Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper

Definition and Purpose of Abstracts
An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes:
- an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to read the full paper;
- an abstract prepares readers to follow the detailed information, analyses, and arguments in your full paper;
- and, later, an abstract helps readers remember key points from your paper.
It’s also worth remembering that search engines and bibliographic databases use abstracts, as well as the title, to identify key terms for indexing your published paper. So what you include in your abstract and in your title are crucial for helping other researchers find your paper or article.
If you are writing an abstract for a course paper, your professor may give you specific guidelines for what to include and how to organize your abstract. Similarly, academic journals often have specific requirements for abstracts. So in addition to following the advice on this page, you should be sure to look for and follow any guidelines from the course or journal you’re writing for.
The Contents of an Abstract
Abstracts contain most of the following kinds of information in brief form. The body of your paper will, of course, develop and explain these ideas much more fully. As you will see in the samples below, the proportion of your abstract that you devote to each kind of information—and the sequence of that information—will vary, depending on the nature and genre of the paper that you are summarizing in your abstract. And in some cases, some of this information is implied, rather than stated explicitly. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , which is widely used in the social sciences, gives specific guidelines for what to include in the abstract for different kinds of papers—for empirical studies, literature reviews or meta-analyses, theoretical papers, methodological papers, and case studies.
Here are the typical kinds of information found in most abstracts:
- the context or background information for your research; the general topic under study; the specific topic of your research
- the central questions or statement of the problem your research addresses
- what’s already known about this question, what previous research has done or shown
- the main reason(s) , the exigency, the rationale , the goals for your research—Why is it important to address these questions? Are you, for example, examining a new topic? Why is that topic worth examining? Are you filling a gap in previous research? Applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data? Resolving a dispute within the literature in your field? . . .
- your research and/or analytical methods
- your main findings , results , or arguments
- the significance or implications of your findings or arguments.
Your abstract should be intelligible on its own, without a reader’s having to read your entire paper. And in an abstract, you usually do not cite references—most of your abstract will describe what you have studied in your research and what you have found and what you argue in your paper. In the body of your paper, you will cite the specific literature that informs your research.
When to Write Your Abstract
Although you might be tempted to write your abstract first because it will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s a good idea to wait to write your abstract until after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
What follows are some sample abstracts in published papers or articles, all written by faculty at UW-Madison who come from a variety of disciplines. We have annotated these samples to help you see the work that these authors are doing within their abstracts.
Choosing Verb Tenses within Your Abstract
The social science sample (Sample 1) below uses the present tense to describe general facts and interpretations that have been and are currently true, including the prevailing explanation for the social phenomenon under study. That abstract also uses the present tense to describe the methods, the findings, the arguments, and the implications of the findings from their new research study. The authors use the past tense to describe previous research.
The humanities sample (Sample 2) below uses the past tense to describe completed events in the past (the texts created in the pulp fiction industry in the 1970s and 80s) and uses the present tense to describe what is happening in those texts, to explain the significance or meaning of those texts, and to describe the arguments presented in the article.
The science samples (Samples 3 and 4) below use the past tense to describe what previous research studies have done and the research the authors have conducted, the methods they have followed, and what they have found. In their rationale or justification for their research (what remains to be done), they use the present tense. They also use the present tense to introduce their study (in Sample 3, “Here we report . . .”) and to explain the significance of their study (In Sample 3, This reprogramming . . . “provides a scalable cell source for. . .”).
Sample Abstract 1
From the social sciences.
Reporting new findings about the reasons for increasing economic homogamy among spouses
Gonalons-Pons, Pilar, and Christine R. Schwartz. “Trends in Economic Homogamy: Changes in Assortative Mating or the Division of Labor in Marriage?” Demography , vol. 54, no. 3, 2017, pp. 985-1005.
![a research project begins with an abstract “The growing economic resemblance of spouses has contributed to rising inequality by increasing the number of couples in which there are two high- or two low-earning partners. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the topic under study (the “economic resemblance of spouses”). This sentence also implies the question underlying this research study: what are the various causes—and the interrelationships among them—for this trend?] The dominant explanation for this trend is increased assortative mating. Previous research has primarily relied on cross-sectional data and thus has been unable to disentangle changes in assortative mating from changes in the division of spouses’ paid labor—a potentially key mechanism given the dramatic rise in wives’ labor supply. [Annotation for the previous two sentences: These next two sentences explain what previous research has demonstrated. By pointing out the limitations in the methods that were used in previous studies, they also provide a rationale for new research.] We use data from the Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) to decompose the increase in the correlation between spouses’ earnings and its contribution to inequality between 1970 and 2013 into parts due to (a) changes in assortative mating, and (b) changes in the division of paid labor. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The data, research and analytical methods used in this new study.] Contrary to what has often been assumed, the rise of economic homogamy and its contribution to inequality is largely attributable to changes in the division of paid labor rather than changes in sorting on earnings or earnings potential. Our findings indicate that the rise of economic homogamy cannot be explained by hypotheses centered on meeting and matching opportunities, and they show where in this process inequality is generated and where it is not.” (p. 985) [Annotation for the previous two sentences: The major findings from and implications and significance of this study.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-1.png)
Sample Abstract 2
From the humanities.
Analyzing underground pulp fiction publications in Tanzania, this article makes an argument about the cultural significance of those publications
Emily Callaci. “Street Textuality: Socialism, Masculinity, and Urban Belonging in Tanzania’s Pulp Fiction Publishing Industry, 1975-1985.” Comparative Studies in Society and History , vol. 59, no. 1, 2017, pp. 183-210.
![a research project begins with an abstract “From the mid-1970s through the mid-1980s, a network of young urban migrant men created an underground pulp fiction publishing industry in the city of Dar es Salaam. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the context for this research and announces the topic under study.] As texts that were produced in the underground economy of a city whose trajectory was increasingly charted outside of formalized planning and investment, these novellas reveal more than their narrative content alone. These texts were active components in the urban social worlds of the young men who produced them. They reveal a mode of urbanism otherwise obscured by narratives of decolonization, in which urban belonging was constituted less by national citizenship than by the construction of social networks, economic connections, and the crafting of reputations. This article argues that pulp fiction novellas of socialist era Dar es Salaam are artifacts of emergent forms of male sociability and mobility. In printing fictional stories about urban life on pilfered paper and ink, and distributing their texts through informal channels, these writers not only described urban communities, reputations, and networks, but also actually created them.” (p. 210) [Annotation for the previous sentences: The remaining sentences in this abstract interweave other essential information for an abstract for this article. The implied research questions: What do these texts mean? What is their historical and cultural significance, produced at this time, in this location, by these authors? The argument and the significance of this analysis in microcosm: these texts “reveal a mode or urbanism otherwise obscured . . .”; and “This article argues that pulp fiction novellas. . . .” This section also implies what previous historical research has obscured. And through the details in its argumentative claims, this section of the abstract implies the kinds of methods the author has used to interpret the novellas and the concepts under study (e.g., male sociability and mobility, urban communities, reputations, network. . . ).]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-2.png)
Sample Abstract/Summary 3
From the sciences.
Reporting a new method for reprogramming adult mouse fibroblasts into induced cardiac progenitor cells
Lalit, Pratik A., Max R. Salick, Daryl O. Nelson, Jayne M. Squirrell, Christina M. Shafer, Neel G. Patel, Imaan Saeed, Eric G. Schmuck, Yogananda S. Markandeya, Rachel Wong, Martin R. Lea, Kevin W. Eliceiri, Timothy A. Hacker, Wendy C. Crone, Michael Kyba, Daniel J. Garry, Ron Stewart, James A. Thomson, Karen M. Downs, Gary E. Lyons, and Timothy J. Kamp. “Lineage Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Proliferative Induced Cardiac Progenitor Cells by Defined Factors.” Cell Stem Cell , vol. 18, 2016, pp. 354-367.
![a research project begins with an abstract “Several studies have reported reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes; however, reprogramming into proliferative induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPCs) remains to be accomplished. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence announces the topic under study, summarizes what’s already known or been accomplished in previous research, and signals the rationale and goals are for the new research and the problem that the new research solves: How can researchers reprogram fibroblasts into iCPCs?] Here we report that a combination of 11 or 5 cardiac factors along with canonical Wnt and JAK/STAT signaling reprogrammed adult mouse cardiac, lung, and tail tip fibroblasts into iCPCs. The iCPCs were cardiac mesoderm-restricted progenitors that could be expanded extensively while maintaining multipo-tency to differentiate into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells in vitro. Moreover, iCPCs injected into the cardiac crescent of mouse embryos differentiated into cardiomyocytes. iCPCs transplanted into the post-myocardial infarction mouse heart improved survival and differentiated into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. [Annotation for the previous four sentences: The methods the researchers developed to achieve their goal and a description of the results.] Lineage reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs provides a scalable cell source for drug discovery, disease modeling, and cardiac regenerative therapy.” (p. 354) [Annotation for the previous sentence: The significance or implications—for drug discovery, disease modeling, and therapy—of this reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-3.png)
Sample Abstract 4, a Structured Abstract
Reporting results about the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis, from a rigorously controlled study
Note: This journal requires authors to organize their abstract into four specific sections, with strict word limits. Because the headings for this structured abstract are self-explanatory, we have chosen not to add annotations to this sample abstract.
Wald, Ellen R., David Nash, and Jens Eickhoff. “Effectiveness of Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis in Children.” Pediatrics , vol. 124, no. 1, 2009, pp. 9-15.
“OBJECTIVE: The role of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis (ABS) in children is controversial. The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate in the treatment of children diagnosed with ABS.
METHODS : This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Children 1 to 10 years of age with a clinical presentation compatible with ABS were eligible for participation. Patients were stratified according to age (<6 or ≥6 years) and clinical severity and randomly assigned to receive either amoxicillin (90 mg/kg) with potassium clavulanate (6.4 mg/kg) or placebo. A symptom survey was performed on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30. Patients were examined on day 14. Children’s conditions were rated as cured, improved, or failed according to scoring rules.
RESULTS: Two thousand one hundred thirty-five children with respiratory complaints were screened for enrollment; 139 (6.5%) had ABS. Fifty-eight patients were enrolled, and 56 were randomly assigned. The mean age was 6630 months. Fifty (89%) patients presented with persistent symptoms, and 6 (11%) presented with nonpersistent symptoms. In 24 (43%) children, the illness was classified as mild, whereas in the remaining 32 (57%) children it was severe. Of the 28 children who received the antibiotic, 14 (50%) were cured, 4 (14%) were improved, 4(14%) experienced treatment failure, and 6 (21%) withdrew. Of the 28children who received placebo, 4 (14%) were cured, 5 (18%) improved, and 19 (68%) experienced treatment failure. Children receiving the antibiotic were more likely to be cured (50% vs 14%) and less likely to have treatment failure (14% vs 68%) than children receiving the placebo.
CONCLUSIONS : ABS is a common complication of viral upper respiratory infections. Amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate results in significantly more cures and fewer failures than placebo, according to parental report of time to resolution.” (9)
Some Excellent Advice about Writing Abstracts for Basic Science Research Papers, by Professor Adriano Aguzzi from the Institute of Neuropathology at the University of Zurich:

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Abstract Writing: A Step-by-Step Guide With Tips & Examples

Table of Contents

Introduction
Abstracts of research papers have always played an essential role in describing your research concisely and clearly to researchers and editors of journals, enticing them to continue reading. However, with the widespread availability of scientific databases, the need to write a convincing abstract is more crucial now than during the time of paper-bound manuscripts.
Abstracts serve to "sell" your research and can be compared with your "executive outline" of a resume or, rather, a formal summary of the critical aspects of your work. Also, it can be the "gist" of your study. Since most educational research is done online, it's a sign that you have a shorter time for impressing your readers, and have more competition from other abstracts that are available to be read.
The APCI (Academic Publishing and Conferences International) articulates 12 issues or points considered during the final approval process for conferences & journals and emphasises the importance of writing an abstract that checks all these boxes (12 points). Since it's the only opportunity you have to captivate your readers, you must invest time and effort in creating an abstract that accurately reflects the critical points of your research.
With that in mind, let’s head over to understand and discover the core concept and guidelines to create a substantial abstract. Also, learn how to organise the ideas or plots into an effective abstract that will be awe-inspiring to the readers you want to reach.
What is Abstract? Definition and Overview
The word "Abstract' is derived from Latin abstractus meaning "drawn off." This etymological meaning also applies to art movements as well as music, like abstract expressionism. In this context, it refers to the revealing of the artist's intention.
Based on this, you can determine the meaning of an abstract: A condensed research summary. It must be self-contained and independent of the body of the research. However, it should outline the subject, the strategies used to study the problem, and the methods implemented to attain the outcomes. The specific elements of the study differ based on the area of study; however, together, it must be a succinct summary of the entire research paper.
Abstracts are typically written at the end of the paper, even though it serves as a prologue. In general, the abstract must be in a position to:
- Describe the paper.
- Identify the problem or the issue at hand.
- Explain to the reader the research process, the results you came up with, and what conclusion you've reached using these results.
- Include keywords to guide your strategy and the content.
Furthermore, the abstract you submit should not reflect upon any of the following elements:
- Examine, analyse or defend the paper or your opinion.
- What you want to study, achieve or discover.
- Be redundant or irrelevant.
After reading an abstract, your audience should understand the reason - what the research was about in the first place, what the study has revealed and how it can be utilised or can be used to benefit others. You can understand the importance of abstract by knowing the fact that the abstract is the most frequently read portion of any research paper. In simpler terms, it should contain all the main points of the research paper.
What is the Purpose of an Abstract?
Abstracts are typically an essential requirement for research papers; however, it's not an obligation to preserve traditional reasons without any purpose. Abstracts allow readers to scan the text to determine whether it is relevant to their research or studies. The abstract allows other researchers to decide if your research paper can provide them with some additional information. A good abstract paves the interest of the audience to pore through your entire paper to find the content or context they're searching for.
Abstract writing is essential for indexing, as well. The Digital Repository of academic papers makes use of abstracts to index the entire content of academic research papers. Like meta descriptions in the regular Google outcomes, abstracts must include keywords that help researchers locate what they seek.
Types of Abstract
Informative and Descriptive are two kinds of abstracts often used in scientific writing.
A descriptive abstract gives readers an outline of the author's main points in their study. The reader can determine if they want to stick to the research work, based on their interest in the topic. An abstract that is descriptive is similar to the contents table of books, however, the format of an abstract depicts complete sentences encapsulated in one paragraph. It is unfortunate that the abstract can't be used as a substitute for reading a piece of writing because it's just an overview, which omits readers from getting an entire view. Also, it cannot be a way to fill in the gaps the reader may have after reading this kind of abstract since it does not contain crucial information needed to evaluate the article.
To conclude, a descriptive abstract is:
- A simple summary of the task, just summarises the work, but some researchers think it is much more of an outline
- Typically, the length is approximately 100 words. It is too short when compared to an informative abstract.
- A brief explanation but doesn't provide the reader with the complete information they need;
- An overview that omits conclusions and results
An informative abstract is a comprehensive outline of the research. There are times when people rely on the abstract as an information source. And the reason is why it is crucial to provide entire data of particular research. A well-written, informative abstract could be a good substitute for the remainder of the paper on its own.
A well-written abstract typically follows a particular style. The author begins by providing the identifying information, backed by citations and other identifiers of the papers. Then, the major elements are summarised to make the reader aware of the study. It is followed by the methodology and all-important findings from the study. The conclusion then presents study results and ends the abstract with a comprehensive summary.
In a nutshell, an informative abstract:
- Has a length that can vary, based on the subject, but is not longer than 300 words.
- Contains all the content-like methods and intentions
- Offers evidence and possible recommendations.
Informative Abstracts are more frequent than descriptive abstracts because of their extensive content and linkage to the topic specifically. You should select different types of abstracts to papers based on their length: informative abstracts for extended and more complex abstracts and descriptive ones for simpler and shorter research papers.
What are the Characteristics of a Good Abstract?
- A good abstract clearly defines the goals and purposes of the study.
- It should clearly describe the research methodology with a primary focus on data gathering, processing, and subsequent analysis.
- A good abstract should provide specific research findings.
- It presents the principal conclusions of the systematic study.
- It should be concise, clear, and relevant to the field of study.
- A well-designed abstract should be unifying and coherent.
- It is easy to grasp and free of technical jargon.
- It is written impartially and objectively.
What are the various sections of an ideal Abstract?
By now, you must have gained some concrete idea of the essential elements that your abstract needs to convey . Accordingly, the information is broken down into six key sections of the abstract, which include:
An Introduction or Background
Research methodology, objectives and goals, limitations.
Let's go over them in detail.
The introduction, also known as background, is the most concise part of your abstract. Ideally, it comprises a couple of sentences. Some researchers only write one sentence to introduce their abstract. The idea behind this is to guide readers through the key factors that led to your study.
It's understandable that this information might seem difficult to explain in a couple of sentences. For example, think about the following two questions like the background of your study:
- What is currently available about the subject with respect to the paper being discussed?
- What isn't understood about this issue? (This is the subject of your research)
While writing the abstract’s introduction, make sure that it is not lengthy. Because if it crosses the word limit, it may eat up the words meant to be used for providing other key information.
Research methodology is where you describe the theories and techniques you used in your research. It is recommended that you describe what you have done and the method you used to get your thorough investigation results. Certainly, it is the second-longest paragraph in the abstract.
In the research methodology section, it is essential to mention the kind of research you conducted; for instance, qualitative research or quantitative research (this will guide your research methodology too) . If you've conducted quantitative research, your abstract should contain information like the sample size, data collection method, sampling techniques, and duration of the study. Likewise, your abstract should reflect observational data, opinions, questionnaires (especially the non-numerical data) if you work on qualitative research.
The research objectives and goals speak about what you intend to accomplish with your research. The majority of research projects focus on the long-term effects of a project, and the goals focus on the immediate, short-term outcomes of the research. It is possible to summarise both in just multiple sentences.
In stating your objectives and goals, you give readers a picture of the scope of the study, its depth and the direction your research ultimately follows. Your readers can evaluate the results of your research against the goals and stated objectives to determine if you have achieved the goal of your research.
In the end, your readers are more attracted by the results you've obtained through your study. Therefore, you must take the time to explain each relevant result and explain how they impact your research. The results section exists as the longest in your abstract, and nothing should diminish its reach or quality.
One of the most important things you should adhere to is to spell out details and figures on the results of your research.
Instead of making a vague assertion such as, "We noticed that response rates varied greatly between respondents with high incomes and those with low incomes", Try these: "The response rate was higher for high-income respondents than those with lower incomes (59 30 percent vs. 30 percent in both cases; P<0.01)."
You're likely to encounter certain obstacles during your research. It could have been during data collection or even during conducting the sample . Whatever the issue, it's essential to inform your readers about them and their effects on the research.
Research limitations offer an opportunity to suggest further and deep research. If, for instance, you were forced to change for convenient sampling and snowball samples because of difficulties in reaching well-suited research participants, then you should mention this reason when you write your research abstract. In addition, a lack of prior studies on the subject could hinder your research.
Your conclusion should include the same number of sentences to wrap the abstract as the introduction. The majority of researchers offer an idea of the consequences of their research in this case.
Your conclusion should include three essential components:
- A significant take-home message.
- Corresponding important findings.
- The Interpretation.
Even though the conclusion of your abstract needs to be brief, it can have an enormous influence on the way that readers view your research. Therefore, make use of this section to reinforce the central message from your research. Be sure that your statements reflect the actual results and the methods you used to conduct your research.
Good Abstract Examples
Abstract example #1.
Children’s consumption behavior in response to food product placements in movies.
The abstract:
"Almost all research into the effects of brand placements on children has focused on the brand's attitudes or behavior intentions. Based on the significant differences between attitudes and behavioral intentions on one hand and actual behavior on the other hand, this study examines the impact of placements by brands on children's eating habits. Children aged 6-14 years old were shown an excerpt from the popular film Alvin and the Chipmunks and were shown places for the item Cheese Balls. Three different versions were developed with no placements, one with moderately frequent placements and the third with the highest frequency of placement. The results revealed that exposure to high-frequency places had a profound effect on snack consumption, however, there was no impact on consumer attitudes towards brands or products. The effects were not dependent on the age of the children. These findings are of major importance to researchers studying consumer behavior as well as nutrition experts as well as policy regulators."
Abstract Example #2
Social comparisons on social media: The impact of Facebook on young women’s body image concerns and mood. The abstract:
"The research conducted in this study investigated the effects of Facebook use on women's moods and body image if the effects are different from an internet-based fashion journal and if the appearance comparison tendencies moderate one or more of these effects. Participants who were female ( N = 112) were randomly allocated to spend 10 minutes exploring their Facebook account or a magazine's website or an appearance neutral control website prior to completing state assessments of body dissatisfaction, mood, and differences in appearance (weight-related and facial hair, face, and skin). Participants also completed a test of the tendency to compare appearances. The participants who used Facebook were reported to be more depressed than those who stayed on the control site. In addition, women who have the tendency to compare appearances reported more facial, hair and skin-related issues following Facebook exposure than when they were exposed to the control site. Due to its popularity it is imperative to conduct more research to understand the effect that Facebook affects the way people view themselves."
Abstract Example #3
The Relationship Between Cell Phone Use and Academic Performance in a Sample of U.S. College Students
"The cellphone is always present on campuses of colleges and is often utilised in situations in which learning takes place. The study examined the connection between the use of cell phones and the actual grades point average (GPA) after adjusting for predictors that are known to be a factor. In the end 536 students in the undergraduate program from 82 self-reported majors of an enormous, public institution were studied. Hierarchical analysis ( R 2 = .449) showed that use of mobile phones is significantly ( p < .001) and negative (b equal to -.164) connected to the actual college GPA, after taking into account factors such as demographics, self-efficacy in self-regulated learning, self-efficacy to improve academic performance, and the actual high school GPA that were all important predictors ( p < .05). Therefore, after adjusting for other known predictors increasing cell phone usage was associated with lower academic performance. While more research is required to determine the mechanisms behind these results, they suggest the need to educate teachers and students to the possible academic risks that are associated with high-frequency mobile phone usage."
Quick tips on writing a good abstract
There exists a common dilemma among early age researchers whether to write the abstract at first or last? However, it's recommended to compose your abstract when you've completed the research since you'll have all the information to give to your readers. You can, however, write a draft at the beginning of your research and add in any gaps later.
If you find abstract writing a herculean task, here are the few tips to help you with it:
1. Always develop a framework to support your abstract
Before writing, ensure you create a clear outline for your abstract. Divide it into sections and draw the primary and supporting elements in each one. You can include keywords and a few sentences that convey the essence of your message.
2. Review Other Abstracts
Abstracts are among the most frequently used research documents, and thousands of them were written in the past. Therefore, prior to writing yours, take a look at some examples from other abstracts. There are plenty of examples of abstracts for dissertations in the dissertation and thesis databases.
3. Avoid Jargon To the Maximum
When you write your abstract, focus on simplicity over formality. You should write in simple language, and avoid excessive filler words or ambiguous sentences. Keep in mind that your abstract must be readable to those who aren't acquainted with your subject.
4. Focus on Your Research
It's a given fact that the abstract you write should be about your research and the findings you've made. It is not the right time to mention secondary and primary data sources unless it's absolutely required.
Conclusion: How to Structure an Interesting Abstract?
Abstracts are a short outline of your essay. However, it's among the most important, if not the most important. The process of writing an abstract is not straightforward. A few early-age researchers tend to begin by writing it, thinking they are doing it to "tease" the next step (the document itself). However, it is better to treat it as a spoiler.
The simple, concise style of the abstract lends itself to a well-written and well-investigated study. If your research paper doesn't provide definitive results, or the goal of your research is questioned, so will the abstract. Thus, only write your abstract after witnessing your findings and put your findings in the context of a larger scenario.
The process of writing an abstract can be daunting, but with these guidelines, you will succeed. The most efficient method of writing an excellent abstract is to centre the primary points of your abstract, including the research question and goals methods, as well as key results.
Interested in learning more about dedicated research solutions? Go to the SciSpace product page to find out how our suite of products can help you simplify your research workflows so you can focus on advancing science.

The best-in-class solution is equipped with features such as literature search and discovery, profile management, research writing and formatting, and so much more.
But before you go,
You might also like.

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Mastering Project Abstracts - The Ultimate Guide | Grantboost

When it comes to research, grant proposals, and academic writing, project abstracts play a crucial role in summarizing the key elements of a proposal or research paper. However, many nonprofit grant writers, students and researchers often struggle to understand their meaning and purpose. We’ll explore what project abstracts are, why they are important, and provide an example to give you an idea.
Project Abstract Meaning
- How Long Should a Project Abstract Be?
- Why Are Project Abstracts Important?
Elements of a Good Project Abstract
Proposal abstract example, using ai to generate project abstracts.
A project abstract is a brief summary of a research project or proposal that outlines the main objectives, methods, and expected outcomes. It is typically the first section of a research paper or grant proposal and is designed to give readers a clear idea of what the project is about without having to read the entire document. Merriam-Webster defines an abstract as something that summarizes or concentrates the essentials of a larger thing or several things .
How Long Should Project Abstracts Be?
The length of a project abstract can vary depending on the requirements of the specific project or proposal. They are meant to be persuasive, but it’s best practice for an abstract to be concise and to the point.
It’s important to keep in mind that grant reviewers often have a lot of proposals to read and evaluate, so brevity and clarity are key.
As a general guideline, a project abstract should be between 150-250 words or one page in length. This length should be sufficient to convey the essential information about the project and its significance, without overwhelming the reader with unnecessary details. Carefully review the guidelines of each grant application and tailor the length of the project abstract accordingly.
Why are Project Abstracts Important?
Project abstracts serve a variety of important functions in grant writing. Firstly, they help to ensure that the project and/or proposal is clearly defined and that the objectives and expected outcomes are communicated effectively. This is particularly important when applying for grants or funding, as the abstract is often the first thing that reviewers will read.
In addition, project abstracts provide readers with a quick overview of the research topic and can help them to determine whether the project is relevant to their own work or interests. This can be particularly useful for grant proposal reviewers who are conducting dozens of reviews and trying to identify potential collaborators.
Finally, project abstracts can be used to promote the project or proposal to a wider audience. For example, they can be used in conference programs or on websites to promote the project and attract potential collaborators or funders.
A good project abstract is essential to any successful grant application or research proposal. It is the first thing that reviewers or potential collaborators will read, and it plays a crucial role in determining whether or not they will continue to read on. To write a compelling project abstract, it is important to answer the core questions that reviewers will have about your project.
According to Yale’s Center for Teaching and Learning a good project abstract answers these 4 questions.
1. What do you intend to do? 2. Why is the work important? 3. What has already been done? 4. How are you going to do the work?

The first question that a project abstract should seek to answer is: what do you intend to do? This question relates to the overarching problem that your project seeks to address and the background context around it. It is important to clearly articulate the aims and objectives of your project in the abstract, and to do so in a way that is concise and easy to understand. Ideally, the aims and objectives should be framed in a way that highlights the novelty and impact of your project.
The second question that a project abstract should address is: why is the work important? This question relates to the broader context of your research, and should explain why your project is relevant and timely. It is important to demonstrate the potential impact of your research, and to show how it relates to current trends or challenges in your field. This can be achieved by providing a brief overview of the state of the art in your area of research, and by highlighting the potential implications of your work for both theoretical understanding and practical application.
The third question that a project abstract should answer is: what has already been done? This question relates to the background and context of your research, and should demonstrate that you have a good understanding of the existing literature and research in your field. It is important to show how your project builds upon existing work, and to highlight any gaps or limitations in the current understanding of the problem that your research aims to address. This can be achieved by providing a brief overview of the relevant literature and research, and by highlighting any key findings or insights that your project aims to contribute.
The final question that a project abstract should seek to answer is: how are you going to do the work? This question relates to the methodology and approach that you will use to carry out your research. It is important to provide a clear and concise overview of the methods and techniques that you will use to collect and analyze data, and to explain how these methods are appropriate for addressing the research question or problem that you have identified. It is also important to highlight any potential challenges or limitations in your methodology, and to explain how you plan to address these challenges.
In addition to answering these core questions, a good project abstract should also be well-written and well-structured. It should be concise and to-the-point, while still providing enough detail to give reviewers a clear understanding of your project. It should also be free of jargon or technical language that might be difficult for non-specialists to understand.
To help ensure that your project abstract is effective and compelling, it can be useful to seek feedback from colleagues or mentors in your field. They can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of your abstract, and can help you to refine your message and improve your writing. By taking the time to craft a well-written and compelling project abstract, you can increase your chances of securing funding, attracting collaborators, and making a significant contribution to your field of research. If you’re a small nonprofit, reach out to our team for free feedbcack on your proposal.
To help illustrate the key elements of a project abstract, let’s look at an example of a research proposal abstract, courtesy of our friends at Yale:
Global warming is arguably one of the most pressing concerns of our time. However, we lack an effective model to predict precisely by how much the temperature will rise as a consequence of the increased levels of CO2 and other factors.
The width of this range is due to several uncertainties in different elements of the climate models, including the variability in the Sun’s rate of energy output.
To gain greater insight into the relationship between solar energy output and global temperature, we propose to launch the internationally led ABC satellite in April 2018.
Our aim is to collect for 2 years data on the solar diameter and shape, oscillations, and photospheric temperature variation. We will assess these data to model solar variability. Our findings will dramatically advance our understanding of solar activity and its climate effects.
Source: Yale’s Teaching and Learning Center
In recent years, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technology have revolutionized the way we approach proposal writing. AI-powered tools can help writers to automate repetitive tasks, generate ideas, and even write content from scratch. These “AI Grants” are powered by tools and companies that specialize in the writing process. One such tool is Grantboost, a company that specializes in using AI to help researchers and grant writers to write project abstracts more efficiently. Another tool with more broad use cases is ChatGPT.
Grantboost uses Generative AI to take in information about the grant opportunity and information about the problem being solved to create custom proejct abstracts based on the the specific needs of the researcher or grant writer.
One of the key benefits of using an AI-powered tool like Grantboost or ChatGPT is that it can save writers a significant amount of time and effort. Writing a project abstract can be a time-consuming and challenging process, particularly for those who are not experienced in academic writing. When asking for funding, the language being used in the abstract is incredibly important. If you’re not experienced in technical writing or fundraising, it can be a big challenge just to understand what a good proposal looks like. By using an AI-powered tool like Grantboost, writers can generate a high-quality project abstract in a matter of minutes, rather than spending hours focusing on just trying to get the language and tone right.
In addition, using an AI-powered tool can help to ensure that the project abstract is of high quality and meets the requirements of the funding agency or academic institution. Grantboost’s takes in information about the Grant opportunity to make sure that the abstract is aligned with the priorities of the Funder. This means that the project abstract generated by the tool is more likely to be successful in securing funding or attracting attention from potential collaborators.
Of course, it is important to note that using an AI-powered tool to write a project abstract does not mean that the writer can simply sit back and let the tool do all the work. The writer still needs to provide input and guidance to the tool to ensure that the project abstract accurately reflects the research project or proposal. This might involve inputting key information such as the research question, methodology, and expected outcomes, as well as providing feedback on the generated project abstract and making any necessary revisions.
In conclusion, AI-powered tools like Grantboost can be a valuable resource for writers who are looking to streamline the process of writing project abstracts. By using machine learning to generate successful grant proposals and research abstracts, these tools can generate high-quality project abstracts in a matter of minutes, saving writers time and effort. However, it is important to note that these tools should be used in conjunction with human input and guidance to ensure that the project abstract accurately reflects the research project or proposal. By combining the power of AI with human expertise, writers can produce project abstracts that are both efficient and effective.
Project abstracts are an important component of academic writing that provide a brief summary of a research project or proposal. They serve to define the project, communicate objectives and expected outcomes, and can be used to promote the research to a wider audience. By understanding the key elements of a project abstract, researchers and students can ensure that their work is effectively communicated and stands out in a crowded field of academic writing.
Transform Your Grant Writing with Grantboost: Join Our Beta and Try Our Project Abstract Generator Today!
As a nonprofit grant writer, you know the importance of making an impact in your community. That’s why we’re excited to announce Grantboost - a platform designed specifically to help you write better grants faster.
Grantboost is a game-changer, my friends. It’s a one-stop-shop for all your grant writing needs, and it’s completely free. That’s right, free. We’re about to launch our closed beta, and we’re giving you the opportunity to be one of the first to try out our revolutionary ✨ project abstract generator✨
The project abstract generator is a powerful tool that will help you create compelling abstracts for your grant proposals in just a few clicks. No more struggling to find the right words or spending hours writing and rewriting. With Grantboost, you’ll have everything you need to make a real difference in your community.
So what are you waiting for? Sign up for our closed beta today and join the revolution. With Grantboost, you’ll be able to write better grants faster than ever before.
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write an Abstract

Expedite peer review, increase search-ability, and set the tone for your study
The abstract is your chance to let your readers know what they can expect from your article. Learn how to write a clear, and concise abstract that will keep your audience reading.
How your abstract impacts editorial evaluation and future readership
After the title , the abstract is the second-most-read part of your article. A good abstract can help to expedite peer review and, if your article is accepted for publication, it’s an important tool for readers to find and evaluate your work. Editors use your abstract when they first assess your article. Prospective reviewers see it when they decide whether to accept an invitation to review. Once published, the abstract gets indexed in PubMed and Google Scholar , as well as library systems and other popular databases. Like the title, your abstract influences keyword search results. Readers will use it to decide whether to read the rest of your article. Other researchers will use it to evaluate your work for inclusion in systematic reviews and meta-analysis. It should be a concise standalone piece that accurately represents your research.
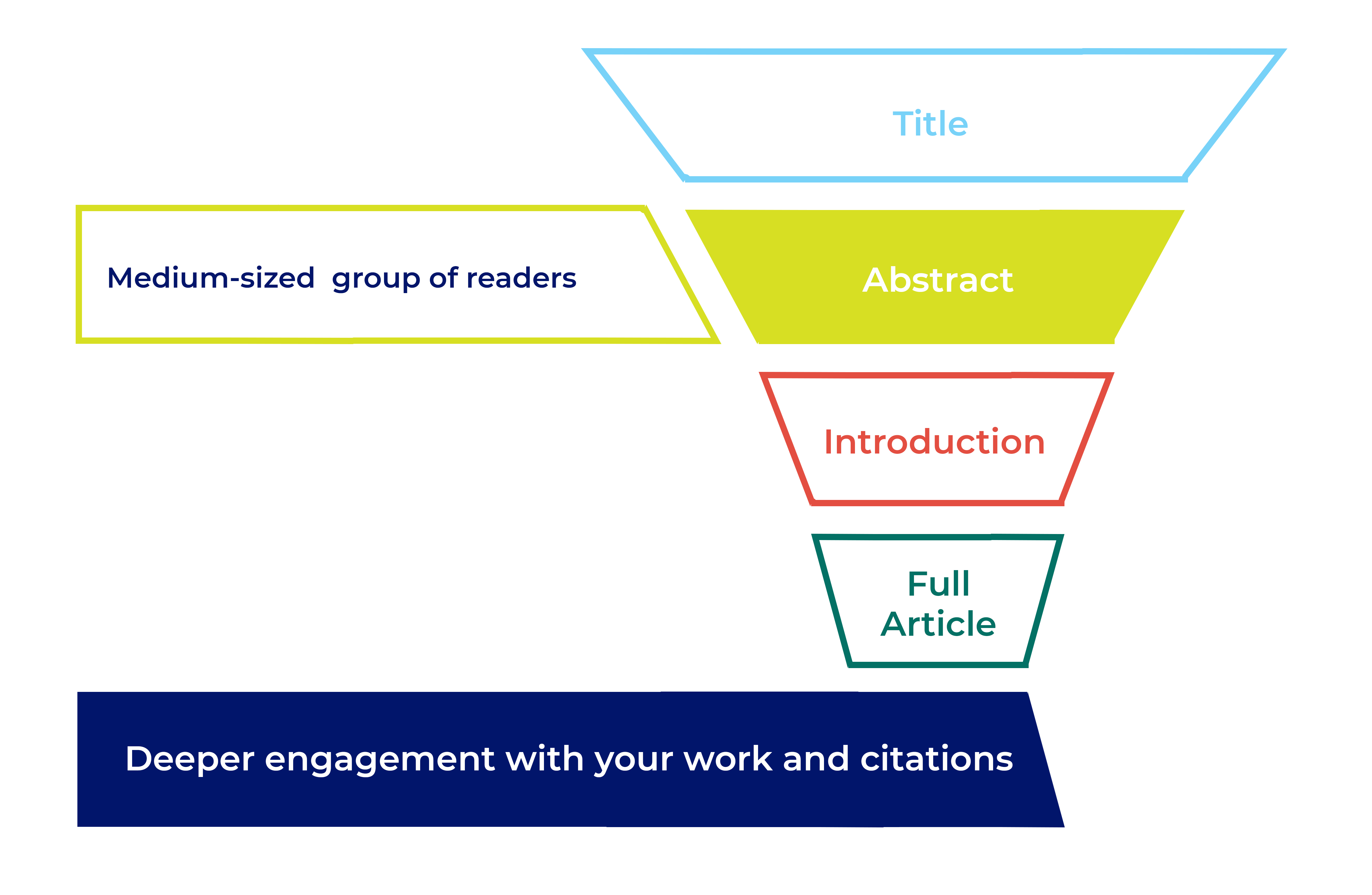
What to include in an abstract
The main challenge you’ll face when writing your abstract is keeping it concise AND fitting in all the information you need. Depending on your subject area the journal may require a structured abstract following specific headings. A structured abstract helps your readers understand your study more easily. If your journal doesn’t require a structured abstract it’s still a good idea to follow a similar format, just present the abstract as one paragraph without headings.
Background or Introduction – What is currently known? Start with a brief, 2 or 3 sentence, introduction to the research area.
Objectives or Aims – What is the study and why did you do it? Clearly state the research question you’re trying to answer.
Methods – What did you do? Explain what you did and how you did it. Include important information about your methods, but avoid the low-level specifics. Some disciplines have specific requirements for abstract methods.
- CONSORT for randomized trials.
- STROBE for observational studies
- PRISMA for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Results – What did you find? Briefly give the key findings of your study. Include key numeric data (including confidence intervals or p values), where possible.
Conclusions – What did you conclude? Tell the reader why your findings matter, and what this could mean for the ‘bigger picture’ of this area of research.
Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your abstract is keeping it concise AND convering all the information you need to.

- Keep it concise and to the point. Most journals have a maximum word count, so check guidelines before you write the abstract to save time editing it later.
- Write for your audience. Are they specialists in your specific field? Are they cross-disciplinary? Are they non-specialists? If you’re writing for a general audience, or your research could be of interest to the public keep your language as straightforward as possible. If you’re writing in English, do remember that not all of your readers will necessarily be native English speakers.
- Focus on key results, conclusions and take home messages.
- Write your paper first, then create the abstract as a summary.
- Check the journal requirements before you write your abstract, eg. required subheadings.
- Include keywords or phrases to help readers search for your work in indexing databases like PubMed or Google Scholar.
- Double and triple check your abstract for spelling and grammar errors. These kind of errors can give potential reviewers the impression that your research isn’t sound, and can make it easier to find reviewers who accept the invitation to review your manuscript. Your abstract should be a taste of what is to come in the rest of your article.

Don’t
- Sensationalize your research.
- Speculate about where this research might lead in the future.
- Use abbreviations or acronyms (unless absolutely necessary or unless they’re widely known, eg. DNA).
- Repeat yourself unnecessarily, eg. “Methods: We used X technique. Results: Using X technique, we found…”
- Contradict anything in the rest of your manuscript.
- Include content that isn’t also covered in the main manuscript.
- Include citations or references.
Tip: How to edit your work
Editing is challenging, especially if you are acting as both a writer and an editor. Read our guidelines for advice on how to refine your work, including useful tips for setting your intentions, re-review, and consultation with colleagues.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
Published on 1 March 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022 by Eoghan Ryan.
An abstract is a short summary of a longer work (such as a dissertation or research paper ). The abstract concisely reports the aims and outcomes of your research, so that readers know exactly what your paper is about.
Although the structure may vary slightly depending on your discipline, your abstract should describe the purpose of your work, the methods you’ve used, and the conclusions you’ve drawn.
One common way to structure your abstract is to use the IMRaD structure. This stands for:
- Introduction
Abstracts are usually around 100–300 words, but there’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check the relevant requirements.
In a dissertation or thesis , include the abstract on a separate page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Abstract example, when to write an abstract, step 1: introduction, step 2: methods, step 3: results, step 4: discussion, tips for writing an abstract, frequently asked questions about abstracts.
Hover over the different parts of the abstract to see how it is constructed.
This paper examines the role of silent movies as a mode of shared experience in the UK during the early twentieth century. At this time, high immigration rates resulted in a significant percentage of non-English-speaking citizens. These immigrants faced numerous economic and social obstacles, including exclusion from public entertainment and modes of discourse (newspapers, theater, radio).
Incorporating evidence from reviews, personal correspondence, and diaries, this study demonstrates that silent films were an affordable and inclusive source of entertainment. It argues for the accessible economic and representational nature of early cinema. These concerns are particularly evident in the low price of admission and in the democratic nature of the actors’ exaggerated gestures, which allowed the plots and action to be easily grasped by a diverse audience despite language barriers.
Keywords: silent movies, immigration, public discourse, entertainment, early cinema, language barriers.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
You will almost always have to include an abstract when:
- Completing a thesis or dissertation
- Submitting a research paper to an academic journal
- Writing a book proposal
- Applying for research grants
It’s easiest to write your abstract last, because it’s a summary of the work you’ve already done. Your abstract should:
- Be a self-contained text, not an excerpt from your paper
- Be fully understandable on its own
- Reflect the structure of your larger work
Start by clearly defining the purpose of your research. What practical or theoretical problem does the research respond to, or what research question did you aim to answer?
You can include some brief context on the social or academic relevance of your topic, but don’t go into detailed background information. If your abstract uses specialised terms that would be unfamiliar to the average academic reader or that have various different meanings, give a concise definition.
After identifying the problem, state the objective of your research. Use verbs like “investigate,” “test,” “analyse,” or “evaluate” to describe exactly what you set out to do.
This part of the abstract can be written in the present or past simple tense but should never refer to the future, as the research is already complete.
- This study will investigate the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
- This study investigates the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
Next, indicate the research methods that you used to answer your question. This part should be a straightforward description of what you did in one or two sentences. It is usually written in the past simple tense, as it refers to completed actions.
- Structured interviews will be conducted with 25 participants.
- Structured interviews were conducted with 25 participants.
Don’t evaluate validity or obstacles here — the goal is not to give an account of the methodology’s strengths and weaknesses, but to give the reader a quick insight into the overall approach and procedures you used.
Next, summarise the main research results . This part of the abstract can be in the present or past simple tense.
- Our analysis has shown a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis shows a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis showed a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
Depending on how long and complex your research is, you may not be able to include all results here. Try to highlight only the most important findings that will allow the reader to understand your conclusions.
Finally, you should discuss the main conclusions of your research : what is your answer to the problem or question? The reader should finish with a clear understanding of the central point that your research has proved or argued. Conclusions are usually written in the present simple tense.
- We concluded that coffee consumption increases productivity.
- We conclude that coffee consumption increases productivity.
If there are important limitations to your research (for example, related to your sample size or methods), you should mention them briefly in the abstract. This allows the reader to accurately assess the credibility and generalisability of your research.
If your aim was to solve a practical problem, your discussion might include recommendations for implementation. If relevant, you can briefly make suggestions for further research.
If your paper will be published, you might have to add a list of keywords at the end of the abstract. These keywords should reference the most important elements of the research to help potential readers find your paper during their own literature searches.
Be aware that some publication manuals, such as APA Style , have specific formatting requirements for these keywords.
It can be a real challenge to condense your whole work into just a couple of hundred words, but the abstract will be the first (and sometimes only) part that people read, so it’s important to get it right. These strategies can help you get started.
Read other abstracts
The best way to learn the conventions of writing an abstract in your discipline is to read other people’s. You probably already read lots of journal article abstracts while conducting your literature review —try using them as a framework for structure and style.
You can also find lots of dissertation abstract examples in thesis and dissertation databases .
Reverse outline
Not all abstracts will contain precisely the same elements. For longer works, you can write your abstract through a process of reverse outlining.
For each chapter or section, list keywords and draft one to two sentences that summarise the central point or argument. This will give you a framework of your abstract’s structure. Next, revise the sentences to make connections and show how the argument develops.
Write clearly and concisely
A good abstract is short but impactful, so make sure every word counts. Each sentence should clearly communicate one main point.
To keep your abstract or summary short and clear:
- Avoid passive sentences: Passive constructions are often unnecessarily long. You can easily make them shorter and clearer by using the active voice.
- Avoid long sentences: Substitute longer expressions for concise expressions or single words (e.g., “In order to” for “To”).
- Avoid obscure jargon: The abstract should be understandable to readers who are not familiar with your topic.
- Avoid repetition and filler words: Replace nouns with pronouns when possible and eliminate unnecessary words.
- Avoid detailed descriptions: An abstract is not expected to provide detailed definitions, background information, or discussions of other scholars’ work. Instead, include this information in the body of your thesis or paper.
If you’re struggling to edit down to the required length, you can get help from expert editors with Scribbr’s professional proofreading services .
Check your formatting
If you are writing a thesis or dissertation or submitting to a journal, there are often specific formatting requirements for the abstract—make sure to check the guidelines and format your work correctly. For APA research papers you can follow the APA abstract format .
Checklist: Abstract
The word count is within the required length, or a maximum of one page.
The abstract appears after the title page and acknowledgements and before the table of contents .
I have clearly stated my research problem and objectives.
I have briefly described my methodology .
I have summarized the most important results .
I have stated my main conclusions .
I have mentioned any important limitations and recommendations.
The abstract can be understood by someone without prior knowledge of the topic.
You've written a great abstract! Use the other checklists to continue improving your thesis or dissertation.
An abstract is a concise summary of an academic text (such as a journal article or dissertation ). It serves two main purposes:
- To help potential readers determine the relevance of your paper for their own research.
- To communicate your key findings to those who don’t have time to read the whole paper.
Abstracts are often indexed along with keywords on academic databases, so they make your work more easily findable. Since the abstract is the first thing any reader sees, it’s important that it clearly and accurately summarises the contents of your paper.
An abstract for a thesis or dissertation is usually around 150–300 words. There’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check your university’s requirements.
The abstract is the very last thing you write. You should only write it after your research is complete, so that you can accurately summarize the entirety of your thesis or paper.
Avoid citing sources in your abstract . There are two reasons for this:
- The abstract should focus on your original research, not on the work of others.
- The abstract should be self-contained and fully understandable without reference to other sources.
There are some circumstances where you might need to mention other sources in an abstract: for example, if your research responds directly to another study or focuses on the work of a single theorist. In general, though, don’t include citations unless absolutely necessary.
The abstract appears on its own page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/abstract/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, dissertation title page.
How to Write an Abstract APA Format
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
An APA abstract is a brief, comprehensive summary of the contents of an article, research paper, dissertation, or report.
It is written in accordance with the guidelines of the American Psychological Association (APA), which is a widely used format in social and behavioral sciences.
An APA abstract summarizes, usually in one paragraph of between 150–250 words, the major aspects of a research paper or dissertation in a prescribed sequence that includes:
- The rationale: the overall purpose of the study, providing a clear context for the research undertaken.
- Information regarding the method and participants: including materials/instruments, design, procedure, and data analysis.
- Main findings or trends: effectively highlighting the key outcomes of the hypotheses.
- Interpretations and conclusion(s): solidify the implications of the research.
- Keywords related to the study: assist the paper’s discoverability in academic databases.
The abstract should stand alone, be “self-contained,” and make sense to the reader in isolation from the main article.
The purpose of the abstract is to give the reader a quick overview of the essential information before reading the entire article. The abstract is placed on its own page, directly after the title page and before the main body of the paper.
Although the abstract will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s good practice to write your abstract after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
Note : This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), released in October 2019.
Structure of the Abstract
[NOTE: DO NOT separate the components of the abstract – it should be written as a single paragraph. This section is separated to illustrate the abstract’s structure.]
1) The Rationale
One or two sentences describing the overall purpose of the study and the research problem(s) you investigated. You are basically justifying why this study was conducted.
- What is the importance of the research?
- Why would a reader be interested in the larger work?
- For example, are you filling a gap in previous research or applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data?
- Women who are diagnosed with breast cancer can experience an array of psychosocial difficulties; however, social support, particularly from a spouse, has been shown to have a protective function during this time. This study examined the ways in which a woman’s daily mood, pain, and fatigue, and her spouse’s marital satisfaction predict the woman’s report of partner support in the context of breast cancer.
- The current nursing shortage, high hospital nurse job dissatisfaction, and reports of uneven quality of hospital care are not uniquely American phenomena.
- Students with special educational needs and disabilities (SEND) are more likely to exhibit behavioral difficulties than their typically developing peers. The aim of this study was to identify specific risk factors that influence variability in behavior difficulties among individuals with SEND.
2) The Method
Information regarding the participants (number, and population). One or two sentences outlining the method, explaining what was done and how. The method is described in the present tense.
- Pretest data from a larger intervention study and multilevel modeling were used to examine the effects of women’s daily mood, pain, and fatigue and average levels of mood, pain, and fatigue on women’s report of social support received from her partner, as well as how the effects of mood interacted with partners’ marital satisfaction.
- This paper presents reports from 43,000 nurses from more than 700 hospitals in the United States, Canada, England, Scotland, and Germany in 1998–1999.
- The study sample comprised 4,228 students with SEND, aged 5–15, drawn from 305 primary and secondary schools across England. Explanatory variables were measured at the individual and school levels at baseline, along with a teacher-reported measure of behavior difficulties (assessed at baseline and the 18-month follow-up).
3) The Results
One or two sentences indicating the main findings or trends found as a result of your analysis. The results are described in the present or past tense.
- Results show that on days in which women reported higher levels of negative or positive mood, as well as on days they reported more pain and fatigue, they reported receiving more support. Women who, on average, reported higher levels of positive mood tended to report receiving more support than those who, on average, reported lower positive mood. However, average levels of negative mood were not associated with support. Higher average levels of fatigue but not pain were associated with higher support. Finally, women whose husbands reported higher levels of marital satisfaction reported receiving more partner support, but husbands’ marital satisfaction did not moderate the effect of women’s mood on support.
- Nurses in countries with distinctly different healthcare systems report similar shortcomings in their work environments and the quality of hospital care. While the competence of and relation between nurses and physicians appear satisfactory, core problems in work design and workforce management threaten the provision of care.
- Hierarchical linear modeling of data revealed that differences between schools accounted for between 13% (secondary) and 15.4% (primary) of the total variance in the development of students’ behavior difficulties, with the remainder attributable to individual differences. Statistically significant risk markers for these problems across both phases of education were being male, eligibility for free school meals, being identified as a bully, and lower academic achievement. Additional risk markers specific to each phase of education at the individual and school levels are also acknowledged.
4) The Conclusion / Implications
A brief summary of your conclusions and implications of the results, described in the present tense. Explain the results and why the study is important to the reader.
- For example, what changes should be implemented as a result of the findings of the work?
- How does this work add to the body of knowledge on the topic?
Implications of these findings are discussed relative to assisting couples during this difficult time in their lives.
- Resolving these issues, which are amenable to managerial intervention, is essential to preserving patient safety and care of consistently high quality.
- Behavior difficulties are affected by risks across multiple ecological levels. Addressing any one of these potential influences is therefore likely to contribute to the reduction in the problems displayed.
The above examples of abstracts are from the following papers:
Aiken, L. H., Clarke, S. P., Sloane, D. M., Sochalski, J. A., Busse, R., Clarke, H., … & Shamian, J. (2001). Nurses’ reports on hospital care in five countries . Health affairs, 20(3) , 43-53.
Boeding, S. E., Pukay-Martin, N. D., Baucom, D. H., Porter, L. S., Kirby, J. S., Gremore, T. M., & Keefe, F. J. (2014). Couples and breast cancer: Women’s mood and partners’ marital satisfaction predicting support perception . Journal of Family Psychology, 28(5) , 675.
Oldfield, J., Humphrey, N., & Hebron, J. (2017). Risk factors in the development of behavior difficulties among students with special educational needs and disabilities: A multilevel analysis . British journal of educational psychology, 87(2) , 146-169.
5) Keywords
APA style suggests including a list of keywords at the end of the abstract. This is particularly common in academic articles and helps other researchers find your work in databases.
Keywords in an abstract should be selected to help other researchers find your work when searching an online database. These keywords should effectively represent the main topics of your study. Here are some tips for choosing keywords:
Core Concepts: Identify the most important ideas or concepts in your paper. These often include your main research topic, the methods you’ve used, or the theories you’re discussing.
Specificity: Your keywords should be specific to your research. For example, suppose your paper is about the effects of climate change on bird migration patterns in a specific region. In that case, your keywords might include “climate change,” “bird migration,” and the region’s name.
Consistency with Paper: Make sure your keywords are consistent with the terms you’ve used in your paper. For example, if you use the term “adolescent” rather than “teen” in your paper, choose “adolescent” as your keyword, not “teen.”
Jargon and Acronyms: Avoid using too much-specialized jargon or acronyms in your keywords, as these might not be understood or used by all researchers in your field.
Synonyms: Consider including synonyms of your keywords to capture as many relevant searches as possible. For example, if your paper discusses “post-traumatic stress disorder,” you might include “PTSD” as a keyword.
Remember, keywords are a tool for others to find your work, so think about what terms other researchers might use when searching for papers on your topic.
The Abstract SHOULD NOT contain:
Lengthy background or contextual information: The abstract should focus on your research and findings, not general topic background.
Undefined jargon, abbreviations, or acronyms: The abstract should be accessible to a wide audience, so avoid highly specialized terms without defining them.
Citations: Abstracts typically do not include citations, as they summarize original research.
Incomplete sentences or bulleted lists: The abstract should be a single, coherent paragraph written in complete sentences.
New information not covered in the paper: The abstract should only summarize the paper’s content.
Subjective comments or value judgments: Stick to objective descriptions of your research.
Excessive details on methods or procedures: Keep descriptions of methods brief and focused on main steps.
Speculative or inconclusive statements: The abstract should state the research’s clear findings, not hypotheses or possible interpretations.
- Any illustration, figure, table, or references to them . All visual aids, data, or extensive details should be included in the main body of your paper, not in the abstract.
- Elliptical or incomplete sentences should be avoided in an abstract . The use of ellipses (…), which could indicate incomplete thoughts or omitted text, is not appropriate in an abstract.
APA Style for Abstracts
An APA abstract must be formatted as follows:
Include the running head aligned to the left at the top of the page (professional papers only) and page number. Note, student papers do not require a running head. On the first line, center the heading “Abstract” and bold (do not underlined or italicize). Do not indent the single abstract paragraph (which begins one line below the section title). Double-space the text. Use Times New Roman font in 12 pt. Set one-inch (or 2.54 cm) margins. If you include a “keywords” section at the end of the abstract, indent the first line and italicize the word “Keywords” while leaving the keywords themselves without any formatting.
Example APA Abstract Page
Download this example as a PDF

Further Information
- APA 7th Edition Abstract and Keywords Guide
- Example APA Abstract
- How to Write a Good Abstract for a Scientific Paper or Conference Presentation
- How to Write a Lab Report
- Writing an APA paper
How long should an APA abstract be?
An APA abstract should typically be between 150 to 250 words long. However, the exact length may vary depending on specific publication or assignment guidelines. It is crucial that it succinctly summarizes the essential elements of the work, including purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions.
Where does the abstract go in an APA paper?
In an APA formatted paper, the abstract is placed on its own page, directly after the title page and before the main body of the paper. It’s typically the second page of the document. It starts with the word “Abstract” (centered and not in bold) at the top of the page, followed by the text of the abstract itself.
What are the 4 C’s of abstract writing?
The 4 C’s of abstract writing are an approach to help you create a well-structured and informative abstract. They are:
Conciseness: An abstract should briefly summarize the key points of your study. Stick to the word limit (typically between 150-250 words for an APA abstract) and avoid unnecessary details.
Clarity: Your abstract should be easy to understand. Avoid jargon and complex sentences. Clearly explain the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of your study.
Completeness: Even though it’s brief, the abstract should provide a complete overview of your study, including the purpose, methods, key findings, and your interpretation of the results.
Cohesion: The abstract should flow logically from one point to the next, maintaining a coherent narrative about your study. It’s not just a list of disjointed elements; it’s a brief story of your research from start to finish.
What is the abstract of a psychology paper?
An abstract in a psychology paper serves as a snapshot of the paper, allowing readers to quickly understand the purpose, methodology, results, and implications of the research without reading the entire paper. It is generally between 150-250 words long.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Abstract
Research Paper Abstract is a brief summary of a research pape r that describes the study’s purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions . It is often the first section of the paper that readers encounter, and its purpose is to provide a concise and accurate overview of the paper’s content. The typical length of an abstract is usually around 150-250 words, and it should be written in a concise and clear manner.
Research Paper Abstract Structure
The structure of a research paper abstract usually includes the following elements:
- Background or Introduction: Briefly describe the problem or research question that the study addresses.
- Methods : Explain the methodology used to conduct the study, including the participants, materials, and procedures.
- Results : Summarize the main findings of the study, including statistical analyses and key outcomes.
- Conclusions : Discuss the implications of the study’s findings and their significance for the field, as well as any limitations or future directions for research.
- Keywords : List a few keywords that describe the main topics or themes of the research.

How to Write Research Paper Abstract
Here are the steps to follow when writing a research paper abstract:
- Start by reading your paper: Before you write an abstract, you should have a complete understanding of your paper. Read through the paper carefully, making sure you understand the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions.
- Identify the key components : Identify the key components of your paper, such as the research question, methods used, results obtained, and conclusion reached.
- Write a draft: Write a draft of your abstract, using concise and clear language. Make sure to include all the important information, but keep it short and to the point. A good rule of thumb is to keep your abstract between 150-250 words.
- Use clear and concise language : Use clear and concise language to explain the purpose of your study, the methods used, the results obtained, and the conclusions drawn.
- Emphasize your findings: Emphasize your findings in the abstract, highlighting the key results and the significance of your study.
- Revise and edit: Once you have a draft, revise and edit it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free from errors.
- Check the formatting: Finally, check the formatting of your abstract to make sure it meets the requirements of the journal or conference where you plan to submit it.
Research Paper Abstract Examples
Research Paper Abstract Examples could be following:
Title : “The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Treating Anxiety Disorders: A Meta-Analysis”
Abstract : This meta-analysis examines the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in treating anxiety disorders. Through the analysis of 20 randomized controlled trials, we found that CBT is a highly effective treatment for anxiety disorders, with large effect sizes across a range of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. Our findings support the use of CBT as a first-line treatment for anxiety disorders and highlight the importance of further research to identify the mechanisms underlying its effectiveness.
Title : “Exploring the Role of Parental Involvement in Children’s Education: A Qualitative Study”
Abstract : This qualitative study explores the role of parental involvement in children’s education. Through in-depth interviews with 20 parents of children in elementary school, we found that parental involvement takes many forms, including volunteering in the classroom, helping with homework, and communicating with teachers. We also found that parental involvement is influenced by a range of factors, including parent and child characteristics, school culture, and socio-economic status. Our findings suggest that schools and educators should prioritize building strong partnerships with parents to support children’s academic success.
Title : “The Impact of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis”
Abstract : This paper presents a systematic review and meta-analysis of the existing literature on the impact of exercise on cognitive function in older adults. Through the analysis of 25 randomized controlled trials, we found that exercise is associated with significant improvements in cognitive function, particularly in the domains of executive function and attention. Our findings highlight the potential of exercise as a non-pharmacological intervention to support cognitive health in older adults.
When to Write Research Paper Abstract
The abstract of a research paper should typically be written after you have completed the main body of the paper. This is because the abstract is intended to provide a brief summary of the key points and findings of the research, and you can’t do that until you have completed the research and written about it in detail.
Once you have completed your research paper, you can begin writing your abstract. It is important to remember that the abstract should be a concise summary of your research paper, and should be written in a way that is easy to understand for readers who may not have expertise in your specific area of research.
Purpose of Research Paper Abstract
The purpose of a research paper abstract is to provide a concise summary of the key points and findings of a research paper. It is typically a brief paragraph or two that appears at the beginning of the paper, before the introduction, and is intended to give readers a quick overview of the paper’s content.
The abstract should include a brief statement of the research problem, the methods used to investigate the problem, the key results and findings, and the main conclusions and implications of the research. It should be written in a clear and concise manner, avoiding jargon and technical language, and should be understandable to a broad audience.
The abstract serves as a way to quickly and easily communicate the main points of a research paper to potential readers, such as academics, researchers, and students, who may be looking for information on a particular topic. It can also help researchers determine whether a paper is relevant to their own research interests and whether they should read the full paper.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...
University of Missouri
- Bias Hotline: Report bias incidents
Undergraduate Research
- How to Write An Abstract
Think of your abstract or artist statement like a movie trailer: it should leave the reader eager to learn more but knowledgeable enough to grasp the scope of your work. Although abstracts and artist statements need to contain key information on your project, your title and summary should be understandable to a lay audience.

Please remember that you can seek assistance with any of your writing needs at the MU Writing Center . Their tutors work with students from all disciplines on a wide variety of documents. And they are specially trained to use the Abstract Review Rubric that will be used on the abstracts reviewed at the Spring Forum.
Types of Research Summaries
Students should submit artist statements as their abstracts. Artist statements should introduce to the art, performance, or creative work and include information on media and methods in creating the pieces. The statements should also include a description of the inspiration for the work, the meaning the work signifies to the artist, the artistic influences, and any unique methods used to create the pieces. Students are encouraged to explain the connections of the work with their inspirations or themes. The statements should be specific to the work presented and not a general statements about the students’ artistic philosophies and approaches. Effective artist statements should provide the viewer with information to better understand the work of the artists. If presentations are based on previous performances, then students may include reflections on the performance experiences and audience reactions.
Abstracts should describe the nature of the project or piece (ex: architectural images used for a charrette, fashion plates, advertising campaign story boards) and its intended purpose. Students should describe the project or problem that they addressed and limitations and challenges that impact the design process. Students may wish to include research conducted to provide context for the project and inform the design process. A description of the clients/end users may be included. Information on inspirations, motivations, and influences may also be included as appropriate to the discipline and project. A description of the project outcome should be included.
Abstracts should include a short introduction or background to put the research into context; purpose of the research project; a problem statement or thesis; a brief description of materials, methods, or subjects (as appropriate for the discipline); results and analysis; conclusions and implications; and recommendations. For research projects still in progress at the time of abstract submission, students may opt to indicate that results and conclusions will be presented [at the Forum].
Tips for writing a clear and concise abstract
The title of your abstract/statement/poster should include some language that the lay person can understand. When someone reads your title they should have SOME idea of the nature of your work and your discipline.
Ask a peer unfamiliar with your research to read your abstract. If they’re confused by it, others will be too.
Keep it short and sweet.
- Interesting eye-catching title
- Introduction: 1-3 sentences
- What you did: 1 sentence
- Why you did it: 1 sentence
- How you did it: 1 sentence
- Results or when they are expected: 2 sentences
- Conclusion: 1-3 sentences
Ideas to Address:
- The big picture your project helps tackle
- The problem motivating your work on this particular project
- General methods you used
- Results and/or conclusions
- The next steps for the project
Things to Avoid:
- A long and confusing title
- Jargon or complicated industry terms
- Long description of methods/procedures
- Exaggerating your results
- Exceeding the allowable word limit
- Forgetting to tell people why to care
- References that keep the abstract from being a “stand alone” document
- Being boring, confusing, or unintelligible!
Artist Statement
The artist statement should be an introduction to the art and include information on media and methods in creating the piece(s). It should include a description of the inspiration for the work, what the work signifies to the artist, the artistic influences, and any unique methods used to create the work. Students are encouraged to explain the connections of the work with their inspiration or theme. The artist statement (up to 300 words) should be written in plain language to invite viewers to learn more about the artist’s work and make their own interpretations. The statement should be specific to the piece(s) that will be on display, and not a general statement about the student’s artistic philosophy and approach. An effective artist statement should provide the viewer with information to better understand and experience viewing the work on display.
Research/Applied Design Abstract
The project abstract (up to 300 words) should describe the nature of the project or piece (ex: architectural images used for a charrette, fashion plates, small scale model of a theater set) and its intended purpose. Students should describe the project or problem that was addressed and limitations and challenges that impact the design process. Students may wish to include research conducted to provide context for the project and inform the design process. A description of the clients/end users may be included. Information on inspirations, motivations, and influences may also be included as appropriate to the discipline and project.
Key Considerations
- What is the problem/ big picture that your project helps to address?
- What is the appropriate background to put your project into context? What do we know? What don’t we know? (informed rationale)
- What is YOUR project? What are you seeking to answer?
- How do you DO your research? What kind of data do you collect? How do you collect it?
- What is the experimental design? Number of subjects or tests run? (quantify if you can!)
- Provide some data (not raw, but analyzed)
- What have you found? What are your results? How do you KNOW this – how did you analyze this?
- What does this mean?
- What are the next steps? What don’t we know still?
- How does this relate (again) to the bigger picture. Who should care and why? (what is your audience?)
More Resources
- Abstract Writing Presentation from University of Illinois – Chicago
- Sample Abstracts
- A 10-Step Guide to Make Your Research Paper More Effective
- Your Artist Statement: Explaining the Unexplainable
- How to Write an Artist Statement

Here is the Forum Abstract Review Rubric for you and your mentor to use when writing your abstract to submit to the Spring Research & Creative Achievements Forum.
Organizing Research for Arts and Humanities Papers and Theses
- General Guide Information
- Developing a Topic
- What are Primary and Secondary Sources
- What are Scholarly and Non-Scholarly Sources
- Writing an Abstract
- Writing Academic Book Reviews
- Writing A Literature Review
- Using Images and other Media
What is an abstract?
Note: This description of a typical abstract and its elements is geared toward researchers in the arts and humanities. Additional information on writing abstracts is available in Dr. Robert Labaree's libguide on organizing research in the social sciences .
An abstract is a summary of a paper, a book, or a presentation. As a general rule, the abstract is written by the author of the work. Most abstracts are informative.
Abstracts are a required part of graduate theses and dissertations. Abstracts are common in academic and scholarly journal articles, as well as in conference presentations and publications of proceedings. The author, the title, and the abstract are the most immediately visible elements of a work of scholarship that other researchers see as they peruse scholarly databases and publications. These are also the elements that may be indexed by search engines such as Google.
Stylistic guidelines : Use active verbs, when possible, and write in complete sentences. Try to imagine yourself in the shoes of a reader who is not familiar with your work, and who might be reading the abstract to decide on the im portance and relevance of your research.
An informative abstract
A common type of abstract is informative. Such an abstract is usually about 300-500 words in length. It is usually composed after the conclusion of the writing of the work, and acts as a surrogate for the work itself.
Generally speaking an informative abstract should include at least the following elements:
1) an overall description of the topic explored;
2) the theoretical, historical, or methodological framework used;
3) an outline of the main argument(s);
4) a brief summary of the conclusion(s).
A descriptive abstract
A somewhat less common type of abstract is descriptive. Descriptive abstracts are short, ordinarily 150 words or less, and briefly describe the work, almost in an outline format.
Remember to keep track of your sources, regardless of the stage of your research. The USC Libraries have an excellent guide to citation styles and to citation management software .
- << Previous: What are Scholarly and Non-Scholarly Sources
- Next: Writing Academic Book Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Jan 19, 2023 3:12 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/ah_writing

The What: Defining a research project
During Academic Writing Month 2018, TAA hosted a series of #AcWriChat TweetChat events focused on the five W’s of academic writing. Throughout the series we explored The What: Defining a research project ; The Where: Constructing an effective writing environment ; The When: Setting realistic timeframes for your research ; The Who: Finding key sources in the existing literature ; and The Why: Explaining the significance of your research . This series of posts brings together the discussions and resources from those events. Let’s start with The What: Defining a research project .
Before moving forward on any academic writing effort, it is important to understand what the research project is intended to understand and document. In order to accomplish this, it’s also important to understand what a research project is. This is where we began our discussion of the five W’s of academic writing.
Q1: What constitutes a research project?
According to a Rutgers University resource titled, Definition of a research project and specifications for fulfilling the requirement , “A research project is a scientific endeavor to answer a research question.” Specifically, projects may take the form of “case series, case control study, cohort study, randomized, controlled trial, survey, or secondary data analysis such as decision analysis, cost effectiveness analysis or meta-analysis”.
Hampshire College offers that “Research is a process of systematic inquiry that entails collection of data; documentation of critical information; and analysis and interpretation of that data/information, in accordance with suitable methodologies set by specific professional fields and academic disciplines.” in their online resource titled, What is research? The resource also states that “Research is conducted to evaluate the validity of a hypothesis or an interpretive framework; to assemble a body of substantive knowledge and findings for sharing them in appropriate manners; and to generate questions for further inquiries.”
TweetChat participant @TheInfoSherpa , who is currently “investigating whether publishing in a predatory journal constitutes blatant research misconduct, inappropriate conduct, or questionable conduct,” summarized these ideas stating, “At its simplest, a research project is a project which seeks to answer a well-defined question or set of related questions about a specific topic.” TAA staff member, Eric Schmieder, added to the discussion that“a research project is a process by which answers to a significant question are attempted to be answered through exploration or experimentation.”
In a learning module focused on research and the application of the Scientific Method, the Office of Research Integrity within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services states that “Research is a process to discover new knowledge…. No matter what topic is being studied, the value of the research depends on how well it is designed and done.”
Wenyi Ho of Penn State University states that “Research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict and control the observed phenomenon.” in an online resource which further shares four types of knowledge that research contributes to education, four types of research based on different purposes, and five stages of conducting a research study. Further understanding of research in definition, purpose, and typical research practices can be found in this Study.com video resource .
Now that we have a foundational understanding of what constitutes a research project, we shift the discussion to several questions about defining specific research topics.
Q2: When considering topics for a new research project, where do you start?
A guide from the University of Michigan-Flint on selecting a topic states, “Be aware that selecting a good topic may not be easy. It must be narrow and focused enough to be interesting, yet broad enough to find adequate information.”
Schmieder responded to the chat question with his approach.“I often start with an idea or question of interest to me and then begin searching for existing research on the topic to determine what has been done already.”
@TheInfoSherpa added, “Start with the research. Ask a librarian for help. The last thing you want to do is design a study thst someone’s already done.”
The Utah State University Libraries shared a video that “helps you find a research topic that is relevant and interesting to you!”
Q2a: What strategies do you use to stay current on research in your discipline?
The California State University Chancellor’s Doctoral Incentive Program Community Commons resource offers four suggestions for staying current in your field:
- Become an effective consumer of research
- Read key publications
- Attend key gatherings
- Develop a network of colleagues
Schmieder and @TheInfoSherpa discussed ways to use databases for this purpose. Schmieder identified using “journal database searches for publications in the past few months on topics of interest” as a way to stay current as a consumer of research.
@TheInfoSherpa added, “It’s so easy to set up an alert in your favorite database. I do this for specific topics, and all the latest research gets delivered right to my inbox. Again, your academic or public #librarian can help you with this.” To which Schmieder replied, “Alerts are such useful advancements in technology for sorting through the myriad of material available online. Great advice!”
In an open access article, Keeping Up to Date: An Academic Researcher’s Information Journey , researchers Pontis, et. al. “examined how researchers stay up to date, using the information journey model as a framework for analysis and investigating which dimensions influence information behaviors.” As a result of their study, “Five key dimensions that influence information behaviors were identified: level of seniority, information sources, state of the project, level of familiarity, and how well defined the relevant community is.”
Q3: When defining a research topic, do you tend to start with a broad idea or a specific research question?
In a collection of notes on where to start by Don Davis at Columbia University, Davis tells us “First, there is no ‘Right Topic.’”, adding that “Much more important is to find something that is important and genuinely interests you.”
Schmieder shared in the chat event, “I tend to get lost in the details while trying to save the world – not sure really where I start though. :O)” @TheInfoSherpa added, “Depends on the project. The important thing is being able to realize when your topic is too broad or too narrow and may need tweaking. I use the five Ws or PICO(T) to adjust my topic if it’s too broad or too narrow.”
In an online resource , The Writing Center at George Mason University identifies the following six steps to developing a research question, noting significance in that “the specificity of a well-developed research question helps writers avoid the ‘all-about’ paper and work toward supporting a specific, arguable thesis.”
- Choose an interesting general topic
- Do some preliminary research on your general topic
- Consider your audience
- Start asking questions
- Evaluate your question
- Begin your research
USC Libraries’ research guides offer eight strategies for narrowing the research topic : Aspect, Components, Methodology, Place, Relationship, Time, Type, or a Combination of the above.
Q4: What factors help to determine the realistic scope a research topic?
The scope of a research topic refers to the actual amount of research conducted as part of the study. Often the search strategies used in understanding previous research and knowledge on a topic will impact the scope of the current study. A resource from Indiana University offers both an activity for narrowing the search strategy when finding too much information on a topic and an activity for broadening the search strategy when too little information is found.
The Mayfield Handbook of Technical & Scientific Writing identifies scope as an element to be included in the problem statement. Further when discussing problem statements, this resource states, “If you are focusing on a problem, be sure to define and state it specifically enough that you can write about it. Avoid trying to investigate or write about multiple problems or about broad or overly ambitious problems. Vague problem definition leads to unsuccessful proposals and vague, unmanageable documents. Naming a topic is not the same as defining a problem.”
Schmieder identified in the chat several considerations when determining the scope of a research topic, namely “Time, money, interest and commitment, impact to self and others.” @TheInfoSherpa reiterated their use of PICO(T) stating, “PICO(T) is used in the health sciences, but it can be used to identify a manageable scope” and sharing a link to a Georgia Gwinnett College Research Guide on PICOT Questions .
By managing the scope of your research topic, you also define the limitations of your study. According to a USC Libraries’ Research Guide, “The limitations of the study are those characteristics of design or methodology that impacted or influenced the interpretation of the findings from your research.” Accepting limitations help maintain a manageable scope moving forward with the project.
Q5/5a: Do you generally conduct research alone or with collaborative authors? What benefits/challenges do collaborators add to the research project?
Despite noting that the majority of his research efforts have been solo, Schmieder did identify benefits to collaboration including “brainstorming, division of labor, speed of execution” and challenges of developing a shared vision, defining roles and responsibilities for the collaborators, and accepting a level of dependence on the others in the group.
In a resource on group writing from The Writing Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, both advantages and pitfalls are discussed. Looking to the positive, this resource notes that “Writing in a group can have many benefits: multiple brains are better than one, both for generating ideas and for getting a job done.”
Yale University’s Office of the Provost has established, as part of its Academic Integrity policies, Guidance on Authorship in Scholarly or Scientific Publications to assist researchers in understanding authorship standards as well as attribution expectations.
In times when authorship turns sour , the University of California, San Francisco offers the following advice to reach a resolution among collaborative authors:
- Address emotional issues directly
- Elicit the problem author’s emotions
- Acknowledge the problem author’s emotions
- Express your own emotions as “I feel …”
- Set boundaries
- Try to find common ground
- Get agreement on process
- Involve a neutral third party
Q6: What other advice can you share about defining a research project?
Schmieder answered with question with personal advice to “Choose a topic of interest. If you aren’t interested in the topic, you will either not stay motivated to complete it or you will be miserable in the process and not produce the best results from your efforts.”
For further guidance and advice, the following resources may prove useful:
- 15 Steps to Good Research (Georgetown University Library)
- Advice for Researchers and Students (Tao Xie and University of Illinois)
- Develop a research statement for yourself (University of Pennsylvania)
Whatever your next research project, hopefully these tips and resources help you to define it in a way that leads to greater success and better writing.
Share this:

- Share on Tumblr
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Latest science news, discoveries and analysis

The Maldives is racing to create new land. Why are so many people concerned?
Mini-colon and brain 'organoids' shed light on cancer and other diseases

Retractions are part of science, but misconduct isn’t — lessons from a superconductivity lab
Monkeypox virus: dangerous strain gains ability to spread through sex, new data suggest
Dna from ancient graves reveals the culture of a mysterious nomadic people, atomic clock keeps ultra-precise time aboard a rocking naval ship, who redefines airborne transmission: what does that mean for future pandemics, ecologists: don’t lose touch with the joy of fieldwork chris mantegna, european ruling linking climate change to human rights could be a game changer — here’s how charlotte e. blattner.

Lethal AI weapons are here: how can we control them?

Living on Mars would probably suck — here's why

Dozens of genes are linked to post-traumatic stress disorder

What toilets can reveal about COVID, cancer and other health threats
How gliding marsupials got their ‘wings’, plastic pollution: three numbers that support a crackdown, first glowing animals lit up the oceans half a billion years ago, how to freeze a memory: putting worms on ice stops them forgetting.

Any plan to make smoking obsolete is the right step

Will AI accelerate or delay the race to net-zero emissions?

Citizenship privilege harms science
We must protect the global plastics treaty from corporate interference martin wagner, un plastics treaty: don’t let lobbyists drown out researchers, current issue.

Surprise hybrid origins of a butterfly species
Stripped-envelope supernova light curves argue for central engine activity, optical clocks at sea, research analysis.
A chemical method for selective labelling of the key amino acid tryptophan
Charles Darwin investigates: the curious case of primrose punishment
Nanoparticle fix opens up tricky technique to forensic applications
Coupled neural activity controls working memory in humans
Robust optical clocks promise stable timing in a portable package, targeting rna opens therapeutic avenues for timothy syndrome, bioengineered ‘mini-colons’ shed light on cancer progression, ancient dna traces family lines and political shifts in the avar empire.

Breaking ice, and helicopter drops: winning photos of working scientists

Shrouded in secrecy: how science is harmed by the bullying and harassment rumour mill

Londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs
How ground glass might save crops from drought on a caribbean island, deadly diseases and inflatable suits: how i found my niche in virology research, books & culture.

How volcanoes shaped our planet — and why we need to be ready for the next big eruption

Dogwhistles, drilling and the roots of Western civilization: Books in brief

Cosmic rentals
Las boriqueñas remembers the forgotten puerto rican women who tested the first pill, dad always mows on summer saturday mornings, nature podcast.

Latest videos
Nature briefing.
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Our approach
- Responsibility
- Infrastructure
- Try Meta AI
COMPUTER VISION
Imagine flash: accelerating emu diffusion models with backward distillation.
April 18, 2024
Diffusion models are a powerful generative framework, but come with expensive inference. Existing acceleration methods often compromise image quality or fail under complex conditioning when operating in an extremely low-step regime. In this work, we propose a novel distillation framework tailored to enable high-fidelity, diverse sample generation using just one to three steps. Our approach comprises three key components: (i) Backward Distillation, which mitigates training-inference discrepancies by calibrating the student on its own backward trajectory; (ii) Shifted Reconstruction Loss that dynamically adapts knowledge transfer based on the current time step; and (iii) Noise Correction, an inference time technique that enhances sample quality by addressing singularities in noise prediction. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our method outperforms existing competitors in quantitative metrics and human evaluations. Remarkably, it achieves performance comparable to the teacher model using only three denoising steps, enabling efficient high-quality generation.
Jonas Kohler
Albert Pumarola
Edgar Schoenfeld
Artsiom Sanakoyeu
Roshan Sumbaly
Peter Vajda
Research Topics
Computer Vision
Related Publications
March 20, 2024
SceneScript: Reconstructing Scenes With An Autoregressive Structured Language Model
Armen Avetisyan , Chris Xie , Henry Howard-Jenkins , Tsun-Yi Yang , Samir Aroudj , Suvam Patra , Fuyang Zhang , Duncan Frost , Luke Holland , Campbell Orme , Jakob Julian Engel , Edward Miller , Richard Newcombe , Vasileios Balntas
February 13, 2024
IM-3D: Iterative Multiview Diffusion and Reconstruction for High-Quality 3D Generation
Luke Melas-Kyriazi , Iro Laina , Christian Rupprecht , Natalia Neverova , Andrea Vedaldi , Oran Gafni , Filippos Kokkinos
January 25, 2024
LRR: Language-Driven Resamplable Continuous Representation against Adversarial Tracking Attacks
Felix Xu , Di Lin , Jianjun Zhao , Jianlang Chen , Lei Ma , Qing Guo , Wei Feng , Xuhong Ren
December 08, 2023
Learning Fine-grained View-Invariant Representations from Unpaired Ego-Exo Videos via Temporal Alignment
Sherry Xue , Kristen Grauman

Help Us Pioneer The Future of AI
We share our open source frameworks, tools, libraries, and models for everything from research exploration to large-scale production deployment..
Product experiences
Foundational models
Latest news
Meta © 2024

The IFRS Foundation is a not-for-profit, public interest organisation established to develop high-quality, understandable, enforceable and globally accepted accounting and sustainability disclosure standards.
Our Standards are developed by our two standard-setting boards, the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB).
About the IFRS Foundation
Ifrs foundation governance, stay updated.

IFRS Accounting Standards are developed by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). The IASB is an independent standard-setting body within the IFRS Foundation.
IFRS Accounting Standards are, in effect, a global accounting language—companies in more than 140 jurisdictions are required to use them when reporting on their financial health. The IASB is supported by technical staff and a range of advisory bodies.
IFRS Accounting
Standards and frameworks, using the standards, project work, products and services.
IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards are developed by the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB). The ISSB is an independent standard-setting body within the IFRS Foundation.
IFRS Sustainability Standards are developed to enhance investor-company dialogue so that investors receive decision-useful, globally comparable sustainability-related disclosures that meet their information needs. The ISSB is supported by technical staff and a range of advisory bodies.
IFRS Sustainability
Education, membership and licensing, issb to commence research projects about risks and opportunities related to nature and human capital.
You need to Sign in to use this feature
Informed by its recent consultation on future priorities , the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) will commence projects to research disclosure about risks and opportunities associated with:
- biodiversity, ecosystems and ecosystem services; and
- human capital.
The research projects will focus on the common information needs of investors in assessing whether and how these risks and opportunities could reasonably be expected to affect a company’s prospects.
As with the approach to the ISSB’s inaugural Standards, the ISSB will look at how it might build from relevant pre-existing initiatives. This includes those already under its purview—the SASB Standards and CDSB guidance—and, additionally, relevant aspects of the work of the Task Force on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD).
Disclosure of material information about all sustainability-related risks and opportunities is already required under IFRS S1, with companies asked to refer to sources of guidance—including the SASB Standards—to provide appropriate disclosures beyond climate. These projects will enable the ISSB to embark on its own standard-setting work in key areas needed to establish more specific disclosures to build out the global baseline of sustainability-related financial disclosures.
Through the research projects, the ISSB will assess and define the limitations with current disclosure in these areas, identifying possible solutions and decide whether standard setting is required.
The ISSB’s priority for the next two years will be supporting the implementation of the ISSB’s inaugural Standards—IFRS S1 and IFRS S2. The two new research projects and work to enhance the SASB Standards will be the ISSB’s other key focus areas. Capacity will be reserved for addressing emerging needs and engaging with the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
Informed by market feedback, the ISSB decided not to embark on projects related to risks and opportunities associated with human rights—beyond risks and opportunities relating to a company's own workforce and workers in its value chain—or integration in reporting at this time. However, the ISSB agreed to closely monitor developments in these important areas and may consider including them in a future agenda consultation.
Both the ISSB and IASB will continue to support the use of the Integrated Reporting Framework as a resource that drives high-quality corporate reporting and a cohesive information package for investors.
In June, the ISSB expects to publish a summary of the feedback on its agenda consultation, together with its response to the feedback and its work plan for the next two years.
ISSB Chair Emmanuel Faber, said:
Beyond climate, we are committed to building out the global baseline of sustainability-related financial disclosure to meet the needs of investors. Feedback indicated a significant and growing need among investors for improved disclosures around biodiversity, ecosystems and ecosystems services as well as human capital, as a key source of value for companies. Our industry-specific SASB Standards continue to be used as a cost-effective way of providing decision-useful information to investors. We are committed to enhancing the SASB Standards further given they will also support our new research areas. We look forward to sharing our work plan for the next two years in June.
Related information
International Sustainability Standards Board
April 2024 ISSB meeting
IFRS S1 General Requirements for Disclosure of Sustainability-related Financial Information
IFRS S2 Climate-related Disclosures
Followable tags
Your action was not processed, please try again later
Related news
Your privacy.
IFRS Foundation cookies
We use cookies on ifrs.org to ensure the best user experience possible. For example, cookies allow us to manage registrations, meaning you can watch meetings and submit comment letters. Cookies that tell us how often certain content is accessed help us create better, more informative content for users.
We do not use cookies for advertising, and do not pass any individual data to third parties.
Some cookies are essential to the functioning of the site. Other cookies are optional. If you accept all cookies now you can always revisit your choice on our privacy policy page.
Cookie preferences
Essential cookies, always active.
Essential cookies are required for the website to function, and therefore cannot be switched off. They include managing registrations.
Analytics cookies
We use analytics cookies to generate aggregated information about the usage of our website. This helps guide our content strategy to provide better, more informative content for our users. It also helps us ensure that the website is functioning correctly and that it is available as widely as possible. None of this information can be tracked to individual users.
Preference cookies
Preference cookies allow us to offer additional functionality to improve the user experience on the site. Examples include choosing to stay logged in for longer than one session, or following specific content.
Share this page

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Methods. Next, indicate the research methods that you used to answer your question. This part should be a straightforward description of what you did in one or two sentences. It is usually written in the past simple tense, as it refers to completed actions.
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes: an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to….
You can, however, write a draft at the beginning of your research and add in any gaps later. If you find abstract writing a herculean task, here are the few tips to help you with it: 1. Always develop a framework to support your abstract. Before writing, ensure you create a clear outline for your abstract.
A project abstract is a brief summary of a research project or proposal that outlines the main objectives, methods, and expected outcomes. It is typically the first section of a research paper or grant proposal and is designed to give readers a clear idea of what the project is about without having to read the entire document.
4. How to Start an Abstract. The first line of your abstract should give your reader the context of your report by providing background information. You can use this sentence to imply the motivation for your research. You don't need to use a hook phrase or device in your first sentence to grab the reader's attention.
Methodology: An abstract of a scientific work may include specific models or approaches used in the larger study. Other abstracts may describe the types of evidence used in the research. Results: Again, an abstract of a scientific work may include specific data that indicates the results of the project. Other abstracts may discuss the findings ...
Write your paper first, then create the abstract as a summary. Check the journal requirements before you write your abstract, eg. required subheadings. Include keywords or phrases to help readers search for your work in indexing databases like PubMed or Google Scholar. Double and triple check your abstract for spelling and grammar errors.
An abstract is a 150- to 250-word paragraph that provides readers with a quick overview of your essay or report and its organization. It should express your thesis (or central idea) and your key points; it should also suggest any implications or applications of the research you discuss in the paper. According to Carole Slade, an abstract is ...
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text. Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes. Table of contents. Abstract example. When to write an abstract. Step 1: Introduction. Step 2: Methods. Step 3: Results.
An APA abstract must be formatted as follows: Include the running head aligned to the left at the top of the page (professional papers only) and page number. Note, student papers do not require a running head. On the first line, center the heading "Abstract" and bold (do not underlined or italicize).
An abstract should be a stand-alone summary of a research project. 1 Although abstracts are most used to provide an overview of a research project, they may also be used to summarize an implementation project related to practice, policy, or education in nursing. The abstract may be a precursor to a scientific manuscript, chapter, thesis, or ...
Research Paper Abstract. Research Paper Abstract is a brief summary of a research paper that describes the study's purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions. It is often the first section of the paper that readers encounter, and its purpose is to provide a concise and accurate overview of the paper's content.
Here are the basic steps to follow when writing an abstract: 1. Write your paper. Since the abstract is a summary of a research paper, the first step is to write your paper. Even if you know what you will be including in your paper, it's always best to save your abstract for the end so you can accurately summarize the findings you describe in ...
The project abstract (up to 300 words) should describe the nature of the project or piece (ex: architectural images used for a charrette, fashion plates, small scale model of a theater set) and its intended purpose. Students should describe the project or problem that was addressed and limitations and challenges that impact the design process.
Qualitative studies also have clearly defined research methods. Therefore, it is important to keep in mind the general principles of informative abstract writing. Always begin with the research question or problem statement, and proceed to offer a one-sentence description of study methods and results. Informative Abstract Example 5
An abstract is a brief summary of a completed research/innovation project. What should an abstract include? An abstract should include the following components: 1. Background: What is the motivation behind the research? Provide a short paragraph that details the background information. 2. Objectives: What problem are you attempting to solve ...
Additional information on writing abstracts is available in Dr. Robert Labaree's libguide on organizing research in the social sciences. An abstract is a summary of a paper, a book, or a presentation. As a general rule, the abstract is written by the author of the work. ... Abstracts are common in academic and scholarly journal articles, as ...
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page
Abstracts present the essential elements of a longer work in a short and powerful statement. The purpose of an abstract is to provide prospective readers the opportunity to judge the relevance of the longer work to their projects. Abstracts also include the key terms found in the longer work and the purpose and methods of the research.
According to a Rutgers University resource titled, Definition of a research project and specifications for fulfilling the requirement, "A research project is a scientific endeavor to answer a research question.". Specifically, projects may take the form of "case series, case control study, cohort study, randomized, controlled trial ...
A research project begins with an abstract construct that researchers want to measure. That idea is referred to as a(n) ____. Researchers then create a tangible way to measure that idea, known as a(n) ____. For example, if researchers wanted to measure the abstract concept of ____, they might create a study that records specific ____.
A research project begins with an abstract idea of what researchers want to measure. That idea is referred to as a/an ? ... Buckeye Healthcare Corp. is proposing to spend $186,725 on an eight-year project that has estimated net cash flows of$35,000 for each of the eight years. a. Compute the net present value, using a rate of return of 12%.
Abstract Studied the variables associated with successful single-parent families. Information was sought from 25 single parents (aged 24-47 yrs) on the following topics: ages of family members and length of single-parent family status, education level and income, relations with absent parent, relations with children, use of social networks ...
Find breaking science news and analysis from the world's leading research journal.
Abstract. Diffusion models are a powerful generative framework, but come with expensive inference. Existing acceleration methods often compromise image quality or fail under complex conditioning when operating in an extremely low-step regime.
The research projects will focus on the common information needs of investors in assessing whether and how these risks and opportunities could reasonably be expected to affect a company's prospects. As with the approach to the ISSB's inaugural Standards, the ISSB will look at how it might build from relevant pre-existing initiatives. ...
With the research projects, the ISSB will now undertake its own standard-setting in these areas, with the objective to provide more specific disclosure requirements and thereby expanding the global baseline of sustainability-related financial disclosures. For more information, please see the press release on the IFRS Foundation website.