Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


Assignment on Coca-Cola Company

As the leading beverages company in the world, Coca Cola almost monopolizes the entire carbonated beverages segment. Beside it, Coca Cola also maintain their reputation as the leading company in the world using PESTLE analysis so that Coca Cola can examine the macro-environment of Coca Cola’s operations.
Related Papers
puti andani
International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences
J. Tshibangu
Ethnobotany of Mountain Regions
Rainer W Bussmann
SouKaina Azouanate
Theriogenology
William Velander
joglo lawas
Jual joglo yogyakarta
CALL/WA : +62 878-9554-4111 Spesialis penyedia dan kontraktor rumah kayu tradisional jawa kuno limasan maupun joglo. Wujudkan impian anda. LimasanJoglo.Com merupakan perusahaan penyedia dan kontraktor pembuatan rumah kayu tradisional jawa kuno dengan desain Limasan Jawa maupun Joglo. Misi kami yaitu mewujudkan impian anda memiliki rumah limasan maupun joglo yang merupakan passion anda. Silakan hubungi kami kapan saja dengan kontak person: Bpk. Beny Riss +62 857-1616-1701
EPJ Web of Conferences
Dra. Lizbet Ñaupari Tolentino
Esta investigación titulada “Motivación Laboral y Liderazgo Pedagógico en directivos de Instituciones Educativas de la UGEL 03 - 2015. Nos permite determinar la relación significativa entre motivación laboral y liderazgo pedagógico. La población en esta investigación consta de 105 directivos de distintas IIEE. Muchos directores se negaron por distintas circunstancias a participar de la aplicación del cuestionario; sin embargo, se perseveró logrando un muestreo no probabilístico intencional, es decir trabajar con la población de 105 directores de la UGEL 03, se empleó la escala de Likert, estos datos de procesaron empleando el programa estadístico de SPSS v.15. El resultado final son los siguientes: El resultado de 0.708 indica que existe relación positiva entre las variables además se encuentra en el nivel de correlación alta y siendo el nivel de significancia bilateral p=0.000<0.05 se rechaza la hipótesis nula y se acepta la hipótesis general; se concluye que: La motivación labo...
Sharon Guan
When planning a distance education program, providers should determine their purpose in offering distance learning, how distance learning will benefit students, what resources they will need, and whether instructors are prepared to teach on the Web. (JOW)
RELATED PAPERS
Microelectronic Engineering
Furio Gramatica
Marcelino Cuesta Izquierdo
Pharmacological Reviews
David Tweardy
Bangladesh Journal of Animal Science
ismartoyo ismartoyo
Cadernos de História da Educação
Carlota Boto
Zoe Childerley
New Media & Society
Critical Pathways in Cardiology: A Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine
German Malaga
I saggi di Lexia
Cristina Voto
Rastislav Jakus
OSTI OAI (U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information)
Erika Cooley
Animus Revista Interamericana de Comunicação Midiática
Viviane Borelli
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Theresa Ramelot
Obra abierta Ediciones
Fernando Torres
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Assignment on Business Management: Quick Guide

What is Business Management Assignment
College curriculums are loaded with unfamiliar subjects, and students often feel lost. The first assignments are usually the hardest to get done, and a little help would be nice. If you are a beginner facing this challenge and are asking all around 'what is business management' or how it differs from business administration, you have come to the right place. This quick guide will explain the basics of the management of business and will provide topics of business management essays.
To put it simply, business management is a process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the organizational resources to achieve the company's objectives. While business administration concentrates on the organization's day-to-day operations, business management focuses on the overall process.
Business management is vital for a successful business. A business manager's job is to make strategic decisions, allocate resources, hire the best employees, and ensure the company meets its business objectives.
A business management assignment helps students demonstrate their ability to apply theoretical knowledge to real scenarios and prepare them for future challenges. While the structure of the assignment is not foreign to experienced students, it covers a wide range of topics. It could involve operations management, financial and human resources management, organizational behavior, etc.
In the following chapters, you will find useful tips, a formal structure, and a general outline of a business management essay. Down below, there is a list of essay topics you could write a magnificent essay about. To clarify things, here is a business assignment sample essay. Our college essay writing services will provide a business essay crafted to meet the highest standards of your university.
How to Write a Business Assignment: Helpful Tips
Even though every essay structure and general outline resembles one another for each type, there are still many intricate details that you should consider when writing a business management assignment.
Let's move on to discuss constructing an impressive business paper without wasting time making mistakes. The following guide will save you the trouble of extensive research on how to polish an academic paper and help you reach the academic success you deserve.
If you don't have much free time on your hands, our exceptional custom essay writing service is also a great option. Let us know what is due, and we will deliver unforgettable reports on business management.

Choose Relevant Business Management Topics
Start by implementing a general to a specific approach. Think about the areas of your expertise and how it links with the business assignment. A topic you feel comfortable writing will help you construct a high-quality and meaningful research paper.
Writing about the topics of business you feel passionate about will make the process more engaging and enjoyable. Consider your audience, and make the topic meet their needs. This will help you write an informative and engaging paper. Be relevant. Stay up to date with trending topics of business management. Choose a topic about an important issue and provide new perspectives or even a solution. Filling in the existing gaps will help your essay stand out.
Narrowing down the scope is always a good idea. The specific topic will make your work more manageable and keep you focused. A broad topic is always difficult to cover, but narrowing it down too much can limit your research options. Thus, balance is the key!
Maintain Your Management Assignment Structure
Maintaining the structure of the assignment is crucial. Make sure to keep your ideas coherent and your essay easy to follow. Whether you are writing about international business management or organizational structure, the most important thing is simply communicating your ideas to the readers.
Start by following the course guideline. Make sure you understand every component. Usually, professors give out this kind of map to determine the structure, format, and length of the management of business assignments.
Before you start writing, create an outline. Organize your thoughts and ideas and stay on track. Use headings and subheadings to break up your assignment into sections. Start with a strong introduction and an easy-to-digest thesis statement. Follow it with comprehensive body paragraphs. Here you can provide your arguments, show other people's work, and communicate with the audience about the problems you've discovered. Use transitional sentences to connect your ideas and eventually to the bigger picture. Finally, write a powerful conclusion that ties everything up. Showcase your ability to link various arguments to one another.
Following our guidelines will bring clarity and coherence to your writing. Well-structured and easy-to-follow essays always get positive feedback from their readers.
Analyze Topics of Business, Don't Repeat
Analyzing business paper topics can get tricky, especially for beginners who have to develop their writing style. Chances are you will repeat the same argument several times to make it look more convincing. But answering the question 'what is business management' several times with different words will only make your paper look unprofessional.
It's tricky, but there are ways to avoid repeating the arguments. Do the prior research. Acquiring knowledge will expand your horizon, and you won't feel the need to repeat the same sentence couple of times. Create the general outline. Knowing the order of your essay elements will help you avoid restating the same information twice.
Besides the general outline, it's a good idea to list all the key points and prioritize them. This way, you will cover every important detail in your essay. Last but not least, consider alternative perspectives. If you incorporate opposing viewpoints, you will enrich the paper and show off your writing skill level.
Provide Rationale for Your Business Assignment
It is trivial, but for safety reasons, let's point out: an argument without supporting evidence is not valid. The same goes for the topics of business management essay. You must provide a rationale for every stage of the essay.
Being able to provide supporting evidence demonstrates strong research abilities. Writing a well-reasoned essay requires thorough research. Providing rationale and citing sources in the assignment shows that the writer has done their best. Besides looking professional, it will be easier to convince the reader about the credibility of your argument if they can see the reasoning behind it. If you can explain why you think what you think, it shows that you have considered opposing viewpoints. Critical thinking is one of the most important aspects of the writing process.
Writing essays about the management of business takes extensive research. If the deadline is too close and there is not enough time to master the art of writing, you can go to the website and check out our custom research papers writing service . Our team of professional writers is always here to help you.
Use Formal Language in Your Business Assignment
In business, academia, or any other professional setting, we use formal language. It strictly adheres to the rules of grammar, tone, and vocabulary.
Formal language helps to establish a professional tone in A management assignment which supports creating a positive impression on the reader. Using formal language also increases the clarity of the arguments. Formal language is more precise, which can help avoid ambiguity and confusion.
No matter which business management topic assignment you write, having a respectful relationship with your audience is crucial. Formal language and correctly chosen vocabulary can take you a long way. It shows respect to the reader and the topic also.
Thus, you must avoid using slang, vocabulary unsuitable for the audience, contractions, and other unprofessional language or tone forms. And if you are reading all these, you are thinking, 'why can't somebody else write an essay for me ,' visit our website, and your wish will become a reality in no time. Get top-notch essays tailored to your specific requirements.
Need a Great Essay?
Get top-quality essays written by professionals today!
Business Management Topics
Mastering the art of constructing an impressive essay is only one-half of the job. First of all, you need an engaging topic. Our team has prepared a comprehensive list of business management topics to write about. From operations to business process management, explore a list of topics covering a wide range of fields, choose the one that excites you the most, and start implementing the freshly acquired knowledge.
International Business Management Topics
Our experienced writers have gathered the 20 most engaging topics about international business management. Explore the list and find the most attractive one:
- Exploring management concepts in international business
- Cross-cultural challenges in achieving Organizational goals
- The challenges of the first line managers in international organizations
- Key strategies for managing international business operations in an efficient and effective manner
- Maximizing international business success through effective human resource management strategies
- Navigating global business challenges through effective management of cultural intelligence
- Effective leadership strategies for international business management
- Cross-cultural communication as an essential part of international business management
- The link between happy employees and successful international business management
- Maximizing global business performance through effective staff managers
- Leveraging various resources for competitive advantage
- Understanding the universal phenomenon of cross-cultural communication challenges
- Foreign direct investment and risks for international businesses
- Sustainability in international business
- Challenges of corporate governance in international businesses
- The role of ethical leadership as an essential part of international business management
- Developing a high degree of cross-cultural competence
- Managing global value chains: integrating all the activities in international business management
- The importance of cultural awareness in international business management
- The role of self-confidence in international business management
Operations Management Assignment Topics
Below you will find the most relevant and moderns operations management assignment topics:
- Enhancing Organizational Performance through Effective Operations Management and Managerial Skills
- The role of organizational chart in effective operations management
- The impact of executive functions on operations management
- The role of operations management in achieving success at a shareholder meeting
- The importance of understanding human behavior in operations management
- Leveraging consumer insights based on market research
- Optimizing group dynamics in operations management
- Leadership and strategies of general managers in operations management
- Planning effectively: best practices for operations management
- Tools, techniques, and approaches for a good knowledge base in operations management
- How to manage an organization effectively: operations management strategies
- The role of operations management in organizational development
- Achieving efficiency and productivity through simple form and process
- The role of independent decision-making in operations management
- Management theories: How to plan effectively toward organizational success
- Optimizing human activities for the entire organization's success
- Streamlining operations management for a particular job: important strategies for effectiveness
- From plans decided to action implemented: the importance of effective operations management
- Provide guidance for upper management: strategies for leadership and direction
- Balancing technology and human beings for global success
Business Process Management Topics
Explore 20 more topics about business process management:
- Strategies for implementing effective business process management principles across the entire organization
- The role of human effort and organizational structure in achieving operational excellence
- How successful managers utilize basic principles for achieving operational excellence
- Interplay between management principles and executive function in driving business process
- Achieving synergy between top management and other employees for improved operational efficiency
- The crucial role of company leadership in aligning objectives and strengthening decision making
- A critical analysis of management theories: exploring the role of functional managers in achieving goals
- Optimizing the management process to achieve organizational goals
- Effective business process management consists of strategic allocation for company growth
- How to manage challenges created by leadership and top management
- Optimizing business process management through collaborative efforts between top managers and the best employees
- Crucial managerial skills: Optimizing processes through nurturing talent and celebrating human efforts
- The role of the functional manager in talent acquisition and optimizing human resource management
- Why business process management involves determining the journey, not just the destination
- Aligning employee decision-making with business objectives
- How process-centered leadership empowers organizations to manage change
- Process improvement through agile methodologies
- The evolution of process management thought
- The role of information technology in business process management
- The impact of business process management on customer satisfaction and retention
Additional Interesting Topics of Business
If you can choose from a wide range of topics, this list is for you. Impress your professor with an intriguing topic assignment:
- Measuring the ROI: Key metrics and techniques for demonstrating value to stakeholders
- Effective change management: how to implement and adapt
- Digital transformation in business management
- Strategies for handling and overcoming business crises
- Strategies for reducing environmental impact and promoting social responsibility
- Best practices and emerging trends for effective online branding
- Strategies for driving innovation and creating a culture of creativity
- Managing human resources in small business
- Strategies for managing cash flow, budgets, and investments
- The importance of market research and analysis for effective business management
- Using game mechanics to improve employee performance and engagement
- Strategies for effective time management and priorities in a busy workplace
- Strategies and tactics for successful business deals
- Emerging trends in remote work, automation, and AI
- Benefits and best practices for reducing stress and improving productivity
- Creating a workplace culture that fosters happy employees
- How understanding human behavior can inform business decision making
- Is servant leadership a new paradigm for effective business management?
- Techniques for handling uncertainty and complexity in an organization
- The role of entrepreneurial mindset and creativity in business success
Business Assignment Sample Essay
In the next section of the article, you will find a sample business management essay to help you understand how to structure and write a successful business assignment. Read through it carefully and take notes on the techniques used.
Further Academic Help
Are you struggling to come up with an assignment on management topic? Let us help you! Our online assignment writing service provides a comprehensive list of essay titles across various subjects to choose from, whether it's topics of business management or history assignment.
Don't stress yourself out; rely on our expertise to deliver outstanding results. Contact us today and take advantage of our reliable and affordable writing services.
Struggling with Your College Essay?
Order now and experience the best essay-writing service availabl
Related Articles
%20(1).webp)
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Company Overview for a Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
When you start a company, you ideally want it to grow. If you’re seeking business funding to scale your business or an initial investment to get your business off the ground, you’re going to need a business plan . Putting together a business plan can be an intimidating process that involves a lot of steps and writing — but breaking it down piece by piece can help you accomplish this seemingly insurmountable task.
One small piece of your business plan is the company overview, so let’s take a look at what that is, exactly, check out some company overview examples and go over how to make a company overview of your very own.

ZenBusiness
What is a company overview?
A company overview provides the reader of your business plan with basic background information about your company so they have an understanding of what you do, who the management team is and what customers your business serves.
The company description is the second piece of a business plan, falling right after the executive summary. Similar to the executive summary, your company overview will be short and succinct. Your reader needs to have a grasp on what your business does and who your customers are, even if they have limited time.

Why do I need a company overview?
The company overview is the part of your business plan that gives the basics and background of your business. It’s the foundation on which you will build the rest of your business plan.
If you’re looking to appeal to investors or potential clients, you need a reader to make an informed decision about your company. Before they can do that, they must know what your company does and who your customer is. Lenders in particular need a reason to keep reading, since they see tons of business plans regularly. The company overview provides those answers, and it will help you get a better sense of your business so you can firm up things like your marketing plan.
Compare cards
How much do you need.
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
What should I include in a company overview?
The exact elements that you need in your company overview will depend upon what details of your business are important, but there are some foundational elements that will be included in every company overview.
Once you’ve covered the basics, you can include any other minor details that will benefit a reader who will need to make an informed decision about your business.
Basic company information
Consider the company overview like an introduction for your business. In the opening paragraph of your company overview, you’ll want to include basic company information. That includes:
Your company name: This should be the official name of your business, exactly as it is written when you registered your business with the state.
Business structure: Your reader will want to know what business entity your company comes in: sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership or corporation.
Location(s): Share where your business is headquartered and other locations the business owns.
Ownership and management team
Break down who owns your business and how each owner is involved with the business. What shares of the company belong to whom? If you have a highly involved management team, share their names and key roles with the company as well.
Company history
Part of what makes your company unique is its history. And, even startups have some history. Don’t put too much focus on this section, but do add some personality and interesting details if possible, especially if they relate to your company culture.
Mission statement
Your company’s mission statement should be included in the company overview. If you don’t yet have a company mission statement, that’s okay. Think of a mission statement as the purpose of your company.
If you don’t have one, you can create one with your team. Or you can simply replace the mission statement with a problem statement. Your business idea should exist to solve a problem or pain point faced by your customers. Share what that problem is and what your business does to solve it. That’s essentially your mission statement.
Product/service and customer
This section of the company overview is where you can share the nitty-gritty details of your business. Talk about what product or service you provide and to whom you provide it. You can share some numbers here, but in general, save the numbers for later in your business plan.
The company overview should give the reader a general understanding of your business, your product or service, and your customer. If they’re interested to know more, they’ll reach out to you for a meeting or take the time to read the rest of your business plan. Keep it simple and straightforward here.
Future goals
While concrete details and facts about your business are important to whoever is reading your company overview, it’s also important to share your dreams and your vision. If you’re writing a business plan for a business that’s already in place, it’s very likely you’re looking for business financing to scale or solve a business problem. If you’re just starting out, though, then it’s likely you’re hoping to find startup funding.
The section on your future business goals should include a brief description of your growth goals for your business. Where you are now tells the reader a lot, but they also want to know where you plan to go.
A company overview is comprised of many small parts. Each part shares just a little bit more about your company with your reader.
Tips for writing a company overview
While a company overview is simply the details of your company written out, it might not be easy to write. Break it down into small steps and use these tips to make putting together your company overview just a little bit easier.
Start with the elevator pitch
If your business is already in operation, then you likely have an elevator pitch. Your company overview can start off with your elevator pitch.
The first paragraph of your company overview should include just a few sentences that explain your business and what you do. The shorter and clearer this is, the more likely your reader will understand and keep reading.
Stick to the basics
It’s tempting to pile on all the details when you’re writing a company overview. Remember, many of the details of your company, including the numbers, will be included in later sections of your business plan.
Your company overview should include only the most basic details about your company that the reader needs to know.
Be passionate
When you share the history, mission statement, and vision for the future of your company, it’s okay to show your passion. You wouldn’t be in business if you didn’t love what you do.
Your excitement for your business could spark interest for the reader and keep them engaged with your company overview and business plan.
Keep it succinct
When you’re passionate about something, it’s easy to get carried away. Remember that you’ve got plenty of space for details in your business plan. The company overview should be just the most basic information someone needs to understand your business.
It’s OK if your first draft of your company overview is long. Simply go through and edit it to be shorter, removing unnecessary details and words each time you read through it. Clear, concise descriptions are more likely to be read and to keep the reader reading to other sections of your business plan.
Have structure
Your company overview is just one piece of a multi-tiered business plan. Creating a clear structure for your business plan makes it easier to read. The same is true for your company overview.
Your business plan should have chapters, one of which is the company overview. Then, you can further break down the content for easy skimming and reading by adding sub-chapters. You can denote these breaks in content with bold headers.
While you can break down each section of the company overview with bold headers based on the above suggestions, you can also interweave some information together, such as the company structure and leadership structure. Each section should be only a few sentences long.
Write it later
If you’re struggling to write your company overview, come back to it. Write the rest of your business plan first and then write your company overview.
While this might seem like the opposite way of doing things, knowing what will be contained in the rest of your business plan can help you to focus in on the very most essential details in the company overview and to leave everything else out.
Get a test reader
If you’re struggling to edit down your company overview, get a test reader. Ideally, you’ll want to ask someone who doesn’t know a lot about your business. They’ll help you understand whether or not you’ve clearly communicated your message.
Proofreading is the final step in editing something you’ve written. This type of editing looks for typos, misspellings and grammatical errors that have been missed. Many of these small errors can be difficult to spot in our own writing, so be sure to ask someone who hasn’t seen multiple drafts of your company overview.
Start Your Dream Business
Company overview examples
If you don’t want to shell out for business planning software, but would still like some company overview examples to get you started, there are many places online you can look to for help getting started, like the Small Business Administration and SCORE.
Many successful companies also have some version of their company overview made public as their company profile page online. There are some variations from the company overview steps we’ve listed above, of course, but you can use the language and style of these company overview examples for inspiration:
Starbucks company profile .
Puma company page .
TaskRabbit About page .
Peloton company page .
Nestlé About page .
If you’re still feeling stuck, or want more company overview examples, try searching the websites of your favorite companies for more information. You might be surprised what you find — the Nestlé page, for example, has more information about their strategy and business principles.
On a similar note...

- assignments basic law
Assignments: The Basic Law
The assignment of a right or obligation is a common contractual event under the law and the right to assign (or prohibition against assignments) is found in the majority of agreements, leases and business structural documents created in the United States.
As with many terms commonly used, people are familiar with the term but often are not aware or fully aware of what the terms entail. The concept of assignment of rights and obligations is one of those simple concepts with wide ranging ramifications in the contractual and business context and the law imposes severe restrictions on the validity and effect of assignment in many instances. Clear contractual provisions concerning assignments and rights should be in every document and structure created and this article will outline why such drafting is essential for the creation of appropriate and effective contracts and structures.
The reader should first read the article on Limited Liability Entities in the United States and Contracts since the information in those articles will be assumed in this article.
Basic Definitions and Concepts:
An assignment is the transfer of rights held by one party called the “assignor” to another party called the “assignee.” The legal nature of the assignment and the contractual terms of the agreement between the parties determines some additional rights and liabilities that accompany the assignment. The assignment of rights under a contract usually completely transfers the rights to the assignee to receive the benefits accruing under the contract. Ordinarily, the term assignment is limited to the transfer of rights that are intangible, like contractual rights and rights connected with property. Merchants Service Co. v. Small Claims Court , 35 Cal. 2d 109, 113-114 (Cal. 1950).
An assignment will generally be permitted under the law unless there is an express prohibition against assignment in the underlying contract or lease. Where assignments are permitted, the assignor need not consult the other party to the contract but may merely assign the rights at that time. However, an assignment cannot have any adverse effect on the duties of the other party to the contract, nor can it diminish the chance of the other party receiving complete performance. The assignor normally remains liable unless there is an agreement to the contrary by the other party to the contract.
The effect of a valid assignment is to remove privity between the assignor and the obligor and create privity between the obligor and the assignee. Privity is usually defined as a direct and immediate contractual relationship. See Merchants case above.
Further, for the assignment to be effective in most jurisdictions, it must occur in the present. One does not normally assign a future right; the assignment vests immediate rights and obligations.
No specific language is required to create an assignment so long as the assignor makes clear his/her intent to assign identified contractual rights to the assignee. Since expensive litigation can erupt from ambiguous or vague language, obtaining the correct verbiage is vital. An agreement must manifest the intent to transfer rights and can either be oral or in writing and the rights assigned must be certain.
Note that an assignment of an interest is the transfer of some identifiable property, claim, or right from the assignor to the assignee. The assignment operates to transfer to the assignee all of the rights, title, or interest of the assignor in the thing assigned. A transfer of all rights, title, and interests conveys everything that the assignor owned in the thing assigned and the assignee stands in the shoes of the assignor. Knott v. McDonald’s Corp ., 985 F. Supp. 1222 (N.D. Cal. 1997)
The parties must intend to effectuate an assignment at the time of the transfer, although no particular language or procedure is necessary. As long ago as the case of National Reserve Co. v. Metropolitan Trust Co ., 17 Cal. 2d 827 (Cal. 1941), the court held that in determining what rights or interests pass under an assignment, the intention of the parties as manifested in the instrument is controlling.
The intent of the parties to an assignment is a question of fact to be derived not only from the instrument executed by the parties but also from the surrounding circumstances. When there is no writing to evidence the intention to transfer some identifiable property, claim, or right, it is necessary to scrutinize the surrounding circumstances and parties’ acts to ascertain their intentions. Strosberg v. Brauvin Realty Servs., 295 Ill. App. 3d 17 (Ill. App. Ct. 1st Dist. 1998)
The general rule applicable to assignments of choses in action is that an assignment, unless there is a contract to the contrary, carries with it all securities held by the assignor as collateral to the claim and all rights incidental thereto and vests in the assignee the equitable title to such collateral securities and incidental rights. An unqualified assignment of a contract or chose in action, however, with no indication of the intent of the parties, vests in the assignee the assigned contract or chose and all rights and remedies incidental thereto.
More examples: In Strosberg v. Brauvin Realty Servs ., 295 Ill. App. 3d 17 (Ill. App. Ct. 1st Dist. 1998), the court held that the assignee of a party to a subordination agreement is entitled to the benefits and is subject to the burdens of the agreement. In Florida E. C. R. Co. v. Eno , 99 Fla. 887 (Fla. 1930), the court held that the mere assignment of all sums due in and of itself creates no different or other liability of the owner to the assignee than that which existed from the owner to the assignor.
And note that even though an assignment vests in the assignee all rights, remedies, and contingent benefits which are incidental to the thing assigned, those which are personal to the assignor and for his sole benefit are not assigned. Rasp v. Hidden Valley Lake, Inc ., 519 N.E.2d 153, 158 (Ind. Ct. App. 1988). Thus, if the underlying agreement provides that a service can only be provided to X, X cannot assign that right to Y.
Novation Compared to Assignment:
Although the difference between a novation and an assignment may appear narrow, it is an essential one. “Novation is a act whereby one party transfers all its obligations and benefits under a contract to a third party.” In a novation, a third party successfully substitutes the original party as a party to the contract. “When a contract is novated, the other contracting party must be left in the same position he was in prior to the novation being made.”
A sublease is the transfer when a tenant retains some right of reentry onto the leased premises. However, if the tenant transfers the entire leasehold estate, retaining no right of reentry or other reversionary interest, then the transfer is an assignment. The assignor is normally also removed from liability to the landlord only if the landlord consents or allowed that right in the lease. In a sublease, the original tenant is not released from the obligations of the original lease.
Equitable Assignments:
An equitable assignment is one in which one has a future interest and is not valid at law but valid in a court of equity. In National Bank of Republic v. United Sec. Life Ins. & Trust Co. , 17 App. D.C. 112 (D.C. Cir. 1900), the court held that to constitute an equitable assignment of a chose in action, the following has to occur generally: anything said written or done, in pursuance of an agreement and for valuable consideration, or in consideration of an antecedent debt, to place a chose in action or fund out of the control of the owner, and appropriate it to or in favor of another person, amounts to an equitable assignment. Thus, an agreement, between a debtor and a creditor, that the debt shall be paid out of a specific fund going to the debtor may operate as an equitable assignment.
In Egyptian Navigation Co. v. Baker Invs. Corp. , 2008 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 30804 (S.D.N.Y. Apr. 14, 2008), the court stated that an equitable assignment occurs under English law when an assignor, with an intent to transfer his/her right to a chose in action, informs the assignee about the right so transferred.
An executory agreement or a declaration of trust are also equitable assignments if unenforceable as assignments by a court of law but enforceable by a court of equity exercising sound discretion according to the circumstances of the case. Since California combines courts of equity and courts of law, the same court would hear arguments as to whether an equitable assignment had occurred. Quite often, such relief is granted to avoid fraud or unjust enrichment.
Note that obtaining an assignment through fraudulent means invalidates the assignment. Fraud destroys the validity of everything into which it enters. It vitiates the most solemn contracts, documents, and even judgments. Walker v. Rich , 79 Cal. App. 139 (Cal. App. 1926). If an assignment is made with the fraudulent intent to delay, hinder, and defraud creditors, then it is void as fraudulent in fact. See our article on Transfers to Defraud Creditors .
But note that the motives that prompted an assignor to make the transfer will be considered as immaterial and will constitute no defense to an action by the assignee, if an assignment is considered as valid in all other respects.
Enforceability of Assignments:
Whether a right under a contract is capable of being transferred is determined by the law of the place where the contract was entered into. The validity and effect of an assignment is determined by the law of the place of assignment. The validity of an assignment of a contractual right is governed by the law of the state with the most significant relationship to the assignment and the parties.
In some jurisdictions, the traditional conflict of laws rules governing assignments has been rejected and the law of the place having the most significant contacts with the assignment applies. In Downs v. American Mut. Liability Ins. Co ., 14 N.Y.2d 266 (N.Y. 1964), a wife and her husband separated and the wife obtained a judgment of separation from the husband in New York. The judgment required the husband to pay a certain yearly sum to the wife. The husband assigned 50 percent of his future salary, wages, and earnings to the wife. The agreement authorized the employer to make such payments to the wife.
After the husband moved from New York, the wife learned that he was employed by an employer in Massachusetts. She sent the proper notice and demanded payment under the agreement. The employer refused and the wife brought an action for enforcement. The court observed that Massachusetts did not prohibit assignment of the husband’s wages. Moreover, Massachusetts law was not controlling because New York had the most significant relationship with the assignment. Therefore, the court ruled in favor of the wife.
Therefore, the validity of an assignment is determined by looking to the law of the forum with the most significant relationship to the assignment itself. To determine the applicable law of assignments, the court must look to the law of the state which is most significantly related to the principal issue before it.
Assignment of Contractual Rights:
Generally, the law allows the assignment of a contractual right unless the substitution of rights would materially change the duty of the obligor, materially increase the burden or risk imposed on the obligor by the contract, materially impair the chance of obtaining return performance, or materially reduce the value of the performance to the obligor. Restat 2d of Contracts, § 317(2)(a). This presumes that the underlying agreement is silent on the right to assign.
If the contract specifically precludes assignment, the contractual right is not assignable. Whether a contract is assignable is a matter of contractual intent and one must look to the language used by the parties to discern that intent.
In the absence of an express provision to the contrary, the rights and duties under a bilateral executory contract that does not involve personal skill, trust, or confidence may be assigned without the consent of the other party. But note that an assignment is invalid if it would materially alter the other party’s duties and responsibilities. Once an assignment is effective, the assignee stands in the shoes of the assignor and assumes all of assignor’s rights. Hence, after a valid assignment, the assignor’s right to performance is extinguished, transferred to assignee, and the assignee possesses the same rights, benefits, and remedies assignor once possessed. Robert Lamb Hart Planners & Architects v. Evergreen, Ltd. , 787 F. Supp. 753 (S.D. Ohio 1992).
On the other hand, an assignee’s right against the obligor is subject to “all of the limitations of the assignor’s right, all defenses thereto, and all set-offs and counterclaims which would have been available against the assignor had there been no assignment, provided that these defenses and set-offs are based on facts existing at the time of the assignment.” See Robert Lamb , case, above.
The power of the contract to restrict assignment is broad. Usually, contractual provisions that restrict assignment of the contract without the consent of the obligor are valid and enforceable, even when there is statutory authorization for the assignment. The restriction of the power to assign is often ineffective unless the restriction is expressly and precisely stated. Anti-assignment clauses are effective only if they contain clear, unambiguous language of prohibition. Anti-assignment clauses protect only the obligor and do not affect the transaction between the assignee and assignor.
Usually, a prohibition against the assignment of a contract does not prevent an assignment of the right to receive payments due, unless circumstances indicate the contrary. Moreover, the contracting parties cannot, by a mere non-assignment provision, prevent the effectual alienation of the right to money which becomes due under the contract.
A contract provision prohibiting or restricting an assignment may be waived, or a party may so act as to be estopped from objecting to the assignment, such as by effectively ratifying the assignment. The power to void an assignment made in violation of an anti-assignment clause may be waived either before or after the assignment. See our article on Contracts.
Noncompete Clauses and Assignments:
Of critical import to most buyers of businesses is the ability to ensure that key employees of the business being purchased cannot start a competing company. Some states strictly limit such clauses, some do allow them. California does restrict noncompete clauses, only allowing them under certain circumstances. A common question in those states that do allow them is whether such rights can be assigned to a new party, such as the buyer of the buyer.
A covenant not to compete, also called a non-competitive clause, is a formal agreement prohibiting one party from performing similar work or business within a designated area for a specified amount of time. This type of clause is generally included in contracts between employer and employee and contracts between buyer and seller of a business.
Many workers sign a covenant not to compete as part of the paperwork required for employment. It may be a separate document similar to a non-disclosure agreement, or buried within a number of other clauses in a contract. A covenant not to compete is generally legal and enforceable, although there are some exceptions and restrictions.
Whenever a company recruits skilled employees, it invests a significant amount of time and training. For example, it often takes years before a research chemist or a design engineer develops a workable knowledge of a company’s product line, including trade secrets and highly sensitive information. Once an employee gains this knowledge and experience, however, all sorts of things can happen. The employee could work for the company until retirement, accept a better offer from a competing company or start up his or her own business.
A covenant not to compete may cover a number of potential issues between employers and former employees. Many companies spend years developing a local base of customers or clients. It is important that this customer base not fall into the hands of local competitors. When an employee signs a covenant not to compete, he or she usually agrees not to use insider knowledge of the company’s customer base to disadvantage the company. The covenant not to compete often defines a broad geographical area considered off-limits to former employees, possibly tens or hundreds of miles.
Another area of concern covered by a covenant not to compete is a potential ‘brain drain’. Some high-level former employees may seek to recruit others from the same company to create new competition. Retention of employees, especially those with unique skills or proprietary knowledge, is vital for most companies, so a covenant not to compete may spell out definite restrictions on the hiring or recruiting of employees.
A covenant not to compete may also define a specific amount of time before a former employee can seek employment in a similar field. Many companies offer a substantial severance package to make sure former employees are financially solvent until the terms of the covenant not to compete have been met.
Because the use of a covenant not to compete can be controversial, a handful of states, including California, have largely banned this type of contractual language. The legal enforcement of these agreements falls on individual states, and many have sided with the employee during arbitration or litigation. A covenant not to compete must be reasonable and specific, with defined time periods and coverage areas. If the agreement gives the company too much power over former employees or is ambiguous, state courts may declare it to be overbroad and therefore unenforceable. In such case, the employee would be free to pursue any employment opportunity, including working for a direct competitor or starting up a new company of his or her own.
It has been held that an employee’s covenant not to compete is assignable where one business is transferred to another, that a merger does not constitute an assignment of a covenant not to compete, and that a covenant not to compete is enforceable by a successor to the employer where the assignment does not create an added burden of employment or other disadvantage to the employee. However, in some states such as Hawaii, it has also been held that a covenant not to compete is not assignable and under various statutes for various reasons that such covenants are not enforceable against an employee by a successor to the employer. Hawaii v. Gannett Pac. Corp. , 99 F. Supp. 2d 1241 (D. Haw. 1999)
It is vital to obtain the relevant law of the applicable state before drafting or attempting to enforce assignment rights in this particular area.
Conclusion:
In the current business world of fast changing structures, agreements, employees and projects, the ability to assign rights and obligations is essential to allow flexibility and adjustment to new situations. Conversely, the ability to hold a contracting party into the deal may be essential for the future of a party. Thus, the law of assignments and the restriction on same is a critical aspect of every agreement and every structure. This basic provision is often glanced at by the contracting parties, or scribbled into the deal at the last minute but can easily become the most vital part of the transaction.
As an example, one client of ours came into the office outraged that his co venturer on a sizable exporting agreement, who had excellent connections in Brazil, had elected to pursue another venture instead and assigned the agreement to a party unknown to our client and without the business contacts our client considered vital. When we examined the handwritten agreement our client had drafted in a restaurant in Sao Paolo, we discovered there was no restriction on assignment whatsoever…our client had not even considered that right when drafting the agreement after a full day of work.
One choses who one does business with carefully…to ensure that one’s choice remains the party on the other side of the contract, one must master the ability to negotiate proper assignment provisions.
Founded in 1939, our law firm combines the ability to represent clients in domestic or international matters with the personal interaction with clients that is traditional to a long established law firm.
Read more about our firm
© 2024, Stimmel, Stimmel & Roeser, All rights reserved | Terms of Use | Site by Bay Design

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.23: Assignment- Marketing Plan, Part I
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 47975
- Lumen Learning
Student Instructions: Complete the following information about the organization and products and/or services you will focus on as you develop a complete marketing plan throughout the course. You may need to do research to get answers to the questions below. Be sure the organization and offering you select will 1) remain interesting to you for the duration of the course, and 2) have sufficient information available for you to conduct research and make informed recommendations in your marketing plan.
Company Profile
- Company Name:
- Major products and/or services (names, types):
- Products and/or services your marketing plan will focus on:
- Target customers:
- Distribution channel(s):
- Headquarters (city, state, country):
- Year founded:
- Number of employees:
- Annual revenue (estimated)
- Key competitors:
- Link to Web site:
- Link to Yahoo! Finance information page (for public companies):
Market Segmentation and Targeting
- What problem does your product or service solve?
- Describe the total market for your solution: Who are potential customers?
- What are the key segments within this market?
- Identify and briefly describe 1–3 segments that this company serves.
- Which segment does this marketing plan focus on, and why? Why do you believe this segment will offer growth and profit opportunities?
Situation and Company Analysis
Economic environment.
Discuss factors that affect your consumers’ purchasing power and spending patterns. What is the economic environment that you are operating in? Is it a growth, recovery or recession? Will it be easy to find staff? What is the current interest rate i.e. is it increasing or decreasing? What is consumer confidence like?
Technical Environment
The technological environment changes rapidly. You need to make sure that you are aware of trends in your industry and other industries could affect your business. New technologies create new markets and can influence you consumers and competitors. Industry environment What are the trends in your industry? Are there new entrants in the market? Has a substitute product been introduced? Are there changes in industry practices or new benchmarks to use?
Competitive Environment
How many competitors do you have? Who are the key competitors? What are the key selling points or competitive advantages of each one. What is your advantage over competitors? Is the market large enough to support you and competitors?
Political Environment
Consider the political environment for the areas that your business will trade and operate in. Is there a stable political system? Are there any licenses and regulations that you should be aware of? Do you need to win support to be able to operate?
SWOT Analysis
Instruction: Complete the table below with descriptive responses and explanation as you answer the questions below.
- Does the organization have a strong brand presence?
- What resources are available for marketing activities?
- Does the the company have unique products or services that satisfy the needs of their target market?
- What makes the company’s products or services unique?
- What value is brought to customers?
- Does the organization have a weak brand presence?
- Are resources insufficient for marketing activities?
- Does the company lack distinctive products or services?
- Do current products or services fail to satisfy the needs of customers?
- Do current products or services fail to bring value to customers?

Opportunities
- What is the unique opportunity that the company is trying to take advantage of?
- Does the target market have any unfulfilled needs that the company can satisfy?
- Are there emerging target markets with needs that the company can satisfy?
- Are there ways the company and its competitors can benefit by working together?
- Are there opportunities for collaborating with customers to build brand presence?
- Describe and analyze if market demand is increasing?
- Are there changes in the government regulations that will affect the company?
- Describe any emerging global issues that will affect the company?
- What are the tactics that competitors use to pursue customers?
- What are the strengths of the company’s biggest and or emerging competitors?
- In what ways are the competitors’ products or services superior to the company’s offerings?
- How are competitors likely to respond to any changes in the way the company markets?
- Is the company behind in adopting new technologies for marketing?
- Describe any ways in which international competitors are taking away market share?
- What do customers dislike about the company?
- Describe and analyze if market demand is decreasing?
Mission, Objectives, and Goals
State the mission or business purpose: what the organization wants to achieve, in market-oriented terms. (Example: Disney’s mission could be, “We create happiness by providing the finest in entertainment for people of all ages.)
List 1–3 objectives that move the organization a step closer to achieving the mission. (Example: A Disney objective could be, “To be the most popular theme park for international visitors.”)
Convert objectives into specific marketing goals that are easy to measure and evaluate. (Example: Our goal is to increase market share of international theme park visitors by 10% in the next two years.”)
Sample Grading Rubric
Company profile grading rubric.
Total points possible for Company Profile Assignment: 10 pts.
Market Segmentation and Targeting Grading Rubric
Total points possible for Market Segmentation and Targeting Assignment: 10 pts.
Situation and Company Analysis Grading Rubric
Total points possible for Situation and Company Analysis Assignment: 50 pts.
Total points possible for Marketing Plan, Part 1 Assignment (Consists of Company Profile Assignment, Market Segmentation and Targeting Assignment, and Situation and Company Analysis Assignment combined): 100 pts.
Contributors and Attributions
- Assignment: Marketing Plan, Part I . Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- SWOT and Integrated Marketing Communications Templates. Authored by : Melissa Barker. License : CC BY: Attribution

MGT 2220: Principles of Management (Assignment)
- Company Information
- Industry Information
- Case Studies
- Additional Resources
- Writing & Citing This link opens in a new window
Chat with a Librarian
Term assignment.
TERM PROJECT
- Background and Context: Discuss type of industry, products/services, and how organizational vision and strategies have influenced their management.
- Analysis of current managerial style and organizational culture.
- One NEW recommendation by you that the company can embark on in the near future meaning the next one to three years. This can be a goal to fix issues the company may be experiencing, or to address new endeavors from a growth perspective. Ensure that these align with the organization’s vision and values. This recommendation must not be identical or very similar to anything the organization is planning already or is currently involved in. The management involves the four functions of management being applied to achieve some type of organizational goal.
- For your recommendation you will select one goal that will be accomplish. This goal must be a specific goal following the SMART goal setting theory. That means the goal must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time bound.
- Once your goal is selected for your new strategic initiative you will complete the following four areas regarding the four functions of management.
List and describe the 4 functions of management. Then, for each of the functions describe how your goal will be achieved by the organization. This section should be approximately eight paragraphs. Four paragraphs to describe the four functions, and then four paragraphs to apply the four functions to how the organization will address your recommendation.
Getting Started
A published SWOT report or company profile is always a good starting point for your company analysis. These reports will also provide the name of the top management executives at your company.
To Locate SWOT Reports:
- Business Insights - From the main page in Business Insights, select a company or search for the name of your company. There are Company Profiles for 400,000+ companies, and the largest 1000 public companies have a SWOT analysis right next to the Company Overview.
- ProQuest Central - From the main search page in ProQuest Central, type the name of your company and SWOT into the search bar. From the results, choose the relevant record
To Locate Company Profiles:
Business Market Research Collection - This collection includes Hoover’s Company Profiles for thousands of public and non-public companies. From the main search page, type the name of your company and HOOVERS into the search bar. From the results, choose the relevant record.
- Next: Company Information >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://berkeleycollege.libguides.com/c.php?g=784823
Module 6: Organizational Structures
Assignment: organizational structures.
Step 1: To view this assignment, click on Assignment: Organizational Structures.
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Assignment: Organizational Structures. Authored by : Nina Burokas. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Options and Derivatives
- Strategy & Education
Assignment: Definition in Finance, How It Works, and Examples
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
What Is an Assignment?
Assignment most often refers to one of two definitions in the financial world:
- The transfer of an individual's rights or property to another person or business. This concept exists in a variety of business transactions and is often spelled out contractually.
- In trading, assignment occurs when an option contract is exercised. The owner of the contract exercises the contract and assigns the option writer to an obligation to complete the requirements of the contract.
Key Takeaways
- Assignment is a transfer of rights or property from one party to another.
- Options assignments occur when option buyers exercise their rights to a position in a security.
- Other examples of assignments can be found in wages, mortgages, and leases.
Uses For Assignments
Assignment refers to the transfer of some or all property rights and obligations associated with an asset, property, contract, or other asset of value. to another entity through a written agreement.
Assignment rights happen every day in many different situations. A payee, like a utility or a merchant, assigns the right to collect payment from a written check to a bank. A merchant can assign the funds from a line of credit to a manufacturing third party that makes a product that the merchant will eventually sell. A trademark owner can transfer, sell, or give another person interest in the trademark or logo. A homeowner who sells their house assigns the deed to the new buyer.
To be effective, an assignment must involve parties with legal capacity, consideration, consent, and legality of the object.
A wage assignment is a forced payment of an obligation by automatic withholding from an employee’s pay. Courts issue wage assignments for people late with child or spousal support, taxes, loans, or other obligations. Money is automatically subtracted from a worker's paycheck without consent if they have a history of nonpayment. For example, a person delinquent on $100 monthly loan payments has a wage assignment deducting the money from their paycheck and sent to the lender. Wage assignments are helpful in paying back long-term debts.
Another instance can be found in a mortgage assignment. This is where a mortgage deed gives a lender interest in a mortgaged property in return for payments received. Lenders often sell mortgages to third parties, such as other lenders. A mortgage assignment document clarifies the assignment of contract and instructs the borrower in making future mortgage payments, and potentially modifies the mortgage terms.
A final example involves a lease assignment. This benefits a relocating tenant wanting to end a lease early or a landlord looking for rent payments to pay creditors. Once the new tenant signs the lease, taking over responsibility for rent payments and other obligations, the previous tenant is released from those responsibilities. In a separate lease assignment, a landlord agrees to pay a creditor through an assignment of rent due under rental property leases. The agreement is used to pay a mortgage lender if the landlord defaults on the loan or files for bankruptcy . Any rental income would then be paid directly to the lender.
Options Assignment
Options can be assigned when a buyer decides to exercise their right to buy (or sell) stock at a particular strike price . The corresponding seller of the option is not determined when a buyer opens an option trade, but only at the time that an option holder decides to exercise their right to buy stock. So an option seller with open positions is matched with the exercising buyer via automated lottery. The randomly selected seller is then assigned to fulfill the buyer's rights. This is known as an option assignment.
Once assigned, the writer (seller) of the option will have the obligation to sell (if a call option ) or buy (if a put option ) the designated number of shares of stock at the agreed-upon price (the strike price). For instance, if the writer sold calls they would be obligated to sell the stock, and the process is often referred to as having the stock called away . For puts, the buyer of the option sells stock (puts stock shares) to the writer in the form of a short-sold position.
Suppose a trader owns 100 call options on company ABC's stock with a strike price of $10 per share. The stock is now trading at $30 and ABC is due to pay a dividend shortly. As a result, the trader exercises the options early and receives 10,000 shares of ABC paid at $10. At the same time, the other side of the long call (the short call) is assigned the contract and must deliver the shares to the long.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/novation.asp-final-f5904e1fe68047ba9d8b6feaf53c1736.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Sample Profile
FREE 8+ Company Profile Assignment Samples [ Construction, Project, Business ]

According to the book “ Knowledge Management Strategies and Applications ”, there are many organizations that start with their vision statement as a beginning point to facilitate organizational performance as core values occupy a supporting role in a company’s vision. If you are working as a project manager or team leader, you must consider effectively assigning relevant tasks, roles, and responsibilities to each of the members of your team or office department. In this article, here are some guides on creating a company profile assignment and downloadable company or business assignment samples to assist you. Keep on reading!
Company Profile Assignment
Free 8+ company profile assignment samples, 1. company profile accounting assignment, 2. company profile project assignment, 3. company profile consultant experience assignment, 4. company profile description assignment, 5. company profile market analysis assignment, 6. company work profile assignment, 7. company profile analytical assignment, 8. company profile recycling plan assignment, 9. company business profile assignment, what is a company profile assignment, how to create a company profile assignment, 1. structure a simple format, 2. explain the concept or plan, 3. gather information for the content, 4. evaluate goals and strategies, what are the important elements in a company profile, what is a business assignment, how to assess a company, what is the use of assignment for business.
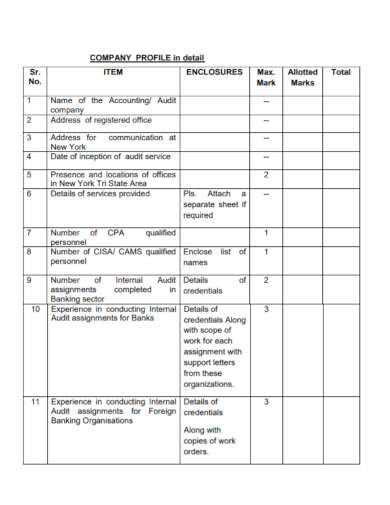
Size: 803 KB
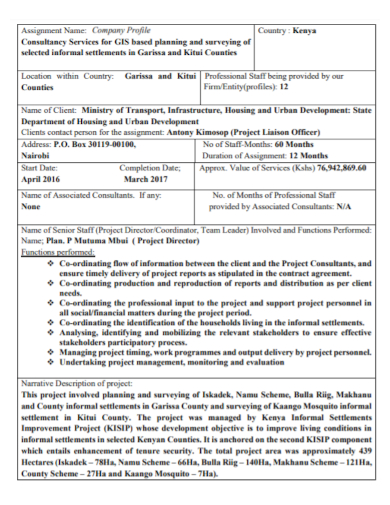
Size: 497 KB

Size: 109 KB
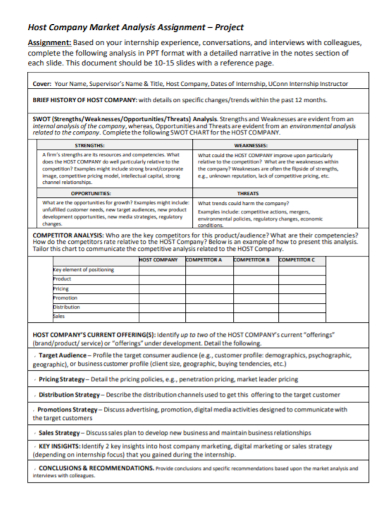
Size: 659 KB

Size: 114 KB

Size: 101 KB

Size: 287 KB

Size: 55 KB
A company profile assignment is a clear and well-detailed document containing primary information and other details concerning different kinds of assignments to be managed and utilized in a particular company such as accounting, project, consultant experience, profile description, market analysis , recycling plan, and many more.
A clear and comprehensive company profile and business analysis of your company will be advantageous for your business in presenting the financial position to your business partners, prospective clients, potential investors, and stakeholders. In this section, we provide some useful tips that you can learn and apply in creating a company profile assignment for your business firm:
Start your company assignment by structuring a simple format of a list consisting of information with different kinds of sections. Write solid goals, requirements, case studies, adn reports or any other data for this document. Provide a clear overview of all topics which you will later explain in the assignment.
The next step is to thoroughly explain your concepts and plans for your company . Again, familiarize yourself with every little detail of your project or ideas. Learning and discerning various concepts will assist you in creating a positive effect on assignments.
In this part, you will need to gather necessary information for the content of your business assignment. Use research tools, and comparison charts to match reports and articles that may significantly help in your business assignment writing.
One of the essential steps that you need to do is performing an assessment of evaluation of diverse goals and strategies available to your company or organization. This method will help you comprehend the fundamentals of strategy-based business management.
The important elements in a company profile are mission and vision statements, business description, product and service descriptions, history, expansion and growth, advertising, industry information, and many more.
A business assignment is the act of transferring a person’s rights or property to another person or business. It may also pertain to transferring obligations or roles to another employee inside the company.
To assess your company , you need to calculate the total value of your company’s assets and subtract any debts or liabilities. Then, determine the financial worth of your business through a stockbroker or a business broker. You can also estimate your company’s earnings for upcoming years. And you can also consider the geographical location and other factors that affect your business.
This method is integral in various business firms in terms of identifying the specific type of resources that are assigned to a certain department, machine, or center or operation in the process of production. Assigning resources is a beneficial way with the aim to improve production efficiency, manage costs, and boost profits.
Creating a structured and well-detailed company profile assignment for your business is very beneficial in terms of elevating the value and impact of your overall brand identity or company. Several research studies have shown that an organized worker assignment is vital in every business. There are people who designed various frameworks for integrating human factors into planning models while others presented this matter in project scheduling and innovative optimization approaches.
If you’re currently looking for some inspiration in developing an information sheet and company profile assignment, w e provide you with some downloadable and printable assignments on company profile templates here in different types of formats. Click the templates in this article and start downloading now!
Related Posts
Free 11+ professional writing samples, free 10+ company quotation samples, free 9+ sample assignment letter, free 9+ patent assignment samples, free 9+ immigration business plan samples, free 7+ sample patent assignment forms, free 7+ board resolution samples in pdf ms word, free 6+ sample assignment of contract, assignment of intellectual property rights, free 25+ fact sheet templates, free 15+ company flowchart samples, free 14+ travel business plan templates, free 10+ company analysis templates, free 9+ job evaluation samples, free 9+ sample seo proposal, free 10+ general assignment samples, free 8+ sample company profiles, free 16+ deed of assignment samples, free 15+ assignment agreement templates.
Assignment on Company Law
Harmonization of the rules relating to company law and corporate governance, as well as to accounting and auditing, is essential for creating a Single Market for Financial Services and products. In the fields of company law and corporate governance, objectives include: providing equivalent protection for shareholders and other parties concerned with companies; ensuring freedom of establishment for companies throughout the EU; fostering efficiency and competitiveness of business; promoting cross-border cooperation between companies in different Member States; and stimulating discussions between Member States on the modernization of company law and corporate governance. This report is a diagnostic assessment of the corporate governance regulations and practices in Bangladesh. The assessment is measured against international norms and current practices as recognized by the OECD Guidelines on Corporate Governance. The report identifies critical areas where institutions, regulations, or other economic factors in the corporate sector could be strengthened to improve corporate governance (CG). As such, the authors identify strengths and weaknesses of legal requirements, regulations, and corporate practices. To identify the current strengths and weaknesses, the authors drew heavily on a review of laws and a survey of businesses organisations carried out by the research team as well as a series of interviews with key stakeholders. This analysis will serve as a basis on which further study can build. In fact, this report comprises the first stage of a three-stage project; Stage 2 will frame detailed recommendations to strengthen corporate governance in Bangladesh and Stage 3 will formulate implementation strategies. The Companies Act 1994 (the Act) defines the rights of both majority and minority shareholders. Shareholders are not intended to, and do not in practice get involved in the day-to-day management of a company. However, the Act provides for certain supervisory functions to be undertaken by the shareholders in the form of these rights to attend meetings, appoint and remove directors and to obtain financial information as well as approve the balance sheet annually. The law also provides for various mechanisms for shareholders to enforce these rights, the principal among them being a suit for minority protection under Section 233 of the Act.
I NTRODUCTION
In this term paper we will discuss the dictum derived from Lord Halsbury’s judgement in Salomon v Salomon what are the pros and cons of the dictum, the reasoning why the House of Lords reached their conclusion reversing what the Court of Appeal said in relation to the agency point. The assessment of the limited liability doctrine which was originally intended to encourage passive investors to contribute to encourage trade and commerce, the most fundamental criticism to this doctrine, group of companies and when the court will lift the veil between the parent and its subsidiary .A mention must be made of shareholders as the owners of the company and creditors ’interest who lend the company money which directors have to take into consideration when they are conducting the affairs of the company.
C ompany D efinition
The term company is used to describe an association of a number of person , formed for some common purpose and registered according to the law relating to companies .Section 3(1)(i) of the companies act , 1994 states that a company means , A Company formed and registered under this actor an existing company.
Lord justice lindley defines a company as follows: By a company is meant an association of many person who contribute money or money’s worth to a common stock and employ it for a common purpose. The common stock so contributed is denoted in money and is the capital of the company. The people who contribute it or to whom it belongs are member. The proportion of capital to which each member is entitled is his share
Company is a voluntary association of persons formed for the purpose of doing business having a distinct name and limited liability. It is a juristic person having a separate legal entity distinct from the members who constitute it, capable of rights and duties of its own and endowed with the potential of perpetual succession. The Companies Act, 1956, states that ‘company’ includes company formed and registered under the Act or an existing company i.e. a company formed or registered under any of the previous company laws.
However, company is not a citizen so as to claim fundamental rights granted to citizens.
A voluntary association formed and organized to carry on a business. Types of companies include sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability, corporation, and public limited company.
A legal entity, allowed by legislation, which permits a group of people, as shareholders, to apply to the government for an independent organization to be created, which can then focus on pursuing set objectives, and empowered with legal rights which are usually only reserved for individuals, such as to sue and be sued, own property, hire employees or loan and borrow money.
E ssential features of a company
1. Registration:
A company comes into existence only after registration under the Companies Act. But a Statutory Corporation is formed and commence business as notified or stated in the Act and as passed in Legislature. In case of partnership, registration is not compulsory.
2. Voluntary Association:
A company is an association of many persons on a voluntary basis. Therefore a company is formed by the choice and consent of the members.
3. Legal Personality:
A company is regarded by law as a single person. It has a legal personality. This rule applies even in the case of “One-man Company.”
4. Contractual Capacity:
A shareholder of a company, in its individual capacity, cannot bind the company in any way. The shareholder of a company can enter into contract with the company and can be an employee of the company.
5. Management
A company is managed by the Board of Directors, whole time Directors, Managing Directors or Manager. These persons are selected in the manner provided by the Act and the Articles of Association of the company. A shareholder, as such, cannot participate in the management.
A company must have a capital, otherwise it cannot work.
7. Permanent Existence
The company has perpetual succession. The death or insolvency of a shareholder does not affect its existence. A company comes into end only when it is liquidated according to provision of the Companies Act.
8. Registered Office
A company must have a registered office.
9. Common Seal
A company must have a Common Seal. The company being an artificial person cannot sign its name on a contract. The common seal is used as a subsititute for its signature. The common seal bears the name and place of the company, and date of its incorporation engraved on it.
10. Limited Liability
The liabilities of shareholder of a company are usually limited. The creditors of a company are not creditors of individual shareholders and a decree obtained against a company cannot be executed against any shareholders. It can only be executed against the assets of the company.
11. Transferability
The shareholder of a company can transfer its share and ordinarily the transferee becomes a member of the company.
12. Statutory Obligations
A company is required to comply with various statutory obligations regarding management, e.g., filing balance sheets, maintaining proper account books and registers etc.
13. Not a Citizen
A company is an artificial person, not a natural person. Therefore a company is not a citizen, although it may have a Domicile
14. Residence
A company has a residence (for taxation and other purpose). A company does not posses any fundamental rights.
15. Social Objective
The present view as regard the legal nature of Company Law is that the Company is a social institution having duties and responsibilities toward the community, its workers, the national economy and progress.
16. Centrally Administrated
The administration of company Law is entrusted to the Central Government.
T ypes of company
There are two types of companies –
- Private Limited Company
- Public Limited Company
P rivate Limited Company
Section 3(1) (iii) defines a private company as one which:-
(a) has a minimum paid-up share capital of Rs.1 Lakh or such higher capital as may be prescribed; and
(b) by its Articles Association:
- restricts the right of transfer of its share; limits the number of its members to 50 which will not include:-
- members who are employees of the company; and
- members who are ex-employees of the company and were members while in such employment and who have continued to be members after ceasing to be employees;
- prohibits any invitation to the public to subscribe for any shares or debentures of the company; and
- Prohibits any invitation or acceptance of deposits from persons other than its members, directors or their relatives.
This goes to say that a private company, in addition to the earlier conditions, shall have a minimum paid-up share capital of Rupees One Lakh or such higher capital as may be prescribed and its Articles shall prohibit invitation or acceptance of deposits from persons other than its members, directors or their relatives. In case of such companies, public interest is not involved.
The basic characteristics of a private company in terms of section 3(1)(iii) of the Act do not get altered just because it is a subsidiary of a public company in view of the fiction in terms of section 3(1)(iv)(c) of the Act that it is a public company. May be it is a public company in relation to other provisions of the Act but not with reference to its basic characteristics. In terms of that section, a company is a private company when its articles restrict the right of transfer of shares, restrict its membership to 50 (other than employees shareholders) and prohibits invitation to public to subscribe to its shares. Therefore, all the provisions in the articles to maintain the basic characteristics of a private company in terms of that section is restriction on the right to transfer and the same will apply even if a private company is a subsidiary of a public company.
P ublic Limited Company
The standard legal designation of a company which has offered shares to the general public and has limited liability. A Public Limited Company’s stock can be acquired by anyone and holders are only limited to potentially lose the amount paid for the shares. It is a legal form more commonly used in the U.K. Two or more people are required to form such a company, assuming it has a lawful purpose.
A company whose securities are traded on a stock exchange and can be bought and sold by anyone. Public companies are strictly regulated, and are required by law to publish their complete and true financial position so that investors can determine the true worth of its stock (shares). Also called publicly held company. Public limited company and its abbreviation Plc are commonly used in the UK in the way that corporation and Inc. is used in the United States.
The Company defined under section 3(1)(iv) of the Companies Act, 1956 is a public company which-
- is not a private company;
- has a minimum paid-up capital of Rs. 5 lakhs or such higher capital as may be prescribed;
- is a private company but subsidiary of a public company.
M emorandum of Association:
The Memorandum of Association is the constitution of the company and provides the foundation on which its structure is built. It is the principal document of the company and no company can be registered without the memorandum of association. It defines the scope of the company’s activities as well as its relation with the outside world.
According to Lord Macmillan , “The purpose of the memorandum is to enable the shareholder, creditors and those who deal with the company to know what is permitted range of enterprise.”
In the words of Charles Worth, “the memorandum of association is the company’s charter and defines the limitations of its powers. Its purpose is to enable shareholders; creditors and those who deal with the company, to know what its permitted range of enterprise is. It is the document which informs all persons dealing with the company, what the company is formed to do. How capital will it raise its nationality is? It regulates the company’s external affairs, while the articles of association regulate its internal affairs.” This is an exhaustive definition which explains the nature and scope of memorandum.
Section 2 (28) of the Companies Act defines a memorandum as “the memorandum of association of a company as originally framed or as altered from time to time in pursuance of any previous Company Law or of this Act.” The contents of the memorandum are explained in Section B of the Act.
The main purpose of the memorandum is to explain the scope of activities of the company. The prospective shareholders know the areas where company will invest their money and the risk they are taking in investing the money. The outsiders will understand the limits of the working of the company and their dealings with it should remain within the prescribed scope.
I mportance of Memorandum
Memorandum is the fundamental document of a company which contain conditions upon which the company is incorporated. This document is important for the following reasons.
- Memorandum defines the limitations on the powers of the company established under the Act.
- The whole structure of the company is built upon memorandum.
- It explains the scope of activities of the company. The investment knows where their money will be spent and outsiders also know the nature of activities the company is authorized to take up.
- It is a basic document of the company with regard to its constitution
- It is a charter of the company which sets out its written goals.
C lauses of Memorandum
The memorandum of association contains the following clauses:
T he Name Clause
A company being a separate legal entity must have a name. A company may select any name which does not resemble the name of any other company and it should not contain the words like king, queen, emperor, government bodies and the names of world bodies like UNO, WHO, World Bank etc. The name should not be objectionable in the opinion of the government. The word ‘limited’ must be used at the end of the name of a Public and ‘Private Limited’ is used by a Private Company. These words are used to ensure that all persons dealing with the company should know that the liability of its members is limited. The name of the company must be painted outside every place where business of the company is carried on.
If the company has a name which is undesirable or resembles the name of any other existing company, this name can be changed by passing an ordinary resolution.
R egistered Office Clause
Every company should have a registered office, the address of which should be communicated to the Registrar of Companies. This helps the Registrar to have correspondence with the company. The place of registered office can be intimated to the Registrar within 30 days of incorporation or commencement of business, whichever is earlier.
A company can shift its registered office from one play to another n the same town with intimation to the Register. But if the company wants to shift its registered office from one town to another town in the same state, a special resolution is required to be passed. If the office is to be shifted from one state to another state it involves alteration in the memorandum.
O bject Clause
This is one of the important clauses of the Memorandum of Association. It determines the rights and powers of the company and also defines its sphere of activities. The object clause should decide carefully because it is difficult to alter this clause later on. No activity can be taken up by the company which is not mentioned in the object clause Moreover, the investors i.e., shareholders will not mentioned in the object clause. Moreover, the investors i.e., shareholders will know the sphere of activities which the company can undertake. The choice of the object clause lies with the subscribers to the memorandum. They are free to add anything to it provided it is not contrary to the provisions of the Companies Act and other laws of the land.
The Companies (Amendment) Act 1965 requires that in cause of companies formed after this amendment, the memorandum must state separately (a) main objects, and (b) other objects. Main objects will include objects to be pursued by the company on incorporation and objects incidental or ancillary to the attainment of the main objects. Other objects will include all other objects which are not included in the main objects.
The object clause offers protection to the shareholders by ensuring that the funds raised for the undertaking are not going to be risked in any other undertaking. The creditors also feel protected by this clause. By confining the activities within a specified field, it serves the public interest also.
The object clause can be changed to enable a company to carry on its activities more economically, or by improved means to carry on some business which under existing circumstances may conveniently by combined with the object clause.
L iability Clause
This clause states that the liability of the members is limited to the value of shares held by them. It means that the memes will be liable to pay only the unpaid balance of their shares. The liability of the members may be limited by guarantee. It also states the amount which every member will undertake to contribute to the assets of the company in the event of its winding up.
C apital Clause
The clause states the total capital of the proposed company. The division of capital into equity share capital and preference share capital should also be mentioned. The number of shares in each category and their value should be given. If some special rights and privileges are conferred on any type of shareholders, mention may also be made in the clause to enable the public to know the exact nature of capital structure of the company.
A ssociation Clause
This clause contains the names of signatories to the memorandum of association. The memorandum must be singed by at least seven persons in the cause of public limited company and by at least two persons in the case of private limited company. Each subscriber must take at least one share in the company. The subscribers declare that they agree to incorporate the company and agree to take the shares stated against their names. The signatures of subscriber are attested by at least one witness each. The full addresses and occupations of subscribers and the witnesses are also given.
A lteration of a Memorandum of Association
Memorandum of Association is a basic document of the company. Any change in various clauses of memorandum may have an adverse effect on any of the parties connected with the company. Company Law has prescribed a particular procedure for making a change in the memorandum. The procedure provided for different clauses varies. The following procedure is followed for carrying out a change in the memorandum:
N ame clause (Section 25)
the Central government. If the company is registered with an undesirable name then it can change it with an ordinary resolution with the approval of the Central Government. The Central Government can also direct the comapny within 12 months of its registration to change its name and this will have to be done within three months. The change in name will be effective when it is resisted with the Registrar.
R egistered Office (Section 17)
The change in registered office place from one state to another requires a change in memorandum. This change affects the interests of shareholders, investors, creditors, employees etc. This change can be affected only with the approval of Company Law Board. Earlier this power was vested with the court but the Company Law (Amended) Act, 1974 has transferred it to Company Law Board.
O bject Clause (Section 17)
The object clause is the most important clause in the memorandum; its change may affect the activities of the company. This clause is a limitation on the company beyond which it cannot carry its activities. The object clause can be changed by passing a special resolution and by getting the permission of the Company Law Board. A copy of the resolution should be field with the Registrar within 30 days of passing the resolution. A petition is also made to the Company Law Board for issuing a confirmation. When this change is allowed by the Board, then printed copy of the Memorandum as altered must be field with the Registrar within three months of the order.
The change in situation and objects clause is allowed only under certain situations. It will be allowed when it necessary for any of the following reasons:
- The change is necessary to allow the company to carry on its business more economically or efficiently.
- The company will be able to attain its objectives by new and improved means.
- The company may enlarge the local area of its operations.
- The company is enabled by change to carry on some new business with convenience and advantage.
- To restrict or abandon any of the objects specified in the memorandum.
- To sell whole of part of the company’s property.
- To amalgamate with any other company or body of persons.
L iability clause :
If articles so permit, the liability of the Directors Managing Directors or Manager can be made unlimited by passing a special resolution. The officer concerned should also accord his consent for making the liability unlimited.
A change in capital clause involving an increase in the authorized capital can affected by passing an ordinary resolution in the general Meeting .
A rticle of Association
The rules and regulations which are framed of the internal management of the company are set out in a document named Articles of Association. The arties are framed to help the company in achieving its objectives set out in a memorandum of association. It is a supplementary document to the memorandum. According to Section 2(2) of the
Companies Act, “Articles of association of the company as originally framed or as altered from time to time in pursuance of any previous companies’ law or of this act.”
The private companies limited by shares, companies limited by guarantee and unlimited companies must have their articles of association. A public company limited by shares may or may not have its own Articles. As per Section 26 of Companies Act, it is not obligatory on the part of a public company limited by shares to prepare and register Articles of Association along with Memorandum of Association. However, such a company may adopt all or any of the regulations contained in the model set of Articles given in table A in the Schedule I of the Act. It means the company can partly frame it sown articles and partly incorporate some of the regulations in Table A. Unless the company prepares its own articles then regulations of Table A shall be applicable in the same manner as if they were contained in its own registered articles.
The articles cannot contain anything contrary to the Companies Act and also to the memorandum of association. If the document contains anything contrary to the Companies Act or memorandum, it will be inoperative. When articles are proposed to be registered, they must be printed, divided into paragraphs and numbered consecutively. Each subscriber to the memorandum must sign the articles in the presence of at least one witness.
- The nature of Articles may be explained as follows:
- Articles of association are subordinate to memorandum of association.
- The articles are controlled by memorandum.
- Articles help in achieving the objectives laid down in the memorandum.
- Articles are only internal regulation over which members exercise control.
- Articles lay down the regulations of governance of the company.
Some of the contents of articles of association are follows:
- The amount of share capital issued, different types of shares, calls on shares, forfeiture of shares, transfer and transmission of share and rights and privileges of different categories of shareholders.
- Powers to alter as well as reduce share capital.
- The appointment of directors, powers, duties and their remuneration.
- The appointment of manager, managing director, etc.
- The procedure for holding and conducting of various meetings.
- Matters relating to maintaining of accounts, declaration of dividends and keeping of reserves, etc.
- Procedure for winding up the company.
A lteration of Articles of Association
- The articles of association can be altered by assign a special resolution. Certain restrictions are imposed on the nature and extent of the alternation that may be made.
- The change should not be violating the provisions of the Companies Act.
- It should not be contrary to the provisions of the memorandum of association.
- The alteration must not have anything illegal.
- The alteration should not adversely affect the minority shareholders.
Prospectus of a Company
After the receipt of certificate of incorporation, if the promoters of a public limited company wishes to issue shares to the public, he will issue a document called prospectus. It is an invitation to the public to subscribe to the share capital of the company. The companies Act, 1956 defines prospectus as any document described or issued as a prospectus and include any notice, circular, advertisement or other documents inviting deposits from the public or inviting offer from the public for the subscription of shares. It is circulated among the public in printed pamphlets.
It gives all necessary information about the company so that the prospective shareholders may fully understand the objectives and the plans of the company.
After getting the company incorporated, promoters will raise finances. The public is invited to purchase s A document containing detailed information about the company and an invitation to the public subscribing to the share capital and debentures is issued. This document is called ‘prospectuses. Private companies cannot issue a prospectus because they are strictly prohibited from inviting the public to subscribe to their shares. Only public companies can issue a prospectus. Section 2 (36) of the Companies Act defines prospectus as, “A prospectus means any document described or issued as prospectus and includes any notice, circular, advertisement or other documents invent deposits from public or inviting offers from the public for the subscription or purchase of any shares in or debentures of a body corporate.”
The prospectus is not an offer in the contractual sense but only an invitation to offer. A document constructed to be a prospectus should be issued to the public. A prospectus should have the following essentials.
- There must be an invitation offering to the public.
- The invitation must be made on behalf of the company or intended company.
- The invitation must to be subscribed or purchase.
- The invitation must relate to shares or debentures.
A prospectus must be field with the Registrar of companies before it is issued to the public. The issue of prospectus is essential when the company wishes the public to purchase its shares or debentures.
If the promoters are confident of obtaining the required capital through private contacts, even a public company may not issue a prospectus. The promoters prepare a draft prospectus containing required information and this document is known as ‘a statement is lieu of prospectus.’ A prospectus duly dated and signed by all the directors should be field with Register of Company before it is issued to the public.
A prospectus brings to the notice of the public that a new company has been formed. The company tries to convince the public that it offers best opportunity for their investment. A prospectus outlines a detail the terms and conditions on which the shares or debentures have been offered to the public. Every prospectus contains an application from on which an intending investor can apply for the purchase of shares or debentures. A company must get minimum subscription within 120 days from the issue of prospectus. If it fails to obtain minimum subscription from the members of the public within the specified period, then the amount already received from public is returned. The company cannot get a certificate of commencement of business because the public is not interested in that company.
The following important matter are included in the prospectus:
- The prospectus contains the main objectives of the company, the name and addresses of the signatories of the memorandum of association and the number of shares held by them.
- The name, addresses and occupation of directors and managing directors.
- The number and classes of shares and debentures issued.
- The qualification share of directors and the interest of directors for the promotion of company.
- The number, description and the document of shares or debentures which within the two preceding years have been agreed to be issed other than cash.
- The name and addresses of the vendors of any property acquired by the company and the amount paid or to be paid.
- particulars about the directors, secretaries and the treasures and their remuneration.
- The amount for the minimum subscription.
- If the company carrying on business, the length of time of such businesses.
- The estimated amount of preliminary expenses.
- Name and address of the auditors, bankers and solicitors of the company.
- Time and place where copies of balance sheets, profits and loss account and the auditors report may be inspected.
- The auditor’s report so submitted must deal with the profit and loss of the company for each year of five financial years immediately preceding the issue of prospectus.
- If any profit or reserve has been capitalized, the particulars of such capitalization will be stated in the prospectus.
- Name and full address of the company.
- Full particulars about the signatories to the memorandum of association and the number of shares taken up by them.
- The number and classes of shares. The interest of shareholders in the property and profits of the company.
- Name, address and occupations of members of the Board of Directors or proposed Directors.
- The minimum subscription fixed by promoters after taking into account all financial requirements at the beginning.
- If the company acquires any property from vendors, their full particulars are to be given.
- The full address of underwriters, if any, and the opinion of directors that the underwriters have sufficient resources to meet their obligations.
- The time of opening of the subscription list.
- The nature and extent of interest of every promoter in the promotion of the company.
- The amount payable on application, allotment and calls.
- The particulars of preferential treatment given to any person for subscribing shares or debentures.
- Particulars about reserves and surpluses.
- The amount of preliminary expenses.
- The name and address of the auditor.
- Particulars regarding voting rights at the meeting of the company.
- A report by the auditors regarding the profits and losses of the company.
- These are some of the contents which every prospectus must include. The prospectus is an advertisement of the company, so the company may give any information which promotes its interest. Any information given in the prospectus must be true, otherwise the subscribe can beheld guilty for misrepresentation.
S tatement in Lieu of Prospectus
A public company raises its capital from the public and it issues prospectus for this purpose. Sometimes, the promoters of a company decide not to approach the public for raising necessary capital. They are hopeful of raising funds from the friends and relations or through underwriters. In that case a prospectus need not be issued but a Statement in Lieu of Prospectus must be field with the registrar at least three days before the first allotment of shares. Such a statement must be singed by every person who is named therein as a director or proposed director of the company. This statement will be drafted strictly in accordance with the particulars set out in a part I of Schedule III of the Act.
G eneral Meetings 1994
General meetings of a company are the fora where shareholders can raise their concerns and make their influence felt over the management of a company. A company must hold at least one general meeting of its shareholders, normally called the annual general meeting (AGM), in every calendar year. If an AGM is not duly called, then the RJSC or the Court may authorize the holding of the meeting out of time. In some circumstances, holders of at least 10% of the shares of a company can require an extraordinary general meeting to be called and held.
For a general meeting (AGM or EGM) to be valid all members of the company must be served with the notice of the meeting. The location of the meeting is decided by the directors, but should normally be at the registered office of the company, so that all the books and records are at hand. In Bangladesh, space constraints mean that general meetings are often held other than in the registered office of the company.
The quorum requisite is generally provided in the articles. There are usually no veto provisions regarding company meetings. Unless otherwise specified in the Act or the articles, decisions are by a simplemajority.
In an AGM, the agenda must include the following items, and may include other items as necessary:
- Approval of the annual report and audited accounts of the company
- Appointment of auditors
- Resignation by rotation and appointment of directors (as required)
Special majorities of three-fourths of the shareholders present and voting are required for passing special and extraordinary resolutions. These special majorities give a measure of protection to shareholders, particularly in widely held companies, in that there is a lower possibility of decisions being forced through by brute majority.
A special resolution is required for the following reasons, among others:
- To change provisions of the objects clause of the memorandum of the company
- To alter or add to the articles of association of the company
- To reduce share capital
- To reserve capital
- To remove a director from office
- To remove an auditor before the expiry of his term
- On winding up through the Court
An extraordinary resolution is required for the following reasons.
C onclusion
As is documented in this report, failings in institutions, government agencies, legal enforcement, and market behaviour have resulted in weak corporate governance in Bangladesh. The report is designed as a diagnostic tool from which a consensus will emerge regarding the way forward for Bangladesh. The authors hope that this report will start a dialogue amongst stakeholders about specific measures that can be taken to improve the transparency and accountability of the corporate sector and streng then institutional support for good corporate governance. At this stage, only very broad recommendations are provided, identifying institutions or sectors that should be studied further. Specific recommendations will be framed in subsequent stages of this project.
Corporate Governance is a term that describes the interaction of government regulators, shareholders, Boards of directors, independent observers, auditors, accountants and managers to provide quality Information to shareholders, the market, and society at large. Each stakeholder plays an important part to Creating an environment where transparency and accountability are encouraged, enforced, and rewarded. For Bangladesh, the first step in strengthening the role of stakeholders in corporate governance is raising their awareness regarding these issues. This report attempts to start that process. For companies to have Sufficient motivation to disclose information and improve governance practices, the relevant stakeholders must place a value on that information and there must be consequences for corporate governance practices.
Civil Justice System
Islamic law of inheritance, client counseling for lawyers, define and discuss on federal courts, why are kitchen sponges ideal bacteria habitats, population explosion, stochastic volatility, changi airport in singapore will expand significantly once t5 construction plans come to fruition, define and discuss on organic farming, consumer price index (cpi), latest post, mid-ocean ridge (mor), harnessing hydrogen at the genesis of life, ngc 5728’s faint characteristics are exposed, astronomers discover the oldest black hole ever observed, atomic hydrogen welding, variable-frequency transformer (vft).
13 February 2023
Notice of Assignment in Factoring in the U.S
When a business uses invoice factoring, they transfer ownership of its accounts receivable to a factoring company, which then has the responsibility to collect payment for those invoices.
Therefore, a document is issued to alert its customers of this. This is known as a notice of assignment.
Meaning of Notice of Assignment
A notice of assignment is a document that notifies clients that a factoring company has acquired ownership of their accounts receivable, or invoices, from the original business.
The notice's objective is to alert customers to the ownership change and specify who should receive payments.
Importance of Notice of Assignment
A notice of assignment is vital because it officially notifies customers that the ownership of an invoice has changed hands and that they should now direct payments to the factoring company.
The notice helps ensure that payments are sent to the appropriate parties , avoiding misunderstandings and potential conflicts and preventing uncertainty.
In the event of a disagreement, having a detailed and official notice of assignment can safeguard the legal interests of both the company and the factoring company.
Impact of Notice of Assignment on Businesses
The possible impacts faced by businesses by using a factoring company and sending their customers a notice of assignment are:
1. Enhanced customer relationships: By providing clear and official notification to customers of the change in ownership of invoices, a business can help maintain and strengthen its relationship with them.
2. Improved cash flow: By transferring ownership of invoices to a factoring company, a business can receive payment more quickly and improve its overall cash flow.
3. Increased operational efficiency: By using a factoring company to manage the collections process, a business can free up internal resources and focus on its core operations, leading to increased efficiency.
4. Reduced risk: By transferring the responsibility of collecting payment to a factoring company, a business can reduce its exposure to the risk of non-payment and bad debt.
However, before deciding to utilize factoring , it's crucial to consider any potential drawbacks, such as losing control over the collection process and the expense of the factoring service.
Factors Covered in a Notice of Assignment The main sections covered are:
- The company's accounts receivable have been transferred to a third-party financial institution, and payment should now be made to them
- The customer should now send payments to a new address, typically a secure payment processing location
- The customer will be responsible if they make a payment to the wrong address
Information in a Notice of Assignment
In a factoring notice of assignment, the following details are covered to notify the business’ customer about the transfer of ownership of accounts receivable:
- Particulars of the accounts receivable being assigned , including the amount and invoice numbers
- Details of the factor and the client/debtor
- Specifics of the assignment of the accounts receivable, including the effective date and any conditions of the assignment
- Instructions for the customer on how to direct future payments to the factor
- Any other relevant terms and conditions of the factoring agreement
What Happens When an Obligor Doesn’t Receive Notice of Agreement
A business that sells its accounts receivables (invoices) to a third-party factor must send a notice of agreement to its customers.
The purpose of the notice is to inform the customer that the factor has taken ownership of the invoice, and the payments should be made directly to the factor instead of the business.
If the customer does not receive the notice, they may continue to make the payments to the business, leading to confusion, delayed payments to the factor and potential disputes.
In some cases, the customer may have the right to demand a return of the payment made to the factor or stop payment if the notice of assignment was not correctly given.
How to Receive Notice of Agreement
A factoring notice of agreement is typically provided by the factoring company or third-party factor that has purchased the accounts receivable (invoices) from the business.
The notice is usually generated by the factor and given to the business to send to its customers.
The business may also be responsible for ensuring that the notice of assignment is delivered correctly to its customers.
Some factoring companies provide templates or sample notices that the business can use.
Requirements for a Notice of Assignment
To obtain a notice of assignment (NOA) from a factoring company, the following requirements are necessary:
- Monthly revenue of at least $300,000
- A stable financial track record of 1-2 years
- Accurate and trustworthy financial reports
- Effective management of accounts receivable
- No significant financial difficulties
1. Who Sends a Factoring Notice of Assignment? A factoring notice of assignment is typically sent by the business that has sold its accounts receivables or invoices to a third-party factor or factoring company.
The factor usually provides the notice of assignment, and the business may have to sign a factoring agreement with the factor to obtain the notice.
The notice informs the business’ customers that the factor has taken over the ownership of the invoices, and the payments should be made directly to the factoring company instead of the business.
2. How Much Does a Notice of Assignment Cost? The cost for issuing a notice of assignment in factor can differ based on various elements, such as the amount assigned, the state where the assignment is taking place and the particular provisions of the assignment agreement.
This cost may include legal fees, filing paperwork fees and other administrative expenses. It's crucial to examine the assignment agreement thoroughly to determine the precise cost and be aware of any additional fees that may be incurred.
3. How Long Does a Notice of Assignment Take? The duration of issuing a notice of assignment in factoring can differ based on particular circumstances. Usually, the process can take anywhere between a few days to weeks.
The length of the time may be influenced by factors such as the state in which the assignment is getting issued, the complexity of the assignment agreement and the accessibility of relevant parties.
Moreover, the time needed for the notice of assignment may be affected by any legal challenges or hindrances.
4. Does Notice of Assessment Mean You Owe Money? In the United States, a notice of assessment usually implies that you owe money to the government.
However, it is contingent on particular circumstances. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) sends out the notice of assessment to inform taxpayers of any modification to their tax obligations.
If the notice displays an increase in the amount owed, it implies that the taxpayer has an outstanding balance with the IRS and should pay it promptly to prevent further interest and penalties.
On the other hand, if it shows a decrease in the amount owed, it showcases that the taxpayer has paid more taxes than required and may be eligible for a refund.
It is, therefore, always advisable to thoroughly examine the notice and to get help from a professional.
5. Is Notice of Agreement a Proof of Debt? A notice of agreement alone is not considered proof of a debt. The document merely outlines the terms and conditions agreed upon by the parties involved.
It is not enough evidence to confirm the presence of debt but rather serves as a record of the agreement between the parties.
To establish proof of debt, other financial documents such as receipts, invoices or other documentation may be necessary.
The specific requirements for proving a debt depend upon the type of debt and the laws of the jurisdiction where it is being established.
6. What is a Letter of Release? A letter of release from a factoring company is a declaration that a debt has been satisfied and is no longer the company's responsibility.
In factoring, a business sells its accounts receivable to a factoring company for a fee to receive cash quickly.
Upon receiving the payment on the accounts receivable by the business’ customer, the factoring company issues a letter of release, confirming that the debt has been fully paid off and the company is no longer obligated to it.
The letter serves as proof that the debt has been fully resolved. It can be used to clear the debt from the business's financial records.
The specifics of the letter of release, including the terms and conditions, will depend on the particular factoring agreement and the laws in the jurisdiction where it is formed and drafted.
Siddhi Parekh
Finance manager at drip capital.
Table of Content
- Information in a NOA
- What Happens When an Obligor Doesn’t Receive NOA
- How to Receive NOA
- Requirements for NOA
We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website. By continuing to browse this site, you give consent for cookies to be used in accordance with and for the purposes set out in our Privacy Policy and acknowledge that your have read, understood and consented to all terms and conditions therein.
Assignment on IT
This section of the online library serves the students and teachers with a wide range of IT assignments for inspiration. Students with an acquiring mind and a proactive approach learn a good deal on IT topics for assistance in their courses within high school and undergraduate IT subjects. The given section of IT assignments is not only for IT students but also for students in other respects who have IT subjects in their courses.
Computer Systems
- Click to Read More
Database Design Concepts
Inter organizational cyber security policies, charles babbage, group policy software deployments, telecommunication, data on fixed line vs. cellular debate, cabling design, standards, codes and definitions, fiber optic connector assembly, fiber-optic and copper cable installation safety, generate free bibliography in all citation styles.
Researchomatic helps you cite your academic research in multiple formats, such as APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago & Many more. Try it for Free!
- Aeronautics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Empowering Businesses to Achieve More. ASGN helps commercial and government businesses realize their digital innovation and transformation goals. Our industry knowledge, and qualifications get us in the door, while our investments in our clients' future growth and success support our growing market share.
Assignment on Coca-Cola Company. Amirul Islam Lisan Ruhul Amin. As the leading beverages company in the world, Coca Cola almost monopolizes the entire carbonated beverages segment. Beside it, Coca Cola also maintain their reputation as the leading company in the world using PESTLE analysis so that Coca Cola can examine the macro-environment of ...
On Assignment (please see ASGN Incorporated) Staffing and Recruiting Calabasas, California 12,072 followers
This quick guide will explain the basics of the management of business and will provide topics of business management essays. To put it simply, business management is a process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the organizational resources to achieve the company's objectives. While business administration concentrates on the ...
On Assignment is a provider of professional and technical employees for long- and short-term assignments. The company operates four divisions: Lab Support, which provides scientific professionals ...
On Assignment Inc. | 103 followers on LinkedIn. Engineering and Technical, IT, Staffing and Recruiting, Technical | On Assignment, Inc. (NYSE: ASGN), is a leading global provider of in-demand ...
Half of the written assignments and discussions (32 in total) are based on a case study, whose focus is a fictional dog-treats business called "Salty Pawz." Many of these assignments take the form of asking students to give Wanda, the company's inexperienced owner, advice about how she can run her business more effectively.
Many of these assignments take the form of asking students to give Tom, the company's inexperienced owner, advice about how he can run his business more effectively. The Sun City Boards assignments create a common framework for applying knowledge and skills developed through the course, encouraging students to demonstrate mastery of the ...
That includes: Your company name: This should be the official name of your business, exactly as it is written when you registered your business with the state. Business structure: Your reader will ...
On Assignment Unveils Dramatic Rebranding. CALABASAS, Calif.-- ( BUSINESS WIRE )-- On Assignment, Inc. (NYSE: ASGN), a leading provider of diversified staffing solutions today announced a new logo, brand mark, and website design. Peter Dameris, CEO of On Assignment said, "Our new branding scheme is a bold new look for the digital age.".
Introduction of Amazon (Company) Amazon, Inc. is an American multinational technology company which focuses on e-commerce, cloud computing, digital streaming, and artificial intelligence. It has been referred to as "one of the most influential economic and cultural forces in the world and is one of the world's most valuable brands. It is
Complete a written assignment that contains the following information: A brief (one-paragraph) summary of the business you selected. According to your research, how does the company rank with regard to CSR? Be sure to provide a source for this ranking! Describe specific examples of corporate actions that resulted in this company's ranking.
Ordinarily, the term assignment is limited to the transfer of rights that are intangible, like contractual rights and rights connected with property. Merchants Service Co. v. Small Claims Court, 35 Cal. 2d 109, 113-114 (Cal. 1950). An assignment will generally be permitted under the law unless there is an express prohibition against assignment ...
4: Marketing Strategy. Expand/collapse global location. 4.23: Assignment- Marketing Plan, Part I. Page ID. Lumen Learning. Lumen Learning. Student Instructions: Complete the following information about the organization and products and/or services you will focus on as you develop a complete marketing plan throughout the course.
A published SWOT report or company profile is always a good starting point for your company analysis. These reports will also provide the name of the top management executives at your company. To Locate SWOT Reports: Business Insights - From the main page in Business Insights, select a company or search for the name of your company. There are ...
Step 1: To view this assignment, click on Assignment: Organizational Structures. Step 2: Follow the instructions in the assignment and submit your completed assignment into the LMS.
Assignment: An assignment is the transfer of an individual's rights or property to another person or business. For example, when an option contract is assigned, an option writer has an obligation ...
What is a Company Profile Assignment? A company profile assignment is a clear and well-detailed document containing primary information and other details concerning different kinds of assignments to be managed and utilized in a particular company such as accounting, project, consultant experience, profile description, market analysis, recycling plan, and many more.
Voluntary Association: A company is an association of many persons on a voluntary basis. Therefore a company is formed by the choice and consent of the members. 3. Legal Personality: A company is regarded by law as a single person. It has a legal personality. This rule applies even in the case of "One-man Company.". 4.
Fashion Simona Company collaborated with other logistic companies such as Ninja Van and JNT for item pickup and delivery. In this current situation, almost the customers are not able to go outside for shopping clothes because covid-19 cases increase rapidly. The Company uses this opportunity to sell the clothes at an online platform.
Meaning of Notice of Assignment. A notice of assignment is a document that notifies clients that a factoring company has acquired ownership of their accounts receivable, or invoices, from the original business. The notice's objective is to alert customers to the ownership change and specify who should receive payments.
Researchomatic helps you cite your academic research in multiple formats, such as APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago & Many more. Try it for Free! Researchomatic is the largest e-library that contains millions of free IT Assignment topics & IT Assignment examples for students of all academic levels.
MGMT 6046 Group Assignment #1: TEMPLATES Company Details Globacom Limited Globacom Limited commonly known as Glo, is a Nigerian multinational telecommunications company founded in 2003 by Mike Adenuga. It is one of the leading telecommunications service providers in Nigeria and has expanded its operations to other African countries. Glo offers a range of services, including mobile telephony ...