September 5, 2024

Managing PTSD with exercise: What do clinicians think?
Researchers from UCL highlight the need for more guidance for trauma clinicians on how to effectively use exercise to help treat PTSD
Image credit: Pete Linforth from Pixabay
Patient expectations are a feature of treatment strategy rather than a source of bias
Ralph Horwitz and colleagues suggest that expectations could be a useful factor in the management of mental health
Image credit: germ, by congerdesign from Pixabay
Climate & mental health: A roadmap to global heat resilience
The Wellcome Trust and The Physiological Society share their plans to help tackle mental health effects of climate change
Image credit: Environmental, by Pete Linforth from Pixabay
Is it time to change mental health crisis responses?
Psychiatrist Rupinder Legha advocates for change to mental health crisis management
Image credit: Police, Max from Pixabay
Equipping the next generation of clinicians for addressing conflict mental health: A role for Geopsychiatry
Section Editor Joseph El-Khoury and colleagues share recommendations for training mental health professionals in conflict medicine
Image credit: War, by Alexa from Pixabay
mental health psychology
Gender differences in severity and parental estimation of adolescent’s pandemic-related stress in the United States
Kristen D. Holtz and colleagues find that parents could be more likely to underestimate the mental health needs of their daughters compared to their sons.
Image credit: Family, by Pexels from Pixabay
What are the effects of diagnostic labels?
Nick Haslam and colleagues examine how diagnostic labels affect empathy, help-seeking and stigma
Image credit: Woman, by lisa runnels from Pixabay
behavioural medicine and mental health economics
Cost-effectiveness of automated digital CBT ( Daylight ) for generalized anxiety disorder: A Markov simulation model in the United States
The cost-effectiveness and cost-benefits of digital CBT are assessed by Christopher Miller and colleagues
Image credit: Hands, by Pexels from Pixabay
epidemiology of mental health
Prevalence and covariates of depression among older adults in Nepal: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Image credit: woman, by Pexels from Pixabay
public mental health & policy
Psychological support for older crime victims - understanding barriers using Metropolitan Police data
Image credit: Hands, by Sabine van Erp, Pixabay
socio-economics & political approaches
The role of social determinants of health in mental health: An examination of the moderating effects of race, ethnicity, and gender on depression through the all of us research program dataset
Image credit: Line, by Peggy from Pixabay
Mental health psychology
Psychopathy, psychological distress, and treatment history among perpetrators of intimate partner femicide, homicide, and other violent crimes in Buenos Aires, Argentina
Image credit: Barbed wire, by vero_vig_050 from Pixabay
Community Case Studies - NTDs
Get to know our sections neurodiversity & mental health, get to know our sections epidemiology of mental health, get to know our sections community mental health, journeys in mental health: an anonymous blog series on lived experiences from plos mental health, journeys in mental health for world refugee day, june 2024, schizophrenia, overturning a ‘death sentence’, mental health awareness month at plos mental health, publish with plos.
- Submission Instructions
- Submit Your Manuscript
Connect with Us
- PLOS Mental Health on Twitter
- PLOS on Facebook
Get new content from PLOS Mental Health in your inbox
Advertisement
Social Media and Mental Health: Benefits, Risks, and Opportunities for Research and Practice
- Published: 20 April 2020
- Volume 5 , pages 245–257, ( 2020 )
Cite this article

- John A. Naslund 1 ,
- Ameya Bondre 2 ,
- John Torous 3 &
- Kelly A. Aschbrenner 4
406k Accesses
221 Citations
186 Altmetric
19 Mentions
Explore all metrics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Social media has become a prominent fixture in the lives of many individuals facing the challenges of mental illness. Social media refers broadly to web and mobile platforms that allow individuals to connect with others within a virtual network (such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Snapchat, or LinkedIn), where they can share, co-create, or exchange various forms of digital content, including information, messages, photos, or videos (Ahmed et al. 2019 ). Studies have reported that individuals living with a range of mental disorders, including depression, psychotic disorders, or other severe mental illnesses, use social media platforms at comparable rates as the general population, with use ranging from about 70% among middle-age and older individuals to upwards of 97% among younger individuals (Aschbrenner et al. 2018b ; Birnbaum et al. 2017b ; Brunette et al. 2019 ; Naslund et al. 2016 ). Other exploratory studies have found that many of these individuals with mental illness appear to turn to social media to share their personal experiences, seek information about their mental health and treatment options, and give and receive support from others facing similar mental health challenges (Bucci et al. 2019 ; Naslund et al. 2016b ).
Across the USA and globally, very few people living with mental illness have access to adequate mental health services (Patel et al. 2018 ). The wide reach and near ubiquitous use of social media platforms may afford novel opportunities to address these shortfalls in existing mental health care, by enhancing the quality, availability, and reach of services. Recent studies have explored patterns of social media use, impact of social media use on mental health and wellbeing, and the potential to leverage the popularity and interactive features of social media to enhance the delivery of interventions. However, there remains uncertainty regarding the risks and potential harms of social media for mental health (Orben and Przybylski 2019 ) and how best to weigh these concerns against potential benefits.
In this commentary, we summarized current research on the use of social media among individuals with mental illness, with consideration of the impact of social media on mental wellbeing, as well as early efforts using social media for delivery of evidence-based programs for addressing mental health problems. We searched for recent peer reviewed publications in Medline and Google Scholar using the search terms “mental health” or “mental illness” and “social media,” and searched the reference lists of recent reviews and other relevant studies. We reviewed the risks, potential harms, and necessary safety precautions with using social media for mental health. Overall, our goal was to consider the role of social media as a potentially viable intervention platform for offering support to persons with mental disorders, promoting engagement and retention in care, and enhancing existing mental health services, while balancing the need for safety. Given this broad objective, we did not perform a systematic search of the literature and we did not apply specific inclusion criteria based on study design or type of mental disorder.
Social Media Use and Mental Health
In 2020, there are an estimated 3.8 billion social media users worldwide, representing half the global population (We Are Social 2020 ). Recent studies have shown that individuals with mental disorders are increasingly gaining access to and using mobile devices, such as smartphones (Firth et al. 2015 ; Glick et al. 2016 ; Torous et al. 2014a , b ). Similarly, there is mounting evidence showing high rates of social media use among individuals with mental disorders, including studies looking at engagement with these popular platforms across diverse settings and disorder types. Initial studies from 2015 found that nearly half of a sample of psychiatric patients were social media users, with greater use among younger individuals (Trefflich et al. 2015 ), while 47% of inpatients and outpatients with schizophrenia reported using social media, of which 79% reported at least once-a-week usage of social media websites (Miller et al. 2015 ). Rates of social media use among psychiatric populations have increased in recent years, as reflected in a study with data from 2017 showing comparable rates of social media use (approximately 70%) among individuals with serious mental illness in treatment as compared with low-income groups from the general population (Brunette et al. 2019 ).
Similarly, among individuals with serious mental illness receiving community-based mental health services, a recent study found equivalent rates of social media use as the general population, even exceeding 70% of participants (Naslund et al. 2016 ). Comparable findings were demonstrated among middle-age and older individuals with mental illness accessing services at peer support agencies, where 72% of respondents reported using social media (Aschbrenner et al. 2018b ). Similar results, with 68% of those with first episode psychosis using social media daily were reported in another study (Abdel-Baki et al. 2017 ).
Individuals who self-identified as having a schizophrenia spectrum disorder responded to a survey shared through the National Alliance of Mental Illness (NAMI) and reported that visiting social media sites was one of their most common activities when using digital devices, taking up roughly 2 h each day (Gay et al. 2016 ). For adolescents and young adults ages 12 to 21 with psychotic disorders and mood disorders, over 97% reported using social media, with average use exceeding 2.5 h per day (Birnbaum et al. 2017b ). Similarly, in a sample of adolescents ages 13–18 recruited from community mental health centers, 98% reported using social media, with YouTube as the most popular platform, followed by Instagram and Snapchat (Aschbrenner et al. 2019 ).
Research has also explored the motivations for using social media as well as the perceived benefits of interacting on these platforms among individuals with mental illness. In the sections that follow (see Table 1 for a summary), we consider three potentially unique features of interacting and connecting with others on social media that may offer benefits for individuals living with mental illness. These include: (1) Facilitate social interaction; (2) Access to a peer support network; and (3) Promote engagement and retention in services.
Facilitate Social Interaction
Social media platforms offer near continuous opportunities to connect and interact with others, regardless of time of day or geographic location. This on demand ease of communication may be especially important for facilitating social interaction among individuals with mental disorders experiencing difficulties interacting in face-to-face settings. For example, impaired social functioning is a common deficit in schizophrenia spectrum disorders, and social media may facilitate communication and interacting with others for these individuals (Torous and Keshavan 2016 ). This was suggested in one study where participants with schizophrenia indicated that social media helped them to interact and socialize more easily (Miller et al. 2015 ). Like other online communication, the ability to connect with others anonymously may be an important feature of social media, especially for individuals living with highly stigmatizing health conditions (Berger et al. 2005 ), such as serious mental disorders (Highton-Williamson et al. 2015 ).
Studies have found that individuals with serious mental disorders (Spinzy et al. 2012 ) as well as young adults with mental illness (Gowen et al. 2012 ) appear to form online relationships and connect with others on social media as often as social media users from the general population. This is an important observation because individuals living with serious mental disorders typically have few social contacts in the offline world and also experience high rates of loneliness (Badcock et al. 2015 ; Giacco et al. 2016 ). Among individuals receiving publicly funded mental health services who use social media, nearly half (47%) reported using these platforms at least weekly to feel less alone (Brusilovskiy et al. 2016 ). In another study of young adults with serious mental illness, most indicated that they used social media to help feel less isolated (Gowen et al. 2012 ). Interestingly, more frequent use of social media among a sample of individuals with serious mental illness was associated with greater community participation, measured as participation in shopping, work, religious activities, or visiting friends and family, as well as greater civic engagement, reflected as voting in local elections (Brusilovskiy et al. 2016 ).
Emerging research also shows that young people with moderate to severe depressive symptoms appear to prefer communicating on social media rather than in-person (Rideout and Fox 2018 ), while other studies have found that some individuals may prefer to seek help for mental health concerns online rather than through in-person encounters (Batterham and Calear 2017 ). In a qualitative study, participants with schizophrenia described greater anonymity, the ability to discover that other people have experienced similar health challenges and reducing fears through greater access to information as important motivations for using the Internet to seek mental health information (Schrank et al. 2010 ). Because social media does not require the immediate responses necessary in face-to-face communication, it may overcome deficits with social interaction due to psychotic symptoms that typically adversely affect face-to-face conversations (Docherty et al. 1996 ). Online social interactions may not require the use of non-verbal cues, particularly in the initial stages of interaction (Kiesler et al. 1984 ), with interactions being more fluid and within the control of users, thereby overcoming possible social anxieties linked to in-person interaction (Indian and Grieve 2014 ). Furthermore, many individuals with serious mental disorders can experience symptoms including passive social withdrawal, blunted affect, and attentional impairment, as well as active social avoidance due to hallucinations or other concerns (Hansen et al. 2009 ), thus potentially reinforcing the relative advantage, as perceived by users, of using social media over in person conversations.
Access to a Peer Support Network
There is growing recognition about the role that social media channels could play in enabling peer support (Bucci et al. 2019 ; Naslund et al. 2016b ), referred to as a system of mutual giving and receiving where individuals who have endured the difficulties of mental illness can offer hope, friendship, and support to others facing similar challenges (Davidson et al. 2006 ; Mead et al. 2001 ). Initial studies exploring use of online self-help forums among individuals with serious mental illnesses have found that individuals with schizophrenia appeared to use these forums for self-disclosure and sharing personal experiences, in addition to providing or requesting information, describing symptoms, or discussing medication (Haker et al. 2005 ), while users with bipolar disorder reported using these forums to ask for help from others about their illness (Vayreda and Antaki 2009 ). More recently, in a review of online social networking in people with psychosis, Highton-Williamson et al. ( 2015 ) highlight that an important purpose of such online connections was to establish new friendships, pursue romantic relationships, maintain existing relationships or reconnect with people, and seek online peer support from others with lived experience (Highton-Williamson et al. 2015 ).
Online peer support among individuals with mental illness has been further elaborated in various studies. In a content analysis of comments posted to YouTube by individuals who self-identified as having a serious mental illness, there appeared to be opportunities to feel less alone, provide hope, find support and learn through mutual reciprocity, and share coping strategies for day-to-day challenges of living with a mental illness (Naslund et al. 2014 ). In another study, Chang ( 2009 ) delineated various communication patterns in an online psychosis peer-support group (Chang 2009 ). Specifically, different forms of support emerged, including “informational support” about medication use or contacting mental health providers, “esteem support” involving positive comments for encouragement, “network support” for sharing similar experiences, and “emotional support” to express understanding of a peer’s situation and offer hope or confidence (Chang 2009 ). Bauer et al. ( 2013 ) reported that the main interest in online self-help forums for patients with bipolar disorder was to share emotions with others, allow exchange of information, and benefit by being part of an online social group (Bauer et al. 2013 ).
For individuals who openly discuss mental health problems on Twitter, a study by Berry et al. ( 2017 ) found that this served as an important opportunity to seek support and to hear about the experiences of others (Berry et al. 2017 ). In a survey of social media users with mental illness, respondents reported that sharing personal experiences about living with mental illness and opportunities to learn about strategies for coping with mental illness from others were important reasons for using social media (Naslund et al. 2017 ). A computational study of mental health awareness campaigns on Twitter provides further support with inspirational posts and tips being the most shared (Saha et al. 2019 ). Taken together, these studies offer insights about the potential for social media to facilitate access to an informal peer support network, though more research is necessary to examine how these online interactions may impact intentions to seek care, illness self-management, and clinically meaningful outcomes in offline contexts.
Promote Engagement and Retention in Services
Many individuals living with mental disorders have expressed interest in using social media platforms for seeking mental health information (Lal et al. 2018 ), connecting with mental health providers (Birnbaum et al. 2017b ), and accessing evidence-based mental health services delivered over social media specifically for coping with mental health symptoms or for promoting overall health and wellbeing (Naslund et al. 2017 ). With the widespread use of social media among individuals living with mental illness combined with the potential to facilitate social interaction and connect with supportive peers, as summarized above, it may be possible to leverage the popular features of social media to enhance existing mental health programs and services. A recent review by Biagianti et al. ( 2018 ) found that peer-to-peer support appeared to offer feasible and acceptable ways to augment digital mental health interventions for individuals with psychotic disorders by specifically improving engagement, compliance, and adherence to the interventions and may also improve perceived social support (Biagianti et al. 2018 ).
Among digital programs that have incorporated peer-to-peer social networking consistent with popular features on social media platforms, a pilot study of the HORYZONS online psychosocial intervention demonstrated significant reductions in depression among patients with first episode psychosis (Alvarez-Jimenez et al. 2013 ). Importantly, the majority of participants (95%) in this study engaged with the peer-to-peer networking feature of the program, with many reporting increases in perceived social connectedness and empowerment in their recovery process (Alvarez-Jimenez et al. 2013 ). This moderated online social therapy program is now being evaluated as part of a large randomized controlled trial for maintaining treatment effects from first episode psychosis services (Alvarez-Jimenez et al. 2019 ).
Other early efforts have demonstrated that use of digital environments with the interactive peer-to-peer features of social media can enhance social functioning and wellbeing in young people at high risk of psychosis (Alvarez-Jimenez et al. 2018 ). There has also been a recent emergence of several mobile apps to support symptom monitoring and relapse prevention in psychotic disorders. Among these apps, the development of PRIME (Personalized Real-time Intervention for Motivational Enhancement) has involved working closely with young people with schizophrenia to ensure that the design of the app has the look and feel of mainstream social media platforms, as opposed to existing clinical tools (Schlosser et al. 2016 ). This unique approach to the design of the app is aimed at promoting engagement and ensuring that the app can effectively improve motivation and functioning through goal setting and promoting better quality of life of users with schizophrenia (Schlosser et al. 2018 ).
Social media platforms could also be used to promote engagement and participation in in-person services delivered through community mental health settings. For example, the peer-based lifestyle intervention called PeerFIT targets weight loss and improved fitness among individuals living with serious mental illness through a combination of in-person lifestyle classes, exercise groups, and use of digital technologies (Aschbrenner et al. 2016b , c ). The intervention holds tremendous promise as lack of support is one of the largest barriers towards exercise in patients with serious mental illness (Firth et al. 2016 ), and it is now possible to use social media to counter such. Specifically, in PeerFIT, a private Facebook group is closely integrated into the program to offer a closed platform where participants can connect with the lifestyle coaches, access intervention content, and support or encourage each other as they work towards their lifestyle goals (Aschbrenner et al. 2016a ; Naslund et al. 2016a ). To date, this program has demonstrated preliminary effectiveness for meaningfully reducing cardiovascular risk factors that contribute to early mortality in this patient group (Aschbrenner, Naslund, Shevenell, Kinney, et al., 2016), while the Facebook component appears to have increased engagement in the program, while allowing participants who were unable to attend in-person sessions due to other health concerns or competing demands to remain connected with the program (Naslund et al. 2018 ). This lifestyle intervention is currently being evaluated in a randomized controlled trial enrolling young adults with serious mental illness from real world community mental health services settings (Aschbrenner et al. 2018a ).
These examples highlight the promise of incorporating the features of popular social media into existing programs, which may offer opportunities to safely promote engagement and program retention, while achieving improved clinical outcomes. This is an emerging area of research, as evidenced by several important effectiveness trials underway (Alvarez-Jimenez et al. 2019 ; Aschbrenner et al. 2018a ), including efforts to leverage online social networking to support family caregivers of individuals receiving first episode psychosis services (Gleeson et al. 2017 ).
Challenges with Social Media for Mental Health
The science on the role of social media for engaging persons with mental disorders needs a cautionary note on the effects of social media usage on mental health and wellbeing, particularly in adolescents and young adults. While the risks and harms of social media are frequently covered in the popular press and mainstream news reports, careful consideration of the research in this area is necessary. In a review of 43 studies in young people, many benefits of social media were cited, including increased self-esteem and opportunities for self-disclosure (Best et al. 2014 ). Yet, reported negative effects were an increased exposure to harm, social isolation, depressive symptoms, and bullying (Best et al. 2014 ). In the sections that follow (see Table 1 for a summary), we consider three major categories of risk related to use of social media and mental health. These include: (1) Impact on symptoms; (2) Facing hostile interactions; and (3) Consequences for daily life.
Impact on Symptoms
Studies consistently highlight that use of social media, especially heavy use and prolonged time spent on social media platforms, appears to contribute to increased risk for a variety of mental health symptoms and poor wellbeing, especially among young people (Andreassen et al. 2016 ; Kross et al. 2013 ; Woods and Scott 2016 ). This may partly be driven by the detrimental effects of screen time on mental health, including increased severity of anxiety and depressive symptoms, which have been well documented (Stiglic and Viner 2019 ). Recent studies have reported negative effects of social media use on mental health of young people, including social comparison pressure with others and greater feeling of social isolation after being rejected by others on social media (Rideout and Fox 2018 ). In a study of young adults, it was found that negative comparisons with others on Facebook contributed to risk of rumination and subsequent increases in depression symptoms (Feinstein et al. 2013 ). Still, the cross-sectional nature of many screen time and mental health studies makes it challenging to reach causal inferences (Orben and Przybylski 2019 ).
Quantity of social media use is also an important factor, as highlighted in a survey of young adults ages 19 to 32, where more frequent visits to social media platforms each week were correlated with greater depressive symptoms (Lin et al. 2016 ). More time spent using social media is also associated with greater symptoms of anxiety (Vannucci et al. 2017 ). The actual number of platforms accessed also appears to contribute to risk as reflected in another national survey of young adults where use of a large number of social media platforms was associated with negative impact on mental health (Primack et al. 2017 ). Among survey respondents using between 7 and 11 different social media platforms compared with respondents using only 2 or fewer platforms, there were 3 times greater odds of having high levels of depressive symptoms and a 3.2 times greater odds of having high levels of anxiety symptoms (Primack et al. 2017 ).
Many researchers have postulated that worsening mental health attributed to social media use may be because social media replaces face-to-face interactions for young people (Twenge and Campbell 2018 ) and may contribute to greater loneliness (Bucci et al. 2019 ) and negative effects on other aspects of health and wellbeing (Woods and Scott 2016 ). One nationally representative survey of US adolescents found that among respondents who reported more time accessing media such as social media platforms or smartphone devices, there were significantly greater depressive symptoms and increased risk of suicide when compared with adolescents who reported spending more time on non-screen activities, such as in-person social interaction or sports and recreation activities (Twenge et al. 2018 ). For individuals living with more severe mental illnesses, the effects of social media on psychiatric symptoms have received less attention. One study found that participation in chat rooms may contribute to worsening symptoms in young people with psychotic disorders (Mittal et al. 2007 ), while another study of patients with psychosis found that social media use appeared to predict low mood (Berry et al. 2018 ). These studies highlight a clear relationship between social media use and mental health that may not be present in general population studies (Orben and Przybylski 2019 ) and emphasize the need to explore how social media may contribute to symptom severity and whether protective factors may be identified to mitigate these risks.
Facing Hostile Interactions
Popular social media platforms can create potential situations where individuals may be victimized by negative comments or posts. Cyberbullying represents a form of online aggression directed towards specific individuals, such as peers or acquaintances, which is perceived to be most harmful when compared with random hostile comments posted online (Hamm et al. 2015 ). Importantly, cyberbullying on social media consistently shows harmful impact on mental health in the form of increased depressive symptoms as well as worsening of anxiety symptoms, as evidenced in a review of 36 studies among children and young people (Hamm et al. 2015 ). Furthermore, cyberbullying disproportionately impacts females as reflected in a national survey of adolescents in the USA, where females were twice as likely to be victims of cyberbullying compared with males (Alhajji et al. 2019 ). Most studies report cross-sectional associations between cyberbullying and symptoms of depression or anxiety (Hamm et al. 2015 ), though one longitudinal study in Switzerland found that cyberbullying contributed to significantly greater depression over time (Machmutow et al. 2012 ).
For youth ages 10 to 17 who reported major depressive symptomatology, there were over 3 times greater odds of facing online harassment in the last year compared with youth who reported mild or no depressive symptoms (Ybarra 2004 ). Similarly, in a 2018 national survey of young people, respondents ages 14 to 22 with moderate to severe depressive symptoms were more likely to have had negative experiences when using social media and, in particular, were more likely to report having faced hostile comments or being “trolled” from others when compared with respondents without depressive symptoms (31% vs. 14%) (Rideout and Fox 2018 ). As these studies depict risks for victimization on social media and the correlation with poor mental health, it is possible that individuals living with mental illness may also experience greater hostility online compared to individuals without mental illness. This would be consistent with research showing greater risk of hostility, including increased violence and discrimination, directed towards individuals living with mental illness in in-person contexts, especially targeted at those with severe mental illnesses (Goodman et al. 1999 ).
A computational study of mental health awareness campaigns on Twitter reported that while stigmatizing content was rare, it was actually the most spread (re-tweeted) demonstrating that harmful content can travel quickly on social media (Saha et al. 2019 ). Another study was able to map the spread of social media posts about the Blue Whale Challenge, an alleged game promoting suicide, over Twitter, YouTube, Reddit, Tumblr, and other forums across 127 countries (Sumner et al. 2019 ). These findings show that it is critical to monitor the actual content of social media posts, such as determining whether content is hostile or promotes harm to self or others. This is pertinent because existing research looking at duration of exposure cannot account for the impact of specific types of content on mental health and is insufficient to fully understand the effects of using these platforms on mental health.
Consequences for Daily Life
The ways in which individuals use social media can also impact their offline relationships and everyday activities. To date, reports have described risks of social media use pertaining to privacy, confidentiality, and unintended consequences of disclosing personal health information online (Torous and Keshavan 2016 ). Additionally, concerns have been raised about poor quality or misleading health information shared on social media and that social media users may not be aware of misleading information or conflicts of interest especially when the platforms promote popular content regardless of whether it is from a trustworthy source (Moorhead et al. 2013 ; Ventola 2014 ). For persons living with mental illness, there may be additional risks from using social media. A recent study that specifically explored the perspectives of social media users with serious mental illnesses, including participants with schizophrenia spectrum disorders, bipolar disorder, or major depression, found that over one third of participants expressed concerns about privacy when using social media (Naslund and Aschbrenner 2019 ). The reported risks of social media use were directly related to many aspects of everyday life, including concerns about threats to employment, fear of stigma and being judged, impact on personal relationships, and facing hostility or being hurt (Naslund and Aschbrenner 2019 ). While few studies have specifically explored the dangers of social media use from the perspectives of individuals living with mental illness, it is important to recognize that use of these platforms may contribute to risks that extend beyond worsening symptoms and that can affect different aspects of daily life.
In this commentary, we considered ways in which social media may yield benefits for individuals living with mental illness, while contrasting these with the possible harms. Studies reporting on the threats of social media for individuals with mental illness are mostly cross-sectional, making it difficult to draw conclusions about direction of causation. However, the risks are potentially serious. These risks should be carefully considered in discussions pertaining to use of social media and the broader use of digital mental health technologies, as avenues for mental health promotion or for supporting access to evidence-based programs or mental health services. At this point, it would be premature to view the benefits of social media as outweighing the possible harms, when it is clear from the studies summarized here that social media use can have negative effects on mental health symptoms, can potentially expose individuals to hurtful content and hostile interactions, and can result in serious consequences for daily life, including threats to employment and personal relationships. Despite these risks, it is also necessary to recognize that individuals with mental illness will continue to use social media given the ease of accessing these platforms and the immense popularity of online social networking. With this in mind, it may be ideal to raise awareness about these possible risks so that individuals can implement necessary safeguards, while highlighting that there could also be benefits. Being aware of the risks is an essential first step, before then recognizing that use of these popular platforms could contribute to some benefits like finding meaningful interactions with others, engaging with peer support networks, and accessing information and services.
To capitalize on the widespread use of social media and to achieve the promise that these platforms may hold for supporting the delivery of targeted mental health interventions, there is need for continued research to better understand how individuals living with mental illness use social media. Such efforts could inform safety measures and also encourage use of social media in ways that maximize potential benefits while minimizing risk of harm. It will be important to recognize how gender and race contribute to differences in use of social media for seeking mental health information or accessing interventions, as well as differences in how social media might impact mental wellbeing. For example, a national survey of 14- to 22-year olds in the USA found that female respondents were more likely to search online for information about depression or anxiety and to try to connect with other people online who share similar mental health concerns when compared with male respondents (Rideout and Fox 2018 ). In the same survey, there did not appear to be any differences between racial or ethnic groups in social media use for seeking mental health information (Rideout and Fox 2018 ). Social media use also appears to have a differential impact on mental health and emotional wellbeing between females and males (Booker et al. 2018 ), highlighting the need to explore unique experiences between gender groups to inform tailored programs and services. Research shows that lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender individuals frequently use social media for searching for health information and may be more likely compared with heterosexual individuals to share their own personal health experiences with others online (Rideout and Fox 2018 ). Less is known about use of social media for seeking support for mental health concerns among gender minorities, though this is an important area for further investigation as these individuals are more likely to experience mental health problems and online victimization when compared with heterosexual individuals (Mereish et al. 2019 ).
Similarly, efforts are needed to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health among ethnic and racial minorities. A recent study found that exposure to traumatic online content on social media showing violence or hateful posts directed at racial minorities contributed to increases in psychological distress, PTSD symptoms, and depression among African American and Latinx adolescents in the USA (Tynes et al. 2019 ). These concerns are contrasted by growing interest in the potential for new technologies including social media to expand the reach of services to underrepresented minority groups (Schueller et al. 2019 ). Therefore, greater attention is needed to understanding the perspectives of ethnic and racial minorities to inform effective and safe use of social media for mental health promotion efforts.
Research has found that individuals living with mental illness have expressed interest in accessing mental health services through social media platforms. A survey of social media users with mental illness found that most respondents were interested in accessing programs for mental health on social media targeting symptom management, health promotion, and support for communicating with health care providers and interacting with the health system (Naslund et al. 2017 ). Importantly, individuals with serious mental illness have also emphasized that any mental health intervention on social media would need to be moderated by someone with adequate training and credentials, would need to have ground rules and ways to promote safety and minimize risks, and importantly, would need to be free and easy to access.
An important strength with this commentary is that it combines a range of studies broadly covering the topic of social media and mental health. We have provided a summary of recent evidence in a rapidly advancing field with the goal of presenting unique ways that social media could offer benefits for individuals with mental illness, while also acknowledging the potentially serious risks and the need for further investigation. There are also several limitations with this commentary that warrant consideration. Importantly, as we aimed to address this broad objective, we did not conduct a systematic review of the literature. Therefore, the studies reported here are not exhaustive, and there may be additional relevant studies that were not included. Additionally, we only summarized published studies, and as a result, any reports from the private sector or websites from different organizations using social media or other apps containing social media–like features would have been omitted. Although, it is difficult to rigorously summarize work from the private sector, sometimes referred to as “gray literature,” because many of these projects are unpublished and are likely selective in their reporting of findings given the target audience may be shareholders or consumers.
Another notable limitation is that we did not assess risk of bias in the studies summarized in this commentary. We found many studies that highlighted risks associated with social media use for individuals living with mental illness; however, few studies of programs or interventions reported negative findings, suggesting the possibility that negative findings may go unpublished. This concern highlights the need for a future more rigorous review of the literature with careful consideration of bias and an accompanying quality assessment. Most of the studies that we described were from the USA, as well as from other higher income settings such as Australia or the UK. Despite the global reach of social media platforms, there is a dearth of research on the impact of these platforms on the mental health of individuals in diverse settings, as well as the ways in which social media could support mental health services in lower income countries where there is virtually no access to mental health providers. Future research is necessary to explore the opportunities and risks for social media to support mental health promotion in low-income and middle-income countries, especially as these countries face a disproportionate share of the global burden of mental disorders, yet account for the majority of social media users worldwide (Naslund et al. 2019 ).
Future Directions for Social Media and Mental Health
As we consider future research directions, the near ubiquitous social media use also yields new opportunities to study the onset and manifestation of mental health symptoms and illness severity earlier than traditional clinical assessments. There is an emerging field of research referred to as “digital phenotyping” aimed at capturing how individuals interact with their digital devices, including social media platforms, in order to study patterns of illness and identify optimal time points for intervention (Jain et al. 2015 ; Onnela and Rauch 2016 ). Given that most people access social media via mobile devices, digital phenotyping and social media are closely related (Torous et al. 2019 ). To date, the emergence of machine learning, a powerful computational method involving statistical and mathematical algorithms (Shatte et al. 2019 ), has made it possible to study large quantities of data captured from popular social media platforms such as Twitter or Instagram to illuminate various features of mental health (Manikonda and De Choudhury 2017 ; Reece et al. 2017 ). Specifically, conversations on Twitter have been analyzed to characterize the onset of depression (De Choudhury et al. 2013 ) as well as detecting users’ mood and affective states (De Choudhury et al. 2012 ), while photos posted to Instagram can yield insights for predicting depression (Reece and Danforth 2017 ). The intersection of social media and digital phenotyping will likely add new levels of context to social media use in the near future.
Several studies have also demonstrated that when compared with a control group, Twitter users with a self-disclosed diagnosis of schizophrenia show unique online communication patterns (Birnbaum et al. 2017a ), including more frequent discussion of tobacco use (Hswen et al. 2017 ), symptoms of depression and anxiety (Hswen et al. 2018b ), and suicide (Hswen et al. 2018a ). Another study found that online disclosures about mental illness appeared beneficial as reflected by fewer posts about symptoms following self-disclosure (Ernala et al. 2017 ). Each of these examples offers early insights into the potential to leverage widely available online data for better understanding the onset and course of mental illness. It is possible that social media data could be used to supplement additional digital data, such as continuous monitoring using smartphone apps or smart watches, to generate a more comprehensive “digital phenotype” to predict relapse and identify high-risk health behaviors among individuals living with mental illness (Torous et al. 2019 ).
With research increasingly showing the valuable insights that social media data can yield about mental health states, greater attention to the ethical concerns with using individual data in this way is necessary (Chancellor et al. 2019 ). For instance, data is typically captured from social media platforms without the consent or awareness of users (Bidargaddi et al. 2017 ), which is especially crucial when the data relates to a socially stigmatizing health condition such as mental illness (Guntuku et al. 2017 ). Precautions are needed to ensure that data is not made identifiable in ways that were not originally intended by the user who posted the content as this could place an individual at risk of harm or divulge sensitive health information (Webb et al. 2017 ; Williams et al. 2017 ). Promising approaches for minimizing these risks include supporting the participation of individuals with expertise in privacy, clinicians, and the target individuals with mental illness throughout the collection of data, development of predictive algorithms, and interpretation of findings (Chancellor et al. 2019 ).
In recognizing that many individuals living with mental illness use social media to search for information about their mental health, it is possible that they may also want to ask their clinicians about what they find online to check if the information is reliable and trustworthy. Alternatively, many individuals may feel embarrassed or reluctant to talk to their clinicians about using social media to find mental health information out of concerns of being judged or dismissed. Therefore, mental health clinicians may be ideally positioned to talk with their patients about using social media and offer recommendations to promote safe use of these sites while also respecting their patients’ autonomy and personal motivations for using these popular platforms. Given the gap in clinical knowledge about the impact of social media on mental health, clinicians should be aware of the many potential risks so that they can inform their patients while remaining open to the possibility that their patients may also experience benefits through use of these platforms. As awareness of these risks grows, it may be possible that new protections will be put in place by industry or through new policies that will make the social media environment safer. It is hard to estimate a number needed to treat or harm today given the nascent state of research, which means the patient and clinician need to weigh the choice on a personal level. Thus, offering education and information is an important first step in that process. As patients increasingly show interest in accessing mental health information or services through social media, it will be necessary for health systems to recognize social media as a potential avenue for reaching or offering support to patients. This aligns with growing emphasis on the need for greater integration of digital psychiatry, including apps, smartphones, or wearable devices, into patient care and clinical services through institution-wide initiatives and training clinical providers (Hilty et al. 2019 ). Within a learning healthcare environment where research and care are tightly intertwined and feedback between both is rapid, the integration of digital technologies into services may create new opportunities for advancing use of social media for mental health.
As highlighted in this commentary, social media has become an important part of the lives of many individuals living with mental disorders. Many of these individuals use social media to share their lived experiences with mental illness, to seek support from others, and to search for information about treatment recommendations, accessing mental health services and coping with symptoms (Bucci et al. 2019 ; Highton-Williamson et al. 2015 ; Naslund et al. 2016b ). As the field of digital mental health advances, the wide reach, ease of access, and popularity of social media platforms could be used to allow individuals in need of mental health services or facing challenges of mental illness to access evidence-based treatment and support. To achieve this end and to explore whether social media platforms can advance efforts to close the gap in available mental health services in the USA and globally, it will be essential for researchers to work closely with clinicians and with those affected by mental illness to ensure that possible benefits of using social media are carefully weighed against anticipated risks.
Abdel-Baki, A., Lal, S., Charron, D.-C., Stip, E., & Kara, N. (2017). Understanding access and use of technology among youth with first-episode psychosis to inform the development of technology-enabled therapeutic interventions. Early Intervention in Psychiatry, 11 (1), 72–76.
PubMed Google Scholar
Ahmed, Y. A., Ahmad, M. N., Ahmad, N., & Zakaria, N. H. (2019). Social media for knowledge-sharing: a systematic literature review. Telematics and Informatics, 37 , 72–112.
Google Scholar
Alhajji, M., Bass, S., & Dai, T. (2019). Cyberbullying, mental health, and violence in adolescents and associations with sex and race: data from the 2015 youth risk behavior survey. Global Pediatric Health, 6 , 2333794X19868887.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Alvarez-Jimenez, M., Bendall, S., Lederman, R., Wadley, G., Chinnery, G., Vargas, S., Larkin, M., Killackey, E., McGorry, P., & Gleeson, J. F. (2013). On the HORYZON: moderated online social therapy for long-term recovery in first episode psychosis. Schizophrenia Research, 143 (1), 143–149.
Alvarez-Jimenez, M., Gleeson, J., Bendall, S., Penn, D., Yung, A., Ryan, R., et al. (2018). Enhancing social functioning in young people at ultra high risk (UHR) for psychosis: a pilot study of a novel strengths and mindfulness-based online social therapy. Schizophrenia Research, 202 , 369–377.
Alvarez-Jimenez, M., Bendall, S., Koval, P., Rice, S., Cagliarini, D., Valentine, L., et al. (2019). HORYZONS trial: protocol for a randomised controlled trial of a moderated online social therapy to maintain treatment effects from first-episode psychosis services. BMJ Open, 9 (2), e024104.
Andreassen, C. S., Billieux, J., Griffiths, M. D., Kuss, D. J., Demetrovics, Z., Mazzoni, E., & Pallesen, S. (2016). The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 30 (2), 252.
Aschbrenner, K. A., Naslund, J. A., & Bartels, S. J. (2016a). A mixed methods study of peer-to-peer support in a group-based lifestyle intervention for adults with serious mental illness. Psychiatric Rehabilitation Journal, 39 (4), 328–334.
Aschbrenner, K. A., Naslund, J. A., Shevenell, M., Kinney, E., & Bartels, S. J. (2016b). A pilot study of a peer-group lifestyle intervention enhanced with mHealth technology and social media for adults with serious mental illness. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 204 (6), 483–486.
Aschbrenner, K. A., Naslund, J. A., Shevenell, M., Mueser, K. T., & Bartels, S. J. (2016c). Feasibility of behavioral weight loss treatment enhanced with peer support and mobile health technology for individuals with serious mental illness. Psychiatric Quarterly, 87 (3), 401–415.
Aschbrenner, K. A., Naslund, J. A., Gorin, A. A., Mueser, K. T., Scherer, E. A., Viron, M., et al. (2018a). Peer support and mobile health technology targeting obesity-related cardiovascular risk in young adults with serious mental illness: protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Contemporary Clinical Trials, 74 , 97–106.
Aschbrenner, K. A., Naslund, J. A., Grinley, T., Bienvenida, J. C. M., Bartels, S. J., & Brunette, M. (2018b). A survey of online and mobile technology use at peer support agencies. Psychiatric Quarterly , 1–10.
Aschbrenner, K. A., Naslund, J. A., Tomlinson, E. F., Kinney, A., Pratt, S. I., & Brunette, M. F. (2019). Adolescents’ use of digital technologies and preferences for mobile health coaching in mental health settings. Frontiers in Public Health. 7 , 178.
Badcock, J. C., Shah, S., Mackinnon, A., Stain, H. J., Galletly, C., Jablensky, A., & Morgan, V. A. (2015). Loneliness in psychotic disorders and its association with cognitive function and symptom profile. Schizophrenia Research, 169 (1–3), 268–273.
Batterham, P. J., & Calear, A. J. (2017). Preferences for internet-based mental health interventions in an adult online sample: findings from ann online community survey. JMIR Mental Health, 4 (2), e26.
Bauer, R., Bauer, M., Spiessl, H., & Kagerbauer, T. (2013). Cyber-support: an analysis of online self-help forums (online self-help forums in bipolar disorder). Nordic Journal of Psychiatry, 67 (3), 185–190.
Berger, M., Wagner, T. H., & Baker, L. C. (2005). Internet use and stigmatized illness. Social Science & Medicine, 61 (8), 1821–1827.
Berry, N., Lobban, F., Belousov, M., Emsley, R., Nenadic, G., & Bucci, S. (2017). # WhyWeTweetMH: understanding why people use Twitter to discuss mental health problems. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 19 (4), e107.
Berry, N., Emsley, R., Lobban, F., & Bucci, S. (2018). Social media and its relationship with mood, self-esteem and paranoia in psychosis. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 138 , 558–570.
Best, P., Manktelow, R., & Taylor, B. (2014). Online communication, social media and adolescent wellbeing: a systematic narrative review. Children and Youth Services Review, 41 , 27–36.
Biagianti, B., Quraishi, S. H., & Schlosser, D. A. (2018). Potential benefits of incorporating peer-to-peer interactions into digital interventions for psychotic disorders: a systematic review. Psychiatric Services, 69 (4), 377–388.
Bidargaddi, N., Musiat, P., Makinen, V.-P., Ermes, M., Schrader, G., & Licinio, J. (2017). Digital footprints: facilitating large-scale environmental psychiatric research in naturalistic settings through data from everyday technologies. Molecular Psychiatry, 22 (2), 164.
Birnbaum, M. L., Ernala, S. K., Rizvi, A. F., De Choudhury, M., & Kane, J. M. (2017a). A collaborative approach to identifying social media markers of schizophrenia by employing machine learning and clinical appraisals. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 19 (8), e289.
Birnbaum, M. L., Rizvi, A. F., Correll, C. U., Kane, J. M., & Confino, J. (2017b). Role of social media and the Internet in pathways to care for adolescents and young adults with psychotic disorders and non-psychotic mood disorders. Early Intervention in Psychiatry, 11 (4), 290–295.
Booker, C. L., Kelly, Y. J., & Sacker, A. (2018). Gender differences in the associations between age trends of social media interaction and well-being among 10-15 year olds in the UK. BMC Public Health, 18 (1), 321.
Brunette, M., Achtyes, E., Pratt, S., Stilwell, K., Opperman, M., Guarino, S., & Kay-Lambkin, F. (2019). Use of smartphones, computers and social media among people with SMI: opportunity for intervention. Community Mental Health Journal , 1–6.
Brusilovskiy, E., Townley, G., Snethen, G., & Salzer, M. S. (2016). Social media use, community participation and psychological well-being among individuals with serious mental illnesses. Computers in Human Behavior, 65 , 232–240.
Bucci, S., Schwannauer, M., & Berry, N. (2019). The digital revolution and its impact on mental health care. Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice, 92 (2), 277–297.
Chancellor, S., Birnbaum, M. L., Caine, E. D., Silenzio, V. M., & De Choudhury, M. (2019). A taxonomy of ethical tensions in inferring mental health states from social media. In Proceedings of the Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, 79–88.
Chang, H. J. (2009). Online supportive interactions: using a network approach to examine communication patterns within a psychosis social support group in Taiwan. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 60 (7), 1504–1517.
Davidson, L., Chinman, M., Sells, D., & Rowe, M. (2006). Peer support among adults with serious mental illness: a report from the field. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 32 (3), 443–450.
De Choudhury, M., Gamon, M., & Counts, S. (2012). Happy, nervous or surprised? classification of human affective states in social media. Paper presented at the sixth international Association for Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) Conference on Weblogs and Social Meedia, 435–438.
De Choudhury, M., Gamon, M., Counts, S., & Horvitz, E. (2013). Predicting depression via social media. Paper presented at the seventh international Association for Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, 128–137.
Docherty, N. M., Hawkins, K. A., Hoffman, R. E., Quinlan, D. M., Rakfeldt, J., & Sledge, W. H. (1996). Working memory, attention, and communication disturbances in schizophrenia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 105 (2), 212–219.
Ernala, S. K., Rizvi, A. F., Birnbaum, M. L., Kane, J. M., & De Choudhury, M. (2017). Linguistic markers indicating therapeutic outcomes of social media disclosures of schizophrenia. Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, 1 (1), 43.
Feinstein, B. A., Hershenberg, R., Bhatia, V., Latack, J. A., Meuwly, N., & Davila, J. (2013). Negative social comparison on Facebook and depressive symptoms: rumination as a mechanism. Psychology of Popular Media Culture, 2 (3), 161.
Firth, J., Cotter, J., Torous, J., Bucci, S., Firth, J. A., & Yung, A. R. (2015). Mobile phone ownership and endorsement of “mHealth” among people with psychosis: a meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 42 (2), 448–455.
Firth, J., Rosenbaum, S., Stubbs, B., Gorczynski, P., Yung, A. R., & Vancampfort, D. (2016). Motivating factors and barriers towards exercise in severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychological Medicine, 46 (14), 2869–2881.
Gay, K., Torous, J., Joseph, A., Pandya, A., & Duckworth, K. (2016). Digital technology use among individuals with schizophrenia: results of an online survey. JMIR Mental Health, 3 (2), e15.
Giacco, D., Palumbo, C., Strappelli, N., Catapano, F., & Priebe, S. (2016). Social contacts and loneliness in people with psychotic and mood disorders. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 66 , 59–66.
Gleeson, J., Lederman, R., Herrman, H., Koval, P., Eleftheriadis, D., Bendall, S., Cotton, S. M., & Alvarez-Jimenez, M. (2017). Moderated online social therapy for carers of young people recovering from first-episode psychosis: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials, 18 (1), 27.
Glick, G., Druss, B., Pina, J., Lally, C., & Conde, M. (2016). Use of mobile technology in a community mental health setting. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare, 22 (7), 430–435.
Goodman, L. A., Thompson, K. M., Weinfurt, K., Corl, S., Acker, P., Mueser, K. T., & Rosenberg, S. D. (1999). Reliability of reports of violent victimization and posttraumatic stress disorder among men and women with serious mental illness. Journal of Traumatic Stress: Official Publication of the International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies, 12 (4), 587–599.
Gowen, K., Deschaine, M., Gruttadara, D., & Markey, D. (2012). Young adults with mental health conditions and social networking websites: seeking tools to build community. Psychiatric Rehabilitation Journal, 35 (3), 245–250.
Guntuku, S. C., Yaden, D. B., Kern, M. L., Ungar, L. H., & Eichstaedt, J. C. (2017). Detecting depression and mental illness on social media: an integrative review. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 18 , 43–49.
Haker, H., Lauber, C., & Rössler, W. (2005). Internet forums: a self-help approach for individuals with schizophrenia? Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 112 (6), 474–477.
Hamm, M. P., Newton, A. S., Chisholm, A., Shulhan, J., Milne, A., Sundar, P., Ennis, H., Scott, S. D., & Hartling, L. (2015). Prevalence and effect of cyberbullying on children and young people: a scoping review of social media studies. JAMA Pediatrics, 169 (8), 770–777.
Hansen, C. F., Torgalsbøen, A.-K., Melle, I., & Bell, M. D. (2009). Passive/apathetic social withdrawal and active social avoidance in schizophrenia: difference in underlying psychological processes. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 197 (4), 274–277.
Highton-Williamson, E., Priebe, S., & Giacco, D. (2015). Online social networking in people with psychosis: a systematic review. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 61 (1), 92–101.
Hilty, D. M., Chan, S., Torous, J., Luo, J., & Boland, R. J. (2019). Mobile health, smartphone/device, and apps for psychiatry and medicine: competencies, training, and faculty development issues. Psychiatric Clinics, 42 (3), 513–534.
Hswen, Y., Naslund, J. A., Chandrashekar, P., Siegel, R., Brownstein, J. S., & Hawkins, J. B. (2017). Exploring online communication about cigarette smoking among Twitter users who self-identify as having schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 257 , 479–484.
Hswen, Y., Naslund, J. A., Brownstein, J. S., & Hawkins, J. B. (2018a). Monitoring online discussions about suicide among Twitter users with schizophrenia: exploratory study. JMIR Mental Health, 5 (4), e11483.
Hswen, Y., Naslund, J. A., Brownstein, J. S., & Hawkins, J. B. (2018b). Online communication about depression and anxiety among twitter users with schizophrenia: preliminary findings to inform a digital phenotype using social media. Psychiatric Quarterly, 89 (3), 569–580.
Indian, M., & Grieve, R. (2014). When Facebook is easier than face-to-face: social support derived from Facebook in socially anxious individuals. Personality and Individual Differences, 59 , 102–106.
Jain, S. H., Powers, B. W., Hawkins, J. B., & Brownstein, J. S. (2015). The digital phenotype. Nature Biotechnology, 33 (5), 462–463.
Kiesler, S., Siegel, J., & McGuire, T. W. (1984). Social psychological aspects of computer-mediated communication. American Psychologist, 39 , 1123–1134.
Kross, E., Verduyn, P., Demiralp, E., Park, J., Lee, D. S., Lin, N., Shablack, H., Jonides, J., & Ybarra, O. (2013). Facebook use predicts declines in subjective well-being in young adults. PLoS One, 8 (8), e69841.
Lal, S., Nguyen, V., & Theriault, J. (2018). Seeking mental health information and support online: experiences and perspectives of young people receiving treatment for first-episode psychosis. Early Intervention in Psychiatry, 12 (3), 324–330.
Lin, L. Y., Sidani, J. E., Shensa, A., Radovic, A., Miller, E., Colditz, J. B., Hoffman, B. L., Giles, L. M., & Primack, B. A. (2016). Association between social media use and depression among US young adults. Depression and Anxiety, 33 (4), 323–331.
Machmutow, K., Perren, S., Sticca, F., & Alsaker, F. D. (2012). Peer victimisation and depressive symptoms: can specific coping strategies buffer the negative impact of cybervictimisation? Emotional and Behavioural Difficulties, 17 (3–4), 403–420.
Manikonda, L., & De Choudhury, M. (2017). Modeling and understanding visual attributes of mental health disclosures in social media. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 170–181.
Mead, S., Hilton, D., & Curtis, L. (2001). Peer support: a theoretical perspective. Psychiatric Rehabilitation Journal, 25 (2), 134–141.
Mereish, E. H., Sheskier, M., Hawthorne, D. J., & Goldbach, J. T. (2019). Sexual orientation disparities in mental health and substance use among Black American young people in the USA: effects of cyber and bias-based victimisation. Culture, Health & Sexuality, 21 (9), 985–998.
Miller, B. J., Stewart, A., Schrimsher, J., Peeples, D., & Buckley, P. F. (2015). How connected are people with schizophrenia? Cell phone, computer, email, and social media use. Psychiatry Research, 225 (3), 458–463.
Mittal, V. A., Tessner, K. D., & Walker, E. F. (2007). Elevated social Internet use and schizotypal personality disorder in adolescents. Schizophrenia Research, 94 (1–3), 50–57.
Moorhead, S. A., Hazlett, D. E., Harrison, L., Carroll, J. K., Irwin, A., & Hoving, C. (2013). A new dimension of health care: systematic review of the uses, benefits, and limitations of social media for health communication. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 15 (4), e85.
Naslund, J. A., & Aschbrenner, K. A. (2019). Risks to privacy with use of social media: understanding the views of social media users with serious mental illness. Psychiatric Services, 70 (7), 561–568.
Naslund, J. A., Grande, S. W., Aschbrenner, K. A., & Elwyn, G. (2014). Naturally occurring peer support through social media: the experiences of individuals with severe mental illness using YouTube. PLoS One, 9 (10), e110171.
Naslund, J. A., Aschbrenner, K. A., & Bartels, S. J. (2016). How people living with serious mental illness use smartphones, mobile apps, and social media. Psychiatric Rehabilitation Journal, 39 (4), 364–367.
Naslund, J. A., Aschbrenner, K. A., Marsch, L. A., & Bartels, S. J. (2016a). Feasibility and acceptability of Facebook for health promotion among people with serious mental illness. Digital Health, 2 , 2055207616654822.
PubMed Central Google Scholar
Naslund, J. A., Aschbrenner, K. A., Marsch, L. A., & Bartels, S. J. (2016b). The future of mental health care: peer-to-peer support and social media. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences, 25 (2), 113–122.
Naslund, J. A., Aschbrenner, K. A., McHugo, G. J., Unützer, J., Marsch, L. A., & Bartels, S. J. (2019). Exploring opportunities to support mental health care using social media: A survey of social media users with mental illness. Early Intervention in Psychiatry, 13 (3), 405–413.
Naslund, J. A., Aschbrenner, K. A., Marsch, L. A., McHugo, G. J., & Bartels, S. J. (2018). Facebook for supporting a lifestyle intervention for people with major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia: an exploratory study. Psychiatric Quarterly, 89 (1), 81–94.
Naslund, J. A., Gonsalves, P. P., Gruebner, O., Pendse, S. R., Smith, S. L., Sharma, A., & Raviola, G. (2019). Digital innovations for global mental health: opportunities for data science, task sharing, and early intervention. Current Treatment Options in Psychiatry , 1–15.
Onnela, J.-P., & Rauch, S. L. (2016). Harnessing smartphone-based digital phenotyping to enhance behavioral and mental health. Neuropsychopharmacology, 41 (7), 1691–1696.
Orben, A., & Przybylski, A. K. (2019). The association between adolescent well-being and digital technology use. Nature Human Behaviour, 3 (2), 173–182.
Patel, V., Saxena, S., Lund, C., Thornicroft, G., Baingana, F., Bolton, P., et al. (2018). The Lancet Commission on global mental health and sustainable development. The Lancet, 392 (10157), 1553–1598.
Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: a nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69 , 1–9.
Reece, A. G., & Danforth, C. M. (2017). Instagram photos reveal predictive markers of depression. EPJ Data Science, 6 (1), 15.
Reece, A. G., Reagan, A. J., Lix, K. L., Dodds, P. S., Danforth, C. M., & Langer, E. J. (2017). Forecasting the onset and course of mental illness with Twitter data. Scientific Reports, 7 (1), 13006.
Rideout, V., & Fox, S. (2018). Digital health practices, social media use, and mental well-being among teens and young adults in the U.S. Retrieved from San Francisco, CA: https://www.hopelab.org/reports/pdf/a-national-survey-by-hopelab-and-well-being-trust-2018.pdf . Accessed 10 Jan 2020.
Saha, K., Torous, J., Ernala, S. K., Rizuto, C., Stafford, A., & De Choudhury, M. (2019). A computational study of mental health awareness campaigns on social media. Translational behavioral medicine, 9 (6), 1197–1207.
Schlosser, D. A., Campellone, T., Kim, D., Truong, B., Vergani, S., Ward, C., & Vinogradov, S. (2016). Feasibility of PRIME: a cognitive neuroscience-informed mobile app intervention to enhance motivated behavior and improve quality of life in recent onset schizophrenia. JMIR Research Protocols, 5 (2).
Schlosser, D. A., Campellone, T. R., Truong, B., Etter, K., Vergani, S., Komaiko, K., & Vinogradov, S. (2018). Efficacy of PRIME, a mobile app intervention designed to improve motivation in young people with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 44 (5), 1010–1020.
Schrank, B., Sibitz, I., Unger, A., & Amering, M. (2010). How patients with schizophrenia use the internet: qualitative study. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 12 (5), e70.
Schueller, S. M., Hunter, J. F., Figueroa, C., & Aguilera, A. (2019). Use of digital mental health for marginalized and underserved populations. Current Treatment Options in Psychiatry, 6 (3), 243–255.
Shatte, A. B., Hutchinson, D. M., & Teague, S. J. (2019). Machine learning in mental health: a scoping review of methods and applications. Psychological Medicine, 49 (9), 1426–1448.
Spinzy, Y., Nitzan, U., Becker, G., Bloch, Y., & Fennig, S. (2012). Does the Internet offer social opportunities for individuals with schizophrenia? A cross-sectional pilot study. Psychiatry Research, 198 (2), 319–320.
Stiglic, N., & Viner, R. M. (2019). Effects of screentime on the health and well-being of children and adolescents: a systematic review of reviews. BMJ Open, 9 (1), e023191.
Sumner, S. A., Galik, S., Mathieu, J., Ward, M., Kiley, T., Bartholow, B., et al. (2019). Temporal and geographic patterns of social media posts about an emerging suicide game. Journal of Adolescent Health, 65 (1), 94–100.
Torous, J., & Keshavan, M. (2016). The role of social media in schizophrenia: evaluating risks, benefits, and potential. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 29 (3), 190–195.
Torous, J., Chan, S. R., Tan, S. Y.-M., Behrens, J., Mathew, I., Conrad, E. J., et al. (2014a). Patient smartphone ownership and interest in mobile apps to monitor symptoms of mental health conditions: a survey in four geographically distinct psychiatric clinics. JMIR Mental Health, 1 (1), e5.
Torous, J., Friedman, R., & Keshavan, M. (2014b). Smartphone ownership and interest in mobile applications to monitor symptoms of mental health conditions. JMIR mHealth and uHealth, 2 (1), e2.
Torous, J., Wisniewski, H., Bird, B., Carpenter, E., David, G., Elejalde, E., et al. (2019). Creating a digital health smartphone app and digital phenotyping platform for mental health and diverse healthcare needs: an interdisciplinary and collaborative approach. Journal of Technology in Behavioral Science, 4 (2), 73–85.
Trefflich, F., Kalckreuth, S., Mergl, R., & Rummel-Kluge, C. (2015). Psychiatric patients' internet use corresponds to the internet use of the general public. Psychiatry Research, 226 , 136–141.
Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2018). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: evidence from a population-based study. Preventive Medicine Reports, 12 , 271–283.
Twenge, J. M., Joiner, T. E., Rogers, M. L., & Martin, G. N. (2018). Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among US adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen time. Clinical Psychological Science, 6 (1), 3–17.
Tynes, B. M., Willis, H. A., Stewart, A. M., & Hamilton, M. W. (2019). Race-related traumatic events online and mental health among adolescents of color. Journal of Adolescent Health, 65 (3), 371–377.
Vannucci, A., Flannery, K. M., & Ohannessian, C. M. (2017). Social media use and anxiety in emerging adults. Journal of Affective Disorders, 207 , 163–166.
Vayreda, A., & Antaki, C. (2009). Social support and unsolicited advice in a bipolar disorder online forum. Qualitative Health Research, 19 (7), 931–942.
Ventola, C. L. (2014). Social media and health care professionals: benefits, risks, and best practices. Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 39 (7), 491–520.
We Are Social. (2020). Digital in 2020. Retrieved from https://wearesocial.com/global-digital-report-2019 . Accessed 10 Jan 2020.
Webb, H., Jirotka, M., Stahl, B. C., Housley, W., Edwards, A., Williams, M., ... & Burnap, P. (2017). The ethical challenges of publishing Twitter data for research dissemination . Paper presented at the proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Web Science Conference, 339–348.
Williams, M. L., Burnap, P., & Sloan, L. (2017). Towards an ethical framework for publishing twitter data in social research: taking into account users’ views, online context and algorithmic estimation. Sociology, 51 (6), 1149–1168.
Woods, H. C., & Scott, H. (2016). # Sleepyteens: social media use in adolescence is associated with poor sleep quality, anxiety, depression and low self-esteem. Journal of Adolescence, 51 , 41–49.
Ybarra, M. L. (2004). Linkages between depressive symptomatology and internet harassment among young regular Internet users. Cyberpsychology & Behavior, 7 (2), 247–257.
Download references
Dr. Naslund is supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (U19MH113211). Dr. Aschbrenner is supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (1R01MH110965-01).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Global Health and Social Medicine, Harvard Medical School, 641 Huntington Avenue, Boston, MA, 02115, USA
John A. Naslund
Digital Mental Health Research Consultant, Mumbai, India
Ameya Bondre
Division of Digital Psychiatry, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
John Torous
Department of Psychiatry, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, NH, USA
Kelly A. Aschbrenner
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to John A. Naslund .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Naslund, J.A., Bondre, A., Torous, J. et al. Social Media and Mental Health: Benefits, Risks, and Opportunities for Research and Practice. J. technol. behav. sci. 5 , 245–257 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-020-00134-x
Download citation
Received : 19 October 2019
Revised : 24 February 2020
Accepted : 17 March 2020
Published : 20 April 2020
Issue Date : September 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-020-00134-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 24 October 2019
A scoping review of the literature on the current mental health status of physicians and physicians-in-training in North America
- Mara Mihailescu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6878-1024 1 &
- Elena Neiterman 2
BMC Public Health volume 19 , Article number: 1363 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
27k Accesses
66 Citations
11 Altmetric
Metrics details
This scoping review summarizes the existing literature regarding the mental health of physicians and physicians-in-training and explores what types of mental health concerns are discussed in the literature, what is their prevalence among physicians, what are the causes of mental health concerns in physicians, what effects mental health concerns have on physicians and their patients, what interventions can be used to address them, and what are the barriers to seeking and providing care for physicians. This review aims to improve the understanding of physicians’ mental health, identify gaps in research, and propose evidence-based solutions.
A scoping review of the literature was conducted using Arksey and O’Malley’s framework, which examined peer-reviewed articles published in English during 2008–2018 with a focus on North America. Data were summarized quantitatively and thematically.
A total of 91 articles meeting eligibility criteria were reviewed. Most of the literature was specific to burnout ( n = 69), followed by depression and suicidal ideation ( n = 28), psychological harm and distress ( n = 9), wellbeing and wellness ( n = 8), and general mental health ( n = 3). The literature had a strong focus on interventions, but had less to say about barriers for seeking help and the effects of mental health concerns among physicians on patient care.
Conclusions
More research is needed to examine a broader variety of mental health concerns in physicians and to explore barriers to seeking care. The implication of poor physician mental health on patients should also be examined more closely. Finally, the reviewed literature lacks intersectional and longitudinal studies, as well as evaluations of interventions offered to improve mental wellbeing of physicians.
Peer Review reports
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines mental health as “a state of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her community.” [ 41 ] One in four people worldwide are affected by mental health concerns [ 40 ]. Physicians are particularly vulnerable to experiencing mental illness due to the nature of their work, which is often stressful and characterized by shift work, irregular work hours, and a high pressure environment [ 1 , 21 , 31 ]. In North America, many physicians work in private practices with no access to formal institutional supports, which can result in higher instances of social isolation [ 13 , 27 ]. The literature on physicians’ mental health is growing, partly due to general concerns about mental wellbeing of health care workers and partly due to recognition that health care workers globally are dissatisfied with their work, which results in burnout and attrition from the workforce [ 31 , 34 ]. As a consequence, more efforts have been made globally to improve physicians’ mental health and wellness, which is known as “The Quadruple Aim.” [ 34 ] While the literature on mental health is flourishing, however, it has not been systematically summarized. This makes it challenging to identify what is being done to improve physicians’ wellbeing and which solutions are particularly promising [ 7 , 31 , 33 , 37 , 38 ]. The goal of our paper is to address this gap.
This paper explores what is known from the existing peer-reviewed literature about the mental health status of physicians and physicians-in-training in North America. Specifically, we examine (1) what types of mental health concerns among physicians are commonly discussed in the literature; (2) what are the reported causes of mental health concerns in physicians; (3) what are the effects that mental health concerns may have on physicians and their patients; (4) what solutions are proposed to improve mental health of physicians; and (5) what are the barriers to seeking and providing care to physicians with mental health concerns. Conducting this scoping review, our goal is to summarize the existing research, identifying the need for a subsequent systematic review of the literature in one or more areas under the study. We also hope to identify evidence-based interventions that can be utilized to improve physicians’ mental wellbeing and to suggest directions for future research [ 2 ]. Evidence-based interventions might have a positive impact on physicians and improve the quality of patient care they provide.
A scoping review of the academic literature on the mental health of physicians and physicians-in-training in North America was conducted using Arksey and O’Malley’s [ 2 ] methodological framework. Our review objectives and broad focus, including the general questions posed to conduct the review, lend themselves to a scoping review approach, which is suitable for the analysis of a broader range of study designs and methodologies [ 2 ]. Our goal was to map the existing research on this topic and identify knowledge gaps, without making any prior assumptions about the literature’s scope, range, and key findings [ 29 ].
Stage 1: identify the research question
Following the guidelines for scoping reviews [ 2 ], we developed a broad research question for our literature search, asking what does the academic literature tell about mental health issues among physicians, residents, and medical students in North America ? Burnout and other mental health concerns often begin in medical training and continue to worsen throughout the years of practice [ 31 ]. Recognizing that the study and practice of medicine plays a role in the emergence of mental health concerns, we focus on practicing physicians – general practitioners, specialists, and surgeons – and those who are still in training – residents and medical students. We narrowed down the focus of inquiry by asking the following sub-questions:
What types of mental health concerns among physicians are commonly discussed in the literature?
What are the reported causes of mental health problems in physicians and what solutions are available to improve the mental wellbeing of physicians?
What are the barriers to seeking and providing care to physicians suffering from mental health problems?
Stage 2: identify the relevant studies
We included in our review empirical papers published during January 2008–January 2018 in peer-reviewed journals. Our exclusive focus on peer-reviewed and empirical literature reflected our goal to develop an evidence-based platform for understanding mental health concerns in physicians. Since our focus was on prevalence of mental health concerns and promising practices available to physicians in North America, we excluded articles that were more than 10 years old, suspecting that they might be too outdated for our research interest. We also excluded papers that were not in English or outside the region of interest. Using combinations of keywords developed in consultation with a professional librarian (See Table 1 ), we searched databases PUBMed, SCOPUS, CINAHL, and PsychNET. We also screened reference lists of the papers that came up in our original search to ensure that we did not miss any relevant literature.
Stage 3: literature selection
Publications were imported into a reference manager and screened for eligibility. During initial abstract screening, 146 records were excluded for being out of scope, 75 records were excluded for being outside the region of interest, and 4 papers were excluded because they could not be retrieved. The remaining 91 papers were included into the review. Figure 1 summarizes the literature search and selection.
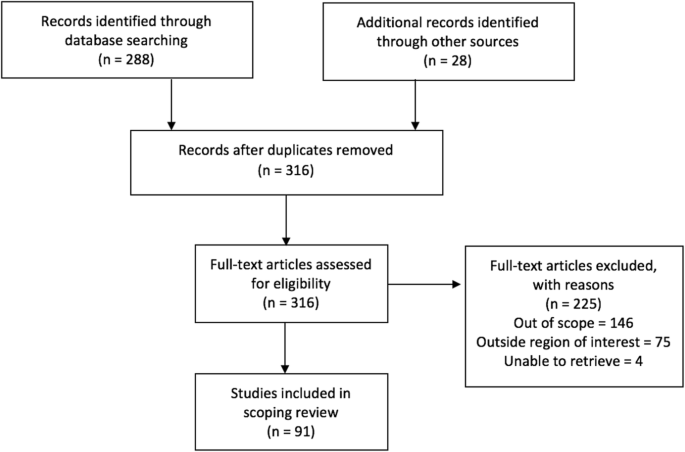
PRISMA Flow Diagram
Stage 4: charting the data
A literature extraction tool was created in Microsoft Excel to record the author, date of publication, location, level of training, type of article (empirical, report, commentary), and topic. Both authors coded the data inductively, first independently reading five articles and generating themes from the data, then discussing our coding and developing a coding scheme that was subsequently applied to ten more papers. We then refined and finalized the coding scheme and used it to code the rest of the data. When faced with disagreements on narrowing down the themes, we discussed our reasoning and reached consensus.
Stage 5: collating, summarizing, and reporting the results
The data was summarized by frequency and type of publication, mental health topics, and level of training. The themes inductively derived from the data included (1) description of mental health concerns affecting physicians and physicians-in-training; (2) prevalence of mental health concerns among this population; (3) possible causes that can explain the emergence of mental health concerns; (4) solutions or interventions proposed to address mental health concerns; (5) effects of mental health concerns on physicians and on patient outcomes; and (6) barriers for seeking and providing help to physicians afflicted with mental health concerns. Each paper was coded based on its relevance to major theme(s) and, if warranted, secondary focus. Therefore, one paper could have been coded in more than one category. Upon analysis, we identified the gaps in the literature.
Characteristics of included literature
The initial search yielded 316 records of which 91 publications underwent full-text review and were included in our scoping review. Our analysis revealed that the publications appear to follow a trend of increase over the course of the last decade reflecting the growing interest in physicians’ mental health. More than half of the literature was published in the last 4 years included in the review, from 2014 to 2018 ( n = 55), with most publications in 2016 ( n = 18) (Fig. 2 ). The majority of papers ( n = 36) focused on practicing physicians, followed by papers on residents ( n = 22), medical students ( n = 21), and those discussing medical professionals with different level of training ( n = 12). The types of publications were mostly empirical ( n = 71), of which 46 papers were quantitative. Furthermore, the vast majority of papers focused on the United States of America (USA) ( n = 83), with less than 9% focusing on Canada ( n = 8). The frequency of identified themes in the literature is broken down into prevalence of mental health concerns ( n = 15), causes of mental health concerns ( n = 18), effects of mental health concerns on physicians and patients ( n = 12), solutions and interventions for mental health concerns ( n = 46), and barriers to seeking and providing care for mental health concerns ( n = 4) (Fig. 3 ).
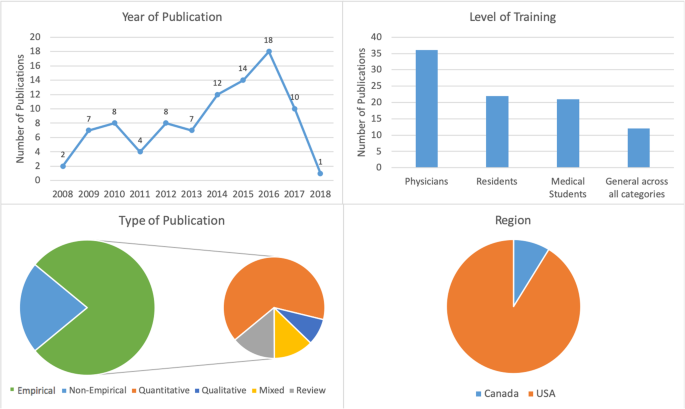
Number of sources by characteristics of included literature
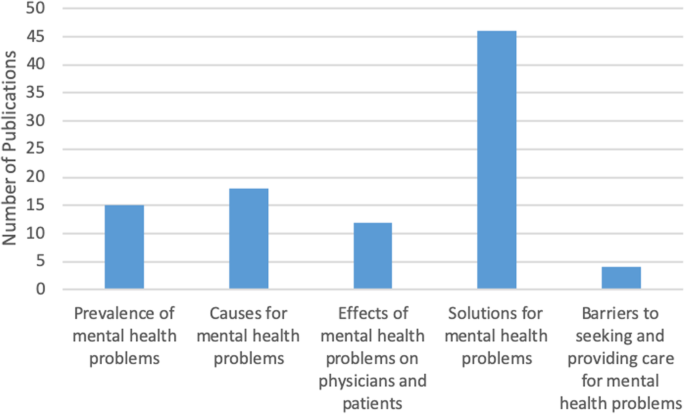
Frequency of themes in literature ( n = 91)
Mental health concerns and their prevalence in the literature
In this thematic category ( n = 15), we coded the papers discussing the prevalence of specific mental health concerns among physicians and those comparing physicians’ mental health to that of the general population. Most papers focused on burnout and stress ( n = 69), which was followed by depression and suicidal ideation ( n = 28), psychological harm and distress ( n = 9), wellbeing and wellness ( n = 8), and general mental health ( n = 3) (Fig. 4 ). The literature also identified that, on average, burnout and mental health concerns affect 30–60% of all physicians and residents [ 4 , 5 , 8 , 9 , 15 , 25 , 26 ].
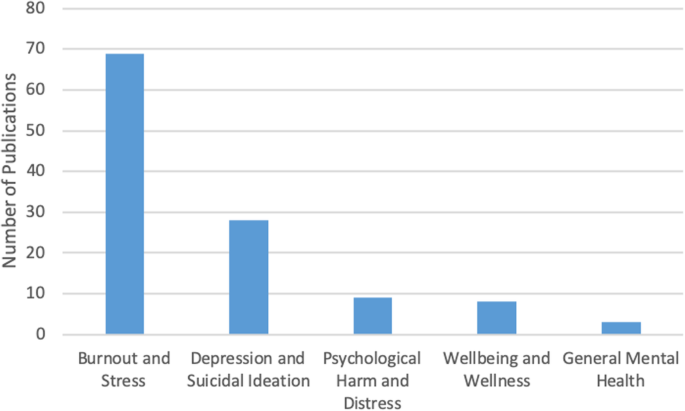
Number of sources by mental health topic discussed ( n = 91)
There was some overlap between the papers discussing burnout, depression, and suicidal ideation, suggesting that work-related stress may lead to the emergence of more serious mental health problems [ 3 , 12 , 21 ], as well as addiction and substance abuse [ 22 , 27 ]. Residency training was shown to produce the highest rates of burnout [ 4 , 8 , 19 ].
Causes of mental health concerns
Papers discussing the causes of mental health concerns in physicians formed the second largest thematic category ( n = 18). Unbalanced schedules and increasing administrative work were defined as key factors in producing poor mental health among physicians [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 13 , 15 , 27 ]. Some papers also suggested that the nature of the medical profession itself – competitive culture and prioritizing others – can lead to the emergence of mental health concerns [ 23 , 27 ]. Indeed, focus on qualities such as rigidity, perfectionism, and excessive devotion to work during the admission into medical programs fosters the selection of students who may be particularly vulnerable to mental illness in the future [ 21 , 24 ]. The third cluster of factors affecting mental health stemmed from structural issues, such as pressure from the government and insurance, fragmentation of care, and budget cuts [ 13 , 15 , 18 ]. Work overload, lack of control over work environment, lack of balance between effort and reward, poor sense of community among staff, lack of fairness and transparency by decision makers, and dissonance between one’s personal values and work tasks are the key causes for mental health concerns among physicians [ 20 ]. Govardhan et al. conceptualized causes for mental illness as having a cyclical nature - depression leads to burnout and depersonalization, which leads to patient dissatisfaction, causing job dissatisfaction and more depression [ 19 ].
Effects of mental health concerns on physicians and patients
A relatively small proportion of papers (13%) discussed the effects of mental health concerns on physicians and patients. The literature prioritized the direct effect of mental health on physicians ( n = 11) with only one paper focusing solely on the indirect effects physicians’ mental health may have on patients. Poor mental health in physicians was linked to decreased mental and physical health [ 3 , 14 , 15 ]. In addition, mental health concerns in physicians were associated with reduction in work hours and the number of patients seen, decrease in job satisfaction, early retirement, and problems in personal life [ 3 , 5 , 15 ]. Lu et al. found that poor mental health in physicians may result in increased medical errors and the provision of suboptimal care [ 25 ]. Thus physicians’ mental wellbeing is linked to the quality of care provided to patients [ 3 , 4 , 5 , 10 , 17 ].
Solutions and interventions
In this largest thematic category ( n = 46) we coded the literature that offered solutions for improving mental health among physicians. We identified four major levels of interventions suggested in the literature. A sizeable proportion of literature discussed the interventions that can be broadly categorized as primary prevention of mental illness. These papers proposed to increase awareness of physicians’ mental health and to develop strategies that can help to prevent burnout from occurring in the first place [ 4 , 12 ]. Some literature also suggested programs that can help to increase resilience among physicians to withstand stress and burnout [ 9 , 20 , 27 ]. We considered the papers referring to the strategies targeting physicians currently suffering from poor mental health as tertiary prevention . This literature offered insights about mindfulness-based training and similar wellness programs that can increase self-awareness [ 16 , 18 , 27 ], as well as programs aiming to improve mental wellbeing by focusing on physical health [ 17 ].
While the aforementioned interventions target individual physicians, some literature proposed workplace/institutional interventions with primary focus on changing workplace policies and organizational culture [ 4 , 13 , 23 , 25 ]. Reducing hours spent at work and paperwork demands or developing guidelines for how long each patient is seen have been identified by some researchers as useful strategies for improving mental health [ 6 , 11 , 17 ]. Offering access to mental health services outside of one’s place of employment or training could reduce the fear of stigmatization at the workplace [ 5 , 12 ]. The proposals for cultural shift in medicine were mainly focused on promoting a less competitive culture, changing power dynamics between physicians and physicians-in-training, and improving wellbeing among medical students and residents. The literature also proposed that the medical profession needs to put more emphasis on supporting trainees, eliminating harassment, and building strong leadership [ 23 ]. Changing curriculum for medical students was considered a necessary step for the cultural shift [ 20 ]. Finally, while we only reviewed one paper that directly dealt with the governmental level of prevention, we felt that it necessitated its own sub-thematic category because it identified the link between government policy, such as health care reforms and budget cuts, and the services and care physicians can provide to their patients [ 13 ].
Barriers to seeking and providing care
Only four papers were summarized in this thematic category that explored what the literature says about barriers for seeking and providing care for physicians suffering from mental health concerns. Based on our analysis, we identified two levels of factors that can impact access to mental health care among physicians and physicians-in-training.
Individual level barriers stem from intrinsic barriers that individual physicians may experience, such as minimizing the illness [ 21 ], refusing to seek help or take part in wellness programs [ 14 ], and promoting the culture of stoicism [ 27 ] among physicians. Another barrier is stigma associated with having a mental illness. Although stigma might be experienced personally, literature suggests that acknowledging the existence of mental health concerns may have negative consequences for physicians, including loss of medical license, hospital privileges, or professional advancement [ 10 , 21 , 27 ].
Structural barriers refer to the lack of formal support for mental wellbeing [ 3 ], poor access to counselling [ 6 ], lack of promotion of available wellness programs [ 10 ], and cost of treatment. Lack of research that tests the efficacy of programs and interventions aiming to improve mental health of physicians makes it challenging to develop evidence-based programs that can be implemented at a wider scale [ 5 , 11 , 12 , 18 , 20 ].
Our analysis of the existing literature on mental health concerns in physicians and physicians-in-training in North America generated five thematic categories. Over half of the reviewed papers focused on proposing solutions, but only a few described programs that were empirically tested and proven to work. Less common were papers discussing causes for deterioration of mental health in physicians (20%) and prevalence of mental illness (16%). The literature on the effects of mental health concerns on physicians and patients (13%) focused predominantly on physicians with only a few linking physicians’ poor mental health to medical errors and decreased patient satisfaction [ 3 , 4 , 16 , 24 ]. We found that the focus on barriers for seeking and receiving help for mental health concerns (4%) was least prevalent. The topic of burnout dominated the literature (76%). It seems that the nature of physicians’ work fosters the environment that causes poor mental health [ 1 , 21 , 31 ].
While emphasis on burnout is certainly warranted, it might take away the attention paid to other mental health concerns that carry more stigma, such as depression or anxiety. Establishing a more explicit focus on other mental health concerns might promote awareness of these problems in physicians and reduce the fear such diagnosis may have for doctors’ job security [ 10 ]. On the other hand, utilizing the popularity and non-stigmatizing image of “burnout” might be instrumental in developing interventions promoting mental wellbeing among a broad range of physicians and physicians-in-training.
Table 2 summarizes the key findings from the reviewed literature that are important for our understanding of physician mental health. In order to explicitly summarize the gaps in the literature, we mapped them alongside the areas that have been relatively well studied. We found that although non-empirical papers discussed physicians’ mental wellbeing broadly, most empirical papers focused on medical specialty (e.g. neurosurgeons, family medicine, etc.) [ 4 , 8 , 15 , 19 , 25 , 28 , 35 , 36 ]. Exclusive focus on professional specialty is justified if it features a unique context for generation of mental health concerns, but it limits the ability to generalize the findings to a broader population of physicians. Also, while some papers examined the impact of gender on mental health [ 7 , 32 , 39 ], only one paper considered ethnicity as a potential factor for mental health concerns and found no association [ 4 ]. Given that mental health in the general population varies by gender, ethnicity, age, and sexual orientation, it would be prudent to examine mental health among physicians using an intersectional analysis [ 30 , 32 , 39 ]. Finally, of the empirical studies we reviewed, all but one had a cross-sectional design. Longitudinal design might offer a better understanding of the emergence and development of mental health concerns in physicians and tailor interventions to different stages of professional career. Additionally, it could provide an opportunity to evaluate programs’ and policies’ effectiveness in improving physicians’ mental health. This would also help to address the gap that we identified in the literature – an overarching focus on proposing solutions with little demonstrated evidence they actually work.
This review has several limitations. First, our focus on academic literature may have resulted in overlooking the papers that are not peer-reviewed but may provide interesting solutions to physician mental health concerns. It is possible that grey literature – reports and analyses published by government and professional organizations – offers possible solutions that we did not include in our analysis or offers a different view on physicians’ mental health. Additionally, older papers and papers not published in English may have information or interesting solutions that we did not include in our review. Second, although our findings suggest that the theme of burnout dominated the literature, this may be the result of the search criteria we employed. Third, following the scoping review methodology [ 2 ], we did not assess the quality of the papers, focusing instead on the overview of the literature. Finally, our research was restricted to North America, specifically Canada and the USA. We excluded Mexico because we believed that compared to the context of medical practice in Canada and the USA, which have some similarities, the work experiences of Mexican physicians might be different and the proposed solutions might not be readily applicable to the context of practice in Canada and the USA. However, it is important to note that differences in organization of medical practice in Canada and the USA do exist, as do differences across and within provinces in Canada and the USA. A comparative analysis can shed light on how the structure and organization of medical practice shapes the emergence of mental health concerns.
The scoping review we conducted contributes to the existing research on mental wellbeing of American and Canadian physicians by summarizing key knowledge areas and identifying key gaps and directions for future research. While the papers reviewed in our analysis focused on North America, we believe that they might be applicable to the global medical workforce. Identifying key gaps in our knowledge, we are calling for further research on these topics, including examination of medical training curricula and its impact on mental wellbeing of medical students and residents, research on common mental health concerns such as depression or anxiety, studies utilizing intersectional and longitudinal approaches, and program evaluations assessing the effectiveness of interventions aiming to improve mental wellbeing of physicians. Focus on the effect physicians’ mental health may have on the quality of care provided to patients might facilitate support from government and policy makers. We believe that large-scale interventions that are proven to work effectively can utilize an upstream approach for improving the mental health of physicians and physicians-in-training.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
United States of America
World Health Organization
Ahmed N, Devitt KS, Keshet I, Spicer J, Imrie K, Feldman L, et al. A systematic review of the effects of resident duty hour restrictions in surgery: impact on resident wellness, training, and patient outcomes. Ann Surg. 2014;259(6):1041–53.
Article Google Scholar
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Atallah F, McCalla S, Karakash S, Minkoff H. Please put on your own oxygen mask before assisting others: a call to arms to battle burnout. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215(6):731.e1.
Baer TE, Feraco AM, Tuysuzoglu Sagalowsky S, Williams D, Litman HJ, Vinci RJ. Pediatric resident burnout and attitudes toward patients. Pediatrics. 2017;139(3):e20162163. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-2163 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Blais R, Safianyk C, Magnan A, Lapierre A. Physician, heal thyself: survey of users of the Quebec physicians health program. Can Fam Physician. 2010;56(10):e383–9.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Brennan J, McGrady A. Designing and implementing a resiliency program for family medicine residents. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2015;50(1):104–14.
Cass I, Duska LR, Blank SV, Cheng G, NC dP, Frederick PJ, et al. Stress and burnout among gynecologic oncologists: a Society of Gynecologic Oncology Evidence-based Review and Recommendations. Gynecol Oncol. 2016;143(2):421–7.
Chan AM, Cuevas ST, Jenkins J 2nd. Burnout among osteopathic residents: a cross-sectional analysis. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2016;116(2):100–5.
Chaukos D, Chad-Friedman E, Mehta DH, Byerly L, Celik A, McCoy TH Jr, et al. Risk and resilience factors associated with resident burnout. Acad Psychiatry. 2017;41(2):189–94.
Compton MT, Frank E. Mental health concerns among Canadian physicians: results from the 2007-2008 Canadian physician health study. Compr Psychiatry. 2011;52(5):542–7.
Cunningham C, Preventing MD. Burnout. Trustee. 2016;69(2):6–7 1.
PubMed Google Scholar
Daskivich TJ, Jardine DA, Tseng J, Correa R, Stagg BC, Jacob KM, et al. Promotion of wellness and mental health awareness among physicians in training: perspective of a national, multispecialty panel of residents and fellows. J Grad Med Educ. 2015;7(1):143–7.
Dyrbye LN, Shanafelt TD. Physician burnout: a potential threat to successful health care reform. JAMA. 2011;305(19):2009–10.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Epstein RM, Krasner MS. Physician resilience: what it means, why it matters, and how to promote it. Acad Med. 2013;88(3):301–3.
Evans RW, Ghosh K. A survey of headache medicine specialists on career satisfaction and burnout. Headache. 2015;55(10):1448–57.
Fahrenkopf AM, Sectish TC, Barger LK, Sharek PJ, Lewin D, Chiang VW, et al. Rates of medication errors among depressed and burnt out residents: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2008;336(7642):488–91.
Fargen KM, Spiotta AM, Turner RD, Patel S. The importance of exercise in the well-rounded physician: dialogue for the inclusion of a physical fitness program in neurosurgery resident training. World Neurosurg. 2016;90:380–4.
Gabel S. Demoralization in Health Professional Practice: Development, Amelioration, and Implications for Continuing Education. J Contin Educ Health Prof 2013 Spring. 2013;33(2):118–26.
Google Scholar
Govardhan LM, Pinelli V, Schnatz PF. Burnout, depression and job satisfaction in obstetrics and gynecology residents. Conn Med. 2012;76(7):389–95.
Jennings ML, Slavin SJ. Resident wellness matters: optimizing resident education and wellness through the learning environment. Acad Med. 2015;90(9):1246–50.
Keller EJ. Philosophy in medical education: a means of protecting mental health. Acad Psychiatry. 2014;38(4):409–13.
Krall EJ, Niazi SK, Miller MM. The status of physician health programs in Wisconsin and north central states: a look at statewide and health systems programs. WMJ. 2012;111(5):220–7.
Lemaire JB, Wallace JE. Burnout among doctors. BMJ. 2017;358:j3360.
Linzer M, Bitton A, Tu SP, Plews-Ogan M, Horowitz KR, Schwartz MD, et al. The end of the 15-20 minute primary care visit. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30(11):1584–6.
Lu DW, Dresden S, McCloskey C, Branzetti J, Gisondi MA. Impact of burnout on self-reported patient care among emergency physicians. West J Emerg Med. 2015;16(7):996–1001.
Maslach C, Schaufeli WB, Leiter MP. Job burnout. Annu Rev Psychol. 2001;52:397–422.
McClafferty H, Brown OW. Section on integrative medicine, committee on practice and ambulatory medicine, section on integrative medicine. Physician health and wellness. Pediatrics. 2014;134(4):830–5.
Miyasaki JM, Rheaume C, Gulya L, Ellenstein A, Schwarz HB, Vidic TR, et al. Qualitative study of burnout, career satisfaction, and well-being among US neurologists in 2016. Neurology. 2017;89(16):1730–8.
Peterson J, Pearce P, Ferguson LA, Langford C. Understanding scoping reviews: definition, purpose, and process. JAANP. 2016;29:12–6.
Przedworski JM, Dovidio JF, Hardeman RR, Phelan SM, Burke SE, Ruben MA, et al. A comparison of the mental health and well-being of sexual minority and heterosexual first-year medical students: a report from the medical student CHANGE study. Acad Med. 2015;90(5):652–9.
Ripp JA, Privitera MR, West CP, Leiter R, Logio L, Shapiro J, et al. Well-being in graduate medical education: a call for action. Acad Med. 2017;92(7):914–7.
Salles A, Mueller CM, Cohen GL. Exploring the relationship between stereotype perception and Residents’ well-being. J Am Coll Surg. 2016;222(1):52–8.
Shiralkar MT, Harris TB, Eddins-Folensbee FF, Coverdale JH. A systematic review of stress-management programs for medical students. Acad Psychiatry. 2013;37(3):158–64.
Sikka R, Morath J, Leape L. The quadruple aim: care, health, cost and meaning in work. BMJ Qual Saf. 2015;24(10):608–10. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004160 .
Tawfik DS, Phibbs CS, Sexton JB, Kan P, Sharek PJ, Nisbet CC, et al. Factors Associated With Provider Burnout in the NICU. Pediatrics. 2017;139(5):608. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-4134 Epub 2017 Apr 18.
Turner TB, Dilley SE, Smith HJ, Huh WK, Modesitt SC, Rose SL, et al. The impact of physician burnout on clinical and academic productivity of gynecologic oncologists: a decision analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 2017;146(3):642–6.
West CP, Dyrbye LN, Erwin PJ, Shanafelt TD. Interventions to prevent and reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2016;388(10057):2272.
Williams D, Tricomi G, Gupta J, Janise A. Efficacy of burnout interventions in the medical education pipeline. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(1):47–54.
Woodside JR, Miller MN, Floyd MR, McGowen KR, Pfortmiller DT. Observations on burnout in family medicine and psychiatry residents. Acad Psychiatry. 2008;32(1):13–9.
World Health Organization. (2001). Mental disorders affect one in four people.
World Health Organization. Promoting mental health: concepts, emerging evidence, practice (Summary Report). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not Applicable.
Not Applicable
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Telfer School of Management, University of Ottawa, 55 Laurier Ave E, Ottawa, ON, K1N 6N5, Canada
Mara Mihailescu
School of Public Health and Health Systems, University of Waterloo, 200 University Avenue West, Waterloo, ON, N2L 3G1, Canada
Elena Neiterman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M.M. and E.N. were involved in identifying the relevant research question and developing the combinations of keywords used in consultation with a professional librarian. M.M. performed the literature selection and screening of references for eligibility. Both authors were involved in the creation of the literature extraction tool in Excel. Both authors coded the data inductively, first independently reading five articles and generating themes from the data, then discussing their coding and developing a coding scheme that was subsequently applied to ten more papers. Both authors then refined and finalized the coding scheme and M.M. used it to code the rest of the data. M.M. conceptualized and wrote the first copy of the manuscript, followed by extensive drafting by both authors. E.N. was a contributor to writing the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mara Mihailescu .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Mihailescu, M., Neiterman, E. A scoping review of the literature on the current mental health status of physicians and physicians-in-training in North America. BMC Public Health 19 , 1363 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7661-9
Download citation
Received : 29 April 2019
Accepted : 20 September 2019
Published : 24 October 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7661-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mental health
- Mental illness
- Medical students
- Scoping review
- Interventions
- North America
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 10 May 2023
Mental health awareness: uniting advocacy and research
Nature Mental Health volume 1 , pages 295–296 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
4188 Accesses
16 Altmetric
Metrics details
Mental Health Month has been observed to reduce the stigma that is associated with mental illness and to educate the public and encourage individuals to make their mental health and wellbeing a priority. It is an important moment to bring the strengths of advocacy groups and researchers together to promote mental health awareness and to improve equity.
Observances have become a popular tool to garner media and notice for topics deserving attention, from medical conditions to public health concerns, commemoration of notable events, or celebration of cultural groups. Codifying the scope and needs connected to an issue or illness through awareness campaigns can provide opportunities for imparting useful information, reducing stigma and marshalling support for policy change. The impact of awareness campaigns can be difficult to measure beyond tallying social media mentions or news stories. Effective advocacy, however, extends beyond traffic and paves the way for the creation of knowledge and partnerships among allies and with those whose interests are being represented. When the magnitude of an issue and the potential for improvement are great and are matched by broad involvement and recognition by stakeholders, the possibility for impact is also great.

Held annually in May, Mental Health Month , also called Mental Health Awareness Month, is an observance with such reach, resonating with many people. Nearly everyone has experience with the challenges that are associated with mental health, either first-hand or through loved ones or in their community. There is a need for education, support and initiative to improve our understanding of the causes of mental health disorders and to increase the availability of resources for prevention and treatment. Mental Health Month also offers the possibility of bringing together groups who often work in parallel, such as mental health advocates and mental health research organizations, that can mutually benefit from each other’s functions and expertise.
Mental Health Month was first established in the US in 1949 by the National Mental Health Association, now known as Mental Health America . At a time more often associated with the outset of the Cold War and Marshall Plan than setting an agenda for domestic mental health and wellbeing advocacy, in the more than 70 years since, Mental Health Month has grown into an international event designed to reduce exclusion, stigma and discrimination against people with mental health conditions or disorders. Mental Health America are joined by other prominent mental health advocacy groups to sponsor related observances: Mental Health Awareness Week Canada (1–7 May, 2023) and Europe (22–28 May, 2023); and federal agencies such as the Substance Use Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration ( SAMSHA ) in the US, promoting related public education platforms, including National Prevention Week (7–13 May, 2023).
Observances and awareness campaigns also provide occasions to put mental health in context. Increasing acknowledgment of the role of social determinants, for example, as mechanisms that can increase vulnerability for developing disorders and that drive disparities in mental health are an important framework to underscore as part of promoting mental health awareness. Given the complex and broad scope of people, disorders, conditions and issues under the umbrella of mental health, observances also give us the chance to focus more closely on specific problems or experiences. The theme for Mental Health Month in 2023 is ‘Look Around, Look Within’, which emphasizes the interdependence of mental health and wellness with an individual’s internal and external experiences and environments.
“The ‘Look Around, Look Within’ theme builds on the growing recognition that all humans have mental health needs and that our available resources to build resilience and heal come in many forms — including in the natural world,” explains Jennifer Bright, Mental Health America Board Chair and President of Momentum Health Strategies. “Mental Health America’s strategic plan, focused on NextGen Prevention, carries a similar theme — that the social factors supporting mental health are essential building blocks. These encompass basic needs like healthy food, stable housing, and access to treatment and supports, but they also include spirituality, connection with peers with lived experience, and safe and natural spaces.”
Overlapping with Mental Health Month, Mental Health Foundation sponsors Mental Health Week in the UK (15–21 May, 2023), dedicating this year to raising awareness around anxiety. It shares an individual-centered approach to advocacy. In addition to providing toolkits and resources that point to how prevalent stress and anxiety can be to reduce stigma, it also promotes the accessibility of coping strategies for managing anxiety. As part of the Mental Health Awareness Week campaign, Mental Health Foundation and others use the international symbol of wearing a green ribbon or clothing to physically raise awareness around mental health. Nature Mental Health also incorporates the symbol of the green ribbon on the cover of this month’s issue and as our journal theme color. Green evokes the ideas of vitality, growth, new beginnings and hope — powerful imagery in mental health awareness.
Alongside stories, sponsorships and social media resources, mental health advocacy toolkits and strategy documents include fact sheets and messaging that are shaped and informed by research. Yet, there is often a perception that a divide exists between the mental health advocacy and research spaces, but observances such as Mental Health Month can bridge the two.
According to Lea Milligan, Chief Executive Officer of MQ: Transforming Mental Health , an international mental health research organization, there are complementary approaches and priorities in advocacy and research: “Mental health research can be used to bolster awareness by providing evidence-based information and resources that can help individuals and communities better understand mental health and the factors that contribute to mental health problems. This can include information on risk factors, prevention strategies, and available treatments.”
In addition, increased efforts to involve people with lived experience of mental illness in the research enterprise is a goal that is well-served through connection with advocacy. “While MQ is primarily focused on promoting mental health research, it also recognizes the importance of advocacy in advancing the mental health agenda” suggests Milligan. “MQ advocates for increased funding and support for mental health research, as well as policies that promote mental health and wellbeing. Additionally, MQ seeks to empower individuals with lived experience of mental health conditions to be involved in research and advocacy efforts, and to have their voices heard in the development of policies and programs that affect their lives. MQ provides resources and support for individuals with lived experience who wish to be involved in research or advocacy efforts, including training programs, research grants, and opportunities to participate in research studies.”
Involvement or engagement is certainly one of the most important metrics of advocacy. By strengthening collaboration between advocacy and research organizations and identifying the mutual areas of benefit, such as engagement and increased funding, we may find new ways to green light mental health awareness and action toward mental health equity.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Mental health awareness: uniting advocacy and research. Nat. Mental Health 1 , 295–296 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44220-023-00072-6
Download citation
Published : 10 May 2023
Issue Date : May 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s44220-023-00072-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

Transforming the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses.
Información en español
Celebrating 75 Years! Learn More >>
Research funded by nimh, research conducted at nimh (intramural research program), priority research areas.
- Research Resources
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), is the lead federal agency for research on mental disorders, supporting research that aims to transform the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses through basic and clinical research. Learn more about NIMH-funded research areas, policies, resources, initiatives, and research conducted by NIMH.

Notify the NIMH Press Team about NIMH-funded research that has been submitted to a journal for publication, and we may be able to promote the findings.

NIMH Strategic Plan
The NIMH Strategic Plan for Research outlines the Institute's research goals and priorities over the next five years. Learn more about the Strategic Plan.
NIMH supports research at universities, medical centers, and other institutions via grants, contracts, and cooperative agreements. Learn more about NIMH research areas, policies, resources, and initiatives:
- Research Domain Criteria (RDoC)
- Policies and Procedures
- Inside NIMH - Funding and Research News
The Division of Intramural Research Programs (IRP) is the internal research division of the NIMH. Over 40 research groups conduct basic neuroscience research and clinical investigations of mental illnesses, brain function, and behavior at the NIH campus in Bethesda, Maryland. Learn more about research conducted at NIMH:
- Intramural Investigators
- Intramural Research Groups
- Fellowships and Training
- Office of the Scientific Director
- Collaborations and Partnerships
- Join a Study
- IRP News and Events

- NIMH Priority Research Areas
- Highlighted Research Initiatives
Resources for Researchers
- Psychosocial Research at NIMH: A Primer
- Genomics Research Guidance for Grant Applicants
NIMH Women Leading Mental Health Research
Diversity in the scientific workforce enhances excellence, creativity, and innovation. NIMH and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are committed to increasing diversity in the scientific workforce. Learn more about early-career women scientists whose NIMH-funded research is playing a role in advancing our mission of transforming the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses.
Mental Health, Substance Use, and Child Maltreatment
Child maltreatment is a pressing concern in the United States, with more than four million children referred to child protective services in 2022. Reducing child maltreatment is a national health objective given the substantial, negative consequences for children who experience maltreatment, both in the short- and long-term. Parental mental health and substance use disorders are strongly associated with child maltreatment. In this study, we use administrative data over the period 2004 to 2021 to study the relationship between the number of mental health and substance use treatment centers per county and child maltreatment reports. Our findings provide evidence that better access to mental health and substance use treatment reduces child maltreatment reports. In particular, an 8% increase in the supply of treatment would reduce maltreatment reports by 1%. These findings suggest that recent and ongoing efforts by the federal government to expand mental health and substance use treatment availability may lead to reduced child maltreatment.
All authors contributed equally to this study. Authors are listed in alphabetical order. Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute on Mental Health of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number 1R01MH132552 (PI: Johanna Catherine Maclean). Dr. Meinhofer acknowledges support from the Foundation for Opioid Response Efforts GR00015582 and the National Institute on Drug Abuse K01DA051777. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Institutes of Health or the Foundation for Opioid Response Efforts. We thank Douglas Webber and Jiaxin Wei for excellent comments. All errors are our own. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
More from NBER
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

- Open access
- Published: 30 August 2024
Research landscape analysis on dual diagnosis of substance use and mental health disorders: key contributors, research hotspots, and emerging research topics
- Waleed M. Sweileh 1
Annals of General Psychiatry volume 23 , Article number: 32 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Substance use disorders (SUDs) and mental health disorders (MHDs) are significant public health challenges with far-reaching consequences on individuals and society. Dual diagnosis, the coexistence of SUDs and MHDs, poses unique complexities and impacts treatment outcomes. A research landscape analysis was conducted to explore the growth, active countries, and active journals in this field, identify research hotspots, and emerging research topics.
A systematic research landscape analysis was conducted using Scopus to retrieve articles on dual diagnosis of SUDs and MHDs. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied to focus on research articles published in English up to December 2022. Data were processed and mapped using VOSviewer to visualize research trends.
A total of 935 research articles were found. The number of research articles on has been increasing steadily since the mid-1990s, with a peak of publications between 2003 and 2012, followed by a fluctuating steady state from 2013 to 2022. The United States contributed the most articles (62.5%), followed by Canada (9.4%). The Journal of Dual Diagnosis , Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment , and Mental Health and Substance Use Dual Diagnosis were the top active journals in the field. Key research hotspots include the comorbidity of SUDs and MHDs, treatment interventions, quality of life and functioning, epidemiology, and the implications of comorbidity. Emerging research topics include neurobiological and psychosocial aspects, environmental and sociocultural factors, innovative interventions, special populations, and public health implications.
Conclusions
The research landscape analysis provides valuable insights into dual diagnosis research trends, active countries, journals, and emerging topics. Integrated approaches, evidence-based interventions, and targeted policies are crucial for addressing the complex interplay between substance use and mental health disorders and improving patient outcomes.
Introduction
Substance use disorders (SUDs) refer to a range of conditions characterized by problematic use of psychoactive substances, leading to significant impairment in physical, psychological, and social functioning [ 1 ]. These substances may include alcohol, tobacco, illicit drugs (e.g., cocaine, opioids, cannabis), and prescription medications. The global burden of SUDs is substantial, with far-reaching consequences on public health, socio-economic development, and overall well-being. For instance, alcohol abuse accounts for 3 million deaths worldwide annually, while the opioid crisis has escalated to unprecedented levels in certain regions, such as North America, resulting in tens of thousands of overdose deaths per year [ 2 , 3 , 4 ]. Mental health disorders (MHDs) encompass a wide range of conditions that affect mood, thinking, behavior, and emotional well-being [ 5 ]. Examples of MHDs include depression, anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and eating disorders. These conditions can significantly impair an individual's ability to function, negatively impacting their quality of life, relationships, and overall productivity [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Furthermore, certain MHD such as major depressive disorder and anxiety are often associated with specific affective temperaments, hopelessness, and suicidal behavior and grasping such connections can help in crafting customized interventions to reduce suicide risk [ 9 ]. In addition, a systematic review of 18 studies found that demoralization with somatic or psychiatric disorders is a significant independent risk factor for suicide and negative clinical outcomes across various populations [ 10 ]. The coexistence of SUDs and MHDs, often referred to as dual diagnosis or comorbidity, represents a complex and prevalent phenomenon that significantly impacts affected individuals and healthcare systems [ 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. For instance, individuals with depression may be more likely to self-medicate with alcohol or drugs to cope with emotional distress [ 16 ]. Similarly, PTSD has been linked to increased rates of substance abuse, as individuals attempt to alleviate the symptoms of trauma [ 17 , 18 ]. Moreover, chronic substance use can lead to changes in brain chemistry, increasing the risk of developing MHDs or exacerbating existing conditions [ 17 , 19 , 20 , 21 ]. The coexistence of SUDs and MHDs presents unique challenges from a medical and clinical standpoint. Dual diagnosis often leads to more severe symptoms, poorer treatment outcomes, increased risk of relapse, and higher rates of hospitalization compared to either disorder alone [ 22 ]. Additionally, diagnosing and treating dual diagnosis cases can be complex due to overlapping symptoms and interactions between substances and psychiatric medications. Integrated treatment approaches that address both conditions simultaneously are essential for successful recovery and improved patient outcomes [ 20 ]. Patients grappling with dual diagnosis encounter a multifaceted web of barriers when attempting to access essential mental health services. These barriers significantly compound the complexity of their clinical presentation. The first barrier pertains to stigma, where societal prejudices surrounding mental health and substance use disorders deter individuals from seeking help, fearing discrimination or social repercussions [ 23 ]. A lack of integrated care, stemming from fragmented healthcare systems, poses another significant hurdle as patients often struggle to navigate separate mental health and addiction treatment systems [ 24 ]. Insurance disparities contribute by limiting coverage for mental health services and imposing strict criteria for reimbursement [ 25 ]. Moreover, there is a shortage of adequately trained professionals equipped to address both substance use and mental health issues, creating a workforce barrier [ 26 ]. Geographical disparities in access further hinder care, particularly in rural areas with limited resources [ 27 ]. These barriers collectively serve to exacerbate the clinical complexity of patients with dual diagnosis, and ultimately contributing to poorer outcomes.
A research landscape analysis involves a systematic review and synthesis of existing literature on a specific topic to identify key trends, knowledge gaps, and research priorities [ 28 , 29 ]. Scientific research landscape analysis, is motivated by various factors. First, the rapid growth of scientific literature poses a challenge for researchers to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their respective fields. Research landscape analysis provides a structured approach to comprehend the vast body of literature, identifying crucial insights and emerging trends. Additionally, it plays a vital role in identifying knowledge gaps, areas with limited research, or inadequate understanding. This pinpointing allows researchers to focus on critical areas that demand further investigation, fostering more targeted and impactful research efforts [ 30 ]. Furthermore, in the realm of policymaking and resource allocation, evidence-based decision-making is crucial. Policymakers and funding agencies seek reliable information to make informed decisions about research priorities. Research landscape analysis offers a comprehensive view of existing evidence, facilitating evidence-based decision-making processes [ 28 ]. When it comes to the research landscape analysis of dual diagnosis of SUDs and MHDs, there are several compelling justifications to explore this complex comorbidity and gain a comprehensive understanding of its interplay and impact on patient outcomes. Firstly, the complexity of the interplay between SUDs and MHDs demands a comprehensive examination of current research to unravel the intricacies of this comorbidity [ 31 ]. Secondly, dual diagnosis presents unique challenges for treatment and intervention strategies due to the overlapping symptoms and interactions between substances and psychiatric medications. A research landscape analysis can shed light on effective integrated treatment approaches and identify areas for improvement [ 18 ]. Moreover, the public health impact of co-occurring SUDs and MHDs is substantial, resulting in more severe symptoms, poorer treatment outcomes, increased risk of relapse, and higher rates of hospitalization. Understanding the research landscape can inform public health policies and interventions to address this issue more effectively [ 32 ]. Lastly, the holistic approach of research landscape analysis enables a comprehensive understanding of current knowledge, encompassing epidemiological data, risk factors, treatment modalities, and emerging interventions. This integrative approach can lead to more coordinated and effective care for individuals with dual diagnosis [ 22 ]. Based on the above argument, the current study aims to conduct a research landscape analysis of dual diagnosis of SUDs and MHDs. The research landscape analysis bears a lot of significance for individuals and society. First and foremost, it’s a beacon of hope for individuals seeking help. Research isn’t just about dry statistics; it's about finding better ways to treat and support those facing dual diagnosis. By being informed about the latest breakthroughs, healthcare professionals can offer more effective, evidence-backed care, opening the door to improved treatment outcomes and a brighter future for those they serve. Beyond the individual level, this understanding has profound societal implications. It has the power to chip away at the walls of stigma that often surround mental health and substance use issues. Greater awareness and knowledge about the complexities of dual diagnosis can challenge stereotypes and biases, fostering a more compassionate and inclusive society. Additionally, society allocates resources based on research findings. When we understand the prevalence and evolving nature of dual diagnosis, policymakers and healthcare leaders can make informed decisions about where to channel resources most effectively. This ensures that the needs of individuals struggling with co-occurring disorders are not overlooked or under-prioritized. Moreover, research helps identify risk factors and early warning signs related to dual diagnosis. Armed with this information, we can develop prevention strategies and early intervention programs, potentially reducing the incidence of co-occurring disorders and mitigating their impact. Legal and criminal justice systems also stand to benefit. Understanding dual diagnosis trends can inform policies related to diversion programs, treatment alternatives to incarceration, and the rehabilitation of individuals with co-occurring disorders, potentially reducing rates of reoffending. Moreover, dual diagnosis research contributes to public health planning by highlighting the need for integrated mental health and addiction services. This knowledge can guide the development of comprehensive healthcare systems that offer holistic care to individuals with co-occurring disorders. Families and communities, too, are vital players in this narrative. With a grasp of research findings, they can provide informed, empathetic, and effective support to their loved ones, contributing to better outcomes.
The present research landscape analysis of dual diagnosis of SUDs and MHDs was conducted using a systematic approach to retrieve, process, and analyze relevant articles. The following methodology outlines the key steps taken to address the research questions:
Research Design The present study constitutes a thorough and robust analysis of the research landscape concerning the dual diagnosis of SUD and MHD. It's important to note that the research landscape analysis differs from traditional systematic or scoping reviews. In conducting research landscape analysis, we made deliberate methodological choices aimed at achieving both timely completion and unwavering research quality. These choices included a strategic decision to focus our search exclusively on a single comprehensive database, a departure from the customary practice of utilizing multiple databases. Furthermore, we streamlined the quality control process by assigning specific quality checks to a single author, rather than following the conventional dual-reviewer approach. This approach prioritized efficiency and expediency without compromising the rigor of our analysis. To expedite the research process further, we opted for a narrative synthesis instead of a quantitative one, ensuring that we provide a succinct yet highly informative summary of the available evidence. We place a premium on research transparency and, as such, are committed to sharing the detailed search string employed for data retrieval. This commitment underscores our dedication to fostering reproducibility and transparency in research practices.
Ethical considerations Since the research landscape analysis involved the use of existing and publicly available literature, and no human subjects were directly involved, no formal ethical approval was required.
Article retrieval Scopus, a comprehensive bibliographic database, was utilized to retrieve articles related to the dual diagnosis of SUDs and MHDs. Scopus is a multidisciplinary abstract and citation database that covers a wide range of scientific disciplines, including life sciences, physical sciences, social sciences, and health sciences. It includes content from thousands of scholarly journals.
Keywords used To optimize the search process and ensure the inclusion of pertinent articles, a set of relevant keywords and equivalent terms were employed. Keywords for “dual diagnosis” included dual diagnosis, co-occurring disorders, comorbid substance use, comorbid addiction, coexisting substance use, combined substance use, simultaneous substance use, substance use and psychiatric, co-occurring substance use and psychiatric, concurrent substance use and mental, coexisting addiction and mental, combined addiction and mental, simultaneous addiction and mental, substance-related and psychiatric, comorbid mental health and substance use, co-occurring substance use and psychiatric, concurrent mental health and substance use, coexisting mental health and substance use, combined mental health and substance use, simultaneous mental health and substance use, substance-related and coexisting psychiatric, comorbid psychiatric and substance abuse, co-occurring mental health and substance-related, concurrent psychiatric and substance use, coexisting psychiatric and substance abuse, combined psychiatric and substance use, simultaneous psychiatric and substance use, substance-related and concurrent mental, substance abuse comorbidity. Keywords for “Substance use disorders” included substance abuse, substance dependence, drug use disorders, addiction, substance-related disorders, drug abuse, opioid use disorder, cocaine use disorder, alcohol use disorder, substance misuse, substance use disorder, substance-related, substance addiction. Keywords for “Mental health disorders” included psychiatric disorders, mental illnesses, mental disorders, emotional disorders, psychological disorders, schizophrenia, depression, PTSD, ADHD, anxiety, bipolar disorder, eating disorders, personality disorders, mood disorders, psychotic disorders, mood and anxiety disorders, mental health conditions. To narrow down the search to focus specifically on dual diagnosis, we adopted a strategy that involved the simultaneous presence of SUDs and MHDs in the presence of specific keywords in the titles and abstracts such as “dual,” “co-occurring,” “concurrent,” “co-occurring disorders,” “dual disorders,” “dual diagnosis,” “comorbid psychiatric,” “cooccurring psychiatric,” “comorbid*,” and “coexisting”.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria To maintain the study’s focus and relevance, specific inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied. Included articles were required to be research article, written in English, and published in peer-reviewed journals up to December 31, 2022, Articles focusing on animal studies, internet addiction, obesity, pain, and validity of instruments and tools were excluded.
Flow chart of the search strategy Supplement 1 shows the overall search strategy and the number of articles retrieved in each step. The total number of research articles that met the inclusion and exclusion criteria were 935.
Validation of search strategy The effectiveness of our search strategy was rigorously assessed through three distinct methods, collectively demonstrating its ability to retrieve pertinent articles while minimizing false positives. First, to gauge precision, we meticulously examined a sample of 30 retrieved articles, scrutinizing their alignment with our research question and their contributions to the topic of dual diagnosis. This manual review revealed that the majority of the assessed articles were highly relevant to our research focus. Second, for a comprehensive evaluation, we compared the articles obtained through our search strategy with a set of randomly selected articles from another source. This set comprised 10 references sourced from Google Scholar [ 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 ], and the aim was to determine if our strategy successfully identified articles selected at random from an alternative database. Impressively, our analysis showed that the search strategy had a notably high success rate in capturing these randomly selected articles. Lastly, to further corroborate the relevance of our retrieved articles, we investigated the research interests of the top 10 active authors and the subject scope of the top 10 active journals. This exploration confirmed that their areas of expertise and the journal scopes were in alignment with the field of mental health and/or substance use disorders. These three validation methods collectively reinforce the reliability of our search strategy, affirming that the vast majority of the retrieved articles are indeed pertinent to our research inquiry.
Data processing and mapping Data extracted from the selected articles were processed and organized using Microsoft Excel. Information on the titles/abstracts/author keywords, year of publication, journal name, authors, institution and country affiliation, and number of citations received by the article were extracted. To visualize and analyze the research landscape, VOSviewer, a bibliometric analysis tool, was employed [ 43 ]. This software enables mapping and clustering of co-occurring terms, authors, and countries, providing a comprehensive overview of the dual diagnosis research domain.
Interpreting VOSviewer maps and generating research topics
We conducted a rigorous analysis and generated a comprehensive research landscape using VOSviewer, a widely acclaimed software tool renowned for its expertise in mapping research domains. We seamlessly integrated pertinent data extracted from the Scopus database, including publication metadata, into VOSviewer to delve into the frequency of author keywords and terminologies. The resulting visualizations provided us with profound insights into the intricate web of interconnected research topics and their relationships within the field. Interpreting VOSviewer maps is akin to navigating a vibrant and interconnected tapestry of knowledge. Each term or keyword in the dataset is depicted as a point on the map, represented by a circle or node. These nodes come in varying sizes and colors and are interconnected by lines of differing thicknesses. The size of a node serves as an indicator of the term’s significance or prevalence within the dataset. Larger nodes denote that a specific term is frequently discussed or plays a pivotal role in the body of research, while smaller nodes signify less commonly mentioned concepts. The colors assigned to these nodes serve a dual purpose. Firstly, they facilitate the categorization of terms into thematic groups, with terms of the same color typically belonging to the same cluster or sharing a common thematic thread. Secondly, they aid in the identification of distinct research clusters or thematic groups within the dataset. For instance, a cluster of blue nodes might indicate that these terms are all associated with a particular area of research. The spatial proximity of nodes on the map reflects their closeness in meaning or concept. Nodes positioned closely together share a robust semantic or contextual connection and are likely to be co-mentioned in research articles or share a similar thematic focus. Conversely, nodes situated farther apart indicate less commonality in terms of their usage in the literature. The lines that link these nodes represent the relationships between terms. The thickness of these lines provides insights into the strength and frequency of these connections. Thick lines indicate that the linked terms are frequently discussed together or exhibit a robust thematic association, while thinner lines imply weaker or less frequent connections. In essence, VOSviewer maps offer a visual narrative of the underlying structure and relationships within your dataset. By examining node size and color, you can pinpoint pivotal terms and thematic clusters. Simultaneously, analyzing the distance between nodes and line thickness unveils the semantic closeness and strength of associations between terms. These visual insights are invaluable for researchers seeking to unearth key concepts, identify research clusters, and track emerging trends within their field of study.
Growth pattern, active countries, and active journals
The growth pattern of the 935 research articles on dual diagnosis of substance use disorders and mental health disorders shows an increasing trend in the number of published articles over the years. Starting from the late 1980s and early 1990s with only a few publications, the research interest gradually picked up momentum, and the number of articles has been consistently rising since the mid-1990s. Table 1 shows the number of articles published in three different periods. The majority of publications (52.2%) were produced between 2003 and 2012, indicating a significant surge in research during that decade. The subsequent period from 2013 to 2022 saw a continued interest in the subject, accounting for 35.5% of the total publications. The number of articles published per year during the period from 2013 to 2022 showed a fluctuating steady state with an average of approximately 33 articles per year. The earliest period from 1983 to 2002 comprised 12.3% of the total publications, reflecting the initial stages of research and the gradual development of interest in the field.
Out of the total 935 publications, the United States contributed the most with 585 publications, accounting for approximately 62.5% of the total research output. Canada follows with 88 publications, making up around 9.4% of the total. The United Kingdom and Australia also made substantial contributions with 70 and 53 publications, accounting for 7.5 and 5.7%, respectively. Table 2 shows the top 10 active countries.
Based on the list of top active journals in the field of dual diagnosis of substance use and mental health disorders, it is evident that there are several reputable and specialized journals that focus on this important area of research (Table 3 ). These journals cover a wide range of topics related to dual diagnosis, including comorbidity, treatment approaches, intervention strategies, and epidemiological studies. The Journal of Dual Diagnosis appears to be a leading and comprehensive platform for research on dual diagnosis. It covers a broad spectrum of studies related to substance use disorders and mental health conditions. The Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment ranked second while the Mental Health and Substance Use Dual Diagnosis journal ranked third and seems to be dedicated specifically to the intersection of substance use disorder and mental health disorders, providing valuable insights and research findings related to comorbidities and integrated treatment approaches.
Most frequent author keywords
Mapping author keywords with a minimum occurrence of five (n = 96) provides insights in research related to dual diagnosis. Figure 1 shows the 96 author keywords and their links with other keywords. The number of occurrences represent the number of times each author keyword appears in the dataset, while the total link strength (TLS) indicates the combined strength of connections between keywords based on their co-occurrence patterns. The most frequent author keywords with high occurrences and TLS represent the key areas of focus in research on the dual diagnosis of substance use and mental health disorders.
“Comorbidity” is the most frequent keyword, with 144 occurrences and a high TLS of 356. This reflects the central theme of exploring the co-occurrence of substance use disorders and mental health conditions and their complex relationship. “Substance use disorder” and “dual diagnosis” are also highly prevalent keywords with 122 and 101 occurrences, respectively. These terms highlight the primary focus on studying individuals with both substance use disorders and mental health disorders, underscoring the significance of dual diagnosis in research. “Co-occurring disorders” and “substance use disorders” are frequently used, indicating a focus on understanding the relationship between different types of disorders and the impact of substance use on mental health. Several specific mental health disorders such as “schizophrenia,” “depression,” “bipolar disorder,” and “PTSD” are prominent keywords, indicating a strong emphasis on exploring the comorbidity of these disorders with substance use. “Mental health” and “mental illness” are relevant keywords, reflecting the broader context of research on mental health conditions and their interaction with substance use. “Treatment” is a significant keyword with 34 occurrences, indicating a focus on investigating effective interventions and treatment approaches for individuals with dual diagnosis. “Addiction” and “recovery” are important keywords, highlighting the interest in understanding the addictive nature of substance use and the potential for recovery in this population. The mention of “veterans” as a keyword suggests a specific focus on the dual diagnosis of substance use and mental health disorders in the veteran population. “Integrated treatment” is an important keyword, indicating an interest in studying treatment approaches that address both substance use and mental health disorders together in an integrated manner.
Network visualization map of author keywords with a minimum occurrence of five in the retrieved articles on dual diagnosis of substance use and mental health disorders
Most impactful research topics
To have an insight into the most impactful research topics on dual diagnosis, the top 100 research articles were visualized and the terms with the largest node size and TLS were used to. To come up with the five most common investigated research topics:
Dual diagnosis and comorbidity of SUDs and MHDs: This topic focuses on the co-occurrence of substance use disorders and various mental health conditions, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, PTSD, anxiety disorders, and major depressive disorder. This research topic explored the prevalence, characteristics, and consequences of comorbidity in different populations, including veterans, adolescents, and individuals experiencing homelessness [ 13 , 19 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 ].
Treatment and interventions for co-occurring disorders: This topic involves studies on different treatment approaches and interventions for individuals with dual diagnosis. These interventions may include motivational interviewing, cognitive-behavioral therapy, family intervention, integrated treatment models, assertive community treatment, and prolonged exposure therapy. The goal is to improve treatment outcomes and recovery for individuals with co-occurring substance use and mental health disorders [ 48 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 ].
Quality of life and functioning in individuals with dual diagnosis: This research topic explores the impact of dual diagnosis on the quality of life and functioning of affected individuals. It assesses the relationship between dual diagnosis and various aspects of well-being, including social functioning, physical health, and overall quality of life [ 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 ].
Epidemiology and prevalence of co-occurring disorders: This topic involves population-based studies that investigate the prevalence of comorbid substance use and mental health disorders. It examines the demographic and clinical correlates of dual diagnosis, as well as risk factors associated with the development of co-occurring conditions [ 50 , 52 , 60 , 65 , 66 , 67 ].
Implications and consequences of comorbidity: This research topic explores the consequences of comorbidity between substance use and mental health disorders, such as treatment utilization, service access barriers, criminal recidivism, and the impact on suicidality. It also investigates the implications of comorbidity for treatment outcomes and the potential risks associated with specific comorbidities [ 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 ].
Emerging research topics
Upon scrutinizing the titles, abstracts, author keywords, and a visualization map of the 100 recently published articles, the research themes listed below came to the forefront. It’s worth noting that some of the research themes in the 100 recently published articles were not groundbreaking; rather, they represented a natural progression of ongoing research endeavors, and that is why they were not listed as emerging research themes. For instance, there was a continuation of research into the prevalence and epidemiology of co-occurring mental illnesses and substance use disorders and characteristics of various cases of co-morbid cases of SUDs and MHDs. The list below included such emergent themes. It might seem that certain aspects within these research themes duplicate the initial research topics, but it’s crucial to emphasize that this is not the case. For example, both themes delve into investigations concerning treatment, yet the differentiation lies in the treatment approach adopted.
Neurobiological and psychosocial aspects of dual diagnosis: This research topic focuses on exploring the neurobiological etiology and underlying mechanisms of comorbid substance use and mental health disorders. It investigates brain regions, neurotransmitter systems, hormonal pathways, and other neurobiological factors contributing to the development and maintenance of dual diagnosis. Additionally, this topic may examine psychosocial aspects, such as trauma exposure, adverse childhood experiences, and social support, that interact with neurobiological factors in the context of comorbidity [ 76 ].
Impact of environmental and sociocultural factors on dual diagnosis: This research topic delves into the influence of environmental and sociocultural factors on the occurrence and course of comorbid substance use and mental health disorders. It may explore how cultural norms, socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, and societal attitudes toward mental health and substance use affect the prevalence, treatment outcomes, and quality of life of individuals with dual diagnosis [ 77 , 78 ].
New interventions and treatment approaches for dual diagnosis: This topic involves studies that propose and evaluate innovative interventions and treatment approaches for individuals with dual diagnosis. These interventions may include novel psychotherapeutic techniques, pharmacological treatments, digital health interventions, and integrated care models. The research aims to improve treatment effectiveness, adherence, and long-term recovery outcomes in individuals with comorbid substance use and mental health disorders [ 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 ].
Mental health and substance use in special populations with dual diagnosis: This research topic focuses on exploring the prevalence and unique characteristics of comorbid substance use and mental health disorders in specific populations, such as individuals with eating disorders, incarcerated individuals, and people with autism spectrum disorder. It aims to identify the specific needs and challenges faced by these populations and develop tailored interventions to address their dual diagnosis [ 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 ].
Public health implications and policy interventions for dual diagnosis: This topic involves research that addresses the public health implications of dual diagnosis and the need for policy interventions to address this complex issue. It may include studies on the economic burden of comorbidity, the impact on healthcare systems, and the evaluation of policy initiatives aimed at improving prevention, early intervention, and access to integrated care for individuals with dual diagnosis [ 81 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 ].
Comparison in research topics
The comparison between the most impactful research topics and emerging research topics in the field of dual diagnosis reveals intriguing insights into the evolving landscape of this critical area of study (Table 4 ). In the most impactful research topics, there is a strong emphasis on the epidemiology of dual diagnosis, indicating a well-established foundation in understanding the prevalence, characteristics, and consequences of comorbid SUDs and MHDs. Treatment and interventions also receive considerable attention, highlighting the ongoing efforts to improve outcomes and recovery for individuals with dual diagnosis. Quality of life and medical consequences are additional focal points, reflecting the concern for the holistic well-being of affected individuals and the health-related implications of comorbidity.
On the other hand, emerging research topics signify a shift towards newer methods and interventions. The exploration of neurobiology in the context of dual diagnosis reflects a growing interest in unraveling the underlying neurobiological mechanisms contributing to comorbidity. This shift suggests a deeper understanding of the neural pathways and potential targets for intervention. The consideration of dual diagnosis in special groups underscores a recognition of the unique needs and challenges faced by specific populations, such as individuals with autism spectrum disorder. This tailored approach acknowledges that one size does not fit all in addressing dual diagnosis. Finally, the exploration of environmental and psychosocial contexts highlights the importance of socio-cultural factors, policy interventions, and societal attitudes in shaping the experience of individuals with dual diagnosis, signaling a broader perspective that extends beyond clinical interventions. In summary, while the most impactful research topics have laid a strong foundation in epidemiology, treatment, quality of life, and medical consequences, the emerging research topics point to a promising future with a deeper dive into the neurobiology of dual diagnosis, a focus on special populations, and a broader consideration of the environmental and psychosocial context. This evolution reflects the dynamic nature of dual diagnosis research as it strives to advance our understanding and improve the lives of those affected by comorbid substance use and mental health disorders.
The main hypothesis underlying the study was that dual diagnosis, or the comorbidity of SUDs and MHDs, was historically underrecognized and under-researched. Over time, however, there has been a significant increase in understanding, appreciation, and research into this complex interplay in clinical settings. This was expected to manifest through a growing number of publications, increased attention to integrated treatment approaches, and a heightened recognition of the complexities and public health implications associated with dual diagnosis. The study aims to analyze this progression and its implications through a research landscape analysis, identifying key trends, knowledge gaps, and research priorities. The research landscape analysis of the dual diagnosis of SUDs and MHDs has unveiled a substantial and evolving body of knowledge, with a notable rise in publications since the mid-1990s and a significant surge between 2003 and 2012. This growing research interest underscores the increasing recognition of the importance and complexity of dual diagnosis in clinical and public health contexts. The United States has emerged as the most active contributor, followed by Canada, the United Kingdom, and Australia, with specialized journals such as the Journal of Dual Diagnosis playing a pivotal role in disseminating research findings. Common keywords such as “comorbidity,” “substance use disorder,” “dual diagnosis,” and specific mental health disorders highlight the primary focus areas, with impactful research topics identified as the comorbidity of SUDs and MHDs, treatment and interventions, quality of life, epidemiology, and the implications of comorbidity. Emerging research themes emphasize neurobiological and psychosocial aspects, the impact of environmental and sociocultural factors, innovative treatment approaches, and the needs of special populations with dual diagnosis, reflecting a shift towards a more holistic and nuanced understanding. The study highlights a shift from traditional epidemiological studies towards understanding the underlying mechanisms and broader social determinants of dual diagnosis, with a need for continued research into integrated treatment models, specific needs of diverse populations, and the development of tailored interventions.
The findings of this research landscape analysis have significant implications for clinical practice, public health initiatives, policy development, and future research endeavors. Clinicians and healthcare providers working with individuals with dual diagnosis can benefit from the identified research hotspots, as they highlight crucial aspects that require attention in diagnosis, treatment, and support. The prominence of treatment and intervention topics indicates the need for evidence-based integrated approaches that address both substance use and mental health disorders concurrently [ 102 , 103 , 104 ]. The research on the impact of dual diagnosis on quality of life and functioning underscores the importance of holistic care that addresses psychosocial and functional well-being [ 63 ]. For public health initiatives, understanding the prevalence and epidemiological aspects of dual diagnosis is vital for resource allocation and the development of effective prevention and early intervention programs. Policymakers can use the research landscape analysis to inform policies that promote integrated care, reduce barriers to treatment, and improve access to mental health and substance abuse services [ 15 , 105 ]. Furthermore, the identification of emerging topics offers opportunities for investment in research areas that are gaining momentum and importance.
The present study lays a robust groundwork, serving as a catalyst for the advancement of research initiatives and the formulation of comprehensive policies and programs aimed at elevating the quality of life for individuals grappling with the intricate confluence of SUDs and MHDs. Within the realm of significance, it underscores a critical imperative—the urgent necessity to revolutionize the landscape of tailored mental health services offered to patients harboring this challenging comorbidity. The paper distinctly illuminates the exigency for a heightened quantity of research endeavors that delve deeper into unraveling the temporal intricacies underpinning the relationship between SUDs and MHDs. In so doing, it not only unveils potential risk factors but also delves into the far-reaching consequences of treatment modalities over the extended course of time. This illumination, therefore, not only beckons but virtually ushers in a promising trajectory for prospective research endeavors, a path designed to uncover the intricate and evolving journey of dual diagnosis. A profound implication of this study is the direct applicability of its findings in the corridors of policymaking. By leveraging the insights encapsulated within the paper, policymakers stand uniquely equipped to sculpt policies that unequivocally champion the cause of integrated care. The remarkable emphasis on themes of treatment and intervention, permeating the research's core, emphatically underscores the urgent demand for dismantling barriers obstructing access to mental health and substance abuse services. It is incumbent upon policymakers to heed this call, for policies fostering the integration of care can inexorably elevate the outcomes experienced by patients grappling with dual diagnosis. Furthermore, this study artfully directs policymakers to allocate their resources judiciously by identifying burgeoning areas of research that are surging in prominence and pertinence. These emergent topics, discerned within the study, are not just topics; they are emblematic of windows of opportunity. By investing in these areas, policymakers can tangibly bolster research initiatives that are primed to tackle the multifaceted challenges inherent in the realm of dual diagnosis, addressing both current exigencies and future prospects. Additionally, the paper furnishes the foundational blueprint essential for the development of screening guidelines and clinical practice protocols that truly grasp the complexity of dual diagnosis. Clinical practitioners and healthcare establishments would be remiss not to harness this invaluable information to augment their own practices, thereby delivering more effective and empathetic care to individuals contending with dual diagnosis. In essence, this study serves as the compass guiding the way toward a more compassionate, comprehensive, and efficacious approach to mental health and substance abuse care for those in need.
The current landscape analysis of reveals significant implications and highlights the growing research interest in this field since the late 1980s. This increasing trend underscores the complexities and prevalence of comorbid conditions, which necessitate focused research and intervention strategies. The results can be generalized to guide future research priorities, inform clinical guidelines, shape healthcare policies, and provide a framework for other countries to adapt and build upon in their context.
The key take-home message emphasizes the importance of recognizing the high prevalence and intricate relationship between SUDs and MHDs, necessitating integrated and tailored treatment approaches. Additionally, the study advocates for employing efficient research methodologies to synthesize vast amounts of literature and identify emerging trends, focusing on quality of life, treatment outcomes, and the broader socio-cultural and policy contexts to improve care and support for individuals with dual diagnosis. Finally, the research underscores the critical need for continued focus on dual diagnosis, advocating for comprehensive, integrated, and innovative approaches to research, clinical practice, and policymaking to improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Despite the comprehensive approach adopted in this research landscape analysis, several limitations must be acknowledged. The exclusive reliance on Scopus, while extensive, inherently limits the scope of the analysis, potentially omitting relevant articles indexed in other databases such as the Chinese scientific database, thus not fully representing the entire research landscape on dual diagnosis of SUDs and MHDs. Assigning quality control responsibilities to a single author, rather than employing a dual-reviewer system, may introduce bias and affect the reliability of the quality assessment. Although this approach was chosen to expedite the process, it might have compromised the thoroughness of quality checks. The use of narrative synthesis instead of a quantitative synthesis limits the ability to perform meta-analytical calculations that could provide more robust statistical insights. This choice was made for efficiency, but it may affect the depth of the analysis and the generalizability of the conclusions. The reliance on specific keywords to retrieve articles means that any relevant studies not containing these exact terms in their titles or abstracts may have been overlooked, potentially leading to an incomplete representation of the research domain. The restriction to English-language articles and peer-reviewed journals may exclude significant research published in other languages or in non-peer-reviewed formats, introducing linguistic and publication type bias that could skew the results towards predominantly English-speaking regions and established academic journals. The inclusion of articles up to December 31, 2022, means that any significant research published after this date is not considered, potentially missing the latest developments in the field. The validation of the search strategy using a small sample of 30 articles and a comparison with 10 randomly selected articles from Google Scholar may not be sufficient to comprehensively assess the effectiveness of the search strategy; a larger sample size might provide a more accurate validation. Some of the research topics and findings may be specific to particular populations (e.g., veterans) and might not be generalizable to other groups, highlighting the need for caution when extrapolating the results to broader contexts. Although no formal ethical approval was required due to the use of existing literature, ethical considerations related to the interpretation and application of findings must still be acknowledged, particularly in terms of representing vulnerable populations accurately and sensitively. Acknowledging these limitations is crucial for interpreting the findings of this research landscape analysis and for guiding future research efforts to address these gaps and enhance the robustness and comprehensiveness of studies on the dual diagnosis of SUDs and MHDs.
In conclusion, the research landscape analysis of dual diagnosis of substance abuse and mental health disorders provides valuable insights into the growth, active countries, and active journals in this field. The identification of research hotspots and emerging topics informs the scientific community about prevailing interests and potential areas for future investigation. Addressing research gaps can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of dual diagnosis, while the implications of the findings extend to clinical practice, public health initiatives, policy development, and future research priorities. This comprehensive understanding is crucial in advancing knowledge, improving care, and addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by dual diagnosis to individuals and society.
Availability of data and materials
All data presented in this manuscript are available on the Scopus database using the search query listed in the methodology section.
Hasin DS, O’Brien CP, Auriacombe M, Borges G, Bucholz K, Budney A, et al. DSM-5 criteria for substance use disorders: recommendations and rationale. Am J Psychiatry. 2013;170(8):834–51. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12060782 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Collaborators GA. Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet. 2018;392(10152):1015–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31310-2 .
Article Google Scholar
Ayalew M, Tafere M, Asmare Y. Prevalence, trends, and consequences of substance use among university students: implication for intervention. Int Q Community Health Educ. 2018;38(3):169–73. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272684x17749570 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Raftery D, Kelly PJ, Deane FP, Baker AL, Ingram I, Goh MCW, et al. Insight in substance use disorder: a systematic review of the literature. Addict Behav. 2020;111:106549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106549 .
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the national comorbidity survey replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593–602. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.593 .
Hossain MM, Nesa F, Das J, Aggad R, Tasnim S, Bairwa M, et al. Global burden of mental health problems among children and adolescents during COVID-19 pandemic: an umbrella review. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317:114814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114814 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kurdyak P, Patten S. The burden of mental illness and evidence-informed mental health policy development. Can J Psychiatry. 2022;67(2):104–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/07067437211021299 .
Stumbrys D, Jasilionis D, Pūras D. The burden of mental health-related mortality in the Baltic States in 2007–2018. BMC Public Health. 2022;22(1):1776. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14175-9 .
Pompili M, Innamorati M, Gonda X, Serafini G, Sarno S, Erbuto D, et al. Affective temperaments and hopelessness as predictors of health and social functioning in mood disorder patients: a prospective follow-up study. J Affect Disord. 2013;150(2):216–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2013.03.026 .
Costanza A, Vasileios C, Ambrosetti J, Shah S, Amerio A, Aguglia A, et al. Demoralization in suicide: a systematic review. J Psychosom Res. 2022;157:110788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2022.110788 .
Arias F, Szerman N, Vega P, Mesías B, Basurte I, Rentero D. Bipolar disorder and substance use disorders. Madrid study on the prevalence of dual disorders/pathology. Adicciones. 2017;29(3):186–94. https://doi.org/10.2088/adicciones.782 .
Brewer S, Godley MD, Hulvershorn LA. Treating mental health and substance use disorders in adolescents: what is on the menu? Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2017;19(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-017-0755-0 .
Jones CM, McCance-Katz EF. Co-occurring substance use and mental disorders among adults with opioid use disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;197:78–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2018.12.030 .
Murthy P, Mahadevan J, Chand PK. Treatment of substance use disorders with co-occurring severe mental health disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2019;32(4):293–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/yco.0000000000000510 .
Saddichha S, Schütz CG, Sinha BN, Manjunatha N. Substance use and dual diagnosis disorders: future epidemiology, determinants, and policies. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:145905. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/145905 .
Hammen C. Adolescent depression: stressful interpersonal contexts and risk for recurrence. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2009;18(4):200–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8721.2009.01636.x .
Wolitzky-Taylor K, Bobova L, Zinbarg RE, Mineka S, Craske MG. Longitudinal investigation of the impact of anxiety and mood disorders in adolescence on subsequent substance use disorder onset and vice versa. Addict Behav. 2012;37(8):982–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2012.03.026 .
Mueser KT, Drake RE, Wallach MA. Dual diagnosis: a review of etiological theories. Addict Behav. 1998;23(6):717–34.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hartz SM, Pato CN, Medeiros H, Cavazos-Rehg P, Sobell JL, Knowles JA, et al. Comorbidity of severe psychotic disorders with measures of substance use. JAMA Psychiat. 2014;71(3):248–54. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.3726 .
Carroll KM, Kiluk BD, Nich C, Babuscio TA, Brewer JA, Potenza MN, et al. Cognitive function and treatment response in a randomized clinical trial of computer-based training in cognitive-behavioral therapy. Subst Use Misuse. 2011;46(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.3109/10826084.2011.521069 .
Drake RE, Mueser KT. Psychosocial approaches to dual diagnosis. Schizophr Bull. 2000;26(1):105–18. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.schbul.a033429 .
Ruggeri M, Leese M, Thornicroft G, Bisoffi G, Tansella M. Definition and prevalence of severe and persistent mental illness. Br J Psychiatry. 2000;177:149–55. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.177.2.149 .
Reavley NJ, Jorm AF. Stigmatizing attitudes towards people with mental disorders: findings from an Australian national survey of mental health literacy and stigma. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2011;45(12):1086–93. https://doi.org/10.3109/00048674.2011.621061 .
Torrey WC, Tepper M, Greenwold J. Implementing integrated services for adults with co-occurring substance use disorders and psychiatric illnesses: a research review. J Dual Diagn. 2011;7(3):150–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/15504263.2011.592769 .
Bouchery EE, Harwood HJ, Dilonardo J, Vandivort-Warren R. Type of health insurance and the substance abuse treatment gap. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2012;42(3):289–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2011.09.002 .
Abuse S, Administration MHS. National Mental Health Services Survey (N-MHSS): 2014. Data on mental health treatment facilities. Department of Health and Human Services, Substance Abuse and Mental Health …; 2014.
Shiner B, Gottlieb D, Rice K, Forehand JA, Snitkin M, Watts BV. Evaluating policies to improve access to mental health services in rural areas. J Rural Health. 2022;38(4):805–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/jrh.12674 .
Ioannidis JP, Greenland S, Hlatky MA, Khoury MJ, Macleod MR, Moher D, et al. Increasing value and reducing waste in research design, conduct, and analysis. Lancet. 2014;383(9912):166–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(13)62227-8 .
Bornmann L, Bowman BF, Bauer J, Marx W, Schier H, Palzenberger MJBbHmiosi. (2014): 11 Bibliometric standards for evaluating research institutes in the natural sciences.201.
Hicks D, Wouters P, Waltman L, de Rijcke S, Rafols I. Bibliometrics: the Leiden manifesto for research metrics. Nature. 2015;520(7548):429–31. https://doi.org/10.1038/520429a .
Ziedonis D, Brady K. Dual diagnosis in primary care. Detecting and treating both the addiction and mental illness. Med Clin North Am. 1997;81(4):1017–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-7125(05)70561-7 .
Kim JI, Kim B, Kim BN, Hong SB, Lee DW, Chung JY, et al. Prevalence of psychiatric disorders, comorbidity patterns, and repeat offending among male juvenile detainees in South Korea: a cross-sectional study. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2017;11:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-017-0143-x .
Astals M, Domingo-Salvany A, Buenaventura CC, Tato J, Vazquez JM, Martín-Santos R, et al. Impact of substance dependence and dual diagnosis on the quality of life of heroin users seeking treatment. Subst Use Misuse. 2008;43(5):612–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826080701204813 .
Buckley PF. Prevalence and consequences of the dual diagnosis of substance abuse and severe mental illness. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(Suppl 7):5–9.
PubMed Google Scholar
Buckley PF, Brown ES. Prevalence and consequences of dual diagnosis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67(7):e01. https://doi.org/10.4088/jcp.0706e01 .
Canaway R, Merkes M. Barriers to comorbidity service delivery: the complexities of dual diagnosis and the need to agree on terminology and conceptual frameworks. Aust Health Rev. 2010;34(3):262–8. https://doi.org/10.1071/ah08723 .
Edward KL, Munro I. Nursing considerations for dual diagnosis in mental health. Int J Nurs Pract. 2009;15(2):74–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-172X.2009.01731.x .
Healey C, Peters S, Kinderman P, McCracken C, Morriss R. Reasons for substance use in dual diagnosis bipolar disorder and substance use disorders: a qualitative study. J Affect Disord. 2009;113(1–2):118–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2008.05.010 .
Horsfall J, Cleary M, Hunt GE, Walter G. Psychosocial treatments for people with co-occurring severe mental illnesses and substance use disorders (dual diagnosis): a review of empirical evidence. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2009;17(1):24–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/10673220902724599 .
Kerfoot KE, Petrakis IL, Rosenheck RA. Dual diagnosis in an aging population: prevalence of psychiatric disorders, comorbid substance abuse, and mental health service utilization in the department of veterans affairs. J Dual Diagn. 2011;7(1–2):4–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/15504263.2011.568306 .
Morojele NK, Saban A, Seedat S. Clinical presentations and diagnostic issues in dual diagnosis disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2012;25(3):181–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0b013e328351a429 .
Thylstrup B, Johansen KS. Dual diagnosis and psychosocial interventions–introduction and commentary. Nord J Psychiatry. 2009;63(3):202–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/08039480802571069 .
van Eck NJ, Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3 .
Arndt S, Tyrrell G, Flaum M, Andreasen NC. Comorbidity of substance abuse and schizophrenia: the role of pre-morbid adjustment. Psychol Med. 1992;22(2):379–88. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291700030324 .
Barnes TRE, Mutsatsa SH, Hutton SB, Watt HC, Joyce EM. Comorbid substance use and age at onset of schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 2006;188:237–42. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.104.007237 .
Brady KT, Killeen T, Saladin ME, Dansky B, Becker S. Comorbid substance abuse and posttraumatic stress disorder: characteristics of women in treatment. Am J Addict. 1994;3(2):160–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1521-0391.1994.tb00383.x .
Brière FN, Rohde P, Seeley JR, Klein D, Lewinsohn PM. Comorbidity between major depression and alcohol use disorder from adolescence to adulthood. Compr Psychiatry. 2014;55(3):526–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2013.10.007 .
Brown PJ, Stout RL, Mueller T. Substance use disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder comorbidity: addiction and psychiatric treatment rates. Psychol Addict Behav. 1999;13(2):115–22. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-164X.13.2.115 .
Bulik CM, Klump KL, Thornton L, Kaplan AS, Devlin B, Fichter MM, et al. Alcohol use disorder comorbidity in eating disorders: a multicenter study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;65(7):1000–6. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.v65n0718 .
Compton WM, Conway KP, Stinson FS, Grant BF. Changes in the prevalence of major depression and comorbid substance use disorders in the United States between 1991–1992 and 2001–2002. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(12):2141–7. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.2006.163.12.2141 .
Green AI, Drake RE, Brunette MF, Noordsy DL. Schizophrenia and co-occurring substance use disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(3):402–8. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.2007.164.3.402 .
Morgenstern J, Langenbucher J, Labouvie E, Miller KJ. The comorbidity of alcoholism and personality disorders in a clinical population: prevalence rates and relation to alcohol typology variables. J Abnorm Psychol. 1997;106(1):74–84. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.106.1.74 .
Back SE, Waldrop AE, Brady KT. Treatment challenges associated with comorbid substance use and posttraumatic stress disorder: clinicians’ perspectives. Am J Addict. 2009;18(1):15–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10550490802545141 .
Brown PJ, Recupero PR, Stout R. PTSD substance abuse comorbidity and treatment utilization. Addict Behav. 1995;20(2):251–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4603(94)00060-3 .
Harris KM, Edlund MJ. Use of mental health care and substance abuse treatment among adults with co-occurring disorders. Psychiatr Serv. 2005;56(8):954–9. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.56.8.954 .
Hien DA, Cohen LR, Miele GM, Litt LC, Capstick C. Promising treatments for women with comorbid PTSD and substance use disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161(8):1426–32. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.161.8.1426 .
Manwani SG, Szilagyi KA, Zablotsky B, Hennen J, Griffin ML, Weiss RD. Adherence to pharmacotherapy in bipolar disorder patients with and without co-occurring substance use disorders. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(8):1172–6. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.v68n0802 .
Minkoff K. An integrated treatment model for dual diagnosis of psychosis and addiction. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1989;40(10):1031–6. https://doi.org/10.1176/ps.40.10.1031 .
Smith JP, Book SW. Comorbidity of generalized anxiety disorder and alcohol use disorders among individuals seeking outpatient substance abuse treatment. Addict Behav. 2010;35(1):42–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2009.07.002 .
Kamali M, Kelly L, Gervin M, Browne S, Larkin C, O’Callaghan E. The prevalence of comorbid substance misuse and its influence on suicidal ideation among in-patients with schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2000;101(6):452–6. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0447.2000.101006452.x .
Padgett DK, Gulcur L, Tsemberis S. Housing first services for people who are homeless with co-occurring serious mental illness and substance abuse. Res Soc Work Pract. 2006;16(1):74–83. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049731505282593 .
Schmidt LM, Hesse M, Lykke J. The impact of substance use disorders on the course of schizophrenia-A 15-year follow-up study. Dual diagnosis over 15 years. Schizophr Res. 2011;130(1–3):228–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2011.04.011 .
Singh J, Mattoo SK, Sharan P, Basu D. Quality of life and its correlates in patients with dual diagnosis of bipolar affective disorder and substance dependence. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(2):187–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-5618.2004.00173.x .
Urboanoski KA, Cairney J, Bassani DG, Rush BR. Perceived unmet need for mental health care for Canadians with co-occurring mental and substance use disorders. Psychiatr Serv. 2008;59(3):283–9. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.59.3.283 .
Kingston REF, Marel C, Mills KL. A systematic review of the prevalence of comorbid mental health disorders in people presenting for substance use treatment in Australia. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2017;36(4):527–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/dar.12448 .
Klinkenberg WD, Caslyn RJ, Morse GA, Yonker RD, McCudden S, Ketema F, et al. Prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C among homeless persons with co-occurring severe mental illness and substance use disorders. Compr Psychiatry. 2003;44(4):293–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-440X(03)00094-4 .
Wallace C, Mullen PE, Burgess P. Criminal offending in schizophrenia over a 25-year period marked by deinstitutionalization and increasing prevalence of comorbid substance use disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161(4):716–27. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.161.4.716 .
Bronisch T, Wittchen HU. Suicidal ideation and suicide attempts: comorbidity with depression, anxiety disorders, and substance abuse disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1994;244(2):93–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02193525 .
Hatzenbuehler ML, Keyes KM, Narrow WE, Grant BF, Hasin DS. Racial/ethnic disparities in service utilization for individuals with co-occurring mental health and substance use disorders in the general population: Results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008;69(7):1112–21. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.v69n0711 .
Hodgins S, Tiihonen J, Ross D. The consequences of conduct disorder for males who develop schizophrenia: associations with criminality, aggressive behavior, substance use, and psychiatric services. Schizophr Res. 2005;78(2–3):323–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2005.05.021 .
Hunt GE, Bergen J, Bashir M. Medication compliance and comorbid substance abuse in schizophrenia: impact on community survival 4 years after a relapse. Schizophr Res. 2002;54(3):253–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-9964(01)00261-4 .
Link BG, Struening EL, Rahav M, Phelan JC, Nuttbrock L. On stigma and its consequences: evidence from a longitudinal study of men with dual diagnoses of mental illness and substance abuse. J Health Soc Behav. 1997;38(2):177–90. https://doi.org/10.2307/2955424 .
Priester MA, Browne T, Iachini A, Clone S, DeHart D, Seay KD. Treatment access barriers and disparities among individuals with co-occurring mental health and substance use disorders: an integrative literature review. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2016;61:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2015.09.006 .
Talamo A, Centorrino F, Tondo L, Dimitri A, Hennen J, Baldessarini RJ. Comorbid substance-use in schizophrenia: relation to positive and negative symptoms. Schizophr Res. 2006;86(1–3):251–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2006.04.004 .
Teplin LA, Elkington KS, McClelland GM, Abram KM, Mericle AA, Washburn JJ. Major mental disorders, substance use disorders, comorbidity, and HIV-AIDS risk behaviors in juvenile detainees. Psychiatr Serv. 2005;56(7):823–8. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.56.7.823 .
Hinckley JD, Danielson CK. Elucidating the neurobiologic etiology of comorbid PTSD and substance use disorders. Brain Sci. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12091166 .
Jarnecke AM, Saraiya TC, Brown DG, Richardson J, Killeen T, Back SE. Examining the role of social support in treatment for co-occurring substance use disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder. Addict Behav Rep. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abrep.2022.100427 .
Kyster NB, Tranberg K, Osler M, Hjorthøj C, Mårtensson S. The influence of childhood aspirations on the risk of developing psychotic disorders, substance use disorders, and dual diagnosis in adulthood based on the Metropolit 1953 Danish male birth cohort. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-022-02091-7 .
Cunill R, Castells X, González-Pinto A, Arrojo M, Bernardo M, Sáiz PA, et al. Clinical practice guideline on pharmacological and psychological management of adult patients with attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder and comorbid substance use. Adicciones. 2022;34(2):168–78. https://doi.org/10.2088/adicciones.1569 .
Margolese HC, Boucher M, Therrien F, Clerzius G. Treatment with aripiprazole once-monthly injectable formulation is effective in improving symptoms and global functioning in schizophrenia with and without comorbid substance use—a post hoc analysis of the ReLiAM study. BMC Psychiatry. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-022-04397-x .
Minkoff K, Covell NH. Recommendations for integrated systems and services for people with co-occurring mental health and substance use conditions. Psychiatric Serv. 2022;73(6):686–9. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.202000839 .
Oliva V, De Prisco M, Pons-Cabrera MT, Guzmán P, Anmella G, Hidalgo-Mazzei D, et al. Machine learning prediction of comorbid substance use disorders among people with bipolar disorder. J Clin Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11143935 .
Somohano VC, Kaplan J, Newman AG, O’Neil M, Lovejoy T. Formal mindfulness practice predicts reductions in PTSD symptom severity following a mindfulness-based intervention for women with co-occurring PTSD and substance use disorder. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13722-022-00333-2 .
Watkins LE, Patton SC, Drexler K, Rauch SAM, Rothbaum BO. Clinical effectiveness of an intensive outpatient program for integrated treatment of comorbid substance abuse and mental health disorders. Cogn Behav Pract. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpra.2022.05.005 .
Bertulies-Esposito B, Ouellet-Plamondon C, Jutras-Aswad D, Gagnon J, Abdel-Baki A. The impact of treatment orders for residential treatment of comorbid severe substance use disorders for youth suffering from early psychosis: a case series. Int J Ment Heal Addict. 2021;19(6):2233–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-020-00317-w .
Butler A, Nicholls T, Samji H, Fabian S, Lavergne MR. Prevalence of mental health needs, substance use, and co-occurring disorders among people admitted to prison. Psychiatric Serv. 2022;73(7):737–44. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.202000927 .
Henderson JL, Wilkins LK, Hawke LD, Wang W, Sanches M, Brownlie EB, et al. Longitudinal emergence of concurrent mental health and substance use concerns in an ontario school-based sample: the research and action for teens study. J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021;30(4):249–63.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Huang JS, Yang FC, Chien WC, Yeh TC, Chung CH, Tsai CK, et al. Risk of substance use disorder and its associations with comorbidities and psychotropic agents in patients with autism. JAMA Pediatr. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.5371 .
Lu W, Muñoz-Laboy M, Sohler N, Goodwin RD. Trends and disparities in treatment for co-occurring major depression and substance use disorders among US adolescents from 2011 to 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.30280 .
Melkonian AJ, Flanagan JC, Calhoun CD, Hogan JN, Back SE. Craving moderates the effects of intranasal oxytocin on anger in response to social stress among veterans with co-occurring posttraumatic stress disorder and alcohol use disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2021;41(4):465–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/JCP.0000000000001434 .
Otasowie J. Co-occurring mental disorder and substance use disorder in young people: aetiology, assessment and treatment. BJPsych Adv. 2021;27(4):272–81. https://doi.org/10.1192/bja.2020.64 .
Saraiya TC, Badour CL, Jones AC, Jarnecke AM, Brown DG, Flanagan JC, et al. The role of posttraumatic guilt and anger in integrated treatment for PTSD and co-occurring substance use disorders among primarily male veterans. Psychol Trauma: Theory Res Pract Policy. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1037/tra0001204 .
Walhout SJN, Zanten JV, DeFuentes-Merillas L, Sonneborn CKME, Bosma M. Patients with autism spectrum disorder and co-occurring substance use disorder: a clinical intervention study. Subst Abuse: Res Treat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1177/11782218221085599 .
Walker D, Infante AA, Knight D. Examining the impact of mental health, substance use, and co-occurring disorders on juvenile court outcomes. J Res Crime Delinq. 2022;59(6):820–53. https://doi.org/10.1177/00224278221084981 .
Warfield SC, Pack RP, Degenhardt L, Larney S, Bharat C, Ashrafioun L, et al. The next wave? Mental health comorbidities and patients with substance use disorders in under-resourced and rural areas. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2020.108189 .
Hien DA, Fitzpatrick S, Saavedra LM, Ebrahimi CT, Norman SB, Tripp J, et al. What’s in a name? A data-driven method to identify optimal psychotherapy classifications to advance treatment research on co-occurring PTSD and substance use disorders. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/20008198.2021.2001191 .
Leonhardt M, Brodahl M, Cogan N, Lien L. How did the first COVID-19 lockdown affect persons with concurrent mental health and substance use disorders in Norway? A qualitative study. BMC Psychiatry. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-022-03812-7 .
Leonhardt M, Kyrdalen E, Holstad A, Hurlen-Solbakken H, Chiu MYL, Lien L. Norwegian cross-cultural adaptation of the social and communities opportunities profile-mini for persons with concurrent mental health and substance use disorders. J Psychosoc Rehabil Mental Health. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40737-022-00309-0 .
Sell L, Lund HL, Johansen KS. Past, present, and future labor market participation among patients admitted to hospital with concurrent substance use and mental health disorder, and what we can learn from it. J Occup Environ Med. 2022;64(12):1041–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/JOM.0000000000002633 .
Sverdlichenko I, Hawke LD, Henderson J. Understanding the service needs of youth with opioid use: a descriptive study of demographics and co-occurring substance use and mental health concerns. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108592 .
Yerriah J, Tomita A, Paruk S. Surviving but not thriving: Burden of care and quality of life for caregivers of patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders and comorbid substance use in South Africa. Early Interv Psychiatry. 2022;16(2):153–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/eip.13141 .
Murthy P, Chand P. Treatment of dual diagnosis disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2012;25(3):194–200. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0b013e328351a3e0 .
Schneier M. Better treatment for dual diagnosis patients. Psychiatr Serv. 2000;51(9):1079. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.51.9.1079 .
Tirado Muñoz J, Farré A, Mestre-Pintó J, Szerman N, Torrens M. Dual diagnosis in depression: treatment recommendations. Adicciones. 2018;30(1):66–76. https://doi.org/10.2088/adicciones.868 .
Carrà G, Clerici M. Dual diagnosis–policy and practice in Italy. Am J Addict. 2006;15(2):125–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/10550490500528340 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Author information, authors and affiliations.
Department of Physiology and Pharmacology/Toxicology, Division of Biomedical Sciences, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, An-Najah National University, Nablus, Palestine
Waleed M. Sweileh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
W.S started the idea, designed the methodology; did the data analysis, graphics, and data interpretation; wrote and submitted the manuscript. This was a single-authored manuscript. W.S wrote and submitted the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Waleed M. Sweileh .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
IRB at An-Najah National University (Palestine) requires no approval for bibliometric studies.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Sweileh, W.M. Research landscape analysis on dual diagnosis of substance use and mental health disorders: key contributors, research hotspots, and emerging research topics. Ann Gen Psychiatry 23 , 32 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12991-024-00517-x
Download citation
Received : 28 July 2023
Accepted : 21 August 2024
Published : 30 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12991-024-00517-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Substance use disorders
- Mental health disorders
- Dual diagnosis
- Research landscape analysis
- Treatment interventions
- Comorbidity
Annals of General Psychiatry
ISSN: 1744-859X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 30.8.2024 in Vol 11 (2024)
Evaluation of Digital Mental Health Technologies in the United States: Systematic Literature Review and Framework Synthesis
Authors of this article:

- Julianna Catania 1 , MPH ;
- Steph Beaver 1 , MChem ;
- Rakshitha S Kamath 1 , MS, MSL ;
- Emma Worthington 2 , MPH ;
- Minyi Lu 3 , PhD ;
- Hema Gandhi 3 , PhD ;
- Heidi C Waters 3 , PhD ;
- Daniel C Malone 4 , PhD
1 Costello Medical, Boston, MA, United States
2 Costello Medical, Cambridge, United Kingdom
3 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization Inc, Princeton, NJ, United States
4 Department of Pharmacotherapy, Skaggs College of Pharmacy, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States
Corresponding Author:
Daniel C Malone, PhD
Department of Pharmacotherapy
Skaggs College of Pharmacy
University of Utah
30 S 2000 East
Salt Lake City, UT, 84112
United States
Phone: 1 801 581 6257
Email: [email protected]
Background: Digital mental health technologies (DMHTs) have the potential to enhance mental health care delivery. However, there is little information on how DMHTs are evaluated and what factors influence their use.
Objective: A systematic literature review was conducted to understand how DMHTs are valued in the United States from user, payer, and employer perspectives.
Methods: Articles published after 2017 were identified from MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, Cochrane Library, the Health Technology Assessment Database, and digital and mental health congresses. Each article was evaluated by 2 independent reviewers to identify US studies reporting on factors considered in the evaluation of DMHTs targeting mental health, Alzheimer disease, epilepsy, autism spectrum disorder, or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Study quality was assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program Qualitative and Cohort Studies Checklists. Studies were coded and indexed using the American Psychiatric Association’s Mental Health App Evaluation Framework to extract and synthesize relevant information, and novel themes were added iteratively as identified.
Results: Of the 4353 articles screened, data from 26 unique studies from patient, caregiver, and health care provider perspectives were included. Engagement style was the most reported theme (23/26, 88%), with users valuing DMHT usability, particularly alignment with therapeutic goals through features including anxiety management tools. Key barriers to DMHT use included limited internet access, poor technical literacy, and privacy concerns. Novel findings included the discreetness of DMHTs to avoid stigma.
Conclusions: Usability, cost, accessibility, technical considerations, and alignment with therapeutic goals are important to users, although DMHT valuation varies across individuals. DMHT apps should be developed and selected with specific user needs in mind.
Introduction
Digital health comprises a broad range of technologies, including mobile health, health information technology, wearable devices, and personalized medicine, which serve as tools to enhance health care delivery. Recently, several digital mental health (MH) therapeutics, a category of digital MH technologies (DMHTs), have received US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval to prevent, manage, or treat a medical disorder or disease based on evidence from superiority trials and compliance with technical guidelines [ 1 , 2 ]. However, most DMHTs, particularly apps, fall outside FDA jurisdiction because they are not intended to diagnose, treat, or prevent disease and because they are “low risk” in that they would not cause harm in the event of malfunction [ 3 ]. Due to this lack of regulatory framework, few DMHTs are supported by published efficacy studies. One study found that only 16% of MH apps recommended by college counseling centers were supported by efficacy studies published in peer-reviewed journals [ 4 ].
Nonetheless, many health care providers (HCPs) use MH apps in clinical practice. Up to 83% of behavioral health providers in a small study covering the Greater Boston area reported using apps as part of their clinical care, particularly mindfulness apps for patient anxiety management [ 5 ]. As many DMHTs are currently widely used in clinical practice without undergoing any formal assessment for quality or relevance, understanding how DMHTs should be assessed based on factors impacting their value from the perspective of key stakeholders, such as patients, caregivers, providers, payers, and employers, could improve the selection of DMHTs for use by patients, thereby increasing care quality and outcomes for those seeking MH support.
To address identified gaps, a systematic literature review (SLR) was conducted using a published framework to synthesize emerging themes from mixed methods evidence in order to understand how digital health solutions, encompassing both digital therapeutics and direct-to-consumer digital health technologies, are valued, with a focus on MH disorders, Alzheimer disease, epilepsy, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in the United States.
The SLR was performed in accordance with a prespecified protocol and reported in line with the Enhancing Transparency in Reporting the Synthesis of Qualitative Research and PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines [ 6 , 7 ]. The protocol was not registered.
Search Strategy
Electronic databases, encompassing MEDLINE (including MEDLINE In-Process, MEDLINE Daily, and MEDLINE Epub Ahead of Print); Embase; the Cochrane Library (including Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials); PsycINFO; and the Health Technology Assessment Database, were selected in alignment with this SLR’s target indications and were searched on June 17, 2022. The search terms included combinations of free-text and Medical Subject Heading or Emtree terms related to indications of interest, DMHTs, and relevant outcomes or assessment types (eg, technology assessments and cost; Tables S1-S5 in Multimedia Appendix 1 ). Searches were limited to studies performed in the United States and to those published from 2017 onward.
Manual hand searches of gray literature, namely, the bibliographies of relevant SLRs identified from the electronic database searches and key conference proceedings (2019-2022), were performed to identify additional studies of relevance (Table S6 in Multimedia Appendix 1 ). The FDA website was also searched to identify factors involved in the FDA’s appraisal of relevant MH apps, which could supplement the factors identified in this SLR (Table S7 in Multimedia Appendix 1 ).
Study Selection
Studies were included in the SLR if they met prespecified criteria defined using the SPIDER (Sample, Phenomenon of Interest, Design, Evaluation, Research type) framework, which is appropriate for mixed methods research questions. Eligible studies were published in the English language, were set in the United States, and reported quantitative or qualitative outcomes relating to the factors considered in the evaluation of DMHTs. Only studies published in 2017 or later were included because of the rapidly evolving research area. Eligible studies reported on MH, Alzheimer disease, epilepsy, ASD, or ADHD from user, payer, or employer perspectives (Table S8 in Multimedia Appendix 1 ). While the primary focus of the SLR was MH, neurological conditions were also of interest because their pathologies, symptoms, and treatment strategies can overlap with those of mental illnesses. Alzheimer disease, epilepsy, ASD, and ADHD were selected because they are highly researched and represent diverse types of neurological conditions.
The titles and abstracts of records were assessed for inclusion against these eligibility criteria by 2 independent reviewers, and discrepancies were resolved by consensus, with arbitration by a third reviewer if necessary. Full texts of potentially relevant articles were acquired and screened using the same methodology.
Study Prioritization
Due to the large volume of the evidence identified, additional eligibility criteria were applied to prioritize primary research on theoretical DMHT valuation factors. In line with the thematic framework synthesis objective, theoretical valuation factors were defined as user or DMHT attributes that impact interaction with or perception of DMHTs; therefore, studies that reported only efficacy outcomes, such as mental illness symptom improvement, were deprioritized for full-text review. Secondary research was also deprioritized for full-text review. Studies that reviewed a select app against a framework and studies that reported only the outcomes specific to a select app were deprioritized for data extraction. For example, a study reporting the usability of a specific app’s features would have been deprioritized, while a study reporting what types of features increase MH app usability in general would not.
Data Extraction
All relevant data were extracted into a prespecified Microsoft Excel grid, and a quality assessment was performed for each study. Studies that reported only qualitative data were assessed with the Critical Appraisal Skills Program Qualitative Studies Checklist. Studies that reported only quantitative data were evaluated with the Critical Appraisal Skills Program Cohort Study Checklist, and studies reporting both qualitative and quantitative data were evaluated with both checklists [ 8 ]. Data extractions and quality assessments were performed by a single individual for each study, with the information verified by a second independent individual. Discrepancies were resolved by consensus, with arbitration by a third individual if necessary.
Framework Synthesis
A framework synthesis approach was undertaken to synthesize qualitative and quantitative data identified from the SLR. In line with the “best fit” framework synthesis approach, data were indexed deductively against an existing framework where possible, and novel themes were added inductively as needed [ 9 , 10 ]. The American Psychiatric Association (APA) Mental Health App Evaluation framework was considered the most appropriate framework to address the research objectives of this SLR because its key valuation themes were developed using psychiatrist and patient input, are broadly shared by other evaluation frameworks, are widely acknowledged in the literature, and have been described as durable and adaptable [ 11 - 13 ].
The APA model follows a hierarchical and chronological order whereby the evaluator moves through the framework using prompting questions (eg, “Does the app work offline?”). For this SLR, these questions were either thematically grouped into subthemes or left as prompting questions, as appropriate. The framework was therefore ultimately adapted into 3 levels: themes, subthemes, and more granular valuation criteria. It should be emphasized that this SLR did not aim to formally develop an updated framework to be used in practice by HCPs and their patients but rather was used to form a theoretical basis for understanding DMHT valuation factors, for which novel themes were expected to emerge.
A data-based convergent approach was used to synthesize quantitative and qualitative data [ 14 ]. Data were initially indexed deductively against the prespecified themes within the data collection instrument and then further synthesized within Docear [ 15 ], a mind-map software used to organize and connect data and concepts. Indexing was performed by 1 reviewer and checked by a second independent reviewer. New themes and subthemes that emerged from the literature through inductive coding were added post hoc to the thematic framework, with all extracted data then considered against both the prespecified and novel themes. The evidence identified for each theme was synthesized narratively, taking into consideration the context and design of each study.
Included Studies
A total of 4974 records were retrieved from the electronic databases. Of the 3374 (67.83%) unique records identified following deduplication across the databases, 2891 (85.68%) were excluded based on the eligibility criteria, and an additional 456 (13.52%) were deprioritized because they were not directly related to the topic of interest for this SLR. Excluded and deprioritized full texts are listed in Tables S9 and S10 in Multimedia Appendix 1 , respectively. Therefore, 27 (0.54%) articles were included from the electronic database searches. In addition, 1 article reporting on the same study as an already-included conference abstract was identified during supporting targeted searches and included as a supplementary record, resulting in a total of 28 articles reporting on 26 unique studies (Figure S1 in Multimedia Appendix 1 ). No relevant FDA appraisals were identified in the supplementary search.
Of the 26 included studies, 8 (31%) were quantitative, 12 (46%) were qualitative, and 6 (23%) used a mixed methods approach. While 5 (19%) studies assessed prospective cohorts, 22 (85%) used a cross-sectional approach, including 1 (4%) study that contained both a prospective cohort and a cross-sectional cohort ( Table 1 ). All studies (26/26, 100%) investigated a user perspective, with none specifically investigating payer or employer perspectives. Only 1 (4%) study, which examined ingestible sensor pills and smart pill dispensers to track adherence, investigated a DMHT that was not an app [ 16 ].
| Study (author, year) | Design | Perspective and population | Objectives | Data collection methods |
| Afra et al [ ], 2018 | Cross-sectional, quantitative | To develop a drug-device combination product using an app in combination with antiseizure medications as an epilepsy treatment | Custom survey | |
| Beard et al [ ], 2019 | Cross-sectional, quantitative | , BD , anxiety, OCD , stress-related disorders, and psychotic disorders (N=322) | To characterize general smartphone app and social media use in an acute transdiagnostic psychiatric sample with high smartphone ownership, characterize current engagement and interest in the use of smartphone apps to support MH , and test demographic and clinical predictors of smartphone use | Custom survey |
| Borghouts et al [ ], 2022 | Cross-sectional, mixed methods | : members of the Center on Deafness Inland Empire, comprised people with lived experience as members of the deaf or hard-of-hearing community (N=10) | To investigate the MH needs of the deaf or hard-of-hearing community and how MH apps might support these needs | Custom survey; focus group |
| Boster and McCarthy [ ], 2018 | Cross-sectional, qualitative | recruited through social media and professional listserves (N=8) | To gain insight from speech-language pathologists and parents of children with ASD regarding appealing features of augmentative and alternative communication apps | Focus groups; poll questions |
| Buck et al [ ], 2021a | Cross-sectional, quantitative | referrals or ads (N=43) | To assess caregivers’ interest in an array of specific potential mHealth functions to guide the development of mHealth for caregivers of young adults with early psychosis | Custom survey |
| Buck et al [ ], 2021b | Cross-sectional, quantitative | To understand the needs, interests, and preferences of young adults with early psychosis regarding mHealth by surveying interest in mHealth features and delivery modalities and by collecting information about their digital and web-based behaviors | Custom survey | |
| Carpenter-Song et al [ ], 2018 | Prospective cohort, qualitative | To examine current practices and orientations toward technology among consumers in 3 mental health settings in the United States | Semistructured interviews | |
| Casarez et al [ ], 2019 | Cross-sectional, qualitative | To explore how the well-being of spouses and partners of patients with BD can be improved through mHealth technology | Focus groups; minimally structured, open-ended individual interviews | |
| Connolly et al [ ], 2018 | Cross-sectional, qualitative | , alcohol use disorder, or MDD during the previous year at 9 community-based VA outpatient clinics (N=66) | To examine veterans’ attitudes toward smartphone apps and to assess whether openness toward this technology varies by age or rurality | Semistructured interviews informed by the State of the Art Access Model |
| Cummings et al [ ], 2019 | Cross-sectional, qualitative | treatment at 4 safety-net clinics (N=37) | To examine stakeholder perspectives regarding whether mHealth tools can improve MH treatment for low-income youth with ADHD in safety-net settings and what functions would improve treatment | Focus groups (caregivers) and interviews (HCPs and staff), both semistructured and including open-ended questions and targeted probes |
| Dinkel et al [ ], 2021 | Cross-sectional, qualitative | To explore patient and clinic-level perceptions of the use of depression self-management apps within an integrated primary care setting | Semistructured focus groups; semistructured interviews | |
| Forma et al [ ], 2022 | Cross-sectional, quantitative | To assess caregivers’ preferences and willingness to pay for digital (ingestible sensor pill, medication containers with electronic monitoring, mobile apps, and smart pill dispensers) and nondigital (medication diary and simple pill organizer) tools | Custom discrete choice experiment survey | |
| Hoffman et al [ ], 2019 | Prospective interventional, mixed methods | To test the feasibility of using mHealth apps to augment integrated primary care services, solicit feedback from patients and providers to guide implementation, and develop an MH app toolkit for system-wide dissemination | Custom survey | |
| Huberty et al [ ], 2022 | Cross-sectional (current Calm (Calm.com, Inc) users) and prospective interventional (nonusers of Calm, HCPs), qualitative | : patients with cancer and survivors of cancer with smartphones, some of whom were current subscribers of Calm, a meditation app (N=17) | To develop a mobile meditation app prototype specifically designed for patients with cancer and survivors of cancer | Custom surveys; focus groups |
| Kern et al [ ], 2018 | Cross-sectional, quantitative | : students from a midwestern university with smartphones (N=721) | To investigate the potential usefulness of MH apps and attitudes toward using them | Custom survey |
| Knapp et al [ ], 2021 | Prospective cohort, qualitative | To learn about considerations and perspectives of community behavioral HCPs on incorporating digital tools into their clinical care for children and adolescents | Focus groups | |
| Kornfield et al [ ], 2022 | Prospective cohort, qualitative | or GAD-7 questionnaires, but without serious mental illnesses (eg, BD, schizophrenia), who were not receiving formal care and recruited upon completing free web-based MH self-screening surveys hosted by Mental Health America (N=28) | To investigate how digital technologies can engage young adults in self-managing their MH outside the formal care system | Web-based asynchronous discussion; synchronous web-based design workshop |
| Lipschitz et al [ ], 2019 | Cross-sectional, quantitative | To assess patients’ interest in mHealth interventions for MH, to identify whether provider endorsement would impact interest, to determine reasons for nonuse of mHealth interventions for MH, and to identify what mHealth content or features are of most interest to patients | Custom survey | |
| Mata-Greve et al [ ], 2021 | Cross-sectional, mixed methods | : essential workers during the COVID-19 pandemic or workers who were unemployed or furloughed because of the COVID-19 pandemic, recruited from a web-based research platform (N=1987) | To document psychological stress, to explore DMHT use in response to COVID-19–related stress, to explore the usability and user burden of DMHTs, and to explore which aspects and features of DMHTs were seen as necessary for managing stress during a pandemic by having participants design their own ideal DMHTs | Survey combining custom and validated measures (System Usability Scale, Use Burden Scale) |
| Melcher et al [ ], 2022 and Melcher and Torous [ ], 2020 | Cross-sectional, mixed methods | : college students aged 18-25 years, recruited through social media and word of mouth (N=100) | To examine why college students show poor engagement with MH apps and how apps may be adapted to suit this population | Custom survey; interviews |
| Schueller et al [ ], 2018 | Cross-sectional, mixed methods | : smartphone owners recruited from a research registry (N=827) | To understand where users search for MH apps, what aspects of MH apps they find appealing, and what factors influence their decisions to use MH apps | Custom survey; focus group interviews |
| Schueller et al [ ], 2021 | Cross-sectional, qualitative | : participants who had used an app that allowed them to track their mood, feelings, or mental well-being for ≥2 weeks, recruited from a research registry (N=22) | To understand motivations for and experiences in using mood-tracking apps from people who used them in real-world contexts | Semistructured interviews |
| Stiles-Shields et al [ ], 2017 | Cross-sectional, qualitative | : participants recruited from web-based postings; approximately equal numbers of participants were above and below the criteria for a referral for psychotherapy for depression (N=20) | To identify the barriers to the use of a mobile app to deliver treatment for depression and to provide design implications on the basis of identified barriers | Card sorting task |
| Storm et al [ ], 2021 | Cross-sectional, qualitative | To identify stakeholders’ perspectives on partnering to inform the software development life cycle of a smartphone health app intervention for people with serious mental illness | Semistructured interviews | |
| Torous et al [ ], 2018 | Cross-sectional, quantitative | To understand how individuals with mental illness use their mobile phones by exploring their access to mobile phones and their use of MH apps | Custom survey | |
| Zhou and Parmanto [ ], 2020 | Cross-sectional, mixed methods | To determine user preferences among the several privacy protection methods used in current mHealth apps and the reasons behind those preferences | Custom survey; interview |
a Only information relevant to this systematic literature review is reported in this table.
b MDD: major depressive disorder.
c BD: bipolar disorder.
d OCD: obsessive-compulsive disorder.
e MH: mental health.
f General users are participants who were not necessarily diagnosed with indications of interest.
g ASD: autism spectrum disorder.
h HCP: Health care provider.
i mHealth: mobile health.
j PTSD: posttraumatic stress disorder.
k VA: Veterans Affairs.
l ADHD: attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
m PHQ-9: Personal Health Questionnaire-9.
n GAD-7: Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7.
o DMHT: digital mental health technology.
Most frequently, studies focused on indications for mood, anxiety, or psychotic disorders (15/26, 58%), with other indications of focus including ADHD (2/26, 8%), ASD (1/26, 4%), and epilepsy (1/26, 4%). No relevant studies focused on Alzheimer disease were identified.
A total of 8 (31%) studies assessed the perspectives toward DMHTs of general population participants who were not necessarily diagnosed with relevant conditions [ 19 , 28 , 29 , 33 - 37 ]. Of these populations, several were identified as having an increased risk of MH conditions, such as patients with cancer [ 28 ], college students [ 29 , 34 ], deaf or hard-of-hearing individuals [ 19 ], and people who were unemployed or furloughed during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 33 ]. In addition, 1 (4%) study included a mix of patients who were above and below the referral criteria for psychotherapy for depression [ 37 ].
Thematic Analysis
Evidence was identified for all 5 themes included in the APA framework: engagement style (23/26, 88%), background and accessibility (16/26, 62%), privacy and security (13/26, 50%), therapeutic goal (12/26, 46%), and clinical foundation (8/26, 31%; Table 2 ). Five novel criteria were identified and added to the framework post hoc, 1 each under engagement style (forgetting or feeling unmotivated to use DMHTs) and privacy and security (personal image and stigma) and 3 under background and accessibility (willingness to pay, insurance restrictions, and cost savings compared with professional care).
| Subtheme | Criteria (study reference) | ||
| Short-term usability | , , , ] - , , , , , , ] | ||
| Long-term usability | , - , , , - , - ] [ , , , ] | ||
| Customizability | , , , , , , ] | ||
| Technical | , , , , , ] , , , - , , , ] | ||
| Business model | | ||
| Costs | , ] , , , ] [ ] [ ] - , ] | ||
| Medical claims | | ||
| Stability | , ] | ||
| No specific subtheme | , , ] | ||
| Data collection and storage | , , , , ] | ||
| Privacy policy | , , ] ] ] | ||
| Personal health information | ] , , , ] | ||
| Security measures | , , ] | ||
| Impressions of use | , ] | ||
| User feedback | , ] | ||
| Clinical validity | , ] , - ] , , ] | ||
| Clinically actionable | , , - , , , , ] - , ] | ||
| Therapeutic alliance | , , , , , ] , ] | ||
| Data ownership, access, and export | | ||
a Novel findings that emerged from this systematic literature review.
b These subthemes and criteria were included in the American Psychiatric Association’s framework but were not reported on by studies included in this systematic literature review.
c HCP: health care provider.
Theme 1: Engagement Style
Engagement style was the most reported theme, with evidence identified from 23 (88%) of the 26 studies. Engagement style encompasses how and why users do or do not interact with DMHTs. The long-term usability subtheme was reported by 96% (22/23) of studies, short-term usability by 12 (52%) studies, and customizability by 7 (30%) studies. Findings from short- and long-term usability subthemes were highly interconnected.
A total of 4 studies reported that ease of use promoted short-term DMHT engagement. In the study by Schueller et al [ 35 ], 89.6% of a general population of smartphone users reported ease of use for MH apps as “important” or “very important,” and users qualitatively reported dislike of “overwhelming,” difficult-to-navigate apps. In addition, users valued apps that were “simplistic” [ 34 ], fit into their daily schedules, and were available when needed (eg, during acute symptom experiences) [ 5 , 25 ]. Select supporting qualitative data are presented in Table 3 .
| Subtheme and criteria: findings | Key quotes | |||
| Ease of use | ] ] | |||
| Available engagement styles: use of animation and visuals | ] ] [ ] | |||
| Alignment of app with needs and priorities: gamification | ] | |||
| Alignment of app with needs and priorities: anxiety management | center peer support specialist] [ ] ] | |||
| Alignment of app with needs and priorities: tracking mood, symptoms, or sleep | ] ] [ ] | |||
| Alignment of app with needs and priorities: social media–like features | ] | |||
| Alignment of app with needs and priorities: peer support and chat functions | ] ] [ ] | |||
| Forgot or unmotivated to use | ] ] ] | |||
| Accessibility: mobility barriers | ] | |||
| Accessibility: technical literacy | ] | |||
| Offline functionality: internet and mobile data access as a barrier to use | ] ] | |||
| Willingness to pay | ] ] | |||
| Security associated with collection, use, and transmission of sensitive data (including personal health information) | ] ] | |||
| Transparency and accessibility of privacy policy | ] | |||
| Personal image and stigma | that is protected in the same way my EMR is protected.” [Patient in routine behavioral health care] [ ] | |||
| Security systems used | ] | |||
| Positive change or skill acquisition: apps that impart skills and encourage positive change, in an easy way | ] in cancer care] [ ] | |||
| Ease of sharing and interpretation of data: increase of engagement and symptom reporting | ] | |||
| Therapeutic alliance between patient and HCP | ] | |||
| Evidence of specific benefit: HCP recommendations | ] | |||
| Evidence of specific benefit: increased usage if supported by research, academic institution, or reputable professional society | ] ] | |||
a ASD: autism spectrum disorder.
b MH: mental health.
c ADHD: attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
d BD: bipolar disorder.
e Novel criteria identified by this systematic literature review.
f CHA: Cambridge Health Alliance.
g EMR: electronic medical record.
h HCP: health care provider.
Users valued DMHT features that aligned with their needs and priorities, as reflected by findings within the long-term usability subtheme. Across 9 studies, quantitative and qualitative findings demonstrated high interest in anxiety management features such as relaxation tools, breathing exercises, and mindfulness or meditation activities, and 10 studies identified interest in mood, symptom, or sleep tracking ( Tables 3 and 4 ). While most studies (24/26, 92%) focused on MH, patients with epilepsy also reported high interest in features to record seizure dates and types [ 17 ]. Importantly, users in 2 studies emphasized the need for developers to tailor DMHTs to the needs and priorities of the target population ( Table 3 ) [ 28 , 31 ]. Relatedly, mixed attitudes were reported toward positive affirmations and words of encouragement, with many users expressing interest but others emphasizing the value of a human component to DMHTs or cautioning against blanket encouragement and automated messages that could feel insincere [ 19 , 25 , 31 ].
| Features, study, perspective, and finding | Patients, n (%) | Likert score, mean (SD) | |||||
| ], 2021b | |||||||
| Interest in skill practices for managing stress and improving mood | 64 (84.2) | 3.30 (0.98) | |||||
| Interest in skill practices for relaxation | 57 (76) | 3.09 (1.12) | |||||
| Interest in information about relaxation exercises | 59 (77.6) | 3.00 (1.16) | |||||
| Interest in information about healthy sleep practices | 56 (73.7) | 2.93 (1.15) | |||||
| Interest in mindfulness or meditation practices | 44 (59.4) | 2.61 (1.34) | |||||
| ], 2018 | |||||||
| Interest in music to help seizure control | — (75) | — | |||||
| Interest in relaxing music that may help alleviate stress | — (68) | — | |||||
| Interest in relaxing imagery that may help alleviate stress | — (40) | — | |||||
| Interest in drawing or writing while listening to music | — (35) | — | |||||
| Interest in practicing mindfulness | — (63) | — | |||||
| ], 2018 | |||||||
| Comfort level for mindfulness and therapy | — | 3.75 | |||||
| Comfort level for mindfulness and therapy | — | 3.17 | |||||
| ], 2019 | |||||||
| Current use of an MH app with the primary purpose being mindfulness or meditation | — (71) | — | |||||
| ], 2021 | |||||||
| Most frequently endorsed mindfulness tools as a feature when provided options to build their own app | 687 (67.8) | — | |||||
| Most frequently endorsed mindfulness tools as a feature when provided options to build their own app | 584 (60) | — | |||||
| Most frequently endorsed mindfulness tools as a feature when provided options to build their own app | 305 (61.4) | — | |||||
| Most frequently endorsed mindfulness tools as a feature when provided options to build their own app | 966 (65.3) | — | |||||
| ], 2019 | |||||||
| The ability to manage mood, anxiety, or substance use through the use of DMHTs was seen as a benefit of incorporating DMHTs into clinical care | 13 (57) | — | |||||
| ], 2018 | |||||||
| Willingness to use an MH app to track mood or anxiety | 41 (10.3) | — | |||||
| ], 2018 | |||||||
| Interest in a diary to record the date of seizures | — (85) | — | |||||
| Interest in a digital diary to record the type of seizure | — (73) | — | |||||
| Interest in digital diary to log the missed dosages of their medications | — (78) | — | |||||
| ], 2019 | |||||||
| , or PTSD | |||||||
| Interested in progress monitoring (track mood, stress, anxiety, or PTSD symptoms) | 95 (63.8) | — | |||||
| Interested in progress monitoring (track mood, stress, anxiety, or PTSD symptoms) | 80 (67.2) | — | |||||
| ], 2021b | |||||||
| Interest in a feature to set and track goals | 60 (78) | 3.10 (1.05) | |||||
| Interest in a feature to track symptoms over time | 70 (90.9) | 3.44 (0.90) | |||||
| Interest in a feature to track changes in progress toward goals | 66 (86.9) | 3.37 (0.86) | |||||
| Interest in a feature to track wellness behaviors (eg, steps or activity) | 48 (64.9) | 2.86 (1.22) | |||||
| ], 2019 | |||||||
| Current use of an MH app with the primary purpose being mood tracking | — (10) | — | |||||
| Willingness to use an MH app daily to monitor condition | 262 (81) | — | |||||
| Willingness to use an MH app daily to monitor condition | — (85) | — | |||||
| Willingness to use an MH app daily to monitor condition | — (77) | — | |||||
| ], 2021 | |||||||
| Most frequently endorsed symptom tracking (tracking sleep or mood) as a feature when provided options to build their app | 605 (59.7) | — | |||||
| Most frequently endorsed symptom tracking (tracking sleep or mood) as a feature when provided options to build their app | 555 (57) | — | |||||
| Most frequently endorsed symptom tracking (tracking sleep or mood) as a feature when provided options to build their app | 270 (54.3) | — | |||||
| Most frequently endorsed symptom tracking (tracking sleep or mood) as a feature when provided options to build their own app | 890 (60.2) | — | |||||
| ], 2018 | |||||||
| Comfort level for in-app symptom surveys | — | 3.50 | |||||
| Comfort level for in-app symptom surveys | — | 3.11 | |||||
| Comfort level for passive call or text monitoring | — | 2.32 | |||||
| Comfort level for passive call or text monitoring | — | 2.39 | |||||
| Comfort level for passive GPS monitoring | — | 2.31 | |||||
| Comfort level for passive GPS monitoring | — | 2.78 | |||||
a A 5-point Likert scale (0-4) was used.
b Not available.
c A 5-point Likert scale (1-5) was used.
d MH: mental health.
e DMHT: digital mental health technology.
f MDD: major depressive disorder.
g PTSD: posttraumatic stress disorder.
Both patients and caregivers expressed interest in psychoeducational content that aligned with their needs and priorities. When surveyed, >60% of veterans with anxiety or major depressive disorder (MDD), patients with epilepsy, young adults with psychosis, and essential and furloughed workers during the COVID-19 pandemic expressed interest in relevant psychoeducational content [ 17 , 22 , 32 , 33 ]. In contrast, only 4% of college students in another study reported using an MH app for information about MH, although an MH diagnosis was not required for study participation [ 29 ].
Caregivers of young adults with psychosis, caregivers of children with ADHD, and spouses and partners of people with bipolar disorder (BD) were all interested in information related to caring for the individual with the given disorder, such as information on psychological and pharmacological treatments, symptoms and symptom changes, and the MH system [ 21 , 24 , 26 ]. Comparatively smaller, but still notable, proportions of caregivers of patients with psychosis were interested in caregiver-focused information; for instance, 62% to 69% were interested in relaxation exercises, stress and mood management, and community events for caregivers, while 85% to 90% were interested in the aforementioned patient-focused information [ 21 ].
Information delivery–style preference was captured under the short-term usability subtheme. One study in young adults with psychosis and another study with their caregivers revealed that delivering information in a variety of formats was important; when presented with nonmutually exclusive options, >50% of both populations were interested in text content, video content, audio content, and discussion boards [ 21 , 22 ].
Social interaction promoted long-term engagement. Qualitatively, 3 studies found that users valued learning about similar experiences from others via social media–like features, which normalized their experiences and could provide new symptom management strategies ( Table 3 ) [ 28 , 31 , 36 ]. Similarly, 67% of both young adults with psychosis and deaf or hard-of-hearing survey participants (N=9) reported interest in peer support via chat features [ 19 , 22 ]. However, a comparatively smaller proportion of veterans with anxiety or MDD (48.3% of the full cohort and 51.3% of the smartphone user subgroup) were interested in peer support [ 32 ].
Overall, users endorsed social features to support their MH. In the study by Casarez et al [ 24 ], spouses and partners of people with BD likewise desired features to communicate with other caregivers and also emphasized that DMHTs could facilitate conversation and understanding with patients, a sentiment echoed by peer support specialists by Storm et al [ 38 ] ( Table 3 ). However, one oncology HCP cautioned that similar to support groups, “very strict guidelines of what is said” should be implemented to manage potential risks from shared social media–like content, although little additional context was provided [ 28 ].
Spouses and partners of people with BD also suggested both in-app information on accessing professional resources and direct counseling for the patient at times when other support might be inaccessible [ 24 ]. More than half of all workers, employed or unemployed during the COVID-19 pandemic, likewise endorsed links to resources, counseling, and crisis support as DMHT features, and 81.6% of young adults with psychosis endorsed a feature to communicate with professional experts [ 22 , 33 ]. Importantly, compared with patients attending public clinics, patients attending private psychiatric clinics expressed a higher comfort level for in-app communication with HCPs, suggesting demographic differences in the valuation of access to professional support through DMHTs [ 39 ].
A total of 9 studies reported an interest in DMHT reminders and notifications. Across 3 studies, >70% of patients or caregivers were interested in appointment reminders [ 17 , 21 , 22 ]. In addition, 73% and 68% of patients with epilepsy reported interest in reminders for medication refills and adherence, respectively [ 17 ]. Beyond apps, caregivers of patients with MDD, BD, and schizophrenia preferred an ingestible pill sensor that tracked medication adherence, physical activity, mood, and rest 9.79 (95% CI 4.81-19.9), 7.47 (95% CI 3.81-14.65), and 6.71 (95% CI 3.29-13.69) times more than a nondigital pill organizer, respectively [ 16 ]. Qualitatively, patients and caregivers also appreciated reminders, especially if reasonably timed or delivered via text messages [ 27 , 31 ].
Short-term DMHT engagement was also supported by games and graphics, which could communicate information in an accessible way [ 24 ], provide tools for stress management [ 17 , 33 ], and be used therapeutically with children [ 20 , 30 ]. However, some HCPs and caregivers expressed concerns that graphics and games may be distracting for certain children ( Table 3 ) [ 20 ].
In a novel finding, 3 studies reported forgetfulness or lack of motivation as an influence on DMHT engagement. In some cases, disuse was related to stress, other MH symptoms, or poor technical literacy ( Table 3 ) [ 5 , 25 , 31 ]. In contrast, “forgetting to use” DMHTs and “lack of motivation” were perceived as relatively small barriers to use in the study by Stiles-Shields et al [ 37 ].
The third subtheme under engagement style was customizability, which was generally valued by users; 70.9% of a general population of smartphone users noted customization was an important factor [ 35 ]. Similarly, 9.4% of all surveyed veterans and 10.9% of those with smartphones reported disliking a prior DMHT due to a lack of personalization [ 32 ]. Users specifically wanted to be able to opt out of irrelevant features, customize audiovisual and design elements, add personal notes to tracked mood data, and provide ongoing feedback to facilitate personalization [ 20 , 24 , 28 , 31 , 34 ].
Theme 2: Background and Accessibility
A total of 16 (62%) studies reported findings related to DMHT background and accessibility, which considers the developer of the DMHT, as well as functionality and accessibility. Of these, 12 (75%) studies reported on the technical considerations subtheme, 9 (56%) on costs, and 2 (13%) on stability.
Under technical considerations, 9 studies assessed diverse accessibility concerns. Broadly, Storm et al [ 38 ] emphasized that DMHTs should be developed in consideration of patients’ social, cognitive, and environmental needs to avoid overwhelming users. Specifically, 2 studies reported language as a barrier. Deaf or hard-of-hearing participants recommended visual content presentation, such as videos and icons, alongside text and American Sign Language translations where possible [ 19 ]. Similarly, when discussing English-only apps, 1 provider stated as follows: “language is a barrier for some [patients]” [ 5 ]. Mobility issues related to MH symptoms or other conditions and technical literacy, such as difficulties remembering passwords and navigating smartphones or apps, created accessibility barriers as well ( Table 3 ) [ 5 , 25 , 27 , 28 ]. Additional concerns included apps that restricted use based on geographic location [ 19 ], user difficulty in finding relevant, useful apps [ 32 ], and limited mobile device memory for downloading apps [ 5 , 19 ].
Offline functionality, reported by 6 studies, was also captured under the technical considerations subtheme. A majority (5/9, 56%) of participants included in the study by Borghouts et al [ 19 ] expressed concern about their mobile data plans when using their devices. Correspondingly, “availability of Wi-Fi” was noted as a top barrier to the use of apps for depression by Stiles-Shields et al [ 37 ], and several veterans in another study reported that home Wi-Fi connectivity facilitated app use by eliminating cellular data fees [ 25 , 37 ]. Quotes from patients and HCPs echoed the concern about apps without offline functionality ( Table 3 ) [ 23 , 30 ].
Data fees were also captured under the costs subtheme, with hidden or additional costs described as a barrier to app use by 2 studies [ 26 , 37 ]. Parents of children with ADHD reported that difficulty paying phone bills could result in their phones being shut off, limiting DMHT use; one MH clinic administrator stated as follows: “We often encounter parents’ phones being shut off because they haven’t paid their bill...If the app were free or low cost, I imagine it could be very helpful” [ 26 ]. In addition to hidden costs, this quote identifies up-front app costs as a barrier. Quantitatively, more than half of a general population of surveyed college students expressed that cost was a top concern for the use of MH apps [ 34 ]. Qualitative findings from 2 additional studies likewise identified cost as a barrier to DMHT use [ 25 , 27 ].
Three novel cost attributes were identified by this SLR: willingness to pay, insurance restrictions, and cost savings compared with professional care. Four studies, 3 of which focused on apps, explored willingness to pay for DMHTs from a user perspective. Willingness to pay varied based on user preference; some surveyed college students and smartphone users among general populations valued free apps due to financial restrictions or uncertainty around app effectiveness, although 1 student commented that the quality of free trials might be inferior [ 34 , 35 ]. Some smartphone users also voiced a limit on how much they would be willing to spend for an app subscription ( Table 3 ) [ 35 ]. Forma et al [ 16 ] found that caregivers were willing to pay US $255.04 (95% CI US $123.21-US $386.86) more per month for a pill with an ingestible sensor that tracked medication adherence, physical activity, and rest and could connect to an app that also collected self-reported mood data. Moreover, the caregivers were willing to pay US $124.50 (95% CI US $48.18-US $200.81) more per month for an app-connected pill organizer alone than for a nondigital pill organizer [ 16 ]. In contrast, some veterans expressed total disinterest in paid apps, with 1 user citing poor technical literacy (“don’t have the knowledge”) in addition to cost as affecting willingness to pay [ 25 ].
In another novel finding, a speech-language pathologist working with children with ASD preferred a single app including multiple features over separate apps for particular features due to insurance restrictions: “I agree that teaching Apps should be an in-App feature versus their own app because sometimes insurance doesn’t allow us to open the iPads purchased through insurance” [ 20 ]. Although no further detail was provided for this finding, it suggests that there may be restrictions on the use of other apps on devices purchased under insurance, which may have implications for DMHT use in formal care settings due to the lack of financial support.
In a third novel cost-related finding, a small number of participants from a general population of students (3.6%) in one study preferred using an MH app to seeing an MH professional due to cost savings [ 29 ].
A total of 13% (2/16) of studies reported on the subtheme of app stability and technical difficulties, with crashes and poor display quality decreasing DMHT value [ 35 , 37 ]. Participants in the study by Schueller et al [ 35 ] reported that technical difficulties were often an issue for apps developed by medical institutions, which might be effective and safe but less usable than apps from other developers.
Theme 3: Privacy and Security
A total of 13 (50%) out of 26 studies reported findings related to the privacy and security theme, which covered the use and protection of user data by DMHTs. Subthemes were reported relatively equally: data collection and storage (5/13, 38%), personal health information (PHI; 5/13, 38%), privacy policies (4/13, 31%), general privacy (3/13, 23%), and security measures (3/13, 23%).
Quantitative and qualitative findings on general privacy (ie, evidence not categorized under any specific subtheme), the data collection and storage subtheme, and the privacy policies subtheme revealed heterogeneous concerns ( Table 3 ). A total of 74% of a general population of college students reported privacy as a top concern for MH apps, although further details on the specific area of concern were unclear [ 34 ]. In the study by Stiles-Shields et al [ 37 ], participants were highly concerned with data access but less so with general privacy. Echoing the concerns about data collection and storage, 59.1% of veterans with anxiety or MDD in 1 study were concerned about in-app PHI protection [ 32 ]; however, a qualitative study in veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder, alcohol use disorder, or MDD reported that a relatively small number of participants expressed privacy concerns. In the latter study, reasons for the concerns included distrust in Veterans Affairs, belief that digital data are inherently not confidential, and fear of phone hacking [ 25 ]. From an HCP perspective, none of the surveyed behavioral health HCPs agreed with the statement “My patients are concerned about data security,” despite multiple patients within the same study reporting privacy concerns [ 5 ].
Still, privacy policies were important overall, with 70.5% of smartphone MH app users rating having a privacy policy as “very important” or “important” [ 35 ]. Melcher et al [ 34 ] found that although users valued data protection, some reported a lack of awareness about data privacy, and others were concerned about obscure privacy policies and PHI use. As noted in the data collection and storage subtheme, veteran concerns about government use of PHI were heterogeneous [ 25 ].
A novel valuation factor not included in the APA framework related to user concern with PHI privacy and security regarding MH diagnoses and MH app use is a desire to upkeep their personal image or avoid stigma ( Table 3 ) [ 5 , 25 , 29 , 40 ]. For instance, 21.1% of a general college student population preferred MH app use to seeing an MH professional due to anonymity or reduced stigma [ 29 ]. One participant in a study of Veterans Affairs health service users described access to professional care via MH apps as convenient because they could avoid disclosing their use of MH services to explain leaving work early for an appointment [ 25 ].
In line with the overarching concern about PHI privacy and security, users valued app security measures. Schueller et al [ 35 ] reported that 74.2% of users rated data encryption as “important” or “very important.” Users in another study perceived the level of privacy protection as the highest for apps using a combination of a generic app name (ie, not reflecting the indicated MH disorder); easily hidden modules; and secure, user-authenticated web portals for making module changes [ 40 ]. Behavioral health clinic staff echoed the importance of discreet MH app names ( Table 3 ) [ 30 ].
Theme 4: Therapeutic Goal
There were 12 (46%) studies that reported on the factors relating to the integration of DMHTs with users’ therapeutic goals. The clinical actionability and therapeutic alliance subthemes were reported by 83% (10/12) and 58% (7/12) of studies, respectively.
A total of 9 studies reported the value of clinically actionable insights from apps where the users could acquire and practice new skills to make positive changes in their lives ( Table 3 ). For instance, patient and caregiver app users reported interests in “daily tips,” “new ideas,” and “solutions or recommendations” for symptom management [ 26 , 27 , 36 ]. Furthermore, an app that could serve as a resource for multiple management strategies was preferable [ 26 , 28 , 31 ]. Quantitatively, 4% of patients receiving acute treatment in a partial hospitalization program for MH conditions, including mood and psychotic disorders, reported that the primary purpose of their DMHT use was therapy skills practice [ 18 ]. HCPs similarly appreciated that DMHTs could facilitate patients practicing skills outside of formal treatment sessions [ 5 ]. In particular, clinicians from a youth behavioral health clinic noted that DMHTs might be especially beneficial for young users because they could be conveniently and discreetly incorporated into their daily lives [ 30 ].
Users valued easy data sharing with clinicians, particularly for mood- or symptom-tracking features, which could improve communication and the accuracy of symptom reporting during clinical visits [ 5 , 25 - 27 , 34 , 36 ]. For instance, 53% of a general college student population believed that the potential to share information with their clinician was “one of the top benefits” of using DMHTs [ 34 ]. In addition, many HCPs reported active use or interest in the use of DMHTs in clinical practice to facilitate asynchronous communication and increase patient engagement with treatments outside of formal appointments; however, some preferred traditional care strategies for their personalization and flexibility ( Table 3 ) [ 5 , 26 , 30 ].
Theme 5: Clinical Foundation
A total of 8 (31%) studies reported findings related to the clinical foundation of DMHTs, that is, their utility and appropriateness for patients. Clinical validity was the most reported subtheme, with evidence identified from 6 (75%) studies; 2 (25%) studies reported on the user feedback subtheme and 2 (25%) on the impressions of use subtheme, which captured users’ perceptions of app content as accurate and relevant.
Across subthemes, users valued evidence of DMHT benefit or efficacy from various sources. A total of 71.8% of surveyed veterans said that they would use a DMHT if they “saw proof that it worked” for their MH conditions [ 32 ]. Similarly, among the 811 general population participants surveyed, 69.5% ranked direct research evidence as “important” or “very important” for DMHT, and 66.8% ranked indirect research evidence the same [ 35 ]. Qualitative data identified recommendations from HCPs or academic institutions, as well as evidence of DMHT benefit from publications or research studies, as specific sources for clinically valid evidence of benefits ( Table 3 ) [ 27 , 34 , 35 ].
In addition to academic and professional support, the user feedback subtheme captured user interest in whether DMHTs were beneficial for peers or recommended by other trusted individuals. Patients with depression reported that other users’ experiences influenced their app use, with one user wanting to know “...if other people had success using it” [ 27 ]. Quantitatively, user ratings and user reviews were ranked as “important” or “very important” factors in DMHT use by 59.4% and 58.7% of the general population participants, respectively [ 35 ].
Quality Assessment
The risk of bias was overall moderate. Of the 14 studies including quantitative components, only 1 (7%) used relevant validated outcome measurement instruments [ 33 ]; all others used custom questionnaires. Of the 18 studies with qualitative components, 4 (22%) were at risk of selection bias due to participants being exclusively recruited using web-based postings and research registries [ 33 - 35 , 37 ], and only 1 (6%) considered the relationship between researcher and participant when interpreting the results [ 36 ]. Full quality assessments for qualitative and quantitative study components can be found in Tables S11 and S12 in Multimedia Appendix 1 , respectively.
Principal Findings
This SLR aimed to identify and synthesize qualitative and quantitative evidence on how DMHTs are valued by users, payers, and employers in the United States. Evidence from users with or without diagnosed relevant disorders, caregivers, and HCPs was captured across a wide range of demographics. No study reported evaluating an app from a payer or employer perspective. Furthermore, all but one included study focused on mobile apps.
No relevant appraisals of DMHTs were identified from the FDA website searches; however, 8 relevant FDA approval labels or notifications for MH apps or guidance documents for industry and FDA staff were identified. The content of these materials overlapped with some valuation factors identified in this SLR, including evidence of clinical efficacy and safety, app maintenance, and privacy and security.
Engagement style, although not covered by the FDA materials, was the most reported theme by the studies included in this SLR and was found to overlap heavily with other themes. Engagement may be a key consideration for app developers, as app user retention can be low: 1 study showed that >90% of users had abandoned free MH apps within 30 days of installation [ 41 ]. Engagement is also a key clinical concern in terms of DMHT efficacy; one meta-analysis of 25 studies showed that increased use of DMHT modules was significantly associated with positive outcomes regardless of the target MH condition [ 42 ]. The findings of this SLR may therefore be informative to both DMHT designers and HCPs who integrate DMHTs into clinical care by providing insight on DMHT valuation and thus how use and benefit can be improved. For instance, users valued DMHTs that were easy to use and aligned with their needs and priorities, particularly through features that supported their therapeutic goals. In addition, content presented through multiple delivery modes, such as both text and visuals, promoted engagement as well as accessibility.
However, engagement and feature preference varied across populations. For instance, DMHT valuation was affected by technical literacy, which may relate to user demographics; in this SLR, veterans repeatedly emphasized technical literacy as a barrier to DMHT use [ 25 ]. Similarly, offline functionality may be more important for some users. Although 85% of the total United States population owns smartphones, only 59% of Medicare beneficiaries have access to a smartphone with a wireless plan. Moreover, beneficiaries who are older, less educated, disabled, or Black or Hispanic have even lower digital access [ 43 , 44 ]. These findings emphasize the importance of customizability and suggest that app development and selection in the clinical setting should consider the demographics of the target population, particularly in relation to ease of use and offline functionality.
Background and accessibility findings also identified up-front and hidden costs as barriers to DMHT use, with the willingness to pay varying among individuals. This has important implications for app development, considering that many MH apps currently on the market are direct-to-consumer sales and require out-of-pocket payment. App developers often take this approach as it does not require the accumulation of formal evidence of clinical benefit for FDA approval [ 45 ], but it may present a financial barrier to use for consumers.
Privacy and security, reported by 13 (50%) out of 26 studies, was a prevalent theme, with users primarily concerned with data and PHI security within apps. This finding reflects wider research; a 2019 review of 116 depression-related apps retrieved from iTunes and Google Play stores in 2017 found that only 4% of the identified apps had acceptable transparency in privacy and security, with many completely lacking a privacy policy [ 46 ]. Similarly, 39% of MH apps recommended by college counseling centers had no privacy policy, and of those with a policy, 88% collected user data, and 49% shared that data with third parties [ 4 ]. Most evidence identified in this SLR under this theme, as well as findings previously published in the wider literature, focuses on these remote privacy risks. However, local privacy concerns are also important to users. In particular, inconspicuous naming and the ability to hide sensitive modules within MH apps were rated as highly important by both patients and HCPs to maintain user privacy. Users emphasized a desire to avoid the stigma associated with mental illness, which was also reflected by the findings in the engagement style theme: more young adults with psychosis were more interested in in-app messaging with other patients in psychosis recovery (67.1%) than a provider and family member together (47.3%) or their personal support network (59.8%) [ 22 ]. Similarly, youths were interested in apps that could be used discreetly in school or other public settings to avoid potential MH stigma. This is a key, novel finding of this SLR, considering that many app or DMHT components on the market are named after their target disorder.
The use of DMHTs to achieve therapeutic goals was discussed from patient, caregiver, and HCP perspectives, all of which valued DMHTs that had evidence of efficacy, presented clinically actionable information, and facilitated patient-clinician relationships. Of the 5 studies that explored how HCPs value DMHTs in clinical practice, 2 (40%) were restricted to the oncology or ASD settings and were not readily generalizable to wider MH settings [ 20 , 28 ]. In other studies, providers reported interest in using DMHTs to facilitate asynchronous communication with patients and their caregivers, promote patient skill practice, and improve care for children through the use of games and visuals [ 26 , 30 ]. However, while HCPs overall believed that DMHTs improved care, some believed that their clinical training allowed for care personalization beyond what DMHTs could provide. Feature customizability and receipt of input from HCPs and users during app development and testing may be a way to mitigate these concerns, as well as concerns about safety and efficacy, as many available apps do not appropriately address user health concerns [ 47 ].
Findings additionally suggested that training and resources on DMHTs would be beneficial to ensure that HCPs were equipped to integrate DMHTs into their practices [ 5 ]. Collaboration between DMHT specialists and HCPs, along with a shift from randomized controlled trials to effectiveness-implementation hybrid trials, may be a way to streamline the integration of DMHTs into clinical care and provide more training and resources for HCPs [ 30 , 48 ].
This review followed a prespecified protocol and used systematic methods in line with the York Centre for Reviews and Dissemination guidelines [ 49 ] to conduct an exhaustive search of the literature, identifying evidence relevant to the review objectives from multiple databases and supplementary sources. The framework synthesis approach allowed for the inclusion and analysis of both qualitative and quantitative data, providing a detailed picture of not only what DMHT features users value but why they value them, especially in areas where valuation varies across patient demographics. In addition, the APA framework is a robust model created with patient and HCP input that incorporates key valuation themes broadly shared by other frameworks and widely acknowledged in the literature [ 11 - 13 ].
Limitations
Methodological limitations should be considered when interpreting the findings of this SLR. Only publications in English and in United States populations were included. As perceptions of value are influenced by factors including cultures, laws, and health care settings, the findings of this SLR should not be generalized to other countries. For instance, trust in HCPs and rates of longstanding relationships between patients and primary care providers are lower in the United States than in many European nations [ 50 , 51 ], which could impact the type of support users want from DMHTs (ie, engagement style) or interest in DMHT integration with therapeutic goals.
In addition to the prespecified eligibility criteria, deprioritization strategies were implemented due to the large volume of the identified evidence, and this may have resulted in missing relevant articles. In particular, the deprioritization of secondary research and opinion pieces likely led to the exclusion of relevant discussion around payer perspectives and reimbursement, for which no evidence was included in this SLR. Furthermore, although unlikely, there may have been reporting biases in the included studies due to missing results, which this SLR was not able to assess.
This SLR identified no evidence for 3 subthemes included in the APA framework: business model (background and accessibility), which covers DMHT funding sources and potential sources of conflict, medical claims (background and accessibility), which examines whether DMHTs claim to be medical and the trustworthiness of their creators, and data ownership, access, and export (therapeutic goal), which includes sharing data with eHealth records or wellness devices (eg, Apple HealthKit [Apple Inc], Fitbit [Google LLC]). The valuation of these subthemes should be evaluated in future research.
Conclusions
In summary, app usability, cost, accessibility and other technical considerations, and alignment with therapeutic goals were the most reported valuation factors identified by this SLR. Many studies also reported user preference for apps that incorporated privacy and security features that provided protection from stigma. However, individual DMHTs and their features are valued differently across individuals based on demographics and personal preferences. MH apps should be developed and selected with these specific user needs in mind. Feature customizability and input from users and HCPs during development may improve app usability and clinical benefit.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Max Lee, Costello Medical, US, for medical writing and editorial assistance based on the authors’ input and direction.
Conflicts of Interest
DCM is a consultant for Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization (OPDC) Inc for this project and has received consulting funds from Pear Therapeutics, Sanofi, Avidity, Sarepta, Novartis, and BioMarin. ML, HG, and HCW are employees of OPDC. JC, SB, RSK, and EW are employees of Costello Medical. This research was funded by OPDC.
Electronic database and supplementary search terms, systematic literature review eligibility criteria, publications excluded or deprioritized at full-text review, quality assessments of included studies, and the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram of the identified publications.
PRISMA checklist.
- Content of premarket submissions for device software functions: guidance for industry and Food and Drug Administration staff. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Jun 14, 2023. URL: https://www.fda.gov/media/153781/download [accessed 2024-07-19]
- Patel NA, Butte AJ. Characteristics and challenges of the clinical pipeline of digital therapeutics. NPJ Digit Med. Dec 11, 2020;3(1):159. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Policy for device software functions and mobile medical applications: guidance for industry and Food and Drug Administration staff. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. URL: https://www.fda.gov/media/80958/download [accessed 2023-01-06]
- Melcher J, Torous J. Smartphone apps for college mental health: a concern for privacy and quality of current offerings. Psychiatr Serv. Nov 01, 2020;71(11):1114-1119. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hoffman L, Benedetto E, Huang H, Grossman E, Kaluma D, Mann Z, et al. Augmenting mental health in primary care: a 1-year study of deploying smartphone apps in a multi-site primary care/behavioral health integration program. Front Psychiatry. 2019;10:94. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E, Oliver S, Craig J. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ. BMC Med Res Methodol. Nov 27, 2012;12(1):181. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. Jul 21, 2009;339(jul21 1):b2535. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- CASP critical appraisal checklists. Critical Appraisal Skills Programme. URL: https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/ [accessed 2022-01-06]
- Carroll C, Booth A, Cooper K. A worked example of "best fit" framework synthesis: a systematic review of views concerning the taking of some potential chemopreventive agents. BMC Med Res Methodol. Mar 16, 2011;11(1):29. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Carroll C, Booth A, Leaviss J, Rick J. "Best fit" framework synthesis: refining the method. BMC Med Res Methodol. Mar 13, 2013;13(1):37. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kolasa K, Kozinski G. How to value digital health interventions? a systematic literature review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. Mar 23, 2020;17(6):2119. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lagan S, Aquino P, Emerson MR, Fortuna K, Walker R, Torous J. Actionable health app evaluation: translating expert frameworks into objective metrics. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3:100. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lagan S, Emerson MR, King D, Matwin S, Chan SR, Proctor S, et al. Mental health app evaluation: updating the American Psychiatric Association's framework through a stakeholder-engaged workshop. Psychiatr Serv. Sep 01, 2021;72(9):1095-1098. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hong QN, Pluye P, Bujold M, Wassef M. Convergent and sequential synthesis designs: implications for conducting and reporting systematic reviews of qualitative and quantitative evidence. Syst Rev. Mar 23, 2017;6(1):61. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Beel J, Gipp B, Langer S, Genzmehr M. Docear: an academic literature suite for searching, organizing and creating academic literature. In: Proceedings of the 11th annual international ACM/IEEE joint conference on Digital libraries. 2011. Presented at: JCDL '11; June 13-17, 2011:565-566; Ottawa, ON. URL: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1998076.1998188 [ CrossRef ]
- Forma F, Chiu K, Shafrin J, Boskovic DH, Veeranki SP. Are caregivers ready for digital? caregiver preferences for health technology tools to monitor medication adherence among patients with serious mental illness. Digit Health. 2022;8:20552076221084472. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Afra P, Bruggers CS, Sweney M, Fagatele L, Alavi F, Greenwald M, et al. Mobile software as a medical device (SaMD) for the treatment of epilepsy: development of digital therapeutics comprising behavioral and music-based interventions for neurological disorders. Front Hum Neurosci. 2018;12:171. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Beard C, Silverman AL, Forgeard M, Wilmer MT, Torous J, Björgvinsson T. Smartphone, social media, and mental health app use in an acute transdiagnostic psychiatric sample. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. Jun 07, 2019;7(6):e13364. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Borghouts J, Neary M, Palomares K, de Leon C, Schueller SM, Schneider M, et al. Understanding the potential of mental health apps to address mental health needs of the deaf and hard of hearing community: mixed methods study. JMIR Hum Factors. Apr 11, 2022;9(2):e35641. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Boster JB, McCarthy JW. Designing augmentative and alternative communication applications: the results of focus groups with speech-language pathologists and parents of children with autism spectrum disorder. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. May 10, 2018;13(4):353-365. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Buck B, Chander A, Monroe-DeVita M, Cheng SC, Stiles B, Ben-Zeev D. Mobile health for caregivers of young adults with early psychosis: a survey study examining user preferences. Psychiatr Serv. Aug 01, 2021;72(8):955-959. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Buck B, Chander A, Tauscher J, Nguyen T, Monroe-DeVita M, Ben-Zeev D. mHealth for young adults with early psychosis: user preferences and their relationship to attitudes about treatment-seeking. J Technol Behav Sci. 2021;6(4):667-676. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Carpenter-Song E, Noel VA, Acquilano SC, Drake RE. Real-world technology use among people with mental illnesses: qualitative study. JMIR Ment Health. Nov 23, 2018;5(4):e10652. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Casarez RL, Barlow E, Iyengar SM, Soares JC, Meyer TD. Understanding the role of m-health to improve well-being in spouses of patients with bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord. May 01, 2019;250:391-396. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Connolly SL, Miller CJ, Koenig CJ, Zamora KA, Wright PB, Stanley RL, et al. Veterans' attitudes toward smartphone app use for mental health care: qualitative study of rurality and age differences. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. Aug 22, 2018;6(8):e10748. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Cummings JR, Gaydos LM, Mensa-Kwao A, Song M, Blake SC. Perspectives on caregiver-focused mHealth technologies to improve mental health treatment for low-income youth with ADHD. J Technol Behav Sci. Mar 9, 2019;4(1):6-16. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Dinkel D, Harsh Caspari J, Fok L, Notice M, Johnson DJ, Watanabe-Galloway S, et al. A qualitative exploration of the feasibility of incorporating depression apps into integrated primary care clinics. Transl Behav Med. Sep 15, 2021;11(9):1708-1716. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Huberty J, Bhuiyan N, Neher T, Joeman L, Mesa R, Larkey L. Leveraging a consumer-based product to develop a cancer-specific mobile meditation app: prototype development study. JMIR Form Res. Jan 14, 2022;6(1):e32458. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kern A, Hong V, Song J, Lipson SK, Eisenberg D. Mental health apps in a college setting: openness, usage, and attitudes. Mhealth. Jun 2018;4:20. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Knapp AA, Cohen K, Nicholas J, Mohr DC, Carlo AD, Skerl JJ, et al. Integration of digital tools into community mental health care settings that serve young people: focus group study. JMIR Ment Health. Aug 19, 2021;8(8):e27379. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kornfield R, Meyerhoff J, Studd H, Bhattacharjee A, Williams JJ, Reddy MC, et al. Meeting users where they are: user-centered design of an automated text messaging tool to support the mental health of young adults. In: Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. 2022. Presented at: CHI '22; April 29-May 5 2022:1-6; New Orleans, LA. URL: https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3491102.3502046
- Lipschitz J, Miller CJ, Hogan TP, Burdick KE, Lippin-Foster R, Simon SR, et al. Adoption of mobile apps for depression and anxiety: cross-sectional survey study on patient interest and barriers to engagement. JMIR Ment Health. Jan 25, 2019;6(1):e11334. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Mata-Greve F, Johnson M, Pullmann MD, Friedman EC, Griffith Fillipo I, Comtois KA, et al. Mental health and the perceived usability of digital mental health tools among essential workers and people unemployed due to COVID-19: cross-sectional survey study. JMIR Ment Health. Aug 05, 2021;8(8):e28360. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Melcher J, Camacho E, Lagan S, Torous J. College student engagement with mental health apps: analysis of barriers to sustained use. J Am Coll Health. Oct 13, 2022;70(6):1819-1825. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Schueller SM, Neary M, O'Loughlin K, Adkins EC. Discovery of and interest in health apps among those with mental health needs: survey and focus group study. J Med Internet Res. Jun 11, 2018;20(6):e10141. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Schueller SM, Neary M, Lai J, Epstein DA. Understanding people's use of and perspectives on mood-tracking apps: interview study. JMIR Ment Health. Aug 11, 2021;8(8):e29368. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Stiles-Shields C, Montague E, Lattie EG, Kwasny MJ, Mohr DC. What might get in the way: barriers to the use of apps for depression. Digit Health. Jun 08, 2017;3:2055207617713827. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Storm M, Venegas M, Gocinski A, Myers A, Brooks J, Fortuna KL. Stakeholders' perspectives on partnering to inform the software development lifecycle of smartphone applications for people with serious mental illness: enhancing the software development lifecycle through stakeholder engagement. In: Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference. 2021. Presented at: GHTC '21; October 19-23, 2021:195-199; Seattle, WA. URL: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9612444 [ CrossRef ]
- Torous J, Wisniewski H, Liu G, Keshavan M. Mental health mobile phone app usage, concerns, and benefits among psychiatric outpatients: comparative survey study. JMIR Ment Health. Nov 16, 2018;5(4):e11715. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Zhou L, Parmanto B. User preferences for privacy protection methods in mobile health apps: a mixed-methods study. Int J Telerehabil. Dec 08, 2020;12(2):13-26. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Baumel A, Muench F, Edan S, Kane JM. Objective user engagement with mental health apps: systematic search and panel-based usage analysis. J Med Internet Res. Sep 25, 2019;21(9):e14567. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gan DZ, McGillivray L, Han J, Christensen H, Torok M. Effect of engagement with digital interventions on mental health outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Digit Health. 2021;3:764079. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Mobile fact sheet. Pew Research Center. 2021. URL: https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/fact-sheet/mobile/ [accessed 2024-04-29]
- Roberts ET, Mehrotra A. Assessment of disparities in digital access among Medicare beneficiaries and implications for telemedicine. JAMA Intern Med. Oct 01, 2020;180(10):1386-1389. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Powell AC, Torous JB, Firth J, Kaufman KR. Generating value with mental health apps. BJPsych Open. Feb 05, 2020;6(2):e16. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- O'Loughlin K, Neary M, Adkins EC, Schueller SM. Reviewing the data security and privacy policies of mobile apps for depression. Internet Interv. Mar 2019;15:110-115. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Akbar S, Coiera E, Magrabi F. Safety concerns with consumer-facing mobile health applications and their consequences: a scoping review. J Am Med Inform Assoc. Feb 01, 2020;27(2):330-340. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Curran GM, Bauer M, Mittman B, Pyne JM, Stetler C. Effectiveness-implementation hybrid designs: combining elements of clinical effectiveness and implementation research to enhance public health impact. Med Care. Mar 2012;50(3):217-226. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Systematic reviews: CRD's guidance for undertaking reviews in health care. Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. 2008. URL: https://www.york.ac.uk/media/crd/Systematic_Reviews.pdf [accessed 2024-04-29]
- Gumas ED, Lewis C, Horstman C, Gunja MZ. Finger on the pulse: the state of primary care in the U.S. and nine other countries. The Commonwealth Fund. URL: https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2024/mar/finger-on-pulse-primary-care-us-nine-countries [accessed 2024-04-29]
- Huang EC, Pu C, Chou YJ, Huang N. Public trust in physicians-health care commodification as a possible deteriorating factor: cross-sectional analysis of 23 countries. Inquiry. Mar 05, 2018;55:46958018759174. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
Abbreviations
| attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder |
| American Psychiatric Association |
| autism spectrum disorder |
| bipolar disorder |
| digital mental health technology |
| Food and Drug Administration |
| health care provider |
| major depressive disorder |
| mental health |
| personal health information |
| Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| systematic literature review |
| Sample, Phenomenon of Interest, Design, Evaluation, Research type |
Edited by J Torous; submitted 15.02.24; peer-reviewed by A Mathieu-Fritz, K Stawarz; comments to author 05.05.24; revised version received 20.06.24; accepted 21.06.24; published 30.08.24.
©Julianna Catania, Steph Beaver, Rakshitha S Kamath, Emma Worthington, Minyi Lu, Hema Gandhi, Heidi C Waters, Daniel C Malone. Originally published in JMIR Mental Health (https://mental.jmir.org), 30.08.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in JMIR Mental Health, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://mental.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.

Research & Studies
- Research Videos
- WTC Medical Working Group

WTC Medical Working Group , a group of scientists and medical experts appointed by former Mayor Bloomberg, met from 2007 to 2013 to review 9/11 health research, identify gaps in research and services, and advise city government on ways to communicate health risk information.
Find Current Studies on 9/11 health funded under the Zadroga Act .
WTC Scientific Bibliography lists WTC-related research published in the past years, by category:
- Mental Health Effects
- Physical Effects
- Exposures
- Tower Survivors and Fatalities
- Residential, Commercial and Building Occupants
Find published reports about 9/11 health from the World Trade Center Health Program.
- DOI: 10.55041/ijsrem29138
- Corpus ID: 268429998
An Investigation on Students Learnings & Mental Health Influenced by Artificial Intelligence
- Ijsrem Journal
- Published in INTERANTIONAL JOURNAL OF… 7 March 2024
- Computer Science, Education, Psychology
Related Papers
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
September National Health Observances: Healthy Aging, Sickle Cell Disease, and More
Each month, we feature select National Health Observances (NHOs) that align with our priorities for improving health across the nation. In September, we’re raising awareness about healthy aging, sickle cell disease, substance use recovery, and HIV/AIDS.
Below, you’ll find resources to help you spread the word about these NHOs with your audiences.
- Healthy Aging Month Each September, we celebrate Healthy Aging Month to promote ways people can stay healthy as they age. Explore our healthy aging resources , bookmark the Healthy People 2030 and Older Adults page , share our Move Your Way® materials for older adults , and check out the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans Midcourse Report . You can also share resources related to healthy aging from the National Institute on Aging — and register for the 2024 National Healthy Aging Symposium to hear from experts on innovations to improve the health and well-being of older adults.
- National Recovery Month The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) sponsors National Recovery Month to raise awareness about mental health and addiction recovery. Share our MyHealthfinder resources on substance use and misuse — and be sure to check out Healthy People 2030’s evidence-based resources related to drug and alcohol use .
- National Sickle Cell Awareness Month National Sickle Cell Awareness Month is a time to raise awareness and support people living with sickle cell disease. Help your community learn about sickle cell disease by sharing these resources from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) . You can also encourage new and expecting parents to learn about screening their newborn baby for sickle cell . And be sure to view our Healthy People 2030 objectives on improving health for people who have blood disorders .
- National HIV/AIDS and Aging Awareness Day (September 18) On September 18, we celebrate HIV/AIDS and Aging Awareness Day to encourage older adults to get tested for HIV. Share CDC’s Let’s Stop HIV Together campaign to help promote HIV testing, prevention, and treatment. MyHealthfinder also has information for consumers about getting tested for HIV and actionable questions for the doctor about HIV testing . Finally, share these evidence-based resources on sexually transmitted infections from Healthy People 2030.
- National Gay Men’s HIV/AIDS Awareness Day (September 27) National Gay Men’s HIV/AIDS Awareness Day on September 27 highlights the impact of HIV on gay and bisexual men and promotes strategies to encourage testing. Get involved by sharing CDC’s social media toolkit and HIV information to encourage men to get tested — and share our MyHealthfinder resources to help people get tested for HIV and talk with their doctor about testing .
We hope you’ll join us in promoting these important NHOs with your networks to help improve health across the nation!
The Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (ODPHP) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by ODPHP or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- Follow University of Limerick on Facebook
- Follow University of Limerick on X/Twitter
- Follow University of Limerick on Instagram
- Follow University of Limerick on LinkedIn
- Follow University of Limerick on YouTube
- Follow University of Limerick on TikTok
- Search University of Limerick website
Ireland’s youngest female councillor graduates from University of Limerick

Newly elected Clare County Councillor, Rachel Hartigan credits her success to working twice as hard as the average candidate, as she graduated from University of Limerick today (Thursday) with a Bachelor of Arts in European Studies .
Aged 22, Cllr Hartigan might be the youngest female councillor in the country, but she is no stranger to politics, having studied it in UL, been an active member of Ógra Fianna Fáil, and interned for Clare TD Cathal Crowe.
It was during her summer internship with Deputy Crowe that Rachel first considered running in the local elections.
“I never would have seen myself running for elected politics”, she explained, “but working in Cathal's office, a lot of the queries coming in were what I would imagine a local councillor should really be dealing with.
“And that's when I realised I didn't know who my local councillor was, which seemed bizarre because I'm a politics student, interning in my TD's office, so I'm politically engaged.
“And there's a lot that a local councillor deals with that has a huge impact on people's day-to-day lives, and I felt like we were really missing that strong voice.”
Cllr Hartigan also credits a lack of representation amongst local councillors as a key factor that “spurred” her to action: “I think the median age of a councillor in Ireland is somewhere in the 70s bracket and I felt like that was extremely unfair.
“When we look at why younger people don't come out in droves to vote a lot of the time, what stood out to me was we can't identify with our politicians.
“We don't feel like they speak for us and they don't take the time to get to know what our issues are and what's important to us.
“We're kind of written off and cast aside a lot of the time, and that really spurred me to action as well.”
Rachel was one of more than 3,600 students to graduate at UL this week, and as a first-time local representative, she said her degree in European Studies has “without a doubt” helped to prepare her for her new role.
“I could probably go through reams of actual content and papers and academic research that I did, I could give you exact examples that will come into play now in my role, but the main thing is critical thinking. It is the ability to be open minded and have the skills to do your own research, that is the biggest thing.
“Because there is no guidebook, there is no induction to becoming a councillor, so I'm dealing with queries on housing, medical cards, roads, and footpaths, it's a broad range of issues and I've just started, so having the skills to be able to research properly and effectively and efficiently is huge and I genuinely wouldn't be able to do what I'm doing now had I not learned those really important research skills in UL.
“Obviously studying politics comes into it but in terms of the other subjects I studied, my time studying marketing was hugely helpful, particularly in planning the campaign.
“It was massively beneficial to have an understanding of consumer culture and behavior and being able to approach social media strategically, not just throwing something up for the sake of it. And they're all skills and habits that I picked up in my time as a student in UL.”
Commenting on the landscape for a young woman running an election campaign, Cllr Hartigan said: “I did get a lot of ‘Oh you'll get elected because you're a woman, so you'll get the woman vote or you'll get elected because you're a young person.’
“I got elected because I worked my ass off, that's why I got elected.
“There wasn't an army of young people or an army of women heading to the polling station for me, that's just not what happened, as much as that would have been really cool to see.
“I got elected because I was canvassing for six or seven hours a day, I was on top of my social media, I was planning and hosting public meetings.
“I was doing all of the things that you need to do to win, but I was working twice as hard as the average candidate because I had a lot to prove because I am a young woman, so it doesn't make it easier to run as a woman or a young person like some people suggest.
“You actually have to prove yourself twice as much, and that's not fair, but I think the only way that that will change is if we get more women in and more young people in.”
Cllr Hartigan credits the support of her family and lecturers in helping her throughout her election campaign.
“My lecturer Dr Scott Fitzsimmons was very supportive, as was course director Dr Xosé Boan, who advised me to watch myself and my own mental health and well-being as well.
“Sometimes you get these grand ideas and you're just all go, all the time and you forget to take the time to mind yourself, so I was really glad to have been told that.”
Rachel does not hail from a political family, with her mother Rosaleen working as a medical secretary and her father Paul the Chief Information Officer for Electric Ireland Superhomes. However, that did not stop Paul from taking on the role of campaign manager.
“We both learned together and he came out with me every single night, as did my mom. I could not have done it without them,” explained Rachel.
“Obviously, the focus and the attention is on the candidate, but behind the scenes nobody does it alone, your family has to be on board.
“It's a huge, massive team effort and for all the work that I was doing with my final year in UL and campaigning, they were out canvassing with me just as much, spending just as many hours at the doors.”
A native of Parteen, Co. Clare, Rachel attended Parteen National School and now represents the Shannon Electoral Area.
Reflecting on achieving the two major milestones of graduating university and winning her first election, she said it hasn’t fully sunk in yet.
“I really felt like I was a campaign/Final Year Project robot, and it’s only the last few weeks I've had time to sit and process and reflect.
“You never really look at your own accomplishments and achievements and say ‘oh my God, that was really good’. I think Irish people in particular, and women too, are really bad at giving themselves a pat on the back, even when it's well deserved.
“I'm trying to take in the huge accomplishment, but it's hard to come out and say that and to even feel it, so that's something I'm working on at the moment, giving myself a little pat on the back.”
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.15(7); 2023 Jul
- PMC10460242

A Comprehensive Analysis of Mental Health Problems in India and the Role of Mental Asylums
Vanee r meghrajani.
1 Community Medicine, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Higher Education and Research, Wardha, IND
Manvi Marathe
2 Medicine, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Higher Education and Research, Wardha, IND
Ritika Sharma
3 Medicine and Surgery, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Higher Education and Research, Wardha, IND
Ashwini Potdukhe
4 Medical Surgical Nursing, Smt. Radhikabai Meghe Memorial College of Nursing, Datta Meghe Institute of Higher Education and Research, Wardha, IND
Mayur B Wanjari
5 Research Scientist, Department of Research and Development, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Higher Education and Research, Wardha, IND
Avinash B Taksande
6 Physiology, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Datta Meghe Institute of Higher Education and Research, Wardha, IND
This review article provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of mental health in India, highlighting the challenges faced, the existing initiatives, and the future directions for improving mental healthcare delivery. India is grappling with a high prevalence of mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and substance use disorders. The burden of mental health issues on individuals, families, and society is immense, leading to reduced quality of life, impaired functioning, and significant economic and social consequences. Various social and cultural factors, such as stigma, discrimination, gender inequalities, poverty, rapid urbanization, and cultural beliefs surrounding mental illness, further exacerbate the challenges of addressing mental health problems. Access to mental healthcare remains a significant concern, with considerable gaps in access to and quality of treatment and limited availability of mental health professionals, especially in rural areas. Inadequate infrastructure, a lack of awareness, and insufficient integration into primary healthcare systems hinder access to appropriate care. The historical development of mental asylums in India is examined, highlighting their establishment, purpose, and evolution over time. Critiques and challenges associated with mental asylums are discussed, including stigmatization, human rights concerns, the absence of human center approaches, quality of care, and the need for alternative approaches to mental healthcare.
Introduction and background
With its vast population and diverse demographics, India confronts a substantial mental health burden that warrants urgent attention [ 1 ]. Mental disorders cut across various age groups, socioeconomic backgrounds, and geographical regions, impacting individuals from all walks of life [ 1 ]. The repercussions of these conditions encompass personal suffering, impaired daily functioning, and extensive societal costs [ 1 ]. The prevalence of mental health disorders in India has risen steadily in recent years, contributing to the escalating public health concern. Estimates suggest that nearly 15% of the Indian population grapples with some form of mental health issue. This figure encompasses many disorders, including anxiety disorders, depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, substance use disorders, and neurodevelopmental disorders [ 2 ].
The consequences of these mental health challenges reverberate throughout society. Firstly, individuals struggling with mental health problems face immense personal anguish and distress, as these conditions often impede their ability to lead fulfilling lives. They may encounter difficulties maintaining relationships, pursuing education or employment opportunities, and participating in social activities [ 3 ]. Moreover, mental health problems substantially affect the overall functioning of communities and the nation. Decreased productivity, both in the workplace and within households, is a significant economic consequence. Mental health issues often lead to absenteeism, reduced work efficiency, and long-term disability, negatively impacting workforce productivity and economic growth [ 4 , 5 ].
The financial burden associated with mental health problems cannot be overlooked. Increased healthcare expenditure is incurred due to the need for mental healthcare services, including diagnosis, treatment, medication, and therapy [ 6 ]. The indirect costs, such as lost productivity and an increased burden on caregivers, further exacerbate the economic impact [ 6 ]. Beyond the economic aspect, mental health problems in India also have far-reaching social implications. Stigma and discrimination surrounding mental disorders persist in many communities, hindering individuals from seeking help and support. This leads to delays in diagnosis and treatment, perpetuating the cycle of suffering and exacerbating the long-term consequences [ 7 ].
The rising prevalence of mental health disorders in India and their multifaceted impacts necessitate a comprehensive understanding of the challenges. Addressing mental health issues becomes crucial not only for the well-being of affected individuals but also for the overall progress and development of the nation. By investigating the role of mental asylums in this context, this review article aims to shed light on potential strategies to tackle mental health problems and improve the lives of individuals grappling with these conditions in India [ 1 , 2 , 6 ]. This review article aims to comprehensively analyze mental health problems in India and explore the role of mental asylums in addressing these challenges. By examining the historical and current context, this review aims to shed light on the strengths, limitations, and potential future directions of mental asylums in the Indian mental health landscape.
Methodology
The literature search strategy involved a comprehensive approach to identifying relevant studies on mental health problems in India. Multiple databases, including PubMed, PsycINFO, and Google Scholar, were searched using a combination of keywords such as "mental health," "India," "prevalence," "burden," "access to care," and "mental health disorders." The search was conducted without any language or date restrictions to ensure the inclusion of a wide range of studies. In addition to academic literature, reports from government agencies, international organizations, and non-governmental organizations were reviewed to capture a holistic understanding of the topic. To ensure the selection of appropriate studies, specific inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied. Inclusion criteria included studies on mental health problems in India, prevalence rates, types of mental health disorders, access to mental healthcare, social and cultural factors influencing mental health, and mental health policies and initiatives in India. Both quantitative and qualitative studies were considered. Studies that provided insights into the challenges, current practices, and future directions for mental healthcare in India were prioritized. Exclusion criteria involved studies that were not specific to mental health or did not pertain to the Indian context. Studies with insufficient data, case reports, editorials, and opinion pieces were also excluded. The focus was primarily on peer-reviewed articles, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and research reports that provided substantial evidence and analysis of mental health problems in India. The selection of studies involved a two-step process. Initially, titles and abstracts were screened to assess their relevance to the research topic. Subsequently, full-text articles were reviewed based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Any discrepancies or uncertainties during the study selection process were resolved through discussion and consensus among the research team members.
Mental health problems in India
Prevalence and Types of Mental Health Disorders
In India, mental health disorders have a high prevalence, impacting a considerable proportion of the population. Epidemiological studies report prevalence rates for psychiatric disorders varying from 9.5 to 370 per 1000 people in India [ 8 ]. This prevalence encompasses a broad spectrum of mental health disorders, reflecting the diverse challenges individuals face in the country [ 8 ]. The prevalence rates of mental health disorders in India highlight the need for effective interventions and support systems to address the mental well-being of the population. Conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and substance use disorders are commonly observed mental health disorders in India [ 8 ].
Depression: Depression is a common mental health disorder characterized by persistent sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in activities. At the population level, 3.5% of deaths were attributable to anxiety or depression [ 9 ]. It can negatively impact an individual's mood, thoughts, behavior, and physical well-being. Symptoms of depression may include fatigue, changes in appetite, sleep disturbances, difficulty concentrating, and thoughts of self-harm or suicide. Depression can significantly impair a person's daily functioning, interpersonal relationships, and overall quality of life [ 9 ].
Anxiety disorders: Anxiety disorders are characterized by excessive and persistent worry, fear, or anxiety that significantly interfere with daily functioning. Generalized anxiety disorder involves chronic and excessive worry about various aspects of life. Panic disorder is characterized by recurrent panic attacks, which are intense periods of overwhelming fear and physical symptoms such as heart palpitations and shortness of breath. Phobias involve an intense fear of specific objects, situations, or activities. Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is characterized by intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) performed to alleviate anxiety. Anxiety disorders can cause significant distress, avoidance behaviors, and impaired functioning [ 10 ].
Bipolar disorder: Bipolar disorder is characterized by alternating periods of elevated mood (mania or hypomania) and episodes of depression. During manic episodes, individuals may experience heightened energy levels, decreased sleep, racing thoughts, inflated self-esteem, impulsive behavior, and an exaggerated sense of self-importance. Depressive episodes are marked by sadness, loss of interest, fatigue, and changes in appetite and sleep patterns. Bipolar disorder can profoundly impact an individual's emotions, behavior, relationships, and overall functioning [ 11 ].
Schizophrenia: Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects a person's perception of reality, thinking processes, emotions, and behavior. Common symptoms include hallucinations (perceiving things that are not there), delusions (false beliefs), disorganized speech and behavior, reduced emotional expression, and social withdrawal. Individuals with schizophrenia may experience difficulties in cognitive functioning, such as problems with memory, attention, and executive functioning. Schizophrenia can significantly impair an individual's ability to think, interact with others, and function in society [ 12 ].
Substance use disorders: Substance use disorders involve the excessive and compulsive use of substances, such as alcohol or drugs, despite negative consequences. These disorders can have significant impacts on mental health. Substance abuse can lead to addiction, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms when the substance is unavailable. Substance use disorders can cause various mental health issues, including mood disorders, anxiety disorders, psychosis, cognitive impairments, and social and occupational problems. The associated problems may include financial difficulties, legal issues, relationship conflicts, and physical health complications [ 13 ].
Social and cultural factors influencing mental health in India
Societal Stigma and Discrimination
Mental illness carries a significant social stigma in Indian society, leading to discrimination and social exclusion for individuals with mental health problems. The stigma surrounding mental illness often stems from misconceptions, fear, and a lack of awareness. This stigma creates barriers to seeking help and support, as individuals may fear judgment, rejection, or negative consequences. Consequently, individuals may delay or avoid seeking treatment, resulting in inadequate or delayed care and further exacerbating their condition [ 14 ].
Gender Inequalities
Gender inequalities in India have a profound impact on mental health. Women, in particular, face unique challenges and are more vulnerable to mental health problems. Factors such as domestic violence, sexual abuse, unequal power dynamics, limited access to education and employment opportunities, and societal expectations can contribute to increased stress, anxiety, and depression among women. The intersectionality of gender with other factors, such as socioeconomic status and caste, further compounds mental health disparities [ 15 ].
Poverty and Socioeconomic Factors
Poverty and socioeconomic disparities play a crucial role in developing and exacerbating mental health disorders in India. Limited resources, including access to quality healthcare, mental health services, and essential social support systems, significantly impact mental well-being. Stressful living conditions, financial instability, and a lack of opportunities for upward mobility contribute to heightened psychological distress and the risk of mental health problems [ 16 ].
Rapid Urbanization and Migration
India's rapid urbanization and migration patterns have significant implications for mental health. Urban areas often present challenges such as social dislocation, loss of social support networks, increased competition, and higher stress levels. The migration process, whether from rural to urban areas or within urban areas, can disrupt social cohesion, traditional support systems, and stability, leading to an increased risk of mental health problems [ 17 ].
Family Dynamics and Societal Pressure
Family dynamics and societal expectations pressure individuals, impacting their mental well-being. Expectations related to education, career success, marriage, and gender roles can create significant stress and anxiety. Interpersonal conflicts, strained relationships, and dysfunctional family dynamics can also contribute to developing mental health issues. In some cases, the stigma associated with mental illness within families can lead to a lack of understanding and support, further hindering the individual's ability to seek help [ 18 ].
Cultural Beliefs Surrounding Mental Illness
Cultural beliefs and traditional practices related to mental illness vary across different regions and communities in India. These beliefs can influence help-seeking behaviors, treatment approaches, and perceptions of mental health. Sometimes, cultural beliefs may stigmatize mental illness, discourage open discussions, and promote harmful practices or ineffective remedies. This can hinder access to evidence-based care and perpetuate the cycle of mental health-related challenges [ 19 ].
The Burden of Mental Health Issues on Individuals and Society
Mental health problems substantially burden individuals and society as a whole in India. Individuals with mental health disorders often experience a reduced quality of life, impaired functioning in various domains (such as work, relationships, and education), and an increased risk of suicide [ 20 ]. Societally, mental health problems lead to significant productivity losses due to absenteeism, decreased work performance, and disability. The economic impact includes increased healthcare costs and decreased productivity, impeding social and economic development [ 21 ]. Additionally, mental health problems contribute to the overall burden on the healthcare system, straining resources and diverting attention from other areas of healthcare.
Access to mental healthcare in India
Shortage of Mental Health Professionals
The availability of mental health professionals, including psychiatrists, psychologists, and psychiatric nurses, is insufficient to meet the growing demand for mental healthcare in India. The shortage is particularly prominent in rural areas, where access to mental health professionals is limited. This uneven distribution of services creates a significant barrier for individuals seeking timely and appropriate mental healthcare [ 22 - 23 ].
Inadequate Infrastructure and Resources
Mental healthcare facilities, especially in rural areas, often lack the necessary infrastructure, equipment, and resources to provide comprehensive care. There is a shortage of psychiatric hospitals, outpatient clinics, and community-based services. The lack of appropriate infrastructure hinders the delivery of mental healthcare services and limits the capacity to meet the diverse needs of individuals with mental health disorders [ 24 ].
Lack of Awareness and Stigma
Limited awareness and pervasive stigma surrounding mental health issues in India contribute to the underutilization of mental healthcare services. The stigma associated with mental illness leads to discrimination, social isolation, and prejudice against individuals seeking help. This stigma discourages individuals from openly discussing their mental health concerns and seeking timely treatment [ 25 ].
Insufficient Integration into Primary Healthcare
Mental health services are not adequately integrated into primary healthcare systems in India. This lack of integration results in a fragmented approach to mental healthcare, hindering early detection, timely intervention, and continuity of care for individuals with mental health problems. The separation of mental health from primary healthcare reinforces the notion that mental health is separate from physical health, perpetuating the treatment gap [ 26 ].
Historical development of mental asylums in India
Establishment and Purpose of Mental Asylums
Mental asylums were established in India during the colonial era, primarily under British rule. The first mental asylum in India, the Indian Lunatic Asylum, was established in 1745 in Calcutta (now Kolkata). These institutions were initially established to confine and segregate individuals with mental illness from the rest of society. The focus was primarily on custodial care, with little emphasis on therapeutic interventions [ 27 ].
The main objectives of mental asylums were to provide a secure and controlled environment for those deemed "insane" and to manage and control perceived threats posed by individuals with mental illness. Asylums were often located in remote areas away from urban centers and were designed to isolate individuals with mental illness from the general population [ 28 ].
Changes and Evolution of Mental Asylums Over Time
Over time, mental asylums in India have undergone significant changes and evolution. With advancements in medical understanding and changes in societal attitudes towards mental illness, the approach to care within mental asylums shifted from custodial confinement to a more humane and therapeutic approach [ 29 ].
In the mid-19th century, mental asylums began adopting moral treatment principles influenced by European reform movements. Moral treatment aims to provide a more humane and respectful environment for individuals with mental illness. It focused on promoting moral and spiritual development, engaging patients in meaningful activities, and creating a supportive therapeutic milieu [ 30 ].
In the 20th century, developing psychiatric research institutes and training centers in India further contributed to the evolution of mental healthcare practices. These institutions played a crucial role in advancing the understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of mental health disorders. They also provided opportunities to train mental health professionals and conduct research to improve care [ 31 ].
Role of Mental Asylums in Addressing Mental Health Problems
Mental asylums significantly addressed mental health problems in India, particularly when alternative options were limited. They provided a place of refuge for individuals with mental illness, offering shelter, basic care, and some level of treatment. The asylums acted as custodial institutions, ensuring the containment and management of individuals considered "insane" by societal standards [ 32 ].
Although mental asylums' quality of care and conditions varied widely, some asylums did strive to provide treatment and rehabilitation to their residents. Occupational therapy, recreation, and vocational training were introduced to promote functional improvement and reintegration into society. Some mental asylums also contributed to the understanding and treatment of mental health disorders through research and training initiatives [ 33 ].
However, it is important to acknowledge that mental asylums face significant criticism and challenges. Stigmatization, abuse, overcrowding, a lack of resources, and inadequate staff training were pervasive issues. These concerns led to an evaluation of the asylum model and the recognition of the need for broader reforms in mental healthcare delivery [ 34 ]. The role of mental asylums has evolved, and today, the focus is shifting towards community-based care, deinstitutionalization, and integrating mental health services into mainstream healthcare systems.
Critiques and challenges of mental asylums in India
Stigmatization and Social Attitudes Towards Mental Asylums
Mental asylums in India have historically faced stigmatization and negative societal attitudes. They have been associated with neglect, abuse, and human rights violations. The perception of mental asylums as places of confinement and isolation perpetuates the stigma surrounding mental health and hampers efforts to promote community-based care. This stigma often prevents individuals from seeking help and reinforces the idea that mental health conditions should be dealt with in isolation rather than as part of a broader community [ 35 ].
Human Rights Concerns and Ethical Considerations
Human rights concerns have been raised regarding mental asylums in India. Reports have documented overcrowding, a lack of privacy, and inadequate living conditions in some institutions. Patients' rights, including dignity, autonomy, and privacy, can be compromised in these settings. Additionally, the ethical considerations of involuntary admissions, the use of restraints, and the need for informed consent in psychiatric treatment are critical issues that must be addressed to protect individuals' rights and well-being [ 36 ].
Quality of Care and Treatment Modalities
The quality of care provided in mental asylums varies widely across India. While some institutions adhere to evidence-based treatments, rehabilitation programs, and a multidisciplinary approach, others struggle with resource constraints, inadequate staffing, and outdated practices. Using outdated treatments and over-reliance on medications without adequate psychosocial support services remain challenges within the mental asylum system. Improving the quality of care requires a focus on the training and capacity-building of mental health professionals, ensuring access to evidence-based treatments, and promoting holistic approaches that address the individual's social, psychological, and emotional needs [ 37 ].
Alternative Approaches to Mental Healthcare
The criticisms and challenges surrounding mental asylums have spurred the exploration of alternative approaches to mental healthcare in India. Community-based care has gained recognition as a more humane and effective approach that emphasizes the involvement of families, communities, and social support networks. Integrating mental health into primary healthcare settings allows for early detection, timely intervention, and holistic management of mental health problems. Other alternative approaches include mobile mental health units to reach underserved populations, telemedicine for remote consultations, and the implementation of psychosocial interventions that prioritize individual empowerment, resilience, and well-being. These alternative approaches promote a shift towards person-centered care and community support, reducing reliance on institutionalized care and enhancing India's overall mental health ecosystem [ 38 ].
Current mental health initiatives in India
Government Programs and Policies
The Government of India has implemented several programs and policies to address mental health issues. The National Mental Health Program (NMHP) is a flagship initiative to improve mental healthcare services. The program aims to provide accessible and affordable mental healthcare, promote community participation, train mental health professionals, and raise awareness about mental health. It also emphasizes integrating mental health into primary healthcare systems [ 39 ].
In addition, the Mental Healthcare Act of 2017 is significant legislation that prioritizes the rights and dignity of individuals with mental illness. It provides a legal framework for delivering mental healthcare, protects the rights of individuals with mental illness, decriminalizes suicide, and promotes community-based care [ 40 ].
Community-Based Mental Health Services
Community-based mental health services have gained prominence in India as a strategy to bridge the treatment gap and improve access to mental healthcare. These services adopt a decentralized approach, delivering mental healthcare at the community level through trained professionals. Community mental health programs involve outreach activities, awareness campaigns, counseling services, and support for individuals with mental health disorders and their families. The aim is to reduce stigma, enhance accessibility, and provide holistic care sensitive to communities' cultural context [ 38 ].
Integration of Mental Health into Primary Healthcare
Integrating mental health into primary healthcare is a key strategy to improve access to mental healthcare services. The District Mental Health Program (DMHP) is a notable initiative. The DMHP focuses on strengthening mental health services at the primary care level by training primary healthcare workers to identify and manage common mental health conditions. It involves capacity building, the provision of essential psychotropic medications, referral systems, and community-based rehabilitation services. This integration ensures that mental health is given equal importance to physical health, leading to early detection, timely intervention, and continuity of care [ 41 ].
Awareness Campaigns and Advocacy Efforts
Awareness campaigns and advocacy efforts are critical to promoting mental health literacy, reducing stigma, and raising public awareness about mental health issues. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs), mental health professionals, and community groups actively engage in advocacy, education, and destigmatization initiatives. These efforts aim to challenge stereotypes, provide accurate information about mental health, promote help-seeking behaviors, and create supportive environments for individuals with mental health disorders. Awareness campaigns often utilize various media platforms, community events, and workshops to reach a wide audience and promote positive attitudes toward mental health [ 42 ]. These current mental health initiatives in India demonstrate a multifaceted approach that combines government policies, community-based services, integration into primary healthcare, and awareness campaigns. Such comprehensive efforts are crucial in addressing the complex challenges of mental health and improving the overall mental well-being of individuals in the country.
Future directions for mental health in India
Increasing the Number of Mental Health Professionals
Addressing the shortage of mental health professionals requires a multi-pronged approach. One strategy is to increase the number of psychiatrists, psychologists, psychiatric nurses, and other mental health specialists. This can be achieved through expanded training programs that attract more individuals to the field and provide them with the necessary skills and knowledge to practice effectively. Scholarships and incentives can also be offered to encourage professionals to work in underserved areas where the shortage is more pronounced. By increasing the workforce in mental health, access to care can be improved [ 43 ].
Enhancing Training and Capacity-Building
To ensure the delivery of high-quality mental healthcare, it is crucial to provide comprehensive and specialized training to mental health professionals. This includes continuous professional development programs that keep professionals updated with the latest evidence-based practices. Professionals can provide more effective and targeted interventions by enhancing their knowledge and skills in diagnosing and treating mental health disorders. Training programs should focus on culturally sensitive approaches and address the specific needs of diverse populations [ 44 ].
Decentralizing Mental Health Services
To bridge the gap in mental healthcare between urban and rural areas, it is essential to strengthen mental healthcare infrastructure and services at the district and community levels. This involves establishing mental health facilities, outpatient clinics, and community-based services in rural and remote areas. By bringing mental health services closer to where people live, access to care can be improved, and individuals can receive timely interventions. This also helps reduce the burden on tertiary care centers and psychiatric hospitals [ 45 ].
Integrating Mental Health into Primary Healthcare
Recognizing the importance of early detection and intervention, integrating mental health services into primary healthcare settings is crucial. This integration involves training primary healthcare providers to identify and manage common mental health conditions. It also includes establishing referral systems between primary care and specialized mental health services. Individuals can receive timely support and treatment by integrating mental health into primary healthcare, and the stigma associated with seeking mental healthcare can be reduced [ 46 ].
Strengthening Referral Systems
To ensure seamless transitions between different levels of care, robust referral systems must be developed. Effective communication and coordination between primary healthcare providers, specialized mental health services, and other relevant sectors (such as education and employment) are essential. Referral systems should ensure that individuals with mental health problems receive continuous support and follow-up care as they move through different stages of their treatment journey. This helps maintain continuity of care and address individuals' holistic needs [ 47 ].
Public-Private Partnerships and Leveraging Technology
To improve mental healthcare delivery, collaborations between the public and private sectors can be fostered through public-private partnerships. Such partnerships can enhance resource allocation, capacity-building, and the development of innovative approaches to mental health. Private sector involvement can bring additional expertise and resources to complement public sector efforts. Furthermore, leveraging technology can significantly improve access to mental healthcare, particularly in remote and underserved areas. Telemedicine, mobile health applications, and online platforms can facilitate virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and self-help interventions, expanding the reach of mental health services [ 48 ].
By implementing these recommendations, India can make significant strides in improving mental healthcare delivery, addressing workforce shortages, enhancing training and capacity-building, decentralizing services, integrating mental health into primary care, strengthening referral systems, and harnessing the potential of public-private partnerships and technology. These strategies contribute to a more comprehensive and accessible mental health system that meets the diverse needs of individuals nationwide.
Policy reforms and resource allocation
Allocating Adequate Resources
Increasing budgetary allocations specifically for mental health is essential. Sufficient funds should be allocated to support infrastructure development, including the establishment of mental health facilities, outpatient clinics, and community-based services. Adequate resources are also necessary to recruit and train mental health professionals, implement training programs for primary healthcare providers, conduct research, and address mental health disparities across regions [ 49 ].
Prioritizing Mental Health in the Healthcare Agenda
Recognizing mental health as a priority area within the broader healthcare system is essential for effective reform. This involves integrating mental health into national health policies, strategic plans, and programs. Setting measurable targets and indicators for improving mental healthcare outcomes helps ensure that progress is monitored and interventions are evidence-based [ 50 ].
Developing a Robust Regulatory Framework
Establishing and implementing a comprehensive regulatory framework is crucial for ensuring quality standards, ethics, and guidelines for mental health services. This includes developing licensing and accreditation processes for mental healthcare providers, monitoring compliance with professional standards, and enforcing ethical guidelines. Additionally, monitoring and evaluation mechanisms should be in place to assess the quality and effectiveness of mental healthcare delivery, identify areas for improvement, and ensure accountability [ 51 ].
Ensuring Policy Implementation
Strengthening coordination and collaboration among government departments responsible for mental health, social welfare, education, and employment is necessary for effective policy implementation. Intersectoral collaboration facilitates a holistic approach to addressing mental health issues and ensures that policies and initiatives are coordinated. This coordination can include sharing resources, data, and expertise, as well as joint planning and monitoring of mental health programs [ 52 ].
Holistic and multidisciplinary approaches to mental health
Integrating Psychological, Social, and Biological Perspectives
Recognizing that mental health disorders have complex causes and manifestations, it is essential to adopt an integrated approach that addresses mental health's biological, psychological, and social determinants. This means acknowledging the interplay between genetic factors, brain chemistry, individual experiences, and social contexts in developing and managing mental health disorders [ 53 ].
Collaborative Care Models
Collaborative care models involve a coordinated and team-based approach to mental healthcare delivery. These models bring together multiple stakeholders, including mental health professionals, primary healthcare providers, social workers, and community organizations, to work collaboratively to address the needs of individuals with mental health disorders [ 54 ].
Promoting community participation and support systems
Engaging Community Leaders and Organizations
Collaborating with community leaders, religious and cultural organizations, and community-based groups is crucial for promoting mental health awareness, reducing stigma, and improving access to care. Community leaders and organizations have significant influence and reach within their communities. By partnering with them, it is possible to conduct awareness campaigns, organize educational events, and disseminate accurate information about mental health. This collaboration can help create supportive environments where individuals feel comfortable seeking help and accessing mental healthcare services. Community-based organizations can also play a role in identifying individuals in need of support and connecting them with appropriate resources [ 55 ].
Involving Individuals with Lived Experience
It is essential to involve individuals with personal experience with mental health problems in decision-making, service planning, and advocacy efforts. Their unique insights and perspectives can contribute to more person-centered and recovery-oriented mental healthcare services. These individuals can provide valuable input on the challenges they faced, the types of support that were helpful to them, and the gaps in existing services. Their involvement can help shape policies, programs, and interventions more responsive to the needs and preferences of individuals with mental health disorders. It also empowers them to become advocates for mental health and reduce stigma through sharing their stories and experiences [ 56 ].
Peer Support Networks and Community-Based Rehabilitation
Establishing peer support networks, self-help groups, and community-based rehabilitation programs is essential for fostering a sense of belonging and support among individuals with mental health disorders. Peer support networks provide a platform for individuals to connect, share experiences, and offer mutual support. These networks can help reduce feelings of isolation and provide a sense of community, which is particularly beneficial during recovery. Self-help groups allow individuals to share coping strategies, provide emotional support, and learn from each other's experiences. Community-based rehabilitation programs empower individuals with mental health disorders to develop skills, reintegrate into society, and participate in meaningful activities. These initiatives promote social inclusion, recovery, and well-being [ 57 ]. By implementing these recommendations, India can significantly improve its mental healthcare delivery, ensure better access and quality of care, reduce stigma, and promote holistic well-being for individuals with mental health disorders.
Conclusions
Addressing mental health problems in India holds immense significance, considering the scale of human value impact involved. The country's population size gives added weight to the importance of tackling these barriers. It is crucial to recognize that mental health issues affect a significant portion of the population and can lead to severe consequences if left unaddressed. Therefore, concerted efforts are essential to combating these challenges effectively. Reducing the stigma surrounding mental illness is critical to addressing mental health problems in India. Stigma creates barriers that hinder individuals from seeking the necessary help and support they require. To overcome this, public awareness campaigns and educational initiatives are vital in combating stigma and promoting understanding and empathy toward those with mental health conditions. A comprehensive and compassionate approach is necessary to tackle India's complex mental health challenges. By reducing stigma, improving accessibility, enhancing the quality of services, shifting towards community-based care, protecting human rights, and integrating mental health into mainstream healthcare systems, India can make significant progress in addressing mental health issues. The benefits will extend beyond individuals, contributing to society's overall development and well-being.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
- Ecosystem Ecology
- Natural Environments
Environmental problems of development and population safety in natural environment of Voronezh region
- February 2022
- IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science 981(3):032033
- 981(3):032033
- This person is not on ResearchGate, or hasn't claimed this research yet.
Abstract and Figures
![research papers mental health Biopotential (biocapacity) and ecological footprint (gha. per 1 person) [3].](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358865675/figure/fig1/AS:11431281118564784@1675793268366/Biopotential-biocapacity-and-ecological-footprint-gha-per-1-person-3_Q320.jpg)
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- R E Rogozina
- M V Derevyagina
- E.S. Kulakovskiy
- I Chernyshova
- Yu M Fetisov
- Larisa Nikolaevna Shentseva
- Russia Regions Of
- M Derevyagina
- M Shentseva
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Anxiety, Depression and Quality of Life—A Systematic ...
Mental Health Prevention and Promotion—A Narrative ...
Social Media Use and Its Connection to Mental Health
The role of social determinants of health in mental health: An examination of the moderating effects of race, ethnicity, and gender on depression through the all of us research program dataset. Image credit: Line, by Peggy from Pixabay. 07/24/2024. Mental health psychology.
Challenges and barriers in mental healthcare systems and ...
Mental health professionals can help craft messages to be delivered by trusted leaders. 4. The Covid-19 pandemic has alarming implications for individual and collective health and emotional and ...
Society and Mental Health
Social Media and Mental Health: Benefits, Risks, and ...
A scoping review of the literature on the current mental health ...
A systematic review: the influence of social media on ...
Mental Health America are joined by other prominent mental health advocacy groups to sponsor related observances: Mental Health Awareness Week Canada (1-7 May, 2023) and Europe (22-28 May ...
Then, current and future directions of SMH research are discussed, including (a) the impact of SMH health initiatives and services on schools' achievement, (b) the need to address the mental ...
In The Lancet Psychiatry, Chekroud and colleagues1 presented a large cross-sectional examination of physical activity and mental health. Despite imprecision about the terms mental health and exercise in the study—and the cross-sectional design—the findings overall match the existing body of longitudinal research showing that regular physical activity is associated with better mental health.2
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) is the Nation's leader in research on mental disorders, supporting research to transform the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses. Below you can learn more about NIMH funded research areas, policies, resources, initiatives, and research conducted by NIMH on the NIH campus.
Mental Health Problems among Young People—A Scoping ...
Research; Working Papers; Mental Health, Substance Use, and Child… Mental Health, Substance Use, and Child Maltreatment. Mir M. Ali, Thanh Lu, Johanna Catherine Maclean & Angélica Meinhofer. Share. X LinkedIn Email. Working Paper 32895 DOI 10.3386/w32895 Issue Date ...
Substance use disorders (SUDs) and mental health disorders (MHDs) are significant public health challenges with far-reaching consequences on individuals and society. Dual diagnosis, the coexistence of SUDs and MHDs, poses unique complexities and impacts treatment outcomes. A research landscape analysis was conducted to explore the growth, active countries, and active journals in this field ...
Background: Digital mental health technologies (DMHTs) have the potential to enhance mental health care delivery. However, there is little information on how DMHTs are evaluated and what factors influence their use. Objective: A systematic literature review was conducted to understand how DMHTs are valued in the United States from user, payer, and employer perspectives.
Mental, neurological and substance use (MNS) disorders are a leading, but neglected, cause of morbidity and mortality in sub-Saharan Africa. The treatment gap for MNS is vast with only 10% of people with MNS disorders in low-income countries accessing evidence-based treatments. Reasons for this include low awareness of the burden of MNS disorders and limited evidence to support development ...
The survey also showed that most students used informal networks like friends and family for emotional support, highlighting a shortfall in mental health assistance. The research emphasises the ...
Our paper focuses on the issues of social health and psychological safety of university students involved in digital sustainable education during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Research & Studies. WTC Medical Working Group, a group of scientists and medical experts appointed by former Mayor Bloomberg, met from 2007 to 2013 to review 9/11 health research, identify gaps in research and services, and advise city government on ways to communicate health risk information.. Find Current Studies on 9/11 health funded under the Zadroga Act.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in the ...
A method for the influence of public mental health on the teaching effect of the business administration profession based on artificial intelligence engineering is developed to improve the teaching- learning effect of the business administration major. Artificial intelligence has impacted student's social, emotional, and physical well-being. It has resulted in how a person thinks and reacts ...
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) sponsors National Recovery Month to raise awareness about mental health and addiction recovery. Share our MyHealthfinder resources on substance use and misuse — and be sure to check out Healthy People 2030's evidence-based resources related to drug and alcohol use.
Newly elected Clare County Councillor, Rachel Hartigan credits her success to working twice as hard as the average candidate, as she graduated from University of Limerick today (Thursday) with a Bachelor of Arts in European Studies. Aged 22, Cllr Hartigan might be the youngest female councillor in the country, but she is no stranger to politics, having studied it in UL, been an active member ...
Stress, Anxiety, and Depression Among Undergraduate ...
Select low-income countries have implemented P4P at a national level, strengthening health system capacity through collection and analysis of population health data. Early research at all country ...
A Comprehensive Analysis of Mental Health Problems in ...
The paper presents the results of an assessment of agroecological conditions in the soils of the Azov-Kuban lowland due to the development of technogenic degradation.