

Speech on Globalisation
Globalisation ties the world together. It’s like a giant web, connecting countries through trade, culture, and ideas. It’s why you can find the same fast food joint in different parts of the world.
But it’s not just about burgers and fries. Globalisation impacts your life in many ways. It shapes the clothes you wear, the gadgets you use, and even the movies you watch. It’s a big, complex topic with lots to explore.
1-minute Speech on Globalisation
Ladies and Gentlemen,
Globalisation means the world coming together. It’s like making the whole world one big neighbourhood. Imagine your neighbourhood where everyone knows each other, shares things, and helps when needed. That’s what globalisation is doing to our world.
Think about the clothes you wear, the food you eat, or the music you listen to. They come from different parts of the world. You might be eating pasta from Italy, wearing a shirt made in China, or listening to music from America. This is possible because of globalisation.
Globalisation also helps us to learn and grow. When we share ideas, we learn new things. For example, the internet, a gift of globalisation, allows us to learn about cultures, languages, and traditions from all over the world. It’s like a magic door that opens to different parts of the world.
But, like everything else, globalisation has its challenges. Sometimes, it can lead to job losses in one country when businesses move to another country where things are cheaper. It can also harm our environment, as goods travel long distances, causing pollution.
We must work together to make globalisation a force for good. We can create policies that protect jobs and the environment. We can also use technology to reduce pollution and waste.
In conclusion, globalisation is like a big web connecting us all. It brings both opportunities and challenges. It’s up to us to make the most of the opportunities and find solutions to the challenges. Together, we can make our world a better place. Thank you.
Also check:
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalisation
2-minute Speech on Globalisation
Today, we talk about a topic that touches our lives every day – Globalisation. It’s like a big, invisible web that connects us all. Imagine a spider’s web. Each thread links to another, forming a network. This is what globalisation is. It’s a network that links countries and people.
Now, let’s look at how this web is made. It’s woven by trade and technology. When we buy things, we often see the label ‘Made in China’ or ‘Made in USA’. This is because businesses send their products all over the world. They do this to reach more customers and make more money. This is the trade part of globalisation.
Then, there’s technology. With the internet, we can talk to someone on the other side of the world. We can share ideas and learn from each other. This makes the world feel like a smaller place. We call this the ‘global village’.
Globalisation also brings us closer together through culture. We watch movies from Hollywood, eat sushi from Japan, and dance to music from Africa. We learn about different cultures and become more understanding of each other. This makes the world a more peaceful place.
But, like everything in life, globalisation has its good and bad sides. It creates jobs and wealth, but it can also lead to job losses. Some people get richer, while others may get poorer. It can also harm our planet. When we make and sell more things, we use more resources and create more pollution.
These challenges are big, but they are not impossible to solve. We need to make sure that the benefits of globalisation reach everyone. We need to protect our planet while we grow our economies. We need to make globalisation work for all of us.
So, let’s keep the conversation going. Let’s talk about globalisation at our dinner tables, in our classrooms, and in our communities. Let’s make sure that we understand it, so we can shape it in a way that benefits us all.
- Speech on Health
- Speech on Girls Education
- Speech on Girl Power
We also have speeches on more interesting topics that you may want to explore.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Food & Dining
- Coronavirus
- Real Estate
- Seattle History
- PNW Politics
Globalization Topics for a Persuasive Paper
- College & Higher Education
Related Articles
What effects does propane have on the environment, the contributing factors to deforestation in the amazon rain forest, natural disasters & pollution.
- What Factors Influence the Biodiversity of an Ecosystem?
- How Does Electricity Affect the Environment?
Globalization is not one specific process, but a complex, intertwined set of processes holding varied definitions for different people. Some see it as beneficial to achieving equality and reducing poverty worldwide. Critics see social chaos and political instability resulting directly from globalization trends. Because globalization is so complex and experts disagree about its effects, the subject lends itself to persuasive papers. For example, a writer could argue that workers are victimized while multinational corporations reap enormous profits.
Critical Arguments Against Globalization
Gail Tverberg identifies 12 negative aspects of globalization. According to her perspective, globalization has resulted in natural resources such as gas, oil and coal being used much more rapidly. Nations including China and India are consuming coal quickly as they attempt to prosper economically. An essayist can take the position that this is not sustainable environmentally. An essay can also be constructed to persuade readers that globalization has increased world oil prices consistently since the 1970s. Another frequent criticism of globalization is that it has led to the exploitation of workers, including children, in many countries. Also often reported are inhumane conditions, including unsafe factories and increased human trafficking, which globalization appears to fuel.
The Upside of Globalization
By contrast, a persuasive essayist might argue that world poverty has shown a startling decline recently and that this process can be linked directly to globalization. A writer can also argue that there is now more information traded across and among countries, benefiting both individuals and organizations worldwide. Supporters of global free trade argue that it creates jobs and lowers prices for consumers worldwide and provides opportunities for poorer nations to develop economically. Proponents of globalization also point out the potential for a new world power or order to be created instead of the current political and economic power silos or compartments that exist. These are cogent pro-globalization arguments for persuasive papers.
Exported Pop Culture
Many people express concerns about the Westernization or Americanization of other parts of the world. American movies exert a great deal of cultural influence worldwide. In fact, the U.S. entertainment industry generates tremendous revenues from overseas. Fast food is another Western export that has taken hold across several continents. The rapid spread of American restaurant chains and consumer products is a fact, yet you can argue very persuasively that it tends to overshadow or subvert local cultures and is a factor in obesity rates. It can be also argued that Western rock music is a form that promotes specific values, including blatant sexuality, spontaneity and defiance.
The American Perspective vs. Global Thinking
Mike Collins points out that what might be positive for Third World nations, or developing ones such as China, might not be best for the U.S. Since 1980, for example, American manufacturing shed 6 million jobs. Many service industry jobs in insurance, marketing and customer service have been relocated to cheaper venues like India. According to economists, Americans benefit as consumers from lower prices and a wider array of product from which to choose, but the job market is adversely affected by globalization. Some American research and development facilities have been shipped overseas, while experts simultaneously argue that American-built factories elsewhere are good from a global perspective. The essayist can consider globalization from either the American perspective or from a multinational outlook.
- Gail Tverberg; Twelve Negative Aspects of Globalization
Susie Zappia teaches humanities and research and writing courses online for several colleges. Her research interests include counterculture literature of the 1960 and instructional design for online courses and she enjoys writing about literature, art and instructional design. She holds a Master of Arts in humanities from California State University, Dominguez Hills and a Master of Science in instructional design from Capella University.
How Did Geography Affect Early China Before the Silk Road?
What does natural resources mean in social studies, crucial environmental problems affecting the ocean, rates of deforestation & reforestation in the u.s., the roman republic's contributions to economics, the iconography & symbolism of the lascaux cave paintings, different areas of study for economics, pollution caused by fossil fuels, what event in american history brought the roaring '20s to an end, most popular.
- 1 How Did Geography Affect Early China Before the Silk Road?
- 2 What Does Natural Resources Mean in Social Studies?
- 3 Crucial Environmental Problems Affecting the Ocean
- 4 Rates of Deforestation & Reforestation in the U.S.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Persuasive Speaking
Learning objectives.
- Explain how claims, evidence, and warrants function to create an argument.
- Identify strategies for choosing a persuasive speech topic.
- Identify strategies for adapting a persuasive speech based on an audience’s orientation to the proposition.
- Distinguish among propositions of fact, value, and policy.
- Choose an organizational pattern that is fitting for a persuasive speech topic.
We produce and receive persuasive messages daily, but we don’t often stop to think about how we make the arguments we do or the quality of the arguments that we receive. In this section, we’ll learn the components of an argument, how to choose a good persuasive speech topic, and how to adapt and organize a persuasive message.
Foundation of Persuasion
Persuasive speaking seeks to influence the beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors of audience members. In order to persuade, a speaker has to construct arguments that appeal to audience members. Arguments form around three components: claim, evidence, and warrant. The claim is the statement that will be supported by evidence. Your thesis statement is the overarching claim for your speech, but you will make other claims within the speech to support the larger thesis. Evidence , also called grounds, supports the claim. The main points of your persuasive speech and the supporting material you include serve as evidence. For example, a speaker may make the following claim: “There should be a national law against texting while driving.” The speaker could then support the claim by providing the following evidence: “Research from the US Department of Transportation has found that texting while driving creates a crash risk that is twenty-three times worse than driving while not distracted.” The warrant is the underlying justification that connects the claim and the evidence. One warrant for the claim and evidence cited in this example is that the US Department of Transportation is an institution that funds research conducted by credible experts. An additional and more implicit warrant is that people shouldn’t do things they know are unsafe.
Figure 11.2 Components of an Argument
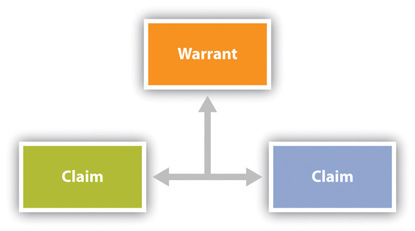
The quality of your evidence often impacts the strength of your warrant, and some warrants are stronger than others. A speaker could also provide evidence to support their claim advocating for a national ban on texting and driving by saying, “I have personally seen people almost wreck while trying to text.” While this type of evidence can also be persuasive, it provides a different type and strength of warrant since it is based on personal experience. In general, the anecdotal evidence from personal experience would be given a weaker warrant than the evidence from the national research report. The same process works in our legal system when a judge evaluates the connection between a claim and evidence. If someone steals my car, I could say to the police, “I’m pretty sure Mario did it because when I said hi to him on campus the other day, he didn’t say hi back, which proves he’s mad at me.” A judge faced with that evidence is unlikely to issue a warrant for Mario’s arrest. Fingerprint evidence from the steering wheel that has been matched with a suspect is much more likely to warrant arrest.
As you put together a persuasive argument, you act as the judge. You can evaluate arguments that you come across in your research by analyzing the connection (the warrant) between the claim and the evidence. If the warrant is strong, you may want to highlight that argument in your speech. You may also be able to point out a weak warrant in an argument that goes against your position, which you could then include in your speech. Every argument starts by putting together a claim and evidence, but arguments grow to include many interrelated units.
Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
As with any speech, topic selection is important and is influenced by many factors. Good persuasive speech topics are current, controversial, and have important implications for society. If your topic is currently being discussed on television, in newspapers, in the lounges in your dorm, or around your family’s dinner table, then it’s a current topic. A persuasive speech aimed at getting audience members to wear seat belts in cars wouldn’t have much current relevance, given that statistics consistently show that most people wear seat belts. Giving the same speech would have been much more timely in the 1970s when there was a huge movement to increase seat-belt use.
Many topics that are current are also controversial, which is what gets them attention by the media and citizens. Current and controversial topics will be more engaging for your audience. A persuasive speech to encourage audience members to donate blood or recycle wouldn’t be very controversial, since the benefits of both practices are widely agreed on. However, arguing that the restrictions on blood donation by men who have had sexual relations with men be lifted would be controversial. I must caution here that controversial is not the same as inflammatory. An inflammatory topic is one that evokes strong reactions from an audience for the sake of provoking a reaction. Being provocative for no good reason or choosing a topic that is extremist will damage your credibility and prevent you from achieving your speech goals.
You should also choose a topic that is important to you and to society as a whole. As we have already discussed in this book, our voices are powerful, as it is through communication that we participate and make change in society. Therefore we should take seriously opportunities to use our voices to speak publicly. Choosing a speech topic that has implications for society is probably a better application of your public speaking skills than choosing to persuade the audience that Lebron James is the best basketball player in the world or that Superman is a better hero than Spiderman. Although those topics may be very important to you, they don’t carry the same social weight as many other topics you could choose to discuss. Remember that speakers have ethical obligations to the audience and should take the opportunity to speak seriously.
You will also want to choose a topic that connects to your own interests and passions. If you are an education major, it might make more sense to do a persuasive speech about funding for public education than the death penalty. If there are hot-button issues for you that make you get fired up and veins bulge out in your neck, then it may be a good idea to avoid those when speaking in an academic or professional context.

Choose a persuasive speech topic that you’re passionate about but still able to approach and deliver in an ethical manner.
Michael Vadon – Nigel Farage – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Choosing such topics may interfere with your ability to deliver a speech in a competent and ethical manner. You want to care about your topic, but you also want to be able to approach it in a way that’s going to make people want to listen to you. Most people tune out speakers they perceive to be too ideologically entrenched and write them off as extremists or zealots.
You also want to ensure that your topic is actually persuasive. Draft your thesis statement as an “I believe” statement so your stance on an issue is clear. Also, think of your main points as reasons to support your thesis. Students end up with speeches that aren’t very persuasive in nature if they don’t think of their main points as reasons. Identifying arguments that counter your thesis is also a good exercise to help ensure your topic is persuasive. If you can clearly and easily identify a competing thesis statement and supporting reasons, then your topic and approach are arguable.
Review of Tips for Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
- Not current. People should use seat belts.
- Current. People should not text while driving.
- Not controversial. People should recycle.
- Controversial. Recycling should be mandatory by law.
- Not as impactful. Superman is the best superhero.
- Impactful. Colleges and universities should adopt zero-tolerance bullying policies.
- Unclear thesis. Homeschooling is common in the United States.
- Clear, argumentative thesis with stance. Homeschooling does not provide the same benefits of traditional education and should be strictly monitored and limited.
Adapting Persuasive Messages
Competent speakers should consider their audience throughout the speech-making process. Given that persuasive messages seek to directly influence the audience in some way, audience adaptation becomes even more important. If possible, poll your audience to find out their orientation toward your thesis. I read my students’ thesis statements aloud and have the class indicate whether they agree with, disagree with, or are neutral in regards to the proposition. It is unlikely that you will have a homogenous audience, meaning that there will probably be some who agree, some who disagree, and some who are neutral. So you may employ all of the following strategies, in varying degrees, in your persuasive speech.
When you have audience members who already agree with your proposition, you should focus on intensifying their agreement. You can also assume that they have foundational background knowledge of the topic, which means you can take the time to inform them about lesser-known aspects of a topic or cause to further reinforce their agreement. Rather than move these audience members from disagreement to agreement, you can focus on moving them from agreement to action. Remember, calls to action should be as specific as possible to help you capitalize on audience members’ motivation in the moment so they are more likely to follow through on the action.
There are two main reasons audience members may be neutral in regards to your topic: (1) they are uninformed about the topic or (2) they do not think the topic affects them. In this case, you should focus on instilling a concern for the topic. Uninformed audiences may need background information before they can decide if they agree or disagree with your proposition. If the issue is familiar but audience members are neutral because they don’t see how the topic affects them, focus on getting the audience’s attention and demonstrating relevance. Remember that concrete and proxemic supporting materials will help an audience find relevance in a topic. Students who pick narrow or unfamiliar topics will have to work harder to persuade their audience, but neutral audiences often provide the most chance of achieving your speech goal since even a small change may move them into agreement.
When audience members disagree with your proposition, you should focus on changing their minds. To effectively persuade, you must be seen as a credible speaker. When an audience is hostile to your proposition, establishing credibility is even more important, as audience members may be quick to discount or discredit someone who doesn’t appear prepared or doesn’t present well-researched and supported information. Don’t give an audience a chance to write you off before you even get to share your best evidence. When facing a disagreeable audience, the goal should also be small change. You may not be able to switch someone’s position completely, but influencing him or her is still a success. Aside from establishing your credibility, you should also establish common ground with an audience.

Build common ground with disagreeable audiences and acknowledge areas of disagreement.
Chris-Havard Berge – Shaking Hands – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Acknowledging areas of disagreement and logically refuting counterarguments in your speech is also a way to approach persuading an audience in disagreement, as it shows that you are open-minded enough to engage with other perspectives.
Determining Your Proposition
The proposition of your speech is the overall direction of the content and how that relates to the speech goal. A persuasive speech will fall primarily into one of three categories: propositions of fact, value, or policy. A speech may have elements of any of the three propositions, but you can usually determine the overall proposition of a speech from the specific purpose and thesis statements.
Propositions of fact focus on beliefs and try to establish that something “is or isn’t.” Propositions of value focus on persuading audience members that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.” Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done. Since most persuasive speech topics can be approached as propositions of fact, value, or policy, it is a good idea to start thinking about what kind of proposition you want to make, as it will influence how you go about your research and writing. As you can see in the following example using the topic of global warming, the type of proposition changes the types of supporting materials you would need:
- Proposition of fact. Global warming is caused by increased greenhouse gases related to human activity.
- Proposition of value. America’s disproportionately large amount of pollution relative to other countries is wrong .
- Proposition of policy. There should be stricter emission restrictions on individual cars.
To support propositions of fact, you would want to present a logical argument based on objective facts that can then be used to build persuasive arguments. Propositions of value may require you to appeal more to your audience’s emotions and cite expert and lay testimony. Persuasive speeches about policy usually require you to research existing and previous laws or procedures and determine if any relevant legislation or propositions are currently being considered.
“Getting Critical”
Persuasion and Masculinity
The traditional view of rhetoric that started in ancient Greece and still informs much of our views on persuasion today has been critiqued for containing Western and masculine biases. Traditional persuasion has been linked to Western and masculine values of domination, competition, and change, which have been critiqued as coercive and violent (Gearhart, 1979).
Communication scholars proposed an alternative to traditional persuasive rhetoric in the form of invitational rhetoric. Invitational rhetoric differs from a traditional view of persuasive rhetoric that “attempts to win over an opponent, or to advocate the correctness of a single position in a very complex issue” (Bone et al., 2008). Instead, invitational rhetoric proposes a model of reaching consensus through dialogue. The goal is to create a climate in which growth and change can occur but isn’t required for one person to “win” an argument over another. Each person in a communication situation is acknowledged to have a standpoint that is valid but can still be influenced through the offering of alternative perspectives and the invitation to engage with and discuss these standpoints (Ryan & Natalle, 2001). Safety, value, and freedom are three important parts of invitational rhetoric. Safety involves a feeling of security in which audience members and speakers feel like their ideas and contributions will not be denigrated. Value refers to the notion that each person in a communication encounter is worthy of recognition and that people are willing to step outside their own perspectives to better understand others. Last, freedom is present in communication when communicators do not limit the thinking or decisions of others, allowing all participants to speak up (Bone et al., 2008).
Invitational rhetoric doesn’t claim that all persuasive rhetoric is violent. Instead, it acknowledges that some persuasion is violent and that the connection between persuasion and violence is worth exploring. Invitational rhetoric has the potential to contribute to the civility of communication in our society. When we are civil, we are capable of engaging with and appreciating different perspectives while still understanding our own. People aren’t attacked or reviled because their views diverge from ours. Rather than reducing the world to “us against them, black or white, and right or wrong,” invitational rhetoric encourages us to acknowledge human perspectives in all their complexity (Bone et al., 2008).
- What is your reaction to the claim that persuasion includes Western and masculine biases?
- What are some strengths and weaknesses of the proposed alternatives to traditional persuasion?
- In what situations might an invitational approach to persuasion be useful? In what situations might you want to rely on traditional models of persuasion?
Organizing a Persuasive Speech
We have already discussed several patterns for organizing your speech, but some organization strategies are specific to persuasive speaking. Some persuasive speech topics lend themselves to a topical organization pattern, which breaks the larger topic up into logical divisions. Earlier, in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , we discussed recency and primacy, and in this chapter we discussed adapting a persuasive speech based on the audience’s orientation toward the proposition. These concepts can be connected when organizing a persuasive speech topically. Primacy means putting your strongest information first and is based on the idea that audience members put more weight on what they hear first. This strategy can be especially useful when addressing an audience that disagrees with your proposition, as you can try to win them over early. Recency means putting your strongest information last to leave a powerful impression. This can be useful when you are building to a climax in your speech, specifically if you include a call to action.

Putting your strongest argument last can help motivate an audience to action.
Celestine Chua – The Change – CC BY 2.0.
The problem-solution pattern is an organizational pattern that advocates for a particular approach to solve a problem. You would provide evidence to show that a problem exists and then propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action. One main point addressing the problem and one main point addressing the solution may be sufficient, but you are not limited to two. You could add a main point between the problem and solution that outlines other solutions that have failed. You can also combine the problem-solution pattern with the cause-effect pattern or expand the speech to fit with Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
As was mentioned in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , the cause-effect pattern can be used for informative speaking when the relationship between the cause and effect is not contested. The pattern is more fitting for persuasive speeches when the relationship between the cause and effect is controversial or unclear. There are several ways to use causes and effects to structure a speech. You could have a two-point speech that argues from cause to effect or from effect to cause. You could also have more than one cause that lead to the same effect or a single cause that leads to multiple effects. The following are some examples of thesis statements that correspond to various organizational patterns. As you can see, the same general topic area, prison overcrowding, is used for each example. This illustrates the importance of considering your organizational options early in the speech-making process, since the pattern you choose will influence your researching and writing.
Persuasive Speech Thesis Statements by Organizational Pattern
- Problem-solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that we can solve by finding alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Problem–failed solution–proposed solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that shouldn’t be solved by building more prisons; instead, we should support alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Cause-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-cause-effect. State budgets are being slashed and prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to increased behavioral problems among inmates and lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-solution. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals; therefore we need to find alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence is an organizational pattern designed for persuasive speaking that appeals to audience members’ needs and motivates them to action. If your persuasive speaking goals include a call to action, you may want to consider this organizational pattern. We already learned about the five steps of Monroe’s Motivated Sequence in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , but we will review them here with an example:
- Hook the audience by making the topic relevant to them.
- Imagine living a full life, retiring, and slipping into your golden years. As you get older you become more dependent on others and move into an assisted-living facility. Although you think life will be easier, things get worse as you experience abuse and mistreatment from the staff. You report the abuse to a nurse and wait, but nothing happens and the abuse continues. Elder abuse is a common occurrence, and unlike child abuse, there are no laws in our state that mandate complaints of elder abuse be reported or investigated.
- Cite evidence to support the fact that the issue needs to be addressed.
- According to the American Psychological Association, one to two million elderly US Americans have been abused by their caretakers. In our state, those in the medical, psychiatric, and social work field are required to report suspicion of child abuse but are not mandated to report suspicions of elder abuse.
- Offer a solution and persuade the audience that it is feasible and well thought out.
- There should be a federal law mandating that suspicion of elder abuse be reported and that all claims of elder abuse be investigated.
- Take the audience beyond your solution and help them visualize the positive results of implementing it or the negative consequences of not.
- Elderly people should not have to live in fear during their golden years. A mandatory reporting law for elderly abuse will help ensure that the voices of our elderly loved ones will be heard.
- Call your audience to action by giving them concrete steps to follow to engage in a particular action or to change a thought or behavior.
- I urge you to take action in two ways. First, raise awareness about this issue by talking to your own friends and family. Second, contact your representatives at the state and national level to let them know that elder abuse should be taken seriously and given the same level of importance as other forms of abuse. I brought cards with the contact information for our state and national representatives for this area. Please take one at the end of my speech. A short e-mail or phone call can help end the silence surrounding elder abuse.
Key Takeaways
- Arguments are formed by making claims that are supported by evidence. The underlying justification that connects the claim and evidence is the warrant. Arguments can have strong or weak warrants, which will make them more or less persuasive.
- Good persuasive speech topics are current, controversial (but not inflammatory), and important to the speaker and society.
- When audience members agree with the proposal, focus on intensifying their agreement and moving them to action.
- When audience members are neutral in regards to the proposition, provide background information to better inform them about the issue and present information that demonstrates the relevance of the topic to the audience.
- When audience members disagree with the proposal, focus on establishing your credibility, build common ground with the audience, and incorporate counterarguments and refute them.
- Propositions of fact focus on establishing that something “is or isn’t” or is “true or false.”
- Propositions of value focus on persuading an audience that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.”
- Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done.
- Persuasive speeches can be organized using the following patterns: problem-solution, cause-effect, cause-effect-solution, or Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
- Getting integrated: Give an example of persuasive messages that you might need to create in each of the following contexts: academic, professional, personal, and civic. Then do the same thing for persuasive messages you may receive.
- To help ensure that your persuasive speech topic is persuasive and not informative, identify the claims, evidence, and warrants you may use in your argument. In addition, write a thesis statement that refutes your topic idea and identify evidence and warrants that could support that counterargument.
- Determine if your speech is primarily a proposition of fact, value, or policy. How can you tell? Identify an organizational pattern that you think will work well for your speech topic, draft one sentence for each of your main points, and arrange them according to the pattern you chose.
Bone, J. E., Cindy L. Griffin, and T. M. Linda Scholz, “Beyond Traditional Conceptualizations of Rhetoric: Invitational Rhetoric and a Move toward Civility,” Western Journal of Communication 72 (2008): 436.
Gearhart, S. M., “The Womanization of Rhetoric,” Women’s Studies International Quarterly 2 (1979): 195–201.
Ryan, K. J., and Elizabeth J. Natalle, “Fusing Horizons: Standpoint Hermenutics and Invitational Rhetoric,” Rhetoric Society Quarterly 31 (2001): 69–90.
Communication in the Real World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Programs submenu
Regions submenu, topics submenu, poni 2024 capstone conference, dod's gaza pier and the maritime corridor—gaza: the human toll, lessons from myanmar.
- Abshire-Inamori Leadership Academy
- Aerospace Security Project
- Africa Program
- Americas Program
- Arleigh A. Burke Chair in Strategy
- Asia Maritime Transparency Initiative
- Asia Program
- Australia Chair
- Brzezinski Chair in Global Security and Geostrategy
- Brzezinski Institute on Geostrategy
- Chair in U.S.-India Policy Studies
- China Power Project
- Chinese Business and Economics
- Defending Democratic Institutions
- Defense-Industrial Initiatives Group
- Defense 360
- Defense Budget Analysis
- Diversity and Leadership in International Affairs Project
- Economics Program
- Emeritus Chair in Strategy
- Energy Security and Climate Change Program
- Europe, Russia, and Eurasia Program
- Freeman Chair in China Studies
- Futures Lab
- Geoeconomic Council of Advisers
- Global Food and Water Security Program
- Global Health Policy Center
- Hess Center for New Frontiers
- Human Rights Initiative
- Humanitarian Agenda
- Intelligence, National Security, and Technology Program
- International Security Program
- Japan Chair
- Kissinger Chair
- Korea Chair
- Langone Chair in American Leadership
- Middle East Program
- Missile Defense Project
- Project on Critical Minerals Security
- Project on Fragility and Mobility
- Project on Nuclear Issues
- Project on Prosperity and Development
- Project on Trade and Technology
- Renewing American Innovation Project
- Scholl Chair in International Business
- Smart Women, Smart Power
- Southeast Asia Program
- Stephenson Ocean Security Project
- Strategic Technologies Program
- Transnational Threats Project
- Wadhwani Center for AI and Advanced Technologies
- All Regions
- Australia, New Zealand & Pacific
- Middle East
- Russia and Eurasia
- American Innovation
- Civic Education
- Climate Change
- Cybersecurity
- Defense Budget and Acquisition
- Defense and Security
- Energy and Sustainability
- Food Security
- Gender and International Security
- Geopolitics
- Global Health
- Human Rights
- Humanitarian Assistance
- Intelligence
- International Development
- Maritime Issues and Oceans
- Missile Defense
- Nuclear Issues
- Transnational Threats
- Water Security
So Long, Globalization?

Photo: JIM WATSON/AFP via Getty Images
Commentary by William Alan Reinsch
Published May 1, 2023
Last week I wrote about Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen’s speech that was largely about China. It was followed a week later by National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan’s speech on international economic policy, which is the topic of today’s column.
On Sullivan’s speech, I have long supported the industrial policy initiatives he identified as key elements of the administration’s policy—the infrastructure law, the CHIPS and Science Act, and the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). Helping our companies run faster and making our economy more competitive is something I’ve supported for more than 40 years, and I’m happy to see progress on that front, which is overdue, although some of the restrictions will delay the green transition rather than accelerate it.
Where I get off the boat is on his description of trade policy, both past and present. With respect to the past, I think his description of the failures of globalization misses some important points.
- The trade policy he attacked has lifted more than a billion people out of poverty and made the world a better place. Granted, most of them were not in the United States, but the policy deserves respect for its successes, and ignoring that is a reflection on the self-centered nature of our new policy.
- Arguing that past policy was just about tariffs is simply wrong. That may have been true in the 1950s and 60s, but even in the Tokyo Round in 1979 and certainly in the 1994 Uruguay Round, countries were refocusing their attention on nontariff barriers and issues like protection of intellectual property, government procurement, and later on, trade facilitation.
- The implication that trade policy was responsible for everything bad that happened economically in the past 50 years is also a gross oversimplification. Trade agreements create benefits; they do not distribute them. The trickle-down policies he also attacked have had much more to do with the inequality that currently plagues our population.
- Companies did indeed move offshore, sometimes for cheaper labor, sometimes because it was the best way to serve foreign consumers, and we were indeed buried in imports, many of them Chinese. I think, though, that was less a result of our trade policy than the application of basic economic principles, which the administration cannot repeal. David Ricardo may be dead, but his principle of comparative advantage is not, and saying the world now is more complicated than making cloth and wine is true but irrelevant. The real problem is that countries have figured out how to create comparative advantage through subsidies and protection. We are now responding in kind, which is the best short-term tactic, but not the best economics. Blaming U.S. companies for responding to economic realities at the time misses the point.
Sullivan’s defense of the new policy is equally flawed and ignores the contrast between the principles he articulates and what the United States is actually doing on the ground.
Most important, he ignores the concept of reciprocity in both the past and present. Those trade agreements he blames for our problems opened doors for U.S. exports, which for a mature economy like ours are essential for growth. Those doors were not opened for free. We had to give something to get something, which is the way all negotiations work.
In contrast, in the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) talks, the United States has been clear it does not intend to make concessions but is looking for an agreement that will reflect current U.S. standards and practices. That is not likely to produce significant results. CSIS’s research indicates the Asian parties are looking for “tangible benefits.” Instead, we are asking for many good things on labor, sustainability, decarbonization, anti-corruption, etc. but are offering little in return. As my colleague and fellow Trade Guy, Scott Miller, channeling Larry Summers, put it on our most recent podcast : When a developing country talks to the Chinese, they get an airport. When the country talks to the Americans, they get a lecture. It’s not hard to figure out which policy is more successful.
Our new policy is not really about trade. Instead of talking about the exchange of goods and services, we are talking about worker rights, sustainability, climate, human rights, and cooperation on supply chains, and so on. As I said above, these are all good things, but they cut much closer to how a country chooses to organize its society than dealing with non-tariff barriers. That makes the cost of agreement much higher, both economically and politically, which means the United States will have to pay a higher price to achieve its goals.
In fairness, trade agreements are often not about trade. They’re about geopolitics—cementing the U.S. profile in a region and displaying our commitment. But reaching any agreement requires give and take, and so far our policy is only offering words.
I am particularly sad at the gap between word and deed. We spent 75 years rebuilding war-devastated Europe, creating rule-of-law institutions, and arguing for economic policies that would promote global growth and prosperity—with a good deal of success, I might add. We say we are still for that but in fact are turning inward and focusing on what is good for us. We give lip service to global institutions like the World Trade Organization (WTO), but our actions undermine what we claim to support via protectionist restrictions designed to promote reshoring and lack of enthusiasm for getting the WTO back on its feet. In a long-ago column , I wrote that American exceptionalism has become a myth, that in reality we are just like everybody else. Sullivan’s remarks put an eloquent gloss on our policy, but our actions fall short of the promise.
William Reinsch holds the Scholl Chair in International Business at the Center for Strategic and International Studies in Washington, D.C.
Commentary is produced by the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), a private, tax-exempt institution focusing on international public policy issues. Its research is nonpartisan and nonproprietary. CSIS does not take specific policy positions. Accordingly, all views, positions, and conclusions expressed in this publication should be understood to be solely those of the author(s).
© 2024 by the Center for Strategic and International Studies. All rights reserved.

William Alan Reinsch
Programs & projects.

15 Persuasive Speeches
Speeches that Make a Change
In this chapter . . .
For many public speeches, the specific purpose is to convince the audience of a particular opinion or claim or to convince them to take some action in response to the speech. When your intention is to affect change in your audience (not just the acquisition of knowledge) then you are delivering a persuasive speech. In this chapter you will learn about the elements of persuasion, why persuasion is difficult, and how to overcome people’s resistance to change by using effective and ethical methods.
Although a persuasive speech involves information—even as much as an informative speech—the key difference is that a persuasive speech is designed for “creating, reinforcing, or changing people’s beliefs or actions” (Lucas, 2015. p. 306). A persuasive speech makes something happen. In other words, it performs a job.
Traditional Views of Persuasion
In the fourth century BCE, the classic philosopher Aristotle took up the study of the public practices of the ruling class in Athenian society. For two years he observed the rhetoric (the art of persuasion) of the men who spoke in the assembly and the courts. In the end, he developed a theory about persuasiveness that has come down to us in history as a treatise called Rhetoric. Among his many ideas was the identification of three elements essential to persuasion: ethos, logos, and pathos. In short, they mean credibility, reasonability, and emotion.
Ethos has come to mean speaker character and credentials. It is the element that establishes the audience’s trust in you as a speaker. A speaker’s credibility is based on who the speaker is and what they know: experience, education, expertise, and background. If you’re delivering a persuasive speech about adopting a pet from a shelter and you have raised several shelter dogs, then you have credibility through experience and should share that fact about yourself with the audience to enhance their trust in your persuasive argument. Another way to establish your credibility is through research sources. You may not be an expert in climate change, but if you were giving a persuasive speech about it, you can cite reliable authoritative sources.
The word ethos looks very much like the word “ethics,” and there are many close parallels to the trust an audience has in a speaker and their honesty and ethical stance. In terms of ethics, it goes without saying that your speech will be truthful.
In addition to expertise and truthfulness is your personal involvement in the topic. Ideally you have chosen the topic because it means something to you personally. Audiences will have more trust in you if they feel you have something as stake or something personal in the subject. For example, perhaps your speech is designed to motivate audience members to take action against bullying in schools, and it’s important to you because you work with the Boys and Girls Club organization and have seen how anti-bullying programs can have positive results. Sharing your own involvement and commitment is key to establishing your credibility on this topic.
Logos is the second key element in Aristotle’s theory of rhetoric. Related to our word “logic,” the Greek term logos in persuasion means presenting ideas that appeal to logic or reason. Logos in a speech pertain to arguments that the audience would find acceptable. Imagine a speech, for example, which has the goal of persuading an audience to adopt healthier eating habits. Would the speech be effective if the arguments focused on how expensive organic foods are? Of course not.
Logic and reason are persuasive not only as matters of content. Logos pertains to organization, as well. An effective persuasive speech presents arguments in an organized fashion.
In words like “empathy,” “sympathy,” and “compassion” we see the root word behind the Greek word pathos. Pathos, for Aristotle, meant exciting emotions such as anger, joy, hate, love, and desire to persuade the audience of the rightness of a proposition. In a positive sense, appealing to the emotions of the audience is a highly effective persuasive tool. In the earlier example of a speech designed to encourage an audience to take action against bullying in schools, including a touching story about a student experiencing bullying would make the audience more likely to support your call for action.
However, we recognize that pathos can be used in a negative way. Emotional appeals that use anger, guilt, hatred, inflammatory language like name-calling, or that try to frighten the audience with horrible images, are counter-productive and even unethical. They might incite emotion in the audience, but they are poor uses of pathos.
One negative emotion used frequently by persuasive speakers is fear. Candidates for political office, for example, often try to provoke fear to move us to vote for them. Intense, over-the-top fear appeals, based on factual falsehoods or cherry-picking, and/or including shocking photos, are not ethical and are often dismissed by discerning audience members. Appealing to the emotion of fear can be ethical if it’s managed carefully. This means being strictly factual and avoiding extremes.
Persuasion and the Audience
It makes sense that if a speaker wants to affect the audience’s beliefs or actions, then the speaker must be perfectly clear about their expectations. If you were listening to a persuasive speech call for your audience to support animals, wouldn’t you want to know exactly what “support” the speaker was talking about? Giving money to charities? Volunteering at an animal shelter? Writing state legislators and urging them to change laws? Your job as a persuasive speaker is to be clear about what you want to create, reinforce, or change in your audience.
For your speech to have persuasive power, you must also consider your audience and choose a goal that is feasible for them. Persuasion isn’t an on/off switch. It’s more like a thermometer. Skillful persuasive speakers respect and identify a persuasive goal that is calibrated to the audience. Think of persuasion as a continuum or line going both directions. At one end is strong disagreement. At the other end is strong agreement. Your audience members, either as a group or individually, are sitting somewhere on that line in relation to your central idea statement, or what we are going to call a proposition in this chapter.
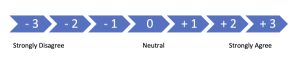
For example, your speech proposition might be something like “The main cause of climate change is human activity.” You are claiming that climate change is due to the harmful things that humans have done to the environment. To be an effective persuasive speaker, one of your first jobs after choosing this topic would be to determine where your audience “sits” on the continuum.
+ 3 means strongly agree to the point of making lifestyle choices to lessen climate change (such as riding a bike instead of driving a car, recycling, eating certain kinds of foods, and advocating for government policy changes). + 2 means agree but not to the point of acting upon it or only acting on it in small ways. + 1 as mildly agrees with your proposition; that is, they think it’s probably true, but the issue doesn’t affect them personally. 0 means neutral, no opinion, or feeling too uninformed to decide. – 1 means mildly opposed to the proposition but willing to listen to those with whom they disagree. – 2 means disagreement to the point of dismissing the idea pretty quickly. – 3 means strong opposition to the point that the concept of climate change itself isn’t even listened to or acknowledged as a valid subject.
Since everyone in the audience is somewhere on this line or continuum, you can accept the fact that any movement toward +3 or to the right is a win. Trying to change an audience from -3 (strong disagreement) to +3 (strong agreement) in a single speech would be quite impossible. When you understand this, you can make strategic choices about the content of your speech.
In this example, if you knew that most of the audience was at -2 or -3, your speech could focus on opening their minds to the possibility of climate change and provide the science behind human causes. On the other hand, if you knew your audience was at +1 or +2, you could focus on urging them to take bold steps, like giving up their gasoline-powered vehicles.
A proposition is assumed to be in some way controversial, or a “stretch” for the audience. Some people in the audience will disagree with your proposition or at least have no opinion; they are not “on your side.”
There will be those in the audience who disagree with your proposition but who are willing to listen. Some members of the audience may already agree with you, although they don’t know why. Both groups could be called the target audience . At the same time, another cluster of your audience may be extremely opposed to your position to the degree that they probably will not give you a fair hearing. They probably can’t be persuaded. Focus on your target audience, they are the one you can persuade.
Why is Persuasion Hard?
Persuasion is hard mainly because we have a bias against change. We go out of our way to protect our beliefs, attitudes, and values. We selectively expose ourselves to messages that we already agree with, rather than those that confront or challenge us. We find it uncomfortable to be confronted with conflicting information or viewpoints.
Additionally, during a persuasive speech the audience members are holding a mental dialogue with the speaker or at least the speaker’s content. The processes that the human mind goes through while it listens to a persuasive message is like a silent conversation. In their minds, audience members are producing doubts or reservations about your proposal. If we could listen in on one of these conversations, it might go something like this:
Speaker: Switching to a plant-based diet is the best action you can take to support a reduction in the CO-2 emissions harming the climate. Audience Member Mind: Yeah, I hear what you’re saying, but eating like that won’t give me enough protein.
The audience member has a doubt or reservation about the speaker’s proposal. We can call these doubts “yeah, buts” because the audience members are thinking, “Yeah, but what about—?” It’s a skill of good persuasion speechwriting to anticipate reservations.
Solutions to the Difficulty of Persuasion
With these reasons for the resistance audience members have to persuasion, what is a speaker to do? Here are some strategies.
First, choose a feasible goal for the persuasive action you want the audience to take. Going back to our continuum, trying to move an audience from -3 to +2 or +3 is too big a move. Having reasonable persuasive goals is the first way to meet resistance. Even moving someone from -3 to -2 is progress, and over time these small shifts can eventually result in a significant amount of persuasion.
Secondly, as speakers we must address reservations. While speechwriters aren’t mind-readers, we can easily imagine reservations about our proposition and build a response to those reservations into the speech. Using the example above, a speaker might say:
Switching to a plant-based diet is the best action you can take to support a reduction in the CO-2 emissions harming the climate. I urge all of you to consider this important dietary change. Perhaps you are thinking that a plant-based diet won’t provide enough protein. That is a common concern. Nutritionists at the website Forks Over Knives explain how the staples of a PB diet—whole grains, legumes, and nuts—provide ample protein.
Here, the speaker acknowledges a valid reservation and then offers a rebuttal. This is called a two-tailed argument. The speaker articulates a possible argument against their proposition and then refutes it.
The third strategy is to keep in mind that since you are asking the audience to change something, they must view the benefits of the change as worth the stress of the change. In effect, audiences want to know: “What’s in it for me?” (WIIFM). As a speaker, you should give thought to that question and in your speech address the benefit, advantage, or improvement that the audience will gain by taking the action you propose.
Structure of a Persuasive Speech
A persuasive speech shares with an informational speech the same four elements for a strongly structured speech: introduction, body, conclusion, and connectors. Like informative speeches, preparation requires thoughtful attention to the given circumstances of the speech occasion, as well as audience analysis in terms of demographic and psychographic features. That said, there are some elements unique to a persuasive speech.
General and Specific Purpose General Purpose: To Persuade Specific Purpose: To motivate my audience of campus administrators to provide LGBTQ+ safe spaces on campus.
This looks familiar up to this point. The general purpose is one of the three broad speech goals (to instruct, to persuade, to inspire or entertain). The specific purpose statement follows a clear T.W.A.C. pattern:
T o + W ord: To convince A udience: campus administrators C ontent: LGBTQ+ safe spaces
What is unique to persuasive speeches is what comes next, the proposition.
Propositions
Informational speeches require a thesis. This is the central idea of the speech; its “takeaway.” Persuasive speeches equally require a strong focus on the main idea, but we call this something else: a proposition . A proposition is a statement that expresses a judgement or opinion about which you want audience in agreement. Remember that propositions must be something that can be argued. To say, “The earth is round” isn’t a proposition. “The earth is flat” is a proposition.
- Converting to solar energy saves homeowners money.
- A vegan diet is the most ethical way to eat.
- Universities should provide on-line learning options for all classes.
- The Constitution’s Second Amendment does not include possession of automatic weapons for private use.
Like a thesis statement for an informative speech, a proposition statement is best when it not only clearly states the judgment or opinion for which you seek audience agreement, but also provides a succinct preview of the reasons for that judgement.
Universities should provide LGBTQ+ safe spaces on campus to promote visibility, build community, and protect well-being for LGBTQ+ students and their allies.
Types of Propositions
If you take a closer look at the propositions above, you’ll notice that they suggest several types of persuasion. In fact, there are several broad categories of propositions, determined by their primary goal. These are: a) propositions of fact, b) propositions of value, c) propositions of policy, and d) propositions of definition.
Proposition of Fact
Speeches with this type of proposition attempt to establish the truth of a statement. The core of the proposition isn’t whether something is morally right or wrong, only that a statement is supported by evidence or not. These propositions are not facts such as “the chemical symbol for water is H20.” Rather, propositions of fact are statements over which people disagree and there is evidence on both sides. Some examples of propositions of fact are:
- Experiments using animals are essential to the development of many life-saving medical procedures.
- Climate change has been caused by human activity.
Notice that in none of these are any values—good or bad—mentioned. The point of these propositions is to prove with evidence the truth of a statement.
Proposition of Value
Propositions of fact have the primary purpose of arguing that something exists in a particular way. Propositions of value, on the other hand, have as their primary purpose to argue that one thing is better than another. When the proposition has a word such as “good,” “bad,” “best,” “worst,” “just,” “unjust,” “ethical,” “unethical,” “moral,” “immoral,” “beneficial,” “harmful,” “advantageous,” or “disadvantageous,” then it’s a proposition of value. Some examples include:
- Hybrid cars are the best form of automobile transportation available today.
- Mascots that involve Native American names, characters, and symbols are unjust.
Propositions of value require a first step: defining the “value” word. If you are trying to convince your audience that something is “unjust,” you will have to make clear what you mean by that term. For different people, “best” might mean “safest,” “least expensive,” “most environmentally responsible,” “stylish,” “powerful,” or “prestigious.” Obviously, in the case of the first proposition above, it means “environmentally responsible.” It’s the first job of the speaker, after introducing the speech and stating the proposition, to explain what “best form of automobile transportation” means. Then the proposition would be defended with separate arguments.
Proposition of Policy
These propositions are easy to identify because they almost always have the word “should” in them. These propositions call for a change in policy or practice (including those in a government, community, or school), or they can call for the audience to adopt a certain behavior.
- The federal government should act to ensure clean water standards for all citizens.
- Universities should eliminate attendance requirements.
- States should lower taxes on food.
The proposition determines the approach to the speech, especially the organization. The exact phrasing of the proposition should be carefully done to be reasonable, positive, and appropriate for the context and audience.
Propositions of Definition
Propositions of definitions argue that a word, phrase, or concept has a particular meaning. Lawyers, legislators, and scholars often write briefs, present persuasive speeches, or compose articles to define terms that are vital to defendants, citizens, or disciplines. Some examples might be:
- The Second Amendment to the Constitution does not include possession of automatic weapons for private use.
- Alcoholism should be considered a disease because…
- Thomas Jefferson’s definition of inalienable rights did not include a right to privacy.
In each of these examples, the proposition is that the definition of these things needs to be changed or viewed differently, but the audience isn’t asked to change an attitude or action.
These are not strict categories. A proposition of value most likely contains elements of facts and definitions, for example. However, identifying the primary category for a persuasive speech focuses the speaker on the ultimate purpose of the speech.
Pro-Arguments
Once you know your proposition, the next step is to make your case for your judgement or opinion through clear and distinct points. These are the main points of the body of your persuasive speech. We call these the “pro” or “for” arguments. You should present at least three distinct arguments in favor of your proposition. Expanding on the example above,
General Purpose: To Persuade Specific Purpose: To motivate my audience of campus administrators to provide LGBTQ+ safe spaces on campus. Proposition: Universities should provide LGBTQ+ safe spaces on campus in order to promote visibility, build community, and protect well-being for LGBTQ+ students and their allies.
Three pro-arguments for the proposition are:
Pro-Argument #1: Creating a safe space makes LGBTQ+ community more visible and central to campus life, instead of marginalized. Pro-Argument #2: Safe spaces create a place where LGBTQ+ and their allies learn to build networks, friendship, and support circles. Pro-Argument #3: With a safe and centralized space bringing together this community, instances of bias or harassment can be brought to counselors, making for a safer community.
Two-Tailed Arguments
There is one more crucial element following pro-arguments. These are unique to persuasive speeches. As discussed above, it’s essential to anticipate and address audience reservations about your propositions. These are the two-tailed arguments that articulate the reservation and then address it or refute it. In the example we’re using, such a statement might look like this:
“Perhaps you are thinking that an LGBTQ+ safe space isn’t necessary on campus because there are already places on campus that provide this function. I understand that concern. However, a space that is officially provided by the University provides access to resources with trained personnel. The national organization CampusPride provides training to university facilitators for exactly this reason.”
There are some techniques for rebuttal or refutation that work better than others. You would not want to say, “If you are one of the people who believe this about my proposition, you are wrong.” It’s better to say that their reservations are “misconceptions,” “myths,” or “mistaken ideas” that are commonly held about the proposition.
Building Upon Your Persuasive Speech’s Arguments
Once you have constructed the key arguments, it’s time to be sure the main points are well supported with evidence.
First, your evidence should be from sources that the audience will find credible. If you can find the same essential information from two sources but know that the audience will find the information more credible from one source than another, use and cite the information from the more credible one. For example, if you find the same statistical data on Wikipedia and the US Department of Labor’s website, cite the US Department of Labor. Audiences also accept information from sources they consider unbiased or indifferent. Gallup polls, for example, have been considered reliable sources of survey data because unlike some organizations, Gallup does not have a cause (political or otherwise) it’s supporting.
Secondly, your evidence should be new to the audience. New evidence is more attention-getting, and you will appear more credible if you tell the audience something new (as long as you cite it well) than if you use the “same old, same old” evidence they have heard before.
Third, in order to be effective and ethical, your supporting evidence should be relevant and not used out of context, manipulated, or edited to change its meaning.
After choosing the evidence and apportioning it to the correct parts of the speech, you will want to consider the use of metaphors, quotations, rhetorical devices, and narratives that will enhance the language and “listenability” of your speech. Narratives are especially good for introduction and conclusions, to get attention and to leave the audience with something dramatic. You might refer to the narrative in the introduction again in the conclusion to give the speech a sense of finality.
Lastly, you will want to decide if you should use any type of presentation aid for the speech. The decision to use visuals such as PowerPoint slides or a video clip in a persuasive speech should take into consideration the effect of the visuals on the audience and the time allotted for the speech. The charts, graphs, or photographs you use should be focused and credibly done.
Organization of a Persuasive Speech
You can see that the overall structure of a persuasive speech follows a common model: introduction, body (arguments and support), two-tailed arguments, and conclusion. Study the example at the end of this chapter to see this structure in action.
In speechwriting, you can think of a speech structure like the building of a house and organization like the arrangement of the rooms within it. As with other speeches, persuasive speeches can be organized topically, chronologically, or spatially. However, persuasive speeches often follow a problem-solution or problem-cause-solution pattern.
Organization for a proposition of fact
If your proposition is one of fact or definition, it will be best to use a topical organization for the body of your speech. That means that you will have two to four discrete, separate topics in support of the proposition.
Proposition: Converting to solar energy saves homeowners money.
- (Pro-Argument 1) Solar energy can be economical to install.
- (Pro-Argument 2) The government awards grants for solar.
- (Pro-Argument 3) Solar energy reduces power bills.
- (Pro-Argument 4) Solar energy requires less money for maintenance.
Organization for a proposition of value
A persuasive speech that incorporates a proposition of value will have a slightly different structure. A proposition of value must first define the “value” word for clarity and provide a basis for the other arguments of the speech. Then the pro-arguments for the proposition based on the definition.
Proposition: Hybrid cars are the best form of automotive transportation available today.
- (Definition of value) Automotive transportation that is best meets three standards: dependable, economical, and environmentally responsible.
- (Pro-Argument 1) Studies show that hybrid cars are durable and dependable.
- (Pro-Argument 2) Hybrid cars are fuel-efficient.
- (Pro-Argument 3) Hybrid cars are environmentally responsible.
Organization for a propositions of policy
The most common type of outline organizations for speeches with propositions of policy is problem-solution or problem-cause-solution. Typically, we don’t feel any motivation to change unless we are convinced that some harm, problem, need, or deficiency exists, and even more, that it affects us personally. Therefore, the organization of a speech about policy needs to first explain the problem and its cause, followed by the solution in the form of 3-5 pro-arguments.
Proposition: Universities should provide on-line learning options for all classes.
- (Problem) Regular attendance in a physical classroom is no longer possible for all students.
- (Cause) Changes brought about by the COVID pandemic have made guaranteed classroom attendance difficult.
- (Pro-Argument 1) Providing on-line learning options protects the health of students.
- (Pro-Argument 2) On-line learning serves students who cannot come to campus.
- (Pro-Argument 3) Access to on-line learning allows students to maintain employment while still going to school.
To complete this outline, along with introduction and conclusion, your pro-arguments should be supported with fact, quotations, and statistics.
Your persuasive speech in class, as well as in real life, is an opportunity to share a passion or cause that you believe will matter to society and help the audience live a better life. Even if you are initially uncomfortable with the idea of persuasion, we use it all the time in diverse ways. Choose your topic based on your commitment and experience, look for quality evidence, craft your proposition so that it will be clear and audience appropriate, and put the finishing touches on it with an eye toward enhancing your logos , ethos , and pathos .
Media Attributions
- Persuasion Scale © Mechele Leon is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
Public Speaking as Performance Copyright © 2023 by Mechele Leon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

47 Persuasion Across Cultures
Learning Objectives
- Explain the causes of cross-cultural miscommunication.
- Identify fundamental cross-cultural communication strategies.
- Practice cross-cultural dialogue.

Persuasion Across Cultures
NASEER ALOMARI, PH.D.
The Swedish journalist Thomas Larsson has defined globalization as “the process of world shrinkage, of distances getting shorter, things moving closer. It pertains to the increasing ease with which somebody on one side of the world can interact, to mutual benefit, with somebody on the other side of the world” (p. 9). Enhanced by the revolutionary advances in communication technologies, globalization has facilitated direct contact among people from various countries, cultural, and linguistic backgrounds. Face-to-face or technology-mediated, cross-cultural encounters are typically friendly, respectful, and positive despite cultural and linguistic barriers and differences. This chapter will explore the nature and causes of cross-cultural miscommunication and identify key strategies for effective cross-cultural persuasion.
The Root of Cross-Cultural Miscommunication
When people from different linguistic and cultural backgrounds meet, the interaction is usually friendly and respectful. In cross-cultural communication, people are typically proud of their acceptance and tolerance and emphasize shared values with different people. Many people dream of traveling to foreign countries to learn about other nations, cultures, traditions, and religions. Unfortunately, misunderstandings and conflicts may occur when people from differing linguistic and cultural worldviews argue about controversial political or social issues.
While respect and tolerance can go a long way in reducing conflict among people from different linguistic and cultural backgrounds, misunderstandings can still result in severe disagreements and conflicts due to differences in worldviews and communication styles. Personal, social, and cultural factors usually shape a person’s communication style. However, how individuals express themselves reflects their socio-economic status and the influence and power in society. For instance, people who belong to a dominant or privileged group tend to speak in a way that reflects their influential status. Privileged individuals in some societies may project their dominant position over less privileged groups or individuals by using direct, assertive, and goal-oriented language. On the other hand, individuals with less power may reflect their lack of influence by using indirect or implicit expressions.
Despite sharing universally accepted values such as harmony, trust, sincerity, honesty, and loyalty among world cultures, traditions, and religions, cross-cultural communication can still be distrustful and tense due to differences in values, beliefs, and worldviews. Gender roles are perceived differently in different cultures and religions and are usually controversial. For example, in many cultures, men are protective of women and show respect by preventing or shielding them from working or doing demanding jobs. In contrast, barring women from work or doing challenging jobs is viewed as violating gender equality and fundamental workplace rights in other cultures. Thus, the different perceptions of gender roles may lead to miscommunication and serious misunderstandings in cross-cultural settings.
Miscommunication between people from different linguistic or cultural backgrounds may result from differences in values, beliefs, or communication styles. For example, people in some cultures emphasize direct and explicit communication to express individualism, independence, and pride. Furthermore, the straightforward communication style is viewed positively in Western cultures as an honest and practical approach to personal and professional interactions.
Cross-Cultural Persuasion Strategies
Persuasion involves influencing others to do or believe something by presenting convincing reasons or evidence. Cialdini (2001) has identified six persuasion techniques that can help speakers win hearts and minds. The six techniques can be used in different combinations and include persuading listeners to like and trust the speaker as someone who has something valuable to offer. To like you, your listeners have to feel appreciated and respected by you, and to trust you; they need to trust your knowledge or expertise and trust your commitment to your ideas. Effective cross-cultural communication should be based on effective persuasion techniques and the strategies specific to communication in diverse linguistic and cultural settings. The following are fundamental cross-cultural communication strategies:
Emphasizing Shared Values
The first cross-cultural persuasion strategy is to build rapport and establish by emphasizing your values with your audience from a different linguistic or cultural background. New York City is an excellent example of how millions of people from all corners of the globe overcome countless linguistic and cultural barriers. New Yorkers live, work, and prosper in their diverse communities by championing such values as freedom, equality, and justice, which serve as a solid foundation for communication and persuasion.
A practical example of building rapport by emphasizing shared values is loyalty to family and community to a listener who grew up in Saudi Arabian society. Al-Zahrani (1993) explored the differences between Americans and Saudis and concluded that Saudis are more collectivist than Americans. People from collectivist cultures tend to be family- and group-serving than people from individualist cultures who are more self-serving. By sharing one’s loyalty and love for family, people from a collectivist culture like the Saudis and others from individualist cultures like Americans establish a solid ground for persuasion.
Focusing on Meaning and Intention
Focus on meaning and intention is critical since it helps reduce or eliminate minor distractions, common in cross-cultural communication and persuasion. For instance, while people in some cultures express themselves indirectly and implicitly to maintain harmony and show courtesy, others do so directly and explicitly to show honesty and trustworthiness. Consequently, it is not uncommon for two people from the abovementioned cultures to misunderstand each other as direct and explicit speakers may appear bold and disrespectful, while indirect and implicit speakers may seem elusive or non-committal. Recognizing the difference between implicit and explicit communication styles reduces the chance of misunderstanding and conflict.
Speakers from individualist cultures may appear to listeners from collectivist cultures as self-centered and self-important. Conversely, speakers from collectivist cultures may appear to listeners from individualistic cultures as selfless and lacking in self-esteem. But, of course, both impressions can be completely wrong since communication styles reflect social norms, power structure, and relationships rather than individual traits. Therefore, distinguishing between personal qualities and cultural styles of communication is crucial for establishing and maintaining rapport and avoiding conflict.
Persuasion requires understanding what the person you are speaking with says and means. While this might be straightforward in a language and tradition you are familiar with, it is trickier when engaging in cross-cultural persuasion. For example, many Japanese prefer to show disagreement indirectly while many Americans do so directly. Therefore, it is common for the Japanese to perceive Americans as aggressive or uncourteous. Conversely, Americans may perceive the Japanese as elusive, indecisive, or weak. Both perceptions can be completely mistaken, backfire, and undermine “trust and developing relationships” (Rahman 11).
Engaging in Empathetic Listening
Global and social media can intensify cultural and political tensions, contribute to miscommunication, and divide communities. Cross-cultural communication can be particularly fraught with miscommunication challenges due to the linguistic and cultural barriers that separate people from different backgrounds. Therefore, applying empathetic listening and suspending judgment are critical strategies for effective communication and persuasion. Furthermore, eliminating or reducing misunderstandings and tension necessitates approaching cross-cultural communication with open-mindedness and willingness to compromise and find solutions to problems (Putnam & Roloff, 1992).

Understanding other people’s cultural context and perspective are critical for decreasing conflict and improving persuasiveness. For example, while some cultures adhere to strict rationality as a persuasive strategy, others may view strict adherence to logic as attempts to dictate and impose opinions and solutions without fully understanding the discussion’s political, social, or cultural context. On the other hand, appealing to emotion, which is common in some cultures, can be interpreted as avoiding facts or ignoring logic and reason. Empathetic listening requires showing others your genuine interest in understanding their ideas. One way to show empathy is by paraphrasing speakers’ viewpoints in your own words, asking for clarification, or expressing appreciation of their contribution to the discussion.
Approaching Persuasion as Dialogue
In this era of globalization, ethnic, cultural, and religious diversity, pluralism, and multiculturalism have become the norm in the United States and across the globe. The emerging global, pluralistic culture in which people from different backgrounds work and live together will shape how people view themselves, others, and their perception of reality. In such a pluralistic environment, cross-cultural communication requires dialogue with others “to understand one another’s point of view, to show tolerance, listening, and flexibility of thought in the face of sociocultural gaps” (Eliyahu-Levi 417).
Linguistic and cultural barriers can be decreased or eliminated if communication is focused on meaning and purpose. For example, millions of people use English as a foreign language (EFL) to communicate effectively without necessarily adopting the cultural values, beliefs, or styles of native speakers of English. Adopting dialogue helps maintain a positive tone when speaking with people with different communication styles and cultural etiquette. Thus, it is essential to remember that when communicating with EFL speakers, the latter may not observe the values, opinions, or communication strategies used by native English speakers. Furthermore, it is essential to remember that when engaging in persuasive dialogue with people from different linguistic or cultural backgrounds than yours, the latter filter the ideas through the lens of their communication patterns and social and political experiences. Therefore, suspending judgment and listening carefully to the arguments and evidence help achieve mutual understanding, reach an agreement, and resolve conflicts.
Approaching cross-cultural persuasion as a two-way dialogue helps build trust and reduce disagreements and tension. Dialogue requires participants to listen carefully, be flexible, and give up trying to control the communication process to achieve predetermined outcomes. Kent and Taylor (2002) view dialogue as a means to solidify sympathy, satisfaction, and trust, essential for relationship building between people who would otherwise find no grounds for reasoning and agreement. Hence, cross-cultural communication is essentially a compromise between people committed to searching for ways to engage and remain in constant dialogue that may seem impossible at times.
In many Western cultures, monolog is hailed as a winning method of speech to persuade and change hearts and minds. However, in cross-cultural communication, monologs may be counterproductive. It should, therefore, be replaced by dialogue which is a balanced two-way symmetrical communication process that leads to mutual understanding between participants (Grunig, Grunig & Dozier, 2006).
Building linguistic and cultural bridges are fundamental strategies for effective cross-cultural persuasion. Engaging in genuine dialogue for understanding and being understood is the basis for building trust, reducing tension, and reaching an agreement.
Key Takeaways
- When creating your persuasive outline and rehearsing your speech, be sure to check for common miscommunication pitfalls. Consider revising and editing your work and your delivery to demonstrate intercultural competence and effective linguistic cross-cultural persuasion.
Al-Zahrani, Saad Said A., and Stan A. Kaplowitz. “Attributional biases in individualistic and collectivistic cultures: A comparison of Americans with Saudis.” Social Psychology Quarterly (1993): 223-233.
Cialdini, Robert B. “The science of persuasion.” Scientific American 284.2 (2001): 76-81.
Eliyahu-Levi, Dolly. “Cross-cultural online encounters with peers from different countries.” Distance Education 41.3 (2020): 402-423.
Grunig, James E., Larissa A. Grunig, and David M. Dozier. “The excellence theory.” Public Relations Theory II (2006): 21-62.
Kent, Michael L., and Maureen Taylor. “Toward a dialogic theory of public relations.” Public Relations Review 28.1 (2002): 21-37.
Larsson, Tomas. The Race to the Top: The Real Story of Globalization. Cato Institute, 2001.
Putnam, Linda L., and Michael E. Roloff, eds. Communication and Negotiation . Vol. 20. Sage, 1992.
Rahman, Khairiah A. “Dialogue and persuasion in the Islamic tradition: Implications for journalism.” Global Media Journal , Canadian Edition 9.2 (2016): 9-26.
Public Speaking Copyright © by Dr. Layne Goodman; Amber Green, M.A.; and Various is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
115 Global Issues Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best global issues topic ideas & essay examples, ✍️ global issues essay topics for college, 📌 good essay topics on global issues, 💡 interesting topics to write about global issues, ❓ global issues questions.
- Water Scarcity as a Global Issue: Causes and Solutions Common causes of water scarcity include overpopulation e in regions that have limited water resources, global warming, destruction of water catchment areas by human activities, and pollution of water sources.
- Gender Inequality as a Global Issue This essay will examine some of the causes that affect the gap in the treatment of men and women, and its ramifications, particularly regarding developing countries.
- Tuberculosis as a Global Health Issue Over the years, the bacteria strain that causes tuberculosis has developed a lot of resistance mainly as a result of a lack of compliance to treatment on the part of the patient.
- Reflection on Global Issues: Globalization of the Environment The global conflicts, managing the post-pandemic world, and the need to navigate the social injustices to ensure equality for all are among the most pressing ones.
- Homelessness as a Global Social Issue In the US, homelessness is on the increase because of economic melt- down and foreclosures. Moreover, differences in perception of homelessness by liberal and conservative on homeless have increased homelessness in the US.
- Anthropology in Solving Global Social Issues Artists were moving in the same direction, which excluded the possibility to understand and assess other examples of the art of other nations.
- The Great Global Warming Swindle: Different Views on the Issue According to the film, the main aim of the scientific organizations is to get funding for the research of this problem and attract additional attention to global warming, while in reality, the climate is changing […]
- Global Health Issue in the “Mother Teresa” Movie The movie is devoted to her immense donation to the universal HIV/AIDS struggle in India, but along with the help to HIV infected people, she made the greatest ever contribution to the matters of peace […]
- Global Issues: Addressing an Aging Population An important issue that is currently facing the world community is aging due to the increasing number of older people. Migration leaves the countries in which people are moving with a significant number of older […]
- Global Health Issue of Malaria It can be explained due to the higher density of the population in those areas and the low socioeconomic status of most people.
- Global Health Issues Affecting International Community The HIV and tuberculosis pandemics have caused and will continue to present considerable challenges to emerging nations’ public health care systems, especially in the hardest-hit nations.
- Global Inequality Issues in Modern Society It was evident during the times of colonization when foreign entities tried to impose their sociopolitical and economic institutions on the developing nations.
- Global Issues, Climate Justice, and Human Overpopulation On the one hand, globalization has many positive aspects: the mutual enrichment of the world community, the exchange of best practices, and the availability of goods.
- Sustainability as an Urgent Global Issue Therefore, this shows the importance of integrating technology with other multidisciplinary teams to achieve quick and sustainable designs that can help in solving the urgent global issue.
- Global Issues, Common Good, and Individualism In such a case, the cohesion and commitment of each individual to shared goals and interests seem to solve the mentioned problems.
- Global Issues: Politics, Economics, and Culture by R.Payne The next chapter 14 reveals the issue of cultural homogenization and hybridization due to globalization. From the perspective of the biblical worldview, it largely determines the principles of the world.
- Global Ecological Issues of Covid-19 Pandemic The reduction in carbon dioxide emissions is due to the removal of cars on the streets, which account for about 23% of total CO2 emissions.
- Environmental and Global Health Issues: Measles Measles is among the most contagious disease in the world and is highly frequent and densely distributed in poor developing nations of Africa and Asia.
- Solving Global Issues May Not Be as Easy as It Seems The main point of the essay is to demonstrate how the inaction of those with power and money in the face of human suffering is purely immoral.
- Global Health Issue: The Coronavirus Disease Families have suffered unparalleled grief, anxiety, and distress from the increasing fatality, massive job losses, lockdowns, and movement restrictions to curb the spread of the virus.
- WHO and Its Impact on Global Health Issues The issues which are the center of attention of the World Health Organization are: Women’s Health Health In Africa Eradication of communicable diseases Dr Margaret Chan, the Director-General of World Health Organization said;”I want my […]
- Examination of a Global Population Issue of Russia The country is one of the richest in the world. The country also has the largest forest cover in the world, and the largest fresh water lake.
- Global Health Concerns Overview Title Report 1. Japan nuke risks are minimal The World Health Organization has sent alerts to global health experts to travel to Japan to prevent health hazards caused by radiation. WHO reported the health risks arising from the incident is very low and the current radiation level has no great risk on public health. In […]
- Global Issues Action Plan in the U.S. While drawbacks are the possibility of losing power that other states can use to influence the United States and the lack of protection from emerging military organizations and countries, such as China and Iran, that […]
- Global Health Issue Analysis: HIV – A Relatively New Disease Rapid detection and treatment are crucial to limit the spread of HIV and limit the patient’s effects. As the frequency and intensity of symptoms vary from person to person, testing is the only clear way […]
- Race as a Global Issue in the 1920s The main intention of prohibiting immigrants from entering the country was to block the Germans whom the Americans saw as a threat to their country.
- Global Digital Divide as a Social Issue That is, if societies around the globe are able to bridge the gap between those who have and those who do not in relation to information technology, then the development problems would be minimized at […]
- Global Issue: WWF on Bio-Refineries NGO’s and private communities provide most of the funds, along with the government, for the development of these integrated bio-refineries. Integrated bio-refineries come with the promise of a better lifestyle and enhanced working conditions for […]
- Global Warming Issues Review and Environmental Sustainability Whether it is the melt down of Arctic ice, the damage of the Ozone layer, extra pollution in developing countries; all sums up to one thing in common and that is global warming.
- Modern Global Issues: Drinking Water Shortage The situation is closely linked with the lack of water, and the offered technology to cope with this problem. This is the only way to use naturally filtered and sprang water.
- How Has Globalization Impacted on Issues of Human Rights? William Adler closely examines the disrupted lives of the three women who occupy an assembly-line job as the job and its company moves from New Jersey to rural Mississippi and to Matamoros, Mexico, across the […]
- Malnutrition in Children as a Global Health Issue The peculiarity of this initiative is not to support children and control their feeding processes but prevent pediatric malnutrition even before a child is born.
- Adolescent Pregnancy as a Global Issue The wider the information system is, the more effective methods of solving problems related to the health of pregnant teens are.
- The Doha Round Effectiveness in Solving Global Issues Except for the Dispute Settlement Understanding actions, the attendees of the conference agreed that the outcome of all negotiations was to be done as a single undertaking.
- Cultural Competence in Action: Solutions to Global Health Issues In this paper, the analysis of several case studies about cultural competence will be discussed to clarify how to achieve positive results and reduce the wasting of resources. In the second case, certain attention is […]
- Polar Transformations as a Global Warming Issue Changes in vegetation due to global warming will be varying as the regions are covered with three main vegetation types: polar desert, boreal forest, and the tundra.
- Project Cost Management’s Global Issues and Challenges The results suggest the lack of identity for the profession on the global scale due to the lack of consensus regarding the common descriptor, the scarcity of common standards, terminology, and bodies of knowledge, and […]
- Project Cost Management: Global Issues and Challenges The information revealed by the author is likely to be beneficial for those individuals who are occupied in various fields but provide cost management services in the framework of the global construction industry.
- Natural Disasters and Global Social Issues The hurricane led to a major shift in the social arrangement of the populations in the worst affected areas. This led to a significant loss of jobs in the affected areas.
- Childhood Obesity in Developing Countries – A Global Health Issue Childhood Obesity and the Globe As mentioned earlier, according to the data of WHO, the number of obese children in the world today is more than 42 million, and the vast majority of them are […]
- Differing Views on Global Warming Issues It is crucial to bring on board the views of those who view global warming as a myth that need not to be addressed.
- Ethics-Related Global Workplace Issues Child labor also exposes the children to activities that are illegal. Forced labor is a form of slavery and should not be practiced anywhere in the world.
- Examination of a Global Population Issue Economic Issues The economy of South Africa is one of the fastest developing economies in the world. Being the only African country which is a member of the G-20, this country has been seen to […]
- Global Population Issues and Population in the UAE The natural resources will face exhaustion due to the great pressure of the population. Consequently, the governments of these countries will be forced to take measures to drive the fertility rates up to cover up […]
- Global Issues for Global Citizens: An Introduction to Key Development Challenges
- Are Gender Rights and Gender Discrimination Global Issues
- Global Issues Regarding the Container Shipping
- Analysis of the Global Issues in Business
- Global Issues, Local Solutions: Rethinking Wealth and Health
- Climate Change and Pollution Are Serious Global Issues
- Compounded Global Issues: Terrorism, Nuclear Proliferation, and Climate Change
- Global Issues: Obesity, Inactivity, and Water-Crisis
- Environment-Related Global Issues: Global and Regional Conventions
- How Global Issues Are Resolved With the Scopes of Many Disciplines
- Explaining the Global Issues of Environment and Health
- Global Crimes Cause Global Issues That Affect the National
- The Alarming and Troublesome Global Warming Issue
- Analyzing How Global Issues Affect Tourism
- The Link Between Global Issues and Change in Human Resource Management
- The Relations Between the Global Issues and Institutions
- Global Issues Surrounding the Millennium Development Goals
- Analyzing Human Trafficking as a Global Issue
- Global Warming: An Issue That Is Man-Made?
- Immigration and Migration Described as the Global Issues
- Analyzing Global Issues That Effect Everyone
- Environmental Issues: Chevron’s Contribution to Global Warming
- Global Issues We Are Facing Today
- Cigarette Smoking Relation to Global Issues of the Future
- Six Global Issues Associated With E-Commerce
- Global Issues: The Link Between Water Shortage and Child Mortality
- Analysis of the Innovation and Global Issues in Social Sciences
- The Relationships Between Internet, Computers, and Global Issues
- Global Issues Within the First Civilizations
- Legal and Global Issues Focused On Treating Undocumented Immigrants
- Analysis of the Poor News Coverage and Public Opinion on Global Issues
- Depicting Social and Global Issues and Trends in Adult Education
- The Global Issues Depicted in “Home”, a Documentary by Yann Arthus-Bertrand
- Teaching for Sustainable Development Through Ethical Global Issues Pedagogy
- Terrorism and the Military: Global Issues of Today
- The Concept, Content, and Nature of Contemporary Global Issues
- The Gay Marriage Debate: Contemporary Global Issues
- The Analysis of the Global Issues and Threats of Nuclear Weapons
- Overview of the Significant Global Issues of Nowadays
- The Part of the U.S. and India in Global Issues On Women
- Are Gender Rights and Gender Discrimination Global Issues?
- What Are the Global Issues in Business?
- Are Climate Change and Pollution Serious Global Issues?
- Are Terrorism and Nuclear Proliferation Global Issues?
- What Is the Role of Third World Countries in Global Environmental Issues?
- How Are Global Issues Solved With the Help of Many Disciplines?
- What Are the Social and Global Issues and Trends in Adult Education?
- What Institutions Can Solve Global Issues?
- What Are the Global Issues of Immigration and Migration?
- Do Global Issues Have Local Solutions?
- How Global Is the Issue of Obesity?
- What Are the Global Issues Related to Container Transportation?
- Is Child Mortality a Global Issue?
- What Are the Global Issues Associated With the Millennium Development Goals?
- What Were the Global Issues of the First Civilizations?
- What Global Issues Is Humanity Currently Facing?
- What Are the Global Issues Related to Human Resource Management?
- What Does Smoking Have to Do With Global Issues of the Future?
- How Do Global Issues Affect Individual States?
- What Is Public Opinion About Global Issues?
- What Are the Concepts, Meaning and Nature of Modern Global Issues?
- Gay Marriage: Is It a Modern Global Issue?
- What Are the US and India Global Issues Affecting Women?
- Global Issues: How to Fight Addiction to Video Games?
- What Are the Global Health Issues?
- Is Organized Crime a Global Issue in the World?
- How Can National Governments Solve the Global Issue of Climate Change?
- What Are Starbucks Global Issues?
- Why Is Global Cooperation Important to Address the Global Issues of Postharvest Losses?
- Is It Possible to Solve the Global Issue of PTSD?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 26). 115 Global Issues Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/global-issues-essay-topics/
"115 Global Issues Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 26 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/global-issues-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '115 Global Issues Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 26 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "115 Global Issues Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/global-issues-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "115 Global Issues Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/global-issues-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "115 Global Issues Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/global-issues-essay-topics/.
- Environment Research Topics
- Gender Inequality Research Topics
- Human Rights Essay Ideas
- National Parks Research Topics
- Overpopulation Topics
- Nuclear Energy Essay Titles
- Poverty Essay Titles
- Racism Paper Topics

What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
112 Persuasive Speech Topics That Are Actually Engaging
What’s covered:, how to pick an awesome persuasive speech topic, 112 engaging persuasive speech topics, tips for preparing your persuasive speech.
Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
When it comes time to select a topic for your persuasive speech, you may feel overwhelmed by all the options to choose from—or your brain may be drawing a completely blank slate. If you’re having trouble thinking of the perfect topic, don’t worry. We’re here to help!
In this post, we’re sharing how to choose the perfect persuasive speech topic and tips to prepare for your speech. Plus, you’ll find 112 persuasive speech topics that you can take directly from us or use as creative inspiration for your own ideas!
Choose Something You’re Passionate About
It’s much easier to write, research, and deliver a speech about a cause you care about. Even if it’s challenging to find a topic that completely sparks your interest, try to choose a topic that aligns with your passions.
However, keep in mind that not everyone has the same interests as you. Try to choose a general topic to grab the attention of the majority of your audience, but one that’s specific enough to keep them engaged.
For example, suppose you’re giving a persuasive speech about book censorship. In that case, it’s probably too niche to talk about why “To Kill a Mockingbird” shouldn’t be censored (even if it’s your favorite book), and it’s too broad to talk about media censorship in general.
Steer Clear of Cliches
Have you already heard a persuasive speech topic presented dozens of times? If so, it’s probably not an excellent choice for your speech—even if it’s an issue you’re incredibly passionate about.
Although polarizing topics like abortion and climate control are important to discuss, they aren’t great persuasive speech topics. Most people have already formed an opinion on these topics, which will either cause them to tune out or have a negative impression of your speech.
Instead, choose topics that are fresh, unique, and new. If your audience has never heard your idea presented before, they will be more open to your argument and engaged in your speech.
Have a Clear Side of Opposition
For a persuasive speech to be engaging, there must be a clear side of opposition. To help determine the arguability of your topic, ask yourself: “If I presented my viewpoint on this topic to a group of peers, would someone disagree with me?” If the answer is yes, then you’ve chosen a great topic!
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork for what it takes to choose a great persuasive speech topic, here are over one hundred options for you to choose from.
- Should high school athletes get tested for steroids?
- Should schools be required to have physical education courses?
- Should sports grades in school depend on things like athletic ability?
- What sport should be added to or removed from the Olympics?
- Should college athletes be able to make money off of their merchandise?
- Should sports teams be able to recruit young athletes without a college degree?
- Should we consider video gamers as professional athletes?
- Is cheerleading considered a sport?
- Should parents allow their kids to play contact sports?
- Should professional female athletes be paid the same as professional male athletes?
- Should college be free at the undergraduate level?
- Is the traditional college experience obsolete?
- Should you choose a major based on your interests or your potential salary?
- Should high school students have to meet a required number of service hours before graduating?
- Should teachers earn more or less based on how their students perform on standardized tests?
- Are private high schools more effective than public high schools?
- Should there be a minimum number of attendance days required to graduate?
- Are GPAs harmful or helpful?
- Should schools be required to teach about standardized testing?
- Should Greek Life be banned in the United States?
- Should schools offer science classes explicitly about mental health?
- Should students be able to bring their cell phones to school?
- Should all public restrooms be all-gender?
- Should undocumented immigrants have the same employment and education opportunities as citizens?
- Should everyone be paid a living wage regardless of their employment status?
- Should supremacist groups be able to hold public events?
- Should guns be allowed in public places?
- Should the national drinking age be lowered?
- Should prisoners be allowed to vote?
- Should the government raise or lower the retirement age?
- Should the government be able to control the population?
- Is the death penalty ethical?
Environment
- Should stores charge customers for plastic bags?
- Should breeding animals (dogs, cats, etc.) be illegal?
- Is it okay to have exotic animals as pets?
- Should people be fined for not recycling?
- Should compost bins become mandatory for restaurants?
- Should electric vehicles have their own transportation infrastructure?
- Would heavier fining policies reduce corporations’ emissions?
- Should hunting be encouraged or illegal?
- Should reusable diapers replace disposable diapers?
Science & Technology
- Is paper media more reliable than digital news sources?
- Should automated/self-driving cars be legalized?
- Should schools be required to provide laptops to all students?
- Should software companies be able to have pre-downloaded programs and applications on devices?
- Should drones be allowed in military warfare?
- Should scientists invest more or less money into cancer research?
- Should cloning be illegal?
- Should societies colonize other planets?
- Should there be legal oversight over the development of technology?
Social Media
- Should there be an age limit on social media?
- Should cyberbullying have the same repercussions as in-person bullying?
- Are online relationships as valuable as in-person relationships?
- Does “cancel culture” have a positive or negative impact on societies?
- Are social media platforms reliable information or news sources?
- Should social media be censored?
- Does social media create an unrealistic standard of beauty?
- Is regular social media usage damaging to real-life interactions?
- Is social media distorting democracy?
- How many branches of government should there be?
- Who is the best/worst president of all time?
- How long should judges serve in the U.S. Supreme Court?
- Should a more significant portion of the U.S. budget be contributed towards education?
- Should the government invest in rapid transcontinental transportation infrastructure?
- Should airport screening be more or less stringent?
- Should the electoral college be dismantled?
- Should the U.S. have open borders?
- Should the government spend more or less money on space exploration?
- Should students sing Christmas carols, say the pledge of allegiance, or perform other tangentially religious activities?
- Should nuns and priests become genderless roles?
- Should schools and other public buildings have prayer rooms?
- Should animal sacrifice be legal if it occurs in a religious context?
- Should countries be allowed to impose a national religion on their citizens?
- Should the church be separated from the state?
- Does freedom of religion positively or negatively affect societies?
Parenting & Family
- Is it better to have children at a younger or older age?
- Is it better for children to go to daycare or stay home with their parents?
- Does birth order affect personality?
- Should parents or the school system teach their kids about sex?
- Are family traditions important?
- Should parents smoke or drink around young children?
- Should “spanking” children be illegal?
- Should parents use swear words in front of their children?
- Should parents allow their children to play violent video games?
Entertainment
- Should all actors be paid the same regardless of gender or ethnicity?
- Should all award shows be based on popular vote?
- Who should be responsible for paying taxes on prize money, the game show staff or the contestants?
- Should movies and television shows have ethnicity and gender quotas?
- Should newspapers and magazines move to a completely online format?
- Should streaming services like Netflix and Hulu be free for students?
- Is the movie rating system still effective?
- Should celebrities have more privacy rights?
Arts & Humanities
- Are libraries becoming obsolete?
- Should all schools have mandatory art or music courses in their curriculum?
- Should offensive language be censored from classic literary works?
- Is it ethical for museums to keep indigenous artifacts?
- Should digital designs be considered an art form?
- Should abstract art be considered an art form?
- Is music therapy effective?
- Should tattoos be regarded as “professional dress” for work?
- Should schools place greater emphasis on the arts programs?
- Should euthanasia be allowed in hospitals and other clinical settings?
- Should the government support and implement universal healthcare?
- Would obesity rates lower if the government intervened to make healthy foods more affordable?
- Should teenagers be given access to birth control pills without parental consent?
- Should food allergies be considered a disease?
- Should health insurance cover homeopathic medicine?
- Is using painkillers healthy?
- Should genetically modified foods be banned?
- Should there be a tax on unhealthy foods?
- Should tobacco products be banned from the country?
- Should the birth control pill be free for everyone?
If you need more help brainstorming topics, especially those that are personalized to your interests, you can use CollegeVine’s free AI tutor, Ivy . Ivy can help you come up with original persuasive speech ideas, and she can also help with the rest of your homework, from math to languages.
Do Your Research
A great persuasive speech is supported with plenty of well-researched facts and evidence. So before you begin the writing process, research both sides of the topic you’re presenting in-depth to gain a well-rounded perspective of the topic.
Understand Your Audience
It’s critical to understand your audience to deliver a great persuasive speech. After all, you are trying to convince them that your viewpoint is correct. Before writing your speech, consider the facts and information that your audience may already know, and think about the beliefs and concerns they may have about your topic. Then, address these concerns in your speech, and be mindful to include fresh, new information.
Have Someone Read Your Speech
Once you have finished writing your speech, have someone read it to check for areas of strength and improvement. You can use CollegeVine’s free essay review tool to get feedback on your speech from a peer!
Practice Makes Perfect
After completing your final draft, the key to success is to practice. Present your speech out loud in front of a mirror, your family, friends, and basically, anyone who will listen. Not only will the feedback of others help you to make your speech better, but you’ll become more confident in your presentation skills and may even be able to commit your speech to memory.
Hopefully, these ideas have inspired you to write a powerful, unique persuasive speech. With the perfect topic, plenty of practice, and a boost of self-confidence, we know you’ll impress your audience with a remarkable speech!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Persuasive Speeches — Types, Topics, and Examples

What is a persuasive speech?
In a persuasive speech, the speaker aims to convince the audience to accept a particular perspective on a person, place, object, idea, etc. The speaker strives to cause the audience to accept the point of view presented in the speech.
The success of a persuasive speech often relies on the speaker’s use of ethos, pathos, and logos.

Ethos is the speaker’s credibility. Audiences are more likely to accept an argument if they find the speaker trustworthy. To establish credibility during a persuasive speech, speakers can do the following:
Use familiar language.
Select examples that connect to the specific audience.
Utilize credible and well-known sources.
Logically structure the speech in an audience-friendly way.
Use appropriate eye contact, volume, pacing, and inflection.
Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions. Speakers who create an emotional bond with their audience are typically more convincing. Tapping into the audience’s emotions can be accomplished through the following:
Select evidence that can elicit an emotional response.
Use emotionally-charged words. (The city has a problem … vs. The city has a disease …)
Incorporate analogies and metaphors that connect to a specific emotion to draw a parallel between the reference and topic.
Utilize vivid imagery and sensory words, allowing the audience to visualize the information.
Employ an appropriate tone, inflection, and pace to reflect the emotion.
Logos appeals to the audience’s logic by offering supporting evidence. Speakers can improve their logical appeal in the following ways:
Use comprehensive evidence the audience can understand.
Confirm the evidence logically supports the argument’s claims and stems from credible sources.
Ensure that evidence is specific and avoid any vague or questionable information.
Types of persuasive speeches
The three main types of persuasive speeches are factual, value, and policy.

A factual persuasive speech focuses solely on factual information to prove the existence or absence of something through substantial proof. This is the only type of persuasive speech that exclusively uses objective information rather than subjective. As such, the argument does not rely on the speaker’s interpretation of the information. Essentially, a factual persuasive speech includes historical controversy, a question of current existence, or a prediction:
Historical controversy concerns whether an event happened or whether an object actually existed.
Questions of current existence involve the knowledge that something is currently happening.
Predictions incorporate the analysis of patterns to convince the audience that an event will happen again.
A value persuasive speech concerns the morality of a certain topic. Speakers incorporate facts within these speeches; however, the speaker’s interpretation of those facts creates the argument. These speeches are highly subjective, so the argument cannot be proven to be absolutely true or false.
A policy persuasive speech centers around the speaker’s support or rejection of a public policy, rule, or law. Much like a value speech, speakers provide evidence supporting their viewpoint; however, they provide subjective conclusions based on the facts they provide.
How to write a persuasive speech
Incorporate the following steps when writing a persuasive speech:
Step 1 – Identify the type of persuasive speech (factual, value, or policy) that will help accomplish the goal of the presentation.
Step 2 – Select a good persuasive speech topic to accomplish the goal and choose a position .

Step 3 – Locate credible and reliable sources and identify evidence in support of the topic/position. Revisit Step 2 if there is a lack of relevant resources.
Step 4 – Identify the audience and understand their baseline attitude about the topic.
Step 5 – When constructing an introduction , keep the following questions in mind:
What’s the topic of the speech?
What’s the occasion?
Who’s the audience?
What’s the purpose of the speech?
Step 6 – Utilize the evidence within the previously identified sources to construct the body of the speech. Keeping the audience in mind, determine which pieces of evidence can best help develop the argument. Discuss each point in detail, allowing the audience to understand how the facts support the perspective.
Step 7 – Addressing counterarguments can help speakers build their credibility, as it highlights their breadth of knowledge.
Step 8 – Conclude the speech with an overview of the central purpose and how the main ideas identified in the body support the overall argument.

Persuasive speech outline
One of the best ways to prepare a great persuasive speech is by using an outline. When structuring an outline, include an introduction, body, and conclusion:
Introduction
Attention Grabbers
Ask a question that allows the audience to respond in a non-verbal way; ask a rhetorical question that makes the audience think of the topic without requiring a response.
Incorporate a well-known quote that introduces the topic. Using the words of a celebrated individual gives credibility and authority to the information in the speech.
Offer a startling statement or information about the topic, typically done using data or statistics.
Provide a brief anecdote or story that relates to the topic.
Starting a speech with a humorous statement often makes the audience more comfortable with the speaker.
Provide information on how the selected topic may impact the audience .
Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the audience needs to know to understand the speech in its entirety.
Give the thesis statement in connection to the main topic and identify the main ideas that will help accomplish the central purpose.
Identify evidence
Summarize its meaning
Explain how it helps prove the support/main claim
Evidence 3 (Continue as needed)
Support 3 (Continue as needed)
Restate thesis
Review main supports
Concluding statement
Give the audience a call to action to do something specific.
Identify the overall importan ce of the topic and position.
Persuasive speech topics
The following table identifies some common or interesting persuasive speech topics for high school and college students:
Persuasive speech examples
The following list identifies some of history’s most famous persuasive speeches:
John F. Kennedy’s Inaugural Address: “Ask Not What Your Country Can Do for You”
Lyndon B. Johnson: “We Shall Overcome”
Marc Antony: “Friends, Romans, Countrymen…” in William Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar
Ronald Reagan: “Tear Down this Wall”
Sojourner Truth: “Ain’t I a Woman?”

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
75 Persuasive Speech Topics and Ideas
October 4, 2018 - Gini Beqiri
To write a captivating and persuasive speech you must first decide on a topic that will engage, inform and also persuade the audience. We have discussed how to choose a topic and we have provided a list of speech ideas covering a wide range of categories.
What is persuasive speech?
The aim of a persuasive speech is to inform, educate and convince or motivate an audience to do something. You are essentially trying to sway the audience to adopt your own viewpoint.
The best persuasive speech topics are thought-provoking, daring and have a clear opinion. You should speak about something you are knowledgeable about and can argue your opinion for, as well as objectively discuss counter-arguments.
How to choose a topic for your speech
It’s not easy picking a topic for your speech as there are many options so consider the following factors when deciding.
Familiarity
Topics that you’re familiar with will make it easier to prepare for the speech.
It’s best if you decide on a topic in which you have a genuine interest in because you’ll be doing lots of research on it and if it’s something you enjoy the process will be significantly easier and more enjoyable. The audience will also see this enthusiasm when you’re presenting which will make the speech more persuasive.
The audience’s interest
The audience must care about the topic. You don’t want to lose their attention so choose something you think they’ll be interested in hearing about.
Consider choosing a topic that allows you to be more descriptive because this allows the audience to visualize which consequently helps persuade them.
Not overdone
When people have heard about a topic repeatedly they’re less likely to listen to you as it doesn’t interest them anymore. Avoid cliché or overdone topics as it’s difficult to maintain your audience’s attention because they feel like they’ve heard it all before.
An exception to this would be if you had new viewpoints or new facts to share. If this is the case then ensure you clarify early in your speech that you have unique views or information on the topic.
Emotional topics
Emotions are motivators so the audience is more likely to be persuaded and act on your requests if you present an emotional topic.
People like hearing about issues that affect them or their community, country etc. They find these topics more relatable which means they find them more interesting. Look at local issues and news to discover these topics.
Desired outcome
What do you want your audience to do as a result of your speech? Use this as a guide to choosing your topic, for example, maybe you want people to recycle more so you present a speech on the effect of microplastics in the ocean.

Persuasive speech topics
Lots of timely persuasive topics can be found using social media, the radio, TV and newspapers. We have compiled a list of 75 persuasive speech topic ideas covering a wide range of categories.
Some of the topics also fall into other categories and we have posed the topics as questions so they can be easily adapted into statements to suit your own viewpoint.
- Should pets be adopted rather than bought from a breeder?
- Should wild animals be tamed?
- Should people be allowed to own exotic animals like monkeys?
- Should all zoos and aquariums be closed?
Arts/Culture
- Should art and music therapy be covered by health insurance?
- Should graffiti be considered art?
- Should all students be required to learn an instrument in school?
- Should automobile drivers be required to take a test every three years?
- Are sports cars dangerous?
- Should bicycles share the roads with cars?
- Should bicycle riders be required by law to always wear helmets?
Business and economy
- Do introverts make great leaders?
- Does owning a business leave you feeling isolated?
- What is to blame for the rise in energy prices?
- Does hiring cheaper foreign employees hurt the economy?
- Should interns be paid for their work?
- Should employees receive bonuses for walking or biking to work?
- Should tipping in restaurants be mandatory?
- Should boys and girls should be taught in separate classrooms?
- Should schools include meditation breaks during the day?
- Should students be allowed to have their mobile phones with them during school?
- Should teachers have to pass a test every decade to renew their certifications?
- Should online teaching be given equal importance as the regular form of teaching?
- Is higher education over-rated?
- What are the best ways to stop bullying?
- Should people with more than one DUI lose their drivers’ licenses?
- Should prostitution be legalised?
- Should guns be illegal in the US?
- Should cannabis be legalised for medical reasons?
- Is equality a myth?
- Does what is “right” and “wrong” change from generation to generation?
- Is there never a good enough reason to declare war?
- Should governments tax sugary drinks and use the revenue for public health?
- Has cosmetic surgery risen to a level that exceeds good sense?
- Is the fast-food industry legally accountable for obesity?
- Should school cafeterias only offer healthy food options?
- Is acupuncture a valid medical technique?
- Should assisted suicide be legal?
- Does consuming meat affect health?
- Is dieting a good way to lose weight?
Law and politics
- Should voting be made compulsory?
- Should the President (or similar position) be allowed to serve more than two terms?
- Would poverty reduce by fixing housing?
- Should drug addicts be sent for treatment in hospitals instead of prisons?
- Would it be fair for the government to detain suspected terrorists without proper trial?
- Is torture acceptable when used for national security?
- Should celebrities who break the law receive stiffer penalties?
- Should the government completely ban all cigarettes and tobacco products
- Is it wrong for the media to promote a certain beauty standard?
- Is the media responsible for the moral degradation of teenagers?
- Should advertising be aimed at children?
- Has freedom of press gone too far?
- Should prayer be allowed in public schools?
- Does religion have a place in government?
- How do cults differ from religion?
Science and the environment
- Should recycling be mandatory?
- Should genetically modified foods be sold in supermarkets?
- Should parents be allowed to choose the sex of their unborn children?
- Should selling plastic bags be completely banned in shops?
- Should smoking in public places be banned?
- Should professional female athletes be paid the same as male athletes in the same sport?
- Should doping be allowed in professional sports?
- Should schools be required to teach all students how to swim?
- How does parental pressure affect young athletes?
- Will technology reduce or increase human employment opportunities?
- What age should children be allowed to have mobile phones?
- Should libraries be replaced with unlimited access to e-books?
- Should we recognize Bitcoin as a legal currency?
- Should bloggers and vloggers be treated as journalists and punished for indiscretions?
- Has technology helped connect people or isolate them?
- Should mobile phone use in public places be regulated?
- Do violent video games make people more violent?
World peace
- What is the safest country in the world?
- Is planetary nuclear disarmament possible?
- Is the idea of peace on earth naive?
These topics are just suggestions so you need to assess whether they would be suitable for your particular audience. You can easily adapt the topics to suit your interests and audience, for example, you could substitute “meat” in the topic “Does consuming meat affect health?” for many possibilities, such as “processed foods”, “mainly vegan food”, “dairy” and so on.
After choosing your topic
After you’ve chosen your topic it’s important to do the following:
- Research thoroughly
- Think about all of the different viewpoints
- Tailor to your audience – discussing your topic with others is a helpful way to gain an understanding of your audience.
- How involved are you with this topic – are you a key character?
- Have you contributed to this area, perhaps through blogs, books, papers and products.
- How qualified are you to speak on this topic?
- Do you have personal experience in it? How many years?
- How long have you been interested in the area?
While it may be difficult to choose from such a variety of persuasive speech topics, think about which of the above you have the most knowledge of and can argue your opinion on.
For advice about how to deliver your persuasive speech, check out our blog Persuasive Speech Outline and Ideas .
100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
If you are planning a persuasive speech, you should think about a topic that can engage your audience. For this reason, you may want to consider a few topics before settling on the one that allows you to be more descriptive and entertaining.
Another important factor when picking a persuasive speech topic is to choose one that can provoke your audience. If you stir up a little emotion in your audience members, you'll keep their attention.
The list below is provided to help you brainstorm. Choose a topic from this list, or use it to generate an idea of your own. It could even be an idea that opposes the proposed example. For instance, instead of arguing American workers should be guaranteed a three-day weekend by law, you could argue why this shouldn't be the case.
How to Pick a Good Persuasive Speech Topic
Persuasive speeches are generally meant to convince an audience to agree with an idea you present. The topics can range from political to scientific or societal, and professional to personal—or even fun. They can be almost anything.
Just remember, a persuasive speech is different than a persuasive essay because you are presenting to an audience. So as you decide on a topic, think about your audience and decide on a subject matter that will be appropriate, compelling, and engaging to discuss. Perhaps it's a timely issue attracting a lot of news coverage, or maybe you want to be motivational and encourage a healthy activity. Whatever it is, structure your argument with a hook to capture attention , a clear definition of the topic or issue, and finally, your proposed solution or opinion.
100 Examples of Persuasive Speech Topics
- Studying martial arts is good for mind and health.
- Competitive sports can teach us about life.
- Reality shows are exploiting people.
- Community service should be a graduation requirement for all high school students.
- The characteristics that make a person a hero.
- It's important to grow things in a garden.
- Violent video games are dangerous.
- Lyrics in a song can impact our lives.
- Traveling and studying abroad are positive experiences.
- Journal writing is therapeutic.
- You should spend time with your grandparents.
- A laptop is better than a tablet.
- Religion and science can go hand in hand.
- School uniforms are good.
- All-female colleges and all-male colleges are bad.
- Multiple-choice tests are better than essay tests .
- We should not spend money on space exploration.
- Open-book tests are as effective as closed-book tests.
- Security cameras keep us safer.
- Parents should have access to students' grades.
- Small classes are better than big classes.
- You need to start saving for retirement now.
- Credit cards are harmful to college students.
- We should have a royal family.
- We should protect endangered animals.
- Texting while driving is dangerous.
- You can write a novel.
- Recycling should be required in the U.S.
- State colleges are better than private colleges.
- Private colleges are better than state colleges.
- We should do away with penny coins.
- Fast food containers hurt the environment.
- Plastic straws are harmful to the environment.
- You can eat and enjoy healthy snacks.
- You can become a millionaire.
- Dogs are better pets than cats.
- You should own a bird.
- It's unethical to keep birds in cages.
- Liberal arts degrees prepare graduates to be better workers than other degrees.
- Hunting animals should be banned.
- Football is a dangerous sport.
- School days should start later.
- Night school is better than day school.
- Technical training is better than a college degree.
- Immigration laws should be more lenient.
- Students should be able to choose their schools.
- Everyone should learn to play a musical instrument.
- Grass lawns should be prohibited.
- Sharks should be protected.
- We should do away with cars and go back to horse and carriage for transportation.
- We should use more wind power.
- We should pay more taxes.
- We should do away with taxes.
- Teachers should be tested like students.
- We should not interfere in the affairs of other countries.
- Every student should join a club.
- Homeschooling is better than traditional schooling.
- People should stay married for life.
- Smoking in public should be illegal.
- College students should live on campus .
- Parents should let students fail.
- Giving to charity is good.
- Education makes us happier people.
- The death penalty should be outlawed.
- Bigfoot is real.
- We should increase train travel to save the environment.
- We should read more classic books.
- Fame is bad for young children.
- Athletes should stay loyal to teams.
- We should reform our prisons.
- Juvenile offenders should not go to boot camps.
- Abraham Lincoln was the best president.
- Abraham Lincoln gets too much credit.
- Students should be allowed to have cell phones in elementary, middle, and high school.
- College student-athletes should be paid for playing.
- Elderly citizens on fixed income should receive free public transportation.
- Colleges and universities should be free to attend.
- All American citizens should complete one year of community service.
- Students should be required to take Spanish language classes.
- Every student should be required to learn at least one foreign language .
- Marijuana should be legal for recreational use nationwide.
- Commercial testing of products on animals should no longer be allowed.
- High school students should be required to participate in at least one team sport.
- The minimum drinking age in the U.S. should be 25.
- Replacing fossil fuels with cheaper alternative energy options should be mandated.
- Churches need to contribute their share of taxes.
- The Cuba embargo should be maintained by the U.S.
- America should replace income taxes with a nationwide flat tax.
- Once they reach the age of 18, all U.S. citizens should be automatically registered to vote .
- Doctor-assisted suicide should be legal.
- Spammers—people who bombard the internet with unsolicited email—should be banned from sending junk mail.
- Every automobile driver should be required to take a new driver's test every three years.
- Electroshock treatment is not a humane form of therapy.
- Global warming is not real.
- Single-parent adoption should be encouraged and promoted.
- Gun companies should be held accountable for gun crimes.
- Human cloning is not moral.
- Religion does not belong in public education.
- Juveniles should not be tried as adults.
- American workers should be guaranteed a three-day weekend by law.
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- 40 Writing Topics for Argumentative and Persuasive Essays
- Middle School Debate Topics
- How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Controversial Speech Topics
- High School Debate Topics
- Speech Topics to Meet Oral Communication Standards
- 30 Writing Topics: Persuasion
- Preparing an Argument Essay: Exploring Both Sides of an Issue
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- Impromptu Speech Activities
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- 501 Topic Suggestions for Writing Essays and Speeches
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- 50 Topics for Impromptu Student Speeches
- Deliberative Rhetoric
Example of a Persuasive Speech Global Warming

Global Warming
If you are in need of a persuasive speech for school, college or work, here is an example of a persuasive speech. It is a very informative speech, but why not have a look at the statistics on NASA’s website?
There is little doubt that the planet is warming. Over the last century, the planets temperature has risen by around 1.8 degree fahrenheit (1 degree celsius). The warmest since the mid 1800’s was the 1990s and since then only 1998 has broken this record. The hottest years recorded were 1997, 1998, 2001, 2002, 2003. In fact 14 of the hottest years on record have been in the last 15 years.
The United Nations panel on climate change projects that the global temperatures will rise 3-10 degrees fahrenheit by the century’s end – enough to have the polar caps all but melted. If the ice caps melt, a vast majority of our countries borders will be under water. Monuments and great buildings, as well as homes and lives will be under water, including New York City.
So now we know what some of the causes are for global warming, how can we as individuals do our part to help save the planet?
The answer is simpler than you may think. You don’t have to go miles away from home to protest, or spend masses of money. If you try to follow the few simple steps that I shall now give you, you will have started to help us all.
Firstly, plant a tree. This could be easier than it sounds. Join or help out a local wildlife group and ask to plant a tree. Trees, when fully grown, will help keep the planet cooler. On the same point, you could protest against the demolition of the rainforests. This is the same principle, we need the trees to cool our planet and yet they are chopping them down to create roads or homes.
Something as simple as walking instead of taking the car will help reduce pollution. As well as stopping pollution, you are giving yourself exercise, something important for our bodies. So the next time you get into your car, or your motorbike, think – do I have to make this journey by vehicle or can I walk?
When you are at home, and your getting a little cold. Put a jumper on and do not adjust the heating. The extra heat produced by our homes also affects the planet. So try wearing an extra layer in winter.
If possible, buy your fruit and vegetables from local suppliers. And try to avoid imported goods. The more foreign food that we import the more pollution from aeroplanes and boats it will create.
Keeping to the speed limit can also help the environment. The more you speed the more petrol you are going to use, making the pollution higher. Also, SUV’s make about six times their own weight in CO2 each year. A small efficient diesel car covering the same distance not only uses much less fuel; it makes two thirds less.
If possible use solar energy, after all it is free; all you need to buy is the equipment. You can get much of your hot water and heating from the sun and even generate electricity.
Reduce, reuse and recycle. Only buy what you need; don’t stock the cupboards with things you may or may not use. Reuse whatever you can, like containers and paper, and recycle what you cannot reuse. It really is as simple as that.
Finally turning off unused sources of power such as televisions and heaters will help the environment, as well as save you money.
If everybody stuck to these rules, we would be doing a great thing by protecting the earth. So please take into consideration what I have said, and try to do your part. After all, it will be our next generation that will feel the effects.
Next persuasive speech example >> Diana
Picking a topic
Informative Speech Topic
Essential Presentation Skills
Recommended Pages

thanks vary much now I can Answer my task
Tnks phoe kc nkpagreport aq ng maayoz.,tnks ng mlak
this is an excelent speech, but the opening paragraph could be slightly more grasping, as it doesn’t attract the audience too well, but an overall excellent speech 🙂
actually great speech!
This speech is very informative about what we as individuals can do but it doesn’t give a clear understanding of what affects global warming and what other problems could occur if the polar ice caps melted.The introduction could be a little bit better as it doesn’t grab the audience’s attention. The facts are very good and the things we can do to help are things I can now do to help. Overall a good speech but the intro and the other areas I commented on could be better.
Excellent speech! Can I get the name of the author?
It is copywrited to Presentation Magazine
thanks for everything <3
thx brw, this help me so much
I agree with kieran
that totaly helped me!!!!
Thankx..its help me well!!
i like it all. quite interesting!:)
sounds more like a informative speech to me
Awesome Speech!
how wonderfull
cool i loved it!
Best help ever.!!! Three cheers yay
this speech saved my day it is very interesting
great!!! it is good…
thanks so much! u saved my day! bt yeah da startng could have been a bit more interesting however overall gr8 speech!
It is very helpfull for me . I love it and thnx . I impressed my teachers and freinds ………
Thanx once again !!!!!!
thankz about the information
Omgarshhhh I’m in love with this , thank you so so so much you have made be a better persuasive writer ! You are incredible , words can’t express how I feel right now ! I’m so impacted ! Keep posting you’re doing fine ! And now can you please example please !
Great speech
Why does she didn’t address anyone who is listening or especially the audiences
Sounds great. Liked it
Fantastic speech and good information !!
thankyou, I’m getting a better a better mark for my grade 7 english
Thank u for give me idea for my speech
thats great
this website really help me understand a persuasive speech for an essay
Thank you verymuch for your global warming example that i used it as a referrence to prepare m own speech
It’s great. Thanks for this example. I really need this in our English X.
Really useful for my persuasive writing task and speech, reduce, reuse and recycle – genius!
Great! No matter wat,,I will pass speech nw
That speech is very good to the people that cannot understand the important of nature and people that cannot follow the rules
thanks a lot but it seems that I should not use A lot of quotes
This speech could use some more interesting and persuasive vocabulary in the introduction but has a great topic to focus on the entire way through and could be very useful for the reader. It gives many facts and this helps the reader develop an understanding of what could happen to the next generation as said within your speech!
This is a good speech..May I use this for my students?
thank you! It helped me
does it use rhetoric cause if it does I wanna use it nice job
gosh, our warming problems are getting worse, when will we do something? thanks for the speech!
The speech was good but not formal persuasive speech as there was no Theses and Introduction. It could have 1 or 2 lines for garbing audience’s attention. Anyways this is a very good topic for audience to persuade
good speech =)
plz give the speech about modern media
Thank you for sharing your speech
thanks…
May I know who is the author for this speech please..thanks
agree with Kieran
I like the speech thank you so much
can i know who`s the author? plzz thanks
Yes it is us – Presentation Magazine
simple but nice, thank u writer 🙂
It’s very INTRESTING
Thank you very much …..
I agree with anonymous. It really looks like an informative speech rather than a persuasive one but it’s still impressive.
- All Templates
- Persuasive Speech Topics
- Informative
- Architecture
- Celebration
- Educational
- Engineering
- Food and Drink
- Subtle Waves Template
- Business world map
- Filmstrip with Countdown
- Blue Bubbles
- Corporate 2
- Vector flowers template
- Editable PowerPoint newspapers
- Hands Template
- Red blood cells slide
- Circles Template on white
- Maps of America
- Light Streaks Business Template
- Zen stones template
- Heartbeat Template
- Web icons template
More From Forbes
The world is watching: studying javier milei.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
TOPSHOT - Argentina's President Javier Milei arrives to deliver a speech at the World Economic Forum ... [+] (WEF) meeting in Davos on January 17, 2024. (Photo by Fabrice COFFRINI / AFP) (Photo by FABRICE COFFRINI/AFP via Getty Images)
President Javier Milei’s first major international speech was at the World Economic Forum in Davos in January. Soon after, in February, he spoke at CPAC, and this week, he arrived in the United States for the fourth time since his election. This time, he speaks at the Milken Institute's global conference with many other luminaries, from several former presidents to Elon Musk and other business leaders. Milei continues to be in high demand as a speaker internationally, especially for groups championing free enterprise. This coming June 21, he will speak and receive the Juan de Mariana Award in Madrid, Spain, and in July, he will be in Nevada to speak at Freedom Fest, one of the most significant free-market events in the world.
Javier Milei, Argentina's president, during the Conservative Political Action Conference (CPAC) in ... [+] National Harbor, Maryland, US, on Saturday, Feb. 24, 2024. The Conservative Political Action Conference launched in 1974 brings together conservative organizations, elected leaders, and activists. Photographer: Kent Nishimura/Bloomberg
Why is he attracting so much attention? An Argentine economics professor earning his living as a consultant, with almost no party, no money, and a small team of confidants, with a message that went against eight decades of economic interventionist ideology and control, winning the presidency? It is as if someone were to begin to defy the laws of gravity on live TV and social media. Is it possible? Milei has seemingly pulled off a political magic trick. If Milei fulfills his promises to close the Central Bank (making the “caste,” the entrenched bureaucracies and the interests that live from it, pay most of the cost of the reforms), liberalize the economy, and unapologetically side with the West in issues of national security, he could create a ripple effect through political-economic establishments around the globe. No wonder he is being studied.
One Milei-monitoring effort is Universidad Francisco Marroquin’s UFM Reform Watch . UFM in Guatemala is a university known for its commitment to a free economy. Reform Watch aims to study the reforms conducted by Milei’s government. It is focused mainly on economics, following currency, fiscal, labor, and macroeconomic reforms. Argentine professors have been part of UFM’s faculty almost since its foundation in 1971. Articles in UFM Reform Watch’s analysis include “Milei’s Monetary Plan and Disinflation” by Argentine economist Adrian Ravier and “The Reforms Proposed In Argentina by President Milei” by former Judge Ricardo Manuel Rojas, also from Argentina. Ravier is trained in the tradition of the Austrian School of Economics and currently directs the post-graduate program on Institutional Economics and Political Science at UCEMA, Argentina’s “University of Chicago.” Judge Rojas is a professor and prolific writer who writes in the tradition of Ayn Rand's capitalist and individualist philosophy. UFM Reform Watch posts videos with past and present discussions by Javier Milei that are relevant to understanding his agenda. One of the videos highlights Javier Milei’s criticism of Keynesianism. Another, by Judge Ricardo Rojas, is about monetary inflation as theft. So far, all posted material is in Spanish.
In the United States, the Wilson Center has an Argentina Project that claims to be “the premier institution for policy-relevant research on politics and economics in Argentina.” Its activities include public events, briefings, conferences, publications, polling, and research. The Wilson Center is known for its scholarly work but not for its pro-free-market activism. Until recently, it included Francisco de Santibañes on its team. Santibañes was a Global Fellow at the Wilson Center and is now the head of the Argentine Council for International Relations (CARI), the leading Argentine think tank on international issues. He is well-versed in political economy and has held fellowships and internships at leading U.S. think tanks, including the Heritage Foundation and the Manhattan Institute. Although no longer officially at the Wilson Center, Santibañes should be able to provide sound advice to his former colleagues. I asked Santibañes how he explains the foreign interest in Milei: “I believe that the interest abroad is due to his role as a referent of the anti-establishment liberal/conservative right after Trump and Bolsonaro left power. I believe Milei generates a special interest in the United States as a possible Latin American ally at a time when it does not have many others in the region. His personality also helps him position himself in a particular way.”
New FBI Warning As Hackers Strike Email Senders Must Do This 1 Thing
Apple ipad 2024 release date: your final, complete guide to what and when, drake kendrick lamar feud timeline drive by shooting at drake s house.
Going beyond institutions, two individuals who follow Javier Milei closely and have an even broader reach than many institutions are Spanish economist Juan Ramón Rallo and libertarian U.S. influencer Austin Petersen. Rallo has almost 700,000 followers on YouTube, over 400,000 on X, and over 100,000 on Instagram. Rallo’s reach is impressive as his posts shun entertainment; he frames them as economic analysis, almost like an academic lesson. Rallo received his Ph.D. under Professor Jesús Huerta de Soto, the leading Austrian-inspired anarcho-capitalist economist whom Milei often lauds.
Economist Juan Ramon Rallo (middle) flanked by Daniel Lacalle (to his right) and Pablo Gil (left). ... [+] Rallo follows and analyzes Javier Milei economic policies very closely in his popular blog and video channel.
Austin Petersen, who competed in the presidential primaries of the Libertarian Party and is now the host of the Wake Up America show, is an active supporter and disseminator of Javier Milei’s ideas and government decisions. Many U.S. libertarians take issue with Milei’s aggressive war against drug mafias, principled pro-life stances, and warm embraces with former President Trump and the leading conservative politicians of today, from Jair Bolsonaro in Brazil to Santiago Abascal in Spain. Petersen, though, focuses on the main battle line, namely freedom versus socialism. He tells me, “I support Javier Milei because he is a credible and persuasive politician who supports the principles of limited government. His idealism is inspiring, but even more so is his practical politics. Libertarians have always failed on that front, and we need more freedom fighters like him who can advance our radical ideals in tactical ways.”
Former Libertarian presidential candidate Austin Petersen is an active promoter of the policies of ... [+] President Javier Milei
We are approaching five months with Javier Milei in office. Given the immense economic challenges he inherited, most supporters of Milei’s ideas and goals focus on his battle against inflation and government spending. Economics is essential, but Argentina faces significant challenges with its weak rule of law and external enemies who want to derail Milei’s alignment with Western powers. Chile, Argentina’s neighbor and, until recently, the model country for positive economic reforms, did not change course towards government interventionism due to economic factors. The analysis of this unique period in Argentine history, which can have profound effects in the Americas, needs to include serious efforts to monitor Milei’s government decisions on defense, intelligence, and judicial institutions. They go beyond social and economic policies but can play a decisive role in his success.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1-minute Speech on Globalisation. Ladies and Gentlemen, Globalisation means the world coming together. It's like making the whole world one big neighbourhood. Imagine your neighbourhood where everyone knows each other, shares things, and helps when needed. That's what globalisation is doing to our world.
We've compiled a list of 110 persuasive speech topics—broken down by category—for you to choose from or use as inspiration. Use the set of three questions we shared above to determine which of these interesting persuasive speech topics is right for you. Art, Media, and Culture.
The Upside of Globalization. By contrast, a persuasive essayist might argue that world poverty has shown a startling decline recently and that this process can be linked directly to globalization. A writer can also argue that there is now more information traded across and among countries, benefiting both individuals and organizations worldwide
The role of globalization in promoting peaceful societies. Globalization speech topics. Globalization and how it affects the social environment of America. Globalization of higher education affecting financial operations of colleges and universities. South Korean industry and the influence of globalization.
The Concept. It is the world economy which we think of as being globalized. We mean that the whole of the world is increasingly behaving as though it were a part of a single market, with interdependent production, consuming similar goods, and responding to the same impulses. Globalization is manifested in the growth of world trade as a ...
You can study globalization from the perspective of many topics, such as politics, ecology, countries' economies, and political sciences. Globalization essay topics may include: Positive and negative effects of globalization. The correlation between globalization and democratization: The perspective of developing countries.
By Anne O. Krueger. First Deputy Managing Director. International Monetary Fund. September 26, 2002. I. Introduction. It is a privilege to take part in your deliberations on "The New Global Context for Today's Security Environment". Supporting globalization is one of the best investments we can make to improve today's security environment.
Foundation of Persuasion. Persuasive speaking seeks to influence the beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors of audience members. In order to persuade, a speaker has to construct arguments that appeal to audience members. Arguments form around three components: claim, evidence, and warrant. The claim is the statement that will be supported by ...
So Long, Globalization? Last week I wrote about Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen's speech that was largely about China. It was followed a week later by National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan's speech on international economic policy, which is the topic of today's column. On Sullivan's speech, I have long supported the industrial policy ...
Although a persuasive speech involves information—even as much as an informative speech—the key difference is that a persuasive speech is designed for "creating, reinforcing, or changing people's beliefs or actions" (Lucas, 2015. p. 306). A persuasive speech makes something happen. In other words, it performs a job.
Persuasive Essay About Globalization; Persuasive Essay About Globalization. 1034 Words 5 Pages "Globalization is not a monolithic force but an evolving set of consequences- some good, some bad and some unintended. It is the new reality" (Larson, n.d). I remember myself asking my mom ten years ago how we could talk to someone who were so far ...
Persuasion Across Cultures. NASEER ALOMARI, PH.D. The Swedish journalist Thomas Larsson has defined globalization as "the process of world shrinkage, of distances getting shorter, things moving closer. It pertains to the increasing ease with which somebody on one side of the world can interact, to mutual benefit, with somebody on the other ...
Gender Inequality as a Global Issue. This essay will examine some of the causes that affect the gap in the treatment of men and women, and its ramifications, particularly regarding developing countries. We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 809 writers online. Learn More.
112 Engaging Persuasive Speech Topics. Tips for Preparing Your Persuasive Speech. Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your ...
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples. A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything - voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on. A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing ...
Video playlists about Global issues. TED Explains the World with Ian Bremmer dives into complex geopolitical issues to explore what really matters in the critical news stories of the day. This special series — a partnership with political scientist Ian Bremmer, president and founder of Eurasia Group and GZERO Media — takes us behind the ...
The tax administration reform´s next steps should focus on the use of information technology and third-party data to enhance timely voluntary tax compliance, enforce accurate reporting, and incentivize and monitor revenue mobilization. The TA report also reviewed the next steps to the Value-Added Tax implementation. May 1, 2024.
The three main types of persuasive speeches are factual, value, and policy. A factual persuasive speech focuses solely on factual information to prove the existence or absence of something through substantial proof. This is the only type of persuasive speech that exclusively uses objective information rather than subjective.
Globalization Persuasive Speech. 1496 Words6 Pages. Opening/Attention: First let me introduce you to my topic. The greatest weapon of mass destruction is corporate economic globalization. From dawn to dusk, even all the food items we consume, we use 99% of the corporate products. It can be waking up to an alarm clock made in China, downing a ...
The aim of a persuasive speech is to inform, educate and convince or motivate an audience to do something. You are essentially trying to sway the audience to adopt your own viewpoint. The best persuasive speech topics are thought-provoking, daring and have a clear opinion. You should speak about something you are knowledgeable about and can ...
100 Examples of Persuasive Speech Topics. Studying martial arts is good for mind and health. Competitive sports can teach us about life. Reality shows are exploiting people. Community service should be a graduation requirement for all high school students. The characteristics that make a person a hero.
If everybody stuck to these rules, we would be doing a great thing by protecting the earth. So please take into consideration what I have said, and try to do your part. After all, it will be our next generation that will feel the effects. Next persuasive speech example >> Diana. Picking a topic.
After years of shocks—including the COVID-19 pandemic and Russia's invasion of Ukraine—countries are reevaluating their trading partners based on economic and national security concerns. Foreign direct investment flows are also being re-directed along geopolitical lines. Some countries are reevaluating their heavy reliance on the dollar in their international transactions and reserve ...
President Javier Milei's first major international speech was at the World Economic Forum in Davos in January. Soon after, in February, he spoke at CPAC, and this week, he arrived in the United ...