- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers


What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Introducing SciSpace’s Citation Booster To Increase Research Visibility

AI for Meta-Analysis — A Comprehensive Guide

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


Speechwriting
8 Purpose and Thesis
Speechwriting Essentials
In this chapter . . .
As discussed in the chapter on Speaking Occasion , speechwriting begins with careful analysis of the speech occasion and its given circumstances, leading to the choice of an appropriate topic. As with essay writing, the early work of speechwriting follows familiar steps: brainstorming, research, pre-writing, thesis, and so on.
This chapter focuses on techniques that are unique to speechwriting. As a spoken form, speeches must be clear about the purpose and main idea or “takeaway.” Planned redundancy means that you will be repeating these elements several times over during the speech.
Furthermore, finding purpose and thesis are essential whether you’re preparing an outline for extemporaneous delivery or a completely written manuscript for presentation. When you know your topic, your general and specific purpose, and your thesis or central idea, you have all the elements you need to write a speech that is focused, clear, and audience friendly.
Recognizing the General Purpose
Speeches have traditionally been grouped into one of three categories according to their primary purpose: 1) to inform, 2) to persuade, or 3) to inspire, honor, or entertain. These broad goals are commonly known as the general purpose of a speech . Earlier, you learned about the actor’s tool of intention or objectives. The general purpose is like a super-objective; it defines the broadest goal of a speech. These three purposes are not necessarily exclusive to the others. A speech designed to be persuasive can also be informative and entertaining. However, a speech should have one primary goal. That is its general purpose.
Why is it helpful to talk about speeches in such broad terms? Being perfectly clear about what you want your speech to do or make happen for your audience will keep you focused. You can make a clearer distinction between whether you want your audience to leave your speech knowing more (to inform), or ready to take action (to persuade), or feeling something (to inspire)
It’s okay to use synonyms for these broad categories. Here are some of them:
- To inform could be to explain, to demonstrate, to describe, to teach.
- To persuade could be to convince, to argue, to motivate, to prove.
- To inspire might be to honor, or entertain, to celebrate, to mourn.
In summary, the first question you must ask yourself when starting to prepare a speech is, “Is the primary purpose of my speech to inform, to persuade, or to inspire?”
Articulating Specific Purpose
A specific purpose statement builds upon your general purpose and makes it specific (as the name suggests). For example, if you have been invited to give a speech about how to do something, your general purpose is “to inform.” Choosing a topic appropriate to that general purpose, you decide to speak about how to protect a personal from cyberattacks. Now you are on your way to identifying a specific purpose.
A good specific purpose statement has three elements: goal, target audience, and content.
If you think about the above as a kind of recipe, then the first two “ingredients” — your goal and your audience — should be simple. Words describing the target audience should be as specific as possible. Instead of “my peers,” you could say, for example, “students in their senior year at my university.”
The third ingredient in this recipe is content, or what we call the topic of your speech. This is where things get a bit difficult. You want your content to be specific and something that you can express succinctly in a sentence. Here are some common problems that speakers make in defining the content, and the fix:
Now you know the “recipe” for a specific purpose statement. It’s made up of T o, plus an active W ord, a specific A udience, and clearly stated C ontent. Remember this formula: T + W + A + C.
A: for a group of new students
C: the term “plagiarism”
Here are some further examples a good specific purpose statement:
- To explain to a group of first-year students how to join a school organization.
- To persuade the members of the Greek society to take a spring break trip in Daytona Beach.
- To motivate my classmates in English 101 to participate in a study abroad program.
- To convince first-year students that they need at least seven hours of sleep per night to do well in their studies.
- To inspire my Church community about the accomplishments of our pastor.
The General and Specific Purpose Statements are writing tools in the sense that they help you, as a speechwriter, clarify your ideas.
Creating a Thesis Statement
Once you are clear about your general purpose and specific purpose, you can turn your attention to crafting a thesis statement. A thesis is the central idea in an essay or a speech. In speechwriting, the thesis or central idea explains the message of the content. It’s the speech’s “takeaway.” A good thesis statement will also reveal and clarify the ideas or assertions you’ll be addressing in your speech (your main points). Consider this example:
General Purpose: To persuade. Specific Purpose: To motivate my classmates in English 101 to participate in a study abroad program. Thesis: A semester-long study abroad experience produces lifelong benefits by teaching you about another culture, developing your language skills, and enhancing your future career prospects.
The difference between a specific purpose statement and a thesis statement is clear in this example. The thesis provides the takeaway (the lifelong benefits of study abroad). It also points to the assertions that will be addressed in the speech. Like the specific purpose statement, the thesis statement is a writing tool. You’ll incorporate it into your speech, usually as part of the introduction and conclusion.
All good expository, rhetorical, and even narrative writing contains a thesis. Many students and even experienced writers struggle with formulating a thesis. We struggle when we attempt to “come up with something” before doing the necessary research and reflection. A thesis only becomes clear through the thinking and writing process. As you develop your speech content, keep asking yourself: What is important here? If the audience can remember only one thing about this topic, what do I want them to remember?
Example #2: General Purpose: To inform Specific Purpose: To demonstrate to my audience the correct method for cleaning a computer keyboard. Central Idea: Your computer keyboard needs regular cleaning to function well, and you can achieve that in four easy steps.
Example # 3 General Purpose: To Inform Specific Purpose: To describe how makeup is done for the TV show The Walking Dead . Central Idea: The wildly popular zombie show The Walking Dead achieves incredibly scary and believable makeup effects, and in the next few minutes I will tell you who does it, what they use, and how they do it.
Notice in the examples above that neither the specific purpose nor the central idea ever exceeds one sentence. If your central idea consists of more than one sentence, then you are probably including too much information.
Problems to Avoid
The first problem many students have in writing their specific purpose statement has already been mentioned: specific purpose statements sometimes try to cover far too much and are too broad. For example:
“To explain to my classmates the history of ballet.”
Aside from the fact that this subject may be difficult for everyone in your audience to relate to, it’s enough for a three-hour lecture, maybe even a whole course. You’ll probably find that your first attempt at a specific purpose statement will need refining. These examples are much more specific and much more manageable given the limited amount of time you’ll have.
- To explain to my classmates how ballet came to be performed and studied in the U.S.
- To explain to my classmates the difference between Russian and French ballet.
- To explain to my classmates how ballet originated as an art form in the Renaissance.
- To explain to my classmates the origin of the ballet dancers’ clothing.
The second problem happens when the “communication verb” in the specific purpose does not match the content; for example, persuasive content is paired with “to inform” or “to explain.” Can you find the errors in the following purpose statements?
- To inform my audience why capital punishment is unconstitutional. (This is persuasive. It can’t be informative since it’s taking a side)
- To persuade my audience about the three types of individual retirement accounts. (Even though the purpose statement says “persuade,” it isn’t persuading the audience of anything. It is informative.)
- To inform my classmates that Universal Studios is a better theme park than Six Flags over Georgia. (This is clearly an opinion; hence it is a persuasive speech and not merely informative)
The third problem exists when the content part of the specific purpose statement has two parts. One specific purpose is enough. These examples cover two different topics.
- To explain to my audience how to swing a golf club and choose the best golf shoes.
- To persuade my classmates to be involved in the Special Olympics and vote to fund better classes for the intellectually disabled.
To fix this problem of combined or hybrid purposes, you’ll need to select one of the topics in these examples and speak on that one alone.
The fourth problem with both specific purpose and central idea statements is related to formatting. There are some general guidelines that need to be followed in terms of how you write out these elements of your speech:
- Don’t write either statement as a question.
- Always use complete sentences for central idea statements and infinitive phrases (beginning with “to”) for the specific purpose statement.
- Use concrete language (“I admire Beyoncé for being a talented performer and businesswoman”) and avoid subjective or slang terms (“My speech is about why I think Beyoncé is the bomb”) or jargon and acronyms (“PLA is better than CBE for adult learners.”)
There are also problems to avoid in writing the central idea statement. As mentioned above, remember that:
- The specific purpose and central idea statements are not the same thing, although they are related.
- The central idea statement should be clear and not complicated or wordy; it should “stand out” to the audience. As you practice delivery, you should emphasize it with your voice.
- The central idea statement should not be the first thing you say but should follow the steps of a good introduction as outlined in the next chapters.
You should be aware that all aspects of your speech are constantly going to change as you move toward the moment of giving your speech. The exact wording of your central idea may change, and you can experiment with different versions for effectiveness. However, your specific purpose statement should not change unless there is a good reason to do so. There are many aspects to consider in the seemingly simple task of writing a specific purpose statement and its companion, the central idea statement. Writing good ones at the beginning will save you some trouble later in the speech preparation process.
Public Speaking as Performance Copyright © 2023 by Mechele Leon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

12 Constructing the Thesis and Argument from the Ground Up
Amy Guptill; Liz Delf; Rob Drummond; and Kristy Kelly
Amy Guptill Adapted by Liz Delf, Rob Drummond, and Kristy Kelly
Moving beyond the five-paragraph theme.
As an instructor, I’ve noted that a number of new (and sometimes not-so-new) students are skilled wordsmiths and generally clear thinkers but are nevertheless stuck in a high school style of writing. They struggle to let go of certain assumptions about how an academic paper should be. Some students who have mastered that form, and enjoyed a lot of success from doing so, assume that college writing is simply more of the same. The skills that go into a very basic kind of essay—often called the five-paragraph theme —are indispensable. If you’re good at the five-paragraph theme, then you’re good at identifying a clearfl and consistent thesis, arranging cohesive paragraphs, organizing evidence for key points, and situating an argument within a broader context through the intro and conclusion.
In college you need to build on those essential skills. The five-paragraph theme, as such, is bland and formulaic; it doesn’t compel deep thinking. Your instructors are looking for a more ambitious and arguable thesis, a nuanced and compelling argument, and real-life evidence for all key points, all in an organically structured paper.
Figures 12.1 and 12.2 contrast the standard five-paragraph theme and the organic college paper. The five-paragraph theme (outlined in figure 12.1 ) is probably what you’re used to: the introductory paragraph starts broad and gradually narrows to a thesis, which readers expect to find at the very end of that paragraph. In this idealized format, the thesis invokes the magic number of three: three reasons why a statement is true. Each of those reasons is explained and justified in the three body paragraphs, and then the final paragraph restates the thesis before gradually getting broader. This format is easy for readers to follow, and it helps writers organize their points and the evidence that goes with them. That’s why you learned this format.

In contrast, figure 12.2 represents a paper on the same topic that has the more organic form expected in college. The first key difference is the thesis. Rather than simply positing a number of reasons to think that something is true, it puts forward an arguable statement: one with which a reasonable person might disagree. An arguable thesis gives the paper purpose. It surprises readers and draws them in. You hope your reader thinks, “Huh. Why would they come to that conclusion?” and then feels compelled to read on. The body paragraphs, then, build on one another to carry out this ambitious argument. In the classic five-paragraph theme ( figure 12.1 ), it hardly matters which of the three reasons you explain first or second. In the more organic structure ( figure 12.2 ), each paragraph specifically leads to the next.
The last key difference is seen in the conclusion. Because the organic essay is driven by an ambitious, nonobvious argument, the reader comes to the concluding section thinking, “OK, I’m convinced by the argument. What do you, author, make of it? Why does it matter?” The conclusion of an organically structured paper has a real job to do. It doesn’t just reiterate the thesis; it explains why the thesis matters.
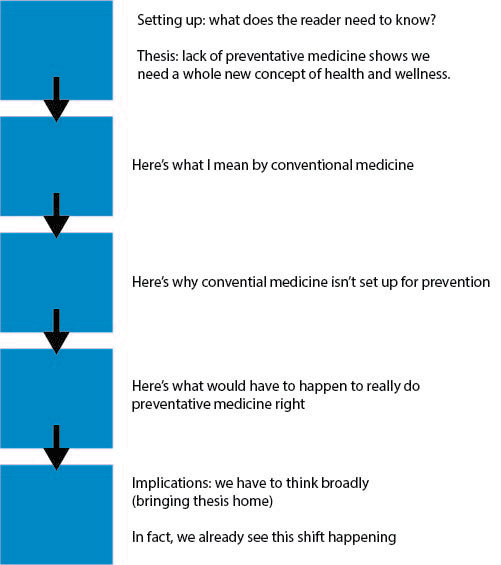
The substantial time you spent mastering the five-paragraph form in figure 12.1 was time well spent; it’s hard to imagine anyone succeeding with the more organic form without the organizational skills and habits of mind inherent in the simpler form. (And it is worth noting that there are limited moments in college where the five-paragraph structure is still useful—in-class essay exams, for example.) But if you assume that you must adhere rigidly to the simpler form, you’re blunting your intellectual ambition. Your instructors will not be impressed by obvious theses, loosely related body paragraphs, and repetitive conclusions. They want you to undertake an ambitious independent analysis, one that will yield a thesis that is somewhat surprising and challenging to explain.
The Three-Story Thesis
From the ground up.
You have no doubt been drilled on the need for a thesis statement and its proper location at the end of the introduction. And you also know that all of the key points of the paper should clearly support the central driving thesis. Indeed, the whole model of the five-paragraph theme hinges on a clearly stated and consistent thesis. However, some students are surprised—and dismayed—when some of their early college papers are criticized for not having a good thesis. Their instructor might even claim that the paper doesn’t have a thesis when, in the author’s view, it clearly does. So what makes a good thesis in college?
- Version A: Linen served as a form of currency in the ancient Mediterranean world, connecting rival empires through circuits of trade.
- Version B: Linen served as a form of currency in the ancient Mediterranean world, connecting rival empires through circuits of trade. The economic role of linen raises important questions about how shifting environmental conditions can influence economic relationships and, by extension, political conflicts.
How do you produce a good, strong thesis? And how do you know when you’ve gotten there? Many instructors and writers embrace a metaphor based on this passage by Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. (1809–1894). He compares a good thesis to a three-story building:
There are one-story intellects, two-story intellects, and three-story intellects with skylights. All fact collectors who have no aim beyond their facts are one-story men. Two-story men compare, reason, generalize using the labor of fact collectors as their own. Three-story men idealize, imagine, predict—their best illumination comes from above the skylight. (50)
In other words,
- One-story theses state inarguable facts. What’s the background?
- Two-story theses bring in an arguable (interpretive or analytical) point . What is your argument?
- Three-story theses nest that point within its larger, compelling implications . Why does it matter?
Thesis: that’s the word that pops at me whenever I write an essay. Seeing this word in the prompt scared me and made me think to myself, “Oh great, what are they really looking for?” or “How am I going to make a thesis for a college paper?” When rehearing that I would be focusing on theses again in a class, I said to myself, “Here we go again!” But after learning about the three-story thesis, I never had a problem with writing another thesis. In fact, I look forward to being asked on a paper to create a thesis.
Timothée Pizarro
writing student
The biggest benefit of the three-story metaphor is that it describes a process for building a thesis. To build the first story or level, you first have to get familiar with the complex, relevant facts surrounding the problem or question. You have to be able to describe the situation thoroughly and accurately. Then with that first story built, you can layer on the second story by formulating the insightful, arguable point that animates the analysis. That’s often the most effortful part: brainstorming, elaborating and comparing alternative ideas, finalizing your point. With that specified, you can frame up the third story by articulating why the point you make matters beyond its particular topic or case.
The concept of a three-story thesis framework was the most helpful piece of information I gained from the writing component of DCC 100. The first time I utilized it in a college paper, my professor included “good thesis” and “excellent introduction” in her notes and graded it significantly higher than my previous papers. You can expect similar results if you dig deeper to form three-story theses. More importantly, doing so will make the actual writing of your paper more straightforward as well. Arguing something specific makes the structure of your paper much easier to design.
Peter Farrell
For example, imagine you have been assigned a paper about the impact of online learning in higher education. You would first construct an account of the origins and multiple forms of online learning and assess research findings on its use and effectiveness. If you’ve done that well, you’ll probably come up with a well-considered opinion that wouldn’t be obvious to readers who haven’t looked at the issue in depth. Maybe you’ll want to argue that online learning is a threat to the academic community. Or perhaps you’ll want to make the case that online learning opens up pathways to college degrees that traditional campus-based learning does not.
In the course of developing your central, argumentative point, you’ll come to recognize its larger context; in this example, you may claim that online learning can serve to better integrate higher education with the rest of society, as online learners bring their educational and career experiences together. Here is an example:
The final thesis would be all three of these pieces together. These stories build on one another; they don’t replace the previous story. Here’s another example of a three-story thesis:
Here’s one more example:
A thesis statement that stops at the first story isn’t usually considered a thesis . A two-story thesis is usually considered competent, though some two-story theses are more intriguing and ambitious than others. A thoughtfully crafted and well-informed three-story thesis puts the author on a smooth path toward an excellent paper.
Three-Story Theses and the Organically Structured Argument
The three-story thesis is a beautiful thing. For one, it gives a paper authentic momentum. The first paragraph doesn’t just start with some broad, vague statement; every sentence is crucial for setting up the thesis. The body paragraphs build on one another, moving through each step of the logical chain. Each paragraph leads inevitably to the next, making the transitions from paragraph to paragraph feel wholly natural. The conclusion, instead of being a mirror-image paraphrase of the introduction, builds out the third story by explaining the broader implications of the argument. It offers new insight without departing from the flow of the analysis.
I should note here that a paper with this kind of momentum often reads like it was knocked out in one inspired sitting. But in reality, just like accomplished athletes, artists, and musicians, masterful writers make the difficult thing look easy. As writer Anne Lamott notes, reading a well-written piece feels like its author sat down and typed it out, “bounding along like huskies across the snow.” However, she continues,
This is just the fantasy of the uninitiated. I know some very great writers, writers you love who write beautifully and have made a great deal of money, and not one of them sits down routinely feeling wildly enthusiastic and confident. Not one of them writes elegant first drafts. All right, one of them does, but we do not like her very much. (21)
Experienced writers don’t figure out what they want to say and then write it. They write in order to figure out what they want to say.
Experienced writers develop theses in dialogue with the body of the essay. An initial characterization of the problem leads to a tentative thesis, and then drafting the body of the paper reveals thorny contradictions or critical areas of ambiguity, prompting the writer to revisit or expand the body of evidence and then refine the thesis based on that fresh look. The revised thesis may require that body paragraphs be reordered and reshaped to fit the emerging three-story thesis. Throughout the process, the thesis serves as an anchor point while the author wades through the morass of facts and ideas. The dialogue between thesis and body continues until the author is satisfied or the due date arrives, whatever comes first. It’s an effortful and sometimes tedious process.
Novice writers, in contrast, usually oversimplify the writing process. They formulate some first-impression thesis, produce a reasonably organized outline, and then flesh it out with text, never taking the time to reflect or truly revise their work. They assume that revision is a step backward when, in reality, it is a major step forward.
Everyone has a different way that they like to write. For instance, I like to pop my earbuds in, blast dubstep music, and write on a whiteboard. I like using the whiteboard because it is a lot easier to revise and edit while you write. After I finish writing a paragraph that I am completely satisfied with on the whiteboard, I sit in front of it with my laptop and just type it up.
Kaethe Leonard
Another benefit of the three-story thesis framework is that it demystifies what a “strong” argument is in academic culture . In an era of political polarization, many students may think that a strong argument is based on a simple, bold, combative statement that is promoted in the most forceful way possible. “Gun control is a travesty!” “Shakespeare is the best writer who ever lived!” When students are encouraged to consider contrasting perspectives in their papers, they fear that doing so will make their own thesis seem mushy and weak.
However, in academics a “strong” argument is comprehensive and nuanced, not simple and polemical. The purpose of the argument is to explain to readers why the author—through the course of his or her in-depth study—has arrived at a somewhat surprising point. On that basis, it has to consider plausible counterarguments and contradictory information. Academic argumentation exemplifies the popular adage about all writing: show, don’t tell. In crafting and carrying out the three-story thesis, you are showing your reader the work you have done.
The model of the organically structured paper and the three-story thesis framework explained here is the very foundation of the paper itself and the process that produces it. Your instructors assume that you have the self-motivation and organizational skills to pursue your analysis with both rigor and flexibility; that is, they envision you developing, testing, refining, and sometimes discarding your own ideas based on a clear-eyed and open-minded assessment of the evidence before you.
The original chapter, Constructing the Thesis and Argument—from the Ground Up by Amy Guptill, is from Writing in College: From Competence to Excellence
Discussion Questions
- What writing “rules” were you taught in the past? This might be about essay structure, style, or something else. Which of these rules seem to be true in college writing? Which ones are not true in college?
- In what contexts is the five-paragraph essay a useful structure? Why is it not helpful in other contexts—what’s the problem?
- Despite their appeal to patients, robotic pets should not be used widely, since they cause more problems than they solve.
- In recent years, robotic pets have been used in medical settings to help children and elderly patients feel emotionally supported and loved.
- Shifting affection to robotic pets rather than live animals suggests a major change in empathy and humanity and could have long-term costs that have not been fully considered.
- Television programming includes content that some find objectionable.
- The percentage of children and youth who are overweight or obese has risen in recent decades.
- First-year college students must learn how to independently manage their time.
- The things we surround ourselves with symbolize who we are.
- Find a scholarly article or book that is interesting to you. Focusing on the abstract and introduction, outline the first, second, and third stories of its thesis.
- Find an example of a five-paragraph theme (online essay mills, your own high school work), produce an alternative three-story thesis, and outline an organically structured paper to carry that thesis out.

Additional Resources
- The Writing Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill offers an excellent, readable rundown on the five-paragraph theme, why most college writing assignments want you to go beyond it, and those times when the simpler structure is actually a better choice.
- There are many useful websites that describe good thesis statements and provide examples. Those from the writing centers at Hamilton College and Purdue University are especially helpful.
Works Cited
Holmes, Oliver Wendell. The Poet at the Breakfast-Table: His Talks with His Fellow-Boarders and the Reader. James R. Osgood, 1872.
Lamott, Anne. Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life. Pantheon, 1994.
Media Attributions
- 12.1 five-paragraph theme © Amy Guptill is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
- 12.2 organic college paper © Amy Guptill is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
Constructing the Thesis and Argument from the Ground Up Copyright © 2022 by Amy Guptill; Liz Delf; Rob Drummond; and Kristy Kelly is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
The Writing Center @ UVa
314 bryan hall, writing theses and claims.
Virtually all genres of academic writing rely to some degree on claims as the engine of arguments, whether as the main point of arguments (the central claim or thesis) or as supporting points (subclaims).
For this reason, writing effective claims is vital to success in academic writing. But what is a claim? How do you distinguish it from other statements. To understand claims, it can be helpful to distinguish them from facts and opinions, as follows.
What is a claim?
- Example: Vanilla ice cream is the highest selling flavor of ice cream in the United States . (This is a fact because it can’t be reasonably argued against. The sales figures are pretty ironclad.)
- Example: Vanilla ice cream is the best flavor of ice cream. (This is an opinion because it isn’t arguable. It’s based solely in someone’s subjectivity, their preferences.)
- Example: The ubiquity of vanilla ice cream disconnects consumers from the complex and unethical agriculture practices that create it. (This is a claim because it can be argued with, and it can be supported with evidence)
Dispelling some myths about claims
Sometimes, people are given a set of rules about claims that don’t apply in all contexts. Here are some common beliefs about claims that aren’t necessarily true or are perhaps only true in some circumstances.
- NOT NECESSARILY TRUE. This may have been true in high school writing contexts, but in college and beyond different audiences have different expectations for where central claims will be located. Sometimes it’s after a few paragraphs. Sometimes it’s in the middle. Sometimes it’s at the end. At the college level, it’s time to start thinking more rhetorically (meaning thinking about audience expectations and impact) about where the central claim should go.
- NOT NECESSARILY TRUE. You can use a formula, but you don’t have to. And the formula’s you’ve learned previously may only be useful in the specific context you in which you learned them.
- NOT TRUE AT ALL. Central claims differ depending on the genre in which you’re writing. They look different in different disciplines (history, english, psychology, biology), and they look different in genres outside of academia, as well.
- NOT NECESSARILY TRUE. Again, they might be, but as writing becomes more sophisticated and topics more complex, it’s likely that you’ll come up with central or supporting claims that are more than one sentence long. That’s fine, potentially good even.
Two Types of claims
- Example: The University of Virginia should change its admissions practices in an effort to admit more low-income students.
- Example: The University of Virginia’s admissions practices create systemic hurdles to the admission of low-income students.
Two ways of doing claims
- Explicit – a claim that is clearly stated
- Implicit – a claim that is implied
Good claims have 3 features
- Focused – typically, the most specific a claim is the better
- Arguable – someone could reasonably argue against it
- This example is bad because it’s not focused enough. It’s technically a claim, but it’s too broad and not revelatory.
- This claim is better because it’s more focused and as a result more arguable and revelatory.
Share this:
One thought on “ writing theses and claims ”.
- Pingback: Literary Analysis | The Writing Center @ UVa
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

Central Idea Mastery: Tips for Identifying Main Themes in Texts
Ever struggled to figure out what a piece of literature is really about?
I have. I’m a math and sciences geek, and English Lit was never my strong suit in school. But I figured out a way to get straight to the central idea.
Studies show that grasping the central idea is one of the most challenging aspects for readers, freelance writers , and in-company writers alike.
This post will take you on a journey to understand clearly what a central idea statement in literature entails, how it differs from themes or thesis statements , and why it matters so much.
Ready for an enlightening ride into the realm of literary analysis? Let’s dive in!
What is the Central Idea in Literature?
The central idea in literature is the main point or message the author wants to convey to the reader. It is often the well written central ideas, expressed through a thesis statement , which serves as the foundation for the entire work of literature.
The central idea statement should be distinct from the story’s theme itself, as it focuses more on the author’s specific argument or perspective. To identify this in literature, readers can analyze key details and keywords as a map and keep their predictions short and straightforward.
The Relationship between Central Idea and Thesis Statement

A central idea is like a map for a story or essay. It guides readers through the words and themes.
On the other hand, a thesis statement is a claim or argument in an essay, article or research work.
This is often based on the central idea but goes further by giving an opinion about the topic. You can think of these as two good friends. Both play key roles in shaping any piece of writing, and they rely on each other to make sense.
For instance, if you write an essay arguing that reading helps improve vocabulary – your central idea might be ‘the benefits of reading,’ while your thesis statement could be ‘reading regularly improves one’s vocabulary.’
The Difference between Central Idea and Theme

The central idea and theme are two critical parts of a story. They may seem the same but tell different parts of the tale. The main topic or message in a text is the central idea .
It’s like telling what a book or essay is about.
A theme, though, dives deeper into the story. It shows us life lessons or morals that we can learn from it.
Think of it as an undercover message hiding inside the words and scenes of a story! An easy way to spot them? Central ideas often pop up more in texts that give information.
Themes make their home primarily in stories with lots of action, conflict and drama.
How to Identify the Central Idea in Literature
Use details and keywords as a map.

Words and clues in a story can help find the main idea. Look for words that repeat . They matter a lot to the writer. Think of keywords as signposts on a map. When you use a map when lost, use these words when stuck on an idea.
Stay away from small details that only discuss one thing in the text. Focus on ideas that cover all parts of the story instead. Those tell you what is most important to know.
Keep Predictions Short and Simple

When identifying the central idea statement in literature, keeping your predictions short and simple is essential. By predicting the answer in your own words, you can narrow down the options and eliminate choices that don’t match the passage.
Keeping your predictions brief makes it easier to compare them with the given choices. If you’re having trouble understanding a passage, try summarizing paragraphs or sentences to help clarify things.
Remember, taking it slow and staying calm can improve your performance in the SAT reading and writing section. So, keep those predictions concise and straightforward!
Importance of Central Ideas in Literature
The central ideas in literature play a crucial role in your content strategy and in understanding the text and its deeper meaning, as they serve as the backbone that holds the entire work together.
The Role of Central Ideas in Understanding Literature
The central idea plays a crucial role in helping us understand literature. It acts as the primary focus or point of the text, providing a clear picture of what the author wants to convey.
By identifying and analyzing the central idea, we can better comprehend the overall message and themes of a piece of writing. The well written central idea guides readers, helping them navigate through the details and supporting evidence presented in the text.
It helps us see how all these elements connect to create a cohesive whole.
The Connection between Central Ideas and Details
The connection between central ideas and details in literature is meaningful because the details provide evidence and examples to support and strengthen the central idea.
Details are specific pieces of information or examples that help to bring the story’s main idea to life and make it more relatable for readers.
By analyzing the central idea and details, readers can engage with the text deeper and uncover hidden meanings and themes.
A central idea can be explicit, stated directly in the text, or implicit, requiring readers to infer and interpret what the author is trying to convey.
So, paying attention to details helps readers understand and appreciate the overall message of a work of literature.
Central Ideas Examples in Literature

Central ideas in literature can vary greatly depending on the genre and themes explored.
For instance, classification essays may focus on a central idea related to categorization and justification, while works of English literature might delve into a central idea about societal norms or personal identity.
Additionally, environmental science literature may explore a central idea surrounding sustainability and conservation. These examples demonstrate the diverse range found across different types of literature.
Central Ideas in Classification Essays
The central idea in a classification essay is the main topic and the categories or subtopics we use to organize our thoughts . It’s like a roadmap for our essay, showing us how to structure it and what message we want to convey.
In other words, it’s the same as the thesis statement in a classification essay .
By stating the main topic and explaining why we’re categorizing things in a certain way, we can say something meaningful about how different parts of the topic are related or how they relate to the whole subject.
So, when writing a classification essay, ensure your central idea is clear and helps guide your readers through your thoughtful categories!
Central Ideas in English Literature
Understanding the central ideas in English literature is crucial for writers. These help us grasp the main themes and messages in literary works. They cover most details and emphasize key points, allowing readers to analyze the text effectively.
When analyzing literature, it’s important to avoid focusing too much on one detail or introducing new ideas not addressed in the text.
Central ideas play a vital role in answering exam questions like the SAT, where students identify the main idea or specific details based on a passage.
Notable Examples
“The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald
Central Idea: The American Dream and its corruption. This novel delves deep into the idea of the American Dream—the pursuit of happiness, wealth, and social status—and the lengths people go to achieve it. Set in the Roaring Twenties, the story showcases the opulence of the time but also the moral bankruptcy and hollowness that often accompanied the pursuit of wealth and social status. The novel questions the true meaning of success and challenges the superficial values of society.
“ To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
Central Idea: Racism and the loss of innocence. Set in the American South during the 1930s, this novel tackles the deep-seated racial prejudices of the time. Through the eyes of a young girl named Scout Finch, readers witness the injustice and cruelty meted out to a Black man, Tom Robinson, who is falsely accused of raping a white woman. The story also deals with the idea of growing up and losing innocence as Scout and her brother Jem navigate the complexities of their small town’s social structure.
“The Catcher in the Rye” by J.D. Salinger
Central Idea: Adolescent alienation and the challenges of growing up. The novel’s protagonist, Holden Caulfield, represents the quintessential disaffected youth. As he navigates the adult world, which he views as “phony,” he struggles with his own sense of identity, his place in the world, and the impending responsibilities of adulthood. The story is a poignant examination of the complexities of adolescence and the inevitable loss of childhood innocence.
Whether it’s contemporary or classic works, central ideas can be found throughout English literature.
Central Ideas in Environmental Science Literature
The central idea in environmental science literature is essential. It helps us understand the main topic and categories/subtopics discussed in the text. It gives us an overview of what the whole thing is about.
The central idea also helps structure the essay and conveys a message about the topic. So, if you’re writing about environmental science, ensure you have a clear main idea that divides your topic into different parts, helping readers quickly grasp the main points.
One way to find the main idea is by locating the thesis statement in your text.
Tips for Writing a Central Idea

Crafting a strong main idea requires clarity and conciseness. Use clear and specific language to express the main point of your work, ensuring that it is debatable and not just a statement of fact.
Consider the purpose of your writing and the audience you are targeting to shape your central idea effectively.
Formulation of the Central Idea
To formulate a well written central idea, you need to think carefully about the main point or message you want to convey.
When formulating the central idea, make sure it covers most of the details introduced in your text and emphasizes any important points. Avoid focusing too much on just one detail or introducing new ideas not addressed in your writing.
Also, be careful not to contradict any information from your text.
To help with formulation, summarize your text in your own words and determine the task or purpose of your writing. If you need clarification on the story’s main character or idea, revisit your summary to find the overarching theme .
Predicting the answer can also be useful as it helps narrow down choices and eliminate options that don’t align with your writing.
The Purpose of a Central Idea in Literature
The purpose of a central idea in literature is to provide a main theme or message that ties together all the different parts of a literary work. It helps readers understand and grasp the overall meaning and purpose of the text.
When writing a central idea, it’s important to consider the main theme or message, analyze key elements in the text, and think about what the author wants to convey. The central idea should cover most of the details introduced in the text and mention any points of emphasis.
However, it shouldn’t focus too much on just one detail, introduce new ideas not addressed in the text, or contradict information from the text.
Wrapping up the Central Idea
Understanding the central idea in literature is crucial for writers and readers alike. By grasping the main message of a text, we can delve deeper into its themes and analyze it with greater clarity.
Through examples and explanations, this blog has highlighted the importance of central ideas and provided tools to identify them effectively. So go forth, writers, armed with this knowledge, and create works that captivate audiences by conveying powerful central ideas!
1. What is the central idea in literature?
The central idea in literature refers to the main point or theme that the author wants to explain or convey through their story or writing.
2. How can I identify the central idea in a piece of literature?
You can identify the central idea by looking for recurring themes, key messages, and important moments that shape the text’s overall meaning.
3. Why is understanding the central idea important when reading literature?
Understanding the central idea helps you grasp the deeper meaning and purpose behind a piece of literature, allowing you to appreciate its message and connect with it more meaningfully.
4. Can multiple central ideas exist in a single piece of literature?
While some texts may have multiple themes or ideas, there is typically one primary central idea that serves as the core focus of the work.
Content Manager, Marketer and Business Development Expert.
Noel is a full-time content manager, marketer, and business development manager. A 25-year veteran and professional project manager (PMP) as well, Noel enjoys writing about content management, AI and the tools and technology shaping the industry.
Similar Posts

Website Budgeting: How Much Does it Cost to Create a Website?
Ever scratched your head, puzzling over the question “How much does it cost to create a website?” Believe me, you’re not alone. The answer’s a bit more intricate…

Why Are Headless CMS So Expensive? Exploring Key Factors
Explore why are headless CMS so expensive, covering customization costs, specialized expertise, and long-term savings potential.

Spotlight on Top WordPress Sites and Designs
Ever found yourself wrestling with the challenge of designing an eye-catching WordPress website? Oh boy, do I understand that struggle. After pouring over countless successful sites powered by…

Enterprise Content Management Tools: Ultimate Guide
Does it feel like you’re drowning in a sea of digital content for your company? Yeah, I can relate to that. Catching your breath may seem impossible, especially…

What Are Conventions In Writing? An Essential Guide
Ever wondered what sets a compelling read apart from an arduous ordeal? Clarity, consistency, and convention-the holy trinity of effective writing. As someone who’s plunged into the labyrinth…

What is WordPress And Why It Is Used As The Preferred Choice for Websites
Feeling a tad swamped by the deluge of website builders cluttering up the online world? Trust me, you’re in good company. In this whirlwind digital maze, one platform…

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
53 Formulating a Central Idea Statement
Learning objectives.
After reading this chapter, the student will be able to:
- Distinguish between the specific purpose, central idea, and main points of a speech;
- Differentiate between a speech to inform, persuade, and inspire or entertain;
- Write a specific purpose statement;
- Write a thesis or central idea statement;
- Distinguish between acceptable and unacceptable specific purpose and central idea statements;
- Compose appropriate specific purpose and central idea statements for informative, persuasive, and inspirational/entertaining speeches.
Formulating a Central Idea Statement – developing the thesis statement
While you will not actually say your specific purpose statement during your speech, you will need to clearly state what your focus and main points are going to be (preferably after using an introductory method such as those described in Chapter 8). The statement that reveals your main points is commonly known as the central idea statement (or just the central idea).
Central Idea Statement
a statement that contains or summarizes a speech’s main points
Now, at this point we need to make a point about terminology. Your instructor may call the central idea statement “the thesis” or “the thesis statement.” Your English composition instructor probably uses that term in your essay writing. Another instructor may call it the “main idea statement.” All of these are basically synonymous and you should not let the terms confuse you, but you should use the term your instructor uses.
That said, is the central idea statement the very same thing as the thesis sentence in an essay? Yes, in that both are letting the audience know without a doubt your topic, purpose, direction, angle and/or point of view. No, in that the rules for writing a “thesis” or central idea statement in a speech are not as strict as in an essay. For example, it is acceptable in a speech to announce the topic and purpose, although it is usually not the most artful or effective way to do it. You may say,
“In this speech I will try to motivate you to join me next month as a volunteer at the regional Special Olympics.”
That would be followed by a preview statement of what the speech’s arguments or reasons for participating will be, such as,
“You will see that it will benefit the community, the participants, and you individually.”
However, another approach is to “capsulize” the purpose, topic, approach, and preview in one succinct statement.
“Your involvement as a volunteer in next month’s regional Special Olympics will be a rewarding experience that will benefit the community, the participants, and you personally.”
This last version is really the better approach and most likely the one your instructor will prefer.
So, you don’t want to just repeat your specific purpose in the central idea statement, but you do want to provide complete information. Also, unlike the formal thesis of your English essays, the central idea statement in a speech can and should use personal language (I, me, we, us, you, your, etc.) and should attempt to be attention-getting and audience-focused. And importantly, just like a formal thesis sentence, it must be a complete, grammatical sentence.
The point of your central idea statement in terms of your audience is to reveal and clarify the ideas or assertions you will be addressing in your speech, more commonly known as your main points, to fulfill your specific purpose. However, as you are processing your ideas and approach, you may still be working on them. Sometimes those main points will not be clear to you immediately. As much as we would like these writing processes to be straightforward, sometimes we find that we have to revise our original approach. This is why preparing a speech the night before you are giving it is a really, really bad idea. You need lots of time for the preparation and then the practice.
Sometimes you will hear the writing process referred to as “iterative.” This word means, among other things, that a speech or document is not always written in the same order as the audience finally experiences it. You may have noticed that we have not said anything about the introduction of your speech yet. Even though that is the first thing the audience hears, it may be one of the last parts you actually compose. It is best to consider your speech flexible as you work on it, and to be willing to edit and revise. If your instructor asks you to turn the outline in before the speech, you should be clear on how much you can revise after that. Otherwise, it helps to know that you can keep editing your speech until you deliver it, especially while you practice.
Here are some examples of pairs of specific purpose statements and central idea statements.
Specific Purpose: To explain to my classmates the effects of losing a pet on the elderly.
Central Idea: When elderly persons lose their animal companions, they can experience serious psychological, emotional, and physical effects.
Specific Purpose: To demonstrate to my audience the correct method for cleaning a computer keyboard.
Central Idea: Your computer keyboard needs regular cleaning to function well, and you can achieve that in four easy steps.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my political science class that labor unions are no longer a vital political force in the U.S.
Central Idea: Although for decades in the twentieth century labor unions influenced local and national elections, in this speech I will point to how their influence has declined in the last thirty years.
Specific Purpose: To motivate my audience to oppose the policy of drug testing welfare recipients.
Central Idea: Many voices are calling for welfare recipients to have to go through mandatory, regular drug testing, but this policy is unjust, impractical, and costly, and fair-minded Americans should actively oppose it.
Specific Purpose: To explain to my fellow civic club members why I admire Representative John Lewis.
Central Idea: John Lewis has my admiration for his sacrifices during the Civil Rights movement and his service to Georgia as a leader and U.S. Representative.
Specific Purpose: To describe how makeup is done for the TV show The Walking Dead.
Central Idea: The wildly popular zombie show The Walking Dead achieves incredibly scary and believable makeup effects, and in the next few minutes I will tell you who does it, what they use, and how they do it.
Notice that in all of the above examples that neither the specific purpose nor the central idea ever exceeds one sentence. You may divide your central idea and the preview of main points into two sentences or three sentences, depending on what your instructor directs. If your central idea consists of more than three sentences, then you probably are including too much information and taking up time that is needed for the body of the speech.
Exploring Communication in the Real World Copyright © 2020 by Chris Miller is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Module 5: Choosing and Researching a Topic
Finding the purpose and central idea of your speech, learning objectives.
- Identify the specific purpose of a speech.
- Explain how to formulate a central idea statement for a speech.
General Purpose
The general purpose of most speeches will fall into one of four categories: to inform , to persuade , to entertain , and to commemorate or celebrate . The first step of defining the purpose of your speech is to think about which category best describes your overall goal with the speech. What do you want your audience to think, feel, or do as a consequence of hearing you speak? Often, the general purpose of your speech will be defined by the speaking situation. If you’re asked to run a training session at work, your purpose isn’t to entertain but rather to inform. Likewise, if you are invited to introduce the winner of an award, you’re not trying to change the audience’s mind about something; you’re honoring the recipient of the award. In a public speaking class, your general purpose may be included in the assignment: for instance, “Give a persuasive speech about . . . .” When you’re assigned a speech project, you should always make sure you know whether the general purpose is included in the assignment or whether you need to decide on the general purpose yourself.
Specific Purpose
Now that you know your general purpose (to inform, to persuade, or to entertain), you can start to move in the direction of the specific purpose. A specific purpose statement builds on your general purpose and makes it more specific (as the name suggests). So if your first speech is an informative speech, your general purpose will be to inform your audience about a very specific realm of knowledge.
In writing your specific purpose statement, you will take three contributing elements and bring them together to help you determine your specific purpose :
- You (your interests, your background, experience, education, etc.)
- Your audience
- The context or setting

There are three elements that combine to create a specific purpose statements: your own interests and knowledge, the interests and needs of your audience, and the context or setting in which you will be speaking.
Keeping these three inputs in mind, you can begin to write a specific purpose statement, which will be the foundation for everything you say in the speech and a guide for what you do not say. This formula will help you in putting together your specific purpose statement:
To _______________ [ Specific Communication Word (inform, explain, demonstrate, describe, define, persuade, convince, prove, argue)] _______________ [ Target Audience (my classmates, the members of the Social Work Club, my coworkers] __________________. [ The Content (how to bake brownies, that Macs are better than PCs].
Example: The purpose of my presentation is to demonstrate to my coworkers the value of informed intercultural communication .
Formulating a Central Idea Statement
While you will not actually say your specific purpose statement during your speech, you will need to clearly state what your focus and main points are going to be. The statement that reveals your main points is commonly known as the central idea statement (or just the central idea). Just as you would create a thesis statement for an essay or research paper, the central idea statement helps focus your presentation by defining your topic, purpose, direction, angle, and/or point of view. Here are two examples:
- Central Idea—When elderly persons lose their animal companions, they can experience serious psychological, emotional, and physical effects.
- Central Idea—Your computer keyboard needs regular cleaning to function well, and you can achieve that in four easy steps.
Please note that your central idea will emerge and evolve as you research and write your speech, so be open to where your research takes you and anticipate that formulating your central idea will be an ongoing process.
Below are four guidelines for writing a strong central idea.
- Your central idea should be one, full sentence.
- Your central idea should be a statement, not a question.
- Your central idea should be specific and use concrete language.
- Each element of your central idea should be related to the others.
Using the topic “Benefits of Yoga for College Students’ Stress,” here are some correct and incorrect ways to write a central idea.
A strong central idea shows that your speech is focused around a clear and concise topic and that you have a strong sense of what you want your audience to know and understand as a result of your speech. Again, it is unlikely that you will have a final central idea before you begin your research. Instead, it will come together as you research your topic and develop your main points.
- Purpose and Central Idea Statements. Provided by : eCampusOntario. Project : Communication for Business Professionals. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Finding the Purpose of Your Speech. Authored by : Susan Bagley-Koyle with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

What is the central thesis?
The central thesis states the main point or argument of the paper. It is stated in the thesis statement in the introductory paragraph, and every paragraph of the paper supports it.
Add your answer:
What is an thesis statement?
A Thesis Statement states the central idea in any essay and sums it up.
The thesis statement summarizes?
the central argument, claim, or premise of the essay.
What is a weak thesis?
Weak thesis is a thesis that is weak
What is a deductive thesis?
A deductive thesis is a thesis that is stated right at the beginning. acctually it is a thesis that was fromed apon carefully analisis of the matter
What is a sub thesis?
It is not necessarily a topic sentence. It is an introduction to an area of support + reference back to your central idea in the form of a topic sentence for each of your body paragraphs
The central idea that explains what your essay is about is included in the what?
The central point appears in your thesis statement.
Should your thesis statement contain two or more central points?
YEs, the classic is 3 main central points in a thesis.
What is a central idea of a speech?
The central idea of a speech is like the thesis statement.
The central idea explains what your essay is about is included in the?
thesis statement
The central idea that explains what your essay is about is included in the?
The central argument claim or premise of an essay is represented in the ., is a sentence that reflects a central idea or theme and can be implied or stated..
Thesis Statement
Which of the following elements of revision would you focus on when you want to make sure that each paragraph relates to the central idea of your piece A tone B Thesis C Grammar D-Diction?
Is the thesis the main point of an essay.
Yes, the thesis is the main point or central idea of an essay. It is usually stated in the introduction and guides the rest of the content in the essay.
What are the answers for chapter 14 in reading across the discipline 5th edition?
the central thesis of this selection is that
Top Categories

Opening statements in Trump's historic trial set to begin Monday after tense day of jury selection
Opening statements are set to begin next week in Donald Trump’s historic criminal trial after the final members of the jury were seated Friday, following a dramatic day in which two prospective jurors broke down in tears, an appeals court judge rejected Trump's request for a stay, and a man set himself on fire in front of the courthouse.
“We’re going to have opening statements on Monday morning. This trial is starting,” Judge Juan Merchan said towards the end of the day, after successfully seating the remaining five alternate jurors that were needed.
The case — the first-ever criminal trial of a former president —will be heard by a panel of 12 jurors and a total of six alternates. It's expected to last roughly six weeks.
The five alternates ultimately selected Friday include an unemployed married woman who’s into art and described herself as not political, an audio professional, a contract specialist, a clothing company executive and a construction company project manager. It took four days of jury selection to find the 18 jurors.
Around the same time the judge declared, "we have our full panel" inside the courtroom in the early afternoon, a man set himself on fire outside the courthouse. The NYPD said the man, identified as Max Azzarello of Florida, later died. He appeared to have had pamphlets describing a conspiracy involving cryptocurrency that he threw around before setting himself ablaze, police said.
Later in the afternoon, Trump's attorneys were in a state appeals court trying again to get an emergency stay of the trial. Trump attorney Cliff Robert argued his client could not get a fair trial in Manhattan, which had been Trump's longtime home before moving to Florida after he was elected president in 2016.
Steven Wu of Manhattan District Attorney Alvin Bragg's office countered that "what the last week has shown is that the jury selection has worked."
"We have 18 ordinary New Yorkers who are ready to serve. It would be unfair to them and the public for this to be delayed further," he argued. The judge rejected Trump's stay request a short time later.
The jury selection process Friday was especially intense, some potential jurors breaking down in tears and others saying they were too anxious to serve.
The day began with the judge calling up the 22 remaining potential jurors from the previous pool of 96 to answer questions designed to indicate whether they could be fair and impartial about the divisive real estate mogul and presumptive Republican nominee for president.
The first of those potential jurors was dismissed after she said she didn’t think she could be fair. “I have really, really bad anxiety and people have found out where I am,” she told the judge. A short time later, two other potential jurors were dismissed after each told the judge that upon further reflection, “I don’t think I can be impartial.”
Other potential jurors included a married father who said he listens to a podcast called “Order of Man,” which is described on Apple’s website as discussions about “reclaiming what it means to be a man.” Some past guests of the podcast include people who’ve been outspoken in their support of Trump and were highly critical of the civil fraud case New York Attorney General Letitia James brought against the former president. The man, an audio specialist, was chosen as one of the alternates.
Another potential juror was a married fund manager who said he’d done “get-out-the-vote” work for former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, Trump’s 2016 presidential opponent. Trump and his attorney Todd Blanche passed notes back and forth while that juror was speaking. He was later dismissed after being asked about a 2020 Facebook post where he apparently called Trump “the devil and a sociopath.”

Trump appeared most interested in jurors whose answers offer ambiguity around their personal political views. When one prospective juror said they were a Fox News viewer, Trump cocked his head, then quickly conferred with his lawyer, Todd Blanche.
Another potential juror was a woman who became emotional as she disclosed she'd served two years in prison on drug-related charges, but said she could be "fair and impartial."
During a morning break, Merchan — who'd chided reporters on Thursday for disclosing too much information about potential jurors — said the woman had shared "very personal things about her life" and was "very brave." “I just wanted to encourage the press to please be kind. Please be kind to this person,” the judge said. He later dismissed her, saying she needed a certificate of release to be qualified for service going forward. On her way out, she cheerfully called out, "Good luck!"
Following that juror's departure, the DA's office began its individual questioning of the jurors. One woman, who'd disclosed that her father is lifelong friends with Trump ally turned critic Chris Christie, broke down in tears when prosecutor Susan Hoffinger asked her an innocuous question about the burden of proof in the case. "I feel so nervous and anxious right now. I’m sorry," she responded, bursting out into tears. "I thought I could do this," she said, adding "I wouldn’t want someone who feels this way to judge my case." She was dismissed.
Hoffinger's questioning was followed by Trump attorney Susan Necheles, who asked a potential juror who'd started their own business how she would assess a witness's credibility. The woman then asked to speak to the judge, saying she was "getting anxiety and self-doubt” from Necheles's line of questioning. She was dismissed.
Necheles later asked another woman — who previously said she was a victim of sexual assault — whether she would hold it against Trump that women outside this case have accused Trump of sexual assault. She said she would not have a problem setting those accusations aside but the judge ultimately excused her, saying, "It’s best to err on the side of caution."
Another man said he has some differences from Trump on his policies but thinks he's “usually awesome.” He was not chosen for the jury.
On his way into court in the morning, Trump again complained the case against him is "unfair," and that the partial gag order preventing him from lashing out at witnesses, prosecutors, court staffers and jurors is not "constitutional." "Everyone else can say whatever they want about me. They can say anything they want. They can continue to make up lies and everything else. They lie. They’re real scum. But you know what? I’m not allowed to speak," he told reporters.
Prosecutors this week asked the judge to fine Trump and hold him in contempt for social media posts that they said violate the gag order. A hearing on the matter is scheduled for Tuesday.
The m a in pa nel of 12 is made up of seven men and five women, including two lawyers, a teacher, a retired wealth manager, a product development manager, a security engineer, a software engineer, a speech therapist and a physical therapist. The foreman — the juror who essentially acts as the leader and spokesperson for the panel — is a married man who works in sales and gets his news from The New York Times, MSNBC and Fox News.
The lone alternate selected Thursday is a woman who works as an asset manager.
Trump vented about the speed of the process in a post on social media shortly after the final jurors were selected, claiming the judge is “‘railroading’ me, at breakneck speed, in order to completely satisfy his ‘friends’.”
Later in the day, Merchan held what's known as a Sandoval hearing . That's a type of hearing designed to let defendants know the scope of questions they could face from prosecutors on cross-examination so they can make informed decisions about whether to take the witness stand in their own defense.
Leaving court on Friday, Trump was asked whether he was still planning to testify and he said he was.
Manhattan District Attorney Alvin Bragg's office disclosed in a court filing that it would like to ask Trump about several items, among them the $464 million civil judgment against him and his company for fraud , the total $88 million verdicts and liability findings for sexual abuse and defamation in lawsuits brought by writer E. Jean Carroll and a number of other adverse court rulings over the past few years.
Trump has denied wrongdoing in all the cases and is appealing the fraud judgment and the Carroll verdicts.
Prosecutors said they want to be able to bring those findings up “to impeach the credibility of the defendant” if he takes the witness stand.
Discussing the findings in the fraud case, prosecutor Matthew Colangelo told the judge it was "hard to think of something that is more squarely in the wheelhouse” for the DA to ask Trump about "than a finding by a judge of persistent and repeated fraud and illegality."
Trump's attorney Emil Bove countered that prosecutors shouldn't be able to breach the topic at all because Trump's appeal is still pending. He made similar arguments over the DA's contention that they should be allowed to ask about a judge's finding that he was untruthful on the witness stand during the fraud trial and had violated a gag order in the case.
“Is it your position that because a case is being appealed or might be appealed, that therefore it can not be used?" Merchan asked the lawyer. "Not necessarily," Bove replied.
The judge said he'd issue his ruling on the dispute on Monday morning.
Trump said last week he “absolutely” plans to testify , but he is under no obligation to do so.
Asked by Necheles at the end of the day who the DA's first witness would be, prosecutor Joshua Steinglass said they wouldn't inform Trump's team of the person's identity until Sunday, given that Trump has been criticizing some witnesses on social media despite the partial gag order in the case. “And if that should be tweeted, that’ll be the last time we provide that courtesy,” Steinglass said.
Merchan called the DA's position "understandable" and told Necheles "I will not compel them to do anything."
Trump has pleaded not guilty to 34 counts of falsifying business records and faces up to four years in prison if he is convicted.
Bragg alleges that Trump falsified records to hide money he was paying his former lawyer Michael Cohen to reimburse him for $130,000 he paid adult film actor Stormy Daniels near the end of the 2016 presidential campaign. Daniels has claimed she had a sexual encounter with Trump in 2006. Trump has denied that he slept with Daniels, but he has acknowledged repaying Cohen.
The DA’s office also alleges that as part of a scheme to boost Trump, National Enquirer publisher American Media Inc. paid $150,000 to model and actor Karen McDougal , who appeared in Playboy magazine and claimed that she had a nine-month affair with Trump before he was elected president “in exchange for her agreement not to speak out about the alleged sexual relationship,” according to a statement of facts filed by Bragg.
Trump has also denied having a sexual relationship with McDougal.
Adam Reiss is a reporter and producer for NBC and MSNBC.
Lisa Rubin is an MSNBC legal correspondent and a former litigator.
Dareh Gregorian is a politics reporter for NBC News.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why. The best thesis statements are: Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don't use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement. What is a thesis statement? A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
Central Claim What is a thesis? A thesis is the central claim or main argument of an essay. Because it provides a unifying theme for the rest of the essay, it typically appears early on—in shorter papers, most often within the first paragraph or two. The thesis should be analytic or interpretive rather than merely descriptive or factual.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay. It usually comes near the end of your introduction. ... You'll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay, so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing.
An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it's the core of any essay or research paper. You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper-not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains ...
Creating a Thesis Statement. Once you are clear about your general purpose and specific purpose, you can turn your attention to crafting a thesis statement. A thesis is the central idea in an essay or a speech. In speechwriting, the thesis or central idea explains the message of the content. It's the speech's "takeaway."
The biggest benefit of the three-story metaphor is that it describes a process for building a thesis. To build the first story or level, you first have to get familiar with the complex, relevant facts surrounding the problem or question. You have to be able to describe the situation thoroughly and accurately.
Central claims (theses) should always appear at the end of the first paragraph. NOT NECESSARILY TRUE. This may have been true in high school writing contexts, but in college and beyond different audiences have different expectations for where central claims will be located. Sometimes it's after a few paragraphs.
Evolving a Central Claim: Example 1. Your central claim (also called a thesis) lies at the heart of your argument. As a contestable and weighty statement, it anchors your essay, encapsulating the most important idea that you will unpack, unveil, and support in your writing. Claims don't blossom fully formed from the phenomenon under ...
In their Writing Analytically, David Rosenwasser and Jill Stephen, outline six steps for evolving a central claim. Getting the central claim to respond more fully to evidence, either by formulating a mostly new central claim and beginning again, or by modifying the existing thesis, is the primary activity of conceptual revision (as opposed to correcting and editing).
The central idea in literature is the main point or message the author wants to convey to the reader. It is often the well written central ideas, expressed through a thesis statement, which serves as the foundation for the entire work of literature. The central idea statement should be distinct from the story's theme itself, as it focuses ...
Central Idea Statement. a statement that contains or summarizes a speech's main points. Now, at this point we need to make a point about terminology. Your instructor may call the central idea statement "the thesis" or "the thesis statement.". Your English composition instructor probably uses that term in your essay writing.
The statement that reveals your main points is commonly known as the central idea statement (or just the central idea). Just as you would create a thesis statement for an essay or research paper, the central idea statement helps focus your presentation by defining your topic, purpose, direction, angle, and/or point of view. Here are two examples:
The central thesis states the main point or argument of the paper. It is stated in the thesis statement in the introductory paragraph, and every paragraph of the paper supports it.
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
The central thesis of the school of ethical universalism is that common moral agreement about right or wrong actions and behaviors across multiple cultures and countries form the basis for universal ethical standards applicable to the members of all societies, all companies, and all business people.
Opening statements are set to begin next week in Donald Trump's historic criminal trial after the final members of the jury were seated Friday, following a dramatic day in which two prospective ...
Question: The central thesis of biography is the _____. Choices: - contributions of the subject - historical times in which the subject lived - personality of the subject. Click the card to flip 👆 ...
Thesis Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore needs
The central thesis of biography is the. Personality of the subject. Settings and historical events play a. Secondary role. Jesse Stuart wrote an autobiography about his life as a. Teacher in rural Kentucky. Bradford's biography of Robert E. Lee reveals him as a general who felt that war was _____.
The thesis here is if we do see the economy falter a bit, it will be a two-way win for gold. First, economic weakness is generally good for defensive assets. And gold is such a defensive asset.