

Research Process :: Step by Step
- Introduction
- Select Topic
- Identify Keywords
- Background Information
- Develop Research Questions
- Refine Topic
- Search Strategy
- Popular Databases
- Evaluate Sources
- Types of Periodicals
- Reading Scholarly Articles
- Primary & Secondary Sources
- Organize / Take Notes
- Writing & Grammar Resources
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Citation Styles
- Paraphrasing
- Privacy / Confidentiality
- Research Process
- Selecting Your Topic
- Identifying Keywords
- Gathering Background Info
- Evaluating Sources

Organize the literature review into sections that present themes or identify trends, including relevant theory. You are not trying to list all the material published, but to synthesize and evaluate it according to the guiding concept of your thesis or research question.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. Occasionally you will be asked to write one as a separate assignment, but more often it is part of the introduction to an essay, research report, or thesis. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries
A literature review must do these things:
- be organized around and related directly to the thesis or research question you are developing
- synthesize results into a summary of what is and is not known
- identify areas of controversy in the literature
- formulate questions that need further research
Ask yourself questions like these:
- What is the specific thesis, problem, or research question that my literature review helps to define?
- What type of literature review am I conducting? Am I looking at issues of theory? methodology? policy? quantitative research (e.g. on the effectiveness of a new procedure)? qualitative research (e.g., studies of loneliness among migrant workers)?
- What is the scope of my literature review? What types of publications am I using (e.g., journals, books, government documents, popular media)? What discipline am I working in (e.g., nursing psychology, sociology, medicine)?
- How good was my information seeking? Has my search been wide enough to ensure I've found all the relevant material? Has it been narrow enough to exclude irrelevant material? Is the number of sources I've used appropriate for the length of my paper?
- Have I critically analyzed the literature I use? Do I follow through a set of concepts and questions, comparing items to each other in the ways they deal with them? Instead of just listing and summarizing items, do I assess them, discussing strengths and weaknesses?
- Have I cited and discussed studies contrary to my perspective?
- Will the reader find my literature review relevant, appropriate, and useful?
Ask yourself questions like these about each book or article you include:
- Has the author formulated a problem/issue?
- Is it clearly defined? Is its significance (scope, severity, relevance) clearly established?
- Could the problem have been approached more effectively from another perspective?
- What is the author's research orientation (e.g., interpretive, critical science, combination)?
- What is the author's theoretical framework (e.g., psychological, developmental, feminist)?
- What is the relationship between the theoretical and research perspectives?
- Has the author evaluated the literature relevant to the problem/issue? Does the author include literature taking positions she or he does not agree with?
- In a research study, how good are the basic components of the study design (e.g., population, intervention, outcome)? How accurate and valid are the measurements? Is the analysis of the data accurate and relevant to the research question? Are the conclusions validly based upon the data and analysis?
- In material written for a popular readership, does the author use appeals to emotion, one-sided examples, or rhetorically-charged language and tone? Is there an objective basis to the reasoning, or is the author merely "proving" what he or she already believes?
- How does the author structure the argument? Can you "deconstruct" the flow of the argument to see whether or where it breaks down logically (e.g., in establishing cause-effect relationships)?
- In what ways does this book or article contribute to our understanding of the problem under study, and in what ways is it useful for practice? What are the strengths and limitations?
- How does this book or article relate to the specific thesis or question I am developing?
Text written by Dena Taylor, Health Sciences Writing Centre, University of Toronto
http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/specific-types-of-writing/literature-review
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliography
- Next: Step 5: Cite Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2024 12:43 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/researchprocess
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Conducting a literature review: why do a literature review, why do a literature review.
- How To Find "The Literature"
- Found it -- Now What?
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed.
You identify:
- core research in the field
- experts in the subject area
- methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
- gaps in knowledge -- or where your research would fit in
It Also Helps You:
- Publish and share your findings
- Justify requests for grants and other funding
- Identify best practices to inform practice
- Set wider context for a program evaluation
- Compile information to support community organizing
Great brief overview, from NCSU
Want To Know More?
- Next: How To Find "The Literature" >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 1:10 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/litreview
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview

- Research Process
Literature Review in Research Writing
- 4 minute read
Table of Contents
Research on research? If you find this idea rather peculiar, know that nowadays, with the huge amount of information produced daily all around the world, it is becoming more and more difficult to keep up to date with all of it. In addition to the sheer amount of research, there is also its origin. We are witnessing the economic and intellectual emergence of countries like China, Brazil, Turkey, and United Arab Emirates, for example, that are producing scholarly literature in their own languages. So, apart from the effort of gathering information, there must also be translators prepared to unify all of it in a single language to be the object of the literature survey. At Elsevier, our team of translators is ready to support researchers by delivering high-quality scientific translations , in several languages, to serve their research – no matter the topic.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a study – or, more accurately, a survey – involving scholarly material, with the aim to discuss published information about a specific topic or research question. Therefore, to write a literature review, it is compulsory that you are a real expert in the object of study. The results and findings will be published and made available to the public, namely scientists working in the same area of research.
How to Write a Literature Review
First of all, don’t forget that writing a literature review is a great responsibility. It’s a document that is expected to be highly reliable, especially concerning its sources and findings. You have to feel intellectually comfortable in the area of study and highly proficient in the target language; misconceptions and errors do not have a place in a document as important as a literature review. In fact, you might want to consider text editing services, like those offered at Elsevier, to make sure your literature is following the highest standards of text quality. You want to make sure your literature review is memorable by its novelty and quality rather than language errors.
Writing a literature review requires expertise but also organization. We cannot teach you about your topic of research, but we can provide a few steps to guide you through conducting a literature review:
- Choose your topic or research question: It should not be too comprehensive or too limited. You have to complete your task within a feasible time frame.
- Set the scope: Define boundaries concerning the number of sources, time frame to be covered, geographical area, etc.
- Decide which databases you will use for your searches: In order to search the best viable sources for your literature review, use highly regarded, comprehensive databases to get a big picture of the literature related to your topic.
- Search, search, and search: Now you’ll start to investigate the research on your topic. It’s critical that you keep track of all the sources. Start by looking at research abstracts in detail to see if their respective studies relate to or are useful for your own work. Next, search for bibliographies and references that can help you broaden your list of resources. Choose the most relevant literature and remember to keep notes of their bibliographic references to be used later on.
- Review all the literature, appraising carefully it’s content: After reading the study’s abstract, pay attention to the rest of the content of the articles you deem the “most relevant.” Identify methodologies, the most important questions they address, if they are well-designed and executed, and if they are cited enough, etc.
If it’s the first time you’ve published a literature review, note that it is important to follow a special structure. Just like in a thesis, for example, it is expected that you have an introduction – giving the general idea of the central topic and organizational pattern – a body – which contains the actual discussion of the sources – and finally the conclusion or recommendations – where you bring forward whatever you have drawn from the reviewed literature. The conclusion may even suggest there are no agreeable findings and that the discussion should be continued.
Why are literature reviews important?
Literature reviews constantly feed new research, that constantly feeds literature reviews…and we could go on and on. The fact is, one acts like a force over the other and this is what makes science, as a global discipline, constantly develop and evolve. As a scientist, writing a literature review can be very beneficial to your career, and set you apart from the expert elite in your field of interest. But it also can be an overwhelming task, so don’t hesitate in contacting Elsevier for text editing services, either for profound edition or just a last revision. We guarantee the very highest standards. You can also save time by letting us suggest and make the necessary amendments to your manuscript, so that it fits the structural pattern of a literature review. Who knows how many worldwide researchers you will impact with your next perfectly written literature review.
Know more: How to Find a Gap in Research .
Language Editing Services by Elsevier Author Services:

What is a Research Gap

- Manuscript Preparation
Types of Scientific Articles
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- Library databases
- Library website
Library Guide to Capstone Literature Reviews: Role of the Literature Review
The role of the literature review.
Your literature review gives readers an understanding of the scholarly research on your topic.
In your literature review you will:
- demonstrate that you are a well-informed scholar with expertise and knowledge in the field by giving an overview of the current state of the literature
- find a gap in the literature, or address a business or professional issue, depending on your doctoral study program; the literature review will illustrate how your research contributes to the scholarly conversation
- provide a synthesis of the issues, trends, and concepts surrounding your research

Be aware that the literature review is an iterative process. As you read and write initial drafts, you will find new threads and complementary themes, at which point you will return to search, find out about these new themes, and incorporate them into your review.
The purpose of this guide is to help you through the literature review process. Take some time to look over the resources in order to become familiar with them. The tabs on the left side of this page have additional information.

Short video: Research for the Literature Review
Short Video: Research for the Literature Review
(4 min 10 sec) Recorded August 2019 Transcript
Literature review as a dinner party
To think about the role of the literature review, consider this analogy: pretend that you throw a dinner party for the other researchers working in your topic area. First, you’d need to develop a guest list.
- The guests of honor would be early researchers or theorists; their work likely inspired subsequent studies, ideas, or controversies that the current researchers pursue.
- Then, think about the important current researchers to invite. Which guests might agree with each other? Which others might provide useful counterpoints?
- You likely won’t be able to include everyone on the guest list, so you may need to choose carefully so that you don’t leave important figures out.
- Alternatively, if there aren’t many researchers working in your topic area, then your guest list will need to include people working in other, related areas, who can still contribute to the conversation.
After the party, you describe the evening to a friend. You’ll summarize the evening’s conversation. Perhaps one guest made a comment that sparked a conversation, and then you describe who responded and how the topic evolved. There are other conversations to share, too. This is how you synthesize the themes and developments that you find in your research. Thinking about your literature research this way will help you to present your dinner party (and your literature review) in a lively and engaging way.
Short video: Empirical research
Video: How to locate and identify empirical research for your literature review
(6 min 16 sec) Recorded May 2020 Transcript
Here are some useful resources from the Writing Center, the Office of Research and Doctoral Services, and other departments within the Office of Academic Support. Take some time to look at what is available to help you with your capstone/dissertation.
- Familiarize yourself with Walden support
- Doctoral Capstone Resources website
- Capstone writing resources
- Office of Student Research Administration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Visit the Writing Center
You can watch recorded webinars on the literature review in our Library Webinar Archives .
- Next Page: Scope
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews


Why is it important to do a literature review in research?
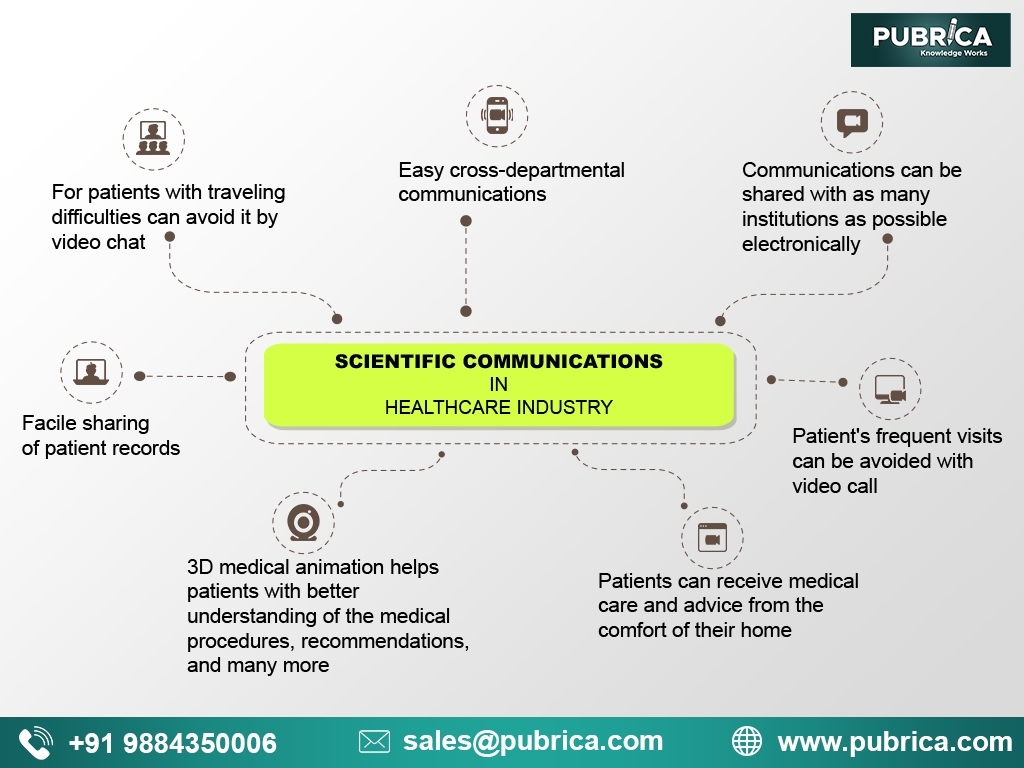
The importance of scientific communication in the healthcare industry
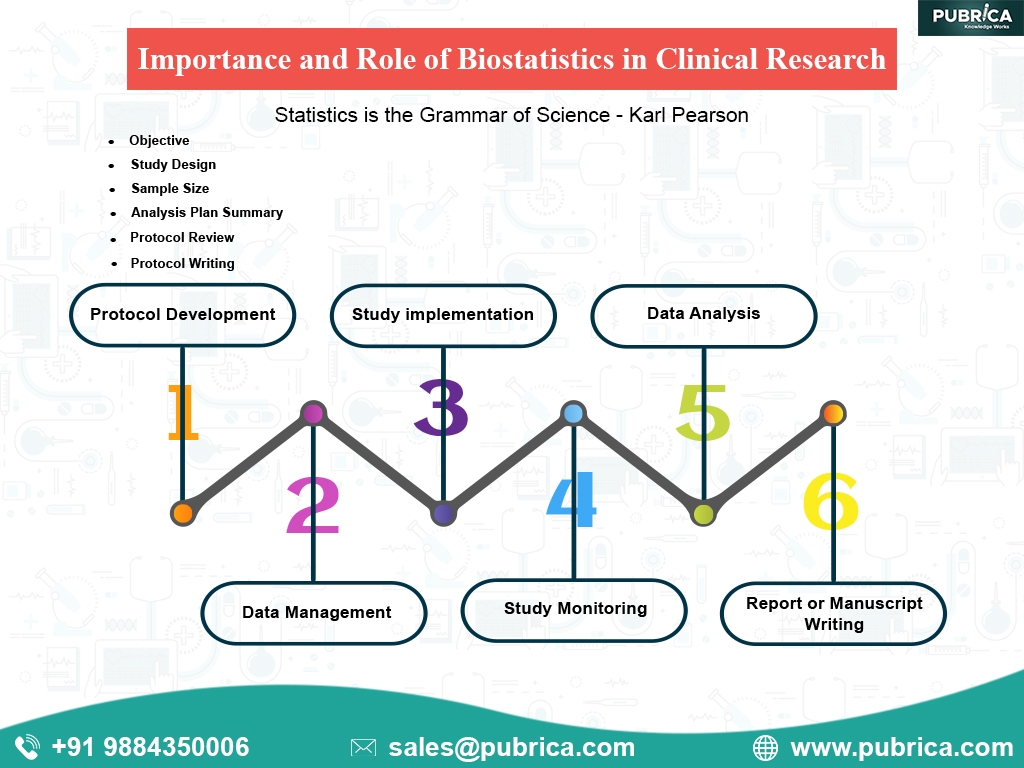
The Importance and Role of Biostatistics in Clinical Research
“A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research”. Boote and Baile 2005
Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review. Since it is one of the basic needs for researches at any level, they have to be done vigilantly. Only then the reader will know that the basics of research have not been neglected.
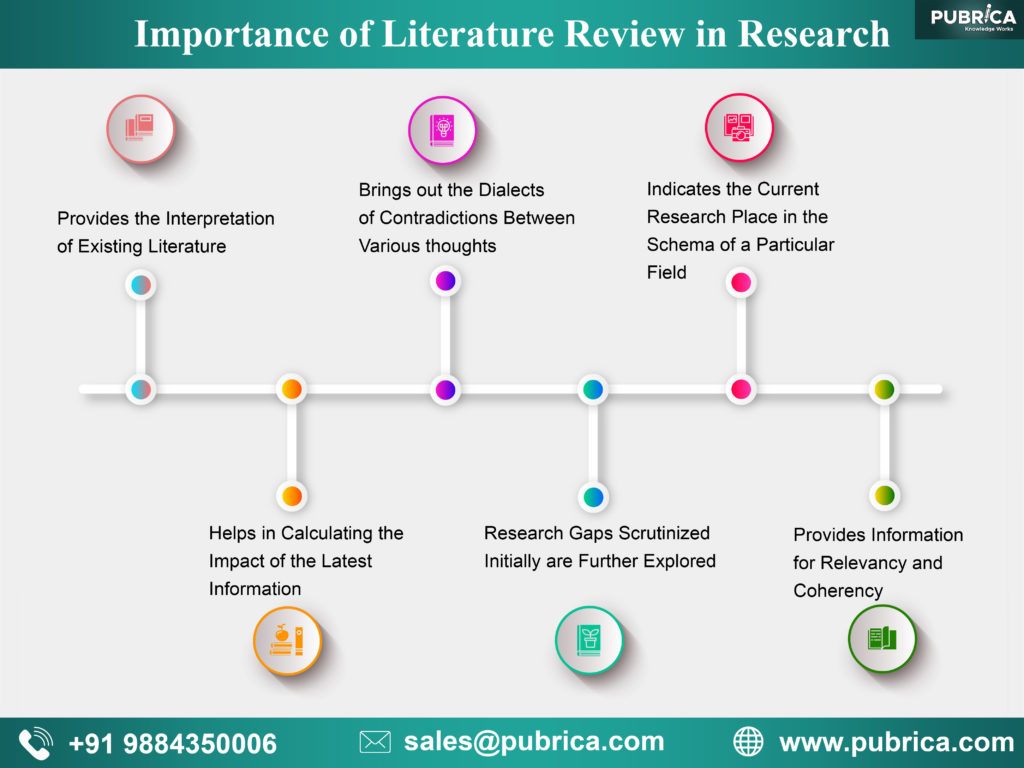
The aim of any literature review is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of existing knowledge in a particular field without adding any new contributions. Being built on existing knowledge they help the researcher to even turn the wheels of the topic of research. It is possible only with profound knowledge of what is wrong in the existing findings in detail to overpower them. For other researches, the literature review gives the direction to be headed for its success.
The common perception of literature review and reality:
As per the common belief, literature reviews are only a summary of the sources related to the research. And many authors of scientific manuscripts believe that they are only surveys of what are the researches are done on the chosen topic. But on the contrary, it uses published information from pertinent and relevant sources like
- Scholarly books
- Scientific papers
- Latest studies in the field
- Established school of thoughts
- Relevant articles from renowned scientific journals
and many more for a field of study or theory or a particular problem to do the following:
- Summarize into a brief account of all information
- Synthesize the information by restructuring and reorganizing
- Critical evaluation of a concept or a school of thought or ideas
- Familiarize the authors to the extent of knowledge in the particular field
- Encapsulate
- Compare & contrast
By doing the above on the relevant information, it provides the reader of the scientific manuscript with the following for a better understanding of it:
- It establishes the authors’ in-depth understanding and knowledge of their field subject
- It gives the background of the research
- Portrays the scientific manuscript plan of examining the research result
- Illuminates on how the knowledge has changed within the field
- Highlights what has already been done in a particular field
- Information of the generally accepted facts, emerging and current state of the topic of research
- Identifies the research gap that is still unexplored or under-researched fields
- Demonstrates how the research fits within a larger field of study
- Provides an overview of the sources explored during the research of a particular topic
Importance of literature review in research:
The importance of literature review in scientific manuscripts can be condensed into an analytical feature to enable the multifold reach of its significance. It adds value to the legitimacy of the research in many ways:
- Provides the interpretation of existing literature in light of updated developments in the field to help in establishing the consistency in knowledge and relevancy of existing materials
- It helps in calculating the impact of the latest information in the field by mapping their progress of knowledge.
- It brings out the dialects of contradictions between various thoughts within the field to establish facts
- The research gaps scrutinized initially are further explored to establish the latest facts of theories to add value to the field
- Indicates the current research place in the schema of a particular field
- Provides information for relevancy and coherency to check the research
- Apart from elucidating the continuance of knowledge, it also points out areas that require further investigation and thus aid as a starting point of any future research
- Justifies the research and sets up the research question
- Sets up a theoretical framework comprising the concepts and theories of the research upon which its success can be judged
- Helps to adopt a more appropriate methodology for the research by examining the strengths and weaknesses of existing research in the same field
- Increases the significance of the results by comparing it with the existing literature
- Provides a point of reference by writing the findings in the scientific manuscript
- Helps to get the due credit from the audience for having done the fact-finding and fact-checking mission in the scientific manuscripts
- The more the reference of relevant sources of it could increase more of its trustworthiness with the readers
- Helps to prevent plagiarism by tailoring and uniquely tweaking the scientific manuscript not to repeat other’s original idea
- By preventing plagiarism , it saves the scientific manuscript from rejection and thus also saves a lot of time and money
- Helps to evaluate, condense and synthesize gist in the author’s own words to sharpen the research focus
- Helps to compare and contrast to show the originality and uniqueness of the research than that of the existing other researches
- Rationalizes the need for conducting the particular research in a specified field
- Helps to collect data accurately for allowing any new methodology of research than the existing ones
- Enables the readers of the manuscript to answer the following questions of its readers for its better chances for publication
- What do the researchers know?
- What do they not know?
- Is the scientific manuscript reliable and trustworthy?
- What are the knowledge gaps of the researcher?
22. It helps the readers to identify the following for further reading of the scientific manuscript:
- What has been already established, discredited and accepted in the particular field of research
- Areas of controversy and conflicts among different schools of thought
- Unsolved problems and issues in the connected field of research
- The emerging trends and approaches
- How the research extends, builds upon and leaves behind from the previous research
A profound literature review with many relevant sources of reference will enhance the chances of the scientific manuscript publication in renowned and reputed scientific journals .
References:
http://www.math.montana.edu/jobo/phdprep/phd6.pdf
journal Publishing services | Scientific Editing Services | Medical Writing Services | scientific research writing service | Scientific communication services
Related Topics:
Meta Analysis
Scientific Research Paper Writing
Medical Research Paper Writing
Scientific Communication in healthcare
pubrica academy
Related posts.

Statistical analyses of case-control studies

PUB - Selecting material (e.g. excipient, active pharmaceutical ingredient) for drug development
Selecting material (e.g. excipient, active pharmaceutical ingredient, packaging material) for drug development

PUB - Health Economics of Data Modeling
Health economics in clinical trials
Comments are closed.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 4:39 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln
- < Previous Thesis
- Next Thesis >
Home > Honors Program > Honors Theses > 693
Honors Program
Honors theses, sarcopenia and the importance of resistance training and protein-rich diets for prevention of muscle loss in older adults: a literature review and informational pamphlet.
Madison Steele , University of Nebraska - Lincoln
Document Type
Date of this version.
Steele, M. 2024. Sarcopenia and the Importance of Resistance Training and Protein-Rich Diets for Prevention of Muscle Loss in Older Adults: A Literature Review and Informational Pamphlet. Undergraduate Honors Thesis. University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
Copyright Madison Steele 2024.
The growing prevalence of sarcopenia among older adults as well as youths has prompted further research aimed at developing effective preventative measures and treatment plans. Sarcopenia is often thought to occur solely due to aging, but several other factors contribute to progressive muscle loss. Previous research studies have found an effect of physical activity and dietary protein levels on the risk of developing sarcopenia as well as its onset age. This study aims to review existing knowledge in the field to compile an extensive list of sarcopenia causes and methods of prevention. The main causes identified in this review are the natural aging process, physical inactivity, and inadequate protein intake. The preventative measures discussed in this review include increasing awareness, resistance training, and protein-rich diets in the general population, but especially in older adults. Future research is needed to determine the extent of the combined effect of these attempts to delay or reverse sarcopenia symptoms. A condensed version of this review was also developed into an informational pamphlet as a tool to spread knowledge about sarcopenia in hopes of reducing the prevalence of this condition in society.
Since April 24, 2024
Included in
Gifted Education Commons , Higher Education Commons , Musculoskeletal Diseases Commons , Nutrition Commons , Other Education Commons , Physiology Commons
Advanced Search
Search Help
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Administrator Resources
- How to Cite Items From This Repository
- Copyright Information
- Collections
- Disciplines
Author Corner
- Guide to Submitting
- Submit your paper or article
- Honors Program Website
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
EDITORIAL article
This article is part of the research topic.
Small non-coding RNAs in Gram negative bacteria
Editorial on the Research Topic: Small non-coding RNAs in Gram negative bacteria Provisionally Accepted

- 1 Long Island University, United States
- 2 Bambino Gesù Children's Hospital (IRCCS), Italy
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
Ongoing efforts to discover and characterize small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs) in bacteria, often known as microRNA-size small RNAs (msRNAs) or more broadly as bacterial-derived small RNAs (bsRNAs), are deepening our knowledge of how they regulate post-transcriptional process. Although poorly described so far, they play an important role in controlling various biological functions of bacteria such as virulence, biofilm formation, antibiotic resistance, pathogenesis, adaptation to stress, and expression of outer membrane proteins. The objective of this research topic was to pool down the knowledge available so far in addition to attract promising new studies in sRNA regulatory network, which would enable forefront studies in the field of regulatory sRNAs to effectively tackle bacterial pathogens. This research topic includes some original articles that explore how bacteria utilize sRNAs to survive under antibiotic stress conditions as well as their involvement in mediating differences in immune response in the case of respiratory syncytial virus versus rhinovirus bronchiolitis. It also includes valuable review articles that discuss Hfq interactions with sRNAs and how bacterial pathogens produce sRNAs encapsulated in outer membrane vesicles (OMVs). Through this process, sRNAs can be transferred into eukaryotic cells and other bacteria, highlighting their potential as therapeutic agents in the treatment of various diseases. Kim et al. reported how bacteria switch from active aerobic respiration to anaerobic adaptation upon exposure to moderately effective first-generation antibiotics (Kim et al., 2024). The overuse and misuse of antibiotics has led to the emergence of multidrug resistant bacteria, and this situation has worsened with the overuse of antibiotics during Corona Virus Disease (COVID-19) pandemic (Andersson and Hughes, 2014;Rawson et al., 2020). The authors used a transcriptome analysis approach to understand the change in gene expression when the bacteria switch to anaerobic respiration (Kim et al., 2024). It has been noticed that the treatment of sublethal concentrations of antibiotics increased the expression of genes related to anaerobic respiration. In addition, the transition was dependent on the transcriptional regulators, AcrA (aerobic respiratory control) and FMR (fumarate and nitrate reduction) (Kim et al., 2024). It has been reported that the expression of these regulators is modulated by oxygen availability (Levanon et al., 2005). The authors in turn report that the antibiotic stress leads to specific reprogramming of non-coding RNAs including small RNAs FnrS and Tp2 (Kim et al., 2024). It was noticed that FnrS is involved in reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, thereby increasing cell survival. Overall, the study demonstrates how bacteria strive to maintain cellular homeostasis via sRNA-mediated gene regulation upon sublethal antibiotic exposure. As the authors pointed out, this study provides insights for developing novel antimicrobial compounds targeting sRNAs to combat multi-drug resistance.Another valuable original article in our research topic demonstrates the role of bacterial sRNAs in mediating immune response in Bronchiolitis (Krohmaly et al., 2024). Bronchiolitis is a viral infection caused by many viruses including respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), rhinovirus (RV), and others (Marguet et al., 2009). It has been reported that bronchiolitis caused by RSV is majorly associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae, while bronchiolitis caused by RV is frequently associated with Haemophilus influenzae (Hasegawa et al., 2018;Stewart et al., 2018). In this study, the authors identified many novel sRNAs from different bacterial species and studied their influence on immune response during bronchiolitis (Krohmaly et al., 2024). Through RNA-Seq database, several bacterial sRNAs were found to be associated with RSV and RV-only bronchiolitis in human nasal. They found that some bacterial sRNAs were differently expressed in infants with RSV compare to RV-only bronchiolitis from the MARC-35 cohort. They found that the sRNAs associated with RSV-only bronchiolitis may relatively activate the IL-6 and IL-8 pathways and relatively inhibit the IL-17A pathway, compared to those associated with RV-only bronchitis (Krohmaly et al., 2024). This is the first study to report that bacterial sRNAs may be contributing to inflammation differences seen in RSV-and RV-only bronchiolitis.Nowadays, it is known that production and regulation of bacterial sRNAs that are involved in facilitating sRNA-mRNA base-pairing is coordinated through several components, including other sRNAs, mRNAs, and sRNA-binding proteins (sRBPs). Among several sRBPs (e.g., Hfq, ProQ, and CsrA), Hfq is the most extensively studied chaperon that protects sRNAs from degradation and aids in their binding to mRNA. Watkins and Arya have written an interesting review on how the structures of Hfq have defined the difference in interactions of the Gram-negative and Grampositive homologues with RNA (Watkins and Arya, 2023). While it appears that Hfq is a vital virulence factor in Gram-negative bacteria, it remains unclear how this chaperone is involved in mediating sRNA-mRNA interactions, a function that is worth exploring.Another interesting review paper published by Ajam-Hosseini et al. discussed bacterial OMVs that can serve as vehicles for the delivery of sRNAs to target cells (Ajam-Hosseini et al., 2024). It has been shown that sRNAs encapsulated in OMVs can regulate gene expression in recipient cells, leading to changes in cellular behavior and function. Additionally, targeting sRNAs involved in bacterial virulence or antibiotic resistance has the potential to disrupt the pathogenicity of bacteria and improve the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment. This suggests that OMV-encapsulated sRNAs could be used as potential therapeutic strategy in treating various bacterial diseases.In summary, the current Research Topic highlights the importance of regulating bacterial sRNAs in shielding bacterial lifestyle under stress conditions and in modulating the immune response. It also provides valuable insights into the clinical significance of Gram-negative bacterial sRNAs in biomedical applications. Despite its importance, detailed studies on the expression patterns of bacterial sRNAs are scarce. Therefore, we believe that further research could enhance our understating of their role as a versatile toolkit for bacterial adaptation to the host environment. Such studies could also reveal their potential utility as novel therapeutics, including their use in natural or synthetic OMVs.We would like to express our gratitude to the authors and reviewers for their valuable contributions to this research topic. We hope that this collection of reviews, and original articles will be helpful for clinicians, researchers, and students seeking for information about sRNAs in bacterial virulence and communication.
Keywords: Small non-coding RNA (sRNA), Hfq, multidrug resistance, antibiotics, Bronchiolitis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Outer membrane vesicles (OMVs)
Received: 30 Apr 2024; Accepted: 02 May 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Subhadra and Sarshar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Dr. Bindu Subhadra, Long Island University, Brookville, United States
People also looked at
- Open access
- Published: 01 May 2024
A clinical guideline for the Iranian women and newborns in the postpartum period
- Leila Abdoli Najmi 1 ,
- Sakineh Mohammad-Alizadeh-Charandabi 2 ,
- Fatemeh Abbasalizadeh 3 ,
- Haniyeh Salehi Poormehr 4 ,
- Fariba Pashazade 5 &
- Mojgan Mirghafourvand 6
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 563 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The postpartum is a vital period for women, newborns, spouses, parents, caregivers, and families. Regarding the importance of postpartum care and the lack of comprehensive and up-to-date clinical guidelines in the country of Iran, the postpartum clinical guidelines have been adapted.
Cultural adaptation was conducted in three stages. In the first stage, the adaptation team was formed and the process was approved. During the second stage, a systematic literature review was conducted using international databases to identify English-language clinical guidelines published within the last 10 years. Out of 17 guidelines and documents initially selected, 5 guidelines meeting the inclusion and exclusion criteria and published within the last 5 years were chosen following a thorough review by the search team. In the secondary selection, the guidelines were investigated by two subject-matter experts based on AGREE II Checklist, and regarding the high evaluation score obtained by the WHO Recommendations on Postnatal Care of the Mother and Newborn (2022), and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE,2021) guideline for postnatal care were selected for cultural adaptation. In the third stage, the opinions of experts from all over the country were collected and scored using the Delphi method, and a final guideline was formulated.
The adapted postpartum clinical guideline has offered 56 recommendations. The recommendations are categorized into four major themes including mother care, newborn care, health system and health promotion interventions and post caesarean care.
Applying evidence-based recommendations for the care of mothers and babies in the postpartum period will enhance the health system, promote the provision of care after vaginal and caesarean births, and ensure a positive postnatal experience for mothers, fathers, babies, and families.
Peer Review reports
The postpartum period is critical for the long-term physical and mental health of mothers and children [ 1 ]. Quality care during the early days and weeks after childbirth significantly influences their experiences [ 2 ]. During this phase, women adapt to physical, mental, and social changes, which can present significant challenges such as insomnia, fatigue, breastfeeding issues, stress, mental health concerns, reduced sexual desire, and urinary incontinence. [ 3 ]. Socio-economic and cultural factors can influence mothers’ experiences, emotions, and behaviors during early motherhood [ 4 ]. Additionally, the support and encouragement provided to mothers by healthcare staff during childbirth, in hospital settings, at home, and through peer support can significantly influence their health and well-being [ 5 ].
Despite its importance, evidence suggests that postpartum care has been undervalued and under-resourced [ 6 ]. Studies indicate that many women are dissatisfied with the postpartum care they receive. For instance, a survey in England revealed that 50% of mothers felt they lacked adequate help, support, and information on newborn feeding [ 4 ]. Furthermore, in the United States, 40% of women do not attend their postpartum checkups, leading to challenges in managing chronic conditions, accessing effective contraception, and increasing the risk of short inter-pregnancy intervals and preterm delivery, particularly among disadvantaged communities [ 7 ].
In Iran, postpartum care often receives less attention compared to the antenatal period, both in terms of quality and quantity [ 8 ]. Research indicates that only 30% of mothers in developing countries receive adequate postpartum care, with approximately 70% expressing dissatisfaction with the care in Iran [ 9 , 10 , 11 ].
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists advocates for continuous, personalized postpartum care to optimize the health of mothers and newborns, emphasizing that postpartum checkups should not be limited to a single visit at 6–8 weeks after delivery [ 7 ]. Similarly, the WHO recommends postpartum care within 24 h after childbirth, followed by at least three additional visits, aiming to improve maternal and newborn health [ 12 ].
Postpartum care plays a vital role in continuous care for mothers, newborns, and children, contributing to the achievement of sustainable development goals in reproductive health, such as reducing maternal and infant mortality [ 13 ]. However, the lack of attention to maternal health needs during the postpartum period contributes to one-third of maternal deaths, highlighting the need for improved clinical knowledge and technology for long-term prevention, particularly in underserved areas [ 14 , 15 ].
Evidence-based guidelines for postpartum care can mitigate mid- and long-term complications, inform clinical management, and contribute to policy-making and unified care across healthcare departments and professions [ 12 , 16 ]. The adaptation of clinical guidelines is essential to ensure their relevance and feasibility in local contexts, requiring significant resources, expertise, and coordination involving multidisciplinary experts, continuous supervision, and evaluation [ 17 , 18 ].
Authentic and comprehensive clinical guidelines, such as the WHO Recommendations on Postnatal Care of the Mother and Newborn and the NICE guideline for postnatal care, provide a basis for routine care for mothers and newborns, with the potential for standardizing postnatal services through adaptation and utilization of international clinical guidelines [ 16 , 19 ].
Considering the absence of comprehensive and current postnatal guidelines in Iran, as well as the WHO’s suggestion for the adaptation and utilization of clinical guidelines, this study aims to provide evidence-based recommendations for enhancing postnatal care in Iran, taking into account the sociocultural and healthcare system context of the country [ 12 , 20 ].
This study is the first phase of a multi-phase research that its protocol has already been published [ 21 ]. It is a multi-stage developmental research using systematic review and qualitative methods. It is aimed at the cultural adaptation of postnatal clinical guidelines in Tabriz University of Medical Sciences in 2023. The ADAPTE method has been used for the cultural adaptation of the clinical guidelines in the present study. Generally, ADAPTE includes three stages [ 18 , 22 ]:
First phase: set-up
During the set-up phase, the adaptation team was formed. The cultural adaptation team consists of 6 people (two reproductive health specialists, a perinatologist, a PhD in evidence-based studies, a PhD student in midwifery, and a senior expert in Medical Library and Information Science). The topic selection criteria were set. Also, the feasibility of adaptation of the clinical guideline was evaluated based on the availability of authentic international postnatal clinical guidelines, and then, the adaptation plan was prepared.
Second phase: adaptation (search, and evaluation of the clinical guidelines)
Since the team aimed to adapt a clinical guideline for postnatal care, the search to find suitable clinical guidelines was conducted. A PIPOH-based search strategy was used to find the clinical guidelines and other relevant documents. The keyword “postpartum” was searched for in the Mesh and the terms “Postpartum Period” and “Postnatal Care” which were related to the searched keyword were retrieved. No Mesh equivalents were found for the keyword “Guideline”, so the search was conducted using the ‘Publication Type’ and ‘title/abstract’. The search for the relative keywords was conducted on the related websites (Table 1 ) in a 10-year period. In this phase, after removing duplicates, 17 guidelines and documents were selected. The selected guidelines are available as a supplementary file. Based on inclusion criteria (using the English language, availability of the full manuscript of the guideline, routine postpartum care, and being the latest or most common manuscript), and exclusion criteria (the target group not being the same and the topic background not matching), after the initial evaluations of the retrieved guidelines by the search team, 5 guidelines that were published within the last 5 years (Table 2 ) were primarily selected, which were evaluated and scrutinized for the second time. As the secondary selection, the guidelines were evaluated by two thematic experts, using the AGREE II Checklist. The AGREE II includes 23 appraisal criteria (items) organized within six domains. These domains are scope and purpose, stakeholder involvement, rigor of development, clarity of presentation, applicability, and editorial independence. Each criterion is given a score ranging from 1 (totally disagree) to 7 (totally agree). The score of each domain is calculated by the sum of the scores given to the criteria of that domain and standardizing the total score based on the maximum obtainable score for that domain. The quality score for all six domains was calculated [ 23 , 24 ].
Regarding the high evaluation scores obtained by the WHO Recommendations on Postnatal Care of the Mother and Newborn (2022), and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guideline for postnatal care (2021) (Table 3 ), these guidelines were selected for cultural adaptation. The recommendations for the preparation of the draft of the clinical guideline were selected and formulated in the form of a table.
Third phase: finalization (reviewing the target users and formulation of the final manuscript)
To reach a consensus on the clinical advantage and feasibility of cultural adaptation, the Delphi technique [ 25 ] was used to survey experts from different regions of the country via email. Eighteen experts from a variety of specialties, including reproductive health, obstetrics, midwifery, health policy, Evidence Based Medicine (EBM) and pediatrics, were invited to participate (Table 4 ). The panel of experts scored the recommendations in terms of the feasibility of cultural adaptation (low, medium, and high). The views and opinions of these experts were scored and summarized using a 9-item Likert scale. These points were scored from 1 to 9. Scores above 7 meant the approval of the recommendation, scores between 5 and 7 needed modifications in a second phase of Delphi, and scores lower than 4 meant the rejection of the recommendation. The most common definition of consensus, which is the agreement percentage, has been used for clinical advantage. An above-75% agreement was considered as the consensus threshold [ 26 ].
The clinical guideline was sent to authorities (Ministry of Health and Medical Education) for consultation and their views were applied to it. Finally, the culturally adapted guideline was formulated after being summarized, judged, and agreed upon by the panel of experts. The evidence grades of the recommendations in this guideline were based on the sum of evidence strength according to the reference clinical guidelines and the opinions of the panel of experts (Table 5 ).
After the Delphi process, 56 clinical recommendations (Table 6 ) were developed in the form of care, prevention, treatment, education, and promotion of the health system themes. These recommendations were produced by a panel of experts from different regions of Iran and took into account the cultural, socio-economic, and health system constraints of the country. Out of those recommendations, 43 recommendations aligned with the WHO’s guidelines while 13 recommendations aligned with the NICE guidelines. As some recommendations in these guidelines overlapped, the WHO’s guideline were used as the main guideline, and the NICE guideline was used for some specific recommendations related to post-caesarean procedures. The recommendations are designed to improve maternal and child health outcomes and address the specific needs and contexts of these groups in Iran.
The recommendations are categorized into four major themes: (1) mother care (recommendations 1–17), (2) newborn care (recommendations 18–32), and (3) health system and health promotion interventions (recommendations 33–43). (4) post caesarean care (recommendations 46–56).
The mother care section, including different themes regarding maternal assessment, preventive interventions, mental health interventions, nutritional and physical activity interventions, and information and services for interval between pregnancies. Additionally, there were 10 recommendations specifically addressing the needs of women who had caesarean delivery, and 1 recommendation about the delivery experience and 2 recommendations about child safety and emotional connection with the child.
The neonatal section covers various areas such as physiological examination, preventive interventions, nutritional interventions, newborn growth and development, and breastfeeding.
The health system and health promotion section provides 11 recommendations addressing important areas such as health promotion, policy formulation, monitoring and evaluation, and evidence-based decision-making.
The postpartum is a very sensitive period for the mothers and the newborn. The lack of comprehensive and up-to-date clinical guidelines in Iran has created a significant gap in the provision of postnatal care. Cultural adaptation of clinical guidelines for postpartum is a vital step to ensure that mothers, newborns, spouses, parents, and families receive suitable and evidence-based care in this critical period.
Among the evaluated guidelines, the WHO Recommendations on Postnatal Care of the Mother and Newborn (2022), and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE, 2021) guideline for postnatal care obtained the highest scores in six appraisal domains with AGREE II. Also, in the study by Yang et al. [ 27 ], these guidelines obtained the highest score in terms of the use of the latest evidence, methodological quality, and the use of a multi-disciplinary team for the formulation of the recommemdations. The AGREE II is used to formulate or adapt the guideline. It was also used as a credible reference to evaluate the quality of clinical guidelines [ 28 ]. This tool has been used in various studies, as a standard benchmark for investigation of the quality of clinical guidelines [ 27 , 29 , 30 ].
The WHO Recommendations on Postnatal Care of the Mother and Newborn are about the common postnatal care for healthy mothers and newborns. This clinical guideline is a comprehensive collection of 55 recommendations that have provided the components of postnatal care in three main categories: a) maternal care (24 recommendations), b) newborn care (19 recommendations), and c) healthcare system and health promotion interventions (12 recommendations). Since the WHO’s guideline only covers vaginal birth and provides no recommendations for cesarean birth, and considering the high statistics of cesarean in our country [ 31 , 32 ], the recommendation by the panel of experts who emphasized that the adapted guideline should be comprehensive and also cover the cesarean delivery, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guideline for postnatal care was also used for post-cesarean care recommendations.
During the initial evaluation of the WHO’s guidelines by the cultural adaptation team, 5 maternal care recommendations were removed (No 3, 9, 15, 16, 17). Due to the low prevalence of tuberculosis, schistosomiasis, parasites (worms) and HIV in our country, recommendations related to tuberculosis screening, prevention of schistosomiasis, drug prevention of parasites (Preventive anthelminthic treatment), and Oral pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention were removed. Medical prevention of mastitis with subcutaneous oxytocin (No. 9) and vitamin A consumption in pregnancy (No. 21), which were not recommended by the WHO, were removed according to experts’ opinion.
The WHO’s recommendations on immediate postnatal evaluation of mother (No. 1) and HIV screening (No. 2) were formulated by some modifications after the first stage of Delphi and with the consensus of the experts. According to the WHO’s guidelines (No. 7), it is not recommended to do exercise to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, but with the consensus of the experts (over 75% agreement), this recommendation was added to the adapted guideline.
Regarding the population policies of the country, and based on the opinions of the experts, the WHO’s recommendation on the provision of contraception information and services (No. 24) was changed into ‘provide information and services related to the interval between pregnancies. According to experts’ opinion, mothers should be advised to start vitamin A + D drops for infants from the 3rd to the 5th day after birth (No. 28).
In terms of post-cesarean pain relief in the NICE guideline, the ‘protocols of the related hospital for pain relief’ and names of some common pain relievers were added based on the experts’ recommendations (No. 47 b). In the recommendation of the NICE clinical guide regarding vaginal childbirth after cesarean section, according to experts, labor induction was omitted, because it is not performed in our country in mothers with a history of cesarean section.
The WHO recommendations related to health system and health promotion interventions, specifically recommendations 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 41, 42 and 43, would require specific infrastructure to be effectively implemented in Iran. These recommendations include the criteria to be assessed prior to discharge after birth, midwifery continuity of care, home-based records, digital targeted client communication, and cultural considerations related to men’s involvement in some regions of the country. Although these recommendations may pose challenges to implement in the current state of the health system, experts agree that they should not be removed from the guideline, but rather should serve as a long-term goal to move the health system towards creating the necessary infrastructure to implement these recommendations effectively in the future.
By implementing evidence-based recommendations for the care of mothers and babies in the postpartum period, the healthcare system will be strengthened in order to promote the provision of care after vaginal and caesarean births. Additionally, a positive postnatal experience will be ensured for mothers, fathers, babies, and families. By adopting these recommendations, the overall health outcomes of mothers and babies during this critical period can be improved. The experts emphasize the importance of integrating these recommendations into healthcare policies and practices in order to promote a comprehensive and evidence-based approach to maternal and child health in Iran.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
World Health Organization
Sustainable development goals
Group name for adaption a Clinical guideline
Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
Belemsaga DY, Kouanda S, Goujon A, Kiendrébéogo J, Duysburgh E, Degomme O, et al. A review of factors associated with the utilization of healthcare services and strategies for improving postpartum care in Africa. Afrika Focus. 2015;28(2):83–105. https://doi.org/10.1163/2031356X-02802006 .
Article Google Scholar
Bick D, MacArthur C, Winter H. Postnatal Care E-Book. 2nd ed. London: Churchill Livingstone; 2008.
Aber C, Weiss M, Fawcett J. Contemporary women’s adaptation to motherhood: the first 3 to 6 weeks postpartum. Nurs Sci Q. 2013;26(4):344–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894318413500345 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Redshaw M, Rowe R, Hockley C, Brocklehurst P. Recorded delivery: a national survey of women’s experience of maternity care 2006: National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit NPEU. Oxford: Joshua Horgan; 2007. Available from: https://www.npeu.ox.ac.uk/assets/downloads/maternity-surveys/reports/Maternity-Survey-Report-2006-Recorded-Delivery.pdf . Accessed 30 Apr 2024.
Barnes J, Ram B, Leach P, Sylva K. Factors associated with negative emotional expression: a study of mothers of young infants. J Reprod Infant Psychol. 2007;25(2):122–38. https://doi.org/10.1080/02646830701292399 .
Bhavnani V, Newburn M. Left to your own devices: The postnatal care experiences of 1260 first-time mothers. National Childbirth Trust; 2010. https://www.nct.org.uk/sites/default/files/related_documents/PostnatalCareSurveyReport5.pdf .
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Optimizing postpartum care. ACOG Committee opinion no. 736. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(5):e140-50. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000002633 .
Sakkaky M, Khairkhah M, Hosseini AF. The effect of home visit after cesarean delivery on exclusive breastfeeding in neonatal period. Iran J Nurs. 2010;23(64):72–80.
Google Scholar
Mojalli M, Basiri Moghadam M, Shamshiri M. Effectiveness of instructional environment and related factors on breastfeeding function of mothers. Intern Med Today. 2010;16(1):59–64.
Mansour Lamadah S, El-Nagger N. Mothers’ satisfaction regarding quality of postpartum nursing care and discharge teaching plan at ain shams maternity and gynecological hospital. Int J Curr Res. 2014;6(7):7545–51.
Mohseni MA, Bahadoran P, Abedi H. The quality of postpartum care from mothers’ viewpoint. Hakim Res J. 2009;12(1):27–40.
World Health Organization. WHO recommendations on maternal and newborn care for a positive postnatal experience. 2022.
Every Woman Every Child. Global Strategy for Women’s, Children’s and Adolescents Health 2016–2030. 2015. Available online. https://www.who.int/life-course/partners/global-strategy/globalstrategyreport2016-2030-lowres.pdf . Accessed 11 Jan 2020.
WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, World Bank Group and the United Nations Population Division. Trends in maternal mortality 2000 to 2017; 2019. Available from: https://www.unfpa.org/resources/trends-maternal-mortality-2000-2017-executive-summary . Accessed 30 Apr 2024.
World Health Organization. Standards for improving quality of maternal and newborn care in health facilities. Genève: World Health Organization; 2016. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241511216 .
World Health Organization. WHO Recommendations: Intrapartum Care for a Positive Childbirth Experience. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/intrapartum-care-guidelines/en/ .
Ministry of Health, Treatment and Medical Education. Department of Standardization and Compilation of Clinical Guidelines. Guidelines Adapting. Available from: https://hetas.behdasht.gov.ir/uploads/422/2021/Mar.pdf : Accessed 5 May 2022.
Harrison MB, Légaré Légaré F, Graham ID, Fervers B. Adapting clinical practice guidelines to local context and assessing barriers to their use. CMAJ. 2010;182(2):E78–84. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.081232 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Postnatal care. Available from:. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng194/resources/postnatal-care-pdf-66142082148037 Accessed 10 Jul 2023.
OliaeiManesh A, Shirvani A, SalehiZelani Gh, Rabanikhah F, MousaGholizadeh R, Nejati M, et al. National guidelines for clinical medicine (2). 1st ed. Tehran: Parse Negar Publications; 2013. (Persian).
AbdoliNajmi L, Mohammad-Alizadeh-Charandabi S, Jahanfar S, Abbasalizadeh F, SalehiPoormehr H, Mirghafourvand M. Adaptation and implementation of clinical guidelines on maternal and newborn postnatal care in Iran: study protocol. Reprod Health. 2023;20(1):135.
Mwangi N, Gachago M, Gichangi M, Gichuhi S, Githeko K, Jalango A, et al. Adapting clinical practice guidelines for diabetic retinopathy in Kenya: process and outputs. Implement Sci. 2018;13(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-018-0773- .
Brouwers MC, Kho ME, Browman GP, Burgers JS, Cluzeau F, Feder G, et al., Development of the AGREE II paovoia. https://doi.org/ttsaCE .
Rashidian A, Yousefi-Nooraie R. Development of a Farsi translation of the AGREE instrument, and the effects of group discussion on improving the reliability of the scores. J Eval Clin Pract. 2012;18(3):676–81. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.091716 .
Diamond IR, Robert C, Feldman BM, Pencharz PB, Ling SC, Moore AM, et al. Defining consensus: a systematic review recommends methodologic criteria for reporting of Delphi studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(4):401–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi .
Habibi A, Izadyar S, Sarafrazi A. Delphi technique theoretical framework in qualitative research. IJES. 2014;3(4):08–13.
Yang M, Yue W, Han X, et al. Postpartum care indications and methodological quality:a systematic review of guidelines. J Public Health. 2022;30(9):2261–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-021-01629-4 . published Online First: Epub Date.
Moradi-Joo M, Olyaeemanesh A, Akbari-Sari A, Rayegani SM. Adaptation frameworks for clinical guidelines and proposing a framework for Iran: a review and comparative study. Med J Islam. 2022;36(1):85–94. https://doi.org/10.47176/mjiri.36.10 .
Tara FDR, Saghafi N, Mirteimouri M, Ghooshkhanei H, Soltanifar A, Salehi M, Dadgar S. Management of Post-Partum Hemorrhage (Clinical Guideline). Iran J Obstet Gynecol Infertil. 2013;16(62):11–7. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJOGI.2013.1719 .
Coronado-Zarco R, de León AOG, Faba-Beaumont MG. Adaptation of clinical practice guidelines for osteoporosis in a Mexican context. Experience using methodologies ADAPTE, GRADE-ADOLOPMENT, and RAND/UCLA. J Clin Epidemiol. 2021;131:30–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2020.10.022 .
Jafarzadeh AHM, Hasanshahi G, Rezaeian M, Vazirinejad R, Aminzadeh F, Sarkoohi A. Cesarean or Cesarean Epidemic? Arch Iran Med. 2019;22(11):663–70 PMID: 31823633.
PubMed Google Scholar
Rafiei M, Ghare MS, Akbari M, Kiani F, Sayehmiri F, Sayehmiri K, et al. Prevalence, causes, and complications of cesarean delivery in Iran: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2018;16(4):221–34 PMID: 29942930.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We should thank the Vice-chancellor for Research of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences for their financial support.
This Study has been funded by Tabriz University of Medical Sciences. The funding source have no role in the design and conduct of the study, and decision to this manuscript writing and submission.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Midwifery, Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
Leila Abdoli Najmi
Sakineh Mohammad-Alizadeh-Charandabi
Women’s Reproductive Health Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
Fatemeh Abbasalizadeh
Research Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, Iranian EBM Center: A Joanna Briggs Institute Center of Excellence, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
Haniyeh Salehi Poormehr
Research Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, Iranian EBM Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
Fariba Pashazade
Social Determinants of Health Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
Mojgan Mirghafourvand
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MM, SMAC, and LAN contributed to the design of the protocol. MM and LAN contributed to the implementation and analysis plan. MM and LAN have written the first draft of this article, MM and LAN evaluated and graded separately the guidelines with AGREE-ll, and SMAC provided supervision to the manuscript drafting and revisions. HSP and FP undertook the literature search, selection, and final review of the results and findings with the guidance of FA. All authors have critically read the text and contributed with inputs and revisions, and all authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors are members of guideline evaluation group.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mojgan Mirghafourvand .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Written informed consent was obtained from each participant. This study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of the Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran (code number: IR.TBZMED.REC.1401.661). All the steps/ methods was performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Najmi, L.A., Mohammad-Alizadeh-Charandabi, S., Abbasalizadeh, F. et al. A clinical guideline for the Iranian women and newborns in the postpartum period. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 563 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11026-8
Download citation
Received : 14 January 2024
Accepted : 22 April 2024
Published : 01 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11026-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Clinical guideline
- Cultural adaptation
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your ...
Literature Review and Research Design by Dave Harris This book looks at literature review in the process of research design, and how to develop a research practice that will build skills in reading and writing about research literature--skills that remain valuable in both academic and professional careers. Literature review is approached as a process of engaging with the discourse of scholarly ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
This book looks at literature review in the process of research design, and how to develop a research practice that will build skills in reading and writing about research literature--skills that remain valuable in both academic and professional careers. Literature review is approached as a process of engaging with the discourse of scholarly ...
Why is it important? A literature review is important because it: Explains the background of research on a topic. Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area. Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas. Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic. Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it ...
This article is organized as follows: The next section presents the methodology adopted by this research, followed by a section that discusses the typology of literature reviews and provides empirical examples; the subsequent section summarizes the process of literature review; and the last section concludes the paper with suggestions on how to improve the quality and rigor of literature ...
In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your ...
The literature review is a vital part of medical education research and should occur throughout the research process to help researchers design a strong study and effectively communicate study results and importance. To achieve these goals, researchers are advised to plan and execute the literature review carefully.
A literature review is a study - or, more accurately, a survey - involving scholarly material, with the aim to discuss published information about a specific topic or research question. Therefore, to write a literature review, it is compulsory that you are a real expert in the object of study. The results and findings will be published and ...
Literature search. Fink has defined research literature review as a "systematic, explicit and reproducible method for identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing the existing body of completed and recorded work produced by researchers, scholars and practitioners."[]Review of research literature can be summarized into a seven step process: (i) Selecting research questions/purpose of the ...
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
Be aware that the literature review is an iterative process. As you read and write initial drafts, you will find new threads and complementary themes, at which point you will return to search, find out about these new themes, and incorporate them into your review. The purpose of this guide is to help you through the literature review process ...
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
"A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research". Boote and Baile 2005 . Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review.
A literature review helps you create a sense of rapport with your audience or readers so they can trust that you have done your homework. As a result, they can give you credit for your due diligence: you have done your fact-finding and fact-checking mission, one of the initial steps of any research writing.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
Some Issues in Liter ature R eview. 1. A continuous and time consuming process runs. through out r esearch work (more whil e selecting. a resear ch problem and writing 'r eview of. liter ature ...
Materials and methods . The authors searched seven databases on 1 August 2022, for publications that utilized physical or biophysical markers in the assessment of medical trainees (medical students, residents, fellows, and synonymous terms used in other countries).
The three main thematic categories that emerged from this rigorous process were not arbitrary but rather a result of a comprehensive and systematic review of the literature. Through a meticulous examination of the selected articles, a discerning pattern of recurring concepts and focal points within the realm of organizational culture surfaced ...
Invention and innovation education and its associated practices (e.g., problem-finding, problem-defining, learning from failure, iterative problem-solving, innovation-focused curricula, collaboration, and maker spaces) are moving from the periphery to the center of education at an ever-increasing pace. Although the research and literature on invention and innovation education, collectively ...
The growing prevalence of sarcopenia among older adults as well as youths has prompted further research aimed at developing effective preventative measures and treatment plans. Sarcopenia is often thought to occur solely due to aging, but several other factors contribute to progressive muscle loss. Previous research studies have found an effect of physical activity and dietary protein levels ...
Systematic reviews that summarize the available information on a topic are an important part of evidence-based health care. There are both research and non-research reasons for undertaking a literature review. It is important to systematically review the literature when one would like to justify the need for a study, to update personal ...
Ongoing efforts to discover and characterize small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs) in bacteria, often known as microRNA-size small RNAs (msRNAs) or more broadly as bacterial-derived small RNAs (bsRNAs), are deepening our knowledge of how they regulate post-transcriptional process. Although poorly described so far, they play an important role in controlling various biological functions of bacteria ...
The postpartum is a vital period for women, newborns, spouses, parents, caregivers, and families. Regarding the importance of postpartum care and the lack of comprehensive and up-to-date clinical guidelines in the country of Iran, the postpartum clinical guidelines have been adapted. Cultural adaptation was conducted in three stages. In the first stage, the adaptation team was formed and the ...
The conservation of marine ecosystems and species is inherently complex, plagued by social, political, economic and ecological uncertainty. Navigating these challenges to sustain marine systems requires the understanding, consideration and uptake of multiple knowledge systems within decision-making processes. Participatory research approaches, such as knowledge co-production, are advocated ...