13.5 Research Process: Making Notes, Synthesizing Information, and Keeping a Research Log
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Employ the methods and technologies commonly used for research and communication within various fields.
- Practice and apply strategies such as interpretation, synthesis, response, and critique to compose texts that integrate the writer’s ideas with those from appropriate sources.
- Analyze and make informed decisions about intellectual property based on the concepts that motivate them.
- Apply citation conventions systematically.
As you conduct research, you will work with a range of “texts” in various forms, including sources and documents from online databases as well as images, audio, and video files from the Internet. You may also work with archival materials and with transcribed and analyzed primary data. Additionally, you will be taking notes and recording quotations from secondary sources as you find materials that shape your understanding of your topic and, at the same time, provide you with facts and perspectives. You also may download articles as PDFs that you then annotate. Like many other students, you may find it challenging to keep so much material organized, accessible, and easy to work with while you write a major research paper. As it does for many of those students, a research log for your ideas and sources will help you keep track of the scope, purpose, and possibilities of any research project.
A research log is essentially a journal in which you collect information, ask questions, and monitor the results. Even if you are completing the annotated bibliography for Writing Process: Informing and Analyzing , keeping a research log is an effective organizational tool. Like Lily Tran’s research log entry, most entries have three parts: a part for notes on secondary sources, a part for connections to the thesis or main points, and a part for your own notes or questions. Record source notes by date, and allow room to add cross-references to other entries.

Summary of Assignment: Research Log
Your assignment is to create a research log similar to the student model. You will use it for the argumentative research project assigned in Writing Process: Integrating Research to record all secondary source information: your notes, complete publication data, relation to thesis, and other information as indicated in the right-hand column of the sample entry.
Another Lens. A somewhat different approach to maintaining a research log is to customize it to your needs or preferences. You can apply shading or color coding to headers, rows, and/or columns in the three-column format (for colors and shading). Or you can add columns to accommodate more information, analysis, synthesis, or commentary, formatting them as you wish. Consider adding a column for questions only or one for connections to other sources. Finally, consider a different visual format , such as one without columns. Another possibility is to record some of your comments and questions so that you have an aural rather than a written record of these.
Writing Center
At this point, or at any other point during the research and writing process, you may find that your school’s writing center can provide extensive assistance. If you are unfamiliar with the writing center, now is a good time to pay your first visit. Writing centers provide free peer tutoring for all types and phases of writing. Discussing your research with a trained writing center tutor can help you clarify, analyze, and connect ideas as well as provide feedback on works in progress.
Quick Launch: Beginning Questions
You may begin your research log with some open pages in which you freewrite, exploring answers to the following questions. Although you generally would do this at the beginning, it is a process to which you likely will return as you find more information about your topic and as your focus changes, as it may during the course of your research.
- What information have I found so far?
- What do I still need to find?
- Where am I most likely to find it?
These are beginning questions. Like Lily Tran, however, you will come across general questions or issues that a quick note or freewrite may help you resolve. The key to this section is to revisit it regularly. Written answers to these and other self-generated questions in your log clarify your tasks as you go along, helping you articulate ideas and examine supporting evidence critically. As you move further into the process, consider answering the following questions in your freewrite:
- What evidence looks as though it best supports my thesis?
- What evidence challenges my working thesis?
- How is my thesis changing from where it started?
Creating the Research Log
As you gather source material for your argumentative research paper, keep in mind that the research is intended to support original thinking. That is, you are not writing an informational report in which you simply supply facts to readers. Instead, you are writing to support a thesis that shows original thinking, and you are collecting and incorporating research into your paper to support that thinking. Therefore, a research log, whether digital or handwritten, is a great way to keep track of your thinking as well as your notes and bibliographic information.
In the model below, Lily Tran records the correct MLA bibliographic citation for the source. Then, she records a note and includes the in-text citation here to avoid having to retrieve this information later. Perhaps most important, Tran records why she noted this information—how it supports her thesis: The human race must turn to sustainable food systems that provide healthy diets with minimal environmental impact, starting now . Finally, she makes a note to herself about an additional visual to include in the final paper to reinforce the point regarding the current pressure on food systems. And she connects the information to other information she finds, thus cross-referencing and establishing a possible synthesis. Use a format similar to that in Table 13.4 to begin your own research log.
Types of Research Notes
Taking good notes will make the research process easier by enabling you to locate and remember sources and use them effectively. While some research projects requiring only a few sources may seem easily tracked, research projects requiring more than a few sources are more effectively managed when you take good bibliographic and informational notes. As you gather evidence for your argumentative research paper, follow the descriptions and the electronic model to record your notes. You can combine these with your research log, or you can use the research log for secondary sources and your own note-taking system for primary sources if a division of this kind is helpful. Either way, be sure to include all necessary information.
Bibliographic Notes
These identify the source you are using. When you locate a useful source, record the information necessary to find that source again. It is important to do this as you find each source, even before taking notes from it. If you create bibliographic notes as you go along, then you can easily arrange them in alphabetical order later to prepare the reference list required at the end of formal academic papers. If your instructor requires you to use MLA formatting for your essay, be sure to record the following information:
- Title of source
- Title of container (larger work in which source is included)
- Other contributors
- Publication date
When using MLA style with online sources, also record the following information:
- Date of original publication
- Date of access
- DOI (A DOI, or digital object identifier, is a series of digits and letters that leads to the location of an online source. Articles in journals are often assigned DOIs to ensure that the source can be located, even if the URL changes. If your source is listed with a DOI, use that instead of a URL.)
It is important to understand which documentation style your instructor will require you to use. Check the Handbook for MLA Documentation and Format and APA Documentation and Format styles . In addition, you can check the style guide information provided by the Purdue Online Writing Lab .
Informational Notes
These notes record the relevant information found in your sources. When writing your essay, you will work from these notes, so be sure they contain all the information you need from every source you intend to use. Also try to focus your notes on your research question so that their relevance is clear when you read them later. To avoid confusion, work with separate entries for each piece of information recorded. At the top of each entry, identify the source through brief bibliographic identification (author and title), and note the page numbers on which the information appears. Also helpful is to add personal notes, including ideas for possible use of the information or cross-references to other information. As noted in Writing Process: Integrating Research , you will be using a variety of formats when borrowing from sources. Below is a quick review of these formats in terms of note-taking processes. By clarifying whether you are quoting directly, paraphrasing, or summarizing during these stages, you can record information accurately and thus take steps to avoid plagiarism.
Direct Quotations, Paraphrases, and Summaries
A direct quotation is an exact duplication of the author’s words as they appear in the original source. In your notes, put quotation marks around direct quotations so that you remember these words are the author’s, not yours. One advantage of copying exact quotations is that it allows you to decide later whether to include a quotation, paraphrase, or summary. ln general, though, use direct quotations only when the author’s words are particularly lively or persuasive.
A paraphrase is a restatement of the author’s words in your own words. Paraphrase to simplify or clarify the original author’s point. In your notes, use paraphrases when you need to record details but not exact words.
A summary is a brief condensation or distillation of the main point and most important details of the original source. Write a summary in your own words, with facts and ideas accurately represented. A summary is useful when specific details in the source are unimportant or irrelevant to your research question. You may find you can summarize several paragraphs or even an entire article or chapter in just a few sentences without losing useful information. It is a good idea to note when your entry contains a summary to remind you later that it omits detailed information. See Writing Process Integrating Research for more detailed information and examples of quotations, paraphrases, and summaries and when to use them.
Other Systems for Organizing Research Logs and Digital Note-Taking
Students often become frustrated and at times overwhelmed by the quantity of materials to be managed in the research process. If this is your first time working with both primary and secondary sources, finding ways to keep all of the information in one place and well organized is essential.
Because gathering primary evidence may be a relatively new practice, this section is designed to help you navigate the process. As mentioned earlier, information gathered in fieldwork is not cataloged, organized, indexed, or shelved for your convenience. Obtaining it requires diligence, energy, and planning. Online resources can assist you with keeping a research log. Your college library may have subscriptions to tools such as Todoist or EndNote. Consult with a librarian to find out whether you have access to any of these. If not, use something like the template shown in Figure 13.8 , or another like it, as a template for creating your own research notes and organizational tool. You will need to have a record of all field research data as well as the research log for all secondary sources.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/13-5-research-process-making-notes-synthesizing-information-and-keeping-a-research-log
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Writing a Research Paper: 5. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- Getting Started
- 1. Topic Ideas
- 2. Thesis Statement & Outline
- 3. Appropriate Sources
- 4. Search Techniques
- 5. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- 6. Evaluating Sources
- 7. Citations & Plagiarism
- 8. Writing Your Research Paper
Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
How to take notes and document sources.
Note taking is a very important part of the research process. It will help you:
- keep your ideas and sources organized
- effectively use the information you find
- avoid plagiarism
When you find good information to be used in your paper:
- Read the text critically, think how it is related to your argument, and decide how you are going to use it in your paper.
- Select the material that is relevant to your argument.
- Copy the original text for direct quotations or briefly summarize the content in your own words, and make note of how you will use it.
- Copy the citation or publication information of the source.
- << Previous: 4. Search Techniques
- Next: 6. Evaluating Sources >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 5:26 PM
- URL: https://kenrick.libguides.com/writing-a-research-paper
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Note-taking for Research
As you determine which sources you will rely on most, it is important to establish a system for keeping track of your sources and taking notes. There are several ways to go about it, and no one system is necessarily superior. What matters is that you keep materials in order; record bibliographical information you will need later; and take detailed, organized notes.
Keeping Track of Your Sources
As you conduct research, taking time to keep track of source information and to organize that information now will help ensure that you are not scrambling to find it at the last minute, which easily leads to problems ranging from incomplete essays to plagiarism. Throughout your research, record bibliographical information for each source as soon as you begin using it. Maintaining an electronic list (even by copying and pasting information) can be quick and efficient, but you may instead feel more in control of the information you’ve collected by using pen-and-paper methods, such as a notebook or note cards.
The table below shows the kinds of details you should record for commonly used source types. Use these details to develop a working bibliography —a preliminary list of sources that you will later use to develop the final Works Cited page of your essay.
Details for Commonly Used Source Types
Your research may involve less common types of sources not listed above. For additional information on citing different sources, see the chapter MLA Format and Citation.
Taking Notes Efficiently
Good researchers stay focused and organized as they gather information from sources. Before you begin taking notes, take a moment to step back and think about your goal as a researcher—to find information that will help you answer your research question. When you write your essay, you will present your conclusions about the subject supported by your research. That goal will determine what information you record and how you organize it.
Writers sometimes get caught up in taking extensive notes, so much so that they lose sight of how their notes relate to the questions and ideas they started out with. Remember that you do not need to write down every detail from your reading. Focus on finding and recording details that will help you answer your research questions. The following strategies will help you take notes efficiently.
Use Headings to Organize Ideas
Whether you use old-fashioned index cards or organize your notes using word-processing software, such as MS Word or Google Docs, record just one major point from each source at a time, and use a heading to summarize the information covered. Keep all your notes in one file, digital or otherwise. Doing so will help you identify connections among different pieces of information. It will also help you make connections between your notes and the research questions and subtopics you identified earlier.
Know When to Summarize, Paraphrase, or Directly Quote a Source
Your notes will fall under three categories—summary notes, paraphrased information, and direct quotations from your sources. Effective researchers make choices about which type of notes is most appropriate for their purpose.
- Summary notes give an overview of the main ideas in a source in a few sentences or a short paragraph. A summary is considerably shorter than the original text and captures only the major ideas. Use summary notes when you do not need to record specific details but you intend to refer to broad concepts the author discusses.
- Paraphrased notes restate a fact or idea from a source using your own words and sentence structure, particularly in a way that better suits your purpose and audience than the way the original source said it.
- Direct quotations use the exact wording used by the original source and enclose the quoted material in quotation marks. It is a good strategy to copy direct quotations when an author expresses an idea in an especially lively or memorable way. However, do not rely exclusively on direct quotations in your note taking.
Most of your notes should be paraphrased from the original source. Paraphrasing as you take notes is usually a better strategy than copying direct quotations, because it forces you to think through the information in your source and understand it well enough to restate it. In short, it helps you stay engaged with the material instead of simply copying and pasting. For more information on this, see the section Summary, Paraphrasis, and Quotation.
Maintain Complete, Accurate Notes
Regardless of the format used, any notes you take should include enough information to help you organize ideas and locate them instantly in the original text if you need to review them. Make sure your notes include the vital bibliographic information noted above.
Throughout the process of taking notes, be scrupulous about making sure you have correctly attributed each idea to its source. Always include source information so you know exactly which ideas came from which sources. Use quotation marks to set off any words for phrases taken directly from the original text. If you add your own responses and ideas, make sure they are distinct from ideas you quoted or paraphrased.
Finally, make sure your notes accurately reflect the content of the original text. Make sure quoted material is copied verbatim. If you omit words from a quotation, use ellipses to show the omission and make sure the omission does not change the author’s meaning. Paraphrase ideas carefully, and check your paraphrased notes against the original text to make sure that you have restated the author’s ideas accurately in your own words. For more information on this, see the section Summary, Paraphrasis, and Quotation.
Use a System That Works for You
There are several formats you can use to take notes. No technique is necessarily better than the others—it is more important to choose a format you are comfortable using. Choosing the format that works best for you will ensure your notes are organized, complete, and accurate. Consider implementing one of these formats when you begin taking notes:
- Use index cards. This traditional format involves writing each note on a separate index card. It takes more time than copying and pasting into an electronic document, which encourages you to be selective in choosing which ideas to record. Recording notes on separate cards makes it easy to later organize your notes according to major topics. Some writers color-code their cards to make them still more organized.
- Use note-taking software. Word-processing and office software packages often include different types of note-taking software. Although you may need to set aside some time to learn the software, this method combines the speed of typing with the same degree of organization associated with handwritten note cards.
- Maintain a research notebook. Instead of using index cards or electronic note cards, you may wish to keep a notebook or electronic folder, allotting a few pages (or one file) for each of your sources. This method makes it easy to create a separate column or section of the document where you add your responses to the information you encounter in your research.
- Annotate your sources. This method involves making handwritten notes in the margins of sources that you have printed or photocopied. If using electronic sources, you can make comments within the source document. For example, you might add comment boxes to a PDF version of an article. This method works best for experienced researchers who have already thought a great deal about the topic because it can be difficult to organize your notes later when starting your draft.
Choose one of the methods from the list to use for taking notes. Continue gathering sources and taking notes. In the next section, you will learn strategies for organizing and synthesizing the information you have found.
The Writing Textbook Copyright © 2021 by Josh Woods, editor and contributor, as well as an unnamed author (by request from the original publisher), and other authors named separately is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1916 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,380 quotes across 1916 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!


Research Paper: A step-by-step guide: 6. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- 1. Getting Started
- 2. Topic Ideas
- 3. Thesis Statement & Outline
- 4. Appropriate Sources
- 5. Search Techniques
- 6. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- 7. Evaluating Sources
- 8. Citations & Plagiarism
- 9. Writing Your Research Paper

Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
How to take notes and document sources.
Note taking is a very important part of the research process. It will help you:
- keep your ideas and sources organized
- effectively use the information you find
- avoid plagiarism
When you find good information to be used in your paper:
- Read the text critically, think how it is related to your argument, and decide how you are going to use it in your paper.
- Select the material that is relevant to your argument.
- Copy the original text for direct quotations or briefly summarize the content in your own words, and make note of how you will use it.
- Copy the citation or publication information of the source.
There are different ways to take notes and organize your research. Check out this video, and try different strategies to find what works best for you.
- << Previous: 5. Search Techniques
- Next: 7. Evaluating Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2023 12:12 PM
- URL: https://butte.libguides.com/ResearchPaper
- Writing Home
- Writing Advice Home
Taking Notes from Research Reading
- Printable PDF Version
- Fair-Use Policy
If you take notes efficiently, you can read with more understanding and also save time and frustration when you come to write your paper. These are three main principles
1. Know what kind of ideas you need to record
Focus your approach to the topic before you start detailed research. Then you will read with a purpose in mind, and you will be able to sort out relevant ideas.
- First, review the commonly known facts about your topic, and also become aware of the range of thinking and opinions on it. Review your class notes and textbook and browse in an encyclopaedia or other reference work.
- Try making a preliminary list of the subtopics you would expect to find in your reading. These will guide your attention and may come in handy as labels for notes.
- Choose a component or angle that interests you, perhaps one on which there is already some controversy. Now formulate your research question. It should allow for reasoning as well as gathering of information—not just what the proto-Iroquoians ate, for instance, but how valid the evidence is for early introduction of corn. You may even want to jot down a tentative thesis statement as a preliminary answer to your question. (See Using Thesis Statements .)
- Then you will know what to look for in your research reading: facts and theories that help answer your question, and other people’s opinions about whether specific answers are good ones.
2. Don’t write down too much
Your essay must be an expression of your own thinking, not a patchwork of borrowed ideas. Plan therefore to invest your research time in understanding your sources and integrating them into your own thinking. Your note cards or note sheets will record only ideas that are relevant to your focus on the topic; and they will mostly summarize rather than quote.
- Copy out exact words only when the ideas are memorably phrased or surprisingly expressed—when you might use them as actual quotations in your essay.
- Otherwise, compress ideas in your own words . Paraphrasing word by word is a waste of time. Choose the most important ideas and write them down as labels or headings. Then fill in with a few subpoints that explain or exemplify.
- Don’t depend on underlining and highlighting. Find your own words for notes in the margin (or on “sticky” notes).
3. Label your notes intelligently
Whether you use cards or pages for note-taking, take notes in a way that allows for later use.
- Save bother later by developing the habit of recording bibliographic information in a master list when you begin looking at each source (don’t forget to note book and journal information on photocopies). Then you can quickly identify each note by the author’s name and page number; when you refer to sources in the essay you can fill in details of publication easily from your master list. Keep a format guide handy (see Documentation Formats ).
- Try as far as possible to put notes on separate cards or sheets. This will let you label the topic of each note. Not only will that keep your notetaking focussed, but it will also allow for grouping and synthesizing of ideas later. It is especially satisfying to shuffle notes and see how the conjunctions create new ideas—yours.
- Leave lots of space in your notes for comments of your own—questions and reactions as you read, second thoughts and cross-references when you look back at what you’ve written. These comments can become a virtual first draft of your paper.
Office of Undergraduate Research
- Office of Undergraduate Research FAQ's
- URSA Engage
- Resources for Students
- Resources for Faculty
- Engaging in Research
- Presenting Your Research
- Earn Money by Participating in Research Studies
- Transcript Notation
- Student Publications
How to take Research Notes
How to take research notes.
Your research notebook is an important piece of information useful for future projects and presentations. Maintaining organized and legible notes allows your research notebook to be a valuable resource to you and your research group. It allows others and yourself to replicate experiments, and it also serves as a useful troubleshooting tool. Besides it being an important part of the research process, taking detailed notes of your research will help you stay organized and allow you to easily review your work.
Here are some common reasons to maintain organized notes:
- Keeps a record of your goals and thoughts during your research experiments.
- Keeps a record of what worked and what didn't in your research experiments.
- Enables others to use your notes as a guide for similar procedures and techniques.
- A helpful tool to reference when writing a paper, submitting a proposal, or giving a presentation.
- Assists you in answering experimental questions.
- Useful to efficiently share experimental approaches, data, and results with others.
Before taking notes:
- Ask your research professor what note-taking method they recommend or prefer.
- Consider what type of media you'll be using to take notes.
- Once you have decided on how you'll be taking notes, be sure to keep all of your notes in one place to remain organized.
- Plan on taking notes regularly (meetings, important dates, procedures, journal/manuscript revisions, etc.).
- This is useful when applying to programs or internships that ask about your research experience.
Note Taking Tips:
Taking notes by hand:.
- Research notebooks don’t belong to you so make sure your notes are legible for others.
- Use post-it notes or tabs to flag important sections.
- Start sorting your notes early so that you don't become backed up and disorganized.
- Only write with a pen as pencils aren’t permanent & sharpies can bleed through.
- Make it a habit to write in your notebook and not directly on sticky notes or paper towels. Rewriting notes can waste time and sometimes lead to inaccurate data or results.
Taking Notes Electronically
- Make sure your device is charged and backed up to store data.
- Invest in note-taking apps or E-Ink tablets
- Create shortcuts to your folders so you have easier access
- Create outlines.
- Keep your notes short and legible.
Note Taking Tips Continued:
Things to avoid.
- Avoid using pencils or markers that may bleed through.
- Avoid erasing entries. Instead, draw a straight line through any mistakes and write the date next to the crossed-out information.
- Avoid writing in cursive.
- Avoid delaying your entries so you don’t fall behind and forget information.
Formatting Tips
- Use bullet points to condense your notes to make them simpler to access or color-code them.
- Tracking your failures and mistakes can improve your work in the future.
- If possible, take notes as you’re experimenting or make time at the end of each workday to get it done.
- Record the date at the start of every day, including all dates spent on research.
Types of media to use when taking notes:
Traditional paper notebook.
- Pros: Able to take quick notes, convenient access to notes, cheaper option
- Cons: Requires a table of contents or tabs as it is not easily searchable, can get damaged easily, needs to be scanned if making a digital copy
Electronic notebook
- Apple Notes
- Pros: Easily searchable, note-taking apps available, easy to edit & customize
- Cons: Can be difficult to find notes if they are unorganized, not as easy to take quick notes, can be a more expensive option
Combination of both
Contact info.
618 Kerr Administration Building Corvallis, OR 97331
541-737-5105
How to Do Research: A Step-By-Step Guide: 4a. Take Notes
- Get Started
- 1a. Select a Topic
- 1b. Develop Research Questions
- 1c. Identify Keywords
- 1d. Find Background Information
- 1e. Refine a Topic
- 2a. Search Strategies
- 2d. Articles
- 2e. Videos & Images
- 2f. Databases
- 2g. Websites
- 2h. Grey Literature
- 2i. Open Access Materials
- 3a. Evaluate Sources
- 3b. Primary vs. Secondary
- 3c. Types of Periodicals
- 4a. Take Notes
- 4b. Outline the Paper
- 4c. Incorporate Source Material
- 5a. Avoid Plagiarism
- 5b. Zotero & MyBib
- 5c. MLA Formatting
- 5d. MLA Citation Examples
- 5e. APA Formatting
- 5f. APA Citation Examples
- 5g. Annotated Bibliographies
Note Taking in Bibliographic Management Tools
We encourage students to use bibliographic citation management tools (such as Zotero, EasyBib and RefWorks) to keep track of their research citations. Each service includes a note-taking function. Find more information about citation management tools here . Whether or not you're using one of these, the tips below will help you.
Tips for Taking Notes Electronically
- Try using a bibliographic citation management tool to keep track of your sources and to take notes.
- As you add sources, put them in the format you're using (MLA, APA, Chicago, etc.).
- Group sources by publication type (i.e., book, article, website).
- Number each source within the publication type group.
- For websites, include the URL information and the date you accessed each site.
- Next to each idea, include the source number from the Works Cited file and the page number from the source. See the examples below. Note that #A5 and #B2 refer to article source 5 and book source 2 from the Works Cited file.
#A5 p.35: 76.69% of the hyperlinks selected from homepage are for articles and the catalog #B2 p.76: online library guides evolved from the paper pathfinders of the 1960s
- When done taking notes, assign keywords or sub-topic headings to each idea, quote or summary.
- Use the copy and paste feature to group keywords or sub-topic ideas together.
- Back up your master list and note files frequently!
Tips for Taking Notes by Hand
- Use index cards to keep notes and track sources used in your paper.
- Include the citation (i.e., author, title, publisher, date, page numbers, etc.) in the format you're using. It will be easier to organize the sources alphabetically when creating the Works Cited page.
- Number the source cards.
- Use only one side to record a single idea, fact or quote from one source. It will be easier to rearrange them later when it comes time to organize your paper.
- Include a heading or key words at the top of the card.
- Include the Work Cited source card number.
- Include the page number where you found the information.
- Use abbreviations, acronyms, or incomplete sentences to record information to speed up the notetaking process.
- Write down only the information that answers your research questions.
- Use symbols, diagrams, charts or drawings to simplify and visualize ideas.
Forms of Notetaking
Use one of these notetaking forms to capture information:
- Summarize : Capture the main ideas of the source succinctly by restating them in your own words.
- Paraphrase : Restate the author's ideas in your own words.
- Quote : Copy the quotation exactly as it appears in the original source. Put quotation marks around the text and note the name of the person you are quoting.
Example of a Work Cited Card
Example notecard.
- << Previous: Step 4: Write
- Next: 4b. Outline the Paper >>
- Last Updated: Feb 21, 2024 11:01 AM
- URL: https://libguides.elmira.edu/research
Research Guides
Gould library, reading well and taking research notes.
- How to read for college
- How to take research notes
- How to use sources in your writing
- Tools for note taking and annotations
- Mobile apps for notes and annotations
- Assistive technology
- How to cite your sources
Be Prepared: Keep track of which notes are direct quotes, which are summary, and which are your own thoughts. For example, enclose direct quotes in quotation marks, and enclose your own thoughts in brackets. That way you'll never be confused when you're writing.
Be Clear: Make sure you have noted the source and page number!
Be Organized: Keep your notes organized but in a single place so that you can refer back to notes about other readings at the same time.
Be Consistent: You'll want to find specific notes later, and one way to do that is to be consistent in the way you describe things. If you use consistent terms or tags or keywords, you'll be able to find your way back more easily.
Recording what you find

Take full notes
Whether you take notes on cards, in a notebook, or on the computer, it's vital to record information accurately and completely. Otherwise, you won't be able to trust your own notes. Most importantly, distinguish between (1) direct quotation; (2) paraphrases and summaries of the text; and (3) your own thoughts. On a computer, you have many options for making these distinctions, such as parentheses, brackets, italic or bold text, etc.
Know when to quote, paraphrase, and summarize
- Summarize when you only need to remember the main point of the passage, chapter, etc.
- Paraphrase when you are able to able to clearly state a source's point or meaning in your own words.
- Quote exactly when you need the author's exact words or authority as evidience to back up your claim. You may also want to be sure and use the author's exact wording, either because they stated their point so well, or because you want to refute that point and need to demonstrate you aren't misrepresenting the author's words.
Get the context right
Don't just record the author's words or ideas; be sure and capture the context and meaning that surrounds those ideas as well. It can be easy to take a short quote from an author that completely misrepresents his or her actual intentions if you fail to take the context into account. You should also be sure to note when the author is paraphrasing or summarizing another author's point of view--don't accidentally represent those ideas as the ideas of the author.
Example of reading notes
Here is an example of reading notes taken in Evernote, with citation and page numbers noted as well as quotation marks for direct quotes and brackets around the reader's own thoughts.

- << Previous: How to read for college
- Next: How to use sources in your writing >>
- Last Updated: Feb 7, 2024 12:22 PM
- URL: https://gouldguides.carleton.edu/activereading
Questions? Contact [email protected]

Powered by Springshare.
Writing a Research Paper
This page lists some of the stages involved in writing a library-based research paper.
Although this list suggests that there is a simple, linear process to writing such a paper, the actual process of writing a research paper is often a messy and recursive one, so please use this outline as a flexible guide.
Discovering, Narrowing, and Focusing a Researchable Topic
- Try to find a topic that truly interests you
- Try writing your way to a topic
- Talk with your course instructor and classmates about your topic
- Pose your topic as a question to be answered or a problem to be solved
Finding, Selecting, and Reading Sources
You will need to look at the following types of sources:
- library catalog, periodical indexes, bibliographies, suggestions from your instructor
- primary vs. secondary sources
- journals, books, other documents
Grouping, Sequencing, and Documenting Information
The following systems will help keep you organized:
- a system for noting sources on bibliography cards
- a system for organizing material according to its relative importance
- a system for taking notes
Writing an Outline and a Prospectus for Yourself
Consider the following questions:
- What is the topic?
- Why is it significant?
- What background material is relevant?
- What is my thesis or purpose statement?
- What organizational plan will best support my purpose?
Writing the Introduction
In the introduction you will need to do the following things:
- present relevant background or contextual material
- define terms or concepts when necessary
- explain the focus of the paper and your specific purpose
- reveal your plan of organization
Writing the Body
- Use your outline and prospectus as flexible guides
- Build your essay around points you want to make (i.e., don’t let your sources organize your paper)
- Integrate your sources into your discussion
- Summarize, analyze, explain, and evaluate published work rather than merely reporting it
- Move up and down the “ladder of abstraction” from generalization to varying levels of detail back to generalization
Writing the Conclusion
- If the argument or point of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to add your points up, to explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction.
- Perhaps suggest what about this topic needs further research.
Revising the Final Draft
- Check overall organization : logical flow of introduction, coherence and depth of discussion in body, effectiveness of conclusion.
- Paragraph level concerns : topic sentences, sequence of ideas within paragraphs, use of details to support generalizations, summary sentences where necessary, use of transitions within and between paragraphs.
- Sentence level concerns: sentence structure, word choices, punctuation, spelling.
- Documentation: consistent use of one system, citation of all material not considered common knowledge, appropriate use of endnotes or footnotes, accuracy of list of works cited.

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.

Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics

- Cambridge Libraries
Study Skills
Research skills.
- Searching the literature
- Note making for dissertations
- Research Data Management
- Copyright and licenses
- Publishing in journals
- Publishing academic books
- Depositing your thesis
- Research metrics
- Build your online profile
- Finding support
Note making for dissertations: First steps into writing

Note making (as opposed to note taking) is an active practice of recording relevant parts of reading for your research as well as your reflections and critiques of those studies. Note making, therefore, is a pre-writing exercise that helps you to organise your thoughts prior to writing. In this module, we will cover:
- The difference between note taking and note making
- Seven tips for good note making
- Strategies for structuring your notes and asking critical questions
- Different styles of note making
To complete this section, you will need:

- Approximately 20-30 minutes.
- Access to the internet. All the resources used here are available freely.
- Some equipment for jotting down your thoughts, a pen and paper will do, or your phone or another electronic device.
Note taking v note making
When you think about note taking, what comes to mind? Perhaps trying to record everything said in a lecture? Perhaps trying to write down everything included in readings required for a course?
- Note taking is a passive process. When you take notes, you are often trying to record everything that you are reading or listening to. However, you may have noticed that this takes a lot of effort and often results in too many notes to be useful.
- Note making , on the other hand, is an active practice, based on the needs and priorities of your project. Note making is an opportunity for you to ask critical questions of your readings and to synthesise ideas as they pertain to your research questions. Making notes is a pre-writing exercise that develops your academic voice and makes writing significantly easier.
Seven tips for effective note making
Note making is an active process based on the needs of your research. This video contains seven tips to help you make brilliant notes from articles and books to make the most of the time you spend reading and writing.
- Transcript of Seven Tips for Effective Notemaking
Question prompts for strategic note making
You might consider structuring your notes to answer the following questions. Remember that note making is based on your needs, so not all of these questions will apply in all cases. You might try answering these questions using the note making styles discussed in the next section.
- Question prompts for strategic note making
- Background question prompts
- Critical question prompts
- Synthesis question prompts
Answer these six questions to frame your reading and provide context.
- What is the context in which the text was written? What came before it? Are there competing ideas?
- Who is the intended audience?
- What is the author’s purpose?
- How is the writing organised?
- What are the author’s methods?
- What is the author’s key argument and conclusions?
Answer these six questions to determine your critical perspectivess and develop your academic voice.
- What are the most interesting/compelling ideas (to you) in this study?
- Why do you find them interesting? How do they relate to your study?
- What questions do you have about the study?
- What could it cover better? How could it have defended its research better?
- What are the implications of the study? (Look not just to the conclusions but also to definitions and models)
- Are there any gaps in the study? (Look not just at conclusions but definitions, literature review, methodology)
Answer these five questions to compare aspects of various studies (such as for a literature review.
- What are the similarities and differences in the literature?
- Critically analyse the strengths, limitations, debates and themes that emerg from the literature.
- What would you suggest for future research or practice?
- Where are the gaps in the literature? What is missing? Why?
- What new questions should be asked in this area of study?
Styles of note making

- Linear notes . Great for recording thoughts about your readings. [video]
- Mind mapping : Great for thinking through complex topics. [video]
Further sites that discuss techniques for note making:
- Note-taking techniques
- Common note-taking methods
- Strategies for effective note making
Did you know?

How did you find this Research Skills module

Image Credits: Image #1: David Travis on Unsplash ; Image #2: Charles Deluvio on Unsplash
- << Previous: Searching the literature
- Next: Research Data Management >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 9:35 AM
- URL: https://libguides.cam.ac.uk/research-skills
© Cambridge University Libraries | Accessibility | Privacy policy | Log into LibApps

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
Refers to notes created by the researcher during the act of conducting a field study to remember and record the behaviors, activities, events, and other features of an observation. Field notes are intended to be read by the researcher as evidence to produce meaning and an understanding of the culture, social situation, or phenomenon being studied. The notes may constitute the whole data collected for a research study [e.g., an observational project] or contribute to it, such as when field notes supplement conventional interview data or other techniques of data gathering.
Schwandt, Thomas A. The SAGE Dictionary of Qualitative Inquiry . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2015.
How to Approach Writing Field Notes
The ways in which you take notes during an observational study is very much a personal decision developed over time as you become more experienced in fieldwork. However, all field notes generally consist of two parts:
- Descriptive information , in which you attempt to accurately document factual data [e.g., date and time] along with the settings, actions, behaviors, and conversations that you observe; and,
- Reflective information , in which you record your thoughts, ideas, questions, and concerns during the observation.
Note that field notes should be fleshed out as soon as possible after an observation is completed. Your initial notes may be recorded in cryptic form and, unless additional detail is added as soon as possible after the observation, important facts and opportunities for fully interpreting the data may be lost.
Characteristics of Field Notes
- Be accurate . You only get one chance to observe a particular moment in time so, before you conduct your observations, practice taking notes in a setting that is similar to your observation site in regards to number of people, the environment, and social dynamics. This will help you develop your own style of transcribing observations quickly and accurately.
- Be organized . Taking accurate notes while you are actively observing can be difficult. Therefore, it is important that you plan ahead how you will document your observation study [e.g., strictly chronologically or according to specific prompts]. Notes that are disorganized will make it more difficult for you to interpret the data.
- Be descriptive . Use descriptive words to document what you observe. For example, instead of noting that a classroom appears "comfortable," state that the classroom includes soft lighting and cushioned chairs that can be moved around by the students. Being descriptive means supplying yourself with enough factual evidence that you don't end up making assumptions about what you meant when you write the final report.
- Focus on the research problem . Since it's impossible to document everything you observe, focus on collecting the greatest detail that relates to the research problem and the theoretical constructs underpinning your research; avoid cluttering your notes with irrelevant information. For example, if the purpose of your study is to observe the discursive interactions between nursing home staff and the family members of residents, then it would only be necessary to document the setting in detail if it in some way directly influenced those interactions [e.g., there is a private room available for discussions between staff and family members].
- Record insights and thoughts . As you take notes, be thinking about the underlying meaning of what you observe and record your thoughts and ideas accordingly. If needed, this will help you to ask questions or seek clarification from participants after the observation. To avoid any confusion, subsequent comments from participants should be included in a separate, reflective part of your field notes and not merged with the descriptive notes.
General Guidelines for the Descriptive Content
The descriptive content of your notes can vary in detail depending upon what needs to be emphasized in order to address the research problem. However, in most observations, your notes should include at least some of the following elements:
- Describe the physical setting.
- Describe the social environment and the way in which participants interacted within the setting. This may include patterns of interactions, frequency of interactions, direction of communication patterns [including non-verbal communication], and patterns of specific behavioral events, such as, conflicts, decision-making, or collaboration.
- Describe the participants and their roles in the setting.
- Describe, as best you can, the meaning of what was observed from the perspectives of the participants.
- Record exact quotes or close approximations of comments that relate directly to the purpose of the study.
- Describe any impact you might have had on the situation you observed [important!].
General Guidelines for the Reflective Content
You are the instrument of data gathering and interpretation. Therefore, reflective content can include any of the following elements intended to contextualize what you have observed based on your perspective and your own personal, cultural, and situational experiences .
- Note ideas, impressions, thoughts, and/or any criticisms you have about what you observed.
- Include any unanswered questions or concerns that have arisen from analyzing the observation data.
- Clarify points and/or correct mistakes and misunderstandings in other parts of field notes.
- Include insights about what you have observed and speculate as to why you believe specific phenomenon occurred.
- Record any thoughts that you may have regarding any future observations.
NOTE: Analysis of your field notes should occur as they are being written and while you are conducting your observations. This is important for at least two reasons. First, preliminary analysis fosters self-reflection and self-reflection is crucial for facilitating deep understanding and meaning-making in any research study. Second, preliminary analysis reveals emergent themes. Identifying emergent themes while observing allows you to shift your attention in ways that can foster a more developed investigation.
Emerson, Robert M. et al. Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes . 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2011; Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gambold, Liesl L. “Field Notes.” In Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Edited by Albert J. Mills, Gabrielle Durepos, and Elden Wiebe. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2010; Pace, Tonio. Writing Field Reports. Scribd Online Library; Pyrczak, Fred and Randall R. Bruce. Writing Empirical Research Reports: A Basic Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences . 5th ed. Glendale, CA: Pyrczak Publishing, 2005; Report Writing. UniLearning. University of Wollongong, Australia; Ravitch, Sharon M. “Field Notes.” In The SAGE Encyclopedia of Educational Research, Measurement, and Evaluation . Edited by Bruce B. Frey. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2018; Tenzek, Kelly E. “Field Notes.” In The SAGE Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods . Edited by Mike Allen. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2017; Wolfinger, Nicholas H. "On Writing Fieldnotes: Collection Strategies and Background Expectancies.” Qualitative Research 2 (April 2002): 85-95; Writing Reports. Anonymous. The Higher Education Academy.
- << Previous: About Informed Consent
- Next: Writing a Policy Memo >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
- Academic Skills
- Reading, writing and referencing
- Literature reviews
Writing a literature review
Find out how to write a lit review.
What is a literature review ?
A literature review explores and evaluates the literature on a specific topic or question. It synthesises the contributions of the different authors, often to identify areas that need further exploration.
You may be required to write a literature review as a standalone document or part of a larger body of research, such as a thesis.
- The point of a standalone literature review is to demonstrate that you have read widely in your field and you understand the main arguments.
- As part of a thesis or research paper, the literature review defines your project by establishing how your work will extend or differ from previous work and what contribution it will make.
What are markers looking for?
In the best literature reviews, the writer:
- Has a clear understanding of key concepts within the topic.
- Clarifies important definitions and terminology.
- Covers the breadth of the specific topic.
- Critically discusses the ideas in the literature and evaluates how authors present them.
- Clearly indicates a research gap for future enquiry.
How do I write a literature review?
This video outlines a step by step approach to help you evaluate readings, organise ideas and write critically. It provides examples of how to connect, interpret and critique ideas to make sure your voice comes through strongly.
Tips for research, reading and writing
You may be given a specific question to research or broad topics which must be refined to a question that can be reasonably addressed in the time and word limit available.
Use your early reading to help you determine and refine your topic.
- Too much literature? You probably need to narrow your scope. Try to identify a more specific issue of interest.
- Not enough literature? Your topic may be too specific and needs to be broader.
Start with readings suggested by your lecturers or supervisors. Then, do your own research - the best place to go is the Library Website .
You can also use the Library Guides or speak to a librarian to identify the most useful databases for you and to learn how to search for sources effectively and efficiently.
Cover the field
Make sure your literature search covers a broad range of views and information relevant to your topic. Focussing on a narrow selection of sources may result in a lack of depth. You are not expected to cover all research and scholarly opinions on your topic, but you need to identify and include important viewpoints. A quality literature review examines and evaluates different viewpoints based on the evidence presented, rather than providing only material that reinforces a bias.
Use reading strategies
Survey, skim and scan to find the most relevant articles, and the most relevant parts of those articles. These can be re-read more closely later when you have acquired an overview of your topic.
Take notes as you read
This helps to organise and develop your thoughts. Record your own reactions to the text in your notes, perhaps in a separate column. These notes can form the basis of your critical evaluation of the text. Record any facts, opinions or direct quotes that are likely to be useful to your review, noting the page numbers, author and year.
Stop reading when you have enough
This depends on the word count required of this literature review. A review of one thousand words can only cover the major ideas and probably less than ten references. Longer reviews that form part of a large research paper will include more than fifty. Your tutor or supervisor should be able to suggest a suitable number.
As you read, ask yourself these questions:
- Have I answered my question without any obvious gaps?
- Have I read this before? Are there any new related issues coming up as I search the literature?
- Have I found multiple references which cover the same material or just enough to prove agreement?
There are many possible ways to organise the material. For example:
- chronologically
- by theoretical perspective
- from most to least important
- by issue or theme
It is important to remember that you are not merely cataloguing or describing the literature you read. Therefore, you need to choose an organisation that will enable you to compare the various authors' treatment of ideas. This is often best achieved by organising thematically, or grouping ideas into sets of common issues tackled in the various texts. These themes will form the basis of the different threads that are the focus of your study.
A standalone literature review
A standalone literature review is structured much like an academic essay.
- Introduction - establish the context for your topic and outline your main contentions about the literature
- Main body - explain and support these inferences in the main body
- Conclusion - summarise your main points and restate the contention.
The main difference between an essay and this kind of literature review is that an essay focuses on a topic and uses the literature as a support for the arguments. In a standalone literature review, the literature itself is the topic of discussion and evaluation. This means you evaluate and discuss not only the informational content but the quality of the author’s handling of the content.
A literature review as part of a larger research paper?
As part of a larger research paper, the literature review may take many forms, depending on your discipline, your topic and the logic of your research. Traditionally, in empirical research, the literature review is included in the introduction, or a standalone chapter immediately following the introduction. For other forms of research, you may need to engage more extensively with the literature and thus, the literature review may spread over more than one chapter, or even be distributed throughout the thesis.
Start writing early. Writing will clarify your thinking on the topic and reveal any gaps in information and logic. If your ideas change, sections and paragraphs can be reworked to change your contentions or include extra information.
Similarly, draft an overall plan for your review as soon as you are ready, but be prepared to rework sections of it to reflect your developing argument.
The most important thing to remember is that you are writing a review . That means you must move past describing what other authors have written by connecting, interpreting and critiquing their ideas and presenting your own analysis and interpretation.

Looking for one-on-one advice?
Get tailored advice from an Academic Skills Adviser by booking an Individual appointment, or get quick feedback from one of our Academic Writing Mentors via email through our Writing advice service.
Go to Student appointments
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Writing Survey Questions
Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions. Creating good measures involves both writing good questions and organizing them to form the questionnaire.
Questionnaire design is a multistage process that requires attention to many details at once. Designing the questionnaire is complicated because surveys can ask about topics in varying degrees of detail, questions can be asked in different ways, and questions asked earlier in a survey may influence how people respond to later questions. Researchers are also often interested in measuring change over time and therefore must be attentive to how opinions or behaviors have been measured in prior surveys.
Surveyors may conduct pilot tests or focus groups in the early stages of questionnaire development in order to better understand how people think about an issue or comprehend a question. Pretesting a survey is an essential step in the questionnaire design process to evaluate how people respond to the overall questionnaire and specific questions, especially when questions are being introduced for the first time.
For many years, surveyors approached questionnaire design as an art, but substantial research over the past forty years has demonstrated that there is a lot of science involved in crafting a good survey questionnaire. Here, we discuss the pitfalls and best practices of designing questionnaires.
Question development
There are several steps involved in developing a survey questionnaire. The first is identifying what topics will be covered in the survey. For Pew Research Center surveys, this involves thinking about what is happening in our nation and the world and what will be relevant to the public, policymakers and the media. We also track opinion on a variety of issues over time so we often ensure that we update these trends on a regular basis to better understand whether people’s opinions are changing.
At Pew Research Center, questionnaire development is a collaborative and iterative process where staff meet to discuss drafts of the questionnaire several times over the course of its development. We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups , cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample ), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on the ATP.
Measuring change over time
Many surveyors want to track changes over time in people’s attitudes, opinions and behaviors. To measure change, questions are asked at two or more points in time. A cross-sectional design surveys different people in the same population at multiple points in time. A panel, such as the ATP, surveys the same people over time. However, it is common for the set of people in survey panels to change over time as new panelists are added and some prior panelists drop out. Many of the questions in Pew Research Center surveys have been asked in prior polls. Asking the same questions at different points in time allows us to report on changes in the overall views of the general public (or a subset of the public, such as registered voters, men or Black Americans), or what we call “trending the data”.
When measuring change over time, it is important to use the same question wording and to be sensitive to where the question is asked in the questionnaire to maintain a similar context as when the question was asked previously (see question wording and question order for further information). All of our survey reports include a topline questionnaire that provides the exact question wording and sequencing, along with results from the current survey and previous surveys in which we asked the question.
The Center’s transition from conducting U.S. surveys by live telephone interviewing to an online panel (around 2014 to 2020) complicated some opinion trends, but not others. Opinion trends that ask about sensitive topics (e.g., personal finances or attending religious services ) or that elicited volunteered answers (e.g., “neither” or “don’t know”) over the phone tended to show larger differences than other trends when shifting from phone polls to the online ATP. The Center adopted several strategies for coping with changes to data trends that may be related to this change in methodology. If there is evidence suggesting that a change in a trend stems from switching from phone to online measurement, Center reports flag that possibility for readers to try to head off confusion or erroneous conclusions.
Open- and closed-ended questions
One of the most significant decisions that can affect how people answer questions is whether the question is posed as an open-ended question, where respondents provide a response in their own words, or a closed-ended question, where they are asked to choose from a list of answer choices.
For example, in a poll conducted after the 2008 presidential election, people responded very differently to two versions of the question: “What one issue mattered most to you in deciding how you voted for president?” One was closed-ended and the other open-ended. In the closed-ended version, respondents were provided five options and could volunteer an option not on the list.
When explicitly offered the economy as a response, more than half of respondents (58%) chose this answer; only 35% of those who responded to the open-ended version volunteered the economy. Moreover, among those asked the closed-ended version, fewer than one-in-ten (8%) provided a response other than the five they were read. By contrast, fully 43% of those asked the open-ended version provided a response not listed in the closed-ended version of the question. All of the other issues were chosen at least slightly more often when explicitly offered in the closed-ended version than in the open-ended version. (Also see “High Marks for the Campaign, a High Bar for Obama” for more information.)
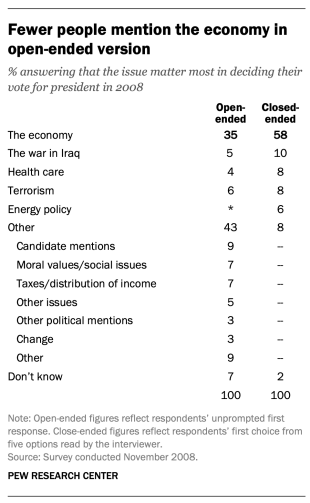
Researchers will sometimes conduct a pilot study using open-ended questions to discover which answers are most common. They will then develop closed-ended questions based off that pilot study that include the most common responses as answer choices. In this way, the questions may better reflect what the public is thinking, how they view a particular issue, or bring certain issues to light that the researchers may not have been aware of.
When asking closed-ended questions, the choice of options provided, how each option is described, the number of response options offered, and the order in which options are read can all influence how people respond. One example of the impact of how categories are defined can be found in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in January 2002. When half of the sample was asked whether it was “more important for President Bush to focus on domestic policy or foreign policy,” 52% chose domestic policy while only 34% said foreign policy. When the category “foreign policy” was narrowed to a specific aspect – “the war on terrorism” – far more people chose it; only 33% chose domestic policy while 52% chose the war on terrorism.
In most circumstances, the number of answer choices should be kept to a relatively small number – just four or perhaps five at most – especially in telephone surveys. Psychological research indicates that people have a hard time keeping more than this number of choices in mind at one time. When the question is asking about an objective fact and/or demographics, such as the religious affiliation of the respondent, more categories can be used. In fact, they are encouraged to ensure inclusivity. For example, Pew Research Center’s standard religion questions include more than 12 different categories, beginning with the most common affiliations (Protestant and Catholic). Most respondents have no trouble with this question because they can expect to see their religious group within that list in a self-administered survey.
In addition to the number and choice of response options offered, the order of answer categories can influence how people respond to closed-ended questions. Research suggests that in telephone surveys respondents more frequently choose items heard later in a list (a “recency effect”), and in self-administered surveys, they tend to choose items at the top of the list (a “primacy” effect).
Because of concerns about the effects of category order on responses to closed-ended questions, many sets of response options in Pew Research Center’s surveys are programmed to be randomized to ensure that the options are not asked in the same order for each respondent. Rotating or randomizing means that questions or items in a list are not asked in the same order to each respondent. Answers to questions are sometimes affected by questions that precede them. By presenting questions in a different order to each respondent, we ensure that each question gets asked in the same context as every other question the same number of times (e.g., first, last or any position in between). This does not eliminate the potential impact of previous questions on the current question, but it does ensure that this bias is spread randomly across all of the questions or items in the list. For instance, in the example discussed above about what issue mattered most in people’s vote, the order of the five issues in the closed-ended version of the question was randomized so that no one issue appeared early or late in the list for all respondents. Randomization of response items does not eliminate order effects, but it does ensure that this type of bias is spread randomly.
Questions with ordinal response categories – those with an underlying order (e.g., excellent, good, only fair, poor OR very favorable, mostly favorable, mostly unfavorable, very unfavorable) – are generally not randomized because the order of the categories conveys important information to help respondents answer the question. Generally, these types of scales should be presented in order so respondents can easily place their responses along the continuum, but the order can be reversed for some respondents. For example, in one of Pew Research Center’s questions about abortion, half of the sample is asked whether abortion should be “legal in all cases, legal in most cases, illegal in most cases, illegal in all cases,” while the other half of the sample is asked the same question with the response categories read in reverse order, starting with “illegal in all cases.” Again, reversing the order does not eliminate the recency effect but distributes it randomly across the population.
Question wording
The choice of words and phrases in a question is critical in expressing the meaning and intent of the question to the respondent and ensuring that all respondents interpret the question the same way. Even small wording differences can substantially affect the answers people provide.
[View more Methods 101 Videos ]
An example of a wording difference that had a significant impact on responses comes from a January 2003 Pew Research Center survey. When people were asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule,” 68% said they favored military action while 25% said they opposed military action. However, when asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule even if it meant that U.S. forces might suffer thousands of casualties, ” responses were dramatically different; only 43% said they favored military action, while 48% said they opposed it. The introduction of U.S. casualties altered the context of the question and influenced whether people favored or opposed military action in Iraq.
There has been a substantial amount of research to gauge the impact of different ways of asking questions and how to minimize differences in the way respondents interpret what is being asked. The issues related to question wording are more numerous than can be treated adequately in this short space, but below are a few of the important things to consider:
First, it is important to ask questions that are clear and specific and that each respondent will be able to answer. If a question is open-ended, it should be evident to respondents that they can answer in their own words and what type of response they should provide (an issue or problem, a month, number of days, etc.). Closed-ended questions should include all reasonable responses (i.e., the list of options is exhaustive) and the response categories should not overlap (i.e., response options should be mutually exclusive). Further, it is important to discern when it is best to use forced-choice close-ended questions (often denoted with a radio button in online surveys) versus “select-all-that-apply” lists (or check-all boxes). A 2019 Center study found that forced-choice questions tend to yield more accurate responses, especially for sensitive questions. Based on that research, the Center generally avoids using select-all-that-apply questions.
It is also important to ask only one question at a time. Questions that ask respondents to evaluate more than one concept (known as double-barreled questions) – such as “How much confidence do you have in President Obama to handle domestic and foreign policy?” – are difficult for respondents to answer and often lead to responses that are difficult to interpret. In this example, it would be more effective to ask two separate questions, one about domestic policy and another about foreign policy.
In general, questions that use simple and concrete language are more easily understood by respondents. It is especially important to consider the education level of the survey population when thinking about how easy it will be for respondents to interpret and answer a question. Double negatives (e.g., do you favor or oppose not allowing gays and lesbians to legally marry) or unfamiliar abbreviations or jargon (e.g., ANWR instead of Arctic National Wildlife Refuge) can result in respondent confusion and should be avoided.
Similarly, it is important to consider whether certain words may be viewed as biased or potentially offensive to some respondents, as well as the emotional reaction that some words may provoke. For example, in a 2005 Pew Research Center survey, 51% of respondents said they favored “making it legal for doctors to give terminally ill patients the means to end their lives,” but only 44% said they favored “making it legal for doctors to assist terminally ill patients in committing suicide.” Although both versions of the question are asking about the same thing, the reaction of respondents was different. In another example, respondents have reacted differently to questions using the word “welfare” as opposed to the more generic “assistance to the poor.” Several experiments have shown that there is much greater public support for expanding “assistance to the poor” than for expanding “welfare.”
We often write two versions of a question and ask half of the survey sample one version of the question and the other half the second version. Thus, we say we have two forms of the questionnaire. Respondents are assigned randomly to receive either form, so we can assume that the two groups of respondents are essentially identical. On questions where two versions are used, significant differences in the answers between the two forms tell us that the difference is a result of the way we worded the two versions.

One of the most common formats used in survey questions is the “agree-disagree” format. In this type of question, respondents are asked whether they agree or disagree with a particular statement. Research has shown that, compared with the better educated and better informed, less educated and less informed respondents have a greater tendency to agree with such statements. This is sometimes called an “acquiescence bias” (since some kinds of respondents are more likely to acquiesce to the assertion than are others). This behavior is even more pronounced when there’s an interviewer present, rather than when the survey is self-administered. A better practice is to offer respondents a choice between alternative statements. A Pew Research Center experiment with one of its routinely asked values questions illustrates the difference that question format can make. Not only does the forced choice format yield a very different result overall from the agree-disagree format, but the pattern of answers between respondents with more or less formal education also tends to be very different.
One other challenge in developing questionnaires is what is called “social desirability bias.” People have a natural tendency to want to be accepted and liked, and this may lead people to provide inaccurate answers to questions that deal with sensitive subjects. Research has shown that respondents understate alcohol and drug use, tax evasion and racial bias. They also may overstate church attendance, charitable contributions and the likelihood that they will vote in an election. Researchers attempt to account for this potential bias in crafting questions about these topics. For instance, when Pew Research Center surveys ask about past voting behavior, it is important to note that circumstances may have prevented the respondent from voting: “In the 2012 presidential election between Barack Obama and Mitt Romney, did things come up that kept you from voting, or did you happen to vote?” The choice of response options can also make it easier for people to be honest. For example, a question about church attendance might include three of six response options that indicate infrequent attendance. Research has also shown that social desirability bias can be greater when an interviewer is present (e.g., telephone and face-to-face surveys) than when respondents complete the survey themselves (e.g., paper and web surveys).
Lastly, because slight modifications in question wording can affect responses, identical question wording should be used when the intention is to compare results to those from earlier surveys. Similarly, because question wording and responses can vary based on the mode used to survey respondents, researchers should carefully evaluate the likely effects on trend measurements if a different survey mode will be used to assess change in opinion over time.
Question order
Once the survey questions are developed, particular attention should be paid to how they are ordered in the questionnaire. Surveyors must be attentive to how questions early in a questionnaire may have unintended effects on how respondents answer subsequent questions. Researchers have demonstrated that the order in which questions are asked can influence how people respond; earlier questions can unintentionally provide context for the questions that follow (these effects are called “order effects”).
One kind of order effect can be seen in responses to open-ended questions. Pew Research Center surveys generally ask open-ended questions about national problems, opinions about leaders and similar topics near the beginning of the questionnaire. If closed-ended questions that relate to the topic are placed before the open-ended question, respondents are much more likely to mention concepts or considerations raised in those earlier questions when responding to the open-ended question.
For closed-ended opinion questions, there are two main types of order effects: contrast effects ( where the order results in greater differences in responses), and assimilation effects (where responses are more similar as a result of their order).
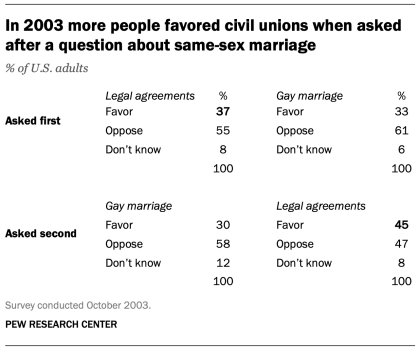
An example of a contrast effect can be seen in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in October 2003, a dozen years before same-sex marriage was legalized in the U.S. That poll found that people were more likely to favor allowing gays and lesbians to enter into legal agreements that give them the same rights as married couples when this question was asked after one about whether they favored or opposed allowing gays and lesbians to marry (45% favored legal agreements when asked after the marriage question, but 37% favored legal agreements without the immediate preceding context of a question about same-sex marriage). Responses to the question about same-sex marriage, meanwhile, were not significantly affected by its placement before or after the legal agreements question.
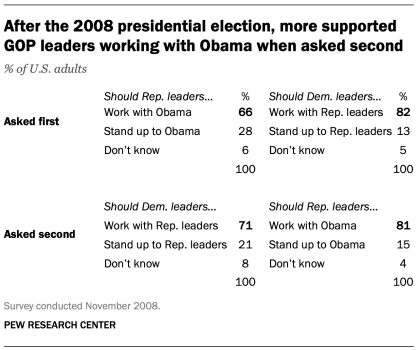
Another experiment embedded in a December 2008 Pew Research Center poll also resulted in a contrast effect. When people were asked “All in all, are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way things are going in this country today?” immediately after having been asked “Do you approve or disapprove of the way George W. Bush is handling his job as president?”; 88% said they were dissatisfied, compared with only 78% without the context of the prior question.
Responses to presidential approval remained relatively unchanged whether national satisfaction was asked before or after it. A similar finding occurred in December 2004 when both satisfaction and presidential approval were much higher (57% were dissatisfied when Bush approval was asked first vs. 51% when general satisfaction was asked first).
Several studies also have shown that asking a more specific question before a more general question (e.g., asking about happiness with one’s marriage before asking about one’s overall happiness) can result in a contrast effect. Although some exceptions have been found, people tend to avoid redundancy by excluding the more specific question from the general rating.
Assimilation effects occur when responses to two questions are more consistent or closer together because of their placement in the questionnaire. We found an example of an assimilation effect in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in November 2008 when we asked whether Republican leaders should work with Obama or stand up to him on important issues and whether Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders or stand up to them on important issues. People were more likely to say that Republican leaders should work with Obama when the question was preceded by the one asking what Democratic leaders should do in working with Republican leaders (81% vs. 66%). However, when people were first asked about Republican leaders working with Obama, fewer said that Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders (71% vs. 82%).
The order questions are asked is of particular importance when tracking trends over time. As a result, care should be taken to ensure that the context is similar each time a question is asked. Modifying the context of the question could call into question any observed changes over time (see measuring change over time for more information).
A questionnaire, like a conversation, should be grouped by topic and unfold in a logical order. It is often helpful to begin the survey with simple questions that respondents will find interesting and engaging. Throughout the survey, an effort should be made to keep the survey interesting and not overburden respondents with several difficult questions right after one another. Demographic questions such as income, education or age should not be asked near the beginning of a survey unless they are needed to determine eligibility for the survey or for routing respondents through particular sections of the questionnaire. Even then, it is best to precede such items with more interesting and engaging questions. One virtue of survey panels like the ATP is that demographic questions usually only need to be asked once a year, not in each survey.
U.S. Surveys
Other research methods, sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Write down your thoughts and shred them to relieve anger, researchers say
Writing negative reactions on paper and shredding it or scrunching and throwing in the bin eliminates angry feelings, study finds
Since time immemorial humans have tried to devise anger management techniques.
In ancient Rome, the Stoic philosopher Seneca believed “my anger is likely to do me more harm than your wrong” and offered avoidance tips in his AD45 work De Ira (On Anger).
More modern methods include a workout on the gym punchbag or exercise bike. But the humble paper shredder may be a more effective – and accessible – way to decompress, according to research.
A study in Japan has found that writing down your reaction to a negative incident on a piece of paper and then shredding it, or scrunching it into a ball and throwing it in the bin, gets rid of anger.
“We expected that our method would suppress anger to some extent,” said Nobuyuki Kawai, lead researcher of the study at Nagoya University. “However, we were amazed that anger was eliminated almost entirely.”
The study, published in Scientific Reports on Nature , builds on research on the association between the written word and anger reduction as well as studies showing how interactions with physical objects can control a person’s mood. For instance, those wanting revenge on an ex-partner may burn letters or destroy gifts.
Researchers believe the shredder results may be related to the phenomenon of “backward magical contagion”, which is the belief that actions taken on an object associated with a person can affect the individuals themselves. In this case, getting rid of the negative physical entity, the piece of paper, causes the original emotion to also disappear.
This is a reversal of “magical contagion” or “celebrity contagion” – the belief that the “essence” of an individual can be transferred through their physical possessions.
Fifty student participants were asked to write brief opinions about an important social problem, such as whether smoking in public should be outlawed. Evaluators then deliberately scored the papers low on intelligence, interest, friendliness, logic, and rationality. For good measure, evaluators added insulting comments such as: “I cannot believe an educated person would think like this. I hope this person learns something while at the university.”
The wound-up participants then wrote down their angry thoughts on the negative feedback on a piece of paper. One group was told to either roll up the paper and throw it in a bin or keep it in a file on their desk. A second group was told to shred the paper, or put it in a plastic box.
Anger levels of the individuals who discarded their paper in the bin or shredded it returned to their initial state, while those who retained a hard copy of the paper experienced only a small decrease in their overall anger.
Researchers concluded that “the meaning (interpretation) of disposal plays a critical role” in reducing anger.
“This technique could be applied in the moment by writing down the source of anger as if taking a memo and then throwing it away,” said Kawai.
Along with its practical benefits, this discovery may shed light on the origins of the Japanese cultural tradition known as hakidashisara ( hakidashi sara refers to a dish or plate) at the Hiyoshi shrine in Kiyosu, just outside Nagoya. Hakidashisara is an annual festival where people smash small discs representing things that make them angry. The study’s findings may explain the feeling of relief that participants report after leaving the festival, the paper concluded.

Fridge magnets can be cool aid to holiday memory recall, study finds

Want to skip that Christmas party? The host probably won’t mind, study shows

‘Succession syndrome’ prevalent among wealthy households, psychiatrists warn

Drugs and alcohol do not make you more creative, research finds

Why being rude to the waiter (or other staff) is the worst strategy

Authors of original dating profiles rated more attractive, research finds

I fear my children are overexposed to technology. Experts say I’m right to worry

I used to be ashamed of being a fangirl. Now I see how joyous and creative it was

Autistic scholar Temple Grandin: ‘The education system is screening out visual thinkers’
Human neurons transplanted into rats to help study brain disorders
Most viewed.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Latest science news, discoveries and analysis
China's Moon atlas is the most detailed ever made
‘Shut up and calculate’: how Einstein lost the battle to explain quantum reality
Rat neurons repair mouse brains — and restore sense of smell
Mini-colon and brain 'organoids' shed light on cancer and other diseases
Scientists urged to collect royalties from the ‘magic money tree’, first glowing animals lit up the oceans half a billion years ago, plastic pollution: three numbers that support a crackdown, the maldives is racing to create new land. why are so many people concerned, ecologists: don’t lose touch with the joy of fieldwork chris mantegna.

Should the Maldives be creating new land?

Lethal AI weapons are here: how can we control them?

Algorithm ranks peer reviewers by reputation — but critics warn of bias

How gliding marsupials got their ‘wings’
Bird flu in us cows: is the milk supply safe, nato is boosting ai and climate research as scientific diplomacy remains on ice, hello puffins, goodbye belugas: changing arctic fjord hints at our climate future, nih pay raise for postdocs and phd students could have us ripple effect.
Retractions are part of science, but misconduct isn’t — lessons from a superconductivity lab

Any plan to make smoking obsolete is the right step

Citizenship privilege harms science
European ruling linking climate change to human rights could be a game changer — here’s how charlotte e. blattner, will ai accelerate or delay the race to net-zero emissions, current issue.

Surprise hybrid origins of a butterfly species
Stripped-envelope supernova light curves argue for central engine activity, optical clocks at sea, research analysis.

Ancient DNA traces family lines and political shifts in the Avar empire
A chemical method for selective labelling of the key amino acid tryptophan
Robust optical clocks promise stable timing in a portable package
Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
Bioengineered ‘mini-colons’ shed light on cancer progression, galaxy found napping in the primordial universe, tumours form without genetic mutations, marsupial genomes reveal how a skin membrane for gliding evolved.

Breaking ice, and helicopter drops: winning photos of working scientists

Shrouded in secrecy: how science is harmed by the bullying and harassment rumour mill
How ground glass might save crops from drought on a caribbean island, londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs, books & culture.

How volcanoes shaped our planet — and why we need to be ready for the next big eruption

Dogwhistles, drilling and the roots of Western civilization: Books in brief

Cosmic rentals
Las borinqueñas remembers the forgotten puerto rican women who tested the first pill, dad always mows on summer saturday mornings, nature podcast.

Latest videos
Nature briefing.
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Instead, you are writing to support a thesis that shows original thinking, and you are collecting and incorporating research into your paper to support that thinking. Therefore, a research log, whether digital or handwritten, is a great way to keep track of your thinking as well as your notes and bibliographic information.
Read the text critically, think how it is related to your argument, and decide how you are going to use it in your paper. Select the material that is relevant to your argument. Copy the original text for direct quotations or briefly summarize the content in your own words, and make note of how you will use it.
memory source. Students take notes to record information and to aid in comprehension and reflection. Note taking is an essential part of writing any research paper because they give you a better understanding of course material. While writing a research paper, you will need to gather and synthesize information from various sources. Knowing what ...
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
We've covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are: To choose a research question and review the literature. To plan your paper structure and draft an outline. To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing.
Note-taking for Research. As you determine which sources you will rely on most, it is important to establish a system for keeping track of your sources and taking notes. There are several ways to go about it, and no one system is necessarily superior. What matters is that you keep materials in order; record bibliographical information you will ...
How to Write an Outline for Your Research Paper. There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline.
Research Paper: A step-by-step guide: 6. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources ... Evaluating Sources; 8. Citations & Plagiarism; 9. Writing Your Research Paper; Taking Notes & Documenting Sources. How to Take Notes and Document Sources. Note taking is a very important part of the research process. ... There are different ways to take notes and ...
Optional: If you are in the process of writing a research paper, you can use this activity as a checklist. Collect all the material you have that relates to your research paper: the prompt, rubric, samples, sources, notes, and other materials. Use these guiding questions are you walk yourself. Research Paper Writing Process, Fall 2022.
Taking Notes from Research Reading. If you take notes efficiently, you can read with more understanding and also save time and frustration when you come to write your paper. These are three main principles. 1. Know what kind of ideas you need to record. Focus your approach to the topic before you start detailed research.
Taking Notes Electronically. Make sure your device is charged and backed up to store data. Invest in note-taking apps or E-Ink tablets. If using your laptop, create folders to organize your notes and data. Create shortcuts to your folders so you have easier access. Create outlines. Keep your notes short and legible.
Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
On each note card: Use only one side to record a single idea, fact or quote from one source. It will be easier to rearrange them later when it comes time to organize your paper. Include a heading or key words at the top of the card. Include the Work Cited source card number. Include the page number where you found the information. Taking notes:
Step 2: Organize Your Schedule. Once you've read the rubric, note in your planner or on your calendar when your research paper is due. Then, make a schedule so that you can accomplish this task in small steps rather than over the course of one (likely stressful) night. Having a plan in place can help you feel better and write a stronger ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
The Craft of Research, Third Edition addresses notetaking in a section called "Recording What You Find" (pp. 95-100). Below is a summary of the system outlined in the book. Take full notes. Whether you take notes on cards, in a notebook, or on the computer, it's vital to record information accurately and completely.
Writing a Research Paper. This page lists some of the stages involved in writing a library-based research paper. Although this list suggests that there is a simple, linear process to writing such a paper, the actual process of writing a research paper is often a messy and recursive one, so please use this outline as a flexible guide.
Note making (as opposed to note taking) is an active practice of recording relevant parts of reading for your research as well as your reflections and critiques of those studies. Note making, therefore, is a pre-writing exercise that helps you to organise your thoughts prior to writing. In this module, we will cover:
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly ...
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
Writing Field Notes ; Writing a Policy Memo; Writing a Reflective Paper; Writing a Research Proposal; Generative AI and Writing; Acknowledgments; Definition. Refers to notes created by the researcher during the act of conducting a field study to remember and record the behaviors, activities, events, and other features of an observation. Field ...
A standalone literature review. A standalone literature review is structured much like an academic essay. Introduction - establish the context for your topic and outline your main contentions about the literature. Main body - explain and support these inferences in the main body. Conclusion - summarise your main points and restate the contention.
A decimal outline is similar in format to the alphanumeric outline, but with a different numbering system: 1, 1.1, 1.2, etc. Text is written as short notes rather than full sentences. Example: 1 Body paragraph one. 1.1 First point. 1.1.1 Sub-point of first point. 1.1.2 Sub-point of first point.
Writing Survey Questions. Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions.
Writing negative reactions on paper and shredding it or scrunching and throwing in the bin eliminates angry feelings, study finds Caroline Davies Tue 9 Apr 2024 09.40 EDT Last modified on Tue 9 ...
Find breaking science news and analysis from the world's leading research journal.
2.2. Vocabulary knowledge and academic writing skills. The linguistic impact of academic writing often depends on how students use forms of words to create connections between their own claims and the claims of others using the knowledge of vocabulary (Hyland, Citation 1999; Hunston & Thompson, Citation 2000).The unsatisfactory use of academic vocabulary and formal vocabulary in the students ...