
Presentation Tips

How to Manage Your Time During a Presentation
You’ve been offered a 60-minute timeslot to present to a group of stakeholders but have 90 minutes of content you want to cover — or worse yet, only 30 minutes. How do you make your message resonate with your audience while not feeling rushed or pressed for time? We offer our best tips for managing your time during a presentation while keeping your audience engaged and talking points heard.
Rehearse and then rehearse again
At a minimum, you should be practicing your presentation between five and 10 times. The goal is not to repeat the same dialogue word for word each time but rather find ways to say something differently or more succinctly each time. You’ll want to not only figure out how long each slide will take to cover, but also when and where to pivot if things don’t go as planned. Stick to the rule of thirds: Spend one-third of your time planning, one-third designing, and one-third rehearsing.
Be ready to cut it short
Life happens, especially when others are in control. Maybe participants are late getting back from a session break, the presenter before you runs long, or the inevitable technical issue happens. If you outline your presentation with key points and sub-points, you should be able to skip along more quickly by only covering the key points when short on time. What’s more, it’s better to engage your audience and encourage questions throughout than finish the presentation. By coming across as the expert in the room, you open the door to scheduling time at a later date with those who want to discuss points not covered during the allotted time.
Arrive early
The best way to avoid the unavoidable is to show up early to your designated location so setup doesn’t factor into your presentation time, and if it doesn’t take that long, give that time to the next presenter for their setup. Simply put, if you’re arriving or finishing on time, you’re running late. Plus, the added bonus of arriving early is you get to know your audience a little bit and find out what’s at the top of their mind. These are golden moments you can integrate into your presentation.
Be realistic
During rehearsal, you’ll quickly get a sense if your presentation is too long or too short. Be realistic about your personal speaking habits. Do you tend to speed up when you’re actually presenting? Do you pause a lot? Do you know if this audience loves to ask questions? Consider those real-world situations as you try to edit your deck. Some extra tips: Don’t linger on a slide for too long; make your point and move on to keep your energy high. Along the same lines, don’t try and cram everything you know into the presentation. Stick to your key points and anecdotes to make sure people are really absorbing the content. Think quality, not quantity.
Never count on a clock being in the room to manage your time in the moment of your presentation. Have your phone (silenced, of course) on the podium ready to glance at, appoint someone in the back of the room to give you cues when you are running out of time, or even discretely glance at your watch while taking a sip of water. Even though you’ve rehearsed enough to know how the time will pan out, taking an obvious break to check the time can be a big distraction.
What time constraints do you run into when making a presentation?

Ace the Presentation

How to Effectively Manage Time During a Presentation? Short and Long Ones!
Slides are one of the best ways to engage an audience and nail a presentation. Nowadays, people use the most efficient and practical skills to make the slides clear, easy to understand. However, most people struggle to plan and manage time in their presentations.
How Many Slides are Suitable for Finishing a Presentation on Time?
The general rule says 1 to 2 slides per minute. However, it is critical to note that the presentation’s number of slides will vary according to the topic complexity, audience, available time, presentation structure and format, and goal. Good planning, rehearsal, and delivery skills are essential!
To be more specific, if you have too many slides in a presentation at the range of 3 to 15 minutes, you will end up confusing your audience or spending a significant part of your time explaining the slides. It does not mean you have to prepare a lot of information and squeeze it into few slides, and the best practice is to summarize your content to understand it easily.
From 25 minutes to 60 minutes, you can make a considerable number of slides. Some experts recommend 1 to 2 slides per minute, but as I said before, it will depend on the topic. Imagine that one of your slides contains graphs about some work you have been doing that can take more than 2 minutes, and it is important to explain it in detail to the audience.
It all starts with planning, researching, organizing all the collected data, prioritizing your key points, and making a structure. After this exercise, it will be easier to know how many slides you will have according to your given time.
To sum this up, there is no exact rule to set a number of slides for a given time frame, and it will vary according to the topic, your research, and your presentation skills. All you have to do is to balance the slides with your speech and time.
How many Slides for a 3-minute Presentation?
For a 3-minute presentation, the presenter should use four slides. Depending on how the slides are structured, 15 seconds to 2 minutes can be spent on each slide.
What really matters is not the amount of the slides but the quality. You can make three powerful slides and nail your presentation or make 5 with too much content and ending up having a boring presentation.
A good practice for a 3 minutes presentation is to keep it clean and straightforward. Keep in mind that slides are more engaging with visuals rather than texts. And on your speech, be as brief as possible, make a 15 to 20 seconds introduction, and do the same on the conclusion.
How many Slides for a 5-minute Presentation?
Five minutes is enough time to deliver your message and engage your audience with content that is straight to the point. The only thing you need to do is keep in mind that every second of your time counts a lot for your presentation.
How many Slides for a 10-minute Presentation?
The Rule of Thumb for a 10-minute presentation is having 10-12 slides. Presenters with good skills use up to 30 seconds per slide to keep it nice and engaging. This time frame is suitable for elaborately introducing the subject or topic, diving deep into it, and highlighting the key points.
According to your topic, you can even make eight slides considering the fact that slides are only the guide of your presentation. That is why it is essential to make an excellent structure to organize your content on the slides properly; this will help you to put aside unnecessary data and focus only on what is essential for the audience.
How many Slides for a 20-minute Presentation?
According to Guy Kawasaki , a 20-minute presentation should have ten slides where each slide utilizes a 30 point font. Using this rule of 10/20/30, the speaker would spend up to 1 minute per slide, which gives time for even allowing 1 or 2 questions from the audience.
To structure a 20 minutes presentation using the rule of 10/20/30 from Guy Kawasaki , you have to use the first slide to introduce your subject, case study, or others, and from the second slide, start diving deep until you get to the conclusion.
In some cases, each slide has a different theme, and you will need to approach them differently. Having different themes per slide will require you to summarize each slide’s content in under a minute.
Although the Rule of Guy Kawasaki is suitable for a 20-minute presentation, you can set your own number of slides according to your subject and how much time you spend on a single slide as long as you deliver the message properly and engage your audience.
How many Slides for a 25-minute Presentation?
For a 25-minute presentation, the general rule is to use 20 to 30 slides. By spending up to two minutes per slide and focusing on the main subject, the speaker can keep the audience engaged for this period of time.
Kawasaki believes that a human being can comprehend at least ten concepts in a meeting. In other words, you have to include in your topic or subject up to ten themes to be discussed. Any More than that can make your audience get confused or bored.
In this given time frame, you now have the opportunity to interact more with the audience, start with a quote, let them raise some clarification questions, and get more involved with them.
How many Slides for a 30-minute Presentation?
Experts recommend 30 to 40 slides to make a memorable presentation. With 30 minutes, the presenter has more options compared to when the given time frame is short. Consider making the content as straightforward as possible. Also, make two paragraphs per slide at the most.
This technique will allow the audience to read all the information on the slide easily and quickly and move to the next one alongside you. If you add too much content on one slide, the audience will likely read something that you are not explaining yet or the opposite.
But you can make more than 40 slides and still have a memorable presentation in just 30 minutes, and I will explain to you how. Well, if you want your audience to understand clearly each content of your slide, make it one paragraph or one sentence, and use more visuals.
Using this method, you will spend 1-2 seconds per slide, and the audience will understand way better seeing the visual (which counts more than text). The explanation is gradual from the beginning to the end.
How many Slides for a 45-minute presentation?
As a general rule, for a 45-minute presentation, between 20 and 50 slides would grant a memorable presentation. Spending 1-2 minutes per slide, the speaker will have time to make a great introduction, interact more with the audience and have a questions and answers session.
A 45-minutes presentation is in the range of long times ones, and in these cases, you have to use the slides very carefully, making them proportional to your presentation time. Consider having a wristwatch to control your time.
A good practice is to use the slides only to guide your speech during the presentation, but you will need to master them. Rehearse the most important of each slide to make sure you spend the right time, or even less. This time management will give you an advantage because you will have enough time to make a great conclusion.
How many Slides for an hour Presentation?
Experts recommend 30 to 60 slides for a 60-minutes presentation. This period of time gives the speaker two main options: summarize the content in 30 slides or make a structure that allows one theme per slide. These two options also give more time to interact with the audience make a great introduction and conclusion.
Both of them are OK. But there are aspects that you have to consider; if you are preparing few slides, you will need to train how to summarize content to make sure you don’t spend too much time explaining all the points or having your audience stuck on reading your slide.
And if you are planning to make one theme per slide to facilitate the understanding to the audience, make sure you spend 30 seconds at the most. But also consider having black screen slides to make pauses or small breaks and entertain or reengage your audience.
How many Slides for a 90-minute Presentation?
A 90-minutes presentation should have not more than 60 slides. In this situation, the speaker will need to know how to keep time on presentations. Experts recommend up to 2 minutes per slide, but depending on how the presentation is flowing, spending more than 2 minutes per slide is possible.
If you fail to make these pauses to double-check if the audience is on the same page with you, you will be running a risk of going back from almost the end of the slides to the first ones to explain something that the audience did not get very well.
How many Slides for a two-hour presentation?
A two-hour presentation would need 60-80 slides to deliver the message memorably. Some experts recommend one theme per slide to make it clear and easily understandable. Keep in mind that a presentation this long requires careful planning and a very well-organized structure.
Generally, a presentation with more than one hour of duration is for professional speakers who can deal with time management. The best way to not have your audience boring is to use the method of one idea per slide; it will make them easily understand each part of your content.
How many Slides for 2+ hours presentations?
Presentations with more than two hours should have not more than 80 slides. Long presentations with over 2 hours, the speaker can organize the information in order to spend 2-3 minutes per slide.
120+ minutes is considered an extended time frame; a good practice is to keep the slides brief and clean to ensure your audience won’t get exhausted.
What are the skills needed to Deliver Long Presentations or Speeches?
For long presentations, several skills are required to ensure successful delivery, such as:
- Time management;
- Engaging the audience
- Solid posture
- Good eye contact
- Controlling your voice, and more.
All these skills will keep your audience engaged and entertained, and make sure you reserve 15-20 minutes for questions and answers after a long presentation or speech.
How to keep time in your presentation?
First of all, to have complete control of your time on stage, you have to write the schedule of time you will spend on each part of your presentation, something like setting time for your opening, how long time you will spend on the introduction, how long time you reserve for questions and answers, etc.
Make sure you start your presentation on time. If you fail this step, then everything that comes ahead may also delay and end the presentation after the scheduled time. You also need to plan how long your speech will take and have a clock to control it.
Planning is also crucial to keep time on your presentation. The main thing in the plan to deliver your message is the structure of your content. A good structure will allow you to know how much time you will spend on each point.
I have an excellent article with a guide for outlining your speech , which should help you nail this part of the process. A good speech outline is key in managing presentation time.
And last but not least, you need to rehearse before you go on stage. It will allow you to know how much time you need for the presentation and practice to see if you need to remove or add something to your presentation to make it perfect.
Why do people usually fail to finish a presentation within the stipulated time?
Generally, people fail to finish a presentation on time because they do not make a good plan, underestimate rehearsing, and fail at an impromptu delivery attempt at the last minute. What commonly happens is that people make too many slides and fail to go from one to another on time. The rule of thumb says that 1-2 minutes per slide is enough using standards.
Another session that makes speakers fail to finish the presentation in time is the question and answers. This mistake happens when the speaker does not practice enough or predict questions that may come and end up thinking about the answer when the question is raised.
Not setting time for each session of your presentation also makes you not finish on time. This mistake will cause you to take longer at one point or another, especially if you don’t have a clock to keep track of the time.
How to keep your Presentation Brief and Clear
To keep a presentation brief and clear, organize your content to be only one theme per slide. To be more specific, consider having one paragraph or idea per slide, one that is concise, straightforward, and should also include minimalist visuals.
The design is also essential to help you get a clean design. Choose a layout that comfortably suits your text and image. Another detail is the color, which has to be neutral to help the reader focus on the content only.
For More Tips on Designing and Nailing a Presentation, open the recommended articles below.
Designing a Killer Presentation in 8 Steps

Planning and performing a presentation that meets expectations and involves the public requires a lot of care. The details involved in holding a talk will be super important to ensure her success and approval from those who participated. Therefore, we have prepared a post with a few crucial steps that you should follow to organize…
What Makes a Great Presenter? 9 Key Qualities to Look for!

Want to Stand Out? 15 Key Tips for an Awesome Presentation

In conclusion, the number of slides a presentation should have for a given time depends on who is presenting and the topic or subject. And also, it varies according to the methods that you use to deliver your message. As long as it reaches the audience properly and on time, the number of slides should be the least of your concerns.
But you can follow the standards that some experts recommend for a presentation from 3 minutes to 120+ minutes. For example, Guy Kawasaki recommends the rule of 10/20/30 for a 20 minutes presentation. This rule of thumb allows you to have ten slides to be presented in 20 minutes, and the font should be 30 points.
This example shows that you can follow the standards and still have a successful presentation. the main thing you have to do, is a good planning, a good structure, and make your content brief and clear, that will help them understand and enjoy your presentation
References and Further Reading
How to Create a Killer 5-Minute Presentation (hubspot.com)
How Many Slides For A Whatever-Minute Presentation? (slidecow.com)
https://www.soappresentations.com/how-many-slides-should-be-used-for-a-60-minute-presentation/
The ideal number of slides for an hour-long presentation, and other thoughts on preparing slides | I’d Rather Be Writing Blog (idratherbewriting.com)
Presentation Slide Counts (duarte.com)
3 Ways to Choose the Right Number of Slides for a Powerpoint Presentation (wikihow.com)
Brevity, Clarity and Wit: 10 Commandments for a 10-Minute Talk | Cath Lab Digest | HMP Global (hmpgloballearningnetwork.com)
How Many Slides to Use For a 5, 10, 15+ Minute Presentation (tutsplus.com)
The 10/20/30 Rule of PowerPoint – Guy Kawasaki
How Many Slides to Use in a Presentation? 5 Tips | Design Shack
Similar Posts

How to bring up salary during the job Interview? (And when?)
If bringing up the subject of salary poses a problem for you during an interview, tell yourself that you are one of the 95% of candidates embarrassed by the question. There is a good chance that your interlocutor has already experienced what you feel… When and how to broach the subject of remuneration during a…

17 Ways to Help Your Child Develop Public Speaking Skills (Public Speaking Tips for Kids)
Speaking in public can be nerve-wracking for a lot of people, and is one area many people shy away from a lot. But if this important skill can be learned at a very early age, kids stand to gain a lot of benefits from it that can serve them well into adulthood. Therefore, today we…

Extemporaneous Presentation: Definition and Actionable tips
There are several forms or methods of speech delivery out there and it can be impromptu (with no warning, more improvisation required), or the most common case: extemporaneous presentations. EXTEMPORANEOUS PRESENTATION DEFINITION We need to define this properly and make sure people don’t get confused here. Because from a literal sense extemporaneous and impromptu have…

3 KEY Things For Delivering a Successful Speech
Have you ever had to give a speech and have no idea how to direct their thoughts or start talking? In this article, we will discuss in a straightforward way how to work the oratory to develop the ability to speak well with different audiences, arousing their attention, respect, and provoking reflections. Speeches are moments…

How to Give An Effective Special Occasion Speech? 2 Main Tips
Almost every now and then we attend special occasions, some organized by our friends, associates, colleagues, family members and some by ourselves. Most times, these special occasions would require us or other colleagues to deliver the so-called ‘special occasion speech’ or sometimes, or we might need to help a friend write a speech. When we…

A 9 Step Guide to Using Humor in Speeches
During a presentation, small touches of humor, added to the main subject, can attract and captivate your audience, helping, including forming ideas of people who are participating. Compelling speakers don’t tell jokes to get laughs. Instead, they use humor to illustrate their message; in this article, we will give you some tips to help you…

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.
- Speech Writing
- Delivery Techniques
- PowerPoint & Visuals
- Speaker Habits
- Speaker Resources
Speech Critiques
- Book Reviews
- Browse Articles
- ALL Articles
- Learn About Us
- About Six Minutes
- Meet Our Authors
- Write for Us
- Advertise With Us
Presentation Timing: 5 Tips to Stay On Time and Avoid Audience Wrath
Were you happy about it? Or were you mad that they now put you behind for your next appointment? Or did you leave before they wrapped up?
In this article, we examine the importance of finishing on time and give 5 tips for staying within your time constraints.
Is finishing your presentation on time important?
In most situations, yes!
Always assume that your audience is busy (because they are).
Always assume that could have chosen other places to be (because they could have).
Always assume that they have something planned immediately after you finish (because they usually do).
Audiences get uneasy if you are approaching your time limit and you aren’t wrapping up.
- They start to consider walking out .
- They start to get nervous thinking about their next appointment , and how they may be late.
- They start wishing you’d wrap it up already.
- Most importantly, they stop listening to you!
Not only do you lose credibility with your audience and risk offending them, but you also lose the opportunity to make a strong conclusion because they either aren’t listening or they aren’t in the room!
Is it better to end early, or right on time?
If it’s really bad to finish over time, then one might assume that you should always try to end well under your allowed time. However, that’s not always good either.
If you finish your presentation considerably under time (e.g. 20 minutes early in a presentation scheduled for one hour), your audience may feel cheated, particularly if they paid to listen to you speak. They may feel that you promised 60 minutes of value, but only delivered 40.
For this reason, one safe rule of thumb is to speak for between 90-100% of your allowed time . So, if your presentation is planned for 60 minutes, you should speak at least 54 (or 55 for a nice round number). This ensures that your audience doesn’t “feel cheated”, but also ensures that you don’t go over time.
There are all sorts of exceptions to the above rule of thumb, so use your judgement and do what makes sense in your situation.
5 Steps To Keep Your Presentation Within Time
It’s really not that hard to finish your presentation on time. Just follow these five simple steps:
#1 — Know Your Allowed Time
Have you ever heard a speaker walking away from a venue muttering: “I thought I had longer”?
This is the result of poor communication between the speaker and the event organizer. Both the speaker and the event organizer end up looking bad in this scenario.
Make sure you are always aware of how long you have to speak. Verify with the event organizer before the event.
#2 — Plan Your Content and Edit as Necessary
For many speakers, the problem is not knowing how much time the audience is giving them. The problem is being unreasonable with how much they can say within that allotted time.
Most people overestimate how much material they can adequately cover within a given time. They want to “share everything” and “leave nothing back”. On the other hand, the wise presenter develops strong self-awareness about how long it takes to effectively deliver their message.
When you are planning, also consider:
- Q&A : Allow time for audience questions, either within your presentation or at the end.
- Activities : Allow adequate time for any planning audience activities or exercises. One of my challenges is that I tend to underestimate how long it takes to explain an activity and “break into groups” before the exercise even starts.
- Breaks : For longer presentations, budget time for breaks for stretching, bathroom visits, coffee, or meals. This all comes out of your allotted time. In a typical full-day (8-hour) training course, for example, you might only have 6 hours of instruction once you subtract out all of the breaks.
Cut mercilessly to make sure the material you intend to deliver can be delivered within your time constraints. It’s better to present the appropriate amount at a pace which the audience can absorb rather than whizzing through too much material so the audience grasps nothing.
#3 — Rehearse Effectively
Until you gain experience as a speaker, you may not be able to accurately gauge how much content fits within a given time. For example, how many pages would you write if delivering a 30 minute commencement address? How many case studies can you cover in a lunch-time seminar?
“ If you go over time while rehearsing, you’ve got to cut material. ”
The best way to measure how long it will take is to time yourself while you rehearse effectively:
- Rehearse standing up and speaking out loud . Don’t fall into the trap of thinking that you can just “whisper” your way through your slides while sitting in front of your computer. Your pace will be different while standing.
- Speak to a test audience , even if all you can arrange is one person. This eliminates the tendency to “practice within yourself” as some speakers do while rehearsing. Just one audience member forces you to make eye contact and look for audience feedback. It also simulates a bit of the pressure you may feel with a real audience. You can also get valuable feedback by asking “How was my pace? Did I go too fast?”
- Make it as close to the real thing as possible . If you’ll be using a presentation remote to advance your slides, then rehearse with one. If you’ll be moving around in the “real presentation”, then do so as you rehearse. If you can rehearse in the room where you’ll be presenting, do so. The more closely you can mimic the real thing, the better your time estimate will be.
- Make it a dress rehearsal . If I’m planning to wear a suit when presenting, I like to rehearse in one. For me, the act of dressing up creates the same nervous energy and tends to give me more accurate timing.
Rehearsing in this way allows you to accurately time your presentation under close-to-real circumstances. If you go over time while rehearsing, you’ve got to cut material.
#4 — Start on Time
How many times have you seen a presenter ask for “just 5 more minutes” at the end of a one-hour presentation, despite having started ten minutes late?
Do everything in your power to start on time. Arrive early, sort out your technology, and make sure everything is set to go when your time starts. Don’t waste a moment.
Your exact start time isn’t always within your control. For example, I know of one company where “lunch-time seminars” always start at 12:15. If you are invited to speak in this forum, you’ve got to know that. A thorough discussion with the event organizer should reveal this.
#5 — Measure Your Progress and Adjust
For short speeches (say, under 15 minutes), you can probably just launch into it and hit your end time target within reason (assuming you have rehearsed it).
For longer presentations, however, you can use a more strategic approach:
- As you rehearse your content, note how long it takes for each “block” of your presentation. (Get someone to time you if necessary.)
- 12:05 – Start presentation
- 12:15 – Introduction and case study introduced
- 12:30 – Case study and lessons learned complete
- 12:50 – Live demonstration complete
- 12:58 – Q&A complete. Applause.
- Write down these targets and have them with you as you present, perhaps on a small notepad by your water. (I do it with red pen and big letters.)
- As you reach the end of each “block”, check the clock . If you are running behind, you can adjust your pace. For example, if you are starting the live demonstration at 12:35, then you know you are 5 minutes behind, and you’ll have to cut planned material to “catch up.”
- If necessary, recruit an assistant with a watch to help you monitor your intermediate targets.
Speaking over your allowed time is disrespectful and will annoy at least some people in your audience. It’s a privilege to have their attention, whether it’s for 5 minutes or 5 hours. Don’t abuse it! End on time — every time.
Share Your Stories
Do you have presentation timing anecdotes to share? Either when you were speaking, or when you were in the audience?
Please share in the comments . We love to hear from readers.
Please share this...
This is one of many public speaking articles featured on Six Minutes . Subscribe to Six Minutes for free to receive future articles.
Image credit: Retro Clock by FreeImages.com/zbyszek80 ( license )
Add a Comment Cancel reply
E-Mail (hidden)
Subscribe - It's Free!
Similar articles you may like....
- The 7 Deadly Sins of Public Speaking
- How to Use Notes in a Speech: A Guide for Speakers
- How to be a Confident Speaker with a Speech Disorder
- What is an Ignite presentation, and why should you try it?
- 10 Presentation Bad Habits My College Students – And You – Must UN-Learn (Part 2)
- 10 Presentation Bad Habits My College Students – And You – Must UN-Learn

Find More Articles Tagged:
We’ve all been there. The speaker speaks for far longer than anyone expects and as an audience member you just sit there thinking “when will this end?” I’ve seen it time after time at public speaking clubs in particular.
It’s worth reinforcing that when you are speaking in front of an audience, it will always take longer to cover the same material adequately. That extra time is necessary to let the message sink in with a real, live audience. Rehearsal time can be misleading, so don’t get caught out!
I would love to share this with clients. Your 5 minutes is not the same as mine, just make sure you finish on time. Great read!
this is great advise ur really smart dude keep doing you
Recent Tweets
5 Tips to Stay On Time and Avoid Audience Wrath http://t.co/6es9Vmug — Presenting Away Dec 19th, 2012
Presentation timing: 5 tips to avoid audience wrath http://t.co/Dw4Je0rz — Diane Dec 21st, 2012
recommend reading for presenters at conferences http://t.co/LfnlikwXp6 — @tweetsimon Jul 7th, 2014
@VMart speaks the truth! 5 tips to keep yourself on time and your audience happy. http://t.co/SWeQFQEcDE #AFS145 https://t.co/bxbn7wDSjQ — @pseanmc Aug 19th, 2015
.@6minutes Andrew! I just read your article on speech timing, so great! Also giving it to my students to read ~ https://t.co/JzheERLxNz — @JacksonHoleRose Oct 25th, 2015
Presentation Timing: 5 Tips to Stay On Time and Avoid Audience Wrath https://t.co/qjXmwcjwZ4 by @6minutes — Sleiman Skaf (@SleimanSkaf) Apr 20th, 2016
#TuesdayTips Good tips by @6minutes about keeping your presentation within the allotted time. https://t.co/Rk2GtzReRv — PitchVantage (@pitchvantage) Jul 26th, 2016
There is nothing worse than when speakers go on and on and on . . . https://t.co/XZVnTmNvHO — @speakers4change Oct 5th, 2016
#DMCIT Might be of interest for the upcoming presentations. https://t.co/oeGhqqc5F8 — @Zeet66 Nov 1st, 2016
Of course, you don’t want to go way under time, but, in my opinion, it’s much better than going over time. I like… https://t.co/4FPFvPxB6R — @justineldees Oct 28th, 2018
Featured Articles
- Majora Carter (TED, 2006) Energy, Passion, Speaking Rate
- Hans Rosling (TED, 2006) 6 Techniques to Present Data
- J.A. Gamache (Toastmasters, 2007) Gestures, Prop, Writing
- Steve Jobs (Stanford, 2005) Figures of speech, rule of three
- Al Gore (TED, 2006) Humor, audience interaction
- Dick Hardt (OSCON, 2005) Lessig Method of Presentation
Books We Recommend
Six Minutes Copyright © 2007-2022 All Rights Reserved.
Read our permissions policy , privacy policy , or disclosure policy .
Comments? Questions? Contact us .
Managing Time Effectively in Your Presentation: 4 Expert Tips – How to Stay on Track!
We’ve all been there. Halfway through a presentation, you suddenly realise that you don‘t have enough time left! This despite the fact that you‘ve practiced the presentation again and again and have always come in under time.
Presentations are often time-limited. In particular, pitch presentations, and occasions where there are several speakers, generally have rigid time limits that you must stick to. This article will give you four great tips for managing time effectively.
How to keep your presentation to time – 4 expert tips
Here are our four best tips for managing time during your presentation effectively – why not give them a try?
Tip #1: Prepare thoroughly
You need to start thinking about the timing of your presentation from the beginning of your preparation . One way of doing this is to take a sheet of paper and sketch out your slides in sequence , making a note of the maximum presentation time you anticipate for each slide.
This helps you see which slides are essential, and which can be left out. You should end up with a coherent narrative line, where each slide adds to your argument.
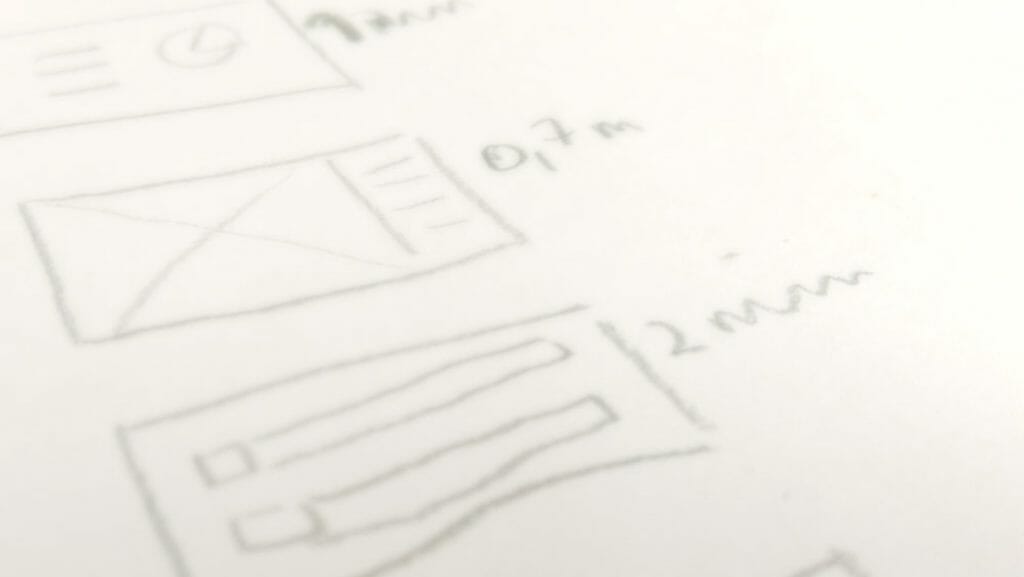

How much speaking time should you allow per slide?
It would be great if we could calculate the speaking time per slide , adding up to the time you’re allowed for your presentation, thus solving the problem of time management. Unfortunately, there aren’t any hard and fast rules. The approximate speaking time per slide depends on the content of that slide and your presentation topic.
As a rule, however, aim to speak for no more than 3-4 minutes per slide. In general, keep it shorter rather than too long – this keeps your audience attentive.
Bonus tip: Keep in mind that your presentation will almost always take longer than when you rehearse it at home beforehand. This is because you are interacting with the audience and follow-up questions are asked. Allow about 20%-40% more time for the actual presentation.
Tip #2: Look at your subject from an outsider’s perspective, and present it accordingly
Think like an outsider. Instead of considering the individual points of your presentation from your own point of view, imagine how long it would take someone without your prior knowledge and background to understand them . Use the latter times as a guide. This way you allow as much room as possible for questions.
You know yourself and your strengths best. When is your energy level at its highest? Do you start strong or do you need a few minutes to get into flow? Tailor your presentation accordingly. Who is your audience and where are you going to give your presentation?
If you are presenting on the evening of the last day of a conference, for example, you need to be prepared for a tired audience. If you are introducing a conference, you may need to clarify terms first. Also, plan your presentation time carefully in light of your surroundings. T hat way, you won’t run out of time or breath.
As a general rule, make sure you meet the needs of your audience . Ask yourself what points you really want to include in your presentation to get your core message across. You can find further tips in our short article “ Focus on audience’s needs “.
Tip #3: Use PowerPoint Speaker View
Another simple trick you can use to keep your presentation time is the PowerPoint Speaker View. This handy PowerPoint feature offers lots of helpful options. For example, you could set it to show the next slide along in your presentation, or display notes that only you, and not your audience, can see.
A really useful feature here is the timer. It shows how much time of your presentation has already passed, allowing you to keep the presentation on time.
We go through how to set the timer in our article “ PowerPoint Presenter View” .
Tip #4: Use shortcuts for PowerPoint for managing time better!
With the right keyboard shortcuts, you can save a lot of time, whether in PowerPoint presentations or generally when working on the computer. The best thing is: they are easy to learn and work on every computer! You can find out exactly which shortcuts there are and how to get the most out of working with shortcuts in our blog post on “ Shortcuts .”
With the help of shortcuts, you can work much more efficiently in the future and invest more time in presenting itself . Not only you, but also your audience will thank you!
Extra Tip: Use add-ins from PresentationLoad!
Our customers often ask whether there is an add-in available that makes it possible to display time periods, countdowns or the current time in presentations . We listened, and developed such an add-in ourselves! With the help of our revolutionary time presentation tool, you can now incorporate time management and efficiency into your next presentation in a professional way.
Until now, the only way to get an overview of time in PowerPoint presentations was to use PowerPoint Speaker View. Unfortunately, this function is only visible to the presenter. That’s why our new Dynamic Time Add-In tool equips your current PowerPoint version with the features needed to show time, date and time periods in the way that best suits your presentation.
The add-in is compatible with:
- Microsoft Office 2010 (32bit & 64bit)
- Microsoft Office 2013 (32bit & 64bit)
- Windows 7 (32bit & 64bit)
- Windows 8.1 (32bit & 64bit)
Four for one: time, date, counter and countdown
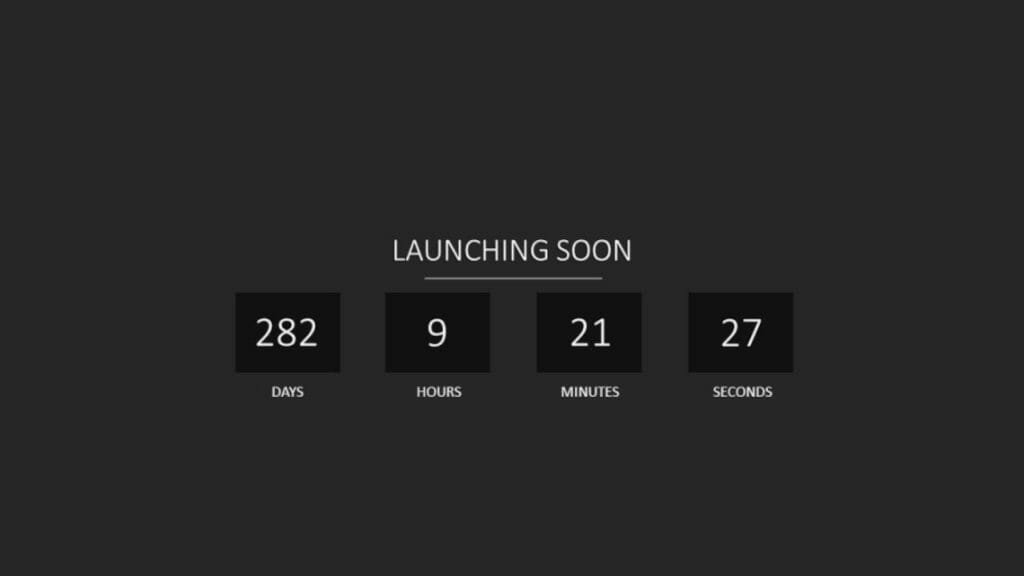
Whether it’s a presentation, a lecture, self-running info screens, or trade fair presentations, showing the time, whether faded in or as a countdown, can be a great tool . For example, you could announce an upcoming deadline for an important product or the launch of your website by fading in a countdown.
By doing so, you not only add interest to your presentation, but also have the use of a unique tool known only to a few. To help you get started, we provide a short tutorial below, to help get you up to speed. Follow the simple instructions to get started!
Just install and go: instructions
The add-in is installed by executing the downloaded file (admin rights may be required) and is automatically integrated within your PowerPoint window as a tab.
To activate the range of functions, click the DynamicElements tab. Then select the Time button to open the Time Panel options window. The editing interface for Dynamic Time now appears on the right of the screen.
As soon as you create a new textbox and select a mode in the Time Panel, it will automatically include the date (or time/countdown) you want.
Any number of text fields can be assigned with time and date display. To do this, create a text field in the conventional way, then activate it via the Time Panel (on the right of the page) by assigning a new mode (the default is none).
We’ve put in four modes (functions with setting options) for this purpose:
- Clock for the time display
- Date to show the date
- Counter to display a counter
- Countdown to see a countdown
When choosing time- or date-based displays, you need to select a time zone if the one you want is not the default.
You can display any time or date using a single field, or split it into components (e.g. the time in hours, minutes and seconds).
To see what the dynamic element looks like once inserted, switch to presentation mode via the Slide Show tab and choose From current slide .
(For further instructions, please see the ReadMeFirst file included in the add-in).
Possible uses:
- Dynamic time display
- Show the current time (including seconds) on your PowerPoint slides during the presentation:

- Show a start screen with live time in digital format (for your event, lecture, self-running presentation/info screen):

- Display a world clock with different time zones. By setting different time zones you can, for example, display an individualized company world clock, including all your company locations:

Display the date in different formats . The days of the week can be automatically included if so desired. Combine the date and time for attractive calendar pages!

3. Dynamic Counter
Show the time which has elapsed since a specified point in time (giving the date and time). For example, show the time since the launch of a new product or of your website, the founding of your company or the opening of a particular location.
4. Dynamic Countdown
Show the time remaining until a particular event (in days, hours, minutes and seconds).
Click here to get to the add-in: Download
To sum up: Managing time in presentations the right way
The chances are that your next presentation is coming up. Using our expert tips, you can plan and achieve sticking to the time you’re given for your presentation . You should find it far easier to manage that time effectively.
If you have any further questions about managing presentation time, or indeed about PowerPoint in general, do feel free to email us at [email protected] . We’re always glad to help!
Looking for professionally designed slide templates for your presentation? Take a look around our store! We have a fabulous range of slides for download covering the business topics you need! ► Shop
You might also be interested in the following articles:
- PowerPoint Presenter View
- Concentrate on Audience’s Needs
- Preparing Presentatios: 11 tips
- Target Group Analysis
Share this post
- share
- save

Design Thinking: Problem Solving with a Difference

Why Corporate Mission Statements Are So Important

7 Tips & Learnings from the Apple Keynote
- Rehearse timings for a slide show Video
- Edit slide timings Video

Edit slide timings

If you have recorded slide timings and find that there are a couple of timings you want to tweak, you don’t need to re-record the whole show.
Rehearse and time the delivery of a presentation
Set the speed and timing of transitions
Record a slide show with narration and slide timings
If you have recorded slide timings and find that there are a couple of timings you want to tweak, you don't need to re-record the whole show.
Instead, click the slide with the timing you want to change. Let's say we need more time for the quick facts on Slide 2.
Then, click the TRANSITIONS tab.
In the Timing group, you'll see the After box, which is checked and shows the recorded timing for the selected slide – 50 seconds.
I need to bump up the timing to 1 minute, so I'll click the up arrow and change the number to 1 minute.
Note that the On Mouse Click box is also checked.
This means that, if I want to, I can click to advance the slide without waiting for the full minute.
If I uncheck On Mouse Click , I have to wait for the automatic timing to elapse on the slide before the slide will advance.
If there is any slide, for which you don't want an automatic timing – for instance, this process slide, which can take a while to step through – select the slide, and uncheck the After box for that slide.
If you want to review all the slide timings and make sure they are set as you expect, click Slide Sorter .
The slide timings appear below each slide thumbnail.
Click Normal to return to Normal view.
To turn off slide timings, the quickest way is to click Slide Show and uncheck Use Timings .
Or, to clear timings completely, click the arrow next to Record Slide Show , point to Clear , and click either Clear Timing on Current Slide , for selected slides, or Clear Timings on All Slides .
For more information, see the course summary and experiment some more with PowerPoint.

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.17(12); 2021 Dec

Ten simple rules for effective presentation slides
Kristen m. naegle.
Biomedical Engineering and the Center for Public Health Genomics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, Virginia, United States of America
Introduction
The “presentation slide” is the building block of all academic presentations, whether they are journal clubs, thesis committee meetings, short conference talks, or hour-long seminars. A slide is a single page projected on a screen, usually built on the premise of a title, body, and figures or tables and includes both what is shown and what is spoken about that slide. Multiple slides are strung together to tell the larger story of the presentation. While there have been excellent 10 simple rules on giving entire presentations [ 1 , 2 ], there was an absence in the fine details of how to design a slide for optimal effect—such as the design elements that allow slides to convey meaningful information, to keep the audience engaged and informed, and to deliver the information intended and in the time frame allowed. As all research presentations seek to teach, effective slide design borrows from the same principles as effective teaching, including the consideration of cognitive processing your audience is relying on to organize, process, and retain information. This is written for anyone who needs to prepare slides from any length scale and for most purposes of conveying research to broad audiences. The rules are broken into 3 primary areas. Rules 1 to 5 are about optimizing the scope of each slide. Rules 6 to 8 are about principles around designing elements of the slide. Rules 9 to 10 are about preparing for your presentation, with the slides as the central focus of that preparation.
Rule 1: Include only one idea per slide
Each slide should have one central objective to deliver—the main idea or question [ 3 – 5 ]. Often, this means breaking complex ideas down into manageable pieces (see Fig 1 , where “background” information has been split into 2 key concepts). In another example, if you are presenting a complex computational approach in a large flow diagram, introduce it in smaller units, building it up until you finish with the entire diagram. The progressive buildup of complex information means that audiences are prepared to understand the whole picture, once you have dedicated time to each of the parts. You can accomplish the buildup of components in several ways—for example, using presentation software to cover/uncover information. Personally, I choose to create separate slides for each piece of information content I introduce—where the final slide has the entire diagram, and I use cropping or a cover on duplicated slides that come before to hide what I’m not yet ready to include. I use this method in order to ensure that each slide in my deck truly presents one specific idea (the new content) and the amount of the new information on that slide can be described in 1 minute (Rule 2), but it comes with the trade-off—a change to the format of one of the slides in the series often means changes to all slides.

Top left: A background slide that describes the background material on a project from my lab. The slide was created using a PowerPoint Design Template, which had to be modified to increase default text sizes for this figure (i.e., the default text sizes are even worse than shown here). Bottom row: The 2 new slides that break up the content into 2 explicit ideas about the background, using a central graphic. In the first slide, the graphic is an explicit example of the SH2 domain of PI3-kinase interacting with a phosphorylation site (Y754) on the PDGFR to describe the important details of what an SH2 domain and phosphotyrosine ligand are and how they interact. I use that same graphic in the second slide to generalize all binding events and include redundant text to drive home the central message (a lot of possible interactions might occur in the human proteome, more than we can currently measure). Top right highlights which rules were used to move from the original slide to the new slide. Specific changes as highlighted by Rule 7 include increasing contrast by changing the background color, increasing font size, changing to sans serif fonts, and removing all capital text and underlining (using bold to draw attention). PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor.
Rule 2: Spend only 1 minute per slide
When you present your slide in the talk, it should take 1 minute or less to discuss. This rule is really helpful for planning purposes—a 20-minute presentation should have somewhere around 20 slides. Also, frequently giving your audience new information to feast on helps keep them engaged. During practice, if you find yourself spending more than a minute on a slide, there’s too much for that one slide—it’s time to break up the content into multiple slides or even remove information that is not wholly central to the story you are trying to tell. Reduce, reduce, reduce, until you get to a single message, clearly described, which takes less than 1 minute to present.
Rule 3: Make use of your heading
When each slide conveys only one message, use the heading of that slide to write exactly the message you are trying to deliver. Instead of titling the slide “Results,” try “CTNND1 is central to metastasis” or “False-positive rates are highly sample specific.” Use this landmark signpost to ensure that all the content on that slide is related exactly to the heading and only the heading. Think of the slide heading as the introductory or concluding sentence of a paragraph and the slide content the rest of the paragraph that supports the main point of the paragraph. An audience member should be able to follow along with you in the “paragraph” and come to the same conclusion sentence as your header at the end of the slide.
Rule 4: Include only essential points
While you are speaking, audience members’ eyes and minds will be wandering over your slide. If you have a comment, detail, or figure on a slide, have a plan to explicitly identify and talk about it. If you don’t think it’s important enough to spend time on, then don’t have it on your slide. This is especially important when faculty are present. I often tell students that thesis committee members are like cats: If you put a shiny bauble in front of them, they’ll go after it. Be sure to only put the shiny baubles on slides that you want them to focus on. Putting together a thesis meeting for only faculty is really an exercise in herding cats (if you have cats, you know this is no easy feat). Clear and concise slide design will go a long way in helping you corral those easily distracted faculty members.
Rule 5: Give credit, where credit is due
An exception to Rule 4 is to include proper citations or references to work on your slide. When adding citations, names of other researchers, or other types of credit, use a consistent style and method for adding this information to your slides. Your audience will then be able to easily partition this information from the other content. A common mistake people make is to think “I’ll add that reference later,” but I highly recommend you put the proper reference on the slide at the time you make it, before you forget where it came from. Finally, in certain kinds of presentations, credits can make it clear who did the work. For the faculty members heading labs, it is an effective way to connect your audience with the personnel in the lab who did the work, which is a great career booster for that person. For graduate students, it is an effective way to delineate your contribution to the work, especially in meetings where the goal is to establish your credentials for meeting the rigors of a PhD checkpoint.
Rule 6: Use graphics effectively
As a rule, you should almost never have slides that only contain text. Build your slides around good visualizations. It is a visual presentation after all, and as they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. However, on the flip side, don’t muddy the point of the slide by putting too many complex graphics on a single slide. A multipanel figure that you might include in a manuscript should often be broken into 1 panel per slide (see Rule 1 ). One way to ensure that you use the graphics effectively is to make a point to introduce the figure and its elements to the audience verbally, especially for data figures. For example, you might say the following: “This graph here shows the measured false-positive rate for an experiment and each point is a replicate of the experiment, the graph demonstrates …” If you have put too much on one slide to present in 1 minute (see Rule 2 ), then the complexity or number of the visualizations is too much for just one slide.
Rule 7: Design to avoid cognitive overload
The type of slide elements, the number of them, and how you present them all impact the ability for the audience to intake, organize, and remember the content. For example, a frequent mistake in slide design is to include full sentences, but reading and verbal processing use the same cognitive channels—therefore, an audience member can either read the slide, listen to you, or do some part of both (each poorly), as a result of cognitive overload [ 4 ]. The visual channel is separate, allowing images/videos to be processed with auditory information without cognitive overload [ 6 ] (Rule 6). As presentations are an exercise in listening, and not reading, do what you can to optimize the ability of the audience to listen. Use words sparingly as “guide posts” to you and the audience about major points of the slide. In fact, you can add short text fragments, redundant with the verbal component of the presentation, which has been shown to improve retention [ 7 ] (see Fig 1 for an example of redundant text that avoids cognitive overload). Be careful in the selection of a slide template to minimize accidentally adding elements that the audience must process, but are unimportant. David JP Phillips argues (and effectively demonstrates in his TEDx talk [ 5 ]) that the human brain can easily interpret 6 elements and more than that requires a 500% increase in human cognition load—so keep the total number of elements on the slide to 6 or less. Finally, in addition to the use of short text, white space, and the effective use of graphics/images, you can improve ease of cognitive processing further by considering color choices and font type and size. Here are a few suggestions for improving the experience for your audience, highlighting the importance of these elements for some specific groups:
- Use high contrast colors and simple backgrounds with low to no color—for persons with dyslexia or visual impairment.
- Use sans serif fonts and large font sizes (including figure legends), avoid italics, underlining (use bold font instead for emphasis), and all capital letters—for persons with dyslexia or visual impairment [ 8 ].
- Use color combinations and palettes that can be understood by those with different forms of color blindness [ 9 ]. There are excellent tools available to identify colors to use and ways to simulate your presentation or figures as they might be seen by a person with color blindness (easily found by a web search).
- In this increasing world of virtual presentation tools, consider practicing your talk with a closed captioning system capture your words. Use this to identify how to improve your speaking pace, volume, and annunciation to improve understanding by all members of your audience, but especially those with a hearing impairment.
Rule 8: Design the slide so that a distracted person gets the main takeaway
It is very difficult to stay focused on a presentation, especially if it is long or if it is part of a longer series of talks at a conference. Audience members may get distracted by an important email, or they may start dreaming of lunch. So, it’s important to look at your slide and ask “If they heard nothing I said, will they understand the key concept of this slide?” The other rules are set up to help with this, including clarity of the single point of the slide (Rule 1), titling it with a major conclusion (Rule 3), and the use of figures (Rule 6) and short text redundant to your verbal description (Rule 7). However, with each slide, step back and ask whether its main conclusion is conveyed, even if someone didn’t hear your accompanying dialog. Importantly, ask if the information on the slide is at the right level of abstraction. For example, do you have too many details about the experiment, which hides the conclusion of the experiment (i.e., breaking Rule 1)? If you are worried about not having enough details, keep a slide at the end of your slide deck (after your conclusions and acknowledgments) with the more detailed information that you can refer to during a question and answer period.
Rule 9: Iteratively improve slide design through practice
Well-designed slides that follow the first 8 rules are intended to help you deliver the message you intend and in the amount of time you intend to deliver it in. The best way to ensure that you nailed slide design for your presentation is to practice, typically a lot. The most important aspects of practicing a new presentation, with an eye toward slide design, are the following 2 key points: (1) practice to ensure that you hit, each time through, the most important points (for example, the text guide posts you left yourself and the title of the slide); and (2) practice to ensure that as you conclude the end of one slide, it leads directly to the next slide. Slide transitions, what you say as you end one slide and begin the next, are important to keeping the flow of the “story.” Practice is when I discover that the order of my presentation is poor or that I left myself too few guideposts to remember what was coming next. Additionally, during practice, the most frequent things I have to improve relate to Rule 2 (the slide takes too long to present, usually because I broke Rule 1, and I’m delivering too much information for one slide), Rule 4 (I have a nonessential detail on the slide), and Rule 5 (I forgot to give a key reference). The very best type of practice is in front of an audience (for example, your lab or peers), where, with fresh perspectives, they can help you identify places for improving slide content, design, and connections across the entirety of your talk.
Rule 10: Design to mitigate the impact of technical disasters
The real presentation almost never goes as we planned in our heads or during our practice. Maybe the speaker before you went over time and now you need to adjust. Maybe the computer the organizer is having you use won’t show your video. Maybe your internet is poor on the day you are giving a virtual presentation at a conference. Technical problems are routinely part of the practice of sharing your work through presentations. Hence, you can design your slides to limit the impact certain kinds of technical disasters create and also prepare alternate approaches. Here are just a few examples of the preparation you can do that will take you a long way toward avoiding a complete fiasco:
- Save your presentation as a PDF—if the version of Keynote or PowerPoint on a host computer cause issues, you still have a functional copy that has a higher guarantee of compatibility.
- In using videos, create a backup slide with screen shots of key results. For example, if I have a video of cell migration, I’ll be sure to have a copy of the start and end of the video, in case the video doesn’t play. Even if the video worked, you can pause on this backup slide and take the time to highlight the key results in words if someone could not see or understand the video.
- Avoid animations, such as figures or text that flash/fly-in/etc. Surveys suggest that no one likes movement in presentations [ 3 , 4 ]. There is likely a cognitive underpinning to the almost universal distaste of pointless animations that relates to the idea proposed by Kosslyn and colleagues that animations are salient perceptual units that captures direct attention [ 4 ]. Although perceptual salience can be used to draw attention to and improve retention of specific points, if you use this approach for unnecessary/unimportant things (like animation of your bullet point text, fly-ins of figures, etc.), then you will distract your audience from the important content. Finally, animations cause additional processing burdens for people with visual impairments [ 10 ] and create opportunities for technical disasters if the software on the host system is not compatible with your planned animation.
Conclusions
These rules are just a start in creating more engaging presentations that increase audience retention of your material. However, there are wonderful resources on continuing on the journey of becoming an amazing public speaker, which includes understanding the psychology and neuroscience behind human perception and learning. For example, as highlighted in Rule 7, David JP Phillips has a wonderful TEDx talk on the subject [ 5 ], and “PowerPoint presentation flaws and failures: A psychological analysis,” by Kosslyn and colleagues is deeply detailed about a number of aspects of human cognition and presentation style [ 4 ]. There are many books on the topic, including the popular “Presentation Zen” by Garr Reynolds [ 11 ]. Finally, although briefly touched on here, the visualization of data is an entire topic of its own that is worth perfecting for both written and oral presentations of work, with fantastic resources like Edward Tufte’s “The Visual Display of Quantitative Information” [ 12 ] or the article “Visualization of Biomedical Data” by O’Donoghue and colleagues [ 13 ].
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank the countless presenters, colleagues, students, and mentors from which I have learned a great deal from on effective presentations. Also, a thank you to the wonderful resources published by organizations on how to increase inclusivity. A special thanks to Dr. Jason Papin and Dr. Michael Guertin on early feedback of this editorial.
Funding Statement
The author received no specific funding for this work.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

suicide prevention
8 templates

46 templates

cybersecurity
6 templates
10 templates

biochemistry
37 templates

18 templates
What Time Is It?
What time is it presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
How to tell time, a question that kids ask and that eventually requires an answer from an adult or a teacher. Why is it that when the long hand points to the 8, it's not "8:00"? Let's make it easy for your students to discover the different types of clocks, what the units of measurement of time are and how to interpret clocks with this template, created with the help of educators. It's very visual thanks to its illustrations and its multiple colors.
Features of this template
- Designed for Elementary
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 16 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
- Available in different languages
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Available in, related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

- USA Time Map
- Canada Time Map
- Europe Time Map
- Australia Map
- Middle East
- Oceania
- Antarctica
- World Time Map
- Time in World Capitals
- North & Central America
- Time in Europe
- Time in Australia & Oceania
- Time in Asia
- Time in South America
- Time in Africa
- Time in Antarctica
- Standard List
Home Blog PowerPoint Tutorials How To Set Time Duration To Switch Slides in PowerPoint
How To Set Time Duration To Switch Slides in PowerPoint
Usually, presenters use mouse clicks, keys from a keyboard or a remote to switch slides in PowerPoint . However, if you have your presentation well-timed or have to account for every second in a presentation due to time constraints, you might want to make sure that your slides are well-timed. To do this, you can add a time duration to switch your slides. In this tutorial we will show you how to set time duration to switch slides in PowerPoint. For the purpose of this post, we will be using the Financial PowerPoint Template .
Select Your Slides from Slides Pane
In the first step, click the slide preview for the slide you wish to set time for. In case you want all your slides to switch according to a set time limit (e.g. 10 seconds), select one slide and hit CTRL+A to select all slides.
In case you want to set a different time for each slide, you will have to select each slide one by one and follow the steps shown below.

Select a Time Duration for Your Slides from the Transitions Tab
From the Transitions tab, go to ‘After’ and add a time duration after which you wish to switch your slide(s). Also make sure that ‘ On Mouse Click’ is unchecked.
The process for switching slides is similar in various versions across PowerPoint and while we are demonstrating this method using PowerPoint 2013, you will find similar options in older versions (e.g. PowerPoint 2010).

For a Single slide: For a single slide, select the respective slide from the Preview pane and add a time duration for switching the slide.

For Multiple Slides: To apply the same time duration to multiple slides, select the slides from the Preview pane using CTRL+Mouse Click, go to the Transitions tab and set a time to switch them. As mentioned earlier, you can also select all slides by clicking a single slide preview, followed by CTRL+A.
In case you have applied slide transitions, you can also set the length of the transitions using the ‘Duration’ option from the same section.

Once you have followed the aforementioned steps, switch to Slide Show mode and your slides will switch according to the set time duration.

While having well-timed slides might help in good time management, you nevertheless need good presentation slides to make an impression on your audience. Slide Model provides High-Quality PowerPoint Templates with editable slide elements which have been designed by expert professionals to give you the imagery that can be attention grabbing and visually appealing. For more details, see our plans and pricing.

Like this article? Please share
PowerPoint 2013, PowerPoint Tips, Presentation, Presentation Tips, Time, Time Management, View Presentation Filed under PowerPoint Tutorials
Related Articles

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • April 19th, 2024
How to Find Trash on Google Slides
Don’t worry if you accidently delete a presentation file. Learn how to find trash on Google Slides with this guide.

Filed under Business • April 10th, 2024
Discovering Coaching Presentation Tools
Discover the best PPT templates to use as coaching presentation tools with this article. Tools explained + examples.

Filed under PowerPoint Tutorials • March 26th, 2024
How to Translate in PowerPoint
Unlock the experience of PowerPoint translation! Learn methods, tools, and expert tips for smooth Spanish conversions. Make your presentations global.
Leave a Reply

Oct 27, 2014
1.44k likes | 2.22k Views
TIME STUDY. Prof.Dr.Yasemin Claire ERENSAL. Time Study. Time Study is a method used to determine the time required by a qualified person working at a normal pace to do a specified task. The Concept of a Labor Standard. An average experienced operator Working with good skill and effort
Share Presentation
- time standard
- total standard time
- time standard includes considerations

Presentation Transcript
TIME STUDY Prof.Dr.Yasemin Claire ERENSAL
Time Study Time Study is a method used to determine the time required by a qualified person working at a normal pace to do a specified task.
The Concept of a Labor Standard • An average experienced operator • Working with good skill and effort • Using a predetermined and documented method • To complete an operation • At an acceptable quality level • The standard represents the expected time for... • The standard does not include rework, repair, • scrap, repeated iteration of work, or any activity not directly related to task completion the “first time through.”
Some Uses for Standards • Determine total labor cost of the product • Determine the size of the work force • Assess quantity of production machinery and • equipment required • Determine overall “throughput” time • Assist in development of production schedules • Set production goals and assess performance • Determine pay policies • Assess improvement possibilities • Check efficiency of the individual/organization
Work Measurement Program Generally before a work measurement program is developed, employees must be convinced it has a need and will produce desirable results.
Time Study • Definition: Time study is used to determine the time required by a qualified well trained person working at a normal pace to perform a specified task. Time Study results in a Time Standard. • Standard includes • standardized method • normal pace • time standard includes considerations of personal time, rest to overcome fatigue and time for unavoidable delays
Time Studies • Labor standards are based on observing worker doing task • Observe only a sample of work • Use average time & pace &allowances in order to set standard • Disadvantages • Requires a trained & experienced analyst • Standard cannot be set before task is performed
Which jobs are suitable for Time Study ? • Job performed by a single worker in a fixed location • Job involves repetitive short cycles • Job expected to continue unchanged for a long period • Job produces large quantities of output • Resulting time standard must be very accurate
Is also known as: Stopwatch Time Study • Pioneered by Fredrich W. Taylor around 1880. • Several types employed: • Snapback: in one hundredths of a minute • Continuous: in one hundredths of a minute • Three watches: continuous watches • Digital: in one thousandths of a minute • TMU (Time-measured units): in one hundred thousandths of an hour • Computer: in one thousandths of a minute
Equipment • Stopwatch • Decimal minute watch – 100 divisions (.01 minute) • Provides continuousorsnapback timing • Electronic watch – accuracy of .001 second (600 times more accurate) • Provides bothcontinuousand snapback timing • Computer Assisted Electronic Stopwatch
Equipment (con’t) • Video cameras • Time study board • Time study forms (TP) • Time study Software • Training equipment
Daywork Work in which pay is based on time rather than performance.
“Fair Days’ Work” Concept The amount of work which is expected daily from an employee. May be established solely by management, or through mutual agreement with employees or a bargaining entity. It is the expected attainment. • In some companies, a Fair Day’s Work is the performance of an operator who effectively follows the specified method.
Basic Equipment 1) Stop watch - electronic, note: decimal minute as opposed to seconds, two modes: snap (fly) back - resets to zero on each press, continuous - the time still increments, (analog: more costly, breakdown, less accurate - time lost on mechanical snap back) 2) Time study board - holding watch and necessary time study forms, L and R-handed boards 3) Time study forms – a)special form for recording times in a certain way b) also a form to analyze and summarize times back in the Office R = rating W = watch time OT = observed time NT = normal time
Time Study types • May use various stopwatches – read in decimal minutes (except TMU) • Continuous time study – short-duration jobs • Long-cycle time study – long jobs (31 minutes or more), 8 hour studies (determine poor performance), or when work elements out-of-sequence
Components of a Labor Standard Observed “Watch” Time Normal Time Allowances
Observed Time (“Watch Time”) The observed and recorded time, as noted from a timing device, for a worker to perform a defined single element of an operation.
Normal Time Observed time (“Watch Time”), adjusted by a performance rating to obtain the time required by an average qualified worker to perform a single element of an operation while working at a normal pace.
Normal Time =Average Observed Time x Rating Factor
Allowance A percentage by which Normal Time is increased in calculation of the labor standard. It usually includes minor unavoidable delays and required personal activities. It may also include some provision for fatigue.
Standard Time Normal Time adjusted by an allowance factor to obtain the time required by an average qualified worker to perform a single element of an operation while working at a normal pace, and considering all normal job delays and personal needs.
Standard Time = Normal Time (OT=ti) x Allowance Factor (R=L)
Typical Allowance - “PF & D” Personal Fatigue Delay
Personal Allowance An allowance in the labor standard to provide time for the personal needs of a worker during the workday.
Fatigue Allowance Time included in the labor standard calculation to allow for the effect of personal bodily fatigue in the performance of work.
Delay Allowance A time allowance in the labor standard which allows for contingencies and minor delays beyond the control of the operator.
Unavoidable Delay A time delay which is outside the control or responsibility of the worker.
Avoidable Delay A time delay not allowed in the labor standard because it is not necessary to completion of the job and caused by factors under worker control.
Making The Time Study 1. Request for time study 2. Ensure that the job is ready for time study 3. Secure and record information about the operation and operator being studied 4. Divide the operation into elements and record a complete description of the method 5. Observe and record the time taken by the operator 6. Determine the number of cycles to be timed 7. Rate the operator’s performance 8. Check to make certain that a sufficient number of cycles have been timed 9. Determine the allowances 10. Determine the standard time for the operation
Making The Time Study- Step1&2 • 1 Select job to be studied: new one, method changes, complaints, 'bottleneck' operation, incentive scheme, excessive costs, want to compare jobs.2.Select operator to be studied: qualified (has the necessary physical attributes, intelligence, education, skills and knowledge to carry out job in satisfactory manner, without undue fatigue) vs. representative (average) worker, slow workers = loose times, uneconomical for company; fast workers = tight times, unfair to workers 'above ground', no sneaking around, talk to supervisor, stand, businesslike attitude, no opinions
Making The Time Study- Step 3 3) record details about the job: sketch layout, info on operator, working conditions
Dividing the Operation into Elements and Recording a Description of the Method (Step 4) • Timing an entire operation as one single element is seldom satisfactory, and an overall study is no substitute for a time study. Breaking the operation down into short elements and timing each of them separately are essential parts of time study, for the following reasons 1. Breaking job down into short meaningful elements with clearly defined beginnings and endings makes job easier to describe 2. Standard times can be determined for each element. Total standard time is sum of element standard times 3. Allows analyst to focus on parts of job where too much and too little time are being spent 4. Operator may not work at the same tempo throughout the cycle. Each element can be performance rated
Dividing the Operation into Elements and Recording a Description of the Method (Step 4) • Three rules for dividing operation into elements • The elements should be as short in duration as can be accurately timed • Handling time should be separated from machine time • Constant elements should be separated from variable elements (the term constant refers to those elements that are independent of the size, weight, length and shape of the workpiece)
Dividing the Operation into Elements and Recording a Description of the Method (Step 4) • Break down into elements (for convenience of analyst, better ratings) using breakpoints, sight and sound, relatively fine but not too small (>.04 min), types (separate within each group): a1) repetitive element: occurs every cycle (sequence of activities for one unit of production) a2) occasional element: not every cycle, at irregular intervals a3) foreign element: not necessary part of job b1) machine element: performed by machine, time so determined b2) manual element: performed by worker c) constant vs. variable: depends on process, leads to standard data
Dividing the Operation into Elements and Recording a Description of the Method (Step 4) Breakpoint A point in a work cycle readily distinguished by sight or sound which is selected as the boundary between two elements in time study.
Dividing the Operation into Elements and Recording a Description of the Method (Step 4) Frequency The recurrence of a work element. If the element occurs once per cycle, the frequency is 1:1. As an example, if an element is done once every six pieces, then the frequency is 1:6, and the observed time must be divided by six when the study is summarized.
Dividing the Operation into Elements and Recording a Description of the Method (Step 4) Irregular (“Foreign”) Elements An element with a random, usually unpredictable, frequency of occurrence, not part of a normal method.
Dividing the Operation into Elements and Recording a Description of the Method (Step 4) Irregular Elements (Method Deviations) • Fumbles Part requires more work than usual • Sticks in die • Has to be tapped into fixture • Excessive burrs • Difficulty in fitting Part requires less work than usual • No burrs • Unusually good fit
Dividing the Operation into Elements and Recording a Description of the Method (Step 4) Irregular Elements(Interruptions, Stoppages) Operator responsible • Blows nose • Wipes perspiration • Talks to others Operator not responsible • Interference by others • Tool breakage • Power failure • Parts shortage
Dividing the Operation into Elements and Recording a Description of the Method (Step 4) Handling Irregular Elements • Discard observations with avoidable or unallowed delays. • Include observation times with allowable delays in element averages. • Subtract the element average time from the observed time containing the delay and prorate the delay time over an estimated quantity (frequency of occurrence).
Making The Time Study- Recording the Data (Timing) Step 5 Information is generally gathered by observing an operator directly or on video tape using a stopwatch • Continuous Timing: starts the watch at the beginning of the first element and permits it to run continuously during the period of the study. Observer reading of the watch at the end of element. Timing is later determined by subtraction. • Repetitive (Snap-back) Timing: With repetitive or snap-back timing, hands of watch are snapped back to zero at the end of each element. Provides direct time for each element.
Making The Time Study- Recording the Data (Timing) Step 5 Continuous Study A stopwatch technique in which the watch runs continuously throughout the study and readings are made accumulatively at the end of each element.
Making The Time Study- Recording the Data (Timing) Step 5 continuous timing stopwatch runs continuously, read incremented time at each stop, watch is never reset, individual element times are obtained by successive subtraction after study is completed Note: 1) don't record decimal point 2) record only two digits, 105=05, except if long element covering several minutes
Figure 9-7 Continuous Study
Making The Time Study- Recording the Data (Timing) Step 5 Continuous Study
Making The Time Study- Recording the Data (Timing) Step 5 Continuous Study-Advantages • Presents a complete record for the entire observation period • All delays and foreign elements are recorded • Better adapted to record short element times • Clerical work required
Making The Time Study- Recording the Data (Timing) Step 5 Snapback Study A stopwatch technique where a time value is read and recorded at each breakpoint and the watch is instantaneously reset to zero to time the next element.
Making The Time Study- Recording the Data (Timing) Step 5 snap-back timing the watch is read at the breakpoint as it is reset, next element increments from zero, thus the exact elemental time is always read directly from the watch Note: 1) record only OT
- More by User

Time and Motion Study
Time and Motion Study. Rebecca Johnston Operations Management Dr. Foster. Time and Motion Study: Defined. A method created to determine the ‘correct time’ it takes to complete a certain task A method to establish ‘the one best way to perform a task’. Time and Motion Study: Purposes.
6.02k views • 18 slides

Stopwatch Time Study
Time Study Procedure. Select the job to studyCollect information about the jobDivide the job into elementsDo the actual time studyExtend the time studyDetermine the number of cycles to be timedRate, level, and normalize the operator's performanceApply allowancesCheck for logicPublish the ti
1.67k views • 6 slides

Random Moment Time Study
Random Moment Time Study. Mental Health & Mental Retardation. Texas Health & Human Services Commission (HHSC) Time Study Unit. 512-491-1715 Ray Wilson - Manager Beverly Tackett – Team Lead Alexandra Young – Rate Analyst E-Mail Address: [email protected]
302 views • 11 slides

Medicaid Time Study 2015
Medicaid Time Study 2015. Special Education . 2014-2015 Time Studies. 1 st Time Study – November 6 th – 12th 2 nd Time Study – February 25 th – March 3rd 3 rd Time Study – April 24 th – 30th Narrative Time Studies always occur on the third day of the study. November 10 February 27
362 views • 11 slides

Study Time. Human Biology Flash cards Nervous System. Arrival of an action potential at an axon terminal results in the release of ________. The contraction of smooth and cardiac muscle is controlled by the ________ division of the peripheral nervous system.
619 views • 30 slides

Mental Health and Intellectual & Developmental Disabilities. Random Moment Time Study. Overview. What is Random Moment Time Study (RMTS) ?. A federally accepted statistically valid random sampling technique that measures the participant’s time performing work activities
343 views • 11 slides

Time Study Method
Time Study Method. Step 1 ... Selecting Work Elements Step 2 ... Timing the Elements Step 3 ... Determining Sample Size Step 4 ... Setting the Standard. Definite starting and stopping points Correspond to a standard work method. Analyst times a worker Continuous method Snap-back method
988 views • 32 slides

Medicaid Time Study
Medicaid Time Study. Online Training Instructions. Log In. Open Time Study – http:// www.c hcf.net/chcfweb /?mode=UserLogin. Type in your user name and password. If you have forgotten, send Shannon an email. Click on “Online Training”.
244 views • 5 slides

Mental Health and Intellectual & Developmental Disabilities. Random Moment Time Study. Texas Health & Human Services Commission (HHSC). Time Study Unit Ray Wilson – Director 512-730-7403 Beverly Tackett – Team Lead Alexandra Young – Rate Analyst
900 views • 67 slides

Part Time Study
Part Time Study. Conference 25 th March 2011 Clare Beckett Head of Student Recruitment. Type name here Type venue here Type date here. The University in West London. Part-time Undergraduate Offer. Undergraduate Areas.
331 views • 20 slides

Time Study Summary
Time Study Summary. Table of Contents. Definitions: Departments ……………………………………………….. Pg 3 Participants ………………………………………………… Pg 4 Work Areas ……………………………………………........ Pg 5 Definition of Intel O/H ……………………………..…….. Pg 6 Definition of Web Products ……………………....... Pg 7 & 8
277 views • 16 slides

Study Time!
Tips on how to improve your study and homework time. Study Time!. Get Your Study Supplies First…. Need a coputer and ditunary ? Someone had this typed in their survey, and YES…a “computer” and “dictionary” would be great! I also found: gasibo for “gazebo” useally for “usually”
317 views • 13 slides

Deb Cooling Time Study
Deb Cooling Time Study. 4s cycle time and changed debuncher cooling OFF timers Data taken: Nominal running…every pulse into Acc DCCT, VSA measurements and production SEM806 ARF1 OFF to measure profile on Injection orbit Every other pulse into Acc (D:ESEPC timer)
181 views • 7 slides

Study Time Analysis
Study Time Analysis. By Johnny Lo IME 301 Winter 2010. Introduction. Problem Analysis - Time spent studying on a daily and weekly basis - Management for four classes and one lab Hypothesis - Most work and study done on weekends - Increased study time during quiz/exam
102 views • 8 slides

TV Time vs. Study Time
TV Time vs. Study Time. By Jason Montgomery IME 301 Winter 2010 Dr. Rosenkrantz. Issue: Analyze the amount of television watching to the amount of study time to see if I am using my spare time wisely.
79 views • 7 slides

NO time to study
NO time to study. By: Nick Hall Andrew Kalfayan Michael Laow Joey Suitonu. Mission Statement. Could the lack of time due to increasing work hours be the cause of lower academic performance?
257 views • 25 slides

Random Moment Time Study. Local Health Departments/Districts. Contact Information. (512) 730 -7403 Time Study Unit Ray Wilson - Director Beverly Tackett – Lead Alexandra Young – Rate Analyst E-Mail Address : [email protected]
530 views • 51 slides

Time Study. Summer Training Industrial Engineering Department. Work Measurement Tools. Time Study Work Sampling Standard Data Predetermined Time Systems Physiological Measures. Time Study. Establishment of Time Standards Estimates Historical records Standards. Estimates.
392 views • 29 slides

4. Time Study
4. Time Study. The major objective of this chapter is to learn how to calculate a time standard based on stopwatch time study procedures. Time Study. A process for measuring the required time for performing a given task, by a given method, by a trained worker, working in a normal pace.
393 views • 35 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
So, here are 6 tips for better time management in presentations: Tip #1: Know your time limits. One of the first things you need to determine is how long your presentation is going to run for. This is because a 10-minute presentation will need to be prepared differently than a 30-minute one.
Plan ahead. Never count on a clock being in the room to manage your time in the moment of your presentation. Have your phone (silenced, of course) on the podium ready to glance at, appoint someone in the back of the room to give you cues when you are running out of time, or even discretely glance at your watch while taking a sip of water.
Experts recommend 30 to 60 slides for a 60-minutes presentation. This period of time gives the speaker two main options: summarize the content in 30 slides or make a structure that allows one theme per slide. These two options also give more time to interact with the audience make a great introduction and conclusion.
Once you've get your presentation planned out, it's time to tackle the design part of creating a presentation. When designing your presentation, keep the following guidelines in mind: 1. Keep the Text to a Minimum. When it comes to your presentation, PowerPoint should assist you in delivering the presentation.
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
As you rehearse your content, note how long it takes for each "block" of your presentation. (Get someone to time you if necessary.) This gives you a number of intermediate time targets. For example: 12:05 - Start presentation. 12:15 - Introduction and case study introduced. 12:30 - Case study and lessons learned complete.
Tip #1: Prepare thoroughly. You need to start thinking about the timing of your presentation from the beginning of your preparation. One way of doing this is to take a sheet of paper and sketch out your slides in sequence, making a note of the maximum presentation time you anticipate for each slide.
Get your main point into the presentation as early as possible (this avoids any risk of audience fatigue or attention span waning), then substantiate your point with facts, figures etc and then reiterate your point at the end in a 'Summary'. 2. Practice Makes Perfect. Also, don't forget to practice your presentation.
Guy Kawasaki believes the ideal presentation has 10 slides, lasts 20 minutes, and has no font smaller than 30 points. That's his 10/20/30 rule. Here are some tips for a 20-minute presentation: 1. Go Longer. With 20 minutes, you can go longer.
Option 1: Insert clock in PowerPoint with built-in feature. Luckily, if you want your PowerPoint presentation to show time, there's a built-in function. You just need to go to the Insert tab > Date &Time option (in the 'Text' group). You'll then get a new window where you can customize what information you want to display.
Guide your team with the help of easy-to-understand standard time presentation templates and Google slides. Toggle Nav. Search. Search. Search . 5. Notifications 5 ... We have an entire team of experts who can work on your custom presentation. Get in touch with our design agency. 5 days ago. SlideGeeks added 23 new products (e.g. Completely ...
Rehearse and time the delivery of a presentation. Set the speed and timing of transitions. Record a slide show with narration and slide timings. Training: If you've recorded slide timings and find that there are a couple of timings you want to tweak, you don't need to re-record the whole show.
Rule 2: Spend only 1 minute per slide. When you present your slide in the talk, it should take 1 minute or less to discuss. This rule is really helpful for planning purposes—a 20-minute presentation should have somewhere around 20 slides. Also, frequently giving your audience new information to feast on helps keep them engaged.
Standard time zone. Science. 1 of 7. Download Now. Download to read offline. Standard time zone - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Time study. Nov 10, 2014 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 59 likes • 44,078 views. Lav Gupta. this contain time study analysis and a case study. Engineering. 1 of 27. Download now. Time Study Presented.
Practice a 1- to 2-minute pitch until you feel comfortable. The poster and your pitch must be aimed at the audience that will be present. The clearer and more rational your poster layout, the easier it will then be for you to make a strong pitch. —Srinivas.
1. Direct Time Study • Direct observation of a task using a stopwatch to record the time taken to accomplish a task. • The task is usually divided into work elements and each work element is timed seperately. • During the observation, the analyst evaluates the worker's pace - performance rating • Normal time Tn=Tobs (PR) where Tn ...
Free Google Slides theme, PowerPoint template, and Canva presentation template. How to tell time, a question that kids ask and that eventually requires an answer from an adult or a teacher. Why is it that when the long hand points to the 8, it's not "8:00"? Let's make it easy for your students to discover the different types of clocks, what the ...
TELLING THE TIME. This is a interactive powerpoint presentation about telling the time. It contains some flash cards and a multiple choice game. There are analog and digital clocks. 49301 uses. 1mada.
Time Zones. Earth Science Chapter 6. Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each about 15 degrees of longitude wide and exactly one hour different from the zones on either side of it. The United States has 6 time zones:Eastern Standard Time, Slideshow 1458155 by kirti
Samoa changed its time zone from -11 (-10 with DST) to +13 (+14 with DST) in Dec 30, 2010. See International Date Line from 2011 to now. American Samoa: Pago Pago. GMT+12:37:12.
Select Your Slides from Slides Pane. In the first step, click the slide preview for the slide you wish to set time for. In case you want all your slides to switch according to a set time limit (e.g. 10 seconds), select one slide and hit CTRL+A to select all slides. In case you want to set a different time for each slide, you will have to select ...
During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher. E N D . Presentation Transcript. ... Total standard time is sum of element standard times 3. Allows analyst to focus on parts of job where too much and too little time are being spent 4. Operator may not work at the same tempo throughout the cycle.