New NPM integration: design with fully interactive components from top libraries!

Creating A User Research Plan (with Examples)

UX research helps to test hypothesis you have about users prior to design. Sadly, not every UX design project starts with user research, and that’s because it takes a lot of time to recruit participants, run UX research projects, and sumamrize findings.
Good research, nevertheless, ensures that your product team doesn’t build the wrong functionality that would cost you valuable resources and make you vulnerable to losing customers.
In this article, you’ll see how you can use UX research plan to get stakeholder’s buy-in and create research reports that’s full of valuable advice for product design. Let’s go.
At the end, when you have your research complete, launch the right tool for your design process. For that, try UXPin, an end-to-end design tool for interactive prototyping that brings design and product development together.
Designers can create a powerful prototypes, show them to product managers who can interact with the design instead of just looking at it. Then, they give the design to engineers who can get all the specs and some code to kickstart front-end design with.
Since with UXPin you work faster, you have ample time for UX research before UX design. Try it for free .
Build advanced prototypes
Design better products with States, Variables, Auto Layout and more.
What is a UX Research Plan?
A UX research plan helps to set expectations and document the essentials you need to communicate to stakeholders and clients. Your company needs a strong business case for every user research session, complete with research objectives, goals, methods, and logistical needs for the study.
UX Research Plan Elements
Every UX research plan should start with a solid outline. That’s where templates come in handy. They help you structure your UX research project in a way that team members and stakeholders see value in completing research process.
Master templates are the best way to create a successful and effective UX research plan. Using a template as a starting point makes planning and writing easier and helps you and your team stay focused on the who, what, why, and when of research. Read on for tips and examples for how you can build a user research plan that works.
UX Research Plan Background
The background section should offer your clients and stakeholders a few sentences on why you are creating a user research plan and what it will accomplish. It should orient readers to the needs and expectations behind the purpose of the study. It should also include a problem statement, which is the primary question you’re setting out to answer with your research findings.
Example Background
The purpose of this study is to understand the major pain points users experience in using our website/app and how these contribute to issues such as cart abandonment, returned items, and low customer loyalty.
We will be using usability testing to follow the user’s experience of our website/app and the obstacles they encounter leading up to the point of purchase. We will also be using generative research techniques to better understand the customer’s experience of our brand and the challenges and needs they face in making a purchase.
UX Research Plan Objectives
Before getting into the nitty-gritty of your user research plan, you first want to focus on your research objectives. This step outlines the reasons you are conducting a UX research plan in the first place. Why are you carrying out this research? What are the end goals you have after completing all the work?
Seeking out answers to these questions should be a collaborative effort between you and your stakeholders. It’s also helpful to consider discussions and learnings from past clients and projects to create metrics for your UX research plan.
Objectives and Success Metrics
Research objectives will be different for every project, but they should always be actionable and specific.
Example Objectives
- Understand how users currently go about tracking orders on our website
- Understand what actions customers take when they consider buying a new [product we offer]
- Learn about competitor websites/apps customers are using to buy [product we offer]
- Evaluate pain points customers are experiencing in using our website/app
And here are some examples to help you determine the success of your UX research plan.
Example Success Metrics
- What information are we trying to collect about users?
- What scales/documents/statistics do we intend to create?
- What decisions will these materials help to make?
UX Research Plan Methodology
This step should be a short and sweet description of the research methods you will use to answer the research objectives. It should include both secondary and primary methods. Generative methods, such as user interviews and open-ended questions, help uncover motivations or more general insights, while UX testing helps to evaluate the usability and experience of your product.
Research Scope & Focus Areas
Clearly outlining the research scope and focus areas helps to facilitate efficient user research planning. The more you’re able to hone in on the specifics of what information you are wanting to collect, the less overwhelmed you will be in the process. It also helps avoid inundating your clients with unnecessary information.
To keep research-focused, this section should include:
- 3-6 question topics (e.g. How do users spend their time on a website?)
- Design Focus Components, including interface qualities (e.g. Usability, Training, Efficiency, Satisfaction)
- Primary User Scenarios (e.g. Scenarios in which pain points are most problematic; scenarios you have the least information about, etc.)
Example Methodology
For this study, we’re conducting a 30-minute usability test to evaluate our user’s experience of our app/website. A secondary method will be to conduct one-on-one generative research interviews to better understand our customers and empathize with their needs.
UX Research Plan Participant Profiles
Once you’ve defined objectives methodology and focus areas, it’s time to outline the participants you’ll need to get the required insights. Participant profiles help you determine who you want to recruit, or an approximation of your users, to optimize recruiting efforts. Here are a few examples of how to ensure you’ll get the best participants for your study.
Define your target user by collaborating with internal stakeholders, marketing, sales, and customer support. With their help, you can create approximations about who your users are. This is a great starting point for finding the right participants for your study.
Compare yourself to your competitors and create participant profiles based on their audiences. Recruiting people who use a competitor’s product can be an excellent way to glean insights into how to further improve your product.
Outline a screening process. Participant profiles should include any relevant information concerning your target audience, including behaviors, needs, demographics, geography, etc. Including the right criteria will help you evaluate whether or not to include certain individuals in your user research plan.
This Nielsen Norman article offers some great information about defining and recruiting the right participants for your study.
UX Research Plan Timeline
This is optional, but many UX research plans include a timeline that offers clients and stakeholders a general overview of how long the research will take. It helps to set expectations for the final results as well as allowing you to create a schedule for research sessions, debriefing, follow-up, and deliverables.
Timeline Example:
Approximately 6-8 weeks for identifying objectives, creating participant profiles, recruitment, in-person meetings, qualitative research, and analysis.
Try an End-to-End Design Solution
UX research plan templates are essential tools for executing a successful project. Having a master template helps you to remember what the process entails, communicate essential information to the right people, and stay on track throughout the user research plan.
UXPin, besides being a great prototyping tool, makes creating such research templates fast and easy. Especially since each project will be a little different and plans will need tweaking in terms of structure and content. Try UXPin for free .
Build prototypes that are as interactive as the end product. Try UXPin
by UXPin on 8th October, 2020
UXPin is a product design platform used by the best designers on the planet. Let your team easily design, collaborate, and present from low-fidelity wireframes to fully-interactive prototypes.
No credit card required.
These e-Books might interest you

Design Systems & DesignOps in the Enterprise
Spot opportunities and challenges for increasing the impact of design systems and DesignOps in enterprises.

DesignOps Pillar: How We Work Together
Get tips on hiring, onboarding, and structuring a design team with insights from DesignOps leaders.
We use cookies to improve performance and enhance your experience. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies in accordance with our cookie policy.
UX Research: Objectives, Assumptions, and Hypothesis
by Rick Dzekman
An often neglected step in UX research
Introduction
UX research should always be done for a clear purpose – otherwise you’re wasting the both your time and the time of your participants. But many people who do UX research fail to properly articulate the purpose in their research objectives. A major issue is that the research objectives include assumptions that have not been properly defined.
When planning UX research you have some goal in mind:
- For generative research it’s usually to find out something about users or customers that you previously did not know
- For evaluative research it’s usually to identify any potential issues in a solution
As part of this goal you write down research objectives that help you achieve that goal. But for many researchers (especially more junior ones) they are missing some key steps:
- How will those research objectives help to reach that goal?
- What assumptions have you made that are necessary for those objectives to reach that goal?
- How does your research (questions, tasks, observations, etc.) help meet those objectives?
- What kind of responses or observations do you need from your participants to meet those objectives?

One approach people use is to write their objectives in the form of research hypothesis. There are a lot of problems when trying to validate a hypothesis with qualitative research and sometimes even with quantitative.
This article focuses largely on qualitative research: interviews, user tests, diary studies, ethnographic research, etc. With qualitative research in mind let’s start by taking a look at a few examples of UX research hypothesis and how they may be problematic.
Research hypothesis
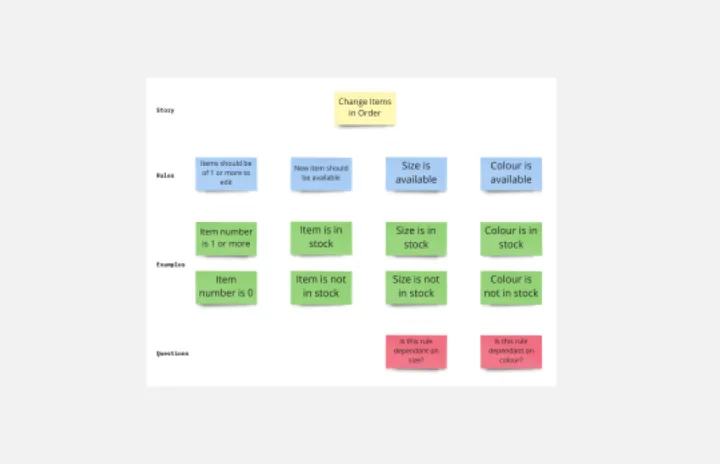
Example hypothesis: users want to be able to filter products by colour.
At first it may seem that there are a number of ways to test this hypothesis with qualitative research. For example we might:
- Observe users shopping on sites with and without colour filters and see whether or not they use them
- Ask users who are interested in our products about how narrow down their choices
- Run a diary study where participants document the ways they narrowed down their searches on various stores
- Make a prototype with colour filters and see if participants use them unprompted
These approaches are all effective but they do not and cannot prove or disprove our hypothesis. It’s not that the research methods are ineffective it’s that the hypothesis itself is poorly expressed.
The first problem is that there are hidden assumptions made by this hypothesis. Presumably we would be doing this research to decide between a choice of possible filters we could implement. But there’s no obvious link between users wanting to filter by colour and a benefit from us implementing a colour filter. Users may say they want it but how will that actually benefit their experience?
The second problem with this hypothesis is that we’re asking a question about “users” in general. How many users would have to want colour filters before we could say that this hypothesis is true?
Example Hypothesis: Adding a colour filter would make it easier for users to find the right products
This is an obvious improvement to the first example but it still has problems. We could of course identify further assumptions but that will be true of pretty much any hypothesis. The problem again comes from speaking about users in general.
Perhaps if we add the ability to filter by colour it might make the possible filters crowded and make it more difficult for users who don’t need colour to find the filter that they do need. Perhaps there is a sample bias in our research participants that does not apply broadly to our user base.
It is difficult (though not impossible) to design research that could prove or disprove this hypothesis. Any such research would have to be quantitative in nature. And we would have to spend time mapping out what it means for something to be “easier” or what “the right products” are.
Example Hypothesis: Travelers book flights before they book their hotels
The problem with this hypothesis should now be obvious: what would it actually mean for this hypothesis to be proved or disproved? What portion of travelers would need to book their flights first for us to consider this true?
Example Hypothesis: Most users who come to our app know where and when they want to fly
This hypothesis is better because it talks about “most users” rather than users in general. “Most” would need to be better defined but at least this hypothesis is possible to prove or disprove.
We could address this hypothesis with quantitative research. If we found out that it was true we could focus our design around the primary use case or do further research about how to attract users at different stages of their journey.
However there is no clear way to prove or disprove this hypothesis with qualitative research. If the app has a million users and 15/20 research participants tell you that this is true would your findings generalise to the entire user base? The margin of error on that finding is 20-25%, meaning that the true results could be closer to 50% or even 100% depending on how unlucky you are with your sample.
Example Hypothesis: Customers want their bank to help them build better savings habits
There are many things wrong with this hypothesis but we will focus on the hidden assumptions and the links to design decisions. Two big assumptions are that (1) it’s possible to find out what research participants want and (2) people’s wants should dictate what features or services to provide.
Research objectives
One of the biggest problem with using hypotheses is that they set the wrong expectations about what your research results are telling you. In Thinking, Fast and Slow, Daniel Kahneman points out that:
- “extreme outcomes (both high and low) are more likely to be found in small than in large samples”
- “the prominence of causal intuitions is a recurrent theme in this book because people are prone to apply causal thinking inappropriately, to situations that require statistical reasoning”
- “when people believe a conclusion is true, they are also very likely to believe arguments that appear to support it, even when these arguments are unsound”
Using a research hypothesis primes us to think that we have found some fundamental truth about user behaviour from our qualitative research. This leads to overconfidence about what the research is saying and to poor quality research that could simply have been skipped in exchange for simply making assumption. To once again quote Kahneman: “you do not believe that these results apply to you because they correspond to nothing in your subjective experience”.
We can fix these problems by instead putting our focus on research objectives. We pay attention to the reason that we are doing the research and work to understand if the results we get could help us with our objectives.
This does not get us off the hook however because we can still create poor research objectives.
Let’s look back at one of our prior hypothesis examples and try to find effective research objectives instead.
Example objectives: deciding on filters
In thinking about the colour filter we might imagine that this fits into a larger project where we are trying to decide what filters we should implement. This is decidedly different research to trying to decide what order to implement filters in or understand how they should work. In this case perhaps we have limited resources and just want to decide what to implement first.
A good approach would be quantitative research designed to produce some sort of ranking. But we should not dismiss qualitative research for this particular project – provided our assumptions are well defined.
Let’s consider this research objective: Understand how users might map their needs against the products that we offer . There are three key aspects to this objective:
- “Understand” is a common form of research objective and is a way that qualitative research can discover things that we cannot find with quant. If we don’t yet understand some user attitude or behaviour we cannot quantify it. By focusing our objective on understanding we are looking at uncovering unknowns.
- By using the word “might” we are not definitively stating that our research will reveal all of the ways that users think about their needs.
- Our focus is on understanding the users’ mental models. Then we are not designing for what users say that they want and we aren’t even designing for existing behaviour. Instead we are designing for some underlying need.
The next step is to look at the assumptions that we are making. One assumption is that mental models are roughly the same between most people. So even though different users may have different problems that for the most part people tend to think about solving problems with the same mental machinery. As we do more research we might discover that this assumption is not true and there are distinctly different kinds of behaviours. Perhaps we know what those are in advance and we can recruit our research participants in a way that covers those distinct behaviours.
Another assumption is that if we understand our users’ mental models that we will be able to design a solution that will work for most people. There are of course more assumptions we could map but this is a good start.
Now let’s look at another research objective: Understand why users choose particular filters . Again we are looking to understand something that we did not know before.
Perhaps we have some prior research that tells us what the biggest pain points are that our products solve. If we have an understanding of why certain filters are used we can think about how those motivations fit in with our existing knowledge.
Mapping objectives to our research plan
Our actual research will involve some form of asking questions and/or making observations. It’s important that we don’t simply forget about our research objectives and start writing questions. This leads to completing research and realising that you haven’t captured anything about some specific objective.
An important step is to explicitly write down all the assumptions that we are making in our research and to update those assumptions as we write our questions or instructions. These assumptions will help us frame our research plan and make sure that we are actually learning the things that we think we are learning. Consider even high level assumptions such as: a solution we design with these insights will lead to a better experience, or that a better experience is necessarily better for the user.
Once we have our main assumptions defined the next step is to break our research objective down further.
Breaking down our objectives
The best way to consider this breakdown is to think about what things we could learn that would contribute to meeting our research objective. Let’s consider one of the previous examples: Understand how users might map their needs against the products that we offer
We may have an assumption that users do in fact have some mental representation of their needs that align with the products they might purchase. An aspect of this research objective is to understand whether or not this true. So two sub-objectives may be to (1) understand why users actually buy these sorts of products (if at all), and (2) understand how users go about choosing which product to buy.
Next we might want to understand what our users needs actually are or if we already have research about this understand which particular needs apply to our research participants and why.
And finally we would want to understand what factors go into addressing a particular need. We may leave this open ended or even show participants attributes of the products and ask which ones address those needs and why.
Once we have a list of sub-objectives we could continue to drill down until we feel we’ve exhausted all the nuances. If we’re happy with our objectives the next step is to think about what responses (or observations) we would need in order to answer those objectives.
It’s still important that we ask open ended questions and see what our participants say unprompted. But we also don’t want our research to be so open that we never actually make any progress on our research objectives.
Reviewing our objectives and pilot studies
At the end it’s important to review every task, question, scenario, etc. and seeing which research objectives are being addressed. This is vital to make sure that your planning is worthwhile and that you haven’t missed anything.
If there’s time it’s also useful to run a pilot study and analyse the responses to see if they help to address your objectives.
Plan accordingly
It should be easy to see why research hypothesis are not suitable for most qualitative research. While it is possible to create suitable hypothesis it is more often than not going to lead to poor quality research. This is because hypothesis create the impression that qualitative research can find things that generalise to the entire user base. In general this is not true for the sample sizes typically used for qualitative research and also generally not the reason that we do qualitative research in the first place.
Instead we should focus on producing effective research objectives and making sure every part of our research plan maps to a suitable objective.
Detailed Guide On Developing UX Research Plan
When you decide to travel to a country you’ve never visited before, you’ll probably start with a plan. You need to check the price of the tickets, transfer options, find somewhere to stay and what places to visit, and probably learn some basic phrases in the local language just in case. Without planning, there’s a chance that your trip will turn into a real challenge, and you won’t enjoy it at all.
The same goes for UX research – without a clear plan, you’ll waste time and money and won’t be able to align your business goals with a research strategy. Think about UX research as the starting point of your product development, and always start with a problem, never an idea. When you understand what issues users have, you can come up with a solution more easily.
At IntelliSoft, creating UX research plans has been one of our main tasks for more than 16 years of working with clients, so we know how nuanced this process is. Fortunately, this experience now allows us to guide our clients through the process of UX research and help them build a base for their future products.
If you want to learn more about research planning and how to become a master in it, keep on reading.
Table of Contents
What is a UX research plan?
Planning ahead is the key to conducting usability testing or user research. A research plan is a detailed description of the steps you will take during your UX research. Think of it as a roadmap and guide that helps you conduct research easier and faster because you have everything outlined in front of you in a document.
A UX research plan usually includes details about the methodology of the research, types of studies, and information about the timing, scope, and respondents.

Don’t confuse a UX research plan with a strategy – they are two separate things. A strategy contains goals, expectations, vision, and business goals, while a plan explains how a team will achieve those goals. A strategy is a guide, but a plan is what helps put it into action.
When to use UX research plans
Research plans are useful if you want to have a clear outline of your project scope and know what steps to follow. It also helps teams answer questions regarding customers’ needs and who the target audience is. Moreover, it helps companies identify whether their current design works for customers or needs to be altered somehow.
A detailed plan also helps researchers to:
- Clarify ideas, research approaches, and issues that need to be solved
- Identify what works for stakeholders
- Keep stakeholders invested in the research results
With a plan, there’s less chance that everyone will switch the research goal in the middle by mistake, or get lost in all the details. Moreover, plans allow researchers to ensure that all set goals will be met in the most efficient way and according to the timeline.
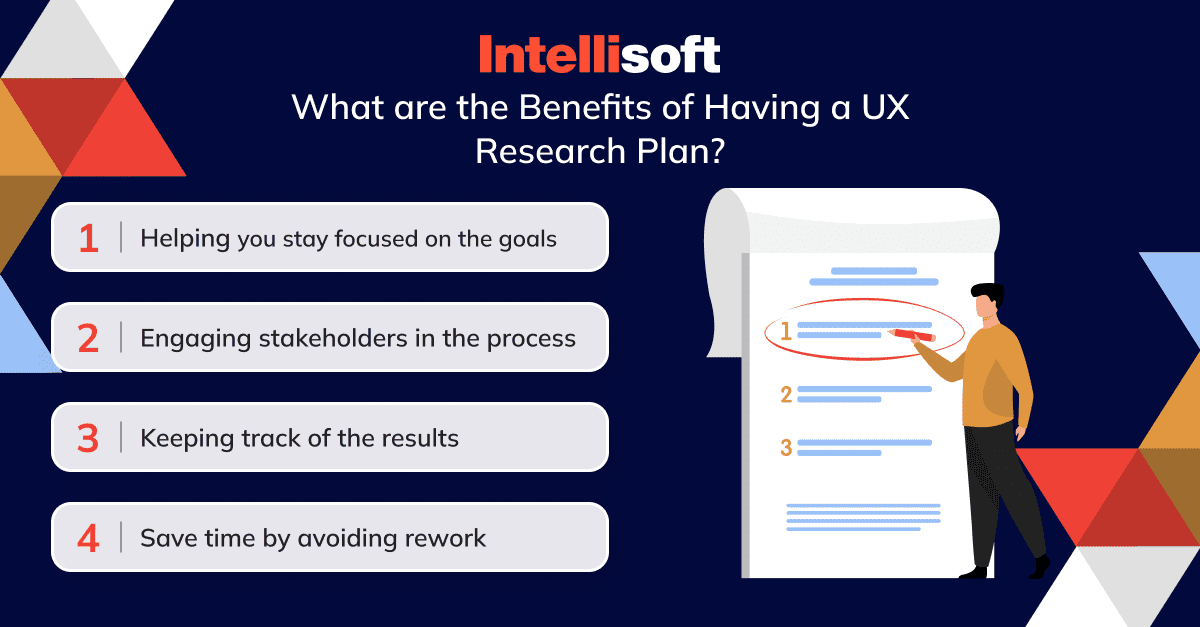
What are the benefits of having a UX research plan?
You can’t start any research without having clear goals in mind, so having a UX research plan is incredibly beneficial for your product’s success and your business as a whole. Let’s take a look at the main benefits of creating a detailed plan.
Helping you stay focused on the goals
Setting goals is one of the primary aspects of creating a research plan. You need to know what you’re moving towards and how you’ll get there. A research plan helps you stay focused on those goals and not get distracted. When you have goals outlined in a document, your entire team is constantly reminded of the end goal and works towards it. With a clear plan, all your goals become measurable rather than vague and unachievable. Moreover, you can turn it into a UX research plan template and reuse it for future projects to save time.
Engaging stakeholders in the process
A written plan is an awesome way to engage your stakeholders in the project and ensure that they are on the same page regarding the timeline, scope, and goals before you start working. When you align all the details of your research in one document, updating stakeholders on the progress of your project and the achieved goals is a piece of cake. Your stakeholders need to see your achievements and that your project is going somewhere, so a research plan will help you keep them invested.
Keeping track of the results
You can’t keep track of your UX research results in your head because it will explode. A plan will serve as a handy roadmap of everything that has already been done and what’s in the process, keeping all data in one place and structuring it efficiently. You also need this plan to monitor your progress or see what areas require improvement.
Save time by avoiding rework
If you don’t have a clear plan, the chances are you’ll have to redo certain tasks, fix usability issues, and waste a lot of time. With a plan, you can make changes during the design or prototyping phase, which is far less expensive and time-consuming. Once you launch your product, making even small alterations can cost you a fortune and affect the usability of the product. Moreover, when your team has a plan in front of them, they know what direction to take in their research, so it positively influences the use of resources.
What should a UX research plan include?
Your plan is a detailed guide that will help you follow the steps you need to go through during research, and ensure that your study is more effective. This is what a plan should include:
- Background information about the project, reasons for the study, and information about internal stakeholders
- Research goals and what the team wants to learn
- Data about research participants, who they are, sample size, and how people will be recruited
- Research methodology , the way the research is conducted, and explanation of why you chose the specific test methods
- An interview guide/template and list of questions
- A list of expectations , including deliverables, type of results, and timing
- Resources that can help the team, such as scripts, previous studies, etc
- The test set up and/or guidelines such as screening questions, scenarios, and duration of pilot tests
- When and how the results will be presented
- Estimations about costs or requests to go over budget
How to create a UX research plan
Now that you know exactly why you need a research plan, it’s time to explain all the hows. Here is a detailed guide on how to create a plan that you can later use as a UX research plan template.
1. Define the problem statement
You need to start with the problem. Identify what exactly you want to solve and what you want to achieve with your research. Don’t do it by yourself, though. You can sit with the stakeholders and brainstorm, looking at the problem space. You can also perform team sessions, analyze customer feedback, or interview your stakeholders to better understand what issues might need solving. The problem statement is all about defining the research scope and understanding the deliverables and end goals.
Related readings
- Assembling Your Dream Design Team: A Comprehensive Guide
- User Story Acceptance Criteria Explained with Examples
- Who Does What? Understanding Roles in a Software Development Startup
- What Is Iterative Design Process?
2. Identify your objectives
After you have identified the issue, move on to identifying the objectives. The research objectives should align with the UX strategy and your business goals as well as meet the targets you have set for the research. Your plan should include information about what you are doing, why you are doing it, and what you expect from the UX research.
These are the research plan example objectives:
- Improve customer loyalty
- Discover what technology your competitors are using
- Prioritize new features and learn how people use them
- Understand why people spend a specific amount of time on your website and (don’t) return to your web page/app
- Learn when people interact most with your web page/product
If you don’t set valuable objectives, you can suffer from scope creep and let your stakeholders ask any types of questions they want, leading your research in a wrong direction. When you set objectives, they influence the type of questions asked, giving your research more focus.
To help you identify the objectives, ask yourself and your research team these questions:
- What do you plan to do with this information?
- What decisions will it influence?
- How are you going to use these insights?
3. Involve stakeholders
It is essential that you involve stakeholders at the earliest stages of plan creation. Your goal should be to ensure that everyone is on the same page about the goals of the research. Moreover, involving stakeholders helps you gather more context, make adjustments based on their feedback, and focus on what matters the most to them.
Identify key stakeholders and present the plan to them, aligning the scope of the research and letting them know when and how you will present the research findings. Moreover, this step helps you broaden your vision and take into account stakeholders’ opinions on the product. Listen to what they have to say, analyze this information, and use it to your benefit. Your stakeholders should be participants, not just viewers.
4. Choose the research method
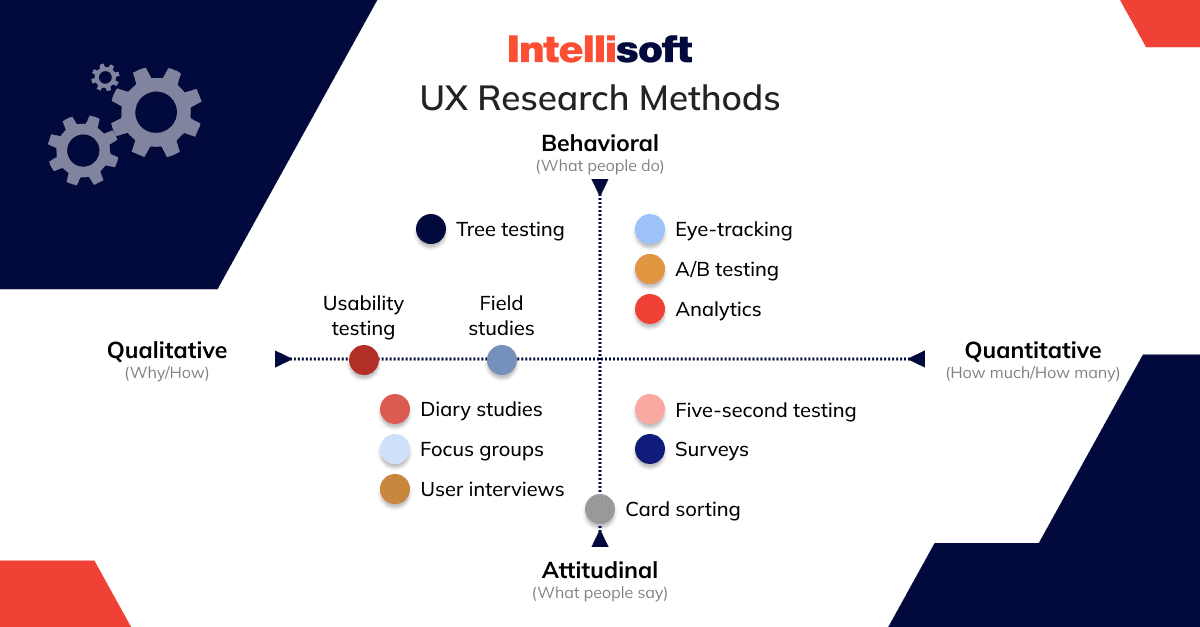
There are numerous research methods to choose from, but you need to go back to your research goals first. The method of research will also depend on the stage of product development, your resources, constraints, and the timeline of the project. You can also mix different research methods to get a clearer picture of the issues you need to solve.
For example, performing user interviews or field studies is a great way to generate new insights about your target audience at the early stages of the design process. If you have already created a new design and want to see how people use it, you can run usability tests and gather feedback.
Let’s look at the list of UX research methods you should consider:
- Five-second testing: It helps you gather insights about what information users take away and what their impression is within the first five seconds of viewing the design. The participants view the design for five seconds and then answer some questions, usually about the purpose of the page, the main elements that a person can recall, or whether the design looks trustworthy.
- User interviews: This is a fast and easy way to gather user feedback and learn about users’ perceptions of your design. You need to set a goal for the interview, prepare a list of questions, and ask follow-up questions based on your research goals.
- Surveys: Surveys allow you to collect both qualitative and quantitative insights from users. They should be conducted across all customer journey stages to identify what is blocking users from progress.
- Tree testing: This research method is used to evaluate the hierarchy and findability of topics in a website/app. It consists of category or text labels that are organized hierarchically. The goal of this method is to answer the question of whether the user can easily find what they are looking for. It also helps identify gaps in navigation, see whether the content is grouped logically, and identify how easily users can access specific functionalities.
- Field studies: When using this research method, you observe people in their natural environment to gather insights about their behavior, obstacles, preferences, and so on. This method helps identify how digital products or services can be better integrated into the daily lives of users.
- Card sorting: Card sorting helps you see how users categorize information, making your UX more user-oriented and competitive. During card sorting, people are asked to group labels according to the criteria that make more sense to them. As a result, you can learn more about peoples’ domain knowledge and meet their user expectations with your app/website design.
- Diary studies: Diary research is used to collect qualitative data from users’ diaries where they collect their thoughts and feelings while using the product. Users should report data during an extended period of time, allowing you to understand the user experience better and what influences it. This research method functions as a window into the real way people interact with the product.
5. Recruit participants
Your plan should always include data about the participants and the way you will recruit them. You should identify who your perfect candidate for the research is by revisiting your goals and the list of questions you need answering. Build a target user persona based on this information, including the demographics and use cases.
These are the questions you need to answer during this step:
- Do you already have a user base you can collect information from?
- What is your recruiting budget?
- Is there a need to hire external participants?
- How many users do you need to interact with?
You should have several target personas, so keep that in mind when recruiting participants. This means that you should recruit people who are your target base and those who aren’t, but will still interact with the product. Moreover, if you create an app for different devices and OSs, recruit people for testing it, too. Some participants will use your app on iPhones, while the other group will test it on Android phones.
Always reward your participants for their time and effort. That’s why you need to plan your budget ahead and take into account this spending. If your budget is limited, run moderated or unmoderated research.
6. Prepare the brief
The next step is preparing the brief for your research session. The type of brief will depend on your research method, but if you choose to conduct user interviews, focus groups, or field studies, you need to outline the questions you will ask and create a script.
Your script should cover the following:
- Introduction: A message you will say to the participants before the session. This will help you start the conversation, set the tone for the meeting, and explain the purpose of the research.
- Interview questions: Always include the list of questions you will be asking. You can include pre-planned questions or test tasks for your participants to perform.
- Outro message: Finally, you should inform your participants about the next steps, ask if they are open to future research, and thank them for their time.
7. Establish the timeline
Even though it’s challenging to estimate objectively how long the project will take, it is essential to determine an approximate timeline at least. You should set deadlines for the project and findings review and present this timeline to the stakeholders. Moreover, this step will allow you to manage their expectations better. You can also add milestones to indicate your progress and see how much time each activity takes.
8. Decide how you’ll present your findings
Presenting your findings to the team during UX research is one of the key steps. The format of the presentation matters because you should present the findings in a concise and easy way so that everyone understands how the research will influence the design and development of the product.
You can present your findings in the following ways:
- A PDF report (either physical or digital) with key takeaways and statistics
- A digital whiteboard
- An interactive online report
- A presentation with information about the results
UX research plan template
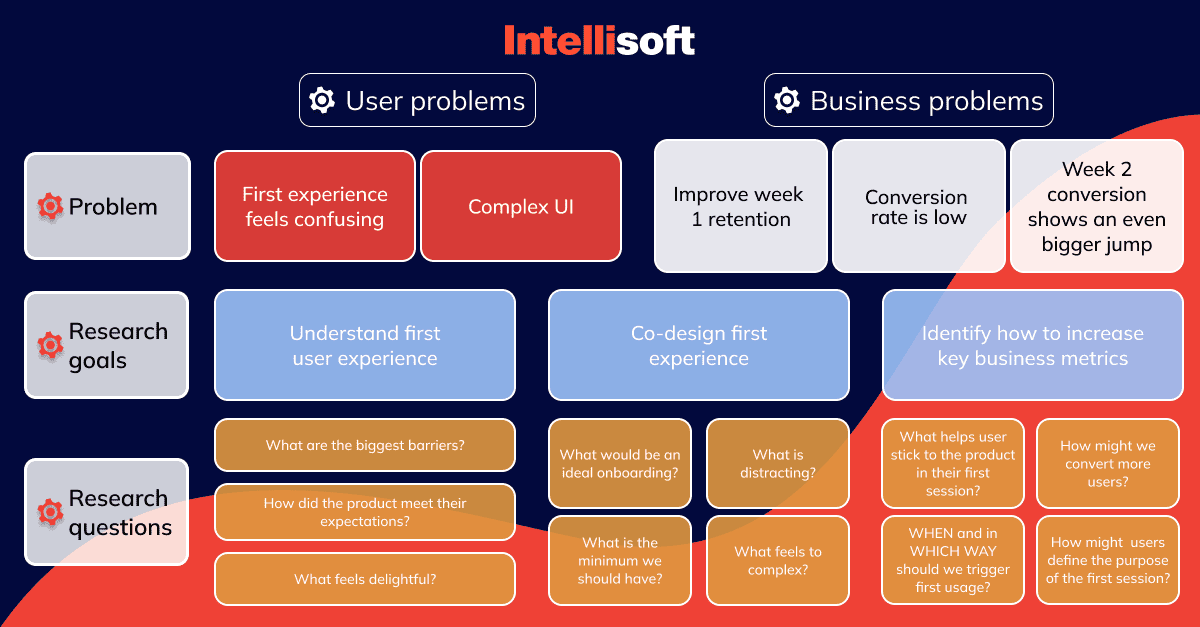
If you want to create plans quickly, you can either use an existing UX research plan template or turn your previous plan into one. Either way, a UX research plan template should consist of the following:
1. Background
This first section should include information on why you decided to initiate this research. Think of it as a brief explanation for anyone wondering why you’re doing this.
You can break this section down into 3 paragraphs:
1 – What led to the research? What needs to be explored? 2 – What has already been done prior to this research? 3 – What insights will this research bring? How will this data be used and what decision can be made based on it?
2. Objectives
Your plan should cover two types of data: business/product objectives and KPIs, and research success criteria.
The business/product objectives and KPIs section should cover information about what your stakeholders/teams are trying to achieve. Some of the objectives might include customer loyalty, revenue growth, customer growth, or efficiency.
The research success criteria usually consist of the following:
- What qualitative and quantitative data about the users will be collected?
- What documents should be created?
- What decisions should be made with the insights generated during the research?
3. Research methods
Next, you should list all research methods you will use, both primary and secondary. You should also include brief explanations of each method for your stakeholders if they are not familiar with some of them.
4. Research scope & focus areas
In this section, write down approximately 6 topics of questions (can be less) and rank them by importance. Next, design focus components that include interface qualities. Finally, include primary user scenarios. All this will help identify the research scope and not get overwhelmed while collecting information.
5. Research participant profiles
Include information about user segments, where and when you will recruit them, and information about the criteria used to screen them.
6. Appendix
This is the final part of the plan. It should include the information discussed prior to creating the research plan. For example:
- Highlights of meeting notes
- Initial hypotheses
- User ecosystem map
A UX research plan is what lets you breathe out and be sure that the research process will go smoothly and without unpredictable issues. Once you have the plan in front of you, you know what to focus on, how to talk to the stakeholders, and manage your team. It’s one of the easiest ways to align everyone’s expectations, gather feedback, and ensure that everyone knows exactly what to do during the research. If you have never created research project templates and need guidance, Intellisoft is there to help, just contact us .
What’s the difference between a UX research plan and a UX research strategy?
The plan and strategy cover different levels of scope and detail. A plan is a document that guides UX research projects, while a UX research strategy outlines more high-level goals, expectations, and the demographics of the discovery.
What should you include in a user research plan?
Here’s what you should include in your UX plan:Problem statement Background information Research goals Data about research participants Research methodology An interview guide A list of expectations Resources The test set up Estimations about costs
How to write a research plan for UX design?
The first thing you need to do is create a problem statement and outline your objectives. Then, you choose the research method or several methods, recruit participants, brief them, and establish a timeline for the project.
What are the 7 elements of the UX plan?
The 7 elements of a plan includeProject background Research Goals Research Questions Key Performance Indicators (KPI) Methodology Participants Script
What are the four key things to include in your research plan?
You should answer these 4 questions: What do you intend to do? Why is the work important? What has already been done? How are you going to do the work?
What are the six 6 steps in implementing the research plan?
The 6 key steps are: Identify the opportunity Develop a plan Collect the data Analyze the data Present the results Incorporate findings
What is a UX research brief?
A brief is a document that outlines your research goals, important milestones and dates, key contributors, and timelines. It can also cover budget information, recruitment details, and access to past research.
What are UX research goals?
UX research goals are the things you want to achieve with your research, and the reason why you’re conducting your research. The goals are the driving force of the research and every task you assign to the team.
What are the UX research deliverables?
UX research deliverables are the tangible outputs and documentation that result from conducting user experience research. Common UX research deliverables include a research plan, a user recruitment screener, a discussion guide, user interviews, personas, user journey maps, wireframes and prototypes, and actionable insights.
How do you write a good UX research objective?
To write a good UX research objective, you first need to clearly identify the purpose and goals of the research study. You need to understand the context of the problem you’re addressing, define the scope, identify the research goal, specify the research questions, consider your audience, and keep it focused and realistic.

About Kosta Mitrofanskiy

Related Posts


Home > Blog >
How to write a ux research plan that actually works: 7-step tutorial, saviour egbe, august 29, 2023.
A UX research plan is like a map that will help you navigate the complexity of running a research project. It will help you define your goals, choose the right methods, and collect the data you need to make informed design decisions.
But UX research plans don't have to be boring. In fact, they can be quite funny. For example, one UX researcher I know has a section in his plan called " The Things That Make Me Cry ." This is where he lists all the things that he's learned about his users that make him sad, such as the fact that they often have to deal with frustrating interfaces or unhelpful customer service.
But the primary use of a research plan of course is to make sure that your research is effective. So, while it’s helpful to have a sense of humor, you also need to be serious about your research.
In this article, we'll consider:
- What a UX research plan is and why it's important
- How to create a UX research plan
- An example of a well-structured UX research plan and
- A template for a UX research plan you can use to get started
So, whether you're a UX newbie or a seasoned pro, read on for everything you need to know about UX research plans!
What is a UX Research Plan?
A UX research plan is a document that outlines the goals, methods, and timeline for your research. It's a roadmap that will help you stay on track and ensure that your research is productive.
A good UX research plan should include the following:
- A clear statement of the research goals: What do you hope to learn from your research? What are the specific questions you're trying to answer?
- A description of the target audience: Who are the people you're designing for? What are their needs and pain points?
- A selection of research methods: There are many different research methods available, so it's important to choose the ones that are right for your goals and target audience.
- A timeline and budget: How long will your research take? How much money will it cost?
- A plan for data analysis and presentation: How will you analyze your data and communicate the findings to others?
Why is a UX Research Plan Important?
A UX research plan is important for several reasons. It helps you:
- Stay focused and avoids wasting time and resources.
- Ensures that your research is relevant to the needs of your users.
- Get buy-in from stakeholders & align on the goals for the project.
- Provides a framework for organizing and analyzing your data.
- Helps you communicate the findings of your research to others.
How to Create a UX Research Plan
Creating a UX research plan is an important step in ensuring that your product or service is user-friendly and meets the needs of your target audience. Here are the essential steps to create a research plan that drives meaningful insights and successful user experiences:
Step 1: Alignment & Requirements Gathering
Research rarely will happen in a vacuum. Usually you are working with a team—product, engineering, design, for example.
When the need for a research study arises, the first thing you want to do is meet with your team to understand the questions they're trying to answer.
Depending on how formally set up your research practice is, you may even want to supplement this step with a Research Request document where stakeholders can explain the key questions they'd like to answer, why they're important, and any constraints (budgets, timelines) they're working with.
Step 2: Define Your Goals
Once you've gathered your data, the next step is to clearly define & write out your goals. What do you hope to learn from your research? What specific questions are you trying to answer?
Here are some things to consider when framing your goals:
- What are the business objectives for your product or service? Are you trying to grow active users? Or reduce churn? What should the final results of this research project help you do?
- Who are your target users? These are the people you’d like to learn more about.
- What do you want to learn about their behavior and preferences? This will help you determine your research questions. Ideally the answers to these questions should also tie to your business goals so there’s a clear line between what you’re trying to learn and what that learning will do for the company.
Once you’ve thought about and drafted the answers to these questions, make sure to follow the below steps before starting interviews:
i. Assess Internal Data and Identify Research Needs
Before you start collecting new data, take some time to assess any existing data you have. This could include analytics, customer feedback, or previous research findings. This will help you identify any gaps in your knowledge and determine what areas need to be explored further.
Sometimes you’ll find you already have the answer to your research question in-house—saving you weeks of research effort and thousands of dollars of investment!
If you’re trying to build a repository to help you do this more effectively, check out this definitive guide on research repositories .
ii. Link Research Goals to Business Objectives
It's also important to link your research goals to the business objectives of your organization. This will help you justify the time and resources that will be required for your research. By demonstrating how your research will help you achieve your business goals, you'll be more likely to get the support you need.
As a bonus, once your research is complete, you can go back and track its impact against these business goals. This will help you build a case for your own work and the research practice at your company.
As you proceed through Step 1, keep in mind that your research goals should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). This framework will help you ensure that your goals are well-defined and actionable.
Step 3: Identify Your Target Audience & Plan a Recruiting Strategy
Knowing your audience is essential for creating a UX research plan that delivers relevant and actionable insights. In this step, we'll talk about how to define your target audience and plan a recruiting strategy for this set of users.
The target audience you’re considering this research study may overlap with your standard target users, or you may want to speak with a subset of this group.
For instance, if you’re doing a research study on why users churn, speaking to a regular active user won’t help. You’ll need to define and recruit users who can actually answer your questions well—in this case it could be “users who have churned in the last 2 weeks”.
When defining the audience for this study, think about whether your target user falls in a specific category based on one of these characteristics:
- Demographics: This includes basic characteristics, such as age, gender, location, and occupation.
- Behaviors and habits: Are you interested in users who have or have not conducted certain actions on your product? For research on how well your Slack integration works, you may want to speak to users who have already installed it, for example.
- Needs and use cases: Sometimes one product can have multiple use cases. For example, a transcription product could be used by researchers, or journalists, or students trying to capture their class notes. Which use case or needs are relevant to your research study?
- Payment type: In today’s world products may have free, freemium / trial, or paid users and each of these groups may behave differently. Think about whether you need one or all of these user types as part of your research.
Now that you know who you need to reach, you also need to think about how to reach them.
Recruiting, as we all know, is a major pain point for (most) researchers. There are some ways to speed it up though.
If you’re running research for a B2C product or an easy to find B2B cohort, you may want to turn to an external recruiting software like UserInterview.com or Respondent.io. There are also local agencies to help you find more local audiences in international markets.
If you are trying to recruit via an external paid channel like this, make sure to budget it in your research plan. These channels are very quick to set up research calls with, but they do come with an added cost.
If you’re running research with a niche B2B audience or are defining your audience based on behaviour on your product (e.g., user who churned in the last 2 weeks), you may need to use internal recruiting methods. This means reaching out to your own users via email, intercom, or via your sales / support team.
If you are recruiting existing customers, make sure to budget in the time it takes to recruit these users. It may take a few days to weeks to gather the relevant user emails and schedule calls, although paid incentives for research help this move much faster.
If you are planning to recruit your own customers, use our Ultimate Guide to Recruiting Your Users for Interviews and Usability Tests . This article has templates for outreach, incentive payment options, and many tactical tips to help you streamline internal recruiting.
Remember, the accuracy and relevance of your research findings depend on the quality of your participants. Take the time to identify and engage users who genuinely reflect your intended audience. This will help you create a research plan that generates insights that drive impactful design decisions.
Step 4: Choose Your Research Methods
Choosing the right research methods is necessary for getting the most out of your UX research plan. Before kicking off your study, make sure to review the possible ways you can answer your research question as well as any constraints you face regarding time, money, or tooling.
If you’re not sure which methods exist, read through this article on UX Research Methods . This article provides an overview of the different methods, so you can choose the ones that are right for your project. It covers everything from usability testing to card sorting, and it includes practical advice on how to conduct each UX research method effectively.
When you’re actually selecting the right method out of the available options, here are the key questions you need to ask yourself:
- Your research goals: What do you hope to learn from your research? The methods you choose should be aligned with your specific goals. For example, if you need to deeply understand user motivations, a user interview is much better fit than a survey.
- Quantitative vs. qualitative: Do you want to collect quantitative data (numbers and statistics) or qualitative insights (in-depth understanding)? Different methods are better suited for different types of data. If you need to know the percentage of users using Zoom vs GoogleMeet, a 5-person user interview won’t get you that data but a 100 person survey with a representative sample might.
- Resources and time: How much time and money do you have to spend on your research? Some methods are more time-consuming or expensive than others. For instance, an ethnographic study where you travel to see your users is obviously more expensive and time-consuming than a 30-minute remote user interview.
By considering these factors, you can choose a combination of research methods that will help you understand your users better.
Step 5: Define your timelines & budgets
Now that you know your target audience (and therefore recruiting method) and your research methods, you can define the timelines and budgets your stakeholders care about.
- Timelines: How long will it take to conduct your research? This will depend on the methods you choose, the number of participants you need to recruit, and the amount of data you need to collect. For example, user interviews can typically be conducted within a few weeks, but usability testing can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the number of participants and the complexity of the product or service being tested.
- Budgets: How much money will you need to conduct your research? This will depend on the methods you choose, the number of participants you need to recruit, and the cost of data collection and analysis. For example, user interviews can be conducted for a few hundred dollars, but usability testing can cost several thousand dollars, depending on the number of participants and the complexity of the product or service being tested.
Step 6: Identify your assumptions
Sometimes without realising it, our research study comes packaged with a set of assumptions about who users are and what they want.
Before kicking off your study, it’s important to identify these assumptions in writing and align on them with your team.
For instance, if you’re running research on how to improve a Slack integration, your in-built assumptions may be:
- Users already use this integration
- It’s worth improving this integration further
Once you’ve laid out these assumptions in advance of your research, you can check them against existing data and keep them in mind when you’re reviewing your research findings.
For example, if analytics data shows that no users use your Slack integration, it may call into question the research you’re running today or change the audience you speak to about it.
Instead of speaking to existing Slack integration users, your audience may need to be companies that have Slack but have not downloaded your Slack integration.
Your research questions may also shift from “Why do you use the Slack integration?” to “Why not? ”
In general, taking a moment to review research assumptions helps you be more aware of them throughout your research study.
Step 7: Define the research questions
This is a pivotal phase in the UX research process. It's when you define the questions that will guide your data collection efforts. These questions will be your compass, directing your research toward meaningful insights that drive product improvements.
Here are some tips for crafting and structuring your research questions:
- Make sure each question is aligned with your overall research objectives. This will ensure that your findings address the core goals of your project.
- Make your questions clear, concise, and specific. Ambiguity can lead to varied interpretations and muddy insights.
- Frame your questions from the user's perspective. Use language that aligns with your target audience to ensure your questions are relatable.
- Avoid leading questions. These are questions that nudge participants towards a particular response. Aim for neutrality to get real insights.
- Use a mix of open-ended and closed-ended questions. Open-ended questions allow participants to provide detailed responses, while closed-ended questions offer predefined answer choices.
- Structure your questions logically, moving from broader inquiries to more specific ones. This will help participants to follow your thought process.
- Limit the number of questions. You want to get comprehensive insights but don't want to overwhelm participants with too many questions.
- Cover the core areas relevant to your project. This could include user pain points, needs, preferences, expectations, and perceptions.
- Pilot-test your questions with a small group of participants. Their feedback can help you to identify unclear or misleading questions.
- Make sure your questions are relevant to the research methods you will be using. For example, usability testing may focus on task-oriented questions, while interviews explore broader experiences.
Here are some examples of well-defined research questions:
1. Usability testing:
- How easily can users navigate the Looppanel account setup process?
- What challenges do users face when uploading their recorded calls to Looppanel?
- How intuitive is the process of setting up Calendar integration on Looppanel?
2. Interviews:
- Can you describe a recent experience you had with the Looppanel customer support?
- What motivated you to sign up for Looppanel for your user research needs instead of other platforms?
- In your view, how does the platform assist in taking your user interview notes effectively?
By carefully defining your research questions, you can ensure that your data collection efforts are focused and meaningful. This will help you to gather the insights you need to improve your product or service and deliver a better experience to your users.
Step 8: Align with your team
Now that you’ve thought through the basics, it's essential to get buy-in from your team and stakeholders on the final plan.
A lot may have happened between your first requirement-gathering meeting and when your plan is finalized. Take the final plan to stakeholders and make sure they are aligned:
- The research question you’re going to answer
- How your study ties to business goals
- Which users you’ll be engaging with
- Which method you’ll be using
- What your timelines look like
- What your budget looks like (if applicable)
This step is really important because if there’s a lack of alignment between you and your key stakeholder, you may end up with findings nobody is going to act on.
Example UX Research Plan
Here is an example UX research plan for improving the onboarding experience of a mobile app. Use this example as a guide to help you create your own plan!
Psst… we also have a template below that you can copy and use!
Project Title: Research study to improve onboarding experience on DuoLingo
Business Goal: We want to increase the activation rate of new users on the app.
Project Goal(s) :
- Identify key drop-off points on the onboarding flow
- Identify why users are dropping off at these points
Target Users: People from the 15-40 age group in North America who have not used Duolingo before.
- MixPanel analytics data to identify existing drop-off points for users
- Usability testing with the think aloud protocol to understand why users are dropping off at those points
Timelines: The study will run for 4 weeks:
- Week 1: Analyzing existing analytics data & recruiting participants
- Week 2: Running usability tests
- Week 3: Analyzing results
- Week 4: Presenting findings
Budget (if applicable): Anticipated spend of $500 on recruiting.
Key Research Questions These are the research questions we’ll be gathering data on :
- At which point(s) in the onboarding process are users most likely to drop off?
- What are the common reasons users cite for discontinuing the onboarding process?
- How do users perceive the clarity of instructions during the initial setup stages?
- Are there any specific usability issues that lead users to abandon the onboarding flow?
- How do users' prior experiences with language learning apps impact their expectations of DuoLingo's onboarding?
UX Research plan template

We’ve also created a UX Research plan template you can use easily duplicate and use for your own work.
Click here to get Looppanel's UX Research Plan template.
This template contains sections for:
- Project Title
- Business Goals
- Project Goals
- Target Users
- Research Methods
- Timelines & Budgets
- Key Research Questions
Follow us on
Get the best resources for ux research, in your inbox, related articles.

Resources & Guides
April 21, 2023
15 Best UX Research Tools for User Researchers - 2024

August 1, 2023
How to Choose the Right UX Research Method

November 8, 2022
A Definitive Guide to the UX Research Repository [2024]
Looppanel automatically records your calls, transcribes them, and centralizes all your research data in one place
UX Research Plan Template
Create a strong business case for UX research and streamline your process with the UX research plan template.
Trusted by 65M+ users and leading companies
About the UX Research Plan Template
A UX research plan, also known as a user research plan, is a brief reference document that outlines your research project’s goals, key contributors, important dates, and timelines.
Think of your research plan as a UX-focused kick-off document for your project. The plan offers an overview of the research initiative, encourages well-defined and agreed-upon goals, and acts as a written guarantee that the research will meet these goals.
What is a UX research plan?
When conducting usability testing or user research with a goal in mind, researchers need to plan. UX researchers often present their findings to stakeholders, like product managers, developers, marketers, and executives, to act on those results.
You should present your UX research plan in plain language with a single document. Keep your findings clear, collaborative, easily accessed, and digestible to get buy-in for your research and your team’s next steps.
A user research plan typically has up to seven segments:
Project background: Reasons for the study and internal stakeholders involved.
Research goals and objectives: What your teams want to learn, or their ideal research outcome.
Research participants: Who they are and how they’ll be recruited.
Method: How you conducted research, and any other information about how the research will be conducted.
Guides: An interview guide or cheat sheet of instructions and questions to follow during the session.
Duration: A rough timeline of how long the research will take and when the team can review the report.
Other helpful information: Additional resources for your team, such as previous studies, scripts, or results, can inform this new round of research.
Research plans keep your team focused on outcomes rather than getting lost in the details or changing the research goal midway through the project. By the end of the project, UX researchers should feel confident that their questions were answered and presented in both the plan and actual research.
When to use UX research plans
UX research plans are useful for teams who need to decide on questions such as:
What do our customers need? Who is our target persona?
Does the proposed or current design work well for our customers? How can we make it better?
Planning UX research also gives researchers an opportunity to:
Decide what works for your stakeholders, especially the questions they’re trying to answer.
Engage stakeholders and keep them invested in your research results.
Clarify your ideas, problems to be solved, and research approaches.
Treat your research plan as a blueprint for aligning expectations, asking for feedback, or generating enthusiasm and support for increasing the value of user research in your organization.
Create your own UX research plan template
Making your own UX research plans is easy, and Miro is the perfect tool to create and share them. Get started by selecting the UX research plan template, then take the following steps to make one of your own.
Give your team or stakeholders a quick project introduction. You can hop on a video chat with up to 25 team members and remind everyone what you’re trying to achieve. Remember that research proves its value when it satisfies a single objective rather than many. If you seem to have lots of different goals or objectives, avoid overreaching and start fresh: what’s the one customer problem and business problem you’re trying to solve?
Define the user and business problems your research needs to solve. The default sticky notes are simply for inspiration — feel free to edit each of these to fix your own context. If you want your team to focus on this area instead of skipping ahead, you can select the “problem” frame and click the “hide frame” (closed eye) icon that appears in the frame’s menu.
Define your research goals. Ask your team to brainstorm their top three research goals or priorities. Remember that the best research sessions are chasing a single objective, so out of the two to three you note down, ask your team to vote for their preferences. Try Miro’s Voting Plugin to help your team reach a decision.
Draft your research questions. Pick three to five questions with your team or stakeholders that are most important to your research. Aim for no more than 10. The more focused your questions, the more focused your research will be.
Link to useful supporting information as needed. Keep this plan to the point in order to get buy-in. For stakeholders who need more detail, there may be other useful data to link to. If you have previous UX research results or relevant studies, link to them on your Miro Board. You can also import survey data, embed tables and charts , or link sticky notes to external sources .
Dive even deeper into how to conduct UX research – and see examples – in our expert guide to user research .
Why should you use the UX Research Template?
Centralized planning: Centralize your UX research plans in one shared space. This ensures that all relevant information, including research objectives, methodologies, and timelines, is easily accessible in one place, reducing the risk of scattered or lost documentation.
Collaborative research: Multiple stakeholders, including designers, researchers, and product managers, can collaborate on your UX research plan template simultaneously, fostering a more inclusive and collaborative approach to research planning.
Visual representation of research steps: Create diagrams, flowcharts, and visual representations of the research process. This visual mapping helps teams better understand the sequence of research activities, identify dependencies, and effectively communicate the overall research strategy.
Iterative refinement: Provide feedback, comments, and suggestions directly on the UX research plan template. Promote continuous improvement, allowing the team to refine the research plan based on insights and changing project requirements.
Integration with user flows and personas: Integrate with other templates, such as user flows and persona maps. By connecting these elements, teams can create a holistic view of the user experience journey. This integration helps align research activities with the overall UX strategy and ensures a more cohesive and user-centric product design.
How can I ensure that a UX Research Plan remains effective?
Regularly review and update the research plan as project requirements evolve. It's crucial to stay flexible and adapt the plan based on the findings and changing project needs.
Get started with this template right now.
Example Mapping Template
Works best for:.
Product Management, Mapping, Diagrams
To update your product in valuable ways—to recognize problem areas, add features, and make needed improvements—you have to walk in your users’ shoes. Example mapping (or user story mapping) can give you that perspective by helping cross-functional teams identify how users behave in different situations. These user stories are ideal for helping organizations form a development plan for Sprint planning or define the minimum amount of features needed to be valuable to customers.

PESTLE Analysis Template
Ideation, Strategic Planning, Business Management
Want to keep your company secure and performing soundly? You have to first know how you’ll be affected by outside elements and factors — especially those that are political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental in nature. A PESTLE Analysis helps you identify them and prepare for them. With this easy-to-use template, you can conduct a PESTLE Analysis, then use the results to shape your strategic planning, budget allocation, marketing, product updates, and organizational change initiatives.
Jobs to be Done template
Ideation, Design Thinking, Brainstorming
It’s all about a job done right — customers “hire” a product or service to do a “job,” and if it's not done right, the customer will find someone to do it better. Built on that simple premise, the Jobs To Be Done (JTBD) framework helps entrepreneurs, start-ups, and business managers define who their customer is and see unmet needs in the market. A standard job story lets you see things from your customers’ perspective by telling their story with a “When I…I Want To…So That I …” story structure.
HEART Framework Template
Desk Research, Project Management, User Experience
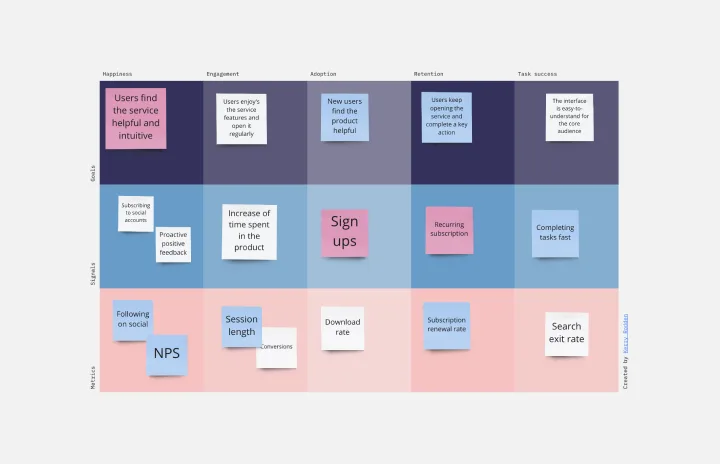
Happiness, Engagement, Adoption, Retention, and Task Success. Those are the pillars of user experience — which is why they serve as the key metrics in the HEART framework. Developed by the research team at Google, this framework gives larger companies an accurate way to measure user experience at scale, which you can then reference throughout the product development lifecycle. While the HEART framework uses five metrics, you might not need all five for every project — choose the ones that will be most useful for your company and project.

Customer Journey Mapping Template Pack
Mapping, User Experience, Workshops
A customer journey map (CJM) is a visual representation of your customer’s experience. It allows you to capture the path that a customer follows when they buy a product, sign up for a service, or otherwise interact with your site. Most maps include a specific persona, outlines their customer experience from beginning to end, and captures the potential emotional highs and lows of interacting with the product or service. Use this template to easily create customer journey maps for projects of all kinds.

Daily Stand-up Meeting Template
Agile Methodology, Meetings, Software Development
The entire team meets to review the day before and discuss the day ahead. These daily meetings, also known as “scrums,” are brief but powerful — they identify roadblocks, give each team member a voice, foster collaboration, keep progress on track, and ultimately keep teams working together effectively. This template makes it so easy for you to plan daily standups for your sprint team. It all starts with picking a date and time, creating an agenda, and sticking with the same format throughout the sprint.
How to create an effective UX research plan (2024)
Last updated
23 January 2024
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
You wouldn’t build a home without a solid architectural plan. The plan ensures what you create fits the brief and will delight future residents. The same level of planning is needed when it comes to research.
Think of your research plan as the building blocks of your UX research, helping to streamline the process, firm up your goals, and ensure the results are reliable and actionable.
Let’s take a look at what a UX research plan is, and how to create one.
- What is a UX research plan?
A UX research plan outlines the research problem, objectives, strategies, participant profiles, budget, timeline, and methodology. It serves as a guide for researchers, designers, and project managers to understand the scope of the project and carry it out efficiently.
There’s no one format for UX research plans––they may be compiled into a slideshow, a simple document, or a more comprehensive report. The important thing is not the format, but that the plan covers all the essential elements of the research your team will perform.
In some cases, a UX research plan could also be required to secure funding or approval for the project.
- What's the difference between a research plan and research design?
A research plan and research design are two related, but distinct concepts. A research plan includes a summary of the intended research design.
Research plan
This outlines the goals, methodology, and strategies of the research. The research plan is typically compiled into a document or slideshow.
A research plan outlines the goals of the project while providing an overall structure.
Research design
This is the specific method by which the research will be conducted. It includes the UX research methodologies and tools that will be used to conduct the research, the sampling size, and the data collection process.
The focus of research design is to decide which research techniques will be used, how the information will be gathered, and how the analysis will be conducted.
- What are the benefits of using a UX research plan?
Having a solid foundation, or specific outline, for any UX research you wish to conduct can make the process much faster, more accurate, and more specific.
The UX research plan helps teams to firm up their goals, set clear research questions, decide on the research methods they’ll use––ones that will be most effective––and consider how the results will be analyzed. This process allows teams to consider contingencies and differing methods, and to make adjustments accordingly.
An effective research plan can also save organizations money by providing a clear path to success, highlighting potential challenges, and helping a team gather all the elements for success.
Some key benefits of research plans include:
Problem definition: having a research plan helps you clarify the problem you’re solving. A well-defined problem statement can firm up the focus and direction of the research, outlining specific issues and challenges you’ll look to address.
Goal clarity: all research projects should begin with clear goals. This ensures your research is relevant, useful, and measurable for your team’s needs. Creating a UX research plan can help you not only create goals but also consider if they are feasible and relevant for the business and the user.
Stakeholder alignment: creating a detailed UX research plan can help align all key stakeholders. This guides everyone toward the same goal, provides clarity for objectives, ensures teams don’t work in silos, and helps the whole organization work together to improve the customers’ user experience. It can also be useful to collect questions and requirements from stakeholders to keep them engaged with the research.
Method choices: through the process of defining the UX research goals, strategies, and data-collection process, it can be simpler to see the right research method for your project. Potential issues or roadblocks will become clear, allowing your research to be conducted more effectively.
- What should a UX research plan include?
While there is no one way to create a UX research plan, the most effective plans include a few core elements.
Some of the most essential aspects of a UX research plan include:
Challenges: identify challenges that users and the business may encounter. These may be fluctuations in revenue, friction in the user experience, insufficient information, or issues related to customer service. Addressing these challenges ensures the research aligns with the pertinent issues from user and business perspectives.
Research questions: pinpoint the specific questions that will be asked during the project to check they align with the overall project goals.
Methodology: note the UX research methods that will be used during the project. These should also be relevant to the overall goals and challenges.
Timeline: clarify timings so teams won’t complete research that’s too big for the budget or time available. Timings will impact what can be researched and even the results.
Participant selection: as part of UX research, usually participants are required to answer questions or complete exercises. Choosing the right number of relevant participants can be challenging. Having a plan in place for this can streamline that part of the process and prevent teams from getting bogged down by delays.
Data-collection methods: make sure your team knows how the data will be collected and analyzed. Having this as part of your plan can ensure the data collection aligns with the project goals and access to your team’s resources.
Budget: include your research budget to help you allocate resources, estimate overall costs, and prioritize activities. A clear budget will support the approval process, aid in risk management, and increase accountability for teams.
Ethical considerations: ethics are important in any research, whether or not it involves humans. UX studies typically involve participants, so it’s important to consider a range of critical factors. Personal privacy, potential for harm, and persuasion are just a few areas to be aware of.
Risk: all projects have the potential for risk. Considering what those risks are before the project starts can help the team consider potential contingencies.
- How to create a UX research plan
Creating a UX research plan doesn’t have to be intimidating. By following a framework and including essential elements, you’ll streamline the research process and reduce work down the line.
Let’s look at some best-practice steps.
1. Define the challenge
UX research seeks to understand the pain points, wants, and needs of your customers so you can develop better products and services. Before beginning UX research, you need to understand what challenge you are looking to understand, and solve, for your business and customers. Here are three examples:
We seek to uncover the root causes behind the significant drop-off rates at the shopping cart, aiming to identify user behaviors and potential barriers to retention.
Our focus is on understanding and evaluating the factors influencing user behavior to transition from free to paying platform members, aiming to optimize our conversion rate.
Our current challenge is to identify functionalities and features for our B2B fitness coaching app that will drive conversion and revenue.
Before diving in, it’s important to know what the challenge is, and therefore, what the UX research will be focused on.
2. Set your goals
Once the challenge is clear, it’s essential to set your specific goals for the research. The goals you set at the start will define the entire project, so this aspect is worth spending time on.
There may be several areas that your team would like to research, but, for the best results, keep things simple. Set a small number of goals that relate to the core challenge. You can order your goals by priority to select the most essential ones for your project.
An example of a goal could be:
To decrease shopping cart drop-off rates by 25% by identifying and solving the challenges our customers experience.
3. Select your research method
Based on the goals you’ve set, choose a relevant research method. With many research methods to choose from––customer interviews, focus groups, user testing, A/B testing, surveys, diary studies, analytics, and more––choosing the right method is important.
First, consider whether quantitative or qualitative research (or a mixed approach) will be most helpful for your project. Then select a method that aligns with your project objectives.
To discover why users are abandoning their shopping cart, for example, a range of methods may be relevant. These include:
User testing: users could be tasked with adding items to a shopping cart and completing a purchase while being observed by researchers. This may reveal moments of friction or difficulty in the checkout process.
Surveys: users could also be asked to provide feedback immediately after using the shopping cart. This would help researchers gain insights into customers’ feelings and frustrations directly after interacting with the product.
Heatmaps: some tools show where users are clicking and using their cursor. This can help identify areas where users pause, suggesting they are challenging or confusing.
A/B testing: presenting users with two different options for the shopping cart could help teams refine what elements, design features, and interfaces work better for conversion.
4. Identify participant sources
Once you’ve chosen your method or methods, determine how you’ll select participants. Don’t select them merely based on demographic factors; also focus on key behavioral patterns. This can be a challenging aspect of UX research, and it’s helpful to include it in your UX research plan to make the process more efficient.
Your current customers can be an ideal source of participants. Other ways to attract participants include reaching out to recruitment research agencies, putting a callout on social media, sending an email to customers, or using incentives. Pop-up surveys on your website and app could also prove useful.
5. Run a test
At this stage, it’s helpful to run a test of your plan methodology to check it works effectively. That could mean having a team member try out your survey or trialing a usability test within the team to spot any issues.
By running a test, and ironing out any issues that may arise, you’re more likely to have fewer challenges when conducting the actual research.
6. Analyze the data
Deciding how the data will be collected and analyzed––including how those results will be shared with the broader team, is an essential aspect of a UX research plan.
Keep in mind that the data you collect and analyze should link back to your goals and the overall challenge your team is looking to solve.
- Tips for your UX research plan
To save time and make your UX plan as effective as possible, here are some best-practice tips:
Set clear goals: to get the best results from your research and ensure your UX research plan is comprehensive and effective, insist on clarity in your goals. Clear goals lead to cohesion among stakeholders, useful results, and addressing of business and customer challenges.
Understand your target market: your UX research should speak to your target market, solving their problems. Deeply understanding your market will direct you to the right type of research to keep delivering better products and services.
Set out an accurate timeline: to keep your project on track and ensure you have the appropriate resources to complete it, an accurate timeline is essential. The timeline should be well thought out, taking into account potential roadblocks and challenges.
Allow for flexibility: as you conduct the research, you may discover unexpected data or new insights. Some degree of flexibility in a UX plan, and your timeline, can be useful to allow for these potential diversions.
- Examples of a good UX research plan
To help you get started with your UX research plan, we’ve created this UX research plan template for your next project.
Feel free to use this as a guide, adding or removing elements as you see fit.
This example covers a UX team wanting to boost resubscriptions for their dog-sitting app.
50% of users are not renewing their app subscription.
To understand why some users are not renewing their app subscriptions and use this information to increase app resubscribes by 20%.
Research questions
What areas of the app are causing friction for users?
What aspects of the app provide the most value?
How can the app be streamlined for a boosted user experience?
How do user preferences and expectations align with the current offerings of the app, and are there opportunities for adjustments to better meet user needs?
How does the app compare to competitors in terms of subscription models, features, and overall user satisfaction?
Methodology
Surveys: conduct surveys with a relevant number of participants [the number you survey will depend on the population size, confidence level, and margin of error you are willing to have] who have just failed to renew their app subscription. Understand from these users what areas of the app caused the most friction and where more value could be added.
Usability testing: perform usability testing with a representative user sample to identify any usability issues that might be contributing to the drop in subscription renewals. Observe users interacting with the app and gather feedback on the user interface, navigation, and overall user experience.
Analytics: assess the analytics of customers who decide not to renew their subscriptions against those who do. Look for any differences in demographics, the way they use the app, and more.
Participants
[Choose existing or recent customers as participants so their insights are relevant to the project.]
Week 1: establish participants
Week 2–3: perform surveys and usability tests
Week 4: gather key analytics
Week 5: perform analysis
Week 6: collate and share results
Stakeholders and responsibilities
[Identify key stakeholders including project managers, product owner, vice president (VP) of product, researchers, UX managers, designers, data engineers, and more.]
Risks and mitigation
Some potential risks include:
Low participant turnout: ensure a sufficient number of participants complete the survey so that the results are valid. The use of incentives may be necessary to boost completion rates.
Data challenges: there may be challenges when collating customer analytics. To ensure this is seamless, use a platform where all data can be housed in one place. And use an experienced engineer who can solve challenges if they arise.
Success metrics
Deeply understand what customers value in the app and what areas cause friction
Use the information gathered to make changes to the app to provide more value and less friction
Increase app resubscriptions by 20%
- What's next after your user research plan?
Rather than diving straight into the research once your plan is in place, make sure your team validates your research plan. This will help you yield the results you are hoping for.
The plan should engage the relevant stakeholders to get them on board. Some research plans may also need to be approved by a funding body before further steps are taken.
Once all relevant parties are in agreement, the next step is to get started in line with the agreed timeline.
- An effective UX research plan
Good pre-planning helps your UX research meet your goals and pleases your customers.
While it might be tempting to jump into UX research, having a solid plan in place will ensure you take the necessary steps at the right time, you won’t overlook key aspects of research, and all stakeholders are aligned before the research begins.
Ultimately, a good plan can help your team perform effective UX research that benefits those who matter the most––your customers.
What are the key questions for UX research?
The questions you ask in UX research will be unique to your project goals and objectives. Some example UX research questions include:
User questions:
What are our user’s demographics?
What problems do people seek to solve with our app?
What are our user’s key pain points?
Satisfaction:
How satisfied are our users with our product offering?
Would our users recommend us to a friend?
Efficiency:
Are our products providing efficiency?
Are our products giving a streamlined user experience?
What is a good UX research process?
A beneficial UX research process is one that ultimately improves the product experience for users. Typically, the process includes:
A specific challenge: rather than researching too generally, understand the challenge or challenges the research is looking to understand better.
Clear goals: have clarity in your UX research goals, otherwise the data will not necessarily benefit the end user.
Relevant methodology: the right research method, which aligns with the goals and overall challenge, will ensure you gather relevant data.
Deep analysis: once you have amassed your data, analyze it to ensure insights can be found and acted upon.
What are the 5 stages of UX research?
There are five core steps in UX research:
Setting goals
Selecting participants
Choosing a relevant research method
Data analysis
Reporting on and sharing the results with stakeholders
How do you plan a UX research roadmap?
A UX research roadmap helps to keep a team on track when working toward the overarching goals and objectives.
When creating a UX research roadmap, it’s helpful to:
Establish the strategy: that’s the challenge you’re looking to solve and the goals you’ve set.
Choose an effective tool: a tool for tracking the entire project—not just timings, but all the key steps—can save time and act as a source of truth for all parties to reference.
Define key check-in points: to keep a team on track and working toward the key goals, it’s essential to have check-ins. This will help establish progress across different members of the team and provide a chance to change tack if needed.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 January 2023
Last updated: 27 April 2023
Last updated: 26 March 2024
Last updated: 24 June 2023
Last updated: 29 May 2023
Last updated: 28 February 2023
Last updated: 14 November 2023
Last updated: 3 April 2024
Last updated: 21 June 2023
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 6 April 2023
Last updated: 31 July 2023
Last updated: 22 June 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
What is UX Research? Methods, Process, Tools, Examples
Appinio Research · 15.02.2024 · 40min read

Ever wondered how successful products and services are meticulously crafted to cater to your needs and preferences? User Experience (UX) research is the key that unlocks the secrets behind creating user-centered designs. In this guide, we will delve deep into UX research, uncovering its methods, strategies, and practical applications. Whether you're a designer, developer, product manager, or simply curious about the science of user satisfaction, this guide will empower you with the knowledge and tools to understand, implement, and benefit from UX research principles.
What is UX Research?
User Experience (UX) Research is a systematic process of understanding and evaluating how users interact with a product, service, or system. It encompasses a wide range of research methods and techniques to gain insights into user behaviors, preferences, needs, and pain points. The ultimate goal of UX research is to inform and improve the design and functionality of products and services to enhance user satisfaction and usability.
Importance of UX Research
Effective UX research plays a pivotal role in shaping user-centered design and development processes. Its significance can be understood through several key points:
- User-Centered Design : UX research places users at the forefront of design decisions, ensuring that products and services are tailored to meet their needs and preferences.
- Enhanced Usability : Research findings lead to improvements that enhance the overall usability of products, reducing user frustration and increasing engagement.
- Cost Reduction : Identifying and addressing usability issues early in the design process can save time and resources by avoiding costly redesigns or post-launch fixes.
- Competitive Advantage : Organizations prioritizing UX research gain a competitive edge by delivering superior user experiences that attract and retain customers.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction : User satisfaction is closely linked to loyalty and positive word-of-mouth, making UX research an investment in long-term customer relationships.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making : Research data provides valuable insights that inform strategic decisions, reducing the guesswork and subjectivity in design choices.
UX Research Goals and Objectives
The primary goals and objectives of UX research revolve around understanding user needs, improving usability, and driving user-centered design. Here are the key objectives that guide UX research efforts:
- User Understanding : Gain a deep understanding of the target audience, including their demographics, behaviors, motivations, and pain points.
- Usability Evaluation : Identify usability issues and challenges users encounter during interactions with a product or service.
- Task Efficiency : Determine how efficiently users can accomplish tasks within a system, with a focus on minimizing friction and errors.
- User Satisfaction : Measure user satisfaction and gather feedback to uncover areas where improvements can enhance overall user experience.
- Feature Prioritization : Assess which features or functionalities are most valuable to users, guiding feature prioritization in development.
- Validation and Iteration : Validate design decisions through testing and iteration, ensuring that changes align with user expectations and preferences.
- Benchmarking : Establish benchmarks to track improvements over time and compare performance to industry standards.
- Evidence-Based Design : Base design decisions on empirical data and user insights, fostering a user-centered and data-driven design culture.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity : Ensure that products and services are accessible to a diverse range of users, including those with disabilities.
- Risk Mitigation : Identify and mitigate potential risks and challenges early in the design process, reducing the likelihood of post-launch issues.
- Continuous Improvement : Embrace a culture of constant improvement, where UX research is an ongoing process that informs product enhancements and updates.
By aligning research efforts with these objectives, organizations can create products and services that resonate with users, leading to increased user satisfaction and business success.
How to Plan UX Research?
Planning is the foundation of any successful UX research project. It sets the direction, defines your objectives, and ensures that your efforts are focused on achieving meaningful outcomes.
Setting Clear Objectives
Setting clear objectives is the first and most crucial step in planning UX research. Your objectives guide the entire research process, helping you stay on track and measure success effectively. When defining objectives, consider the following:
- Specificity : Objectives should be clear and specific. Vague goals can lead to ambiguous research outcomes.
- Relevance : Ensure that your objectives align with the overall goals of your product or project. How will the research contribute to the success of the endeavor?
- Measurability : Define objectives that are measurable. You should be able to determine whether you've achieved them or not.
- Timeframe : Consider the timeline for your research. Are your objectives achievable within the given time frame?
A well-defined objective might look something like this: "To identify pain points in our mobile app's onboarding process by conducting usability testing with 15 participants, with the aim of reducing drop-off rates by 20% within the next quarter."
Identifying Target Audience
Understanding your target audience is fundamental to effective UX research. Your product or service is designed for specific users, and knowing them intimately is essential. When identifying your target audience, keep the following in mind:
- Demographics : Who are your users? What are their age, gender, location, and other relevant demographics?
- Psychographics : Dig deeper into their lifestyles, values, interests, and behaviors. What motivates them, and what are their pain points?
- User Personas : Create user personas to visualize your target audience. Personas help in humanizing and empathizing with your users.
- User Journeys : Map out the typical user journeys to understand the various touchpoints and interactions users have with your product.
Defining Research Questions
Research questions act as the compass that guides your journey through the UX research landscape. They should be well-crafted and directly tied to your objectives. When defining research questions, consider the following:
- Open-Endedness : Craft questions that allow for open-ended responses . Closed-ended questions with yes/no answers can limit the depth of insights.
- Unbiased Language : Ensure that your questions are phrased in a neutral and impartial manner. Biased questions can lead to skewed results.
- Relevance : Are your research questions directly related to your objectives? Avoid asking questions that do not contribute to your research goals.
- User-Centered : Frame questions from the user's perspective. What would users want to know or share about their experience?
For instance, if your objective is to improve the checkout process of an e-commerce website, a research question could be: "What challenges do users encounter during the checkout process, and how can we simplify it to enhance their experience?"

Budgeting and Resource Allocation
Effective UX research requires proper allocation of resources, both in terms of budget and personnel. Before embarking on your research journey:
- Financial Resources : Determine the budget available for your research project. This budget should cover participant incentives, research tools, and any other associated costs.
- Time Allocation : Allocate time appropriately for each phase of the research process, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and reporting.
- Human Resources : Identify the team members or researchers responsible for conducting the research. Ensure they have the necessary skills and expertise.
- Tools and Software : Assess whether you have access to the required research tools, such as usability testing software, survey platforms, or analytics tools.
Proper budgeting and resource allocation prevent unexpected obstacles and ensure a seamless research process. Remember that investing in UX research is an investment in the overall success of your product or service.
Types of UX Research
When it comes to User Experience (UX) research, understanding the different types of research methodologies is crucial. Each type has its own strengths and applications, allowing you to gather specific insights into user behavior, preferences, and interactions. These are the three primary types of UX research.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research focuses on collecting numerical data to quantify user behaviors, preferences, or attitudes. It involves systematic data collection and statistical analysis. Here's a deeper look into quantitative research:
- Data Collection : Quantitative research relies on structured data collection methods, such as surveys, questionnaires, or data analytics tools. These methods yield data in numerical form.
- Objective Measurement : It aims to provide objective and measurable data. This is particularly useful for answering questions like "How many users performed a specific action?" or "What percentage of users prefer feature A over feature B?"
- Large Sample Sizes : Quantitative research often involves larger sample sizes to ensure statistical significance. This allows for generalizable findings.
- Statistical Analysis : Statistical analysis plays a central role in quantitative research. It helps identify trends, correlations, and patterns within the data.
- A/B Testing : A common application of quantitative research is A/B testing, where two versions of a design or feature are compared to determine which performs better based on quantifiable metrics.
Quantitative research provides valuable insights when you need to make data-driven decisions and understand the broader user trends and preferences within your target audience.
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research dives deep into the subjective aspects of the user experience. It seeks to understand the "why" behind user behaviors and motivations. Here's a closer look at qualitative research:
- Data Collection : Qualitative research relies on methods such as user interviews, usability testing, focus groups, and ethnographic studies. These methods capture rich, non-numerical data.
- Subjective Insights : Qualitative research aims to uncover subjective insights. It helps answer questions like "Why do users find a particular feature frustrating?" or "What emotions do users experience during a specific interaction?"
- Small Sample Sizes : Qualitative research typically involves smaller sample sizes but offers in-depth insights into individual experiences.
- Contextual Understanding : Researchers often engage with users in their natural environment or within the context of product use. This provides a holistic understanding of user behaviors.
- Thematic Analysis : Qualitative data is analyzed through techniques like thematic coding, where common themes and patterns in user feedback are identified.
Qualitative research is particularly valuable when you want to gain a deeper understanding of user needs, pain points, and the emotional aspects of their interactions with your product or service.
Mixed-Methods Research
Mixed-methods research combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research approaches. It offers a comprehensive view of the user experience by leveraging the strengths of both methodologies. Here's what you need to know about mixed-methods research:
- Data Variety : Mixed-methods research involves collecting both numerical and non-numerical data. This includes quantitative data from surveys and qualitative data from interviews or observations.
- Holistic Insights : By combining quantitative and qualitative data, researchers can gain a more complete and nuanced understanding of user behavior and preferences.
- Sequential or Concurrent : Mixed-methods research can be conducted sequentially (first quantitative, then qualitative) or concurrently (simultaneously collecting both types of data).
- Data Integration : Researchers must carefully integrate and analyze the data from both sources to draw comprehensive conclusions.
- Complementary Insights : The aim is to complement the strengths of one method with the weaknesses of the other, providing a more well-rounded perspective.
Mixed-methods research is valuable when you want to explore complex user experiences, understand the reasons behind quantitative trends, or validate findings from one method with the other. It offers a holistic approach to UX research that can lead to more informed design decisions.
How to Conduct UX Research?
Now that you've laid the groundwork and explored the types of UX research, it's time to delve into the practical aspects of conducting UX research.
Recruitment: Finding the Right Participants
Recruiting participants is a crucial step in UX research. The quality of your research outcomes depends on selecting the right participants who represent your target audience. Here's how to do it effectively:
- Define Participant Criteria : Begin by defining specific criteria for your participants. These criteria should align with your research objectives. For instance, if you're testing a healthcare app, you might require participants who have experience with healthcare services.
- Recruitment Channels : Determine where and how you will find participants. Common recruitment channels include online platforms, user testing services, or in-house databases.
- Incentives : Consider offering incentives to motivate participants. This could be monetary compensation, gift cards, or access to your product or service.
- Screening : Screen potential participants to ensure they meet your criteria. Conducting a screening interview or questionnaire can help filter out inappropriate candidates.
Sampling: Choosing the Right Sample Size
Sampling involves selecting a subset of your target audience for research. The size and representativeness of your sample are critical for obtaining reliable results:
- Sample Size : Determine the appropriate sample size based on your research goals and statistical requirements. Larger samples enhance the reliability of your findings.
- Random Sampling : Whenever possible, aim for random sampling to reduce bias. Randomly selecting participants from your target population increases the likelihood of obtaining a representative sample.
- Stratified Sampling : In cases where certain user segments are essential, consider stratified sampling. This ensures that each segment is adequately represented in your sample.
Recruitment and sampling are foundational elements of UX research, ensuring that the data collected accurately reflects the perspectives of your intended user base.
Choosing the Right Data Collection Methods
Selecting the most suitable data collection methods is vital for gathering relevant and meaningful information. Depending on your research objectives, you can utilize various methods:
- Usability Testing : Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with your product or prototype. It provides direct insights into how users navigate and use your design.
- Surveys and Questionnaires : Surveys are useful for gathering structured, quantitative data. They allow you to collect responses from a large number of participants quickly.
- Interviews : Interviews offer a deeper understanding of user experiences by engaging participants in open-ended conversations. They are particularly effective for uncovering motivations and pain points.
- Observations : Observational studies involve watching users in their natural context, providing insights into real-world behavior.
- Eye-Tracking : Eye-tracking technology can reveal where users focus their attention within your design, helping to optimize layouts and content placement.
- Heatmaps : Heatmaps display aggregated user interactions, highlighting areas of interest and interaction intensity within your design.
- Card Sorting : Card sorting exercises help organize information and navigation structures based on how users group and label items.
Choosing the proper data collection methods depends on your research goals, the type of insights you seek, and the available resources. When it comes to data collection, Appinio offers a streamlined solution that simplifies the process and ensures actionable results.
With Appinio , you can effortlessly design surveys, target specific demographics, and gather insights from a diverse pool of respondents. Whether you're conducting usability testing, administering surveys, or conducting interviews, Appinio provides the tools you need to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
Ready to elevate your UX research? Book a demo with Appinio today and experience the power of real-time consumer insights firsthand!
Book a Demo
Making Sense of Collected Data
Once data is collected, the next step is to analyze it effectively. Proper data analysis is critical for drawing meaningful insights and conclusions:
- Quantitative Analysis : For quantitative data collected through surveys or analytics, use statistical analysis techniques to identify patterns, correlations, and statistically significant findings.
- Qualitative Analysis : Qualitative data, such as interview transcripts or open-ended survey responses, requires thematic coding and content analysis to uncover themes, trends, and user sentiments.
- Mixed-Methods Integration : In mixed-methods research, integrate both quantitative and qualitative data to provide a comprehensive understanding of the user experience.
- Usability Metrics : When conducting usability testing, use established usability metrics such as task completion rates, time on task, and error rates to evaluate user performance.
- Data Visualization : Visualize your data using charts, graphs, and diagrams to make complex information more accessible and understandable.
Data analysis transforms raw data into actionable insights that inform design improvements and decision-making.
Improving User Experience Through Testing
Usability testing is a fundamental UX research method that involves observing users as they interact with your product or prototype. It helps identify usability issues and gather direct feedback for improvement:
- Test Planning : Begin by creating test scenarios and tasks that align with your research objectives. Determine what you want participants to accomplish during the test.
- Recruitment : Recruit participants who match your target audience and meet your criteria. Ensure they represent the diversity of your user base.
- Moderated vs. Unmoderated Testing : Choose between moderated (where a facilitator guides participants) and unmoderated (participants complete tasks independently) usability testing, depending on your needs and resources.
- Task Observation : Observe participants as they navigate your design, paying attention to their interactions, struggles, and feedback.
- Think-Aloud Protocol : Encourage participants to vocalize their thoughts and feelings during the test. This provides insights into their cognitive processes.
- Post-Test Interviews : Conduct post-test interviews to gather deeper insights. Ask participants about their overall experience, pain points, and suggestions for improvement.
- Iterative Testing : Usability testing is often an iterative process. After making design changes based on feedback, conduct additional tests to validate improvements.
Usability testing helps uncover issues that may not be apparent through other research methods, leading to improved user satisfaction and product usability.
Collecting Quantitative Insights
Surveys and questionnaires are valuable tools for collecting structured, quantitative data from a large number of participants. They can provide insights into user preferences, satisfaction, and demographics:
- Survey Design : Carefully design your survey or questionnaire , ensuring questions are clear, concise, and relevant to your research objectives.
- Sampling : Distribute your survey to a representative sample of your target audience to obtain meaningful results.
- Response Scale : Choose an appropriate response scale, such as Likert scales or multiple-choice questions, depending on the type of data you want to collect.
- Pre-Testing : Before launching your survey, conduct pre-testing to identify and address any potential issues with question wording or survey flow.
- Data Analysis : Once survey responses are collected, perform statistical analysis to uncover patterns and correlations within the data.
Surveys and questionnaires are efficient tools for gathering quantitative data, making them ideal for measuring user satisfaction, preferences, and trends.
Interviews and Observations
Interviews and observations provide qualitative insights that can help you understand the "why" behind user behaviors and motivations:
- Interview Types : Choose between structured, semi-structured, or unstructured interviews, depending on your research goals. Structured interviews use predefined questions, while unstructured interviews allow for open-ended conversations.
- Participant Selection : Select participants who represent your target audience and can provide diverse perspectives.
- Interview Moderation : During interviews, create a comfortable environment for participants to share their thoughts openly. Encourage them to expand on their responses.
- Observations : When conducting observational research, carefully observe users in their natural context or during product use. Take notes on their actions, gestures, and expressions.
- Contextual Inquiry : Contextual inquiries involve observing users while they perform specific tasks related to your product or service. This approach provides insights into real-world behavior.
- Data Interpretation : Analyze interview transcripts and observational notes using thematic coding or content analysis to identify recurring themes and patterns.
Interviews and observations allow you to gain a deep understanding of user experiences, uncover pain points, and inform design decisions from a user-centered perspective.
With these data collection methods at your disposal, you can tailor your approach to gather the most relevant insights for your specific UX research objectives. Whether you choose to observe user interactions, administer surveys, conduct interviews, or run usability tests , each method offers unique advantages for understanding and improving the user experience.
How to Interpret UX Research Data?
As you gather data through various UX research methods, the next critical step is to analyze and interpret this data effectively. This process involves transforming raw information into actionable insights that can drive design improvements and strategic decisions.
Visualizing Insights for Clarity
Data visualization is a powerful technique for making complex data more accessible and understandable. It involves representing data graphically through charts, graphs, and diagrams. Here's why data visualization matters and how to use it effectively:
- Simplify Complex Data : Data visualization simplifies large datasets and helps users quickly grasp trends and patterns.
- Enhance Communication : Visual representations of data are often more effective in conveying information than raw numbers or text.
- Choose the Right Visualization : Select the appropriate type of visualization based on the data and the story you want to tell. Common types include bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, and heatmaps.
- Labels and Legends : Ensure that your visualizations have clear labels, legends, and scales. This makes it easier for viewers to understand and interpret the data.
- Interactivity : In digital formats, consider adding interactivity to allow users to explore data further by hovering, clicking, or filtering.
- Data Storytelling : Use data visualizations to tell a compelling story. Explain the context, highlight key findings, and guide viewers through the insights.
Data visualization aids in identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies within your data, helping you make informed decisions based on a visual representation of your research findings.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
Identifying patterns and trends within your data is essential for understanding user behavior and preferences. Here's how to effectively uncover these insights:
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) : Begin with an exploratory analysis of your data. Visualizations, such as histograms, box plots, and scatterplots, can reveal patterns and outliers.
- Segmentation : Segment your data by relevant variables (e.g., demographics , psychographic , user behaviors) to identify patterns within specific groups.
- Statistical Analysis : Use statistical methods to analyze your data quantitatively. Techniques like regression analysis, correlation, and hypothesis testing can uncover relationships and trends.
- Time Series Analysis : If your data includes time-based information, such as user interactions over time, use time series analysis to identify temporal trends and seasonality.
- Qualitative Data : For qualitative data from interviews or open-ended survey responses, use thematic coding to identify recurring themes and insights.
- Comparative Analysis : Compare data before and after design changes or between different user groups to assess the impact of interventions.
Identifying patterns and trends in your data allows you to deeply understand user behaviors, preferences, and pain points, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Turning Data into Actionable Knowledge
Drawing insights and conclusions from your data is the ultimate goal of UX research. It's the stage where you transform data into actionable knowledge that informs design improvements and strategic decisions:
- Hypothesis Validation : Determine whether your research findings align with your initial hypotheses and objectives.
- Prioritization : Prioritize the most significant insights and findings. Focus on those that have the most substantial impact on the user experience.
- User-Centered Recommendations : Frame your insights in a user-centered manner. Consider how the findings can benefit users and enhance their interactions with your product or service.
- Iterative Design : Use insights to inform iterative design improvements. Test and validate changes based on research findings to ensure they address identified issues.
- Communicate Effectively : Communicate your insights and conclusions clearly to stakeholders, designers, and developers. Use data-driven evidence to support your recommendations.
- Continuous Learning : UX research is an ongoing process. Continue to learn and adapt based on user feedback and new research findings.
Ultimately, the ability to draw meaningful insights and conclusions from your UX research data is what drives the improvement of user experiences and the success of your products and services. It's the bridge between data collection and impactful action.
Examples of UX Research
To gain a deeper understanding of how UX research is applied in real-world scenarios, let's explore some concrete examples that illustrate its importance and impact.
E-Commerce Website Optimization
Scenario : An e-commerce company notices a high cart abandonment rate on their website, with users frequently leaving before completing their purchases.
UX Research Approach : The company conducts usability testing with a group of participants. They observe users as they navigate the website, add products to their carts, and attempt to complete the checkout process.
Findings : Through usability testing, the research team identifies several issues contributing to cart abandonment. Users struggle with unclear product descriptions, a complex checkout process, and a lack of payment options. Additionally, users express concerns about data security during the payment phase.
Impact : Armed with these insights, the company makes a series of improvements. They streamline the checkout process, improve product descriptions, add multiple payment options, and prominently display security certifications. As a result, cart abandonment rates decrease significantly, leading to a notable increase in completed purchases and revenue.
Mobile App Redesign
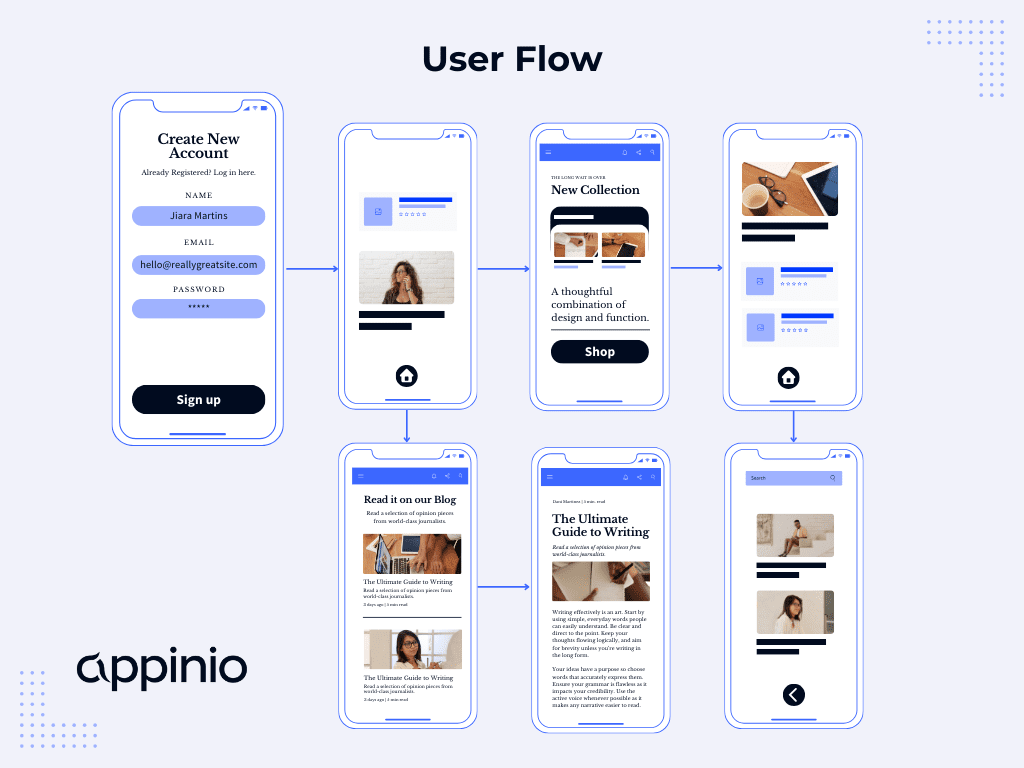
Scenario : A mobile app development company receives user feedback indicating that their app is challenging to navigate and lacks key features.
UX Research Approach : The company initiates a comprehensive research effort that includes user interviews, surveys, and competitor analysis. They aim to understand user expectations, pain points, and the strengths of competing apps.
Findings : User interviews reveal that users desire a more intuitive navigation structure and specific features that rival apps offer. Surveys confirm these preferences and competitor analysis uncovers successful design patterns.
Impact : The company embarks on a redesign project based on user feedback and industry best practices. They restructure the app's interface, add requested features, and enhance the overall user experience. As a result, user satisfaction increases, app ratings improve, and user engagement metrics rise.
Healthcare Information Portal Enhancement
Scenario : A healthcare organization operates an online portal where patients access medical records and communicate with healthcare providers. Users report difficulties in finding information and engaging with the portal.
UX Research Approach : The organization employs a mixed-methods research approach, combining quantitative data analysis with qualitative research. They analyze user interactions and survey responses while also conducting in-depth interviews with patients.
Findings : Quantitative data analysis reveals that users frequently abandon tasks without completion, such as accessing test results. Surveys and interviews uncover confusion related to navigation, terminology, and information layout.
Impact : Armed with a comprehensive understanding of user challenges, the organization revamps the portal's navigation, rewrites content in plain language, and introduces user-friendly features such as task wizards. User engagement with the portal increases, and patients report improved satisfaction with the online experience, leading to enhanced patient-provider interactions.
Social Media Platform Feature Expansion
Scenario : A popular social media platform aims to expand its feature set to stay competitive and retain users. However, the platform's leadership wants to ensure that any new features align with user preferences.
UX Research Approach : The social media platform initiates a series of surveys and user feedback sessions. They present users with potential feature concepts and gather their opinions, expectations, and concerns.
Findings : Through surveys and user feedback sessions, the platform discovers that users desire enhanced privacy controls, a more user-friendly post creation process, and better content filtering options. Additionally, users express concerns about the potential impact of new features on their data privacy.
Impact : Armed with user insights, the platform introduces new features while addressing user concerns. They implement robust privacy settings, simplify post creation, and provide users with customizable content filters. User engagement increases as users appreciate the platform's responsiveness to their needs, and user satisfaction remains high.
These examples highlight how UX research methods, such as usability testing, interviews, surveys, and data analysis, can identify specific issues, inform design improvements, and ultimately enhance the user experience. By investing in UX research, organizations can address user pain points, improve product offerings, and stay competitive in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
How to Report UX Research Findings?
After conducting UX research and drawing valuable insights, the next crucial step is effectively communicating your findings to stakeholders and team members.
Creating Research Reports
Research reports are comprehensive documents that encapsulate your entire UX research process and findings. They serve as a valuable reference for team members and stakeholders. Here's how to create effective research reports:
- Structured Format : Organize your report in a structured format that includes sections such as an executive summary, methodology, key findings, and recommendations.
- Visual Aids : Use visuals such as charts, graphs, and screenshots to illustrate your findings. Visual aids make complex data more accessible.
- Clear Language : Write in clear, concise language that is easily understandable by both technical and non-technical readers.
- Methodology Details : Provide a detailed account of your research methodology, including participant recruitment, data collection methods, and analysis techniques.
- Key Insights : Summarize the most critical findings and insights that emerged from your research. Highlight what these findings mean for the user experience.
- Actionable Recommendations : Include actionable recommendations for improving the product or service based on your research insights.
Creating a well-structured research report ensures that your findings are documented comprehensively and can be referred to as a reference for future decision-making.
Presenting to Stakeholders
Presenting your research findings to stakeholders is essential in the UX research process. It's an opportunity to convey the significance of your insights and garner support for implementing changes.
- Know Your Audience : Understand the background and interests of your audience. Tailor your presentation to their level of expertise and concerns.
- Storytelling : Craft a compelling narrative around your research. Use storytelling techniques to engage your audience and convey the user experience effectively.
- Visuals : Incorporate visuals, such as charts, graphs, and user personas, to illustrate key points and findings.
- Interactive Demonstrations : If possible, demonstrate user interactions or showcase usability improvements through interactive prototypes.
- Key Takeaways : Summarize the main takeaways and actionable recommendations. Highlight how implementing these changes can benefit the organization and users.
- Address Questions : Be prepared to answer questions and provide additional context during the presentation.
Effective presentations not only convey the value of your research but also foster collaboration and support for user-centered improvements.
Making Recommendations
One of the most critical aspects of UX research is translating findings into actionable recommendations that drive improvements in the user experience. Here's how to make recommendations effectively:
- Prioritize Recommendations : Identify and prioritize recommendations based on their potential impact and feasibility. Consider short-term and long-term goals.
- User-Centered Focus : Frame recommendations in a user-centered manner. Explain how implementing each recommendation will directly benefit users.
- Specificity : Make recommendations specific and actionable. Avoid vague suggestions. For example, instead of saying "improve navigation," specify "simplify the main menu structure."
- Data-Backed Evidence : Support recommendations with data-backed evidence from your research. Reference specific findings or user feedback that led to each recommendation.
- Collaboration : Collaborate with designers, developers, and other stakeholders to implement recommendations effectively. Provide guidance and support during the implementation phase.
- Iterative Approach : Recognize that UX research is an ongoing process. Encourage an iterative approach where recommendations are tested, refined, and re-evaluated over time.
Effective recommendations bridge the gap between research findings and meaningful changes that enhance the user experience. They guide product development efforts toward user-centered design and improved satisfaction.
Iterative UX Research
Iterative UX research is a fundamental practice that involves continuous feedback and improvement throughout the product development lifecycle. It emphasizes the importance of ongoing research, testing, and refinement to create user-centered designs.
Here's how it works:
- Feedback Loops : Establish feedback loops where user feedback and insights are collected continuously, not just at specific project phases.
- Regular Testing : Conduct regular usability testing, user interviews, or surveys to gather insights and validate design decisions.
- A/B Testing : Implement A/B testing to compare different design variations and make data-driven decisions on feature implementations.
- Prototyping : Create prototypes and gather user feedback early in the design process. Use this feedback to refine and iterate on designs.
- Monitoring Metrics : Continuously monitor key performance metrics, such as user engagement and conversion rates, to identify areas for improvement.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration : Promote collaboration between UX researchers, designers, developers, and product managers to ensure that research findings inform design and development decisions.
Iterative UX research ensures that user feedback is integrated into the design and development process, leading to products and services that continually evolve to meet user needs and preferences.
Ethical Considerations in UX Research
Ethical considerations in UX research are paramount to protect the rights and well-being of participants and ensure the integrity of the research process. Here are some ethical principles to adhere to:
- Informed Consent : Obtain informed consent from participants, clearly explaining the research purpose, procedures, and any potential risks involved.
- Privacy and Data Security : Safeguard participant privacy by anonymizing and securely storing sensitive data. Follow data protection regulations, such as GDPR.
- Transparency : Be transparent about the research objectives, methodologies, and the use of collected data. Avoid misleading or deceptive practices.
- Avoiding Harm : Ensure that research activities do not harm participants physically or emotionally. Minimize any potential discomfort or stress.
- Respect and Dignity : Treat participants with respect and dignity. Avoid any form of discrimination, bias, or exploitation.
- Bias Awareness : Be aware of potential biases in research design and analysis . Strive for inclusivity and fairness in participant selection and interpretation of findings.
- Debriefing : Provide participants with a debriefing session after their involvement in research, explaining the purpose of the study and addressing any questions or concerns.
Ethical UX research practices uphold the principles of integrity, transparency, and respect, fostering trust between researchers and participants and ensuring the ethical integrity of the research process.
Conclusion for UX Research
UX research is the compass that guides the creation of products and services with you, the user, at the center. By understanding your needs, preferences, and challenges, organizations can craft experiences that truly resonate with you. From setting clear objectives and conducting research to analyzing data and making improvements, the journey of UX research is a continuous cycle of enhancement, ensuring that the digital world becomes more user-friendly with each iteration. Remember, UX research is a powerful tool that empowers teams to create products that delight users and drive success. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just beginning your journey into UX, the principles and practices outlined in this guide can help you make a positive impact in the ever-evolving landscape of user experience.
How to Conduct UX Research in Minutes?
Introducing Appinio , the ultimate solution for lightning-fast UX research! As a real-time market research platform, Appinio specializes in providing companies with instantaneous consumer insights, revolutionizing the way businesses make data-driven decisions.
With our intuitive platform, conducting your own market research becomes a breeze, allowing you to focus on what truly matters: swift, informed choices for your business. Say goodbye to lengthy research processes and hello to quick, reliable results with Appinio.
Here's why you should choose Appinio:
- Instant Insights : From questions to actionable insights in a matter of minutes, empowering you to make decisions on the fly.
- User-Friendly Interface : No need for a research degree; our platform is designed for simplicity and ease of use, making it accessible to everyone.
- Global Reach : Reach your target audience anywhere in the world, with the ability to define precise demographics and survey respondents across over 90 countries.
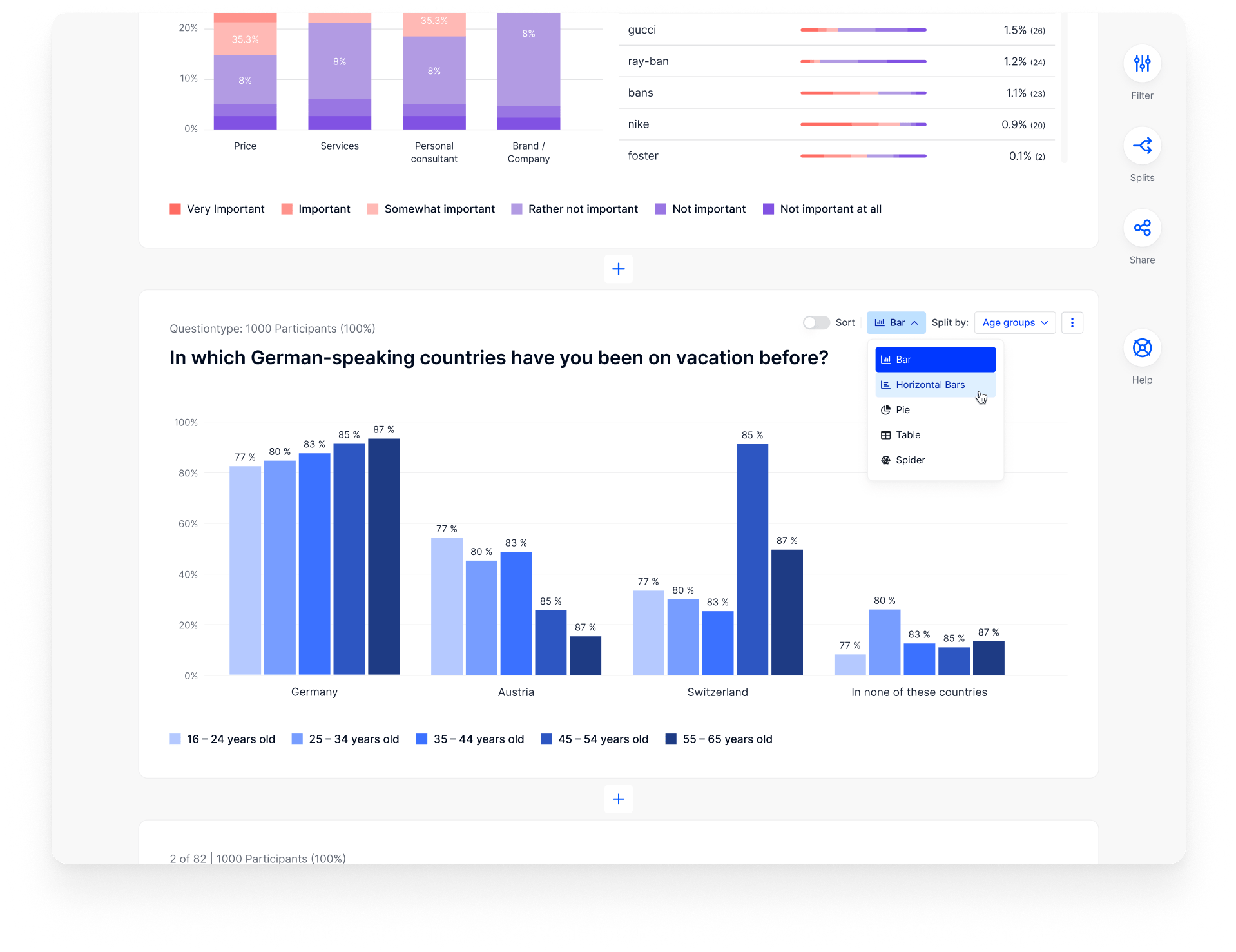
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

17.04.2024 | 25min read
Quota Sampling: Definition, Types, Methods, Examples

15.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Market Share? Definition, Formula, Examples

11.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Data Analysis? Definition, Tools, Examples
Integrations
What's new?
Prototype Testing
Live Website Testing
Feedback Surveys
Interview Studies
Card Sorting
Tree Testing
In-Product Prompts
Participant Management
Automated Reports
Templates Gallery
Choose from our library of pre-built mazes to copy, customize, and share with your own users
Browse all templates
Financial Services
Tech & Software
Product Designers
Product Managers
User Researchers
By use case
Concept & Idea Validation
Wireframe & Usability Test
Content & Copy Testing
Feedback & Satisfaction
Content Hub
Educational resources for product, research and design teams
Explore all resources
Question Bank
Research Maturity Model
Guides & Reports
Help Center
Future of User Research Report
The Optimal Path Podcast
Maze Guides | Resources Hub
What is UX Research: The Ultimate Guide for UX Researchers
0% complete
11 Key UX research methods: How and when to use them
After defining your objectives and planning your research framework, it’s time to choose the research technique that will best serve your project's goals and yield the right insights. While user research is often treated as an afterthought, it should inform every design decision. In this chapter, we walk you through the most common research methods and help you choose the right one for you.

What are UX research methods?
A UX research method is a way of generating insights about your users, their behavior, motivations, and needs. You can use methods like user interviews, surveys, focus groups, card sorting, usability testing to identify user challenges and turn them into opportunities to improve the user experience.
More of a visual learner? Check out this video for a speedy rundown. If you’re ready to get stuck in, jump straight to our full breakdown .
The most common types of user research
First, let’s talk about the types of UX research. Every individual research method falls under these types, which reflect different goals and objectives for conducting research.
Here’s a quick overview:

Qualitative vs. quantitative
All research methods are either quantitative or qualitative . Qualitative research focuses on capturing subjective insights into users' experiences. It aims to understand the underlying reasons, motivations, and behaviors of individuals. Quantitative research, on the other hand, involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and significance. It aims to quantify user behaviors, preferences, and attitudes, allowing for generalizations and statistical insights.
Qualitative research also typically involves a smaller sample size than quantitative research (40 participants, as recommended by Nielsen Norman Group ).
Attitudinal vs. behavioral
Attitudinal research is about understanding users' attitudes, perceptions, and beliefs. It delves into the 'why' behind user decisions and actions. It often involves surveys or interviews where users are asked about their feelings, preferences, or perceptions towards a product or service. It's subjective in nature, aiming to capture people's emotions and opinions.
Behavioral research is about what users do rather than what they say they do or would do. This kind of research is often based on observation methods like usability testing, eye-tracking, or heat maps to understand user behavior.
Generative vs. evaluative
Generative research is all about generating new ideas, concepts, and insights to fuel the design process. You might run brainstorming sessions with groups of users, card sorting, and co-design sessions to inspire creativity and guide the development of user-centered solutions.
On the other hand, evaluative research focuses on assessing the usability, effectiveness, and overall quality of existing designs or prototypes. Once you’ve developed a prototype of your product, it's time to evaluate its strengths and weaknesses. You can compare different versions of a product design or feature through A/B testing—ensuring your UX design meets user needs and expectations.
Remove the guesswork from product decisions
Collect both quantitative and qualitative insights from your customers and build truly user-centric products with Maze.
11 Best UX research methods and when to use them
There are various UX research techniques—each method serves a specific purpose and can provide unique insights into user behaviors and preferences. In this section, we’ll highlight the most common research techniques you need to know.
Read on for an at-a-glance table, and full breakdown of each method.
User interviews
User interviews are a qualitative research method that involves having open-ended and guided discussions with users to gather in-depth insights about their experiences, needs, motivations, and behaviors.
Typically, you would ask a few questions on a specific topic and analyze participants' answers. The results you get will depend on how well you form and ask questions, as well as follow up on participants’ answers.
“As a researcher, it's our responsibility to drive the user to their actual problems,” says Yuliya Martinavichene , User Experience Researcher at Zinio. She adds, “The narration of incidents can help you analyze a lot of hidden details with regard to user behavior.”
That’s why you should:
- Start with a wide context : Make sure that your questions don’t start with your product
- Ask questions that focus on the tasks that users are trying to complete
- Invest in analysis : Get transcripts done and share the findings with your team
Tanya Nativ , Design Researcher at Sketch recommends defining the goals and assumptions internally. “Our beliefs about our users’ behavior really help to structure good questions and get to the root of the problem and its solution,” she explains.
It's easy to be misunderstood if you don't have experience writing interview questions. You can get someone to review them for you or use our Question Bank of 350+ research questions .
When to conduct user interviews
This method is typically used at the start and end of your project. At the start of a project, you can establish a strong understanding of your target users, their perspectives, and the context in which they’ll interact with your product. By the end of your project, new user interviews—often with a different set of individuals—offer a litmus test for your product's usability and appeal, providing firsthand accounts of experiences, perceived strengths, and potential areas for refinement.
Field studies
Field studies are research activities that take place in the user’s environment rather than in your lab or office. They’re a great method for uncovering context, unknown motivations, or constraints that affect the user experience.
An advantage of field studies is observing people in their natural environment, giving you a glimpse at the context in which your product is used. It’s useful to understand the context in which users complete tasks, learn about their needs, and collect in-depth user stories.
When to conduct field studies
This method can be used at all stages of your project—two key times you may want to conduct field studies are:
- As part of the discovery and exploration stage to define direction and understand the context around when and how users interact with the product
- During usability testing, once you have a prototype, to evaluate the effectiveness of the solution or validate design assumptions in real-world contexts
3. Focus groups
A focus group is a qualitative research method that includes the study of a group of people, their beliefs, and opinions. It’s typically used for market research or gathering feedback on products and messaging.
Focus groups can help you better grasp:
- How users perceive your product
- What users believe are a product’s most important features
- What problems do users experience with the product
As with any qualitative research method, the quality of the data collected through focus groups is only as robust as the preparation. So, it’s important to prepare a UX research plan you can refer to during the discussion.
Here’s some things to consider:
- Write a script to guide the conversation
- Ask clear, open-ended questions focused on the topics you’re trying to learn about
- Include around five to ten participants to keep the sessions focused and organized
When to conduct focus groups
It’s easier to use this research technique when you're still formulating your concept, product, or service—to explore user preferences, gather initial reactions, and generate ideas. This is because, in the early stages, you have flexibility and can make significant changes without incurring high costs.
Another way some researchers employ focus groups is post-launch to gather feedback and identify potential improvements. However, you can also use other methods here which may be more effective for identifying usability issues. For example, a platform like Maze can provide detailed, actionable data about how users interact with your product. These quantitative results are a great accompaniment to the qualitative data gathered from your focus group.
4. Diary studies
Diary studies involve asking users to track their usage and thoughts on your product by keeping logs or diaries, taking photos, explaining their activities, and highlighting things that stood out to them.
“Diary studies are one of the few ways you can get a peek into how users interact with our product in a real-world scenario,” says Tanya.
A diary study helps you tell the story of how products and services fit into people’s daily lives, and the touch-points and channels they choose to complete their tasks.
There’s several key questions to consider before conducting diary research, from what kind of diary you want—freeform or structured, and digital or paper—to how often you want participants to log their thoughts.
- Open, ‘freeform’ diary: Users have more freedom to record what and when they like, but can also lead to missed opportunities to capture data users might overlook
- Closed, ‘structured; diary: Users follow a stricter entry-logging process and answer pre-set questions
Remember to determine the trigger: a signal that lets the participants know when they should log their feedback. Tanya breaks these triggers down into the following:
- Interval-contingent trigger : Participants fill out the diary at specific intervals such as one entry per day, or one entry per week
- Signal-contingent trigger : You tell the participant when to make an entry and how you would prefer them to communicate it to you as well as your preferred type of communication
- Event-contingent trigger : The participant makes an entry whenever a defined event occurs
When to conduct diary studies
Diary studies are often valuable when you need to deeply understand users' behaviors, routines, and pain points in real-life contexts. This could be when you're:
- Conceptualizing a new product or feature: Gain insights into user habits, needs, and frustrations to inspire your design
- Trying to enhance an existing product: Identify areas where users are having difficulties or where there are opportunities for better user engagement
Although surveys are primarily used for quantitative research, they can also provided qualitative data, depending on whether you use closed or open-ended questions:
- Closed-ended questions come with a predefined set of answers to choose from using formats like rating scales, rankings, or multiple choice. This results in quantitative data.
- Open-ended question s are typically open-text questions where test participants give their responses in a free-form style. This results in qualitative data.
Matthieu Dixte , Product Researcher at Maze, explains the benefit of surveys: “With open-ended questions, researchers get insight into respondents' opinions, experiences, and explanations in their own words. This helps explore nuances that quantitative data alone may not capture.”
So, how do you make sure you’re asking the right survey questions? Gregg Bernstein , UX Researcher at Signal, says that when planning online surveys, it’s best to avoid questions that begin with “How likely are you to…?” Instead, Gregg says asking questions that start with “Have you ever… ?” will prompt users to give more specific and measurable answers.
Make sure your questions:
- Are easy to understand
- Don't guide participants towards a particular answer
- Include both closed-ended and open-ended questions
- Respect users and their privacy
- Are consistent in terms of format
To learn more about survey design, check out this guide .
When to conduct surveys
While surveys can be used at all stages of project development, and are ideal for continuous product discovery , the specific timing and purpose may vary depending on the research goals. For example, you can run surveys at:
- Conceptualization phase to gather preliminary data, and identify patterns, trends, or potential user segments
- Post-launch or during iterative design cycles to gather feedback on user satisfaction, feature usage, or suggestions for improvements
6. Card sorting
Card sorting is an important step in creating an intuitive information architecture (IA) and user experience. It’s also a great technique to generate ideas, naming conventions, or simply see how users understand topics.
In this UX research method, participants are presented with cards featuring different topics or information, and tasked with grouping the cards into categories that make sense to them.
There are three types of card sorting:
- Open card sorting: Participants organize topics into categories that make sense to them and name those categories, thus generating new ideas and names
- Hybrid card sorting: Participants can sort cards into predefined categories, but also have the option to create their own categories
- Closed card sorting: Participants are given predefined categories and asked to sort the items into the available groups
You can run a card sorting session using physical index cards or digitally with a UX research tool like Maze to simulate the drag-and-drop activity of dividing cards into groups. Running digital card sorting is ideal for any type of card sort, and moderated or unmoderated sessions.
Read more about card sorting and learn how to run a card sorting session here .
When to conduct card sorting
Card sorting isn’t limited to a single stage of design or development—it can be employed anytime you need to explore how users categorize or perceive information. For example, you may want to use card sorting if you need to:
- Understand how users perceive ideas
- Evaluate and prioritize potential solutions
- Generate name ideas and understand naming conventions
- Learn how users expect navigation to work
- Decide how to group content on a new or existing site
- Restructure information architecture
7. Tree testing
During tree testing a text-only version of the site is given to your participants, who are asked to complete a series of tasks requiring them to locate items on the app or website.
The data collected from a tree test helps you understand where users intuitively navigate first, and is an effective way to assess the findability, labeling, and information architecture of a product.
We recommend keeping these sessions short, ranging from 15 to 20 minutes, and asking participants to complete no more than ten tasks. This helps ensure participants remain focused and engaged, leading to more reliable and accurate data, and avoiding fatigue.
If you’re using a platform like Maze to run remote testing, you can easily recruit participants based on various demographic filters, including industry and country. This way, you can uncover a broader range of user preferences, ensuring a more comprehensive understanding of your target audience.
To learn more about tree testing, check out this chapter .
When to conduct tree testing
Tree testing is often done at an early stage in the design or redesign process. That’s because it’s more cost-effective to address errors at the start of a project—rather than making changes later in the development process or after launch.
However, it can be helpful to employ tree testing as a method when adding new features, particularly alongside card sorting.
While tree testing and card sorting can both help you with categorizing the content on a website, it’s important to note that they each approach this from a different angle and are used at different stages during the research process. Ideally, you should use the two in tandem: card sorting is recommended when defining and testing a new website architecture, while tree testing is meant to help you test how the navigation performs with users.
8. Usability testing
Usability testing evaluates your product with people by getting them to complete tasks while you observe and note their interactions (either during or after the test). The goal of conducting usability testing is to understand if your design is intuitive and easy to use. A sign of success is if users can easily accomplish their goals and complete tasks with your product.
There are various usability testing methods that you can use, such as moderated vs. unmoderated or qualitative vs. quantitative —and selecting the right one depends on your research goals, resources, and timeline.
Usability testing is usually performed with functional mid or hi-fi prototypes . If you have a Figma, InVision, Sketch, or prototype ready, you can import it into a platform like Maze and start testing your design with users immediately.
The tasks you create for usability tests should be:
- Realistic, and describe a scenario
- Actionable, and use action verbs (create, sign up, buy, etc)
Be mindful of using leading words such as ‘click here’ or ‘go to that page’ in your tasks. These instructions bias the results by helping users complete their tasks—something that doesn’t happen in real life.
Product tip ✨
With Maze, you can test your prototype and live website with real users to filter out cognitive biases, and gather actionable insights that fuel product decisions.
When to conduct usability testing
To inform your design decisions, you should do usability testing early and often in the process . Here are some guidelines to help you decide when to do usability testing:
- Before you start designing
- Once you have a wireframe or prototype
- Prior to the launch of the product
- At regular intervals after launch
To learn more about usability testing, check out our complete guide to usability testing .
9. Five-second testing
In five-second testing , participants are (unsurprisingly) given five seconds to view an image like a design or web page, and then they’re asked questions about the design to gauge their first impressions.
Why five seconds? According to data , 55% of visitors spend less than 15 seconds on a website, so it;s essential to grab someone’s attention in the first few seconds of their visit. With a five-second test, you can quickly determine what information users perceive and their impressions during the first five seconds of viewing a design.
Product tip 💡
And if you’re using Maze, you can simply upload an image of the screen you want to test, or browse your prototype and select a screen. Plus, you can star individual comments and automatically add them to your report to share with stakeholders.
When to conduct five-second testing
Five-second testing is typically conducted in the early stages of the design process, specifically during initial concept testing or prototype development. This way, you can evaluate your design's initial impact and make early refinements or adjustments to ensure its effectiveness, before putting design to development.
To learn more, check out our chapter on five-second testing .
10. A/B testing
A/B testing , also known as split testing, compares two or more versions of a webpage, interface, or feature to determine which performs better regarding engagement, conversions, or other predefined metrics.
It involves randomly dividing users into different groups and giving each group a different version of the design element being tested. For example, let's say the primary call-to-action on the page is a button that says ‘buy now’.
You're considering making changes to its design to see if it can lead to higher conversions, so you create two versions:
- Version A : The original design with the ‘buy now’ button positioned below the product description—shown to group A
- Version B : A variation with the ‘buy now’ button now prominently displayed above the product description—shown to group B
Over a planned period, you measure metrics like click-through rates, add-to-cart rates, and actual purchases to assess the performance of each variation. You find that Group B had significantly higher click-through and conversion rates than Group A. This indicates that showing the button above the product description drove higher user engagement and conversions.
Check out our A/B testing guide for more in-depth examples and guidance on how to run these tests.
When to conduct A/B testing
A/B testing can be used at all stages of the design and development process—whenever you want to collect direct, quantitative data and confirm a suspicion, or settle a design debate. This iterative testing approach allows you to continually improve your website's performance and user experience based on data-driven insights.
11. Concept testing
Concept testing is a type of research that evaluates the feasibility, appeal, and potential success of a new product before you build it. It centers the user in the ideation process, using UX research methods like A/B testing, surveys, and customer interviews.
There’s no one way to run a concept test—you can opt for concept testing surveys, interviews, focus groups, or any other method that gets qualitative data on your concept.
*Dive into our complete guide to concept testing for more tips and tricks on getting started. *
When to conduct concept testing
Concept testing helps gauge your audience’s interest, understanding, and likelihood-to-purchase, before committing time and resources to a concept. However, it can also be useful further down the product development line—such as when defining marketing messaging or just before launching.
Which is the best UX research type?
The best research type varies depending on your project; what your objectives are, and what stage you’re in. Ultimately, the ideal type of research is one which provides the insights required, using the available resources.
For example, if you're at the early ideation or product discovery stage, generative research methods can help you generate new ideas, understand user needs, and explore possibilities. As you move to the design and development phase, evaluative research methods and quantitative data become crucial.
Discover the UX research trends shaping the future of the industry and why the best results come from a combination of different research methods.
How to choose the right user experience research method
In an ideal world, a combination of all the insights you gain from multiple types of user research methods would guide every design decision. In practice, this can be hard to execute due to resources.
Sometimes the right methodology is the one you can get buy-in, budget, and time for.

Gregg Bernstein , UX Researcher at Signal
UX research tools can help streamline the research process, making regular testing and application of diverse methods more accessible—so you always keep the user at the center of your design process. Some other key tips to remember when choosing your method are:
Define the goals and problems
A good way to inform your choice of user experience research method is to start by considering your goals. You might want to browse UX research templates or read about examples of research.
Michael Margolis , UX Research Partner at Google Ventures, recommends answering questions like:
- “What do your users need?”
- “What are your users struggling with?”
- “How can you help your users?”
Understand the design process stage
If your team is very early in product development, generative research —like field studies—make sense. If you need to test design mockups or a prototype, evaluative research methods—such as usability testing—will work best.
This is something they’re big on at Sketch, as we heard from Design Researcher, Tanya Nativ. She says, “In the discovery phase, we focus on user interviews and contextual inquiries. The testing phase is more about dogfooding, concept testing, and usability testing. Once a feature has been launched, it’s about ongoing listening.”
Consider the type of insights required
If you're looking for rich, qualitative data that delves into user behaviors, motivations, and emotions, then methods like user interviews or field studies are ideal. They’ll help you uncover the ‘why’ behind user actions.
On the other hand, if you need to gather quantitative data to measure user satisfaction or compare different design variations, methods like surveys or A/B testing are more suitable. These methods will help you get hard numbers and concrete data on preferences and behavior.
*Discover the UX research trends shaping the future of the industry and why the best results come from a combination of different research methods. *
Build a deeper understanding of your users with UX research
Think of UX research methods as building blocks that work together to create a well-rounded understanding of your users. Each method brings its own unique strengths, whether it's human empathy from user interviews or the vast data from surveys.
But it's not just about choosing the right UX research methods; the research platform you use is equally important. You need a platform that empowers your team to collect data, analyze, and collaborate seamlessly.
Simplifying product research is simple with Maze. From tree testing to card sorting, prototype testing to user interview analysis—Maze makes getting actionable insights easy, whatever method you opt for.
Meanwhile, if you want to know more about testing methods, head on to the next chapter all about tree testing .
Get valuable insights from real users
Conduct impactful UX research with Maze and improve your product experience and customer satisfaction.
Frequently asked questions
How do you choose the right UX research method?
Choosing the right research method depends on your goals. Some key things to consider are:
- The feature/product you’re testing
- The type of data you’re looking for
- The design stage
- The time and resources you have available
What is the best UX research method?
The best research method is the one you have the time, resources, and budget for that meets your specific needs and goals. Most research tools, like Maze, will accommodate a variety of UX research and testing techniques.
When to use which user experience research method?
Selecting which user research method to use—if budget and resources aren’t a factor—depends on your goals. UX research methods provide different types of data:
- Qualitative vs quantitative
- Attitudinal vs behavioral
- Generative vs evaluative
Identify your goals, then choose a research method that gathers the user data you need.
Tree Testing: Your Guide to Improve Navigation and UX
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
UX Research
What is ux research.
UX (user experience) research is the systematic study of target users and their requirements, to add realistic contexts and insights to design processes. UX researchers adopt various methods to uncover problems and design opportunities. Doing so, they reveal valuable information which can be fed into the design process.
See why UX research is a critical part of the UX design process.
- Transcript loading…
UX Research is about Finding Insights to Guide Successful Designs
When you do UX research, you’ll be better able to give users the best solutions—because you can discover exactly what they need. You can apply UX research at any stage of the design process. UX researchers often begin with qualitative measures, to determine users’ motivations and needs . Later, they might use quantitative measures to test their results . To do UX research well, you must take a structured approach when you gather data from your users. It’s vital to use methods that 1) are right for the purpose of your research and 2) will give you the clearest information. Then, you can interpret your findings so you can build valuable insights into your design .
“I get very uncomfortable when someone makes a design decision without customer contact.” – Dan Ritzenthaler, Senior Product Designer at HubSpot
We can divide UX research into two subsets:
Qualitative research – Using methods such as interviews and ethnographic field studies, you work to get an in-depth understanding of why users do what they do (e.g., why they missed a call to action, why they feel how they do about a website). For example, you can do user interviews with a small number of users and ask open-ended questions to get personal insights into their exercise habits. Another aspect of qualitative research is usability testing , to monitor (e.g.) users’ stress responses. You should do qualitative research carefully. As it involves collecting non-numerical data (e.g., opinions, motivations), there’s a risk that your personal opinions will influence findings.
Quantitative research – Using more-structured methods (e.g., surveys, analytics), you gather measurable data about what users do and test assumptions you drew from qualitative research. For example, you can give users an online survey to answer questions about their exercise habits (e.g., “How many hours do you work out per week?”). With this data, you can discover patterns among a large user group. If you have a large enough sample of representative test users, you’ll have a more statistically reliable way of assessing the population of target users. Whatever the method, with careful research design you can gather objective data that’s unbiased by your presence, personality or assumptions. However, quantitative data alone can’t reveal deeper human insights.
We can additionally divide UX research into two approaches:
Attitudinal – you listen to what users say—e.g., in interviews.
Behavioral – you see what users do through observational studies.
When you use a mix of both quantitative and qualitative research as well as a mix of attitudinal and behavioral approaches, you can usually get the clearest view of a design problem.

© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Use UX Research Methods throughout Development
The Nielsen Norman Group—an industry-leading UX consulting organization—identifies appropriate UX research methods which you can use during a project’s four stages . Key methods are:
Discover – Determine what is relevant for users.
Contextual inquiries – Interview suitable users in their own environment to see how they perform the task/s in question.
Diary studies – Have users record their daily interactions with a design or log their performance of activities.
Explore – Examine how to address all users’ needs.
Card sorting – Write words and phrases on cards; then let participants organize them in the most meaningful way and label categories to ensure that your design is structured in a logical way.
Customer journey maps – Create user journeys to expose potential pitfalls and crucial moments.
Test – Evaluate your designs.
Usability testing – Ensure your design is easy to use.
Accessibility evaluations – Test your design to ensure it’s accessible to everyone.
Listen – Put issues in perspective, find any new problems and notice trends.
Surveys/Questionnaires – Use these to track how users’ feel about your product.
Analytics – Collect analytics/metrics to chart (e.g.) website traffic and build reports.
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://pixabay.com/en/clay-hands-sculpting-art-69...
- Copyright holder: Unsplash. Copyright terms and license: CCO Public Domain. Link: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-black-shirt-an...
- Copyright holder: Indecent Proposer. Copyright terms and license: CC BY-NC 2.0 Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/indecent_proposal/14...
- Copyright holder: Anna Langova. Copyright terms and license: CC0 1.0 Link: http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/view-image.php...
- Copyright holder: Conmongt. Copyright terms and license: CC0 Public Domain Link: https://pixabay.com/en/hourglass-time-time-lapse-clock-1623517/
Whichever UX research method you choose, you need to consider the pros and cons of the different techniques . For instance, card sorting is cheap and easy, but you may find it time-consuming when it comes to analysis. Also, it might not give you in-depth contextual meaning. Another constraint is your available resources , which will dictate when, how much and which type of UX research you can do. So, decide carefully on the most relevant method/s for your research . Moreover, involve stakeholders from your organization early on . They can reveal valuable UX insights and help keep your research in line with business goals. Remember, a design team values UX research as a way to validate its assumptions about users in the field , slash the cost of the best deliverables and keep products in high demand —ahead of competitors’.
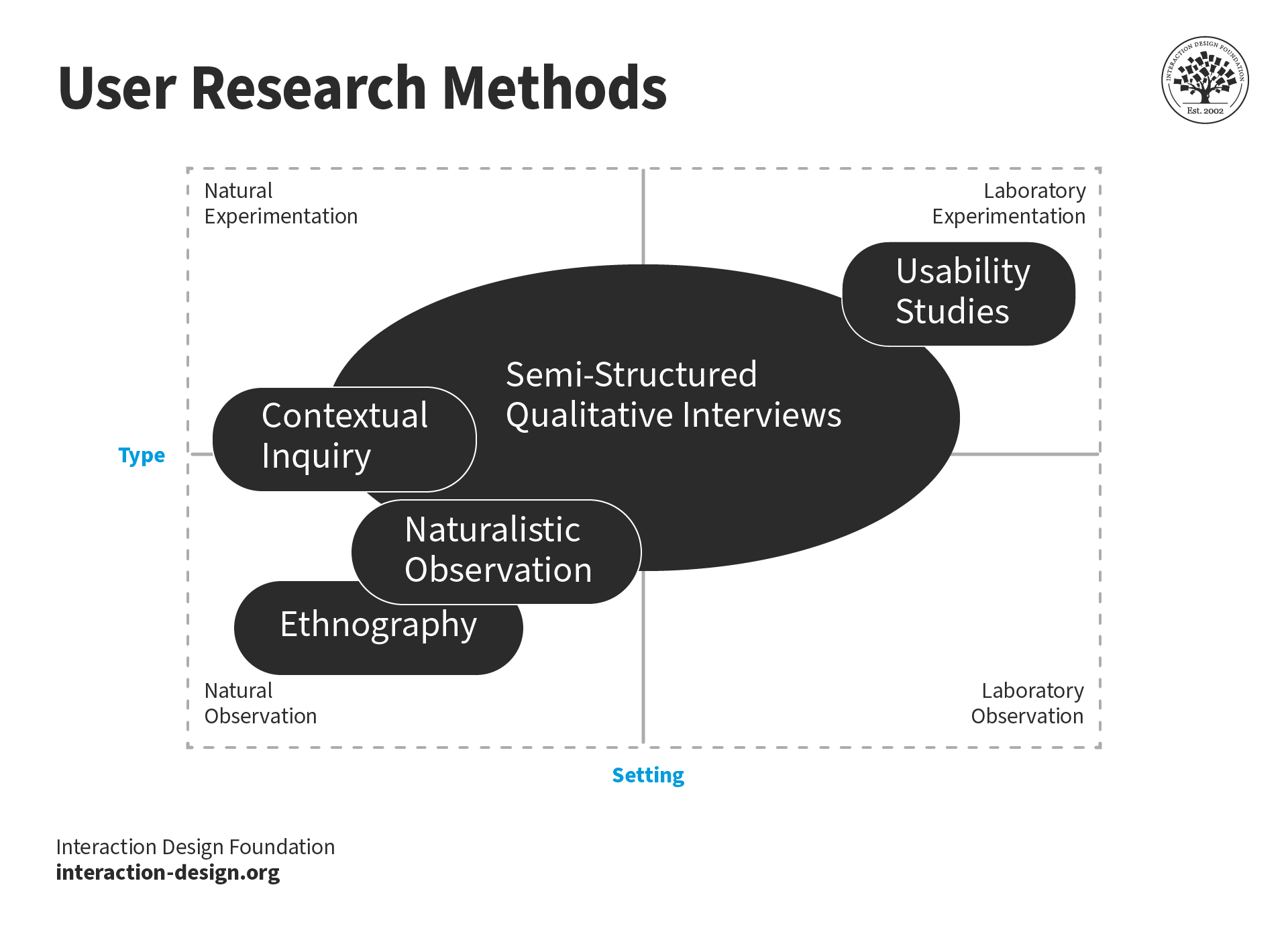
User research methods have different pros and cons,and vary from observations of users in context to controlled experiments in lab settings.
Learn More about UX Research
For a thorough grasp of UX research, take our course here: User Research – Methods and Best Practices
Read an extensive range of UX research considerations, discussed in Smashing Magazine: A Comprehensive Guide To UX Research
See the Nielsen Norman Group’s list of UX research tips: UX Research Cheat Sheet
Here’s a handy, example-rich catalog of UX research tools: 43 UX research tools for optimizing your product
Questions related to UX Research
UX research is a good career for those who enjoy working with a team and have strong communication skills. As a researcher, you play a crucial role in helping your team understand users and deliver valuable and delightful experiences. You will find a UX research career appealing if you enjoy scientific and creative pursuits.
Start exploring this career option; see the User Researcher Learning Path .
Studies suggest that companies are also willing to pay well for research roles. The average salary for a UX researcher ranges from $92,000 to $146,000 per year.
In smaller companies, user research may be one of the responsibilities of a generalist UX designer. How much can your salary vary based on your region? Find out in UI & UX Designer Salaries: How Much Can I Earn .
Research is one part of the overall UX design process. UX research helps inform the design strategy and decisions made at every step of the design process. In smaller teams, a generalist designer may end up conducting research.
A UX researcher aims to understand users and their needs. A UX designer seeks to create a product that meets those needs.
A UX researcher gathers information. A UX designer uses that information to create a user-friendly and visually appealing product.
Learn more about the relationship between UX research and UX design in the course:
User Experience: The Beginner’s Guide
If we consider a very broad definition of UX, then all user research is UX research.
However, in practice, there is a subtle difference between user research and UX research. While both involve understanding people, user research can involve users in any kind of research question, and some questions may not be that directly connected to user experience.
For example, you might do user research relating to a customer’s experience in relation to pricing, delivery or the experience across multiple channels.
Common UX research methods are usability testing, A/B testing, surveys, card sorting, user interviews, usage analytics and ethnographic research. Each method has its pros and cons and is useful in different scenarios. Hence, you must select the appropriate research method for the research question and target audience. Learn more about these methods in 7 Great, Tried and Tested UX Research Techniques .
Get started with user research. Download the User Research template bundle .

For a deep dive into usability testing—the most common research method, take the course Conducting Usability Testing .
Having a degree in a related field can give you an advantage. However, you don’t need a specific degree to become a UX researcher. A combination of relevant education, practical experience, and continuous learning can help you pursue a career in UX research. Many UX researchers come from diverse educational backgrounds, including psychology, statistics, human-computer interaction, information systems, design and anthropology.
Some employers may prefer candidates with at least a bachelor’s degree. However, it does not have to be in a UX-related field. There are relatively fewer degrees that focus solely on user research.
Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX
User Research – Methods and Best Practices
Every research project will vary. However, there are some common steps in conducting research, no matter which method or tool you decide to use:
Define the research question
Select the appropriate research method
Recruit participants
Conduct the research
Analyze the data
Present the findings
You can choose from various UX research tools . Your choice depends on your research question, how you're researching, the size of your organization, and your project. For instance:
Survey tools such as Typeform and Google Forms.
Card sorting tools such as Maze and UXtweak.
Heatmap tools such as HotJar and CrazyEgg
Usability testing (through first-click testing and tree-testing) tools such as Optimal Workshop and Loop 11
Diagramming applications such as Miro and Whimsical to analyze qualitative data through affinity diagramming.
Spreadsheet tools such as Google Sheets and Microsoft Excel for quantitative data analysis
Interface design and prototyping tools like Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch and Marvel to conduct usability testing.
Presentation tools such as Keynote, Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Many of these tools offer additional features you can leverage for multiple purposes. To understand how you can make the most of these tools, we recommend these courses:
There are relatively fewer degrees that focus solely on user research.
While there are no universal research case study formats, here’s one suggested outline:
An overview of the project: Include the problem statement, goals and objectives.
The research methods and methodology: For example, surveys, interviews, or usability testing).
Research findings
The design process: How the research findings led to design decisions.
Impact of design decisions on users and the business: Include metrics such as conversion and error rates to demonstrate the impact.
Optionally, include notes on what you learned and how you can improve the process in the future.
Learn how to showcase your portfolio to wow your future employer/client in the How to Create a UX Portfolio course.
While AI can help automate tasks and help UX researchers, it will not completely replace them. AI lacks the creativity and empathy that human designers bring to the table.
Human researchers are better at understanding the nuances of human behavior and emotions. They can also think outside the box and develop creative solutions that AI cannot. So, AI can help researchers be more efficient and effective through data analysis, smart suggestions and automation. But it cannot replace them.
Watch AI-Powered UX Design: How to Elevate Your UX Career to learn how you can work with AI.
Agile teams often struggle to incorporate user research in their workflows due to the time pressure of short sprints. However, that doesn’t mean agile teams can’t conduct research. Instead of seeing research as one big project, teams can break it into bite-sized chunks. Researchers regularly conduct research and share their findings in every sprint.
Researchers can involve engineers and other stakeholders in decision-making to give everyone the context they need to make better decisions. When engineers participate in the decision-making process, they can ensure that the design will be technically feasible. There will also be lower chances of errors when the team actually builds the feature. Here’s more on how to make research a team effort .
For more on bite-sized research, see this Master Class: Continuous Product Discovery: The What and Why
For more practical tips and methods to work in an agile environment, take our Agile Methods for UX Design course.
User research is very important in designing products people will want and use. It helps us avoid designing based on what we think instead of what users actually want.
UX research helps designers understand their users’ needs, behaviors, attitudes and how they interact with a product or service. Research helps identify usability problems, gather feedback on design concepts, and validate design decisions. This ultimately benefits businesses by improving the product, brand reputation and loyalty. A good user experience provides a competitive edge and reduces the risk of product failure.
Learn more about the importance of user research in the design process in these courses:
Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide
Literature on UX Research
Here’s the entire UX literature on UX Research by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about UX Research
Take a deep dive into UX Research with our course User Research – Methods and Best Practices .
How do you plan to design a product or service that your users will love , if you don't know what they want in the first place? As a user experience designer, you shouldn't leave it to chance to design something outstanding; you should make the effort to understand your users and build on that knowledge from the outset. User research is the way to do this, and it can therefore be thought of as the largest part of user experience design .
In fact, user research is often the first step of a UX design process—after all, you cannot begin to design a product or service without first understanding what your users want! As you gain the skills required, and learn about the best practices in user research, you’ll get first-hand knowledge of your users and be able to design the optimal product—one that’s truly relevant for your users and, subsequently, outperforms your competitors’ .
This course will give you insights into the most essential qualitative research methods around and will teach you how to put them into practice in your design work. You’ll also have the opportunity to embark on three practical projects where you can apply what you’ve learned to carry out user research in the real world . You’ll learn details about how to plan user research projects and fit them into your own work processes in a way that maximizes the impact your research can have on your designs. On top of that, you’ll gain practice with different methods that will help you analyze the results of your research and communicate your findings to your clients and stakeholders—workshops, user journeys and personas, just to name a few!
By the end of the course, you’ll have not only a Course Certificate but also three case studies to add to your portfolio. And remember, a portfolio with engaging case studies is invaluable if you are looking to break into a career in UX design or user research!
We believe you should learn from the best, so we’ve gathered a team of experts to help teach this course alongside our own course instructors. That means you’ll meet a new instructor in each of the lessons on research methods who is an expert in their field—we hope you enjoy what they have in store for you!
All open-source articles on UX Research
7 great, tried and tested ux research techniques.

- 1.2k shares
- 3 years ago
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding UX Roles and Which One You Should Go For
Shadowing in User Research - Do You See What They See?

Contextual Interviews and How to Handle Them

15 Guiding Principles for UX Researchers

Ethnography

Porter’s 5 Forces Model - Design in Context, Understand the Market
- 7 years ago
Ideas for Conducting UX Research with Children

Laddering Questions Drilling Down Deep and Moving Sideways in UX Research

Action Research
4 common pitfalls in usability testing and how to avoid them to get more honest feedback.
Confirmation Bias – It’s Not What We Think We Know That Counts

User Research Methods for Mobile UX

- 10 mths ago
The Top UX Design Books You Need to Read in 2024: Beginner to Expert

6 Tips for Better International UX Research

Team Research

- 2 years ago
Adding Quality to Your Design Research with an SSQS Checklist
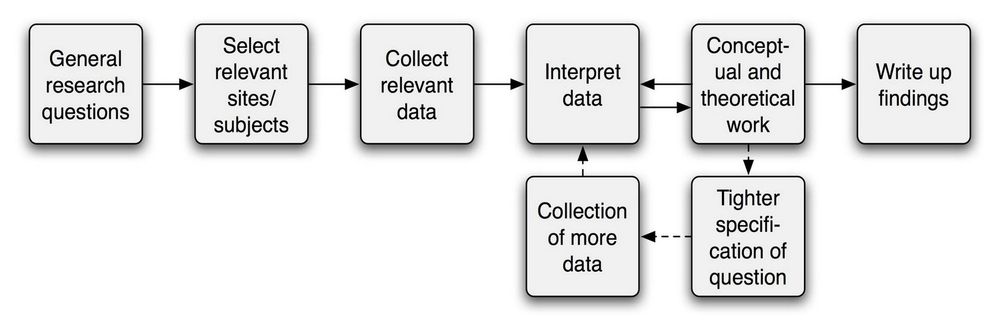
- 8 years ago
Common UX Research Interview Questions

How to Fit Quantitative Research into the Project Lifecycle
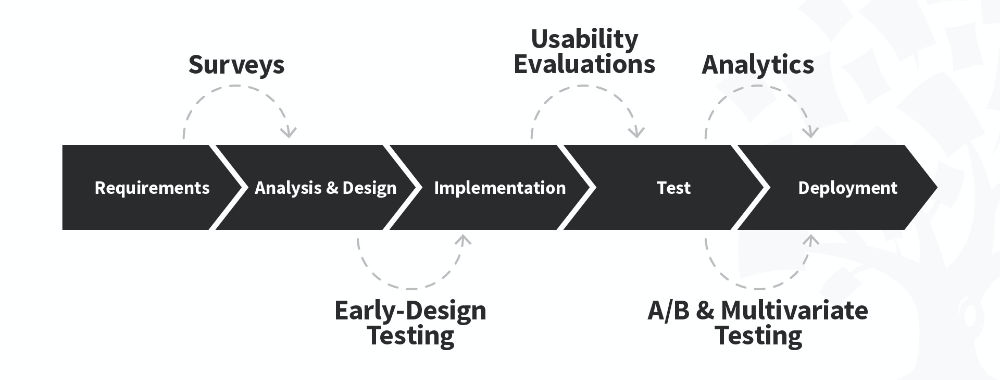
The Best Free UX Design Courses in 2024

Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share the knowledge!
Share this content on:
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Learn / Guides / UX research guide
Back to guides
7 powerful examples of UX research in action
After a lengthy planning and designing process, you’ve turned your website or app vision into a reality. But maybe you've noticed that despite its visual appeal, conversions are low while bounce rates keep soaring. Often, a poor user experience (UX) is to blame, affecting your brand perceptions and customer conversions.
Last updated
Reading time.
So, how can you create a frictionless, user-centric experience? Strong UX research and smart use of UX research tools are key.
While the research process can be a challenge, analyzing how other brands have successfully conducted UX research can inspire your own approach. This article dives into seven detailed case studies and shows you how to use UX research tools to identify and solve UX challenges and delight your customers.
Empower your team to do great UX research
Use Hotjar for effective end-to-end UX research campaigns that help you deeply understand user needs
Why and when should you perform UX research?
UX research is the strategic process of analyzing target users to understand their needs, behavior, and experience. Teams use UX research, feedback tools, and experimentation techniques to collect contextual insights.
Then, they translate these insights into a user-centric design that generates strong conversions and higher user retention rates.
UX research offers several other benefits, including:
Helping create customer delight: by understanding how users behave, you can design your product more accessibly and empathetically. UX research equips teams to create tailored experiences, maximizing customer satisfaction and improving product experience (PX).
Replacing guesswork with data-driven insights : UX research involves collecting and assessing qualitative and quantitative data to make decisions based on comprehensive insights, rather than gut feelings.
Providing insight into the user’s needs : the better you know your audience's pain points, the better you can design a product that truly addresses their needs. UX research tells you exactly where your users struggle—so you can come up with solutions.
Helping you achieve critical KPIs : research methods like concept validation and user feedback ensure every iteration moves you toward better user engagement, conversions, increased retention, and reduced churn, positively impacting your revenue.
The benefits of UX research are clear. So when should you start the process?
Since you are creating a product for someone else and not for yourself, any time is good to start UX research. The beginning doesn't have to be sophisticated. It can start simple and evolve, adapting to the amount/complexity of the questions about the users and the resources of your business.
You only need curiosity, some time, and a willingness to base your product on facts and not assumptions.
Let’s take a look at how seven companies aced UX research and produced incredible results.
7 UX research examples to get inspired
UX research offers you opportunities for conversion rate optimization and personalization that can significantly increase business growth and enhance customer satisfaction.
Contrary to popular belief, you don’t always need a dedicated UX research team: a cost-effective tech stack can do most of the heavy lifting. Product experience insights tools like Hotjar help you assess your users’ experience, measure their behavior, and garner constructive feedback for UX analysis .
Here are seven examples of great UX research with the help of product experience insights tools to get you inspired.
1. Zenprint: 7% reduction in bounce rate
Zenprint provides order and wholesale digital printing services in the Australian market.
Zenprint’s biggest challenge was identifying factors leading to drop-offs on their website. The brand’s marketing team struggled to figure out:
Where people spent their time
What users were interested in
What caused them to drop off
They wanted actionable insights into how users interacted with their site .
Action plan
Zenprint’s marketing team leveraged Hotjar (👋) to analyze web performance and understand user behavior at a granular level. They used:
Funnels to locate the exact drop-off points in the customer journey
Session Recordings to understand how each user behaved on the site, tracing mouse and scroll movements to see which elements users click on
Heatmaps to view color-coded representations of popular and unpopular site elements to help discover areas where users spend the most time and determine those that need improvement
This action plan helped the team zero in on their pricing table as a major blocker.
Once Zenprint identified the problem, the next step was split testing multiple layouts to optimize the pricing table. With a simple change in their pricing plan, the Zenprint team reduced drop-off rates by 7% and boosted its conversion rate by 2%.
Key takeaways
For stellar UX research, collect real-time insights from users across different stages of the conversion funnel to identify bottlenecks. Supplement quantitative analytics with qualitative feedback by analyzing Hotjar Recordings and Heatmaps to understand user behavior.
2. Matalan: 400% ROI
Matalan is a British fashion and homeware retail and ecommerce brand.
Without qualitative UX research to interpret data points, Matalan's UX team was forced to make decisions based on gut feelings, relying on quantitative data alone, which gave them limited visibility. The checkout process was showing high drop-offs and they weren’t sure why.
When Matalan migrated to a responsive website, its UX team used Hotjar to record and assess user responses to this change, and compare performance through A/B testing. They also viewed Session Recordings that flagged bugs and glitches early in the migration process.
They used Hotjar's Feedback tools to collect user feedback in real-time to capture the customer’s voice and make product changes to improve the user experience. Combined with user recordings, these provided a complete overview of the user journey, which helped eliminate areas of friction.
Using recordings to closely monitor user behavior, Matalan optimized its checkout process and increased conversions by 1.23%.
They created a bespoke experience dashboard by combining qualitative insights gathered by Hotjar with Google Data Studio analytics for a comprehensive UX research process.
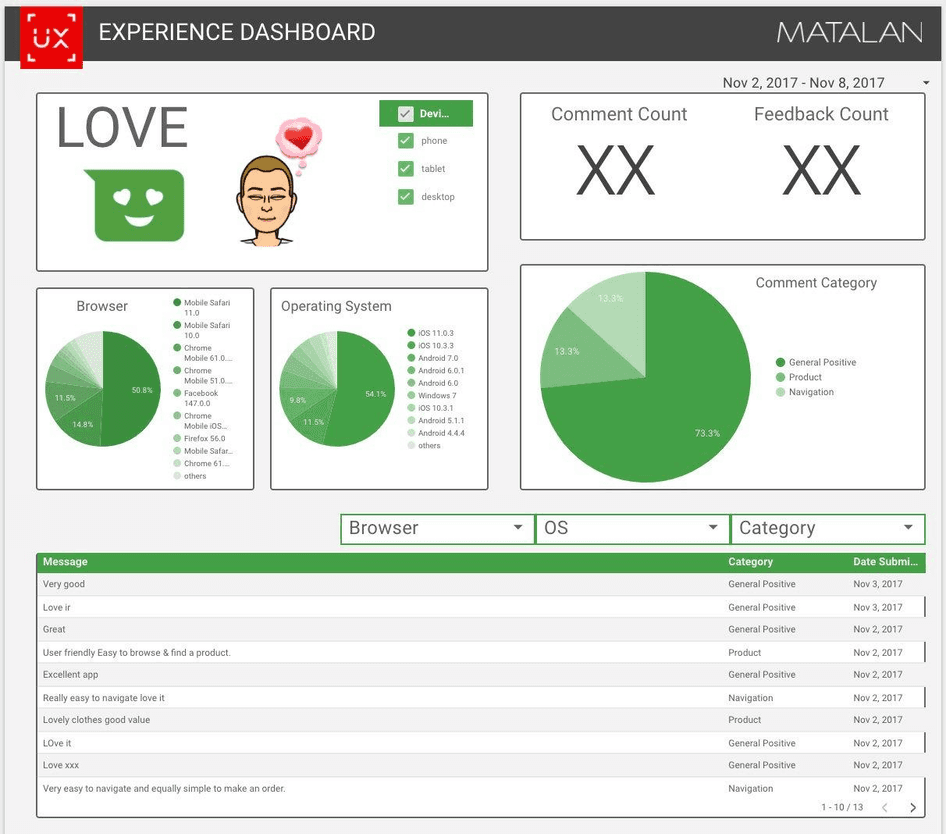
Instead of relying solely on numbers, collect user perspectives to add depth to your UX research . This concrete feedback can make your team aware of flaws in the user experience so you can proactively offer fixes.
3. Materials Market: 3x conversions
Materials Market is a UK-based marketplace for construction material manufacturers and customers.
Materials Market’s co-founder wanted to optimize their website experience by improving three problem areas:
Poorly placed calls to action (CTAs), where mobile users couldn’t see the CTA clearly enough to click on it
Customer drop-offs at the checkout step because users only wanted to check the delivery time
A complicated cookie policy that caused visitors to bounce as soon as they landed on the website
Materials Market used Hotjar Recordings and Heatmaps to dig deeper into these UX research issues . The result was a gradual upgrade of the website to meet—and exceed—customer expectations. Here’s what happened:
They improved the visibility of CTAs with changes to font, color, and design. The team also included a rating widget next to the CTAs to display social proof.
They removed the need to set up an account to place an order and added an estimated delivery date for every product
They implemented design changes in the cookie policy pop-up to make it 30% bigger with better color and copy. They also placed the banner on the top of the page.
Redesigning the checkout flow decreased drop-offs by 86%. On the flip side, the conversion rate more than tripled to 1.6% —massively boosting yearly revenue by more than £10,000.
UX research tools like recordings are a great way to understand user behavior on your website—you can sort and filter recordings with Hotjar by relevance. This can boost your UX research efforts without relying heavily on technical expertise and development knowledge.
4. Totally Promotional: increased sales while enhancing UX
Totally Promotional is a US-based manufacturer and retailer that produces customized promotional products for brands.
Totally Promotional wanted to evaluate on-site user behavior and improve the brand's UX quality but was struggling to collect meaningful user data that offered a complete insight into the user experience.
Relying on Google Analytics alone, the team lacked qualitative feedback to interpret customer needs and design empathetically.
The team added Hotjar to its tech stack to get a better view of user interaction and web experience. They used Hotjar Heatmaps to assess where users spent their time and dropped off—identifying underperforming pages and bugs.
Hotjar’s Feedback and Survey tools were useful in capturing Voice of the Customer (VoC) insights, allowing Totally Promotional to examine why users behaved the way they did. They also watched Session Recordings to pinpoint where buyers felt stuck in the order process.
This mix of UX research tools removed the guesswork from Totally Promotional’s website optimization process. The team took an evidence-based approach and incorporated both minor tweaks and significant updates in the ecommerce storefront design.
However, the most crucial action they took was changing the order process for their branded pens page, which tripled sales for this product.
Behavioral data and user perspectives are both necessary for excellent UX research. Intuitive tools like Hotjar’s Feedback widget can help you collate meaningful information to supercharge your UX research campaign and implement strategic website changes.
5. Hussle: fixed one bug every week
Hussle is a subscription-based network of gyms, spas, and digital fitness solutions.
Hussle’s biggest challenge was high customer churn: the brand’s product team wanted to better understand why this was happening and deploy UX research to reduce churn with an unparalleled product experience.
Hussle’s team leveraged Surveys and Recordings to find answers as to why users were leaving.
It turned out there were three core reasons behind churn:
High subscription cost
Changes in the user’s location
Purchase of direct gym membership
Deploying UX research tools to understand churn led to an improved UX and user interface and boosted Hussle’s growth. The team saw great results, including:
A preemptive bug fix that would’ve hindered the buying process
Streamlined the bug-fixing process by detecting and deleting at least one bug weekly
Gathered meaningful insights from users through 1000+ survey responses and over 73,000 seconds of Hotjar Session Recordings
The team has continued to use Session Recordings and Heatmaps to stay one step ahead—whether detecting bugs or finding where users get stuck.
User feedback is a great way to understand the reasons behind churn so you can address them and improve retention . Additionally, you can also gather data to proactively fix bugs and improve UX.
6. Turum-burum: +55% conversion rate
Turum-burum is a digital UX design agency that provides conversion rate optimization strategies for clients like Intertop, one of Ukraine's biggest shoe retailers.
Intertop saw a rapid increase in traffic on their website and used Turum-burum’s services to maximize conversions from this influx of visitors. They used UX research to address three crucial challenges:
Simplifying and enhancing the customer journey once a visitor lands on Intertop’s homepage
Testing and implementing UX changes as quickly as possible
Anticipating and mitigating any potential risks resulting from UX changes
Using Hotjar’s exit-intent Surveys , the Turum-burum team identified a major problem in the conversion funnel: their complicated checkout process.
Hotjar helped the team in two main ways:
They used the user feedback coming in through Surveys to prioritize improvements
They used Heatmaps and Session Recordings to understand customer blockers and pain points
Drawing on these UX research insights, the team decided to add a few small but crucial details to Intertop’s storefront, such as filters, intuitive product lists, and an improved checkout flow.
Product experience insights helped the team pinpoint exact bottlenecks and run feedback-driven experiments.
These changes skyrocketed Intertop's conversion rate by 54.68% and reduced bounce rates by 13.35%. They also enhanced the product page and lists to increase conversion from the cart to the checkout page by 36.6%.
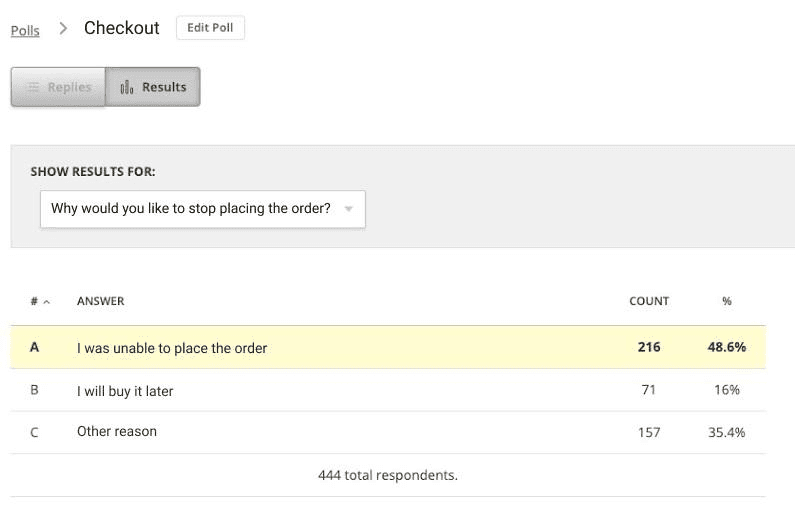
Mapping the customer journey through your sales funnel is a critical part of successful ecommerce UX research. Monitor user needs at every stage through heatmaps, recordings, and feedback tools.
7. eShopWorld: better UX and conversion fluctuation awareness
eShopWorld delivers global ecommerce solutions to help brands scale their business at the international level.
One of eShopWorld’s key services is conversion rate optimization. They monitor conversions for every client to identify drops and discrepancies.
However, the team didn't have a reliable tool for evaluating user behavior and countering occasional dips in the conversion rate.
eShopWorld used Hotjar Feedback tools on its checkout page to collect real-time user opinions: customers were able to flag issues right before ordering, and the eShopWorld team could dig deeper into understanding the context behind their comments via Session Recordings .
Heatmaps also provided actionable insights into customer behavior so the team could holistically review user issues and prioritize them according to their impact on the UX.
eShopWorld studied all the user feedback to get to the root of key problems. They used research data to plan and communicate UX design and user flow changes to tackle each blocker.
The team also analyzed Hotjar Heatmaps and watched Session Recordings to assess whether UX redesigns and changes produced the intended effect for users.
UX research is a continuous process of striving to understand your customers and their preferences at every stage of design and development. By using research tools to identify key issues and dig deeper into their context, teams can produce user-centric interfaces and make data-informed decisions.
UX research is paramount to product success
For your site to attract quality traffic, deliver seamless buying experiences, and move the needle on conversion rates, you need to understand how your users behave and what they expect.
UX research tools can help you stay on top of your customer needs. Feature-packed PX insights tools allow you to easily observe user behavior, synthesize user feedback, and perform experiments to drive product growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does ux research involve.
UX research is the process of studying the target audience to examine user behavior and identify opportunities for improving designs and workflows. UX research typically involves:
Monitoring user behavior
Assessing what users like and dislike based on their activity
Collecting feedback and suggestions for potential bugs or friction areas
Experimenting to see user reactions and validate any design improvements
Asking users for feedback to bring the users’ voice into the design and development process.
What are some UX research methods?
UX research varies in terms of methodology. You can use qualitative, quantitative, behavioral, and attitudinal methods for conducting your research. Each method uncovers unique insights about the user experience, such as:
Qualitative : why and how users behave on a page
Quantitative : numerical assessment of their activity
Behavioral : what users do on a website/product
Attitudinal : how users perceive a website/product
Why do you need UX research?
UX research lays the groundwork for successful UX design strategies. It helps you understand your customers and their needs to create more empathetic designs tailored to your audience.
It’s an essential factor for achieving goals such as lowering churn, bounce rate, cart abandonment, and improving UX. By helping you iterate your site or product informed by user feedback, UX research allows you to create a bulletproof website that meets user expectations.
UX research tools
Previous chapter
UX research methods
Next chapter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research Aim Example 1:Assess the impact and usability of our daily meditation feature in the app. Objective Examples: Uncover usability issues for new users looking to find a relevant meditation that meets their needs. Understand typical usage patterns of our most dedicated daily meditators.
A UX research plan helps to set expectations and document the essentials you need to communicate to stakeholders and clients. Your company needs a strong business case for every user research session, complete with research objectives, goals, methods, and logistical needs for the study. UX Research Plan Elements. Every UX research plan should ...
UX research plan template: This editable Miro research project plan example helps you brainstorm user and business-facing problems, objectives, and questions. UX research brief: You need a clear brief before you conduct UX research—Milanote shares a template that will help you simplify the writing process.
These objectives should be focused on particular features or processes on your product. As a UX researcher, I've learned that the more specific the objectives, the easier it is to write tasks and questions, and the easier it is to extract answers later on in analysis.
Keep your objective action-oriented and specific. If you need help, you might start drafting your objective by filling in the blanks of "I want to learn ____," "I want to understand ____," or "I want to identify ____.". Many UX researchers agree that the more specific the objectives, the easier it is to write tasks and UX research ...
Research objectives. One of the biggest problem with using hypotheses is that they set the wrong expectations about what your research results are telling you. In Thinking, Fast and Slow, Daniel Kahneman points out that: "extreme outcomes (both high and low) are more likely to be found in small than in large samples".
How to plan a UX research study. This is a step-by-step guide to planning user research. It explains the process by which a research plan comes together into a shareable document (like the one above) that enables team alignment, accountability, and efficiency throughout your study. 1. Identify your research goals.
A UX research strategy is the guiding plan for everything you do related to UX research. This means what research you do, when and how you do it. Your UX research strategy is also a way of democratizing research and cultivating an atmosphere of constant iteration and investigation through timely research.
A UX research plan usually includes details about the methodology of the research, types of studies, and information about the timing, scope, and respondents. Don't confuse a UX research plan with a strategy - they are two separate things. A strategy contains goals, expectations, vision, and business goals, while a plan explains how a team ...
Step 1: Alignment & Requirements Gathering. Research rarely will happen in a vacuum. Usually you are working with a team—product, engineering, design, for example. When the need for a research study arises, the first thing you want to do is meet with your team to understand the questions they're trying to answer.
A UX research plan, also known as a user research plan, is a brief reference document that outlines your research project's goals, key contributors, important dates, and timelines. Think of your research plan as a UX-focused kick-off document for your project. The plan offers an overview of the research initiative, encourages well-defined and ...
Research questions: pinpoint the specific questions that will be asked during the project to check they align with the overall project goals. Methodology: note the UX research methods that will be used during the project. These should also be relevant to the overall goals and challenges.
The objective should be used as a way to sell your research in order to get stakeholder buy-in; Make them care about this research project by showing how it affects them. Keep in mind who you are ...
Below is an example structure on how to write an interview script. Try not to be too structured with your approach as part of being a good researcher is to listen to what the user has to say and ask meaningful follow up questions. a. Introduction. Introduce yourself, your role and the purpose of the interview.
User research is the parent of UX research; it's a broader research effort that aims to understand the demographics, behaviors, and sentiments of your users and personas. UX research, on the other hand, is a type of user research that's specific to your product or platform. Where user research focuses on the user as a whole, UX research ...
User Experience (UX) Research is a systematic process of understanding and evaluating how users interact with a product, service, or system. It encompasses a wide range of research methods and techniques to gain insights into user behaviors, preferences, needs, and pain points. The ultimate goal of UX research is to inform and improve the ...
Research Objectives. In the book Interviewing Users by Steve Portigal, two researchers, Nate Bolt, UX Research Manager at Facebook and Cyd Harrel, a former VP of UX Research at BOLT/Peters, talk about a time when they were approached by a client who needed UX research conducted but did not have the time or budget for full-blown research.
10 UI Designer Portfolio Examples. A UI design portfolio showcases a designer's top projects, creativity and problem-solving skills. ... "Defining the Objectives of User Research ... Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design. In 9 chapters, we'll cover: conducting user interviews ...
11. Concept testing. Concept testing is a type of research that evaluates the feasibility, appeal, and potential success of a new product before you build it. It centers the user in the ideation process, using UX research methods like A/B testing, surveys, and customer interviews.
UX (user experience) research is the systematic study of target users and their requirements, to add realistic contexts and insights to design processes. UX researchers adopt various methods to uncover problems and design opportunities. Doing so, they reveal valuable information which can be fed into the design process.
Today's post on UX research objectives is an excerpt from our eBook, The complete guide to user testing websites, apps, and prototypes. Enjoy! User feedback is the key to making any business successful—whether you're launching an app, redesigning a website, refining product features, or making ongoing improvements to your customer experience.
Product experience insights tools like Hotjar help you assess your users' experience, measure their behavior, and garner constructive feedback for UX analysis . Here are seven examples of great UX research with the help of product experience insights tools to get you inspired. 1. Zenprint: 7% reduction in bounce rate.