

1 Introduction to Microbiology
Welcome to the wonderful world of microbiology ! Yay! So. What is microbiology? If we break the word down it translates to “the study of small life,” where the small life refers to microorganisms or microbes . But who are the microbes? And how small are they?
Generally microbes can be divided into two categories: the cellular microbes (or organisms) and the acellular microbes (or agents). In the cellular camp we have the bacteria, the archaea, the fungi, and the protists (a bit of a grab bag composed of algae, protozoa, slime molds, and water molds). Cellular microbes can be either unicellular , where one cell is the entire organism, or multicellular , where hundreds, thousands or even billions of cells can make up the entire organism. In the acellular camp we have the viruses and other infectious agents, such as prions and viroids.
In this textbook the focus will be on the bacteria and archaea (traditionally known as the “prokaryotes,”) and the viruses and other acellular agents.
Characteristics of Microbes
Obviously microbes are small. The traditional definition describes microbes as organisms or agents that are invisible to the naked eye, indicating that one needs assistance in order to see them. That assistance is typically in the form of a microscope of some type. The only problem with that definition is that there are microbes that you can see without a microscope. Not well, but you can see them. It would be easy to dismiss these organisms as non-microbes, but in all other respects they look/act/perform like other well-studied microbes (who follow the size restriction).
So, the traditional definition is modified to describe microbes as fairly simple agents/organisms that are not highly differentiated , meaning even the multicellular microbes are composed of cells that can act independently– there is no set division of labor. If you take a giant fungus and chop half the cells off, the remaining cells will continue to function unimpeded. Versus if you chopped half my cells off, well, that would be a problem. Multicellular microbes, even if composed of billions of cells, are relatively simple in design, usually composed of branching filaments.
It is also acknowledged that research in the field of microbiology will require certain common techniques, largely related to the size of the quarry. Because microbes are so small and there are so many around, it is important to be able to isolate the one type that you are interested in. This involves methods of sterilization , to prevent unwanted contamination, and observation , to confirm that you have fully isolated the microbe that you want to study.
Microbe Size
Since size is a bit of theme in microbiology, let us talk about actual measurements. How small is small? The cellular microbes are typically measured in micrometers ( µm ). A typical bacterial cell (let us say E. coli ) is about 1 µm wide by 4 µm long. A typical protozoal cell (let us say Paramecium ) is about 25 µm wide by 100 µm long. There are 1000 µm in every millimeter, so that shows why it is difficult to see most microbes without assistance. (An exception would be a multicellular microbe, such as a fungus. If you get enough cells together in one place, you can definitely see them without a microscope!)
When we talk about the acellular microbes we have to use an entirely different scale. A typical virus (let us say influenza virus) has a diameter of about 100 nanometers ( nm ). There are 1000 nanometers in every micrometer, so that shows why you need a more powerful microscope to see a virus. If a typical bacterium (let us pick on E.coli again) were inflated to be the size of the Statue of Liberty, a typical virus (again, influenza virus works) would be the size of an adult human, if we keep the correct proportions.
http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/cells/scale/
The Discovery of Microbes
The small size of microbes definitely hindered their discovery. It is hard to get people to believe that their skin is covered with billions of small creatures, if you cannot show it to them. “Seeing is believing,” that is what I always say. Or someone says that.
In microbiology, there are two people that are given the credit for the discovery of microbes. Or at least providing the proof of their discovery, both around the same time period:
Robert Hooke (1635-1703)
Robert Hooke was a scientist who used a compound microscope , or microscope with two lenses in tandem, to observe many different objects. He made detailed drawings of his observations, publishing them in the scientific literature of the day, and is credited with publishing the first drawings of microorganisms. In 1665 he published a book by the name of Micrographia , with drawing of microbes such as fungi, as well as other organisms and cell structures. His microscopes were restricted in their resolution, or clarity, which appeared to limit what microbes he was able to observe.
Antony van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723)
Antony van Leeuwenhoek was a Dutch cloth merchant, who also happened to dabble in microscopes. He constructed a simple microscope (which has a single lens), where the lens was held between two silver plates. Apparently he relished viewing microbes from many different sample types – pond water, fecal material, teeth scrapings, etc. He made detailed drawings and notes about his observations and discoveries, sending them off to the Royal Society of London , the scientific organization of that time. This invaluable record clearly indicates that he saw both bacteria and a wide variety of protists. Some microbiologists refer to van Leeuwenhoek as the “ Father of Microbiology ,” because of his contributions to the field.
Microbial Groups
Classification of organisms, or the determination of how to group them, continually changes as we acquire new information and new tools of assessing the characteristics of an organism. Currently all organisms are grouped into one of three categories or domains: Bacteria , Archaea , and Eukarya . The Three Domain Classification , first proposed by Carl Woese in the 1970s, is based on ribosomal RNA ( rRNA ) sequences and widely accepted by scientists today as the most accurate current portrayal of organism relatedness.
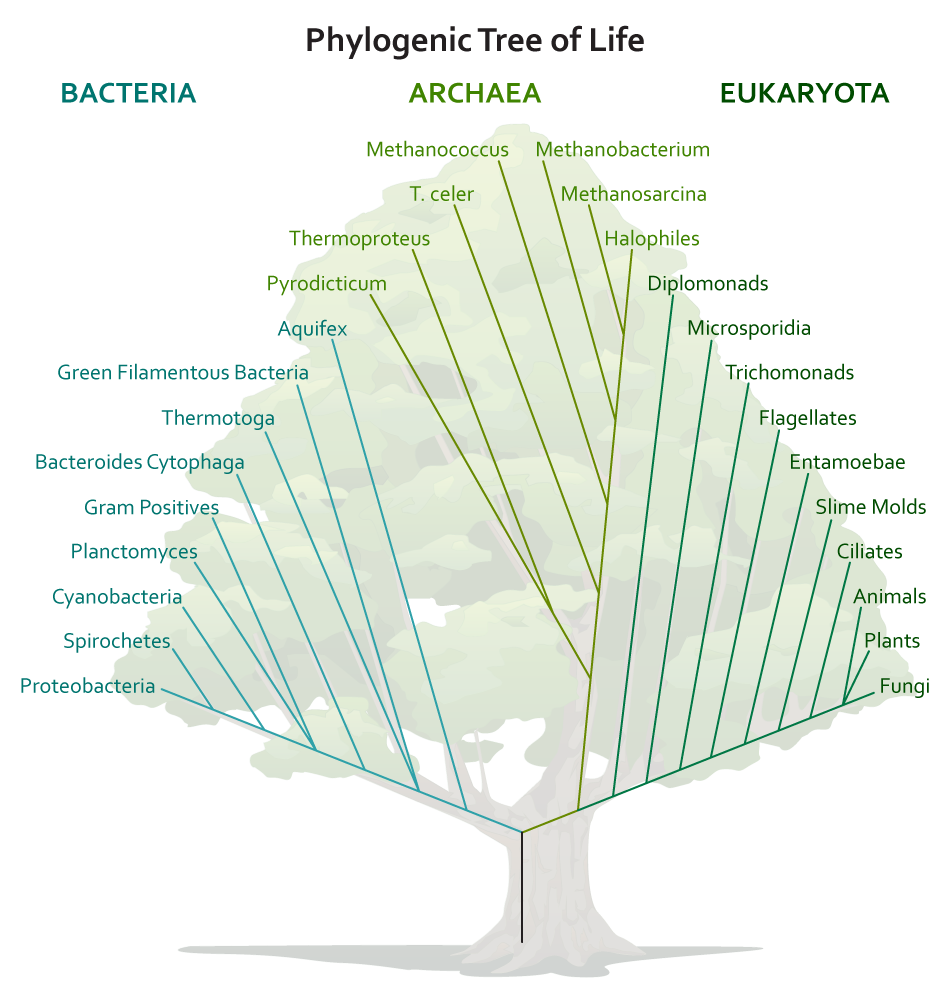
The Bacteria domain contains some of the best known microbial examples ( E. coli , anyone?). Most of the members are unicellular (but not all!), most members lack a nucleus or any other organelle , most members have a cell wall with a particular substance known as peptidoglycan (not found anywhere else but in bacteria!), they have 70S ribosomes, and humans are intimately familiar with many members, since they are common in soil, water, our foods, and our own bodies. All Bacteria are considered microbes.
Archaea is a relatively new domain, since these organisms used to be grouped with the bacteria. There are some obvious similarities, since they are mostly (but not all!) unicellular, cells lack a nucleus or any other organelle, they have 70S ribosomes, and all Archaea are microbes. But they have completely different cell walls that can vary markedly in composition (but notably lack peptidoglycan and might have pseudomurien instead). In addition, their rRNA sequences have shown that they are not closely related to Bacteria at all.
The Eukarya Domain includes many non-microbes, such as animals and plants, but there are numerous microbial examples as well, such as fungi, protists, slime molds, and water molds. The eukaryotic cell type has a nucleus, as well as many organelles, such as mitochondria or an endoplasmic reticulum. They have 80S ribosomes and are commonly found as unicellular or multicellular.
Viruses are not part of the Three Domain Classification, since they lack ribosomes and therefore lack rRNA sequences for comparison. They are classified separately, using characteristics specific to viruses. Viruses are typically described as “ obligate intracellular parasites ,” a reference to their strict requirement for a host cell in order to replicate or increase in number. These acellular entities are often agents of disease, a result of their cell invasion.
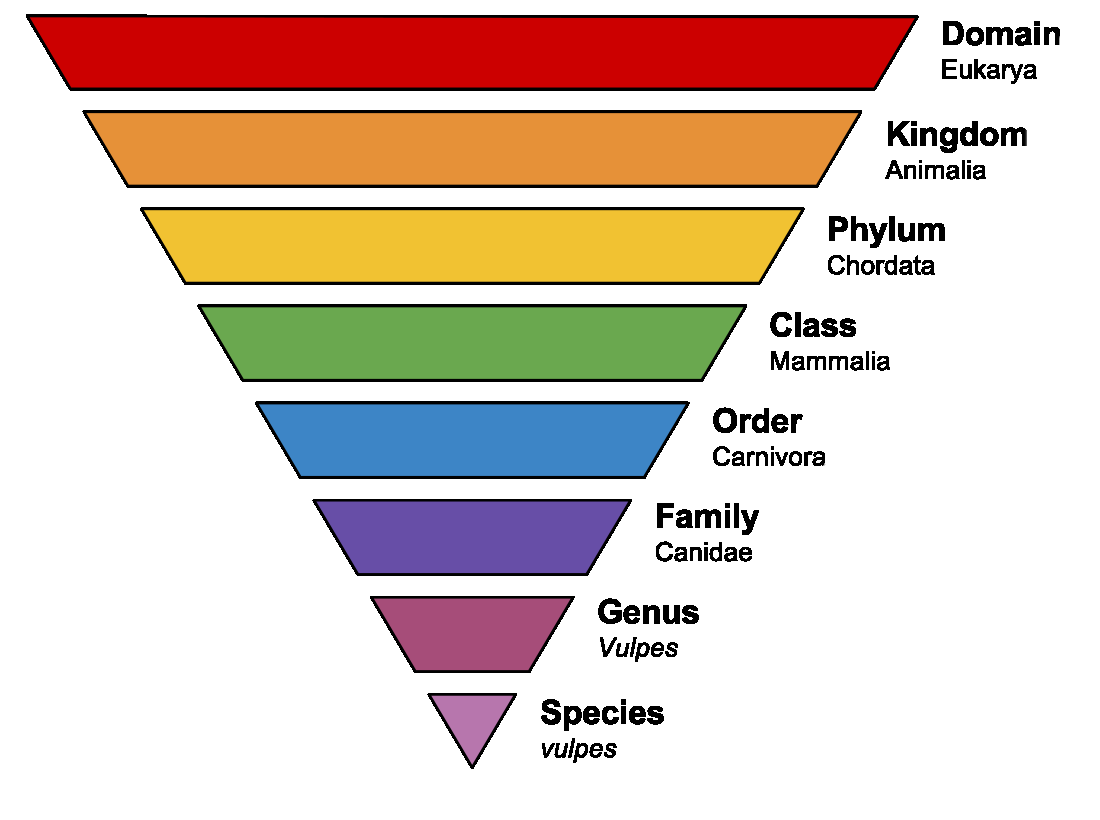
Taxonomic Ranks
Taxonomic ranks are a way for scientists to organize information about organisms, by determining relatedness. Domains are the largest grouping used, followed by numerous smaller groupings, where each smaller grouping consists of organisms that share specific features in common. Each level becomes more and more restrictive as to whom can be a member. Eventually we get down to genus and species , the groupings used for formation of a scientific name. This is the binomial nomenclature devised by Carl Linnaeus in the 1750s.
Binomial Nomenclature
When referring to the actual scientific name assigned to an organism, it is important to follow convention, so it is clear to everyone that you are referring to the scientific name. There are rules in science (just like in English class, where you would never refer to “mr. robert louis stevenson,” or at least not without expecting to get your paper back with red all over it).
A scientific name is composed of a genus and a species, where the genus is a generic name and the species is specific. The species name, once assigned, is permanent for the organism, while the genus can change if new information becomes available. For example, the bacterium previously known as Streptococcus faecalis is now Enterococcus faecalis because sequencing information indicates that it is more closely related to the members of the Enterococcus genus. It is important to note that it is inappropriate to refer to an organism by the species alone (i.e. you should never refer to E. coli as “ coli ” alone. Other bacteria can have the species “ coli ” as well.)
Now for the rules: The genus is always capitalized. The species is always lowercase. And both the genus and the species are italicized (common if typewritten) or underlined (common if handwritten). The genus may be shortened to its starting letter, but only if the name has been referred to in the text in its entirety at least once first (the exception to this is E. coli , due to its commonality, where hardly anyone spells out the Escherichia genus anymore).
microbiology, microorganisms, microbes, unicellular, multicellular, differentiation, sterilization, observation, micrometers (µm), nanometers (nm), Robert Hooke, compound microscope, Antony van Leeuwenhoek, simple microscope, Royal Society of London, Father of Microbiology, Three Domain Classification, ribosomal RNA (rRNA), Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya , obligate intracellular parasites, taxonomic ranks, genus, species, binomial nomenclature
Study Questions
- Who are the members of the microbial world?
- What is the complete definition of microbiology? What characteristics are relevant?
- What size are different groups of microbes?
- What were the contributions of Hooke and Van Leeuwenhoek to the field of microbiology? How did they make these contributions?
- What is the basis for Woese’s classification and what are the three domains?
- What are the basic characteristics of members of the three domains? Where do microbes fit in?
- What are the basic characteristics of viruses? Why are they not classified in one of the three domains?
- What are taxonomic ranks? What is the system of binomial nomenclature? What are the basic rules? How are bacteria named? What is a genus and species? Be able to write a bacterial name correctly.
General Microbiology Copyright © 2019 by Linda Bruslind is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Microbiology: Powerpoint Slides & Handouts
- Powerpoint Slides & Handouts
- Hints and Tips
- Web Resources
Look through the various powepoint presentations. They are all availible in ppt form - perfect for reviewing and printing.
Printing from PowerPoint - how to change from slides to handouts.
- C lick the office button
- Click Print Print what: – on lower left side click the down pointing arrow and then click handouts from the drop-down list Change Color to pure black & white Under Handouts choose 3 or 6 slides per page
- Click on the preview button and zoom to 100% - this will show you what the pages will look like if in your hands. This is a great way to determine how many slides you want on a page.
***You must change from slides to handouts for EACH chapter.
Power Points for Microbiology
- Chapter 18 Part 1
- Chapter 18 Part 2
- Chapter 24 Part 1
- Chapter 24 Part 2
PJC Library
- << Previous: Microbiology
- Next: Hints and Tips >>
- Last Updated: Aug 7, 2023 8:55 AM
- URL: https://parisjc.libguides.com/Microbiology2420

Microbiology PPT
Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, that exist in the world around us. It is a vast field that encompasses numerous areas of study, including immunology, genetics, and biochemistry. Our Microbiology PPT (PowerPoint presentations) will help you to study the basic and applied aspects of Microbiology and it can be used for a variety of purposes, including educational lectures. You can download all our Microbiology PPT absolutely free without any subscription or payments.
Microbiology Notes | Microbiology MCQs
@. Prokarytes vs Eukaryotes PPT
@. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Transcription PPT
@. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Translation PPT
<<< Back to BIOLOGY PPT Page

No related posts.
Privacy Overview

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1: Introduction to Microbiology
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 8629

Microbiology is a broad term which includes virology, mycology, parasitology, bacteriology, immunology, and other branches. A microbiologist is a specialist in microbiology and these related topics. Microbiological procedures usually must be aseptic and use a variety of tools such as light microscopes with a combination of stains and dyes. As microbes are absolutely required for most facets of human life (including the air we breathe and the food we eat) and are potential causes of many human diseases, microbiology is paramount for human society.
- 1.1A: Defining Microbes
- 1.1B: History of Microbiology - Hooke, van Leeuwenhoek, and Cohn
- 1.1C: Pasteur and Spontaneous Generation
- 1.1D: Koch and Pure Culture
- 1.2.1: 1.2A Types of Microorganisms
- 1.2B: Classification of Microorganisms
- 1.2C: Microbes and the Origin of Life on Earth
- 1.2D: Environmental Diversity of Microbes
- 1.3.1: 1.3B Applied Microbiology
- 1.3A: Basic Microbiology
- 1.3C: Immunization, Antiseptics, and Antibiotics
- 1.3D: Modern Microbiology
Thumbnail: A cluster of Escherichia coli bacteria magnified 10,000 times. (Public Domain; Eric Erbe, digital colorization by Christopher Pooley, both of USDA, ARS, EMU).
Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Resource Library
- LOUIS Course Transformation
- louis-course-transformation
Education Standards
Louisiana common course catalogue.
Learning Domain: Biological Sciences
Standard: Microbiology for Nursing & Allied Health
Standard: General Microbiology (Science Majors)
BIOL 2230 Chapter 10 OER
Biol 2230 chapter 5 oer, biol 2230 chapter 6 oer, biol 2230 chapter 7 oer, biol 2230 chapter 8 oer, biol 2230 chapter 9 oer, frazier_biol2230sp20, microbiology chapter 1 oer ppt, microbiology chapter 2 oer ppt, microbiology chapter 3 oer ppt, microbiology chapter 4 oer, microbiology powerpoint slides.

Hi. This OER contains PowerPoint Presentation slides for the Microbiology OpenStax textbook. Chapters 1 - 10 have been uploaded to this platform. All PowerPoint presentations will be refined during implementation. In the meantime, please feel free to use these resources and modify to your liking as I have a different arrangement of slides that are most suitable to my student's needs and course learning outcomes.
Thank you for taking time to stop by!
"OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Introduction to Resources
Hi. Thank you for stopping by. I have created PowerPoint slides for the Microbiology OpenStax textbook. Please feel free to use these resources in your class.
Microbiology Chapter 1 PowerPoint Slides
This OER contains Chapter 1 PowerPoint slides for content in the OpenStax textbook, Microbiology. "OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Microbiology Chapter 2 PowerPoint Slides
This OER contains Chapter 2 PowerPoint slides for content in the OpenStax textbook, Microbiology. "OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Microbiology Chapter 3 PowerPoint Slides
This OER contains Chapter 3 PowerPoint slides for content in the OpenStax textbook, Microbiology. "OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Microbiology Chapter 4 PowerPoint Slides
This OER contains Chapter 4 PowerPoint slides for content in the OpenStax textbook, Microbiology. "OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Microbiology Chapter 5 PowerPoint Slides
This OER contains Chapter 5 PowerPoint slides for content in the OpenStax textbook, Microbiology. "OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Microbiology Chapter 6 PowerPoint Slides
This OER contains Chapter 6 PowerPoint slides for content in the OpenStax textbook, Microbiology. "OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Microbiology Chapter 7 PowerPoint Slides
This OER contains Chapter 7 PowerPoint slides for content in the OpenStax textbook, Microbiology. "OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Microbiology Chapter 8 PowerPoint Slides
This OER contains Chapter 8 PowerPoint slides for content in the OpenStax textbook, Microbiology. "OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Microbiology Chapter 9 PowerPoint Slides
This OER contains Chapter 9 PowerPoint slides for content in the OpenStax textbook, Microbiology. "OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Microbiology Chapter 10 PowerPoint Slides
This OER contains Chapter 10 PowerPoint slides for content in the OpenStax textbook, Microbiology. "OpenStax Microbiology Slides" by Adronisha Frazier, Louisiana Community and Technical College System, Northshore Technical Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Lecture 1 - Introduction to Microbiology

Related Papers
Benedict Zunchi Okoro
microbiology research work in my laboratory
adelokun shakirat
ABSTRACT: We discuss the roles of microbes in the ecosystem services provided by soils to humans. The diversity of microbes in soil is enormous and they drive many soil services. We examine the functional, metabolic, and phylogenetic diversity of soil bacteria, archaea, and fungi. The roles of these soil microbes are highlighted in the cycling of major biological elements (C, N, P), in the recycling of wastes, and the detoxifi cation of environmental pollutants. Microbes play a pivotal role in the cycling of nitrogen; they exclusively mediate nitrogen fi xation, denitrifi cation, and nitrifi cation. We also discuss recent theoretical advances in understanding of ecosystem processes that were made possible through explicit consideration of the roles of soil microbes. Global knowledge of soil microbial diversity and functioning is increasing rapidly, but knowledge of New Zealand’s soil microbial resources is sparse, despite their importance in the provisioning and regulating services provided by soil ecosystems.
magendira mani vinayagam
Pheladi Naka
International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering
ElKamil Tola
Aaron Paul Pineda
The globalization age have brought business organizations all over the world to find innovative strategies to gain advantage it the global markets. Social entrepreneurship is regarded as a new concept that is still yet to gain interests among enterprises in Turkey. However, the context of social entrepreneurship may not be fully embraced by the business sector in the country because of the perceived deficiencies both in the social and legislative structure. Consequently, the way for local enterprises to gain grounds towards globalization will require more than just a sense of responsibility, but rather an initiative, which the social entrepreneurship model tends to provide. The discussion explores the context of social entrepreneurship from a business perspective and examines the various challenges that organizations in Turkey would be facing if they decided to employ social entrepreneurship as a strategic position when venturing towards the global markets.
Jurnal Ilmiah STOK Bina Guna Medan
Agung Nugroho
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui peningkatan hasil belajar passing Chest pass dalam bermain bola basket dengan penerapan variasi pembelajaran dan modifikasi bola basket pada siswa kelas VIII SMP Santa Maria tahun ajaran 2019/2020. Metode penelitian ini adalah metode penelitian tindakan kelas (PTK). Dari analisis data yang telah dilakukan dapat disimpulkan bahwa melalui penerapan variasi pembelajaran dan modifikasi bola basket, siswa dapat meningkatkan hasil belajarnya pada materi belajar passing Chest pass. Subjek dalam penelitian ini adalah siswa Kelas VIII SMP Santa Maria Medan Tahun Ajaran 2019/2020, yang berjumlah 30 orang. Hasil penelitian pada siklus I menunjukkan bahwa hasil belajar passing chest pass yaitu (43,33%) siswa yang tuntas dalam belajarnya, dan (56,67%) siswa yang tidak tuntas belajarnya. Hasil belajar siswa dalam melakukan teknik passing chest pass pada siklus I secara klasikal ketuntasan belajar hanya mencapai (43,33%). Pada siklus II menunjukkan bahwa h...
South American Journal of Herpetology
Cristian Abdala
Recherche et pratiques pédagogiques en langues de spécialité - Cahiers de l APLIUT
Martine Derivry-Plard
L’histoire de la recherche en sciences sociales, dans laquelle s’inscrit celle de la didactique des langues et des cultures (DLC), est fondamentalement une histoire sur le sens des mots, des notions et des concepts qui decrivent, expliquent ou justifient des pratiques. L’enquete empirique justifie ainsi la demarche scientifique de nommer, en fonction des donnees collectees, mais surtout selon les outils utilises qui lui ont permis de comparer, de mesurer et d’evaluer. Si la DLC en France privilegie l’approche qualitative pour ses enquetes empiriques, l’apport du quantitatif ne devrait pas etre neglige. Cet article s’appuie sur un travail de type quantitatif concernant les resultats des enseignants d’anglais « locuteurs natifs » et « locuteurs non natifs » (Derivry-Plard 2003, 2005). Il presente les differentes etapes de sa construction theorique et methodologique et souligne l’apport d’une demarche quantitative et d’une approche sociologique pour la recherche en DLC.
Etlik Veteriner Mikrobiyoloji Dergisi
ersin istanbulluoğlu
RELATED PAPERS
Journal of Linguistics
Science (New York, N.Y.)
Josephine Elizabeth Siregar
CENTRAL ASIAN JOURNAL OF INNOVATIONS ON TOURISM MANAGEMENT AND FINANCE
Central Asian Studies
Chemistry - An Asian Journal
Edgar Guzman
European Journal of Literature, Language, and Linguistic Studies
Brant von Goble
ai julaerah
Journal of Liaquat University of Medical & Health Sciences
Prof. Uzma Zaidi
Revista Argentina de Microbiología
José Gutiérrez-Fernández
Revista Psicologia e Saúde
Silvio Yasui
Felippe Oliveira
Applied Surface Science
margarita elena beatriz campo
Lo Yoga della Tradizione
Fabio Milioni , liliana bordoni
Journal of clinical & experimental ophthalmology
Patricia Becerra
INTELLIGENT SYSTEMS: A STEP TOWARDS SMARTER ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONIC AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING: Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Mechatronics, Electrical and Mechanical Power (IEMPOWER), 2021.
diksha chauhan
Protestantismo em Revista
Adriana Weege
Antibiotics
M. Popovic , Gordana Zavišić , Vera Gusman , Deana Medić
Canadian family physician Médecin de famille canadien
Nandini Natarajan
Mrinalini Prasad
PILAR LOPEZ GONZALEZ-NIETO
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

- Houston Community College
- Eagle Online

- IDOWU FAMUYIWA
- MICROBIOLOGY (BIOL 2320)
Microbiology Lecture Power Points Presentation
Introduction
Chapter outline.
From boiling thermal hot springs to deep beneath the Antarctic ice, microorganisms can be found almost everywhere on earth in great quantities. Microorganisms (or microbes, as they are also called) are small organisms. Most are so small that they cannot be seen without a microscope.
Most microorganisms are harmless to humans and, in fact, many are helpful. They play fundamental roles in ecosystems everywhere on earth, forming the backbone of many food webs. People use them to make biofuels, medicines, and even foods. Without microbes, there would be no bread, cheese, or beer. Our bodies are filled with microbes, and our skin alone is home to trillions of them. 1 Some of them we can’t live without; others cause diseases that can make us sick or even kill us.
Although much more is known today about microbial life than ever before, the vast majority of this invisible world remains unexplored. Microbiologists continue to identify new ways that microbes benefit and threaten humans.
- 1 J. Hulcr et al. “A Jungle in There: Bacteria in Belly Buttons are Highly Diverse, but Predictable.” PLoS ONE 7 no. 11 (2012): e47712. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047712.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Nina Parker, Mark Schneegurt, Anh-Hue Thi Tu, Philip Lister, Brian M. Forster
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Microbiology
- Publication date: Nov 1, 2016
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction
© Jan 10, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Microbiology
A collection of TED Talks (and more) on the topic of Microbiology.
Video playlists about Microbiology

How microbes shape our world

The fabulous life of germs

What's the big deal about Mars?

Weird facts about the human body
Talks about microbiology.

Do gut microbes control your personality?

CRISPR's next advance is bigger than you think

How to harness the ancient partnership between forests and fungi


The fingerprints of life beyond Earth

The search for microscopic aliens

What causes dandruff, and how do you get rid of it?

Why didn't this 2,000 year old body decompose?

What ocean microbes reveal about the changing climate

The urgent case for antibiotic-free animals

How the gut microbes you're born with affect your lifelong health

Humanity at the intersection of science and archaeology

How sharks could inspire a new generation of medical devices

The mysterious microbes living deep inside the earth -- and how they could help humanity

These bacteria eat plastic

To detect diseases earlier, let's speak bacteria's secret language

How a long-forgotten virus could help us solve the antibiotics crisis
Exclusive articles about microbiology, inside the fascinating (and delicious) science of sourdough bread, watch: a cellular biologist animates the life cycle of hiv in this hypnotic video, for healthier buildings, just add bacteria.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Microbiology articles from across Nature Portfolio
Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, archaea, fungi and protozoa. This discipline includes fundamental research on the biochemistry, physiology, cell biology, ecology, evolution and clinical aspects of microorganisms, including the host response to these agents.
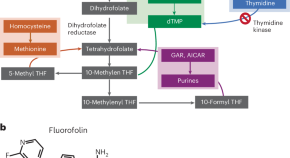
Narrow-spectrum antibiotic exploits metabolic differences to inhibit Pseudomonas aeruginosa
We characterize the activity of fluorofolin, a potent inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase, against Pseudomonas aeruginosa . By exploiting a divergence in thymidine metabolism, fluorofolin becomes selective for P. aeruginosa in the presence of thymine, demonstrating that it can be a narrow-spectrum antibiotic for this bacterial pathogen.
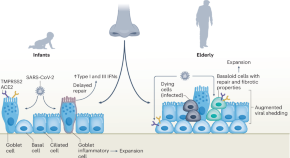
Aged nasal epithelium is more prone to severe COVID-19
Age is the single greatest risk factor driving mortality after encounter with SARS-CoV-2. A new study shows that the composition of nasal epithelial cells varies across ages, facilitating SARS-CoV-2 growth and spread in older people.
- Ivan Zanoni
Video game unleashes millions of citizen scientists on microbiome research
Borderlands Science is a casual mini-game released within a mass-market video game that crowdsources the alignment of one million RNA sequences from the human microbiome. In 3 years, 4 million participants generated over 135 million puzzle solutions that were used to build a reference alignment and improve microbial phylogeny.
Related Subjects
- Antimicrobials
- Applied microbiology
- Bacteriology
- Bacteriophages
- Biogeochemistry
- Cellular microbiology
- Clinical microbiology
- Microbial communities
- CRISPR-Cas systems
- Environmental microbiology
- Industrial microbiology
- Infectious-disease diagnostics
- Microbial genetics
- Parasitology
- Phage biology
- Policy and public health in microbiology
Latest Research and Reviews
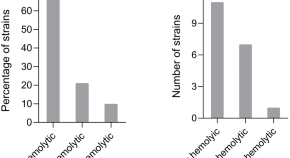
Bacillus velezensis iturins inhibit the hemolytic activity of Staphylococcus aureus
- Yasmin Neves Vieira Sabino
- Katialaine Corrêa de Araújo Domingues
- Hilario Cuquetto Mantovani
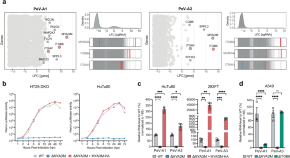
MYADM binds human parechovirus 1 and is essential for viral entry
Host factors required for parechovirus entry are not well understood. Here, the authors identify MYADM as an essential host entry factor that directly binds human parechovirus 1 and that is required for PeV-A infection in cell lines and human gastrointestinal epithelial organoids.
- Wenjie Qiao
- Christopher M. Richards
- Jan E. Carette
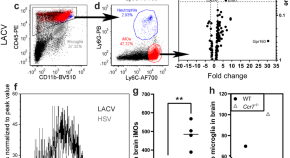
C-C motif chemokine receptor 2 and 7 synergistically control inflammatory monocyte recruitment but the infecting virus dictates monocyte function in the brain
The chemokine receptors CCR2 and CCR7 synergistically regulate recruitment of inflammatory monocytes from the bone marrow to the brain of mice infected with La Crosse and Herpes Simplex virus.
- Clayton W. Winkler
- Alyssa B. Evans
- Karin E. Peterson
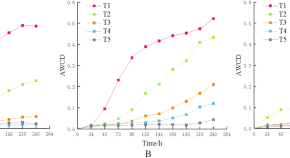
Vertical differences in carbon metabolic diversity and dominant flora of soil bacterial communities in farmlands
- Bufan Zheng
- Zhipeng Xiao
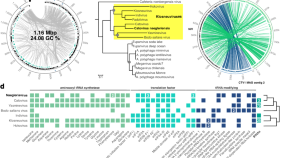
A giant virus infecting the amoeboflagellate Naegleria
This is the first report on a virus infecting the amoeboflagellate Naegleria , including the lethal human pathogen N. fowleri . The new virus isolate, Catovirus naegleriensis (Naegleriavirus, NiV), shows hallmarks of giant viruses (Nucleocytoviricota) and unique adaptations to its protist host.
- Patrick Arthofer
- Florian Panhölzl
- Matthias Horn
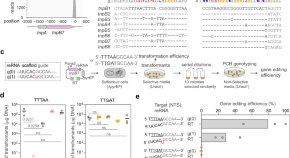
Flexible TAM requirement of TnpB enables efficient single-nucleotide editing with expanded targeting scope
Here the authors report that a thermophilic archaeal TnpB enables efficient gene editing in the natural host: they see that the TnpB has different TAM requirements for eliciting cell death and for facilitating gene editing. They show that TnpB can be harnessed for flexible single-nucleotide editing with templated repair.
News and Comment
Nitroplast organelle unveiled.
A recent study reports the existence of a nitrogen-fixing organelle called the ‘nitroplast’.
- Ashley York
The complex life of the HIV-1 full-length RNA
In this Journal Club, Ricardo Soto-Rifo discusses a study on intron-containing HIV-1 RNA, revealing its role as a pathogen-associated molecular pattern in myeloid cells, which has implications for immune activation, inflammation and clinical outcomes.
- Ricardo Soto-Rifo

WHO redefines airborne transmission: what does that mean for future pandemics?
The World Health Organization was criticized for being too slow to classify COVID-19 as airborne. Will the new terminology help next time?
- Bianca Nogrady
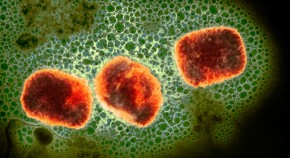
Monkeypox virus: dangerous strain gains ability to spread through sex, new data suggest
A cluster of mpox cases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo sparks worries of a wider outbreak.
Phages get snappy
This study shows that a single-stranded RNA phage binds to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type IV pilus, leading to phage entry into the cell and the detachment of the pilus, which impairs bacterial motility.
- Andrea Du Toit
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

suicide prevention
8 templates

46 templates

tropical rainforest
29 templates

spring season
34 templates

american football
16 templates

32 templates
Microbiology Breakthrough
Microbiology breakthrough presentation, premium google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Advances in medicine are always important events, and it’s great if the new findings can be presented in a clear manner. If you want to make a contribution to the medical community and share what you found out in your research, this new breakthrough presentation template is for you.
We think the look of these slides will not only impress you, but also your audience as well. For starters, let’s say you are talking about microbiology, so we’ve thought that a little visual detail on the backgrounds, such as the illustrations of chemical compounds and molecules, would be a nice addition to go with your data. All of them are colored in black and red, which are the main tones of the palette, along with the white hue used in the backgrounds. The design is not complicated at all; the slides use lines as content dividers, separators, ornaments or as part of infographics. Speaking of which, we’ve made sure to include graphs, charts and a timeline, because you’ll need all of these to properly explain the information, the results, the analysis and the statistics. We’ve also included some linear icons, whose color can be changed at will, that you can use in conjunction with text or other resources. Did we say that everything is customizable? Well, it is! What’s more, there are alternative illustrations and even a set of icons related to health in case you need them. Download this template and open Google Slides or PowerPoint to get started. Keynote is also fine too!
Features of this template
- Has a formal design with white backgrounds and chemical-themed elements
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 22 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics and maps
- Includes 1000+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the free resources used
What are the benefits of having a Premium account?
What Premium plans do you have?
What can I do to have unlimited downloads?
Don’t want to attribute Slidesgo?
Gain access to over 22700 templates & presentations with premium from 1.67€/month.
Are you already Premium? Log in
Related posts on our blog

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
32. The Golden Age of Microbiology ~1857-1914 (about 50 years) Beginning with Pasteur's work, discoveries included relationship between microbes and disease, immunity, and antimicrobial drugs Robert Koch a. Identified a bacterium as cause of anthrax b. Introduced agar, inoculating loop to transfer bacteria and prepare pure cultures.
Pioneers of Microbiology Louis Pasteur (1822-1895), Chemist •Fermentation •Pasteurization: heat liquid enough to kill spoilage bacteria • Vaccine development •Proposed the germ theory of disease •Proposed aseptic techniques (prevent contamination by unwanted microbes) •discovered forms of life that can exist in the presence
A typical bacterial cell (let us say E. coli) is about 1 µm wide by 4 µm long. A typical protozoal cell (let us say Paramecium) is about 25 µm wide by 100 µm long. There are 1000 µm in every millimeter, so that shows why it is difficult to see most microbes without assistance. (An exception would be a multicellular microbe, such as a fungus.
Print what: - on lower left side click the down pointing arrow and then click handouts from the drop-down list. Change Color to pure black & white. Under Handouts choose 3 or 6 slides per page. Click on the preview button and zoom to 100% - this will show you what the pages will look like if in your hands. This is a great way to determine how ...
Microbiology PPT. Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, that exist in the world around us. It is a vast field that encompasses numerous areas of study, including immunology, genetics, and biochemistry. Our Microbiology PPT (PowerPoint presentations) will help you to study the basic and ...
Microbiology is a broad term which includes virology, mycology, parasitology, bacteriology, immunology, and other branches. A microbiologist is a specialist in microbiology and these related topics. Microbiological procedures usually must be aseptic and use a variety of tools such as light microscopes with a combination of stains and dyes. As ...
This OER contains PowerPoint Presentation slides for the Microbiology OpenStax textbook. Chapters 1 - 10 have been uploaded to this platform. All PowerPoint presentations will be refined during implementation. In the meantime, please feel free to use these resources and modify to your liking as I have a different arrangement of slides that are ...
Sign up here and try our FREE content: http://lectur.io/freecontentyt If you're an medical educator or faculty member, visit: http://lectur.io/medytb2u T...
We examine the functional, metabolic, and phylogenetic diversity of soil bacteria, archaea, and fungi. The roles of these soil microbes are highlighted in the cycling of major biological elements (C, N, P), in the recycling of wastes, and the detoxifi cation of environmental pollutants. Microbes play a pivotal role in the cycling of nitrogen ...
Microbiology seems tough? Here we simplify this subject and make it an enjoyable one! Start with us in microbiology, and hopefully you will enjoy and learn a...
Microbiology Lecture Power Points Presentation. Chapter 7 (9th) Chapter 8 (9th edition) Chapter 1 (9th Edition) Chapter 3 (9th Edition) Chapter 4 (9th Edition) Chapter 6 (9th Edition) Chapter 11 (9th Edition) Chapter 12 (9th Edition) Chapter 13 (9th Edition) Chapter 9 (9th Edition) Chapter 14 (9th Edition) Chapter 15 (9th Edition) Chapter 16 ...
Microbiology, the study of microscopic organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, has become more relevant than ever before in our modern world. See? Potential students are already queuing up in the conference room, waiting for your introductory presentation to begin. Use this blue-colored template to prepare the slides that ...
Figure 1.1 A veterinarian gets ready to clean a sea turtle covered in oil following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010. After the spill, the population of a naturally occurring oil-eating marine bacterium called Alcanivorax borkumensis skyrocketed, helping to get rid of the oil. Scientists are working on ways to genetically engineer this bacterium to be more ...
Video playlists about Microbiology. Learn how these microorganisms influence everything from the air we breathe and how healthy we are, to forming life itself. Germs -- they get around. Learn what their travels and overall existence can teach us about not just ourselves, but the past, present and future of humanity.
Austin Community College District | Start Here. Get There.
Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, archaea, fungi and protozoa. This discipline includes fundamental research on the biochemistry, physiology, cell ...
The design of this PowerPoint template suits perfectly a wide range of microbiology branches such as bacteriology, parasitology, immunology, virology, and others. Get your presentation custom designed by us, starting at just $10 per slide. STEP 1. UPLOAD PRESENTATION. Share your presentation and design preferences via our easy-to-use order form.
Microbiology is a fascinating field because it covers the study of incredibly small organisms like bacteria, fungi, protozoa and viruses. These tiny creatures have an incredibly large impact on our lives - from the helpful microbes that help keep our bodies healthy, to the pesky bugs that can make us sick. It's an amazing science! To share this ...
19. Bacterial Classification Based on Staining MethodsBacteria are grouped as 'Gram positive' and 'Gram negative' bacteria, based on the results of Gram staining method, wherein an agent is used to bind to the cell wall of the bacteria.
Free Google Slides theme, PowerPoint template, and Canva presentation template. A bachelor's degree in microbiology opens doors to a wide range of possibilities. Studying bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms can be a fascinating challenge. This presentation template will help you convey your knowledge in a professional format so that your ...
Microbiology Breakthrough Presentation . Medical . Premium Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template . Advances in medicine are always important events, and it's great if the new findings can be presented in a clear manner. If you want to make a contribution to the medical community and share what you found out in your research, this new ...