Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Pregnancy week by week
- Fetal presentation before birth
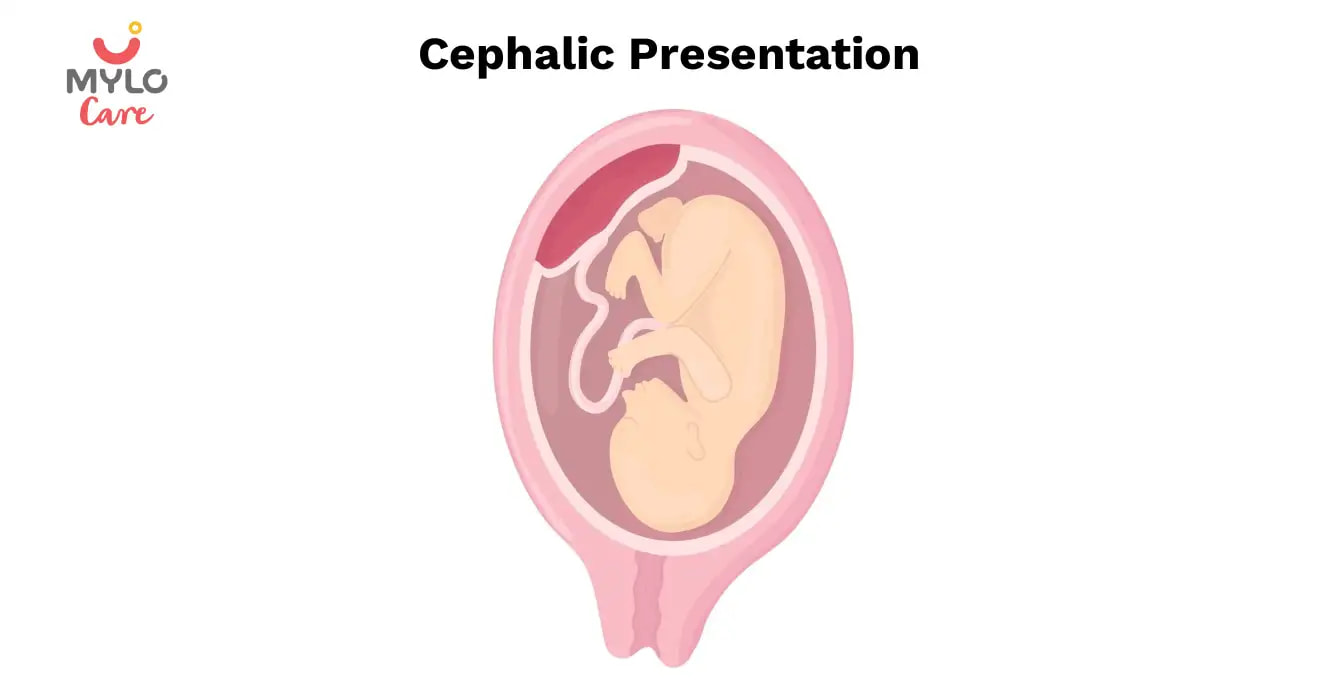
The way a baby is positioned in the uterus just before birth can have a big effect on labor and delivery. This positioning is called fetal presentation.
Babies twist, stretch and tumble quite a bit during pregnancy. Before labor starts, however, they usually come to rest in a way that allows them to be delivered through the birth canal headfirst. This position is called cephalic presentation. But there are other ways a baby may settle just before labor begins.
Following are some of the possible ways a baby may be positioned at the end of pregnancy.

Head down, face down
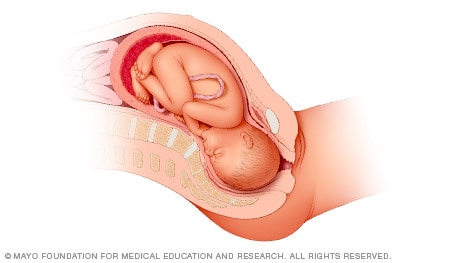
When a baby is head down, face down, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput anterior position. This the most common position for a baby to be born in. With the face down and turned slightly to the side, the smallest part of the baby's head leads the way through the birth canal. It is the easiest way for a baby to be born.
Head down, face up
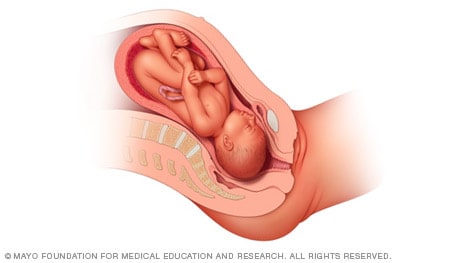
When a baby is head down, face up, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput posterior position. In this position, it might be harder for a baby's head to go under the pubic bone during delivery. That can make labor take longer.
Most babies who begin labor in this position eventually turn to be face down. If that doesn't happen, and the second stage of labor is taking a long time, a member of the health care team may reach through the vagina to help the baby turn. This is called manual rotation.
In some cases, a baby can be born in the head-down, face-up position. Use of forceps or a vacuum device to help with delivery is more common when a baby is in this position than in the head-down, face-down position. In some cases, a C-section delivery may be needed.
Frank breech
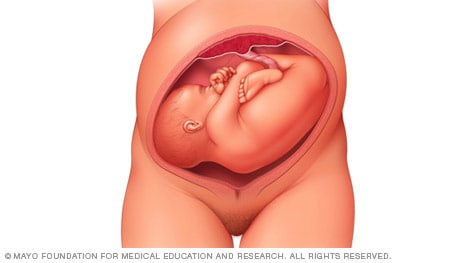
When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a frank breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Most babies in a frank breech position are born by planned C-section.

Complete and incomplete breech
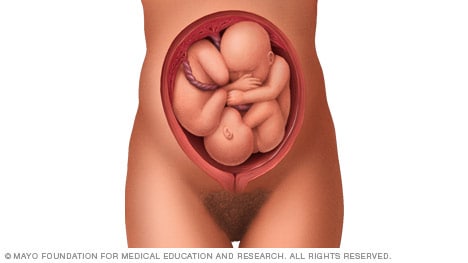
A complete breech presentation, as shown below, is when the baby has both knees bent and both legs pulled close to the body. In an incomplete breech, one or both of the legs are not pulled close to the body, and one or both of the feet or knees are below the baby's buttocks. If a baby is in either of these positions, you might feel kicking in the lower part of your belly.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a complete or incomplete breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies in a complete or incomplete breech position are born by planned C-section.

When a baby is sideways — lying horizontal across the uterus, rather than vertical — it's called a transverse lie. In this position, the baby's back might be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal.
- Sideways, with one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal.
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal.
Although many babies are sideways early in pregnancy, few stay this way when labor begins.
If your baby is in a transverse lie during week 37 of your pregnancy, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of your health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a transverse lie, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies who are in a transverse lie are born by C-section.
If you're pregnant with twins and only the twin that's lower in the uterus is head down, as shown below, your health care provider may first deliver that baby vaginally.
Then, in some cases, your health care team may suggest delivering the second twin in the breech position. Or they may try to move the second twin into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
Your health care team may suggest delivery by C-section for the second twin if:
- An attempt to deliver the baby in the breech position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to have the baby delivered vaginally in the breech position.
- An attempt to move the baby into a head-down position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to move the baby to a head-down position.
In some cases, your health care team may advise that you have both twins delivered by C-section. That might happen if the lower twin is not head down, the second twin has low or high birth weight as compared to the first twin, or if preterm labor starts.
- Landon MB, et al., eds. Normal labor and delivery. In: Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Holcroft Argani C, et al. Occiput posterior position. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Frequently asked questions: If your baby is breech. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/if-your-baby-is-breech. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Hofmeyr GJ. Overview of breech presentation. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Strauss RA, et al. Transverse fetal lie. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Chasen ST, et al. Twin pregnancy: Labor and delivery. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Cohen R, et al. Is vaginal delivery of a breech second twin safe? A comparison between delivery of vertex and non-vertex second twins. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2021; doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005569.
- Marnach ML (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. May 31, 2023.
Products and Services
- A Book: Obstetricks
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- 3rd trimester pregnancy
- Fetal development: The 3rd trimester
- Overdue pregnancy
- Pregnancy due date calculator
- Prenatal care: 3rd trimester
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
Make twice the impact
Your gift can go twice as far to advance cancer research and care!
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Key Points |
Abnormal fetal lie or presentation may occur due to fetal size, fetal anomalies, uterine structural abnormalities, multiple gestation, or other factors. Diagnosis is by examination or ultrasonography. Management is with physical maneuvers to reposition the fetus, operative vaginal delivery , or cesarean delivery .
Terms that describe the fetus in relation to the uterus, cervix, and maternal pelvis are
Fetal presentation: Fetal part that overlies the maternal pelvic inlet; vertex (cephalic), face, brow, breech, shoulder, funic (umbilical cord), or compound (more than one part, eg, shoulder and hand)
Fetal position: Relation of the presenting part to an anatomic axis; for transverse presentation, occiput anterior, occiput posterior, occiput transverse
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse
Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position.
Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with
Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
Fetal congenital anomalies
Uterine structural abnormalities (eg, fibroids, synechiae)
Multiple gestation
Several common types of abnormal lie or presentation are discussed here.

Transverse lie
Fetal position is transverse, with the fetal long axis oblique or perpendicular rather than parallel to the maternal long axis. Transverse lie is often accompanied by shoulder presentation, which requires cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation
There are several types of breech presentation.
Frank breech: The fetal hips are flexed, and the knees extended (pike position).
Complete breech: The fetus seems to be sitting with hips and knees flexed.
Single or double footling presentation: One or both legs are completely extended and present before the buttocks.
Types of breech presentations
Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the presenting part is narrower than the head that follows. The head, which is the part with the largest diameter, can then be trapped during delivery.
Additionally, the trapped fetal head can compress the umbilical cord if the fetal umbilicus is visible at the introitus, particularly in primiparas whose pelvic tissues have not been dilated by previous deliveries. Umbilical cord compression may cause fetal hypoxemia.

Predisposing factors for breech presentation include
Preterm labor
Uterine abnormalities
Fetal anomalies
If delivery is vaginal, breech presentation may increase risk of
Umbilical cord prolapse
Birth trauma
Perinatal death

Face or brow presentation
In face presentation, the head is hyperextended, and position is designated by the position of the chin (mentum). When the chin is posterior, the head is less likely to rotate and less likely to deliver vaginally, necessitating cesarean delivery.
Brow presentation usually converts spontaneously to vertex or face presentation.
Occiput posterior position
The most common abnormal position is occiput posterior.
The fetal neck is usually somewhat deflexed; thus, a larger diameter of the head must pass through the pelvis.
Progress may arrest in the second phase of labor. Operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
Position and Presentation of the Fetus
If a fetus is in the occiput posterior position, operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord.
For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.

- Learn /
Why Is Cephalic Presentation Ideal For Childbirth?

5 Dec 2017 | 8 min Read
During labour, contractions stretch your birth canal so that your baby has adequate room to come through during birth. The cephalic presentation is the safest and easiest way for your baby to pass through the birth canal.
If your baby is in a non-cephalic position, delivery can become more challenging. Different fetal positions pose a range of difficulties and varying risks and may not be considered ideal birthing positions.
Two Kinds of Cephalic Positions
There are two kinds of cephalic positions:
- Cephalic occiput anterior , where your baby’s head is down and is facing toward your back.
- Cephalic occiput posterior , where your baby is positioned head down, but they are facing your abdomen instead of your back. This position is also nicknamed ‘sunny-side-up’ and can increase the chances of prolonged and painful delivery.
How to Know if Your Baby is In a Cephalic Position?
You can feel your baby’s position by rubbing your hand on your belly. If you feel your little one’s stomach in the upper stomach, then your baby is in a cephalic position. But if you feel their kicks in the lower stomach, then it could mean that your baby is in a breech position.
You can also determine whether your baby is in the anterior or posterior cephalic position. If your baby is in the anterior position, you may feel their movement underneath your ribs and your belly button could also pop out. If your baby is in the posterior position, then you may feel their kicks in their abdomen, and your stomach may appear rounded up instead of flat.
You can also determine your baby’s position through an ultrasound scan or a physical examination at your healthcare provider’s office.
Benefits of Cephalic Presentation in Pregnancy
Cephalic presentation is one of the most ideal birth positions, and has the following benefits:
- It is the safest way to give birth as your baby’s position is head-down and prevents the risk of any injuries.
- It can help your baby move through the delivery canal as safely and easily as possible.
- It increases the chances of smooth labour and delivery.
Are There Any Risks Involved in Cephalic Position?
Conditions like a cephalic posterior position in addition to a narrow pelvis of the mother can increase the risk of pregnancy complications during delivery. Some babies in the head-first cephalic presentation might have their heads tilted backward. This may, in some rare cases, cause preterm delivery.
What are the Risks Associated with Other Birth Positions?
A small percentage of babies may settle into a non-cephalic position before their birth. This can pose risks to both your and your baby’s health, and also influence the way in which you deliver.
In the next section, we have discussed a few positions that your baby can settle in throughout pregnancy, as they move around the uterus. But as they grow old, there will be less space for them to tumble around, and they will settle into their final position. This is when non-cephalic positions can pose a risk.
Breech Position
There are three types of breech fetal positioning:
- Frank breech : Your baby’s legs stick straight up along with their feet near their head.
- Footling breech: One or both of your baby’s legs are lowered over your cervix.
- Complete breech: Your baby is positioned bottom-first with their knees bent.
If your baby is in a breech position , vaginal delivery is considered complicated. When a baby is born in breech position, the largest part of their body, that is, their head is delivered last. This can lead to injury or even fetal distress. Moreover, the umbilical cord may also get damaged or get wrapped around your baby’s neck, cutting off their oxygen supply.
If your baby is in a breech position, your healthcare provider may recommend a c-section, or they may try ways to flip your baby’s position in a cephalic presentation.
Transverse Lie
In this position, your baby settles in sideways across the uterus rather than being in a vertical position. They may be:
- Head-down, with their back facing the birth canal
- One shoulder pointing toward the birth canal
- Up with their hands and feet facing the birth canal
If your baby settles in this position, then your healthcare provider may suggest a c-section to reduce the risk of distress in your baby and other pregnancy complications.
Turning Your Baby Into A Cephalic Position
External cephalic version (ECV) is a common, and non-invasive procedure that helps turn your baby into a cephalic position while they are in the womb. However, your healthcare provider may only consider this procedure if they consider you have a stable health condition in the last trimester, and if your baby hasn’t changed their position by the 36th week.
You can also try some natural remedies to change your baby’s position, such as:
- Lying in a bridge position: Movements like bridge position can sometimes help move your baby into a more suitable position. Lie on your back with your feet flat on the ground and your legs bent. Raise your pelvis and hips into a bridge position and hold for 5-10 minutes. Repeat several times daily.
- Chiropractic care: A chiropractor can help with the adjustment of your baby’s position and also reduce stress in them.
- Acupuncture: After your doctor’s go-ahead, you can also consider acupuncture to get your baby to settle into an ideal birthing position.
While most babies settle in a cephalic presentation by the 36th week of pregnancy, some may lie in a breech or transverse position before birth. Since the cephalic position is considered the safest, your doctor may recommend certain procedures to flip your baby’s position to make your labour and delivery smooth. You may also try the natural methods that we discussed above to get your baby into a safe birthing position and prevent risks or other pregnancy complications.
When Should A Baby Be In A Cephalic Position?
Your baby would likely naturally drop into a cephalic position between weeks 37 to 40 of your pregnancy .
Is Cephalic Position Safe?
Research shows that 95% of babies take the cephalic position a few weeks or days before their due date. It is considered to be the safest position. It ensures a smooth birthing process.
While most of the babies are in cephalic position at delivery, this is not always the case. If you have a breech baby, you can discuss the available options for delivery with your doctor.
Does cephalic presentation mean labour is near?
Head-down is the ideal position for your baby within your uterus during birth. This is known as the cephalic position. This posture allows your baby to pass through the delivery canal more easily and safely.
Can babies change from cephalic to breech?
The external cephalic version (ECV) is the most frequent procedure used for turning a breech infant.
How can I keep my baby in a cephalic position?
While your baby naturally gets into this position, you can try some exercises to ensure that they settle in cephalic presentation. Exercises such as breech tilt, forward-leaning position (spinning babies program), cat and camel pose can help.
Stitches after a normal delivery : How many stitches do you need after a vaginal delivery? Tap this post to know.
Vaginal birth after caesarean delivery : Learn all about the precautions to consider before having a vaginal delivery after a c-section procedure.
How many c-sections can you have : Tap this post to know the total number of c-sections that you can safely have.
Cover Image Credit: Freepik.com

Related Topics for you
babychakraenglish
cephalicposition
cephalicpresentation
fetaldevelopment
fetalmovement
preganancycare
Suggestions offered by doctors on BabyChakra are of advisory nature i.e., for educational and informational purposes only. Content posted on, created for, or compiled by BabyChakra is not intended or designed to replace your doctor's independent judgment about any symptom, condition, or the appropriateness or risks of a procedure or treatment for a given person.
Need to talk? Call 1800 882 436. It's a free call with a maternal child health nurse. *call charges may apply from your mobile
Is it an emergency? Dial 000 If you need urgent medical help, call triple zero immediately.
Share via email
There is a total of 5 error s on this form, details are below.
- Please enter your name
- Please enter your email
- Your email is invalid. Please check and try again
- Please enter recipient's email
- Recipient's email is invalid. Please check and try again
- Agree to Terms required
Error: This is required
Error: Not a valid value
Presentation and position of baby through pregnancy and at birth
9-minute read
If you are concerned about your baby’s movements, contact your doctor or midwife for advice immediately.
- If you baby is in a breech presentation, your doctor may recommend trying a technique called an external cephalic version to try and move your baby while they are still in the uterus for an easier birth.
What does presentation and position mean?
Presentation refers to the part of your baby’s body that is facing downwards in the direction of the birth canal.
Position refers to where your baby’s occiput (the bottom part of the back of their head) is in relation to your body.
If your baby is in a breech presentation , then position refers to where your baby’s sacrum (lower back) is in relation to your body.
People — including medical professionals — sometimes use these terms incorrectly. Sometimes when speaking about babies in breech presentation, the word ‘position’ will be used to refer to their presentation. For example, you may read information or hear people say ‘breech position’ instead of ‘breech presentation’.
What are the different types of presentation my baby could be in during pregnancy and birth?
Most babies present headfirst, also known as cephalic presentation. Most babies that are headfirst will be vertex presentation. This means that the crown of their head sits at the opening of your birth canal.
In rare cases, your baby can be headfirst but in face or brow presentation, which may not be suitable for vaginal birth.

If your baby is in a breech presentation, their feet or bottom will be closest to your birth canal. The 3 most common types of breech presentation are:
- frank or extended breech — where your baby’s legs are straight up in front of their body, with their feet up near their face
- complete or flexed breech — where your baby is in a sitting position with their legs crossed in front of their body and their feet near their bottom
- footling breech — where one or both of your baby’s feet are hanging below their bottom, so the foot or feet are coming first
Read more on breech presentation .
What are the different positions my baby could be in during pregnancy and birth?
If your baby is headfirst, the 3 main types of presentation are:
- anterior – when the back of your baby’s head is at the front of your belly
- lateral – when the back of your baby’s head is facing your side
- posterior – when the back of your baby’s head is towards your back

How will I know what presentation and position my baby is in?
Your doctor or midwife can usually work out your baby’s presentation by feeling your abdomen. They may also double check it with a portable ultrasound. Your baby’s presentation is usually checked around 36 weeks .
Your doctor or midwife will also confirm your baby’s head position in labour by examining your belly and using an ultrasound , and they may also do a vaginal examination . During the vaginal examination they are feeling for certain ridges on your baby’s head called sutures and fontanelles that help them work out which way your baby is positioned.
What is the ideal presentation and position for baby to be in for a vaginal birth?
For a vaginal birth, your baby will ideally be headfirst with the back of their head at the front of your belly, also known as being in the anterior position. This position is best for labour and birth since it means that the smallest part of your baby’s head goes down the birth canal first.

When does a baby usually get in the ideal presentation and position for birth?
Your baby will usually be in a headfirst position by 37 weeks of pregnancy. Around 3 in every 100 babies will be in breech presentation after 37 weeks.
Your baby’s position can change with your contractions during labour as they move down the birth canal, so their exact position can change during labour.
What are my options if baby isn't in the ideal presentation or position for a vaginal birth?
If your baby is in a breech presentation, your doctor may recommend a technique called an external cephalic version (ECV) to try and move your baby while they are still in the uterus . An ECV involves your doctor using their hands to apply pressure on your belly and help turn your baby to a headfirst position. It has a 1 in 2 chance of success and is a safe option in most pregnancies.
There is no evidence to show that alternative therapies, such as exercises, acupuncture or chiropractic treatments, help your baby change from a breech presentation to headfirst.
If your baby remains breech, your doctor may discuss having a breech vaginal birth. Not all doctors and hospitals offer this option. They may also suggest you birth your baby with a planned caesarean section .
If your baby’s presentation is headfirst but the position of your baby’s head is not ideal for labour, it can lead to a longer labour, and potential complications . The position of your baby’s head will often change as your labour progresses. If it doesn’t, sometimes you can still give birth without assistance, or you may need your doctor to help turn your baby’s head or help your birth with a vacuum or forceps .
Any procedure or decision for a type of birth will only go ahead with your consent . You will be able to discuss all the options with your doctor, and based on your preferences for yourself and your baby’s safety, make a decision together .
Resources and support
The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology has a factsheet about the options available to you if your baby is in a breech presentation at the end of your pregnancy .
Mercy Perinatal has information on external cephalic version (ECV) safety and benefits if your baby is in a breech presentation at the end of your pregnancy.
The Women’s Hospital has information about the different presentations and positions your baby could be in, and how it can affect your birthing experience.

Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call . Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content .
Last reviewed: October 2023
Related pages
External cephalic version (ecv), malpresentation, breech pregnancy, search our site for.
- Foetal Version
- Breech Presentation
Need more information?
Top results
Breech presentation and turning the baby
In preparation for a safe birth, your health team will need to turn your baby if it is in a bottom first ‘breech’ position.
Read more on WA Health website

Breech Presentation at the End of your Pregnancy
Breech presentation occurs when your baby is lying bottom first or feet first in the uterus (womb) rather than the usual head first position. In early pregnancy, a breech position is very common.
Read more on RANZCOG - Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists website

External Cephalic Version for Breech Presentation - Pregnancy and the first five years
This information brochure provides information about an External Cephalic Version (ECV) for breech presentation
Read more on NSW Health website

When a baby is positioned bottom-down late in pregnancy, this is called the breech position. Find out about 3 main types and safe birthing options.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website

Malpresentation is when your baby is in an unusual position as the birth approaches. Sometimes it’s possible to move the baby, but a caesarean maybe safer.
Labour complications
Even if you’re healthy and well prepared for childbirth, there’s always a chance of unexpected problems. Learn more about labour complications.
ECV is a procedure to try to move your baby from a breech position to a head-down position. This is performed by a trained doctor.
Having a baby
The articles in this section relate to having a baby – what to consider before becoming pregnant, pregnancy and birth, and after your baby is born.
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth - pelvis
Your pelvis helps to carry your growing baby and is tailored for vaginal births. Learn more about the structure and function of the female pelvis.
Birth injury (to the baby)
Giving birth in Australia is very safe, but sometimes during birth, the baby suffers an injury. Learn about birth injury causes, types and treatments.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Call us and speak to a Maternal Child Health Nurse for personal advice and guidance.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Government Accredited with over 140 information partners
We are a government-funded service, providing quality, approved health information and advice

Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
© 2024 Healthdirect Australia Limited
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
Fetal Positions for Labor and Birth
Knowing your baby's position can you help ease pain and speed up labor
In the last weeks of pregnancy , determining your baby's position can help you manage pain and discomfort. Knowing your baby's position during early labor can help you adjust your own position during labor and possibly even speed up the process.
Right or Left Occiput Anterior
Illustration by JR Bee, Verywell
Looking at where the baby's head is in the birth canal helps determine the fetal position.The front of a baby's head is referred to as the anterior portion and the back is the posterior portion. There are two different positions called occiput anterior (OA) positions that may occur.
The left occiput anterior (LOA) position is the most common in labor. In this position, the baby's head is slightly off-center in the pelvis with the back of the head toward the mother's left thigh.
The right occiput anterior (ROA) presentation is also common in labor. In this position, the back of the baby is slightly off-center in the pelvis with the back of the head toward the mother's right thigh.
In general, OA positions do not lead to problems or additional pain during labor or birth.
Right or Left Occiput Transverse
Illustration by JR Bee, Verywell
When facing out toward the mother's right thigh, the baby is said to be left occiput transverse (LOT). This position is halfway between a posterior and anterior position. If the baby was previously in a posterior position (in either direction), the LOT position indicates positive movement toward an anterior position.
When the baby is facing outward toward the mother's left thigh, the baby is said to be right occiput transverse (ROT). Like the previous presentation, ROT is halfway between a posterior and anterior position. If the baby was previously in a posterior position, ROT is a sign the baby is making a positive move toward an anterior position.
When a baby is in the left occiput transverse position (LOT) or right occiput transverse (ROT) position during labor, it may lead to more pain and a slower progression.
Tips to Reduce Discomfort
There are several labor positions a mother can try to alleviate pain and encourage the baby to continue rotating toward an anterior position, including:
- Pelvic tilts
- Standing and swaying
A doula , labor nurse, midwife , or doctor may have other suggestions for positions.
Right or Left Occiput Posterior
When facing forward, the baby is in the occiput posterior position. If the baby is facing forward and slightly to the left (looking toward the mother's right thigh) it is in the left occiput posterior (LOP) position. This presentation can lead to more back pain (sometimes referred to as " back labor ") and slow progression of labor.
In the right occiput posterior position (ROP), the baby is facing forward and slightly to the right (looking toward the mother's left thigh). This presentation may slow labor and cause more pain.
To help prevent or decrease pain during labor and encourage the baby to move into a better position for delivery, mothers can try a variety of positions, including:
- Hands and knees
- Pelvic rocking
Mothers may try other comfort measures, including:
- Bathtub or shower (water)
- Counter pressure
- Movement (swaying, dancing, sitting on a birth ball )
- Rice socks (heat packs)
How a Doctor Determines Baby's Position
Leopold's maneuvers are a series of hands-on examinations your doctor or midwife will use to help determine your baby's position. During the third trimester , the assessment will be done at most of your prenatal visits. Knowing the baby's position before labor begins can help you prepare for labor and delivery.
Once labor begins, a nurse, doctor, or midwife will be able to get a more accurate sense of your baby's position by performing a vaginal exam. When your cervix is dilated enough, the practitioner will insert their fingers into the vagina and feel for the suture lines of the baby's skull as it moves down in the birth canal. It's important to ensure the baby is head down and moving in the right direction.
Labor and delivery may be more complicated if the baby is not in a head-down position, such as in the case of a breech presentation.
How You Can Determine Baby's Position
While exams by health practitioners are an important part of your care, from the prenatal period through labor and delivery, often the best person to assess a baby's position in the pelvis is you. Mothers should pay close attention to how the baby moves and where different movements are felt.
A technique called belly mapping can help mothers ask questions of themselves to assess their baby's movement and get a sense of the position they are in as labor approaches.
For example, the position of your baby's legs can be determined by asking questions about the location and strength of the kicking you feel. The spots where you feel the strongest kicks are most likely where your baby's feet are.
Other landmarks you can feel for include a large, flat plane, which is most likely your baby's back. Sometimes you can feel the baby arching his or her back.
At the top or bottom of the flat plane, you may feel either a hard, round shape (most likely your baby's head) or a soft curve (most likely to be your baby's bottom).
Guittier M, Othenin-Girard V, de Gasquet B, Irion O, Boulvain M. Maternal positioning to correct occiput posterior fetal position during the first stage of labour: a randomised controlled trial . BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology . 2016;123(13):2199-2207. doi:10.1111/1471-0528.13855
Gizzo S, Di Gangi S, Noventa M, Bacile V, Zambon A, Nardelli G. Women’s Choice of Positions during Labour: Return to the Past or a Modern Way to Give Birth? A Cohort Study in Italy . Biomed Res Int . 2014;2014:1-7. doi:10.1155/2014/638093
Ahmad A, Webb S, Early B, Sitch A, Khan K, MacArthur C. Association between fetal position at onset of labor and mode of delivery: a prospective cohort study . Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology . 2014;43(2):176-182. doi:10.1002/uog.13189
Nishikawa M, Sakakibara H. Effect of nursing intervention program using abdominal palpation of Leopold’s maneuvers on maternal-fetal attachment . Reprod Health . 2013;10(1). doi:10.1186/1742-4755-10-12
Choi S, Park Y, Lee D, Ko H, Park I, Shin J. Sonographic assessment of fetal occiput position during labor for the prediction of labor dystocia and perinatal outcomes . The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine . 2016;29(24):3988-3992. doi:10.3109/14767058.2016.1152250
Bamberg C, Deprest J, Sindhwani N et al. Evaluating fetal head dimension changes during labor using open magnetic resonance imaging . J Perinat Med . 2017;45(3). doi:10.1515/jpm-2016-0005
Gabbe S, Niebyl J, Simpson J et al. Obstetrics . Philadelphia, Pa.: Elsevier; 2012.
By Robin Elise Weiss, PhD, MPH Robin Elise Weiss, PhD, MPH is a professor, author, childbirth and postpartum educator, certified doula, and lactation counselor.
Article Continues below advertisement

In this Article
The ABCs of Cephalic Presentation: A Comprehensive Guide for Moms-to-Be
Updated on 24 November 2023
As expectant mothers eagerly anticipate the arrival of their little ones, understanding the intricacies of pregnancy becomes crucial. One term that frequently arises in discussions about childbirth is "cephalic presentation." In this article, we will understand its meaning, types, benefits associated with it, the likelihood of normal delivery and address common concerns expectant mothers might have.
What is the meaning of cephalic presentation in pregnancy?
Cephalic presentation means the baby's head is positioned down towards the birth canal, which is the ideal fetal position for childbirth. This position is considered optimal for a smoother and safer delivery. In medical terms, a baby in cephalic presentation is said to be in a "vertex" position.
The majority of babies naturally assume a cephalic presentation before birth. Other presentations, such as breech presentation (where the baby's buttocks or feet are positioned to enter the birth canal first) or transverse presentation (where the baby is lying sideways), may complicate the delivery process and may require medical intervention.
Cephalic presentation types
There are different types of cephalic presentation, each influencing the birthing process. The primary types include:
1. Vertex Presentation
Article continues below advertisment
2. Brow Presentation
The baby's head is slightly extended, and the forehead presents first.
3. Face Presentation
The baby is positioned headfirst, but the face is the presenting part instead of the crown of the head.
Understanding these variations is essential for expectant mothers and healthcare providers to navigate potential challenges during labor.
You may also like: How to Get Baby in Right Position for Birth?
What are the benefits of cephalic presentation?
1. easier engagement.
This presentation facilitates the baby's engagement in the pelvis, aiding in a smoother descent during labor.
2. Reduced Risk of Complications
Babies in head-first position typically experience fewer complications during delivery compared to other presentations.
3. Faster Labor Progression
This position is associated with quicker labor progression, leading to a potentially shorter and less stressful birthing process.
4. Lower Cesarean Section Rates
The chances of a cesarean section are significantly reduced when the baby is in cephalic presentation in pregnancy.
5. Optimal Fetal Oxygenation
What are the chances of normal delivery in cephalic presentation.
The chances of a normal delivery are significantly higher when the baby is in cephalic or head-first presentation. Vaginal births are the natural outcome when the baby's head leads the way, aligning with the natural mechanics of childbirth.
While this presentation increases the chances of a normal delivery, it's important to note that individual factors, such as the mother's pelvic shape, the size of the baby, and the progress of labor, can also influence the delivery process. Sometimes complications may arise during labor and medical interventions or a cesarean section may be necessary.
You may also like: Normal Delivery Tips: An Expecting Mother's Guide to a Smooth Childbirth Experience
How to achieve cephalic presentation in pregnancy?
While fetal positioning is largely influenced by genetic and environmental factors, there are strategies to encourage head-first fetal position:
1. Regular Exercise
2. correct posture.
Maintaining good posture, particularly during the third trimester , can influence fetal positioning.
3. Hands and Knees Position
Spend some time on your hands and knees. This position may help the baby settle into the pelvis with the head down.

4. Forward-leaning Inversion
Under the guidance of a qualified professional, some women try forward-leaning inversions to encourage the baby to move into a head-down position. This involves positioning the body with the hips higher than the head.
5. Prenatal Yoga
Prenatal yoga focuses on strengthening the pelvic floor and promoting flexibility, potentially aiding in cephalic presentation.
6. Professional Guidance
1. cephalic presentation is good or bad.
Cephalic position is generally considered good as it aligns with the natural process of childbirth. It reduces the likelihood of complications and increases the chances of a successful vaginal delivery . However, it's essential to note that the overall health of both the mother and baby determines its appropriateness.
2. How to increase the chances of normal delivery in cephalic presentation?
Increasing the chances of normal delivery in cephalic presentation involves adopting healthy practices during pregnancy, such as maintaining good posture, engaging in appropriate exercises, and seeking professional guidance. However, individual circumstances vary, and consultation with a healthcare provider is paramount.
Final Thoughts
Navigating the journey of pregnancy involves understanding various aspects, and cephalic presentation plays a crucial role in determining the birthing experience. The benefits of a head-first position, coupled with strategies to encourage it, empower expectant mothers to actively participate in promoting optimal fetal positioning. As always, consulting with healthcare professionals ensures personalized care and guidance, fostering a positive and informed approach towards childbirth.
2. Boos R, Hendrik HJ, Schmidt W. (1987). Das fetale Lageverhalten in der zweiten Schwangerschaftshälfte bei Geburten aus Beckenendlage und Schädellage [Behavior of fetal position in the 2d half of pregnancy in labor with breech and vertex presentations]. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd

Anupama Chadha
Anupama Chadha, born and raised in Delhi is a content writer who has written extensively for industries such as HR, Healthcare, Finance, Retail and Tech.
Get baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
ಬೇಬಿ ತೂಕ ಚಾರ್ಟ್: ಬೆಳವಣಿಗೆಯ ಮಾದರಿಗಳಿಗೆ ಭಾರತೀಯ ಪೋಷಕರ ಮಾರ್ಗದರ್ಶಿ | baby weight chart: an indian parent's guide to growth patterns in kannada.

ನಿಮ್ಮ ಮೊದಲ ತ್ರೈಮಾಸಿಕದಲ್ಲಿ ನಿಮ್ಮ ಜೀವ ಉಳಿಸುವ 14 ಸಲಹೆಗಳು | 14 Lifesavers For Your First Trimester in Kannada

What are the home remedies to get rid of mosquitoes in Hindi |मच्छर भगाने के घरेलू उपाय क्या हैं

Menstrual cup use in Hindi | मेंस्ट्रुअल कप क्या है और कैसे करें इसका उपयोग
Related questions, influenza and boostrix injection kisiko laga hai kya 8 month pregnancy me and q lagta hai ye plz reply me, hai.... my last period was in feb 24. i tested in 40 th day morning 3:30 .. that is faint line .. i conculed mylo thz app also.... and i asked tha dr wait for 3 to 5 days ... im also waiting ... then i test today 4:15 test is sooooo faint ... and i feel in ma body no pregnancy symptoms. what can i do ., baby kicks kb marta hai plz tell mi, pcod kya hota hai, how to detect pcos, related topics, labour & delivery, baby movements, tips for normal delivery, recently published articles, our most recent articles.

Diet & Nutrition
The Ultimate Guide to Consuming Chia Seeds in Pregnancy

Essential Tips for Normal Delivery After Cesarean

Crab During Pregnancy: Benefits, Risks and Smart Choices

Normal Delivery Tips: An Expecting Mother's Guide to a Smooth Childbirth Experience

Top 10 Panchatantra Stories in English You Must Read to Your Children

Health & Wellness
What Helps in Improving Mental Health of Women
- Childhood Disorders: Meaning, Symptoms & Treatment
- Bleeding During Pregnancy 8 Weeks: Should You See a Doctor?
- The Ultimate Guide to Having Sex After C Section
- The Ultimate Guide to Baby Brain Development Food During Pregnancy
- Nappy Rash: Your Ultimate Guide to Symptoms and Quick Relief
- How to Get Periods Immediately to Avoid Pregnancy?
- Loss of Appetite During Pregnancy: Causes and Solutions
- How to Increase Newborn Baby Weight: Expert Tips and Tricks
- Fertisure M: The Comprehensive Solution to Male Infertility and Reproductive Health
- All You Need to Know About the New COVID Variant: Pirola
- Endometrial Polyp and Pregnancy: How Uterine Polyps Can Affect Your Chances of Conception
- How to Stop Heavy Bleeding During Periods: Home Remedies (Part 2)
- How Many Times Should You Have Sex to Get Pregnant?
- A Guide to Planning the Perfect Godh Bharai for the Mom-to-Be
Start Exploring

- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
baby carrier | baby soap | baby wipes | baby shampoo | baby lotion | baby powder | baby body wash | stretch marks cream | stretch marks oil | baby cream | baby massage oil | baby hair oil |
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What Is a Transverse Baby Position?
Why It Happens, How to Turn Your Baby, and Tips for a Safe Delivery
Causes and Risk Factors
Turning the fetus, complications, frequently asked questions.
A transverse baby position, also called transverse fetal lie, is when the fetus is sideways—at a 90-degree angle to your spine—instead of head up or head down. This development means that a vaginal delivery poses major risks to both you and the fetus.
Sometimes, a transverse fetus will turn itself into the head-down position before you go into labor. Other times, a healthcare provider may be able to turn the position.
If a transverse fetus can't be turned to the right position before birth, you're likely to have a cesarean section (C-section).
This article looks at causes and risk factors for a transverse baby position. It also covers how it's diagnosed and treated, the possible complications, and how you can plan ahead for delivery.
Marko Geber / Getty Images
How Common Is Transverse Baby Position?
An estimated 2% to 13% of babies are in an unfavorable position at delivery —meaning they're not in the head-down position .
Certain physiological issues can lead to a transverse fetal lie. These include:
- A bicornuate uterus : The uterus has a deep V in the top that separates the uterus into two sides; it may only be able to hold a near-term fetus sideways.
- Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios : Abnormally low or high amniotic fluid volume (respectively).
Several risk factors can make it more likely for the fetus to be in a transverse lie, such as:
- The placenta being in an unusual position, such as blocking the opening to the cervix ( placenta previa ), which doesn't allow the fetus to reach the head-down position
- Going into labor early, before the fetus has had a chance to get into the right position
- Being pregnant with twins or other multiples, as the uterus is crowded and may not allow for much movement
- An abnormal pelvic structure that limits fetal movement
- Having a cyst or fibroid tumor blocking the cervix
Transverse fetal positioning is also more common after your first pregnancy.
It’s not uncommon for a fetus to be in a transverse position during the earlier stages of pregnancy. In most cases, though, they shift on their own well before labor begins. The transverse fetal position doesn't cause any signs or symptoms.
Healthcare professionals diagnose a transverse lie through an examination called Leopold’s Maneuvers. That involves feeling your abdomen to determine the fetal position. It's usually confirmed by an ultrasound.
You may also discover a transverse fetal lie during a routine ultrasound.
Timing of Transverse Position Diagnosis
The ultrasound done at your 36-week checkup lets your healthcare provider see the fetal position as you get closer to labor and delivery. If it's still a transverse lie at that time, your medical team will look at options for the safest labor and delivery.
Approximately 97% of deliveries involve a fetus positioned with the head down, in the best position to slide out. That makes a vaginal delivery easier and safer.
A transverse position only happens in about 1% of deliveries. In that position, the shoulder, arm, or trunk of the fetus may present first. This isn't a good scenario for either of you because a vaginal delivery is nearly impossible.
In these cases, you have two options:
- Turning the fetal position
- Having a C-section
If the fetus is in a transverse lie late in pregnancy, you or your healthcare provider may be able to change the position. Turning into the proper head-down position may help you avoid a C-section.
Medical Options
A healthcare provider can use one of the following techniques to attempt re-positioning a fetus:
- External cephalic version (ECV) : This procedure typically is performed at or after 36 weeks of pregnancy; involves using pressure on your abdomen where the fetal head and buttocks are.
- Webster technique : This is a chiropractic method in which a healthcare professional moves your hips to allow your uterus to relax and make more room for the fetus to move itself. (Note: No evidence supports this method.)
A 2020 study reported a 100% success rate for trained practitioners who used turning to change a transverse fetal lie. Real-world success rates are closer to 60%.
At-Home Options
You may be able to encourage a move out of the transverse position at home. You can try:
- Getting on your hands and knees and gently rocking back and forth
- Lying on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor, then pushing your hips up in the air (bridge pose)
- Talking or playing music to stimulate the fetus to become more active
- Applying some cold to your abdomen where the fetal head is, which may make them want to move away from it
These methods may or may not work for you. While there's anecdotal evidence that they sometimes work, they haven't been researched.
Talk to your healthcare provider before attempting any of these techniques to ensure you're not doing anything unsafe.
Can Babies Go Back to Transverse After Being Turned?
Even if the fetus does change position or is successfully moved, it is possible that it could return to a transverse position prior to delivery.
Whether your child is born via C-section or is successfully moved so you can have a vaginal delivery, potential complications remain.
Cesarean Sections
C-sections are extremely common and are generally safe for both you and the fetus. Still, some inherent risks are associated with the procedure, as there are with any surgery.
The transverse position can force the surgeon to make a different type of incision, as the fetal lie may be right where they'd usually cut. Possible C-section complications for you can include:
- Increased bleeding
- Bladder or bowel injury
- Reactions to medicines
- Blood clots
- Death (very rare)
In rare cases, a C-section can result in potential complications for the baby , including:
- Breathing problems, if fluid needs to be cleared from their lungs
Most C-sections are safe and result in a healthy baby and parent. In some situations, a surgical delivery is the safest option available.
Vaginal Delivery
If the fetus is successfully moved out of the transverse lie position, you'll likely be able to deliver it vaginally. However, a few complications are possible even after the fetus has been moved:
- Labor typically takes longer.
- Your baby’s face may be swollen and appear bruised for a few days.
- The umbilical cord may be compressed, potentially causing distress and leading to a C-section.
Studies suggest that ECV is safe, effective, and may help lower the C-section rate.
Planning Ahead
As with any birth, if you experience a transverse fetal position, you should work with your healthcare provider to develop a delivery plan. If the transverse position has been maintained throughout the pregnancy, the medical team will evaluate the position at about 36 weeks and make plans accordingly.
Remember that even if the fetal head is down late in pregnancy, things can change quickly during labor and delivery. That means it's worthwhile to discuss options for different types of delivery in case they become necessary.
A transverse baby position, or transverse fetal lie, is the term for a fetus that's lying sideways in the uterus. Vaginal delivery usually isn't possible in these cases.
If the fetus is in this position near the time of delivery, the options are to turn it to make vaginal delivery possible or to have a C-section. A trained healthcare provider can use turning techniques. You may also be able to get the fetus to turn at home with some simple techniques.
Both C-section and vaginal delivery pose a risk of certain complications. However, these problems are rare and the vast majority of deliveries end with a healthy baby and parent.
A Word From Verywell
Pregnancy comes with many unknowns, and the surprises can continue up through labor and delivery.
Talking to your healthcare provider early on about possible scenarios can give you time to think about possible outcomes. This helps to avoid a situation where you’re considering risks and benefits during labor when quick decisions need to be made.
Ideally, a baby should be in the cephalic position (head down) at 32 weeks. If not, a doctor will examine the fetal position at around the 36-week mark and determine what should happen next to ensure a smooth delivery. Whether this involves a cesarian section will depend on the specific case.
Less than 1% of babies are born in the transverse position. In many cases, a doctor might recommend a cesarian delivery to ensure a more safe delivery. The risk of giving birth in the transverse lie position is greater before a due date or if twins or triplets are also born.
A planned cesarian section , or C-section, is typically performed in the 39th week of gestation. This is done so the fetus is given enough time to grow and develop so that it is healthy.
In some cases, a doctor may perform an external cephalic version (ECV) to change a transverse fetal lie. This involves the doctor using their hands to apply firm pressure to the abdomen so the fetus is moved into the cephalic (head-down) position.
Most attempts of ECV are successful, but there is a chance the fetus can move back to its previous position; in these cases, a doctor can attempt ECV again.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. If your baby is breech .
Tempest N, Lane S, Hapangama D. Babies in occiput posterior position are significantly more likely to require an emergency cesarean birth compared with babies in occiput transverse position in the second stage of labor: a prospective observational study . Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand . 2020;99(4):537-545. doi:10.1111/aogs.13765
National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine: MedlinePlus. Congenital uterine anomalies .
Figueroa L, McClure EM, Swanson J, et al. Oligohydramnios: a prospective study of fetal, neonatal and maternal outcomes in low-middle income countries . Reprod Health. 2020;17 (article 19). doi:10.1186/s12978-020-0854-y
National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine: MedlinePlus. Placenta previa .
National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine: MedlinePlus. Your baby in the birth canal .
Van der Kaay DC, Horsch S, Duvekot JJ. Severe neonatal complication of transverse lie after preterm premature rupture of membranes . BMJ Case Rep . 2013;bcr2012008399. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-008399
Oyinloye OI, Okoyomo AA. Longitudinal evaluation of foetal transverse lie using ultrasonography . Afr J Reprod Health ; 14(1):129-133.
Nishikawa M, Sakakibara H. Effect of nursing intervention program using abdominal palpation of Leopold’s maneuvers on maternal-fetal attachment . Reprod Health 2013;10 (article 12). doi.org/10.1186/1742-4755-10-12
National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine: MedlinePlus. Delivery presentations .
Dalvi SA. Difficult deliveries in Cesarean section . J Obstet Gynaecol India . 2018;68(5):344-348. doi:10.1007/s13224-017-1052-x
Zhi Z, Xi L. Clinical analysis of 40 cases of external cephalic version without anesthesia . J Int Med Res . 2021;49(1):300060520986699. doi:10.1177/0300060520986699
National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine: MedlinePlus. Questions to ask your doctor about labor and delivery .
Nemours KidsHealth. Cesarean sections .
By Elizabeth Yuko, PhD Yuko has a doctorate in bioethics and medical ethics and is a freelance journalist based in New York.
- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games
How your twins’ fetal positions affect labor and delivery

Twin fetal presentation – also known as the position of your babies in the womb – dictates whether you'll have a vaginal or c-section birth. Toward the end of pregnancy, most twins will move in the head-down position (vertex), but there's a risk that the second twin will change position after the first twin is born. While there are options to change the second twin's position, this can increase the risk of c-section and other health issues. Learn about the six possible twin fetal presentations: vertex-vertex, vertex-breech, breech-breech, vertex-transverse, breech-transverse, and transverse-transverse – and how they'll impact your delivery and risks for complications.
What is fetal presentation and what does it mean for your twins?
As your due date approaches, you might be wondering how your twins are currently positioned in the womb, also known as the fetal presentation, and what that means for your delivery. Throughout your pregnancy, your twin babies will move in the uterus, but sometime during the third trimester – usually between 32 and 36 weeks – their fetal presentation changes as they prepare to go down the birth canal.
The good news is that at most twin births, both babies are head-down (vertex), which means you can have a vaginal delivery. In fact, nearly 40 percent of twins are delivered vaginally.
But if one baby has feet or bottom first (breech) or is sideways (transverse), your doctor might deliver the lower twin vaginally and then try to rotate the other twin so that they face head-down (also called external cephalic version or internal podalic version) and can be delivered vaginally. But if that doesn't work, there's still a chance that your doctor will be able to deliver the second twin feet first vaginally via breech extraction (delivering the breech baby feet or butt first through the vagina).
That said, a breech extraction depends on a variety of factors – including how experienced your doctor is in the procedure and how much the second twin weighs. Studies show that the higher rate of vaginal births among nonvertex second twins is associated with labor induction and more experienced doctors, suggesting that proper delivery planning may increase your chances of a vaginal birth .
That said, you shouldn't totally rule out a Cesarean delivery with twins . If the first twin is breech or neither of the twins are head-down, then you'll most likely have a Cesarean delivery.
Research also shows that twin babies who are born at less than 34 weeks and have moms with multiple children are associated with intrapartum presentation change (when the fetal presentation of the second twin changes from head-down to feet first after the delivery of the first twin) of the second twin. Women who have intrapartum presentation change are more likely to undergo a Cesarean delivery for their second twin.
Here's a breakdown of the different fetal presentations for twin births and how they will affect your delivery.
Head down, head down (vertex, vertex)
This fetal presentation is the most promising for a vaginal delivery because both twins are head-down. Twins can change positions, but if they're head-down at 28 weeks, they're likely to stay that way.
When delivering twins vaginally, there is a risk that the second twin will change position after the delivery of the first. Research shows that second twins change positions in 20 percent of planned vaginal deliveries. If this happens, your doctor may try to rotate the second twin so it faces head-down or consider a breech extraction. But if neither of these work or are an option, then a Cesarean delivery is likely.
In vertex-vertex pairs, the rate of Cesarean delivery for the second twin after a vaginal delivery of the first one is 16.9 percent.
Like all vaginal deliveries, there's also a chance you'll have an assisted birth, where forceps or a vacuum are needed to help deliver your twins.
Head down, bottom down (vertex, breech)
When the first twin's (the lower one) head is down, but the second twin isn't, your doctor may attempt a vaginal delivery by changing the baby's position or doing breech extraction, which isn't possible if the second twin weighs much more than the first twin.
The rates of emergency C-section deliveries for the second twin after a vaginal delivery of the first twin are higher in second twins who have a very low birth weight. Small babies may not tolerate labor as well.
Head down, sideways (vertex, transverse)
If one twin is lying sideways or diagonally (oblique), there's a chance the baby may shift position as your labor progresses, or your doctor may try to turn the baby head-down via external cephalic version or internal podalic version (changing position in the uterus), which means you may be able to deliver both vaginally.
Bottom down, bottom down (breech, breech)
When both twins are breech, a planned C-section is recommended because your doctor isn't able to turn the fetuses. Studies also show that there are fewer negative neonatal outcomes for planned C-sections than planned vaginal births in breech babies.
As with any C-section, the risks for a planned one with twins include infection, loss of blood, blood clots, injury to the bowel or bladder, a weak uterine wall, placenta abnormalities in future pregnancies and fetal injury.
Bottom down, sideways (breech, transverse)
When the twin lowest in your uterus is breech or transverse (which happens in 25 percent of cases), you'll need to have a c-section.
Sideways, sideways (transverse, transverse)
This fetal presentation is rare with less than 1 percent of cases. If both babies are lying horizontally, you'll almost definitely have a C-section.
Learn more:
- Twin fetal development month by month
- Your likelihood of having twins or more
- When and how to find out if you’re carrying twins or more
Was this article helpful?
32 weeks pregnant with twins

28 weeks pregnant with twins

36 weeks pregnant with twins

24 weeks pregnant with twins

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
Cleveland Clinic. Fetal Positions for Birth: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9677-fetal-positions-for-birth Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Mayo Clinic. Fetal Presentation Before Birth: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/multimedia/fetal-positions/sls-20076615?s=7 Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
NHS. Giving Birth to Twins or More: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29016498/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Science Direct. Breech Extraction: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/breech-extraction Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Obstetrics & Gynecology. Clinical Factors Associated With Presentation Change of the Second Twin After Vaginal Delivery of the First Twin https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29016498/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Fetal presentation and successful twin vaginal delivery: https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(04)00482-X/fulltext [Accessed July 2021]
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. Changes in fetal presentation in twin pregnancies https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14767050400028592 Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Reviews in Obstetrics & Gynecology. An Evidence-Based Approach to Determining Route of Delivery for Twin Gestations https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3252881/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Nature. Neonatal mortality and morbidity in vertex–vertex second twins according to mode of delivery and birth weight: https://www.nature.com/articles/7211408 Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Cochrane. Planned cesarean for a twin pregnancy: https://www.cochrane.org/CD006553/PREG_planned-caesarean-section-twin-pregnancy Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Kids Health. What Is the Apgar Score?: https://www.kidshealth.org/Nemours/en/parents/apgar0.html Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. Neonatal mortality in second twin according to cause of death, gestational age, and mode of delivery https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15467540/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Lancet. Planned cesarean section versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: a randomised multicentre trial. Term Breech Trial Collaborative Group https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11052579/ Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
Cleveland Clinic. Cesarean Birth (C-Section): https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/7246-cesarean-birth-c-section Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]
St. Jude Medical Staff. Delivery of Twin Gestation: http://www.sjmedstaff.org/documents/Delivery-of-twins.pdf Opens a new window [Accessed July 2021]

Where to go next

- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Labor & Delivery
What Causes Breech Presentation?
Learn more about the types, causes, and risks of breech presentation, along with how breech babies are typically delivered.
What Is Breech Presentation?
Types of breech presentation, what causes a breech baby, can you turn a breech baby, how are breech babies delivered.
FatCamera/Getty Images
Toward the end of pregnancy, your baby will start to get into position for delivery, with their head pointed down toward the vagina. This is otherwise known as vertex presentation. However, some babies turn inside the womb so that their feet or buttocks are poised to be delivered first, which is commonly referred to as breech presentation, or a breech baby.
As you near the end of your pregnancy journey, an OB-GYN or health care provider will check your baby's positioning. You might find yourself wondering: What causes breech presentation? Are there risks involved? And how are breech babies delivered? We turned to experts and research to answer some of the most common questions surrounding breech presentation, along with what causes this positioning in the first place.
During your pregnancy, your baby constantly moves around the uterus. Indeed, most babies do somersaults up until the 36th week of pregnancy , when they pick their final position in the womb, says Laura Riley , MD, an OB-GYN in New York City. Approximately 3-4% of babies end up “upside-down” in breech presentation, with their feet or buttocks near the cervix.
Breech presentation is typically diagnosed during a visit to an OB-GYN, midwife, or health care provider. Your physician can feel the position of your baby's head through your abdominal wall—or they can conduct a vaginal exam if your cervix is open. A suspected breech presentation should ultimately be confirmed via an ultrasound, after which you and your provider would have a discussion about delivery options, potential issues, and risks.
There are three types of breech babies: frank, footling, and complete. Learn about the differences between these breech presentations.
Frank Breech
With frank breech presentation, your baby’s bottom faces the cervix and their legs are straight up. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
Footling Breech
Like its name suggests, a footling breech is when one (single footling) or both (double footling) of the baby's feet are in the birth canal, where they’re positioned to be delivered first .
Complete Breech
In a complete breech presentation, baby’s bottom faces the cervix. Their legs are bent at the knees, and their feet are near their bottom. A complete breech is the least common type of breech presentation.
Other Types of Mal Presentations
The baby can also be in a transverse position, meaning that they're sideways in the uterus. Another type is called oblique presentation, which means they're pointing toward one of the pregnant person’s hips.
Typically, your baby's positioning is determined by the fetus itself and the shape of your uterus. Because you can't can’t control either of these factors, breech presentation typically isn’t considered preventable. And while the cause often isn't known, there are certain risk factors that may increase your risk of a breech baby, including the following:
- The fetus may have abnormalities involving the muscular or central nervous system
- The uterus may have abnormal growths or fibroids
- There might be insufficient amniotic fluid in the uterus (too much or too little)
- This isn’t your first pregnancy
- You have a history of premature delivery
- You have placenta previa (the placenta partially or fully covers the cervix)
- You’re pregnant with multiples
- You’ve had a previous breech baby
In some cases, your health care provider may attempt to help turn a baby in breech presentation through a procedure known as external cephalic version (ECV). This is when a health care professional applies gentle pressure on your lower abdomen to try and coax your baby into a head-down position. During the entire procedure, the fetus's health will be monitored, and an ECV is often performed near a delivery room, in the event of any potential issues or complications.
However, it's important to note that ECVs aren't for everyone. If you're carrying multiples, there's health concerns about you or the baby, or you've experienced certain complications with your placenta or based on placental location, a health care provider will not attempt an ECV.
The majority of breech babies are born through C-sections . These are usually scheduled between 38 and 39 weeks of pregnancy, before labor can begin naturally. However, with a health care provider experienced in delivering breech babies vaginally, a natural delivery might be a safe option for some people. In fact, a 2017 study showed similar complication and success rates with vaginal and C-section deliveries of breech babies.
That said, there are certain known risks and complications that can arise with an attempt to deliver a breech baby vaginally, many of which relate to problems with the umbilical cord. If you and your medical team decide on a vaginal delivery, your baby will be monitored closely for any potential signs of distress.
Ultimately, it's important to know that most breech babies are born healthy. Your provider will consider your specific medical condition and the position of your baby to determine which type of delivery will be the safest option for a healthy and successful birth.
ACOG. If Your Baby Is Breech .
American Pregnancy Association. Breech Presentation .
Gray CJ, Shanahan MM. Breech Presentation . [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-.
Mount Sinai. Breech Babies .
Takeda J, Ishikawa G, Takeda S. Clinical Tips of Cesarean Section in Case of Breech, Transverse Presentation, and Incarcerated Uterus . Surg J (N Y). 2020 Mar 18;6(Suppl 2):S81-S91. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1702985. PMID: 32760790; PMCID: PMC7396468.
Shanahan MM, Gray CJ. External Cephalic Version . [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-.
Fonseca A, Silva R, Rato I, Neves AR, Peixoto C, Ferraz Z, Ramalho I, Carocha A, Félix N, Valdoleiros S, Galvão A, Gonçalves D, Curado J, Palma MJ, Antunes IL, Clode N, Graça LM. Breech Presentation: Vaginal Versus Cesarean Delivery, Which Intervention Leads to the Best Outcomes? Acta Med Port. 2017 Jun 30;30(6):479-484. doi: 10.20344/amp.7920. Epub 2017 Jun 30. PMID: 28898615.
Related Articles

- Mammary Glands
- Fallopian Tubes
- Supporting Ligaments
- Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Placental Development
- Maternal Adaptations
- Menstrual Cycle
- Antenatal Care
- Small for Gestational Age
- Large for Gestational Age
- RBC Isoimmunisation
- Prematurity
- Prolonged Pregnancy
- Multiple Pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Recurrent Miscarriage
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
- Breech Presentation
- Abnormal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
- Oligohydramnios
- Polyhydramnios
- Placenta Praevia
- Placental Abruption
- Pre-Eclampsia
- Gestational Diabetes
- Headaches in Pregnancy
- Haematological
- Obstetric Cholestasis
- Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy
- Epilepsy in Pregnancy
- Induction of Labour
- Operative Vaginal Delivery
- Prelabour Rupture of Membranes
- Caesarean Section
- Shoulder Dystocia
- Cord Prolapse
- Uterine Rupture
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism
- Primary PPH
- Secondary PPH
- Psychiatric Disease
- Postpartum Contraception
- Breastfeeding Problems
- Primary Dysmenorrhoea
- Amenorrhoea and Oligomenorrhoea
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Endometriosis
- Endometrial Cancer
- Adenomyosis
- Cervical Polyps
- Cervical Ectropion
- Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia + Cervical Screening
- Cervical Cancer
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Ovarian Cysts & Tumours
- Urinary Incontinence
- Genitourinary Prolapses
- Bartholin's Cyst
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Vulval Carcinoma
- Introduction to Infertility
- Female Factor Infertility
- Male Factor Infertility
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Barrier Contraception
- Combined Hormonal
- Progesterone Only Hormonal
- Intrauterine System & Device
- Emergency Contraception
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Genital Warts
- Genital Herpes
- Trichomonas Vaginalis
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
- Obstetric History
- Gynaecological History
- Sexual History
- Obstetric Examination
- Speculum Examination
- Bimanual Examination
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling
- Hysterectomy
- Endometrial Ablation
- Tension-Free Vaginal Tape
- Contraceptive Implant
- Fitting an IUS or IUD
Abnormal Fetal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
Original Author(s): Anna Mcclune Last updated: 1st December 2018 Revisions: 12
- 1 Definitions
- 2 Risk Factors
- 3.2 Presentation
- 3.3 Position
- 4 Investigations
- 5.1 Abnormal Fetal Lie
- 5.2 Malpresentation
- 5.3 Malposition
The lie, presentation and position of a fetus are important during labour and delivery.
In this article, we will look at the risk factors, examination and management of abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition.
Definitions
- Longitudinal, transverse or oblique
- Cephalic vertex presentation is the most common and is considered the safest
- Other presentations include breech, shoulder, face and brow
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) – this is ideal for birth
- Other positions include occipito-posterior and occipito-transverse.
Note: Breech presentation is the most common malpresentation, and is covered in detail here .
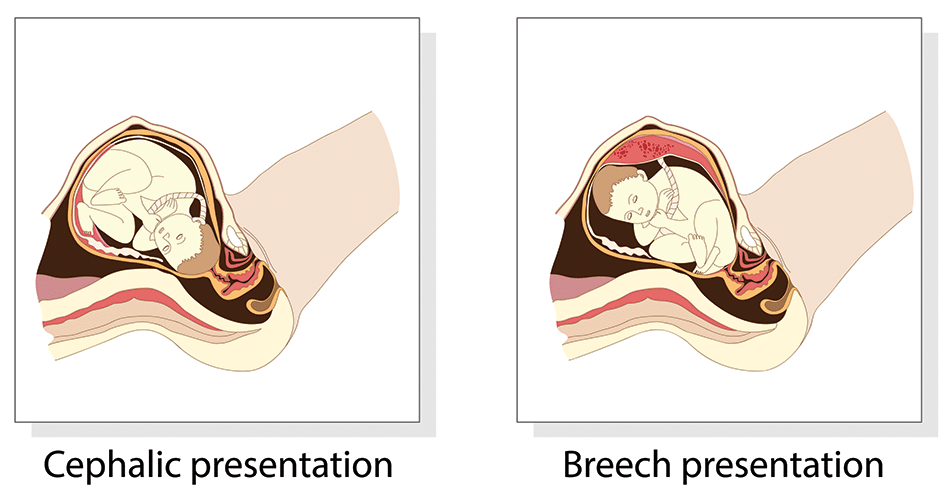
Fig 1 – The two most common fetal presentations: cephalic and breech.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition include:
- Multiple pregnancy
- Uterine abnormalities (e.g fibroids, partial septate uterus)
- Fetal abnormalities
- Placenta praevia
- Primiparity
Identifying Fetal Lie, Presentation and Position
The fetal lie and presentation can usually be identified via abdominal examination. The fetal position is ascertained by vaginal examination.
For more information on the obstetric examination, see here .
- Face the patient’s head
- Place your hands on either side of the uterus and gently apply pressure; one side will feel fuller and firmer – this is the back, and fetal limbs may feel ‘knobbly’ on the opposite side
Presentation
- Palpate the lower uterus (above the symphysis pubis) with the fingers of both hands; the head feels hard and round (cephalic) and the bottom feels soft and triangular (breech)
- You may be able to gently push the fetal head from side to side
The fetal lie and presentation may not be possible to identify if the mother has a high BMI, if she has not emptied her bladder, if the fetus is small or if there is polyhydramnios .
During labour, vaginal examination is used to assess the position of the fetal head (in a cephalic vertex presentation). The landmarks of the fetal head, including the anterior and posterior fontanelles, indicate the position.
Fig 2 – Assessing fetal lie and presentation.
Investigations
Any suspected abnormal fetal lie or malpresentation should be confirmed by an ultrasound scan . This could also demonstrate predisposing uterine or fetal abnormalities.
Abnormal Fetal Lie
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted – ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen.
It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women. Only 8% of breech presentations will spontaneously revert to cephalic in primiparous women over 36 weeks gestation.
Complications of ECV are rare but include fetal distress , premature rupture of membranes, antepartum haemorrhage (APH) and placental abruption. The risk of an emergency caesarean section (C-section) within 24 hours is around 1 in 200.
ECV is contraindicated in women with a recent APH, ruptured membranes, uterine abnormalities or a previous C-section .
Fig 3 – External cephalic version.
Malpresentation
The management of malpresentation is dependent on the presentation.
- Breech – attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
- Brow – a C-section is necessary
- If the chin is anterior (mento-anterior) a normal labour is possible; however, it is likely to be prolonged and there is an increased risk of a C-section being required
- If the chin is posterior (mento-posterior) then a C-section is necessary
- Shoulder – a C-section is necessary
Malposition
90% of malpositions spontaneously rotate to occipito-anterior as labour progresses. If the fetal head does not rotate, rotation and operative vaginal delivery can be attempted. Alternatively a C-section can be performed.
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) - this is ideal for birth
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
- Breech - attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
Found an error? Is our article missing some key information? Make the changes yourself here!
Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. To find out more, read our privacy policy .
Privacy Overview
We have a new app!
Take the Access library with you wherever you go—easy access to books, videos, images, podcasts, personalized features, and more.
Download the Access App here: iOS and Android . Learn more here!
- Remote Access
- Save figures into PowerPoint
- Download tables as PDFs

Chapter 6. Normal Pregnancy and Prenatal Care
Helene B. Bernstein, MD, PhD; George VanBuren, MD
- Download Chapter PDF
Disclaimer: These citations have been automatically generated based on the information we have and it may not be 100% accurate. Please consult the latest official manual style if you have any questions regarding the format accuracy.
Download citation file:
- Search Book
Jump to a Section
- Normal Pregnancy
- Prenatal Care
- Full Chapter
- Supplementary Content
Pregnancy (gestation) is the physiologic process of a developing fetus within the maternal body. Several terms are used to define the developmental stage of human conception and the duration of pregnancy. For obstetric purposes, the gestational age or menstrual age is the time elapsed since the first day of the last normal menstrual period (LNMP), which actually precedes the time of oocyte fertilization. The gestational age is expressed in completed weeks. The start of the gestation (based on the LNMP) is usually 2 weeks before ovulation, assuming a 28-day regular menstrual cycle. The developmental or fetal age is the age of the conception calculated from the time of implantation, which is 4 to 6 days after ovulation is completed. The menstrual gestational age of pregnancy is calculated at 280 days or 40 completed weeks. The estimated due date (EDD) may be estimated by adding 7 days to the first day of the last menstrual period and subtracting 3 months plus 1 year (Naegele's rule).
The period of gestation can be divided into units consisting of 3 calendar months each or 3 trimesters. The first trimester can be subdivided into the embryonic and fetal periods. The embryonic period starts at the time of fertilization (developmental age) or at 2 through 10 weeks' gestational age. The embryonic period is the stage at which organogenesis occurs and the time period during which the embryo is most sensitive to teratogens. The end of the embryonic period and the beginning of the fetal period occurs 8 weeks after fertilization (developmental age) or 10 weeks after the onset of the last menstrual period.
Definitions
The term gravid means “pregnant”; gravida is the total number of pregnancies that a women has had, regardless of the outcome. Parity is the number of births, both before and after 20 weeks' gestation, and comprises 4 components:
Full-term births
Preterm births: having given birth to an infant (alive or deceased) weighing 500 g or more, or at or beyond 20 completed weeks (based on the first day of the last menstrual period)
Abortions: pregnancies ending before 20 weeks, either induced or spontaneous
Living children
When gravidity and parity are calculated as part of the obstetric history, multiple births are designated as a single gravid event, and each infant is included as part of the parity total.
Live birth is the delivery of any infant (regardless of gestational age) that demonstrates evidence of life (eg, a heartbeat, umbilical cord pulsation, voluntary or involuntary movement), independent of whether the umbilical cord has been cut or the placenta detached. An infant is a live-born human from the moment of birth until the completion of 1 year of life (365 days).
Sign in or create a free Access profile below to access even more exclusive content.
With an Access profile, you can save and manage favorites from your personal dashboard, complete case quizzes, review Q&A, and take these feature on the go with our Access app.
Pop-up div Successfully Displayed
This div only appears when the trigger link is hovered over. Otherwise it is hidden from view.
Please Wait
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Womens Health (Lond)
Maternal and fetal characteristics to predict c-section delivery: A scoring system for pregnant women
Rima irwinda.
1 Maternal-Fetal Medicine Division, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia and Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia
Rabbania Hiksas
2 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia and Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia
Angga Wiratama Lokeswara
Noroyono wibowo, introduction:.
Cesarean section is one of the most common obstetrical interventions that has been performed at an increasing rate globally, due to both medical and non-medical reasons. This study aims to develop a prediction tool for pregnant women potentially needing c-section, such that necessary preparations from the mothers, families, and health providers can be made.
A total of 603 pregnant women were recruited in the first phase of c-section prediction tool development. The association between the maternal and fetal factors on the risk of c-section were analyzed, followed by a stepwise multivariate regression analysis. In the next phase, 61 pregnant women were enrolled for external validation. Discrimination was assessed using area under the curve. The calibration plot was then made and assessed using the Hosmer–Lemeshow test.
There were 251 (41.6%) cases of vaginal delivery and 352 (58.4%) of c-section assessed. Multivariate analysis showed that gestational age < 37 wg (OR: 1.66, 95% CI: 1.10–2.51), pre-pregnancy body mass index (underweight) (OR: 0.40, 95% CI: 0.22–0.76), no history of vaginal delivery (OR: 2.66, 95% CI: 1.76–4.02), history of uterine surgery (OR: 8.34, 95% CI: 4.54–15.30), obstetrical complications (OR: 5.61, 95% CI: 3.53–8.90), birthweight ⩾ 3500 g (OR: 4.28, 95% CI: 2.16–8.47), and non-cephalic presentation (OR: 2.74, 95% CI: 1.53–4.89) were independently associated with c-section delivery. Those parameters were included in a 7-item scoring tool, with consecutive predictive scores of 1,–1,2,3,3,2,2,1. The area under the curve result was 0.813 (95% CI: 0.779–0.847), indicating a good predictive ability. The external validation showed AUC: 0.806, 95% CI: 0.694–0.917, Hosmer–Lemeshow test p = 0.666 and calibration plot coefficient of r = 0.939.
Conclusion:
A total of 7 maternal-fetal factors were found to be strongly associated with c-section delivery, including gestational age < 37, maternal underweight body mass index, previous uterine surgery, obstetrical complications, birthweight ⩾ 3500, history of vaginal delivery, and non-cephalic presentation. Using these factors, a prediction tool was developed and validated with good quality.
Introduction
Cesarean section, or more commonly known as c-section, has become the main alternative delivery method in pregnancy with life-threatening complications. 1 The decision to perform c-section should be made under conditions where vaginal delivery is impossible, or poses more risks, and is therefore taken only with certain maternal or fetal indications. 2
Based on the Statement on Cesarean Section Rates by the WHO, 3 a systematic review and ecological analysis have found that a population-based c-section rates above 10% does not correlate with reductions in maternal and neonatal mortality, thus is considered non-optimal, considering the adverse complications in future pregnancies. 4 , 5 Nevertheless, in the last decade, WHO found that the rates of c-section has dramatically increased from 7% in 1990 to more than 1 in 5 childbirths (21%) in 2021, and is projected to reach 29% in 2030, globally. If the trend continues, Eastern Asia and Latin America are projected to reach the highest rates at 63% and 54% respectively. 6
Although c-section can be an imperative, lifesaving surgery in certain cases, one concerning reason behind the trend is the increasing c-section by maternal request, without any medical indications. 7 A systematic review by Begum et al. 8 in 2020 found that c-section by maternal request makes up 0.2%–42% of all childbirths, and 0.9%–60% of all c-sections, with 11-fold increase in c-section by maternal request in upper middle-income countries compared with either high or lower-middle income countries.
In Indonesia, the rate of c-section mimics the global trend, as it increased from 9.8% in 2013 to 17.6% in 2018, with the highest rate found in Jakarta (31.1%). 9 In recent years, the rate of c-section in Cipto Mangunkusumo National Referral Hospital alone reached almost 50%. Despite advanced surgical techniques, c-section poses short-term and long-term complications. Several risks are associated with c-section, including miscarriage and stillbirth, placenta previa, and placenta accreta in the following pregnancy, as well as development of childhood asthma. 10 In Cipto Mangunkusumo hospital, the cases of placenta accreta was found to be at 76 out of 2660 c-section deliveries (2.86%) in 2019. 11 A multi-country survey has also found that c-section performed without medical indications increases risks for severe maternal outcome. 12
Furthermore, in Indonesia, the high maternal morbidity and mortality rates were highly influenced by the poor infrastructure of the healthcare system in remote areas as well as poor awareness of the pregnant mothers, resulting in delayed referrals. 13 In developing countries like Indonesia, poor awareness of the early signs of obstetrical complications also contributes to late consultation to obstetricians. This could eventually delay the c-section, resulting in life-threatening conditions. Therefore, by educating pregnant women with regards to their risks of c-section, maternal and fetal outcomes could potentially be improved.
With varying trends in c-section and its medical and non-medical reasons, the medical risk factors behind today’s trend of c-section becomes unclear. Numbers of scoring system related maternal and fetal characteristics to predict the risk of c-sections have been developed for obstetricians in order to ensure the procedure was done only if indicated. 14 , 15 However, the existing scoring systems were built for obstetrician, hence are too difficult for pregnant women in general population to comprehend, thus many pregnant women remain unaware of their obstetrical condition. Therefore, this study aims to assess the maternal and fetal risk factors of c-section and develop a prediction tool for mothers potentially needing c-section. Hence, necessary preparations from the mothers and families, especially in third trimester, and health providers can be made.
Study setting
The study was carried out at Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital, Fatmawati Hospital, and Tangerang General hospital, located in Jakarta-Tangerang, Indonesia. All of the hospitals are tertiary referral hospital, which receive and treat referred cases from primary and secondary healthcare facilities. Moreover, Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital is a national referral hospital in Indonesia, handling patients not only from Jakarta, Indonesia, but also other referred patients from other provinces in Indonesia, mainly the ones with adverse pregnancy complications. These hospitals are also teaching hospitals, where examination and procedures were performed by residents of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia, under close supervision by highly qualified Obstetrics and Gynecology subspecialists and consultants.
Study design and sample recruitment
This was a retrospective cohort study using data from the hospital’s medical records. The first phase of the study was development of a scoring system, which took place in Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital and Fatmawati Hospital. The minimum sample size calculated was 273; on the basis incidence of c-section rate in Jakarta, 2018 (31.1%), 9 along with 95% confidence interval (CI), and 80% power. 16 The study was restricted to women delivered in those two hospitals from January to April 2019, with gestational age of 22–42 weeks. A total of 753 cases met the criteria. We excluded deliveries with babies weighing 500 g or less (n = 13), cases of intrauterine fetal death at less than 28 weeks (n = 28), and cases with incomplete antenatal data (n = 109). After exclusions, a total of 603 cases complied our eligibility criteria and were put to analysis.
The next phase was a validation of the scoring system, which took place in Tangerang General Hospital. The minimum sample size was also calculated with 95% CI and 80% power. 16 With the effect size 0.26 (low-risk and high-risk difference from the first part of study), the minimum sample requirement for the external validation was 46. Applying similar inclusion and exclusion criteria, the study was restricted to women delivered in the hospital from July to August 2021, with gestational age of 22–42 weeks. Within the period of study, a total 89 cases met the criteria. We excluded deliveries with babies weighing 500 g or less (n = 5), cases of intrauterine fetal death at less than 28 weeks (n = 4), and cases with incomplete antenatal data (n = 19). We continued the external validation using 61 samples. Figure 1 shows the workflow diagram.

The workflow diagram.
This study has been approved by The Ethical Committee for Research in Humans from The Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia (KET-1491/UN2.F1/ETIK/PPM.00.02/2020). Since this was a retrospective study, we extracted only clinically relevant information from medical records with ensuring patient’s privacy protection. This study also did not affect patients treatment and health, thus written informed consent from all participants was waived by the Ethical Committee.
Outcome measures
All data extracted from medical records were classified into demographic characteristics, pregnancy history, current pregnancy characteristics, and neonatal features. Demographic characteristics; maternal age, gestational age, body height, body weight before pregnancy and during last trimester, body mass index (BMI) before pregnancy and during last trimester which was categorized based on Asia-Pacific BMI criteria including underweight (< 18.5), normal (18.5–22.9), overweight (23–24.9), and obese (⩾ 25). Pregnancy history; gravidity, parity, previous uterine surgery (c-section or myomectomy), history of vaginal delivery. Current pregnancy characteristics; antenatal care (ANC) visit, types of pregnancy (single or twin), pregnancy program, presence of chronic diseases (diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, kidney disease, autoimmune diseases, infections including syphilis, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), or hepatitis B, and cancer), obstetrical complications [hypertensive disorder in pregnancy, 17 gestational diabetes mellitus (severe hyperglycaemia in pregnancy), 18 intrauterine growth restriction (i.e. estimated fetal weight or abdominal circumference below the 10th percentile, abnormal doppler/amniotic fluid index/biophysical profile), 19 placenta previa, and placental abruption], and the presence of premature rupture of membrane (later than 6 or 12 h). Neonatal features: birth weight, and fetal presentation at the last trimester.
All women were classified into two groups: vaginal delivery and c-section. C-section included both emergency and elective c-section. Vaginal delivery included spontaneous delivery, with or without induction, vacuum extraction, or forceps delivery. The primary outcome of this study was to identify the possible independent factors associated with c-section, which are comprehensible for both non-health care workers and health-care providers.
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS statistics, version 25 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, Illinois, USA). Mean and standard deviation were used to describe continuous variables with normal distribution, while median and interquartile range for non-normal distribution data. Comparison of proportions was performed by Pearson’s chi-square (χ 2 ) for categorial variables. Variables with p-value < 0.250 in bivariate analysis were put into logistic regression analysis. Each odds ratio (OR) with multivariable log-binomial regression models was estimated with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). A p-value of less than 5% was considered statistically significant.
A predictive scoring tool was developed through stepwise calculations: (1) dividing each prognostic factor’s coefficient B by its standard error (coefficient B/SE); (2) choosing the lowest B/SE value as a reference (3) dividing each B/SE value by the reference value; and (4) picking the rounded number nearest to the result from step 3. In order to evaluate the performance of our scoring system, we analyzed calibration score using the Hosmer–Lemeshow test and discrimination score using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). These were followed by internal validation using repeated backward logistic regression model for each of predictors with 1000 bootstrap resampling. Finally, the result of external validation of the scoring system were evaluated using repeated discrimination and calibration test using the same method.
Characteristics of study population
There were 603 cases assessed in this study, including 251 (41.6%) cases with vaginal delivery and 352 (58.4%) with c-section delivery. The characteristics of study population is shown in Table 1 . Bivariate and multivariate analysis were performed to evaluate the significances of variables associated with mode of delivery. Among the 18 variables which were analyzed for their association with the risk of c-section, 11 variables found to be significant ( Table 2 ). These 11 variables were then included in the logistic regression analysis, resulting in 7 variables found to be significantly associated with c-section delivery (p < 0.05). The odds ratio of the 11 variables are showed in Table 3 .
Baseline characteristics of study population.
IQR: interquartile range; BMI: body mass index; BP: blood pressure.
Bivariate analysis of factors associated with c-section.
OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; BMI: body mass index; ANC: antenatal care.
Odds ratio for independent variables in multivariate logistic regression analysis.
OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; wg: weeks of gestation; BMI: body mass index.
Development of c-section scoring system
There were seven variables identified in development of scoring system for the final model ( Table 4 ), including gestational age < 37 weeks, underweight pre-pregnancy BMI, previous uterine surgery, obstetrical complications, birth weight ⩾ 3500 g, no history of vaginal delivery, and non-cephalic presentation. Following that, a 7-item scoring system was developed (gestational age < 37 weeks = 1, underweight pre-pregnancy BMI = –1, non-cephalic presentation = 1, no history of vaginal delivery = 2, birthweight ⩾ 3500 g = 2, previous uterine surgery = 3, and obstetrical complications = 3), with a total score 11. The full scoring system is shown in Table 5 .
Derivation of 7-point scoring system to the risk of c-section from stepwise multivariate analysis.
SE: standard error; OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; wg: weeks of gestation; BMI: body mass index.
Sensitivity, specificity, and probability analysis of the scoring system.
Furthermore, the area of AUC was 0.813 (95% CI: 0.779–0.847). ( Figure 2 ). This was considered good as sensitivity of 81% were shown when the score ⩾3 was categorized as high risk for c-section, with a probability score of 53.13% ( Table 5 ). Calibration using Hosmer–Lemeshow showed a good calibration score with p = 0.555 (p > 0.05). An internal validation using 1000× boostraping also showed the same p value (p = 0.555). As the p values of before and after bootstrapping are the same, the scoring system can likely be expected to have similar results in a bigger population.

The ROC curve of the scoring system development the AUC = 0.813, 95% CI: 0.779–0.847.
External validation
We then enrolled 61 subjects for external validation of the scoring tool. Among them, 24 subjects underwent vaginal delivery and 37 subjects underwent c-section delivery. The performance of c-section risk scoring tool was assessed for calibration and discrimination results. As the calibration plot showed a coefficient of r = 0.939 ( Figure 3 ), and the Hosmer–Lemeshow test showed p = 0.624, the scoring system was considered to have a good calibration. In Figure 4 , The AUC was 0.806, with 95% CI (0.694–0.917), showing an excellent discrimination with no big difference from the first part of the study.

The plot calibration diagram of the scoring system in external validation (r = 0.939).

The ROC curve of the scoring system in external validation. The AUC = 0.806, 95% CI: 0.694–0.917.
There were seven variables identified to be independently associated with c-section delivery, including gestational age < 37 weeks, maternal underweight pre-pregnancy, previous uterine surgery, obstetrical complications, no history of vaginal delivery, birth weight ⩾ 3500 g, and non-cephalic presentation. From these variables, a scoring system for the risk of c-section has been developed. Since this scoring system was intended for those without medical background, certain variables which were deemed too technical for general population to understand were not included in the analysis. Therefore, variables such as characteristics of amniotic fluid or umbilical cord were not included in the analysis despite their known associations with the risk of c-section based on previous studies. 14
Among the maternal demographical characteristics, maternal underweight BMI pre-pregnancy was the only variable to independently reduce the risk of c-section by OR: 0.40, 95% CI: 0.22–0.76. This finding was consistent with numbers of study from Asia to Europe, where pre-pregnancy underweight BMI were found to lower the risk of cesarean delivery by almost half, with OR: 0.45–0.66. 20 – 22 In contrast, obese patients who were thought to have increased risks for c-section, showed no significant difference in our study. This was surprising as a previous study had suggested that nulliparous obese pregnant women might have increased risk of c-section. 23 A different cut off value for BMI category between the two criteria, Asian-Pacific and WHO criteria, might have influenced the differing results.
In terms of the obstetrical history, the history of uterine surgery and no history of vaginal delivery were found to be highly associated with c-section. Our study found that the history of uterine surgery was one of two variables with the highest scores in predicting c-section. This finding is in agreement with previous studies which found that a history of c-section in previous births increased the risk of c-section in the following pregnancy, with RR 4.30 (4.24–4.36) and OR: 3.5 (3.4–3.6). 15 , 24 This value may also be increased in deliveries with a history of previous c-section with a gestational distance of less than 19 months. 25 , 26 Although a history of previous c-section is not an absolute indication of c-section in subsequent pregnancies, vaginal birth after cesarean (VBAC) might cause numerous adverse effects including uterine rupture, fetal death, or fetal brain damage due to hypoxia. In addition, other previous uterine surgeries such as myomectomy or resection of adenomyosis were also known as a risk factor for c-section, and are considered indications for c-section in subsequent deliveries. 27 Moreover, history of vaginal delivery also affects the risk of c-section. Mothers in their first pregnancy have a greater risk of having a cesarean delivery compared to those who have already had a vaginal delivery before. This is because the pelvic of multiparous women with previous vaginal delivery was considered to be more flexible and easier to undergo vaginal delivery in the following pregnancies. 15 , 23 , 28
Furthermore, obstetrical complications are also well-established major risk factors of c-section procedure. In this study, we included preeclampsia/eclampsia, gestational diabetes mellitus, IUGR, placenta previa, and placental abruption, since those are the most common pregnancy problems in Indonesia. 9 Previous studies have suggested that those complications of pregnancy had relative risk of around 1.45–1.75 for c-section. 14 , 15 , 24 Our study found that preterm birth (gestational age < 37 wg) increased the risk of c-section. This was consistent with another previous study which showed that birth at < 37 wg increased the risk of c-section with an OR: 1.45, 95% CI: 1.16–1.72. 29 This findings imply that pregnant women who felt the signs of labor such as uterine contractions, bloody mucous discharge or water breaking before 37 weeks of gestation, were predicted to had increased risk of c-section.
The characteristics of the fetus during pregnancy may also affect the risk of c-section delivery, especially during the third trimester. Our study found that birthweight ⩾ 3500 g had OR of 4.28 (95% CI: 2.16–8.47), thus is given a score of “2” in our prediction tool. This is in agreement with a previous study which found that heavier fetal weight was associated with the increased risk of c-section. 14 , 30 Another previous study also supports our finding, suggesting that a total of 60.7% of pregnancies with a fetal weight more than 3500 were delivered by c-section, compared to 39.3% for a fetus weighing < 3500 g. 28 Although our study used the clinical birthweight rather than the estimated fetal weight, previous studies have found that there was no significant difference between estimated fetal weight and actual birth weight in normal weight population. 31 Significant difference of fetal weight usually found in small for gestational age fetus, with differences up to 200 g. 32 Thus, a clinically-determined estimated fetal weight of ⩾ 3500 g, can still be a predictive factor for an increased risk of c-section. In addition, our study also found that non-cephalic presentation is associated with increased risk of c-section. This was not surprising, as numbers of studies have also found its association with increased risk of c-section. A previous study found that the incidence of c-section in non-cephalic presentation was 93.3% (p < 0.001) compared to head presentation, the incidence of which is 37.3%. 28 Nevertheless, studies have suggested that non-cephalic presentation was best diagnosed at 36 weeks of gestational age. 33 Therefore, pregnant women who uses our scoring tool with diagnosed fetal presentation before 36 weeks of gestation, is recommended to repeat the examination in the subsequent weeks of pregnancy. Moreover, interestingly, in our first part of study, we also found 37.18 per 1000 rate of early fetal death. This high number was due to the fact that our study was conducted in tertiary and national referral hospitals, thus the number of cases of adverse pregnancy complications was higher than the national data. 9
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to propose a scoring system in the risk of c-section for both non-medical and medical personnel, with variables which were considered simple and easy to evaluate. The internal and external validations have reflected satisfactory calibration and discrimination values of the scoring system. Nevertheless, there were certain limitations of the study. Pregnant women that could confidently use this scoring were the ones with late trimester, as most of variables could only be evaluated during the last trimester. Also, this was a retrospective study, thus the conclusions were limited by the results of this present study. Further studies should explore the application of this predictive scoring tool in a wider range of population with a prospective cohort design.
There were seven independent factors found to be highly associated with c-section delivery, including gestational age < 37, underweight pre-pregnancy BMI, previous uterine surgery, no history of vaginal delivery, obstetrical complications, birthweight ⩾ 3500, and non-cephalic presentation. A predictive scoring tool has been developed and validated with a good quality. Pregnant women were expected to use this scoring tool as a self-administered questionnaire so they are able to self-assess their risks of c-section. High risk of c-section results would encourage mothers, families, and healthcare professionals to arrange for early consultations with obstetricians and make better preparations for the mothers to deliver at the hospitals.
Acknowledgments
We thank Danone Specialized Nutrition Indonesia for supporting this research, as they will further create an online application for the tools.
Author contributions: R.I. and N.W. designed the study. R.H. and A.W.L. conducted the research, performed the analysis, interpretation of data, and wrote the manuscript. R.I. validated the data, revised the paper, and had primary responsibility for the final content. All authors agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.

Data availability: The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Frank breech. When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head.
Occiput or cephalic anterior: This is the best fetal position for childbirth. It means the fetus is head down, facing the birth parent's spine (facing backward). Its chin is tucked towards its chest. The fetus will also be slightly off-center, with the back of its head facing the right or left. This is called left occiput anterior or right ...
Fetal presentation, or how your baby is situated in your womb at birth, is determined by the body part that's positioned to come out first, and it can affect the way you deliver. ... Like the transverse lie, this position is more common earlier in pregnancy, and it's likely your provider will intervene if your baby is still in the oblique lie ...
Toward the end of pregnancy, the fetus moves into position for delivery. Normally, the presentation is vertex (head first), and the position is occiput anterior (facing toward the pregnant patient's spine) with the face and body angled to one side and the neck flexed. Abnormal presentations include face, brow, breech, and shoulder.
Benefits of Cephalic Presentation in Pregnancy. Cephalic presentation is one of the most ideal birth positions, and has the following benefits: It is the safest way to give birth as your baby's position is head-down and prevents the risk of any injuries. It can help your baby move through the delivery canal as safely and easily as possible.
Your provider will likely order an ultrasound toward the end of your pregnancy if they suspect your baby is in a breech position. Breech positions come with a higher likelihood of a C-section delivery in order to protect both you and your little one during childbirth. There are several different types of breech presentation:
Presentation refers to which part of your baby's body is facing towards your birth canal. Position refers to the direction your baby's head or back is facing. Your baby's presentation will be checked at around 36 weeks of pregnancy. Your baby's position is most important during labour and birth.
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation, where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations ...
This presentation can lead to more back pain (sometimes referred to as "back labor") and slow progression of labor. In the right occiput posterior position (ROP), the baby is facing forward and slightly to the right (looking toward the mother's left thigh). This presentation may slow labor and cause more pain. Tips to Reduce Discomfort
In the last weeks of pregnancy, a fetus usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation.A breech presentation occurs when the fetus's buttocks, feet, or both are in place to come out first during birth. This happens in 3-4% of full-term births.
What is the meaning of cephalic presentation in pregnancy? Cephalic presentation means the baby's head is positioned down towards the birth canal, which is the ideal fetal position for childbirth. This position is considered optimal for a smoother and safer delivery. In medical terms, a baby in cephalic presentation is said to be in a "vertex ...
Presentation of twins in Der Rosengarten ("The Rose Garden"), a standard medical text for midwives published in 1513. In obstetrics, the presentation of a fetus about to be born specifies which anatomical part of the fetus is leading, that is, is closest to the pelvic inlet of the birth canal. According to the leading part, this is identified as a cephalic, breech, or shoulder presentation.
Compound presentation means that a fetal hand is coming out with the fetal head. This is a problem because: The amount of baby that must come through the birth canal at one time is increased. There is increased risk of mechanical injury to the arm and shoulder, including fractures, nerve injuries and soft tissue injury.
The vertex presentation describes the orientation a fetus should be in for a safe vaginal delivery. It becomes important as you near your due date because it tells your pregnancy care provider how they may need to deliver your baby. Vertex means "crown of the head.". This means that the crown of the fetus's head is presenting towards the ...
Toward the end of pregnancy, the fetus moves into position for delivery. Normally, the presentation is vertex (head first), and the position is occiput anterior (facing toward the pregnant person's spine) and with the face and body angled to one side and the neck flexed. Variations in fetal presentations include face, brow, breech, and shoulder.
Approximately 97% of deliveries involve a fetus positioned with the head down, in the best position to slide out. That makes a vaginal delivery easier and safer. A transverse position only happens in about 1% of deliveries. In that position, the shoulder, arm, or trunk of the fetus may present first. This isn't a good scenario for either of you ...
Twin fetal presentation - also known as the position of your babies in the womb - dictates whether you'll have a vaginal or c-section birth. Toward the end of pregnancy, most twins will move in the head-down position (vertex), but there's a risk that the second twin will change position after the first twin is born.
Breech presentation is typically diagnosed during a visit to an OB-GYN, midwife, or health care provider. Your physician can feel the position of your baby's head through your abdominal wall—or ...
Abnormal Fetal Lie. If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation. ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen. It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women.
Pregnancy (gestation) is the physiologic process of a developing fetus within the maternal body. Several terms are used to define the developmental stage of human conception and the duration of pregnancy. For obstetric purposes, the gestational age or menstrual age is the time elapsed since the first day of the last normal menstrual period (LNMP), which actually precedes the time of oocyte ...
Introduction. Cesarean section, or more commonly known as c-section, has become the main alternative delivery method in pregnancy with life-threatening complications. 1 The decision to perform c-section should be made under conditions where vaginal delivery is impossible, or poses more risks, and is therefore taken only with certain maternal or fetal indications. 2