- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In

abbreviation or noun
Definition of phd, examples of phd in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'PhD.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
New Latin philosophiae doctor
1839, in the meaning defined above
Dictionary Entries Near PhD
Cite this entry.
“PhD.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/PhD. Accessed 2 May. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
What’s the difference between ‘hillbilly’ and ‘redneck’, more commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 26, 9 superb owl words, 'gaslighting,' 'woke,' 'democracy,' and other top lookups, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, your favorite band is in the dictionary, games & quizzes.


What is a PhD?
- Types of Doctorates
- A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the highest globally recognized postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award.
- PhDs are awarded to candidates who undertake original and extensive research in a particular field of study.
- Full time PhD programmes typically last three to four years, whilst part time PhD programmes typically last six to seven years.
- A PhD can lead to an academia teaching role or a career in research. A PhD can also equip you with skills suitable for a wide range of jobs unrelated to your research topic or academia.
Definition of a PhD – A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD , Ph.D or a DPhil ) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible.
PhDs differ from undergraduate and master’s degrees in that PhDs are entirely research-based rather than involving taught modules (although doctoral training centres (DTCs) offer programmes that start with a year of lecture-based teaching to help develop your research skills prior to starting your project).
In most English-speaking countries, those that complete a PhD use the title “Doctor” (typically abbreviated to Dr) in front of their names and are referred to as such within academic and/or research settings. Those that work in fields outside of academia may decide not to use the formal doctor title but use post-nominal letters (e.g. John Smith PhD); it’s unusual though for someone to use both the Doctor title and post-nominal letters in their name.
PhD vs Doctorate
A PhD and a professional doctorate are both research-based terminal degrees.
However, where a PhD focuses on original research mostly around theoretical concepts, a professional doctorate focuses on examining existing knowledge to solve real-life, practical problems.
While there is much crossover between the two, a PhD is generally better suited for an individual to wants to advance the knowledge and understanding in their field, and a professional doctorate degree is better suited to a working professional who wants to better be able to apply knowledge and understanding to their field.
What Are the Entry Requirements for a PhD?
To be accepted on to a PhD programme, students usually need to hold at least a high ( 2:1 and above ) undergraduate degree that is related to the field of research that they want to pursue. A PhD candidate may also be expected to hold a Master’s degree , however, this does not mean you must have one, as it is still possible to enrol into a PhD without a Master’s .
Self-funded courses may sometimes be more relaxed in relation to entry requirements. It may be possible to be accepted onto a self-funded PhD programme with lower grades, though these students typically demonstrate their suitability for the role through professional work experience.
Whilst a distance learning project is possible , most PhD candidates will carry out their research over at least three years based at their university, with regular contact with two academic supervisors (primary and secondary). This is particularly the case for lab-based projects, however, some PhD projects require spending time on-site away from university (e.g. at a specialist research lab or at a collaborating institution abroad).
How Long Does a PhD Take?
Typically, full-time PhDs last 3-4 years and part-time PhDs last 6-7 years. However, at the discretion of the university, the thesis writing-up period can be extended by up to four years.
Although most doctoral programmes start in September or October, they are generally much more flexible than taught-courses and can start at any time of the year.
How Much Does a PhD Cost?
Tuition fees for UK and EU students vary between £3,000 and £6,000 per year, with the average tuition fee of £4,712 per year for 2023/24 programmes.
Tuition fees increase considerably for international students, varying between £16,000 to £25,000 per year, with an average tuition fee of £19,600 per year .
Nonetheless, most students will secure PhD funding in the form of studentships, scholarships and bursaries to help pay for these fees. These funding opportunities can either be partial, which cover tuition fees only, or full, which cover both tuition fees and living expenses.
UK national students can also apply for Doctoral Loans from Student Finance England if they are unable to secure funding.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
What Does a PhD Involve?
To be awarded a PhD, a doctoral student is required to produce a substantial body of work that adds new knowledge to their chosen field.
A PhD programme will typically involve four key stages:
Stage 1: Literature Review
The first year of a PhD involves attending regular meetings with your supervisors and carrying out a search on previously published work in your subject area. This search will be used to produce a literature review which should set the context of the project by explaining the foundation of what is currently known within the field of research, what recent developments have occurred, and where the gaps in knowledge are. In most cases, this will be an extension of your research proposal should you have produced one as part of your application. The literature review should conclude by outlining the overarching aims and objectives of the research project. This stage of setting achievable goals which are original and contribute to the field of research is an essential first step in a successful PhD.
The supervisor is the main point of contact through the duration of a PhD – but remember: they are there to mentor, not to teach, or do it for you . It will be your responsibility to plan, execute and monitor your own work as well as to identify gaps in your own knowledge and address them.
Stage 2: Research
The second year (and prehapse some of your third year) is when you work on your research. Having identified novel research questions from your review of the literature, this is where you collect your data to help answer these questions. How you do this will depend on the nature of your doctoral research: for example, you may design and run experiments in a lab alongside other PhD students or visit excavation sites in remote regions of the world. You should check in regularly with your supervisors to update them and run any ideas or issues past them.
Have the structure and chapters of your thesis in mind as you develop and tackle your research questions. Working with a view of publishing your work will be very valuable later on.
Stage 3: Write up of Thesis
The next key stage of a PhD is writing a doctoral thesis , which typically takes from anywhere between three months to one year. A thesis is a substantial body of work that describes the work and outcomes of the research over the previous two to three years. It should tell a detailed story of the PhD project – focusing on:
- The motivations for the research questions identified from the literature review.
- The methodologies used, results obtained, and a comprehensive analysis and discussion of the findings.
- A detailed discussion of the key findings with an emphasis on the original contributions made to your field of research and how this has been impactful.
There is no universal rule for the length of a PhD thesis, but general guidelines set the word count between 80,000 to 100,000 words.
For your thesis to be successful, it needs to adequately defend your argument and provide a unique or increased insight into your field that was not previously available.
Stage 4: Attending the Viva
A viva voce , most commonly referred to as just a ‘ viva ‘, is an interview-style examination where the PhD student is required to engage in a critical appraisal of their work and defend their thesis against at least two examiners. The examiners will ask questions to check the PhD student has an in-depth understanding of the ideas and theories proposed in their thesis, and whether they have developed the research skills that would be expected of them.
The viva is one of the final steps in achieving a PhD, and typically lasts at least two hours, but this duration can vary depending on the examiners, the university and the PhD project itself.
Once you have done the viva – you’re on the home stretch. You will typically be asked to make some amendments to your thesis based on the examiner’s feedback. You are then ready to submit your final thesis for either:
- PhD – If you pass the requirements you will be awarded a PhD degree (most common outcome),
- MPhil – If you failed to meet requirements for a PhD, you may be downgraded to an MPhil degree (uncommon outcome),
- Fail – No award is given, typically for cases of plagiarism (extremely uncommon outcome).
What Is It Like to Undertake a PhD?
We’re often asked what it is like to undertake a PhD study. Unfortunately, this isn’t a simple answer to this question as every research project is different.
To help give insight into the life of a PhD student, we’ve interviewed PhD students at various stages of their programmes and put together a series of PhD Student Interviews . Check out the link to find out what a PhD is like and what advice they have to offer you.
What Are the Benefits of A PhD?
A PhD is the highest globally recognised postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award. The degree, which is awarded to candidates who demonstrate original and independent research in a particular field of study, is not only invaluable in itself, but sets you up with invaluable skills and traits.
Career Opportunities
First, a PhD prepares you for a career in academia if you wish to continue in this area. This takes form as a career in the Higher Education sector, typically as a lecturer working their way to becoming a professor leading research on the subject you’ve studied and trained in.
Second, a PhD also enables the opportunity for landing a job in a research & development role outside of the academic environment. Examples of this include laboratory work for a private or third sector company, a governmental role and research for commercial and industrial applications.
Transferable Skills
Finally, in possessing a PhD degree, you can show to employers that you have vital skills that make you an asset to any company. Three examples of the transferable skills that you gain through a PhD are effective communication, time management, and report writing.
- Communication – presenting your work in written and oral forms using journal papers and podium presentations, shows your ability to share complex ideas effectively and to those with less background knowledge than you. Communication is key in the professional environment, regardless of the job.
- Time management – The ability to prioritise and organise tasks is a tremendous asset in the professional industry. A PhD holder can use their qualification to demonstrate that they are able to manage their time, arrange and follow a plan, and stick to deadlines.
- Report writing – Condensing three years of work into a thesis demonstrates your ability to filter through massive amounts of information, identify the key points, and get these points across to the reader. The ability to ‘cut out the waffle’ or ‘get to the point’ is a huge asset in the professional industry.
Aside from the above, you also get to refer to yourself as a Doctor and add fancy initials after your name!
What Can I Do After a PhD?
One of the most desirable postdoctoral fields is working within independent Research and Development (R&D) labs and new emerging companies. Both industries, especially R&D labs, have dedicated groups of PhD graduates who lead research activities, design new products and take part in crucial strategic meetings. Not only is this a stimulating line of work, but the average salaries in R&D labs and emerging start-ups are lucrative. In comparison, an undergraduate with five years of experience within their given field will, on average, likely earn less than a new PhD graduate taking on a R&D position.
It’s a common misunderstanding that PhDs only opens the door for an academic career such as university lecturers and training providers. Although obtaining a PhD opens these doors, the opportunities extend far beyond educational roles. In fact, recent data from the UK’s Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA) indicates only 23% of PhD graduates take a position in educational roles . This low percentage is primarily because PhD graduates have a wide range of skills that make them suitable for a broad spectrum of roles. This is being seen first hand by the increasing number of PhD graduates who are entering alternative roles such as research, writing, law and investment banking.
How Do I Find a PhD?
We appreciate that finding a PhD programme to undertake can be a relatively daunting process. According to Higher Education Student Statistics , over 22,000 PhDs were awarded in 2016/17 within the United Kingdom alone. Clearly there are a huge number of PhD programmes available. This can sometimes be confusing for prospective doctorates, particularly when different programmes are advertised in different places. Often, it is difficult to know where to look or where to even start. We’ve put together a list of useful sources to find the latest PhD programmes:
- A great place to start is with our comprehensive and up-to-date database of available PhD positions .
- Assuming you are still at university, speak to an existing PhD supervisor within your department.
- Attend as many postgraduate open days as you can. Whilst there, speak to current PhD students and career advisors to get an awareness of what PhDs are on offer.
- Visit the postgraduate section of university websites and the PhD Research Council section of the UKRI website.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of PhD in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- associate's degree
- baccalaureate
- bachelor's degree
- double major
- first degree
- Master's degree
- second degree
- summa cum laude
Ph.D. | Intermediate English
Translations of phd.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
mum's the word
said when you tell someone, or agree with someone, to keep something a secret

Hidden in plain sight: words and phrases connected with hiding

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- Intermediate Noun
- Translations
- All translations
To add PhD to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add PhD to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of PhD noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- to do/have/be a PhD
- Anne Thomas, PhD
- acquire/get/lack (an) education/training/ (British English) (some) qualifications
- receive/provide somebody with training/tuition
- develop/design/plan a curriculum/ (especially British English) course/ (North American English) program/syllabus
- give/go to/attend a class/lesson/lecture/seminar
- hold/run/conduct a class/seminar/workshop
- sign up for/take a course/classes/lessons
- go to/start preschool/kindergarten/nursery school
- be in (North American English) the first, second, etc. grade/ (British English) year 1, 2. etc. (at school)
- study/take/drop history/chemistry/German, etc.
- (British English) leave/finish/drop out of/ (North American English) quit school
- (North American English) graduate high school/college
- be the victim/target of bullying
- (British English) play truant from/ (both British English, informal) bunk off/skive off school (= not go to school when you should)
- (both especially North American English) skip/cut class/school
- (British English) cheat in/ (North American English) cheat on an exam/a test
- get/be given a detention (for doing something)
- be expelled from/be suspended from school
- do your homework/ (British English) revision/a project on something
- work on/write/do/submit an essay/a dissertation/a thesis/an assignment/ (North American English) a paper
- finish/complete your dissertation/thesis/studies/coursework
- hand in/ (North American English) turn in your homework/essay/assignment/paper
- study/prepare/ (British English) revise/ (North American English) review/ (North American English, informal) cram for a test/an exam
- take/ (both British English) do/sit a test/an exam
- (especially British English) mark/ (especially North American English) grade homework/a test
- (British English) do well in/ (North American English) do well on/ (especially North American English, informal) ace a test/an exam
- pass/fail/ (especially North American English, informal) flunk a test/an exam/a class/a course/a subject
- apply to/get into/go to/start college/ (British English) university
- leave/graduate from law school/college/ (British English) university (with a degree in computer science)
- study for/take/ (British English) do/complete a law degree/a degree in physics
- (both North American English) major/minor in biology/philosophy
- earn/receive/be awarded/get/have/hold a master’s degree/a bachelor’s degree/a PhD in economics
- dissertation
Join our community to access the latest language learning and assessment tips from Oxford University Press!
Nearby words

- April 2, 2024
- Academic Advice
What Does Ph.D. Stand For?
UOTP Marketing

Ever wondered why someone with the title “Doctor of Philosophy” isn’t necessarily pondering the mysteries of existence like Descartes or Nietzsche? That’s because the term encompasses many disciplines beyond its traditional confines. Whether it’s exploring the mysteries of the cosmos, deciphering intricate economic systems or unraveling the complexities of human behavior, a Ph.D. can be earned in any field ranging from science and economics to humanities and beyond.
In this article, we’ll explore the multifaceted world of Ph.D. studies, beginning with the fundamental question: What does Ph.D. stand for?
Beyond merely defining the acronym, we provide crucial information to assist you in determining whether pursuing this advanced degree aligns with your goals, aspirations and intellectual passions.
Meaning of Ph.D.
A Ph.D., short for Doctor of Philosophy, is an esteemed academic degree marking the pinnacle of in-depth study and innovative research in a specific area of expertise. Attaining a Ph.D. involves not just a broad mastery of the field at large but also acquiring specialized knowledge and insights into a distinct facet of that discipline.
For instance, pursuing a Ph.D. in literature involves acquiring a thorough understanding of literary theory and criticism while also focusing deeply on a particular literary period or genre, such as Victorian literature, postcolonial literature, or contemporary poetry. This process ensures that Ph.D. candidates achieve a comprehensive grasp of their broader discipline while also cultivating an expert-level specialization.
Education Requirements for a Ph.D.
In order to pursue a Ph.D. program, you must first fulfill some education prerequisites. Both a bachelor’s degree and often a master’s degree serve as essential stepping stones toward this advanced academic pursuit.
Bachelor’s degree
A bachelor’s degree is a fundamental requirement for individuals who aspire to pursue higher education, including Ph.D. studies. Although having a major directly related to the intended Ph.D. field is not mandatory, it can undoubtedly provide a beneficial foundation for handling advanced coursework. Therefore, aligning undergraduate studies with future graduate pursuits can significantly ease the transition into more advanced academic pursuits, ensuring a smoother progression through graduate coursework.
Master’s degree
To be eligible for Ph.D. programs, candidates typically need to have completed a master’s degree. The duration of a master’s degree program can vary depending on whether a student is enrolled part-time or full-time, but typically it lasts between one and three years.
Maintaining a high GPA during master’s studies can improve your chances of getting into a Ph.D. program. Generally, a GPA of 3.0 or higher is seen as favorable. However, this can vary based on factors like your field of study and the program’s competitiveness.
How Long Does a Ph.D. Take?
The typical duration of a Ph.D. program ranges from five to six years, yet this timeframe can vary significantly depending on the academic field and individual circumstances.
Several factors play a pivotal role in determining the length of Ph.D. studies. Firstly, the depth and breadth of the research project can significantly influence the timeline. The dissertation phase, which involves original research, data analysis, and presenting your findings, often requires a considerable amount of time. Secondly, the availability of funding and resources is crucial. Access to financial support and adequate research facilities can either speed up the process or cause delays.
Moreover, specific program or institutional requirements, such as compulsory coursework, teaching commitments, or comprehensive exams, may affect the overall timeline. These obligations can increase the academic workload, potentially prolonging the time necessary to fulfill all degree requirements.
The Process of Obtaining a Ph.D.
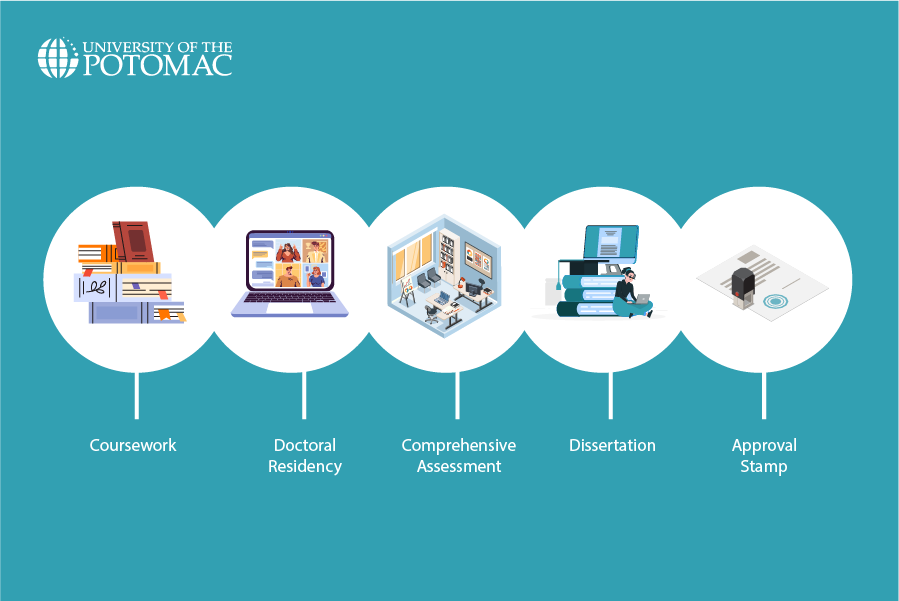
The process of obtaining a Ph.D. is a journey that involves passing through various milestones and academic achievements, each contributing to the culmination of advanced scholarly expertise. Let’s go through some of the steps below:
Completing coursework
Coursework is a foundational step in the Ph.D. process, helping students cultivate profound subject-matter expertise and establish essential knowledge within the field. These courses equip students with the requisite theoretical framework and shape potential dissertation research topics.
Completing one or more doctoral residency experiences
Doctoral residencies provide a structured platform for refining research skills, receiving guidance, and engaging in scholarly discourse. Often conducted virtually, these experiences allow students to focus on specific study and dissertation preparation activities while fostering connections with faculty and peers for invaluable mentorship and collaboration.
Passing a comprehensive assessment or exam
The purpose of the comprehensive examination process is to comprehensively evaluate the student’s depth of knowledge in their area of specialization and their familiarity with the published research within the field. Additionally, the examination verifies whether the student possesses the critical thinking and analytical skills required for dissertation research.

Developing and completing an independent research project
The dissertation is a comprehensive written document that typically consists of five chapters and addresses a unique question or problem within the field. Faculty experts and the ethical review board play integral roles in assessing the rigor and ethical aspects of the research project, ensuring scholarly integrity and adherence to ethical guidelines.
Seeking approval of your completed dissertation manuscript
The approval process entails evaluation by a faculty committee and the school dean, culminating in a final defense where students defend their research, analysis, and conclusions. Meeting specific professional standards, as applicable to the field, is often a requirement before the publication of the approved dissertation, marking the culmination of the Ph.D. journey.
Career Opportunities for Ph.D. Holders
Ph.D. holders are equipped with a wealth of specialized knowledge and advanced skills, opening doors to many career opportunities that vary depending on their field of study. The roles they can pursue encompass a wide range of leadership, managerial, research, academic, and consulting positions, such as:
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. we will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours. if there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:.
By clicking the Send me more information button above, I represent that I am 18+ years of age, that I have read and agreed to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy , and agree to receive email marketing and phone calls from UOTP. I understand that my consent is not required to apply for online degree enrollment. To speak with a representative without providing consent, please call +1 (202) 274-2300
- We value your privacy.
- Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
- Chief Operating Officer (COO)
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
- Chief Technology Officer (CTO)
- Chief Information Officer (CIO)
- Vice President (VP) of Research and Development
- Vice President (VP) of Innovation
- Director of Research
- Director of Development
- Research Scientist
- Principal Investigator
- Senior Consultant
- Academic Dean
- Head of Department
- Professor or Lecturer
- Senior Policy Analyst
- Executive Director of a Nonprofit Organization
- Editor-in-Chief
- Senior Analyst
- Entrepreneur
5 Reasons to Get a Ph.D.
The decision to pursue a Ph.D. is a significant one that holds the potential to shape both your career trajectory and personal growth. Here are five compelling reasons why pursuing a Ph.D. may be worth considering:
Become an expert in the field
One of the primary motivations for pursuing a Ph.D. is the opportunity to become an expert in a specific field. Obtaining expert-level knowledge allows you to contribute significantly to your chosen field while providing you with a sense of fulfillment and accomplishment.
You can make a difference through research
The true value of a Ph.D. lies in the potential to make a positive impact through research. Across various fields, impactful research has the power to drive innovation, solve pressing societal challenges, and advance human knowledge. Whether it’s discovering new treatments for diseases, developing sustainable technologies, or understanding complex social phenomena, Ph.D. research has the potential to change the world for the better.
Broaden your job opportunities
In today’s competitive job market, a Ph.D. can set you apart from the crowd. While it’s highly relevant for academic careers, a Ph.D. also opens doors to diverse opportunities in industries ranging from technology and healthcare to finance and government. Employers value the advanced research, analytical, and critical thinking skills that Ph.D. holders bring to the table, making them highly sought after in various professional settings.
Increase your salary potential
Earning a Ph.D. can lead to significant financial benefits in the long run. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics , Ph.D. holders typically command higher salaries and have lower unemployment rates. While the journey toward a Ph.D. may require dedication and perseverance, the potential for increased earning potential is a compelling incentive for many aspiring scholars.
You can reach your full potential
Perhaps the most rewarding aspect of pursuing a Ph.D. is the opportunity for personal growth and development. Along the way, you’ll acquire valuable skills, including resilience, problem-solving, and effective communication, that will serve you well professionally and personally. By pushing yourself to tackle complex problems and overcome obstacles, you’ll reach your full potential not only as a scholar but also as an individual ready to leave their mark and make a meaningful difference in the world.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, Ph.D. programs are indispensable components of the academic journey for individuals seeking to enhance their expertise, enrich scholarly knowledge, and pursue fulfilling careers in academia, industry, and beyond.
As you reflect on your academic and professional aspirations, consider the transformative potential of pursuing a Ph.D. program tailored to your passions and ambitions. So, dare to delve deeper, embrace the challenge, and pursue this path of intellectual discovery and personal growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a ph.d. harder than a master’s degree.
While both degrees require significant dedication and effort, a Ph.D. typically involves more extensive research and independent study, making it a more demanding academic pursuit than a master’s degree.
Which is higher: Ph.D. or doctorate?
A Ph.D. lies within the category of doctorate degrees, so one is not inherently higher than the other.
Share it with your friends!
Explore more.

Accounting vs. Finance Degree: Which Major to Choose?

12 Important Bookkeeping Skills You Need for a Successful Career
Recent resources.

What Can You Do With a Hospitality Management Degree? Best Hospitality Careers

What Can You Do with an International Studies Degree [2024]

9 Benefits of Learning a Second Language

Associate’s vs. Bachelor’s: Which One To Choose?
INTERESTED IN LEARNING MORE?
Chat with an Admissions Officer Now!

- Associates Degree
- Bachelors Degrees
- Masters Degrees
- Doctoral Degrees
- Faculty & Staff
- Accreditation
- Student Experience
QUICK LINKS
- Admission Requirements
- Military Students
- Financial Aid
Request More Information
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

PhD: so what does it really stand for?
Recently, during some particularly thorough literature research, I stumbled on a list of alternative interpretations of the acronym PhD. Most were funny: protein has degraded, parents have doubts. But one froze my face in a bittersweet grimace: paid half of what I deserve.
When I was still a rookie PhD student, I read with outrage an Economist article entitled the disposable academic , which argued that doing a PhD is mostly needless. Lately, I've come to think of the PhD as more of a heavily spicy meal. It doesn't matter how much you enjoy the process, once you're done, you still have half of the pain ahead.
The years of academic slog to work your way up to a full tenure slot (professorship? ha – dream on!) are not much different from the work of a PhD in terms of relentless benchwork (pipetting hand disease) and unceasing literature research (pound head on desk), served on a fixed menu with professional uncertainty (please hire: desperate). All of which result in, if not professorship, then potential heavy drinking.
PhD students and postdocs are the working class of academic research and paid accordingly. Although postgraduates are crucial to the generation, discussion and dissemination of knowledge, 50% pay (i.e half of what they deserve) is standard for PhDs in natural sciences and not even guaranteed in the arts and humanities. It's depressing to think that the overall salary of a PhD candidate is less than the cost of much lab equipment. Lab devices are meant to last years – but, hell, what about the work of PhD students in a system where knowledge is incremental?
There could be several reasons for this discrepancy. Equipment and consumables are costly and have a substantial impact on future budget setting. The number of PhDs, meanwhile, is inflated and international competition is fierce. PhD candidates are earning a degree, which shouldn't come for free, and demands motivation and not a little self-denial – including financially.
PhD candidates are at their infancy in science and being trained to do something different from their education to date – lessons in theory combined with practical labwork – as they move into more independent, innovative research. And contributing to the advancement of knowledge requires a certain naive idealism, right? But does this mean it's okay to exploit highly educated individuals ( probably heavily in debt )? No.
The possible solutions are simple. The most obvious is: raise the salary of PhD students. A remedy for the resulting scarcity of resources would be stricter selection so that only the best candidates started a PhD. Realistically though, this is never going to happen. It's not because policymakers are greedy but because it would mean a reduction of PhDs and thus a slowdown of science.
A second option wouldn't hinder research, and might even enhance it: cut the salary of professors by half. If there are solid reasons for PhDs being paid half of what they deserve, then the same hold good for professors. They too are doing something different from their previous jobs. After tenure, natural scientists move out of the lab and into an office from where they supervise the research of their team members. The knowledge acquired before (both theoretical and practical) still counts, but the job looks quite different.
Political and managerial skills are equally essential, and nurtured for the sake of tenure, not science. Top-tier staff write proposals, manage funds and coordinate subaltern research units and are sometimes scarcely involved with the generation, presentation and discussion of results which is the core purpose of science. Some department chairs merely take note of advancements generated from the institutes they preside over, but co-author papers nonetheless.
Wages of these academic administrators, then, don't deserve to sit even at 50%. And however grim this may sound to today's professors and those postdocs close to a permanent role, the benefits might appeal to future professors much more. Reduction in salaries for tenured staff will create new professorial appointments and reduce the imbalance between the number of temporary researchers and professors, while smaller research units will favour better supervision of PhD candidates and reduce fixed costs.
Today's professors probably already earn too little, after so many years of being underpaid. As one reader wrote in response to that Economist article: "The PhD student is someone who forgoes current income in order to forgo future income." But if some of the surplus resulting from a slash in professorial salaries flowed down to PhDs and postdocs, then entry level professors would be put in a better financial position.
In this light, cuts to science funding (like those we have seen recently in the US) could be an opportunity. Will they slow down scientific advancement? Most probably, yes. But here is a chance for the elite to rethink the way science is done and stop placing merit only on the levels of grant money they gain, the papers they publish, and the prestige they acquire, but instead taking a closer look at the predicament of those who prop this community up.
Advocates of competition see it as a positive outcome of the current shortage of funding and resources. But to defend job insecurity as the main incentive to scientific advancement is offensive. Science would benefit more from a harmonious coexistence of its members than by favouring ruthless competition.
Jorge Cham, creator of the wittily depressing PhD Comics series, revealed that a major motivation for his sketches was to give solace to fellow PhDs struggling as he did through their postgraduate years. He interprets the acronym as piled higher and deeper. You might think of the paper bulk on your desk, but I believe he had something else in mind.
PhD actually stands for philosophiae doctor , or doctor of philosophy. As we say in my native Italian: prendila con filosofia (take it easy, take it as it comes). And waiting for a change in the current system, or for a global PhD manifesto to emerge, one cannot take it any other way.
This blog was written by a current PhD student in Italy
This content is brought to you by Guardian Professional . Looking for your next university role? Browse Guardian jobs for thousands of the latest academic, administrative and research posts
- Universities
- Professional development
- University recruitment and HR
- Higher education
Comments (…)
Most viewed.
Definition of 'PhD'

Browse alphabetically PhD
- PhD student
- All ENGLISH words that begin with 'P'
Related terms of PhD
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

Wordle Helper

Scrabble Tools
“M.D.” vs. “Ph.D.” vs. “Dr.”: Are They Synonyms?
Quick: when you hear the word doctor , what do you picture?
Most would probably describe someone in a white lab coat with a stethoscope hanging around their neck or someone in medical scrubs—someone you would seek out if you have a deep cut that needed stitches.
That word doctor , however, is a title assigned to many who don’t come close to that description, many of whom you wouldn’t want stitching up that cut. Take your English professor, for instance. No offense, Dr. Barrett.
It can all be a bit confusing, which is why it’s important to know who and why someone might be called a doctor , as well as what all those initials and abbreviations after their name mean. Here we break it all down.
What does Dr. mean?
Let’s start with doctor or D r . for short. While the first definition of the word is “ a person licensed to practice medicine,” that doesn’t mean you want to take medical advice from anyone who calls themselves a doctor . There are many looser definitions of the word that follow and, frankly, make things a bit confusing.
For example, the third definition is older slang for a “cook, as at a camp or on a ship,” while the seventh entry is “an eminent scholar and teacher.” Bugs Bunny didn’t help matters either by plying anyone and everyone with his famous greeting,“What’s up, doc?”
The term doctor can be traced back to the late 1200s, and it stems from a Latin word meaning “to teach.” It wasn’t used to describe a licensed medical practitioner until about 1400, and it wasn’t used as such with regularity until the late 1600s. It replaced the former word used for medical doctors— leech , which is now considered archaic.
WATCH: When Did The Word "Doctor" Become Medical?
Physician vs. doctor : are these synonyms.
While the term physician is a synonym for doctor , it’s typically used to refer to those who practice general medicine rather than those who perform surgery, aka surgeons .
A quack , on the other hand, is defined as “ a fraudulent or ignorant pretender to medical skill.”
What does M.D. mean?
Moving on to initials that carry more weight than a nod from Bugs, let’s look at M.D.s .
M.D. , which can be used with or without the periods ( M.D. or MD ) is the designation for a medical doctor. This is earned by attending medical school (typically a four-year program after completing at least one undergraduate degree, plus a residency program), and learning to diagnose patients’ symptoms and offer treatment.
The initials M and D stem from the Latin title Medicīnae Doctor. There are many different types of doctors, with different specialties, but if you have a physical ailment, visiting a doctor with the initials M.D. is a good place to start.
Specialty doctors may add even more initials to their title, such as DCN (doctor of clinical nutrition), DDS (doctor of dental surgery), or countless others they acquire with additional training. To make things even more confusing, some may add abbreviations from medical associations they belong to, such as FAAEM (Fellow of the American Academy of Emergency Medicine).
Go Behind The Words!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
What does Ph.D. mean?
As for Ph.D. , this stands for “doctor of philosophy.” It stems from the Latin term Philosophiae Doctor.
You can get a Ph.D. in any number of subjects, from anthropology to mythological studies. It’s not an easy feat, however, as to earn one, you must do original research and write a dissertation .
Ph.D. vs. M.D .: are these synonyms?
There are two big differences between Ph.D. s and M.D .s. When it comes to medicine, M.D.s can prescribe medications, and Ph.D.s can’t. And yes, it’s possible to be both an M.D. and a Ph.D. In fact, some med schools offer programs in which you can achieve both simultaneously.
You can also get a professional doctorate degree in a number of fields. For example, you might receive a doctorate of education, an Ed.D .
So, in a nutshell, both M.D.s and Ph.Ds can be referred to as doctors . If you’re looking for someone to treat what ails you physically, then you want at least an M.D. following their name. If you want to dig deep into a subject and get advice from someone who has done their own research and who likely knows the latest and greatest developments in a particular area, then you’re probably looking for a Ph.D. And if someone has both, even better—depending on your needs, it may be just what the doctor ordered.
Want more synonyms? Get Thesaurus.com’s sizzling synonyms right in your inbox!
Commonly Confused

Trending Words
[ pri- pon -der- uh nt ]
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- TheFreeDictionary
- Word / Article
- Starts with
- Free toolbar & extensions
- Word of the Day
- Free content
- PHD Finger Protein 9
- PhD in Business Administration
- PhD Network University of Twente
- PhD program candidate
- PhD Research in Microelectronics and Electronics
- PhD student
- PhD Students in Information and Knowledge Management
- Facebook Share
- abbreviation
- word in meaning
Examples: NFL , NASA , PSP , HIPAA , random Word(s) in meaning: chat "global warming" Postal codes: USA: 81657 , Canada: T5A 0A7
What does PHD stand for?
Your abbreviation search returned 58 meanings
- MLA style: "PHD." Acronym Finder . 2024. AcronymFinder.com 2 May. 2024 https://www.acronymfinder.com/Slang/PHD.html
- Chicago style: Acronym Finder . S.v. "PHD." Retrieved May 2 2024 from https://www.acronymfinder.com/Slang/PHD.html
- APA style: PHD. (n.d.) Acronym Finder. (2024). Retrieved May 2 2024 from https://www.acronymfinder.com/Slang/PHD.html
- Category Filters
- All definitions (58)
- Information Technology (6)
- Military & Government (7)
- Science & Medicine (16)
- Organizations, Schools, etc. (7)
- Business & Finance (15)
- Slang, Chat & Pop culture (20)
Sort results: alphabetical | rank ?
showing only Slang/Internet Slang definitions ( show all 58 definitions )
Note: We have 135 other definitions for PHD in our Acronym Attic
- suggest new definition
Search for PHD in Online Dictionary Encyclopedia
- Abbreviation Database Surfer
- « Previous
- Next »

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The meaning of PHD is the academic degree, title, or rank of doctor of philosophy; also : a person who has earned the academic degree of doctor of philosophy. How to use PhD in a sentence.
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: philosophiae doctor or doctor philosophiae) is the most common degree at the highest academic level, awarded following a course of study and research. The degree is abbreviated PhD and sometimes, especially in the U.S., as Ph.D. It is derived from the Latin Philosophiae Doctor, pronounced as three separate letters (/ p iː eɪ tʃ ˈ d iː ...
A PhD is a terminal academic degree students typically pursue when they're interested in an academic or research career. A PhD is the highest possible academic degree a student can obtain. PhD stands for "Doctor of Philosophy," which refers to the immense knowledge a student gains when earning the degree. While you can actually get a PhD in ...
Definition of a PhD - A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD, Ph.D or a DPhil) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible. PhDs differ from undergraduate and master's degrees in that PhDs are ...
PhD definition: 1. abbreviation for doctor of philosophy: the highest college or university degree, or someone who…. Learn more.
PhD meaning: 1. abbreviation for doctor of philosophy: the highest college or university degree, or someone who…. Learn more.
PhD definition: the highest degree, a doctorate, awarded by a graduate school in a field of academic study, usually to a person who has completed at least three years of graduate study and a dissertation approved by a committee of professors.. See examples of PHD used in a sentence.
Ph.D. definition: the highest degree, a doctorate, awarded by a graduate school in a field of academic study, usually to a person who has completed at least three years of graduate study and a dissertation approved by a committee of professors.. See examples of PH.D. used in a sentence.
1 a university degree of a very high level that is given to someone who has done research in a particular subject (the abbreviation for "Doctor of Philosophy") to be/have/do a Ph.D. Anne Thomas, Ph.D. Topic Collocations Education learning. acquire/get/lack experience/training/(an) education; receive/provide somebody with training
a university degree of a very high level that is given to somebody who has done research in a particular subject; a person who has this degree (the abbreviation for ' Doctor of Philosophy ') . to do/have/be a PhD; Anne Thomas, PhD
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term 'philosophy' does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to 'lover of wisdom'.
Meaning of Ph.D. A Ph.D., short for Doctor of Philosophy, is an esteemed academic degree marking the pinnacle of in-depth study and innovative research in a specific area of expertise. Attaining a Ph.D. involves not just a broad mastery of the field at large but also acquiring specialized knowledge and insights into a distinct facet of that ...
He interprets the acronym as piled higher and deeper. You might think of the paper bulk on your desk, but I believe he had something else in mind. PhD actually stands for philosophiae doctor, or ...
2 meanings: Doctor of Philosophy Also: DPhil. a doctorate awarded for original research in any subject except law, medicine, or.... Click for more definitions.
PhD: Pothole Dodger (driver on poorly maintained roads) PHD: Portable Handheld Device: PHD: Phased-History Data: PHD: Parametric High Definition: PhD: Poor Helpless and Desperate: PhD: Phenomenally Dumb: PHD: Pre-Hearing Detention: PHD: Process Historian Database: Phd: Pathfinder Healthcare Developments (Smethwick, West Midlands, UK) PHD
M.D., which can be used with or without the periods (M.D. or MD) is the designation for a medical doctor. This is earned by attending medical school (typically a four-year program after completing at least one undergraduate degree, plus a residency program), and learning to diagnose patients' symptoms and offer treatment.
There are two parts; one can classify the educational level of the degree: "B" stands for bachelor's degree; "M" stands for master's degree; and "D" stands for doctoral degree. The second part denotes the discipline of the degree, like "S" for science, "A" for arts, or "Ph" for Philosophy. What are the distinctions ...
Looking for online definition of PhD or what PhD stands for? PhD is listed in the World's most authoritative dictionary of abbreviations and acronyms. PhD - What does PhD stand for? ... Acronym Definition; PhD: Philosophiae Doctor (doctor of philosophy) PhD: Psychology and Human Development (various organizations) PhD:
As many noted, both are accepted, so it is a matter of convention and taste. The important is to be consistent with the other abbreviations you use throughout your text. Compare: I got a Ph.D. in A.I. at U.C.L.A in the U.S. I got a PhD in AI at UCLA in the US.
Capitalization within the abbreviation "PhD" or "Ph.D.". As you may already figure, both "D" and "P" are capitalized but "h" is written in lowercase both in "PhD" and "Ph.D.". This is because "P" and "h" are both parts of the word "Philosophiae" or "Philosophy," while "D" is a separate initial ...
PHD Abbreviation Meaning. Explore the diverse meanings of PHD abbreviation, including its most popular usage as "Project Half Done" in Quilting contexts. This page also provides a comprehensive look at what does PHD stand for in other various sectors such as Doctorate, as well as related terms and more.
PHD: Pull Him/Her Down (Internet slang) PhD: Piled High in Debt: PhD: Pizza Hut Dude: PHD: Praising Him Daily: PHD: Plumbing Hardware Dispatcher (Google TiSP spoof) PhD: Poor Hungry Doctor: PHD: Post Holiday Depression: PHD: Permanent Head Damage (slang) PHD: Player Hater Degree: PHD: Public High Diploma