Eight tips to effectively supervise students during their Master's thesis
Jul 30, 2021 PhD
I am a fan of knowledge transfer between peers, teaching what I know to others and learning back from them. At University I frequently helped my fellow course mates with the material, so I was very interested in formally mentoring students when I started my PhD. Luckily my supervisor, who is really talented at this, agreed to let me help him with supervising some Master’s theses. In this article, also published as a Nature Career Column , I present eight lessons that I learned by watching him at work and trying on my own.
I supervised three Master’s students in the past year. One of them was quite good and independent, did not need a lot of guidance and could take care of most things on his own, while the other two required a fair amount of help from us, one of them even coming close to not graduating successfully. Dealing with the difficult situations is when I learned the most important lessons, but regardless of the ability of the students a common thread soon appeared.
But first, here’s a brief digression on how that happened. While I was writing a draft for this blog, I noticed an interesting article on Nature’s newsletter. While I was reading it, I felt its style was quite similar to what I usually aim for in this blog: use headlines to highlight the important points, and elaborate on those with a few paragraphs. I then noticed the author of that column was a PhD student, and I thought: “how comes she has an article there? Why can she do that? Can I do that?”. I quickly found how to do it , finished the draft and sent it to them, and, after eight rounds of review in the course of two months, the article was finally up! The editor was very responsive and we could iterate quickly on the manuscript, and the quality of the writing is so much better than what I had originally sent in. On the other hand, I sometimes felt the message was being warped a bit too much. After the editing process was finished I had to agree to an Embargo Period of six months during which Nature had the exclusive right of publishing the final version on their website. As those six months are now over, I am finally allowed to publish the final version here, too. Enjoy!
This is a post-peer-review, pre-copyedit version of an article published in Nature Career Column . The final authenticated version is available online at: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-02028-1 .

The lessons I learnt supervising master’s students for the first time
PhD student Emilio Dorigatti supported three junior colleagues during their degrees.
I started my PhD wanting to improve not only my scientific abilities, but also ‘soft skills’ such as communication, mentoring and project management. To this end, I joined as many social academic activities as I could find, including journal clubs, seminars, teaching assistance, hackathons, presentations and collaborations.
I am a bioinformatics PhD student at the Munich School for Data Science in Germany, jointly supervised by Bernd Bischl at the Ludwig Maximilian University Munich and Benjamin Schubert at the Helmholtz Centre Munich, the German Research Center for Environmental Health. When I went to them asking to gain some experience in communication and mentoring soft skills, they suggested that I co-supervise three of Benjamin’s master’s students.
At first, I felt out of my depth, so I simply sat in on their meetings and listened. After a few months, I began offering technical advice on programming. I then started proposing new analyses and contributions. Eventually I became comfortable enough to propose a new master’s project based on part of my PhD research; Benjamin and I are now interviewing candidates.
I gained a great deal from this experience and I am grateful to both of my supervisors for supporting me, as well as to the students for staying motivated, determined and friendly throughout. Here are some of the things I learnt about how to ensure smooth collaboration and a happy outcome for all of us.
Draft a project plan
With Benjamin and Bernd, I put together a project plan for each of the master’s students. Drafting a two-page plan that ended up resembling an extended abstract for a conference forced us to consider each project in detail and helped to ensure that it was feasible for a student to carry out in their last semester of study.
If you’re a PhD student supervising others, sit down with your own supervisor and agree on your respective responsibilities as part of the project plan. At first, you might want your supervisor to follow you closely to help keep the project on the right path, but as you gain more experience and trust, you might request more autonomy and independence.
Use the project plan to advertise the position and find a suitable student: share it online on the group’s website or on Twitter, as well as on the job board at your department. Advertise it to your students if you are teaching a related topic, and sit back and wait for applicants.
We structured the plans to include a general introduction to the research subject as well as a few key publications. We described the gap in the literature that the project aimed to close, with the proposed methodology and a breakdown of four or five tasks to be achieved during the project. My supervisors and I also agreed on and included specific qualifications that candidates should have, and formalities such as contact information, starting dates and whether a publication was expected at the end.
Benjamin and I decided to propose publishable projects, sometimes as part of a larger paper. We always list the student as one of the authors.
Meet your student regularly
I found that I met with most students for less than an hour per week, but some might require more attention. Most of the time, Benjamin joined the meeting, too. We started with the students summarizing what they had done the previous week and any issues they had encountered. We then had a discussion and brainstorming session, and agreed on possible next steps. I learnt that I do not need to solve all the student’s problems (it is their thesis, after all). Instead, Benjamin and I tried to focus on suggesting a couple of things they could try out. At the end of the meeting, we made sure it was clear what was expected for the next week.
We used the first few weeks to get the students up to speed with the topic, encouraging them to read publications listed in the plan, and a few others, to familiarize themselves with the specific methods that they would be working with. We also addressed administrative matters such as making sure that the students had accounts to access computational resources: networks, e-mail, Wi-Fi, private GitHub repositories and so on.
Encourage regular writing
Good writing takes time, especially for students who are not used to it, or who are writing in a foreign language. It is important to encourage them to write regularly, and to keep detailed notes of what should be included in the manuscript, to avoid missing key details later on. We tried to remind our students frequently how the manuscript should be structured, what chapters should be included, how long each should be, what writing style was expected, what template to use, and other specifics. We used our meetings to provide continuous feedback on the manuscript.
The first two to four weeks of the project are a good time to start writing the first chapters, including an introduction to the topic and the background knowledge. We suggested allocating the last three or four weeks to writing the remaining chapters — results and conclusions — ensuring that the manuscript forms a coherent whole, and preparing and rehearsing the presentation for the oral examination.
Probe for correct understanding
In our weekly meetings, or at other times when I was teaching, I quickly realized that asking ‘did you understand?’ or ‘is that OK?’ every five minutes is not enough. It can even be counterproductive, scaring away less-assertive students.
I learnt to relax a little and take a different approach: when I explained something, I encouraged the students to explain it back in their own words, providing detailed breakdowns of a certain task, anticipating possible problems, and so on.
Ultimately, this came down to probing for understanding of the science, rather than delivering a lecture or grilling an interviewee. Sometimes this approach helps when a student thinks they fully understand something but actually don’t. For example, one of our students was less experienced in programming than others, so for more difficult tasks, we broke the problem down and wrote a sketch of the computer code that they would fill in on their own during the week.
Adapt supervision to the student
Each student requires a different type of supervision, and we tried to adapt our styles to accommodate that. That could mean using Trello project-management boards or a shared Google Doc to record tasks; defining tasks in detail and walking through them carefully; or taking extra time to explain and to fill knowledge gaps. I tried to be supportive by reminding students that they could always send an e-mail if they were stuck on a problem for too long. One of the students found it very helpful to text brief updates outside of scheduled meetings, as a way to hold themselves accountable.
Sometimes, if we felt a student needed to be challenged, we proposed new tasks that were not in the original plan or encouraged them to follow their interest, be it diving into the literature or coming up with further experiments and research questions.
One student conducted a literature review and summarized the pros and cons of the state-of-the-art technology for a follow-up idea we had. That saved some time when we picked up the project after the student left; they learnt lots of interesting things; and the discussion section of the manuscript was much more interesting as a result.
When things go badly, make another plan
Not all projects can be successful, despite your (and your student’s) best efforts. So, as part of each project, my supervisors and I prepared a plan B (and C), working out which tasks were essential and which were just a nice addition. This included a simpler research question that required less work than the original. The initial plan for one of our projects was to compare a newly proposed method with the usual way of doing things, but the new method turned out to be much more difficult than anticipated, so we decided not to do the comparison, and just showed how the new method performed.
Halfway through the project is a good time to evaluate how likely it is that the thesis will be handed in on time and as originally planned. The top priority is to help the student graduate. That might entail either forgoing some of the tasks planned at the beginning, or obtaining an extension of a few months if possible.
Have a final feedback round
After the oral examinations, Benjamin and I met to decide the students’ final grades on the basis of the university’s rubric. We then met the students one last time to tell them our decision, going through each item in the rubric and explaining the motivation for the score we had given. We tried to recall relevant events from the past months to make each student feel the grading was fair.
We also remembered to ask the student for feedback on our supervision and to suggest things they thought we could do better.
Lastly, I encouraged those students to apply for open positions in our lab, and offered to write recommendation letters for them.
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 22 August 2019
The journey of thesis supervisors from novice to expert: a grounded theory study
- Leila Bazrafkan 1 ,
- Alireza Yousefy 2 ,
- Mitra Amini 1 &
- Nikoo Yamani 2
BMC Medical Education volume 19 , Article number: 320 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
9520 Accesses
6 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Supervision is a well-defined interpersonal relationship between the thesis supervisors and their students. The purpose of this study was to identify the patterns which can explain the process of expertise attainment by thesis supervisors. We aimed at developing a conceptual framework/model to explain this development based on the experience of both students and supervisors.
We have conducted a qualitative grounded theory study in 20 universities of medical sciences in Iran since 2017 by using purposive, snowball sampling, and theoretical sampling and enrolled 84 participants. The data were gathered through semi-structured interviews. Based on the encoding approach of Strauss and Corbin (1998), the data underwent open, axial, and selective coding by constant comparative analysis. Then, the core variables were selected, and a model was developed.
We could obtain three themes and seven related subthemes, the central variable, which explains the process of expertise as the phenomenon of concentration and makes an association among the subthemes, was interactive accountability. The key dimensions during expertise process which generated the supervisors’ competence development in research supervision consisted maturation; also, seven subthemes as curious observation, evaluation of the reality, poorly structured rules, lack of time, reflection in action, reflection on action, and interactive accountability emerged which explain the process of expertise attainment by thesis supervisors.
Conclusions
As the core variable in the expertise process, accountability must be considered in expertise development program planning and decision- making. In other words, efforts must be made to improve responsibility and responsiveness.
Peer Review reports
Supervision is a well-defined term in the interpersonal relationship between thesis supervisors and students. A supervisor is designated to assist the student’s development in terms of their research project [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Faculty members supervise the students because qualified supervision leads to success on the part of the student, and it has moral, reputational, and financial outcomes for the institution. Supervisors are expected to train students to gain competence in areas such as specialist skills, generalist skills, self-reliance skills, and group/team skills [ 4 ]. Expertise is derived from the three essential elements of knowledge, experience, and the ability to solve problems in society [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. .According to Dreyfus, acquisition of expertise or practical wisdom represents a higher level of “self-actualization.” At this point, one reaches a level in which they can flourish in their talents and abilities. This enables the teachers to function in scientific communities and multicultural environments [ 7 ].
Wiscer has identified three stages in the thesis supervision process and describes the duties of the supervisors in each of them [ 8 ]. Pearson and Brew state that maturation in specialist skills, generalist skills, self-reliance skills, and group/team skills are the major areas that need to be promoted in the student. Moreover, these are the generic processes in which the supervisors should be involved for efficacious supervision if they aim to help the students develop in various institutional, disciplinary and professional settings; acquire appropriate expertise and features needed for employment; and make an outline of what might form a flexible professional development program for supervisors in this setting [ 3 ]. Vereijken et al. emphasized novice supervisors’ approaches to reach expertise in supervision and explained the relationship between practice and dilemmas among novice supervisors [ 9 ].
.Despite the importance of expertise in higher education and particularly research supervision, research abilities are not considered as one of the priorities in the employment of the academic staff. Furthermore, the newly employed faculty members are often involved in teaching, administrative tasks, and services in health care; this inhibits them from expertise attainment in other aspects such as research supervision [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. In this regard, Malekafzali believes that in the area of research activities, the faculty members have serious weaknesses in defining the problem, choosing the appropriate method for research, analyzing the data, interpreting the results, and publishing scientific articles. Besides, there is a lack of coherent and compiled training programs which can enhance their research capabilities [ 13 ].
One of the most important factors contributing to the thesis and research quality is the process of developing expertise in supervisors’ research supervision. Most studies in our country have focused on research abilities during the research, and fewer studies have focused on the process of expertise acquisition in thesis supervision, and no actual model has been proposed for this [ 11 , 12 , 13 ]. The quantitative researches could not explain exactly how and through which process the faculty members, as thesis supervisors, become experts in thesis supervision since the expertise process is multi-factorial and has many unknown aspects. Considering the effective role of qualitative research in clarifying ambiguous and unknown aspects, we chose the grounded theory approach for this study [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. This theory will be used when the investigator intends to determine the patterns of actions and social interactions needed for the development of expertise by specific groups of people in a specific setting [ 17 , 18 ].
In this study, we aimed to identify the themes that explain the expertise development process among thesis supervisors in Iran, and also to develop a conceptual framework/model to explain this development based on the experience of both students and supervisors.
This study was carried out in 20 universities of medical sciences with different ranks in Iran because universities are the places where supervisors and students interact purposefully to discourse the needs of experts on specific occasions and in specific conditions. In these universities, different students study with various disciplines. There are three types of universities in Iran. Type 1 universities are the ones with the most facilities, faculties, research presentations, international collaborations, and scientific outcomes. The second rank belongs to type 2, and the one with the least mentioned qualities is type 3 universities. All three types of universities were included in this study. In all these courses, writing a thesis is one of the requirements with the same role and regulation. The majority of the students in this research project were in the late stages of both undergraduate and postgraduate educational programs within the same function and regulation.
Study design
We conducted this qualitative study based on a grounded theory approach in a systematic form [ 17 , 18 ]. Grounded theory is a symbolic interaction which is derived from systematic data collection during the research process. In this strategy, collecting and analyzing data and the theory derived from the data have a close association [ 17 , 19 ]. The investigator’s purpose in using grounded theory is to describe and clarify a phenomenon in the social condition and to identify the essential processes working within [ 17 ].
Participants
In this study, 84 subjects including 56 faculty members of medical sciences, 20 undergraduate and postgraduate students (medical students, MS of Science, Ph.D. and residents), and eight managers in the field of research supervision participated. Using purposive sampling, snowball sampling with maximum variation, we selected the participants from a variety of academic ranks with different work experiences, as the key informants in thesis supervisors. Then, to continue the sampling, we used theoretical sampling and data saturation. The inclusion criterion was 5 years of work experience in thesis supervision, and the exclusion criterion was the unwillingness to participate in the study. Firstly, we collected data in Shiraz University with the help of a research supervisor who is known for his high quality of supervision and then data gathering was initiated in the university of Isfahan. There were 34 key informants from the two universities and 22 individuals from other universities. Students were selected based on their willingness to participate.
Theoretical sampling was used next to develop the tentative theory. The basis for theoretical sampling was the queries that emerged during data analysis. At this stage, the researcher interviewed the supervisor, administrators, and students. Theoretical sampling facilitated in verifying the supervisors’ responses and credibility of categories and resulted in more conceptual density. Data saturation was obtained when no new data emerged in the last five interviews. Therefore, data gathering by interviews was terminated.
Data collection
We collected the data primarily by semi-structured interviews from September 2017 to September 2018. The participants were recognized with unknown codes based on their field of work and setting, and each participant was interviewed in one or two sessions. Having obtained the participants’ informed consent, we recorded the interviews and they were transcribed verbatim immediately. The interviews began with open-ended general questions such as, “What did you experience during research supervision?” and then the participants were asked to describe their perceptions regarding their expertise process. Leading questions were also used to deeply explore the conditions, processes, and other factors that participants recognized as significant issues. The interview was based mostly on the questions which came up during the interview. On average, each interview lasted for an hour, during which field notes and memos were taken. At the end of each session, the participants were asked to give an opinion on other important topics which did not come up during the interview, followed by data collection and analysis which are simultaneously done in grounded theory; analytic thought and queries that arose from one interview were carried to the next one [ 20 ].
The data were also collected by unstructured observations of the educational atmosphere in the laboratory, and the faculty member and students’ counseling offices. These observations lasted 5 weeks, during which the faculties and students’ interactions and the manner of supervision were closely monitored. The observation was arranged to sample the maximum variety of research supervisor activity for some faculty member who is known to be a good or poor supervisor and detailed organized field notes were kept.
Also, we used the field notes to reflect emergent analytic concepts as a source of three angulations of data, frequently reconsidering the data, and referring to field notes in the context of each participant’s explanation. Analysis of the field notes facilitated in shaping contextual conditions and clarifying variations in the supervisors’ responses in each context. This led to the arrangement of several assumptions in the effect of contexts.
Data analysis
We simultaneously performed data collection and analysis. We read the scripts carefully several times and then entered them into MAXQDA (version10). We collected and analyzed the data practically and simultaneously by using a constant comparative method. Data were analyzed based on the 3-stage coding approach, including open, axial, and selective coding by Strauss and Corbin In the open coding stage, we extracted the basic concepts or meaning units from the gathered information. Then, more general concepts were formed by grouping similar concepts into one theme. The themes became clearer throughout the interviews. Then, the constructs of them were compared with each other to form tentative categories. After that, we conducted axial coding by using the guidelines given in Corbin and Strauss’s (2008) Paradigm Model [ 21 ]. The extracted themes (codes) in the previous (open coding) stage were summarized in 3 main themes during the axial coding stage, and then the core variables were selected in the selective coding stage [ 20 ]. To generate a reasonable theory to the community, a grounded theorist needs to condense the studied happenings a the precise sequence. To check the data against categories, the researcher asks questions related to certain categories and returns to the data to seek evidence. After developing a theory, the researcher is required to confirm the theory by comparing it with existing theories found in the recently available research [ 21 ]. We finalized the model after 5 days; during this time, we explained the relations between subcategories and the core category for realizing theoretical saturation and clarifying the theoretical power of the analysis explained about work as narration.
In terms of accuracy improvement, we used the Lincoln and Guba’s criteria, including credibility, dependability, conformability, and transferability [ 22 , 23 ].
To increase credibility, we collected data from different universities in Iran, and their credibility was also confirmed by three reviewers and experts in qualitative research. Also, some of the participants rechecked the data and the investigators’ description and interpretation of their experiences carefully. Prolonged engagement and tenacious observation facilitated the data credibility. In this way, the process of data collection and analysis took 12 months. Data triangulation and method triangulation also confirmed credibility [ 20 ]. The use of the maximum variation sampling method contributed to the dependability and conformability of data. Furthermore, once the explanation of the phenomenon was full, it was returned for confirmation to 3 participants of each university, and they validated the descriptions. Finally, to attain transferability, we adequately described the data in this article, so that a judgment of transferability can be made by readers.
Ethical considerations
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (92–6746). The participants were informed about the research aim and interviews. Informed consent for conducting and recording the interview was obtained. The confidentiality of the participants’ information was maintained throughout the study.
In this study, the mean age of the faculty members and students was 44.34 ± 14.60 and 28.54 ± 2.38 years, respectively. All the faculty members and most of the students were married. Only three students were single. Three themes and seven interrelated sub-themes emerged from the data (Table 1 ). The main variable, which explains the process of expertise as the phenomenon of concentration and makes an association among the categories, was interactive accountability. The key dimensions of the expertise process are displayed in a model (Fig. 1 ).
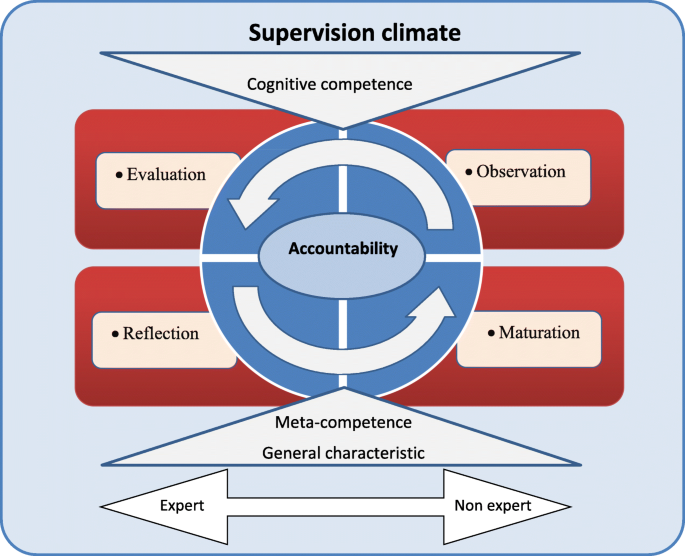
The process of expertise attainment in research supervisor model
Theme 1: engagement
In this theme, the initial phase of expertise, the supervisor starts to observe the others’ behavior in the students’ supervision and guidance based on the practical and cognitive skills previously acquired. They attempt to recognize the different needs based on the amount of their motivation and previous competence so that the models become important for them, and they recognize the scope of the needs based on their importance. Then, they try to understand the needs and values of real thesis supervision in this context. In this theme, two sub-themes, curious observation, and evaluation with reality emerged.
Curious observation
In this sub-theme, several concepts such as personal interest, self-awareness, ability to meet the students’ needs, ability to detect weaknesses in research skills, and observation of role models in this area act as the impellent factors in expertise attainment in research supervision.
Regarding personal interest, a successful faculty member in the area of research supervision said:
“…In my experience, faculties must be selected from those who have curious personalities as well as being good observers, first of all. In this way, they will have the appropriate intrinsic character to acquire knowledge in guidance and supervision)…” (Faculty member N0.3)
According to our participants, the most important intrinsic motivation is the desire to update the content knowledge and skills in research supervision. An experienced professor said:
“ … The knowledge gap between the new and old generations of faculty members is what forced me to update my knowledge...and it has been detected by myself…” (Faculty member N0.3).
Another important intrinsic motivation is the ability to meet the educational and research needs of students. However, usually these needs are combined; one of the faculty members put it:
“…I would like to be an expert in this process (thesis supervision) to meet my students’ needs. Because I have seen and felt this need many times before…” (Faculty member N0.12).
Since the publication of research directly affects the promotion of a faculty, some professors seek skills that are practical in article publication such as several statistical and basic skills for thesis writing. The participants considered the self-awareness and consciousness elements as very important. Through consciousness, one can better understand their needs.
Evaluation with reality
In this sub-theme, in the initial phase maintaining academic dignity and competition motivates the faculty members to obtain expertise in research supervision. At this point, the supervisor evaluates themself and their potentialities considering more precise features and acquired information (or data), so that they can find the distance between the optimal state and the existing conditions. They also evaluate the others’ potentialities in this field realistically and compete. Good supervision is then highlighted for them. Based on the supervisors’ experience, at this stage, they are seriously engaged in evaluation and competition.
Another motivation was obtaining academic and social promotion. Although the number of theses supervised by them can affect the academic promotion of supervisors, this effect is insignificant. The real motivation is maintaining academic dignity and competition amongst peers. A member of the clinical faculties stated:
“ … To enhance academic dignity, a faculty member should master various skills such as patient care, teaching, educational skills, and last but not least, research supervision. I got involved in research and thesis supervision because I felt I should not be left behind…” ( Faculty member N0.17).
At this stage, the junior supervisor tries to increase the cognitive knowledge in research supervision such as increasing specific knowledge of the discipline, planning, directing of a project effectively, and developing good interpersonal skills presented in research supervision.
Theme 2: supervision climate
In this theme, we describe the contextual factor which changes the process of expertise attainment in thesis supervisors. The result of the study reflects some concerns about the relationship between individuals in the context in that they interact purposefully but with barriers. The supervision climate in the thesis supervision process in this theme led to the emergence of two sub-themes, challenging shortcomings and role ambiguity. These challenges include poorly structured rules and regulations which, in turn, can cause confusion and role ambiguity.
Challenging shortcomings
This report shows that contextual factor plays a significant role in promoting the quality of a thesis in a university, but the process is faced with altered challenges such as inadequate resources, inadequate time, and ineffective evaluation and rule and regulation deficit. These challenges include the following. Most faculty members and students have experienced these shortcomings.
Various inadequate resources, such as access to new and online journals, laboratory equipment were one of the challenges for supervisors in certain aspects which required more competency, and the constraints on communication with the other academic centers worldwide undermine the sense of competition and hinder the effort put in to become an expert. One of the students said: “… I see how difficult it is to gain access to a good article or laboratory materials in this situation …we try, but it just isn’t possible...” (Faculty member N0.17).
Based on our results, the sudden changes in personal life, work position, and organizational change can affect the path to expertise. These changes such as marriage, work overload, admission of students over the capacity, new rules and regulation of scholar citizenship, promotion and so on can have both positive and negative impacts, depending on whether they facilitate or restrict the professional development of faculties as supervisors. For instance, an increase in student admission causes work overload, which results in neglecting self-improvement.
“…As you know, we are over- loaded with students (they have increased the number of admissions), which is beyond our capacity. This means that most of our time will be dedicated to teaching. Self-improvement is difficult due to lack of time…” (Faculty member N0.6).
Role ambiguity
Poorly structured supervision can occur where there is an ambiguous context of supervision structure, supervisors and students’ roles. Most participants, as faculty members, managers, and students have experienced some difficulties in this regard, due to poorly structured rules(EDITORS NOTE; do you mean ‘rules and regulations ‘here) and regulations and its impact on the thesis supervision. It is not only the rules themselves but also the way they are implemented. One of the faculty members expressed confusion over the rules related to the dissertation as follows:
“…It should be made clear what I must do exactly. It is obvious regarding supervision on the work of students; there are not the same expectations from an Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, and a professor. Most problems occur as a result of the gap in legislation; For example, the rules imply a full Professor does not need a statistical consult, while many supervisors like me do not have enough knowledge and skills in statistical analysis...” (Faculty member N0.1).
Failure to implement the rules also increases the sense of this ambiguity, and there are no specific rules for verifying capability and audits to determine inadequate experts in thesis supervision. The role ambiguity or unclear roles and responsibilities of the supervisor and student in the thesis process were other limitations that were emphasized by the majority of participants. A faculty member stated:
“… Supervisors have different roles during the thesis process. To enhance this process, one must exactly know one’s responsibilities. For instance, in the beginning, the supervisor should guide the students through the process of finding a suitable research topic, but if the teacher's role is unclear, then instead of guiding they may actually choose the topic, and if so, the students will be prevented from exploring, using their creative thinking, and improving their problem-solving abilities…” (Faculty member N0.1).
Various performance
Based on the participants’ experiences, in this situation in which there are inadequate resources and organizational and social problems, some faculty members are well-trained in the field of supervision. One of the senior faculty members said: “It is my honor to mention that despite the existence of many obstacles, I have been able to train well-educated students, who have become researchers and contribute to the development of science in my country.”
One of the most important causes of poor performance is ineffective evaluation. Based on the participants experiences, two main problems can result in ineffective evaluation. First of all is the inadequate feedback from the supervisor which leads to unmotivated learners and the second one is lack of feedback from the stakeholders and educational institutes which in turn diminishes the supervisor’s efforts toward self-improvement. These can lead to poor performance both in students and supervisors.
In one of the Ph.D. student’s words:
“…In this system, there is no supervision on the supervisors; there is no control or evaluation of their work. Also, the supervisors don't get feedback from their students during the research process, and there is no third person who investigates whether the report is real or not…” (student N0. 7).
Evidence from data suggests that an unfair judgment and evaluation of academic theses are other problems in the process of acquiring the merit of teachers. If there isn’t proper evaluation, students and supervisors would not have the right standards to correct their performance.
The professors do not always consider the lack of expertise to be the only cause of poor performance. Many believe that inadequate monitoring can also reduce the motivation for quality performance. This means that supervisors may obtain the necessary expertise, but they are not motivated to enhance their performance since they are not expected to do this. One student had experienced:
“…I was so thrilled that my thesis supervisor was an experienced, older and well-known professor, but unfortunately, I soon found out that not only was his scientific knowledge outdated, but also he lacked the necessary supervision skills, so he let the students do all the work unsupervised. He did not take any responsibility during the process…” (Student N0.4).
Another point which leads to poor performance is the fact that some faculty members do not comprehend the main purpose of the thesis writing process; actually, they do not know the difference between teaching and guiding in the project or thesis supervision. One of the basic science supervisors said: “… Some faculties consider a thesis as research work and not a lesson in which research methodology should be taught...” (Faculty member N0.5).
Performing poorly along with ignoring professional ethics can also lead to increased tension and stress in student-teacher relationships. This can result in despondency and frustration in both students and teachers and create a vicious cycle of inefficient supervisors who will train inefficient students or future supervisors.
One of the students put it this way:
“...I feel the absence of a supervisor in my research; I would have been more successful, and my results would have been better if I had had more guidance.” (Student N0.6).
Theme 3: maturation
In this theme, the secondary phase of expertise, the individual is emotionally involved and feels that success or failure is important. This is a stage in which the learner needs an integrated schedule to be competent, and as a result, success or failure will follow. The supervisors frequently think about personal promotion and takes action in this way. They try out different approaches, and sometimes due to disappointment and embarrassment they fail. Some individuals quit at this stage and never reach competence, or they have what may be called an artificial competence. And this does not mean that they are not considered to be well-known supervisors; rather, they know, as do the students, that they are not competent. At this stage, the supervisor attempts to acquire the identity of a researcher and tries to enhance his availability, and be dutiful, knowledgeable, and enthusiastic in research supervision. Along the lines of this theme, three sub-themes of Reflection in action, Reflection on action, and Interactive accountability emerged.
Reflection in action
In this sub-theme, the patterns of expertise development begin, and self-directed learning, participatory teaching and learning strategies through a hidden curriculum are considered. At this stage, the supervisor tries to follow self-directed learning, and the amount of time allocated to expertise acquirement seems to be one of the most important factors. In this regard, one stated:
“…My success in this case (research supervision) is, first of all, due to self-evaluation and self-effort. For instance, to be in control and take full responsibility, I think about everything related to the guidance of the students, and I felt the need to master every aspect of research, even the statistical skills needed for analysis…” (Faculty member N0.8).
The supervisors’ activities were divided into two groups: self-directed –learning strategy and gaining experience through individual effort. Expertise requires continuous interaction and experience. They evaluate their learning, and by this, they experience the manner of managing and allocating time for effective supervision. According to participants, the amount of time allocation for expertise seems to be one of the most important factors for self-directed learning and expertise acquirement.
The formal training workshops provided an opportunity for supervisors with similar terms and the same problems in terms of learning experiences, environmental features, students, and educational problems to come together in one place. Participants also considered the formal participatory teaching necessary since it can provide an opportunity for the peers to get together and exchange their experiences. As a clinical faculty member put it:
“…Collaborative strategies can be beneficial in many ways. One of them is the facilitation of experience exchanges amongst teachers, peers, and colleagues and modeling the behavior of teachers and teaching workshops that emphasize the importance of their expertise in research supervision…” (Faculty member N0.1).
In our participants’ experience, this self-directed learning is effective if, and only if, it is done accompanied by proper training and participatory teaching. Otherwise, it is a waste of time. As an example, one of the students in this field said:
“…my supervisor was a great teacher and put in a lot of time and effort on my thesis supervision; however, due to his lack of research skills, I had to change my thesis proposal three times. However, after he participated in a training course at the University of Oxford, his progress was unbelievable and impressive…and I saw his expertise…” (Student N0.11).
One of the faculty members also quoted:
“…When the teachers feel a gap in their knowledge or skill, the university must provide a comfortable, appropriate, and easy way for learning them …” (Faculty member N0.10).
Regarding this subject, one of the Managers in this field stated:
“…Another improvement strategy is the use of interpersonal interactions among faculty members, these instructive interpersonal interactions among the faculty members in similar conditions make it possible to benefit from peers’ feedback …” (Manager N0.1).
A hidden curriculum strategy, like learning through trial and error can also affect the expertise process. One of the professors expressed:
“… Learning through trial and error is very effective; through the supervision of each thesis, we learn some of our mistakes and try not to remake them in the next one …” (Faculty member N0.3).
The professors do not always consider the lack of expertise to be the only cause of poor performance. Many believe that inadequate monitoring can also reduce the motivation for quality performance. This means that supervisors may obtain the necessary expertise, but they are not motivated to enhance their performance since they are not expected to do this. One student’s experience:
Reflection on action
The learner provides an integrated schedule for their competence and uses all the facilitators and facilities around them for further efficiency and promotion. This stage is named Conditional Self-efficacy by expertise experience. At this stage, the supervisor is considered a competent individual who can guide the students based on the experiences of specialized and non-specialized faculty members.
In this regard, one of the students said:
“…I can acknowledge that my supervisor functioned very impressively in this thesis, but guidance and supervision are not static; rather, it is an active process. To be a good supervisor, the faculty members should try to keep up to date and revise their attitudes, duties, and their specialty and knowledge. …” (Student N0.3).
According to the participants, at this stage the supervisors have achieved meta-competence and general characteristics or professional value; are able to guide the students and others; and develop characteristics such as acquiring specific knowledge of the discipline, especially well-organized knowledge, planning, directing of a project effectively, having good interpersonal skills, and being dutiful, knowledgeable and enthusiastic in research.
One of the PhD students states: “… My supervisor is typical of an expert. His ingenious inquiries, extraordinary attention to science and his personality have always been admired and he has been a role model for me…” (Student N0.6).
For example, the supervisors attend educational programs on scientific writing and thesis evaluation as well as ethics in research and apply them in team work. Gradually, their competency can enable them to function as a good supervisor for their students. At this stage, the supervisor develops so that they can respond due to discovery and intuition. These responses replace their dubious and unskilled reactions. The supervisor now reflects various stages of supervision and guidance. They take action, and in fact, a part of their reactions are achieved through observation and recognition. In this stage, they not only recognize what should be done but also distinguish how to achieve it with more precise discretion. A competent person does the appropriate task in the most appropriate time using the right platform.
The time period required for training or acquiring expertise varies from one person to another. Some individuals become experts very soon, whilst it takes others longer.. As one of the professors said:
“…In the beginning, I was too concerned with my responsibility as a thesis supervisor and was not sure what I should do. However, after ten years of experience, I have gained a sense of awareness which makes supervision easier for me. Of course, up to date knowledge and skill as to managing a thesis are always necessary. It took me about 12 years to reach where I am today. Furthermore, an individual who is expert at present, will not be so in two years, so I want to say that the expertise in thesis supervision in a continuum, which depends on the supervisor’s reflections on work and activity …” (Faculty member N0.15).
The continuous path of expertise in supervision can be affected by various factors. This has resulted in a range of expertise and performance in supervisors. This range and continuum is a theme that most of our participants agreed with. One of the managers revealed:
“…There is surely a continuum of expertise. We cannot deny the expert supervisors; however, the existence of those with poor supervising skills must also be acknowledged (in thesis supervision). There are those on whose ethics, honesty, and knowledge we can rely on. On the other hand, there are a few who are not as trustworthy as needed.” (Manager N0.1).
The core variable: interactive accountability
As shown in Fig. 1 , through this survey, we found that the core variable in thesis supervision process is the interactive accountability shaped by interactions of supervisors and students in an academic setting, so to enhance the accountability, each group must take responsibility and do his or her job. In this regard, one of the managers claimed:
“…When supervisors find themselves responsible, and the university officials recognize this responsibility, the supervisors are motivated to seek expertise and try to enhance their competencies and acquire learning strategies because of being accountable…” (Manager N0.2)
This means that teachers must be responsive to the needs of students, university and community. Accountability is a mutual interaction between the students and their supervisor, in other words, if the student is responsive to his duties, he creates motivation in his supervisor. One of the participants commented;
“…I've always tried to be a competent thesis supervisor, so that I have the ability to meet the needs of the community and university as well as students. I say to myself when I accept the supervision of a thesis, I should be well accountable for its results…” (Faculty member N0.32)
This study aimed at exploring the processes of expertise among thesis supervisors based on the experience of faculty members, students, and managers of Iranian universities of medical sciences. The section concludes with an explanation of how these themes are a cohesive relationship, which enables the expertise development of supervisors. It seems that the core variable in the expertise process is the concept of interactive accountability and efforts to acquire the capacity to respond to the students and academic needs. This will help them to promote their professional behavior in research supervision. The importance of accountability and various types of ability in thesis supervision has also been emphasized by other studies [ 24 , 25 , 26 ]. It was also mentioned as the major feature of the supervisor in other studies [ 26 , 27 ].
In this study, “accountability” emerged as the behavioral pattern through which the supervisors resolved their main concern of being an expert in being responsive to academic and students’ needs. Supervision training is complex since academic choices in the real world can depend on supervisor characteristics. The results of this study revealed that in the initial phase of supervision, observation, evaluation, and reflection in action and maturation stage in the secondary phase were the major themes that emerged. This result compared with Bandura’s social learning and self-efficacy theory was significant in similarity and difference. Bandura believes that achieving self-efficacy is one of the most important contributors to competence. In his model, he suggested four sources of self-efficacy, including previous accomplishments, vicarious experiences such as having a role model, verbal persuasion such as coaching and evaluative feedback, and emotional arousal [ 28 , 29 ]. Likewise, in this study, we found that the emotional arousals such as personal interest in cooperative learning, peer competition, meeting the needs of students, self-awareness and the need for upgrading are the significant factors for the faculties’ expertise. Also, our participants found that the utilization of previous experiences is the most effective method of achieving personal competence. However, this study indicates conditional expertise, which means if an expert’s information is not up to date and they do not make any effort in this regard, being an expert and having expertise is not a permanent condition.
This study also revealed that self-effort, workshops, and role models, as part of a hidden curriculum, are influential methods of teacher empowerment which agrees with the results of some studies such as those of Britzman et al. and Patel et al. Patel et al. have also suggested the importance of role modeling; they believe that modeling and observing other faculty members behavior is an effective tool for promoting and strengthening the sense of efficacy in learners [ 30 , 31 ].
Based on our study results, among the learning methods used in Iran, the collaborative education and problem-based learning is the widely accepted method which is preferred by most faculties. Therefore, cooperative and collaborative learning strategies can be used in educating the faculty members towards expertise in supervision, as revealed in other studies [ 32 , 33 ].
Lack of time is reported by supervisors to be one of the most common barriers in trying to become an expert and carry out respectable worthy supervision, and taking one’s time is acknowledged as a motivating factor for putting in more effort in thesis supervision [ 34 , 35 , 36 ].
The effect of contextual factors is studied in several surveys [ 36 , 37 , 38 ]. Gillet et al. state that contextual and organizational factors play a key role in the competence of teachers in research supervision [ 36 ]. This study also showed that faculty expertise in thesis supervision was significantly affected by the impact of contextual interventional factors such as sudden changes, structural shortcomings, and educational environment. Based on our and other studies’ results, among the sudden changes, increased workload due to the increase in the student population has greatly affected expertise. Moreover, while an increase in the workload can lead to more experienced faculty members, it is very time-consuming and, therefore, reduces the chance to obtain new information and skills in thesis supervision [ 33 , 37 ].
Similar to our study, other studies such as those of Al-Naggar et al. and Yousefi et al. have also found insufficient monitoring and lack of formative evaluations to be one of the main obstacles in the thesis supervision process. Studies have indicated that to improve the supervision process, careful planning and incentive rules must be applied [ 5 , 34 ]. Similarly, our participants mentioned that rules and regulations which have resulted in the positive effect of research on scholarship and promotion had truly motivated them. Like our study, other studies in Iran have also found that the amount of time allocated to learning is one of the influential factors affecting the faculty members’ expertise [ 13 , 38 ]. A malfunctioning relationship between the student and supervisors can affect both of them negatively; that is, it can compel the students to misbehave and also reduce the teachers’ motivation to develop better skills. This malfunction may be due to the lack of constructive interactions or paternalism leadership in research supervision [ 39 , 40 ]. As shown in Fig. 1 , this study provided a conceptual framework that can be used in policy making and studies of expertise development in research supervision. This framework is based on the perception and experience of the majority of those involved in the thesis process. It also provides teachers with an opportunity to compare and share their experiences.
This model has three fields of experience, which yields a comprehensive gradient of the factors used for the development and progress of thesis supervision quality. In other words, it is a rational structure that makes an effort to cover a comprehensible number of stages, of concept, achievement, and impact or consequence. In other words, this model is a combination of a great number of items that help to recognize the present and future processes of expertise in thesis supervision, and future challenges in this area which predict results and impacts of supervisor’s knowledge, attitude and research supervision. Table one offers the categories and clarifications [ 17 ].
This study is based on our overall model of expertise attainment. This model reveals that specific personal efforts such as observation of prior knowledge, evaluation or self-assessments alongside the university contextual dynamics help to figure out how supervisors select their approaches and engagements, and respond carefully to their task, which in turn impacts the supervisors’ level of expertise and, finally, outcomes such as work and perseverance, which then help them to become an expert. Similar to the social learning theory of Bandura, this model also states that there is a mutual relationship between different parts that can mutually affect one another. For instance, faculty members have shown in various studies how one’s previous academic success and failure can affect the future levels of involvement and motivation. Based on the study aims, we focused on only three of the components of the model: observation, evaluation, and self-efficacy; in terms of motivational processes, we focused on four motivational components. The first is self-efficacy, defined as students’ judgments of supervisor abilities to carry out a task, and their beliefs about their ability to do so show the highest levels of academic achievement and also engagement in academic behaviors promoting learning.
Through the use of this grounded theory, we can begin to understand the supervisors’ challenges and why it may be difficult to become an expert in research supervision in practice. The junior supervisors curiously observe and evaluate their environment by reflection and in action and do their best to attain knowledge and skills in the supervision of the theses, so that they can reach maturation. They are mainly supported by prior knowledge of the research supervision, which they had acquired when they were students. The concept of “interactive accountability” refers to the fact that if the supervisor is responsive to the students’ needs, they can be an expert in supervision. If they cannot overcome the barriers and shortcomings such as lack of time, they will not attain expertise in thesis supervision.
Strengths and limitations of the study
This grounded theory study describes the main dimensions of expertise in research supervision from straight reports of a large qualitative sample ( n = 84) which consists of thesis supervisors, from all Iranian universities in three different data collection phases. Like other qualitative research, the results of this study cannot be generalized; therefore, it is recommended that the researchers conduct further qualitative research in other contexts to support these findings.
Despite the above limitations, we believe that this model can be useful for supervisors in the thesis supervision area, not only in analyzing the supervisors’ experience of supervision and being an expert but also in recognizing the areas of intervention or development of teacher training.
Implications of the study
The findings of the present study will help administrators to choose the supervisor with definite criteria in medical sciences institutes and facilitate the expertise in the supervision process through elimination of the shortcomings and improvement of the educational climate. The supervisor’s interest, talent, and capabilities should be assessed at the beginning of their employment as academic staff. Supervisors should attend educational workshops for updating their knowledge about supervision. It is recommended that collaborative strategies and methods should be used, so that we can contribute to the process of becoming an expert. The assessment of supervisors’ functioning in supervising and provision of feedback can contribute to the process of expertise. Feedback received from students about their supervisors will improve the supervisor’s further expertise and capabilities. For future studies survey on the impact of successful models in thesis supervision, disclosure analysis studies about student and supervisor are recommended.
In this study, we aimed to find out how thesis supervisors achieve expertise in supervision. The results of our study indicated that thesis supervisors achieve expertise in supervision in two stages of engagement and maturation. The emotional need to be responsive towards peers and students is the main motivation for the acquisition of competency at observation and evaluation phase of engagement. Through the evaluation and observation phase, the supervisors reach cognitive competence, such as research skills. Also, in the maturation phases, they reach meta-competence in research supervision such as problem-solving and resolving dilemmas by reflection in and when exposed to dilemmas. Meanwhile, the effects of supervision climate include shortcomings and role ambiguities which should be taken into account. According to this model, when supervisors are exposed to such problems, they apply multiple strategies, such as self-directed and collaborative learning; and learning by trial and error and from the role models. This will help them to promote their professional behavior in research supervision. This study indicated that interactive accountability, as the core variable, can be guaranteed in thesis supervisors by making the role clear, creating a supportive context, and improving the academic competencies of staff in an ongoing fashion. Therefore, this can promote constructive expertise in supervisors and foster a deeper understanding of the supervisor’s expertise in thesis supervision.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets produced and analyzed during the present study are not publicly accessible due to participant confidentiality, but are obtainable from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Harwood N, Petrić B. Adaptive master’s dissertation supervision: a longitudinal case study. Teach High Educ. 2018; https://doi.org/10.1080/13562517.2018.1541881 .
Hal de Kleijn RA, Meijer PC, Brekelmans M, Pilot A. Adaptive research supervision: exploring expert thesis supervisors’ practical knowledge. High Educ Res Dev. 2015;34(1):117–30.
Article Google Scholar
Pearson M, Brew A. Research training and supervision development. Stud High Educ. 2002;27(2):135–50.
Light, G, Cox R, Calkins S. Learning and teaching in higher education: the reflective professional. 2nd ed. London: Paul Chapman; 2009.
Youseffi A, Bazrafkan L, Yamani N. A qualitative inquiry into the challenges and complexities of research supervision: viewpoints of postgraduate students and faculty members. J Adv Med Educ Prof. 2015;3(3):91.
Google Scholar
Lee AM. Developing effective supervisors: concepts of research supervision. South Afr J High Educ. 2007;21(4):680–93.
Hall-Ellis SD, Grealy DS. The Dreyfus model of skill acquisition: a career development framework for succession planning and management in academic libraries. Coll Res Libr. 2013;74(6):587–603.
Wisker G. The good supervisor: Supervising postgraduate and undergraduate research for doctoral theses and dissertations. 2nd ed. Palgrave Macmillan; 2012.
Vereijken MW, van der Rijst RM, van Driel JH, Dekker FW. Novice supervisors’ practices and dilemmatic space in supervision of student research projects. Teach High Educ. 2018;23(4):522–42.
Haghdoost AA, Ghazi M, Rafiee Z, Afshari M. The trend of governmental support from post-graduated Iranian students in medical fields to study abroad. Iran J Public Health. 2013;42(Suppl 1):141–6.
Malekzadeh R, Mokri A, & , Azarmina P. Medical science and research in Iran. Arch Iran Med (2001)4(1):27–39.
Samari A, Sorkhabi E, Omran S, Geraeenejed. Research and identify the factors contributing to the process of “academic development”. Iran Univ Stud Educ Plann. 2014;2(4):67–100.
Malekafzali H, Majdzadeh S, Fotouhi A, Tavakoli S. Applied research methodology in medical sciences. Tehran: Tehran University of Medical Sciences; 2004.
Creswell JW. Qualitative inquiry and research design: choosing among five approaches. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publication; 2012.
Strauss AJC. Basic of qualitative research: techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. London: Sage Co; 1998.
Jeon Y-H. The application of grounded theory and symbolic interactionism. Scand J Caring Sci. 2004;18(3):249–56.
Denzin NK. The research act: A theoretical introduction to sociological methods. 2nd edition. Routledge: Taylor and Francis group; 2017.
Book Google Scholar
Dilley P. Interviews and the philosophy of qualitative research. J High Educ. 2004;75(1):127–32.
Strauss AJC. Basic of qualitative research: techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. London: Sage Co; 2008.
Cho JY, Lee E-H. Reducing confusion about grounded theory and qualitative content analysis: similarities and differences. Qual Rep. 2014;19(32):1–20.
Gioia DACK, Hamilton AL. Seeking qualitative rigor in inductive research notes on the Gioia methodology. Organ Res Methods. 2013;16(1):15–31.
Skeith L, Ridinger H, Srinivasan S, Givi B, Youssef N, Harris I. Exploring the thesis experience of master of health professions education graduates: a qualitative study. Int J Med Educ. 2018;9:113.
Yeatman A. Making supervision relationships accountable: graduate student logs. Aust Univ Rev. 1995;38(2):9–11.
Saaban A, Abu B, Jiar YK. Students and supervisors’ roles and responsibilities in doctoral research supervision. Adv Sci Lett. 2018;24(1):66–8.
Carter S, Laurs D, Chant L, Wolfgramm-Foliaki E. Indigenous knowledges and supervision: changing the lens. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2018;55(3):384–93.
Boston P. The three faces of supervision: Individual learning, group learning, and supervisor accountability. In C. Burck and G. Daniel (2010) (Eds.) Mirrors and Reflections Processes of Systemic Supervision. Routledge, Taylor, and Francis; 2010:27–48.
Chapter Google Scholar
Manathunga C. The development of research supervision: “turning the light on a private space”. Int J Acad Dev. 2005;10(1):17–30.
Bandura A. On the functional properties of perceived self-efficacy revisited. J Manag. 2012;38(1):9–44.
Bandura A. On deconstructing commentaries regarding alternative theories of self-regulation. J Manag. 2015;41(4):1025–44.
Britzman DP. Practice makes practice: A critical study of learning to teach. -State University of New York Press; 2003.
Patel M, Reed D, Smith C, Arora V. Role-modeling cost-conscious care—a national evaluation of perceptions of faculty at teaching hospitals in the United States. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30(9):1294–8.
Howard M, Steensma HK, Lyles M, Dhanaraj C. Learning to collaborate through collaboration: how allying with expert firms influences collaborative innovation within novice firms. Strateg Manag J. 2015:n/a.
Steinert Y. Faculty development: core concepts and principles. Steinert Y, editor. Faculty development in the health professions. Innovation and change in professional education. 11: Springer Netherlands; 2014. 3–25.
Al-Naggar R, et al. Doctorate international students’ satisfaction and stress on academic supervision in a Malaysian University: a qualitative approach. Educ Res. 2012;3(3):264–9.
Gillet N, Gagné M, Sauvagère S, Fouquereau E. The role of supervisor autonomy support, organizational support, and autonomous and controlled motivation in predicting employees’ satisfaction and turnover intentions. Eur J Work Organ Psy. 2012;22(4):450–60.
Harden RM. AMEE guide no. 14: outcome-based education: part 1-an introduction to outcome-based education. Med Teach. 1999;21(1):7–14.
Bazrafkan L, Shokrpour N, Yousefi A, Yamani N. Management of stress and anxiety among phd students during thesis writing: a qualitative study. Health Care Manag. 2016;35(3):231–40.
Ghadirian L, Sayarifard A, Majdzadeh R, Rajabi F, Yunesian M. Challenges for better thesis supervision. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2014;28:32.
Vehviläinen S, Löfström E. ‘I wish I had a crystal ball’: discourses and potentials for developing academic supervising. Stud High Educ. 2016;41(3):508–24.
Grossman ES. ‘My supervisor is so busy...’ informal spaces for postgraduate learning in the health sciences. South Afr J High Educ. 2016;30(2):94–109.
Download references
Acknowledgments
The researchers would like to thank all research participants of Medical Sciences Universities (faculty, student, and managers) who contributed to the study. The authors would also like to thank the Education Development Center of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences for cooperation in this study and special thanks to Professor Shokrpoour for her editing.
The present article was extracted from the thesis written by Leila Bazrafkan. The design and implementation of the project was financially supported by Esfahan University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 92–6746).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Clinical Education Research Center, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran
Leila Bazrafkan & Mitra Amini
Department of Medical Education, Medical Education Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
Alireza Yousefy & Nikoo Yamani
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LB developed the study design, conducted the interviews and analysis, ensured trustworthiness, and drafted the manuscript. AY, as the supervisor participated in the study design, supervised the codes and data analysis process, and revised the manuscripts. NY as research advisor participated in the study and provided guidance during the study and MA revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
LB is an assistant professor of medical education in Medical Education Research Center, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences,
AY is Professor of Medical Education Dept., Medical Education Research Center, University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan
MA is Professor of Medical Education in the Medical Education Research Center, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences,
NY Associate Professor of Medical Education Dept., Medical Education Research Center, University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nikoo Yamani .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (92–6746). The participants were justified about the research aim and interviews. Informed consent for conducting and recording the interview was obtained. The confidentiality of the participants’ information was maintained throughout the study.
Consent for publication
Participants gave printed informed consent for the use of passages for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Bazrafkan, L., Yousefy, A., Amini, M. et al. The journey of thesis supervisors from novice to expert: a grounded theory study. BMC Med Educ 19 , 320 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1739-z
Download citation
Received : 07 February 2019
Accepted : 29 July 2019
Published : 22 August 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1739-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Medical sciences faculty
- Grounded theory
- Thesis supervision
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

- Get in touch
Supervising Thesis Students: How Does LLInC Help?

“Attending the UTQ module ‘Supervising Thesis Students’ enabled me…to apply supervising skills, use my time in an efficient way and give constructive feedback … I learned when to use different kind of supervisor roles and I became aware of the importance of guiding the student throughout the process… I would like to keep myself updated on this matter. A refresher would be nice ” – UTQ module participant
Supervising students, whether for a thesis or in another project setting, requires lots of skills and time – investment. For this reason, it’s important to be aware of the type of supervisor you are or want to be, as well as ways to help the student grow.
To learn (more) about the skill of supervising , teachers can enrol themselves to participate in one of the five so called UTQ (University Teacher Qualification) modules provided by LLInC .
Since, a t LLInC , we continuously try to innovate and improve our products, when a faculty approached us to develop an accessible module which would enable teachers to refresh their supervising skills, we jumped at the opportunity.
This blog is about supervising students and our newly-created e-learning module, helping you to become the best supervisor you can be!

Looking back – What is the module ‘Supervising Thesis Students’ about?
Supervising Thesis Students is a UTQ module consisting of two meetings. During the first meeting, the role of a supervisor is discussed. We look at some of the challenges, how to set boundaries, and how to give constructive feedback.
During the second meeting, we practice scenarios in which different conversational techniques can be used to discover the causes of student and supervisor miscommunications . We also discuss one or more personal experiences of supervising, analysing what possible next steps could be.
Reflecting – How can we continuously help teachers in their supervising roles?
Although supervisors receive lots of information and insights within these two meetings, they cannot be expected to remember every tip and trick for the rest of their careers. S ince not everyone is constantly supervising students, teachers need to be offered the opportunity to update their supervising skills. This is where we once again come into play!
Moving forward – Time to create an e-learning module!
We knew that having teachers redo the UTQ module was not a viable option. Consequently, we decided it was time to create an e-learning module which could be made accessible to all teachers across Leiden University, helping them refresh their knowledge about supervising students.
Luckily, our intern Érica was there to help us! Based on the information we provided her, she was able to distil the most important parts of the module ‘Supervising Thesis Students’, adapting these into an interactive and inspiring e-learning module able to be followed at any time.
But don’t take our word for it – have a look yourself at the English or Dutch version!
Published: 21 March 2024
Related stories
Home About Stories Events Team Get in touch
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 23 July 2021
The lessons I learnt supervising master’s students for the first time
- Emilio Dorigatti 0
Emilio Dorigatti is a PhD student in data science and bioinformatics at the Munich School for Data Science in Germany, working on new ways to design vaccines for cancer.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
I started my PhD wanting to improve not only my scientific abilities, but also ‘soft skills’ such as communication, mentoring and project management. To this end, I joined as many social academic activities as I could find, including journal clubs, seminars, teaching assistance, hackathons, presentations and collaborations.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-02028-1
This is an article from the Nature Careers Community, a place for Nature readers to share their professional experiences and advice. Guest posts are encouraged .
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Related Articles

- Research management

Breaking ice, and helicopter drops: winning photos of working scientists
Career Feature 23 APR 24

Londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs
Career News 18 APR 24
Deadly diseases and inflatable suits: how I found my niche in virology research
Spotlight 17 APR 24

Ecologists: don’t lose touch with the joy of fieldwork
World View 24 APR 24
Chemistry lab destroyed by Taiwan earthquake has physical and mental impacts
Correspondence 23 APR 24

Algorithm ranks peer reviewers by reputation — but critics warn of bias
Nature Index 25 APR 24

Researchers want a ‘nutrition label’ for academic-paper facts
Nature Index 17 APR 24

How young people benefit from Swiss apprenticeships
Postdoctoral Associate- Computational Spatial Biology
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Staff Scientist - Genetics and Genomics
Technician - senior technician in cell and molecular biology.
APPLICATION CLOSING DATE: 24.05.2024 Human Technopole (HT) is a distinguished life science research institute founded and supported by the Italian ...
Human Technopole
Postdoctoral Fellow
The Dubal Laboratory of Neuroscience and Aging at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) seeks postdoctoral fellows to investigate the ...
San Francisco, California
University of California, San Francsico
Postdoctoral Associate
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Teaching & Learning
- Education Excellence
- Professional development
- Case studies
- Teaching toolkits
- MicroCPD-UCL
- Assessment resources
- Student partnership
- Generative AI Hub
- Community Engaged Learning
- UCL Student Success

Research and project supervision (all levels): an introduction
Supervising projects, dissertations and research at UCL from undergraduate to PhD.

1 August 2019
Many academics say supervision is one of their favourite, most challenging and most fulfilling parts of their job.
Supervision can play a vital role in enabling students to fulfil their potential. Helping a student to become an independent researcher is a significant achievement – and can enhance your own teaching and research.
Supervision is also a critical element in achieving UCL’s strategic aim of integrating research and education. As a research-intensive university, we want all students, not just those working towards a PhD, to engage in research.
Successful research needs good supervision.
This guide provides guidance and recommendations on supervising students in their research. It offers general principles and tips for those new to supervision, at PhD, Master’s or undergraduate level and directs you to further support available at UCL.

What supervision means
Typically, a supervisor acts as a guide, mentor, source of information and facilitator to the student as they progress through a research project.
Every supervision will be unique. It will vary depending on the circumstances of the student, the research they plan to do, and the relationship between you and the student. You will have to deal with a range of situations using a sensitive and informed approach.
As a supervisor at UCL, you’ll help create an intellectually challenging and fulfilling learning experience for your students.
This could include helping students to:
- formulate their research project and question
- decide what methods of research to use
- become familiar with the wider research community in their chosen field
- evaluate the results of their research
- ensure their work meets the necessary standards expected by UCL
- keep to deadlines
- use feedback to enhance their work
- overcome any problems they might have
- present their work to other students, academics or interested parties
- prepare for the next steps in their career or further study.
At UCL, doctoral students always have at least two supervisors. Some faculties and departments operate a model of thesis committees, which can include people from industry, as well as UCL staff.
Rules and regulations
Phd supervision.
The supervision of doctoral students’ research is governed by regulation. This means that there are some things you must – and must not – do when supervising a PhD.
- All the essential information is found in the UCL Code of Practice for Research Degrees .
- Full regulations in the UCL Academic Manual .
All staff must complete the online course Introduction to Research Supervision at UCL before beginning doctoral supervision.
Undergraduate and Masters supervision
There are also regulations around Master’s and undergraduate dissertations and projects. Check with the Programme Lead, your Department Graduate Tutor or Departmental Administrator for the latest regulations related to student supervision.
You should attend other training around research supervision.
- Supervision training available through UCL Arena .
Doctoral (PhD) supervision: introducing your student to the university
For most doctoral students, you will often be their main point of contact at UCL and as such you are responsible for inducting them into the department and wider community.
Check that your student:
- knows their way around the department and about the facilities available to them locally (desk space, common room, support staff)
- has attended the Doctoral School induction and has received all relevant documents (including the Handbook and code of practice for graduate research degrees )
- has attended any departmental or faculty inductions and has a copy of the departmental handbook.
Make sure your student is aware of:
- key central services such as: Student Support and Wellbeing , UCL Students' Union (UCLU) and Careers
- opportunities to broaden their skills through UCL’s Doctoral Skills Development Programme
- the wider disciplinary culture, including relevant networks, websites and mailing lists.
The UCL Good Supervision Guide (for PhD supervisors)
Establishing an effective relationship
The first few meetings you have with your student are critical and can help to set the tone for the whole supervisory experience for you and your student.
An early discussion about both of your expectations is essential:
- Find out your student’s motivations for undertaking the project, their aspirations, academic background and any personal matters they feel might be relevant.
- Discuss any gaps in their preparation and consider their individual training needs.
- Be clear about who will arrange meetings, how often you’ll meet, how quickly you’ll respond when the student contacts you, what kind of feedback they’ll get, and the norms and standards expected for academic writing.
- Set agendas and coordinate any follow-up actions. Minute meetings, perhaps taking it in turns with your student.
- For PhD students, hold a meeting with your student’s other supervisor(s) to clarify your expectations, roles, frequency of meetings and approaches.
Styles of supervision
Supervisory styles are often conceptualized on a spectrum from laissez-faire to more contractual or from managerial to supportive. Every supervisor will adopt different approaches to supervision depending on their own preferences, the individual relationship and the stage the student is at in the project.
Be aware of the positive and negative aspects of different approaches and styles.
Reflect on your personal style and what has prompted this – it may be that you are adopting the style of your own supervisor, or wanting to take a certain approach because it is the way that it would work for you.
No one style fits every situation: approaches change and adapt to accommodate the student and the stage of the project.
However, to ensure a smooth and effective supervision process, it is important to align your expectations from the very beginning. Discuss expectations in an early meeting and re-visit them periodically.
Checking the student’s progress
Make sure you help your student break down the work into manageable chunks, agreeing deadlines and asking them to show you work regularly.
Give your student helpful and constructive feedback on the work they submit (see the various assessment and feedback toolkits on the Teaching & Learning Portal ).
Check they are getting the relevant ethical clearance for research and/or risk assessments.
Ask your student for evidence that they are building a wider awareness of the research field.
Encourage your student to meet other research students and read each other’s work or present to each other.
Encourage your student to write early and often.
Checking your own performance
Regularly review progress with your student and any co-supervisors. Discuss any problems you might be having, and whether you need to revise the roles and expectations you agreed at the start.
Make sure you know what students in your department are feeding back to the Student Consultative Committee or in surveys, such as the Postgraduate Research Experience Survey (PRES) .
Responsibility for the student’s research project does not rest solely on you. If you need help, talk to someone more experienced in your department. Whatever the problem is you’re having, the chances are that someone will have experienced it before and will be able to advise you.
Continuing students can often provide the most effective form of support to new students. Supervisors and departments can foster this, for example through organising mentoring, coffee mornings or writing groups.
Be aware that supervision is about helping students carry out independent research – not necessarily about preparing them for a career in academia. In fact, very few PhD students go on to be academics.
Make sure you support your student’s personal and professional development, whatever direction this might take.
Every research supervision can be different – and equally rewarding.
Where to find help and support
Research supervision web pages from the UCL Arena Centre, including details of the compulsory Research Supervision online course.
Appropriate Forms of Supervision Guide from the UCL Academic Manual
the PhD diaries
Good Supervision videos (Requires UCL login)
The UCL Doctoral School
Handbook and code of practice for graduate research degrees
Doctoral Skills Development programme
Student skills support (including academic writing)
Student Support and Wellbeing
UCL Students' Union (UCLU)
UCL Careers
External resources
Vitae: supervising a docorate
UK Council for Graduate Education
Higher Education Academy – supervising international students (pdf)
Becoming a Successful Early Career Researcher , Adrian Eley, Jerry Wellington, Stephanie Pitts and Catherine Biggs (Routledge, 2012) - book available on Amazon
This guide has been produced by the UCL Arena Centre for Research-based Education . You are welcome to use this guide if you are from another educational facility, but you must credit the UCL Arena Centre.
Further information
More teaching toolkits - back to the toolkits menu
Research supervision at UCL
UCL Education Strategy 2016–21
Connected Curriculum: a framework for research-based education
The Laidlaw research and leadership programme (for undergraduates)
[email protected] : contact the UCL Arena Centre
Download a printable copy of this guide
Case studies : browse related stories from UCL staff and students.
Sign up to the monthly UCL education e-newsletter to get the latest teaching news, events & resources.
Education events
Funnelback feed: https://search2.ucl.ac.uk/s/search.json?collection=drupal-teaching-learn... Double click the feed URL above to edit
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Enrichment Programs
Individualized & Interdisciplinary Studies Program
Guide for thesis supervisors.
Thank you for supervising an individualized major senior thesis project. Your expertise is critical in guiding the student’s project and setting the criteria for its evaluation. The guidelines below outline some considerations particular to individualized major students. They are most appropriate for traditional research projects but may also be relevant to less traditional final projects.
All individualized majors complete a capstone, which provides them an opportunity to integrate knowledge they have acquired during the course of their majors. About 40-45 percent of individualized majors do so by completing a thesis. (The rest complete our capstone course or an approved alternative.)
Thesis projects usually take the form of a traditional research study, but other formats, such as a photo essay, film, website, or piece of creative writing are also possible. Thesis projects, whatever their form, should contribute to the development of knowledge or practice in new ways, involve significant background research, and require sustained attention in the implementation of the project. If the final product takes a less traditional form, it should include a piece of writing that describes the student’s learning process.
Thesis Courses
Some thesis projects will comprise six credits completed over the course of two semesters. This is mandatory for students completing Honors Scholar requirements in their individualized major. Non-honors students may complete a one-semester, three-credit thesis project. Students intending to complete a thesis project must submit a thesis proposal which they have discussed with their thesis supervisor no later than the last day of classes of the semester before they begin their thesis.
In the social sciences and humanities : In the Fall semester of the senior year, students will typically begin their research by enrolling in a thesis-related research seminar, graduate course, or independent study in their thesis supervisor’s department. During the Spring semester, students will enroll in UNIV 4697W Senior Thesis (for which the thesis supervisor serves as instructor) in which they will complete the research and write the thesis. During this process, the student meets regularly with the thesis supervisor for feedback on data collection, evidence gathering, analysis, and writing.
In the sciences , students may follow a more extended sequence, perhaps two to three semesters of data collection and laboratory work (independent studies or research courses) followed by thesis writing (UNIV 4697W) in the final semester.
Learning Outcomes
Individual faculty will differ in expectations regarding research methodology, theoretical approaches, and presentation of findings. Nonetheless, there are some general criteria and intended learning outcomes for all individualized major thesis projects.
- The student’s research, analysis, and writing on the thesis project should be relevant to their individualized major and represent an opportunity for them to integrate and deepen at least several aspects of study in the major.
- A thesis should do more than summarize the existing literature on a particular topic. It should make an original contribution to the field of study, present new findings in the form of new data, or new, critical interpretations of existing material. It should reflect a good command of the research methodologies in the relevant discipline(s).
Upon completion of the thesis project the student should be able to:
- Define a research question and design a substantial research project.
- Select a methodological approach to address the research question.
- Identify appropriate sources and collect relevant and reliable data that addresses the research question.
- Analyze the strengths and limitations of different scholarly approaches to the question, and recognize the resulting interpretative conflicts.
- Develop an argument that is sustained by the available evidence
- Present that argument in a clear, well-organized manner.
Requirements for Honors Students
As noted above, all Honors students are expected to complete at least six credits of thesis-relevant coursework. In addition, all Honors students are expected to have a second reader and make a public presentation of their thesis project.
Second Reader
We ask Honors students to identify a second reader for their thesis from a relevant discipline, which may be the same as, or different from, the supervisor’s discipline. The second reader will provide the student with a different perspective and may provide additional insights on how to achieve the intended learning outcomes of the thesis. The thesis supervisor, in consultation with the student, determines when to bring the second reader on board. It is the supervisor’s prerogative to define how the grade for the thesis will be determined.
Public Presentation
Honors students are required to make a public presentation of their thesis research in a format negotiated with the thesis supervisor. Where possible, the audience should include the thesis supervisor, the second reader, and an IISP staff member. Other faculty members and the student’s peers may be invited to join the audience, as well.
Existing departmental exhibitions or “Frontiers in Undergraduate Research” make excellent venues for student presentations. If a student cannot find a venue for his or her presentation, please consult with IISP and we will coordinate one.
Note: Although non-Honors students who are completing a thesis are not required to have a second reader or make a public presentation, we would certainly welcome them to do so.
Honors Advising
An IISP staff member serves as Honors Advisor to each individualized major following an Honors Scholar plan of study. The staff member’s role as an Honors advisor is to coordinate and facilitate students’ plans for completing Honors Scholar requirements, including the thesis, and to monitor progress toward completion.
Thesis Course Registration
Specific instructions for registering for UNIV 4697W are available on the Capstone page .
We very much appreciate your willingness to supervise an individualized major’s senior thesis. If you have any questions about the Individualized Major Program or about supervising an individualized major thesis, please contact IISP staff .

Thesis supervision
Find a thesis supervisor.
Thesis supervisors must be authorized by their Faculty to supervise theses.
Finding a thesis supervisor arrow_drop_down
Before thinking about a supervisor, students should make sure they are committing to the area of study that most interests them. They should ask themselves whether they are enthusiastic enough about a topic area to sustain this enthusiasm over the period of time it will take to prepare the thesis. Speaking to students and professors who do research in the proposed area of study will help clarify the students’ thoughts. The students should make sure they are well-informed before they approach any potential supervisors.
A professor is not obligated to take on a student if he or she feels the match-up would not be a good one, or if the professor lacks lab space, time or funding.
A student may have more than one supervisor. When mention is made of the thesis supervisor, it is implicit that there may be a co-supervisor.
- Information to collect before contacting a potential supervisor
- Questions to ask after the meeting with the potential supervisor
- Professors, by research interest
Appointment of a thesis supervisor arrow_drop_down
From the uoZone Application tab, click Service Requests to create a service request and appoint a thesis supervisor.
Meetings between the supervisor and the student arrow_drop_down
Preliminary meetings.
Before a student begins researching and writing a thesis, the supervisor and the student should have a detailed discussion of expectations and requirements. Below are examples of general and specific issues to be discussed during the preliminary meetings.
As soon as possible, the student should obtain ethics approvals or any other required approvals to conduct research. The student should discuss with the thesis supervisor and visit the Office of Research Ethics and Integrity Website.
- General and specific topics to be discussed
Regular meetings
The student and the supervisor should plan to meet regularly whether or not the student has any finished work to show to the supervisor.
If it is a major meeting, the student should draw up and deliver to the supervisor an agenda beforehand. If the meeting is to discuss text that has already been written, the student must send the draft well in advance of the meeting.
After the meeting, and based on this agenda, the student prepares a brief report on what was discussed and decided, and shares this report with the supervisor.
It is important to be productive at these major meetings, but it is also crucial to just keep in touch.
Components of a typical agenda
- a summary of the purpose of the meeting
- a review of what was discussed at the previous meeting and what has been accomplished to date
- a discussion and clarification of the current topics, ideas and issues
- next steps as a result of this discussion
- agree with a date for the next meeting
Feedback and revision arrow_drop_down
All along during the thesis preparation process, a student will receive feedback and should expect to do revisions. Revising a thesis based on feedback from the thesis supervisor, advisory committee (if applicable) and from the jury is an important part of the thesis preparation process.
Part of the advancement of knowledge that preparing a thesis fosters involves engaging in dialogue and learning from these discussions, learning how to communicate clearly, and responding appropriately to suggestions for improvement

Already a student?
Types of supervision, co-supervision arrow_drop_down.
A joint management with a professor in another discipline may be considered if the research project of a student is favoured.
Cotutelle arrow_drop_down
A doctoral student may prepare a thesis under a cotutelle agreement. You find below additional information to help familiarize yourself with the roles played by each of the stakeholders.
Learn more about Cotutelle.
Thesis advisory committee arrow_drop_down
In many academic units, a thesis advisory committee, also referred to as thesis committee, is assembled as soon as a student finds a thesis supervisor. Please note that not all academic units have thesis committees, the students must check on the protocol in their own academic unit.
Constitution of the thesis committee
How the thesis committee is formed varies from academic unit to academic unit. The thesis supervisor plays the biggest role by approaching colleagues who have the expertise and inviting them to join the committee.
A thesis committee is made up of:
- the student
- the thesis supervisor, and
- usually at least two other professors.
The thesis supervisor is usually the chair of the thesis committee.
Role of the thesis committee
While the roles and responsibilities of thesis committees may vary from one academic unit to another, members of the committee should provide guidance to the student on thesis planning, research and writing; be available to discuss ideas or for consultation on any other matter related to the thesis; and, if this is the practice within the discipline, evaluate the thesis after submission.
Thesis committees meet according to a schedule set either by the academic unit or by the committee itself. The student is usually responsible for initiating the meetings. When concerns about the progress of the research arise, the supervisor and/or academic unit may require meetings at more frequent intervals.
Useful information
Contracts arrow_drop_down.
Some supervisors and students have contracts or agreements to formalize the expectations and delineate the responsibilities in the preparation of a thesis.
Although these agreements are not considered official documents with force of law, they set out the expectations of the student and supervisor in relation to many of the issues covered in this Website section and help avoid conflict and misunderstandings.
A student should not make assumptions about who will do what in the research and who gets credit for any new discoveries or inventions. A supervisor should not assume the supervised student is aware of any assumptions the supervisor has or any authorship or credit protocols that may exist in the area of research.
Professors who use contracts do so because they have found such agreements are a good tool for helping students achieve their goals and finish their theses. However, while a written agreement can be very useful, one of the keys to a successful supervisor–student relationship is good communication and mutual trust. Both sides need to foster and build on that.
Absences arrow_drop_down
Sometimes a potential supervisor is approached by a student looking for a thesis supervisor and both the student and professor agree it would be a good match, but the professor is going on an academic leave partway through the period in which the student will be preparing this thesis. In the event of a scheduled absence from the University for more than one month, the thesis supervisor must make the necessary arrangements with his students and the academic unit concerned to ensure that students continue to be accompanied during the supervisor's absence.
A thesis supervisor who is going to be away should let the student know well in advance. The same goes for the student. The student should discuss this with the thesis supervisor well ahead of time. In case of illness, the student should let the supervisor know the expected timeline for recovery.
If the student is planning to suspend work on the thesis for a term or more, for whatever reason, the student needs to apply for and receive approval for a leave of absence. Please note that absence has an impact on eligibility for funding.
Form - Request for leave of absence (PDF)
Professionalism arrow_drop_down
As a student, the development of professional skills—for example, communicating appropriately in writing and in person, responding promptly to e-mails, coming prepared to meetings, following up after meetings, respecting deadlines, tracking changes to the text so that it is easy for the supervisor to review each draft after revisions—is important in the preparation of the thesis. Some faculties offer courses in professional skills.
If the student feels aspects of the supervisor’s behavior are unprofessional, he or she should consult the graduate program director or the chair of the academic unit.
Changing supervisors arrow_drop_down
As for changing supervisors partway through a thesis, this is not recommended. Keep in mind that as long as the thesis is logical and the conclusions drawn from the data are valid, the student and the supervisor do not need to be in total agreement on methodology, analysis or interpretation.
The thesis committee may be able to fill in whatever gaps the student perceives in the relationship with the supervisor. If the research goes off in an unexpected direction, one that is not very familiar to the thesis supervisor, the student could see what opportunities are available and what guidelines the academic unit has for this situation. The student could consider joint supervision as an alternative to finding a new supervisor.
If the student has explored all other options and still wish to change supervisors, he or she should talk to the graduate program director. If the supervisor happens to be the graduate program director, the student should talk to the director of the academic unit. If the student remains uncertain or dissatisfied, he or she should talk to the vice-dean graduate studies of his/her home faculty. Beyond that, the student can talk to the university ombudsperson. The student can request that the exchanges with any or all of these individuals (directors, vice-dean, ombudsperson) remain confidential.
The student should be sure to explore options carefully before withdrawing from the supervisory arrangement—a student who terminates the relationship with a supervisor before finding another supervisor may have difficulty securing another supervisor and compromise the thesis project.
- Roles and responsibilities of supervisors
Introduction
- Knowledge of regulations, policies and procedures
- Advice on program of study, research and professional development
- Meetings/consultation
- Financial assistance
- Intellectual property
- Publications
- Withdrawal of supervisory duties
- Accommodation
Introduction
Effective graduate student supervision requires complex interactions between graduate students and their supervisors. The role of a supervisor is threefold: to advise graduate students, monitor their academic progress, and act as a mentor. Supervisors not only provide guidance, instruction and encouragement in the research activities of their students, but also take part in the evaluation and examination of their students’ progress, performance and navigation through the requirements of their academic program with the goal to ensure that their students are successful.
Supervisors are responsible for fostering the intellectual and scholarly development of their students. They also play an important role in providing advice about professional development and both academic and non-academic career opportunities, as they are able, and based upon the student’s career interests.
While these expectations apply to all graduate students, supervising PhD students reflects a longer-term, more substantive commitment. The privilege to supervise PhD students requires that the supervisor hold Approved Doctoral Dissertation Supervisor (ADDS) status. The intent of ADDS policy is to ensure that faculty have the appropriate knowledge to facilitate excellence in PhD supervision.
return to top
Knowledge of regulations, policies and procedures
Effective graduate student supervision requires a knowledge and understanding of the University’s requirements and expectations. To this end, supervisors should:
2.1 Be knowledgeable and remain updated on department, Faculty and University regulations, policies and procedures, and have these protocols guide the supervisors’ decision-making and behaviour as they interact with graduate students. Supervisors are encouraged to take the necessary steps to be well-informed with those Policies identified in section 1.2 .
2.2 Be familiar with the support services available to students and faculty at the University including those articulated in section 1.2 . This information is normally available through department graduate co-ordinators, Faculty Graduate Studies Offices, Graduate Studies and Postdoctoral Affairs (GSPA), the Graduate Student Association (GSA) or the University Secretariat.
2.3 Be informed about University of Waterloo policies and procedures that inform academic integrity (Office of Research).
2.4 Be aware of the University of Waterloo and Tri-Agency policies and procedures associated with the conduct of research. Where appropriate, supervisors should be prepared to provide guidance to students on:
- The responsible conduct of research, with particular emphasis on the Tri-Agency Framework as defined in the Faculty Association of University of Waterloo (FAUW) /University of Waterloo memorandum of Agreement (Section 14).
- The ethical conduct of research (Office of Research) involving animals, animal or human tissues, and human participants
2.5 Have knowledge of the policies and procedures that govern international travel and security that can be found at Waterloo International.
return to top
Advice on program of study, research and professional development
As noted above, supervisors are expected to serve as mentors to their graduate students. To this end, supervisors should be prepared to provide well-informed advice on academics and professional development. More specifically, supervisors should be prepared to advise students on:
2.6 An academic program that is challenging, at the appropriate level for the degree being sought, and that can be accomplished within commonly understood and desirable time and resource expectations of the student and the supervisor.
2.7 The choice of courses and seminars needed to fulfil the degree requirements.
2.8 The development and construct of a research topic and proposal.
2.9 The development of a communication plan with the supervisory/advisory committee as to how the student’s progress will be assessed (including during thesis writing and completion), and the role of advisory committee members in the assessment.
2.10 The availability of internships, practica, co-op or other experiential learning opportunities as part of the program.
2.11 The availability of professional development resources for Waterloo graduate students to help advance the students’ career objectives.
Meetings/consultation
The establishment and communication of common expectations are critical elements to positive experiences for both graduate students and their supervisors. Achieving these outcomes can be facilitated by regular meetings and/or consultation between students, their supervisors, and where appropriate advisory committees. Especially important is timely feedback on students’ written submissions.
The University encourages supervisors to:
2.12 Ensure, especially important in the case of doctoral students, that the student has:
- An advisory committee as required.
- A program of study consistent with department and Faculty requirements that has been approved by the advisory committee as required.
- A research plan that is appropriate in breadth, depth and time to completion (see Milestones in master's and doctoral programs ).
2.13 Arrange for regular (as agreed by the student and supervisor) meetings (which may involve the advisory committee) with students for consultation to ensure steady progress. The frequency of such meetings will depend on the discipline/field of study, type of program, and the student’s progress. At least two, preferably more, meetings should be arranged in each academic term. Supervisors should also be reasonably accessible for meetings requested by their students. The approach to these student meetings should be individualized to reflect the needs of the student. For example, some students may need more support while other may need less.
2.14 Communicate their evaluation of student progress to the department once a year or more often if required. The report should clearly indicate the status of the student’s progress (i.e., satisfactory or unsatisfactory). In the latter case, the report must include a clearly articulated set of conditions that if satisfied will restore the student’s status to satisfactory. Where the supervisor feels that the student will have serious difficulties finishing the program, the supervisor, in consultation with the advisory committee as appropriate, will inform in writing, both the student and the graduate officer of the nature of the problem(s), suggested remedies and may recommend withdrawal from the program. More information on assessing students’ progress can be found in the Graduate Studies Academic Calendar.
2.15 Thoroughly review and provide constructive feedback on all written materials relevant to the thesis or research paper submitted by their students. The supervisor and the student are encouraged to establish in writing expectations on what constitutes timely feedback; a timeframe of two to three weeks depending on the complexity of the document is commonly applied. However, this can vary depending on various circumstances such as travel or vacation. These circumstances should be discussed between the supervisor and student.
2.16 Have knowledge of the guidelines for evaluating students’ progress in a research program (Graduate Studies Academic Calendar).
2.17 Inform students about the broad spectrum of resources available (Writing and Communication Centre) to facilitate development of oral communication and writing skills.
2.18 Be active and supportive in promoting students’ well-being. This may include:
- Inquiring about a student’s well-being, as appropriate.
- Directing students to appropriate support services , including Mental Health and Wellness resources (Campus Wellness).
- Displaying empathy towards the student.
2.19 Complete as appropriate the University requirements for Sexual violence awareness, referral and support training (Human Rights, Equity and Inclusion Office) to understand how to respond to disclosures of sexual violence and refer students to the appropriate supports.
The University recognizes that supervisors will be away from the University for extended periods of time (e.g., sabbatical, satellite campus, visiting professorship). Being physically away from the University does not preclude a supervisor from remaining engaged with their graduate students. In cases where the supervisor will not be available either in person or via electronic communications, the supervisor should:
2.20 Inform students, prospective students and the department of any anticipated extended period where communication will not be occurring. In cases when the absence is for a period of two months or more, supervisors should arrange for suitable communication methods. Interim supervision also must be arranged, for example, using members of advisory committees. Supervisors must inform the student’s department (chair/graduate officer) of the arrangements made for the period of absence, including supervision of laboratory or field work where graduate students continue to work during the absence.
2.21 Ensure students know that in situations where a supervisor works away from campus for two months or more and where their students can accompany the supervisor, the decision to remain on campus or to follow the supervisor rests entirely with the student. Students shall face no pressure (explicit or implicit) or consequences when making this choice and are not required to provide any reason.
As with the departmental representatives, supervisors have responsibility to advance safety. More specifically, supervisors should:
2.22 Ensure a safe working environment both on and off campus (working alone, field work) by assessing hazards and implementing appropriate controls. This must be in accordance with the Occupational Health and Safety Act, Policy 34 (Secretariat) and department and Faculty regulations. All supervisors must complete mandatory health and safety supervisor awareness training (Safety Office) and must ensure that graduate students complete both mandatory and work-specific safety training. More information can be found on the Safety Office website.
2.23 Ensure that students obtain additional training when new safety risks arise and ensure training is kept up to date.
Inherent to graduate education are the dissemination of knowledge and the participation in scholarly activities away from the University campus. Travel (domestic and international) can include fieldwork, conferences, course work and other work related to the thesis. Supervisors are encouraged to support students’ travel to accomplish these important objectives. Supervisors should:
2.24 Follow or encourage students to follow Policy 31 (Secretariat) that governs University-sanctioned travel.
2.25 Categorize and report risk associated with travel. Low risk (Safety Office) are activities for which it is expected that participants will encounter hazards that are no greater than what they encounter in their everyday lives. Examples of significant risk (e.g. industrial sites, remote regions etc.) are noted on the Safety Office website . Travel or field work that involves significant risk must be documented using the Fieldwork Risk Management Form from the Safety Office . For low risk activities off campus, supervisors should:
- Provide advice on preparation for pre-departure orientation and planning for any travel and including associated risk, as they are able;
2.26 Document the student(s) location and duration of travel, including personal and emergency contact information. Review the material provided by Waterloo International to understand how to best mitigate risk and ensure safety for international travel.
2.27 Encourage students to register using the Pre-departure Travel Form at Waterloo International .
2.28 Consult the Government of Canada Travel Advice and Advisories web page for the international destination and discuss the mitigation of risk with the students to the destination.
Financial assistance
Supervisors regularly provide financial support for their graduate students. Both the supervisor and the student benefit when a clear understanding exists of the value of funding, and the academic outcomes that should occur from the supported activities. Specifically, supervisors should:
2.29 Be informed about the spectrum of funding opportunities available through the department, Faculty and Graduate Studies and Postdoctoral Affairs (GSPA) for students in financial need and to communicate these sources to student.
2.30 Communicate clearly and in writing to their students the terms (e.g., amounts, length of time, conditions) of the financial commitment being made when financial assistance is to be provided from research grants or contracts under the supervisor’s direction.
2.31 Support students’ understanding of their funding, including a consideration of student expenses (primarily tuition and housing) and taxation, if appropriate.
Intellectual property
Increasingly, students and supervisors enter into their academic relationships with previously established intellectual property (IP). Moreover, students and supervisors may have an expectation that their collective work may produce new IP. Best practices include the articulation of students’ and supervisors’ understanding of IP relationships at regular intervals throughout the students’ academic program. More specifically, supervisors should:
2.32 Discuss issues related to intellectual property such as patents, software, copyright, and income from sales and royalties, and inform students of University policies about intellectual property and the conduct of research. It should be recognized that, in accordance with Policy 73 (Secretariat), intellectual property normally is owned by the creators. However, the University retains a royalty-free right to use, for educational and research purposes, any intellectual property created by faculty, staff and students. Ideally, supervisors and students should enter into a written agreement that expresses IP owned by either party prior to beginning the research relationship and the default way in which IP created by the researchers’ joint activities will be owned. A common example is an assumption in the absence of an explicit agreement of joint IP ownership, with each researcher owning an equal share.
2.33 Ensure that students are aware of implications and/or obligations regarding intellectual property of research conducted under contract. If appropriate, discuss with their students and any research partners the protection of intellectual property by patent or copyright. Any significant intellectual contribution by a student must be recognized in the form of co-authorship. Supervisors must convey to students, in advance of publication, whether they intend to recognize the student as co-author for work under contract.
Publications
Academic outputs – in various forms – document and demonstrate ownership of creative research and other scholarly activities. These outputs are important for advancing knowledge and catalyzing additional scholarly activity in these areas and should be encouraged. When supervisors and graduate students work collectively on these academic works, it is important for both that their relative contributions are represented appropriately. To achieve these goals, supervisors should:
2.34 Discuss with their students, at an early stage of their program, authorship practices within the discipline and University policies about publications ( Policy 73 on the Secretariat website).
2.35 Discuss and reach agreement with students, well in advance of publication and ideally at the outset of collaboration, the way in which authorship will be shared, if appropriate, between the supervisor, the student and other contributors for work conducted under contract.
2.36 Encourage the dissemination of students’ research results by publication in scholarly and research journals, presentation at conferences (domestic or international) and seminars;
2.37 Motivate the dissemination of research through non-traditional or non-academic avenues (e.g. Open Access resources, public presentations, and popular media).
Withdrawal of supervisory duties
In rare cases supervisors may determine that they are not prepared or able to continue in a supervisory capacity. When this occurs, the supervisor is required to:
2.38 Follow the guidelines in the Graduate Studies Academic Calendar regarding University Responsibilities Regarding Supervisory Relationships that outlines the steps for dissolution of the supervisory relationship.
back to top
Accommodation
The University is eager to establish conditions that maximize graduate students’ likelihood of success. To this end, supervisors:
2.39 Have a duty to engage in accommodations processes with AccessAbility Services , as requested, and to provide appropriate accommodation to the point of undue hardship.
2.40 Remain informed of their roles and responsibilities with respect to accommodations.
<< previous section : Roles and responsibilities of departments, graduate officers and graduate co-ordinators
>> next section : Roles and responsibilities of graduate students

Related links
- Home - Guide for Graduate Research and Supervision
- Introduction to the Guide for Graduate Research and Supervision
- Roles and responsibilities of departments, graduate officers and graduate co-ordinators
- Roles and responsibilities of graduate students
- Roles and responsibilities of advisory committees
- Key university policies and reference materials
Graduate Studies and Postdoctoral Affairs (GSPA)
Needles Hall, second floor, room 2201
Graduate Studies Academic Calendar
Website feedback
- Contact Waterloo
- Maps & Directions
- Accessibility
The University of Waterloo acknowledges that much of our work takes place on the traditional territory of the Neutral, Anishinaabeg and Haudenosaunee peoples. Our main campus is situated on the Haldimand Tract, the land granted to the Six Nations that includes six miles on each side of the Grand River. Our active work toward reconciliation takes place across our campuses through research, learning, teaching, and community building, and is co-ordinated within the Office of Indigenous Relations .
Duties of a thesis supervisor and the supervision plan
The instruction belongs to the following themes.
- Supervising theses
Search for degree programme
Open university programmes.
- Open university Flag this item
Bachelor's Programmes
- Bachelor's Programme for Teachers of Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Agricultural Sciences Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Applied Psychology Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Art Studies Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Biology Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Chemistry Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Computer Science (TKT) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Cultural Studies Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Economics Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Education: Class Teacher (KLU, in Swedish) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Education: Class Teacher, Education (LO-KT) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Education: Class Teacher, Educational Psychology (LO-KP) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Education: Craft Teacher Education (KÄ) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Education: Early Education Teacher (SBP) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Education: Early Education Teacher (VO) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Education: General and Adult Education (PED, in Swedish) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Education: General and Adult Education (YL and AKT) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Education: Home Economics Teacher (KO) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Education: Special Education (EP) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Environmental and Food Economics Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Environmental Sciences Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Food Sciences Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Forest Sciences Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Geography Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Geosciences Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in History Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Languages Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Law Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Logopedics Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Mathematical Sciences Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Molecular Biosciences Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Pharmacy Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Philosophy Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Physical Sciences Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Politics, Media and Communication Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Psychology Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Science (BSC) Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Social Research Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Social Sciences Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Society and Change Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in the Languages and Literatures of Finland Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Theology and Religious Studies Flag this item
- Bachelor's Programme in Veterinary Medicine Flag this item
Master's and Licentiate's Programmes
- Degree Programme in Dentistry Flag this item
- Degree Programme in Medicine Flag this item
- Degree Programme in Veterinary Medicine Flag this item
- International Masters in Economy, State & Society Flag this item
- Master ́s Programme in Development of health care services Flag this item
- Master's Programme for Teachers of Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Agricultural Sciences Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Agricultural, Environmental and Resource Economics Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Area and Cultural Studies Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Art Studies Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Atmospheric Sciences (ATM) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Changing Education Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Chemistry and Molecular Sciences Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Computer Science (CSM) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Contemporary Societies Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Cultural Heritage Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Culture and Communication (in Swedish) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Data Science Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Ecology and Evolutionary Biology Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Economics Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Education: Class Teacher (KLU, in Swedish) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Education: Class Teacher, Education (LO-KT) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Education: Class Teacher, Educational Psychology (LO-KP) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Education: Craft Teacher Education (KÄ) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Education: Early Education (VAKA) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Education: General and Adult Education (PED, in Swedish) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Education: General and Adult Education (YL and AKT) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Education: Home Economics Teacher (KO) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Education: Special Education (EP) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in English Studies Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Environmental Change and Global Sustainability Flag this item
- Master's Programme in European and Nordic Studies Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Finnish and Finno-Ugrian Languages and Cultures Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Food Economy and Consumption Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Food Sciences Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Forest Sciences Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Gender Studies Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Genetics and Molecular Biosciences Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Geography Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Geology and Geophysics Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Global Politics and Communication Flag this item
- Master's Programme in History Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Human Nutrition and Food-Related Behaviour Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Integrative Plant Sciences Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Intercultural Encounters Flag this item
- Master's Programme in International Business Law Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Languages Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Law Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Life Science Informatics (LSI) Flag this item
- Master's programme in Linguistic Diversity and Digital Humanities Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Literary Studies Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Logopedics Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Materials Research (MATRES) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Mathematics and Statistics (MAST) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Microbiology and Microbial Biotechnology Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Neuroscience Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Particle Physics and Astrophysical Sciences (PARAS) Flag this item
- Master's programme in Pharmaceutical Research, Development and Safety Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Pharmacy Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Philosophy Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Politics, Media and Communication Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Psychology Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Russian, Eurasian and Eastern European Studies Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Scandinavian Languages and Literature Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Social and Health Research and Management Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Social Research Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Social Sciences (in Swedish) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Society and Change Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Theology and Religious Studies Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Theoretical and Computational Methods (TCM) Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Translation and Interpreting Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Translational Medicine Flag this item
- Master's Programme in Urban Studies and Planning (USP) Flag this item
- Master’s Programme in Global Governance Law Flag this item
- Nordic Master Programme in Environmental Changes at Higher Latitudes (ENCHIL) Flag this item
Doctoral Programmes
- Doctoral Programme Brain and Mind Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Atmospheric Sciences (ATM-DP) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Biomedicine (DPBM) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Chemistry and Molecular Sciences (CHEMS) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Clinical Research (KLTO) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Clinical Veterinary Medicine (CVM) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Cognition, Learning, Instruction and Communication (CLIC) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Computer Science (DoCS) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Drug Research (DPDR) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Economics Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Food Chain and Health Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Gender, Culture and Society (SKY) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Geosciences (GeoDoc) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in History and Cultural Heritage Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Human Behaviour (DPHuB) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Integrative Life Science (ILS) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Interdisciplinary Environmental Sciences (DENVI) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Language Studies (HELSLANG) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Law Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Materials Research and Nanoscience (MATRENA) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Mathematics and Statistics (Domast) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Microbiology and Biotechnology Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Oral Sciences (FINDOS) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Particle Physics and Universe Sciences (PAPU) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Philosophy, Arts and Society Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Plant Sciences (DPPS) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Political, Societal and Regional Changes (PYAM) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Population Health (DOCPOP) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in School, Education, Society and Culture Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Social Sciences Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Sustainable Use of Renewable Natural Resources (AGFOREE) Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Theology and Religious Studies Flag this item
- Doctoral Programme in Wildlife Biology (LUOVA) Flag this item
Specialist training programmes
- Multidisciplinary studies for class teachers (teaching in Finnish) Flag this item
- Multidisciplinary studies for class teachers (teaching in Swedish) Flag this item
- Non-degree studies for special education teachers (ELO) Flag this item
- Non-degree studies for special education teachers (LEO) Flag this item
- Non-degree studies for special education teachers (VEO) Flag this item
- Non-degree studies in subject teacher education Flag this item
- Specific Training in General Medical Practice Flag this item
- Specialisation Programme in Clinical Mental Health Psychology Flag this item
- Specialisation Programme in Neuropsychology Flag this item
- Specialisation Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Environmental Health and Food Control (old) Flag this item
- Specialisation Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Equine Medicine (old) Flag this item
- Specialisation Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Food Production Hygiene Flag this item
- Specialisation Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Infectious Animal Diseases (new) Flag this item
- Specialisation Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Production Animal Medicine (old) Flag this item
- Specialisation Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Small Animal Medicine (old) Flag this item
- Specialisation Studies in Community and Hospital Pharmacy (for B.Sc.Pharm.) Flag this item
- Specialisation Studies in Community and Hospital Pharmacy (for M.Sc.Pharm.) Flag this item
- Specialisation Studies in Industrial Pharmacy (for B.Sc.Pharm.) Flag this item
- Specialisation Studies in Industrial Pharmacy (for M.Sc.Pharm.) Flag this item
- Specialist Training in Dentistry Flag this item
- Specialist Training in Hospital Chemistry Flag this item
- Specialist Training in Hospital Microbiology Flag this item
- Specialist Training in Medicine, 5-year training Flag this item
- Specialist Training in Medicine, 6-year training Flag this item
- Specialist's Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Environmental Health and Food Control Flag this item
- Specialist's Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Equine Medicine (new) Flag this item
- Specialist's Programme in Veterinary Medicine, general veterinary medicine Flag this item
- Specialist's Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Infectious Animal Diseases (new) Flag this item
- Specialist's Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Production Animal Medicine (new) Flag this item
- Specialist's Programme in Veterinary Medicine, Small Animal Medicine (new) Flag this item
- Trainer Training Programme in Integrative Psychotherapy Flag this item
- Training Programme for Psychotherapists Flag this item
- Language Centre
- Open University
Supervision work is closely linked to the intended learning outcomes of the degree and thesis as well as the related grading criteria. In accordance with the Regulations on Degrees and the Protection of Students’ Rights at the University of Helsinki, the student must receive instruction both during their studies and while writing their thesis. See here for instructions on ensuring that your supervision is aligned with the learning outcomes.
On this page
Supervision principles.
The Rector decides on the principles of supervision, including the rights and obligations of the student and the supervisor. The degree programme’s curriculum must contain instructions on how to prepare a personal study plan, along with the practices for approving and updating the plan. Please review the curriculum of your faculty and the thesis grading criteria in order to ensure that your supervision is aligned with the learning outcomes.
In the Rector’s decision, supervision refers to the support provided for the student’s or doctoral candidate’s learning process as they change, gain experience and grow as an expert. As a whole, supervision consists of communication, advice, instruction and special guidance. Supervision and counselling can be organised in a group led by the supervisor, at a seminar, in a peer group of students or doctoral candidates organised by the supervisor or in a personal meeting separately agreed between the supervisor and the student/doctoral candidate. Supervision and counselling can also be provided electronically through, for example, Moodle or other teaching tools available.
Members of the teaching and research staff provide counselling that is related to teaching and research and requires knowledge of the content of different studies and disciplines. This counselling may concern, for example, personal study plans or thesis supervision.
Guidance and counselling are provided in the Finnish and Swedish-language and multilingual degree programmes in Finnish or Swedish depending on the student’s native language or in English or another language as agreed with the student. If the student’s native language is a language other than Finnish or Swedish, guidance and counselling are provided in English or, if agreed with the student, in another language. In English-language master’s programmes and doctoral programmes, guidance can also be provided solely in English.
The degree programme steering group is responsible for ensuring that each student is appointed with a primary supervisor who is responsible for the supervision of their thesis. Additional supervisors may also be appointed. Your supervision plan can be used to agree on the responsibilities related to the supervision.
Supervision as interaction and the supervision plan
Supervision is about interaction with responsibilities that are divided between the different parties of the supervision relationship. Ambiguities related to supervision are often due to the parties’ different expectations regarding the content and responsibilities of the supervision and the fact that the parties are often unaware of the others’ expectations. Below, you can find a table that serves as a great tool for considering the different rights and obligations related to supervision
The policies and practices of supervision should be discussed in the early stages of the thesis process. The supervisor and the student may also prepare a written supervision plan that clarifies the schedule for the supervision and the thesis work as well as the content of the supervision. The plan can also be utilised if any problems arise or you fall behind schedule.
Topics the supervisor should incorporate in the supervision
When supervising a student’s thesis work, remember to pay attention to the following topics:
- the responsible conduct of research and avoiding cheating
- guiding the student in matters related to data protection
- matters related to open access publications and the public availability of theses
- inform the student of the general process of thesis examination and approval and the related schedule
Different faculties may have their own decisions and instructions on thesis supervision. Please read the instructions provided by your faculty.
See also the Instructions for Students
You will find related content for students in the Studies Service.
Bachelor’s theses and maturity tests
Thesis and maturity test in master's and licentiate's programmes.
- Instructions for students
- Notifications for students
Supervising BSc & MSc thesis students
Course schedule, course description.
Course Description
From Sept 2024 onwards this course will become an one-day course and a follow-up after 'Start to Supervise BSc & MSc thesis students'. New dates will be published in May.
! the course is only open for supervisors having supervised at least two (WUR)students .
The thesis is the final subject of the BSc and MSc programme; and in most cases the most important individual project of a student. Due to the importance and size of the project, the meetings between supervisor and student are more intense and personal compared to those contacts in courses. The relationship between supervisor and student is therefore very important. Students expect certain behaviour of their supervisor, but the supervisor also has expectations of his/her student. Questions about responsibilities for supervisor and student arise.
As a supervisor it is important to be aware of the Wageningen requirements, your own vision about effective supervising, your expectations of your student and the different phases in a thesis project. On the other hand, you should be able to adapt your supervision to the needs of the student when asking questions and giving feedback.
In this course we will on the one hand exchange experiences, theory and models about effective supervising thesis students. On the other hand we will practice a lot and you will develop a vision on supervision that fits Wageningen University and an awareness of your own expectations and preferred supervision style. You will discuss or play different situations and you will practice several skills, like giving feedback, switching communication levels and asking open questions. All these elements come together when you apply everything you learned in a real life case simulation with an actor as your student.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, you are able to:
- formulate your own perspective about the thesis’ function and the supervisors role
- offer an effective and motivating supervision
- distinguish possible phases of a thesis
- explain different supervision styles and argue how you can use different styles to adapt your supervision to the needs of the student
- apply the basic communication skills like giving feedback, listening, summarizing, asking questions and switching between communication levels
Target group & Prerequisites
The course is meant for teachers and PhD‘s who are already supervising thesis-students in Wageningen University. So the course is only open for beginning (having supervised at least two students, preferably in a WUR-context) to experienced supervisors.
At the lastest one week before the start of the course you will receive more information about the course, background material and some preparation assignments. It is a two day course.
This course can be chosen as elective course in the UTQ. It is also suitable as part of an Orientation on Teaching and Supervision (Pre-UTQ). If you are not supervising yet sign up for the short workshop Start to supervise BSc & MSc thesis students.
On this page you will find some basic information in relation to supervising thesis student. You will receive course notes before the start of the course.
Certificate
You will be awarded your certificate at the end of day 2.
18 hours – 0.64 ECTS
Participation is free for Wageningen University & Research staff involved in teaching WU courses.
Recommendation
Apply at least 3 months in advance since this course is fully booked rapidly.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In working on their thesis, students are guided by a master's thesis supervisor (or advisor) who is responsible for fostering the required skills and competences through one-on-one or small-group teaching over an extended period of time, making master's thesis supervision a key teaching role for student development, as well as an increasingly ...
Draft a project plan. With Benjamin and Bernd, I put together a project plan for each of the master's students. Drafting a two-page plan that ended up resembling an extended abstract for a conference forced us to consider each project in detail and helped to ensure that it was feasible for a student to carry out in their last semester of study.
Supervision is a well-defined term in the interpersonal relationship between thesis supervisors and students. A supervisor is designated to assist the student's development in terms of their research project [1,2,3].Faculty members supervise the students because qualified supervision leads to success on the part of the student, and it has moral, reputational, and financial outcomes for the ...
Five supportive roles. of a supervisor involving the supervision system are specific technical support, broader intellectual support, administrative support, management, and personal support brings about the output of the study. A supervisor's roles. for successful thesis and dissertation is reported by using the survey on graduate students ...
This study focuses on the perspectives of supervisors and students on the undergraduate thesis supervision. When students are writing their undergraduate thesis about a research project, they need several research skills: e.g., they have to write a research plan; review the literature to develop a conceptual framework; determine the aim and ...
Supervising Thesis Students is a UTQ module consisting of two meetings. During the first meeting, the role of a supervisor is discussed. We look at some of the challenges, how to set boundaries, and how to give constructive feedback. During the second meeting, we practice scenarios in which different conversational techniques can be used to ...
Adapt supervision to the student. ... Halfway through the project is a good time to evaluate how likely it is that the thesis will be handed in on time and as originally planned. The top priority ...
At UCL, doctoral students always have at least two supervisors. Some faculties and departments operate a model of thesis committees, which can include people from industry, as well as UCL staff. Rules and regulations PhD supervision. The supervision of doctoral students' research is governed by regulation.
Berlach, R.G. (2010). Supervising a research thesis: A practical guide. Fremantle, Western Australia: The University of Notre Dame Australia. This Text Book is brought to you by the School of Education at ResearchOnline@ND. It has been accepted for inclusion in Education Books by an authorized administrator of ResearchOnline@ND.
In order to investigate how teachers and students view thesis supervision at the Bachelor level, we pose the research question 'What supervisor and student roles can be extracted from the focus group and questionnaire data?'. To help contextualise these institutional roles, we refer to official documents/guidelines that apply to the Swedish ...
Here are some tips on where to start: 1. Check out their profile on their chair's website (many people list research interests there). 2. Take a look at their publications: if they have not ...
During the Spring semester, students will enroll in UNIV 4697W Senior Thesis (for which the thesis supervisor serves as instructor) in which they will complete the research and write the thesis. During this process, the student meets regularly with the thesis supervisor for feedback on data collection, evidence gathering, analysis, and writing.
Find a thesis supervisor. Thesis supervisors must be authorized by their Faculty to supervise theses. Finding a thesis supervisor arrow_drop_down. Appointment of a thesis supervisor arrow_drop_down. Meetings between the supervisor and the student arrow_drop_down. Feedback and revision arrow_drop_down.
Minor thesis supervision requires attention to the specific needs of the student, scale and scope associated with timelines and requires particular supervisory expertise. The findings have implications for the enhancement of educational strategies for research supervision of minor thesis students and for targeted supervisor training.
Supervising a Master's Thesis. Are you supervising a master's student writing a thesis and curious about how to guide him/her effectively? This online module challenges you to think and reflect on your supervising skills. It focuses on the supervising process and its possible challenges. Watch this video to find out more.
2.15 Thoroughly review and provide constructive feedback on all written materials relevant to the thesis or research paper submitted by their students. The supervisor and the student are encouraged to establish in writing expectations on what constitutes timely feedback; a timeframe of two to three weeks depending on the complexity of the ...
In this study, we regard research supervision as a teaching process for the supervisor and a learning process for the student (Bruce & Stoodley, 2013; Franke & Arvidsson, 2011). Research on academic supervision is. CONTACT Bas T. Agricola [email protected] Faculty of Social and Behavioural Sciences, Utrecht University, Heidelberglaan 1 ...
Your student currently expects responses within minutes. Matters are rarely so urgent that they need responses the same day. When supervising a thesis, it might be best to minimize such informal messages except for truly urgent issues, and instead have regular meetings for which the student can prepare questions.
Supervision Guidelines for Masters Students and Supervisors (THESIS)i. These guidelines should be regarded as something to help in the planning and conduct during the MA Thesis program. The purpose is to make expectations explicit between supervisors and masters students at an early stage. Clear expectations about the responsibilities of both ...
Supervision and BSc thesis student performance: hypotheses development. In most European countries, the final assessment in a degree programme is a thesis (Meeus, Van Looy, and Libotton Citation 2004), in which students individually perform a supervised piece of empirical research.This applies to Bachelor's and Master's degree programmes, whereby 'the Bachelor's thesis is in most cases ...
Supervision work is closely linked to the intended learning outcomes of the degree and thesis as well as the related grading criteria. In accordance with the Regulations on Degrees and the Protection of Students' Rights at the University of Helsinki, the student must receive instruction both during their studies and while writing their thesis.
1 Commonwealth countries use the term "supervision" for guiding students' thesis or dissertation research. Advising is the term in North America. We use the terms supervision and supervisor in this paper to be consistent with our context, New Zealand, a Commonwealth country. ways: relative to existing literature on interna
Course description. Course Description. From Sept 2024 onwards this course will become an one-day course and a follow-up after 'Start to Supervise BSc & MSc thesis students'. New dates will be published in May. ! the course is only open for supervisors having supervised at least two (WUR)students. The thesis is the final subject of the BSc and ...