Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.

Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing

- Section 1: Home
- Narrowing Your Topic
- Problem Statement
Purpose Statement Overview
Writing an effective purpose statement, best practices for writing your purpose statement, sample purpose statements.
- Conceptual Framework
- Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Synthesis and Analysis in Writing Support This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research Support with the ASC This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Research Process This link opens in a new window
- ASC Guide: Outlining and Annotating This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Organizing Research & Citations This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: RefWorks This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Copyright Information This link opens in a new window
Purpose Statement
The purpose statement succinctly explains the objectives of the doctoral project or dissertation-in-practice. These objectives must directly address the problem. The purpose statement also identifies the project methodology and design.
A problem and a missing piece in combination can lead to different objectives, and hence, different purpose statements.
The purpose of the applied doctoral project or dissertation-in-practice must not only align with the problem and address a missing piece; it must also align with the chosen project method. In fact, the template requires you to name the research method at the very beginning of the purpose statement. In general, quantitative studies involve “closed-ended” research verbs such as determine, measure, correlate, explain, compare, validate, identify, or examine; whereas qualitative studies involve “open-ended” research verbs such as explore, understand, narrate, articulate [meanings], discover, or develop.
Qualitative Purpose Statement
A qualitative purpose statement following the color-coded problem statement (assumed here to be low well-being among financial sector employees) + missing piece (lack of research on followers of mid-level managers), might start like this:
In response to declining levels of employee well-being, the purpose of the qualitative phenomenology was to explore and understand the lived experiences related to the well-being of the followers of novice mid-level managers in the financial services industry. The levels of follower well-being have been shown to correlate to employee morale, turnover intention, and customer orientation (Eren et al., 2013). A combined framework of Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory and the employee well-being concept informed the research questions and supported the inquiry, analysis, and interpretation of the findings to be applied in the financial services industry.
Quantitative Purpose Statement
A quantitative purpose statement for the same problem and gap might start like this:
In response to declining levels of employee well-being, the purpose of the quantitative correlational study was to determine which leadership factors predict employee well-being of the followers of novice mid-level managers to be applied in the financial services industry. Leadership factors were measured by the Leader Member Exchange (LMX) assessment framework by Mantlekow (2015), and employee well-being was conceptualized as a compound variable consisting of self-reported turnover-intent and psychological test scores from the Mental Health Survey (MHS) developed by Johns Hopkins University researchers.
Both of these purpose statements reflect viable research strategies and both align with the problem and gap so it’s up to the practitioner to design a doctoral project or dissertation-in-practice in a manner that reflects personal preferences and desired study outcomes. Note that the quantitative research purpose incorporates operationalized concepts, or variables; that reflect the way the practitioner intends to measure the key concepts under study; whereas the qualitative purpose statement isn’t about translating the concepts under study as variables but instead aim to explore and understand the core research phenomenon.
An important step in the successful completion of an Applied Doctoral Project/Dissertation in Practice is starting off with an accurate and precise purpose statement. Read through the information below to get some general ideas or guidelines related to effective purpose statements and how to compose them. All this information comes from faculty who want you to succeed in the process.
General Guidelines
Keep these in mind as you begin to compose your purpose statement
Good purpose statements:
- Flow from the problem statement and actually address the proposed problem
- Are concise and clear
- Answer the question ‘Why are you doing this project?’
- Match the methodology to your questions
- Have a ‘hook’ to get the reader’s attention
- Set the stage by clearly stating, “The purpose of this (qualitative or quantitative) study is to ...”
Writing your Purpose Statement:
- The Problem Statement is why I am doing the project or dissertation-in-practice
- The Purpose Statement is what type of project or study I am doing to fit or address the problem
The Purpose Statement includes:
- Design and Method of Study
- Specific Population
Creswell (2002) suggested that purpose statements in qualitative projects or studies include deliberate phrasing to alert the reader to the purpose statement. Verbs are key to indicate what will take place in the project or study research and the use of non-directional language that does not suggest an outcome. A purpose statement should focus on a single idea or concept with a broad definition of that idea or concept. How the concept will be investigated should also be included, as well as participants in the study and study locations to give the reader a sense of with whom and where the project or study will occur.
Creswell (2003) advised the following script for purpose statements in qualitative methodology:
“The purpose of this qualitative_________________ (strategy of inquiry, such as ethnography, case study, or other type) study is (was? will be?) to ________________ (understand? describe? develop? discover?) the _________________(central phenomenon being studied) for ______________ (the participants, such as the individual, groups, organization) at __________(site). At this stage in the project, the __________ (central phenomenon being studied) will be generally defined as ___________________ (provide a general definition)” (pg. 90).
Quantitative Purpose Statement
Creswell (2003) offers vast differences between the purpose statements written for qualitative methodology and those written for quantitative methodology, particularly with respect to language and the inclusion of variables. The comparison of variables is often a focus of quantitative methodology with the variables distinguishable by either the temporal order or how they are measured. As with qualitative purpose statements, Creswell (2003) recommends the use of deliberate language to alert the reader to the purpose of the project or study, though quantitative purpose statements also include the theory or conceptual framework guiding the project or study, the variables that are being studied, and how those variables are related.
Creswell (2003) suggests the following script for drafting purpose statements in quantitative projects:
“The purpose of this _____________________ (experiment? survey?) project is (was? will be?) to test the theory of _________________that _________________ (compares? relates?) the ___________(independent variable) to _________________________(dependent variable), controlling for _______________________ (control variables) for ___________________ (participants) at _________________________ (site). The independent variable(s) _____________________ will be generally defined as _______________________ (provide a general definition). The dependent variable(s) will be generally defined as _____________________ (provide a general definition), and the control and intervening variables(s), _________________ (identify the control and intervening variables) will be statistically controlled in this project” (pg. 97).
Creswell, J. (2002). Educational research: Planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research. Merrill Prentice Hall. 7. Creswell, J. (2003). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approaches (2nd ed.). SAGE Publications.
Always keep in mind that the process is iterative, and your writing, over time, will be refined as clarity is gradually achieved. Most of the time, greater clarity for the purpose statement and other components is the result of a growing understanding of the literature in the field. As you increasingly master the literature you will also increasingly clarify the purpose of your project or study.
The purpose statement should flow directly from the problem statement. There should be clear and obvious alignment between the two, and that alignment will get tighter and more pronounced as your work progresses.
The purpose statement should specifically address the reason for conducting the project or study, with emphasis on the word specifically. There should not be any doubt in your readers’ minds as to the purpose of your project or study. To achieve this level of clarity, you will need to also ensure there is no doubt in your mind as to the purpose of your project or study.
You may benefit from stopping your work during the process when insight strikes you in order to write about that insight while it is still fresh in your mind. This pause can help you clarify all aspects of the project or study, including clarifying its purpose.
Your Chair and your committee members can help you to clarify the purpose of your project or dissertation-in-practice, so carefully attend to any feedback they offer.
The purpose statement should reflect the questions proposed and vice versa. The chain of alignment that began with the problem description and continues on to the purpose, questions, and methodology must be respected at all times during development. You are to succinctly describe the overarching goal of the project or dissertation-in-practice that reflects the questions. Each question narrows and focuses the purpose statement. Conversely, the purpose statement encompasses all of the questions.
Identify in the purpose statement the methodology as quantitative, qualitative or mixed (i.e., “The purpose of this [qualitative/quantitative/mixed] study is to ...)
Follow the initial declaration of purpose with a brief overview of how the project or study will be conducted, including instruments, data, with whom (sample), and where (as applicable). Identify variables/constructs and/or phenomenon/concept/idea. Since this section is to be a concise paragraph, emphasis must be placed on the word brief. However, adding these details will give your readers a very clear picture of the purpose of your project or dissertation-in-practice.
Developing the purpose section is usually not achieved in a single flash of insight. The process involves a great deal of reading to find out what other practitioners have done to address the problem you have identified. The purpose section could well be the most important paragraph you write during your academic career, and every word should be carefully selected. Think of it as the DNA of your project or study. Everything else you write should emerge directly and clearly from your purpose statement. In turn, your purpose statement should emerge directly and clearly from your problem description. It is good practice to print out your problem statement and purpose statement and keep them in front of you as you work on each part of your project or dissertation-in-practice in order to ensure alignment.
It is helpful to collect several project or dissertation-in-practice reports or literature similar to the one you envision creating. Extract the problem descriptions and purpose statements of other authors and compare them in order to sharpen your thinking about your own work. Comparing how other authors have handled the many challenges you are facing can be an invaluable exercise. Keep in mind that individual universities use their own tailored protocols for presenting key components, so your review of these purpose statements should focus on content rather than form.
Once your purpose statement is set, it must be consistently presented throughout the project or dissertation-in-practice. This consistency may require some recursive editing because the way you articulate your purpose may evolve as you work on various aspects of your project or dissertation-in-practice. Whenever you make an adjustment to your purpose statement, you should carefully follow up on the editing and conceptual ramifications throughout the entire document.
In establishing your purpose, you should NOT advocate for a particular outcome. Your review of the literature should be done to answer questions, not to prove a point. As a scholar-practitioner, you are to inquire with an open mind, and even when you come to the work with clear assumptions, your job is to support the validity of the conclusions reached. For example, you would not say the purpose of your project or study is to demonstrate that there is a relationship between two variables. Such a statement presupposes you know the answer before your review of the literature conducted and promotes or supports (advocates on behalf of) a particular outcome. A more appropriate purpose statement would be to examine or explore the relationship between two variables.
Your purpose statement should not imply that you are going to prove something. You may be surprised to learn that we cannot prove anything in scholarly review of the literature for two reasons. First, in quantitative analyses, statistical tests calculate the probability that something is true rather than establishing it as true. Second, in qualitative methodology, the study can only purport to describe what is occurring from the perspective of the participants. Whether or not the phenomenon they are describing is true in a larger context is not knowable. We cannot observe the phenomenon in all settings and in all circumstances.
Here are some example purpose statements for your consideration.
Purpose Statement 1
The purpose of this qualitative project was to determine how participation in service-learning in an alternative school impacted students academically, civically, and personally. There is ample evidence demonstrating the failure of schools for students at-risk; however, there is still a need to demonstrate why these students are successful in non-traditional educational programs like the service-learning model used at TDS. This study was unique in that it examined one alternative school’s approach to service-learning in a setting where students not only serve, but faculty serve as volunteer teachers. The use of a constructivist approach in service-learning in an alternative school setting was examined in an effort to determine whether service-learning participation contributes positively to academic, personal, and civic gain for students, and to examine student and teacher views regarding the overall outcomes of service-learning. This study was completed using an ethnographic approach that included observations, content analysis, and interviews with teachers at The David School.
Purpose Statement 2
The purpose of this quantitative, non-experimental, cross-sectional linear, multiple regression design study was to investigate the relationship among early childhood teachers’ self-reported assessment of multicultural awareness as measured by responses from the Teacher Multicultural Attitude Survey (TMAS) and supervisors’ observed assessment of teachers’ multicultural competency skills as measured by the Multicultural Teaching Competency Scale (MTCS) survey. Demographic data such as number of multicultural training hours, years teaching in Dubai, curriculum program at current school, and age were also examined and their relationship to multicultural teaching competency. The study took place in the emirate of Dubai where there were 14,333 expatriate teachers employed in private schools (KHDA, 2013b).
Purpose Statement 3
The purpose of this quantitative, non-experimental project is to examine the degree to which stages of change, gender, acculturation level and trauma types predicts the reluctance of Arab refugees, aged 18 and over, in the Dearborn, MI area, to seek professional help for their mental health needs. This study will utilize four instruments to measure these variables: University of Rhode Island Change Assessment (URICA: DiClemente & Hughes, 1990); Cumulative Trauma Scale (Kira, 2012); Acculturation Rating Scale for Arabic Americans-II Arabic and English (ARSAA-IIA, ARSAA-IIE: Jadalla & Lee, 2013), and a demographic survey. This study will examine 1) the relationship between stages of change, gender, acculturation levels, and trauma types and Arab refugees’ help-seeking behavior, 2) the degree to which any of these variables can predict Arab refugee help-seeking behavior. Additionally, the outcome of this study could provide researchers and clinicians with a stage-based model, TTM, for measuring Arab refugees’ help-seeking behavior and lay a foundation for how TTM can help target the clinical needs of Arab refugees. Lastly, this attempt to apply the TTM model to Arab refugees’ condition could lay the foundation for future research to investigate the application of TTM to clinical work among refugee populations.
Purpose Statement 4
The purpose of this qualitative, phenomenological project is to describe the lived experiences of LLM for 10 EFL learners in rural Guatemala and to utilize that data to determine how it conforms to, or possibly challenges, current theoretical conceptions of LLM. In accordance with Morse’s (1994) suggestion that a phenomenological study should utilize at least six participants, this study utilized semi-structured interviews with 10 EFL learners to explore why and how they have experienced the motivation to learn English throughout their lives. The methodology of horizontalization was used to break the interview protocols into individual units of meaning before analyzing these units to extract the overarching themes (Moustakas, 1994). These themes were then interpreted into a detailed description of LLM as experienced by EFL students in this context. Finally, the resulting description was analyzed to discover how these learners’ lived experiences with LLM conformed with and/or diverged from current theories of LLM.
Purpose Statement 5
The purpose of this qualitative, embedded, multiple case project was to examine how both parent-child attachment relationships are impacted by the quality of the paternal and maternal caregiver-child interactions that occur throughout a maternal deployment, within the context of dual-military couples. In order to examine this phenomenon, an embedded, multiple case study was conducted, utilizing an attachment systems metatheory perspective. The study included four dual-military couples who experienced a maternal deployment to Operation Iraqi Freedom (OIF) or Operation Enduring Freedom (OEF) when they had at least one child between 8 weeks-old to 5 years-old. Each member of the couple participated in an individual, semi-structured interview with the researcher and completed the Parenting Relationship Questionnaire (PRQ). “The PRQ is designed to capture a parent’s perspective on the parent-child relationship” (Pearson, 2012, para. 1) and was used within the proposed study for this purpose. The PRQ was utilized to triangulate the data (Bekhet & Zauszniewski, 2012) as well as to provide some additional information on the parents’ perspective of the quality of the parent-child attachment relationship in regards to communication, discipline, parenting confidence, relationship satisfaction, and time spent together (Pearson, 2012). The researcher utilized the semi-structured interview to collect information regarding the parents' perspectives of the quality of their parental caregiver behaviors during the deployment cycle, the mother's parent-child interactions while deployed, the behavior of the child or children at time of reunification, and the strategies or behaviors the parents believe may have contributed to their child's behavior at the time of reunification. The results of this project may be utilized by the military, and by civilian providers, to develop proactive and preventive measures that both providers and parents can implement, to address any potential adverse effects on the parent-child attachment relationship, identified through the proposed study. The results of this project may also be utilized to further refine and understand the integration of attachment theory and systems theory, in both clinical and research settings, within the field of marriage and family therapy.
Compiled by Dr. Darren Adamson, Department Chair, School of Social and Behavioral Sciences
- << Previous: Problem Statement
- Next: Alignment >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 2:48 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1013602

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information

9 Examples: How to Write a Purpose Statement
By Status.net Editorial Team on September 30, 2023 — 15 minutes to read
- Key Elements of a Purpose Statement Part 1
- How to Write a Purpose Statement Step-by-Step Part 2
- Identifying Your Goals Part 3
- Defining Your Audience Part 4
- Outlining Your Methods Part 5
- Stating the Expected Outcomes Part 6
- Purpose Statement Example for a Research Paper Part 7
- Purpose Statement Example For Personal Goals Part 8
- Purpose Statement Example For Business Objectives Part 9
- Purpose Statement Example For an Essay Part 10
- Purpose Statement Example For a Proposal Part 11
- Purpose Statement Example For a Report Part 12
- Purpose Statement Example For a Project Part 13
- Purpose Statement Templates Part 14
A purpose statement is a vital component of any project, as it sets the tone for the entire piece of work. It tells the reader what the project is about, why it’s important, and what the writer hopes to achieve.
Part 1 Key Elements of a Purpose Statement
When writing a purpose statement, there are several key elements that you should keep in mind. These elements will help you to create a clear, concise, and effective statement that accurately reflects your goals and objectives.
1. The Problem or Opportunity
The first element of a purpose statement is the problem or opportunity that you are addressing. This should be a clear and specific description of the issue that you are trying to solve or the opportunity that you are pursuing.
2. The Target Audience
The second element is the target audience for your purpose statement. This should be a clear and specific description of the group of people who will benefit from your work.
3. The Solution
The third element is the solution that you are proposing. This should be a clear and specific description of the action that you will take to address the problem or pursue the opportunity.
4. The Benefits
The fourth element is the benefits that your solution will provide. This should be a clear and specific description of the positive outcomes that your work will achieve.
5. The Action Plan
The fifth element is the action plan that you will follow to implement your solution. This should be a clear and specific description of the steps that you will take to achieve your goals.
Part 2 How to Write a Purpose Statement Step-by-Step
Writing a purpose statement is an essential part of any research project. It helps to clarify the purpose of your study and provides direction for your research. Here are some steps to follow when writing a purpose statement:
- Start with a clear research question: The first step in writing a purpose statement is to have a clear research question. This question should be specific and focused on the topic you want to research.
- Identify the scope of your study: Once you have a clear research question, you need to identify the scope of your study. This involves determining what you will and will not include in your research.
- Define your research objectives: Your research objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. They should also be aligned with your research question and the scope of your study.
- Determine your research design: Your research design will depend on the nature of your research question and the scope of your study. You may choose to use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods approach.
- Write your purpose statement: Your purpose statement should be a clear and concise statement that summarizes the purpose of your study. It should include your research question, the scope of your study, your research objectives, and your research design.
Research question: What are the effects of social media on teenage mental health?
Scope of study: This study will focus on teenagers aged 13-18 in the United States.
Research objectives: To determine the prevalence of social media use among teenagers, to identify the types of social media used by teenagers, to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health, and to provide recommendations for parents, educators, and mental health professionals.
Research design: This study will use a mixed-methods approach, including a survey and interviews with teenagers and mental health professionals.
Purpose statement: The purpose of this study is to examine the effects of social media on teenage mental health among teenagers aged 13-18 in the United States. The study will use a mixed-methods approach, including a survey and interviews with teenagers and mental health professionals. The research objectives are to determine the prevalence of social media use among teenagers, to identify the types of social media used by teenagers, to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health, and to provide recommendations for parents, educators, and mental health professionals.
Part 3 Section 1: Identifying Your Goals
Before you start writing your purpose statement, it’s important to identify your goals. To do this, ask yourself the following questions:
- What do I want to achieve?
- What problem do I want to solve?
- What impact do I want to make?
Once you have a clear idea of your goals, you can start crafting your purpose statement. Your purpose statement should be a clear and concise statement that outlines the purpose of your work.
For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a business, your statement might look something like this:
“Our purpose is to provide high-quality products and services that improve the lives of our customers and contribute to the growth and success of our company.”
If you’re writing a purpose statement for a non-profit organization, your statement might look something like this:
“Our purpose is to improve the lives of underserved communities by providing access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.”
Remember, your purpose statement should be specific, measurable, and achievable. It should also be aligned with your values and goals, and it should inspire and motivate you to take action.
Part 4 Section 2: Defining Your Audience
Once you have established the purpose of your statement, it’s important to consider who your audience is. The audience for your purpose statement will depend on the context in which it will be used. For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a research paper, your audience will likely be your professor or academic peers. If you’re writing a purpose statement for a business proposal, your audience may be potential investors or clients.
Defining your audience is important because it will help you tailor your purpose statement to the specific needs and interests of your readers. You want to make sure that your statement is clear, concise, and relevant to your audience.
To define your audience, consider the following questions:
- Who will be reading your purpose statement?
- What is their level of knowledge or expertise on the topic?
- What are their needs and interests?
- What do they hope to gain from reading your purpose statement?
Once you have a clear understanding of your audience, you can begin to craft your purpose statement with their needs and interests in mind. This will help ensure that your statement is effective in communicating your goals and objectives to your readers.
For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a research paper on the effects of climate change on agriculture, your audience may be fellow researchers in the field of environmental science. In this case, you would want to make sure that your purpose statement is written in a way that is clear and concise, using technical language that is familiar to your audience.
Or, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a business proposal to potential investors, your audience may be less familiar with the technical aspects of your project. In this case, you would want to make sure that your purpose statement is written in a way that is easy to understand, using clear and concise language that highlights the benefits of your proposal.
The key to defining your audience is to put yourself in their shoes and consider what they need and want from your purpose statement.
Part 5 Section 3: Outlining Your Methods
After you have identified the purpose of your statement, it is time to outline your methods. This section should describe how you plan to achieve your goal and the steps you will take to get there. Here are a few tips to help you outline your methods effectively:
- Start with a general overview: Begin by providing a brief overview of the methods you plan to use. This will give your readers a sense of what to expect in the following paragraphs.
- Break down your methods: Break your methods down into smaller, more manageable steps. This will make it easier for you to stay organized and for your readers to follow along.
- Use bullet points: Bullet points can help you organize your ideas and make your methods easier to read. Use them to list the steps you will take to achieve your goal.
- Be specific: Make sure you are specific about the methods you plan to use. This will help your readers understand exactly what you are doing and why.
- Provide examples: Use examples to illustrate your methods. This will make it easier for your readers to understand what you are trying to accomplish.
Part 6 Section 4: Stating the Expected Outcomes
After defining the problem and the purpose of your research, it’s time to state the expected outcomes. This is where you describe what you hope to achieve by conducting your research. The expected outcomes should be specific and measurable, so you can determine if you have achieved your goals.
It’s important to be realistic when stating your expected outcomes. Don’t make exaggerated or false claims, and don’t promise something that you can’t deliver. Your expected outcomes should be based on your research question and the purpose of your study.
Here are some examples of expected outcomes:
- To identify the factors that contribute to employee turnover in the company.
- To develop a new marketing strategy that will increase sales by 20% within the next year.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of a new training program for improving customer service.
- To determine the impact of social media on consumer behavior.
When stating your expected outcomes, make sure they align with your research question and purpose statement. This will help you stay focused on your goals and ensure that your research is relevant and meaningful.
In addition to stating your expected outcomes, you should also describe how you will measure them. This could involve collecting data through surveys, interviews, or experiments, or analyzing existing data from sources such as government reports or industry publications.
Part 7 Purpose Statement Example for a Research Paper
If you are writing a research paper, your purpose statement should clearly state the objective of your study. Here is an example of a purpose statement for a research paper:
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of social media on the mental health of teenagers in the United States.
This purpose statement clearly states the objective of the study and provides a specific focus for the research.
Part 8 Purpose Statement Example For Personal Goals
When writing a purpose statement for your personal goals, it’s important to clearly define what you want to achieve and why. Here’s a template that can help you get started:
“I want to [goal] so that [reason]. I will achieve this by [action].”
Example: “I want to lose 10 pounds so that I can feel more confident in my body. I will achieve this by going to the gym three times a week and cutting out sugary snacks.”
Remember to be specific and realistic when setting your goals and actions, and to regularly review and adjust your purpose statement as needed.
Part 9 Purpose Statement Example For Business Objectives
If you’re writing a purpose statement for a business objective, this template can help you get started:
[Objective] [Action verb] [Target audience] [Outcome or benefit]
Here’s an example using this template:
Increase online sales by creating a more user-friendly website for millennial shoppers.
This purpose statement is clear and concise. It identifies the objective (increase online sales), the action verb (creating), the target audience (millennial shoppers), and the outcome or benefit (a more user-friendly website).
Part 10 Purpose Statement Example For an Essay
“The purpose of this essay is to examine the causes and consequences of climate change, with a focus on the role of human activities, and to propose solutions that can mitigate its impact on the environment and future generations.”
This purpose statement clearly states the subject of the essay (climate change), what aspects will be explored (causes, consequences, human activities), and the intended outcome (proposing solutions). It provides a clear roadmap for the reader and sets the direction for the essay.
Part 11 Purpose Statement Example For a Proposal
“The purpose of this proposal is to secure funding and support for the establishment of a community garden in [Location], aimed at promoting sustainable urban agriculture, fostering community engagement, and improving local access to fresh, healthy produce.”
Why this purpose statement is effective:
- The subject of the proposal is clear: the establishment of a community garden.
- The specific goals of the project are outlined: promoting sustainable urban agriculture, fostering community engagement, and improving local access to fresh produce.
- The overall objective of the proposal is evident: securing funding and support.
Part 12 Purpose Statement Example For a Report
“The purpose of this report is to analyze current market trends in the electric vehicle (EV) industry, assess consumer preferences and buying behaviors, and provide strategic recommendations to guide [Company Name] in entering this growing market segment.”
- The subject of the report is provided: market trends in the electric vehicle industry.
- The specific goals of the report are analysis of market trends, assessment of consumer preferences, and strategic recommendations.
- The overall objective of the report is clear: providing guidance for the company’s entry into the EV market.
Part 13 Purpose Statement Example For a Project
“The purpose of this project is to design and implement a new employee wellness program that promotes physical and mental wellbeing in the workplace.”
This purpose statement clearly outlines the objective of the project, which is to create a new employee wellness program. The program is designed to promote physical and mental wellbeing in the workplace, which is a key concern for many employers. By implementing this program, the company aims to improve employee health, reduce absenteeism, and increase productivity. The purpose statement is concise and specific, providing a clear direction for the project team to follow. It highlights the importance of the project and its potential benefits for the company and its employees.
Part 14 Purpose Statement Templates
When writing a purpose statement, it can be helpful to use a template to ensure that you cover all the necessary components:
Template 1: To [action] [target audience] in order to [outcome]
This template is a straightforward way to outline your purpose statement. Simply fill in the blanks with the appropriate information:
- The purpose of […] is
- To [action]: What action do you want to take?
- [Target audience]: Who is your target audience?
- In order to [outcome]: What outcome do you hope to achieve?
For example:
- The purpose of our marketing campaign is to increase brand awareness among young adults in urban areas, in order to drive sales and revenue growth.
- The purpose of our employee training program is to improve customer service skills among our frontline staff, in order to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- The purpose of our new product launch is to expand our market share in the healthcare industry, by offering a unique solution to the needs of elderly patients with chronic conditions.
Template 2: This [project/product] is designed to [action] [target audience] by [method] in order to [outcome].
This template is useful for purpose statements that involve a specific project or product. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate information:
- This [project/product]: What is your project or product?
- Is designed to [action]: What action do you want to take?
- By [method]: What method will you use to achieve your goal?
- This app is designed to provide personalized nutrition advice to athletes by analyzing their training data in order to optimize performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key elements of a purpose statement.
A purpose statement should clearly communicate the main goal or objective of your writing. It should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your work. The key elements of a purpose statement include the topic or subject matter, the intended audience, and the overall goal or objective of your writing.
How can a purpose statement benefit your writing?
A purpose statement can help you stay focused and on track when writing. It can also help you to avoid going off-topic or getting bogged down in unnecessary details. By clearly identifying the main goal or objective of your writing, a purpose statement can help you to stay organized and ensure that your writing is effective and impactful.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when writing a purpose statement?
One common mistake is being too vague or general in your purpose statement. Another mistake is making your purpose statement too long or complex, which can make it difficult to understand. Additionally, it’s important to avoid including unnecessary information or details that are not directly relevant to your main goal or objective.
How can you tailor your purpose statement to your audience?
When writing a purpose statement, it’s important to consider your audience and their needs. You should tailor your purpose statement to your audience by using language and terminology that they will understand. You should also consider their level of knowledge or expertise on the subject matter and adjust your purpose statement accordingly.
What are some effective templates for writing a purpose statement?
There are many effective templates for writing a purpose statement, but one common approach is to use the following structure: “The purpose of this writing is to [insert goal or objective] for [insert audience] regarding [insert topic or subject matter].”
Can you provide examples of successful purpose statements?
- “The purpose of this report is to provide an analysis of the current market trends and make recommendations for future growth strategies for our company.”
- “The purpose of this essay is to explore the impact of social media on modern communication and its implications for society.”
- “The purpose of this proposal is to secure funding for a new community center that will provide educational and recreational opportunities for local residents.”
- 20 Inspiring Examples: How to Write a Personal Mission Statement
- 5 Examples: How to Write a Letter of Employment
- 6 Example Emails: How to Ask for a Letter of Recommendation
- 2 Templates and Examples: Individual Development Plan
- 5 Effective Examples: How to Write a Two-Week Notice
- 3 Examples: Job Application Email (with Tips)

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.1 The Purpose of Research Writing
Learning objectives.
- Identify reasons to research writing projects.
- Outline the steps of the research writing process.
Why was the Great Wall of China built? What have scientists learned about the possibility of life on Mars? What roles did women play in the American Revolution? How does the human brain create, store, and retrieve memories? Who invented the game of football, and how has it changed over the years?
You may know the answers to these questions off the top of your head. If you are like most people, however, you find answers to tough questions like these by searching the Internet, visiting the library, or asking others for information. To put it simply, you perform research.
Whether you are a scientist, an artist, a paralegal, or a parent, you probably perform research in your everyday life. When your boss, your instructor, or a family member asks you a question that you do not know the answer to, you locate relevant information, analyze your findings, and share your results. Locating, analyzing, and sharing information are key steps in the research process, and in this chapter, you will learn more about each step. By developing your research writing skills, you will prepare yourself to answer any question no matter how challenging.
Reasons for Research
When you perform research, you are essentially trying to solve a mystery—you want to know how something works or why something happened. In other words, you want to answer a question that you (and other people) have about the world. This is one of the most basic reasons for performing research.
But the research process does not end when you have solved your mystery. Imagine what would happen if a detective collected enough evidence to solve a criminal case, but she never shared her solution with the authorities. Presenting what you have learned from research can be just as important as performing the research. Research results can be presented in a variety of ways, but one of the most popular—and effective—presentation forms is the research paper . A research paper presents an original thesis, or purpose statement, about a topic and develops that thesis with information gathered from a variety of sources.
If you are curious about the possibility of life on Mars, for example, you might choose to research the topic. What will you do, though, when your research is complete? You will need a way to put your thoughts together in a logical, coherent manner. You may want to use the facts you have learned to create a narrative or to support an argument. And you may want to show the results of your research to your friends, your teachers, or even the editors of magazines and journals. Writing a research paper is an ideal way to organize thoughts, craft narratives or make arguments based on research, and share your newfound knowledge with the world.
Write a paragraph about a time when you used research in your everyday life. Did you look for the cheapest way to travel from Houston to Denver? Did you search for a way to remove gum from the bottom of your shoe? In your paragraph, explain what you wanted to research, how you performed the research, and what you learned as a result.
Research Writing and the Academic Paper
No matter what field of study you are interested in, you will most likely be asked to write a research paper during your academic career. For example, a student in an art history course might write a research paper about an artist’s work. Similarly, a student in a psychology course might write a research paper about current findings in childhood development.
Having to write a research paper may feel intimidating at first. After all, researching and writing a long paper requires a lot of time, effort, and organization. However, writing a research paper can also be a great opportunity to explore a topic that is particularly interesting to you. The research process allows you to gain expertise on a topic of your choice, and the writing process helps you remember what you have learned and understand it on a deeper level.
Research Writing at Work
Knowing how to write a good research paper is a valuable skill that will serve you well throughout your career. Whether you are developing a new product, studying the best way to perform a procedure, or learning about challenges and opportunities in your field of employment, you will use research techniques to guide your exploration. You may even need to create a written report of your findings. And because effective communication is essential to any company, employers seek to hire people who can write clearly and professionally.
Writing at Work
Take a few minutes to think about each of the following careers. How might each of these professionals use researching and research writing skills on the job?
- Medical laboratory technician
- Small business owner
- Information technology professional
- Freelance magazine writer
A medical laboratory technician or information technology professional might do research to learn about the latest technological developments in either of these fields. A small business owner might conduct research to learn about the latest trends in his or her industry. A freelance magazine writer may need to research a given topic to write an informed, up-to-date article.
Think about the job of your dreams. How might you use research writing skills to perform that job? Create a list of ways in which strong researching, organizing, writing, and critical thinking skills could help you succeed at your dream job. How might these skills help you obtain that job?
Steps of the Research Writing Process
How does a research paper grow from a folder of brainstormed notes to a polished final draft? No two projects are identical, but most projects follow a series of six basic steps.
These are the steps in the research writing process:
- Choose a topic.
- Plan and schedule time to research and write.
- Conduct research.
- Organize research and ideas.
- Draft your paper.
- Revise and edit your paper.
Each of these steps will be discussed in more detail later in this chapter. For now, though, we will take a brief look at what each step involves.
Step 1: Choosing a Topic
As you may recall from Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , to narrow the focus of your topic, you may try freewriting exercises, such as brainstorming. You may also need to ask a specific research question —a broad, open-ended question that will guide your research—as well as propose a possible answer, or a working thesis . You may use your research question and your working thesis to create a research proposal . In a research proposal, you present your main research question, any related subquestions you plan to explore, and your working thesis.
Step 2: Planning and Scheduling
Before you start researching your topic, take time to plan your researching and writing schedule. Research projects can take days, weeks, or even months to complete. Creating a schedule is a good way to ensure that you do not end up being overwhelmed by all the work you have to do as the deadline approaches.
During this step of the process, it is also a good idea to plan the resources and organizational tools you will use to keep yourself on track throughout the project. Flowcharts, calendars, and checklists can all help you stick to your schedule. See Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , Section 11.2 “Steps in Developing a Research Proposal” for an example of a research schedule.
Step 3: Conducting Research
When going about your research, you will likely use a variety of sources—anything from books and periodicals to video presentations and in-person interviews.
Your sources will include both primary sources and secondary sources . Primary sources provide firsthand information or raw data. For example, surveys, in-person interviews, and historical documents are primary sources. Secondary sources, such as biographies, literary reviews, or magazine articles, include some analysis or interpretation of the information presented. As you conduct research, you will take detailed, careful notes about your discoveries. You will also evaluate the reliability of each source you find.
Step 4: Organizing Research and the Writer’s Ideas
When your research is complete, you will organize your findings and decide which sources to cite in your paper. You will also have an opportunity to evaluate the evidence you have collected and determine whether it supports your thesis, or the focus of your paper. You may decide to adjust your thesis or conduct additional research to ensure that your thesis is well supported.
Remember, your working thesis is not set in stone. You can and should change your working thesis throughout the research writing process if the evidence you find does not support your original thesis. Never try to force evidence to fit your argument. For example, your working thesis is “Mars cannot support life-forms.” Yet, a week into researching your topic, you find an article in the New York Times detailing new findings of bacteria under the Martian surface. Instead of trying to argue that bacteria are not life forms, you might instead alter your thesis to “Mars cannot support complex life-forms.”
Step 5: Drafting Your Paper
Now you are ready to combine your research findings with your critical analysis of the results in a rough draft. You will incorporate source materials into your paper and discuss each source thoughtfully in relation to your thesis or purpose statement.
When you cite your reference sources, it is important to pay close attention to standard conventions for citing sources in order to avoid plagiarism , or the practice of using someone else’s words without acknowledging the source. Later in this chapter, you will learn how to incorporate sources in your paper and avoid some of the most common pitfalls of attributing information.
Step 6: Revising and Editing Your Paper
In the final step of the research writing process, you will revise and polish your paper. You might reorganize your paper’s structure or revise for unity and cohesion, ensuring that each element in your paper flows into the next logically and naturally. You will also make sure that your paper uses an appropriate and consistent tone.
Once you feel confident in the strength of your writing, you will edit your paper for proper spelling, grammar, punctuation, mechanics, and formatting. When you complete this final step, you will have transformed a simple idea or question into a thoroughly researched and well-written paper you can be proud of!
Review the steps of the research writing process. Then answer the questions on your own sheet of paper.
- In which steps of the research writing process are you allowed to change your thesis?
- In step 2, which types of information should you include in your project schedule?
- What might happen if you eliminated step 4 from the research writing process?
Key Takeaways
- People undertake research projects throughout their academic and professional careers in order to answer specific questions, share their findings with others, increase their understanding of challenging topics, and strengthen their researching, writing, and analytical skills.
- The research writing process generally comprises six steps: choosing a topic, scheduling and planning time for research and writing, conducting research, organizing research and ideas, drafting a paper, and revising and editing the paper.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Cookies & Privacy
- GETTING STARTED
- Introduction
- FUNDAMENTALS
- Acknowledgements
- Research questions & hypotheses
- Concepts, constructs & variables
- Research limitations
- Getting started
- Sampling Strategy
- Research Quality
- Research Ethics
- Data Analysis
The purpose statement
The purpose statement is made up of three major components: (1) the motivation driving your dissertation; (2) the significance of the research you plan to carry out; and (3) the research questions you are going to address. Starting the first major chapter of your dissertation (usually Chapter One: Introduction ), the purpose statement establishes the intent of your entire dissertation. Just like a great song that needs a great "hook", the purpose statement needs to draw the reader in and keep their attention. This article explains the purpose of each of these three components that make up the purpose statement.
The "motivation" driving your dissertation
The "significance" of the research you plan to carry out, the "research questions" you are going to address.
Your choice of dissertation topic should be driven by some kind of motivation . This motivation is usually a problem or issue that you feel needs to be addressed or solved. This part of the purpose statement aims to answer the question: Why should we care? In other words, why should we be interested in the research problem or issue that you want to address?
The types of motivation that may drive your dissertation will vary depending on the subject area you are studying, as well as the specific dissertation topic you are interested in. However, some of the broad types of motivation that undergraduate and master's level dissertation students try to address are based around (a) individuals , (b) organisations , and/or (c) society .
Individuals face many problems and issues ranging from those associated with welfare , to health , prosperity , freedoms , security , and so on. From a health perspective, you may be concerned with the rise in childhood obesity and the potential need for regulation to combat the advertising of fast food to children. In terms of welfare and freedoms , you may be interested in the introduction of new legislation that aims to protect discrimination in the workplace, and its implications for small businesses.
Organisations also have a wide range of problems and issues that need to be addressed, whether relating to people , finances , operations , competition , regulations , and so forth. From a people perspective, you may be interested in how organisations use flexible working options to alleviate employee stress and burnout. In terms of regulations , you may be concerned with the growth in Internet piracy and the ways that organisations are dealing with such a threat.
Society is another lens through which you can view problems and issues that need to be addressed. These may relate to a wide range of societal risks or other problems and issues such as factory farming, the potential legalisation of marijuana, the health-related effects of talking on cell phones, and so forth. You may be interested in understanding individuals? views towards the potential legalisation of marijuana; or how these views are influenced by individuals? knowledge of the side-effects of marijuana use.
When communicating the motivation driving your dissertation to the reader, it is important to explain why the problem or issue you are addressing is interesting : that is, why should the reader care? It is not sufficient to simply state what the problem or issue is.
Whilst the motivation component of your purpose statement explains why the reader should care about your dissertation, the significance component justifies the value of the dissertation. In other words: What contribution will the dissertation make to the literature? Why should anyone bother to perform this research? What is its value?
Even though dissertations are rarely "ground-breaking" at the undergraduate or master's level (and are not expected to be), they should still be significant in some way. This component of the Introduction chapter, which follows the motivation section, should explain what this significance is. In this respect, your research may be significant in one of a number of ways. It may:
Capitalise on a recent event
Reflect a break from the past
Target a new audience
Address a flaw in a previous study
Expand a particular field of study
Help an individual, group, organisation, or community
When writing your purpose statement, you will need to explain the relationship between the motivation driving your dissertation and the significance of the research you plan to carry out. These two factors - motivation and significance - must be intrinsically linked; that is, you cannot have one without the other. The key point is that you must be able to explain the relationship between the motivation driving your dissertation and one (or more) of the types of significance highlighted in the bullets above.
The motivation and significance components of your Introduction chapter should signal to the reader the general intent of your dissertation. However, the research questions that you set out indicate the specific intent of your dissertation. In other words, your research questions tell the reader exactly what you intend to try and address (or answer) throughout the dissertation process.
In addition, since there are different types of research question (i.e., quantitative , qualitative and mixed methods research questions), it should be obvious from the significance component of your purpose statement which of these types of research question you intend to tackle [see the section, Research Questions , to learn more].
Having established the research questions you are going to address, this completes the purpose statement. At this point, the reader should be clear about the overall intent of your dissertation. If you are in the process of writing up your dissertation, we would recommend including a Chapter Summaries section after the Research Questions section of your Introduction chapter. This helps to let the reader know what to expect next from your dissertation.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 6. The Methodology
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study’s overall validity and reliability. The methodology section of a research paper answers two main questions: How was the data collected or generated? And, how was it analyzed? The writing should be direct and precise and always written in the past tense.
Kallet, Richard H. "How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004): 1229-1232.
Importance of a Good Methodology Section
You must explain how you obtained and analyzed your results for the following reasons:
- Readers need to know how the data was obtained because the method you chose affects the results and, by extension, how you interpreted their significance in the discussion section of your paper.
- Methodology is crucial for any branch of scholarship because an unreliable method produces unreliable results and, as a consequence, undermines the value of your analysis of the findings.
- In most cases, there are a variety of different methods you can choose to investigate a research problem. The methodology section of your paper should clearly articulate the reasons why you have chosen a particular procedure or technique.
- The reader wants to know that the data was collected or generated in a way that is consistent with accepted practice in the field of study. For example, if you are using a multiple choice questionnaire, readers need to know that it offered your respondents a reasonable range of answers to choose from.
- The method must be appropriate to fulfilling the overall aims of the study. For example, you need to ensure that you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings.
- The methodology should discuss the problems that were anticipated and the steps you took to prevent them from occurring. For any problems that do arise, you must describe the ways in which they were minimized or why these problems do not impact in any meaningful way your interpretation of the findings.
- In the social and behavioral sciences, it is important to always provide sufficient information to allow other researchers to adopt or replicate your methodology. This information is particularly important when a new method has been developed or an innovative use of an existing method is utilized.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects . 5th edition. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Groups of Research Methods
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences:
- The e mpirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences . This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured. The empirical-analytical group employs deductive reasoning that uses existing theory as a foundation for formulating hypotheses that need to be tested. This approach is focused on explanation.
- The i nterpretative group of methods is focused on understanding phenomenon in a comprehensive, holistic way . Interpretive methods focus on analytically disclosing the meaning-making practices of human subjects [the why, how, or by what means people do what they do], while showing how those practices arrange so that it can be used to generate observable outcomes. Interpretive methods allow you to recognize your connection to the phenomena under investigation. However, the interpretative group requires careful examination of variables because it focuses more on subjective knowledge.
II. Content
The introduction to your methodology section should begin by restating the research problem and underlying assumptions underpinning your study. This is followed by situating the methods you used to gather, analyze, and process information within the overall “tradition” of your field of study and within the particular research design you have chosen to study the problem. If the method you choose lies outside of the tradition of your field [i.e., your review of the literature demonstrates that the method is not commonly used], provide a justification for how your choice of methods specifically addresses the research problem in ways that have not been utilized in prior studies.
The remainder of your methodology section should describe the following:
- Decisions made in selecting the data you have analyzed or, in the case of qualitative research, the subjects and research setting you have examined,
- Tools and methods used to identify and collect information, and how you identified relevant variables,
- The ways in which you processed the data and the procedures you used to analyze that data, and
- The specific research tools or strategies that you utilized to study the underlying hypothesis and research questions.
In addition, an effectively written methodology section should:
- Introduce the overall methodological approach for investigating your research problem . Is your study qualitative or quantitative or a combination of both (mixed method)? Are you going to take a special approach, such as action research, or a more neutral stance?
- Indicate how the approach fits the overall research design . Your methods for gathering data should have a clear connection to your research problem. In other words, make sure that your methods will actually address the problem. One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper.
- Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use , such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data, such as a data set or archival documents, describe how it was originally created or gathered and by whom. Also be sure to explain how older data is still relevant to investigating the current research problem.
- Explain how you intend to analyze your results . Will you use statistical analysis? Will you use specific theoretical perspectives to help you analyze a text or explain observed behaviors? Describe how you plan to obtain an accurate assessment of relationships, patterns, trends, distributions, and possible contradictions found in the data.
- Provide background and a rationale for methodologies that are unfamiliar for your readers . Very often in the social sciences, research problems and the methods for investigating them require more explanation/rationale than widely accepted rules governing the natural and physical sciences. Be clear and concise in your explanation.
- Provide a justification for subject selection and sampling procedure . For instance, if you propose to conduct interviews, how do you intend to select the sample population? If you are analyzing texts, which texts have you chosen, and why? If you are using statistics, why is this set of data being used? If other data sources exist, explain why the data you chose is most appropriate to addressing the research problem.
- Provide a justification for case study selection . A common method of analyzing research problems in the social sciences is to analyze specific cases. These can be a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis that are either examined as a singular topic of in-depth investigation or multiple topics of investigation studied for the purpose of comparing or contrasting findings. In either method, you should explain why a case or cases were chosen and how they specifically relate to the research problem.
- Describe potential limitations . Are there any practical limitations that could affect your data collection? How will you attempt to control for potential confounding variables and errors? If your methodology may lead to problems you can anticipate, state this openly and show why pursuing this methodology outweighs the risk of these problems cropping up.
NOTE: Once you have written all of the elements of the methods section, subsequent revisions should focus on how to present those elements as clearly and as logically as possibly. The description of how you prepared to study the research problem, how you gathered the data, and the protocol for analyzing the data should be organized chronologically. For clarity, when a large amount of detail must be presented, information should be presented in sub-sections according to topic. If necessary, consider using appendices for raw data.
ANOTHER NOTE: If you are conducting a qualitative analysis of a research problem , the methodology section generally requires a more elaborate description of the methods used as well as an explanation of the processes applied to gathering and analyzing of data than is generally required for studies using quantitative methods. Because you are the primary instrument for generating the data [e.g., through interviews or observations], the process for collecting that data has a significantly greater impact on producing the findings. Therefore, qualitative research requires a more detailed description of the methods used.
YET ANOTHER NOTE: If your study involves interviews, observations, or other qualitative techniques involving human subjects , you may be required to obtain approval from the university's Office for the Protection of Research Subjects before beginning your research. This is not a common procedure for most undergraduate level student research assignments. However, i f your professor states you need approval, you must include a statement in your methods section that you received official endorsement and adequate informed consent from the office and that there was a clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university. This statement informs the reader that your study was conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. In some cases, the approval notice is included as an appendix to your paper.
III. Problems to Avoid
Irrelevant Detail The methodology section of your paper should be thorough but concise. Do not provide any background information that does not directly help the reader understand why a particular method was chosen, how the data was gathered or obtained, and how the data was analyzed in relation to the research problem [note: analyzed, not interpreted! Save how you interpreted the findings for the discussion section]. With this in mind, the page length of your methods section will generally be less than any other section of your paper except the conclusion.
Unnecessary Explanation of Basic Procedures Remember that you are not writing a how-to guide about a particular method. You should make the assumption that readers possess a basic understanding of how to investigate the research problem on their own and, therefore, you do not have to go into great detail about specific methodological procedures. The focus should be on how you applied a method , not on the mechanics of doing a method. An exception to this rule is if you select an unconventional methodological approach; if this is the case, be sure to explain why this approach was chosen and how it enhances the overall process of discovery.
Problem Blindness It is almost a given that you will encounter problems when collecting or generating your data, or, gaps will exist in existing data or archival materials. Do not ignore these problems or pretend they did not occur. Often, documenting how you overcame obstacles can form an interesting part of the methodology. It demonstrates to the reader that you can provide a cogent rationale for the decisions you made to minimize the impact of any problems that arose.
Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method [i.e., the choice of a survey should include any citations to the works you used to help construct the survey].
It’s More than Sources of Information! A description of a research study's method should not be confused with a description of the sources of information. Such a list of sources is useful in and of itself, especially if it is accompanied by an explanation about the selection and use of the sources. The description of the project's methodology complements a list of sources in that it sets forth the organization and interpretation of information emanating from those sources.
Azevedo, L.F. et al. "How to Write a Scientific Paper: Writing the Methods Section." Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia 17 (2011): 232-238; Blair Lorrie. “Choosing a Methodology.” In Writing a Graduate Thesis or Dissertation , Teaching Writing Series. (Rotterdam: Sense Publishers 2016), pp. 49-72; Butin, Dan W. The Education Dissertation A Guide for Practitioner Scholars . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin, 2010; Carter, Susan. Structuring Your Research Thesis . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012; Kallet, Richard H. “How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper.” Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004):1229-1232; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008. Methods Section. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Rudestam, Kjell Erik and Rae R. Newton. “The Method Chapter: Describing Your Research Plan.” In Surviving Your Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Content and Process . (Thousand Oaks, Sage Publications, 2015), pp. 87-115; What is Interpretive Research. Institute of Public and International Affairs, University of Utah; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Methods and Materials. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Writing Tip
Statistical Designs and Tests? Do Not Fear Them!
Don't avoid using a quantitative approach to analyzing your research problem just because you fear the idea of applying statistical designs and tests. A qualitative approach, such as conducting interviews or content analysis of archival texts, can yield exciting new insights about a research problem, but it should not be undertaken simply because you have a disdain for running a simple regression. A well designed quantitative research study can often be accomplished in very clear and direct ways, whereas, a similar study of a qualitative nature usually requires considerable time to analyze large volumes of data and a tremendous burden to create new paths for analysis where previously no path associated with your research problem had existed.
To locate data and statistics, GO HERE .
Another Writing Tip
Knowing the Relationship Between Theories and Methods
There can be multiple meaning associated with the term "theories" and the term "methods" in social sciences research. A helpful way to delineate between them is to understand "theories" as representing different ways of characterizing the social world when you research it and "methods" as representing different ways of generating and analyzing data about that social world. Framed in this way, all empirical social sciences research involves theories and methods, whether they are stated explicitly or not. However, while theories and methods are often related, it is important that, as a researcher, you deliberately separate them in order to avoid your theories playing a disproportionate role in shaping what outcomes your chosen methods produce.
Introspectively engage in an ongoing dialectic between the application of theories and methods to help enable you to use the outcomes from your methods to interrogate and develop new theories, or ways of framing conceptually the research problem. This is how scholarship grows and branches out into new intellectual territory.
Reynolds, R. Larry. Ways of Knowing. Alternative Microeconomics . Part 1, Chapter 3. Boise State University; The Theory-Method Relationship. S-Cool Revision. United Kingdom.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Methods and the Methodology
Do not confuse the terms "methods" and "methodology." As Schneider notes, a method refers to the technical steps taken to do research . Descriptions of methods usually include defining and stating why you have chosen specific techniques to investigate a research problem, followed by an outline of the procedures you used to systematically select, gather, and process the data [remember to always save the interpretation of data for the discussion section of your paper].
The methodology refers to a discussion of the underlying reasoning why particular methods were used . This discussion includes describing the theoretical concepts that inform the choice of methods to be applied, placing the choice of methods within the more general nature of academic work, and reviewing its relevance to examining the research problem. The methodology section also includes a thorough review of the methods other scholars have used to study the topic.
Bryman, Alan. "Of Methods and Methodology." Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal 3 (2008): 159-168; Schneider, Florian. “What's in a Methodology: The Difference between Method, Methodology, and Theory…and How to Get the Balance Right?” PoliticsEastAsia.com. Chinese Department, University of Leiden, Netherlands.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Next: Qualitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2024 8:54 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
- How to write an APA methods section
How to Write an APA Methods Section | With Examples
Published on February 5, 2021 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
The methods section of an APA style paper is where you report in detail how you performed your study. Research papers in the social and natural sciences often follow APA style. This article focuses on reporting quantitative research methods .
In your APA methods section, you should report enough information to understand and replicate your study, including detailed information on the sample , measures, and procedures used.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Structuring an apa methods section.
Participants
Example of an APA methods section
Other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing an apa methods section.
The main heading of “Methods” should be centered, boldfaced, and capitalized. Subheadings within this section are left-aligned, boldfaced, and in title case. You can also add lower level headings within these subsections, as long as they follow APA heading styles .
To structure your methods section, you can use the subheadings of “Participants,” “Materials,” and “Procedures.” These headings are not mandatory—aim to organize your methods section using subheadings that make sense for your specific study.
| Heading | What to include |
|---|---|
| Participants | |
| Materials | |
| Procedure |
Note that not all of these topics will necessarily be relevant for your study. For example, if you didn’t need to consider outlier removal or ways of assigning participants to different conditions, you don’t have to report these steps.
The APA also provides specific reporting guidelines for different types of research design. These tell you exactly what you need to report for longitudinal designs , replication studies, experimental designs , and so on. If your study uses a combination design, consult APA guidelines for mixed methods studies.
Detailed descriptions of procedures that don’t fit into your main text can be placed in supplemental materials (for example, the exact instructions and tasks given to participants, the full analytical strategy including software code, or additional figures and tables).
Are your APA in-text citations flawless?
The AI-powered APA Citation Checker points out every error, tells you exactly what’s wrong, and explains how to fix it. Say goodbye to losing marks on your assignment!
Get started!

Begin the methods section by reporting sample characteristics, sampling procedures, and the sample size.
Participant or subject characteristics
When discussing people who participate in research, descriptive terms like “participants,” “subjects” and “respondents” can be used. For non-human animal research, “subjects” is more appropriate.
Specify all relevant demographic characteristics of your participants. This may include their age, sex, ethnic or racial group, gender identity, education level, and socioeconomic status. Depending on your study topic, other characteristics like educational or immigration status or language preference may also be relevant.
Be sure to report these characteristics as precisely as possible. This helps the reader understand how far your results may be generalized to other people.
The APA guidelines emphasize writing about participants using bias-free language , so it’s necessary to use inclusive and appropriate terms.
Sampling procedures
Outline how the participants were selected and all inclusion and exclusion criteria applied. Appropriately identify the sampling procedure used. For example, you should only label a sample as random if you had access to every member of the relevant population.
Of all the people invited to participate in your study, note the percentage that actually did (if you have this data). Additionally, report whether participants were self-selected, either by themselves or by their institutions (e.g., schools may submit student data for research purposes).
Identify any compensation (e.g., course credits or money) that was provided to participants, and mention any institutional review board approvals and ethical standards followed.
Sample size and power
Detail the sample size (per condition) and statistical power that you hoped to achieve, as well as any analyses you performed to determine these numbers.
It’s important to show that your study had enough statistical power to find effects if there were any to be found.
Additionally, state whether your final sample differed from the intended sample. Your interpretations of the study outcomes should be based only on your final sample rather than your intended sample.
Write up the tools and techniques that you used to measure relevant variables. Be as thorough as possible for a complete picture of your techniques.
Primary and secondary measures
Define the primary and secondary outcome measures that will help you answer your primary and secondary research questions.
Specify all instruments used in gathering these measurements and the construct that they measure. These instruments may include hardware, software, or tests, scales, and inventories.
- To cite hardware, indicate the model number and manufacturer.
- To cite common software (e.g., Qualtrics), state the full name along with the version number or the website URL .
- To cite tests, scales or inventories, reference its manual or the article it was published in. It’s also helpful to state the number of items and provide one or two example items.
Make sure to report the settings of (e.g., screen resolution) any specialized apparatus used.
For each instrument used, report measures of the following:
- Reliability : how consistently the method measures something, in terms of internal consistency or test-retest reliability.
- Validity : how precisely the method measures something, in terms of construct validity or criterion validity .
Giving an example item or two for tests, questionnaires , and interviews is also helpful.
Describe any covariates—these are any additional variables that may explain or predict the outcomes.
Quality of measurements
Review all methods you used to assure the quality of your measurements.
These may include:
- training researchers to collect data reliably,
- using multiple people to assess (e.g., observe or code) the data,
- translation and back-translation of research materials,
- using pilot studies to test your materials on unrelated samples.
For data that’s subjectively coded (for example, classifying open-ended responses), report interrater reliability scores. This tells the reader how similarly each response was rated by multiple raters.
Report all of the procedures applied for administering the study, processing the data, and for planned data analyses.
Data collection methods and research design
Data collection methods refers to the general mode of the instruments: surveys, interviews, observations, focus groups, neuroimaging, cognitive tests, and so on. Summarize exactly how you collected the necessary data.
Describe all procedures you applied in administering surveys, tests, physical recordings, or imaging devices, with enough detail so that someone else can replicate your techniques. If your procedures are very complicated and require long descriptions (e.g., in neuroimaging studies), place these details in supplementary materials.
To report research design, note your overall framework for data collection and analysis. State whether you used an experimental, quasi-experimental, descriptive (observational), correlational, and/or longitudinal design. Also note whether a between-subjects or a within-subjects design was used.
For multi-group studies, report the following design and procedural details as well:
- how participants were assigned to different conditions (e.g., randomization),
- instructions given to the participants in each group,
- interventions for each group,
- the setting and length of each session(s).
Describe whether any masking was used to hide the condition assignment (e.g., placebo or medication condition) from participants or research administrators. Using masking in a multi-group study ensures internal validity by reducing research bias . Explain how this masking was applied and whether its effectiveness was assessed.
Participants were randomly assigned to a control or experimental condition. The survey was administered using Qualtrics (https://www.qualtrics.com). To begin, all participants were given the AAI and a demographics questionnaire to complete, followed by an unrelated filler task. In the control condition , participants completed a short general knowledge test immediately after the filler task. In the experimental condition, participants were asked to visualize themselves taking the test for 3 minutes before they actually did. For more details on the exact instructions and tasks given, see supplementary materials.
Data diagnostics
Outline all steps taken to scrutinize or process the data after collection.
This includes the following:
- Procedures for identifying and removing outliers
- Data transformations to normalize distributions
- Compensation strategies for overcoming missing values
To ensure high validity, you should provide enough detail for your reader to understand how and why you processed or transformed your raw data in these specific ways.
Analytic strategies
The methods section is also where you describe your statistical analysis procedures, but not their outcomes. Their outcomes are reported in the results section.
These procedures should be stated for all primary, secondary, and exploratory hypotheses. While primary and secondary hypotheses are based on a theoretical framework or past studies, exploratory hypotheses are guided by the data you’ve just collected.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries
This annotated example reports methods for a descriptive correlational survey on the relationship between religiosity and trust in science in the US. Hover over each part for explanation of what is included.
The sample included 879 adults aged between 18 and 28. More than half of the participants were women (56%), and all participants had completed at least 12 years of education. Ethics approval was obtained from the university board before recruitment began. Participants were recruited online through Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk; www.mturk.com). We selected for a geographically diverse sample within the Midwest of the US through an initial screening survey. Participants were paid USD $5 upon completion of the study.
A sample size of at least 783 was deemed necessary for detecting a correlation coefficient of ±.1, with a power level of 80% and a significance level of .05, using a sample size calculator (www.sample-size.net/correlation-sample-size/).
The primary outcome measures were the levels of religiosity and trust in science. Religiosity refers to involvement and belief in religious traditions, while trust in science represents confidence in scientists and scientific research outcomes. The secondary outcome measures were gender and parental education levels of participants and whether these characteristics predicted religiosity levels.
Religiosity
Religiosity was measured using the Centrality of Religiosity scale (Huber, 2003). The Likert scale is made up of 15 questions with five subscales of ideology, experience, intellect, public practice, and private practice. An example item is “How often do you experience situations in which you have the feeling that God or something divine intervenes in your life?” Participants were asked to indicate frequency of occurrence by selecting a response ranging from 1 (very often) to 5 (never). The internal consistency of the instrument is .83 (Huber & Huber, 2012).
Trust in Science
Trust in science was assessed using the General Trust in Science index (McCright, Dentzman, Charters & Dietz, 2013). Four Likert scale items were assessed on a scale from 1 (completely distrust) to 5 (completely trust). An example question asks “How much do you distrust or trust scientists to create knowledge that is unbiased and accurate?” Internal consistency was .8.
Potential participants were invited to participate in the survey online using Qualtrics (www.qualtrics.com). The survey consisted of multiple choice questions regarding demographic characteristics, the Centrality of Religiosity scale, an unrelated filler anagram task, and finally the General Trust in Science index. The filler task was included to avoid priming or demand characteristics, and an attention check was embedded within the religiosity scale. For full instructions and details of tasks, see supplementary materials.
For this correlational study , we assessed our primary hypothesis of a relationship between religiosity and trust in science using Pearson moment correlation coefficient. The statistical significance of the correlation coefficient was assessed using a t test. To test our secondary hypothesis of parental education levels and gender as predictors of religiosity, multiple linear regression analysis was used.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Thematic analysis
- Cohort study
- Peer review
- Ethnography
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Conformity bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Availability heuristic
- Attrition bias
- Social desirability bias
In your APA methods section , you should report detailed information on the participants, materials, and procedures used.
- Describe all relevant participant or subject characteristics, the sampling procedures used and the sample size and power .
- Define all primary and secondary measures and discuss the quality of measurements.
- Specify the data collection methods, the research design and data analysis strategy, including any steps taken to transform the data and statistical analyses.
You should report methods using the past tense , even if you haven’t completed your study at the time of writing. That’s because the methods section is intended to describe completed actions or research.
In a scientific paper, the methodology always comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion . The same basic structure also applies to a thesis, dissertation , or research proposal .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). How to Write an APA Methods Section | With Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/methods-section/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, how to write an apa results section, apa format for academic papers and essays, apa headings and subheadings, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Yale J Biol Med
- v.84(3); 2011 Sep

Focus: Education — Career Advice
How to write your first research paper.
Writing a research manuscript is an intimidating process for many novice writers in the sciences. One of the stumbling blocks is the beginning of the process and creating the first draft. This paper presents guidelines on how to initiate the writing process and draft each section of a research manuscript. The paper discusses seven rules that allow the writer to prepare a well-structured and comprehensive manuscript for a publication submission. In addition, the author lists different strategies for successful revision. Each of those strategies represents a step in the revision process and should help the writer improve the quality of the manuscript. The paper could be considered a brief manual for publication.
It is late at night. You have been struggling with your project for a year. You generated an enormous amount of interesting data. Your pipette feels like an extension of your hand, and running western blots has become part of your daily routine, similar to brushing your teeth. Your colleagues think you are ready to write a paper, and your lab mates tease you about your “slow” writing progress. Yet days pass, and you cannot force yourself to sit down to write. You have not written anything for a while (lab reports do not count), and you feel you have lost your stamina. How does the writing process work? How can you fit your writing into a daily schedule packed with experiments? What section should you start with? What distinguishes a good research paper from a bad one? How should you revise your paper? These and many other questions buzz in your head and keep you stressed. As a result, you procrastinate. In this paper, I will discuss the issues related to the writing process of a scientific paper. Specifically, I will focus on the best approaches to start a scientific paper, tips for writing each section, and the best revision strategies.
1. Schedule your writing time in Outlook
Whether you have written 100 papers or you are struggling with your first, starting the process is the most difficult part unless you have a rigid writing schedule. Writing is hard. It is a very difficult process of intense concentration and brain work. As stated in Hayes’ framework for the study of writing: “It is a generative activity requiring motivation, and it is an intellectual activity requiring cognitive processes and memory” [ 1 ]. In his book How to Write a Lot: A Practical Guide to Productive Academic Writing , Paul Silvia says that for some, “it’s easier to embalm the dead than to write an article about it” [ 2 ]. Just as with any type of hard work, you will not succeed unless you practice regularly. If you have not done physical exercises for a year, only regular workouts can get you into good shape again. The same kind of regular exercises, or I call them “writing sessions,” are required to be a productive author. Choose from 1- to 2-hour blocks in your daily work schedule and consider them as non-cancellable appointments. When figuring out which blocks of time will be set for writing, you should select the time that works best for this type of work. For many people, mornings are more productive. One Yale University graduate student spent a semester writing from 8 a.m. to 9 a.m. when her lab was empty. At the end of the semester, she was amazed at how much she accomplished without even interrupting her regular lab hours. In addition, doing the hardest task first thing in the morning contributes to the sense of accomplishment during the rest of the day. This positive feeling spills over into our work and life and has a very positive effect on our overall attitude.
Rule 1: Create regular time blocks for writing as appointments in your calendar and keep these appointments.
2. start with an outline.
Now that you have scheduled time, you need to decide how to start writing. The best strategy is to start with an outline. This will not be an outline that you are used to, with Roman numerals for each section and neat parallel listing of topic sentences and supporting points. This outline will be similar to a template for your paper. Initially, the outline will form a structure for your paper; it will help generate ideas and formulate hypotheses. Following the advice of George M. Whitesides, “. . . start with a blank piece of paper, and write down, in any order, all important ideas that occur to you concerning the paper” [ 3 ]. Use Table 1 as a starting point for your outline. Include your visuals (figures, tables, formulas, equations, and algorithms), and list your findings. These will constitute the first level of your outline, which will eventually expand as you elaborate.
| 1. What is the topic of my paper? |
| 2. Why is this topic important? |
| 3. How could I formulate my hypothesis? |
| 4. What are my results (include visuals)? |
| 5. What is my major finding? |
The next stage is to add context and structure. Here you will group all your ideas into sections: Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion/Conclusion ( Table 2 ). This step will help add coherence to your work and sift your ideas.
| 1. Why is your research important? |
| 2. What is known about the topic? |
| 3. What are your hypotheses? |
| 4. What are your objectives? |
| 1. What materials did you use? |
| 2. Who were the subjects of your study? |
| 3. What was the design of your research? |
| 4. What procedure did you follow? |
| 1. What are your most significant results? |
| 2. What are your supporting results? |
| 1. What are the studies major findings? |
| 2. What is the significance/implication of the results? |
Now that you have expanded your outline, you are ready for the next step: discussing the ideas for your paper with your colleagues and mentor. Many universities have a writing center where graduate students can schedule individual consultations and receive assistance with their paper drafts. Getting feedback during early stages of your draft can save a lot of time. Talking through ideas allows people to conceptualize and organize thoughts to find their direction without wasting time on unnecessary writing. Outlining is the most effective way of communicating your ideas and exchanging thoughts. Moreover, it is also the best stage to decide to which publication you will submit the paper. Many people come up with three choices and discuss them with their mentors and colleagues. Having a list of journal priorities can help you quickly resubmit your paper if your paper is rejected.
Rule 2: Create a detailed outline and discuss it with your mentor and peers.
3. continue with drafts.
After you get enough feedback and decide on the journal you will submit to, the process of real writing begins. Copy your outline into a separate file and expand on each of the points, adding data and elaborating on the details. When you create the first draft, do not succumb to the temptation of editing. Do not slow down to choose a better word or better phrase; do not halt to improve your sentence structure. Pour your ideas into the paper and leave revision and editing for later. As Paul Silvia explains, “Revising while you generate text is like drinking decaffeinated coffee in the early morning: noble idea, wrong time” [ 2 ].
Many students complain that they are not productive writers because they experience writer’s block. Staring at an empty screen is frustrating, but your screen is not really empty: You have a template of your article, and all you need to do is fill in the blanks. Indeed, writer’s block is a logical fallacy for a scientist ― it is just an excuse to procrastinate. When scientists start writing a research paper, they already have their files with data, lab notes with materials and experimental designs, some visuals, and tables with results. All they need to do is scrutinize these pieces and put them together into a comprehensive paper.
3.1. Starting with Materials and Methods
If you still struggle with starting a paper, then write the Materials and Methods section first. Since you have all your notes, it should not be problematic for you to describe the experimental design and procedures. Your most important goal in this section is to be as explicit as possible by providing enough detail and references. In the end, the purpose of this section is to allow other researchers to evaluate and repeat your work. So do not run into the same problems as the writers of the sentences in (1):
1a. Bacteria were pelleted by centrifugation. 1b. To isolate T cells, lymph nodes were collected.
As you can see, crucial pieces of information are missing: the speed of centrifuging your bacteria, the time, and the temperature in (1a); the source of lymph nodes for collection in (b). The sentences can be improved when information is added, as in (2a) and (2b), respectfully:
2a. Bacteria were pelleted by centrifugation at 3000g for 15 min at 25°C. 2b. To isolate T cells, mediastinal and mesenteric lymph nodes from Balb/c mice were collected at day 7 after immunization with ovabumin.
If your method has previously been published and is well-known, then you should provide only the literature reference, as in (3a). If your method is unpublished, then you need to make sure you provide all essential details, as in (3b).
3a. Stem cells were isolated, according to Johnson [23]. 3b. Stem cells were isolated using biotinylated carbon nanotubes coated with anti-CD34 antibodies.
Furthermore, cohesion and fluency are crucial in this section. One of the malpractices resulting in disrupted fluency is switching from passive voice to active and vice versa within the same paragraph, as shown in (4). This switching misleads and distracts the reader.
4. Behavioral computer-based experiments of Study 1 were programmed by using E-Prime. We took ratings of enjoyment, mood, and arousal as the patients listened to preferred pleasant music and unpreferred music by using Visual Analogue Scales (SI Methods). The preferred and unpreferred status of the music was operationalized along a continuum of pleasantness [ 4 ].
The problem with (4) is that the reader has to switch from the point of view of the experiment (passive voice) to the point of view of the experimenter (active voice). This switch causes confusion about the performer of the actions in the first and the third sentences. To improve the coherence and fluency of the paragraph above, you should be consistent in choosing the point of view: first person “we” or passive voice [ 5 ]. Let’s consider two revised examples in (5).
5a. We programmed behavioral computer-based experiments of Study 1 by using E-Prime. We took ratings of enjoyment, mood, and arousal by using Visual Analogue Scales (SI Methods) as the patients listened to preferred pleasant music and unpreferred music. We operationalized the preferred and unpreferred status of the music along a continuum of pleasantness. 5b. Behavioral computer-based experiments of Study 1 were programmed by using E-Prime. Ratings of enjoyment, mood, and arousal were taken as the patients listened to preferred pleasant music and unpreferred music by using Visual Analogue Scales (SI Methods). The preferred and unpreferred status of the music was operationalized along a continuum of pleasantness.
If you choose the point of view of the experimenter, then you may end up with repetitive “we did this” sentences. For many readers, paragraphs with sentences all beginning with “we” may also sound disruptive. So if you choose active sentences, you need to keep the number of “we” subjects to a minimum and vary the beginnings of the sentences [ 6 ].
Interestingly, recent studies have reported that the Materials and Methods section is the only section in research papers in which passive voice predominantly overrides the use of the active voice [ 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. For example, Martínez shows a significant drop in active voice use in the Methods sections based on the corpus of 1 million words of experimental full text research articles in the biological sciences [ 7 ]. According to the author, the active voice patterned with “we” is used only as a tool to reveal personal responsibility for the procedural decisions in designing and performing experimental work. This means that while all other sections of the research paper use active voice, passive voice is still the most predominant in Materials and Methods sections.
Writing Materials and Methods sections is a meticulous and time consuming task requiring extreme accuracy and clarity. This is why when you complete your draft, you should ask for as much feedback from your colleagues as possible. Numerous readers of this section will help you identify the missing links and improve the technical style of this section.
Rule 3: Be meticulous and accurate in describing the Materials and Methods. Do not change the point of view within one paragraph.
3.2. writing results section.
For many authors, writing the Results section is more intimidating than writing the Materials and Methods section . If people are interested in your paper, they are interested in your results. That is why it is vital to use all your writing skills to objectively present your key findings in an orderly and logical sequence using illustrative materials and text.
Your Results should be organized into different segments or subsections where each one presents the purpose of the experiment, your experimental approach, data including text and visuals (tables, figures, schematics, algorithms, and formulas), and data commentary. For most journals, your data commentary will include a meaningful summary of the data presented in the visuals and an explanation of the most significant findings. This data presentation should not repeat the data in the visuals, but rather highlight the most important points. In the “standard” research paper approach, your Results section should exclude data interpretation, leaving it for the Discussion section. However, interpretations gradually and secretly creep into research papers: “Reducing the data, generalizing from the data, and highlighting scientific cases are all highly interpretive processes. It should be clear by now that we do not let the data speak for themselves in research reports; in summarizing our results, we interpret them for the reader” [ 10 ]. As a result, many journals including the Journal of Experimental Medicine and the Journal of Clinical Investigation use joint Results/Discussion sections, where results are immediately followed by interpretations.
Another important aspect of this section is to create a comprehensive and supported argument or a well-researched case. This means that you should be selective in presenting data and choose only those experimental details that are essential for your reader to understand your findings. You might have conducted an experiment 20 times and collected numerous records, but this does not mean that you should present all those records in your paper. You need to distinguish your results from your data and be able to discard excessive experimental details that could distract and confuse the reader. However, creating a picture or an argument should not be confused with data manipulation or falsification, which is a willful distortion of data and results. If some of your findings contradict your ideas, you have to mention this and find a plausible explanation for the contradiction.
In addition, your text should not include irrelevant and peripheral information, including overview sentences, as in (6).
6. To show our results, we first introduce all components of experimental system and then describe the outcome of infections.
Indeed, wordiness convolutes your sentences and conceals your ideas from readers. One common source of wordiness is unnecessary intensifiers. Adverbial intensifiers such as “clearly,” “essential,” “quite,” “basically,” “rather,” “fairly,” “really,” and “virtually” not only add verbosity to your sentences, but also lower your results’ credibility. They appeal to the reader’s emotions but lower objectivity, as in the common examples in (7):
7a. Table 3 clearly shows that … 7b. It is obvious from figure 4 that …
Another source of wordiness is nominalizations, i.e., nouns derived from verbs and adjectives paired with weak verbs including “be,” “have,” “do,” “make,” “cause,” “provide,” and “get” and constructions such as “there is/are.”
8a. We tested the hypothesis that there is a disruption of membrane asymmetry. 8b. In this paper we provide an argument that stem cells repopulate injured organs.
In the sentences above, the abstract nominalizations “disruption” and “argument” do not contribute to the clarity of the sentences, but rather clutter them with useless vocabulary that distracts from the meaning. To improve your sentences, avoid unnecessary nominalizations and change passive verbs and constructions into active and direct sentences.
9a. We tested the hypothesis that the membrane asymmetry is disrupted. 9b. In this paper we argue that stem cells repopulate injured organs.
Your Results section is the heart of your paper, representing a year or more of your daily research. So lead your reader through your story by writing direct, concise, and clear sentences.
Rule 4: Be clear, concise, and objective in describing your Results.
3.3. now it is time for your introduction.
Now that you are almost half through drafting your research paper, it is time to update your outline. While describing your Methods and Results, many of you diverged from the original outline and re-focused your ideas. So before you move on to create your Introduction, re-read your Methods and Results sections and change your outline to match your research focus. The updated outline will help you review the general picture of your paper, the topic, the main idea, and the purpose, which are all important for writing your introduction.
The best way to structure your introduction is to follow the three-move approach shown in Table 3 .
| a. Show that the general research area is important, central, interesting, and problematic in some way; |
| a. Indicate a gap in the previous research, or extend previous knowledge in some way. |
| a. Outline purposes or state the nature of the present research; |
| b. List research questions or hypotheses; |
| c. Announce principle findings; |
| d. State the value of the present research; |
| e. Indicate the structure of the research paper. |
Adapted from Swales and Feak [ 11 ].
The moves and information from your outline can help to create your Introduction efficiently and without missing steps. These moves are traffic signs that lead the reader through the road of your ideas. Each move plays an important role in your paper and should be presented with deep thought and care. When you establish the territory, you place your research in context and highlight the importance of your research topic. By finding the niche, you outline the scope of your research problem and enter the scientific dialogue. The final move, “occupying the niche,” is where you explain your research in a nutshell and highlight your paper’s significance. The three moves allow your readers to evaluate their interest in your paper and play a significant role in the paper review process, determining your paper reviewers.
Some academic writers assume that the reader “should follow the paper” to find the answers about your methodology and your findings. As a result, many novice writers do not present their experimental approach and the major findings, wrongly believing that the reader will locate the necessary information later while reading the subsequent sections [ 5 ]. However, this “suspense” approach is not appropriate for scientific writing. To interest the reader, scientific authors should be direct and straightforward and present informative one-sentence summaries of the results and the approach.
Another problem is that writers understate the significance of the Introduction. Many new researchers mistakenly think that all their readers understand the importance of the research question and omit this part. However, this assumption is faulty because the purpose of the section is not to evaluate the importance of the research question in general. The goal is to present the importance of your research contribution and your findings. Therefore, you should be explicit and clear in describing the benefit of the paper.
The Introduction should not be long. Indeed, for most journals, this is a very brief section of about 250 to 600 words, but it might be the most difficult section due to its importance.
Rule 5: Interest your reader in the Introduction section by signalling all its elements and stating the novelty of the work.
3.4. discussion of the results.
For many scientists, writing a Discussion section is as scary as starting a paper. Most of the fear comes from the variation in the section. Since every paper has its unique results and findings, the Discussion section differs in its length, shape, and structure. However, some general principles of writing this section still exist. Knowing these rules, or “moves,” can change your attitude about this section and help you create a comprehensive interpretation of your results.
The purpose of the Discussion section is to place your findings in the research context and “to explain the meaning of the findings and why they are important, without appearing arrogant, condescending, or patronizing” [ 11 ]. The structure of the first two moves is almost a mirror reflection of the one in the Introduction. In the Introduction, you zoom in from general to specific and from the background to your research question; in the Discussion section, you zoom out from the summary of your findings to the research context, as shown in Table 4 .
| a. State the study’s major findings. |
| b. Explain the meaning and importance of your finding. |
| c. Consider alternative explanations of the findings. |
| a. Compare and contrast your findings with those of other published results. |
| b. Explain any discrepancies and unexpected findings. |
| c. State the limitations, weaknesses, and assumptions of your study. |
| a. Summarize the answers to the research questions. |
| b. Indicate the importance of the work by stating applications, recommendations, and implications. |
Adapted from Swales and Feak and Hess [ 11 , 12 ].
The biggest challenge for many writers is the opening paragraph of the Discussion section. Following the moves in Table 1 , the best choice is to start with the study’s major findings that provide the answer to the research question in your Introduction. The most common starting phrases are “Our findings demonstrate . . .,” or “In this study, we have shown that . . .,” or “Our results suggest . . .” In some cases, however, reminding the reader about the research question or even providing a brief context and then stating the answer would make more sense. This is important in those cases where the researcher presents a number of findings or where more than one research question was presented. Your summary of the study’s major findings should be followed by your presentation of the importance of these findings. One of the most frequent mistakes of the novice writer is to assume the importance of his findings. Even if the importance is clear to you, it may not be obvious to your reader. Digesting the findings and their importance to your reader is as crucial as stating your research question.
Another useful strategy is to be proactive in the first move by predicting and commenting on the alternative explanations of the results. Addressing potential doubts will save you from painful comments about the wrong interpretation of your results and will present you as a thoughtful and considerate researcher. Moreover, the evaluation of the alternative explanations might help you create a logical step to the next move of the discussion section: the research context.
The goal of the research context move is to show how your findings fit into the general picture of the current research and how you contribute to the existing knowledge on the topic. This is also the place to discuss any discrepancies and unexpected findings that may otherwise distort the general picture of your paper. Moreover, outlining the scope of your research by showing the limitations, weaknesses, and assumptions is essential and adds modesty to your image as a scientist. However, make sure that you do not end your paper with the problems that override your findings. Try to suggest feasible explanations and solutions.
If your submission does not require a separate Conclusion section, then adding another paragraph about the “take-home message” is a must. This should be a general statement reiterating your answer to the research question and adding its scientific implications, practical application, or advice.
Just as in all other sections of your paper, the clear and precise language and concise comprehensive sentences are vital. However, in addition to that, your writing should convey confidence and authority. The easiest way to illustrate your tone is to use the active voice and the first person pronouns. Accompanied by clarity and succinctness, these tools are the best to convince your readers of your point and your ideas.
Rule 6: Present the principles, relationships, and generalizations in a concise and convincing tone.
4. choosing the best working revision strategies.
Now that you have created the first draft, your attitude toward your writing should have improved. Moreover, you should feel more confident that you are able to accomplish your project and submit your paper within a reasonable timeframe. You also have worked out your writing schedule and followed it precisely. Do not stop ― you are only at the midpoint from your destination. Just as the best and most precious diamond is no more than an unattractive stone recognized only by trained professionals, your ideas and your results may go unnoticed if they are not polished and brushed. Despite your attempts to present your ideas in a logical and comprehensive way, first drafts are frequently a mess. Use the advice of Paul Silvia: “Your first drafts should sound like they were hastily translated from Icelandic by a non-native speaker” [ 2 ]. The degree of your success will depend on how you are able to revise and edit your paper.
The revision can be done at the macrostructure and the microstructure levels [ 13 ]. The macrostructure revision includes the revision of the organization, content, and flow. The microstructure level includes individual words, sentence structure, grammar, punctuation, and spelling.
The best way to approach the macrostructure revision is through the outline of the ideas in your paper. The last time you updated your outline was before writing the Introduction and the Discussion. Now that you have the beginning and the conclusion, you can take a bird’s-eye view of the whole paper. The outline will allow you to see if the ideas of your paper are coherently structured, if your results are logically built, and if the discussion is linked to the research question in the Introduction. You will be able to see if something is missing in any of the sections or if you need to rearrange your information to make your point.
The next step is to revise each of the sections starting from the beginning. Ideally, you should limit yourself to working on small sections of about five pages at a time [ 14 ]. After these short sections, your eyes get used to your writing and your efficiency in spotting problems decreases. When reading for content and organization, you should control your urge to edit your paper for sentence structure and grammar and focus only on the flow of your ideas and logic of your presentation. Experienced researchers tend to make almost three times the number of changes to meaning than novice writers [ 15 , 16 ]. Revising is a difficult but useful skill, which academic writers obtain with years of practice.
In contrast to the macrostructure revision, which is a linear process and is done usually through a detailed outline and by sections, microstructure revision is a non-linear process. While the goal of the macrostructure revision is to analyze your ideas and their logic, the goal of the microstructure editing is to scrutinize the form of your ideas: your paragraphs, sentences, and words. You do not need and are not recommended to follow the order of the paper to perform this type of revision. You can start from the end or from different sections. You can even revise by reading sentences backward, sentence by sentence and word by word.
One of the microstructure revision strategies frequently used during writing center consultations is to read the paper aloud [ 17 ]. You may read aloud to yourself, to a tape recorder, or to a colleague or friend. When reading and listening to your paper, you are more likely to notice the places where the fluency is disrupted and where you stumble because of a very long and unclear sentence or a wrong connector.
Another revision strategy is to learn your common errors and to do a targeted search for them [ 13 ]. All writers have a set of problems that are specific to them, i.e., their writing idiosyncrasies. Remembering these problems is as important for an academic writer as remembering your friends’ birthdays. Create a list of these idiosyncrasies and run a search for these problems using your word processor. If your problem is demonstrative pronouns without summary words, then search for “this/these/those” in your text and check if you used the word appropriately. If you have a problem with intensifiers, then search for “really” or “very” and delete them from the text. The same targeted search can be done to eliminate wordiness. Searching for “there is/are” or “and” can help you avoid the bulky sentences.
The final strategy is working with a hard copy and a pencil. Print a double space copy with font size 14 and re-read your paper in several steps. Try reading your paper line by line with the rest of the text covered with a piece of paper. When you are forced to see only a small portion of your writing, you are less likely to get distracted and are more likely to notice problems. You will end up spotting more unnecessary words, wrongly worded phrases, or unparallel constructions.
After you apply all these strategies, you are ready to share your writing with your friends, colleagues, and a writing advisor in the writing center. Get as much feedback as you can, especially from non-specialists in your field. Patiently listen to what others say to you ― you are not expected to defend your writing or explain what you wanted to say. You may decide what you want to change and how after you receive the feedback and sort it in your head. Even though some researchers make the revision an endless process and can hardly stop after a 14th draft; having from five to seven drafts of your paper is a norm in the sciences. If you can’t stop revising, then set a deadline for yourself and stick to it. Deadlines always help.
Rule 7: Revise your paper at the macrostructure and the microstructure level using different strategies and techniques. Receive feedback and revise again.
5. it is time to submit.
It is late at night again. You are still in your lab finishing revisions and getting ready to submit your paper. You feel happy ― you have finally finished a year’s worth of work. You will submit your paper tomorrow, and regardless of the outcome, you know that you can do it. If one journal does not take your paper, you will take advantage of the feedback and resubmit again. You will have a publication, and this is the most important achievement.
What is even more important is that you have your scheduled writing time that you are going to keep for your future publications, for reading and taking notes, for writing grants, and for reviewing papers. You are not going to lose stamina this time, and you will become a productive scientist. But for now, let’s celebrate the end of the paper.
- Hayes JR. In: The Science of Writing: Theories, Methods, Individual Differences, and Applications. Levy CM, Ransdell SE, editors. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum; 1996. A new framework for understanding cognition and affect in writing; pp. 1–28. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silvia PJ. How to Write a Lot. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Whitesides GM. Whitesides’ Group: Writing a Paper. Adv Mater. 2004; 16 (15):1375–1377. [ Google Scholar ]
- Soto D, Funes MJ, Guzmán-García A, Warbrick T, Rotshtein T, Humphreys GW. Pleasant music overcomes the loss of awareness in patients with visual neglect. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009; 106 (14):6011–6016. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hofmann AH. Scientific Writing and Communication. Papers, Proposals, and Presentations. New York: Oxford University Press; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zeiger M. Essentials of Writing Biomedical Research Papers. 2nd edition. San Francisco, CA: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.; 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Martínez I. Native and non-native writers’ use of first person pronouns in the different sections of biology research articles in English. Journal of Second Language Writing. 2005; 14 (3):174–190. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rodman L. The Active Voice In Scientific Articles: Frequency And Discourse Functions. Journal Of Technical Writing And Communication. 1994; 24 (3):309–331. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tarone LE, Dwyer S, Gillette S, Icke V. On the use of the passive in two astrophysics journal papers with extensions to other languages and other fields. English for Specific Purposes. 1998; 17 :113–132. [ Google Scholar ]
- Penrose AM, Katz SB. Writing in the sciences: Exploring conventions of scientific discourse. New York: St. Martin’s Press; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Swales JM, Feak CB. Academic Writing for Graduate Students. 2nd edition. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hess DR. How to Write an Effective Discussion. Respiratory Care. 2004; 29 (10):1238–1241. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Belcher WL. Writing Your Journal Article in 12 Weeks: a guide to academic publishing success. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Single PB. Demystifying Dissertation Writing: A Streamlined Process of Choice of Topic to Final Text. Virginia: Stylus Publishing LLC; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Faigley L, Witte SP. Analyzing revision. Composition and Communication. 1981; 32 :400–414. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flower LS, Hayes JR, Carey L, Schriver KS, Stratman J. Detection, diagnosis, and the strategies of revision. College Composition and Communication. 1986; 37 (1):16–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- Young BR. In: A Tutor’s Guide: Helping Writers One to One. Rafoth B, editor. Portsmouth, NH: Boynton/Cook Publishers; 2005. Can You Proofread This? pp. 140–158. [ Google Scholar ]
How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
The discussion section of a research paper analyzes and interprets the findings, provides context, compares them with previous studies, identifies limitations, and suggests future research directions.
Updated on September 15, 2023

Structure your discussion section right, and you’ll be cited more often while doing a greater service to the scientific community. So, what actually goes into the discussion section? And how do you write it?
The discussion section of your research paper is where you let the reader know how your study is positioned in the literature, what to take away from your paper, and how your work helps them. It can also include your conclusions and suggestions for future studies.
First, we’ll define all the parts of your discussion paper, and then look into how to write a strong, effective discussion section for your paper or manuscript.
Discussion section: what is it, what it does
The discussion section comes later in your paper, following the introduction, methods, and results. The discussion sets up your study’s conclusions. Its main goals are to present, interpret, and provide a context for your results.
What is it?
The discussion section provides an analysis and interpretation of the findings, compares them with previous studies, identifies limitations, and suggests future directions for research.
This section combines information from the preceding parts of your paper into a coherent story. By this point, the reader already knows why you did your study (introduction), how you did it (methods), and what happened (results). In the discussion, you’ll help the reader connect the ideas from these sections.
Why is it necessary?
The discussion provides context and interpretations for the results. It also answers the questions posed in the introduction. While the results section describes your findings, the discussion explains what they say. This is also where you can describe the impact or implications of your research.
Adds context for your results
Most research studies aim to answer a question, replicate a finding, or address limitations in the literature. These goals are first described in the introduction. However, in the discussion section, the author can refer back to them to explain how the study's objective was achieved.
Shows what your results actually mean and real-world implications
The discussion can also describe the effect of your findings on research or practice. How are your results significant for readers, other researchers, or policymakers?
What to include in your discussion (in the correct order)
A complete and effective discussion section should at least touch on the points described below.
Summary of key findings
The discussion should begin with a brief factual summary of the results. Concisely overview the main results you obtained.
Begin with key findings with supporting evidence
Your results section described a list of findings, but what message do they send when you look at them all together?
Your findings were detailed in the results section, so there’s no need to repeat them here, but do provide at least a few highlights. This will help refresh the reader’s memory and help them focus on the big picture.
Read the first paragraph of the discussion section in this article (PDF) for an example of how to start this part of your paper. Notice how the authors break down their results and follow each description sentence with an explanation of why each finding is relevant.
State clearly and concisely
Following a clear and direct writing style is especially important in the discussion section. After all, this is where you will make some of the most impactful points in your paper. While the results section often contains technical vocabulary, such as statistical terms, the discussion section lets you describe your findings more clearly.
Interpretation of results
Once you’ve given your reader an overview of your results, you need to interpret those results. In other words, what do your results mean? Discuss the findings’ implications and significance in relation to your research question or hypothesis.
Analyze and interpret your findings
Look into your findings and explore what’s behind them or what may have caused them. If your introduction cited theories or studies that could explain your findings, use these sources as a basis to discuss your results.
For example, look at the second paragraph in the discussion section of this article on waggling honey bees. Here, the authors explore their results based on information from the literature.
Unexpected or contradictory results
Sometimes, your findings are not what you expect. Here’s where you describe this and try to find a reason for it. Could it be because of the method you used? Does it have something to do with the variables analyzed? Comparing your methods with those of other similar studies can help with this task.
Context and comparison with previous work
Refer to related studies to place your research in a larger context and the literature. Compare and contrast your findings with existing literature, highlighting similarities, differences, and/or contradictions.
How your work compares or contrasts with previous work
Studies with similar findings to yours can be cited to show the strength of your findings. Information from these studies can also be used to help explain your results. Differences between your findings and others in the literature can also be discussed here.
How to divide this section into subsections
If you have more than one objective in your study or many key findings, you can dedicate a separate section to each of these. Here’s an example of this approach. You can see that the discussion section is divided into topics and even has a separate heading for each of them.

Limitations
Many journals require you to include the limitations of your study in the discussion. Even if they don’t, there are good reasons to mention these in your paper.
Why limitations don’t have a negative connotation
A study’s limitations are points to be improved upon in future research. While some of these may be flaws in your method, many may be due to factors you couldn’t predict.
Examples include time constraints or small sample sizes. Pointing this out will help future researchers avoid or address these issues. This part of the discussion can also include any attempts you have made to reduce the impact of these limitations, as in this study .
How limitations add to a researcher's credibility
Pointing out the limitations of your study demonstrates transparency. It also shows that you know your methods well and can conduct a critical assessment of them.
Implications and significance
The final paragraph of the discussion section should contain the take-home messages for your study. It can also cite the “strong points” of your study, to contrast with the limitations section.
Restate your hypothesis
Remind the reader what your hypothesis was before you conducted the study.
How was it proven or disproven?
Identify your main findings and describe how they relate to your hypothesis.
How your results contribute to the literature
Were you able to answer your research question? Or address a gap in the literature?
Future implications of your research
Describe the impact that your results may have on the topic of study. Your results may show, for instance, that there are still limitations in the literature for future studies to address. There may be a need for studies that extend your findings in a specific way. You also may need additional research to corroborate your findings.
Sample discussion section
This fictitious example covers all the aspects discussed above. Your actual discussion section will probably be much longer, but you can read this to get an idea of everything your discussion should cover.
Our results showed that the presence of cats in a household is associated with higher levels of perceived happiness by its human occupants. These findings support our hypothesis and demonstrate the association between pet ownership and well-being.
The present findings align with those of Bao and Schreer (2016) and Hardie et al. (2023), who observed greater life satisfaction in pet owners relative to non-owners. Although the present study did not directly evaluate life satisfaction, this factor may explain the association between happiness and cat ownership observed in our sample.
Our findings must be interpreted in light of some limitations, such as the focus on cat ownership only rather than pets as a whole. This may limit the generalizability of our results.
Nevertheless, this study had several strengths. These include its strict exclusion criteria and use of a standardized assessment instrument to investigate the relationships between pets and owners. These attributes bolster the accuracy of our results and reduce the influence of confounding factors, increasing the strength of our conclusions. Future studies may examine the factors that mediate the association between pet ownership and happiness to better comprehend this phenomenon.
This brief discussion begins with a quick summary of the results and hypothesis. The next paragraph cites previous research and compares its findings to those of this study. Information from previous studies is also used to help interpret the findings. After discussing the results of the study, some limitations are pointed out. The paper also explains why these limitations may influence the interpretation of results. Then, final conclusions are drawn based on the study, and directions for future research are suggested.
How to make your discussion flow naturally
If you find writing in scientific English challenging, the discussion and conclusions are often the hardest parts of the paper to write. That’s because you’re not just listing up studies, methods, and outcomes. You’re actually expressing your thoughts and interpretations in words.
- How formal should it be?
- What words should you use, or not use?
- How do you meet strict word limits, or make it longer and more informative?
Always give it your best, but sometimes a helping hand can, well, help. Getting a professional edit can help clarify your work’s importance while improving the English used to explain it. When readers know the value of your work, they’ll cite it. We’ll assign your study to an expert editor knowledgeable in your area of research. Their work will clarify your discussion, helping it to tell your story. Find out more about AJE Editing.

Adam Goulston, PsyD, MS, MBA, MISD, ELS
Science Marketing Consultant
See our "Privacy Policy"
Ensure your structure and ideas are consistent and clearly communicated
Pair your Premium Editing with our add-on service Presubmission Review for an overall assessment of your manuscript.
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper

Writing a research paper is both an art and a skill, and knowing how to write the methods section of a research paper is the first crucial step in mastering scientific writing. If, like the majority of early career researchers, you believe that the methods section is the simplest to write and needs little in the way of careful consideration or thought, this article will help you understand it is not 1 .
We have all probably asked our supervisors, coworkers, or search engines “ how to write a methods section of a research paper ” at some point in our scientific careers, so you are not alone if that’s how you ended up here. Even for seasoned researchers, selecting what to include in the methods section from a wealth of experimental information can occasionally be a source of distress and perplexity.
Additionally, journal specifications, in some cases, may make it more of a requirement rather than a choice to provide a selective yet descriptive account of the experimental procedure. Hence, knowing these nuances of how to write the methods section of a research paper is critical to its success. The methods section of the research paper is not supposed to be a detailed heavy, dull section that some researchers tend to write; rather, it should be the central component of the study that justifies the validity and reliability of the research.
Are you still unsure of how the methods section of a research paper forms the basis of every investigation? Consider the last article you read but ignore the methods section and concentrate on the other parts of the paper . Now think whether you could repeat the study and be sure of the credibility of the findings despite knowing the literature review and even having the data in front of you. You have the answer!

Having established the importance of the methods section , the next question is how to write the methods section of a research paper that unifies the overall study. The purpose of the methods section , which was earlier called as Materials and Methods , is to describe how the authors went about answering the “research question” at hand. Here, the objective is to tell a coherent story that gives a detailed account of how the study was conducted, the rationale behind specific experimental procedures, the experimental setup, objects (variables) involved, the research protocol employed, tools utilized to measure, calculations and measurements, and the analysis of the collected data 2 .
In this article, we will take a deep dive into this topic and provide a detailed overview of how to write the methods section of a research paper . For the sake of clarity, we have separated the subject into various sections with corresponding subheadings.
Table of Contents
What is the methods section of a research paper ?
The methods section is a fundamental section of any paper since it typically discusses the ‘ what ’, ‘ how ’, ‘ which ’, and ‘ why ’ of the study, which is necessary to arrive at the final conclusions. In a research article, the introduction, which serves to set the foundation for comprehending the background and results is usually followed by the methods section, which precedes the result and discussion sections. The methods section must explicitly state what was done, how it was done, which equipment, tools and techniques were utilized, how were the measurements/calculations taken, and why specific research protocols, software, and analytical methods were employed.
Why is the methods section important?
The primary goal of the methods section is to provide pertinent details about the experimental approach so that the reader may put the results in perspective and, if necessary, replicate the findings 3 . This section offers readers the chance to evaluate the reliability and validity of any study. In short, it also serves as the study’s blueprint, assisting researchers who might be unsure about any other portion in establishing the study’s context and validity. The methods plays a rather crucial role in determining the fate of the article; an incomplete and unreliable methods section can frequently result in early rejections and may lead to numerous rounds of modifications during the publication process. This means that the reviewers also often use methods section to assess the reliability and validity of the research protocol and the data analysis employed to address the research topic. In other words, the purpose of the methods section is to demonstrate the research acumen and subject-matter expertise of the author(s) in their field.
Structure of methods section of a research paper
Similar to the research paper, the methods section also follows a defined structure; this may be dictated by the guidelines of a specific journal or can be presented in a chronological or thematic manner based on the study type. When writing the methods section , authors should keep in mind that they are telling a story about how the research was conducted. They should only report relevant information to avoid confusing the reader and include details that would aid in connecting various aspects of the entire research activity together. It is generally advisable to present experiments in the order in which they were conducted. This facilitates the logical flow of the research and allows readers to follow the progression of the study design.

It is also essential to clearly state the rationale behind each experiment and how the findings of earlier experiments informed the design or interpretation of later experiments. This allows the readers to understand the overall purpose of the study design and the significance of each experiment within that context. However, depending on the particular research question and method, it may make sense to present information in a different order; therefore, authors must select the best structure and strategy for their individual studies.
In cases where there is a lot of information, divide the sections into subheadings to cover the pertinent details. If the journal guidelines pose restrictions on the word limit , additional important information can be supplied in the supplementary files. A simple rule of thumb for sectioning the method section is to begin by explaining the methodological approach ( what was done ), describing the data collection methods ( how it was done ), providing the analysis method ( how the data was analyzed ), and explaining the rationale for choosing the methodological strategy. This is described in detail in the upcoming sections.
How to write the methods section of a research paper
Contrary to widespread assumption, the methods section of a research paper should be prepared once the study is complete to prevent missing any key parameter. Hence, please make sure that all relevant experiments are done before you start writing a methods section . The next step for authors is to look up any applicable academic style manuals or journal-specific standards to ensure that the methods section is formatted correctly. The methods section of a research paper typically constitutes materials and methods; while writing this section, authors usually arrange the information under each category.
The materials category describes the samples, materials, treatments, and instruments, while experimental design, sample preparation, data collection, and data analysis are a part of the method category. According to the nature of the study, authors should include additional subsections within the methods section, such as ethical considerations like the declaration of Helsinki (for studies involving human subjects), demographic information of the participants, and any other crucial information that can affect the output of the study. Simply put, the methods section has two major components: content and format. Here is an easy checklist for you to consider if you are struggling with how to write the methods section of a research paper .
- Explain the research design, subjects, and sample details
- Include information on inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Mention ethical or any other permission required for the study
- Include information about materials, experimental setup, tools, and software
- Add details of data collection and analysis methods
- Incorporate how research biases were avoided or confounding variables were controlled
- Evaluate and justify the experimental procedure selected to address the research question
- Provide precise and clear details of each experiment
- Flowcharts, infographics, or tables can be used to present complex information
- Use past tense to show that the experiments have been done
- Follow academic style guides (such as APA or MLA ) to structure the content
- Citations should be included as per standard protocols in the field
Now that you know how to write the methods section of a research paper , let’s address another challenge researchers face while writing the methods section —what to include in the methods section . How much information is too much is not always obvious when it comes to trying to include data in the methods section of a paper. In the next section, we examine this issue and explore potential solutions.

What to include in the methods section of a research paper
The technical nature of the methods section occasionally makes it harder to present the information clearly and concisely while staying within the study context. Many young researchers tend to veer off subject significantly, and they frequently commit the sin of becoming bogged down in itty bitty details, making the text harder to read and impairing its overall flow. However, the best way to write the methods section is to start with crucial components of the experiments. If you have trouble deciding which elements are essential, think about leaving out those that would make it more challenging to comprehend the context or replicate the results. The top-down approach helps to ensure all relevant information is incorporated and vital information is not lost in technicalities. Next, remember to add details that are significant to assess the validity and reliability of the study. Here is a simple checklist for you to follow ( bonus tip: you can also make a checklist for your own study to avoid missing any critical information while writing the methods section ).
- Structuring the methods section : Authors should diligently follow journal guidelines and adhere to the specific author instructions provided when writing the methods section . Journals typically have specific guidelines for formatting the methods section ; for example, Frontiers in Plant Sciences advises arranging the materials and methods section by subheading and citing relevant literature. There are several standardized checklists available for different study types in the biomedical field, including CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) for randomized clinical trials, PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analysis) for systematic reviews and meta-analysis, and STROBE (STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology) for cohort, case-control, cross-sectional studies. Before starting the methods section , check the checklist available in your field that can function as a guide.
- Organizing different sections to tell a story : Once you are sure of the format required for structuring the methods section , the next is to present the sections in a logical manner; as mentioned earlier, the sections can be organized according to the chronology or themes. In the chronological arrangement, you should discuss the methods in accordance with how the experiments were carried out. An example of the method section of a research paper of an animal study should first ideally include information about the species, weight, sex, strain, and age. Next, the number of animals, their initial conditions, and their living and housing conditions should also be mentioned. Second, how the groups are assigned and the intervention (drug treatment, stress, or other) given to each group, and finally, the details of tools and techniques used to measure, collect, and analyze the data. Experiments involving animal or human subjects should additionally state an ethics approval statement. It is best to arrange the section using the thematic approach when discussing distinct experiments not following a sequential order.
- Define and explain the objects and procedure: Experimental procedure should clearly be stated in the methods section . Samples, necessary preparations (samples, treatment, and drug), and methods for manipulation need to be included. All variables (control, dependent, independent, and confounding) must be clearly defined, particularly if the confounding variables can affect the outcome of the study.
- Match the order of the methods section with the order of results: Though not mandatory, organizing the manuscript in a logical and coherent manner can improve the readability and clarity of the paper. This can be done by following a consistent structure throughout the manuscript; readers can easily navigate through the different sections and understand the methods and results in relation to each other. Using experiment names as headings for both the methods and results sections can also make it simpler for readers to locate specific information and corroborate it if needed.
- Relevant information must always be included: The methods section should have information on all experiments conducted and their details clearly mentioned. Ask the journal whether there is a way to offer more information in the supplemental files or external repositories if your target journal has strict word limitations. For example, Nature communications encourages authors to deposit their step-by-step protocols in an open-resource depository, Protocol Exchange which allows the protocols to be linked with the manuscript upon publication. Providing access to detailed protocols also helps to increase the transparency and reproducibility of the research.
- It’s all in the details: The methods section should meticulously list all the materials, tools, instruments, and software used for different experiments. Specify the testing equipment on which data was obtained, together with its manufacturer’s information, location, city, and state or any other stimuli used to manipulate the variables. Provide specifics on the research process you employed; if it was a standard protocol, cite previous studies that also used the protocol. Include any protocol modifications that were made, as well as any other factors that were taken into account when planning the study or gathering data. Any new or modified techniques should be explained by the authors. Typically, readers evaluate the reliability and validity of the procedures using the cited literature, and a widely accepted checklist helps to support the credibility of the methodology. Note: Authors should include a statement on sample size estimation (if applicable), which is often missed. It enables the reader to determine how many subjects will be required to detect the expected change in the outcome variables within a given confidence interval.
- Write for the audience: While explaining the details in the methods section , authors should be mindful of their target audience, as some of the rationale or assumptions on which specific procedures are based might not always be obvious to the audience, particularly for a general audience. Therefore, when in doubt, the objective of a procedure should be specified either in relation to the research question or to the entire protocol.
- Data interpretation and analysis : Information on data processing, statistical testing, levels of significance, and analysis tools and software should be added. Mention if the recommendations and expertise of an experienced statistician were followed. Also, evaluate and justify the preferred statistical method used in the study and its significance.
What NOT to include in the methods section of a research paper
To address “ how to write the methods section of a research paper ”, authors should not only pay careful attention to what to include but also what not to include in the methods section of a research paper . Here is a list of do not’s when writing the methods section :
- Do not elaborate on specifics of standard methods/procedures: You should refrain from adding unnecessary details of experiments and practices that are well established and cited previously. Instead, simply cite relevant literature or mention if the manufacturer’s protocol was followed.
- Do not add unnecessary details : Do not include minute details of the experimental procedure and materials/instruments used that are not significant for the outcome of the experiment. For example, there is no need to mention the brand name of the water bath used for incubation.
- Do not discuss the results: The methods section is not to discuss the results or refer to the tables and figures; save it for the results and discussion section. Also, focus on the methods selected to conduct the study and avoid diverting to other methods or commenting on their pros or cons.
- Do not make the section bulky : For extensive methods and protocols, provide the essential details and share the rest of the information in the supplemental files. The writing should be clear yet concise to maintain the flow of the section.
We hope that by this point, you understand how crucial it is to write a thoughtful and precise methods section and the ins and outs of how to write the methods section of a research paper . To restate, the entire purpose of the methods section is to enable others to reproduce the results or verify the research. We sincerely hope that this post has cleared up any confusion and given you a fresh perspective on the methods section .
As a parting gift, we’re leaving you with a handy checklist that will help you understand how to write the methods section of a research paper . Feel free to download this checklist and use or share this with those who you think may benefit from it.

References
- Bhattacharya, D. How to write the Methods section of a research paper. Editage Insights, 2018. https://www.editage.com/insights/how-to-write-the-methods-section-of-a-research-paper (2018).
- Kallet, R. H. How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper. Respiratory Care 49, 1229–1232 (2004). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15447808/
- Grindstaff, T. L. & Saliba, S. A. AVOIDING MANUSCRIPT MISTAKES. Int J Sports Phys Ther 7, 518–524 (2012). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3474299/
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

What are the Best Research Funding Sources

Inductive vs. Deductive Research Approach
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
The research process, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Structuring the Research Paper
Formal research structure.
These are the primary purposes for formal research:
enter the discourse, or conversation, of other writers and scholars in your field
learn how others in your field use primary and secondary resources
find and understand raw data and information

For the formal academic research assignment, consider an organizational pattern typically used for primary academic research. The pattern includes the following: introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions/recommendations.
Usually, research papers flow from the general to the specific and back to the general in their organization. The introduction uses a general-to-specific movement in its organization, establishing the thesis and setting the context for the conversation. The methods and results sections are more detailed and specific, providing support for the generalizations made in the introduction. The discussion section moves toward an increasingly more general discussion of the subject, leading to the conclusions and recommendations, which then generalize the conversation again.
Sections of a Formal Structure
The introduction section.
Many students will find that writing a structured introduction gets them started and gives them the focus needed to significantly improve their entire paper.
Introductions usually have three parts:
presentation of the problem statement, the topic, or the research inquiry
purpose and focus of your paper
summary or overview of the writer’s position or arguments
In the first part of the introduction—the presentation of the problem or the research inquiry—state the problem or express it so that the question is implied. Then, sketch the background on the problem and review the literature on it to give your readers a context that shows them how your research inquiry fits into the conversation currently ongoing in your subject area.
In the second part of the introduction, state your purpose and focus. Here, you may even present your actual thesis. Sometimes your purpose statement can take the place of the thesis by letting your reader know your intentions.
The third part of the introduction, the summary or overview of the paper, briefly leads readers through the discussion, forecasting the main ideas and giving readers a blueprint for the paper.
The following example provides a blueprint for a well-organized introduction.
Example of an Introduction
Entrepreneurial Marketing: The Critical Difference
In an article in the Harvard Business Review, John A. Welsh and Jerry F. White remind us that “a small business is not a little big business.” An entrepreneur is not a multinational conglomerate but a profit-seeking individual. To survive, he must have a different outlook and must apply different principles to his endeavors than does the president of a large or even medium-sized corporation. Not only does the scale of small and big businesses differ, but small businesses also suffer from what the Harvard Business Review article calls “resource poverty.” This is a problem and opportunity that requires an entirely different approach to marketing. Where large ad budgets are not necessary or feasible, where expensive ad production squanders limited capital, where every marketing dollar must do the work of two dollars, if not five dollars or even ten, where a person’s company, capital, and material well-being are all on the line—that is, where guerrilla marketing can save the day and secure the bottom line (Levinson, 1984, p. 9).
By reviewing the introductions to research articles in the discipline in which you are writing your research paper, you can get an idea of what is considered the norm for that discipline. Study several of these before you begin your paper so that you know what may be expected. If you are unsure of the kind of introduction your paper needs, ask your professor for more information. The introduction is normally written in present tense.
THE METHODS SECTION
The methods section of your research paper should describe in detail what methodology and special materials if any, you used to think through or perform your research. You should include any materials you used or designed for yourself, such as questionnaires or interview questions, to generate data or information for your research paper. You want to include any methodologies that are specific to your particular field of study, such as lab procedures for a lab experiment or data-gathering instruments for field research. The methods section is usually written in the past tense.
THE RESULTS SECTION
How you present the results of your research depends on what kind of research you did, your subject matter, and your readers’ expectations.
Quantitative information —data that can be measured—can be presented systematically and economically in tables, charts, and graphs. Quantitative information includes quantities and comparisons of sets of data.
Qualitative information , which includes brief descriptions, explanations, or instructions, can also be presented in prose tables. This kind of descriptive or explanatory information, however, is often presented in essay-like prose or even lists.
There are specific conventions for creating tables, charts, and graphs and organizing the information they contain. In general, you should use them only when you are sure they will enlighten your readers rather than confuse them. In the accompanying explanation and discussion, always refer to the graphic by number and explain specifically what you are referring to; you can also provide a caption for the graphic. The rule of thumb for presenting a graphic is first to introduce it by name, show it, and then interpret it. The results section is usually written in the past tense.
THE DISCUSSION SECTION
Your discussion section should generalize what you have learned from your research. One way to generalize is to explain the consequences or meaning of your results and then make your points that support and refer back to the statements you made in your introduction. Your discussion should be organized so that it relates directly to your thesis. You want to avoid introducing new ideas here or discussing tangential issues not directly related to the exploration and discovery of your thesis. The discussion section, along with the introduction, is usually written in the present tense.
THE CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS SECTION
Your conclusion ties your research to your thesis, binding together all the main ideas in your thinking and writing. By presenting the logical outcome of your research and thinking, your conclusion answers your research inquiry for your reader. Your conclusions should relate directly to the ideas presented in your introduction section and should not present any new ideas.
You may be asked to present your recommendations separately in your research assignment. If so, you will want to add some elements to your conclusion section. For example, you may be asked to recommend a course of action, make a prediction, propose a solution to a problem, offer a judgment, or speculate on the implications and consequences of your ideas. The conclusions and recommendations section is usually written in the present tense.
Key Takeaways
- For the formal academic research assignment, consider an organizational pattern typically used for primary academic research.
- The pattern includes the following: introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions/recommendations.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
How to Write an Effective Results Section
Affiliation.
- 1 Rothman Orthopaedics Institute, Philadelphia, PA.
- PMID: 31145152
- DOI: 10.1097/BSD.0000000000000845
Developing a well-written research paper is an important step in completing a scientific study. This paper is where the principle investigator and co-authors report the purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions of the study. A key element of writing a research paper is to clearly and objectively report the study's findings in the Results section. The Results section is where the authors inform the readers about the findings from the statistical analysis of the data collected to operationalize the study hypothesis, optimally adding novel information to the collective knowledge on the subject matter. By utilizing clear, concise, and well-organized writing techniques and visual aids in the reporting of the data, the author is able to construct a case for the research question at hand even without interpreting the data.
PubMed Disclaimer
Similar articles
- Rules to be adopted for publishing a scientific paper. Picardi N. Picardi N. Ann Ital Chir. 2016;87:1-3. Ann Ital Chir. 2016. PMID: 28474609
- How to Write Effective Discussion and Conclusion Sections. Makar G, Foltz C, Lendner M, Vaccaro AR. Makar G, et al. Clin Spine Surg. 2018 Oct;31(8):345-346. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0000000000000687. Clin Spine Surg. 2018. PMID: 29979216
- The rites of writing papers: steps to successful publishing for psychiatrists. Brakoulias V, Macfarlane MD, Looi JC. Brakoulias V, et al. Australas Psychiatry. 2015 Feb;23(1):32-6. doi: 10.1177/1039856214560180. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Australas Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25469001
- How to write a research paper. Alexandrov AV. Alexandrov AV. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004;18(2):135-8. doi: 10.1159/000079266. Epub 2004 Jun 23. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004. PMID: 15218279 Review.
- How to write an original radiological research manuscript. Bannas P, Reeder SB. Bannas P, et al. Eur Radiol. 2017 Nov;27(11):4455-4460. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-4879-8. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Eur Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28616726 Free PMC article. Review.
- Essential Guide to Manuscript Writing for Academic Dummies: An Editor's Perspective. Aga SS, Nissar S. Aga SS, et al. Biochem Res Int. 2022 Sep 1;2022:1492058. doi: 10.1155/2022/1492058. eCollection 2022. Biochem Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36092536 Free PMC article. Review.
- Search in MeSH
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources.
- Ovid Technologies, Inc.
- Wolters Kluwer

- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
- Language Editing Services
- Translation Services

How to write the results section of a research paper
- 3 minute read
- 76.7K views
Table of Contents
At its core, a research paper aims to fill a gap in the research on a given topic. As a result, the results section of the paper, which describes the key findings of the study, is often considered the core of the paper. This is the section that gets the most attention from reviewers, peers, students, and any news organization reporting on your findings. Writing a clear, concise, and logical results section is, therefore, one of the most important parts of preparing your manuscript.
Difference between results and discussion
Before delving into how to write the results section, it is important to first understand the difference between the results and discussion sections. The results section needs to detail the findings of the study. The aim of this section is not to draw connections between the different findings or to compare it to previous findings in literature—that is the purview of the discussion section. Unlike the discussion section, which can touch upon the hypothetical, the results section needs to focus on the purely factual. In some cases, it may even be preferable to club these two sections together into a single section. For example, while writing a review article, it can be worthwhile to club these two sections together, as the main results in this case are the conclusions that can be drawn from the literature.
Structure of the results section
Although the main purpose of the results section in a research paper is to report the findings, it is necessary to present an introduction and repeat the research question. This establishes a connection to the previous section of the paper and creates a smooth flow of information.
Next, the results section needs to communicate the findings of your research in a systematic manner. The section needs to be organized such that the primary research question is addressed first, then the secondary research questions. If the research addresses multiple questions, the results section must individually connect with each of the questions. This ensures clarity and minimizes confusion while reading.
Consider representing your results visually. For example, graphs, tables, and other figures can help illustrate the findings of your paper, especially if there is a large amount of data in the results.
Remember, an appealing results section can help peer reviewers better understand the merits of your research, thereby increasing your chances of publication.
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper
- Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions.
- The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is best to avoid overinterpreting the results.
- If the research addresses more than one hypothesis, use sub-sections to describe the results. This prevents confusion and promotes understanding.
- Ensure that negative results are included in this section, even if they do not support the research hypothesis.
- Wherever possible, use illustrations like tables, figures, charts, or other visual representations to showcase the results of your research paper. Mention these illustrations in the text, but do not repeat the information that they convey.
- For statistical data, it is adequate to highlight the tests and explain their results. The initial or raw data should not be mentioned in the results section of a research paper.
The results section of a research paper is usually the most impactful section because it draws the greatest attention. Regardless of the subject of your research paper, a well-written results section is capable of generating interest in your research.
For detailed information and assistance on writing the results of a research paper, refer to Elsevier Author Services.

Writing a good review article

Why is data validation important in research?
You may also like.

Submission 101: What format should be used for academic papers?

Page-Turner Articles are More Than Just Good Arguments: Be Mindful of Tone and Structure!

A Must-see for Researchers! How to Ensure Inclusivity in Your Scientific Writing

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Library Instruction
Structure of typical research article.
The basic structure of a typical research paper includes Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. Each section addresses a different objective.
- the problem they intend to address -- in other words, the research question -- in the Introduction ;
- what they did to answer the question in Methodology ;
- what they observed in Results ; and
- what they think the results mean in Discussion .
A substantial study will sometimes include a literature review section which discusses previous works on the topic. The basic structure is outlined below:
- Author and author's professional affiliation is identified
- Introduction
- Literature review section (a discussion about what other scholars have written on the topic)
- Methodology section (methods of data gathering are explained)
- Discussion section
- Conclusions
- Reference list with citations (sources of information used in the article)
Thanks for helping us improve csumb.edu. Spot a broken link, typo, or didn't find something where you expected to? Let us know. We'll use your feedback to improve this page, and the site overall.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
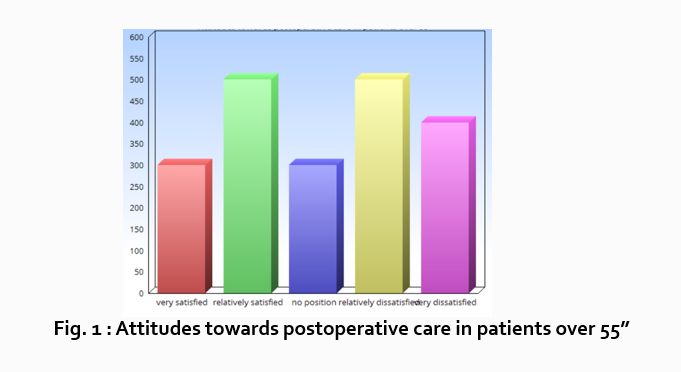
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
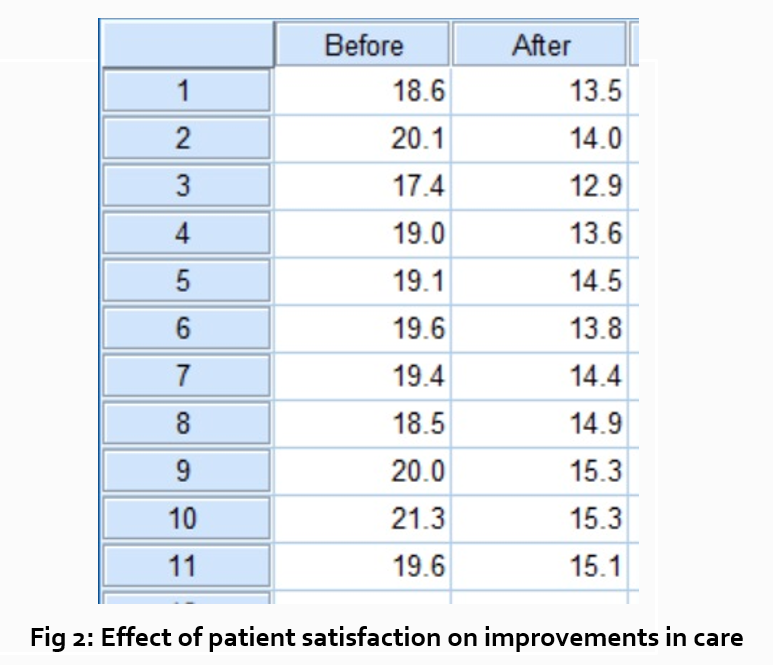
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
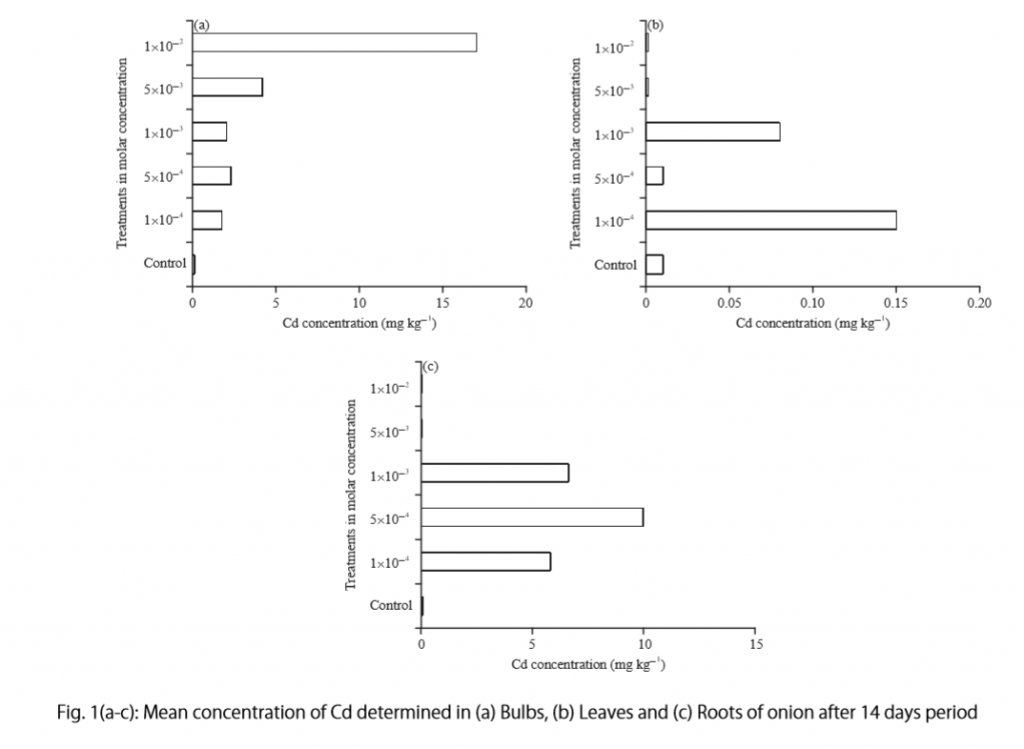
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers
Training videos | Faqs

Research Paper Structure – Main Sections and Parts of a Research Paper
PhD students are expected to write and publish research papers to validate their research work and findings. Writing your first research paper can seem like a daunting task at the start but must be done to validate your work. If you are a beginner writer new to academic writing or a non-native English speaker then it might seem like a daunting process at inception. The best way to begin writing a research paper is to learn about the research paper structure needed in your field, as this may vary between fields. Producing a research paper structure first with various headings and subheadings will significantly simplify the writing process. In this blog, we explain the basic structure of a research paper and explain its various components. We elaborate on various parts and sections of a research paper. We also provide guidance to produce a research paper structure for your work through word cloud diagrams that illustrate various topics and sub-topics to be included under each section. We recommend you to refer to our other blogs on academic writing tools , academic writing resources , and academic phrase-bank , which are relevant to the topic discussed in this blog.
1. Introduction
The Introduction section is one of the most important sections of a research paper. The introduction section should start with a brief outline of the topic and then explain the nature of the problem at hand and why it is crucial to resolve this issue. This section should contain a literature review that provides relevant background information about the topic. The literature review should touch upon seminal and pioneering works in the field and the most recent studies pertinent to your work.

The literature review should end with a few lines about the research gap in the chosen domain. This is where you explain the lack of adequate research about your chosen topic and make a case for the need for more research. This is an excellent place to define the research question or hypothesis. The last part of the introduction should be about your work. Having established the research gap now, you have to explain how you intend to solve the problem and subsequently introduce your approach. You should provide a clear outline that includes both the primary and secondary aims/objectives of your work. You can end the section by providing how the rest of the paper is organized. When you are working on the research paper structure use the word cloud diagrams as a guidance.
2. Material and Methods
The Materials and methods section of the research paper should include detailed information about the implementation details of your method. This should be written in such a way that it is reproducible by any person conducting research in the same field. This section should include all the technical details of the experimental setup, measurement procedure, and parameters of interest. It should also include details of how the methods were validated and tested prior to their use. It is recommended to use equations, figures, and tables to explain the workings of the method proposed. Add placeholders for figures and tables with dummy titles while working on the research paper structure.

Suppose your methodology involves data collection and recruitment. In that case, you should provide information about the sample size, population characteristics, interview process, and recruitment methods. It should also include the details of the consenting procedure and inclusion and exclusion criteria. This section can end with various statistical methods used for data analysis and significance testing.
3. Results and Discussion
Results and Discussion section of the research paper should be the concluding part of your research paper. In the results section, you can explain your experiments’ outcome by presenting adequate scientific data to back up your conclusions. You must interpret the scientific data to your readers by highlighting the key findings of your work. You also provide information on any negative and unexpected findings that came out of your work. It is vital to present the data in an unbiased manner. You should also explain how the current results compare with previously published data from similar works in the literature.

In the discussion section, you should summarize your work and explain how the research work objectives were achieved. You can highlight the benefits your work will bring to the overall scientific community and potential practical applications. You must not introduce any new information in this section; you can only discuss things that have already been mentioned in the paper. The discussion section must talk about your work’s limitations; no scientific work is perfect, and some drawbacks are expected. If there are any inconclusive results in your work, you can present your theories about what might have caused it. You have to end your paper with conclusions and future work . In conclusion, you can restate your aims and objectives and summarize your main findings, preferably in two or three lines. You should also lay out your plans for future work and explain how further research will benefit the research domain. Finally, you can also add ‘Acknowledgments’ and ‘References’ sections to the research paper structure for completion.
Similar Posts

Literature Review Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many literature review examples and understand different ways to present past literature in your paper.

Critical Literature Review : How to Critique a Research Article?
In this blog, we will look at how to use constructive language when critiquing other’s work in your research paper.

How to Make Your Study Limitations Sound Positive?
In this blog, we will look at some clever techniques to present the study limitations without reducing the impact of your work.

Abstract Section Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many abstract examples and understand how to construct a good abstract for your research paper.

Technical Terms, Notations, and Scientific Jargon in Research Papers
In this blog, we will teach you how to use specialized terminology in your research papers with some practical examples.

How to Handle Negative Results in your Research Paper?
In this blog, we will see how to effectively communicate negative and unexpected findings in your paper with detailed examples.
Useful. Thanks.
Thanks your effort of writting research
well articulated
Thank you author
Most usefull to write research article and publish in standard journal
Thank you for the write up. I have really learnt a lot.
Thanks for your efforts
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 26 Share Facebook
- 20 Share Twitter
- 8 Share LinkedIn
- 20 Share Email
Welcome to the new OASIS website! We have academic skills, library skills, math and statistics support, and writing resources all together in one new home.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
General Research Paper Guidelines: Discussion
Discussion section.
The overall purpose of a research paper’s discussion section is to evaluate and interpret results, while explaining both the implications and limitations of your findings. Per APA (2020) guidelines, this section requires you to “examine, interpret, and qualify the results and draw inferences and conclusions from them” (p. 89). Discussion sections also require you to detail any new insights, think through areas for future research, highlight the work that still needs to be done to further your topic, and provide a clear conclusion to your research paper. In a good discussion section, you should do the following:
- Clearly connect the discussion of your results to your introduction, including your central argument, thesis, or problem statement.
- Provide readers with a critical thinking through of your results, answering the “so what?” question about each of your findings. In other words, why is this finding important?
- Detail how your research findings might address critical gaps or problems in your field
- Compare your results to similar studies’ findings
- Provide the possibility of alternative interpretations, as your goal as a researcher is to “discover” and “examine” and not to “prove” or “disprove.” Instead of trying to fit your results into your hypothesis, critically engage with alternative interpretations to your results.
For more specific details on your Discussion section, be sure to review Sections 3.8 (pp. 89-90) and 3.16 (pp. 103-104) of your 7 th edition APA manual
*Box content adapted from:
University of Southern California (n.d.). Organizing your social sciences research paper: 8 the discussion . https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/discussion
Limitations
Limitations of generalizability or utility of findings, often over which the researcher has no control, should be detailed in your Discussion section. Including limitations for your reader allows you to demonstrate you have thought critically about your given topic, understood relevant literature addressing your topic, and chosen the methodology most appropriate for your research. It also allows you an opportunity to suggest avenues for future research on your topic. An effective limitations section will include the following:
- Detail (a) sources of potential bias, (b) possible imprecision of measures, (c) other limitations or weaknesses of the study, including any methodological or researcher limitations.
- Sample size: In quantitative research, if a sample size is too small, it is more difficult to generalize results.
- Lack of available/reliable data : In some cases, data might not be available or reliable, which will ultimately affect the overall scope of your research. Use this as an opportunity to explain areas for future study.
- Lack of prior research on your study topic: In some cases, you might find that there is very little or no similar research on your study topic, which hinders the credibility and scope of your own research. If this is the case, use this limitation as an opportunity to call for future research. However, make sure you have done a thorough search of the available literature before making this claim.
- Flaws in measurement of data: Hindsight is 20/20, and you might realize after you have completed your research that the data tool you used actually limited the scope or results of your study in some way. Again, acknowledge the weakness and use it as an opportunity to highlight areas for future study.
- Limits of self-reported data: In your research, you are assuming that any participants will be honest and forthcoming with responses or information they provide to you. Simply acknowledging this assumption as a possible limitation is important in your research.
- Access: Most research requires that you have access to people, documents, organizations, etc.. However, for various reasons, access is sometimes limited or denied altogether. If this is the case, you will want to acknowledge access as a limitation to your research.
- Time: Choosing a research focus that is narrow enough in scope to finish in a given time period is important. If such limitations of time prevent you from certain forms of research, access, or study designs, acknowledging this time restraint is important. Acknowledging such limitations is important, as they can point other researchers to areas that require future study.
- Potential Bias: All researchers have some biases, so when reading and revising your draft, pay special attention to the possibilities for bias in your own work. Such bias could be in the form you organized people, places, participants, or events. They might also exist in the method you selected or the interpretation of your results. Acknowledging such bias is an important part of the research process.
- Language Fluency: On occasion, researchers or research participants might have language fluency issues, which could potentially hinder results or how effectively you interpret results. If this is an issue in your research, make sure to acknowledge it in your limitations section.
University of Southern California (n.d.). Organizing your social sciences research paper: Limitations of the study . https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/limitations
In many research papers, the conclusion, like the limitations section, is folded into the larger discussion section. If you are unsure whether to include the conclusion as part of your discussion or as a separate section, be sure to defer to the assignment instructions or ask your instructor.
The conclusion is important, as it is specifically designed to highlight your research’s larger importance outside of the specific results of your study. Your conclusion section allows you to reiterate the main findings of your study, highlight their importance, and point out areas for future research. Based on the scope of your paper, your conclusion could be anywhere from one to three paragraphs long. An effective conclusion section should include the following:
- Describe the possibilities for continued research on your topic, including what might be improved, adapted, or added to ensure useful and informed future research.
- Provide a detailed account of the importance of your findings
- Reiterate why your problem is important, detail how your interpretation of results impacts the subfield of study, and what larger issues both within and outside of your field might be affected from such results
University of Southern California (n.d.). Organizing your social sciences research paper: 9. the conclusion . https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/conclusion
- Previous Page: Results
- Next Page: References
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methodology
Definition:
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect , analyze , and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems . Moreover, They are philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process.
Structure of Research Methodology
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section:
I. Introduction
- Provide an overview of the research problem and the need for a research methodology section
- Outline the main research questions and objectives
II. Research Design
- Explain the research design chosen and why it is appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Discuss any alternative research designs considered and why they were not chosen
- Describe the research setting and participants (if applicable)
III. Data Collection Methods
- Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations)
- Explain how the data collection methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or instruments used for data collection
IV. Data Analysis Methods
- Describe the methods used to analyze the data (e.g., statistical analysis, content analysis )
- Explain how the data analysis methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or software used for data analysis
V. Ethical Considerations
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise from the research and how they were addressed
- Explain how informed consent was obtained (if applicable)
- Detail any measures taken to ensure confidentiality and anonymity
VI. Limitations
- Identify any potential limitations of the research methodology and how they may impact the results and conclusions
VII. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the research methodology section
- Explain how the research methodology addresses the research question(s) and objectives
Research Methodology Types
Types of Research Methodology are as follows:
Quantitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. This type of research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Qualitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research. This approach can be particularly useful for studies that aim to explore complex phenomena and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Case Study Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and anthropology to gain a detailed understanding of a particular individual or group.
Action Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves a collaborative process between researchers and practitioners to identify and solve real-world problems. Action research is often used in education, healthcare, and social work.
Experimental Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effects on a dependent variable. Experimental research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Survey Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection of data from a sample of individuals using questionnaires or interviews. Survey research is often used to study attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
Grounded Theory Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the development of theories based on the data collected during the research process. Grounded theory is often used in sociology and anthropology to generate theories about social phenomena.
Research Methodology Example
An Example of Research Methodology could be the following:
Research Methodology for Investigating the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Reducing Symptoms of Depression in Adults
Introduction:
The aim of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. To achieve this objective, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach.
Research Design:
The study will follow a pre-test and post-test design with two groups: an experimental group receiving CBT and a control group receiving no intervention. The study will also include a qualitative component, in which semi-structured interviews will be conducted with a subset of participants to explore their experiences of receiving CBT.
Participants:
Participants will be recruited from community mental health clinics in the local area. The sample will consist of 100 adults aged 18-65 years old who meet the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental group or the control group.
Intervention :
The experimental group will receive 12 weekly sessions of CBT, each lasting 60 minutes. The intervention will be delivered by licensed mental health professionals who have been trained in CBT. The control group will receive no intervention during the study period.
Data Collection:
Quantitative data will be collected through the use of standardized measures such as the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). Data will be collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental group. The interviews will be conducted at the end of the intervention period, and will explore participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and mixed-model analyses of variance (ANOVA) to assess the effectiveness of the intervention. Qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis to identify common themes and patterns in participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Ethical Considerations:
This study will comply with ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects. Participants will provide informed consent before participating in the study, and their privacy and confidentiality will be protected throughout the study. Any adverse events or reactions will be reported and managed appropriately.
Data Management:
All data collected will be kept confidential and stored securely using password-protected databases. Identifying information will be removed from qualitative data transcripts to ensure participants’ anonymity.
Limitations:
One potential limitation of this study is that it only focuses on one type of psychotherapy, CBT, and may not generalize to other types of therapy or interventions. Another limitation is that the study will only include participants from community mental health clinics, which may not be representative of the general population.
Conclusion:
This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled trial and a mixed-methods approach, the study will provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the relationship between CBT and depression. The results of this study will have important implications for the development of effective treatments for depression in clinical settings.
How to Write Research Methodology
Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It’s an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a research methodology:
- Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it’s important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods.
- Describe your research design: Explain the overall approach you used to conduct research. This could be a qualitative or quantitative research design, experimental or non-experimental, case study or survey, etc. Discuss the advantages and limitations of the chosen design.
- Discuss your sample: Describe the participants or subjects you included in your study. Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used.
- Describe your data collection methods : Explain how you collected data from your participants. This could include surveys, interviews, observations, questionnaires, or experiments. Include details on how you obtained informed consent, how you administered the tools, and how you minimized the risk of bias.
- Explain your data analysis techniques: Describe the methods you used to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis. Explain how you dealt with missing data, outliers, and any other issues that arose during the analysis.
- Discuss the validity and reliability of your research : Explain how you ensured the validity and reliability of your study. This could include measures such as triangulation, member checking, peer review, or inter-coder reliability.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your research: Discuss any limitations of your study, including any potential threats to validity or generalizability. This helps readers understand the scope of your findings and how they might apply to other contexts.
- Provide a summary: End the methodology section by summarizing the methods and techniques you used to conduct your research. This provides a clear overview of your research methodology and helps readers understand the process you followed to arrive at your findings.
When to Write Research Methodology
Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the research project.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
The methodology should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be based on established research practices and standards. It is important to provide enough detail so that the reader can understand how the research was conducted and evaluate the validity of the results.
Applications of Research Methodology
Here are some of the applications of research methodology:
- To identify the research problem: Research methodology is used to identify the research problem, which is the first step in conducting any research.
- To design the research: Research methodology helps in designing the research by selecting the appropriate research method, research design, and sampling technique.
- To collect data: Research methodology provides a systematic approach to collect data from primary and secondary sources.
- To analyze data: Research methodology helps in analyzing the collected data using various statistical and non-statistical techniques.
- To test hypotheses: Research methodology provides a framework for testing hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on the analysis of data.
- To generalize findings: Research methodology helps in generalizing the findings of the research to the target population.
- To develop theories : Research methodology is used to develop new theories and modify existing theories based on the findings of the research.
- To evaluate programs and policies : Research methodology is used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies by collecting data and analyzing it.
- To improve decision-making: Research methodology helps in making informed decisions by providing reliable and valid data.
Purpose of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves several important purposes, including:
- To guide the research process: Research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting research. It helps researchers to plan their research, define their research questions, and select appropriate methods and techniques for collecting and analyzing data.
- To ensure research quality: Research methodology helps researchers to ensure that their research is rigorous, reliable, and valid. It provides guidelines for minimizing bias and error in data collection and analysis, and for ensuring that research findings are accurate and trustworthy.
- To replicate research: Research methodology provides a clear and detailed account of the research process, making it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings.
- To advance knowledge: Research methodology enables researchers to generate new knowledge and to contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. It provides a means for testing hypotheses, exploring new ideas, and discovering new insights.
- To inform decision-making: Research methodology provides evidence-based information that can inform policy and decision-making in a variety of fields, including medicine, public health, education, and business.
Advantages of Research Methodology
Research methodology has several advantages that make it a valuable tool for conducting research in various fields. Here are some of the key advantages of research methodology:
- Systematic and structured approach : Research methodology provides a systematic and structured approach to conducting research, which ensures that the research is conducted in a rigorous and comprehensive manner.
- Objectivity : Research methodology aims to ensure objectivity in the research process, which means that the research findings are based on evidence and not influenced by personal bias or subjective opinions.
- Replicability : Research methodology ensures that research can be replicated by other researchers, which is essential for validating research findings and ensuring their accuracy.
- Reliability : Research methodology aims to ensure that the research findings are reliable, which means that they are consistent and can be depended upon.
- Validity : Research methodology ensures that the research findings are valid, which means that they accurately reflect the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Efficiency : Research methodology provides a structured and efficient way of conducting research, which helps to save time and resources.
- Flexibility : Research methodology allows researchers to choose the most appropriate research methods and techniques based on the research question, data availability, and other relevant factors.
- Scope for innovation: Research methodology provides scope for innovation and creativity in designing research studies and developing new research techniques.
Research Methodology Vs Research Methods
| Research Methodology | Research Methods |
|---|---|
| Research methodology refers to the philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process. | refer to the techniques and procedures used to collect and analyze data. |
| It is concerned with the underlying principles and assumptions of research. | It is concerned with the practical aspects of research. |
| It provides a rationale for why certain research methods are used. | It determines the specific steps that will be taken to conduct research. |
| It is broader in scope and involves understanding the overall approach to research. | It is narrower in scope and focuses on specific techniques and tools used in research. |
| It is concerned with identifying research questions, defining the research problem, and formulating hypotheses. | It is concerned with collecting data, analyzing data, and interpreting results. |
| It is concerned with the validity and reliability of research. | It is concerned with the accuracy and precision of data. |
| It is concerned with the ethical considerations of research. | It is concerned with the practical considerations of research. |
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide

Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing...

Background of The Study – Examples and Writing...

Future Research – Thesis Guide

Problem Statement – Writing Guide, Examples and...

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact
Leave your feedback
- Copy URL https://www.pbs.org/newshour/politics/fact-checking-warnings-from-democrats-about-project-2025-and-donald-trump
Fact-checking warnings from Democrats about Project 2025 and Donald Trump
This fact check originally appeared on PolitiFact .
Project 2025 has a starring role in this week’s Democratic National Convention.
And it was front and center on Night 1.
WATCH: Hauling large copy of Project 2025, Michigan state Sen. McMorrow speaks at 2024 DNC
“This is Project 2025,” Michigan state Sen. Mallory McMorrow, D-Royal Oak, said as she laid a hardbound copy of the 900-page document on the lectern. “Over the next four nights, you are going to hear a lot about what is in this 900-page document. Why? Because this is the Republican blueprint for a second Trump term.”
Vice President Kamala Harris, the Democratic presidential nominee, has warned Americans about “Trump’s Project 2025” agenda — even though former President Donald Trump doesn’t claim the conservative presidential transition document.
“Donald Trump wants to take our country backward,” Harris said July 23 in Milwaukee. “He and his extreme Project 2025 agenda will weaken the middle class. Like, we know we got to take this seriously, and can you believe they put that thing in writing?”
Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz, Harris’ running mate, has joined in on the talking point.
“Don’t believe (Trump) when he’s playing dumb about this Project 2025. He knows exactly what it’ll do,” Walz said Aug. 9 in Glendale, Arizona.
Trump’s campaign has worked to build distance from the project, which the Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank, led with contributions from dozens of conservative groups.
Much of the plan calls for extensive executive-branch overhauls and draws on both long-standing conservative principles, such as tax cuts, and more recent culture war issues. It lays out recommendations for disbanding the Commerce and Education departments, eliminating certain climate protections and consolidating more power to the president.
Project 2025 offers a sweeping vision for a Republican-led executive branch, and some of its policies mirror Trump’s 2024 agenda, But Harris and her presidential campaign have at times gone too far in describing what the project calls for and how closely the plans overlap with Trump’s campaign.
PolitiFact researched Harris’ warnings about how the plan would affect reproductive rights, federal entitlement programs and education, just as we did for President Joe Biden’s Project 2025 rhetoric. Here’s what the project does and doesn’t call for, and how it squares with Trump’s positions.
Are Trump and Project 2025 connected?
To distance himself from Project 2025 amid the Democratic attacks, Trump wrote on Truth Social that he “knows nothing” about it and has “no idea” who is in charge of it. (CNN identified at least 140 former advisers from the Trump administration who have been involved.)
The Heritage Foundation sought contributions from more than 100 conservative organizations for its policy vision for the next Republican presidency, which was published in 2023.
Project 2025 is now winding down some of its policy operations, and director Paul Dans, a former Trump administration official, is stepping down, The Washington Post reported July 30. Trump campaign managers Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita denounced the document.
WATCH: A look at the Project 2025 plan to reshape government and Trump’s links to its authors
However, Project 2025 contributors include a number of high-ranking officials from Trump’s first administration, including former White House adviser Peter Navarro and former Housing and Urban Development Secretary Ben Carson.
A recently released recording of Russell Vought, a Project 2025 author and the former director of Trump’s Office of Management and Budget, showed Vought saying Trump’s “very supportive of what we do.” He said Trump was only distancing himself because Democrats were making a bogeyman out of the document.
Project 2025 wouldn’t ban abortion outright, but would curtail access
The Harris campaign shared a graphic on X that claimed “Trump’s Project 2025 plan for workers” would “go after birth control and ban abortion nationwide.”
The plan doesn’t call to ban abortion nationwide, though its recommendations could curtail some contraceptives and limit abortion access.
What’s known about Trump’s abortion agenda neither lines up with Harris’ description nor Project 2025’s wish list.
Project 2025 says the Department of Health and Human Services Department should “return to being known as the Department of Life by explicitly rejecting the notion that abortion is health care.”
It recommends that the Food and Drug Administration reverse its 2000 approval of mifepristone, the first pill taken in a two-drug regimen for a medication abortion. Medication is the most common form of abortion in the U.S. — accounting for around 63 percent in 2023.
If mifepristone were to remain approved, Project 2025 recommends new rules, such as cutting its use from 10 weeks into pregnancy to seven. It would have to be provided to patients in person — part of the group’s efforts to limit access to the drug by mail. In June, the U.S. Supreme Court rejected a legal challenge to mifepristone’s FDA approval over procedural grounds.
WATCH: Trump’s plans for health care and reproductive rights if he returns to White House The manual also calls for the Justice Department to enforce the 1873 Comstock Act on mifepristone, which bans the mailing of “obscene” materials. Abortion access supporters fear that a strict interpretation of the law could go further to ban mailing the materials used in procedural abortions, such as surgical instruments and equipment.
The plan proposes withholding federal money from states that don’t report to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention how many abortions take place within their borders. The plan also would prohibit abortion providers, such as Planned Parenthood, from receiving Medicaid funds. It also calls for the Department of Health and Human Services to ensure that the training of medical professionals, including doctors and nurses, omits abortion training.
The document says some forms of emergency contraception — particularly Ella, a pill that can be taken within five days of unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy — should be excluded from no-cost coverage. The Affordable Care Act requires most private health insurers to cover recommended preventive services, which involves a range of birth control methods, including emergency contraception.
Trump has recently said states should decide abortion regulations and that he wouldn’t block access to contraceptives. Trump said during his June 27 debate with Biden that he wouldn’t ban mifepristone after the Supreme Court “approved” it. But the court rejected the lawsuit based on standing, not the case’s merits. He has not weighed in on the Comstock Act or said whether he supports it being used to block abortion medication, or other kinds of abortions.
Project 2025 doesn’t call for cutting Social Security, but proposes some changes to Medicare
“When you read (Project 2025),” Harris told a crowd July 23 in Wisconsin, “you will see, Donald Trump intends to cut Social Security and Medicare.”
The Project 2025 document does not call for Social Security cuts. None of its 10 references to Social Security addresses plans for cutting the program.
Harris also misleads about Trump’s Social Security views.
In his earlier campaigns and before he was a politician, Trump said about a half-dozen times that he’s open to major overhauls of Social Security, including cuts and privatization. More recently, in a March 2024 CNBC interview, Trump said of entitlement programs such as Social Security, “There’s a lot you can do in terms of entitlements, in terms of cutting.” However, he quickly walked that statement back, and his CNBC comment stands at odds with essentially everything else Trump has said during the 2024 presidential campaign.
Trump’s campaign website says that not “a single penny” should be cut from Social Security. We rated Harris’ claim that Trump intends to cut Social Security Mostly False.
Project 2025 does propose changes to Medicare, including making Medicare Advantage, the private insurance offering in Medicare, the “default” enrollment option. Unlike Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage plans have provider networks and can also require prior authorization, meaning that the plan can approve or deny certain services. Original Medicare plans don’t have prior authorization requirements.
The manual also calls for repealing health policies enacted under Biden, such as the Inflation Reduction Act. The law enabled Medicare to negotiate with drugmakers for the first time in history, and recently resulted in an agreement with drug companies to lower the prices of 10 expensive prescriptions for Medicare enrollees.
Trump, however, has said repeatedly during the 2024 presidential campaign that he will not cut Medicare.
Project 2025 would eliminate the Education Department, which Trump supports
The Harris campaign said Project 2025 would “eliminate the U.S. Department of Education” — and that’s accurate. Project 2025 says federal education policy “should be limited and, ultimately, the federal Department of Education should be eliminated.” The plan scales back the federal government’s role in education policy and devolves the functions that remain to other agencies.
Aside from eliminating the department, the project also proposes scrapping the Biden administration’s Title IX revision, which prohibits discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. It also would let states opt out of federal education programs and calls for passing a federal parents’ bill of rights similar to ones passed in some Republican-led state legislatures.
Republicans, including Trump, have pledged to close the department, which gained its status in 1979 within Democratic President Jimmy Carter’s presidential Cabinet.
In one of his Agenda 47 policy videos, Trump promised to close the department and “to send all education work and needs back to the states.” Eliminating the department would have to go through Congress.
What Project 2025, Trump would do on overtime pay
In the graphic, the Harris campaign says Project 2025 allows “employers to stop paying workers for overtime work.”
The plan doesn’t call for banning overtime wages. It recommends changes to some Occupational Safety and Health Administration, or OSHA, regulations and to overtime rules. Some changes, if enacted, could result in some people losing overtime protections, experts told us.
The document proposes that the Labor Department maintain an overtime threshold “that does not punish businesses in lower-cost regions (e.g., the southeast United States).” This threshold is the amount of money executive, administrative or professional employees need to make for an employer to exempt them from overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act.
In 2019, the Trump’s administration finalized a rule that expanded overtime pay eligibility to most salaried workers earning less than about $35,568, which it said made about 1.3 million more workers eligible for overtime pay. The Trump-era threshold is high enough to cover most line workers in lower-cost regions, Project 2025 said.
The Biden administration raised that threshold to $43,888 beginning July 1, and that will rise to $58,656 on Jan. 1, 2025. That would grant overtime eligibility to about 4 million workers, the Labor Department said.
It’s unclear how many workers Project 2025’s proposal to return to the Trump-era overtime threshold in some parts of the country would affect, but experts said some would presumably lose the right to overtime wages.
Other overtime proposals in Project 2025’s plan include allowing some workers to choose to accumulate paid time off instead of overtime pay, or to work more hours in one week and fewer in the next, rather than receive overtime.
Trump’s past with overtime pay is complicated. In 2016, the Obama administration said it would raise the overtime to salaried workers earning less than $47,476 a year, about double the exemption level set in 2004 of $23,660 a year.
But when a judge blocked the Obama rule, the Trump administration didn’t challenge the court ruling. Instead it set its own overtime threshold, which raised the amount, but by less than Obama.
Support Provided By: Learn more
Educate your inbox
Subscribe to Here’s the Deal, our politics newsletter for analysis you won’t find anywhere else.
Thank you. Please check your inbox to confirm.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
A purpose statement clearly defines the objective of your qualitative or quantitative research. Learn how to create one through unique and real-world examples. ... You might be wondering how a research paper purpose statement is different from a problem statement, thesis statement or research question. In a problem statement, you identify the ...
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic. A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire ...
The purpose section of your dissertation could well be the most important paragraph you write during your academic career, and every word should be carefully selected. Think of it as the DNA of your dissertation. Everything else you write should emerge directly and clearly from your purpose statement. In turn, your purpose statement should ...
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. ... The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new ...
Purpose Statement. The purpose statement succinctly explains the objectives of the doctoral project or dissertation-in-practice. These objectives must directly address the problem. The purpose statement also identifies the project methodology and design. A problem and a missing piece in combination can lead to different objectives, and hence ...
Part 3 Section 1: Identifying Your Goals. Before you start writing your purpose statement, it's important to identify your goals. To do this, ask yourself the following questions: ... Here is an example of a purpose statement for a research paper: The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of social media on the mental health of ...
You will need a way to put your thoughts together in a logical, coherent manner. You may want to use the facts you have learned to create a narrative or to support an argument. And you may want to show the results of your research to your friends, your teachers, or even the editors of magazines and journals. Writing a research paper is an ideal ...
The purpose statement. The purpose statement is made up of three major components: (1) the motivation driving your dissertation; (2) the significance of the research you plan to carry out; and (3) the research questions you are going to address. Starting the first major chapter of your dissertation (usually Chapter One: Introduction), the purpose statement establishes the intent of your entire ...
The discussion section is often considered the most important part of your research paper because it: Most effectively demonstrates your ability as a researcher to think critically about an issue, to develop creative solutions to problems based upon a logical synthesis of the findings, and to formulate a deeper, more profound understanding of the research problem under investigation;
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study's overall validity and reliability.
The main heading of "Methods" should be centered, boldfaced, and capitalized. Subheadings within this section are left-aligned, boldfaced, and in title case. You can also add lower level headings within these subsections, as long as they follow APA heading styles. To structure your methods section, you can use the subheadings of ...
The purpose of the Discussion section is to place your findings in the research context and "to explain the meaning of the findings and why they are important, without appearing arrogant, condescending, or patronizing" . The structure of the first two moves is almost a mirror reflection of the one in the Introduction.
The discussion section provides an analysis and interpretation of the findings, compares them with previous studies, identifies limitations, and suggests future directions for research. This section combines information from the preceding parts of your paper into a coherent story. By this point, the reader already knows why you did your study ...
Methods section is a crucial part of a manuscript and emphasizes the reliability and validity of a research study. And knowing how to write the methods section of a research paper is the first step in mastering scientific writing. Read this article to understand the importance, purpose, and the best way to write the methods section of a research paper.
Formal Research Structure. These are the primary purposes for formal research: enter the discourse, or conversation, of other writers and scholars in your field. learn how others in your field use primary and secondary resources. find and understand raw data and information. For the formal academic research assignment, consider an ...
Developing a well-written research paper is an important step in completing a scientific study. This paper is where the principle investigator and co-authors report the purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions of the study. A key element of writing a research paper is to clearly and objectively report the study's findings in the Results section.
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper. Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions. The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is ...
The basic structure of a typical research paper includes Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. Each section addresses a different objective. what they think the results mean in Discussion. A substantial study will sometimes include a literature review section which discusses previous works on the topic.
Step 1: Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will ...
The discussion section is one of the final parts of a research paper, in which an author describes, analyzes, and interprets their findings. They explain the significance of those results and tie everything back to the research question(s). In this handout, you will find a description of what a discussion section does, explanations of how to ...
1. Introduction. The Introduction section is one of the most important sections of a research paper. The introduction section should start with a brief outline of the topic and then explain the nature of the problem at hand and why it is crucial to resolve this issue. This section should contain a literature review that provides relevant ...
Discussion Section. The overall purpose of a research paper's discussion section is to evaluate and interpret results, while explaining both the implications and limitations of your findings. Per APA (2020) guidelines, this section requires you to "examine, interpret, and qualify the results and draw inferences and conclusions from them ...
This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods. Describe your research design: ... The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research ...
Vice President Kamala Harris, the Democratic presidential nominee, has warned Americans about "Trump's Project 2025" agenda — even though former President Donald Trump doesn't claim the ...