- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons

Difference Between Article and Essay

An article is nothing but a piece of writing commonly found in newspapers or websites which contain fact-based information on a specific topic. It is published with the aim of making the reader aware of something and keeping them up to date.
An essay is a literary work, which often discusses ideas, experiences and concepts in a clear and coherent way. It reflects the author’s personal view, knowledge and research on a specific topic.
Content: Article Vs Essay
Comparison chart, definition of article.
An ‘article’ can be described as any form of written information which is produced either in a printed or electronic form, in newspaper, magazine, journal or website. It aims at spreading news, results of surveys, academic analysis or debates.
An article targets a large group of people, in order to fascinate the readers and engage them. Hence, it should be such that to retain the interest of the readers.
It discusses stories, reports and describes news, present balanced argument, express opinion, provides facts, offers advice, compares and contrast etc. in a formal or informal manner, depending upon the type of audience.
For writing an article one needs to perform a thorough research on the matter, so as to provide original and authentic information to the readers.
Components of Article
- Title : An article contains a noticeable title which should be intriguing and should not be very long and descriptive. However, it should be such that which suggests the theme or issue of the information provided.
- Introduction : The introduction part must clearly define the topic, by giving a brief overview of the situation or event.
- Body : An introduction is followed by the main body which presents the complete information or news, in an elaborative way, to let the reader know about the exact situation.
- Conclusion : The article ends with a conclusion, which sums up the entire topic with a recommendation or comment.
Definition of Essay
An essay is just a formal and comprehensive piece of literature, in which a particular topic is discussed thoroughly. It usually highlights the writer’s outlook, knowledge and experiences on that particular topic. It is a short literary work, which elucidates, argues and analyzes a specific topic.
The word essay is originated from the Latin term ‘exagium’ which means ‘presentation of a case’. Hence, writing an essay means to state the reasons or causes of something, or why something should be done or should be the case, which validates a particular viewpoint, analysis, experience, stories, facts or interpretation.
An essay is written with the intent to convince or inform the reader about something. Further, for writing an essay one needs to have good knowledge of the subject to explain the concept, thoroughly. If not so, the writer will end up repeating the same points again and again.
Components of the Essay
- Title : It should be a succinct statement of the proposition.
- Introduction : The introduction section of the essay, should be so interesting which instantly grabs the attention of the reader and makes them read the essay further. Hence, one can start with a quote to make it more thought-provoking.
- Body : In the main body of the essay, evidence or reasons in support of the writer’s ideas or arguments are provided. One should make sure that there is a sync in the paragraphs of the main body, as well as they, should maintain a logical flow.
- Conclusion : In this part, the writer wraps up all the points in a summarized and simplified manner.
Key Differences Between Article and Essay
Upcoming points will discuss the difference between article and essay:
- An article refers to a written work, published in newspapers, journals, website, magazines etc, containing news or information, in a specific format. On the other hand, an essay is a continuous piece of writing, written with the aim of convincing the reader with the argument or merely informing the reader about the fact.
- An article is objective in the sense that it is based on facts and evidence, and simply describes the topic or narrate the event. As against, an essay is subjective, because it is based on fact or research-based opinion or outlook of a person on a specific topic. It analyses, argues and criticizes the topic.
- The tone used in an article is conversational, so as to make the article easy to understand and also keeping the interest of the reader intact. On the contrary, an essay uses educational and analytical tone.
- An article may contain headings, which makes it attractive and readable. In contrast, an essay does not have any headings, sections or bullet points, however, it is a coherent and organized form of writing.
- An article is always written with a definite objective, which is to inform or make the readers aware of something. Further, it is written to cater to a specific niche of audience. Conversely, an essay is written in response to a particular assertion or question. Moreover, it is not written with a specific group of readers in mind.
- An article is often supported by photographs, charts, statistics, graphs and tables. As opposed, an essay is not supported by any photographs, charts, or graphs.
- Citations and references are a must in case of an essay, whereas there is no such requirement in case of an article.
By and large, an article is meant to inform the reader about something, through news, featured stories, product descriptions, reports, etc. On the flip side, an essay offers an analysis of a particular topic, while reflecting a detailed account of a person’s view on it.
You Might Also Like:

Anna H. Smith says
November 15, 2020 at 6:21 pm
Great! Thank you for explaining the difference between an article and an academic essay so eloquently. Your information is so detailed and very helpful. it’s very educative, Thanks for sharing.
Sunita Singh says
December 12, 2020 at 7:11 am
Thank you! That’s quite helpful.
Saba Zia says
March 8, 2021 at 12:33 am
Great job!! Thank u for sharing this explanation and detailed difference between essay and article. It is really helpful.
Khushi Chaudhary says
February 7, 2021 at 2:38 pm
Thank you so much! It is really very easy to understand & helpful for my test.
Dury Frizza says
July 25, 2022 at 8:18 pm
Thanks a lot for sharing such a clear and easily understood explanation!!!!.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Introduce a Journal Article in an Essay
Last Updated: February 9, 2024
This article was co-authored by Noah Taxis and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Noah Taxis is an English Teacher based in San Francisco, California. He has taught as a credentialed teacher for over four years: first at Mountain View High School as a 9th- and 11th-grade English Teacher, then at UISA (Ukiah Independent Study Academy) as a Middle School Independent Study Teacher. He is now a high school English teacher at St. Ignatius College Preparatory School in San Francisco. He received an MA in Secondary Education and Teaching from Stanford University’s Graduate School of Education. He also received an MA in Comparative and World Literature from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and a BA in International Literary & Visual Studies and English from Tufts University. This article has been viewed 33,908 times.
Using a journal article in your essay can add to your credibility and make your points more persuasive. When you introduce an article to your readers, you help them understand why you're using it as a source. We've gathered a number of different ways you can introduce the journal article and transition between your thoughts and those of the other author. Pick the one that works best for you and your personal writing style.
List the title and the author.

- For example, you might write: "Albus Dumbledore describes the origin of the four Hogwarts houses in his article 'Separating Hogwarts Fact and Fiction.'"
- Put the title of the article in double-quotation marks in your text. [1] X Research source
- If you're quoting directly from the source, include the author's full name the first time you quote them. [2] X Research source
Summarize the article.

- For example, you might write: "The history of Hogwarts makes clear that the houses were never intended to be seen as 'good' or 'evil.' Rather, each house emphasizes and nurtures specific traits students have—how they use those traits is up to them."
- Paraphrasing from the article is similar to summarizing. However, when you summarize, you're covering the entire article in a sentence or two. A paraphrase typically only covers a small portion of the article.
Provide any necessary background.

- For example, you might write: "Professor Slughorn was one of the longest-serving teachers at Hogwarts, schooling generations of students in potions until his retirement."
- You might also include some background if the author of the article is controversial or the article's conclusions have been seriously questioned. If you're doing this, go on to explain why you're using the article in your essay.
Explain the purpose of the source in your essay.

- For example, you might write: "Although this essay doesn't discuss defenses against the dark arts, Gilderoy Lockhart's article provides an example of how you can't learn anything by plagiarizing the work of others."
Frame the source in the context of your own essay.

- For example, you might write: "This article demonstrates broad support for the idea that Hogwarts should continue to sort students into four houses."
Add a signal phrase to distinguish ideas from the source.

- For example, you might write: "McGonagall argues that Slytherin House should be disbanded after the Battle of Hogwarts."
Discuss the source's limitations.

- For example, you might write: "While McGonagall makes a compelling argument that Slytherin House should be disbanded, she was biased by her experiences. In this essay, I will show that the personality traits emphasized by Slytherin are positive traits that can be used for good."
Expert Q&A
- Remember to include an in-text citation for the source if required by your citation guide. You'll also need an entry for the source in your reference list at the end of your paper. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- In an academic essay, you typically introduce a journal article in the first sentence of a paragraph. Then, use the sentences that follow to show how the material from the article relates to the rest of your essay. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about academic writing, check out our in-depth interview with Noah Taxis .
- ↑ https://rasmussen.libanswers.com/faq/32501
- ↑ https://www.ursinus.edu/live/files/1160-integrating-quotespdf
- ↑ https://www.una.edu/writingcenter/docs/Writing-Resources/Source%20Integration.pdf
- ↑ https://www.stetson.edu/other/writing-center/media/Handout%20-%20Incorporating%20Sources%20Effectively.pdf
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
The Difference Between an Article and an Essay
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In composition studies , an article is a short work of nonfiction that typically appears in a magazine or newspaper or on a website. Unlike essays , which often highlight the subjective impressions of the author (or narrator ), articles are commonly written from an objective point of view . Articles include news items, feature stories, reports , profiles , instructions, product descriptions, and other informative pieces of writing.
What Sets Articles Apart From Essays
Though both articles and essays are types of nonfiction writing, they differ in many ways. Here are some features and qualities of articles that differentiate them from essays.
Subject and Theme in Articles
"A useful exercise is to look at some good articles and name the broader subject and the particular aspect each treats. You will find that the subject always deals with a partial aspect examined from some viewpoint; it is never a crammed condensation of the whole.
"...Observe that there are two essential elements of an article: subject and theme . The subject is what the article is about: the issue, event, or person it deals with. (Again, an article must cover only an aspect of a whole.) The theme is what the author wants to say about the subject—what he brings to the subject." (Ayn Rand, The Art of Nonfiction: A Guide for Writers and Readers , ed. by Robert Mayhew. Plume, 2001)
"An article is not everything that's true. It's every important thing that's true." (Gary Provost, Beyond Style: Mastering the Finer Points of Writing . Writer's Digest Books, 1988)
Article Structure
"There are five ways to structure your article . They are:
- The inverted pyramid - The double helix - The chronological double-helix - The chronological report - The storytelling model
Think about how you read a newspaper: you scan the captions and then read the first paragraph or two to get the gist of the article and then read further if you want to know more of the details. That's the inverted pyramid style of writing used by journalists, in which what's important comes first. The double-helix also presents facts in order of importance but it alternates between two separate sets of information. For example, suppose you are writing an article about the two national political conventions. You'll first present Fact 1 about the Democratic convention, then Fact 2 about the Republicans, then Fact 2 about the Democrats, Fact 2 about the Republicans, and so on. The chronological double-helix begins like the double helix but once the important facts from each set of information have been presented, it then goes off to relay the events in chronological order...
"The chronological report is the most straightforward structure to follow since it is written in the order in which the events occurred. The final structure is the storytelling model, which utilizes some of the techniques of fiction writing, so you would want to bring the reader into the story right away even if it means beginning in the middle or even near the end and then filling in the facts as the story unfolds." (Richard D. Bank, The Everything Guide to Writing Nonfiction . Adams Media, 2010)
Opening Sentence of an Article
"The most important sentence in any article is the first one. If it doesn't induce the reader to proceed to the second sentence, your article is dead. And if the second sentence doesn't induce him to continue to the third sentence, it's equally dead. Of such a progression of sentences, each tugging the reader forward until he is hooked, a writer constructs that fateful unit, the ' lead .'" (William Zinsser, On Writing Well: The Classic Guide to Writing Nonfiction , 7th ed. HarperCollins, 2006)
Articles and Media
"More and more, article content written for printed media is also appearing on digital devices (often as an edited version of a longer article) for readers who have short attention spans due to time constraints or their device's small screen. As a result, digital publishers are seeking audio versions of content that is significantly condensed and written in conversational style. Often, content writers must now submit their articles with the understanding they will appear in several media formats." (Roger W. Nielsen, Writing Content: Mastering Magazine and Online Writing . R.W. Nielsen, 2009)
Writer's Voice in Articles and Essays
"Given the confusion of genre minglings and overlaps, what finally distinguishes an essay from an article may just be the author's gumption, the extent to which personal voice , vision, and style are the prime movers and shapers, even though the authorial 'I' may be only a remote energy, nowhere visible but everywhere present. ('We commonly do not remember,' Thoreau wrote in the opening paragraphs of Walden , 'that it is, after all, always the first person that is speaking.')" (Justin Kaplan, quoted by Robert Atwan in The Best American Essays, College Edition , 2nd ed. Houghton Mifflin, 1998)
- How to Write a News Article That's Effective
- What Are the Different Types and Characteristics of Essays?
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Definition and Examples of Paragraphing in Essays
- What Is a Synopsis and How Do You Write One?
- How To Write an Essay
- Paragraph Length in Compositions and Reports
- Learn to Write News Stories
- Unity in Composition
- Writing a Lead or Lede to an Article
- How to Structure an Essay
- How to Write Your Graduate School Admissions Essay
- AP English Exam: 101 Key Terms
- How to Write a Great Book Report
- Writers on Writing: The Art of Paragraphing
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
Things you buy through our links may earn Vox Media a commission
The Case for Marrying an Older Man
A woman’s life is all work and little rest. an age gap relationship can help..

In the summer, in the south of France, my husband and I like to play, rather badly, the lottery. We take long, scorching walks to the village — gratuitous beauty, gratuitous heat — kicking up dust and languid debates over how we’d spend such an influx. I purchase scratch-offs, jackpot tickets, scraping the former with euro coins in restaurants too fine for that. I never cash them in, nor do I check the winning numbers. For I already won something like the lotto, with its gifts and its curses, when he married me.
He is ten years older than I am. I chose him on purpose, not by chance. As far as life decisions go, on balance, I recommend it.
When I was 20 and a junior at Harvard College, a series of great ironies began to mock me. I could study all I wanted, prove myself as exceptional as I liked, and still my fiercest advantage remained so universal it deflated my other plans. My youth. The newness of my face and body. Compellingly effortless; cruelly fleeting. I shared it with the average, idle young woman shrugging down the street. The thought, when it descended on me, jolted my perspective, the way a falling leaf can make you look up: I could diligently craft an ideal existence, over years and years of sleepless nights and industry. Or I could just marry it early.
So naturally I began to lug a heavy suitcase of books each Saturday to the Harvard Business School to work on my Nabokov paper. In one cavernous, well-appointed room sat approximately 50 of the planet’s most suitable bachelors. I had high breasts, most of my eggs, plausible deniability when it came to purity, a flush ponytail, a pep in my step that had yet to run out. Apologies to Progress, but older men still desired those things.
I could not understand why my female classmates did not join me, given their intelligence. Each time I reconsidered the project, it struck me as more reasonable. Why ignore our youth when it amounted to a superpower? Why assume the burdens of womanhood, its too-quick-to-vanish upper hand, but not its brief benefits at least? Perhaps it came easier to avoid the topic wholesale than to accept that women really do have a tragically short window of power, and reason enough to take advantage of that fact while they can. As for me, I liked history, Victorian novels, knew of imminent female pitfalls from all the books I’d read: vampiric boyfriends; labor, at the office and in the hospital, expected simultaneously; a decline in status as we aged, like a looming eclipse. I’d have disliked being called calculating, but I had, like all women, a calculator in my head. I thought it silly to ignore its answers when they pointed to an unfairness for which we really ought to have been preparing.
I was competitive by nature, an English-literature student with all the corresponding major ambitions and minor prospects (Great American novel; email job). A little Bovarist , frantic for new places and ideas; to travel here, to travel there, to be in the room where things happened. I resented the callow boys in my class, who lusted after a particular, socially sanctioned type on campus: thin and sexless, emotionally detached and socially connected, the opposite of me. Restless one Saturday night, I slipped on a red dress and snuck into a graduate-school event, coiling an HDMI cord around my wrist as proof of some technical duty. I danced. I drank for free, until one of the organizers asked me to leave. I called and climbed into an Uber. Then I promptly climbed out of it. For there he was, emerging from the revolving doors. Brown eyes, curved lips, immaculate jacket. I went to him, asked him for a cigarette. A date, days later. A second one, where I discovered he was a person, potentially my favorite kind: funny, clear-eyed, brilliant, on intimate terms with the universe.
I used to love men like men love women — that is, not very well, and with a hunger driven only by my own inadequacies. Not him. In those early days, I spoke fondly of my family, stocked the fridge with his favorite pasta, folded his clothes more neatly than I ever have since. I wrote his mother a thank-you note for hosting me in his native France, something befitting a daughter-in-law. It worked; I meant it. After graduation and my fellowship at Oxford, I stayed in Europe for his career and married him at 23.
Of course I just fell in love. Romances have a setting; I had only intervened to place myself well. Mainly, I spotted the precise trouble of being a woman ahead of time, tried to surf it instead of letting it drown me on principle. I had grown bored of discussions of fair and unfair, equal or unequal , and preferred instead to consider a thing called ease.
The reception of a particular age-gap relationship depends on its obviousness. The greater and more visible the difference in years and status between a man and a woman, the more it strikes others as transactional. Transactional thinking in relationships is both as American as it gets and the least kosher subject in the American romantic lexicon. When a 50-year-old man and a 25-year-old woman walk down the street, the questions form themselves inside of you; they make you feel cynical and obscene: How good of a deal is that? Which party is getting the better one? Would I take it? He is older. Income rises with age, so we assume he has money, at least relative to her; at minimum, more connections and experience. She has supple skin. Energy. Sex. Maybe she gets a Birkin. Maybe he gets a baby long after his prime. The sight of their entwined hands throws a lucid light on the calculations each of us makes, in love, to varying degrees of denial. You could get married in the most romantic place in the world, like I did, and you would still have to sign a contract.
Twenty and 30 is not like 30 and 40; some freshness to my features back then, some clumsiness in my bearing, warped our decade, in the eyes of others, to an uncrossable gulf. Perhaps this explains the anger we felt directed at us at the start of our relationship. People seemed to take us very, very personally. I recall a hellish car ride with a friend of his who began to castigate me in the backseat, in tones so low that only I could hear him. He told me, You wanted a rich boyfriend. You chased and snuck into parties . He spared me the insult of gold digger, but he drew, with other words, the outline for it. Most offended were the single older women, my husband’s classmates. They discussed me in the bathroom at parties when I was in the stall. What does he see in her? What do they talk about? They were concerned about me. They wielded their concern like a bludgeon. They paraphrased without meaning to my favorite line from Nabokov’s Lolita : “You took advantage of my disadvantage,” suspecting me of some weakness he in turn mined. It did not disturb them, so much, to consider that all relationships were trades. The trouble was the trade I’d made struck them as a bad one.
The truth is you can fall in love with someone for all sorts of reasons, tiny transactions, pluses and minuses, whose sum is your affection for each other, your loyalty, your commitment. The way someone picks up your favorite croissant. Their habit of listening hard. What they do for you on your anniversary and your reciprocal gesture, wrapped thoughtfully. The serenity they inspire; your happiness, enlivening it. When someone says they feel unappreciated, what they really mean is you’re in debt to them.
When I think of same-age, same-stage relationships, what I tend to picture is a woman who is doing too much for too little.
I’m 27 now, and most women my age have “partners.” These days, girls become partners quite young. A partner is supposed to be a modern answer to the oppression of marriage, the terrible feeling of someone looming over you, head of a household to which you can only ever be the neck. Necks are vulnerable. The problem with a partner, however, is if you’re equal in all things, you compromise in all things. And men are too skilled at taking .
There is a boy out there who knows how to floss because my friend taught him. Now he kisses college girls with fresh breath. A boy married to my friend who doesn’t know how to pack his own suitcase. She “likes to do it for him.” A million boys who know how to touch a woman, who go to therapy because they were pushed, who learned fidelity, boundaries, decency, manners, to use a top sheet and act humanely beneath it, to call their mothers, match colors, bring flowers to a funeral and inhale, exhale in the face of rage, because some girl, some girl we know, some girl they probably don’t speak to and will never, ever credit, took the time to teach him. All while she was working, raising herself, clawing up the cliff-face of adulthood. Hauling him at her own expense.
I find a post on Reddit where five thousand men try to define “ a woman’s touch .” They describe raised flower beds, blankets, photographs of their loved ones, not hers, sprouting on the mantel overnight. Candles, coasters, side tables. Someone remembering to take lint out of the dryer. To give compliments. I wonder what these women are getting back. I imagine them like Cinderella’s mice, scurrying around, their sole proof of life their contributions to a more central character. On occasion I meet a nice couple, who grew up together. They know each other with a fraternalism tender and alien to me. But I think of all my friends who failed at this, were failed at this, and I think, No, absolutely not, too risky . Riskier, sometimes, than an age gap.
My younger brother is in his early 20s, handsome, successful, but in many ways: an endearing disaster. By his age, I had long since wisened up. He leaves his clothes in the dryer, takes out a single shirt, steams it for three minutes. His towel on the floor, for someone else to retrieve. His lovely, same-age girlfriend is aching to fix these tendencies, among others. She is capable beyond words. Statistically, they will not end up together. He moved into his first place recently, and she, the girlfriend, supplied him with a long, detailed list of things he needed for his apartment: sheets, towels, hangers, a colander, which made me laugh. She picked out his couch. I will bet you anything she will fix his laundry habits, and if so, they will impress the next girl. If they break up, she will never see that couch again, and he will forget its story. I tell her when I visit because I like her, though I get in trouble for it: You shouldn’t do so much for him, not for someone who is not stuck with you, not for any boy, not even for my wonderful brother.
Too much work had left my husband, by 30, jaded and uninspired. He’d burned out — but I could reenchant things. I danced at restaurants when they played a song I liked. I turned grocery shopping into an adventure, pleased by what I provided. Ambitious, hungry, he needed someone smart enough to sustain his interest, but flexible enough in her habits to build them around his hours. I could. I do: read myself occupied, make myself free, materialize beside him when he calls for me. In exchange, I left a lucrative but deadening spreadsheet job to write full-time, without having to live like a writer. I learned to cook, a little, and decorate, somewhat poorly. Mostly I get to read, to walk central London and Miami and think in delicious circles, to work hard, when necessary, for free, and write stories for far less than minimum wage when I tally all the hours I take to write them.
At 20, I had felt daunted by the project of becoming my ideal self, couldn’t imagine doing it in tandem with someone, two raw lumps of clay trying to mold one another and only sullying things worse. I’d go on dates with boys my age and leave with the impression they were telling me not about themselves but some person who didn’t exist yet and on whom I was meant to bet regardless. My husband struck me instead as so finished, formed. Analyzable for compatibility. He bore the traces of other women who’d improved him, small but crucial basics like use a coaster ; listen, don’t give advice. Young egos mellow into patience and generosity.
My husband isn’t my partner. He’s my mentor, my lover, and, only in certain contexts, my friend. I’ll never forget it, how he showed me around our first place like he was introducing me to myself: This is the wine you’ll drink, where you’ll keep your clothes, we vacation here, this is the other language we’ll speak, you’ll learn it, and I did. Adulthood seemed a series of exhausting obligations. But his logistics ran so smoothly that he simply tacked mine on. I moved into his flat, onto his level, drag and drop, cleaner thrice a week, bills automatic. By opting out of partnership in my 20s, I granted myself a kind of compartmentalized, liberating selfishness none of my friends have managed. I am the work in progress, the party we worry about, a surprising dominance. When I searched for my first job, at 21, we combined our efforts, for my sake. He had wisdom to impart, contacts with whom he arranged coffees; we spent an afternoon, laughing, drawing up earnest lists of my pros and cons (highly sociable; sloppy math). Meanwhile, I took calls from a dear friend who had a boyfriend her age. Both savagely ambitious, hyperclose and entwined in each other’s projects. If each was a start-up , the other was the first hire, an intense dedication I found riveting. Yet every time she called me, I hung up with the distinct feeling that too much was happening at the same time: both learning to please a boss; to forge more adult relationships with their families; to pay bills and taxes and hang prints on the wall. Neither had any advice to give and certainly no stability. I pictured a three-legged race, two people tied together and hobbling toward every milestone.
I don’t fool myself. My marriage has its cons. There are only so many times one can say “thank you” — for splendid scenes, fine dinners — before the phrase starts to grate. I live in an apartment whose rent he pays and that shapes the freedom with which I can ever be angry with him. He doesn’t have to hold it over my head. It just floats there, complicating usual shorthands to explain dissatisfaction like, You aren’t being supportive lately . It’s a Frenchism to say, “Take a decision,” and from time to time I joke: from whom? Occasionally I find myself in some fabulous country at some fabulous party and I think what a long way I have traveled, like a lucky cloud, and it is frightening to think of oneself as vapor.
Mostly I worry that if he ever betrayed me and I had to move on, I would survive, but would find in my humor, preferences, the way I make coffee or the bed nothing that he did not teach, change, mold, recompose, stamp with his initials, the way Renaissance painters hid in their paintings their faces among a crowd. I wonder if when they looked at their paintings, they saw their own faces first. But this is the wrong question, if our aim is happiness. Like the other question on which I’m expected to dwell: Who is in charge, the man who drives or the woman who put him there so she could enjoy herself? I sit in the car, in the painting it would have taken me a corporate job and 20 years to paint alone, and my concern over who has the upper hand becomes as distant as the horizon, the one he and I made so wide for me.
To be a woman is to race against the clock, in several ways, until there is nothing left to be but run ragged.
We try to put it off, but it will hit us at some point: that we live in a world in which our power has a different shape from that of men, a different distribution of advantage, ours a funnel and theirs an expanding cone. A woman at 20 rarely has to earn her welcome; a boy at 20 will be turned away at the door. A woman at 30 may find a younger woman has taken her seat; a man at 30 will have invited her. I think back to the women in the bathroom, my husband’s classmates. What was my relationship if not an inconvertible sign of this unfairness? What was I doing, in marrying older, if not endorsing it? I had taken advantage of their disadvantage. I had preempted my own. After all, principled women are meant to defy unfairness, to show some integrity or denial, not plan around it, like I had. These were driven women, successful, beautiful, capable. I merely possessed the one thing they had already lost. In getting ahead of the problem, had I pushed them down? If I hadn’t, would it really have made any difference?
When we decided we wanted to be equal to men, we got on men’s time. We worked when they worked, retired when they retired, had to squeeze pregnancy, children, menopause somewhere impossibly in the margins. I have a friend, in her late 20s, who wears a mood ring; these days it is often red, flickering in the air like a siren when she explains her predicament to me. She has raised her fair share of same-age boyfriends. She has put her head down, worked laboriously alongside them, too. At last she is beginning to reap the dividends, earning the income to finally enjoy herself. But it is now, exactly at this precipice of freedom and pleasure, that a time problem comes closing in. If she would like to have children before 35, she must begin her next profession, motherhood, rather soon, compromising inevitably her original one. The same-age partner, equally unsettled in his career, will take only the minimum time off, she guesses, or else pay some cost which will come back to bite her. Everything unfailingly does. If she freezes her eggs to buy time, the decision and its logistics will burden her singly — and perhaps it will not work. Overlay the years a woman is supposed to establish herself in her career and her fertility window and it’s a perfect, miserable circle. By midlife women report feeling invisible, undervalued; it is a telling cliché, that after all this, some husbands leave for a younger girl. So when is her time, exactly? For leisure, ease, liberty? There is no brand of feminism which achieved female rest. If women’s problem in the ’50s was a paralyzing malaise, now it is that they are too active, too capable, never permitted a vacation they didn’t plan. It’s not that our efforts to have it all were fated for failure. They simply weren’t imaginative enough.
For me, my relationship, with its age gap, has alleviated this rush , permitted me to massage the clock, shift its hands to my benefit. Very soon, we will decide to have children, and I don’t panic over last gasps of fun, because I took so many big breaths of it early: on the holidays of someone who had worked a decade longer than I had, in beautiful places when I was young and beautiful, a symmetry I recommend. If such a thing as maternal energy exists, mine was never depleted. I spent the last nearly seven years supported more than I support and I am still not as old as my husband was when he met me. When I have a child, I will expect more help from him than I would if he were younger, for what does professional tenure earn you if not the right to set more limits on work demands — or, if not, to secure some child care, at the very least? When I return to work after maternal upheaval, he will aid me, as he’s always had, with his ability to put himself aside, as younger men are rarely able.
Above all, the great gift of my marriage is flexibility. A chance to live my life before I become responsible for someone else’s — a lover’s, or a child’s. A chance to write. A chance at a destiny that doesn’t adhere rigidly to the routines and timelines of men, but lends itself instead to roomy accommodation, to the very fluidity Betty Friedan dreamed of in 1963 in The Feminine Mystique , but we’ve largely forgotten: some career or style of life that “permits year-to-year variation — a full-time paid job in one community, part-time in another, exercise of the professional skill in serious volunteer work or a period of study during pregnancy or early motherhood when a full-time job is not feasible.” Some things are just not feasible in our current structures. Somewhere along the way we stopped admitting that, and all we did was make women feel like personal failures. I dream of new structures, a world in which women have entry-level jobs in their 30s; alternate avenues for promotion; corporate ladders with balconies on which they can stand still, have a smoke, take a break, make a baby, enjoy themselves, before they keep climbing. Perhaps men long for this in their own way. Actually I am sure of that.
Once, when we first fell in love, I put my head in his lap on a long car ride; I remember his hands on my face, the sun, the twisting turns of a mountain road, surprising and not surprising us like our romance, and his voice, telling me that it was his biggest regret that I was so young, he feared he would lose me. Last week, we looked back at old photos and agreed we’d given each other our respective best years. Sometimes real equality is not so obvious, sometimes it takes turns, sometimes it takes almost a decade to reveal itself.
More From This Series
- Can You Still Sell Out in This Economy?
- 7 Stories of Dramatic Career Pivots
- My Mother’s Death Blew Up My Life. Opening a Book and Wine Store Helped My Grief
- newsletter pick
- first person
- relationships
- the good life
- best of the cut
- audio article
The Cut Shop
Most viewed stories.
- Anya Taylor-Joy’s Secret Wedding Was Vampire-Themed
- The Case for Marrying an Older Man
- 10 Impressive Questions to Ask in a Job Interview
- What We Know About the Mommy Vlogger Accused of Child Abuse
- Chance the Rapper Is Getting Divorced
- ‘How Do I Find Child Care Without Losing My Mind?’
Editor’s Picks

Most Popular
What is your email.
This email will be used to sign into all New York sites. By submitting your email, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy and to receive email correspondence from us.
Sign In To Continue Reading
Create your free account.
Password must be at least 8 characters and contain:
- Lower case letters (a-z)
- Upper case letters (A-Z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special Characters (!@#$%^&*)
As part of your account, you’ll receive occasional updates and offers from New York , which you can opt out of anytime.

What this handout is about
When we use nouns in English, articles (a, an, and the) specify which and how many nouns we mean. To choose the correct article for your sentence, you need to answer two questions. First, do I mean this one exactly, one of many, or all of them everywhere? Second, is the noun count or non-count? This handout explains these questions and how their answers help determine which article to use.
Using this handout
As you use the handout, try to keep three things in mind:
- First, this handout will be most effective if you use it as a tool. Every time you read this handout, read it along side another piece of writing (a journal article, a magazine, a web page, a novel, a text book, etc.). Locate a few nouns in the reading, and use the handout to analyze the article usage. If you practice a little bit at a time, this kind of analysis can help you develop a natural sensitivity to this complex system.
- Second, using articles correctly is a skill that develops over time through lots of reading, writing, speaking and listening. Think about the rules in this handout, but also try to pay attention to how articles are being used in the language around you. Simply paying attention can also help you develop a natural sensitivity to this complex system.
- Finally, although using the wrong article may distract a reader’s attention, it usually does not prevent the reader from understanding your meaning. So be patient with yourself as you learn.
Basic rules
This is a simple list, but understanding it and remembering it is crucial to using articles correctly.
Rule # 1: Every time a noun is mentioned, the writer is referring to:
- All of them everywhere (“generic” reference),
- One of many, (“indefinite” reference) or
- This one exactly (“definite” reference)
Rule # 2: Every kind of reference has a choice of articles:
- All of them everywhere…(Ø, a/an, the)
- One of many……………..(Ø, a/an)
- This one exactly…………(Ø, the)
(Ø = no article)
Rule # 3: The choice of article depends upon the noun and the context. This will be explained more fully below.
Basic questions
To choose the best article, ask yourself these questions:
- “What do I mean? Do I mean all of them everywhere, one of many, or this one exactly?”
- “What kind of noun is it? Is it countable or not? Is it singular or plural? Does it have any special rules?”
Your answers to these questions will usually determine the correct article choice, and the following sections will show you how.
When you mean “all of them everywhere”
Talking about “all of them everywhere” is also called “generic reference.” We use it to make generalizations: to say something true of all the nouns in a particular group, like an entire species of animal. When you mean “all of them everywhere,” you have three article choices: Ø, a/an, the. The choice of article depends on the noun. Ask yourself, “What kind of noun is it?”
Non-count nouns = no article (Ø)
- Temperature is measured in degrees.
- Money makes the world go around.
Plural nouns = no article (Ø)
- Volcanoes are formed by pressure under the earth’s surface.
- Quagga zebras were hunted to extinction.
Singular nouns = the
- The computer is a marvelous invention.
- The elephant lives in family groups.
Note: We use this form (the + singular) most often in technical and scientific writing to generalize about classes of animals, body organs, plants, musical instruments, and complex inventions. We do not use this form for simple inanimate objects, like books or coat racks. For these objects, use (Ø + plural).
Singular nouns = a/an when a single example represents the entire group
- A rose by any other name would still smell as sweet.
- A doctor is a highly educated person. Generally speaking, a doctor also has tremendous earning potential.
How do you know it’s generic? The “all…everywhere” test
Here’s a simple test you can use to identify generic references while you’re reading. To use this test, substitute “all [plural noun] everywhere” for the noun phrase. If the statement is still true, it’s probably a generic reference. Example:
- A whale protects its young—”All whales everywhere” protect their young. (true—generic reference)
- A whale is grounded on the beach—”All whales everywhere” are grounded on the beach. (not true, so this is not a generic reference; this “a” refers to “one of many”)
You’ll probably find generic references most often in the introduction and conclusion sections and at the beginning of a paragraph that introduces a new topic.
When you mean “one of many”
Talking about “one of many” is also called “indefinite reference.” We use it when the noun’s exact identity is unknown to one of the participants: the reader, the writer, or both. Sometimes it’s not possible for the reader or the writer to identify the noun exactly; sometimes it’s not important. In either case, the noun is just “one of many.” It’s “indefinite.” When you mean “one of many,” you have two article choices: Ø, a/an. The choice of article depends on the noun. Ask yourself, “What kind of noun is it?”
- Our science class mixed boric acid with water today.
- We serve bread and water on weekends.
- We’re happy when people bring cookies!
- We need volunteers to help with community events.
Singular nouns = a/an
- Bring an umbrella if it looks like rain.
- You’ll need a visa to stay for more than ninety days.
Note: We use many different expressions for an indefinite quantity of plural or non-count nouns. Words like “some,” “several,” and “many” use no article (e.g., We need some volunteers to help this afternoon. We really need several people at 3:00.) One exception: “a few” + plural noun (We need a few people at 3:00.) In certain situations, we always use “a” or “an.” These situations include:
- Referring to something that is one of a number of possible things. Example: My lab is planning to purchase a new microscope. (Have you chosen one yet? No, we’re still looking at a number of different models.)
- Referring to one specific part of a larger quantity. Example: Can I have a bowl of cereal and a slice of toast? (Don’t you want the whole box of cereal and the whole loaf of bread? No, thanks. Just a bowl and a slice will be fine.)
- With certain indefinite quantifiers. Example: We met a lot of interesting people last night. (You can also say “a bunch of” or “a ton of” when you want to be vague about the exact quantity. Note that these expressions are all phrases: a + quantifier + of.)
- Exception: “A few of” does not fit this category. See Number 8 in the next section for the correct usage of this expression.
- Specifying information associated with each item of a grouping. Example: My attorney asked for $200 an hour, but I’ll offer him $200 a week instead. (In this case, “a” can substitute for the word “per.”)
- Introducing a noun to the reader for the first time (also called “first mention”). Use “the” for each subsequent reference to that noun if you mean “this one exactly.” Example: I presented a paper last month, and my advisor wants me to turn the paper into an article. If I can get the article written this semester, I can take a break after that! I really need a break!
Note: The writer does not change from “a break” to “the break” with the second mention because she is not referring to one break in particular (“this break exactly”). It’s indefinite—any break will be fine!!
When you mean “this one exactly”
Talking about “this one exactly” is also called “definite reference.” We use it when both the reader and the writer can identify the exact noun that is being referred to. When you mean “this one exactly,” you have two article choices: Ø, the. The choice of article depends on the noun and on the context. Ask yourself, “What kind of noun is it?”
(Most) Proper nouns = no article (Ø)
- My research will be conducted in Luxembourg.
- Dr. Homer inspired my interest in Ontario.
Note: Some proper nouns do require “the.” See the special notes on nouns below.
Non-count nouns = the
- Step two: mix the water with the boric acid.
- The laughter of my children is contagious.
Plural nouns = the
- We recruited the nurses from General Hospital.
- The projects described in your proposal will be fully funded.
- Bring the umbrella in my closet if it looks like rain.
- Did you get the visa you applied for?
In certain situations, we always use “the” because the noun or the context makes it clear that we’re talking about “this one exactly.” The context might include the words surrounding the noun or the context of knowledge that people share. Examples of these situations include:
Unique nouns
- The earth rotates around the sun.
- The future looks bright!
Shared knowledge (both participants know what’s being referred to, so it’s not necessary to specify with any more details)
- The boss just asked about the report.
- Meet me in the parking lot after the show.
Second mention (with explicit first mention)
- I found a good handout on English articles. The handout is available online.
- You can get a giant ice cream cone downtown. If you can eat the cone in five seconds, you get another one free.
Second mention (with implied first mention—this one is very, very common)
- Dr. Frankenstein performed a complicated surgery. He said the patient is recovering nicely. (“The patient” is implied by “surgery”—every surgery has a patient.)
- My new shredder works fabulously! The paper is completely destroyed. (Again, “the paper” is implied by “shredder.”)
Ordinals and superlatives (first, next, primary, most, best, least, etc.)
- The first man to set foot on the moon…
- The greatest advances in medicine…
Specifiers (sole, only, principle, etc.)
- The sole purpose of our organization is…
- The only fact we need to consider is…
Restricters (words, phrases, or clauses that restrict the noun to one definite meaning)
- Study the chapter on osmosis for the test tomorrow.
- Also study the notes you took at the lecture that Dr. Science gave yesterday.
Plural nouns in partitive -of phrases (phrases that indicate parts of a larger whole) (Note: Treat “of the” as a chunk in these phrases—both words in or both words out)
- Most of the international students have met their advisors, but a few of them have appointments next week. (emphasis on part of the group, and more definite reference to a specific group of international students, like the international students at UNC)
- Most international students take advantage of academic advising during their college careers. (emphasis on the group as a whole, and more generic reference to international students everywhere)
- Several of the risk factors should be considered carefully, but the others are only minor concerns. (emphasis on part of the group)
- Several risk factors need to be considered carefully before we proceed with the project. (emphasis on the group as a whole)
- A few of the examples were hard to understand, but the others were very clear. (emphasis on part of the group)
- A few examples may help illustrate the situation clearly. (emphasis on the group as a whole)
Note: “Few examples” is different from “a few examples.” Compare:
- The teacher gave a few good examples. (a = emphasizes the presence of good examples)
- The teacher gave few good examples. (no article = emphasizes the lack of good examples)
Article flowchart
For the more visually oriented, this flowchart sketches out the basic rules and basic questions.
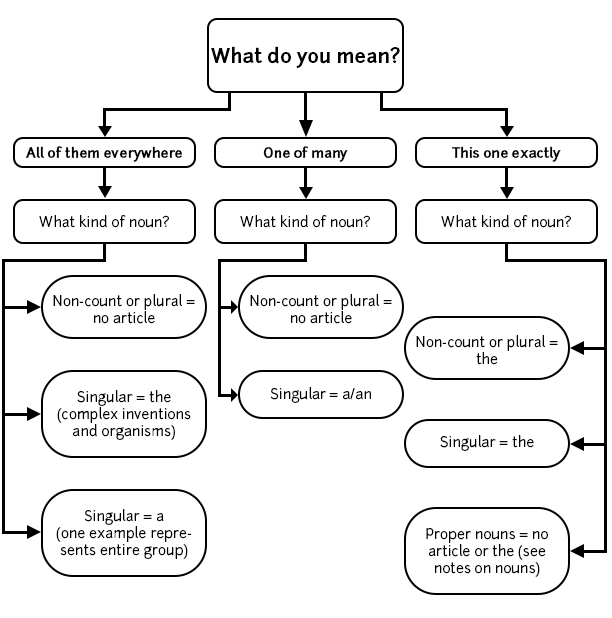
Some notes about nouns
Uncountable nouns.
As the name suggests, uncountable nouns (also called non-count or mass nouns) are things that can not be counted. They use no article for generic and indefinite reference, and use “the” for definite reference. Uncountable nouns fall into several categories:
- Abstractions: laughter, information, beauty, love, work, knowledge
- Fields of study: biology, medicine, history, civics, politics (some end in -s but are non-count)
- Recreational activities: football, camping, soccer, dancing (these words often end in -ing)
- Natural phenomena: weather, rain, sunshine, fog, snow (but events are countable: a hurricane, a blizzard, a tornado)
- Whole groups of similar/identical objects: furniture, luggage, food, money, cash, clothes
- Liquids, gases, solids, and minerals: water, air, gasoline, coffee, wood, iron, lead, boric acid
- Powders and granules: rice, sand, dust, calcium carbonate
- Diseases: cancer, diabetes, schizophrenia (but traumas are countable: a stroke, a heart attack, etc.)
Note: Different languages might classify nouns differently
- “Research” and “information” are good examples of nouns that are non-count in American English but countable in other languages and other varieties of English.
Strategy: Check a dictionary. A learner’s dictionary will indicate whether the noun is countable or not. A regular dictionary will give a plural form if the noun is countable. Note: Some nouns have both count and non-count meanings Some nouns have both count and non-count meanings in everyday usage. Some non-count nouns have count meanings only for specialists in a particular field who consider distinct varieties of something that an average person would not differentiate. Non-count meanings follow the rules for non-count nouns (generic and indefinite reference: no article; definite: “the”); count meanings follow the count rules (a/an for singular, no article for plural). Can you see the difference between these examples?
- John’s performance on all three exams was exceptional.
- John’s performances of Shakespeare were exceptional.
- To be well educated, you need good instruction.
- To assemble a complicated machine, you need good instructions.
Proper nouns
Proper nouns (names of people, places, religions, languages, etc.) are always definite. They take either “the” or no article. Use “the” for regions (like the Arctic) and for a place that’s made up of a collection of smaller parts (like a collection of islands, mountains, lakes, etc.). Examples:
- Places (singular, no article): Lake Erie, Paris, Zimbabwe, Mount Rushmore
- Places (collective, regional, “the”): the Great Lakes, the Middle East, the Caribbean
Note: Proper nouns in theory names may or may not take articles When a person’s name is part of a theory, device, principle, law, etc., use “the” when the name does not have a possessive apostrophe. Do not use “the” when the name has an apostrophe. Examples:
Note: Articles change when proper nouns function as adjectives Notice how the article changes with “Great Lakes” in the examples below. When place names are used as adjectives, follow the article rule for the noun they are modifying. Examples: I’m studying …
- …the Great Lakes. (as noun)
- …a Great Lakes shipwreck.(as adjective with “one of many” singular noun)
- …the newest Great Lakes museum. (as adjective with “this one exactly” singular noun)
- …Great Lakes shipping policies. (as adjective with “one of many” plural noun)
- …Great Lakes history. (as adjective with “one of many” uncountable noun)
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Byrd, Patricia, and Beverly Benson. 1993. Problem/Solution: A Reference for ESL Writers . Boston: Heinle & Heinle.
Celce-Murcia, Marianne, and Diane Larsen-Freeman. 2015. The Grammar Book: An ESL/EFL Teacher’s Course , 3rd ed. Boston: Heinle & Heinle.
Swales, John, and Christine B. Feak. 2012. Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Tasks and Skills , 3rd ed. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

What’s The Difference Between An Article A Paper And An Essay
Table of Contents
When it comes to writing, you may wonder what the difference is between an essay, article, and paper. Even the most experienced writers sometimes confuse these terms, but once you understand what they represent, you’ll be able to choose which kind of writing suits your purposes best. With a little help from an essay writer service, you can be certain that each one of your pieces of writing will be polished and ready to impress upon completion.
Introduction
There are three main types of academic writing: essays, articles, and papers. While these categories are similar, there are some major differences. This post will help you identify what separates these terms from one another. Here’s a quick breakdown of each type of academic writing.
Essay vs. Article vs. Paper
Why are they different? What’s in a title? We hear them used all of the time interchangeably in different contexts, but what makes these three so different from one another? To understand how essay writing differs from articles and papers, we need to look at how each differs from another. So let’s get started by exploring some of their main differences: Essay vs. Article vs. Paper – Key Differences 1. Length 2. Subject Matter 3. Author 4. Purpose 5. Audience.
Essays are typically 1–3 pages long. Articles vary in length but run longer than essays. Papers typically range from 10 to 15 pages or more. It’s important to note that essay writer services have very different writing styles. Some writers write with a conversational tone, while others use a formal style for essays and articles. The best way to figure out which type of writing fits your needs is by looking at samples of their work or asking them about their process.
The three types of writing are intended for different purposes. The purpose is often reflected in both length and tone. For example, a paper is generally longer than an essay or an article because it must be more comprehensive. It also tends to be more formal because it’s intended to be read by experts in a particular field (e.g., doctors reading a medical journal). On the other hand, an essay is usually shorter than a paper because it doesn’t have to cover as much ground and can take a more casual tone since it’s not necessarily directed at experts. Finally, articles tend to fall between essays and papers in terms of length, formality, and audience (i.e., they’re generally shorter than papers but longer than essays).
The difference between essays, articles, and papers can be found in the audience. In other words, you will write them for different people and in different situations. If you need to explain something (from a textbook or another piece of writing) or if you are explaining a procedure to someone new to that topic, then your best bet would be to write an essay. Alternatively, if your purpose is simply to inform someone about something they might find interesting, articles would do just fine. Finally, if you want to share some information with a large group of people with similar interests, then a paper would be your choice. So which one should you choose? It depends on what exactly it is that you want to achieve with your writing.
Subject Matter
There are a few distinct differences in subject matter for these different types of written work. Essays should be focused and concise; articles cover a broader scope. For example, if you were writing about gun control in America from a historical standpoint, your essay would focus on one distinct period throughout American history (likely before modern times), while your articles could each look at a different time during which gun laws were passed, enacted or changed. Papers are similar to essays in that they have a narrow focus, but papers typically take on more of an academic tone than essays do. Papers may also have footnotes, bibliographies, and other citations within them. It’s important to note that there isn’t always a clear distinction between essay and paper; some papers can even read like essays!
Unlike essays and articles, papers do not focus on a single topic. Papers are meant to convey complex information that may have been derived from numerous sources of information. Papers are also typically longer than essays or articles, ranging from five to more than 20 pages in length. This makes papers a relatively demanding form of academic writing. While essays often focus on personal reflections or observations, papers delve into specific topics with objective research findings drawn from secondary sources such as newspapers, journals, or books. An essay writer can be anyone who writes essays for money. An essay writer can be someone who has experience working with students in high school, college, or university-level institutions.
Join the thousands who have sharpened their business writing skills with our award winning courses.
Copyright © 2024 Businesswritingblog.com.
- Written By Gregg Rosenzweig
- Updated: November 8, 2023
We’re here to help you choose the most appropriate content types to fulfill your content strategy. In this series, we’re breaking down the most popular content types to their most basic fundamentals — simple definitions, clarity on formats, and plenty of examples — so you can start with a solid foundation.
What is an article?
An article is a piece of writing that educates, informs and/or colorfully illustrates a topic using purpose-driven writing, provocative insights and a unique perspective designed to engage an audience.
Articles also can be…
- Branded/native content
- Content ladders
- Press releases
- Thought-leadership pieces
- Skyscrapers

The long and short of it
Depending on the outlet and channel you’re publishing in, article lengths will vary . However, as with any writing, you should never write one word more than is necessary to tell your story.
A general guide to article length:
- Short Form (500 words or less)
- Standard (500-1,500 words)
- Long Form (1,500-2,500 words)
- Extra Long Form (2,500+ words)
What can articles do for a business?
Different from advertising, articles allow you to expand on a topic and/or show expertise in your industry or niche, whether an editorial piece or a how-to template . They also afford you an opportunity to enlighten your audience on a deeper level.

Popular use-case examples for articles
Ads only get you so far. If you want to have a conversation with your audience, an article can inspire interactions with a reader, drive traffic to a page, and ultimately convert customers.
- Content for social media channels with viral potential (FB, Twitter, and LinkedIn)
- Content for a company blog and to establish a content cadence
- Thought-leadership pieces that establish instant credibility in a given area
Reasons to write articles
- To inspire inbound marketing and allow you to hit your KPIs
- To expand brand awareness, build loyalty and advocacy
- To boost SEO and “page ranking” through the use of keywords and backlinks
Business types:
Whether you’re a pest control company or hotel chain, there’s always a story to tell. Literally any business, regardless of sector, can use articles to build a greater customer base.
Article examples – short form

Article examples – standard form

Article examples – long form

Article examples – extra long form

Article examples – listicles

Article examples – how-to’s

Article examples – interviews

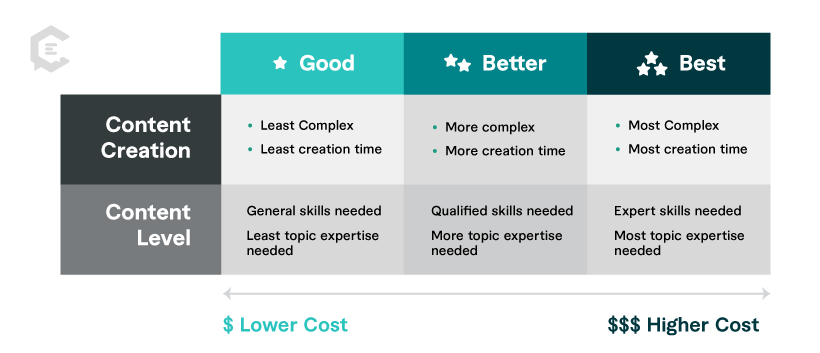
Understanding content quality in examples
Our team has rated content type examples in three degrees of quality ( Good, Better, Best ) to help you better gauge resources needed for your content plan. In general, the degrees of content quality correspond to our three content levels ( General, Qualified, Expert ) based on the criteria below. Please consider there are multiple variables that could determine the cost, completion time, or content level for any content piece with a perceived degree of quality.
More content types with examples:
- What Is an Article?
- What Is an Ebook?
- What Is a White Paper?
- What Is a Customer Story?
- What Is a Product Description?
- What Is an Infographic?
- What Is a Presentation?
- What Is a Motion Graphic?
- What Is an Animated Video?
Need help writing engaging, SEO-friendly articles? Talk to a content specialist at ClearVoice today. Our talented team of writers can easily handle all your content needs, freeing up your team’s time to focus on other parts of your business.
Stay in the know.
We will keep you up-to-date with all the content marketing news and resources. You will be a content expert in no time. Sign up for our free newsletter.

Business Case

How to Measure Success in Content Distribution: Essential Metrics and KPIs

The Ultimate Spring Cleaning Checklist for Your Freelance Business
- Content Production
- Build Your SEO
- Amplify Your Content
- For Agencies
Why ClearVoice
- Talent Network
- How It Works
- Freelance For Us
- Statement on AI
- Talk to a Specialist
Get Insights In Your Inbox
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Intellectual Property Claims
- Data Collection Preferences
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Using Articles

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This handout discusses the differences between indefinite articles (a/an) and definite articles (the).
What is an article? Basically, an article is an adjective. Like adjectives, articles modify nouns.
English has two articles: the and a/an . The is used to refer to specific or particular nouns; a/an is used to modify non-specific or non-particular nouns. We call the the definite article and a/an the indefinite article.
the = definite article
a/an = indefinite article
For example, if I say, "Let's read the book," I mean a specific book. If I say, "Let's read a book," I mean any book rather than a specific book.
Here's another way to explain it: The is used to refer to a specific or particular member of a group. For example, "I just saw the most popular movie of the year." There are many movies, but only one particular movie is the most popular. Therefore, we use the .
"A/an" is used to refer to a non-specific or non-particular member of the group. For example, "I would like to go see a movie." Here, we're not talking about a specific movie. We're talking about any movie. There are many movies, and I want to see any movie. I don't have a specific one in mind.
Let's look at each kind of article a little more closely.
Indefinite Articles: a and an
"A" and "an" signal that the noun modified is indefinite, referring to any member of a group. For example:
- "My daughter really wants a dog for Christmas." This refers to any dog. We don't know which dog because we haven't found the dog yet.
- "Somebody call a policeman!" This refers to any policeman. We don't need a specific policeman; we need any policeman who is available.
- "When I was at the zoo, I saw an elephant!" Here, we're talking about a single, non-specific thing, in this case an elephant. There are probably several elephants at the zoo, but there's only one we're talking about here.
Remember, using a or an depends on the sound that begins the next word. So...
- a + singular noun beginning with a consonant: a boy; a car; a bike; a zoo; a dog
- an + singular noun beginning with a vowel: an elephant; an egg; an apple; an idiot; an orphan
- a + singular noun beginning with a consonant sound: a user (sounds like 'yoo-zer,' i.e. begins with a consonant 'y' sound, so 'a' is used); a university ; a unicycle
- an + nouns starting with silent "h": an hour
- In some cases where "h" is pronounced, such as "historical," you can use an . However, a is more commonly used and preferred. A historical event is worth recording.
Remember that these rules also apply when you use acronyms:
Another case where this rule applies is when acronyms or initialisms start with consonant letters but have vowel sounds:
If the noun is modified by an adjective, the choice between a and an depends on the initial sound of the adjective that immediately follows the article:
- a broken egg
- an unusual problem
- a European country (sounds like 'yer-o-pi-an,' i.e. begins with consonant 'y' sound)
Remember, too, that in English, the indefinite articles are used to indicate membership in a group:
- I am a teacher. (I am a member of a large group known as teachers.)
- Brian is an Irishman. (Brian is a member of the people known as Irish.)
- Seiko is a practicing Buddhist. (Seiko is a member of the group of people known as Buddhists.)
Definite Article: the
The definite article is used before singular and plural nouns when the noun is specific or particular. The signals that the noun is definite, that it refers to a particular member of a group. For example:
" The dog that bit me ran away." Here, we're talking about a specific dog, the dog that bit me.
"I was happy to see the policeman who saved my cat!" Here, we're talking about a particular policeman. Even if we don't know the policeman's name, it's still a particular policeman because it is the one who saved the cat.
"I saw the elephant at the zoo." Here, we're talking about a specific noun. Probably there is only one elephant at the zoo.
Count and Noncount Nouns
The can be used with noncount nouns, or the article can be omitted entirely.
- "I love to sail over the water" (some specific body of water) or "I love to sail over water" (any water).
- "He spilled the milk all over the floor" (some specific milk, perhaps the milk you bought earlier that day) or "He spilled milk all over the floor" (any milk).
"A/an" can be used only with count nouns.
- "I need a bottle of water."
- "I need a new glass of milk."
Most of the time, you can't say, "She wants a water," unless you're implying, say, a bottle of water.
Geographical use of the
There are some specific rules for using the with geographical nouns.
Do not use the before:
- names of most countries/territories: Italy, Mexico, Bolivia ; however, the Netherlands, the Dominican Republic, the Philippines, the United States
- names of cities, towns, or states: Seoul, Manitoba, Miami
- names of streets: Washington Blvd., Main St.
- names of lakes and bays: Lake Titicaca, Lake Erie except with a group of lakes like the Great Lakes
- names of mountains: Mount Everest, Mount Fuji except with ranges of mountains like the Andes or the Rockies or unusual names like the Matterhorn
- names of continents (Asia, Europe)
- names of islands (Easter Island, Maui, Key West) except with island chains like the Aleutians, the Hebrides, or the Canary Islands
Do use the before:
- names of rivers, oceans and seas: the Nile, the Pacific
- points on the globe: the Equator, the North Pole
- geographical areas: the Middle East, the West
- deserts, forests, gulfs, and peninsulas: the Sahara, the Persian Gulf, the Black Forest, the Iberian Peninsula
Omission of Articles
Some common types of nouns that don't take an article are:
- Names of languages and nationalities: Chinese, English, Spanish, Russian (unless you are referring to the population of the nation: " The Spanish are known for their warm hospitality.")
- Names of sports: volleyball, hockey, baseball
- Names of academic subjects: mathematics, biology, history, computer science

What’s The Difference Between An Article, A Paper, And An Essay? (Detailed Analysis)
Categories Culture

School and college life revolves around different types of writing, including opinion articles, review articles, research papers, and essays. Each of these has a different length, structure, and level of research.
You can write articles on various topics and niches if you gather enough information. It is possible to format an interview into an article so that it can be published in a magazine or online publication.
A paper, on the other hand, is longer than an essay or article, and one must follow a specific sequence. There is an abstract at the beginning, followed by a paragraph, a conclusion, and citations at the end.
There are a few paragraphs in the essay, all of which should be transitioned smoothly. The purpose of the essay is to persuade the reader through your logic and ideas. Different types of essays require different thoughts and writing processes.
This article is all about differentiating between an article, paper, and essay, so if it interests you, stick around while we explore these topics. Let’s get into it .
Page Contents
What Is An Article?
Articles are read by thousands of people around the globe and are generally written to educate people about something they’re unaware of. They are either published on an online website, magazine, or newspaper.
In the article, the writer expresses his or her perspective on a certain topic. The articles, mainly, are written to make people aware of a particular topic.

What Is A Paper?
The purpose of writing a research paper is to fill the gaps other authors left while writing on a similar topic.
There’s a structure that one must follow while writing a paper . Before writing a paper, make sure you’ve read the relevant papers.
Another important step is knowing your audience. It’s worth noting that the papers have a different outline of the paper than the essay or article.

Structure of the Paper
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
- References
Steps To Write A Paper
- First of all, you need to pick a topic that you’re interested in. Choosing a topic you’re not interested in is never a good idea.
- Read at least five relevant papers. There’s no need to read the papers thoroughly; you should only go through the abstract part, the introduction paragraph, and the conclusion.
- Write down the findings and gaps that you can work on. Most of your writing covers areas that other papers do not cover.
- The paper always starts with an introduction. Your thesis statement also goes here.
- Since the body part of a paper is almost 8 to 12 pages, you can add as many paragraphs as you want.
- In the end, you conclude your findings and give references to the sources.
What Is An Essay?
The word essay originates from the Latin word ‘exagium’ which refers to the presentation of the case .
An essay is all about giving a verdict on the issue after looking at all sides of the topic with an open mind. However, you need to consider all the evidence .
Essay writing comes with tremendous benefits. It builds a habit of looking at topics from various angles. Additionally, you get an opportunity to express your opinion after thorough research.
There are three parts to the essay: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion.
Introduction
One has to catch the reader’s attention from the first line of the introduction. The purpose of this is to arouse curiosity, which then leads your readers to read more.
In the introduction section, you give a little bit of an overview of the topic you’re writing about. It gives readers an insight into what’s coming next .
This would prevent most people from reading the bottom of your essay. Therefore, it’s really important to keep your audience hooked and curious.
Starting the introduction with some statistics or research findings is the best way to accomplish this. The most important thing to write in the introduction is the thesis statement.
When writing a paragraph in the body section, it’s important to keep sentences linked with each other. They must be coherent.
There should also be backing to your ideas from some relevant studies or sources. The best way to do this is by citing quotations, statistics, and research papers.
Additionally, you should never include irrelevant data in your essay.
The conclusion part includes a summary of the whole essay. You also write your findings or main points in this section of the essay.
Is the Article Different From The Essay?
There is always a thesis statement in an essay, along with reliable sources supporting the argument whereas an article solely represents your idea or opinion.
You’ll see very few articles that are written to persuade someone, while essays are only meant to persuade the readers.

The tone and the structure of the article are indeed different from the essay. The articles are written in simple English, so users of all ages will be able to understand them.
The length of both pieces of writing also differs. There is no limit to the word count when writing an article. An essay can be as long as a page or as short as a paragraph.
It is recommended that an essay be between 1500 and 2000 words in length.
Articles, Papers, and Essays: Differences and Similarities
- Articles, papers, and essays have different purposes in academic and professional writing.
- Articles inform readers on diverse topics. They engagingly present the author’s viewpoint. They’re often found in magazines or online platforms.
- Research papers have sections like abstracts, introductions, reviews, methodologies, findings, and conclusions. They aim to fill gaps in the literature .
- Essays look at different sides of a topic. They give a conclusion backed by facts and careful thinking.
- Articles can be long or short and can be written in many different ways. Papers need a lot of research and must sound serious and smart. Essays use smart arguments to convince people.
- These are different types of writing with different lengths, tones, and reasons for writing. Essays try to convince people of something. Papers are written to share information. Articles give people information that’s easy to understand.
- Knowing these differences is crucial. It helps you communicate well especially when you’re doing school or college work.
- There are different types of academic writing. Each type has its purpose. They each have different ways to make things easy to understand.
- When you get the little details of these types of writing, it makes it easier to understand how they work. This helps both in school and at work.
Other Articles
- Spear and a Lance-What is the difference?
- The Difference Between A High-res Flac 24/96+ and A Normal Uncompressed 16-bit CD
- What’s the Difference Between Tin Foil and Aluminum?
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
José Andrés: Let People Eat

- Share full article
By José Andrés
Mr. Andrés is the founder of World Central Kitchen.
In the worst conditions you can imagine — after hurricanes, earthquakes, bombs and gunfire — the best of humanity shows up. Not once or twice but always.
The seven people killed on a World Central Kitchen mission in Gaza on Monday were the best of humanity. They are not faceless or nameless. They are not generic aid workers or collateral damage in war.
Saifeddin Issam Ayad Abutaha, John Chapman, Jacob Flickinger, Zomi Frankcom, James Henderson, James Kirby and Damian Sobol risked everything for the most fundamentally human activity: to share our food with others.
These are people I served alongside in Ukraine, Turkey, Morocco, the Bahamas, Indonesia, Mexico, Gaza and Israel. They were far more than heroes.
Their work was based on the simple belief that food is a universal human right. It is not conditional on being good or bad, rich or poor, left or right. We do not ask what religion you belong to. We just ask how many meals you need.
From Day 1, we have fed Israelis as well as Palestinians. Across Israel, we have served more than 1.75 million hot meals. We have fed families displaced by Hezbollah rockets in the north. We have fed grieving families from the south. We delivered meals to the hospitals where hostages were reunited with their families. We have called consistently, repeatedly and passionately for the release of all the hostages.
All the while, we have communicated extensively with Israeli military and civilian officials. At the same time, we have worked closely with community leaders in Gaza, as well as Arab nations in the region. There is no way to bring a ship full of food to Gaza without doing so.
That’s how we served more than 43 million meals in Gaza, preparing hot food in 68 community kitchens where Palestinians are feeding Palestinians.
We know Israelis. Israelis, in their heart of hearts, know that food is not a weapon of war.
Israel is better than the way this war is being waged. It is better than blocking food and medicine to civilians. It is better than killing aid workers who had coordinated their movements with the Israel Defense Forces.
The Israeli government needs to open more land routes for food and medicine today. It needs to stop killing civilians and aid workers today. It needs to start the long journey to peace today.
In the worst conditions, after the worst terrorist attack in its history, it’s time for the best of Israel to show up. You cannot save the hostages by bombing every building in Gaza. You cannot win this war by starving an entire population.
We welcome the government’s promise of an investigation into how and why members of our World Central Kitchen family were killed. That investigation needs to start at the top, not just the bottom.
Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has said of the Israeli killings of our team, “It happens in war.” It was a direct attack on clearly marked vehicles whose movements were known by the Israel Defense Forces.
It was also the direct result of a policy that squeezed humanitarian aid to desperate levels. Our team was en route from a delivery of almost 400 tons of aid by sea — our second shipment, funded by the United Arab Emirates, supported by Cyprus and with clearance from the Israel Defense Forces.
The team members put their lives at risk precisely because this food aid is so rare and desperately needed. According to the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification global initiative, half the population of Gaza — 1.1. million people — faces the imminent risk of famine. The team would not have made the journey if there were enough food, traveling by truck across land, to feed the people of Gaza.
The peoples of the Mediterranean and Middle East, regardless of ethnicity and religion, share a culture that values food as a powerful statement of humanity and hospitality — of our shared hope for a better tomorrow.
There’s a reason, at this special time of year, Christians make Easter eggs, Muslims eat an egg at iftar dinners and an egg sits on the Seder plate. This symbol of life and hope reborn in spring extends across religions and cultures.
I have been a stranger at Seder dinners. I have heard the ancient Passover stories about being a stranger in the land of Egypt, the commandment to remember — with a feast before you — that the children of Israel were once slaves.
It is not a sign of weakness to feed strangers; it is a sign of strength. The people of Israel need to remember, at this darkest hour, what strength truly looks like.
José Andrés is a chef and the founder of World Central Kitchen.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
- School Guide
- English Grammar Free Course
- English Grammar Tutorial
- Parts of Speech
- Figure of Speech
- Tenses Chart
- Essay Writing
- Email Writing
- NCERT English Solutions
- English Difference Between
- SSC CGL English Syllabus
- SBI PO English Syllabus
- SBI Clerk English Syllabus
- IBPS PO English Syllabus
- IBPS CLERK English Syllabus
- Get vs Got | Difference Between Get and Got
- Job vs Work | Difference between Job and Work
- Lady vs Girl | Difference Between Lady and Girl
- Difference Between Which and That
- Into vs In To | Difference Between into and in to
- Difference Between Dessert and Desert
- Difference Between Altogether and All Together
- Difference Between Everyone and Everybody
- Difference Between Like and As
- Much vs More | Difference between Much and More
- Lightening vs Lightning | Difference Between Lightening and Lightning
- Difference Between brought and bought
- Difference Between Bear and Bare
- Will vs. Would
- Difference Between Single and Double Quotes
- Difference between May and Might | May vs Might
- Difference Between Concrete and Abstract Nouns
- Difference Between These and Those
- Difference between Till and Until
Difference Between Article and Essay
Articles and essays are both common forms of written communication that are utilized in a variety of sectors of study and vocations. Their goal, organization, and writing style, however, differ.

Articles are pieces of text that are published in a newspaper, magazine, journal, or website, either in print or electronically. It is intended for a big audience. It is founded on surveys, research, data, and analysis, among other things. Articles can be short or somewhat more than 1500 words. It is written with a certain goal in mind and teaches the readers about an idea.
Articles inform readers and keep them up to date by appearing in newspapers, magazines, encyclopedias, and, increasingly, websites. Let us use an example to better understand what an article is. Assume that in a research center, a scientist discovered any new notions and published a brief essay in a popular magazine, so that individuals in the same area found it useful and were also informed about a new thing.
Examples of articles include news articles, feature articles, and opinion pieces.
An essay is a formal and comprehensive piece of literature that describes a particular issue or topic analyzed and discussed. It refers to a short piece of writing on a particular subject. Mainly students in their academics are asked to write essays on some topics as a response to a question or proposition. It does not have a specific readership in mind.
Through essays, the writer or narrator expresses his or her personal views or opinion on a particular topic or a question and it is based on an educational and analytical tone. Let’s take an example and understand what is essay clearly suppose a school student has an exam and in the question paper he has been asked to write something explaining about Floods in India which is an example of an essay.
Examples of essays include academic essays, personal essays, and argumentative essays.
Tabular Differences between Article and Essay:
Conclusion:.
In summary, articles and essays are two different forms of written communication that serve different purposes. Articles are used to provide information about a particular topic, while essays are used to express personal opinions or persuade the reader to take a certain course of action. Understanding the differences between the two can help you choose the appropriate format for your writing task.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

- English-difference-between
- SSC/Banking
- 10 Best Todoist Alternatives in 2024 (Free)
- How to Get Spotify Premium Free Forever on iOS/Android
- Yahoo Acquires Instagram Co-Founders' AI News Platform Artifact
- OpenAI Introduces DALL-E Editor Interface
- Top 10 R Project Ideas for Beginners in 2024
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Newsletters
- Account Activating this button will toggle the display of additional content Account Sign out
That Viral Essay Wasn’t About Age Gaps. It Was About Marrying Rich.
But both tactics are flawed if you want to have any hope of becoming yourself..
Women are wisest, a viral essay in New York magazine’s the Cut argues , to maximize their most valuable cultural assets— youth and beauty—and marry older men when they’re still very young. Doing so, 27-year-old writer Grazie Sophia Christie writes, opens up a life of ease, and gets women off of a male-defined timeline that has our professional and reproductive lives crashing irreconcilably into each other. Sure, she says, there are concessions, like one’s freedom and entire independent identity. But those are small gives in comparison to a life in which a person has no adult responsibilities, including the responsibility to become oneself.
This is all framed as rational, perhaps even feminist advice, a way for women to quit playing by men’s rules and to reject exploitative capitalist demands—a choice the writer argues is the most obviously intelligent one. That other Harvard undergraduates did not busy themselves trying to attract wealthy or soon-to-be-wealthy men seems to flummox her (taking her “high breasts, most of my eggs, plausible deniability when it came to purity, a flush ponytail, a pep in my step that had yet to run out” to the Harvard Business School library, “I could not understand why my female classmates did not join me, given their intelligence”). But it’s nothing more than a recycling of some of the oldest advice around: For women to mold themselves around more-powerful men, to never grow into independent adults, and to find happiness in a state of perpetual pre-adolescence, submission, and dependence. These are odd choices for an aspiring writer (one wonders what, exactly, a girl who never wants to grow up and has no idea who she is beyond what a man has made her into could possibly have to write about). And it’s bad advice for most human beings, at least if what most human beings seek are meaningful and happy lives.
But this is not an essay about the benefits of younger women marrying older men. It is an essay about the benefits of younger women marrying rich men. Most of the purported upsides—a paid-for apartment, paid-for vacations, lives split between Miami and London—are less about her husband’s age than his wealth. Every 20-year-old in the country could decide to marry a thirtysomething and she wouldn’t suddenly be gifted an eternal vacation.
Which is part of what makes the framing of this as an age-gap essay both strange and revealing. The benefits the writer derives from her relationship come from her partner’s money. But the things she gives up are the result of both their profound financial inequality and her relative youth. Compared to her and her peers, she writes, her husband “struck me instead as so finished, formed.” By contrast, “At 20, I had felt daunted by the project of becoming my ideal self.” The idea of having to take responsibility for her own life was profoundly unappealing, as “adulthood seemed a series of exhausting obligations.” Tying herself to an older man gave her an out, a way to skip the work of becoming an adult by allowing a father-husband to mold her to his desires. “My husband isn’t my partner,” she writes. “He’s my mentor, my lover, and, only in certain contexts, my friend. I’ll never forget it, how he showed me around our first place like he was introducing me to myself: This is the wine you’ll drink, where you’ll keep your clothes, we vacation here, this is the other language we’ll speak, you’ll learn it, and I did.”
These, by the way, are the things she says are benefits of marrying older.
The downsides are many, including a basic inability to express a full range of human emotion (“I live in an apartment whose rent he pays and that constrains the freedom with which I can ever be angry with him”) and an understanding that she owes back, in some other form, what he materially provides (the most revealing line in the essay may be when she claims that “when someone says they feel unappreciated, what they really mean is you’re in debt to them”). It is clear that part of what she has paid in exchange for a paid-for life is a total lack of any sense of self, and a tacit agreement not to pursue one. “If he ever betrayed me and I had to move on, I would survive,” she writes, “but would find in my humor, preferences, the way I make coffee or the bed nothing that he did not teach, change, mold, recompose, stamp with his initials.”
Reading Christie’s essay, I thought of another one: Joan Didion’s on self-respect , in which Didion argues that “character—the willingness to accept responsibility for one’s own life—is the source from which self-respect springs.” If we lack self-respect, “we are peculiarly in thrall to everyone we see, curiously determined to live out—since our self-image is untenable—their false notions of us.” Self-respect may not make life effortless and easy. But it means that whenever “we eventually lie down alone in that notoriously un- comfortable bed, the one we make ourselves,” at least we can fall asleep.
It can feel catty to publicly criticize another woman’s romantic choices, and doing so inevitably opens one up to accusations of jealousy or pettiness. But the stories we tell about marriage, love, partnership, and gender matter, especially when they’re told in major culture-shaping magazines. And it’s equally as condescending to say that women’s choices are off-limits for critique, especially when those choices are shared as universal advice, and especially when they neatly dovetail with resurgent conservative efforts to make women’s lives smaller and less independent. “Marry rich” is, as labor economist Kathryn Anne Edwards put it in Bloomberg, essentially the Republican plan for mothers. The model of marriage as a hierarchy with a breadwinning man on top and a younger, dependent, submissive woman meeting his needs and those of their children is not exactly a fresh or groundbreaking ideal. It’s a model that kept women trapped and miserable for centuries.
It’s also one that profoundly stunted women’s intellectual and personal growth. In her essay for the Cut, Christie seems to believe that a life of ease will abet a life freed up for creative endeavors, and happiness. But there’s little evidence that having material abundance and little adversity actually makes people happy, let alone more creatively generativ e . Having one’s basic material needs met does seem to be a prerequisite for happiness. But a meaningful life requires some sense of self, an ability to look outward rather than inward, and the intellectual and experiential layers that come with facing hardship and surmounting it.
A good and happy life is not a life in which all is easy. A good and happy life (and here I am borrowing from centuries of philosophers and scholars) is one characterized by the pursuit of meaning and knowledge, by deep connections with and service to other people (and not just to your husband and children), and by the kind of rich self-knowledge and satisfaction that comes from owning one’s choices, taking responsibility for one’s life, and doing the difficult and endless work of growing into a fully-formed person—and then evolving again. Handing everything about one’s life over to an authority figure, from the big decisions to the minute details, may seem like a path to ease for those who cannot stomach the obligations and opportunities of their own freedom. It’s really an intellectual and emotional dead end.
And what kind of man seeks out a marriage like this, in which his only job is to provide, but very much is owed? What kind of man desires, as the writer cast herself, a raw lump of clay to be molded to simply fill in whatever cracks in his life needed filling? And if the transaction is money and guidance in exchange for youth, beauty, and pliability, what happens when the young, beautiful, and pliable party inevitably ages and perhaps feels her backbone begin to harden? What happens if she has children?
The thing about using youth and beauty as a currency is that those assets depreciate pretty rapidly. There is a nearly endless supply of young and beautiful women, with more added each year. There are smaller numbers of wealthy older men, and the pool winnows down even further if one presumes, as Christie does, that many of these men want to date and marry compliant twentysomethings. If youth and beauty are what you’re exchanging for a man’s resources, you’d better make sure there’s something else there—like the basic ability to provide for yourself, or at the very least a sense of self—to back that exchange up.
It is hard to be an adult woman; it’s hard to be an adult, period. And many women in our era of unfinished feminism no doubt find plenty to envy about a life in which they don’t have to work tirelessly to barely make ends meet, don’t have to manage the needs of both children and man-children, could simply be taken care of for once. This may also explain some of the social media fascination with Trad Wives and stay-at-home girlfriends (some of that fascination is also, I suspect, simply a sexual submission fetish , but that’s another column). Fantasies of leisure reflect a real need for it, and American women would be far better off—happier, freer—if time and resources were not so often so constrained, and doled out so inequitably.
But the way out is not actually found in submission, and certainly not in electing to be carried by a man who could choose to drop you at any time. That’s not a life of ease. It’s a life of perpetual insecurity, knowing your spouse believes your value is decreasing by the day while his—an actual dollar figure—rises. A life in which one simply allows another adult to do all the deciding for them is a stunted life, one of profound smallness—even if the vacations are nice.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates
Published on September 18, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction , a body , and a conclusion . But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
The basics of essay structure, chronological structure, compare-and-contrast structure, problems-methods-solutions structure, signposting to clarify your structure, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about essay structure.
There are two main things to keep in mind when working on your essay structure: making sure to include the right information in each part, and deciding how you’ll organize the information within the body.
Parts of an essay
The three parts that make up all essays are described in the table below.
Order of information
You’ll also have to consider how to present information within the body. There are a few general principles that can guide you here.
The first is that your argument should move from the simplest claim to the most complex . The body of a good argumentative essay often begins with simple and widely accepted claims, and then moves towards more complex and contentious ones.
For example, you might begin by describing a generally accepted philosophical concept, and then apply it to a new topic. The grounding in the general concept will allow the reader to understand your unique application of it.
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay . General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body.
The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the thesis . Ask yourself whether each piece of information advances your argument or provides necessary background. And make sure that the text clearly expresses each piece of information’s relevance.
The sections below present several organizational templates for essays: the chronological approach, the compare-and-contrast approach, and the problems-methods-solutions approach.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The chronological approach (sometimes called the cause-and-effect approach) is probably the simplest way to structure an essay. It just means discussing events in the order in which they occurred, discussing how they are related (i.e. the cause and effect involved) as you go.
A chronological approach can be useful when your essay is about a series of events. Don’t rule out other approaches, though—even when the chronological approach is the obvious one, you might be able to bring out more with a different structure.
Explore the tabs below to see a general template and a specific example outline from an essay on the invention of the printing press.
- Thesis statement
- Discussion of event/period
- Consequences
- Importance of topic
- Strong closing statement
- Claim that the printing press marks the end of the Middle Ages
- Background on the low levels of literacy before the printing press
- Thesis statement: The invention of the printing press increased circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation
- High levels of illiteracy in medieval Europe
- Literacy and thus knowledge and education were mainly the domain of religious and political elites
- Consequence: this discouraged political and religious change
- Invention of the printing press in 1440 by Johannes Gutenberg
- Implications of the new technology for book production
- Consequence: Rapid spread of the technology and the printing of the Gutenberg Bible
- Trend for translating the Bible into vernacular languages during the years following the printing press’s invention
- Luther’s own translation of the Bible during the Reformation
- Consequence: The large-scale effects the Reformation would have on religion and politics
- Summarize the history described
- Stress the significance of the printing press to the events of this period
Essays with two or more main subjects are often structured around comparing and contrasting . For example, a literary analysis essay might compare two different texts, and an argumentative essay might compare the strengths of different arguments.
There are two main ways of structuring a compare-and-contrast essay: the alternating method, and the block method.
Alternating
In the alternating method, each paragraph compares your subjects in terms of a specific point of comparison. These points of comparison are therefore what defines each paragraph.
The tabs below show a general template for this structure, and a specific example for an essay comparing and contrasting distance learning with traditional classroom learning.
- Synthesis of arguments
- Topical relevance of distance learning in lockdown
- Increasing prevalence of distance learning over the last decade
- Thesis statement: While distance learning has certain advantages, it introduces multiple new accessibility issues that must be addressed for it to be as effective as classroom learning
- Classroom learning: Ease of identifying difficulties and privately discussing them
- Distance learning: Difficulty of noticing and unobtrusively helping
- Classroom learning: Difficulties accessing the classroom (disability, distance travelled from home)
- Distance learning: Difficulties with online work (lack of tech literacy, unreliable connection, distractions)
- Classroom learning: Tends to encourage personal engagement among students and with teacher, more relaxed social environment
- Distance learning: Greater ability to reach out to teacher privately
- Sum up, emphasize that distance learning introduces more difficulties than it solves
- Stress the importance of addressing issues with distance learning as it becomes increasingly common
- Distance learning may prove to be the future, but it still has a long way to go
In the block method, each subject is covered all in one go, potentially across multiple paragraphs. For example, you might write two paragraphs about your first subject and then two about your second subject, making comparisons back to the first.
The tabs again show a general template, followed by another essay on distance learning, this time with the body structured in blocks.
- Point 1 (compare)
- Point 2 (compare)
- Point 3 (compare)
- Point 4 (compare)
- Advantages: Flexibility, accessibility
- Disadvantages: Discomfort, challenges for those with poor internet or tech literacy
- Advantages: Potential for teacher to discuss issues with a student in a separate private call
- Disadvantages: Difficulty of identifying struggling students and aiding them unobtrusively, lack of personal interaction among students
- Advantages: More accessible to those with low tech literacy, equality of all sharing one learning environment
- Disadvantages: Students must live close enough to attend, commutes may vary, classrooms not always accessible for disabled students
- Advantages: Ease of picking up on signs a student is struggling, more personal interaction among students
- Disadvantages: May be harder for students to approach teacher privately in person to raise issues
An essay that concerns a specific problem (practical or theoretical) may be structured according to the problems-methods-solutions approach.
This is just what it sounds like: You define the problem, characterize a method or theory that may solve it, and finally analyze the problem, using this method or theory to arrive at a solution. If the problem is theoretical, the solution might be the analysis you present in the essay itself; otherwise, you might just present a proposed solution.
The tabs below show a template for this structure and an example outline for an essay about the problem of fake news.
- Introduce the problem
- Provide background
- Describe your approach to solving it
- Define the problem precisely
- Describe why it’s important
- Indicate previous approaches to the problem
- Present your new approach, and why it’s better
- Apply the new method or theory to the problem
- Indicate the solution you arrive at by doing so
- Assess (potential or actual) effectiveness of solution
- Describe the implications
- Problem: The growth of “fake news” online
- Prevalence of polarized/conspiracy-focused news sources online
- Thesis statement: Rather than attempting to stamp out online fake news through social media moderation, an effective approach to combating it must work with educational institutions to improve media literacy
- Definition: Deliberate disinformation designed to spread virally online
- Popularization of the term, growth of the phenomenon
- Previous approaches: Labeling and moderation on social media platforms
- Critique: This approach feeds conspiracies; the real solution is to improve media literacy so users can better identify fake news
- Greater emphasis should be placed on media literacy education in schools
- This allows people to assess news sources independently, rather than just being told which ones to trust
- This is a long-term solution but could be highly effective
- It would require significant organization and investment, but would equip people to judge news sources more effectively
- Rather than trying to contain the spread of fake news, we must teach the next generation not to fall for it
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Signposting means guiding the reader through your essay with language that describes or hints at the structure of what follows. It can help you clarify your structure for yourself as well as helping your reader follow your ideas.
The essay overview
In longer essays whose body is split into multiple named sections, the introduction often ends with an overview of the rest of the essay. This gives a brief description of the main idea or argument of each section.
The overview allows the reader to immediately understand what will be covered in the essay and in what order. Though it describes what comes later in the text, it is generally written in the present tense . The following example is from a literary analysis essay on Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
Transitions
Transition words and phrases are used throughout all good essays to link together different ideas. They help guide the reader through your text, and an essay that uses them effectively will be much easier to follow.
Various different relationships can be expressed by transition words, as shown in this example.
Because Hitler failed to respond to the British ultimatum, France and the UK declared war on Germany. Although it was an outcome the Allies had hoped to avoid, they were prepared to back up their ultimatum in order to combat the existential threat posed by the Third Reich.
Transition sentences may be included to transition between different paragraphs or sections of an essay. A good transition sentence moves the reader on to the next topic while indicating how it relates to the previous one.
… Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
However , considering the issue of personal interaction among students presents a different picture.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarized in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-structure/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, how to write the body of an essay | drafting & redrafting, transition sentences | tips & examples for clear writing, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Opinion Christine Blasey Ford is no hero, if justice is the measure

An earlier version of this column misspelled the name of Mollie Hemingway. This version has been corrected.
Christine Blasey Ford is promoting her new memoir to acclaim from certain quarters, including a glowing review by the New York Times. Meanwhile, the man she accused of being a witness to her alleged sexual assault by now-Supreme Court Justice Brett M. Kavanaugh more than 40 years ago can’t get his own book reviewed or even mentioned by mainstream newspapers.
You know me. I can’t resist flipping over a cow patty to see what’s underneath.
Ford, you’ll recall, is the California psychologist with two front doors in her house who, in testimony to the Senate Judiciary Committee in 2018, accused Kavanaugh of assaulting her at a high-school-era party while another boy, Mark Judge, allegedly stood by. Judge, who kept his distance and silence during Kavanaugh’s confirmation hearings — in part, he has said , to avoid further harassment by Democratic interlocutors — released his own version of those events and the aftermath in “ The Devil’s Triangle: Mark Judge vs the New American Stasi ” (2022).
As with Kavanaugh, Ford’s accusation against Judge was embraced by most of the news media despite an absence of evidence or corroborating testimony. No one who was supposed to have been at the party where Ford was allegedly assaulted remembered it, or her. Ford herself was unable to nail down the year the party took place (but settled on 1982 after several stabs) or where it was held, how she got there, how she got home or any other details, except that she herself had consumed just one beer, according to her testimony. Her claims against Kavanaugh ultimately were unsubstantiated.

Even so, the awards and accolades for Ford keep coming. During a recent appearance on “The View,” she was nearly sanctified for her “bravery.” Not one of the “View” chin-wags seemed to have done any research. They merely checked the box next to “female” and continued to hold in contempt the male who became a Supreme Court justice. Whoopi Goldberg summed it up: “To face those people the way they were looking and dealing with you, that is bravery under a whole different kind of fire.”
A fair-minded person would also wonder what it was like to be in Kavanaugh’s seat.
And what about Judge? “Roadkill” is the way constitutional lawyer Jonathan Turley described Judge’s invisible role in this tale. Of course, Judge and Kavanaugh were and are distinct people whose adult lives could not be more different. Kavanaugh was the kind of boy who kept a detailed calendar of his busy activities and who had a stellar career as a federal judge.
Judge, who chronicled his heavy-drinking school days in his 1997 book, “ Wasted: Tales of a Gen X Drunk ,” was a teenage alcoholic who had to claw his way to sobriety and suffered accordingly. He told Martha MacCallum during a recent Fox News interview that the effects of being essentially locked in a stockade for public ridicule and condemnation included “suicidal ideation” and “economic issues.”
Under interrogation by Democrats on the Senate Judiciary Committee, Kavanaugh was forced to review his youthful beer consumption, which he admitted was gustatory. He wasn’t alone; Ford was a drinker, too, according to friends and outlined in the deeply researched book “ Justice on Trial ” by Mollie Hemingway and Carrie Severino.
In my own research for a book that never came to fruition, I also learned that Ford was a party girl, which means she and I would have been friends. Her real “best friend” at the time, Leland Keyser, was known as her designated driver in those days, according to several of her friends cited in yet another book, “ The Education of Brett Kavanaugh ” by New York Times writers Robin Pogrebin and Kate Kelly.
A straight-A student and athlete who became a professional golfer, Keyser had her driver’s license at the time of the alleged assault.
Keyser, who felt pressured by Ford’s supporters to confirm Ford’s story, testified to the FBI that she had no recollection of any such party and didn’t know Kavanaugh.
When intimidation didn’t work, Ford and her friends implied that Keyser’s testimony couldn’t be trusted because she had “significant health challenges,” as Ford put it during her testimony. It didn’t take long for the meaning here to become public. Keyser had at one point become addicted to painkillers prescribed for golf-related back and neck injuries. She has suffered years of surgeries and pain that continues today, thanks to her commitment to recovery. No meds. She also has had to cope with the psychological effects of her persecution by the anti-Kavanaugh brigade. At least one person from Team Ford tried to persuade her to adjust her story. She refused.
Meanwhile, after five years of silence, Judge has emerged from his bunker with both barrels blazing. One can stand only so much smearing. He was, after all, accused in the public arena of variously urging Kavanaugh on or trying to stop him, all the while laughing, according to Ford. Like Kavanaugh, Judge was presumed guilty — a tragic by-product of the “believe the woman” orthodoxy that emerged during the #MeToo movement — and justly wants to have his say.
It takes guts to try to breach the #MeToo iron curtain, as Judge is attempting to do. It takes no courage at all to enrich yourself at other people’s expense, as Ford has done. Even if she believes her own story or suffered some traumatic event at some time, in the absence of evidence or corroboration, a measure of doubt is called for. This doesn’t necessarily mean she lied, as Hemingway and Severino have noted.
Both Judge and Keyser, it seems, deserve the applause Ford is receiving for perpetuating a questionable history that has damaged so many people, not to mention the judicial system she says she has sought to protect. We know the truth is otherwise, thanks to a video capture of Ford’s lawyer, Debra Katz, saying that her client wanted to block Kavanaugh because of fears he would vote to reverse Roe v. Wade . Ford’s fears might have been justified, but her tactics — which have netted her $1 million in donations plus overnights at Oprah’s — were not.
Nothing good grows under a cow patty, but Ford sure did step in one.
- Opinion | Here’s why Americans under 40 are so disillusioned with capitalism April 1, 2024 Opinion | Here’s why Americans under 40 are so disillusioned with capitalism April 1, 2024
- Opinion | What we have learned about the Supreme Court’s right-wingers April 1, 2024 Opinion | What we have learned about the Supreme Court’s right-wingers April 1, 2024
- Opinion | This Easter, let’s not try to pretend Jesus was a ‘Palestinian Jew’ March 28, 2024 Opinion | This Easter, let’s not try to pretend Jesus was a ‘Palestinian Jew’ March 28, 2024


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cite this Scribbr article. If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the "Cite this Scribbr article" button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator. Bryson, S. (2023, July 23). Example of a Great Essay | Explanations, Tips & Tricks. Scribbr.
An article is nothing but a piece of writing commonly found in newspapers or websites which contain fact-based information on a specific topic. It is published with the aim of making the reader aware of something and keeping them up to date. An essay is a literary work, which often discusses ideas, experiences and concepts in a clear and coherent way. . It reflects the author's personal view ...
In an academic essay, you typically introduce a journal article in the first sentence of a paragraph. Then, use the sentences that follow to show how the material from the article relates to the rest of your essay. Submit a Tip. All tip submissions are carefully reviewed before being published. Submit.
In composition studies, an article is a short work of nonfiction that typically appears in a magazine or newspaper or on a website. Unlike essays, which often highlight the subjective impressions of the author (or narrator ), articles are commonly written from an objective point of view. Articles include news items, feature stories, reports ...
Using "article" instead of "essay". An article is a written work that provides information on a topic, while an essay is a more formal piece of writing that presents an argument or point of view. Make sure you understand the purpose of your writing. If you're simply providing information, use the term "article.".
A series about ways to take life off "hard mode," from changing careers to gaming the stock market, moving back home, or simply marrying wisely. Illustration: Celine Ka Wing Lau. In the summer, in the south of France, my husband and I like to play, rather badly, the lottery. We take long, scorching walks to the village — gratuitous beauty ...
Basic rules. This is a simple list, but understanding it and remembering it is crucial to using articles correctly. Rule # 1: Every time a noun is mentioned, the writer is referring to: All of them everywhere ("generic" reference), One of many, ("indefinite" reference) or. This one exactly ("definite" reference)
The Issues of Defining an Article, An Essay And A Paper The point is, in different situations of communication and in a different context, article, paper and essay can be interchangeable notions. For example, experimental sciences tend to use words 'article' and 'paper' for pieces of writing that non-experimental sciences would call ...
Essays are typically 1-3 pages long. Articles vary in length but run longer than essays. Papers typically range from 10 to 15 pages or more. It's important to note that essay writer services have very different writing styles. Some writers write with a conversational tone, while others use a formal style for essays and articles.
An article is a piece of writing that educates, informs and/or colorfully illustrates a topic using purpose-driven writing, provocative insights and a unique perspective designed to engage an audience. Articles also can be… Blog posts; Branded/native content; Content ladders; Essays; Guides; FAQs; Features; How-to's; Interviews; Listicles ...
Like adjectives, articles modify nouns. English has two articles: the and a/an. The is used to refer to specific or particular nouns; a/an is used to modify non-specific or non-particular nouns. We call the the definite article and a/an the indefinite article. the = definite article. a/an = indefinite article.
Before you start writing, you will need to take some steps to get ready for your critique: Choose an article that meets the criteria outlined by your instructor. Read the article to get an understanding of the main idea. Read the article again with a critical eye. As you read, take note of the following: What are the credentials of the author/s?
The tone and the structure of the article are indeed different from the essay. The articles are written in simple English, so users of all ages will be able to understand them. The length of both pieces of writing also differs. There is no limit to the word count when writing an article. An essay can be as long as a page or as short as a paragraph.
By José Andrés. Mr. Andrés is the founder of World Central Kitchen. In the worst conditions you can imagine — after hurricanes, earthquakes, bombs and gunfire — the best of humanity shows ...
Article. Essay. Written on a specific topic. Expresses the author's opinion on a particular topic. Informative in nature. Persuasive in nature. Usually published in a magazine, newspaper, or website. Can be published in various formats, such as a book or academic journal. Can be written in a formal or informal style.
The Image Bank/Getty Images. Women are wisest, a viral essay in New York magazine's the Cut argues, to maximize their most valuable cultural assets— youth and beauty—and marry older men when ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
An essay is a composition which belongs to a specific issue, or topic. 2. Articles tend to be objective. Essays tend to be subjective. 3. The purpose of the article is to tell the readers about some prospects, information and concepts. The major goal of the essay is to respond to a query. 4.
March 31, 2024 at 6:30 a.m. EDT. Christine Blasey Ford at a Senate Judiciary Committee hearing in September 2018. (Melina Mara/The Washington Post) Christine Blasey Ford is promoting her new ...