Edinburgh Research Archive

- ERA Home
- Philosophy, Psychology and Language Sciences, School of

Psychology PhD thesis collection
Show simple item record
Management by objectives: a case study
Files in this item, this item appears in the following collection(s).

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
The objective of a literature review
Questions to Consider
B. In some fields or contexts, a literature review is referred to as the introduction or the background; why is this true, and does it matter?
The elements of a literature review • The first step in scholarly research is determining the “state of the art” on a topic. This is accomplished by gathering academic research and making sense of it. • The academic literature can be found in scholarly books and journals; the goal is to discover recurring themes, find the latest data, and identify any missing pieces. • The resulting literature review organizes the research in such a way that tells a story about the topic or issue.
The literature review tells a story in which one well-paraphrased summary from a relevant source contributes to and connects with the next in a logical manner, developing and fulfilling the message of the author. It includes analysis of the arguments from the literature, as well as revealing consistent and inconsistent findings. How do varying author insights differ from or conform to previous arguments?

Language in Action
A. How are the terms “critique” and “review” used in everyday life? How are they used in an academic context?
In terms of content, a literature review is intended to:
• Set up a theoretical framework for further research • Show a clear understanding of the key concepts/studies/models related to the topic • Demonstrate knowledge about the history of the research area and any related controversies • Clarify significant definitions and terminology • Develop a space in the existing work for new research
The literature consists of the published works that document a scholarly conversation or progression on a problem or topic in a field of study. Among these are documents that explain the background and show the loose ends in the established research on which a proposed project is based. Although a literature review focuses on primary, peer -reviewed resources, it may begin with background subject information generally found in secondary and tertiary sources such as books and encyclopedias. Following that essential overview, the seminal literature of the field is explored. As a result, while a literature review may consist of research articles tightly focused on a topic with secondary and tertiary sources used more sparingly, all three types of information (primary, secondary, tertiary) are critical.
The literature review, often referred to as the Background or Introduction to a research paper that presents methods, materials, results and discussion, exists in every field and serves many functions in research writing.
Adapted from Frederiksen, L., & Phelps, S. F. (2017). Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students. Open Textbook Library
Review and Reinforce
Two common approaches are simply outlined here. Which seems more common? Which more productive? Why? A. Forward exploration 1. Sources on a topic or problem are gathered. 2. Salient themes are discovered. 3. Research gaps are considered for future research. B. Backward exploration 1. Sources pertaining to an existing research project are gathered. 2. The justification of the research project’s methods or materials are explained and supported based on previously documented research.
Media Attributions
- 2589960988_3eeca91ba4_o © Untitled blue is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
Sourcing, summarizing, and synthesizing: Skills for effective research writing Copyright © 2023 by Wendy L. McBride is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Bridging the gap: a systematic analysis of circular economy, supply chain management, and digitization for sustainability and resilience
- Published: 13 May 2024
Cite this article

- Bhawna ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3032-0104 1 , 2 ,
- Parminder Singh Kang 2 , 3 &
- Sanjeev Kumar Sharma 1
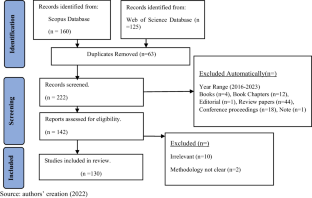
The primary objective of this research paper is to conduct a comprehensive and systematic literature review (SLR) focusing on Sustainable Supply Chain Management (SSCM) practices that promote Circular Economy (CE), sustainability, and resilience through adopting emerging digital technologies. A SLR of 130 research articles published between 1991 and 2023 was used to analyze emerging trends in CE, supply chain management (SCM), and digitalization. This study meticulously examined research publication patterns, the intricate themes explored, influential scholars, leading countries, and substantial scientific contributions that have shaped this multifaceted domain. This paper contributed to the collective understanding of how SSCM practices, driven by the principles of CE and empowered by the adoption of digital technologies, foster sustainability, resilience, and innovation within contemporary SCs. The research findings presented herein are primarily based on an analysis of the current literature from only Scopus and Web of Science (WoS) databases, which may restrict the generalizability of implementing these results. Based on this study, organizations and practitioners can assess the maturity of their SCM practices, gauge the resilience and digitalization levels of their SCs, and align them with academic literature trends. This enables practitioners to bridge the gap between scholarly advancements and real-world SCM implementation. Through its systematic review, the study provides a structured literature review that offers a collective understanding of SSCM practices driven by CE principles and empowered by digital technologies. This understanding enables sustainability, resilience, and innovation within contemporary SCs, benefiting academicians and practitioners.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Data availability
Data can be provided upon request.
Alamelu R, Jayanthi M, Dinesh S, Nalini R, Shobhana N, Amudha R (2023) Sustainable supply chain and circular economy ingenuities in small manufacturing firms-a stimulus for sustainable development. Mater Today: Proc 92:17–23
Google Scholar
Bag S, Pretorius JHC (2022) Relationships between industry 4.0, sustainable manufacturing and circular economy: proposal of a research framework. Int J Organ Anal 30(4):864–898. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-04-2020-2120
Article Google Scholar
Bag S, Wood LC, Xu L, Dhamija P, Kayikci Y (2020) Big data analytics as an operational excellence approach to enhance sustainable supply chain performance. Resour Conserv Recycl 153:104559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104559
Birkel H, Hohenstein N-O, Hähner S (2023) How have digital technologies facilitated supply chain resilience in the COVID-19 pandemic? An exploratory case study. Comput Ind Eng 183:109538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2023.109538
Branke J, Farid SS, Shah N (2016) Industry 4.0: a vision for personalized medicine supply chains? Cell Gene Therapy Insights 2(2):263–270. https://doi.org/10.18609/cgti.2016.027
Carter CR, Rogers DS (2008) A framework of sustainable supply chain management: moving toward new theory. Int J Phys Distribution Logistics Manage 38(5):360–387
Centobelli P, Cerchione R, Esposito E, Passaro R, Shashi (2021) Determinants of the transition towards circular economy in SMEs: a sustainable supply chain management perspective. Int J Prod Econ 242:108297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108297
Cerqueira-Streit J, Endo G, Guarnieri P, Batista L (2021) Sustainable supply Chain Management in the Route for a circular economy: an integrative literature review. Logistics 5(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics5040081
Chadegani AA, Salehi H, Yunus MM, Farhadi H, Fooladi M, Farhadi M, Ebrahim NA (2013) A comparison between two Main Academic Literature collections: web of Science and Scopus databases. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.1305.0377
Chari A, Niedenzu D, Despeisse M, Machado CG, Azevedo JD, Boavida-Dias R, Johansson B (2022) Dynamic capabilities for circular manufacturing supply chains—exploring the role of industry 4.0 and resilience. Bus Strategy Environ 31(5):2500–2517. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3040
Chauhan C, Singh A (2019) A review of industry 4.0 in supply chain management studies. J Manuf Technol Manage 31(5):863–886
Dentoni D, Pinkse J, Lubberink R (2021) Linking Sustainable Business models to Socio-Ecological Resilience through Cross-sector partnerships: a Complex Adaptive systems View. Bus Soc 60(5):1216–1252. https://doi.org/10.1177/0007650320935015
Donthu N, Kumar S, Pattnaik D (2020) Forty-five years of Journal of Business Research: a bibliometric analysis. J Bus Res 109:1–14
Edwin Cheng TC, Kamble SS, Belhadi A, Ndubisi NO, Lai K, Kharat MG (2022) Linkages between big data analytics, circular economy, sustainable supply chain flexibility, and sustainable performance in manufacturing firms. Int J Prod Res 60(22):6908–6922. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2021.1906971
El Baz J, Tiwari S, Akenroye T, Cherrafi A, Derrouiche R (2022) A framework of sustainability drivers and externalities for industry 4.0 technologies using the best-worst method. J Clean Prod 344:130909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130909
Esmaeilian B, Sarkis J, Lewis K, Behdad S (2020) Blockchain for the future of sustainable supply chain management in industry 4.0. Resour Conserv Recycl 163:105064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105064
Ferasso M, Beliaeva T, Kraus S, Clauss T, Ribeiro-Soriano D (2020) Circular economy business models: the state of research and avenues ahead. Bus Strategy Environ 29(8):3006–3024. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2554
Fisher O, Watson N, Porcu L, Bacon D, Rigley M, Gomes RL (2018) Cloud manufacturing as a sustainable process manufacturing route. J Manuf Syst 47:53–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.03.005
Gaur V, Gaiha A (2020) Building a transparent supply chain blockchain can enhance trust, efficiency, and speed. Harvard Business Rev 98(3):94–103
Ghisellini P, Cialani C, Ulgiati S (2016) A review on circular economy: the expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. J Clean Prod 114:11–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.007
Golicic SL, Smith CD (2013) A meta-analysis of environmentally sustainable supply chain management practices and firm performance. J Supply Chain Manage 49(2):78–95
Govindan K, Hasanagic M (2018) A systematic review on drivers, barriers, and practices towards circular economy: a supply chain perspective. Int J Prod Res 56(1–2):278–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1402141
Graham G, Hardaker G (2000) Supply-chain management across the Internet. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 30(3/4):286–295. https://doi.org/10.1108/09600030010326055
Hendry LC, Stevenson M, MacBryde J, Ball P, Sayed M, Liu L (2019) Local food supply chain resilience to constitutional change: the Brexit effect. Int J Oper Prod Manage 39(3):429–453. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-03-2018-0184
Hofmann E, Rüsch M (2017) Industry 4.0 and the current status as well as future prospects on logistics. Comput Ind 89:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2017.04.002
Ingemarsdotter E, Jamsin E, Kortuem G, Balkenende R (2019) Circular strategies enabled by the internet of things—A framework and analysis of current practice. Sustainability 11(20):5689
Jabbarzadeh A, Fahimnia B, Sabouhi F (2018) Resilient and sustainable supply chain design: sustainability analysis under disruption risks. Int J Prod Res 56(17):5945–5968. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1461950
Lopes de Sousa Jabbour AB, Jabbour CJ, Godinho Filho M, Roubaud D (2018) Industry 4.0 and the circular economy: a proposed research agenda and original roadmap for sustainable operations. Ann Oper Res 270:273–286
Kähkönen A-K, Lintukangas K, Hallikas J (2018) Sustainable supply management practices: making a difference in a firm’s sustainability performance. Supply Chain Management: Int J 23(6):518–530
Karmaker CL, Aziz A, Ahmed R, Misbauddin T, Moktadir MA (2023) Impact of industry 4.0 technologies on sustainable supply chain performance: the mediating role of green supply chain management practices and circular economy. J Clean Prod 419:138249
Lu HE, Potter A, Sanchez Rodrigues V, Walker H (2018) Exploring sustainable supply chain management: a social network perspective. Supply Chain Management: Int J 23(4):257–277
Luthra S, Mangla SK (2018) Evaluating challenges to industry 4.0 initiatives for supply chain sustainability in emerging economies. Process Saf Environ Prot 117:168–179
MacArthur E (2013) Towards the circular economy. J Ind Ecol 2(1):23–44
MacArthur E (2017) A new textiles economy: redesigning fashion’s future. Ellen MacArthur Foundation 1–150
Merli R, Preziosi M, Acampora A (2018) How do scholars approach the circular economy? A systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 178:703–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.112
Morali O, Searcy C (2013) A review of sustainable supply Chain Management practices in Canada. J Bus Ethics 117(3):635–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-012-1539-4
Nandi S, Sarkis J, Hervani AA, Helms MM (2021) Redesigning Supply chains using blockchain-enabled circular economy and COVID-19 experiences. Sustainable Prod Consum 27:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2020.10.019
Obeidat SM, Abdalla S, Al Bakri AAK (2023) Integrating green human resource management and circular economy to enhance sustainable performance: an empirical study from the Qatari service sector. Empl Relations: Int J 45(2):535–563. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-01-2022-0041
Pagell M, Wu Z (2009) Building a more complete theory of sustainable supply chain management using case studies of 10 exemplars. J Supply Chain Manage 45(2):37–56
Pettit TJ, Fiksel J, Croxton KL (2010) Ensuring supply chain resilience: development of a conceptual framework. J Bus Logistics 31(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2158-1592.2010.tb00125.x
Ren Y, Li R, Wu K-J, Tseng M-L (2023) Discovering the systematic interlinkages among the circular economy, supply chain, industry 4.0, and technology transfer: a bibliometric analysis. Clean Responsible Consum 9:100123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clrc.2023.100123
Schmidt CVH, Kindermann B, Behlau CF, Flatten TC (2021) Understanding the effect of market orientation on circular economy practices: the mediating role of closed-loop orientation in German SMEs. Bus Strategy Environ 30(8):4171–4187. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2863
Shin N, Park S (2021) Supply chain leadership driven strategic resilience capabilities management: a leader-member exchange perspective. J Bus Res 122:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.08.056
Singh G, Singh S, Daultani Y, Chouhan M (2023) Measuring the influence of digital twins on the sustainability of manufacturing supply chain: a mediating role of supply chain resilience and performance. Comput Ind Eng 186:109711
Stock T, Seliger G (2016) Opportunities of Sustainable Manufacturing in Industry 4.0. Procedia CIRP 40:536–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.01.129
Talla A, McIlwaine S (2022) Industry 4.0 and the circular economy: using design-stage digital technology to reduce construction waste. Smart Sustainable Built Environ. https://doi.org/10.1108/SASBE-03-2022-0050
Tavera Romero CA, Castro DF, Ortiz JH, Khalaf OI, Vargas MA (2021) Synergy between circular economy and industry 4.0: a literature review. Sustainability 13(8):4331. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084331
Tortorella G, Fogliatto FS, Gao S, Chan T-K (2022) Contributions of industry 4.0 to supply chain resilience. Int J Logistics Manage 33(2):547–566
Yadav G, Luthra S, Jakhar SK, Mangla SK, Rai DP (2020) A framework to overcome sustainable supply chain challenges through solution measures of industry 4.0 and circular economy: an automotive case. J Clean Prod 254:120112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120112
Download references
This research paper is part of a funded research project under Mitacs, Canada (Funding Ref. FR106245).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University Institute of Applied Management Sciences (UIAMS), Panjab University, Chandigarh, India
Bhawna & Sanjeev Kumar Sharma
Department of Decision Sciences, School of Business, MacEwan University, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Bhawna & Parminder Singh Kang
School of Engineering and Sustainable Development, Faculty of Technology, De Montfort University, Leicester, UK
Parminder Singh Kang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bhawna .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
There are no relevant financial or non-financial competing interests to report.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Bhawna, Kang, P.S. & Sharma, S.K. Bridging the gap: a systematic analysis of circular economy, supply chain management, and digitization for sustainability and resilience. Oper Manag Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-024-00490-4
Download citation
Received : 12 October 2023
Revised : 20 March 2024
Accepted : 16 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-024-00490-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Sustainable supply chain management
- Circular economy
- Supply chain sustainability
- Supply chain digitalization
- Research trends
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Literature review. Managing objectives as a modern method to evaluate individual and organized performance is evaluated by a lot of researchers. For the first time "Management by Objectives" is created and named by Drucker (1954) as a contemporary management creator in his book "The Practice of Management". Since that time continuously ...
This review of the literature includes: (a) a history of MBO, (b) a description of the MBO process, (c) advantages and disadvantages of using this process, and (d) guidelines for managers to use ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Management by objective is a cooperative approach in which the administrator and each inferior set the inferiors objects together (Oshogbunu et al., 2022). Akrani (2010) observed that the MBO ...
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a systems approach that can assist managers with these functions. This review of the literature includes: (a) a history of MBO, (b) a description of the MBO process, (c) advantages and disadvantages of using this process, and (d) guidelines for managers to use in implementing this participative goal setting ...
The application of systematic or structured literature reviews (SLRs) has developed into an established approach in the management domain (Kraus et al. 2020), with 90% of management-related SLRs published within the last 10 years (Clark et al. 2021).Such reviews help to condense knowledge in the field and point to future research directions, thereby enabling theory development (Fink 2010 ...
An overview of the subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review. Division of works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative theses entirely)
A plethora of management studies has discussed performance and goal setting since 1911 until today. Drucker was a pioneer in introducing a combination of a three-process management philosophy that reshaped the manager-subordinate relationship from dictating objectives to a flexible approach involving all organizational layers; this approach was tagged as MBO.
The objectives of the literature review should be the driving force behind all methodologies and reporting of findings (Xiao & Watson ... Kar A. K., & Ilavarasan P. V. (2021). Applications of text mining in services management: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 1(1), 100008. Crossref.
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a management approach that is frequently discussed and extensively employed, but seldom sufficiently evaluated. ... Literature review . Management by Objectives: The Team Approach. Show details Hide details. Wendell L. French and more... Fundamentals of Organization Development. 2010.
These examples illustrate a few objectives that management researchers may pursue through SLRs (for a categorization of SLR objectives, see Paul & Criado, 2020). ... Six tips for your (systematic) literature review in business and, management research. Management Review Quarterly, 68 (2018), pp. 103-106. CrossRef View in Scopus Google Scholar.
The present methodological literature review (cf. Aguinis et al., 2020) addresses this void and aims to identify the dominant approaches to sample selection and provide insights into essential choices in this step of systematic reviews, with a particular focus on management research.To follow these objectives, I have critically reviewed systematic reviews published in the two most prominent ...
Peter Drucker is often credited with "inventing" ment by objectives is simply defined as measuring management by objectives. He himself has never work against stated objectives. I will use as a defini- claimed the distinction, but a perusal of the tion for MBO the often cited one of George Odiorne literature would lead one to a proper ...
This review paper presents the second half of the 20th century research of Management by objectives (MBO) approach. The relevant research is spanning over the last five decades and an approach to ...
Comparing systematic literature review to other review forms. In management research, SLRs have taken several different forms in seeking various research objectives. For instance, McLeod, Payne, and Evert (2016) applied an SLR to analyze methods and analytical techniques applied in organizational ethics research - a methods objective.
The review of literature was followed by a case study in which management by objectives was introduced into an industrial organisation,, Field conditions that need to be satisfied if action research of this kind is to be conducted were carefully examined. Working according to the principle of management by objectives involved several phases of ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
Since the objective of a research paper is to develop a new perspective on a topic, these papers contain literature reviews to offer an explanation - to in fact tell the backstory - of the research issue. When students conduct their own original research (for a capstone paper, thesis, or dissertation), they write the literature review ...
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
Abstract. The underlining presuppo sition and the supposition of performance management as a st udy field have been controversial. or have a non -defined concept ever s ince the field was introd ...
The objective of this work is to review the literature of the main concepts that lead to determining the strategic approach, creation of strategies, organizational structures, strategy formulation, and strategic evaluation as a guide for the organizational management, taking into account the effects produced by the different types of strategies on the performance of organizations.
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
Kerzner (2003) defines project management as the planning, organizing, directing, and controlling of company resources for a relatively short term objective that has been established to complete specific goals and objectives. Project Management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to project activities to meet project
The objective of this article is to provide guidance on how to conduct systematic literature review. By surveying publications on the methodology of literature review, we summarize the typology of literature review, describe the procedures for conducting the review, and provide tips to planning scholars.
The primary objective of this research paper is to conduct a comprehensive and systematic literature review (SLR) focusing on Sustainable Supply Chain Management (SSCM) practices that promote Circular Economy (CE), sustainability, and resilience through adopting emerging digital technologies. A SLR of 130 research articles published between 1991 and 2023 was used to analyze emerging trends in ...
Given this background, we add to the literature on PM through an examination of three research objectives: (a) to conduct a scoping review of PM research, with a particular focus on the contribution within the HRD field; (b) to identify research gaps for future investigation; and (c) to identify the prevalence of research into PM versus PA.
of the management by objectives (MBO) literature has reviewed on describing the steps, suggesting the methods for implementation, and listing the pros and cons of adopting an MBO program. 2.
The major objective of the study is to review academic articles published previously concerning the relationship between supply chain management practices and competitive advantage to indicate a ...
Demand-side energy management's primary objective is to maximize the economical utilization of renewable resources without sacrificing overall energy efficiency. ... A pie chart illustrating the distribution of publications identified in the literature review. 2.2. Contributions. The study contrasts residential Demand Response (DR) designs from ...