personal reasons”
- Intruding on grief
- Intruding on private pain
- Privacy case settled against TV station
- Seeing both sides
- Two views on “outing”
- Unwanted spotlight
- Whose right is it anyway?
- Other views on the Christine Busalacchi case
- The death of a soldier
- Firing at Round Rock
- A kinder, gentler news media
- Operation: Buy yourself a parade
- Rallying ’round the flag
- “Salute to military” ads canceled
- Tell the truth, stay alive
- The windbags of war
- Absent with no malice
- Anonymity for rape victims . . .
- An exception to the rule
- The boy with a broken heart
- Civilly suitable
- Creating a victim
- “Everyone already knew”
- An exceptional case
- Innocent victims
- Minor infraction
- Names make news
- Naming a victim
- Naming “johns”
- Profile of controversy
- What the media all missed
- Punishing plagiarizers
- Sounding an alarm on AIDS
- Suffer the children
- Anchor’s away
- The day the earth stood still
- Doing your own ethics audit
- Good guys, bad guys and TV news
- Is it just me, or . . . ?
- The Post’s exam answer story
- TV station “teases” suicide
- Yanking Doonesbury
- The year in review
- Colorado media’s option play
- Deadly lesson
- Deciding which critically ill person gets coverage
- When journalists play God . . .
- A delicate balance
- The Fallen Servant
- Handle with care
- It’s the principle, really
- Killing news
- Maybe what seems so right is wrong
- On the line
- Protest and apology after Daily Beacon story
- Red flag for badgering
- Sharing the community’s grief
- The “super-crip” stereotype
- “And then he said *&%*!!!”
- When big is not better
- When the KKK comes calling
- Not the straight story
- Agreeing to disagree
- All in the family
- Family feud
- Author! Author!
- The Bee that roared
- Brewing controversy
- Building barriers
- Other views from librarians
- The ethics of information selling
- Close to home
- Family ties
- How now, sacred cow?
- The ties that bind
- “Like any other story”
- When your newspaper is the news
- Not friendly fire
- Overdraft on credibility?
The problem is the writing
- Written rules can be hazardous
- Project censored, sins of omission and the hardest “W” of all – “why”
- Risking the newsroom’s image
- The Media School
Ethics Case Studies
- Browse Ethics Case Studies
Workplace issues
Agreeing to disagree: How one newspaper handles off-hour activities
All in the family: When a journalist’s spouse creates a conflict of interests
Family feud: Handling conflicts between journalists and partners
Author! Author!: Ethical dilemmas when reporters turn author
The Bee that roared: Taking a stand for editorial independence
Brewing controversy: The commercialization of Linda Ellerbee
Building barriers: The case against financial involvement
Other views from librarians: When interests of client and newsroom conflict
The ethics of information selling: Problems for library reference services
Close to home: When your newsroom is part of the story
Family Ties: When are relationships relationships relevant?
How now, sacred cow?: United Way’s favored treatment by the media
The ties that bind: Publisher’s link to United Way raises questions
“Like any other story”: Can it be when it’s your union vs. your paper?
When your newspaper is the news: Editors discuss their experiences
Not friendly fire: News director at odds with CBS over story
Overdraft on credibility?: Reporter faces conflict-of-interest charges
Written rules can be hazardous: A lawyer views ethics codes
Project censored, sins of omission and the hardest “W” of all – “why”
Risking the newsroom’s image: How editors, in a good cause, can strain independence
Ethics Case Studies resources and social media channels
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Lessons from Beyoncé on Navigating Exclusion
- Ella F. Washington,
- Hildana Haileyesus,
- Laura Morgan Roberts

The star’s path from CMA Awards backlash to Cowboy Carter is a case study in strategic response.
In 2016, Beyoncé’s performance at the CMA Awards sparked backlash from fans complaining about everything from her attire to her lack of connection to the genre. This year, she released her first country album, which debuted at number one on the Billboard 200. Her actions over the past eight years have been a case study in how to navigate workplace exclusion. As a first step, it often makes sense to exit the conversation and wait for a better moment to respond. Then, work behind the scenes, ideally with collaborators, to push for change. Finally, consider focusing on your own authenticity and strengths to create your own lane within your organization or outside it.
Beyoncé, the globally revered singer, songwriter, and entrepreneur, last month released her new album Cowboy Carter. However, this project is much more than another musical release from a leading star. It offers a case study in how to navigate workplace exclusion.
- Ella F. Washington is an organizational psychologist; the founder and CEO of Ellavate Solutions, a DEI strategy firm; and a professor of practice at Georgetown University’s McDonough School of Business. She is the author of The Necessary Journey: Making Real Progress on Equity and Inclusion (HBR Press, November 2022) and Unspoken: A Guide to Cracking the Hidden Corporate Code (Forbes Books, May 2024).
- Hildana Haileyesus is a DEI consultant at Ellavate Solutions with a background in training and facilitation, client strategy, and research. She has worked across higher education and business and applies a sociological lens to equity-driven change efforts.
- Laura Morgan Roberts is a Frank M. Sands Sr. Associate Professor of Business Administration at the University of Virginia’s Darden School of Business. She is an organizational psychologist and the coeditor of Race, Work and Leadership: New Perspectives on the Black Experience (Harvard Business Review Press, 2019).
Partner Center
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Education, training and skills
- Further and higher education, skills and vocational training
- Sector-based Work Academy Programme: qualitative case study research
- Department for Work & Pensions
Summary: Sector-based Work Academy Programme: qualitative case study research
Published 3 May 2024

© Crown copyright 2024
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: [email protected] .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/sector-based-work-academy-programme-qualitative-case-study-research/summary-sector-based-work-academy-programme-qualitative-case-study-research
This summary outlines key findings from in-house qualitative case study research on the Sector-based Work Academy Programme ( SWAP ). The research took place in four Jobcentre Plus ( JCP ) district areas across England in June to November 2022 and involved a total of 93 in-depth interviews/focus groups with 118 participants. The research was conducted to generate insight into how the programme is delivered, and the value of the support it provides for employers and claimants. In each area, fieldwork was conducted with Department for Work and Pensions ( DWP ) staff involved in delivering the programme locally, alongside claimants, employers and training providers who had participated in a SWAP in recent months.
Key findings
Overview of district-level programme delivery.
Districts varied in the way that staffing was set-up to support the delivery of SWAPs , and this was mostly driven by their operational priorities. This ranged from a centralised model with a central, co-located team to launch and manage SWAPs for the whole district, to a clustered approach in another area, which saw staff working on SWAPs embedded within operational sites and account managing SWAPs for their sites. The staffing models had implications for SWAP delivery and quality, although the research didn’t identify any trends in outcomes based on these models. A reliance on Adult Education Budget funding also influenced what types of SWAPs were delivered. DWP staff reported a bias within the funding towards generalist skills training which wasn’t always thought to equip claimants with the career-enabling skills required for more specialist roles.
Local SWAPs
The SWAPs delivered across all areas were highly diverse in content and format, reflecting the flexibility of the SWAP model. While SWAPs were thought to align well with local labour market needs, DWP staff identified some gaps in provision in terms of specific sectors claimants were interested in (for example, a lack of administration SWAPs outside of the Civil Service in Areas 2 and 3). Other gaps mentioned included a lack of SWAPs with shorter or more flexible hours for claimants with caring commitments, and district-specific gaps such as few SWAPs in areas outside the main urban centre in Area 1.
Partnership working
The most effective model of partnership working entailed all three parties ( DWP , training providers and employers) being actively engaged in the set-up and management of SWAPs . This included all parties being aligned with expectations of the SWAP , employers specifying their training requirements, employers contributing to pre- SWAP information sessions, and regular cross-party communication throughout the duration of the programme. If a training provider initiated a SWAP , however, this could minimise the level of engagement DWP had with end employers and reduce the flow of information to DWP concerning outcomes.
Referrals were a crucial stage influencing the effectiveness of the SWAPs delivered. Claimants tended to describe receiving minimal information about the programme which mainly concerned course logistics, although most still felt they had a choice in taking part. Overall, most employers reflected that the calibre of candidates was mixed. The poor suitability of some claimants, alongside lower than anticipated referral numbers, was seen as one of the main reasons why SWAPs didn’t meet all these employers’ vacancy needs. Both DWP -related factors such as Work Coach time and knowledge of SWAP , and external factors such as claimant interest and personal circumstances, were thought to determine the volume and quality of referrals received.
Claimant experiences of programme delivery
Overall claimants were positive about their participation in a SWAP , with components such as the pre-employment training considered more useful when it was specific to the end role on offer or wider sector. The work experience placement and guaranteed job interview ( GJI ) components of SWAP were not consistently offered to the claimants interviewed, and when the GJI wasn’t delivered this could be particularly disappointing. Claimants mostly valued the support received from Work Coaches during the SWAP , although there were some gaps reported, notably in the period immediately following SWAP completion.
Employer experiences of programme delivery
Employers shared diverse experiences of SWAP . While some employers valued the bespoke nature of the training provided, and felt candidates were well prepared and confident at interview, for a minority, they weren’t sure what training had been delivered and/or considered it less necessary for their sector. Some employers linked poor suitability among some of the claimants referred to negative claimant attitudes towards the role or work in general. A small number of employers felt that more robust screening of claimants was needed as part of the referral process to avoid these issues reoccurring.
Outcomes from SWAP
Claimants reported a range of outcomes from their participation in a SWAP , and most of these improved their overall employability (for example, qualifications gained or improved confidence). There was less evidence from this research that SWAPs moved claimants directly into employment, despite this being a key intended outcome for the programme. For employers, SWAPs could help with job-matching and filling vacancies, however, there was doubt about the magnitude of the effectiveness of the SWAP for employers in terms of the number of vacancies filled. Overall, participants found it difficult to attribute positive outcomes to specific types of SWAPs . In general, effective SWAPs were linked to face-to-face training, the delivery of a qualification and the presence of a GJI as part of the offer.
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.

The Coca-Cola Company and Microsoft announce five-year strategic partnership to accelerate cloud and generative AI initiatives
- Share on Facebook (opens new window)
- Share on LinkedIn (opens new window)
- Share on Twitter (opens new window)

Editor’s note – April 23, 2024 – The quotation from Judson Althoff was updated following initial publication.
ATLANTA and REDMOND, Wash . — April 23, 2024 — Microsoft Corp. and The Coca-Cola Company on Tuesday announced a five-year strategic partnership to align Coca-Cola’s core technology strategy systemwide; enable the adoption of leading-edge technology; and foster innovation and productivity globally.
As part of the partnership, Coca-Cola has made a $1.1 billion commitment to the Microsoft Cloud and its generative AI capabilities. The collaboration underscores Coca-Cola’s ongoing technology transformation, underpinned by the Microsoft Cloud as Coca-Cola’s globally preferred and strategic cloud and AI platform.
Through the partnership, the companies will jointly experiment with groundbreaking new technology like Azure OpenAI Service to develop innovative generative AI use cases across various business functions. This includes testing how Copilot for Microsoft 365 could help improve workplace productivity.
“Through our long-term partnership, we have made significant progress to accelerate system-wide AI Transformation across The Coca-Cola Company and its network of independent bottlers worldwide,” said Judson Althoff, executive vice president and chief commercial officer at Microsoft. “We are proud to support Coca-Cola as it continues to embrace the era of AI and looks to solutions like Azure OpenAI Service and Copilot for Microsoft 365 to drive innovation across every area of its business.”
Coca-Cola has migrated all its applications to Microsoft Azure, with most major independent bottling partners following suit. As a pioneer in AI adoption, Coca-Cola has been innovating with generative AI for nearly a year and has already leveraged Azure OpenAI Service to reimagine everything from marketing to manufacturing and supply chain and beyond. The company is currently exploring the use of generative AI-powered digital assistants on Azure OpenAI Service to help employees improve customer experiences, streamline operations, foster innovation, gain a competitive advantage, boost efficiency and uncover new growth opportunities.
“This new agreement builds on the success of Coca-Cola’s partnership strategy with Microsoft, showing our commitment to ongoing digital transformation,” said John Murphy, president and chief financial officer of The Coca-Cola Company. “Our partnership with Microsoft has grown exponentially, from the $250 million agreement we initially announced in 2020 to $1.1 billion today.”
The agreement reflects a significant step in advancing Coca-Cola’s digital transformation, focused on providing expanded access to Microsoft’s cloud and AI platforms — as well as solutions such as Microsoft 365, Power BI, Dynamics 365, Defender and Fabric — to enhance efficiency and scalability while fostering innovation across the system.
“Our expanded partnership with Microsoft is an important next chapter in Coca-Cola’s journey toward a digital-first enterprise powered by emerging technologies,” said Neeraj Tolmare, senior vice president and global chief information officer for The Coca-Cola Company. “Microsoft’s capabilities help accelerate our adoption of AI to create incremental enterprise value.”
About The Coca-Cola Company
The Coca-Cola Company (NYSE: KO) is a total beverage company with products sold in more than 200 countries and territories. Our company’s purpose is to refresh the world and make a difference. We sell multiple billion-dollar brands across several beverage categories worldwide. Our portfolio of sparkling soft drink brands includes Coca-Cola, Sprite and Fanta. Our water, sports, coffee and tea brands include Dasani, Smartwater, Vitaminwater, Topo Chico, BODYARMOR, Powerade, Costa, Georgia, Gold Peak and Ayataka. Our juice, value-added dairy and plant-based beverage brands include Minute Maid, Simply, innocent, Del Valle, fairlife and AdeS. We’re constantly transforming our portfolio, from reducing sugar in our drinks to bringing innovative new products to market. We seek to positively impact people’s lives, communities and the planet through water replenishment, packaging recycling, sustainable sourcing practices and carbon emissions reductions across our value chain. Together with our bottling partners, we employ more than 700,000 people, helping bring economic opportunity to local communities worldwide. Learn more at www.coca-colacompany.com and follow us on Instagram , Facebook and LinkedIn .
About Microsoft
Microsoft (Nasdaq “MSFT” @microsoft) enables digital transformation for the era of an intelligent cloud and an intelligent edge. Its mission is to empower every person and every organization on the planet to achieve more.
For more information, press only:
Microsoft Media Relations, WE Communications for Microsoft, (425) 638-7777, [email protected]
The Coca-Cola Company, Scott Leith, [email protected]
Note to editors: For more information, news and perspectives from Microsoft, please visit Microsoft Source at http://news.microsoft.com/source . Web links, telephone numbers and titles were correct at time of publication but may have changed. For additional assistance, journalists and analysts may contact Microsoft’s Rapid Response Team or other appropriate contacts listed at https://news.microsoft.com/microsoft-public-relations-contacts .
Related Posts
Axel Springer and Microsoft expand partnership across advertising, AI, content and Azure services
The Estée Lauder Companies and Microsoft increase collaboration to power prestige beauty with generative AI
Microsoft earnings press release available on Investor Relations website
Microsoft Cloud strength fuels third quarter results
Cognizant and Microsoft announce global partnership to expand adoption of generative AI in the enterprise, and drive industry transformation
- Check us out on RSS
Share this page:

NIOSH Science Blog: The Problem of Falls from Elevation in Construction and Prevention Resources
The current situation with falls.
In 2022 falls from elevation represented approximately 81% of all fatal and 20% of all nonfatal slips, trips, and falls for all industry workers (BLS 2023a, BLS 2023b). Many of these falls occurred in the construction industry, and significantly impact construction employers, workers, and their families. In fact, construction workers made up nearly half (49%) of all fatal occupational slips, trips, and falls (BLS 2023). Since 2013, construction workers have suffered approximately 300 fatal and 20,000 nonfatal fall-related injuries per year (CPWR 2024). Four out of 10 of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s (OSHA) top citations involved falls, including general fall protection, ladders, scaffolding, and fall protection training.
Roofing contractors, residential building construction, and commercial/institutional building construction had the highest number of fatalities in 2022 compared to previous years and other industries (CPWR 2024). In addition, approximately 70% of all fatal falls in construction occurred to those working for employers with less than 10 employees (CPWR 2024).
Causes of Falls
The causes of construction workers’ falls from elevation are complex and multifaceted. There are many different factors at play. In 2021, CPWR conducted a fall experience survey that found that insufficient or ineffective planning is a key underlying cause of falls.
In addition, lack of planning was associated with reduced likelihood of using fall protection. Using fall protection was 71% lower for workers whose employer did not do any planning. Approximately half (49%) of survey respondents said that no fall protection was being used at the time of the fall. Lack of fall protection is particularly problematic for small residential construction firms with fewer than 10 employees (CPWR 2022).
Ladders and Ladder Safety
Falls from ladders are a common cause of injury for construction workers (CPWR 2024). Employers should be familiar with safety and regulatory requirements before using a ladder, including:
Planning work tasks to eliminate or reduce the need to work at elevation.
Providing the right equipment. This includes alternative equipment for extended work periods at elevation, such as aerial lifts, supported scaffolds, or mast climbing platforms. If a ladder must be used, properly select the ladder for the location and height of the task and the weight of the worker. Ensure it is thoroughly inspected before each use.
Training all workers in a language they understand on the proper use, care, and inspection of each type of ladder being used.
A recent webinar hosted by CPWR – The Center for Construction Research and Training (CPWR) discussed ladder safety and ways to improve ladder design, usage, and training. The webinar included a panel of experts who conduct laboratory research on ways to prevent common ladder fall injuries, such as slipping off a ladder and falling with the ladder. The audio from the webinar is also available in Spanish .
Ladder Safety Resources
Ladder Safety App
National Ladder Safety Month website
ALI Training
ANSI blog on 5 most common causes of ladder incidents based on ALI study
OSHA Stairways and Ladders
OSHA Letter of Interpretation on three points of contact
Rescue Planning
Falls can occur quickly, even when all precautions are taken and using proper fall prevention and protection methods. Personal Fall Arrest Systems are a critical option to keep workers safe when performing tasks at heights, but rescue planning is essential.
If a fall occurs and a worker is suspended in a harness for more than a few minutes, a lack of circulation can cause unconsciousness, suspension trauma, and even death.
Every fall protection plan must include a rescue strategy to help workers after a fall and reduce fall-related injuries including suspension trauma even when using a Personal Fall Arrest System. Another finding from CPWR’s fall experience survey was that the odds of a fall being fatal were 76% lower for those who had self-rescue training compared to those who did not have this training. The rescue plan should be tailored to each jobsite and prioritize methods to preserve blood circulation for the worker. Ensure equipment for self-rescue is available, such as trauma straps and self-rescue harness units. The rescue plan should ensure other equipment is available, ready to be used, and in good condition, such as a ladder, aerial lift, or bucket truck.
Rescue Planning Resources
CPWR General Fall Protection Plan (English)
CPWR General Fall Protection Plan (Spanish)
OSHA Model Fall Protection Plan
OSHA Standard Interpretations – Rescue of a suspended worker following a fall event
CPWR Fall Rescue Planning Tipsheet
CPWR Fall Rescue Planning Tipsheet (Spanish)
The National Safety Stand-Down to Prevent Falls in Construction
The National Campaign to Prevent Falls in Construction (Falls Campaign) began in 2012 and was followed in 2014 by the National Safety Stand-Down to Prevent Falls in Construction (Stand-Down). The Falls Campaign idea originated with the National Occupational Research Agenda (NORA) Construction Sector Council. The Sector Council consists of industry experts on health and safety representing contractors, trade associations, labor, government, and academia. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), OSHA, and CPWR are the Falls Campaign organizing partners. The Falls Campaign and Stand-Down are important events because of the high burden falls place on construction workers and their families.
Safety stand-downs originated in the military and are a time to focus on worker safety by stopping work and reinforcing the importance of fall prevention and fall protection.
This year’s Stand-Down will take place May 6-10, 2024. CPWR, NIOSH, and OSHA are hosting a virtual event on Tuesday May 7 th at 2 pm (Eastern Time) to educate employers and crew leaders on how rescue planning can save lives. Click here to register and submit a question in advance. Attendees will learn more about identifying a competent person to lead fall prevention and rescue planning, incorporating key components of a rescue plan into the pre-job planning process, and using FREE resources and templates to tailor your plans to each unique jobsite. The webinar will be in English with simultaneous translation into Spanish available.
On May 8 th at 2pm (Eastern Time) a second Stand-Down webinar presented entirely in Spanish will be hosted. Click here to register and submit a question in advance.
Hosting a Stand-Down
Thousands of companies have held fall safety stand-downs , reaching millions of workers across all 50 states and internationally. Industry and business leaders, universities, labor organizations, and community groups have all participated. In 2023, there were 3,554 stand-downs reaching more than 463,000 workers.
Construction employers and workers are invited to host a Safety Stand-Down or join one.
Your involvement can be as simple as sharing NIOSH, OSHA, or CPWR resources at your worksite. If you would like to host or join a free event that is open to the public, contact your Regional Stand-Down Coordinator . You can find resources to host a Stand-Down and activities at CPWR’s Promotion and Planning Page .
If you do participate in the Stand-Down, make sure you get a Certificate of Participation from OSHA. The certificates provide recognition for your event(s). After removing all personal information, CPWR used the data to evaluate and improve the Falls Campaign and Stand-Down every year. Previous evaluation reports and factsheets can be found on the Stop Construction Falls Evaluation page .
Stand-down Resources
About the Campaign
CPWR’S Planning and Promotion Page on StopConstructionFalls.com
Suggestions to prepare successful Stand-Downs
Highlights from previous Stand-Downs
OSHA Regional Stand-Down Coordinators
OSHA Certificates of Participation
Additional Tools and Resources
National Falls Campaign & Safety Stand-Down Website
CPWR Data Bulletin
Bilingual Fall Hazards & Prevention YouTube Playlist
Spanish Fall Safety YouTube Playlist (Prevención de caídas)
Christina Socias-Morales, DrPH is a Research Epidemiologist in the NIOSH Office of Construction Safety and Health.
Scott Earnest, PhD, PE, CSP, is the Associate Director for the NIOSH Office of Construction Safety and Health.
Jessica Bunting, MPH, is the Research to Practice Director at the Center for Construction Research and Training (CPWR).
Rosa Greenberg, MPH, is a Research Analyst in Research to Practice at CPWR
Scott Breloff, Ph.D. is a Senior Biomechanical Research Engineer in the Division of Field Studies & Engineering and the Co-Coordinator for the Construction Program in the Office of Construction Safety and Health at NIOSH.
Asha Brogan, MS, is a Heath Communication Fellow in the NIOSH Division of Field Studies & Engineering.
Douglas Trout, MD, MHS, is Deputy Director, Office of Construction Safety and Health at NIOSH.
Bureau of Labor Statistics (2023a). News Release National Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries in 2022. USDL-23-2615. December 19, 2023. Available from: https://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/cfoi.pdf .
Bureau of Labor Statistics (2023b). Number of nonfatal occupational injuries and illnesses involving days away from work, restricted activity, or job transfer (DART), days away from work (DAFW), and days of restricted work activity, or job transfer (DJTR) by event or exposure leading to injury or illness and industry sector, private industry, 2021-2022 (TABLE R64). November 8, 2023. Available from: https://www.bls.gov/iif/nonfatal-injuries-and-illnesses-tables/case-and-demographic-characteristics-table-r64-2021-2022.xlsx
CPWR (2024). Data Bulletin: Fatal and Nonfatal Falls in the US Construction Industry. The Center for Construction Research and Training. Silver Spring, MD. March 2024. https://www.cpwr.com/wp-content/uploads/DataBulletin-March2024.pdf.
CPWR (2022). Underlying Causes of Falls from Heights (Highlighted Findings from a CPWR Survey). The Center for Construction Research and Training. Silver Spring, MD. March 2022. https://www.cpwr.com/wp-content/uploads/RR-falls_experience_survey.pdf.
Post a Comment
Cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- 50th Anniversary Blog Series
- Additive Manufacturing
- Aging Workers
- Agriculture
- Animal/Livestock hazards
- Artificial Intelligence
- Back Injury
- Bloodborne pathogens
- Cardiovascular Disease
- cold stress
- commercial fishing
- Communication
- Construction
- Cross Cultural Communication
- Dermal Exposure
- Education and Research Centers
- Electrical Safety
- Emergency Response/Public Sector
- Engineering Control
- Environment/Green Jobs
- Epidemiology
- Fire Fighting
- Food Service
- Future of Work and OSH
- Healthy Work Design
- Hearing Loss
- Heat Stress
- Holiday Themes
- Hydraulic Fracturing
- Infectious Disease Resources
- International
- Landscaping
- Law Enforcement
- Manufacturing
- Manufacturing Mondays Series
- Mental Health
- Motor Vehicle Safety
- Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Nanotechnology
- National Occupational Research Agenda
- Needlestick Prevention
- NIOSH-funded Research
- Nonstandard Work Arrangements
- Observances
- Occupational Health Equity
- Oil and Gas
- Outdoor Work
- Partnership
- Personal Protective Equipment
- Physical activity
- Policy and Programs
- Prevention Through Design
- Prioritizing Research
- Reproductive Health
- Research to practice r2p
- Researcher Spotlights
- Respirators
- Respiratory Health
- Risk Assessment
- Safety and Health Data
- Service Sector
- Small Business
- Social Determinants of Health
- Spanish translations
- Sports and Entertainment
- Strategic Foresight
- Struck-by injuries
- Student Training
- Substance Use Disorder
- Surveillance
- Synthetic Biology
- Systematic review
- Take Home Exposures
- Teachers/School Workers
- Temporary/Contingent Workers
- Total Worker Health
- Translations (other than Spanish)
- Transportation
- Uncategorized
- Veterinarians
- Wearable Technologies
- Wholesale and Retail Trade
- Work Schedules
- Workers' Compensation
- Workplace Medical Mystery
- Workplace Supported Recovery
- World Trade Center Health Program
- Young Workers
To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address:
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
World Intellectual Property Report 2024: Making Innovation Policy Work for Growth and Development
Geneva, May 2, 2024 PR/2024/916
A new WIPO report probes the intersection of human innovation, economic diversification and industrial policy and finds that the key to sustainable growth for countries is to focus policy making on developing local innovation capabilities.
The biennial World Intellectual Property Report (WIPR) “Making Innovation Policy Work for Development” documents a recent resurgence in industrial policy making, including in many developing and least developed countries, aimed at ensuring a wide and growing economic structure base - and the innovation, creativity and technology required to achieve it.
Photos on Flickr
The WIPR establishes a novel methodology that maps 20 years of innovation capabilities across 150-plus WIPO member states, pinpointing how different countries have boosted their economic diversification in areas of technology, science and exports. Through this, the WIPR results help governments design their policies in a highly dynamic economic and political environment.

We hope this report will guide policymakers across the world on how to leverage innovation for improved productivity, competitiveness, and development amid global economic shifts, geopolitical tensions and digital acceleration.
Our report shows that countries that leverage on local strengths, build diverse innovation ecosystems and develop deep capabilities are in a better place to win the innovation race.
said WIPO Director General Daren Tang , adding
We hope that policymakers will find the data and insights in this report useful and interesting as they build durable innovation ecosystems that brings real growth over decades.
To help guide policymakers, the report documented:
- Power of local capabilities: Countries often use their existing innovation capabilities as a springboard for diversification. Innovation capabilities based on scientific, technological and production know-how in a particular country or region can be measured by studying the data on scientific publications, patent applications and international trade respectively. For example:
- Economic Specialization and Diversification: Analysis of nearly 40 million patent filings, over 70 million scientific papers and economic activity worth more than 300 trillion dollars in goods and services exports, reveals that innovative outcomes are highly concentrated. Over the past 20 years, for example, the top eight countries account for 50 percent of exports, 60 percent of scientific publications and 80 percent of international patenting. But change is occurring: China, India and the Republic of Korea saw big increases in their technological diversification over the period. China jumped from being specialized in only 16% to 94% of all technological capabilities, the Republic of Korea's technological capabilities went from 40% to 83%, and India saw its technological capabilities double from 9% to 21%.
- Innovation Complexity: Innovation complexity is the knowledge in an economy as expressed in the diversity and sophistication of the science, technologies, and products it generates. Complex capabilities are rare and only diversified innovation ecosystems can make use of them. Of the three types of innovation capabilities, technological capabilities are the most complex and also more likely to generate higher growth.
Case Studies Spotlight
The WIPR focuses on three case studies across eight countries to reveal insights on how innovators and policymakers leveraged and enhanced existing industrial capabilities to create the advanced and sophisticated motorcycles, videogames and agricultural technologies of today.
Motorcycles Industry - full throttle on innovation
The documented evolution of the motorcycle industry is a key example of human innovation and economic diversification, which economists and policymakers can use to spur sustainable, long-term growth across the globe.
The experiences of Italy, Japan and India show how historical ties with closely related sectors - including bicycles, automobiles, and aviation – have allowed them to carve out their own unique specialized trajectories within the same innovative and complex industry.
For instance, Italian motorcycles excel in high-performance and groundbreaking design thanks to vibrant know-how in racing and top of the line craftsmanship; the big four Japanese motorcycles companies (Honda, Yamaha, Kawasaki, Suzuki) dominate the global market by exploiting Japan’s complex innovation capabilities on advanced technologies, product reliability, and sophisticated supply-chain logistics ( keiretsu ) ; and Indian motorcycle companies have emerged as a key global industry player catapulted by India’s capabilities on cost efficient production, particularly prioritizing fuel-efficient engines.
The motorcycle case study provides evidence of strategic implementation of industrial policies, such as those that enhanced the rise of national champions in Japan or faster adoption of electric two- and three-wheelers in India.
Today, the motorcycle industry is in a new and disruptive transformational journey driven by changing consumer preferences, a heightened focus on sustainability and technological shifts. Electrification, artificial intelligence, and enhanced connectivity technologies are revolutionizing the industry.
Agricultural Leveraging Technologies
The agricultural sector is undergoing a spectacular technological transformation as shown by the 239% increase of patent protected agriculture inventions in the last decade. New scientific breakthroughs in genetic engineering and the adoption of frontier robotic and digital technologies are increasing the innovation sophistication of one of the oldest economic activities.
The increase in innovation complexity in the agricultural sector is happening around the world. For instance, scientists in Kenya have leveraged their plant breeding capabilities to create a pest-resistant maize variety successfully being used across the African continent. In Brazil, sugarcane and sugar production capabilities were the standpoint for Brazil's global leadership of ethanol related technologies helping consumers find sustainable fossil-fuel alternatives.
The Rise of the Global Videogame Industry
The videogame case study showcases how seemingly unrelated existing capabilities can be used to create an innovative and sophisticated new industry.
The video game industry is a breeding ground for new businesses, with around 45% of game developers being newly founded companies. This dynamic environment fosters competition and innovation, contributing to the industry's rapid growth.
In addition, the report finds that around 15% of new video games launched each year are based on existing intellectual property (excluding sequels).
The development of the global video game industry has seen regional hubs navigating unique challenges and capitalizing on local strengths. The four video game industry hubs discussed in the chapter demonstrate how local expertise, cultural capital and interconnected industries collectively have influenced the industry's evolution and offer strategic insights for policymakers.
World IP Report 2024: A Guide for Policy Makers
The report provides a new policy toolkit that can help countries replicate these success stories. By identifying over 600 technological, scientific and production capabilities spread around the world, the new framework allow decision takers to design smart policies based on empirical evidence.
Policy makers can see where, when and how to target their innovation policies, either by nurturing their strengths, or by leveraging them to attain new and exciting scientific, technological and production opportunities.
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) is the United Nations agency that serves the world’s innovators and creators, ensuring that their ideas travel safely to the market and improve lives everywhere.
We do so by providing services that enable creators, innovators and entrepreneurs to protect and promote their intellectual property (IP) across borders and acting as a forum for addressing cutting-edge IP issues. Our IP data and information guide decisionmakers the world over. And our impact-driven projects and technical assistance ensure IP benefits everyone, everywhere.
- Tel: (+41 22) 338 81 61 / 338 72 24

Tunisia Quality Infrastructure Green Hydrogen Case Study
Hydrogen is recognized by the international community as a key enabler to accelerate the attainment of an energy transition that is compliant with a 1.5-degree scenario. According to IRENA’s World Energy Transition Outlook (WETO) 2023 , a record 300 GW of renewables was added at the end of 2022. There is also a growing interest in leveraging renewables to produce so called green hydrogen via electrolysis, for use in hard-to-abate sectors like industry and heavy-duty transport.
As the sector starts to grow, the green hydrogen value chain is becoming increasingly complex and capital intensive, across generation, processing, and distribution infrastructure. An often overlooked but important component that needs to be developed in tandem is the corresponding Quality Infrastructure (QI) – to ensure that the production, distribution, use and trade of green hydrogen is safe as well as sustainable.
QI is the national system of organisations, policies, legal framework, and practices required to assure quality, safety and sustainability of products and services. It comprises several key components, including metrology, standardisation, accreditation, and conformity assessment (including testing, certification, and inspection). QI creates the technical basis for assuring the development of the green hydrogen sector. It helps to reduce and mitigate safety, financial and reputational risks in the sector, while supporting the achievement of the intended positive sustainability impacts of investments.
IRENA together with the German Metrology Institute (Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, PTB), with financial support from the Federal Ministry of Economic Cooperation and Development of Germany (Bundesministerium für wirtschaftliche Zusammenarbeit und Entwicklung, BMZ), is implementing a project entitled “Quality Infrastructure (QI) for Green Hydrogen: technical standards and quality control for the production and trade of renewable hydrogen”. The goal of this project is to develop a comprehensive roadmap for the development and implementation of the QI services needed for green hydrogen.
This project also endeavors to apply the proposed roadmap approach to a pilot country (in the form of a case study). The pilot country chosen for this project is Tunisia, where the government has demonstrated a strong commitment to the integration of green hydrogen within its national energy transition strategy.
IRENA together with support from PTB and the Tunisian Department of Industrial Infrastructure and Technology (Direction Générale de l'Infrastructure Industrielle et Technologique, DGIIT) have developed a case study which provides insights on the status of green hydrogen-relevant QI in Tunisia. This analysis provides perspectives on the readiness of its national QI system to cater to the requirements of the ongoing development of the green hydrogen economy.
To validate the findings from this case study, IRENA, PTB and DGIIT are organising an in person half-day in-person workshop with the following objectives:
- Present results from IRENA Tunisia QI green hydrogen case study to national hydrogen stakeholders
- Present the proposed action plan and recommendations on how to address QI gaps
- Solicit comments and feedback from stakeholders on the case study results as well as action plan
- Invite stakeholders to share additional recommendations to be included in the action plan
- Identify at least one recommendation that can be implemented by June 2024 by IRENA and PTB
IRENA would like to thank implementing partner PTB and funder for this work, BMZ. Support, co-ordination and advice from DGIIT is gratefully acknowledged.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A sense of belonging in the workplace contributes greatly to retention and attraction of high-quality candidates, which leads to better productivity, outcomes, creative solutions and more profit. It can also result in 75 per cent fewer sick days and avoid millions of dollars' worth of lost productivity. 'A sense of belonging in the ...
Here are certain strategies for best employee engagement with case studies. 1. Acknowledgment and Appreciation. The first and foremost step to boost employee engagement is making sure your employees are valued, acknowledged, and appreciated. This motivates employees to become more productive, stay on track with tasks, and perform well.
Case Study: Was That Harassment? A version of this article appeared in the May-June 2019 issue (pp.160-165) of Harvard Business Review. J. Neil Bearden is an associate professor at INSEAD.
These Chief Executive Officers show the key role of management leadership in building a culture of safety. The Robert W. Campbell Award Business Case Studies are designed to show future business leaders the business value of environmental, health, and safety (EHS) management. Established in 2004, the award recognizes companies who are the "best ...
Workplace Case Studies. Read More. The 2021 Workplace Customer Success Awards. Download the e-book now. Effective community and connection at AB InBev. ... Explore our inspiring case studies. Find out how organizations like yours use Workplace to connect employees and increase collaboration.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Case Studies. Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina Uses Data-Driven Insight to Empower Managers. Case Studies. Wonolo Turbocharges Recruitment with Great Place To Work Certification. Case Studies. How FinTech Company WEX Uses Data to Drive Culture Forward. Case Studies. Deerfield Public Schools Wins Scarce Talent by Building Employer Brand.
In their book Difficult Conversations: How to Discuss What Matters Most (Penguin Putnam, 2000), authors Douglas Stone, Bruce Patton, and Sheila Heen tell us how to engage in the conversations in our professional or personal lives that make us uncomfortable by examining a case study of conflict management. Tough, honest conversations are critical for managers, whether they need to change the ...
by Michael Blanding. More than 900,000 reviews highlight broad racial disparities in the American working experience. Beyond pay inequities, research by Letian Zhang shows how Black employees are less likely to work at companies known for positive cultures or work-life balance. 26 Jul 2023. Research & Ideas.
Four qualities—awareness, vulnerability, empathy, and compassion—are critical for business leaders to care for people... To truly build a more resilient workforce and rebuild the economy in 2021 and beyond, employers should prioritize well-being, which is the state of being comfortable, healthy, or happy. Businesses should treat well-being ...
an economic case for considering demographic differences in the workplace.14 INCLUSION: The idea that additional work needs to be done to integrate diverse perspectives in the workplace first emerged as a goal in many U.S. companies in the late 1990s/early 2000s.15 A focus on inclusion often emerged in response to
by Michael Blanding. People who seem like they're paying attention often aren't—even when they're smiling and nodding toward the speaker. Research by Alison Wood Brooks, Hanne Collins, and colleagues reveals just how prone the mind is to wandering, and sheds light on ways to stay tuned in to the conversation. 31 Oct 2023. HBS Case.
Case Study This case study examines how curiosity facilitated significant growth in Elizabeth, a mid-level manager at a technology firm facing leadership challenges.
06. Ageism is alive and well in the workplace. In fact, studies show almost 65% of workers say they have experienced age-based discrimination. But even though it's common, leaders can recognize ...
In this research roundup, we share highlights from several new and forthcoming studies that explore the many facets of gender at work. In 2021, the gender gap in U.S. workforce participation hit ...
The value of DEI efforts at work. A majority of workers (56%) say focusing on increasing diversity, equity and inclusion at work is mainly a good thing; 28% say it is neither good nor bad, and 16% say it is a bad thing. Views on this vary along key demographic and partisan lines. Half or more of both men and women say focusing on increasing DEI ...
Diversity Matters Even More is the fourth report in a McKinsey series investigating the business case for diversity, following Why Diversity Matters (2015), Delivering Through Diversity (2018), and Diversity Wins (2020). For almost a decade through our Diversity Matters series of reports, McKinsey has delivered a comprehensive global perspective on the relationship between leadership diversity ...
Cultural Exchange: TalentRupt's approach of celebrating festivals together is more than just a yearly event. It is an opportunity for employees to share their cultural practices, foods, and ...
Workplace Dispute Case Study. It came to the attention of the CEO of a small company that there was a difficulty between two employees who had been working together for some time but recently appeared to have major differences that were affecting their entire department. The CEO was being approached by both employees at different times and also ...
recover from challenges. Studies have shown that resiliency training is effective at reducing stress and anxiety, and improving work performance, mental health and well-being. 11 . Many of these programs apply principles of mindfulness, self-compassion, and cognitive re-framing to help develop a more resilient approach to challenges.
Case Studies Managing Trauma Triggers After Experiencing Assault ... Workplace Options (WPO) received a request from a multinational company.. View Case Study . 14 June 2022. In My Hands. Technology; A 42-year-old married woman living with her spouse and four.. View Case Study . 20 January 2022.
Risking the newsroom's image: How editors, in a good cause, can strain independence. Case studies about workplace issues.
Case Study: What Does Diversity Mean in a Global Organization? "We have a diversity problem.". A version of this article appeared in the May-June 2022 issue of Harvard Business Review. David ...
It offers a case study in how to navigate workplace exclusion. New! HBR Learning. Diversity, Inclusion, and Belonging Course. Accelerate your career with Harvard ManageMentor®. HBR Learning's ...
Published 3 May 2024. This summary outlines key findings from in-house qualitative case study research on the Sector-based Work Academy Programme ( SWAP ). The research took place in four ...
This includes testing how Copilot for Microsoft 365 could help improve workplace productivity. "Through our long-term partnership, we have made significant progress to accelerate system-wide AI Transformation across The Coca-Cola Company and its network of independent bottlers worldwide," said Judson Althoff, executive vice president and ...
Scott Breloff, Ph.D. is a Senior Biomechanical Research Engineer in the Division of Field Studies & Engineering and the Co-Coordinator for the Construction Program in the Office of Construction Safety and Health at NIOSH. Asha Brogan, MS, is a Heath Communication Fellow in the NIOSH Division of Field Studies & Engineering.
The videogame case study showcases how seemingly unrelated existing capabilities can be used to create an innovative and sophisticated new industry. The video game industry is a breeding ground for new businesses, with around 45% of game developers being newly founded companies.
In 2021, there were over 390,000 children and youth in foster care in the U.S., according to the Child Welfare Information Gateway. While 93% of former foster youth state they want to attend college, just 4% obtain a bachelor's degree by the age of 26. Even fewer earn graduate-level degrees. In Julin's case, it wasn't a career choice that ...
To validate the findings from this case study, IRENA, PTB and DGIIT are organising an in person half-day in-person workshop with the following objectives: Present results from IRENA Tunisia QI green hydrogen case study to national hydrogen stakeholders. Present the proposed action plan and recommendations on how to address QI gaps.