Literature Review vs Systematic Review
- Literature Review vs. Systematic Review
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Databases and Articles
- Specific Journal or Article

Subject Guide

Definitions
It’s common to confuse systematic and literature reviews because both are used to provide a summary of the existent literature or research on a specific topic. Regardless of this commonality, both types of review vary significantly. The following table provides a detailed explanation as well as the differences between systematic and literature reviews.
Kysh, Lynn (2013): Difference between a systematic review and a literature review. [figshare]. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.766364
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Primary vs. Secondary Sources >>
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 10:19 AM
- URL: https://libguides.sjsu.edu/LitRevVSSysRev

Systematic Reviews
- The Research Question
- Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Original Studies
- Translating
- Deduplication
- Project Management Tools
- Useful Resources
- What is not a systematic review?
Typology of Reviews
There are other types of reviews, and some are often mistaken for systematic reviews. Some may even call themselves 'systematic reviews.' However, understanding the scope of other reviews and methods can help one distinguish between them and a systematic review proper. Here are some common review types:
- Technique that statistically combines the results of quantitative studies to provide a more precise effect of the results. May be a component of a systematic review.
- Generic term: published materials that provide examination of recent or current literature. Can cover a wide range of subjects at various levels of completeness and comprehensiveness. May include research findings.
- Preliminary assessment of potential size and scope of available research literature. Aims to identify nature and extent of research evidence (usually including ongoing research).
- Assessment of what is already known about a policy or practice issue, by using systematic review methods to search and critically appraise existing research.
- Specifically refers to reviews compiling evidence from multiple reviews into one accessible and usable document. Focuses on broad condition or problem for which there are competing interventions and highlights reviews that address these interventions and their results.
- Attempts to include elements of the systematic review process while stopping short of a systematic review. Typically conducted as a postgraduate student assignment.
The above definitions are taken from A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. The document is listed below.
- A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies
Meta-Analysis
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarise the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analyses can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. Meta-analyses also facilitate investigations of the consistency of evidence across studies, and the exploration of differences across studies ( Cochrane Handbook, 1.2.2 ). More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analyses on the outcomes of similar studies. Systematic reviews may use quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Literature Reviews
Literatures reviews focus on the existing literature of a subject. They lack the rigorous systematic methodology of systematic reviews. They rarely conduct exhaustive search strategies and do not publish the search strategy (although there are exceptions due to the general nature of literature reviews.) Literature reviews may examine the literature that is the most commonly cited within a certain time frame. Synthesis according to some criteria is typically employed. Literature reviews can take many forms: theses, dissertations, a component within a research paper, or lab report. Please see the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill's information on literature reviews here.
Scoping Review or (Mapping Review)
In general, scoping reviews are commonly used for ‘reconnaissance’ – to clarify working definitions and conceptual boundaries of a topic or field. Scoping reviews are useful for when a body of literature has not yet been comprehensively reviewed, or exhibits a complex or heterogeneous nature not amenable to a more precise systematic review of the evidence. While scoping reviews may be conducted to determine the value and probable scope of a full systematic review, they may also be undertaken as exercises in and of themselves to summarize and disseminate research findings, to identify research gaps, and to make recommendations for future research.
From Peters, MD, Godfrey, CM, Khalil , H, McInerney, P, Parker, D & Soares , CB 2015, ' Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews', International Journal of Evidence-Based Healthcare, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 141-146 :
- Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews
- PRISMA for Scoping Reviews The PRISMA extension for scoping reviews was published in 2018. The checklist contains 20 essential reporting items and 2 optional items to include when completing a scoping review. Scoping reviews serve to synthesize evidence and assess the scope of literature on a topic. Among other objectives, scoping reviews help determine whether a systematic review of the literature is warranted. more... less... Check out the Statement/Explanatory paper by Tricco et al. (2018) and the additional Tip Sheets for Items 1-22 in the PRISMA checklist for Scoping Reviews
Rapid reviews
Rapid reviews utilize systematic review methodology, but they have a more streamlined process for possible time constraints. Defining the limitations and the drawbacks of implementing a streamlined process (and a process that may not incorporate all the components of a systematic review for transparency and systematization) must be described. To learn more about rapid reviews, check out the link below.
- A scoping review of rapid review methods
Umbrella Review
An Umbrella review is a synthesis of existing reviews, only including the highest level of evidence such as systematic reviews and meta-analyes. It specifically refers to a review that compiles evidence from multiple reviews into one accessible and usable document. Umbrella reviews focus on either a broad condition or problem for which there are competing interventions. These reviews can highlight the different interventions and their results.
Methodology paper : Aromataris , E, Fernandez, R, Godfrey, CM, Holly, C, Khalil , H & Tungpunkom , P 2015, 'Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach', Int J Evid Based Healthc , vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 132-140.
- Summarizing systematic reviews
Systematized reviews
A systematized review attempts to include elements of the systematic review process while stopping short of the systematic review. Systematized reviews are typically conducted as a postgraduate student assignment, in recognition that they are not able to draw upon the resources required for a full systematic review (such as having two reviewers for extensive literature screening).
- << Previous: Useful Resources
- Last Updated: Oct 12, 2023 12:30 PM
- URL: https://libguides.sph.uth.tmc.edu/SystematicReviews
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Systematic Review | Definition, Example, & Guide
Systematic Review | Definition, Example & Guide
Published on June 15, 2022 by Shaun Turney . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A systematic review is a type of review that uses repeatable methods to find, select, and synthesize all available evidence. It answers a clearly formulated research question and explicitly states the methods used to arrive at the answer.
They answered the question “What is the effectiveness of probiotics in reducing eczema symptoms and improving quality of life in patients with eczema?”
In this context, a probiotic is a health product that contains live microorganisms and is taken by mouth. Eczema is a common skin condition that causes red, itchy skin.
Table of contents
What is a systematic review, systematic review vs. meta-analysis, systematic review vs. literature review, systematic review vs. scoping review, when to conduct a systematic review, pros and cons of systematic reviews, step-by-step example of a systematic review, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about systematic reviews.
A review is an overview of the research that’s already been completed on a topic.
What makes a systematic review different from other types of reviews is that the research methods are designed to reduce bias . The methods are repeatable, and the approach is formal and systematic:
- Formulate a research question
- Develop a protocol
- Search for all relevant studies
- Apply the selection criteria
- Extract the data
- Synthesize the data
- Write and publish a report
Although multiple sets of guidelines exist, the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews is among the most widely used. It provides detailed guidelines on how to complete each step of the systematic review process.
Systematic reviews are most commonly used in medical and public health research, but they can also be found in other disciplines.
Systematic reviews typically answer their research question by synthesizing all available evidence and evaluating the quality of the evidence. Synthesizing means bringing together different information to tell a single, cohesive story. The synthesis can be narrative ( qualitative ), quantitative , or both.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Systematic reviews often quantitatively synthesize the evidence using a meta-analysis . A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis, not a type of review.
A meta-analysis is a technique to synthesize results from multiple studies. It’s a statistical analysis that combines the results of two or more studies, usually to estimate an effect size .
A literature review is a type of review that uses a less systematic and formal approach than a systematic review. Typically, an expert in a topic will qualitatively summarize and evaluate previous work, without using a formal, explicit method.
Although literature reviews are often less time-consuming and can be insightful or helpful, they have a higher risk of bias and are less transparent than systematic reviews.
Similar to a systematic review, a scoping review is a type of review that tries to minimize bias by using transparent and repeatable methods.
However, a scoping review isn’t a type of systematic review. The most important difference is the goal: rather than answering a specific question, a scoping review explores a topic. The researcher tries to identify the main concepts, theories, and evidence, as well as gaps in the current research.
Sometimes scoping reviews are an exploratory preparation step for a systematic review, and sometimes they are a standalone project.
A systematic review is a good choice of review if you want to answer a question about the effectiveness of an intervention , such as a medical treatment.
To conduct a systematic review, you’ll need the following:
- A precise question , usually about the effectiveness of an intervention. The question needs to be about a topic that’s previously been studied by multiple researchers. If there’s no previous research, there’s nothing to review.
- If you’re doing a systematic review on your own (e.g., for a research paper or thesis ), you should take appropriate measures to ensure the validity and reliability of your research.
- Access to databases and journal archives. Often, your educational institution provides you with access.
- Time. A professional systematic review is a time-consuming process: it will take the lead author about six months of full-time work. If you’re a student, you should narrow the scope of your systematic review and stick to a tight schedule.
- Bibliographic, word-processing, spreadsheet, and statistical software . For example, you could use EndNote, Microsoft Word, Excel, and SPSS.
A systematic review has many pros .
- They minimize research bias by considering all available evidence and evaluating each study for bias.
- Their methods are transparent , so they can be scrutinized by others.
- They’re thorough : they summarize all available evidence.
- They can be replicated and updated by others.
Systematic reviews also have a few cons .
- They’re time-consuming .
- They’re narrow in scope : they only answer the precise research question.
The 7 steps for conducting a systematic review are explained with an example.
Step 1: Formulate a research question
Formulating the research question is probably the most important step of a systematic review. A clear research question will:
- Allow you to more effectively communicate your research to other researchers and practitioners
- Guide your decisions as you plan and conduct your systematic review
A good research question for a systematic review has four components, which you can remember with the acronym PICO :
- Population(s) or problem(s)
- Intervention(s)
- Comparison(s)
You can rearrange these four components to write your research question:
- What is the effectiveness of I versus C for O in P ?
Sometimes, you may want to include a fifth component, the type of study design . In this case, the acronym is PICOT .
- Type of study design(s)
- The population of patients with eczema
- The intervention of probiotics
- In comparison to no treatment, placebo , or non-probiotic treatment
- The outcome of changes in participant-, parent-, and doctor-rated symptoms of eczema and quality of life
- Randomized control trials, a type of study design
Their research question was:
- What is the effectiveness of probiotics versus no treatment, a placebo, or a non-probiotic treatment for reducing eczema symptoms and improving quality of life in patients with eczema?
Step 2: Develop a protocol
A protocol is a document that contains your research plan for the systematic review. This is an important step because having a plan allows you to work more efficiently and reduces bias.
Your protocol should include the following components:
- Background information : Provide the context of the research question, including why it’s important.
- Research objective (s) : Rephrase your research question as an objective.
- Selection criteria: State how you’ll decide which studies to include or exclude from your review.
- Search strategy: Discuss your plan for finding studies.
- Analysis: Explain what information you’ll collect from the studies and how you’ll synthesize the data.
If you’re a professional seeking to publish your review, it’s a good idea to bring together an advisory committee . This is a group of about six people who have experience in the topic you’re researching. They can help you make decisions about your protocol.
It’s highly recommended to register your protocol. Registering your protocol means submitting it to a database such as PROSPERO or ClinicalTrials.gov .
Step 3: Search for all relevant studies
Searching for relevant studies is the most time-consuming step of a systematic review.
To reduce bias, it’s important to search for relevant studies very thoroughly. Your strategy will depend on your field and your research question, but sources generally fall into these four categories:
- Databases: Search multiple databases of peer-reviewed literature, such as PubMed or Scopus . Think carefully about how to phrase your search terms and include multiple synonyms of each word. Use Boolean operators if relevant.
- Handsearching: In addition to searching the primary sources using databases, you’ll also need to search manually. One strategy is to scan relevant journals or conference proceedings. Another strategy is to scan the reference lists of relevant studies.
- Gray literature: Gray literature includes documents produced by governments, universities, and other institutions that aren’t published by traditional publishers. Graduate student theses are an important type of gray literature, which you can search using the Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations (NDLTD) . In medicine, clinical trial registries are another important type of gray literature.
- Experts: Contact experts in the field to ask if they have unpublished studies that should be included in your review.
At this stage of your review, you won’t read the articles yet. Simply save any potentially relevant citations using bibliographic software, such as Scribbr’s APA or MLA Generator .
- Databases: EMBASE, PsycINFO, AMED, LILACS, and ISI Web of Science
- Handsearch: Conference proceedings and reference lists of articles
- Gray literature: The Cochrane Library, the metaRegister of Controlled Trials, and the Ongoing Skin Trials Register
- Experts: Authors of unpublished registered trials, pharmaceutical companies, and manufacturers of probiotics
Step 4: Apply the selection criteria
Applying the selection criteria is a three-person job. Two of you will independently read the studies and decide which to include in your review based on the selection criteria you established in your protocol . The third person’s job is to break any ties.
To increase inter-rater reliability , ensure that everyone thoroughly understands the selection criteria before you begin.
If you’re writing a systematic review as a student for an assignment, you might not have a team. In this case, you’ll have to apply the selection criteria on your own; you can mention this as a limitation in your paper’s discussion.
You should apply the selection criteria in two phases:
- Based on the titles and abstracts : Decide whether each article potentially meets the selection criteria based on the information provided in the abstracts.
- Based on the full texts: Download the articles that weren’t excluded during the first phase. If an article isn’t available online or through your library, you may need to contact the authors to ask for a copy. Read the articles and decide which articles meet the selection criteria.
It’s very important to keep a meticulous record of why you included or excluded each article. When the selection process is complete, you can summarize what you did using a PRISMA flow diagram .
Next, Boyle and colleagues found the full texts for each of the remaining studies. Boyle and Tang read through the articles to decide if any more studies needed to be excluded based on the selection criteria.
When Boyle and Tang disagreed about whether a study should be excluded, they discussed it with Varigos until the three researchers came to an agreement.
Step 5: Extract the data
Extracting the data means collecting information from the selected studies in a systematic way. There are two types of information you need to collect from each study:
- Information about the study’s methods and results . The exact information will depend on your research question, but it might include the year, study design , sample size, context, research findings , and conclusions. If any data are missing, you’ll need to contact the study’s authors.
- Your judgment of the quality of the evidence, including risk of bias .
You should collect this information using forms. You can find sample forms in The Registry of Methods and Tools for Evidence-Informed Decision Making and the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations Working Group .
Extracting the data is also a three-person job. Two people should do this step independently, and the third person will resolve any disagreements.
They also collected data about possible sources of bias, such as how the study participants were randomized into the control and treatment groups.
Step 6: Synthesize the data
Synthesizing the data means bringing together the information you collected into a single, cohesive story. There are two main approaches to synthesizing the data:
- Narrative ( qualitative ): Summarize the information in words. You’ll need to discuss the studies and assess their overall quality.
- Quantitative : Use statistical methods to summarize and compare data from different studies. The most common quantitative approach is a meta-analysis , which allows you to combine results from multiple studies into a summary result.
Generally, you should use both approaches together whenever possible. If you don’t have enough data, or the data from different studies aren’t comparable, then you can take just a narrative approach. However, you should justify why a quantitative approach wasn’t possible.
Boyle and colleagues also divided the studies into subgroups, such as studies about babies, children, and adults, and analyzed the effect sizes within each group.
Step 7: Write and publish a report
The purpose of writing a systematic review article is to share the answer to your research question and explain how you arrived at this answer.
Your article should include the following sections:
- Abstract : A summary of the review
- Introduction : Including the rationale and objectives
- Methods : Including the selection criteria, search method, data extraction method, and synthesis method
- Results : Including results of the search and selection process, study characteristics, risk of bias in the studies, and synthesis results
- Discussion : Including interpretation of the results and limitations of the review
- Conclusion : The answer to your research question and implications for practice, policy, or research
To verify that your report includes everything it needs, you can use the PRISMA checklist .
Once your report is written, you can publish it in a systematic review database, such as the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews , and/or in a peer-reviewed journal.
In their report, Boyle and colleagues concluded that probiotics cannot be recommended for reducing eczema symptoms or improving quality of life in patients with eczema. Note Generative AI tools like ChatGPT can be useful at various stages of the writing and research process and can help you to write your systematic review. However, we strongly advise against trying to pass AI-generated text off as your own work.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
A systematic review is secondary research because it uses existing research. You don’t collect new data yourself.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Turney, S. (2023, November 20). Systematic Review | Definition, Example & Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/systematic-review/
Is this article helpful?

Shaun Turney
Other students also liked, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is critical thinking | definition & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 24, Issue 2
- Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0157-5319 Ahtisham Younas 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7839-8130 Parveen Ali 3 , 4
- 1 Memorial University of Newfoundland , St John's , Newfoundland , Canada
- 2 Swat College of Nursing , Pakistan
- 3 School of Nursing and Midwifery , University of Sheffield , Sheffield , South Yorkshire , UK
- 4 Sheffield University Interpersonal Violence Research Group , Sheffield University , Sheffield , UK
- Correspondence to Ahtisham Younas, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John's, NL A1C 5C4, Canada; ay6133{at}mun.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research. 1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis in reviews, the use of literature summary tables is of utmost importance. A literature summary table provides a synopsis of an included article. It succinctly presents its purpose, methods, findings and other relevant information pertinent to the review. The aim of developing these literature summary tables is to provide the reader with the information at one glance. Since there are multiple types of reviews (eg, systematic, integrative, scoping, critical and mixed methods) with distinct purposes and techniques, 2 there could be various approaches for developing literature summary tables making it a complex task specialty for the novice researchers or reviewers. Here, we offer five tips for authors of the review articles, relevant to all types of reviews, for creating useful and relevant literature summary tables. We also provide examples from our published reviews to illustrate how useful literature summary tables can be developed and what sort of information should be provided.
Tip 1: provide detailed information about frameworks and methods
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Tabular literature summaries from a scoping review. Source: Rasheed et al . 3
The provision of information about conceptual and theoretical frameworks and methods is useful for several reasons. First, in quantitative (reviews synthesising the results of quantitative studies) and mixed reviews (reviews synthesising the results of both qualitative and quantitative studies to address a mixed review question), it allows the readers to assess the congruence of the core findings and methods with the adapted framework and tested assumptions. In qualitative reviews (reviews synthesising results of qualitative studies), this information is beneficial for readers to recognise the underlying philosophical and paradigmatic stance of the authors of the included articles. For example, imagine the authors of an article, included in a review, used phenomenological inquiry for their research. In that case, the review authors and the readers of the review need to know what kind of (transcendental or hermeneutic) philosophical stance guided the inquiry. Review authors should, therefore, include the philosophical stance in their literature summary for the particular article. Second, information about frameworks and methods enables review authors and readers to judge the quality of the research, which allows for discerning the strengths and limitations of the article. For example, if authors of an included article intended to develop a new scale and test its psychometric properties. To achieve this aim, they used a convenience sample of 150 participants and performed exploratory (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on the same sample. Such an approach would indicate a flawed methodology because EFA and CFA should not be conducted on the same sample. The review authors must include this information in their summary table. Omitting this information from a summary could lead to the inclusion of a flawed article in the review, thereby jeopardising the review’s rigour.
Tip 2: include strengths and limitations for each article
Critical appraisal of individual articles included in a review is crucial for increasing the rigour of the review. Despite using various templates for critical appraisal, authors often do not provide detailed information about each reviewed article’s strengths and limitations. Merely noting the quality score based on standardised critical appraisal templates is not adequate because the readers should be able to identify the reasons for assigning a weak or moderate rating. Many recent critical appraisal checklists (eg, Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool) discourage review authors from assigning a quality score and recommend noting the main strengths and limitations of included studies. It is also vital that methodological and conceptual limitations and strengths of the articles included in the review are provided because not all review articles include empirical research papers. Rather some review synthesises the theoretical aspects of articles. Providing information about conceptual limitations is also important for readers to judge the quality of foundations of the research. For example, if you included a mixed-methods study in the review, reporting the methodological and conceptual limitations about ‘integration’ is critical for evaluating the study’s strength. Suppose the authors only collected qualitative and quantitative data and did not state the intent and timing of integration. In that case, the strength of the study is weak. Integration only occurred at the levels of data collection. However, integration may not have occurred at the analysis, interpretation and reporting levels.
Tip 3: write conceptual contribution of each reviewed article
While reading and evaluating review papers, we have observed that many review authors only provide core results of the article included in a review and do not explain the conceptual contribution offered by the included article. We refer to conceptual contribution as a description of how the article’s key results contribute towards the development of potential codes, themes or subthemes, or emerging patterns that are reported as the review findings. For example, the authors of a review article noted that one of the research articles included in their review demonstrated the usefulness of case studies and reflective logs as strategies for fostering compassion in nursing students. The conceptual contribution of this research article could be that experiential learning is one way to teach compassion to nursing students, as supported by case studies and reflective logs. This conceptual contribution of the article should be mentioned in the literature summary table. Delineating each reviewed article’s conceptual contribution is particularly beneficial in qualitative reviews, mixed-methods reviews, and critical reviews that often focus on developing models and describing or explaining various phenomena. Figure 2 offers an example of a literature summary table. 4
Tabular literature summaries from a critical review. Source: Younas and Maddigan. 4
Tip 4: compose potential themes from each article during summary writing
While developing literature summary tables, many authors use themes or subthemes reported in the given articles as the key results of their own review. Such an approach prevents the review authors from understanding the article’s conceptual contribution, developing rigorous synthesis and drawing reasonable interpretations of results from an individual article. Ultimately, it affects the generation of novel review findings. For example, one of the articles about women’s healthcare-seeking behaviours in developing countries reported a theme ‘social-cultural determinants of health as precursors of delays’. Instead of using this theme as one of the review findings, the reviewers should read and interpret beyond the given description in an article, compare and contrast themes, findings from one article with findings and themes from another article to find similarities and differences and to understand and explain bigger picture for their readers. Therefore, while developing literature summary tables, think twice before using the predeveloped themes. Including your themes in the summary tables (see figure 1 ) demonstrates to the readers that a robust method of data extraction and synthesis has been followed.
Tip 5: create your personalised template for literature summaries
Often templates are available for data extraction and development of literature summary tables. The available templates may be in the form of a table, chart or a structured framework that extracts some essential information about every article. The commonly used information may include authors, purpose, methods, key results and quality scores. While extracting all relevant information is important, such templates should be tailored to meet the needs of the individuals’ review. For example, for a review about the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, a literature summary table must include information about the intervention, its type, content timing, duration, setting, effectiveness, negative consequences, and receivers and implementers’ experiences of its usage. Similarly, literature summary tables for articles included in a meta-synthesis must include information about the participants’ characteristics, research context and conceptual contribution of each reviewed article so as to help the reader make an informed decision about the usefulness or lack of usefulness of the individual article in the review and the whole review.
In conclusion, narrative or systematic reviews are almost always conducted as a part of any educational project (thesis or dissertation) or academic or clinical research. Literature reviews are the foundation of research on a given topic. Robust and high-quality reviews play an instrumental role in guiding research, practice and policymaking. However, the quality of reviews is also contingent on rigorous data extraction and synthesis, which require developing literature summaries. We have outlined five tips that could enhance the quality of the data extraction and synthesis process by developing useful literature summaries.
- Aromataris E ,
- Rasheed SP ,
Twitter @Ahtisham04, @parveenazamali
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
Advertisement
Toward a framework for selecting indicators of measuring sustainability and circular economy in the agri-food sector: a systematic literature review
- LIFE CYCLE SUSTAINABILITY ASSESSMENT
- Published: 02 March 2022
Cite this article
- Cecilia Silvestri ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2528-601X 1 ,
- Luca Silvestri ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6754-899X 2 ,
- Michela Piccarozzi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9717-9462 1 &
- Alessandro Ruggieri 1
2853 Accesses
11 Citations
9 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
A Correction to this article was published on 24 March 2022
This article has been updated
The implementation of sustainability and circular economy (CE) models in agri-food production can promote resource efficiency, reduce environmental burdens, and ensure improved and socially responsible systems. In this context, indicators for the measurement of sustainability play a crucial role. Indicators can measure CE strategies aimed to preserve functions, products, components, materials, or embodied energy. Although there is broad literature describing sustainability and CE indicators, no study offers such a comprehensive framework of indicators for measuring sustainability and CE in the agri-food sector.
Starting from this central research gap, a systematic literature review has been developed to measure the sustainability in the agri-food sector and, based on these findings, to understand how indicators are used and for which specific purposes.
The analysis of the results allowed us to classify the sample of articles in three main clusters (“Assessment-LCA,” “Best practice,” and “Decision-making”) and has shown increasing attention to the three pillars of sustainability (triple bottom line). In this context, an integrated approach of indicators (environmental, social, and economic) offers the best solution to ensure an easier transition to sustainability.
Conclusions
The sample analysis facilitated the identification of new categories of impact that deserve attention, such as the cooperation among stakeholders in the supply chain and eco-innovation.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
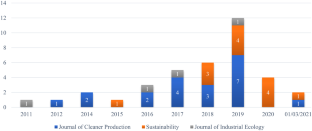
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the temporal distribution of the articles under analysis
Source: Authors’ elaborations. Notes: The graph shows the time distribution of articles from the three major journals
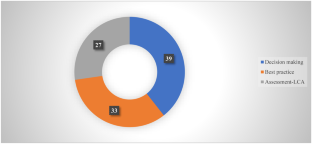
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the composition of the sample according to the three clusters identified by the analysis
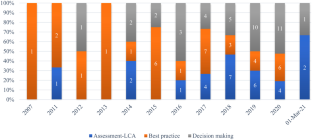
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the distribution of articles over time by cluster
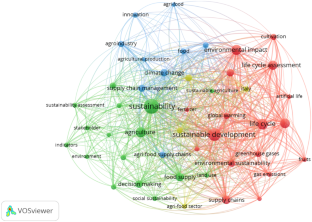
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the network visualization
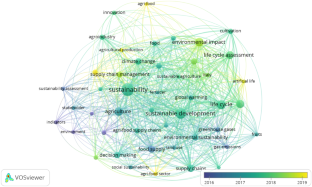
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the overlay visualization
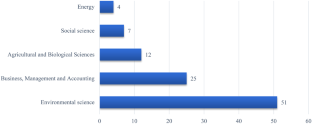
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the classification of articles by scientific field
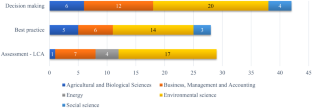
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: Article classification based on their cluster to which they belong and scientific field
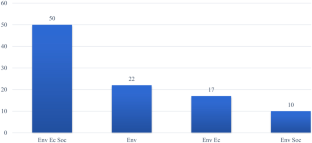
Source: Authors’ elaboration
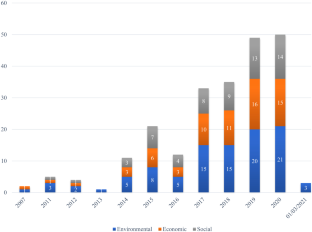
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the distribution of items over time based on TBL
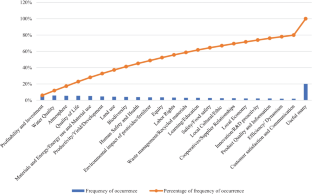
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the Pareto diagram highlighting the most used indicators in literature for measuring sustainability in the agri-food sector
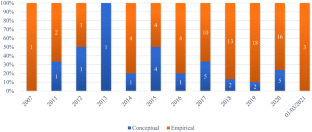
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the distribution over time of articles divided into conceptual and empirical
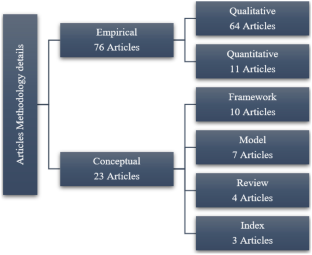
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the classification of articles, divided into conceptual and empirical, in-depth analysis
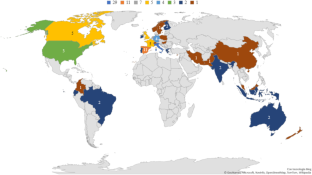
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the geographical distribution of the authors
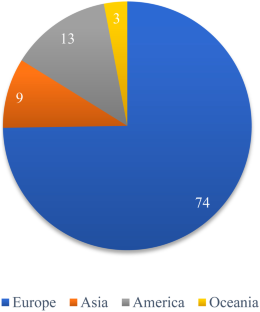
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the distribution of authors according to the continent from which they originate
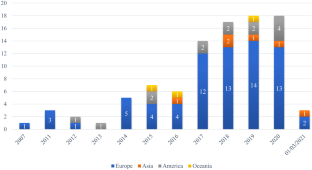
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: The graph shows the time distribution of publication of authors according to the continent from which they originate
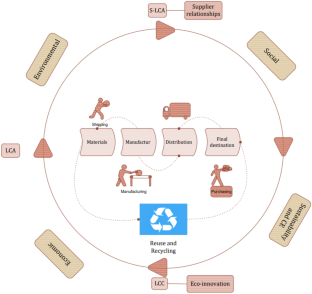
Source: Authors’ elaboration. Notes: Sustainability measurement indicators and impact categories of LCA, S-LCA, and LCC tools should be integrated in order to provide stakeholders with best practices as guidelines and tools to support both decision-making and measurement, according to the circular economy approach
Similar content being viewed by others
The socio-economic performance of agroecology. A review
Ioanna Mouratiadou, Alexander Wezel, … Paolo Bàrberi

The Circular Economy: An Interdisciplinary Exploration of the Concept and Application in a Global Context
Alan Murray, Keith Skene & Kathryn Haynes
The sustainability of “local” food: a review for policy-makers
Alexander J. Stein & Fabien Santini
Change history
24 march 2022.
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-022-02038-9
Acero AP, Rodriguez C, Ciroth A (2017) LCIA methods: impact assessment methods in life cycle assessment and their impact categories. Version 1.5.6. Green Delta 1–23
Accorsi R, Versari L, Manzini R (2015) Glass vs. plastic: Life cycle assessment of extra-virgin olive oil bottles across global supply chains. Sustain 7:2818–2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7032818
Adjei-Bamfo P, Maloreh-Nyamekye T, Ahenkan A (2019) The role of e-government in sustainable public procurement in developing countries: a systematic literature review. Resour Conserv Recycl 142:189–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.12.001
Article Google Scholar
Aivazidou E, Tsolakis N, Vlachos D, Iakovou E (2015) Water footprint management policies for agrifood supply chains: a critical taxonomy and a system dynamics modelling approach. Chem Eng Trans 43:115–120. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1543020
Alhaddi H (2015) Triple bottom line and sustainability: a literature review. Bus Manag Stud 1:6–10
Allaoui H, Guo Y, Sarkis J (2019) Decision support for collaboration planning in sustainable supply chains. J Clean Prod 229:761–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.367
Alshqaqeeq F, Amin Esmaeili M, Overcash M, Twomey J (2020) Quantifying hospital services by carbon footprint: a systematic literature review of patient care alternatives. Resour Conserv Recycl 154:104560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104560
Anwar F, Chaudhry FN, Nazeer S et al (2016) Causes of ozone layer depletion and its effects on human: review. Atmos Clim Sci 06:129–134. https://doi.org/10.4236/acs.2016.61011
Aquilani B, Silvestri C, Ruggieri A (2016). A Systematic Literature Review on Total Quality Management Critical Success Factors and the Identification of New Avenues of Research. https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-01-2016-0003
Aramyan L, Hoste R, Van Den Broek W et al (2011) Towards sustainable food production: a scenario study of the European pork sector. J Chain Netw Sci 11:177–189. https://doi.org/10.3920/JCNS2011.Qpork8
Arfini F, Antonioli F, Cozzi E et al (2019) Sustainability, innovation and rural development: the case of Parmigiano-Reggiano PDO. Sustain 11:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11184978
Assembly UG (2005) Resolution adopted by the general assembly. New York, NY
Avilés-Palacios C, Rodríguez-Olalla A (2021) The sustainability of waste management models in circular economies. Sustain 13:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137105
Azevedo SG, Silva ME, Matias JCO, Dias GP (2018) The influence of collaboration initiatives on the sustainability of the cashew supply chain. Sustain 10:1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10062075
Bajaj S, Garg R, Sethi M (2016) Total quality management: a critical literature review using Pareto analysis. Int J Product Perform Manag 67:128–154
Banasik A, Kanellopoulos A, Bloemhof-Ruwaard JM, Claassen GDH (2019) Accounting for uncertainty in eco-efficient agri-food supply chains: a case study for mushroom production planning. J Clean Prod 216:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.153
Barth H, Ulvenblad PO, Ulvenblad P (2017) Towards a conceptual framework of sustainable business model innovation in the agri-food sector: a systematic literature review. Sustain 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9091620
Bastas A, Liyanage K (2018) Sustainable supply chain quality management: a systematic review
Beckerman W (1992) Economic growth and the environment: whose growth? Whose environment? World Dev 20:481–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-750X(92)90038-W
Belaud JP, Prioux N, Vialle C, Sablayrolles C (2019) Big data for agri-food 4.0: application to sustainability management for by-products supply chain. Comput Ind 111:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2019.06.006
Bele B, Norderhaug A, Sickel H (2018) Localized agri-food systems and biodiversity. Agric 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture8020022
Bilali H El, Calabrese G, Iannetta M et al (2020) Environmental sustainability of typical agro-food products: a scientifically sound and user friendly approach. New Medit 19:69–83. https://doi.org/10.30682/nm2002e
Blanc S, Massaglia S, Brun F et al (2019) Use of bio-based plastics in the fruit supply chain: an integrated approach to assess environmental, economic, and social sustainability. Sustain 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11092475
Bloemhof JM, van der Vorst JGAJ, Bastl M, Allaoui H (2015) Sustainability assessment of food chain logistics. Int J Logist Res Appl 18:101–117. https://doi.org/10.1080/13675567.2015.1015508
Bonisoli L, Galdeano-Gómez E, Piedra-Muñoz L (2018) Deconstructing criteria and assessment tools to build agri-sustainability indicators and support farmers’ decision-making process. J Clean Prod 182:1080–1094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.055
Bonisoli L, Galdeano-Gómez E, Piedra-Muñoz L, Pérez-Mesa JC (2019) Benchmarking agri-food sustainability certifications: evidences from applying SAFA in the Ecuadorian banana agri-system. J Clean Prod 236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.07.054
Bornmann L, Haunschild R, Hug SE (2018) Visualizing the context of citations referencing papers published by Eugene Garfield: a new type of keyword co-occurrence analysis. Scientometrics 114:427–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2591-8
Boulding KE (1966) The economics of the coming spaceship earth. New York, 1-17
Bracquené E, Dewulf W, Duflou JR (2020) Measuring the performance of more circular complex product supply chains. Resour Conserv Recycl 154:104608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104608
Burck J, Hagen U, Bals C et al (2021) Climate Change Performance Index
Calisto Friant M, Vermeulen WJV, Salomone R (2020) A typology of circular economy discourses: navigating the diverse visions of a contested paradigm. Resour Conserv Recycl 161:104917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.104917
Campbell BM, Beare DJ, Bennett EM et al (2017) Agriculture production as a major driver of the earth system exceeding planetary boundaries. Ecol Soc 22. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-09595-220408
Capitanio F, Coppola A, Pascucci S (2010) Product and process innovation in the Italian food industry. Agribusiness 26:503–518. https://doi.org/10.1002/agr.20239
Caputo P, Zagarella F, Cusenza MA et al (2020) Energy-environmental assessment of the UIA-OpenAgri case study as urban regeneration project through agriculture. Sci Total Environ 729:138819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138819
Article CAS Google Scholar
Chabowski BR, Mena JA, Gonzalez-Padron TL (2011) The structure of sustainability research in marketing, 1958–2008: a basis for future research opportunities. J Acad Mark Sci 39:55–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-010-0212-7
Chadegani AA, Salehi H, Yunus M et al (2017) A comparison between two main academic literature collections : Web of Science and Scopus databases. Asian Soc Sci 9:18–26. https://doi.org/10.5539/ass.v9n5p18
Chams N, Guesmi B, Gil JM (2020) Beyond scientific contribution: assessment of the societal impact of research and innovation to build a sustainable agri-food sector. J Environ Manage 264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110455
Chandrakumar C, McLaren SJ, Jayamaha NP, Ramilan T (2019) Absolute sustainability-based life cycle assessment (ASLCA): a benchmarking approach to operate agri-food systems within the 2°C global carbon budget. J Ind Ecol 23:906–917. https://doi.org/10.1111/jiec.12830
Chaparro-Africano AM (2019) Toward generating sustainability indicators for agroecological markets. Agroecol Sustain Food Syst 43:40–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/21683565.2019.1566192
Colicchia C, Strozzi F (2012) Supply chain risk management: a new methodology for a systematic literature review
Conca L, Manta F, Morrone D, Toma P (2021) The impact of direct environmental, social, and governance reporting: empirical evidence in European-listed companies in the agri-food sector. Bus Strateg Environ 30:1080–1093. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2672
Coppola A, Ianuario S, Romano S, Viccaro M (2020) Corporate social responsibility in agri-food firms: the relationship between CSR actions and firm’s performance. AIMS Environ Sci 7:542–558. https://doi.org/10.3934/environsci.2020034
Corona B, Shen L, Reike D et al (2019) Towards sustainable development through the circular economy—a review and critical assessment on current circularity metrics. Resour Conserv Recycl 151:104498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104498
Correia MS (2019) Sustainability: An overview of the triple bottom line and sustainability implementation. Int J Strateg Eng 2:29–38. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJoSE.2019010103
Coteur I, Marchand F, Debruyne L, Lauwers L (2019) Structuring the myriad of sustainability assessments in agri-food systems: a case in Flanders. J Clean Prod 209:472–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.066
CREA (2020) L’agricoltura italiana conta 2019
Crenna E, Sala S, Polce C, Collina E (2017) Pollinators in life cycle assessment: towards a framework for impact assessment. J Clean Prod 140:525–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.058
D’Eusanio M, Serreli M, Zamagni A, Petti L (2018) Assessment of social dimension of a jar of honey: a methodological outline. J Clean Prod 199:503–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.157
Dania WAP, Xing K, Amer Y (2018) Collaboration behavioural factors for sustainable agri-food supply chains: a systematic review. J Clean Prod 186:851–864
De Pascale A, Arbolino R, Szopik-Depczyńska K et al (2021) A systematic review for measuring circular economy: the 61 indicators. J Clean Prod 281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124942
De Schoenmakere M, Gillabel J (2017) Circular by design: products in the circular economy
Del Borghi A, Gallo M, Strazza C, Del Borghi M (2014) An evaluation of environmental sustainability in the food industry through life cycle assessment: the case study of tomato products supply chain. J Clean Prod 78:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.04.083
Del Borghi A, Strazza C, Magrassi F et al (2018) Life cycle assessment for eco-design of product–package systems in the food industry—the case of legumes. Sustain Prod Consum 13:24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2017.11.001
Denyer D, Tranfield D (2009) Producing a systematic review. In: Buchanan B (ed) The sage handbook of organization research methods. Sage Publications Ltd, Cornwall, pp 671–689
Google Scholar
Dietz T, Grabs J, Chong AE (2019) Mainstreamed voluntary sustainability standards and their effectiveness: evidence from the Honduran coffee sector. Regul Gov. https://doi.org/10.1111/rego.12239
Dixon-Woods M (2011) Using framework-based synthesis for conducting reviews of qualitative studies. BMC Med 9:9–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-9-39
do Canto NR, Bossle MB, Marques L, Dutra M, (2020) Supply chain collaboration for sustainability: a qualitative investigation of food supply chains in Brazil. Manag Environ Qual an Int J. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-12-2019-0275
dos Santos RR, Guarnieri P (2020) Social gains for artisanal agroindustrial producers induced by cooperation and collaboration in agri-food supply chain. Soc Responsib J. https://doi.org/10.1108/SRJ-09-2019-0323
Doukidis GI, Matopoulos A, Vlachopoulou M, Manthou V, Manos B (2007) A conceptual framework for supply chain collaboration: empirical evidence from the agri‐food industry. Supply Chain Manag an Int Journal 12:177–186. https://doi.org/10.1108/13598540710742491
Durach CF, Kembro J, Wieland A (2017) A new paradigm for systematic literature reviews in supply chain management. J Supply Chain Manag 53:67–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/jscm.12145
Durán-Sánchez A, Álvarez-García J, Río-Rama D, De la Cruz M (2018) Sustainable water resources management: a bibliometric overview. Water 10:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091191
Duru M, Therond O (2015) Livestock system sustainability and resilience in intensive production zones: which form of ecological modernization? Reg Environ Chang 15:1651–1665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-014-0722-9
Edison Fondazione (2019) Le eccellenze agricole italiane. I primati europei e mondiali dell’Italia nei prodotti vegetali. Milan (IT)
Ehrenfeld JR (2005) The roots of sustainability. MIT Sloan Manag Rev 46(2)46:23–25
Elia V, Gnoni MG, Tornese F (2017) Measuring circular economy strategies through index methods: a critical analysis. J Clean Prod 142:2741–2751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.196
Elkington J (1997) Cannibals with forks : the triple bottom line of 21st century business. Capstone, Oxford
Esposito B, Sessa MR, Sica D, Malandrino O (2020) Towards circular economy in the agri-food sector. A systematic literature review. Sustain 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU12187401
European Commission (2018) Agri-food trade in 2018
European Commission (2019) Monitoring EU agri-food trade: development until September 2019
Eurostat (2018) Small and large farms in the EU - statistics from the farm structure survey
FAO (2011) Biodiversity for food and agriculture. Italy, Rome
FAO (2012) Energy-smart food at FAO: an overview. Italy, Rome
FAO (2014) Food wastage footprint: fool cost-accounting
FAO (2016) The state of food and agriculture climate change, agriculture and food security. Italy, Rome
FAO (2017) The future of food and agriculture: trends and challenges. Italy, Rome
FAO (2020) The state of food security and nutrition in the world. Transforming Food Systems for Affordable Healthy Diets. Rome, Italy
Fassio F, Tecco N (2019) Circular economy for food: a systemic interpretation of 40 case histories in the food system in their relationships with SDGs. Systems 7:43. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems7030043
Fathollahi A, Coupe SJ (2021) Life cycle assessment (LCA) and life cycle costing (LCC) of road drainage systems for sustainability evaluation: quantifying the contribution of different life cycle phases. Sci Total Environ 776:145937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145937
Ferreira VJ, Arnal ÁJ, Royo P et al (2019) Energy and resource efficiency of electroporation-assisted extraction as an emerging technology towards a sustainable bio-economy in the agri-food sector. J Clean Prod 233:1123–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.030
Fiksel J (2006) A framework for sustainable remediation. JOM 8:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1021/es202595w
Flick U (2014) An introduction to qualitative research
Franciosi C, Voisin A, Miranda S et al (2020) Measuring maintenance impacts on sustainability of manufacturing industries : from a systematic literature review to a framework proposal. J Clean Prod 260:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121065
Gaitán-Cremaschi D, Meuwissen MPM, Oude AGJML (2017) Total factor productivity: a framework for measuring agri-food supply chain performance towards sustainability. Appl Econ Perspect Policy 39:259–285. https://doi.org/10.1093/aepp/ppw008
Galdeano-Gómez E, Zepeda-Zepeda JA, Piedra-Muñoz L, Vega-López LL (2017) Family farm’s features influencing socio-economic sustainability: an analysis of the agri-food sector in southeast Spain. New Medit 16:50–61
Gallopín G, Herrero LMJ, Rocuts A (2014) Conceptual frameworks and visual interpretations of sustainability. Int J Sustain Dev 17:298–326. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSD.2014.064183
Gallopín GC (2003) Sostenibilidad y desarrollo sostenible: un enfoque sistémico. Cepal, LATIN AMERICA
Garnett T (2013) Food sustainability: problems, perspectives and solutions. Proc Nutr Soc 72:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665112002947
Garofalo P, D’Andrea L, Tomaiuolo M et al (2017) Environmental sustainability of agri-food supply chains in Italy: the case of the whole-peeled tomato production under life cycle assessment methodology. J Food Eng 200:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.12.007
Gava O, Bartolini F, Venturi F et al (2018) A reflection of the use of the life cycle assessment tool for agri-food sustainability. Sustain 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11010071
Gazzola P, Querci E (2017) The connection between the quality of life and sustainable ecological development. Eur Sci J 7881:1857–7431
Geissdoerfer M, Savaget P, Bocken N, Hultink EJ (2017) The circular economy – a new sustainability paradigm ? The circular economy – a new sustainability paradigm ? J Clean Prod 143:757–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.048
Georgescu-Roegen N (1971) The entropy low and the economic process. Harward University Press, Cambridge Mass
Book Google Scholar
Gerbens-Leenes PW, Moll HC, Schoot Uiterkamp AJM (2003) Design and development of a measuring method for environmental sustainability in food production systems. Ecol Econ 46:231–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(03)00140-X
Gésan-Guiziou G, Alaphilippe A, Aubin J et al (2020) Diversity and potentiality of multi-criteria decision analysis methods for agri-food research. Agron Sustain Dev 40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-020-00650-3
Ghisellini P, Cialani C, Ulgiati S (2016) A review on circular economy: the expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. J Clean Prod 114:11–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.007
Godoy-Durán Á, Galdeano- Gómez E, Pérez-Mesa JC, Piedra-Muñoz L (2017) Assessing eco-efficiency and the determinants of horticultural family-farming in southeast Spain. J Environ Manage 204:594–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.09.037
Gold S, Kunz N, Reiner G (2017) Sustainable global agrifood supply chains: exploring the barriers. J Ind Ecol 21:249–260. https://doi.org/10.1111/jiec.12440
Goucher L, Bruce R, Cameron DD et al (2017) The environmental impact of fertilizer embodied in a wheat-to-bread supply chain. Nat Plants 3:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2017.12
Green A, Nemecek T, Chaudhary A, Mathys A (2020) Assessing nutritional, health, and environmental sustainability dimensions of agri-food production. Glob Food Sec 26:100406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100406
Guinée JB, Heijungs R, Huppes G et al (2011) Life cycle assessment: past, present, and future †. Environ Sci Technol 45:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101316v
Guiomar N, Godinho S, Pinto-Correia T et al (2018) Typology and distribution of small farms in Europe: towards a better picture. Land Use Policy 75:784–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.04.012
Gunasekaran A, Patel C, McGaughey RE (2004) A framework for supply chain performance measurement. Int J Prod Econ 87:333–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2003.08.003
Gunasekaran A, Patel C, Tirtiroglu E (2001) Performance measures and metrics in a supply chain environment. Int J Oper Prod Manag 21:71–87. https://doi.org/10.1108/01443570110358468
Hamam M, Chinnici G, Di Vita G et al (2021) Circular economy models in agro-food systems: a review. Sustain 13
Harun SN, Hanafiah MM, Aziz NIHA (2021) An LCA-based environmental performance of rice production for developing a sustainable agri-food system in Malaysia. Environ Manage 67:146–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-020-01365-7
Harvey M, Pilgrim S (2011) The new competition for land: food, energy, and climate change. Food Policy 36:S40–S51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2010.11.009
Hawkes C, Ruel MT (2006) Understanding the links between agriculture and health. DC: International Food Policy Research Institute. Washington, USA
Hellweg S, Milà i Canals L (2014) Emerging approaches, challenges and opportunities in life cycle assessment. Science (80)344:1109LP–1113. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1248361
Higgins V, Dibden J, Cocklin C (2015) Private agri-food governance and greenhouse gas abatement: constructing a corporate carbon economy. Geoforum 66:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoforum.2015.09.012
Hill T (1995) Manufacturing strategy: text and cases., Macmillan
Hjeresen DD, Gonzales R (2020) Green chemistry promote sustainable agriculture?The rewards are higher yields and less environmental contamination. Environemental Sci Techonology 103–107
Horne R, Grant T, Verghese K (2009) Life cycle assessment: principles, practice, and prospects. Csiro Publishing, Collingwood, Australia
Horton P, Koh L, Guang VS (2016) An integrated theoretical framework to enhance resource efficiency, sustainability and human health in agri-food systems. J Clean Prod 120:164–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.08.092
Hospido A, Davis J, Berlin J, Sonesson U (2010) A review of methodological issues affecting LCA of novel food products. Int J Life Cycle Assess 15:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-009-0130-4
Huffman T, Liu J, Green M et al (2015) Improving and evaluating the soil cover indicator for agricultural land in Canada. Ecol Indic 48:272–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.07.008
Ilbery B, Maye D (2005) Food supply chains and sustainability: evidence from specialist food producers in the Scottish/English borders. Land Use Policy 22:331–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2004.06.002
Ingrao C, Faccilongo N, Valenti F et al (2019) Tomato puree in the Mediterranean region: an environmental life cycle assessment, based upon data surveyed at the supply chain level. J Clean Prod 233:292–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.056
Iocola I, Angevin F, Bockstaller C et al (2020) An actor-oriented multi-criteria assessment framework to support a transition towards sustainable agricultural systems based on crop diversification. Sustain 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135434
Irabien A, Darton RC (2016) Energy–water–food nexus in the Spanish greenhouse tomato production. Clean Technol Environ Policy 18:1307–1316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-1076-9
ISO 14040:2006 (2006) Environmental management — life cycle assessment — principles and framework
ISO 14044:2006 (2006) Environmental management — life cycle assessment — requirements and guidelines
ISO 15392:2008 (2008) Sustainability in building construction–general principles
Istat (2019) Andamento dell’economia agricola
Jaakkola E (2020) Designing conceptual articles : four approaches. AMS Rev 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13162-020-00161-0
Jin R, Yuan H, Chen Q (2019) Science mapping approach to assisting the review of construction and demolition waste management research published between 2009 and 2018. Resour Conserv Recycl 140:175–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.09.029
Johnston P, Everard M, Santillo D, Robèrt KH (2007) Reclaiming the definition of sustainability. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 14:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2007.01.375
Jorgensen SE, Burkhard B, Müller F (2013) Twenty volumes of ecological indicators-an accounting short review. Ecol Indic 28:4–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.12.018
Joshi S, Sharma M, Kler R (2020) Modeling circular economy dimensions in agri-tourism clusters: sustainable performance and future research directions. Int J Math Eng Manag Sci 5:1046–1061. https://doi.org/10.33889/IJMEMS.2020.5.6.080
Kamilaris A, Gao F, Prenafeta-Boldu FX, Ali MI (2017) Agri-IoT: a semantic framework for Internet of Things-enabled smart farming applications. In: 2016 IEEE 3rd World Forum on Internet of Things, WF-IoT 2016. pp 442–447
Karuppusami G, Gandhinathan R (2006) Pareto analysis of critical success factors of total quality management: a literature review and analysis. TQM Mag 18:372–385. https://doi.org/10.1108/09544780610671048
Kates RW, Parris TM, Leiserowitz AA (2005) What is sustainable development? Goals, indicators, values, and practice. Environ Sci Policy Sustain Dev 47:8–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/00139157.2005.10524444
Khounani Z, Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha H, Moustakas K et al (2021) Environmental life cycle assessment of different biorefinery platforms valorizing olive wastes to biofuel, phosphate salts, natural antioxidant, and an oxygenated fuel additive (triacetin). J Clean Prod 278:123916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123916
Kitchenham B, Charters S (2007) Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering version 2.3. Engineering 45. https://doi.org/10.1145/1134285.1134500
Korhonen J, Nuur C, Feldmann A, Birkie SE (2018) Circular economy as an essentially contested concept. J Clean Prod 175:544–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.111
Kuisma M, Kahiluoto H (2017) Biotic resource loss beyond food waste: agriculture leaks worst. Resour Conserv Recycl 124:129–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.04.008
Laso J, Hoehn D, Margallo M et al (2018) Assessing energy and environmental efficiency of the Spanish agri-food system using the LCA/DEA methodology. Energies 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123395
Lee KM (2007) So What is the “triple bottom line”? Int J Divers Organ Communities Nations Annu Rev 6:67–72. https://doi.org/10.18848/1447-9532/cgp/v06i06/39283
Lehmann RJ, Hermansen JE, Fritz M et al (2011) Information services for European pork chains - closing gaps in information infrastructures. Comput Electron Agric 79:125–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2011.09.002
León-Bravo V, Caniato F, Caridi M, Johnsen T (2017) Collaboration for sustainability in the food supply chain: a multi-stage study in Italy. Sustainability 9:1253
Lepage A (2009) The quality of life as attribute of sustainability. TQM J 21:105–115. https://doi.org/10.1108/17542730910938119
Li CZ, Zhao Y, Xiao B et al (2020) Research trend of the application of information technologies in construction and demolition waste management. J Clean Prod 263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121458
Lo Giudice A, Mbohwa C, Clasadonte MT, Ingrao C (2014) Life cycle assessment interpretation and improvement of the Sicilian artichokes production. Int J Environ Res 8:305–316. https://doi.org/10.22059/ijer.2014.721
Lueddeckens S, Saling P, Guenther E (2020) Temporal issues in life cycle assessment—a systematic review. Int J Life Cycle Assess 25:1385–1401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-020-01757-1
Luo J, Ji C, Qiu C, Jia F (2018) Agri-food supply chain management: bibliometric and content analyses. Sustain 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051573
Lynch J, Donnellan T, Finn JA et al (2019) Potential development of Irish agricultural sustainability indicators for current and future policy evaluation needs. J Environ Manage 230:434–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.09.070
MacArthur E (2013) Towards the circular economy. J Ind Ecol 2:23–44
MacArthur E (2017) Delivering the circular economy a toolkit for policymakers, The Ellen MacArthur Foundation
MacInnis DJ (2011) A framework for conceptual. J Mark 75:136–154. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkg.75.4.136
Mangla SK, Luthra S, Rich N et al (2018) Enablers to implement sustainable initiatives in agri-food supply chains. Int J Prod Econ 203:379–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2018.07.012
Marotta G, Nazzaro C, Stanco M (2017) How the social responsibility creates value: models of innovation in Italian pasta industry. Int J Glob Small Bus 9:144–167. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJGSB.2017.088923
Martucci O, Arcese G, Montauti C, Acampora A (2019) Social aspects in the wine sector: comparison between social life cycle assessment and VIVA sustainable wine project indicators. Resources 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8020069
Mayring P (2004) Forum : Qualitative social research Sozialforschung 2. History of content analysis. A Companion to Qual Res 1:159–176
McKelvey B (2002) Managing coevolutionary dynamics. In: 18th EGOS Conference. Barcelona, Spain, pp 1–21
McMichael AJ, Butler CD, Folke C (2003) New visions for addressing sustainability. Science (80- ) 302:1191–1920
Mehmood A, Ahmed S, Viza E et al (2021) Drivers and barriers towards circular economy in agri-food supply chain: a review. Bus Strateg Dev 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/bsd2.171
Mella P, Gazzola P (2011) Sustainability and quality of life: the development model. In: Kapounek S (ed) Enterprise and competitive environment. Mendel University: Brno, Czechia. 542–551
Merli R, Preziosi M, Acampora A (2018) How do scholars approach the circular economy ? A systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 178:703–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.112
Merli R, Preziosi M, Acampora A et al (2020) Recycled fibers in reinforced concrete: a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 248:119207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119207
Miglietta PP, Morrone D (2018) Managing water sustainability: virtual water flows and economic water productivity assessment of the wine trade between Italy and the Balkans. Sustain 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10020543
Mitchell MGE, Chan KMA, Newlands NK, Ramankutty N (2020) Spatial correlations don’t predict changes in agricultural ecosystem services: a Canada-wide case study. Front Sustain Food Syst 4:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2020.539892
Moraga G, Huysveld S, Mathieux F et al (2019) Circular economy indicators: what do they measure?. Resour Conserv Recycl 146:452–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.045
Morrissey JE, Dunphy NP (2015) Towards sustainable agri-food systems: the role of integrated sustainability and value assessment across the supply-chain. Int J Soc Ecol Sustain Dev 6:41–58. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJSESD.2015070104
Moser G (2009) Quality of life and sustainability: toward person-environment congruity. J Environ Psychol 29:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2009.02.002
Muijs D (2010) Doing quantitative research in education with SPSS. London
Muller MF, Esmanioto F, Huber N, Loures ER (2019) A systematic literature review of interoperability in the green Building Information Modeling lifecycle. J Clean Prod 223:397–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.114
Muradin M, Joachimiak-Lechman K, Foltynowicz Z (2018) Evaluation of eco-efficiency of two alternative agricultural biogas plants. Appl Sci 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8112083
Naseer MA, ur R, Ashfaq M, Hassan S, et al (2019) Critical issues at the upstream level in sustainable supply chain management of agri-food industries: evidence from Pakistan’s citrus industry. Sustain 11:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051326
Nattassha R, Handayati Y, Simatupang TM, Siallagan M (2020) Understanding circular economy implementation in the agri-food supply chain: the case of an Indonesian organic fertiliser producer. Agric Food Secur 9:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40066-020-00264-8
Nazari-Sharabian M, Ahmad S, Karakouzian M (2018) Climate change and eutrophication: a short review. Eng Technol Appl Sci Res 8:3668–3672. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2532694
Nazir N (2017) Understanding life cycle thinking and its practical application to agri-food system. Int J Adv Sci Eng Inf Technol 7:1861–1870. https://doi.org/10.18517/ijaseit.7.5.3578
Negra C, Remans R, Attwood S et al (2020) Sustainable agri-food investments require multi-sector co-development of decision tools. Ecol Indic 110:105851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105851
Newsham KK, Robinson SA (2009) Responses of plants in polar regions to UVB exposure: a meta-analysis. Glob Chang Biol 15:2574–2589. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.01944.x
Niemeijer D, de Groot RS (2008) A conceptual framework for selecting environmental indicator sets. Ecol Indic 8:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2006.11.012
Niero M, Kalbar PP (2019) Coupling material circularity indicators and life cycle based indicators: a proposal to advance the assessment of circular economy strategies at the product level. Resour Conserv Recycl 140:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.10.002
Nikolaou IE, Tsagarakis KP (2021) An introduction to circular economy and sustainability: some existing lessons and future directions. Sustain Prod Consum 28:600–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.06.017
Notarnicola B, Hayashi K, Curran MA, Huisingh D (2012) Progress in working towards a more sustainable agri-food industry. J Clean Prod 28:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.02.007
Notarnicola B, Tassielli G, Renzulli PA, Monforti F (2017) Energy flows and greenhouses gases of EU (European Union) national breads using an LCA (life cycle assessment) approach. J Clean Prod 140:455–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.150
Opferkuch K, Caeiro S, Salomone R, Ramos TB (2021) Circular economy in corporate sustainability reporting: a review of organisational approaches. Bus Strateg Environ 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2854
Padilla-Rivera A, do Carmo BBT, Arcese G, Merveille N, (2021) Social circular economy indicators: selection through fuzzy delphi method. Sustain Prod Consum 26:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2020.09.015
Pagotto M, Halog A (2016) Towards a circular economy in Australian agri-food industry: an application of input-output oriented approaches for analyzing resource efficiency and competitiveness potential. J Ind Ecol 20:1176–1186. https://doi.org/10.1111/jiec.12373
Parent G, Lavallée S (2011) LCA potentials and limits within a sustainable agri-food statutory framework. Global food insecurity. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 161–171
Chapter Google Scholar
Pattey E, Qiu G (2012) Trends in primary particulate matter emissions from Canadian agriculture. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 62:737–747. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2012.672058
Pauliuk S (2018) Critical appraisal of the circular economy standard BS 8001:2017 and a dashboard of quantitative system indicators for its implementation in organizations. Resour Conserv Recycl 129:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.10.019
Peano C, Migliorini P, Sottile F (2014) A methodology for the sustainability assessment of agri-food systems: an application to the slow food presidia project. Ecol Soc 19. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-06972-190424
Peano C, Tecco N, Dansero E et al (2015) Evaluating the sustainability in complex agri-food systems: the SAEMETH framework. Sustain 7:6721–6741. https://doi.org/10.3390/su7066721
Pearce DW, Turner RK (1990) Economics of natural resources and the environment. Harvester Wheatsheaf, Hemel Hempstead, Herts
Pelletier N (2018) Social sustainability assessment of Canadian egg production facilities: methods, analysis, and recommendations. Sustain 10:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051601
Peña C, Civit B, Gallego-Schmid A et al (2021) Using life cycle assessment to achieve a circular economy. Int J Life Cycle Assess 26:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-020-01856-z
Perez Neira D (2016) Energy sustainability of Ecuadorian cacao export and its contribution to climate change. A case study through product life cycle assessment. J Clean Prod 112:2560–2568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.11.003
Pérez-Neira D, Grollmus-Venegas A (2018) Life-cycle energy assessment and carbon footprint of peri-urban horticulture. A comparative case study of local food systems in Spain. Landsc Urban Plan 172:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.01.001
Pérez-Pons ME, Plaza-Hernández M, Alonso RS et al (2021) Increasing profitability and monitoring environmental performance: a case study in the agri-food industry through an edge-iot platform. Sustain 13:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010283
Petti L, Serreli M, Di Cesare S (2018) Systematic literature review in social life cycle assessment. Int J Life Cycle Assess 23:422–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-016-1135-4
Pieroni MPP, McAloone TC, Pigosso DCA (2019) Business model innovation for circular economy and sustainability: a review of approaches. J Clean Prod 215:198–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.036
Polit DF, Beck CT (2004) Nursing research: principles and methods. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
Porkka M, Gerten D, Schaphoff S et al (2016) Causes and trends of water scarcity in food production. Environ Res Lett 11:015001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/1/015001
Prajapati H, Kant R, Shankar R (2019) Bequeath life to death: state-of-art review on reverse logistics. J Clean Prod 211:503–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.187
Priyadarshini P, Abhilash PC (2020) Policy recommendations for enabling transition towards sustainable agriculture in India. Land Use Policy 96:104718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104718
Pronti A, Coccia M (2020) Multicriteria analysis of the sustainability performance between agroecological and conventional coffee farms in the East Region of Minas Gerais (Brazil). Renew Agric Food Syst. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742170520000332
Rabadán A, González-Moreno A, Sáez-Martínez FJ (2019) Improving firms’ performance and sustainability: the case of eco-innovation in the agri-food industry. Sustain 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205590
Raut RD, Luthra S, Narkhede BE et al (2019) Examining the performance oriented indicators for implementing green management practices in the Indian agro sector. J Clean Prod 215:926–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.139
Recanati F, Marveggio D, Dotelli G (2018) From beans to bar: a life cycle assessment towards sustainable chocolate supply chain. Sci Total Environ 613–614:1013–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.187
Redclift M (2005) Sustainable development (1987–2005): an oxymoron comes of age. Sustain Dev 13:212–227. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.281
Rezaei M, Soheilifard F, Keshvari A (2021) Impact of agrochemical emission models on the environmental assessment of paddy rice production using life cycle assessment approach. Energy Sources. Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 1–16
Rigamonti L, Mancini E (2021) Life cycle assessment and circularity indicators. Int J Life Cycle Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-021-01966-2
Risku-Norja H, Mäenpää I (2007) MFA model to assess economic and environmental consequences of food production and consumption. Ecol Econ 60:700–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.05.001
Ritzén S, Sandström GÖ (2017) Barriers to the circular economy – integration of perspectives and domains. Procedia CIRP 64:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.005
Rockström J, Steffen W, Noone K et al (2009) A safe operating space for humanity. Nature 461:472–475. https://doi.org/10.1038/461472a
Roos Lindgreen E, Mondello G, Salomone R et al (2021) Exploring the effectiveness of grey literature indicators and life cycle assessment in assessing circular economy at the micro level: a comparative analysis. Int J Life Cycle Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-021-01972-4
Roselli L, Casieri A, De Gennaro BC et al (2020) Environmental and economic sustainability of table grape production in Italy. Sustain 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093670
Ross RB, Pandey V, Ross KL (2015) Sustainability and strategy in U.S. agri-food firms: an assessment of current practices. Int Food Agribus Manag Rev 18:17–48
Royo P, Ferreira VJ, López-Sabirón AM, Ferreira G. (2016) Hybrid diagnosis to characterise the energy and environmental enhancement of photovoltaic modules using smart materials. Energy 101:174–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.01.101
Ruggerio CA (2021) Sustainability and sustainable development: a review of principles and definitions. Sci Total Environ 786:147481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147481
Ruiz-Almeida A, Rivera-Ferre MG (2019) Internationally-based indicators to measure agri-food systems sustainability using food sovereignty as a conceptual framework. Food Secur 11:1321–1337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-019-00964-5
Ryan M, Hennessy T, Buckley C et al (2016) Developing farm-level sustainability indicators for Ireland using the Teagasc National Farm Survey. Irish J Agric Food Res 55:112–125. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijafr-2016-0011
Saade MRM, Yahia A, Amor B (2020) How has LCA been applied to 3D printing ? A systematic literature review and recommendations for future studies. J Clean Prod 244:118803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118803
Saitone TL, Sexton RJ (2017) Agri-food supply chain: evolution and performance with conflicting consumer and societal demands. Eur Rev Agric Econ 44:634–657. https://doi.org/10.1093/erae/jbx003
Salim N, Ab Rahman MN, Abd Wahab D (2019) A systematic literature review of internal capabilities for enhancing eco-innovation performance of manufacturing firms. J Clean Prod 209:1445–1460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.105
Salimi N (2021) Circular economy in agri-food systems BT - strategic decision making for sustainable management of industrial networks. In: International S (ed) Rezaei J. Publishing, Cham, pp 57–70
Salomone R, Ioppolo G (2012) Environmental impacts of olive oil production: a life cycle assessment case study in the province of Messina (Sicily). J Clean Prod 28:88–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.10.004
Sánchez AD, Río DMDLC, García JÁ (2017) Bibliometric analysis of publications on wine tourism in the databases Scopus and WoS. Eur Res Manag Bus Econ 23:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iedeen.2016.02.001
Saputri VHL, Sutopo W, Hisjam M, Ma’aram A (2019) Sustainable agri-food supply chain performance measurement model for GMO and non-GMO using data envelopment analysis method. Appl Sci 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061199
Sassanelli C, Rosa P, Rocca R, Terzi S (2019) Circular economy performance assessment methods : a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 229:440–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.019
Schiefer S, Gonzalez C, Flanigan S (2015) More than just a factor in transition processes? The role of collaboration in agriculture. In: Sutherland LA, Darnhofer I, Wilson GA, Zagata L (eds) Transition pathways towards sustainability in agriculture: case studies from Europe, CPI Group. Croydon, UK, pp. 83
Seuring S, Muller M (2008) From a literature review to a conceptual framework for sustainable supply chain management. J Clean Prod 16:1699–1710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.04.020
Silvestri C, Silvestri L, Forcina A, et al (2021) Green chemistry contribution towards more equitable global sustainability and greater circular economy: A systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126137
Smetana S, Schmitt E, Mathys A (2019) Sustainable use of Hermetia illucens insect biomass for feed and food: attributional and consequential life cycle assessment. Resour Conserv Recycl 144:285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.01.042
Sonesson U, Berlin J, Ziegler F (2010) Environmental assessment and management in the food industry: life cycle assessment and related approaches. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge
Soussana JF (2014) Research priorities for sustainable agri-food systems and life cycle assessment. J Clean Prod 73:19–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.02.061
Soylu A, Oruç C, Turkay M et al (2006) Synergy analysis of collaborative supply chain management in energy systems using multi-period MILP. Eur J Oper Res 174:387–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2005.02.042
Spaiser V, Ranganathan S, Swain RB, Sumpter DJ (2017) The sustainable development oxymoron: quantifying and modelling the incompatibility of sustainable development goals. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 24:457–470. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2016.1235624
Stewart R, Niero M (2018) Circular economy in corporate sustainability strategies: a review of corporate sustainability reports in the fast-moving consumer goods sector. Bus Strateg Environ 27:1005–1022. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2048
Stillitano T, Spada E, Iofrida N et al (2021) Sustainable agri-food processes and circular economy pathways in a life cycle perspective: state of the art of applicative research. Sustain 13:1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052472
Stone J, Rahimifard S (2018) Resilience in agri-food supply chains: a critical analysis of the literature and synthesis of a novel framework. Supply Chain Manag 23:207–238. https://doi.org/10.1108/SCM-06-2017-0201
Strazza C, Del Borghi A, Gallo M, Del Borghi M (2011) Resource productivity enhancement as means for promoting cleaner production: analysis of co-incineration in cement plants through a life cycle approach. J Clean Prod 19:1615–1621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.05.014
Su B, Heshmati A, Geng Y, Yu X (2013) A review of the circular economy in China: moving from rhetoric to implementation. J Clean Prod 42:215–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.11.020
Suárez-Eiroa B, Fernández E, Méndez-Martínez G, Soto-Oñate D (2019) Operational principles of circular economy for sustainable development: linking theory and practice. J Clean Prod 214:952–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.271
Svensson G, Wagner B (2015) Implementing and managing economic, social and environmental efforts of business sustainability. Manag Environ Qual an Int Journal 26:195–213. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-09-2013-0099
Tasca AL, Nessi S, Rigamonti L (2017) Environmental sustainability of agri-food supply chains: an LCA comparison between two alternative forms of production and distribution of endive in northern Italy. J Clean Prod 140:725–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.170
Tassielli G, Notarnicola B, Renzulli PA, Arcese G (2018) Environmental life cycle assessment of fresh and processed sweet cherries in southern Italy. J Clean Prod 171:184–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.227
Teixeira R, Pax S (2011) A survey of life cycle assessment practitioners with a focus on the agri-food sector. J Ind Ecol 15:817–820. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9290.2011.00421.x
Tobergte DR, Curtis S (2013) ILCD Handbook. J Chem Info Model. https://doi.org/10.278/33030
Tortorella MM, Di Leo S, Cosmi C et al (2020) A methodological integrated approach to analyse climate change effects in agri-food sector: the TIMES water-energy-food module. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217703
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidenceinformed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14:207–222
Trivellas P, Malindretos G, Reklitis P (2020) Implications of green logistics management on sustainable business and supply chain performance: evidence from a survey in the greek agri-food sector. Sustain 12:1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410515
Tsangas M, Gavriel I, Doula M et al (2020) Life cycle analysis in the framework of agricultural strategic development planning in the Balkan region. Sustain 12:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051813
Ülgen VS, Björklund M, Simm N (2019) Inter-organizational supply chain interaction for sustainability : a systematic literature review.
UNEP S (2020) Guidelines for social life cycle assessment of products and organizations 2020.
UNEP/SETAC (2009) United Nations Environment Programme-society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. Guidelines for social life cycle assessment of products. France
United Nations (2011) Guiding principles on business and human rights. Implementing the United Nations “protect, respect and remedy” framework
United Nations (2015) Transforming our world: the 2030 agenda for sustainable development. sustainabledevelopment.un.org
Van Asselt ED, Van Bussel LGJ, Van Der Voet H et al (2014) A protocol for evaluating the sustainability of agri-food production systems - a case study on potato production in peri-urban agriculture in the Netherlands. Ecol Indic 43:315–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.02.027
Van der Ploeg JD (2014) Peasant-driven agricultural growth and food sovereignty. J Peasant Stud 41:999–1030. https://doi.org/10.1080/03066150.2013.876997
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84:523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2019) Manual for VOSviwer version 1.6.10. CWTS Meaningful metrics 1–53
Vasa L, Angeloska A, Trendov NM (2017) Comparative analysis of circular agriculture development in selected Western Balkan countries based on sustainable performance indicators. Econ Ann 168:44–47. https://doi.org/10.21003/ea.V168-09
Verdecho MJ, Alarcón-Valero F, Pérez-Perales D et al (2020) A methodology to select suppliers to increase sustainability within supply chains. Cent Eur J Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10100-019-00668-3
Vergine P, Salerno C, Libutti A et al (2017) Closing the water cycle in the agro-industrial sector by reusing treated wastewater for irrigation. J Clean Prod 164:587–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.239
WCED (1987) Our common future - call for action
Webster K (2013) What might we say about a circular economy? Some temptations to avoid if possible. World Futures 69:542–554
Wheaton E, Kulshreshtha S (2013) Agriculture and climate change: implications for environmental sustainability indicators. WIT Trans Ecol Environ 175:99–110. https://doi.org/10.2495/ECO130091
Wijewickrama MKCS, Chileshe N, Rameezdeen R, Ochoa JJ (2021) Information sharing in reverse logistics supply chain of demolition waste: a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 280:124359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124359
Woodhouse A, Davis J, Pénicaud C, Östergren K (2018) Sustainability checklist in support of the design of food processing. Sustain Prod Consum 16:110–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2018.06.008
Wu R, Yang D, Chen J (2014) Social Life Cycle Assessment Revisited Sustain 6:4200–4226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6074200
Yadav S, Luthra S, Garg D (2021) Modelling Internet of things (IoT)-driven global sustainability in multi-tier agri-food supply chain under natural epidemic outbreaks. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16633–16654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11676-1
Yee FM, Shaharudin MR, Ma G et al (2021) Green purchasing capabilities and practices towards Firm’s triple bottom line in Malaysia. J Clean Prod 307:127268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127268
Yigitcanlar T (2010) Rethinking sustainable development: urban management, engineering, and design. IGI Global
Zamagni A, Amerighi O, Buttol P (2011) Strengths or bias in social LCA? Int J Life Cycle Assess 16:596–598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-011-0309-3
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economy, Engineering, Society and Business Organization, University of “Tuscia, ” Via del Paradiso 47, 01100, Viterbo, VT, Italy
Cecilia Silvestri, Michela Piccarozzi & Alessandro Ruggieri
Department of Engineering, University of Rome “Niccolò Cusano, ” Via Don Carlo Gnocchi, 3, 00166, Rome, Italy
Luca Silvestri
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Cecilia Silvestri .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Monia Niero
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: a number of ill-placed paragraph headings were removed and the source indication "Authors' elaborations" was added to Tables 1-3.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 31 KB)
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Silvestri, C., Silvestri, L., Piccarozzi, M. et al. Toward a framework for selecting indicators of measuring sustainability and circular economy in the agri-food sector: a systematic literature review. Int J Life Cycle Assess (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-022-02032-1
Download citation
Received : 15 June 2021
Accepted : 16 February 2022
Published : 02 March 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-022-02032-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Agri-food sector
- Sustainability
- Circular economy
- Triple bottom line
- Life cycle assessment
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 08 April 2024
A systematic review and multivariate meta-analysis of the physical and mental health benefits of touch interventions
- Julian Packheiser ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9805-6755 2 na1 nAff1 ,
- Helena Hartmann 2 , 3 , 4 na1 ,
- Kelly Fredriksen 2 ,
- Valeria Gazzola ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0324-0619 2 ,
- Christian Keysers ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2845-5467 2 &
- Frédéric Michon ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1289-2133 2
Nature Human Behaviour ( 2024 ) Cite this article
18k Accesses
1838 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Human behaviour
- Paediatric research
- Randomized controlled trials
Receiving touch is of critical importance, as many studies have shown that touch promotes mental and physical well-being. We conducted a pre-registered (PROSPERO: CRD42022304281) systematic review and multilevel meta-analysis encompassing 137 studies in the meta-analysis and 75 additional studies in the systematic review ( n = 12,966 individuals, search via Google Scholar, PubMed and Web of Science until 1 October 2022) to identify critical factors moderating touch intervention efficacy. Included studies always featured a touch versus no touch control intervention with diverse health outcomes as dependent variables. Risk of bias was assessed via small study, randomization, sequencing, performance and attrition bias. Touch interventions were especially effective in regulating cortisol levels (Hedges’ g = 0.78, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.24 to 1.31) and increasing weight (0.65, 95% CI 0.37 to 0.94) in newborns as well as in reducing pain (0.69, 95% CI 0.48 to 0.89), feelings of depression (0.59, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.78) and state (0.64, 95% CI 0.44 to 0.84) or trait anxiety (0.59, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.77) for adults. Comparing touch interventions involving objects or robots resulted in similar physical (0.56, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.88 versus 0.51, 95% CI 0.38 to 0.64) but lower mental health benefits (0.34, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.49 versus 0.58, 95% CI 0.43 to 0.73). Adult clinical cohorts profited more strongly in mental health domains compared with healthy individuals (0.63, 95% CI 0.46 to 0.80 versus 0.37, 95% CI 0.20 to 0.55). We found no difference in health benefits in adults when comparing touch applied by a familiar person or a health care professional (0.51, 95% CI 0.29 to 0.73 versus 0.50, 95% CI 0.38 to 0.61), but parental touch was more beneficial in newborns (0.69, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.88 versus 0.39, 95% CI 0.18 to 0.61). Small but significant small study bias and the impossibility to blind experimental conditions need to be considered. Leveraging factors that influence touch intervention efficacy will help maximize the benefits of future interventions and focus research in this field.
Similar content being viewed by others

Touching the social robot PARO reduces pain perception and salivary oxytocin levels
Nirit Geva, Florina Uzefovsky & Shelly Levy-Tzedek
The impact of mindfulness apps on psychological processes of change: a systematic review
Natalia Macrynikola, Zareen Mir, … John Torous
The why, who and how of social touch
Juulia T. Suvilehto, Asta Cekaite & India Morrison
The sense of touch has immense importance for many aspects of our life. It is the first of all the senses to develop in newborns 1 and the most direct experience of contact with our physical and social environment 2 . Complementing our own touch experience, we also regularly receive touch from others around us, for example, through consensual hugs, kisses or massages 3 .
The recent coronavirus pandemic has raised awareness regarding the need to better understand the effects that touch—and its reduction during social distancing—can have on our mental and physical well-being. The most common touch interventions, for example, massage for adults or kangaroo care for newborns, have been shown to have a wide range of both mental and physical health benefits, from facilitating growth and development to buffering against anxiety and stress, over the lifespan of humans and animals alike 4 . Despite the substantial weight this literature gives to support the benefits of touch, it is also characterized by a large variability in, for example, studied cohorts (adults, children, newborns and animals), type and duration of applied touch (for example, one-time hug versus repeated 60-min massages), measured health outcomes (ranging from physical health outcomes such as sleep and blood pressure to mental health outcomes such as depression or mood) and who actually applies the touch (for example, partner versus stranger).
A meaningful tool to make sense of this vast amount of research is through meta-analysis. While previous meta-analyses on this topic exist, they were limited in scope, focusing only on particular types of touch, cohorts or specific health outcomes (for example, refs. 5 , 6 ). Furthermore, despite best efforts, meaningful variables that moderate the efficacy of touch interventions could not yet be identified. However, understanding these variables is critical to tailor touch interventions and guide future research to navigate this diverse field with the ultimate aim of promoting well-being in the population.
In this Article, we describe a pre-registered, large-scale systematic review and multilevel, multivariate meta-analysis to address this need with quantitative evidence for (1) the effect of touch interventions on physical and mental health and (2) which moderators influence the efficacy of the intervention. In particular, we ask whether and how strongly health outcomes depend on the dynamics of the touching dyad (for example, humans or robots/objects, familiarity and touch directionality), demographics (for example, clinical status, age or sex), delivery means (for example, type of touch intervention or touched body part) and procedure (for example, duration or number of sessions). We did so separately for newborns and for children and adults, as the health outcomes in newborns differed substantially from those in the other age groups. Despite the focus of the analysis being on humans, it is widely known that many animal species benefit from touch interactions and that engaging in touch promotes their well-being as well 7 . Since animal models are essential for the investigation of the mechanisms underlying biological processes and for the development of therapeutic approaches, we accordingly included health benefits of touch interventions in non-human animals as part of our systematic review. However, this search yielded only a small number of studies, suggesting a lack of research in this domain, and as such, was insufficient to be included in the meta-analysis. We evaluate the identified animal studies and their findings in the discussion.
Touch interventions have a medium-sized effect
The pre-registration can be found at ref. 8 . The flowchart for data collection and extraction is depicted in Fig. 1 .
Animal outcomes refer to outcomes measured in non-human species that were solely considered as part of a systematic review. Included languages were French, Dutch, German and English, but our search did not identify any articles in French, Dutch or German. MA, meta-analysis.
For adults, a total of n = 2,841 and n = 2,556 individuals in the touch and control groups, respectively, across 85 studies and 103 cohorts were included. The effect of touch overall was medium-sized ( t (102) = 9.74, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.52, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.42 to 0.63; Fig. 2a ). For newborns, we could include 63 cohorts across 52 studies comprising a total of n = 2,134 and n = 2,086 newborns in the touch and control groups, respectively, with an overall effect almost identical to the older age group ( t (62) = 7.53, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.56, 95% CI 0.41 to 0.71; Fig. 2b ), suggesting that, despite distinct health outcomes, touch interventions show comparable effects across newborns and adults. Using these overall effect estimates, we conducted a power sensitivity analysis of all the included primary studies to investigate whether such effects could be reliably detected 9 . Sufficient power to detect such effect sizes was rare in individual studies, as investigated by firepower plots 10 (Supplementary Figs. 1 and 2 ). No individual effect size from either meta-analysis was overly influential (Cook’s D < 0.06). The benefits were similar for mental and physical outcomes (mental versus physical; adults: t (101) = 0.79, P = 0.432, Hedges’ g difference of −0.05, 95% CI −0.16 to 0.07, Fig. 2c ; newborns: t (61) = 1.08, P = 0.284, Hedges’ g difference of −0.19, 95% CI −0.53 to 0.16, Fig. 2d ).
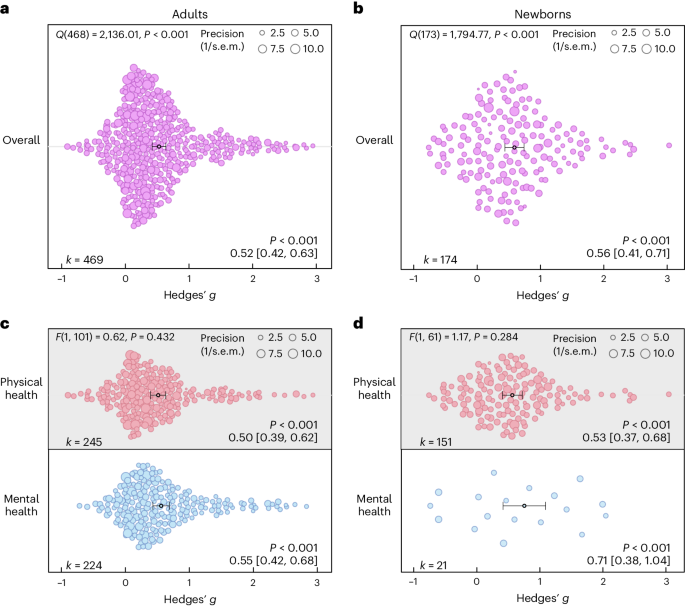
a , Orchard plot illustrating the overall benefits across all health outcomes for adults/children across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. b , The same as a but for newborns across 174 in part dependent effect sizes from 52 studies and 63 cohorts. c , The same as a but separating the results for physical versus mental health benefits across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. d , The same as b but separating the results for physical versus mental health benefits across 172 in part dependent effect sizes from 52 studies and 63 cohorts. Each dot reflects a measured effect, and the number of effects ( k ) included in the analysis is depicted in the bottom left. Mean effects and 95% CIs are presented in the bottom right and are indicated by the central black dot (mean effect) and its error bars (95% CI). The heterogeneity Q statistic is presented in the top left. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test). Note that the P values above the mean effects indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. The dot size reflects the precision of each individual effect (larger indicates higher precision). Small-study bias for the overall effect was significant ( F test, two-sided test) in the adult meta-analysis ( F (1, 101) = 21.24, P < 0.001; Supplementary Fig. 3 ) as well as in the newborn meta-analysis ( F (1, 61) = 5.25, P = 0.025; Supplementary Fig. 4 ).
Source data
On the basis of the overall effect of both meta-analyses as well as their median sample sizes, the minimum number of studies necessary for subgroup analyses to achieve 80% power was k = 9 effects for adults and k = 8 effects for newborns (Supplementary Figs. 5 and 6 ). Assessing specific health outcomes with sufficient power in more detail in adults (Fig. 3a ) revealed smaller benefits to sleep and heart rate parameters, moderate benefits to positive and negative affect, diastolic blood and systolic blood pressure, mobility and reductions of the stress hormone cortisol and larger benefits to trait and state anxiety, depression, fatigue and pain. Post hoc tests revealed stronger benefits for pain, state anxiety, depression and trait anxiety compared with respiratory, sleep and heart rate parameters (see Fig. 3 for all post hoc comparisons). Reductions in pain and state anxiety were increased compared with reductions in negative affect ( t (83) = 2.54, P = 0.013, Hedges’ g difference of 0.31, 95% CI 0.07 to 0.55; t (83) = 2.31, P = 0.024, Hedges’ g difference of 0.27, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.51). Benefits to pain symptoms were higher compared with benefits to positive affect ( t (83) = 2.22, P = 0.030, Hedges’ g difference of 0.29, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.54). Finally, touch resulted in larger benefits to cortisol release compared with heart rate parameters ( t (83) = 2.30, P = 0.024, Hedges’ g difference of 0.26, 95% CI 0.04–0.48).
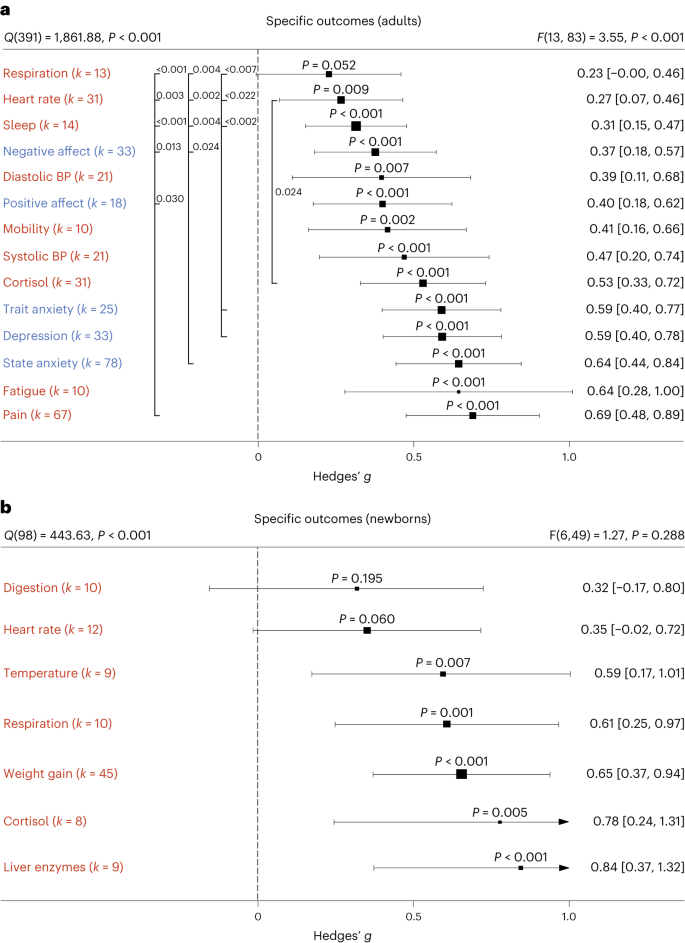
a , b , Health outcomes in adults analysed across 405 in part dependent effect sizes from 79 studies and 97 cohorts ( a ) and in newborns analysed across 105 in part dependent effect sizes from 46 studies and 56 cohorts ( b ). The type of health outcomes measured differed between adults and newborns and were thus analysed separately. Numbers on the right represent the mean effect with its 95% CI in square brackets and the significance level estimating the likelihood that the effect is equal to zero. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test). The F value in the top right represents a test of the hypothesis that all effects within the subpanel are equal. The Q statistic represents the heterogeneity. P values of post hoc tests are depicted whenever significant. P values above the horizontal whiskers indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. Vertical lines indicate significant post hoc tests between moderator levels. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. Physical outcomes are marked in red. Mental outcomes are marked in blue.
In newborns, only physical health effects offered sufficient data for further analysis. We found no benefits for digestion and heart rate parameters. All other health outcomes (cortisol, liver enzymes, respiration, temperature regulation and weight gain) showed medium to large effects (Fig. 3b ). We found no significant differences among any specific health outcomes.
Non-human touch and skin-to-skin contact
In some situations, a fellow human is not readily available to provide affective touch, raising the question of the efficacy of touch delivered by objects and robots 11 . Overall, we found humans engaging in touch with other humans or objects to have medium-sized health benefits in adults, without significant differences ( t (99) = 1.05, P = 0.295, Hedges’ g difference of 0.12, 95% CI −0.11 to 0.35; Fig. 4a ). However, differentiating physical versus mental health benefits revealed similar benefits for human and object touch on physical health outcomes, but larger benefits on mental outcomes when humans were touched by humans ( t (97) = 2.32, P = 0.022, Hedges’ g difference of 0.24, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.44; Fig. 4b ). It must be noted that touching with an object still showed a significant effect (see Supplementary Fig. 7 for the corresponding orchard plot).
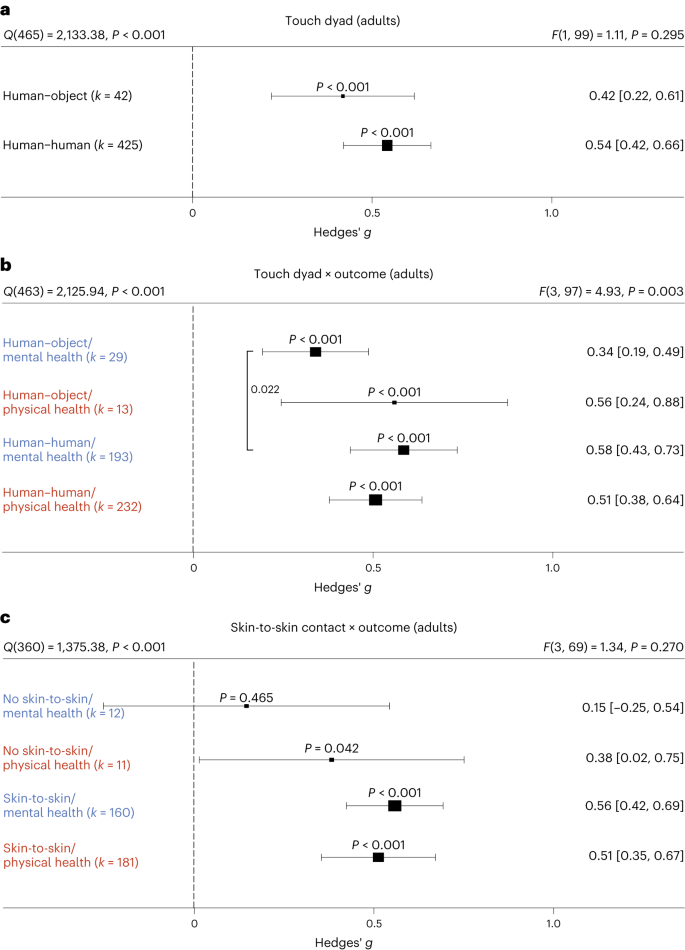
a , Forest plot comparing humans versus objects touching a human on health outcomes overall across 467 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 101 cohorts. b , The same as a but separately for mental versus physical health outcomes across 467 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 101 cohorts. c , Results with the removal of all object studies, leaving 406 in part dependent effect sizes from 71 studies and 88 cohorts to identify whether missing skin-to-skin contact is the relevant mediator of higher mental health effects in human–human interactions. Numbers on the right represent the mean effect with its 95% CI in square brackets and the significance level estimating the likelihood that the effect is equal to zero. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test). The F value in the top right represents a test of the hypothesis that all effects within the subpanel are equal. The Q statistic represents the heterogeneity. P values of post hoc tests are depicted whenever significant. P values above the horizontal whiskers indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. Vertical lines indicate significant post hoc tests between moderator levels. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. Physical outcomes are marked in red. Mental outcomes are marked in blue.
We considered the possibility that this effect was due to missing skin-to-skin contact in human–object interactions. Thus, we investigated human–human interactions with and without skin-to-skin contact (Fig. 4c ). In line with the hypothesis that skin-to-skin contact is highly relevant, we again found stronger mental health benefits in the presence of skin-to-skin contact that however did not achieve nominal significance ( t (69) = 1.95, P = 0.055, Hedges’ g difference of 0.41, 95% CI −0.00 to 0.82), possibly because skin-to-skin contact was rarely absent in human–human interactions, leading to a decrease in power of this analysis. Results for skin-to-skin contact as an overall moderator can be found in Supplementary Fig. 8 .
Influences of type of touch
The large majority of touch interventions comprised massage therapy in adults and kangaroo care in newborns (see Supplementary Table 1 for a complete list of interventions across studies). However, comparing the different types of touch explored across studies did not reveal significant differences in effect sizes based on touch type, be it on overall health benefits (adults: t (101) = 0.11, P = 0.916, Hedges’ g difference of 0.02, 95% CI −0.32 to 0.29; Fig. 5a ) or comparing different forms of touch separately for physical (massage therapy versus other forms: t (99) = 0.99, P = 0.325, Hedges’ g difference 0.16, 95% CI −0.15 to 0.47) or for mental health benefits (massage therapy versus other forms: t (99) = 0.75, P = 0.458, Hedges’ g difference of 0.13, 95% CI −0.22 to 0.48) in adults (Fig. 5c ; see Supplementary Fig. 9 for the corresponding orchard plot). A similar picture emerged for physical health effects in newborns (massage therapy versus kangaroo care: t (58) = 0.94, P = 0.353, Hedges’ g difference of 0.15, 95% CI −0.17 to 0.47; massage therapy versus other forms: t (58) = 0.56, P = 0.577, Hedges’ g difference of 0.13, 95% CI −0.34 to 0.60; kangaroo care versus other forms: t (58) = 0.07, P = 0.947, Hedges’ g difference of 0.02, 95% CI −0.46 to 0.50; Fig. 5d ; see also Supplementary Fig. 10 for the corresponding orchard plot). This suggests that touch types may be flexibly adapted to the setting of every touch intervention.
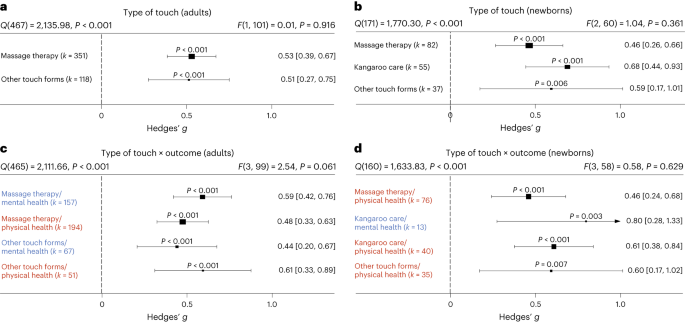
a , Forest plot of health benefits comparing massage therapy versus other forms of touch in adult cohorts across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. b , Forest plot of health benefits comparing massage therapy, kangaroo care and other forms of touch for newborns across 174 in part dependent effect sizes from 52 studies and 63 cohorts. c , The same as a but separating mental and physical health benefits across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. d , The same as b but separating mental and physical health outcomes where possible across 164 in part dependent effect sizes from 51 studies and 62 cohorts. Note that an insufficient number of studies assessed mental health benefits of massage therapy or other forms of touch to be included. Numbers on the right represent the mean effect with its 95% CI in square brackets and the significance level estimating the likelihood that the effect is equal to zero. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test). The F value in the top right represents a test of the hypothesis that all effects within the subpanel are equal. The Q statistic represents heterogeneity. P values of post hoc tests are depicted whenever significant. P values above the horizontal whiskers indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. Vertical lines indicate significant post hoc tests between moderator levels. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. Physical outcomes are marked in red. Mental outcomes are marked in blue.
The role of clinical status
Most research on touch interventions has focused on clinical samples, but are benefits restricted to clinical cohorts? We found health benefits to be significant in clinical and healthy populations (Fig. 6 ), whether all outcomes are considered (Fig. 6a,b ) or physical and mental health outcomes are separated (Fig. 6c,d , see Supplementary Figs. 11 and 12 for the corresponding orchard plots). In adults, however, we found higher mental health benefits for clinical populations compared with healthy ones (Fig. 6c ; t (99) = 2.11, P = 0.037, Hedges’ g difference of 0.25, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.49).
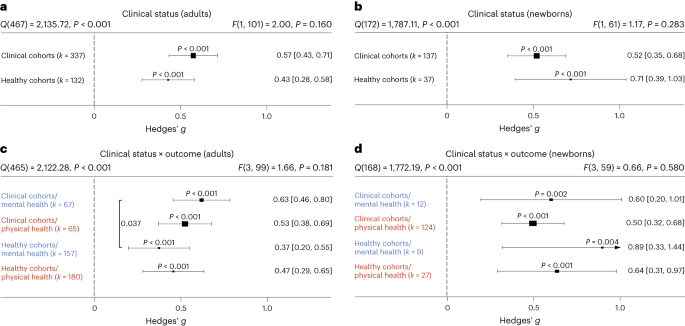
a , Health benefits for clinical cohorts of adults versus healthy cohorts of adults across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. b , The same as a but for newborn cohorts across 174 in part dependent effect sizes from 52 studies and 63 cohorts. c , The same as a but separating mental versus physical health benefits across 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts. d , The same as b but separating mental versus physical health benefits across 172 in part dependent effect sizes from 52 studies and 63 cohorts. Numbers on the right represent the mean effect with its 95% CI in square brackets and the significance level estimating the likelihood that the effect is equal to zero. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test).The F value in the top right represents a test of the hypothesis that all effects within the subpanel are equal. The Q statistic represents the heterogeneity. P values of post hoc tests are depicted whenever significant. P values above the horizontal whiskers indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. Vertical lines indicate significant post hoc tests between moderator levels. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. Physical outcomes are marked in red. Mental outcomes are marked in blue.
A more detailed analysis of specific clinical conditions in adults revealed positive mental and physical health benefits for almost all assessed clinical disorders. Differences between disorders were not found, with the exception of increased effectiveness of touch interventions in neurological disorders (Supplementary Fig. 13 ).
Familiarity in the touching dyad and intervention location
Touch interventions can be performed either by familiar touchers (partners, family members or friends) or by unfamiliar touchers (health care professionals). In adults, we did not find an impact of familiarity of the toucher ( t (99) = 0.12, P = 0.905, Hedges’ g difference of 0.02, 95% CI −0.27 to 0.24; Fig. 7a ; see Supplementary Fig. 14 for the corresponding orchard plot). Similarly, investigating the impact on mental and physical health benefits specifically, no significant differences could be detected, suggesting that familiarity is irrelevant in adults. In contrast, touch applied to newborns by their parents (almost all studies only included touch by the mother) was significantly more beneficial compared with unfamiliar touch ( t (60) = 2.09, P = 0.041, Hedges’ g difference of 0.30, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.59) (Fig. 7b ; see Supplementary Fig. 15 for the corresponding orchard plot). Investigating mental and physical health benefits specifically revealed no significant differences. Familiarity with the location in which the touch was applied (familiar being, for example, the participants’ home) did not influence the efficacy of touch interventions (Supplementary Fig. 16 ).
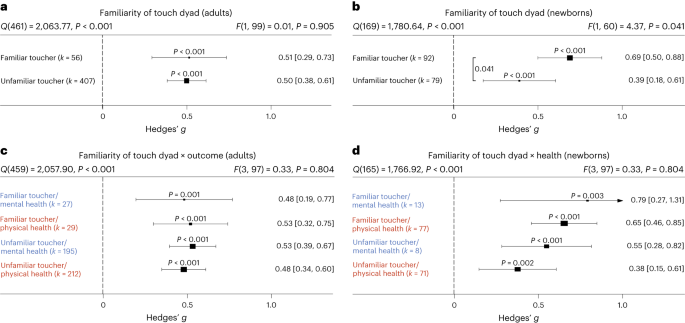
a , Health benefits for being touched by a familiar (for example, partner, family member or friend) versus unfamiliar toucher (health care professional) across 463 in part dependent effect sizes from 83 studies and 101 cohorts. b , The same as a but for newborn cohorts across 171 in part dependent effect sizes from 51 studies and 62 cohorts. c , The same as a but separating mental versus physical health benefits across 463 in part dependent effect sizes from 83 studies and 101 cohorts. d , The same as b but separating mental versus physical health benefits across 169 in part dependent effect sizes from 51 studies and 62 cohorts. Numbers on the right represent the mean effect with its 95% CI in square brackets and the significance level estimating the likelihood that the effect is equal to zero. Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test, and post hoc comparisons were done using t tests (two-sided test). The F value in the top right represents a test of the hypothesis that all effects within the subpanel are equal. The Q statistic represents the heterogeneity. P values of post hoc tests are depicted whenever significant. P values above the horizontal whiskers indicate whether an effect differed significantly from a zero effect. Vertical lines indicate significant post hoc tests between moderator levels. P values were not corrected for multiple comparisons. Physical outcomes are marked in red. Mental outcomes are marked in blue.
Frequency and duration of touch interventions
How often and for how long should touch be delivered? For adults, the median touch duration across studies was 20 min and the median number of touch interventions was four sessions with an average time interval of 2.3 days between each session. For newborns, the median touch duration across studies was 17.5 min and the median number of touch interventions was seven sessions with an average time interval of 1.3 days between each session.
Delivering more touch sessions increased benefits in adults, whether overall ( t (101) = 4.90, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.02, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.03), physical ( t (81) = 3.07, P = 0.003, Hedges’ g = 0.02, 95% CI 0.01–0.03) or mental benefits ( t (72) = 5.43, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.02, 95% CI 0.01–0.03) were measured (Fig. 8a ). A closer look at specific outcomes for which sufficient data were available revealed that positive associations between the number of sessions and outcomes were found for trait anxiety ( t (12) = 7.90, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.03, 95% CI 0.02–0.04), depression ( t (20) = 10.69, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.03, 95% CI 0.03–0.04) and pain ( t (37) = 3.65, P < 0.001, Hedges’ g = 0.03, 95% CI 0.02–0.05), indicating a need for repeated sessions to improve these adverse health outcomes. Neither increasing the number of sessions for newborns nor increasing the duration of touch per session in adults or newborns increased health benefits, be they physical or mental (Fig. 8b–d ). For continuous moderators in adults, we also looked at specific health outcomes as sufficient data were generally available for further analysis. Surprisingly, we found significant negative associations between touch duration and reductions of cortisol ( t (24) = 2.71, P = 0.012, Hedges’ g = −0.01, 95% CI −0.01 to −0.00) and heart rate parameters ( t (21) = 2.35, P = 0.029, Hedges’ g = −0.01, 95% CI −0.02 to −0.00).
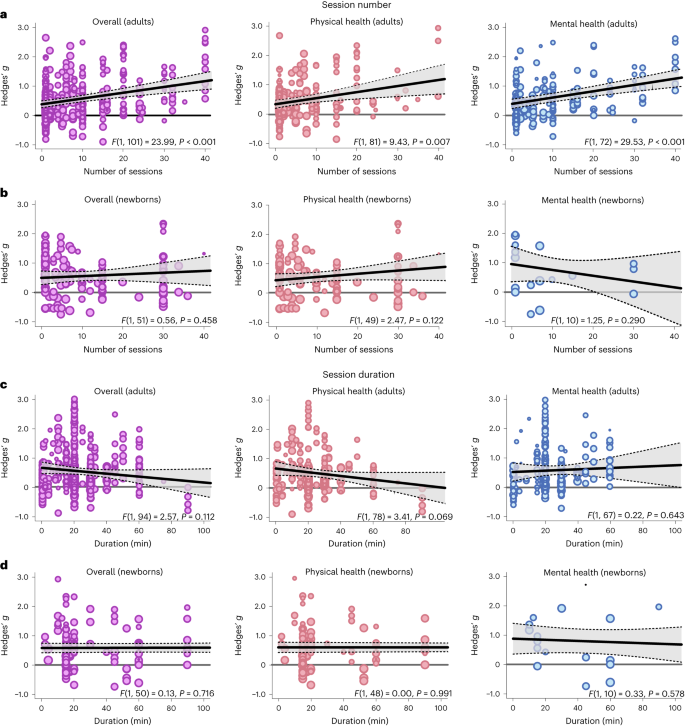
a , Meta-regression analysis examining the association between the number of sessions applied and the effect size in adults, either on overall health benefits (left, 469 in part dependent effect sizes from 85 studies and 103 cohorts) or for physical (middle, 245 in part dependent effect sizes from 69 studies and 83 cohorts) or mental benefits (right, 224 in part dependent effect sizes from 60 studies and 74 cohorts) separately. b , The same as a for newborns (overall: 150 in part dependent effect sizes from 46 studies and 53 cohorts; physical health: 127 in part dependent effect sizes from 44 studies and 51 cohorts; mental health: 21 in part dependent effect sizes from 11 studies and 12 cohorts). c , d the same as a ( c ) and b ( d ) but for the duration of the individual sessions. For adults, 449 in part dependent effect sizes across 80 studies and 96 cohorts were included in the overall analysis. The analysis of physical health benefits included 240 in part dependent effect sizes across 67 studies and 80 cohorts, and the analysis of mental health benefits included 209 in part dependent effect sizes from 56 studies and 69 cohorts. For newborns, 145 in part dependent effect sizes across 45 studies and 52 cohorts were included in the overall analysis. The analysis of physical health benefits included 122 in part dependent effect sizes across 43 studies and 50 cohorts, and the analysis of mental health benefits included 21 in part dependent effect sizes from 11 studies and 12 cohorts. Each dot represents an effect size. Its size indicates the precision of the study (larger indicates better). Overall effects of moderator impact were assessed via an F test (two-sided test). The P values in each panel represent the result of a regression analysis testing the hypothesis that the slope of the relationship is equal to zero. P values are not corrected for multiple testing. The shaded area around the regression line represents the 95% CI.
Demographic influences of sex and age
We used the ratio between women and men in the single-study samples as a proxy for sex-specific effects. Sex ratios were heavily skewed towards larger numbers of women in each cohort (median 83% women), and we could not find significant associations between sex ratio and overall ( t (62) = 0.08, P = 0.935, Hedges’ g = 0.00, 95% CI −0.00 to 0.01), mental ( t (43) = 0.55, P = 0.588, Hedges’ g = 0.00, 95% CI −0.00 to 0.01) or physical health benefits ( t (51) = 0.15, P = 0.882, Hedges’ g = −0.00, 95% CI −0.01 to 0.01). For specific outcomes that could be further analysed, we found a significant positive association of sex ratio with reductions in cortisol secretion ( t (18) = 2.31, P = 0.033, Hedges’ g = 0.01, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.01) suggesting stronger benefits in women. In contrast to adults, sex ratios were balanced in samples of newborns (median 53% girls). For newborns, there was no significant association with overall ( t (36) = 0.77, P = 0.447, Hedges’ g = −0.01, 95% CI −0.02 to 0.01) and physical health benefits of touch ( t (35) = 0.93, P = 0.359, Hedges’ g = −0.01, 95% CI −0.02 to 0.01). Mental health benefits did not provide sufficient data for further analysis.
The median age in the adult meta-analysis was 42.6 years (s.d. 21.16 years, range 4.5–88.4 years). There was no association between age and the overall ( t (73) = 0.35, P = 0.727, Hedges’ g = 0.00, 95% CI −0.01 to 0.01), mental ( t (53) = 0.94, P = 0.353, Hedges’ g = 0.01, 95% CI −0.01 to 0.02) and physical health benefits of touch ( t (60) = 0.16, P = 0.870, Hedges’ g = 0.00, 95% CI −0.01 to 0.01). Looking at specific health outcomes, we found significant positive associations between mean age and improved positive affect ( t (10) = 2.54, P = 0.030, Hedges’ g = 0.01, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.02) as well as systolic blood pressure ( t (11) = 2.39, P = 0.036, Hedges’ g = 0.02, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.04).
A list of touched body parts can be found in Supplementary Table 1 . For the touched body part, we found significantly higher health benefits for head touch compared with arm touch ( t (40) = 2.14, P = 0.039, Hedges’ g difference of 0.78, 95% CI 0.07 to 1.49) and torso touch ( t (40) = 2.23, P = 0.031; Hedges’ g difference of 0.84, 95% CI 0.10 to 1.58; Supplementary Fig. 17 ). Touching the arm resulted in lower mental health compared with physical health benefits ( t (37) = 2.29, P = 0.028, Hedges’ g difference of −0.35, 95% CI −0.65 to −0.05). Furthermore, we found a significantly increased physical health benefit when the head was touched as opposed to the torso ( t (37) = 2.10, P = 0.043, Hedges’ g difference of 0.96, 95% CI 0.06 to 1.86). Thus, head touch such as a face or scalp massage could be especially beneficial.
Directionality
In adults, we tested whether a uni- or bidirectional application of touch mattered. The large majority of touch was applied unidirectionally ( k = 442 of 469 effects). Unidirectional touch had higher health benefits ( t (101) = 2.17, P = 0.032, Hedges’ g difference of 0.30, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.58) than bidirectional touch. Specifically, mental health benefits were higher in unidirectional touch ( t (99) = 2.33, P = 0.022, Hedges’ g difference of 0.46, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.66).
Study location
For adults, we found significantly stronger health benefits of touch in South American compared with North American cohorts ( t (95) = 2.03, P = 0.046, Hedges’ g difference of 0.37, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.73) and European cohorts ( t (95) = 2.22, P = 0.029, Hedges’ g difference of 0.36, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.68). For newborns, we found weaker effects in North American cohorts compared to Asian ( t (55) = 2.28, P = 0.026, Hedges’ g difference of −0.37, 95% CI −0.69 to −0.05) and European cohorts ( t (55) = 2.36, P = 0.022, Hedges’ g difference of −0.40, 95% CI −0.74 to −0.06). Investigating the interaction with mental and physical health benefits did not reveal any effects of study location in both meta-analyses (Supplementary Fig. 18 ).
Systematic review of studies without effect sizes
All studies where effect size data could not be obtained or that did not meet the meta-analysis inclusion criteria can be found on the OSF project 12 in the file ‘Study_lists_final_revised.xlsx’ (sheet ‘Studies_without_effect_sizes’). Specific reasons for exclusion are furthermore documented in Supplementary Table 2 . For human health outcomes assessed across 56 studies and n = 2,438 individuals, interventions mostly comprised massage therapy ( k = 86 health outcomes) and kangaroo care ( k = 33 health outcomes). For datasets where no effect size could be computed, 90.0% of mental health and 84.3% of physical health parameters were positively impacted by touch. Positive impact of touch did not differ between types of touch interventions. These results match well with the observations of the meta-analysis of a highly positive benefit of touch overall, irrespective of whether a massage or any other intervention is applied.
We also assessed health outcomes in animals across 19 studies and n = 911 subjects. Most research was conducted in rodents. Animals that received touch were rats (ten studies, k = 16 health outcomes), mice (four studies, k = 7 health outcomes), macaques (two studies, k = 3 health outcomes), cats (one study, k = 3 health outcomes), lambs (one study, k = 2 health outcomes) and coral reef fish (one study, k = 1 health outcome). Touch interventions mostly comprised stroking ( k = 13 health outcomes) and tickling ( k = 10 health outcomes). For animal studies, 71.4% of effects showed benefits to mental health-like parameters and 81.8% showed positive physical health effects. We thus found strong evidence that touch interventions, which were mostly conducted by humans (16 studies with human touch versus 3 studies with object touch), had positive health effects in animal species as well.
The key aim of the present study was twofold: (1) to provide an estimate of the effect size of touch interventions and (2) to disambiguate moderating factors to potentially tailor future interventions more precisely. Overall, touch interventions were beneficial for both physical and mental health, with a medium effect size. Our work illustrates that touch interventions are best suited for reducing pain, depression and anxiety in adults and children as well as for increasing weight gain in newborns. These findings are in line with previous meta-analyses on this topic, supporting their conclusions and their robustness to the addition of more datasets. One limitation of previous meta-analyses is that they focused on specific health outcomes or populations, despite primary studies often reporting effects on multiple health parameters simultaneously (for example, ref. 13 focusing on neck and shoulder pain and ref. 14 focusing on massage therapy in preterms). To our knowledge, only ref. 5 provides a multivariate picture for a large number of dependent variables. However, this study analysed their data in separate random effects models that did not account for multivariate reporting nor for the multilevel structure of the data, as such approaches have only become available recently. Thus, in addition to adding a substantial amount of new data, our statistical approach provides a more accurate depiction of effect size estimates. Additionally, our study investigated a variety of moderating effects that did not reach significance (for example, sex ratio, mean age or intervention duration) or were not considered (for example, the benefits of robot or object touch) in previous meta-analyses in relation to touch intervention efficacy 5 , probably because of the small number of studies with information on these moderators in the past. Owing to our large-scale approach, we reached high statistical power for many moderator analyses. Finally, previous meta-analyses on this topic exclusively focused on massage therapy in adults or kangaroo care in newborns 15 , leaving out a large number of interventions that are being carried out in research as well as in everyday life to improve well-being. Incorporating these studies into our study, we found that, in general, both massages and other types of touch, such as gentle touch, stroking or kangaroo care, showed similar health benefits.
While it seems to be less critical which touch intervention is applied, the frequency of interventions seems to matter. More sessions were positively associated with the improvement of trait outcomes such as depression and anxiety but also pain reductions in adults. In contrast to session number, increasing the duration of individual sessions did not improve health effects. In fact, we found some indications of negative relationships in adults for cortisol and blood pressure. This could be due to habituating effects of touch on the sympathetic nervous system and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, ultimately resulting in diminished effects with longer exposure, or decreased pleasantness ratings of affective touch with increasing duration 16 . For newborns, we could not support previous notions that the duration of the touch intervention is linked to benefits in weight gain 17 . Thus, an ideal intervention protocol does not seem to have to be excessively long. It should be noted that very few interventions lasted less than 5 min, and it therefore remains unclear whether very short interventions have the same effect.
A critical issue highlighted in the pandemic was the lack of touch due to social restrictions 18 . To accommodate the need for touch in individuals with small social networks (for example, institutionalized or isolated individuals), touch interventions using objects/robots have been explored in the past (for a review, see ref. 11 ). We show here that touch interactions outside of the human–human domain are beneficial for mental and physical health outcomes. Importantly, object/robot touch was not as effective in improving mental health as human-applied touch. A sub-analysis of missing skin-to-skin contact among humans indicated that mental health effects of touch might be mediated by the presence of skin-to-skin contact. Thus, it seems profitable to include skin-to-skin contact in future touch interventions, in line with previous findings in newborns 19 . In robots, recent advancements in synthetic skin 20 should be investigated further in this regard. It should be noted that, although we did not observe significant differences in physical health benefits between human–human and human–object touch, the variability of effect sizes was higher in human–object touch. The conditions enabling object or robot interactions to improve well-being should therefore be explored in more detail in the future.
Touch was beneficial for both healthy and clinical cohorts. These data are critical as most previous meta-analytic research has focused on individuals diagnosed with clinical disorders (for example, ref. 6 ). For mental health outcomes, we found larger effects in clinical cohorts. A possible reason could relate to increased touch wanting 21 in patients. For example, loneliness often co-occurs with chronic illnesses 22 , which are linked to depressed mood and feelings of anxiety 23 . Touch can be used to counteract this negative development 24 , 25 . In adults and children, knowing the toucher did not influence health benefits. In contrast, familiarity affected overall health benefits in newborns, with parental touch being more beneficial than touch applied by medical staff. Previous studies have suggested that early skin-to-skin contact and exposure to maternal odour is critical for a newborn’s ability to adapt to a new environment 26 , supporting the notion that parental care is difficult to substitute in this time period.
With respect to age-related effects, our data further suggest that increasing age was associated with a higher benefit through touch for systolic blood pressure. These findings could potentially be attributed to higher basal blood pressure 27 with increasing age, allowing for a stronger modulation of this parameter. For sex differences, our study provides some evidence that there are differences between women and men with respect to health benefits of touch. Overall, research on sex differences in touch processing is relatively sparse (but see refs. 28 , 29 ). Our results suggest that buffering effects against physiological stress are stronger in women. This is in line with increased buffering effects of hugs in women compared with men 30 . The female-biased primary research in adults, however, begs for more research in men or non-binary individuals. Unfortunately, our study could not dive deeper into this topic as health benefits broken down by sex or gender were almost never provided. Recent research has demonstrated that sensory pleasantness is affected by sex and that this also interacts with the familiarity of the other person in the touching dyad 29 , 31 . In general, contextual factors such as sex and gender or the relationship of the touching dyad, differences in cultural background or internal states such as stress have been demonstrated to be highly influential in the perception of affective touch and are thus relevant to maximizing the pleasantness and ultimately the health benefits of touch interactions 32 , 33 , 34 . As a positive personal relationship within the touching dyad is paramount to induce positive health effects, future research applying robot touch to promote well-being should therefore not only explore synthetic skin options but also focus on improving robots as social agents that form a close relationship with the person receiving the touch 35 .
As part of the systematic review, we also assessed the effects of touch interventions in non-human animals. Mimicking the results of the meta-analysis in humans, beneficial effects of touch in animals were comparably strong for mental health-like and physical health outcomes. This may inform interventions to promote animal welfare in the context of animal experiments 36 , farming 37 and pets 38 . While most studies investigated effects in rodents, which are mostly used as laboratory animals, these results probably transfer to livestock and common pets as well. Indeed, touch was beneficial in lambs, fish and cats 39 , 40 , 41 . The positive impact of human touch in rodents also allows for future mechanistic studies in animal models to investigate how interventions such as tickling or stroking modulate hormonal and neuronal responses to touch in the brain. Furthermore, the commonly proposed oxytocin hypothesis can be causally investigated in these animal models through, for example, optogenetic or chemogenetic techniques 42 . We believe that such translational approaches will further help in optimizing future interventions in humans by uncovering the underlying mechanisms and brain circuits involved in touch.
Our results offer many promising avenues to improve future touch interventions, but they also need to be discussed in light of their limitations. While the majority of findings showed robust health benefits of touch interventions across moderators when compared with a null effect, post hoc tests of, for example, familiarity effects in newborns or mental health benefit differences between human and object touch only barely reached significance. Since we computed a large number of statistical tests in the present study, there is a risk that these results are false positives. We hope that researchers in this field are stimulated by these intriguing results and target these questions by primary research through controlled experimental designs within a well-powered study. Furthermore, the presence of small-study bias in both meta-analyses is indicative that the effect size estimates presented here might be overestimated as null results are often unpublished. We want to stress however that this bias is probably reduced by the multivariate reporting of primary studies. Most studies that reported on multiple health outcomes only showed significant findings for one or two among many. Thus, the multivariate nature of primary research in this field allowed us to include many non-significant findings in the present study. Another limitation pertains to the fact that we only included articles in languages mostly spoken in Western countries. As a large body of evidence comes from Asian countries, it could be that primary research was published in languages other than specified in the inclusion criteria. Thus, despite the large and inclusive nature of our study, some studies could have been missed regardless. Another factor that could not be accounted for in our meta-analysis was that an important prerequisite for touch to be beneficial is its perceived pleasantness. The level of pleasantness associated with being touched is modulated by several parameters 34 including cultural acceptability 43 , perceived humanness 44 or a need for touch 45 , which could explain the observed differences for certain moderators, such as human–human versus robot–human interaction. Moreover, the fact that secondary categorical moderators could not be investigated with respect to specific health outcomes, owing to the lack of data points, limits the specificity of our conclusions in this regard. It thus remains unclear whether, for example, a decreased mental health benefit in the absence of skin-to-skin contact is linked mostly to decreased anxiolytic effects, changes in positive/negative affect or something else. Since these health outcomes are however highly correlated 46 , it is likely that such effects are driven by multiple health outcomes. Similarly, it is important to note that our conclusions mainly refer to outcomes measured close to the touch intervention as we did not include long-term outcomes. Finally, it needs to be noted that blinding towards the experimental condition is essentially impossible in touch interventions. Although we compared the touch intervention with other interventions, such as relaxation therapy, as control whenever possible, contributions of placebo effects cannot be ruled out.
In conclusion, we show clear evidence that touch interventions are beneficial across a large number of both physical and mental health outcomes, for both healthy and clinical cohorts, and for all ages. These benefits, while influenced in their magnitude by study cohorts and intervention characteristics, were robustly present, promoting the conclusion that touch interventions can be systematically employed across the population to preserve and improve our health.
Open science practices
All data and code are accessible in the corresponding OSF project 12 . The systematic review was registered on PROSPERO (CRD42022304281) before the start of data collection. We deviated from the pre-registered plan as follows:
Deviation 1: During our initial screening for the systematic review, we were confronted with a large number of potential health outcomes to look at. This observation of multivariate outcomes led us to register an amendment during data collection (but before any effect size or moderator screening). In doing so, we aimed to additionally extract meta-analytic effects for a more quantitative assessment of our review question that can account for multivariate data reporting and dependencies of effects within the same study. Furthermore, as we noted a severe lack of studies with respect to health outcomes for animals during the inclusion assessment for the systematic review, we decided that the meta-analysis would only focus on outcomes that could be meaningfully analysed on the meta-analytic level and therefore only included health outcomes of human participants.
Deviation 2: In the pre-registration, we did not explicitly exclude non-randomized trials. Since an explicit use of non-randomization for group allocation significantly increases the risk of bias, we decided to exclude them a posteriori from data analysis.
Deviation 3: In the pre-registration, we outlined a tertiary moderator level, namely benefits of touch application versus touch reception. This level was ignored since no included study specifically investigated the benefits of touch application by itself.
Deviation 4: In the pre-registration, we suggested using the RoBMA function 47 to provide a Bayesian framework that allows for a more accurate assessment of publication bias beyond small-study bias. Unfortunately, neither multilevel nor multivariate data structures are supported by the RoBMA function, to our knowledge. For this reason, we did not further pursue this analysis, as the hierarchical nature of the data would not be accounted for.
Deviation 5: Beyond the pre-registered inclusion and exclusion criteria, we also excluded dissertations owing to their lack of peer review.
Deviation 6: In the pre-registration, we stated to investigate the impact of sex of the person applying the touch. This moderator was not further analysed, as this information was rarely given and the individuals applying the touch were almost exclusively women (7 males, 24 mixed and 85 females in studies on adults/children; 3 males, 17 mixed and 80 females in studied on newborns).
Deviation 7: The time span of the touch intervention as assessed by subtracting the final day of the intervention from the first day was not investigated further owing to its very high correlation with the number of sessions ( r (461) = 0.81 in the adult meta-analysis, r (145) = 0.84 in the newborn meta-analysis).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
To be included in the systematic review, studies had to investigate the relationship between at least one health outcome (physical and/or mental) in humans or animals and a touch intervention, include explicit physical touch by another human, animal or object as part of an intervention and include an experimental and control condition/group that are differentiated by touch alone. Of note, as a result of this selection process, no animal-to-animal touch intervention study was included, as they never featured a proper no-touch control. Human touch was always explicit touch by a human (that is, no brushes or other tools), either with or without skin-to-skin contact. Regarding the included health outcomes, we aimed to be as broad as possible but excluded parameters such as neurophysiological responses or pleasantness ratings after touch application as they do not reflect health outcomes. All included studies in the meta-analysis and systematic review 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 , 102 , 103 , 104 , 105 , 106 , 107 , 108 , 109 , 110 , 111 , 112 , 113 , 114 , 115 , 116 , 117 , 118 , 119 , 120 , 121 , 122 , 123 , 124 , 125 , 126 , 127 , 128 , 129 , 130 , 131 , 132 , 133 , 134 , 135 , 136 , 137 , 138 , 139 , 140 , 141 , 142 , 143 , 144 , 145 , 146 , 147 , 148 , 149 , 150 , 151 , 152 , 153 , 154 , 155 , 156 , 157 , 158 , 159 , 160 , 161 , 162 , 163 , 164 , 165 , 166 , 167 , 168 , 169 , 170 , 171 , 172 , 173 , 174 , 175 , 176 , 177 , 178 , 179 , 180 , 181 , 182 , 183 , 184 , 185 , 186 , 187 , 188 , 189 , 190 , 191 , 192 , 193 , 194 , 195 , 196 , 197 , 198 , 199 , 200 , 201 , 202 , 203 , 204 , 205 , 206 , 207 , 208 , 209 , 210 , 211 , 212 , 213 , 214 , 215 , 216 , 217 , 218 , 219 , 220 , 221 , 222 , 223 , 224 , 225 , 226 , 227 , 228 , 229 , 230 , 231 , 232 , 233 , 234 , 235 , 236 , 237 , 238 , 239 , 240 , 241 , 242 , 243 , 244 , 245 , 246 , 247 , 248 , 249 , 250 , 251 , 252 , 253 , 254 , 255 , 256 , 257 , 258 , 259 , 260 , 261 , 262 , 263 are listed in Supplementary Table 2 . All excluded studies are listed in Supplementary Table 3 , together with a reason for exclusion. We then applied a two-step process: First, we identified all potential health outcomes and extracted qualitative information on those outcomes (for example, direction of effect). Second, we extracted quantitative information from all possible outcomes (for example, effect sizes). The meta-analysis additionally required a between-subjects design (to clearly distinguish touch from no-touch effects and owing to missing information about the correlation between repeated measurements 264 ). Studies that explicitly did not apply a randomized protocol were excluded before further analysis to reduce risk of bias. The full study lists for excluded and included studies can be found in the OSF project 12 in the file ‘Study_lists_final_revised.xlsx’. In terms of the time frame, we conducted an open-start search of studies until 2022 and identified studies conducted between 1965 and 2022.
Data collection
We used Google Scholar, PubMed and Web of Science for our literature search, with no limitations regarding the publication date and using pre-specified search queries (see Supplementary Information for the exact keywords used). All procedures were in accordance with the updated Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines 265 . Articles were assessed in French, Dutch, German or English. The above databases were searched from 2 December 2021 until 1 October 2022. Two independent coders evaluated each paper against the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inconsistencies between coders were checked and resolved by J.P. and H.H. Studies excluded/included for the review and meta-analysis can be found on the OSF project.
Search queries
We used the following keywords to search the chosen databases. Agents (human versus animal versus object versus robot) and touch outcome (physical versus mental) were searched separately together with keywords searching for touch.
TOUCH: Touch OR Social OR Affective OR Contact OR Tactile interaction OR Hug OR Massage OR Embrace OR Kiss OR Cradling OR Stroking OR Haptic interaction OR tickling
AGENT: Object OR Robot OR human OR animal OR rodent OR primate
MENTAL OUTCOME: Health OR mood OR Depression OR Loneliness OR happiness OR life satisfaction OR Mental Disorder OR well-being OR welfare OR dementia OR psychological OR psychiatric OR anxiety OR Distress
PHYSICAL OUTCOME: Health OR Stress OR Pain OR cardiovascular health OR infection risk OR immune response OR blood pressure OR heart rate
Data extraction and preparation
Data extraction began on 10 October 2022 and was concluded on 25 February 2023. J.P. and H.H. oversaw the data collection process, and checked and resolved all inconsistencies between coders.
Health benefits of touch were always coded by positive summary effects, whereas adverse health effects of touch were represented by negative summary effects. If multiple time points were measured for the same outcome on the same day after a single touch intervention, we extracted the peak effect size (in either the positive or negative direction). If the touch intervention occurred multiple times and health outcomes were assessed for each time point, we extracted data points separately. However, we only extracted immediate effects, as long-term effects not controlled through the experimental conditions could be due to influences other than the initial touch intervention. Measurements assessing long-term effects without explicit touch sessions in the breaks were excluded for the same reason. Common control groups for touch interventions comprised active (for example, relaxation therapy) as well as passive control groups (for example, standard medical care). In the case of multiple control groups, we always contrasted the touch group to the group that most closely matched the touch condition (for example, relaxation therapy was preferred over standard medical care). We extracted information from all moderators listed in the pre-registration (Supplementary Table 4 ). A list of included and excluded health outcomes is presented in Supplementary Table 5 . Authors of studies with possible effects but missing information to calculate those effects were contacted via email and asked to provide the missing data (response rate 35.7%).
After finalizing the list of included studies for the systematic review, we added columns for moderators and the coding schema for our meta-analysis per our updated registration. Then, each study was assessed for its eligibility in the meta-analysis by two independent coders (J.P., H.H., K.F. or F.M.). To this end, all coders followed an a priori specified procedure: First, the PDF was skimmed for possible effects to extract, and the study was excluded if no PDF was available or the study was in a language different from the ones specified in ‘ Data collection ’. Effects from studies that met the inclusion criteria were extracted from all studies listing descriptive values or statistical parameters to calculate effect sizes. A website 266 was used to convert descriptive and statistical values available in the included studies (means and standard deviations/standard errors/confidence intervals, sample sizes, F values, t values, t test P values or frequencies) into Cohen’s d , which were then converted in Hedges’ g . If only P value thresholds were reported (for example, P < 0.01), we used this, most conservative, value as the P value to calculate the effect size (for example, P = 0.01). If only the total sample size was given but that number was even and the participants were randomly assigned to each group, we assumed equal sample sizes for each group. If delta change scores (for example, pre- to post-touch intervention) were reported, we used those over post-touch only scores. In case frequencies were 0 when frequency tables were used to determine effect sizes, we used a value of 0.5 as a substitute to calculate the effect (the default setting in the ‘metafor’ function 267 ). From these data, Hedges’ g and its variance could be derived. Effect sizes were always computed between the experimental and the control group.
Statistical analysis and risk of bias assessment
Owing to the lack of identified studies, health benefits to animals were not included as part of the statistical analysis. One meta-analysis was performed for adults, adolescents and children, as outcomes were highly comparable. We refer to this meta-analysis as the adult meta-analysis, as children/adolescent cohorts were only targeted in a minority of studies. A separate meta-analysis was performed for newborns, as their health outcomes differed substantially from any other age group.
Data were analysed using R (version 4.2.2) with the ‘rma.mv’ function from the ‘metafor’ package 267 in a multistep, multivariate and multilevel fashion.
We calculated an overall effect of touch interventions across all studies, cohorts and health outcomes. To account for the hierarchical structure of the data, we used a multilevel structure with random effects at the study, cohort and effects level. Furthermore, we calculated the variance–covariance matrix of all data points to account for the dependencies of measured effects within each individual cohort and study. The variance–covariance matrix was calculated by default with an assumed correlation of effect sizes within each cohort of ρ = 0.6. As ρ needed to be assumed, sensitivity analyses for all computed effect estimates were conducted using correlations between effects of 0, 0.2, 0.4 and 0.8. The results of these sensitivity analyses can be found in ref. 12 . No conclusion drawn in the present manuscript was altered by changing the level of ρ . The sensitivity analyses, however, showed that higher assumed correlations lead to more conservative effect size estimates (see Supplementary Figs. 19 and 20 for the adult and newborn meta-analyses, respectively), reducing the type I error risk in general 268 . In addition to these procedures, we used robust variance estimation with cluster-robust inference at the cohort level. This step is recommended to more accurately determine the confidence intervals in complex multivariate models 269 . The data distribution was assumed to be normal, but this was not formally tested.
To determine whether individual effects had a strong influence on our results, we calculated Cook’s distance D . Here, a threshold of D > 0.5 was used to qualify a study as influential 270 . Heterogeneity in the present study was assessed using Cochran’s Q , which determines whether the extracted effect sizes estimate a common population effect size. Although the Q statistic in the ‘rma.mv’ function accounts for the hierarchical nature of the data, we also quantified the heterogeneity estimator σ ² for each random-effects level to provide a comprehensive overview of heterogeneity indicators. These indicators for all models can be found on the OSF project 12 in the Table ‘Model estimates’. To assess small study bias, we visually inspected the funnel plot and used the standard error as a moderator in the overarching meta-analyses.
Before any sub-group analysis, the overall effect size was used as input for power calculations. While such post hoc power calculations might be limited, we believe that a minimum number of effects to be included in subgroup analyses was necessary to allow for meaningful conclusions. Such medium effect sizes would also probably be the minimum effect sizes of interest for researchers as well as clinical practitioners. Power calculation for random-effects models further requires a sample size for each individual effect as well as an approximation of the expected heterogeneity between studies. For the sample size input, we used the median sample size in each of our studies. For heterogeneity, we assumed a value between medium and high levels of heterogeneity ( I ² = 62.5% 271 ), as moderator analyses typically aim at reducing heterogeneity overall. Subgroups were only further investigated if the number of observed effects achieved ~80% power under these circumstances, to allow for a more robust interpretation of the observed effects (see Supplementary Figs. 5 and 6 for the adult and newborn meta-analysis, respectively). In a next step, we investigated all pre-registered moderators for which sufficient power was detected. We first looked at our primary moderators (mental versus physical health) and how the effect sizes systematically varied as a function of our secondary moderators (for example, human–human or human–object touch, duration, skin-to-skin presence, etc.). We always included random slopes to allow for our moderators to vary with the random effects at our clustering variable, which is recommended in multilevel models to reduce false positives 272 . All statistical tests were performed two-sided. Significance of moderators was determined using omnibus F tests. Effect size differences between moderator levels and their confidence intervals were assessed via t tests.
Post hoc t tests were performed comparing mental and physical health benefits within each interacting moderator (for example, mental versus physical health benefits in cancer patients) and mental or physical health benefits across levels of the interacting moderator (for example, mental health benefits in cancer versus pain patients). The post hoc tests were not pre-registered. Data were visualized using forest plots and orchard plots 273 for categorical moderators and scatter plots for continuous moderators.
For a broad overview of prior work and their biases, risk of bias was assessed for all studies included in both meta-analyses and the systematic review. We assessed the risk of bias for the following parameters:
Bias from randomization, including whether a randomization procedure was performed, whether it was a between- or within-participant design and whether there were any baseline differences for demographic or dependent variables.
Sequence bias resulting from a lack of counterbalancing in within-subject designs.
Performance bias resulting from the participants or experiments not being blinded to the experimental conditions.
Attrition bias resulting from different dropout rates between experimental groups.
Note that four studies in the adult meta-analysis did not explicitly mention randomization as part of their protocol. However, since these studies never showed any baseline differences in all relevant variables (see ‘Risk of Bias’ table on the OSF project ) , we assumed that randomization was performed but not mentioned. Sequence bias was of no concern for studies for the meta-analysis since cross-over designs were excluded. It was, however, assessed for studies within the scope of the systematic review. Importantly, performance bias was always high in the adult/children meta-analysis, as blinding of the participants and experimenters to the experimental conditions was not possible owing to the nature of the intervention (touch versus no touch). For studies with newborns and animals, we assessed the performance bias as medium since neither newborns or animals are likely to be aware of being part of an experiment or specific group. An overview of the results is presented in Supplementary Fig. 21 , and the precise assessment for each study can be found on the OSF project 12 in the ‘Risk of Bias’ table.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
All data are available via Open Science Framework at https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/C8RVW (ref. 12 ). Source data are provided with this paper.
Code availability
All code is available via Open Science Framework at https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/C8RVW (ref. 12 ).
Fulkerson, M. The First Sense: a Philosophical Study of Human Touch (MIT Press, 2013).
Farroni, T., Della Longa, L. & Valori, I. The self-regulatory affective touch: a speculative framework for the development of executive functioning. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 43 , 167–173 (2022).
Article Google Scholar
Ocklenburg, S. et al. Hugs and kisses—the role of motor preferences and emotional lateralization for hemispheric asymmetries in human social touch. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 95 , 353–360 (2018).
Ardiel, E. L. & Rankin, C. H. The importance of touch in development. Paediatr. Child Health 15 , 153–156 (2010).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Moyer, C. A., Rounds, J. & Hannum, J. W. A meta-analysis of massage therapy research. Psychol. Bull. 130 , 3–18 (2004).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lee, S. H., Kim, J. Y., Yeo, S., Kim, S. H. & Lim, S. Meta-analysis of massage therapy on cancer pain. Integr. Cancer Ther. 14 , 297–304 (2015).
LaFollette, M. R., O’Haire, M. E., Cloutier, S. & Gaskill, B. N. A happier rat pack: the impacts of tickling pet store rats on human–animal interactions and rat welfare. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 203 , 92–102 (2018).
Packheiser, J., Michon, F. Eva, C., Fredriksen, K. & Hartmann H. The physical and mental health benefits of social touch: a comparative systematic review and meta-analysis. PROSPERO https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42022304281 (2023).
Lakens, D. Sample size justification. Collabra. Psychol. 8 , 33267 (2022).
Quintana, D. S. A guide for calculating study-level statistical power for meta-analyses. Adv. Meth. Pract. Psychol. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1177/25152459221147260 (2023).
Eckstein, M., Mamaev, I., Ditzen, B. & Sailer, U. Calming effects of touch in human, animal, and robotic interaction—scientific state-of-the-art and technical advances. Front. Psychiatry 11 , 555058 (2020).
Packheiser, J. et al. The physical and mental health benefits of affective touch: a comparative systematic review and multivariate meta-analysis. Open Science Framework https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/C8RVW (2023).
Kong, L. J. et al. Massage therapy for neck and shoulder pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013 , 613279 (2013).
Wang, L., He, J. L. & Zhang, X. H. The efficacy of massage on preterm infants: a meta-analysis. Am. J. Perinatol. 30 , 731–738 (2013).
Field, T. Massage therapy research review. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 24 , 19–31 (2016).
Bendas, J., Ree, A., Pabel, L., Sailer, U. & Croy, I. Dynamics of affective habituation to touch differ on the group and individual level. Neuroscience 464 , 44–52 (2021).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Charpak, N., Montealegre‐Pomar, A. & Bohorquez, A. Systematic review and meta‐analysis suggest that the duration of Kangaroo mother care has a direct impact on neonatal growth. Acta Paediatr. 110 , 45–59 (2021).
Packheiser, J. et al. A comparison of hugging frequency and its association with momentary mood before and during COVID-19 using ecological momentary assessment. Health Commun. https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2023.2198058 (2023).
Whitelaw, A., Heisterkamp, G., Sleath, K., Acolet, D. & Richards, M. Skin to skin contact for very low birthweight infants and their mothers. Arch. Dis. Child. 63 , 1377–1381 (1988).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yogeswaran, N. et al. New materials and advances in making electronic skin for interactive robots. Adv. Robot. 29 , 1359–1373 (2015).
Durkin, J., Jackson, D. & Usher, K. Touch in times of COVID‐19: touch hunger hurts. J. Clin. Nurs. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.15488 (2021).
Rokach, A., Lechcier-Kimel, R. & Safarov, A. Loneliness of people with physical disabilities. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 34 , 681–700 (2006).
Palgi, Y. et al. The loneliness pandemic: loneliness and other concomitants of depression, anxiety and their comorbidity during the COVID-19 outbreak. J. Affect. Disord. 275 , 109–111 (2020).
Heatley-Tejada, A., Dunbar, R. I. M. & Montero, M. Physical contact and loneliness: being touched reduces perceptions of loneliness. Adapt. Hum. Behav. Physiol. 6 , 292–306 (2020).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Packheiser, J. et al. The association of embracing with daily mood and general life satisfaction: an ecological momentary assessment study. J. Nonverbal Behav. 46 , 519–536 (2022).
Porter, R. The biological significance of skin-to-skin contact and maternal odours. Acta Paediatr. 93 , 1560–1562 (2007).
Hawkley, L. C., Masi, C. M., Berry, J. D. & Cacioppo, J. T. Loneliness is a unique predictor of age-related differences in systolic blood pressure. Psychol. Aging 21 , 152–164 (2006).
Russo, V., Ottaviani, C. & Spitoni, G. F. Affective touch: a meta-analysis on sex differences. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 108 , 445–452 (2020).
Schirmer, A. et al. Understanding sex differences in affective touch: sensory pleasantness, social comfort, and precursive experiences. Physiol. Behav. 250 , 113797 (2022).
Berretz, G. et al. Romantic partner embraces reduce cortisol release after acute stress induction in women but not in men. PLoS ONE 17 , e0266887 (2022).
Gazzola, V. et al. Primary somatosensory cortex discriminates affective significance in social touch. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109 , E1657–E1666 (2012).
Sorokowska, A. et al. Affective interpersonal touch in close relationships: a cross-cultural perspective. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 47 , 1705–1721 (2021).
Ravaja, N., Harjunen, V., Ahmed, I., Jacucci, G. & Spapé, M. M. Feeling touched: emotional modulation of somatosensory potentials to interpersonal touch. Sci. Rep. 7 , 40504 (2017).
Saarinen, A., Harjunen, V., Jasinskaja-Lahti, I., Jääskeläinen, I. P. & Ravaja, N. Social touch experience in different contexts: a review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 131 , 360–372 (2021).
Huisman, G. Social touch technology: a survey of haptic technology for social touch. IEEE Trans. Haptics 10 , 391–408 (2017).
Lewejohann, L., Schwabe, K., Häger, C. & Jirkof, P. Impulse for animal welfare outside the experiment. Lab. Anim. https://doi.org/10.17169/REFUBIUM-26765 (2020).
Sørensen, J. T., Sandøe, P. & Halberg, N. Animal welfare as one among several values to be considered at farm level: the idea of an ethical account for livestock farming. Acta Agric. Scand. A 51 , 11–16 (2001).
Google Scholar
Verga, M. & Michelazzi, M. Companion animal welfare and possible implications on the human–pet relationship. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 8 , 231–240 (2009).
Coulon, M. et al. Do lambs perceive regular human stroking as pleasant? Behavior and heart rate variability analyses. PLoS ONE 10 , e0118617 (2015).
Soares, M. C., Oliveira, R. F., Ros, A. F. H., Grutter, A. S. & Bshary, R. Tactile stimulation lowers stress in fish. Nat. Commun. 2 , 534 (2011).
Gourkow, N., Hamon, S. C. & Phillips, C. J. C. Effect of gentle stroking and vocalization on behaviour, mucosal immunity and upper respiratory disease in anxious shelter cats. Prev. Vet. Med. 117 , 266–275 (2014).
Oliveira, V. E. et al. Oxytocin and vasopressin within the ventral and dorsal lateral septum modulate aggression in female rats. Nat. Commun. 12 , 2900 (2021).
Burleson, M. H., Roberts, N. A., Coon, D. W. & Soto, J. A. Perceived cultural acceptability and comfort with affectionate touch: differences between Mexican Americans and European Americans. J. Soc. Personal. Relatsh. 36 , 1000–1022 (2019).
Wijaya, M. et al. The human ‘feel’ of touch contributes to its perceived pleasantness. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 46 , 155–171 (2020).
Golaya, S. Touch-hunger: an unexplored consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 43 , 362–363 (2021).
Ng, T. W. H., Sorensen, K. L., Zhang, Y. & Yim, F. H. K. Anger, anxiety, depression, and negative affect: convergent or divergent? J. Vocat. Behav. 110 , 186–202 (2019).
Maier, M., Bartoš, F. & Wagenmakers, E.-J. Robust Bayesian meta-analysis: addressing publication bias with model-averaging. Psychol. Methods 28 , 107–122 (2022).
Ahles, T. A. et al. Massage therapy for patients undergoing autologous bone marrow transplantation. J. Pain. Symptom Manag. 18 , 157–163 (1999).
Albert, N. M. et al. A randomized trial of massage therapy after heart surgery. Heart Lung 38 , 480–490 (2009).
Ang, J. Y. et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of massage therapy on the immune system of preterm infants. Pediatrics 130 , e1549–e1558 (2012).
Arditi, H., Feldman, R. & Eidelman, A. I. Effects of human contact and vagal regulation on pain reactivity and visual attention in newborns. Dev. Psychobiol. 48 , 561–573 (2006).
Arora, J., Kumar, A. & Ramji, S. Effect of oil massage on growth and neurobehavior in very low birth weight preterm neonates. Indian Pediatr. 42 , 1092–1100 (2005).
PubMed Google Scholar
Asadollahi, M., Jabraeili, M., Mahallei, M., Asgari Jafarabadi, M. & Ebrahimi, S. Effects of gentle human touch and field massage on urine cortisol level in premature infants: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. J. Caring Sci. 5 , 187–194 (2016).
Basiri-Moghadam, M., Basiri-Moghadam, K., Kianmehr, M. & Jani, S. The effect of massage on neonatal jaundice in stable preterm newborn infants: a randomized controlled trial. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 65 , 602–606 (2015).
Bauer, B. A. et al. Effect of massage therapy on pain, anxiety, and tension after cardiac surgery: a randomized study. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 16 , 70–75 (2010).
Beijers, R., Cillessen, L. & Zijlmans, M. A. C. An experimental study on mother-infant skin-to-skin contact in full-terms. Infant Behav. Dev. 43 , 58–65 (2016).
Bennett, S. et al. Acute effects of traditional Thai massage on cortisol levels, arterial blood pressure and stress perception in academic stress condition: a single blind randomised controlled trial. J. Bodyw. Mov. Therapies 20 , 286–292 (2016).
Bergman, N., Linley, L. & Fawcus, S. Randomized controlled trial of skin-to-skin contact from birth versus conventional incubator for physiological stabilization in 1200- to 2199-gram newborns. Acta Paediatr. 93 , 779–785 (2004).
Bigelow, A., Power, M., MacLellan‐Peters, J., Alex, M. & McDonald, C. Effect of mother/infant skin‐to‐skin contact on postpartum depressive symptoms and maternal physiological stress. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 41 , 369–382 (2012).
Billhult, A., Bergbom, I. & Stener-Victorin, E. Massage relieves nausea in women with breast cancer who are undergoing chemotherapy. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 13 , 53–57 (2007).
Billhult, A., Lindholm, C., Gunnarsson, R. & Stener-Victorin, E. The effect of massage on cellular immunity, endocrine and psychological factors in women with breast cancer—a randomized controlled clinical trial. Auton. Neurosci. 140 , 88–95 (2008).
Braun, L. A. et al. Massage therapy for cardiac surgery patients—a randomized trial. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 144 , 1453–1459 (2012).
Cabibihan, J.-J. & Chauhan, S. S. Physiological responses to affective tele-touch during induced emotional stimuli. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 8 , 108–118 (2017).
Campeau, M.-P. et al. Impact of massage therapy on anxiety levels in patients undergoing radiation therapy: randomized controlled trial. J. Soc. Integr. Oncol. 5 , 133–138 (2007).
Can, Ş. & Kaya, H. The effects of yakson or gentle human touch training given to mothers with preterm babies on attachment levels and the responses of the baby: a randomized controlled trial. Health Care Women Int. 43 , 479–498 (2021).
Carfoot, S., Williamson, P. & Dickson, R. A randomised controlled trial in the north of England examining the effects of skin-to-skin care on breast feeding. Midwifery 21 , 71–79 (2005).
Castral, T. C., Warnock, F., Leite, A. M., Haas, V. J. & Scochi, C. G. S. The effects of skin-to-skin contact during acute pain in preterm newborns. Eur. J. Pain. 12 , 464–471 (2008).
Cattaneo, A. et al. Kangaroo mother care for low birthweight infants: a randomized controlled trial in different settings. Acta Paediatr. 87 , 976–985 (1998).
Charpak, N., Ruiz-Peláez, J. G. & Charpak, Y. Rey-Martinez kangaroo mother program: an alternative way of caring for low birth weight infants? One year mortality in a two cohort study. Pediatrics 94 , 804–810 (1994).
Chermont, A. G., Falcão, L. F. M., de Souza Silva, E. H. L., de Cássia Xavier Balda, R. & Guinsburg, R. Skin-to-skin contact and/or oral 25% dextrose for procedural pain relief for term newborn infants. Pediatrics 124 , e1101–e1107 (2009).
Chi Luong, K., Long Nguyen, T., Huynh Thi, D. H., Carrara, H. P. O. & Bergman, N. J. Newly born low birthweight infants stabilise better in skin-to-skin contact than when separated from their mothers: a randomised controlled trial. Acta Paediatr. 105 , 381–390 (2016).
Cho, E.-S. et al. The effects of kangaroo care in the neonatal intensive care unit on the physiological functions of preterm infants, maternal–infant attachment, and maternal stress. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 31 , 430–438 (2016).
Choi, H. et al. The effects of massage therapy on physical growth and gastrointestinal function in premature infants: a pilot study. J. Child Health Care 20 , 394–404 (2016).
Choudhary, M. et al. To study the effect of Kangaroo mother care on pain response in preterm neonates and to determine the behavioral and physiological responses to painful stimuli in preterm neonates: a study from western Rajasthan. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 29 , 826–831 (2016).
Christensson, K. et al. Temperature, metabolic adaptation and crying in healthy full-term newborns cared for skin-to-skin or in a cot. Acta Paediatr. 81 , 488–493 (1992).
Cloutier, S. & Newberry, R. C. Use of a conditioning technique to reduce stress associated with repeated intra-peritoneal injections in laboratory rats. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 112 , 158–173 (2008).
Cloutier, S., Wahl, K., Baker, C. & Newberry, R. C. The social buffering effect of playful handling on responses to repeated intraperitoneal injections in laboratory rats. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 53 , 168–173 (2014).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cloutier, S., Wahl, K. L., Panksepp, J. & Newberry, R. C. Playful handling of laboratory rats is more beneficial when applied before than after routine injections. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 164 , 81–90 (2015).
Cong, X. et al. Effects of skin-to-skin contact on autonomic pain responses in preterm infants. J. Pain. 13 , 636–645 (2012).
Cong, X., Ludington-Hoe, S. M., McCain, G. & Fu, P. Kangaroo care modifies preterm infant heart rate variability in response to heel stick pain: pilot study. Early Hum. Dev. 85 , 561–567 (2009).
Cong, X., Ludington-Hoe, S. M. & Walsh, S. Randomized crossover trial of kangaroo care to reduce biobehavioral pain responses in preterm infants: a pilot study. Biol. Res. Nurs. 13 , 204–216 (2011).
Costa, R. et al. Tactile stimulation of adult rats modulates hormonal responses, depression-like behaviors, and memory impairment induced by chronic mild stress: role of angiotensin II. Behav. Brain Res. 379 , 112250 (2020).
Cutshall, S. M. et al. Effect of massage therapy on pain, anxiety, and tension in cardiac surgical patients: a pilot study. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 16 , 92–95 (2010).
Dalili, H., Sheikhi, S., Shariat, M. & Haghnazarian, E. Effects of baby massage on neonatal jaundice in healthy Iranian infants: a pilot study. Infant Behav. Dev. 42 , 22–26 (2016).
Diego, M. A., Field, T. & Hernandez-Reif, M. Vagal activity, gastric motility, and weight gain in massaged preterm neonates. J. Pediatr. 147 , 50–55 (2005).
Diego, M. A., Field, T. & Hernandez-Reif, M. Temperature increases in preterm infants during massage therapy. Infant Behav. Dev. 31 , 149–152 (2008).
Diego, M. A. et al. Preterm infant massage elicits consistent increases in vagal activity and gastric motility that are associated with greater weight gain. Acta Paediatr. 96 , 1588–1591 (2007).
Diego, M. A. et al. Spinal cord patients benefit from massage therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 112 , 133–142 (2002).
Diego, M. A. et al. Aggressive adolescents benefit from massage therapy. Adolescence 37 , 597–607 (2002).
Diego, M. A. et al. HIV adolescents show improved immune function following massage therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 106 , 35–45 (2001).
Dieter, J. N. I., Field, T., Hernandez-Reif, M., Emory, E. K. & Redzepi, M. Stable preterm infants gain more weight and sleep less after five days of massage therapy. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 28 , 403–411 (2003).
Ditzen, B. et al. Effects of different kinds of couple interaction on cortisol and heart rate responses to stress in women. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32 , 565–574 (2007).
Dreisoerner, A. et al. Self-soothing touch and being hugged reduce cortisol responses to stress: a randomized controlled trial on stress, physical touch, and social identity. Compr. Psychoneuroendocrinol. 8 , 100091 (2021).
Eaton, M., Mitchell-Bonair, I. L. & Friedmann, E. The effect of touch on nutritional intake of chronic organic brain syndrome patients. J. Gerontol. 41 , 611–616 (1986).
Edens, J. L., Larkin, K. T. & Abel, J. L. The effect of social support and physical touch on cardiovascular reactions to mental stress. J. Psychosom. Res. 36 , 371–382 (1992).
El-Farrash, R. A. et al. Longer duration of kangaroo care improves neurobehavioral performance and feeding in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatr. Res. 87 , 683–688 (2020).
Erlandsson, K., Dsilna, A., Fagerberg, I. & Christensson, K. Skin-to-skin care with the father after cesarean birth and its effect on newborn crying and prefeeding behavior. Birth 34 , 105–114 (2007).
Escalona, A., Field, T., Singer-Strunck, R., Cullen, C. & Hartshorn, K. Brief report: improvements in the behavior of children with autism following massage therapy. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 31 , 513–516 (2001).
Fattah, M. A. & Hamdy, B. Pulmonary functions of children with asthma improve following massage therapy. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 17 , 1065–1068 (2011).
Feldman, R. & Eidelman, A. I. Skin-to-skin contact (kangaroo care) accelerates autonomic and neurobehavioural maturation in preterm infants. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 45 , 274–281 (2003).
Feldman, R., Eidelman, A. I., Sirota, L. & Weller, A. Comparison of skin-to-skin (kangaroo) and traditional care: parenting outcomes and preterm infant development. Pediatrics 110 , 16–26 (2002).
Feldman, R., Singer, M. & Zagoory, O. Touch attenuates infants’ physiological reactivity to stress. Dev. Sci. 13 , 271–278 (2010).
Feldman, R., Weller, A., Sirota, L. & Eidelman, A. I. Testing a family intervention hypothesis: the contribution of mother–infant skin-to-skin contact (kangaroo care) to family interaction, proximity, and touch. J. Fam. Psychol. 17 , 94–107 (2003).
Ferber, S. G. et al. Massage therapy by mothers and trained professionals enhances weight gain in preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 67 , 37–45 (2002).
Ferber, S. G. & Makhoul, I. R. The effect of skin-to-skin contact (kangaroo care) shortly after birth on the neurobehavioral responses of the term newborn: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 113 , 858–865 (2004).
Ferreira, A. M. & Bergamasco, N. H. P. Behavioral analysis of preterm neonates included in a tactile and kinesthetic stimulation program during hospitalization. Rev. Bras. Fisioter. 14 , 141–148 (2010).
Fidanza, F., Polimeni, E., Pierangeli, V. & Martini, M. A better touch: C-tactile fibers related activity is associated to pain reduction during temporal summation of second pain. J. Pain. 22 , 567–576 (2021).
Field, T. et al. Leukemia immune changes following massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 5 , 271–274 (2001).
Field, T. et al. Benefits of combining massage therapy with group interpersonal psychotherapy in prenatally depressed women. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 13 , 297–303 (2009).
Field, T., Delage, J. & Hernandez-Reif, M. Movement and massage therapy reduce fibromyalgia pain. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 7 , 49–52 (2003).
Field, T. et al. Fibromyalgia pain and substance P decrease and sleep improves after massage therapy. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 8 , 72–76 (2002).
Field, T., Diego, M., Gonzalez, G. & Funk, C. G. Neck arthritis pain is reduced and range of motion is increased by massage therapy. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 20 , 219–223 (2014).
Field, T., Diego, M., Hernandez-Reif, M., Deeds, O. & Figueiredo, B. Pregnancy massage reduces prematurity, low birthweight and postpartum depression. Infant Behav. Dev. 32 , 454–460 (2009).
Field, T. et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 increased in preterm neonates following massage therapy. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 29 , 463–466 (2008).
Field, T. et al. Yoga and massage therapy reduce prenatal depression and prematurity. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 16 , 204–209 (2012).
Field, T., Diego, M., Hernandez-Reif, M., Schanberg, S. & Kuhn, C. Massage therapy effects on depressed pregnant women. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynecol. 25 , 115–122 (2004).
Field, T., Diego, M., Hernandez-Reif, M. & Shea, J. Hand arthritis pain is reduced by massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 11 , 21–24 (2007).
Field, T., Gonzalez, G., Diego, M. & Mindell, J. Mothers massaging their newborns with lotion versus no lotion enhances mothers’ and newborns’ sleep. Infant Behav. Dev. 45 , 31–37 (2016).
Field, T. et al. Children with asthma have improved pulmonary functions after massage therapy. J. Pediatr. 132 , 854–858 (1998).
Field, T., Hernandez-Reif, M., Diego, M. & Fraser, M. Lower back pain and sleep disturbance are reduced following massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 11 , 141–145 (2007).
Field, T. et al. Effects of sexual abuse are lessened by massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 1 , 65–69 (1997).
Field, T. et al. Pregnant women benefit from massage therapy. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynecol. 20 , 31–38 (1999).
Field, T. et al. Juvenilerheumatoid arthritis: benefits from massage therapy. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 22 , 607–617 (1997).
Field, T., Hernandez-Reif, M., Taylor, S., Quintino, O. & Burman, I. Labor pain is reduced by massage therapy. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynecol. 18 , 286–291 (1997).
Field, T. et al. Massage therapy reduces anxiety and enhances EEG pattern of alertness and math computations. Int. J. Neurosci. 86 , 197–205 (1996).
Field, T. et al. Brief report: autistic children’s attentiveness and responsivity improve after touch therapy. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 27 , 333–338 (1997).
Field, T. M. et al. Tactile/kinesthetic stimulation effects on preterm neonates. Pediatrics 77 , 654–658 (1986).
Field, T. et al. Massage reduces anxiety in child and adolescent psychiatric patients. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 31 , 125–131 (1992).
Field, T. et al. Burn injuries benefit from massage therapy. J. Burn Care Res. 19 , 241–244 (1998).
Filho, F. L. et al. Effect of maternal skin-to-skin contact on decolonization of methicillin-oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus in neonatal intensive care units: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0496-1 (2015).
Forward, J. B., Greuter, N. E., Crisall, S. J. & Lester, H. F. Effect of structured touch and guided imagery for pain and anxiety in elective joint replacement patients—a randomized controlled trial: M-TIJRP. Perm. J. 19 , 18–28 (2015).
Fraser, J. & Ross Kerr, J. Psychophysiological effects of back massage on elderly institutionalized patients. J. Adv. Nurs. 18 , 238–245 (1993).
Frey Law, L. A. et al. Massage reduces pain perception and hyperalgesia in experimental muscle pain: a randomized, controlled trial. J. Pain. 9 , 714–721 (2008).
Gao, H. et al. Effect of repeated kangaroo mother care on repeated procedural pain in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 52 , 1157–1165 (2015).
Garner, B. et al. Pilot study evaluating the effect of massage therapy on stress, anxiety and aggression in a young adult psychiatric inpatient unit. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 42 , 414–422 (2008).
Gathwala, G., Singh, B. & Singh, J. Effect of kangaroo mother care on physical growth, breastfeeding and its acceptability. Trop. Dr. 40 , 199–202 (2010).
Geva, N., Uzefovsky, F. & Levy-Tzedek, S. Touching the social robot PARO reduces pain perception and salivary oxytocin levels. Sci. Rep. 10 , 9814 (2020).
Gitau, R. et al. Acute effects of maternal skin-to-skin contact and massage on saliva cortisol in preterm babies. J. Reprod. Infant Psychol. 20 , 83–88 (2002).
Givi, M. Durability of effect of massage therapy on blood pressure. Int. J. Prev. Med. 4 , 511–516 (2013).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Glover, V., Onozawa, K. & Hodgkinson, A. Benefits of infant massage for mothers with postnatal depression. Semin. Neonatol. 7 , 495–500 (2002).
Gonzalez, A. et al. Weight gain in preterm infants following parent-administered vimala massage: a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Perinatol. 26 , 247–252 (2009).
Gray, L., Watt, L. & Blass, E. M. Skin-to-skin contact is analgesic in healthy newborns. Pediatrics 105 , e14 (2000).
Grewen, K. M., Anderson, B. J., Girdler, S. S. & Light, K. C. Warm partner contact is related to lower cardiovascular reactivity. Behav. Med. 29 , 123–130 (2003).
Groër, M. W., Hill, J., Wilkinson, J. E. & Stuart, A. Effects of separation and separation with supplemental stroking in BALB/c infant mice. Biol. Res. Nurs. 3 , 119–131 (2002).
Gürol, A. P., Polat, S. & Nuran Akçay, M. Itching, pain, and anxiety levels are reduced with massage therapy in burned adolescents. J. Burn Care Res. 31 , 429–432 (2010).
Haley, S. et al. Tactile/kinesthetic stimulation (TKS) increases tibial speed of sound and urinary osteocalcin (U-MidOC and unOC) in premature infants (29–32 weeks PMA). Bone 51 , 661–666 (2012).
Harris, M., Richards, K. C. & Grando, V. T. The effects of slow-stroke back massage on minutes of nighttime sleep in persons with dementia and sleep disturbances in the nursing home: a pilot study. J. Holist. Nurs. 30 , 255–263 (2012).
Hart, S. et al. Anorexia nervosa symptoms are reduced by massage therapy. Eat. Disord. 9 , 289–299 (2001).
Hattan, J., King, L. & Griffiths, P. The impact of foot massage and guided relaxation following cardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Issues Innov. Nurs. Pract. 37 , 199–207 (2002).
Haynes, A. C. et al. A calming hug: design and validation of a tactile aid to ease anxiety. PLoS ONE 17 , e0259838 (2022).
Henricson, M., Ersson, A., Määttä, S., Segesten, K. & Berglund, A.-L. The outcome of tactile touch on stress parameters in intensive care: a randomized controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 14 , 244–254 (2008).
Hernandez-Reif, M., Diego, M. & Field, T. Preterm infants show reduced stress behaviors and activity after 5 days of massage therapy. Infant Behav. Dev. 30 , 557–561 (2007).
Hernandez-Reif, M., Dieter, J. N. I., Field, T., Swerdlow, B. & Diego, M. Migraine headaches are reduced by massage therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 96 , 1–11 (1998).
Hernandez-Reif, M. et al. Natural killer cells and lymphocytes increase in women with breast cancer following massage therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 115 , 495–510 (2005).
Hernandez-Reif, M. et al. Children with cystic fibrosis benefit from massage therapy. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 24 , 175–181 (1999).
Hernandez-Reif, M., Field, T., Krasnegor, J. & Theakston, H. Lower back pain is reduced and range of motion increased after massage therapy. Int. J. Neurosci. 106 , 131–145 (2001).
Hernandez-Reif, M. et al. High blood pressure and associated symptoms were reduced by massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 4 , 31–38 (2000).
Hernandez-Reif, M. et al. Parkinson’s disease symptoms are differentially affected by massage therapy vs. progressive muscle relaxation: a pilot study. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 6 , 177–182 (2002).
Hernandez-Reif, M., Field, T. & Theakston, H. Multiple sclerosis patients benefit from massage therapy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2 , 168–174 (1998).
Hernandez-Reif, M. et al. Breast cancer patients have improved immune and neuroendocrine functions following massage therapy. J. Psychosom. Res. 57 , 45–52 (2004).
Hertenstein, M. J. & Campos, J. J. Emotion regulation via maternal touch. Infancy 2 , 549–566 (2001).
Hinchcliffe, J. K., Mendl, M. & Robinson, E. S. J. Rat 50 kHz calls reflect graded tickling-induced positive emotion. Curr. Biol. 30 , R1034–R1035 (2020).
Hodgson, N. A. & Andersen, S. The clinical efficacy of reflexology in nursing home residents with dementia. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 14 , 269–275 (2008).
Hoffmann, L. & Krämer, N. C. The persuasive power of robot touch. Behavioral and evaluative consequences of non-functional touch from a robot. PLoS ONE 16 , e0249554 (2021).
Holst, S., Lund, I., Petersson, M. & Uvnäs-Moberg, K. Massage-like stroking influences plasma levels of gastrointestinal hormones, including insulin, and increases weight gain in male rats. Auton. Neurosci. 120 , 73–79 (2005).
Hori, M. et al. Tickling during adolescence alters fear-related and cognitive behaviors in rats after prolonged isolation. Physiol. Behav. 131 , 62–67 (2014).
Hori, M. et al. Effects of repeated tickling on conditioned fear and hormonal responses in socially isolated rats. Neurosci. Lett. 536 , 85–89 (2013).
Hucklenbruch-Rother, E. et al. Delivery room skin-to-skin contact in preterm infants affects long-term expression of stress response genes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 122 , 104883 (2020).
Im, H. & Kim, E. Effect of yakson and gentle human touch versus usual care on urine stress hormones and behaviors in preterm infants: a quasi-experimental study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 46 , 450–458 (2009).
Jain, S., Kumar, P. & McMillan, D. D. Prior leg massage decreases pain responses to heel stick in preterm babies. J. Paediatr. Child Health 42 , 505–508 (2006).
Jane, S.-W. et al. Effects of massage on pain, mood status, relaxation, and sleep in Taiwanese patients with metastatic bone pain: a randomized clinical trial. Pain 152 , 2432–2442 (2011).
Johnston, C. C. et al. Kangaroo mother care diminishes pain from heel lance in very preterm neonates: a crossover trial. BMC Pediatr. 8 , 13 (2008).
Johnston, C. C. et al. Kangaroo care is effective in diminishing pain response in preterm neonates. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 157 , 1084–1088 (2003).
Jung, M. J., Shin, B.-C., Kim, Y.-S., Shin, Y.-I. & Lee, M. S. Is there any difference in the effects of QI therapy (external QIGONG) with and without touching? a pilot study. Int. J. Neurosci. 116 , 1055–1064 (2006).
Kapoor, Y. & Orr, R. Effect of therapeutic massage on pain in patients with dementia. Dementia 16 , 119–125 (2017).
Karagozoglu, S. & Kahve, E. Effects of back massage on chemotherapy-related fatigue and anxiety: supportive care and therapeutic touch in cancer nursing. Appl. Nurs. Res. 26 , 210–217 (2013).
Karbasi, S. A., Golestan, M., Fallah, R., Golshan, M. & Dehghan, Z. Effect of body massage on increase of low birth weight neonates growth parameters: a randomized clinical trial. Iran. J. Reprod. Med. 11 , 583–588 (2013).
Kashaninia, Z., Sajedi, F., Rahgozar, M. & Noghabi, F. A. The effect of kangaroo care on behavioral responses to pain of an intramuscular injection in neonates . J. Pediatr. Nurs. 3 , 275–280 (2008).
Kelling, C., Pitaro, D. & Rantala, J. Good vibes: The impact of haptic patterns on stress levels. In Proc. 20th International Academic Mindtrek Conference 130–136 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2016).
Khilnani, S., Field, T., Hernandez-Reif, M. & Schanberg, S. Massage therapy improves mood and behavior of students with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Adolescence 38 , 623–638 (2003).
Kianmehr, M. et al. The effect of massage on serum bilirubin levels in term neonates with hyperbilirubinemia undergoing phototherapy. Nautilus 128 , 36–41 (2014).
Kim, I.-H., Kim, T.-Y. & Ko, Y.-W. The effect of a scalp massage on stress hormone, blood pressure, and heart rate of healthy female. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 28 , 2703–2707 (2016).
Kim, M. A., Kim, S.-J. & Cho, H. Effects of tactile stimulation by fathers on physiological responses and paternal attachment in infants in the NICU: a pilot study. J. Child Health Care 21 , 36–45 (2017).
Kim, M. S., Sook Cho, K., Woo, H.-M. & Kim, J. H. Effects of hand massage on anxiety in cataract surgery using local anesthesia. J. Cataract Refr. Surg. 27 , 884–890 (2001).
Koole, S. L., Tjew A Sin, M. & Schneider, I. K. Embodied terror management: interpersonal touch alleviates existential concerns among individuals with low self-esteem. Psychol. Sci. 25 , 30–37 (2014).
Krohn, M. et al. Depression, mood, stress, and Th1/Th2 immune balance in primary breast cancer patients undergoing classical massage therapy. Support. Care Cancer 19 , 1303–1311 (2011).
Kuhn, C. et al. Tactile-kinesthetic stimulation effects sympathetic and adrenocortical function in preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 119 , 434–440 (1991).
Kumar, J. et al. Effect of oil massage on growth in preterm neonates less than 1800 g: a randomized control trial. Indian J. Pediatr. 80 , 465–469 (2013).
Lee, H.-K. The effects of infant massage on weight, height, and mother–infant interaction. J. Korean Acad. Nurs. 36 , 1331–1339 (2006).
Leivadi, S. et al. Massage therapy and relaxation effects on university dance students. J. Dance Med. Sci. 3 , 108–112 (1999).
Lindgren, L. et al. Touch massage: a pilot study of a complex intervention. Nurs. Crit. Care 18 , 269–277 (2013).
Lindgren, L. et al. Physiological responses to touch massage in healthy volunteers. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 158 , 105–110 (2010).
Listing, M. et al. Massage therapy reduces physical discomfort and improves mood disturbances in women with breast cancer. Psycho-Oncol. 18 , 1290–1299 (2009).
Ludington-Hoe, S. M., Cranston Anderson, G., Swinth, J. Y., Thompson, C. & Hadeed, A. J. Randomized controlled trial of kangaroo care: cardiorespiratory and thermal effects on healthy preterm infants. Neonatal Netw. 23 , 39–48 (2004).
Lund, I. et al. Corticotropin releasing factor in urine—a possible biochemical marker of fibromyalgia. Neurosci. Lett. 403 , 166–171 (2006).
Ma, Y.-K. et al. Lack of social touch alters anxiety-like and social behaviors in male mice. Stress 25 , 134–144 (2022).
Massaro, A. N., Hammad, T. A., Jazzo, B. & Aly, H. Massage with kinesthetic stimulation improves weight gain in preterm infants. J. Perinatol. 29 , 352–357 (2009).
Mathai, S., Fernandez, A., Mondkar, J. & Kanbur, W. Effects of tactile-kinesthetic stimulation in preterms–a controlled trial. Indian Pediatr. 38 , 1091–1098 (2001).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Matsunaga, M. et al. Profiling of serum proteins influenced by warm partner contact in healthy couples. Neuroenocrinol. Lett. 30 , 227–236 (2009).
CAS Google Scholar
Mendes, E. W. & Procianoy, R. S. Massage therapy reduces hospital stay and occurrence of late-onset sepsis in very preterm neonates. J. Perinatol. 28 , 815–820 (2008).
Mirnia, K., Arshadi Bostanabad, M., Asadollahi, M. & Hamid Razzaghi, M. Paternal skin-to-skin care and its effect on cortisol levels of the infants. Iran. J. Pediatrics 27 , e8151 (2017).
Mitchell, A. J., Yates, C., Williams, K. & Hall, R. W. Effects of daily kangaroo care on cardiorespiratory parameters in preterm infants. J. Neonatal-Perinat. Med. 6 , 243–249 (2013).
Mitchinson, A. R. et al. Acute postoperative pain management using massage as an adjuvant therapy: a randomized trial. Arch. Surg. 142 , 1158–1167 (2007).
Modrcin-Talbott, M. A., Harrison, L. L., Groer, M. W. & Younger, M. S. The biobehavioral effects of gentle human touch on preterm infants. Nurs. Sci. Q. 16 , 60–67 (2003).
Mok, E. & Pang Woo, C. The effects of slow-stroke back massage on anxiety and shoulder pain in elderly stroke patients. Complement. Ther. Nurs. Midwifery 10 , 209–216 (2004).
Mokaberian, M., Noripour, S., Sheikh, M. & Mills, P. J. Examining the effectiveness of body massage on physical status of premature neonates and their mothers’ psychological status. Early Child Dev. Care 192 , 2311–2325 (2021).
Mori, H. et al. Effect of massage on blood flow and muscle fatigue following isometric lumbar exercise. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 10 , CR173–CR178 (2004).
Moyer-Mileur, L. J., Haley, S., Slater, H., Beachy, J. & Smith, S. L. Massage improves growth quality by decreasing body fat deposition in male preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 162 , 490–495 (2013).
Moyle, W. et al. Foot massage and physiological stress in people with dementia: a randomized controlled trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 20 , 305–311 (2014).
Muntsant, A., Shrivastava, K., Recasens, M. & Giménez-Llort, L. Severe perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury induces long-term sensorimotor deficits, anxiety-like behaviors and cognitive impairment in a sex-, age- and task-selective manner in C57BL/6 mice but can be modulated by neonatal handling. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 13 , 7 (2019).
Negahban, H., Rezaie, S. & Goharpey, S. Massage therapy and exercise therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis: a randomized controlled pilot study. Clin. Rehabil. 27 , 1126–1136 (2013).
Nelson, D., Heitman, R. & Jennings, C. Effects of tactile stimulation on premature infant weight gain. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 15 , 262–267 (1986).
Griffin, J. W. Calculating statistical power for meta-analysis using metapower. Quant. Meth. Psychol . 17 , 24–39 (2021).
Nunes, G. S. et al. Massage therapy decreases pain and perceived fatigue after long-distance Ironman triathlon: a randomised trial. J. Physiother. 62 , 83–87 (2016).
Ohgi, S. et al. Comparison of kangaroo care and standard care: behavioral organization, development, and temperament in healthy, low-birth-weight infants through 1 year. J. Perinatol. 22 , 374–379 (2002).
O′Higgins, M., St. James Roberts, I. & Glover, V. Postnatal depression and mother and infant outcomes after infant massage. J. Affect. Disord. 109 , 189–192 (2008).
Okan, F., Ozdil, A., Bulbul, A., Yapici, Z. & Nuhoglu, A. Analgesic effects of skin-to-skin contact and breastfeeding in procedural pain in healthy term neonates. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 30 , 119–128 (2010).
Oliveira, D. S., Hachul, H., Goto, V., Tufik, S. & Bittencourt, L. R. A. Effect of therapeutic massage on insomnia and climacteric symptoms in postmenopausal women. Climacteric 15 , 21–29 (2012).
Olsson, E., Ahlsén, G. & Eriksson, M. Skin-to-skin contact reduces near-infrared spectroscopy pain responses in premature infants during blood sampling. Acta Paediatr. 105 , 376–380 (2016).
Pauk, J., Kuhn, C. M., Field, T. M. & Schanberg, S. M. Positive effects of tactile versus kinesthetic or vestibular stimulation on neuroendocrine and ODC activity in maternally-deprived rat pups. Life Sci. 39 , 2081–2087 (1986).
Pinazo, D., Arahuete, L. & Correas, N. Hugging as a buffer against distal fear of death. Calid. Vida Salud 13 , 11–20 (2020).
Pope, M. H. et al. A prospective randomized three-week trial of spinal manipulation, transcutaneous muscle stimulation, massage and corset in the treatment of subacute low back pain. Spine 19 , 2571–2577 (1994).
Preyde, M. Effectiveness of massage therapy for subacute low-back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 162 , 1815–1820 (2000).
Ramanathan, K., Paul, V. K., Deorari, A. K., Taneja, U. & George, G. Kangaroo mother care in very low birth weight infants. Indian J. Pediatr. 68 , 1019–1023 (2001).
Reddan, M. C., Young, H., Falkner, J., López-Solà, M. & Wager, T. D. Touch and social support influence interpersonal synchrony and pain. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 15 , 1064–1075 (2020).
Rodríguez-Mansilla, J. et al. The effects of ear acupressure, massage therapy and no therapy on symptoms of dementia: a randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 29 , 683–693 (2015).
Rose, S. A., Schmidt, K., Riese, M. L. & Bridger, W. H. Effects of prematurity and early intervention on responsivity to tactual stimuli: a comparison of preterm and full-term infants. Child Dev. 51 , 416–425 (1980).
Scafidi, F. A. et al. Massage stimulates growth in preterm infants: a replication. Infant Behav. Dev. 13 , 167–188 (1990).
Scafidi, F. A. et al. Effects of tactile/kinesthetic stimulation on the clinical course and sleep/wake behavior of preterm neonates. Infant Behav. Dev. 9 , 91–105 (1986).
Scafidi, F. & Field, T. Massage therapy improves behavior in neonates born to HIV-positive mothers. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 21 , 889–897 (1996).
Scarr-Salapatek, S. & Williams, M. L. A stimulation program for low birth weight infants. Am. J. Public Health 62 , 662–667 (1972).
Serrano, B., Baños, R. M. & Botella, C. Virtual reality and stimulation of touch and smell for inducing relaxation: a randomized controlled trial. Comput. Hum. Behav. 55 , 1–8 (2016).
Seyyedrasooli, A., Valizadeh, L., Hosseini, M. B., Asgari Jafarabadi, M. & Mohammadzad, M. Effect of vimala massage on physiological jaundice in infants: a randomized controlled trial. J. Caring Sci. 3 , 165–173 (2014).
Sharpe, P. A., Williams, H. G., Granner, M. L. & Hussey, J. R. A randomised study of the effects of massage therapy compared to guided relaxation on well-being and stress perception among older adults. Complement. Therap. Med. 15 , 157–163 (2007).
Sherman, K. J., Cherkin, D. C., Hawkes, R. J., Miglioretti, D. L. & Deyo, R. A. Randomized trial of therapeutic massage for chronic neck pain. Clin. J. Pain. 25 , 233–238 (2009).
Shiloh, S., Sorek, G. & Terkel, J. Reduction of state-anxiety by petting animals in a controlled laboratory experiment. Anxiety, Stress Coping 16 , 387–395 (2003).
Shor-Posner, G. et al. Impact of a massage therapy clinical trial on immune status in young Dominican children infected with HIV-1. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 12 , 511–516 (2006).
Simpson, E. A. et al. Social touch alters newborn monkey behavior. Infant Behav. Dev. 57 , 101368 (2019).
Smith, S. L., Haley, S., Slater, H. & Moyer-Mileur, L. J. Heart rate variability during caregiving and sleep after massage therapy in preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 89 , 525–529 (2013).
Smith, S. L. et al. The effect of massage on heart rate variability in preterm infants. J. Perinatol. 33 , 59–64 (2013).
Solkoff, N. & Matuszak, D. Tactile stimulation and behavioral development among low-birthweight infants. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 6 , 3337 (1975).
Srivastava, S., Gupta, A., Bhatnagar, A. & Dutta, S. Effect of very early skin to skin contact on success at breastfeeding and preventing early hypothermia in neonates. Indian J. Public Health 58 , 22–26 (2014).
Stringer, J., Swindell, R. & Dennis, M. Massage in patients undergoing intensive chemotherapy reduces serum cortisol and prolactin: massage in oncology patients reduces serum cortisol. Psycho-Oncol. 17 , 1024–1031 (2008).
Suman Rao, P. N., Udani, R. & Nanavati, R. Kangaroo mother care for low birth weight infants: a randomized controlled trial. Indian Pediatr. 45 , 17–23 (2008).
Sumioka, H. et al. A huggable device can reduce the stress of calling an unfamiliar person on the phone for individuals with ASD. PLoS ONE 16 , e0254675 (2021).
Sumioka, H., Nakae, A., Kanai, R. & Ishiguro, H. Huggable communication medium decreases cortisol levels. Sci. Rep. 3 , 3034 (2013).
Suzuki, M. et al. Physical and psychological effects of 6-week tactile massage on elderly patients with severe dementia. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 25 , 680–686 (2010).
Thomson, L. J. M., Ander, E. E., Menon, U., Lanceley, A. & Chatterjee, H. J. Quantitative evidence for wellbeing benefits from a heritage-in-health intervention with hospital patients. Int. J. Art. Ther. 17 , 63–79 (2012).
Triplett, J. L. & Arneson, S. W. The use of verbal and tactile comfort to alleviate distress in young hospitalized children. Res. Nurs. Health 2 , 17–23 (1979).
Walach, H., Güthlin, C. & König, M. Efficacy of massage therapy in chronic pain: a pragmatic randomized trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 9 , 837–846 (2003).
Walker, S. C. et al. C‐low threshold mechanoafferent targeted dynamic touch modulates stress resilience in rats exposed to chronic mild stress. Eur. J. Neurosci. 55 , 2925–2938 (2022).
Weinrich, S. P. & Weinrich, M. C. The effect of massage on pain in cancer patients. Appl. Nurs. Res. 3 , 140–145 (1990).
Wheeden, A. et al. Massage effects on cocaine-exposed preterm neonates. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 14 , 318–322 (1993).
White, J. L. & Labarba, R. C. The effects of tactile and kinesthetic stimulation on neonatal development in the premature infant. Dev. Psychobiol. 9 , 569–577 (1976).
Wilkie, D. J. et al. Effects of massage on pain intensity, analgesics and quality of life in patients with cancer pain: a pilot study of a randomized clinical trial conducted within hospice care delivery. Hosp. J. 15 , 31–53 (2000).
Willemse, C. J. A. M., Toet, A. & van Erp, J. B. F. Affective and behavioral responses to robot-initiated social touch: toward understanding the opportunities and limitations of physical contact in human–robot interaction. Front. ICT 4 , 12 (2017).
Willemse, C. J. A. M. & van Erp, J. B. F. Social touch in human–robot interaction: robot-initiated touches can induce positive responses without extensive prior bonding. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 11 , 285–304 (2019).
Woods, D. L., Beck, C. & Sinha, K. The effect of therapeutic touch on behavioral symptoms and cortisol in persons with dementia. Res. Complement. Med. 16 , 181–189 (2009).
Yamaguchi, M., Sekine, T. & Shetty, V. A salivary cytokine panel discriminates moods states following a touch massage intervention. Int. J. Affect. Eng. 19 , 189–198 (2020).
Yamazaki, R. et al. Intimacy in phone conversations: anxiety reduction for Danish seniors with hugvie. Front. Psychol. 7 , 537 (2016).
Yang, M.-H. et al. Comparison of the efficacy of aroma-acupressure and aromatherapy for the treatment of dementia-associated agitation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 15 , 93 (2015).
Yates, C. C. et al. The effects of massage therapy to induce sleep in infants born preterm. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 26 , 405–410 (2014).
Yu, H. et al. Social touch-like tactile stimulation activates a tachykinin 1-oxytocin pathway to promote social interactions. Neuron 110 , 1051–1067 (2022).
Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: a practical primer for t -tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 4 , 863 (2013).
Page, M. J., et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4 (2021).
Wilson, D. B. Practical meta-analysis effect size calculator (Version 2023.11.27). https://campbellcollaboration.org/research-resources/effect-size-calculator.html (2023).
Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v036.i03 (2010).
Scammacca, N., Roberts, G. & Stuebing, K. K. Meta-analysis with complex research designs: dealing with dependence from multiple measures and multiple group comparisons. Rev. Educ. Res. 84 , 328–364 (2014).
Pustejovsky, J. E. & Tipton, E. Meta-analysis with robust variance estimation: expanding the range of working models. Prev. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Prev. Res. 23 , 425–438 (2022).
Cook, R. D. in International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science (ed. M. Lovric) S. 301–302 (Springer, 2011).
Higgins, J. P. T., Thompson, S. & Deeks, J. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557 (2003).
Oberauer, K. The importance of random slopes in mixed models for Bayesian hypothesis testing. Psychol. Sci. 33 , 648–665 (2022).
Nakagawa, S. et al. The orchard plot: cultivating a forest plot for use in ecology, evolution, and beyond. Res. Synth. Methods 12 , 4–12 (2021).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Frick and E. Chris for supporting the initial literature search and coding. We also thank A. Dreisoerner, T. Field, S. Koole, C. Kuhn, M. Henricson, L. Frey Law, J. Fraser, M. Cumella Reddan, and J. Stringer, who kindly responded to our data requests and provided additional information or data with respect to single studies. J.P. was supported by the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina (LPDS 2021-05). H.H. was supported by the Marietta-Blau scholarship of the Austrian Agency for Education and Internationalisation (OeAD) and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation, project ID 422744262 – TRR 289). C.K. received funding from OCENW.XL21.XL21.069 and V.G. from the European Research Council (ERC) under European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme, grant ‘HelpUS’ (758703) and from the Dutch Research Council (NWO) grant OCENW.XL21.XL21.069. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Open access funding provided by Ruhr-Universität Bochum.
Author information
Julian Packheiser
Present address: Social Neuroscience, Faculty of Medicine, Ruhr University Bochum, Bochum, Germany
These authors contributed equally: Julian Packheiser, Helena Hartmann.
Authors and Affiliations
Social Brain Lab, Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, Royal Netherlands Academy of Art and Sciences, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
Julian Packheiser, Helena Hartmann, Kelly Fredriksen, Valeria Gazzola, Christian Keysers & Frédéric Michon
Center for Translational and Behavioral Neuroscience, University Hospital Essen, Essen, Germany
Helena Hartmann
Clinical Neurosciences, Department for Neurology, University Hospital Essen, Essen, Germany
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
J.P. contributed to conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing the original draft, review and editing, visualization, supervision and project administration. HH contributed to conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing the original draft, review and editing, visualization, supervision and project administration. K.F. contributed to investigation, data curation, and review and editing. C.K. and V.G. contributed to conceptualization, and review and editing. F.M. contributed to conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing the original draft, and review and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Julian Packheiser .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Human Behaviour thanks Ville Harjunen, Rebecca Boehme and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Supplementary Figs. 1–21 and Tables 1–4.
Reporting Summary
Peer review file, supplementary table 1.
List of studies included in and excluded from the meta-analyses/review.
Supplementary Table 2
PRISMA checklist, manuscript.
Supplementary Table 3
PRISMA checklist, abstract.
Source Data Fig. 2
Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) information for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 3 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (column ‘Outcome’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 4 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (columns ‘dyad_type’ and ‘skin_to_skin’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 5 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (column ‘touch_type’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 6 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (column ‘clin_sample’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 7 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (column ‘familiarity’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis. Source Data Fig. 7 Effect size/error (columns ‘Hedges_g’ and ‘variance’) together with moderator data (columns ‘touch_duration’ and ‘sessions’) for each study/cohort/effect included in the analysis.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Packheiser, J., Hartmann, H., Fredriksen, K. et al. A systematic review and multivariate meta-analysis of the physical and mental health benefits of touch interventions. Nat Hum Behav (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-024-01841-8
Download citation
Received : 16 August 2023
Accepted : 29 January 2024
Published : 08 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-024-01841-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

Patient No-Show Prediction: A Systematic Literature Review
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Statistics, University Carlos III of Madrid, 28911 Leganés, Spain.
- 2 UC3M-Santander Big Data Institute, University Carlos III of Madrid, 28903 Getafe, Spain.
- PMID: 33286447
- PMCID: PMC7517206
- DOI: 10.3390/e22060675
Nowadays, across the most important problems faced by health centers are those caused by the existence of patients who do not attend their appointments. Among others, these patients cause loss of revenue to the health centers and increase the patients' waiting list. In order to tackle these problems, several scheduling systems have been developed. Many of them require predicting whether a patient will show up for an appointment. However, obtaining these estimates accurately is currently a challenging problem. In this work, a systematic review of the literature on predicting patient no-shows is conducted aiming at establishing the current state-of-the-art. Based on a systematic review following the PRISMA methodology, 50 articles were found and analyzed. Of these articles, 82% were published in the last 10 years and the most used technique was logistic regression. In addition, there is significant growth in the size of the databases used to build the classifiers. An important finding is that only two studies achieved an accuracy higher than the show rate. Moreover, a single study attained an area under the curve greater than the 0.9 value. These facts indicate the difficulty of this problem and the need for further research.
Keywords: patient no-show; prediction; systematic review.
Publication types
- Open access
- Published: 06 December 2022
What improves access to primary healthcare services in rural communities? A systematic review
- Zemichael Gizaw 1 ,
- Tigist Astale 2 &
- Getnet Mitike Kassie 2
BMC Primary Care volume 23 , Article number: 313 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
13k Accesses
9 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
To compile key strategies from the international experiences to improve access to primary healthcare (PHC) services in rural communities. Different innovative approaches have been practiced in different parts of the world to improve access to essential healthcare services in rural communities. Systematically collecting and combining best experiences all over the world is important to suggest effective strategies to improve access to healthcare in developing countries. Accordingly, this systematic review of literature was undertaken to identify key approaches from international experiences to enhance access to PHC services in rural communities.
All published and unpublished qualitative and/or mixed method studies conducted to improvement access to PHC services were searched from MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, WHO Global Health Library, and Google Scholar. Articles published other than English language, citations with no abstracts and/or full texts, and duplicate studies were excluded. We included all articles available in different electronic databases regardless of their publication years. We assessed the methodological quality of the included studies using mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT) version 2018 to minimize the risk of bias. Data were extracted using JBI mixed methods data extraction form. Data were qualitatively analyzed using emergent thematic analysis approach to identify key concepts and coded them into related non-mutually exclusive themes.
Our analysis of 110 full-text articles resulted in ten key strategies to improve access to PHC services. Community health programs or community-directed interventions, school-based healthcare services, student-led healthcare services, outreach services or mobile clinics, family health program, empanelment, community health funding schemes, telemedicine, working with traditional healers, working with non-profit private sectors and non-governmental organizations including faith-based organizations are the key strategies identified from international experiences.
This review identified key strategies from international experiences to improve access to PHC services in rural communities. These strategies can play roles in achieving universal health coverage and reducing disparities in health outcomes among rural communities and enabling them to get healthcare when and where they want.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Universal health coverage (UHC) is used to provide expanding services to eliminate access barriers. Universal health coverage is defined by the world health organization (WHO) as access to key promotional, preventive, curative and rehabilitative health services for all at an affordable rate and ensuring equity in access. The term universal has been described as the State's legal obligation to provide healthcare to all its citizens, with particular attention to ensuring that all poor and excluded groups are included [ 1 , 2 , 3 ].
Strengthening primary healthcare (PHC) is the most comprehensive, reliable and productive approach to improving people's physical and mental wellbeing and social well-being, and that PHC is a pillar of a sustainable health system for UHC and health-related sustainable development goals [ 4 , 5 ]. Despite tremendous progress over the last decades, there are still unaddressed health needs of people in all parts of the world [ 6 , 7 ]. Many people, particularly the poor and people living in rural areas and those who are in vulnerable circumstances, face challenges to remain healthy [ 8 ].
Geographical and financial inaccessibility, inadequate funding, inconsistent medication supply and equipment and personnel shortages have left the reach, availability and effect of PHC services in many countries disappointingly limited [ 9 , 10 ]. A recent Astana Declaration recognized those aspects of PHC need to be changed to adapt adequately to current and emerging threats to the healthcare system. This declaration discussed that implementation of a need-based, comprehensive, cost-effective, accessible, efficient and sustainable healthcare system is needed for disadvantaged and rural populations in more local and convenient settings to provide care when and where they want it [ 8 ].
Different innovative approaches have been practiced in different parts of the world to improve access to essential healthcare services in rural communities. Systematically collecting and combining best experiences all over the world is important to suggest effective strategies to improve access to healthcare in developing countries. Accordingly, this systematic review of literature was undertaken to identify key approaches from international experiences to enhance access to PHC services in rural communities. The findings of this systematic literature review can be used by healthcare professionals, researchers and policy makers to improve healthcare service delivery in rural communities.
Methodology
Research question.
What improves access to PHC services in rural communities? We used the PICO (population, issue/intervention, comparison/contrast, and outcome) construct to develop the search question [ 11 ]. The population is rural communities or remote communities in developing countries who have limited access to healthcare services. Moreover, we extended the population to developed countries to capture experiences of both developing and developed countries. The issue/intervention is implementation of different community-based health interventions to access to essential healthcare services. In this systematic review, we focused on PHC health services, mainly essential or basic healthcare services, community or public health services, and health promotion or health education. Primary healthcare is “a health care system that addressed social, economic, and political causes of poor health promotes health though health services at the primary care level enhances health of the community” [ 12 ]. Comparison/contrast is not appropriate for this review. The outcome is improved access to essential healthcare services.
Outcome measures
The outcome of this review is access to PHC services, such as preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative, and palliative health services which are affordable, convenient or acceptable, and available to all who need care.
Criteria for considering studies for this review
All published and unpublished qualitative and/or mixed method studies conducted to improve access to PHC services were included. Government and international or national organizations reports were also included. Different organizations whose primary mission is health or promotion of community health were selected. We included articles based on these eligibility criteria: context or scope of studies (access to PHC services), article type (primary studies), and publication language (English). Articles published other than English language, citations with no abstracts and/or full texts, reviews, and duplicate studies were excluded. We included all articles available in different electronic databases regardless of their publication years. We didn’t use time of publication for screening.
Information sources and search strategy
We searched relevant articles from MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, WHO Global Health Library, and Google Scholar to access all forms of evidence. An initial search of MEDLINE was undertaken followed by analysis of the text words contained in the title and abstract, and of the index terms used to describe articles. We used the aforementioned performance indicators of PHC delivery and the PICO as we described above to choose keywords. A second search using all identified keywords and index terms was undertaken across all included databases. Thirdly, references of all identified articles were searched to get additional studies. The full electronic search strategy for MEDLINE, a major database we used for this review is included as a supplementary file (Additional file 1 : Appendix 1).
Study selection and assessment of methodological quality
Search results from different electronic databases were exported to Endnote reference manager version 7 to remove duplication. Two independent reviewers (ZG and BA) screened out records. An initial screening of titles and abstracts was done based on the PICO criteria and language of publication. Secondary screening of full-text papers was done for studies we included at the initial screening phase. We further investigated and assessed records included in the full-text articles against the inclusion and exclusion criteria. We sat together and discussed the eligibility assessment. The interrater agreement was 90%. We resolved disagreements by consensus for points we had different rating. We used the PRISMA flow diagram to summarize the study selection processes.
Methodological quality of the included studies was assessed using mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT) version 2018 [ 13 ]. As it is clearly indicated in the user guide of the MMAT tool, it is discouraged to calculate an overall score from the ratings of each criterion. Instead, it is advised to provide a more detailed presentation of the ratings of each criterion to better inform quality of the included studies. The rating of each criterion was, therefore, done as per the detail explanations included in the guideline. Almost all the included full text articles fulfilled the criteria and all the included full text articles were found to be better quality.
Data extraction
We independently extracted data from papers included in the review using JBI mixed methods data extraction form. This form is only used for reviews that follow a convergent integrated approach, i.e. integration of qualitative data and qualitative data [ 14 ]. The data extraction form was piloted on randomly selected papers and modified accordingly. One reviewer extracted the data from the included studies and the second reviewer checked the extracted data. Disagreements were resolved by discussion between the two reviewers. Information was extracted from each included study on: list of authors, year of publication, study area, population of interest, study type, methods, focus of the studies, main findings, authors’ conclusion, and limitations of the study.
Synthesis of findings
The included full-text articles were qualitatively analyzed using emergent thematic analysis approach to identify key concepts and coded them into related non-mutually exclusive themes. Themes are strategies mentioned or discussed in the included records to improve access to PHC services. Themes were identified manually by reading the included records again and again. We then synthesized each theme by comparing the discussion and conclusion of the included articles.
Systematic review registration number
The protocol of this review is registered in PROSPERO (the registration number is: CRD42019132592) to avoid unplanned duplication and to enable comparison of reported review methods with what was planned in the protocol. It is available at https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42019132592 .
Schematic of the systematic review and reporting of the search
We used PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) 2009 checklist [ 15 ] for reporting of this systematic review.
Study selection
The search strategy identified 1148 titles and abstracts [914 from PubMed (Table 1 ) and 234 from other sources] as of 10 March 2022. We obtained 900 after we removed duplicated articles. Following assessment by title and abstract, 485 records were excluded because these records did not meet the criteria as mentioned in the method section. Additional 256 records were discarded because the records did not discuss the outcome of interest well and some records were systematic reviews. The full text of the remaining 159 records was examined in more detail. It appeared that 49 studies did not meet the inclusion criteria as described in the method section. One hundred ten records met the inclusion criteria and were included in the systematic review or synthesis (Fig. 1 ).
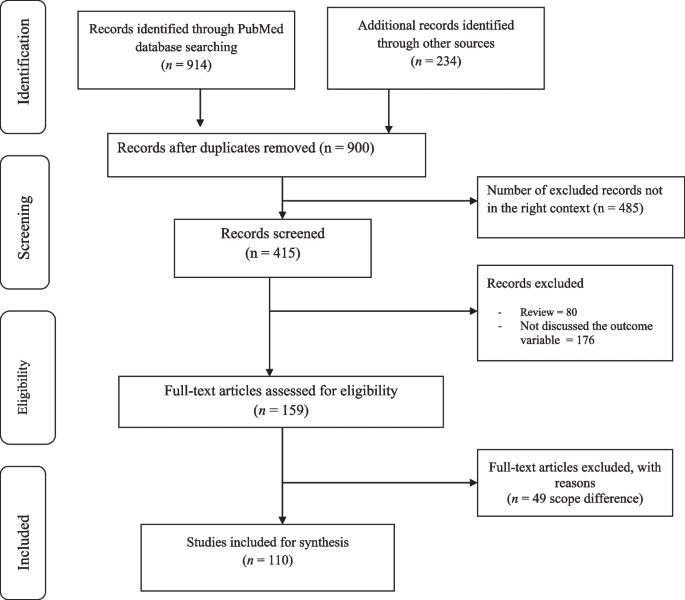
Study selection flow diagram
Of 900 articles resulting from the search term, 110 (12.2%) met the inclusion criteria. The included full-text articles were published between 1993 and 2021. Ninety-two (83.6%) of the included full-text articles were research articles, 5(4.5%) were technical reports, 3 (2.7%) were perspective, 4 (3.6%) was discussion paper, 3(2.7%) were dissertation or thesis, 2 (1.8%) were commentary, and 1 (0.9) was a book. Thirty-six (33%) and 29 (26%) of the included full-text articles were conducted in Africa and North America, respectively (Fig. 2 ).
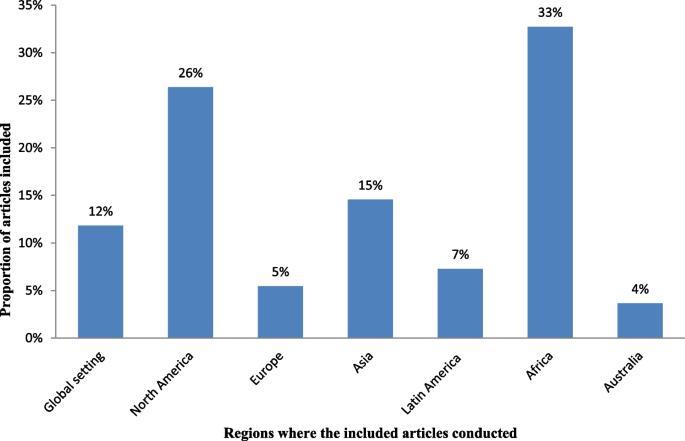
Regions where the included full-test articles conducted
Key strategies identified
The analysis of 110 full-text articles resulted in 10 themes. The themes are key strategies to improve access to PHC services in rural communities. The key strategies identified are community health programs or community-directed healthcare interventions, school-based healthcare services, student-led healthcare services, outreach services or mobile clinics, family health program, empanelment, community health funding schemes, telemedicine, promoting the role of traditional medicine, working with non-profit private sectors and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) including faith-based organizations (Table 2 ).
Description of strategies
a. Community health programs or community-directed healthcare interventions
Twenty-four (21.8%) of the full-text articles included in this review discussed that community health programs (CHPs) or community-directed healthcare interventions are best strategies to provide basic health and medical care close to the community to increase access and coverage of essential health services. Community health programs are locally based health promotion, disease prevention, and treatment programs available typically to communities in need and community-directed intervention strategy is an approach in which communities themselves direct the planning and implementation of intervention delivery. Rural communities, especially, in developing countries have no access to healthcare facilities in the near distance and have less chance to receive healthcare from doctors, health officers, nurses or midwives. In response to this critical problems, many countries have been investing heavily in community based primary health care to bring services to rural and remote areas where most of the population lives. Community health programs include construction of health posts or community health centers close to the community and deployment of community health workers (CHWs), such as health extension workers, to reach-out every village, who play a prominent role as the gatekeepers of healthcare in rural communities. Community-directed healthcare intervention is an approach in which communities themselves direct the planning and implementation of healthcare interventions. Community participation remains crucial in the identification of health problems, planning or designing of health interventions and implementation of the interventions, which enhances need-based and demand-driven provision of health services while promoting sustainability and ownership (Additional file 2 : Appendix 2, Table A1).
b. School-based primary healthcare
In this review, 9 of 110 (8.2%) of the included full-text articles pointed out that school-based healthcare services can be effective to improve access to PHC services. School-based health services are health programs that offer health care to children and youth either in a school or on school grounds and usually staffed according to school community needs and resources. School-based health services provide a variety of healthcare services to underserved children, youth and vulnerable populations in a convenient and accessible environment. Access to comprehensive health services via schools leads to improved access to healthcare (Additional file 3 : Appendix 3, Table A2).
c. Student-led healthcare services
In this review, 5 of 110 (4.5%) of the full-text articles discussed that the use of medical and health science students as healthcare service providers can minimize problems related with shortage of health professionals in rural healthcare system and can play appreciable roles to minimize healthcare service access problems in rural communities. Student-led healthcare services are developed through consultation between universities and local health providers and are purposefully designed clinical placements with a focus on clinical educational activities for pre-registration students. Student-led clinics link students, healthcare professionals, community-based organizations, universities, and communities. In this approach, students can gain practical experience in an interdisciplinary setting and through exposure to a community with unique and severe needs (Additional file 4 : Appendix 4, Table A3).
d. Outreach services or mobile clinics
In this systematic literature review, 18 of 110 (16.4%) of the included studies discussed that outreach services or mobile clinics in primary care and rural hospital settings can improve access to PHC services in rural communities. Mobile outreach service is defined as healthcare services provided by a mobile team of trained providers, from a higher-level health facility to a lower-level health facilities or locally available community facilities that are not used for clinical services, such as schools, health posts, or other community structures. Outreach services improve access to specialists and hospital-based services, strengthen connections between specialists and PHC providers, and give the benefits of consultations in primary care settings. Specialist outreach services have the potential to overcome access barriers faced by disadvantaged rural and remote communities. Furthermore, a community-based mobile clinics can be effective in uncovering illness and in directing patients to a healthcare home (Additional file 5 : Appendix 5, Table A4).
e. Family health program
Four (3.6%) of the included full-text articles discussed that family health program (FHP) is highly cost-effective tool for improving access to healthcare services for deprived areas (such as rural communities). Family health program means the program is a program designed to provide primary care as well as the prevention and early treatment of communicable and non-communicable diseases in defined populations by deploying interdisciplinary healthcare teams include physicians, nurses, nurse assistants, and full-time community health agents. It has evolved into a robust approach to providing primary care for defined populations by deploying interdisciplinary healthcare teams. The nucleus of each team includes a physician, a nurse, a nurse assistant, and full-time community health agents. This approach is effective on improving access to healthcare and eliminating health disparities (Additional file 6 : Appendix 6, Table A5).
f. Empanelment
This systematic review of literature identified that empanelment (also known as rostering) is a best strategy to proactively provide coordinated primary healthcare towards achieving universal health coverage. Empanelment is a continuous, iterative set of processes that identify and assign populations to facilities, care teams, or primary care providers who have a responsibility to know their assigned population. It enables health systems to improve health outcomes and to reduce costs. Empanelment establishes a point of care for individuals and simultaneously holds primary healthcare providers and care teams accountable for actively managing care for a specific group of individuals (Additional file 7 : Appendix 7, Table A6).
g. Community health funding schemes
In this systematic review of literature, 11 (10%) of the included articles discussed that community health funding schemes such as community-based health insurance (CBHI) increases access to healthcare services in low-income rural communities. Community-based health insurance schemes are usually voluntary and characterized by community members pooling funds to offset the cost of healthcare. Moreover, this approach is effective to mobilize domestic resources for health at low income levels. For low-income countries, community health financing has modest ability to increase the total amount of funds for healthcare. Properly structured community health financing system can significantly improve efficiency, reduce the cost of healthcare, improve quality and health outcomes, and pool risks. Community-financing schemes could improve preventive services and reduce the incidence of diseases. It could also improve people’s access to healthcare and the quality of services, thus improving their health status. Community health financing could also improve risk pooling and reduce health-induced impoverishment. Community health insurance has potential positive impacts on health and social security (Additional file 8 : Appendix 8, Table A7).
h. Telemedicine
In this review, 13 of 110 (11.8%) articles discussed that telemedicine is one of the solutions for rural subspecialty healthcare delivery. Telemedicine can be defined as the use of technology (computers, video, phone, messaging) by a medical professional to diagnose and treat patients in a remote location. The provision of subspecialty services using telemedicine to a remote and medically underserved population provides improved access to subspecialty care. Telemedicine brings sustainable healthcare to rural populations. Use of information and communication technologies in support of health and health-related fields, including healthcare services, health surveillance, health education, and health research has the potential to greatly improve health service efficiency, expand or scale up treatment delivery to thousands of patients in the rural populations (Additional file 9 : Appendix 9, Table A8).
i. Promoting the role of traditional medicine
Seven (6.4%) of the included articles showed that incorporating traditional healers into public health system addresses healthcare needs of people with limited access to allopathic medicine. Traditional medicine is the sum total of the knowledge, skill, and practices based on the theories, beliefs, and experiences indigenous to different cultures, whether explicable or not, used in the maintenance of health as well as in the prevention, diagnosis, improvement or treatment of physical and mental illness. Knowledge about traditional medicine has a catalyzing effect in meeting health sector development objectives. Integrating traditional medicine into national health systems in combination with national policy and regulation for products, practices and providers can enhance access to PHC services in remote populations (Additional file 10 : Appendix 10, Table A9).
j. Working with non-profit private sectors and non-governmental organizations
In this systematic review, 15 of 110 (13.6%) of the included articles revealed that working with non-profit private sectors and NGOs strengthens the healthcare system. Involving the non-profit private sectors, faith-based organizations (FBOs), and NGOs for health system strengthening eventually contributes to create a healthcare system reflecting an increased efficiency, more equity and good governance in health. International and local NGOs have endeavored to fill the gaps in access to healthcare services, research and advocacy. Non-profit private sectors and NGOs have a key role in improving health in low- and middle-income countries. With networks that reach even the most remote communities, many FBOs are well positioned to promote demand and access for healthcare services. Partnership among FBOs is critical in increasing access to healthcare services, and ensuring sustainability by influencing behaviors at the community, family and individual level. Faith-based organizations play an integral role in the healthcare system by increasing health seeking behaviors and delivering supportive services that address common access and cultural barriers (Additional file 11 : Appendix 11, Table A10).
This systematic literature review found that community health programs or community-directed healthcare interventions, school-based healthcare services, student-led healthcare services, outreach services or mobile clinics, family health program, empanelment, community health funding schemes, telehealth, integrative medicine, and working with non-profit private sectors and NGOs are key strategies to improve access to PHC services in rural communities. The identified strategies address the four major pillars of primary healthcare (i.e., community participation, inter-sectoral coordination, appropriate technology, and support mechanism made available) [ 126 ]. Moreover, the identified strategies are effective to improve access to healthcare services to rural communities. Moreover, the identified strategies are effective to solve shortage of manpower and to build knowledge and skill of the local health workforces in rural healthcare system. The ability of a healthcare system to meet health needs of the population depends largely on the knowledge, skills, motivation and deployment of the people responsible for organizing and delivering health services. The results of this review can strengthen the health information system, which are core elements of the healthcare system that ensure community engagement through dissemination and use of timely and reliable health information to rural populations. This review also suggests strategies to narrow down the health disparities among rural populations, which is wide in most Least and Middle Income Countries (LMICs). Healthcare services are usually disproportionately concentrated in major urban areas. As a result, rural communities face growing health disparities, largely attributed to weak policies, inefficiencies, poor leadership, and governance in healthcare system.
This review identified that community health programs or community-directed healthcare interventions address health disparities by ensuring equitable access to health resources in communities where health equity is limited by socioeconomic and geographical factors. Community health programs include identifying and prioritizing public health problems in a specific geographic area; designing and implementing public health interventions (such as establishing community health centers, mobile clinics, and outreach programs); providing services (such as health education, screenings, social support, and counseling), and deploying community health workers to promote healthy behaviors; advocating for improved care for populations at risk; and working with stakeholders to address community healthcare needs [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 127 , 128 , 129 , 130 ]. The community-oriented PHC model which is socially responsive medicine makes a healthcare system more rational, accountable, appropriate, and socially relevant to the public. Consequently, this model serves as a paradigm for reforming healthcare systems. Community-directed interventions can be considered as a realistic means to increase accessibility of interventions at community-level in rural areas [ 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 ]. This approach is best in situations where there are cultural barriers to implement interventions because this strategy is effective to develop ownership in the community. In-service and on-the-job training for community health workers, close supervision and government support, and program evaluation is very important to strengthen the community health program [ 131 , 132 , 133 ].
This review identified that school-based PHC services are effective strategies to improve access to PHC services. School-based health services provide a variety of healthcare services to children, youth and vulnerable populations in a convenient and accessible environment which indirectly improve leadership and governance. Science teachers and home room teachers play important roles to implement this strategy. It impacts on delivering preventive care such as immunizations, managing chronic illnesses and providing reproductive health services for adolescents. Comprehensive health services via schools improve access to healthcare information [ 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 ]. Access to school around the world increased drastically in the last century [ 134 ]. This high schooling rate is a good opportunity to provide healthcare services to school learners in accessible places and to disseminate health messages to families. Prior researches suggest that school-based healthcare services increase access to healthcare by increasing utilization of primary care, prevention services, and health maintenance visits [ 135 , 136 ]. Including science teachers, home room teachers, school principals, students, communities, community health workers, and other interested parties in the school-based healthcare system as main actors or promoters must be considered to sustain the impact. Health and education sectors should work in collaboration with the above-mentioned actors to plan, implement and monitor the progress. School-based healthcare services are preferable in situations when there is high schooling rate and limited access to healthcare institutions. This strategy is also an alternative way in areas where the health seeking behavior of the community is low.
The use of medical and health science students in rural healthcare system was identified as a key strategy to minimize health inequalities in rural communities due to shortages in health workforce and distribution of healthcare resources [ 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 ]. Student-led health intervention is an alternative approach to provide essential healthcare services to the community where there is shortage of healthcare workers [ 137 , 138 ]. Students will have opportunities to learn professional skills and competencies while they are providing healthcare services to the community. Moreover, benefits for student learning include increased communication, collaboration, and leadership skills [ 53 , 139 ]. Student-led health intervention also enables increased access to services, more time for assessments and treatments, increased depth of health teaching, holistic and integrated healthcare, and free health supports [ 140 , 141 , 142 , 143 ]. However, the use of medical and health science students in the rural healthcare system may have ethical and competency issues. Supporting strategies such as close supervision, preparing clear protocols, and including senior experts in the team should be considered.
This systematic review of literature found that outreach services or mobile clinics can improve access to PHC service delivery in rural populations [ 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 ]. In developing countries, the highest proportion of people lives in rural areas where doctor services are not available. Rural communities travel to major cities to get specialist services. This reflects a desire for closer integration between primary and secondary care. Specialist outreach services or mobile clinics have become one of the effective solution to solve health disparities, to improve access to healthcare services, and to build capacity of local healthcare workforces. This strategy is preferable in situations when there are high loads in tertiary or referral level hospitals and when there is high patient leakage in the referral system [ 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 ]. However, the implementation may not be easy. It needs well established healthcare system and budget. Moreover, the efficiency of care may be lower compared with hospital-based cares and the effect on patients’ health outcomes might be small [ 56 , 57 , 61 ] . Irregular specialist visits in rural areas may not have real impacts unless the services are sustainable with a strong commitment at national and local levels. Outreach activities should be included in health policies with strong leadership, healthcare financing, and private initiatives must be encouraged to maintain the activities over time.
This review revealed that FHP is highly effective tool for improving health for rural communities. The FHP has provided a new, more robust model of primary healthcare services designed to provide accessible, first contact, comprehensive, and whole person care that is coordinated with other healthcare services. It has positive results to improved availability, access to, and use of health services, and improved health indicators, such as reduced infant mortality, improved detection of cases of neglected diseases, and reduced health disparities [ 73 , 144 , 145 , 146 ]. The FHP deploys interdisciplinary healthcare teams. The team includes a physician, a nurse, a nurse assistant, and full-time community health agents. Family health teams are organized geographically. The teams are responsible for delivering public health interventions [ 72 , 74 ]. Family health program is an alternative strategy in rural healthcare system in situations when there are inequities in access to care; when there is high hospitalization rate; when there is low health seeking behavior in the community; and when there is poor case detecting and reporting system. Despite these remarkable achievements, the FHP has some challenges include difficulties in the recruitment and retention of doctors trained appropriately to deliver primary healthcare, large variations in quality of local care, patchy integration of primary care services with existing secondary and tertiary care, and slow adoption of FHP in large population [ 147 ].
In this review, empanelment has been identified as a best strategy to deliver coordinated primary healthcare towards achieving universal health coverage [ 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 ]. The goal of empanelment is provide people-centered healthcare services based on their needs to ensure that every established patient receives optimal care, whether he/she regularly visits healthcare centers. Major activities in this approach include assignment of all patients to a healthcare provider panel; update panel assignments on a regular basis; and use panel data to educate, and track patients [ 79 ]. Empanelment enables healthcare systems to improve patient experiences, reduce costs, and improve health outcomes. Empanelment is an effective strategy to deliver four key functions: first-contact accessibility, continuity, comprehensiveness, and coordination [ 148 ]. Effective empanelment requires responsibility for the health of a target population, including providing healthcare services based on their health status, which is an important step in moving towards people-centered integrated healthcare [ 79 ].
This review identified that community health funding schemes such as community-based health insurance (CBHI) increases access to healthcare in low-income rural communities. Moreover, this approach is effective to mobilize domestic resources for health at low income levels [ 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 ]. Community-based health insurance is an emerging strategy to provide financial protection against the cost of illness. It is an effective strategy to improve access to quality health services for low-income rural households [ 149 ]. Existence of social capital in the community is a determinant factor for the effectiveness of CBHI as social capital has a positive effect on the community's demand for insurance [ 150 , 151 ]. Moreover, solidarity and trust between the members are the key principles for the good functioning of a CBHI. Solidarity and trust stir-up members who are susceptible to risk to put together their resources for common use [ 149 , 152 , 153 ]. Affordability of premiums or contributions, technical arrangements made by the scheme management, timing of collecting the contributions, trust in the integrity and competence of the managers of the CBHI, The quality of care offered through the CBHI, accessible across different population groups are some of the determinant factors to be considered to increase people’s decision to join the CBHI schemes [ 154 , 155 ].
In this review, telemedicine has been identified as one of the many possible solutions for rural subspecialty healthcare delivery. Telemedicine is a vital technological tool to increase healthcare access, improve care delivery systems, engage in culturally competent outreach, health workforce development, and health information system [ 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 ]. Telemedicine can be a great alternative to the traditional healthcare system in situations like diagnoses of common medical problems; inquiries about various medical issues for home treatments; post-treatment check-ins or follow-up for chronic care; holidays, weekends, late night or any other situation when regular medical care is not possible; patient inability to leave the house; patients who lack regular access to relevant medical expertise in their geographic area ; and etc. However, technological issues are challenges when dealing with telemedicine, especially in developing countries. General problems of Internet connectivity and access to infrastructure can minimize benefits of this strategy. Costs associated with technology can also be a barrier. Furthermore, health technology requires human capacity to use it. Therefore, strengthening the information communication technologies (ICT) and human capacity building on ICT are important to address the health needs of the rural communities.
This systematic review of literature identified that promoting the role of TM solves problems of access to allopathic medicine. Integration of TM in health system will result in increased coverage and access to healthcare services. The role of complementary and alternative medicine for health is undisputed particularly in light of its role in health promotion and well-being. It also supports local health workforces [ 104 , 105 , 106 , 107 , 108 , 109 ]. Incorporating traditional healers into the public health system addresses healthcare needs [ 156 , 157 ]. However, integrating TM to the public healthcare system is challenging. It is a general belief that TM defies scientific procedures in terms of objectivity, measurement, codification and classification [ 157 ]. If integrated, who provides training to medical doctors on the ontology, epistemology and the efficacies of TM in modern medicine [ 157 ]. Due to these, some scholars suggest that both TM and modern medicine be allowed to operate and develop independent of one another [ 158 , 159 ]. Another fundamental challenge to TM is the widespread reported cases of fake healers and healings [ 157 ]. Generally, this strategy is more of feasible in areas where formal trainings on integrative medicine are available. Even though the integration is challenging, the health sector can use traditional healers as health educators or health promoters by providing training and continuous support. It can be also possible to use traditional healers as facilitators in the community-directed approaches. In general TM can be used in the primary healthcare system where no access to allopathic medicine and when conventional medicine is ineffective in treatment of disease [ 160 ].
Working with non-profit private sectors and NGOs has been identified as effective strategies to strengthen the healthcare system in developing countries [ 111 , 112 , 113 , 114 , 115 , 116 , 117 , 118 ]. Since governments in developing countries are challenged to meet the health needs of their populations because of financial constraints, limited human resources, and weak health infrastructure; the private sector (especially the non-profit private sectors) and non-governmental organizations can help expand access to healthcare services through its resources, expertise, and infrastructure. However, the presence of an NGO in the operation, may contribute to unrealistic expectations of health services, affecting perceptions of the latter negatively [ 113 ]. Moreover, reports have it that besides other issues in many instances NGOs allocated funds only to disease specific projects (vertical programming) rather than to broad based investments (horizontal programming) [ 161 ]. There are also concerns that donor expenditures in developing countries are not only unsustainable but may be considered as inadequate considering the enormous healthcare burden [ 161 , 162 , 163 , 164 ]. To avoid unrealistic expectations and dissatisfaction, and to increase and sustain the population’s trust in the organization, NGOs should operate in a manner that is as integrated as possible within the existing structure and should work close to the population it serves, with services anchored in the community. Moreover, faith-based organizations contribute in health such as disease prevention, health education or promotion, and community health development beyond psychological and spiritual care [ 119 , 120 , 121 , 122 , 123 , 124 ]. Religious organizations can reach all segments of rural populations. Therefore, integrating PHC services, especially health education and promotion, diseases prevention and community health development with religious organizations intensifies delivery of healthcare services. Working with FBOs is a best way in situations where cultural and faith-based barriers are common and in areas, where access problems are often related to lack of providers. However, religious organizations need intensive training on health promotion and health system to enable them to respond to local contexts within the framework of national policies. Moreover, there should be strong partnership with government agenesis to sustain the effort [ 165 , 166 , 167 , 168 ].
Contribution of this review
Various studies reported one or more strategies to improve access to primary healthcare services. However, the strategies reported by individual studies are not compiled together and there is lack of pooled evidence on effective strategies to improve access to healthcare system. This systematic literature review was, therefore, conducted to compile effective strategies to improve access to healthcare services in rural communities. The review suggests key strategies to improve access to PHC services in rural communities. These suggested strategies are implementable in countries that suffer from shortage of health workers and healthcare financing because all the strategies used locally available opportunities. The local healthcare system needs, therefore, scan the available opportunities in the locality for implementing the suggested strategies and needs to integrate the strategies in the healthcare system to sustain the impacts. Healthcare providers, researchers and policy makers could use the results of this systematic literature review to increase access to healthcare services in hard-to-reach areas. As the strategies are compiled from experiences of different countries (developed and least developed countries), there might be contextual differences like socio-economic, cultural, institutional, and geographical challenges to adopt the identified strategies. Moreover, some of the experiences only come from one or two countries. Therefore, strategy developers and implementers need to consider these contextual challenges or variation during adopting and implementing different strategies.
Strengths and limitations of the study
As a strength, this systematic review explores international (both developed and developing countries) best experiences on primary healthcare service delivery and identified ten key approaches to improve access to PHC services in rural communities. We also searched relevant published or unpublished articles, dissertations or theses, discussion papers, and perspectives from a wide range of sources, such as MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, WHO Global Health Library, and Google Scholar.
As a limitation, we entirely relied on electronic databases to search relevant articles. We didn’t include locally available printed out records. We also applied limits for language. We excluded articles published other than English language. We believed we could get more relevant articles if we had access to records available in prints and if we include articles published other than English language. Furthermore, since the strategies are compiled from experiences of different countries (developed and least developed countries), there might be contextual differences like socio-economic, cultural, institutional and geographical challenges to adopt the identified strategies. There was also limited evidence for some articles, especially reports to rate their methodological quality. Readers should also note that our review might missed some important work in improving access to PHC services and the identified strategies are not the only strategies to improve access to PHC services. There might be other effective strategies which are not included in this review. In addition generalizability might be affected since some of the experiences only come from one or two countries. Moreover, this review focuses on access not quality of care delivered.
This review identified key strategies from international experiences to improve access to PHC services in rural communities. These strategies are effective to improve access to healthcare services in rural or remote communities. They can also play roles in achieving UHC and reducing disparities in health outcomes and increase access to rural communities to get healthcare when and where they want. Therefore, incorporating these key strategies suggested by this review in to the healthcare system is useful to enhance PHC services and to minimize impacts of health disparity in rural communities. However, the identified strategies may not be easy to implement. Increasing number and capacity of human resource for health; strengthening the healthcare financing system; improving medicine and supplies; working in different partners and communities; establishing monitoring and evaluation system; strong and committed leadership; and encouraging private initiatives must be considered to implement and maintain these strategies over time. Moreover, policy makers, program planners and implementers who want to utilize findings of this review should be aware that these are not the only effective strategies to improve access to primary healthcare services.
Availability of data and materials
All the extracted data are included in the manuscript.
Abbreviations
Community-based health insurance
Faith-based organizations
Family health program
Information communication technologies
Mixed methods appraisal tool
Non-governmental organizations
- Primary healthcare
Primary Health Care Performance Initiative
Population, phenomena of interest and context)
Traditional medicine
Universal health coverage
Hampton MB, Kettle AJ, Winterbourn CC. Inside the neutrophil phagosome: oxidants, myeloperoxidase, and bacterial killing. Blood. 1998;92(9):3007–17.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Kirby M. The right to health fifty years on: Still skeptical? Health Hum Rights. 1999;4(1):6–25.
O’Connell T, Rasanathan K, Chopra M. What does universal health coverage mean? The Lancet. 2014;383(9913):277–9.
White F. Primary health care and public health: foundations of universal health systems. Med Princ Pract. 2015;24(2):103–16.
Article Google Scholar
Sanders D, Nandi S, Labonté R, Vance C, Van Damme W. From primary health care to universal health coverage—one step forward and two steps back. The Lancet. 2019;394(10199):619–21.
Brezzi M, Luongo P. Regional Disparities In Access To Health Care. 2016.
Google Scholar
Hartley D. Rural health disparities, population health, and rural culture. Am J Public Health. 2004;94(10):1675–8.
Walraven G. The 2018 Astana declaration on primary health care, is it useful? J Glob Health. 2019;9(1).
Gillam S. Is the declaration of Alma Ata still relevant to primary health care? BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2008;336(7643):536–8.
Tollman S, Doherty J, Mulligan JA. General Primary Care. In: Jamison DT, Breman JG, Measham AR, Alleyne G, Claeson M, Evans DB, Jha P, Mills A, Musgrove P, editors. Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries. Washington: World Bank The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank Group; 2006. Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK11789/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK11789.pdf .
Stern C, Jordan Z, McArthur A. Developing the review question and inclusion criteria. AJN The Am J Nurs. 2014;114(4):53–6.
World Health Organization. losing the gap in a generation. Commission on Social Determinants of Health FINAL REPORT. 2008. Available at https://www.who.int/social_determinants/final_report/csdh_finalreport_2008.pdf . Accessed on 22 March 2022.
Hong QN, Pluye P, Fàbregues S, Bartlett G, Boardman F, Cargo M, Dagenais P, GagnonM-P GF, Nicolau B, O’Cathain A. Mixed methods appraisal tool (MMAT), version 2018. Canada: IC Canadian Intellectual Property Office, Industry; 2018. Available at https://mixedmethodsappraisaltoolpublicpbworks.com/w/file/fetch/127916259/MMAT_2018_criteria-manual_2018-08-01_ENG.pdf .
JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. Appendix 8.1 JBI Mixed Methods Data Extraction Form following a Convergent Integrated Approach. Available at https://jbi-global-wiki.refined.site/space/MANUAL/3318284375/Appendix+8.1+JBI+Mixed+Methods+Data+Extraction+Form+following+a+Convergent+Integrated+Approach . Accessed on 12 August 2021.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097.
Assefa Y, Gelaw YA, Hill PS, Taye BW, Van Damme W. Community health extension program of Ethiopia, 2003–2018: successes and challenges toward universal coverage for primary healthcare services. Glob Health. 2019;15(1):1–11.
Admassie A, Abebaw D, Woldemichael AD. Impact evaluation of the Ethiopian health services extension programme. J Dev Eff. 2009;1(4):430–49.
Yitayal M, Berhane Y, Worku A, Kebede Y. The community-based Health extension Program significantly improved contraceptive utilization in West gojjam Zone, ethiopia. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2014;7:201.
Croke K, Mengistu AT, O’Connell SD, Tafere K. The impact of a health facility construction campaign on health service utilisation and outcomes: analysis of spatially linked survey and facility location data in Ethiopia. BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(8):e002430.
Arwal S. Health Posts in Afghanistan. J Gen Practice. 2015;3(213):2.
Negussie A, Girma G. Is the role of Health Extension Workers in the delivery of maternal and child health care services a significant attribute? The case of Dale district, southern Ethiopia. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):1–8.
Than KK, Mohamed Y, Oliver V, Myint T, La T, Beeson JG, Luchters S. Prevention of postpartum haemorrhage by community-based auxiliary midwives in hard-to-reach areas of Myanmar: a qualitative inquiry into acceptability and feasibility of task shifting. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2017;17(1):1–10.
Medhanyie A, Spigt M, Kifle Y, Schaay N, Sanders D, Blanco R, GeertJan D, Berhane Y. The role of health extension workers in improving utilization of maternal health services in rural areas in Ethiopia: a cross sectional study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012;12(1):1–9.
Sakeah E, McCloskey L, Bernstein J, Yeboah-Antwi K, Mills S, Doctor HV. Can community health officer-midwives effectively integrate skilled birth attendance in the community-based health planning and services program in rural Ghana? Reprod Health. 2014;11(1):1–13.
Sarmento DR. Traditional birth attendance (TBA) in a health system: what are the roles, benefits and challenges: a case study of incorporated TBA in Timor-Leste. Asia Pac Fam Med. 2014;13(1):1–9.
Rahmawati R, Bajorek B. Peer Reviewed: A Community Health Worker-Based Program for Elderly People with Hypertension in Indonesia: A Qualitative Study, 2013. Prev Chronic Dis. 2015;12:E175.
Feltner FJ, Ely GE, Whitler ET, Gross D, Dignan M. Effectiveness of community health workers in providing outreach and education for colorectal cancer screening in Appalachian Kentucky. Soc Work Health Care. 2012;51(5):430–40.
Hughes MM, Yang E, Ramanathan D, Benjamins MR. Community-based diabetes community health worker intervention in an underserved Chicago population. J Community Health. 2016;41(6):1249–56.
Panday S, Bissell P, Van Teijlingen E, Simkhada P. The contribution of female community health volunteers (FCHVs) to maternity care in Nepal: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):1–11.
Datiko DG, Lindtjørn B. Health extension workers improve tuberculosis case detection and treatment success in southern Ethiopia: a community randomized trial. PLoS ONE. 2009;4(5):e5443.
le Roux KW, Almirol E, Rezvan PH, Le Roux IM, Mbewu N, Dippenaar E, Stansert-Katzen L, Baker V, Tomlinson M, Rotheram-Borus M. Community health workers impact on maternal and child health outcomes in rural South Africa–a non-randomized two-group comparison study. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1–14.
Witmer A, Seifer SD, Finocchio L, Leslie J, O’Neil EH. Community health workers: integral members of the health care work force. Am J Public Health. 1995;85(8 Pt 1):1055–8.
Wright RA. Community-oriented primary care. The cornerstone of health care reform. Jama. 1993;269(19):2544–7.
Makaula P, Bloch P, Banda HT, Mbera GB, Mangani C, de Sousa A, Nkhono E, Jemu S, Muula AS. Primary Health Care in rural Malawi - a qualitative assessment exploring the relevance of the community-directed interventions approach. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012;12:328.
Katabarwa MN, Habomugisha P, Richards FO Jr, Hopkins D. Community-directed interventions strategy enhances efficient and effective integration of health care delivery and development activities in rural disadvantaged communities of Uganda. Trop Med Int Health : TM & IH. 2005;10(4):312–21.
Madon S, Malecela MN, Mashoto K, Donohue R, Mubyazi G, Michael E. The role of community participation for sustainable integrated neglected tropical diseases and water, sanitation and hygiene intervention programs: A pilot project in Tanzania. Soc Sci Med. 1982;2018(202):28–37.
Okeibunor JC, Orji BC, Brieger W, Ishola G, Otolorin E, Rawlins B, Ndekhedehe EU, Onyeneho N, Fink G. Preventing malaria in pregnancy through community-directed interventions: evidence from Akwa Ibom State, Nigeria. Malaria J. 2011;10:227.
Brieger WR, Sommerfeld JU, Amazigo UV. The Potential for Community-Directed Interventions: Reaching Underserved Populations in Africa. Int Q Community Health Educ. 2015;35(4):295–316.
Braimah JA, Sano Y, Atuoye KN, Luginaah I. Access to primary health care among women: the role of Ghana’s community-based health planning and services policy. Prim Health Care Res Dev. 2019;20:e82.
Kaplan DW, Brindis CD, Phibbs SL, Melinkovich P, Naylor K, Ahlstrand K. A comparison study of an elementary school–based health center: effects on health care access and use. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153(3):235–43.
Allison MA, Crane LA, Beaty BL, Davidson AJ, Melinkovich P, Kempe A. School-based health centers: improving access and quality of care for low-income adolescents. Pediatrics. 2007;120(4):e887–94.
Keeton V, Soleimanpour S, Brindis CD. School-based health centers in an era of health care reform: Building on history. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2012;42(6):132–56.
Brindis CD, Klein J, Schlitt J, Santelli J, Juszczak L, Nystrom RJ. School-based health centers: Accessibility and accountability. J Adolesc Health. 2003;32(6):98–107.
Hutchinson P, Carton TW, Broussard M, Brown L, Chrestman S. Improving adolescent health through school-based health centers in post-Katrina New Orleans. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2012;34(2):360–8.
Paschall MJ, Bersamin M. School-based health centers, depression, and suicide risk among adolescents. Am J Prev Med. 2018;54(1):44–50.
Minguez M, Santelli JS, Gibson E, Orr M, Samant S. Reproductive health impact of a school health center. J Adolesc Health. 2015;56(3):338–44.
Gibson EJ, Santelli JS, Minguez M, Lord A, Schuyler AC. Measuring school health center impact on access to and quality of primary care. J Adolesc Health. 2013;53(6):699–705.
Bozigar M. A Cross-Sectional Survey to Evaluate Potential for Partnering With School Nurses to Promote Human Papillomavirus Vaccination. Prev Chronic Dis. 2020;17:E111.
Suen J, Attrill S, Thomas JM, Smale M, Delaney CL, Miller MD. Effect of student-led health interventions on patient outcomes for those with cardiovascular disease or cardiovascular disease risk factors: a systematic review. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020;20(1):1–10.
Atuyambe LM, Baingana RK, Kibira SP, Katahoire A, Okello E, Mafigiri DK, Ayebare F, Oboke H, Acio C, Muggaga K. Undergraduate students’ contributions to health service delivery through communitybased education. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:123.
Stuhlmiller CM, Tolchard B. Developing a student-led health and wellbeing clinic in an underserved community: collaborative learning, health outcomes and cost savings. BMC Nurs. 2015;14(1):1–8.
Campbell DJ, Gibson K, O’Neill BG, Thurston WE. The role of a student-run clinic in providing primary care for Calgary’s homeless populations: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13(1):1–6.
Simpson SA, Long JA. Medical student-run health clinics: important contributors to patient care and medical education. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22(3):352–6.
Gruen RL, O’Rourke IC, Bailie RS, d’Abbs PH, O’Brien MM, Verma N. Improving access to specialist care for remote Aboriginal communities: evaluation of a specialist outreach service. Med J Aust. 2001;174(10):507–11.
Gruen RL, Weeramanthri T, Bailie R. Outreach and improved access to specialist services for indigenous people in remote Australia: the requirements for sustainability. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2002;56(7):517–21.
Gruen RL, Bailie RS, Wang Z, Heard S, O’Rourke IC. Specialist outreach to isolated and disadvantaged communities: a population-based study. The Lancet. 2006;368(9530):130–8.
Bond M, Bowling A, Abery A, McClay M, Dickinson E. Evaluation of outreach clinics held by specialists in general practice in England. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2000;54(2):149–56.
Irani M, Dixon M, Dean JD. Care closer to home: past mistakes, future opportunities. J R Soc Med. 2007;100(2):75–7.
Bailey JJ, Black ME, Wilkin D. Specialist outreach clinics in general practice. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 1994;308(6936):1083–6.
De Roodenbeke E, Lucas S, Rouzaut A, Bana F. Outreach services as a strategy to increase access to health workers in remote and rural areas. Geneva: WHO; 2011.
Bowling A, Stramer K, Dickinson E, Windsor J, Bond M. Evaluation of specialists’ outreach clinics in general practice in England: process and acceptability to patients, specialists, and general practitioners. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1997;51(1):52–61.
Spencer N. Consultant paediatric outreach clinics–a practical step in integration. Arch Dis Child. 1993;68(4):496–500.
Aljasir B, Alghamdi MS. Patient satisfaction with mobile clinic services in a remote rural area of Saudi Arabia. East Mediterr Health J. 2010;16(10):1085–90.
Lee EJ, O’Neal S. A mobile clinic experience: nurse practitioners providing care to a rural population. J Pediatr Health Care. 1994;8(1):12–7.
Cone PH, Haley JM. Mobile clinics in Haiti, part 1: Preparing for service-learning. Nurse Educ Pract. 2016;21:1–8.
Diaz-Perez Mde J, Farley T, Cabanis CM. A program to improve access to health care among Mexican immigrants in rural Colorado. J Rural Health. 2004;20(3):258–64.
Hill C, Zurakowski D, Bennet J, Walker-White R, Osman JL, Quarles A, Oriol N. Knowledgeable Neighbors: a mobile clinic model for disease prevention and screening in underserved communities. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(3):406–10.
Edgerley LP, El-Sayed YY, Druzin ML, Kiernan M, Daniels KI. Use of a community mobile health van to increase early access to prenatal care. Matern Child Health J. 2007;11(3):235–9.
Peters G, Doctor H, Afenyadu G, Findley S, Ager A. Mobile clinic services to serve rural populations in Katsina State, Nigeria: perceptions of services and patterns of utilization. Health Policy Plan. 2014;29(5):642–9.
Neke NM, Gadau G, Wasem J. Policy makers’ perspective on the provision of maternal health services via mobile health clinics in Tanzania—Findings from key informant interviews. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(9):e0203588.
Padmadas SS, Johnson FA, Leone T, Dahal GP. Do mobile family planning clinics facilitate vasectomy use in Nepal? Contraception. 2014;89(6):557–63.
Macinko J, Harris MJ. Brazil’s family health strategy—delivering community-based primary care in a universal health system. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(23):2177–81.
Macinko J, Lima Costa MF. Access to, use of and satisfaction with health services among adults enrolled in Brazil’s Family Health Strategy: evidence from the 2008 National Household Survey. Tropical Med Int Health. 2012;17(1):36–42.
Dourado I, Oliveira VB, Aquino R, Bonolo P, Lima-Costa MF, Medina MG, Mota E, Turci MA, Macinko J. Trends in primary health care-sensitive conditions in Brazil: the role of the Family Health Program (Project ICSAP-Brazil). Medical care. 2011;49:577–84.
Aquino R, De Oliveira NF, Barreto ML. Impact of the family health program on infant mortality in Brazilian municipalities. Am J Public Health. 2009;99(1):87–93.
Chong P-N, Tang WE. Transforming primary care—the way forward with the TEAMS2 approach. Fam Pract. 2019;36(3):369–70.
Primary Health Care Performance Initiatives (phcpi). Improvement strategies model: Population health management: Empanelment. Available at https://improvingphc.org/sites/default/files/Empanelment%20-%20v1.2%20-%20last%20updated%2012.13.2019.pdf . Accessed on 18 March 2022.
McGough P, Chaudhari V, El-Attar S, Yung P. A health system’s journey toward better population health through empanelment and panel management. Healthcare. 2018;6(66):1–9.
Bearden T, Ratcliffe HL, Sugarman JR, Bitton A, Anaman LA, Buckle G, Cham M, Quan DCW, Ismail F, Jargalsaikhan B. Empanelment: A foundational component of primary health care. Gates Open Res. 2019;3:1654.
Hsiao WC. Unmet health needs of two billion: is community financing a solution? 2001.
Wang W, Temsah G, Mallick L. The impact of health insurance on maternal health care utilization: evidence from Ghana, Indonesia and Rwanda. Health Policy Plan. 2017;32(3):366–75.
Atnafu DD, Tilahun H, Alemu YM. Community-based health insurance and healthcare service utilisation, North-West, Ethiopia: a comparative, cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2018;8(8):e019613.
USAID. Ethiopia’s Community-based Health Insurance: A Step on the Road to Universal Health Coverage. Available at https://www.hfgproject.org/ethiopias-community-based-health-insurance-step-road-universal-health-coverage/ . Accessed on 18 March 2022.
Blanchet NJ, Fink G, Osei-Akoto I. The effect of Ghana’s National Health Insurance Scheme on health care utilisation. Ghana Med J. 2012;46(2):76–84.
CAS Google Scholar
Nshakira-Rukundo E, Mussa EC, Nshakira N, Gerber N, von Braun J. Impact of community-based health insurance on utilisation of preventive health services in rural Uganda: a propensity score matching approach. Int J Health Econ Manag. 2021;21(2):203–27.
Mwaura JW, Pongpanich S. Access to health care: the role of a community based health insurance in Kenya. Pan Afr Med J. 2012;12(1):35.
Jutting JP. The Impact Of Health Insurance On The Access To Health Care And Financial Protection In Rural Developing Countries: The Example of Senegal. HNP discussion paper series;. World Bank, Washington, DC. © World Bank. 2011. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/13774 . License: CC BY 3.0 IGO.
Balamiento NC. The impact of social health insurance on healthcare utilization outcomes: evidence from the indigent program of the Philippine National Health Insurance. International Institute of Social Studies. 2018. Available at https://thesis.eur.nl/pub/46445/Balamiento,%20Neeanne_MA_2017_18%20_ECD.pdf . Accessed 30 Nov 2022.
Farrell CM, Gottlieb A. The effect of health insurance on health care utilization in the justice-involved population: United States, 2014–2016. Am J Public Health. 2020;110(S1):S78–84.
Thuong NTT. Impact of health insurance on healthcare utilisation patterns in Vietnam: a survey-based analysis with propensity score matching method. BMJ Open. 2020;10(10):e040062.
Custodio R, Gard AM, Graham G. Health information technology: addressing health disparity by improving quality, increasing access, and developing workforce. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2009;20(2):301–7.
Meier CA, Fitzgerald MC, Smith JM. eHealth: extending, enhancing, and evolving health care. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2013;15:359–82.
Anstey Watkins JOT, Goudge J, Gomez-Olive FX, Griffiths F. Mobile phone use among patients and health workers to enhance primary healthcare: A qualitative study in rural South Africa. Soc Sci Med. 1982;2018(198):139–47.
Kuntalp M, Akar O. A simple and low-cost Internet-based teleconsultation system that could effectively solve the health care access problems in underserved areas of developing countries. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2004;75(2):117–26.
Price M, Yuen EK, Goetter EM, Herbert JD, Forman EM, Acierno R, Ruggiero KJ. mHealth: a mechanism to deliver more accessible, more effective mental health care. Clin Psychol Psychother. 2014;21(5):427–36.
Bashshur RL, Shannon GW, Krupinski EA, Grigsby J, Kvedar JC, Weinstein RS, Sanders JH, Rheuban KS, Nesbitt TS, Alverson DC, et al. National telemedicine initiatives: essential to healthcare reform. Telemed J E Health. 2009;15(6):600–10.
Norton SA, Burdick AE, Phillips CM, Berman B. Teledermatology and underserved populations. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133(2):197–200.
Raza T, Joshi M, Schapira RM, Agha Z. Pulmonary telemedicine–a model to access the subspecialist services in underserved rural areas. Int J Med Informatics. 2009;78(1):53–9.
Shouneez YH. Smartphone hearing screening in mHealth assisted community-based primary care. UPSpace Institutional Repository, Department of Liberary Service. Dissertation (MCommPath)--University of Pretoria. 2016. Available at http://hdl.handle.net/2263/53477 . Accessed 17 Mar 2022.
Marcin JP, Ellis J, Mawis R, Nagrampa E, Nesbitt TS, Dimand RJ. Using telemedicine to provide pediatric subspecialty care to children with special health care needs in an underserved rural community. Pediatrics. 2004;113(1 Pt 1):1–6.
Olu O, Muneene D, Bataringaya JE, Nahimana M-R, Ba H, Turgeon Y, Karamagi HC, Dovlo D. How can digital health technologies contribute to sustainable attainment of universal health coverage in Africa? A perspective. Front Public Health. 2019;7:341.
Ryan MH, Yoder J, Flores SK, Soh J, Vanderbilt AA. Using health information technology to reach patients in underserved communities: A pilot study to help close the gap with health disparities. Global J Health Sci. 2016;8(6):86.
Buckwalter KC, Davis LL, Wakefield BJ, Kienzle MG, Murray MA. Telehealth for elders and their caregivers in rural communities. Fam Community Health. 2002;25(3):31–40.
WHO Regional Committee for Africa. Promoting the role of traditional medicine in health systems: a strategy for the African Region. World Health Organization. Regional Office for Africa. Available at http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/95467. .
Mishra SR, Neupane D, Kallestrup P. Integrating complementary and alternative medicine into conventional health care system in developing countries: an example of Amchi. J Evid-Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015;20(1):76–9.
Mbwambo ZH, Mahunnah RL, Kayombo EJ. Traditional health practitioner and the scientist: bridging the gap in contemporary health research in Tanzania. Tanzan Health Res Bull. 2007;9(2):115–20.
Poudyal AK, Jimba M, Murakami I, Silwal RC, Wakai S, Kuratsuji T. A traditional healers’ training model in rural Nepal: strengthening their roles in community health. Trop Med Int Health : TM & IH. 2003;8(10):956–60.
Payyappallimana U. Role of Traditional Medicine in Primary Health Care: An Overview of Perspectives and Challenges. Yokohama J Social Sciences. 2009;14(6):723–43.
Kange’ethe SM. Traditional healers as caregivers to HIV/AIDS clients and other terminally challenged persons in Kanye community home-based care programme (CHBC), Botswana. SAHARA J. 2009;6(2):83–91.
Habtom GK. Integrating traditional medical practice with primary healthcare system in Eritrea. J Complement Integr Med. 2015;12(1):71–87.
Ejaz I, Shaikh BT, Rizvi N. NGOs and government partnership for health systems strengthening: a qualitative study presenting viewpoints of government, NGOs and donors in Pakistan. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011;11(1):1–7.
Wu FS. International non-governmental actors in HIV/AIDS prevention in China. Cell Res. 2005;15(11):919–22.
Biermann O, Eckhardt M, Carlfjord S, Falk M, Forsberg BC. Collaboration between non-governmental organizations and public services in health–a qualitative case study from rural Ecuador. Glob Health Action. 2016;9(1):32237.
Mercer A, Khan MH, Daulatuzzaman M, Reid J. Effectiveness of an NGO primary health care programme in rural Bangladesh: evidence from the management information system. Health Policy Plan. 2004;19(4):187–98.
Baqui AH, Rosecrans AM, Williams EK, Agrawal PK, Ahmed S, Darmstadt GL, Kumar V, Kiran U, Panwar D, Ahuja RC. NGO facilitation of a government community-based maternal and neonatal health programme in rural India: improvements in equity. Health Policy Plan. 2008;23(4):234–43.
Ricca J, Kureshy N, LeBan K, Prosnitz D, Ryan L. Community-based intervention packages facilitated by NGOs demonstrate plausible evidence for child mortality impact. Health Policy Plan. 2014;29(2):204–16.
Ahmed N, DeRoeck D, Sadr-Azodi N. Private sector engagement and contributions to immunisation service delivery and coverage in Sudan. BMJ Glob Health. 2019;4(2):e001414.
Edimond BJ. The Contribution of Non-Governmental Organizations in Delivery of Basic Health Services in Partnership with Local Government. Doctoral Dissertation, Uganda Martyrs University. 2014.
Chand S, Patterson J: Faith-Based Models for Improving Maternal and Newborn Health. IMA World Health and ActionAid International USA, 2007 Available at https://imaworldhealthorg/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/faith_based_models_for_improving_maternal_and_newborn_health.pdf
Magezi V. Churchdriven primary health care: Models for an integrated church and community primary health care in Africa (a case study of the Salvation Army in East Africa). HTS Teologiese Studies/ Theological Studies. 2018;74(2):4365.
Villatoro AP, Dixon E, Mays VM. Faith-based organizations and the Affordable Care Act: Reducing Latino mental health care disparities. Psychol Serv. 2016;13(1):92–104.
Levin J. Faith-based initiatives in health promotion: history, challenges, and current partnerships. American journal of health promotion : AJHP. 2014;28(3):139–41.
Green A, Shaw J, Dimmock F, Conn C. A shared mission? Changing relationships between government and church health services in Africa. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2002;17(4):333–53.
Bandy G, Crouch A. Building from common foundations : the World Health Organization and faith-based organizations in primary healthcare. World Health Organization; 2008. Available at https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43884 . Accessed 16 Mar 2022.
Zahnd WE, Jenkins WD, Shackelford J, Lobb R, Sanders J, Bailey A. Rural cancer screening and faith community nursing in the era of the Affordable Care Act. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2018;29(1):71–80.
Wagle K. Primary Health Care (PHC): History, Principles, Pillars, Elements & Challenges. Global Health, 2020. Available at https://www.publichealthnotes.com/primary-health-care-phc-history-principles-pillars-elements-challenges/ . Accessed 4 June 2022.
Bhatt J, Bathija P. Ensuring access to quality health care in vulnerable communities. Acad Med. 2018;93(9):1271.
Arvey SR, Fernandez ME. Identifying the core elements of effective community health worker programs: a research agenda. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(9):1633–7.
Pennel CL, McLeroy KR, Burdine JN, Matarrita-Cascante D, Wang J. Community health needs assessment: potential for population health improvement. Popul Health Manag. 2016;19(3):178–86.
Chudgar RB, Shirey LA, Sznycer-Taub M, Read R, Pearson RL, Erwin PC. Local health department and academic institution linkages for community health assessment and improvement processes: a national overview and local case study. J Public Health Manag Pract. 2014;20(3):349–55.
Desta FA, Shifa GT, Dagoye DW, Carr C, Van Roosmalen J, Stekelenburg J, Nedi AB, Kols A, Kim YM. Identifying gaps in the practices of rural health extension workers in Ethiopia: a task analysis study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):1–9.
Lehmann U, Sanders D. Community health workers: what do we know about them. The state of the evidence on programmes, activities, costs and impact on health outcomes of using community health workers Geneva: World Health Organization; 2007. Available at https://www.hrhresourcecenter.org/node/1587.html . Accessed 17 Mar 2022.
Chen N, Raghavan M, Albert J, McDaniel A, Otiso L, Kintu R, West M, Jacobstein D. The community health systems reform cycle: strengthening the integration of community health worker programs through an institutional reform perspective. Global Health: Sci Practice. 2021;9(Supplement 1):S32–46.
Roser M, Ortiz-Ospina E: Global rise of education. Our World in Data 2017. Available at https://ourworldindata.org/global-rise-of-education . Accessed on 29 May 2019.
Santelli J, Morreale M, Wigton A, Grason H. School health centers and primary care for adolescents: a review of the literature. J Adolesc Health. 1996;18(5):357–66.
Wade TJ, Mansour ME, Guo JJ, Huentelman T, Line K, Keller KN. Access and utilization patterns of school-based health centers at urban and rural elementary and middle schools. Public Health Reports. 2008;123(6):739–50.
Johnson I, Hunter L, Chestnutt IG. Undergraduate students’ experiences of outreach placements in dental secondary care settings. Eur J Dent Educ. 2012;16(4):213–7.
Ndira S, Ssebadduka D, Niyonzima N, Sewankambo N, Royall J. Tackling malaria, village by village: a report on a concerted information intervention by medical students and the community in Mifumi Eastern Uganda. Afr Health Sci. 2014;14(4):882–8.
Frakes K-a, Brownie S, Davies L, Thomas JB, Miller M-E, Tyack Z. Capricornia Allied Health Partnership (CAHP): a case study of an innovative model of care addressing chronic disease through a regional student-assisted clinic. Aust Health Rev. 2014;38(5):483–6.
Frakes KA, Brownie S, Davies L, Thomas J, Miller ME, Tyack Z. The sociodemographic and health-related characteristics of a regional population with chronic disease at an interprofessional student-assisted clinic in Q ueensland C apricornia A llied H ealth P artnership. Aust J Rural Health. 2013;21(2):97–104.
Frakes K-A, Tyzack Z, Miller M, Davies L, Swanston A, Brownie S. The Capricornia Project: Developing and implementing an interprofessional student-assisted allied health clinic. 2011.
Frakes K-A, Brownie S, Davies L, Thomas J, Miller M-E, Tyack Z. Experiences from an interprofessional student-assisted chronic disease clinic. J Interprof Care. 2014;28(6):573–5.
Schutte T, Tichelaar J, Dekker RS, van Agtmael MA, de Vries TP, Richir MC. Learning in student-run clinics: A systematic review. Med Educ. 2015;49(3):249–63.
Paim J, Travassos C, Almeida C, Bahia L, Macinko J. The Brazilian health system: history, advances, and challenges. The Lancet. 2011;377(9779):1778–97.
Rocha R, Soares RR. Evaluating the impact of community-based health interventions: evidence from Brazil’s Family Health Program. Health Econ. 2010;19(S1):126–58.
Rasella D, Harhay MO, Pamponet ML, Aquino R, Barreto ML. Impact of primary health care on mortality from heart and cerebrovascular diseases in Brazil: a nationwide analysis of longitudinal data. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2014;349:g4014.
Harris M. Brazil’s Family Health Programme: A cost effective success that higher income countries could learn from. BMJ: Br Med J. 2010;341(7784):1171–2.
Starfield B. Is primary care essential? The lancet. 1994;344(8930):1129–33.
Donfouet HPP, Mahieu P-A. Community-based health insurance and social capital: a review. Heal Econ Rev. 2012;2(1):1–5.
Zhang L, Wang H, Wang L, Hsiao W. Social capital and farmer’s willingness-to-join a newly established community-based health insurance in rural China. Health Policy. 2006;76(2):233–42.
Donfouet HPP. Essombè J-RE, Mahieu P-A, Malin E: Social capital and willingness-to-pay for community-based health insurance in rural Cameroon. Global J Health Sci. 2011;3(1):142.
Grunau J. Exploring people’s motivation to join or not to join the community-based health insurance’Sina Passenang’in Sotouboua, Togo. 2013.
Gitahi JW. Innovative Healthcare Financing and Equity through Community Based Health Insurance Schemes (CBHHIS) In Kenya. United States International University-Africa Digital Repository. Available at http://erepo.usiu.ac.ke/11732/3654 . Accessed 18 May 2022.
Carrin G, Waelkens MP, Criel B. Community-based health insurance in developing countries: a study of its contribution to the performance of health financing systems. Tropical Med Int Health. 2005;10(8):799–811.
Umeh CA, Feeley FG. Inequitable access to health care by the poor in community-based health insurance programs: a review of studies from low-and middle-income countries. Global Health: Science And Practice. 2017;5(2):299–314.
Odebiyi AI. Western trained nurses’ assessment of the different categories of traditional healers in southwestern Nigeria. Int J Nurs Stud. 1990;27(4):333–42.
Abdullahi AA. Trends and challenges of traditional medicine in Africa. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med : AJTCAM. 2011;8(5 Suppl):115–23.
Taye OR. Yoruba Traditional Medicine and the Challenge of Integration. The J Pan Afr Studies. 2009;3(3):73–90.
Konadu K. Medicine and Anthropology in Twentieth Century Africa: Akan Medicine and Encounters with (Medical) Anthropology. African Studies Quarterly. 2008;10(2 & 3).
Benzie IF, Wachtel-Galor S: Herbal medicine: biomolecular and clinical aspects. 2nd Ed. 2011. Available at https://www.crcpress.com/Herbal-Medicine-Biomolecular-and-Clinical-Aspects-Second-Edition/Benzie-Wachtel-Galor/p/book/9781439807132 . Accessed 21 May 2022.
Ejughemre U. Donor support and the impacts on health system strengthening in sub-saharan africa: assessing the evidence through a review of the literature. Am J Public Health Res. 2013;1(7):146–51.
Seppey M, Ridde V, Touré L, Coulibaly A. Donor-funded project’s sustainability assessment: a qualitative case study of a results-based financing pilot in Koulikoro region. Mali Globalization and health. 2017;13(1):1–15.
Shaw RP, Wang H, Kress D, Hovig D. Donor and domestic financing of primary health care in low income countries. Health Systems & Reform. 2015;1(1):72–88.
Gotsadze G, Chikovani I, Sulaberidze L, Gotsadze T, Goguadze K, Tavanxhi N. The challenges of transition from donor-funded programs: results from a theory-driven multi-country comparative case study of programs in Eastern Europe and Central Asia supported by the Global Fund. Global Health: Science and Practice. 2019;7(2):258–72.
Ascroft J, Sweeney R, Samei M, Semos I, Morgan C. Strengthening church and government partnerships for primary health care delivery in Papua New Guinea: Lessons from the international experience. Health policy and health finance knowledge hub Working paper series. 2011(16).
Campbell MK, Hudson MA, Resnicow K, Blakeney N, Paxton A, Baskin M. Church-based health promotion interventions: evidence and lessons learned. Annu Rev Public Health. 2007;28:213–34.
Olivier J, Wodon Q. The role of faith-inspired health care providers in Sub-Saharan Africa and public private partnerships: Strengthening the Evidence for faith-inspired health engagement in Africa, Volume 1. Health, Nutrition and Population (HNP) Discussion Paper Series 76223v1. Available at https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/851911468203673017 . Accessed 20 May 2022.
Schumann C, Stroppa A, Moreira-Almeida A. The contribution of faith-based health organisations to public health. Int Psychiatry. 2011;8(3):62–4.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank IPHC- E for funding this review.
This review was funded by International Institute for Primary Health Care- Ethiopia (IPHC- E).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Environmental and Occupational Health and Safety, Institute of Public Health, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
Zemichael Gizaw
International Institute for Primary Health Care- Ethiopia, Ethiopian Public Health Institute, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Tigist Astale & Getnet Mitike Kassie
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ZG prepared the manuscript. TA and GMK critically reviewed the protocol and manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zemichael Gizaw .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Systematic review does not required ethics approval.
Consent for publication
This manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data.
Competing interests
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: .
Searchstrategy. MEDLINE (PubMed).
Additional file 2: Appendix 2: Table A1.
Description of full-text articles which discussed community health programs or community-directed interventions as a strategy to improve PHC service delivery in ruralcommunities.
Additional file 3:
Appendix 3: Table A2. Description of full-text articles which discussed school-based healthcareservices as a strategy to improve PHCservice delivery in rural communities.
Additional file 4:
Appendix 4: Table A3. Description of full-text articles which discussed student-led healthcareservices as a strategy to improve PHC service delivery in ruralcommunities.
Additional file 5: Appendix 5: Table A4
. Descriptionof full-text articles which discussed outreach services or mobile clinics as astrategy to improve PHC service delivery in ruralcommunities.
Additional file 6:
Appendix 6: Table A5. Description of full-text articles which discussed family health program as astrategy to improve PHC service delivery in rural,communities.
Additional file 7:
Appendix 7: Table A6. Description of full-text articles whichdiscussed empanelment as a strategy to improve PHC service delivery in ruralcommunities.
Additional file 8:
Appendix 9: Table A8. Description of full-text articles which discussed telemedicine or mobile healthas a strategy to improve PHC service delivery in ruralcommunities.
Additional file 9:
Appendix 8: Table A7. Description of full-text articles which discussed community health funding schemes as a strategy to improve PHC service delivery in ruralcommunities.
Additional file 10:
Appendix 10: Table A9. Description of full-text articles which discussed promoting the role of workingwith traditional healers as a strategy toimprove PHC service delivery in rural communities.
Additional file 11:
Appendix 11: Table A10. Description of full-text articles which discussed working with non-profitprivate sectors and non-governmental organizations as a strategy to improve PHC service delivery in rural communities.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Gizaw, Z., Astale, T. & Kassie, G.M. What improves access to primary healthcare services in rural communities? A systematic review. BMC Prim. Care 23 , 313 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12875-022-01919-0
Download citation
Received : 09 August 2022
Accepted : 18 November 2022
Published : 06 December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12875-022-01919-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Access to PHC services
- Rural communities
- Key strategies to improve access to PHC services
BMC Primary Care
ISSN: 2731-4553
- General enquiries: [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PMC10248995

Guidance to best tools and practices for systematic reviews
Kat kolaski.
1 Departments of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pediatrics, and Neurology, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, NC USA
Lynne Romeiser Logan
2 Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY USA
John P. A. Ioannidis
3 Departments of Medicine, of Epidemiology and Population Health, of Biomedical Data Science, and of Statistics, and Meta-Research Innovation Center at Stanford (METRICS), Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA USA
Associated Data
Data continue to accumulate indicating that many systematic reviews are methodologically flawed, biased, redundant, or uninformative. Some improvements have occurred in recent years based on empirical methods research and standardization of appraisal tools; however, many authors do not routinely or consistently apply these updated methods. In addition, guideline developers, peer reviewers, and journal editors often disregard current methodological standards. Although extensively acknowledged and explored in the methodological literature, most clinicians seem unaware of these issues and may automatically accept evidence syntheses (and clinical practice guidelines based on their conclusions) as trustworthy.
A plethora of methods and tools are recommended for the development and evaluation of evidence syntheses. It is important to understand what these are intended to do (and cannot do) and how they can be utilized. Our objective is to distill this sprawling information into a format that is understandable and readily accessible to authors, peer reviewers, and editors. In doing so, we aim to promote appreciation and understanding of the demanding science of evidence synthesis among stakeholders. We focus on well-documented deficiencies in key components of evidence syntheses to elucidate the rationale for current standards. The constructs underlying the tools developed to assess reporting, risk of bias, and methodological quality of evidence syntheses are distinguished from those involved in determining overall certainty of a body of evidence. Another important distinction is made between those tools used by authors to develop their syntheses as opposed to those used to ultimately judge their work.
Exemplar methods and research practices are described, complemented by novel pragmatic strategies to improve evidence syntheses. The latter include preferred terminology and a scheme to characterize types of research evidence. We organize best practice resources in a Concise Guide that can be widely adopted and adapted for routine implementation by authors and journals. Appropriate, informed use of these is encouraged, but we caution against their superficial application and emphasize their endorsement does not substitute for in-depth methodological training. By highlighting best practices with their rationale, we hope this guidance will inspire further evolution of methods and tools that can advance the field.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s13643-023-02255-9.
Part 1. The state of evidence synthesis
Evidence syntheses are commonly regarded as the foundation of evidence-based medicine (EBM). They are widely accredited for providing reliable evidence and, as such, they have significantly influenced medical research and clinical practice. Despite their uptake throughout health care and ubiquity in contemporary medical literature, some important aspects of evidence syntheses are generally overlooked or not well recognized. Evidence syntheses are mostly retrospective exercises, they often depend on weak or irreparably flawed data, and they may use tools that have acknowledged or yet unrecognized limitations. They are complicated and time-consuming undertakings prone to bias and errors. Production of a good evidence synthesis requires careful preparation and high levels of organization in order to limit potential pitfalls [ 1 ]. Many authors do not recognize the complexity of such an endeavor and the many methodological challenges they may encounter. Failure to do so is likely to result in research and resource waste.
Given their potential impact on people’s lives, it is crucial for evidence syntheses to correctly report on the current knowledge base. In order to be perceived as trustworthy, reliable demonstration of the accuracy of evidence syntheses is equally imperative [ 2 ]. Concerns about the trustworthiness of evidence syntheses are not recent developments. From the early years when EBM first began to gain traction until recent times when thousands of systematic reviews are published monthly [ 3 ] the rigor of evidence syntheses has always varied. Many systematic reviews and meta-analyses had obvious deficiencies because original methods and processes had gaps, lacked precision, and/or were not widely known. The situation has improved with empirical research concerning which methods to use and standardization of appraisal tools. However, given the geometrical increase in the number of evidence syntheses being published, a relatively larger pool of unreliable evidence syntheses is being published today.
Publication of methodological studies that critically appraise the methods used in evidence syntheses is increasing at a fast pace. This reflects the availability of tools specifically developed for this purpose [ 4 – 6 ]. Yet many clinical specialties report that alarming numbers of evidence syntheses fail on these assessments. The syntheses identified report on a broad range of common conditions including, but not limited to, cancer, [ 7 ] chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, [ 8 ] osteoporosis, [ 9 ] stroke, [ 10 ] cerebral palsy, [ 11 ] chronic low back pain, [ 12 ] refractive error, [ 13 ] major depression, [ 14 ] pain, [ 15 ] and obesity [ 16 , 17 ]. The situation is even more concerning with regard to evidence syntheses included in clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) [ 18 – 20 ]. Astonishingly, in a sample of CPGs published in 2017–18, more than half did not apply even basic systematic methods in the evidence syntheses used to inform their recommendations [ 21 ].
These reports, while not widely acknowledged, suggest there are pervasive problems not limited to evidence syntheses that evaluate specific kinds of interventions or include primary research of a particular study design (eg, randomized versus non-randomized) [ 22 ]. Similar concerns about the reliability of evidence syntheses have been expressed by proponents of EBM in highly circulated medical journals [ 23 – 26 ]. These publications have also raised awareness about redundancy, inadequate input of statistical expertise, and deficient reporting. These issues plague primary research as well; however, there is heightened concern for the impact of these deficiencies given the critical role of evidence syntheses in policy and clinical decision-making.
Methods and guidance to produce a reliable evidence synthesis
Several international consortiums of EBM experts and national health care organizations currently provide detailed guidance (Table (Table1). 1 ). They draw criteria from the reporting and methodological standards of currently recommended appraisal tools, and regularly review and update their methods to reflect new information and changing needs. In addition, they endorse the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) system for rating the overall quality of a body of evidence [ 27 ]. These groups typically certify or commission systematic reviews that are published in exclusive databases (eg, Cochrane, JBI) or are used to develop government or agency sponsored guidelines or health technology assessments (eg, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence [NICE], Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network [SIGN], Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality [AHRQ]). They offer developers of evidence syntheses various levels of methodological advice, technical and administrative support, and editorial assistance. Use of specific protocols and checklists are required for development teams within these groups, but their online methodological resources are accessible to any potential author.
Guidance for development of evidence syntheses
Notably, Cochrane is the largest single producer of evidence syntheses in biomedical research; however, these only account for 15% of the total [ 28 ]. The World Health Organization requires Cochrane standards be used to develop evidence syntheses that inform their CPGs [ 29 ]. Authors investigating questions of intervention effectiveness in syntheses developed for Cochrane follow the Methodological Expectations of Cochrane Intervention Reviews [ 30 ] and undergo multi-tiered peer review [ 31 , 32 ]. Several empirical evaluations have shown that Cochrane systematic reviews are of higher methodological quality compared with non-Cochrane reviews [ 4 , 7 , 9 , 11 , 14 , 32 – 35 ]. However, some of these assessments have biases: they may be conducted by Cochrane-affiliated authors, and they sometimes use scales and tools developed and used in the Cochrane environment and by its partners. In addition, evidence syntheses published in the Cochrane database are not subject to space or word restrictions, while non-Cochrane syntheses are often limited. As a result, information that may be relevant to the critical appraisal of non-Cochrane reviews is often removed or is relegated to online-only supplements that may not be readily or fully accessible [ 28 ].
Influences on the state of evidence synthesis
Many authors are familiar with the evidence syntheses produced by the leading EBM organizations but can be intimidated by the time and effort necessary to apply their standards. Instead of following their guidance, authors may employ methods that are discouraged or outdated 28]. Suboptimal methods described in in the literature may then be taken up by others. For example, the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) is a commonly used tool for appraising non-randomized studies [ 36 ]. Many authors justify their selection of this tool with reference to a publication that describes the unreliability of the NOS and recommends against its use [ 37 ]. Obviously, the authors who cite this report for that purpose have not read it. Authors and peer reviewers have a responsibility to use reliable and accurate methods and not copycat previous citations or substandard work [ 38 , 39 ]. Similar cautions may potentially extend to automation tools. These have concentrated on evidence searching [ 40 ] and selection given how demanding it is for humans to maintain truly up-to-date evidence [ 2 , 41 ]. Cochrane has deployed machine learning to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and studies related to COVID-19, [ 2 , 42 ] but such tools are not yet commonly used [ 43 ]. The routine integration of automation tools in the development of future evidence syntheses should not displace the interpretive part of the process.
Editorials about unreliable or misleading systematic reviews highlight several of the intertwining factors that may contribute to continued publication of unreliable evidence syntheses: shortcomings and inconsistencies of the peer review process, lack of endorsement of current standards on the part of journal editors, the incentive structure of academia, industry influences, publication bias, and the lure of “predatory” journals [ 44 – 48 ]. At this juncture, clarification of the extent to which each of these factors contribute remains speculative, but their impact is likely to be synergistic.
Over time, the generalized acceptance of the conclusions of systematic reviews as incontrovertible has affected trends in the dissemination and uptake of evidence. Reporting of the results of evidence syntheses and recommendations of CPGs has shifted beyond medical journals to press releases and news headlines and, more recently, to the realm of social media and influencers. The lay public and policy makers may depend on these outlets for interpreting evidence syntheses and CPGs. Unfortunately, communication to the general public often reflects intentional or non-intentional misrepresentation or “spin” of the research findings [ 49 – 52 ] News and social media outlets also tend to reduce conclusions on a body of evidence and recommendations for treatment to binary choices (eg, “do it” versus “don’t do it”) that may be assigned an actionable symbol (eg, red/green traffic lights, smiley/frowning face emoji).
Strategies for improvement
Many authors and peer reviewers are volunteer health care professionals or trainees who lack formal training in evidence synthesis [ 46 , 53 ]. Informing them about research methodology could increase the likelihood they will apply rigorous methods [ 25 , 33 , 45 ]. We tackle this challenge, from both a theoretical and a practical perspective, by offering guidance applicable to any specialty. It is based on recent methodological research that is extensively referenced to promote self-study. However, the information presented is not intended to be substitute for committed training in evidence synthesis methodology; instead, we hope to inspire our target audience to seek such training. We also hope to inform a broader audience of clinicians and guideline developers influenced by evidence syntheses. Notably, these communities often include the same members who serve in different capacities.
In the following sections, we highlight methodological concepts and practices that may be unfamiliar, problematic, confusing, or controversial. In Part 2, we consider various types of evidence syntheses and the types of research evidence summarized by them. In Part 3, we examine some widely used (and misused) tools for the critical appraisal of systematic reviews and reporting guidelines for evidence syntheses. In Part 4, we discuss how to meet methodological conduct standards applicable to key components of systematic reviews. In Part 5, we describe the merits and caveats of rating the overall certainty of a body of evidence. Finally, in Part 6, we summarize suggested terminology, methods, and tools for development and evaluation of evidence syntheses that reflect current best practices.
Part 2. Types of syntheses and research evidence
A good foundation for the development of evidence syntheses requires an appreciation of their various methodologies and the ability to correctly identify the types of research potentially available for inclusion in the synthesis.
Types of evidence syntheses
Systematic reviews have historically focused on the benefits and harms of interventions; over time, various types of systematic reviews have emerged to address the diverse information needs of clinicians, patients, and policy makers [ 54 ] Systematic reviews with traditional components have become defined by the different topics they assess (Table 2.1 ). In addition, other distinctive types of evidence syntheses have evolved, including overviews or umbrella reviews, scoping reviews, rapid reviews, and living reviews. The popularity of these has been increasing in recent years [ 55 – 58 ]. A summary of the development, methods, available guidance, and indications for these unique types of evidence syntheses is available in Additional File 2 A.
Types of traditional systematic reviews
Both Cochrane [ 30 , 59 ] and JBI [ 60 ] provide methodologies for many types of evidence syntheses; they describe these with different terminology, but there is obvious overlap (Table 2.2 ). The majority of evidence syntheses published by Cochrane (96%) and JBI (62%) are categorized as intervention reviews. This reflects the earlier development and dissemination of their intervention review methodologies; these remain well-established [ 30 , 59 , 61 ] as both organizations continue to focus on topics related to treatment efficacy and harms. In contrast, intervention reviews represent only about half of the total published in the general medical literature, and several non-intervention review types contribute to a significant proportion of the other half.
Evidence syntheses published by Cochrane and JBI
a Data from https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/reviews . Accessed 17 Sep 2022
b Data obtained via personal email communication on 18 Sep 2022 with Emilie Francis, editorial assistant, JBI Evidence Synthesis
c Includes the following categories: prevalence, scoping, mixed methods, and realist reviews
d This methodology is not supported in the current version of the JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis
Types of research evidence
There is consensus on the importance of using multiple study designs in evidence syntheses; at the same time, there is a lack of agreement on methods to identify included study designs. Authors of evidence syntheses may use various taxonomies and associated algorithms to guide selection and/or classification of study designs. These tools differentiate categories of research and apply labels to individual study designs (eg, RCT, cross-sectional). A familiar example is the Design Tree endorsed by the Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine [ 70 ]. Such tools may not be helpful to authors of evidence syntheses for multiple reasons.
Suboptimal levels of agreement and accuracy even among trained methodologists reflect challenges with the application of such tools [ 71 , 72 ]. Problematic distinctions or decision points (eg, experimental or observational, controlled or uncontrolled, prospective or retrospective) and design labels (eg, cohort, case control, uncontrolled trial) have been reported [ 71 ]. The variable application of ambiguous study design labels to non-randomized studies is common, making them especially prone to misclassification [ 73 ]. In addition, study labels do not denote the unique design features that make different types of non-randomized studies susceptible to different biases, including those related to how the data are obtained (eg, clinical trials, disease registries, wearable devices). Given this limitation, it is important to be aware that design labels preclude the accurate assignment of non-randomized studies to a “level of evidence” in traditional hierarchies [ 74 ].
These concerns suggest that available tools and nomenclature used to distinguish types of research evidence may not uniformly apply to biomedical research and non-health fields that utilize evidence syntheses (eg, education, economics) [ 75 , 76 ]. Moreover, primary research reports often do not describe study design or do so incompletely or inaccurately; thus, indexing in PubMed and other databases does not address the potential for misclassification [ 77 ]. Yet proper identification of research evidence has implications for several key components of evidence syntheses. For example, search strategies limited by index terms using design labels or study selection based on labels applied by the authors of primary studies may cause inconsistent or unjustified study inclusions and/or exclusions [ 77 ]. In addition, because risk of bias (RoB) tools consider attributes specific to certain types of studies and study design features, results of these assessments may be invalidated if an inappropriate tool is used. Appropriate classification of studies is also relevant for the selection of a suitable method of synthesis and interpretation of those results.
An alternative to these tools and nomenclature involves application of a few fundamental distinctions that encompass a wide range of research designs and contexts. While these distinctions are not novel, we integrate them into a practical scheme (see Fig. Fig.1) 1 ) designed to guide authors of evidence syntheses in the basic identification of research evidence. The initial distinction is between primary and secondary studies. Primary studies are then further distinguished by: 1) the type of data reported (qualitative or quantitative); and 2) two defining design features (group or single-case and randomized or non-randomized). The different types of studies and study designs represented in the scheme are described in detail in Additional File 2 B. It is important to conceptualize their methods as complementary as opposed to contrasting or hierarchical [ 78 ]; each offers advantages and disadvantages that determine their appropriateness for answering different kinds of research questions in an evidence synthesis.

Distinguishing types of research evidence
Application of these basic distinctions may avoid some of the potential difficulties associated with study design labels and taxonomies. Nevertheless, debatable methodological issues are raised when certain types of research identified in this scheme are included in an evidence synthesis. We briefly highlight those associated with inclusion of non-randomized studies, case reports and series, and a combination of primary and secondary studies.
Non-randomized studies
When investigating an intervention’s effectiveness, it is important for authors to recognize the uncertainty of observed effects reported by studies with high RoB. Results of statistical analyses that include such studies need to be interpreted with caution in order to avoid misleading conclusions [ 74 ]. Review authors may consider excluding randomized studies with high RoB from meta-analyses. Non-randomized studies of intervention (NRSI) are affected by a greater potential range of biases and thus vary more than RCTs in their ability to estimate a causal effect [ 79 ]. If data from NRSI are synthesized in meta-analyses, it is helpful to separately report their summary estimates [ 6 , 74 ].
Nonetheless, certain design features of NRSI (eg, which parts of the study were prospectively designed) may help to distinguish stronger from weaker ones. Cochrane recommends that authors of a review including NRSI focus on relevant study design features when determining eligibility criteria instead of relying on non-informative study design labels [ 79 , 80 ] This process is facilitated by a study design feature checklist; guidance on using the checklist is included with developers’ description of the tool [ 73 , 74 ]. Authors collect information about these design features during data extraction and then consider it when making final study selection decisions and when performing RoB assessments of the included NRSI.
Case reports and case series
Correctly identified case reports and case series can contribute evidence not well captured by other designs [ 81 ]; in addition, some topics may be limited to a body of evidence that consists primarily of uncontrolled clinical observations. Murad and colleagues offer a framework for how to include case reports and series in an evidence synthesis [ 82 ]. Distinguishing between cohort studies and case series in these syntheses is important, especially for those that rely on evidence from NRSI. Additional data obtained from studies misclassified as case series can potentially increase the confidence in effect estimates. Mathes and Pieper provide authors of evidence syntheses with specific guidance on distinguishing between cohort studies and case series, but emphasize the increased workload involved [ 77 ].
Primary and secondary studies
Synthesis of combined evidence from primary and secondary studies may provide a broad perspective on the entirety of available literature on a topic. This is, in fact, the recommended strategy for scoping reviews that may include a variety of sources of evidence (eg, CPGs, popular media). However, except for scoping reviews, the synthesis of data from primary and secondary studies is discouraged unless there are strong reasons to justify doing so.
Combining primary and secondary sources of evidence is challenging for authors of other types of evidence syntheses for several reasons [ 83 ]. Assessments of RoB for primary and secondary studies are derived from conceptually different tools, thus obfuscating the ability to make an overall RoB assessment of a combination of these study types. In addition, authors who include primary and secondary studies must devise non-standardized methods for synthesis. Note this contrasts with well-established methods available for updating existing evidence syntheses with additional data from new primary studies [ 84 – 86 ]. However, a new review that synthesizes data from primary and secondary studies raises questions of validity and may unintentionally support a biased conclusion because no existing methodological guidance is currently available [ 87 ].
Recommendations
We suggest that journal editors require authors to identify which type of evidence synthesis they are submitting and reference the specific methodology used for its development. This will clarify the research question and methods for peer reviewers and potentially simplify the editorial process. Editors should announce this practice and include it in the instructions to authors. To decrease bias and apply correct methods, authors must also accurately identify the types of research evidence included in their syntheses.
Part 3. Conduct and reporting
The need to develop criteria to assess the rigor of systematic reviews was recognized soon after the EBM movement began to gain international traction [ 88 , 89 ]. Systematic reviews rapidly became popular, but many were very poorly conceived, conducted, and reported. These problems remain highly prevalent [ 23 ] despite development of guidelines and tools to standardize and improve the performance and reporting of evidence syntheses [ 22 , 28 ]. Table 3.1 provides some historical perspective on the evolution of tools developed specifically for the evaluation of systematic reviews, with or without meta-analysis.
Tools specifying standards for systematic reviews with and without meta-analysis
a Currently recommended
b Validated tool for systematic reviews of interventions developed for use by authors of overviews or umbrella reviews
These tools are often interchangeably invoked when referring to the “quality” of an evidence synthesis. However, quality is a vague term that is frequently misused and misunderstood; more precisely, these tools specify different standards for evidence syntheses. Methodological standards address how well a systematic review was designed and performed [ 5 ]. RoB assessments refer to systematic flaws or limitations in the design, conduct, or analysis of research that distort the findings of the review [ 4 ]. Reporting standards help systematic review authors describe the methodology they used and the results of their synthesis in sufficient detail [ 92 ]. It is essential to distinguish between these evaluations: a systematic review may be biased, it may fail to report sufficient information on essential features, or it may exhibit both problems; a thoroughly reported systematic evidence synthesis review may still be biased and flawed while an otherwise unbiased one may suffer from deficient documentation.
We direct attention to the currently recommended tools listed in Table 3.1 but concentrate on AMSTAR-2 (update of AMSTAR [A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews]) and ROBIS (Risk of Bias in Systematic Reviews), which evaluate methodological quality and RoB, respectively. For comparison and completeness, we include PRISMA 2020 (update of the 2009 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews of Meta-Analyses statement), which offers guidance on reporting standards. The exclusive focus on these three tools is by design; it addresses concerns related to the considerable variability in tools used for the evaluation of systematic reviews [ 28 , 88 , 96 , 97 ]. We highlight the underlying constructs these tools were designed to assess, then describe their components and applications. Their known (or potential) uptake and impact and limitations are also discussed.
Evaluation of conduct
Development.
AMSTAR [ 5 ] was in use for a decade prior to the 2017 publication of AMSTAR-2; both provide a broad evaluation of methodological quality of intervention systematic reviews, including flaws arising through poor conduct of the review [ 6 ]. ROBIS, published in 2016, was developed to specifically assess RoB introduced by the conduct of the review; it is applicable to systematic reviews of interventions and several other types of reviews [ 4 ]. Both tools reflect a shift to a domain-based approach as opposed to generic quality checklists. There are a few items unique to each tool; however, similarities between items have been demonstrated [ 98 , 99 ]. AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS are recommended for use by: 1) authors of overviews or umbrella reviews and CPGs to evaluate systematic reviews considered as evidence; 2) authors of methodological research studies to appraise included systematic reviews; and 3) peer reviewers for appraisal of submitted systematic review manuscripts. For authors, these tools may function as teaching aids and inform conduct of their review during its development.
Description
Systematic reviews that include randomized and/or non-randomized studies as evidence can be appraised with AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS. Other characteristics of AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS are summarized in Table 3.2 . Both tools define categories for an overall rating; however, neither tool is intended to generate a total score by simply calculating the number of responses satisfying criteria for individual items [ 4 , 6 ]. AMSTAR-2 focuses on the rigor of a review’s methods irrespective of the specific subject matter. ROBIS places emphasis on a review’s results section— this suggests it may be optimally applied by appraisers with some knowledge of the review’s topic as they may be better equipped to determine if certain procedures (or lack thereof) would impact the validity of a review’s findings [ 98 , 100 ]. Reliability studies show AMSTAR-2 overall confidence ratings strongly correlate with the overall RoB ratings in ROBIS [ 100 , 101 ].
Comparison of AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS
a ROBIS includes an optional first phase to assess the applicability of the review to the research question of interest. The tool may be applicable to other review types in addition to the four specified, although modification of this initial phase will be needed (Personal Communication via email, Penny Whiting, 28 Jan 2022)
b AMSTAR-2 item #9 and #11 require separate responses for RCTs and NRSI
Interrater reliability has been shown to be acceptable for AMSTAR-2 [ 6 , 11 , 102 ] and ROBIS [ 4 , 98 , 103 ] but neither tool has been shown to be superior in this regard [ 100 , 101 , 104 , 105 ]. Overall, variability in reliability for both tools has been reported across items, between pairs of raters, and between centers [ 6 , 100 , 101 , 104 ]. The effects of appraiser experience on the results of AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS require further evaluation [ 101 , 105 ]. Updates to both tools should address items shown to be prone to individual appraisers’ subjective biases and opinions [ 11 , 100 ]; this may involve modifications of the current domains and signaling questions as well as incorporation of methods to make an appraiser’s judgments more explicit. Future revisions of these tools may also consider the addition of standards for aspects of systematic review development currently lacking (eg, rating overall certainty of evidence, [ 99 ] methods for synthesis without meta-analysis [ 105 ]) and removal of items that assess aspects of reporting that are thoroughly evaluated by PRISMA 2020.
Application
A good understanding of what is required to satisfy the standards of AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS involves study of the accompanying guidance documents written by the tools’ developers; these contain detailed descriptions of each item’s standards. In addition, accurate appraisal of a systematic review with either tool requires training. Most experts recommend independent assessment by at least two appraisers with a process for resolving discrepancies as well as procedures to establish interrater reliability, such as pilot testing, a calibration phase or exercise, and development of predefined decision rules [ 35 , 99 – 101 , 103 , 104 , 106 ]. These methods may, to some extent, address the challenges associated with the diversity in methodological training, subject matter expertise, and experience using the tools that are likely to exist among appraisers.
The standards of AMSTAR, AMSTAR-2, and ROBIS have been used in many methodological studies and epidemiological investigations. However, the increased publication of overviews or umbrella reviews and CPGs has likely been a greater influence on the widening acceptance of these tools. Critical appraisal of the secondary studies considered evidence is essential to the trustworthiness of both the recommendations of CPGs and the conclusions of overviews. Currently both Cochrane [ 55 ] and JBI [ 107 ] recommend AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS in their guidance for authors of overviews or umbrella reviews. However, ROBIS and AMSTAR-2 were released in 2016 and 2017, respectively; thus, to date, limited data have been reported about the uptake of these tools or which of the two may be preferred [ 21 , 106 ]. Currently, in relation to CPGs, AMSTAR-2 appears to be overwhelmingly popular compared to ROBIS. A Google Scholar search of this topic (search terms “AMSTAR 2 AND clinical practice guidelines,” “ROBIS AND clinical practice guidelines” 13 May 2022) found 12,700 hits for AMSTAR-2 and 1,280 for ROBIS. The apparent greater appeal of AMSTAR-2 may relate to its longer track record given the original version of the tool was in use for 10 years prior to its update in 2017.
Barriers to the uptake of AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS include the real or perceived time and resources necessary to complete the items they include and appraisers’ confidence in their own ratings [ 104 ]. Reports from comparative studies available to date indicate that appraisers find AMSTAR-2 questions, responses, and guidance to be clearer and simpler compared with ROBIS [ 11 , 101 , 104 , 105 ]. This suggests that for appraisal of intervention systematic reviews, AMSTAR-2 may be a more practical tool than ROBIS, especially for novice appraisers [ 101 , 103 – 105 ]. The unique characteristics of each tool, as well as their potential advantages and disadvantages, should be taken into consideration when deciding which tool should be used for an appraisal of a systematic review. In addition, the choice of one or the other may depend on how the results of an appraisal will be used; for example, a peer reviewer’s appraisal of a single manuscript versus an appraisal of multiple systematic reviews in an overview or umbrella review, CPG, or systematic methodological study.
Authors of overviews and CPGs report results of AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS appraisals for each of the systematic reviews they include as evidence. Ideally, an independent judgment of their appraisals can be made by the end users of overviews and CPGs; however, most stakeholders, including clinicians, are unlikely to have a sophisticated understanding of these tools. Nevertheless, they should at least be aware that AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS ratings reported in overviews and CPGs may be inaccurate because the tools are not applied as intended by their developers. This can result from inadequate training of the overview or CPG authors who perform the appraisals, or to modifications of the appraisal tools imposed by them. The potential variability in overall confidence and RoB ratings highlights why appraisers applying these tools need to support their judgments with explicit documentation; this allows readers to judge for themselves whether they agree with the criteria used by appraisers [ 4 , 108 ]. When these judgments are explicit, the underlying rationale used when applying these tools can be assessed [ 109 ].
Theoretically, we would expect an association of AMSTAR-2 with improved methodological rigor and an association of ROBIS with lower RoB in recent systematic reviews compared to those published before 2017. To our knowledge, this has not yet been demonstrated; however, like reports about the actual uptake of these tools, time will tell. Additional data on user experience is also needed to further elucidate the practical challenges and methodological nuances encountered with the application of these tools. This information could potentially inform the creation of unifying criteria to guide and standardize the appraisal of evidence syntheses [ 109 ].
Evaluation of reporting
Complete reporting is essential for users to establish the trustworthiness and applicability of a systematic review’s findings. Efforts to standardize and improve the reporting of systematic reviews resulted in the 2009 publication of the PRISMA statement [ 92 ] with its accompanying explanation and elaboration document [ 110 ]. This guideline was designed to help authors prepare a complete and transparent report of their systematic review. In addition, adherence to PRISMA is often used to evaluate the thoroughness of reporting of published systematic reviews [ 111 ]. The updated version, PRISMA 2020 [ 93 ], and its guidance document [ 112 ] were published in 2021. Items on the original and updated versions of PRISMA are organized by the six basic review components they address (title, abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion). The PRISMA 2020 update is a considerably expanded version of the original; it includes standards and examples for the 27 original and 13 additional reporting items that capture methodological advances and may enhance the replicability of reviews [ 113 ].
The original PRISMA statement fostered the development of various PRISMA extensions (Table 3.3 ). These include reporting guidance for scoping reviews and reviews of diagnostic test accuracy and for intervention reviews that report on the following: harms outcomes, equity issues, the effects of acupuncture, the results of network meta-analyses and analyses of individual participant data. Detailed reporting guidance for specific systematic review components (abstracts, protocols, literature searches) is also available.
PRISMA extensions
PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
a Note the abstract reporting checklist is now incorporated into PRISMA 2020 [ 93 ]
Uptake and impact
The 2009 PRISMA standards [ 92 ] for reporting have been widely endorsed by authors, journals, and EBM-related organizations. We anticipate the same for PRISMA 2020 [ 93 ] given its co-publication in multiple high-impact journals. However, to date, there is a lack of strong evidence for an association between improved systematic review reporting and endorsement of PRISMA 2009 standards [ 43 , 111 ]. Most journals require a PRISMA checklist accompany submissions of systematic review manuscripts. However, the accuracy of information presented on these self-reported checklists is not necessarily verified. It remains unclear which strategies (eg, authors’ self-report of checklists, peer reviewer checks) might improve adherence to the PRISMA reporting standards; in addition, the feasibility of any potentially effective strategies must be taken into consideration given the structure and limitations of current research and publication practices [ 124 ].
Pitfalls and limitations of PRISMA, AMSTAR-2, and ROBIS
Misunderstanding of the roles of these tools and their misapplication may be widespread problems. PRISMA 2020 is a reporting guideline that is most beneficial if consulted when developing a review as opposed to merely completing a checklist when submitting to a journal; at that point, the review is finished, with good or bad methodological choices. However, PRISMA checklists evaluate how completely an element of review conduct was reported, but do not evaluate the caliber of conduct or performance of a review. Thus, review authors and readers should not think that a rigorous systematic review can be produced by simply following the PRISMA 2020 guidelines. Similarly, it is important to recognize that AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS are tools to evaluate the conduct of a review but do not substitute for conceptual methodological guidance. In addition, they are not intended to be simple checklists. In fact, they have the potential for misuse or abuse if applied as such; for example, by calculating a total score to make a judgment about a review’s overall confidence or RoB. Proper selection of a response for the individual items on AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS requires training or at least reference to their accompanying guidance documents.
Not surprisingly, it has been shown that compliance with the PRISMA checklist is not necessarily associated with satisfying the standards of ROBIS [ 125 ]. AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS were not available when PRISMA 2009 was developed; however, they were considered in the development of PRISMA 2020 [ 113 ]. Therefore, future studies may show a positive relationship between fulfillment of PRISMA 2020 standards for reporting and meeting the standards of tools evaluating methodological quality and RoB.
Choice of an appropriate tool for the evaluation of a systematic review first involves identification of the underlying construct to be assessed. For systematic reviews of interventions, recommended tools include AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS for appraisal of conduct and PRISMA 2020 for completeness of reporting. All three tools were developed rigorously and provide easily accessible and detailed user guidance, which is necessary for their proper application and interpretation. When considering a manuscript for publication, training in these tools can sensitize peer reviewers and editors to major issues that may affect the review’s trustworthiness and completeness of reporting. Judgment of the overall certainty of a body of evidence and formulation of recommendations rely, in part, on AMSTAR-2 or ROBIS appraisals of systematic reviews. Therefore, training on the application of these tools is essential for authors of overviews and developers of CPGs. Peer reviewers and editors considering an overview or CPG for publication must hold their authors to a high standard of transparency regarding both the conduct and reporting of these appraisals.
Part 4. Meeting conduct standards
Many authors, peer reviewers, and editors erroneously equate fulfillment of the items on the PRISMA checklist with superior methodological rigor. For direction on methodology, we refer them to available resources that provide comprehensive conceptual guidance [ 59 , 60 ] as well as primers with basic step-by-step instructions [ 1 , 126 , 127 ]. This section is intended to complement study of such resources by facilitating use of AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS, tools specifically developed to evaluate methodological rigor of systematic reviews. These tools are widely accepted by methodologists; however, in the general medical literature, they are not uniformly selected for the critical appraisal of systematic reviews [ 88 , 96 ].
To enable their uptake, Table 4.1 links review components to the corresponding appraisal tool items. Expectations of AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS are concisely stated, and reasoning provided.
Systematic review components linked to appraisal with AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS a
CoI conflict of interest, MA meta-analysis, NA not addressed, PICO participant, intervention, comparison, outcome, PRISMA-P Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols, RoB risk of bias
a Components shown in bold are chosen for elaboration in Part 4 for one (or both) of two reasons: 1) the component has been identified as potentially problematic for systematic review authors; and/or 2) the component is evaluated by standards of an AMSTAR-2 “critical” domain
b Critical domains of AMSTAR-2 are indicated by *
Issues involved in meeting the standards for seven review components (identified in bold in Table 4.1 ) are addressed in detail. These were chosen for elaboration for one (or both) of two reasons: 1) the component has been identified as potentially problematic for systematic review authors based on consistent reports of their frequent AMSTAR-2 or ROBIS deficiencies [ 9 , 11 , 15 , 88 , 128 , 129 ]; and/or 2) the review component is judged by standards of an AMSTAR-2 “critical” domain. These have the greatest implications for how a systematic review will be appraised: if standards for any one of these critical domains are not met, the review is rated as having “critically low confidence.”
Research question
Specific and unambiguous research questions may have more value for reviews that deal with hypothesis testing. Mnemonics for the various elements of research questions are suggested by JBI and Cochrane (Table 2.1 ). These prompt authors to consider the specialized methods involved for developing different types of systematic reviews; however, while inclusion of the suggested elements makes a review compliant with a particular review’s methods, it does not necessarily make a research question appropriate. Table 4.2 lists acronyms that may aid in developing the research question. They include overlapping concepts of importance in this time of proliferating reviews of uncertain value [ 130 ]. If these issues are not prospectively contemplated, systematic review authors may establish an overly broad scope, or develop runaway scope allowing them to stray from predefined choices relating to key comparisons and outcomes.
Research question development
a Cummings SR, Browner WS, Hulley SB. Conceiving the research question and developing the study plan. In: Hulley SB, Cummings SR, Browner WS, editors. Designing clinical research: an epidemiological approach; 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 14–22
b Doran, GT. There’s a S.M.A.R.T. way to write management’s goals and objectives. Manage Rev. 1981;70:35-6.
c Johnson BT, Hennessy EA. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses in the health sciences: best practice methods for research syntheses. Soc Sci Med. 2019;233:237–51
Once a research question is established, searching on registry sites and databases for existing systematic reviews addressing the same or a similar topic is necessary in order to avoid contributing to research waste [ 131 ]. Repeating an existing systematic review must be justified, for example, if previous reviews are out of date or methodologically flawed. A full discussion on replication of intervention systematic reviews, including a consensus checklist, can be found in the work of Tugwell and colleagues [ 84 ].
Protocol development is considered a core component of systematic reviews [ 125 , 126 , 132 ]. Review protocols may allow researchers to plan and anticipate potential issues, assess validity of methods, prevent arbitrary decision-making, and minimize bias that can be introduced by the conduct of the review. Registration of a protocol that allows public access promotes transparency of the systematic review’s methods and processes and reduces the potential for duplication [ 132 ]. Thinking early and carefully about all the steps of a systematic review is pragmatic and logical and may mitigate the influence of the authors’ prior knowledge of the evidence [ 133 ]. In addition, the protocol stage is when the scope of the review can be carefully considered by authors, reviewers, and editors; this may help to avoid production of overly ambitious reviews that include excessive numbers of comparisons and outcomes or are undisciplined in their study selection.
An association with attainment of AMSTAR standards in systematic reviews with published prospective protocols has been reported [ 134 ]. However, completeness of reporting does not seem to be different in reviews with a protocol compared to those without one [ 135 ]. PRISMA-P [ 116 ] and its accompanying elaboration and explanation document [ 136 ] can be used to guide and assess the reporting of protocols. A final version of the review should fully describe any protocol deviations. Peer reviewers may compare the submitted manuscript with any available pre-registered protocol; this is required if AMSTAR-2 or ROBIS are used for critical appraisal.
There are multiple options for the recording of protocols (Table 4.3 ). Some journals will peer review and publish protocols. In addition, many online sites offer date-stamped and publicly accessible protocol registration. Some of these are exclusively for protocols of evidence syntheses; others are less restrictive and offer researchers the capacity for data storage, sharing, and other workflow features. These sites document protocol details to varying extents and have different requirements [ 137 ]. The most popular site for systematic reviews, the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO), for example, only registers reviews that report on an outcome with direct relevance to human health. The PROSPERO record documents protocols for all types of reviews except literature and scoping reviews. Of note, PROSPERO requires authors register their review protocols prior to any data extraction [ 133 , 138 ]. The electronic records of most of these registry sites allow authors to update their protocols and facilitate transparent tracking of protocol changes, which are not unexpected during the progress of the review [ 139 ].
Options for protocol registration of evidence syntheses
a Authors are advised to contact their target journal regarding submission of systematic review protocols
b Registration is restricted to approved review projects
c The JBI registry lists review projects currently underway by JBI-affiliated entities. These records include a review’s title, primary author, research question, and PICO elements. JBI recommends that authors register eligible protocols with PROSPERO
d See Pieper and Rombey [ 137 ] for detailed characteristics of these five registries
e See Pieper and Rombey [ 137 ] for other systematic review data repository options
Study design inclusion
For most systematic reviews, broad inclusion of study designs is recommended [ 126 ]. This may allow comparison of results between contrasting study design types [ 126 ]. Certain study designs may be considered preferable depending on the type of review and nature of the research question. However, prevailing stereotypes about what each study design does best may not be accurate. For example, in systematic reviews of interventions, randomized designs are typically thought to answer highly specific questions while non-randomized designs often are expected to reveal greater information about harms or real-word evidence [ 126 , 140 , 141 ]. This may be a false distinction; randomized trials may be pragmatic [ 142 ], they may offer important (and more unbiased) information on harms [ 143 ], and data from non-randomized trials may not necessarily be more real-world-oriented [ 144 ].
Moreover, there may not be any available evidence reported by RCTs for certain research questions; in some cases, there may not be any RCTs or NRSI. When the available evidence is limited to case reports and case series, it is not possible to test hypotheses nor provide descriptive estimates or associations; however, a systematic review of these studies can still offer important insights [ 81 , 145 ]. When authors anticipate that limited evidence of any kind may be available to inform their research questions, a scoping review can be considered. Alternatively, decisions regarding inclusion of indirect as opposed to direct evidence can be addressed during protocol development [ 146 ]. Including indirect evidence at an early stage of intervention systematic review development allows authors to decide if such studies offer any additional and/or different understanding of treatment effects for their population or comparison of interest. Issues of indirectness of included studies are accounted for later in the process, during determination of the overall certainty of evidence (see Part 5 for details).
Evidence search
Both AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS require systematic and comprehensive searches for evidence. This is essential for any systematic review. Both tools discourage search restrictions based on language and publication source. Given increasing globalism in health care, the practice of including English-only literature should be avoided [ 126 ]. There are many examples in which language bias (different results in studies published in different languages) has been documented [ 147 , 148 ]. This does not mean that all literature, in all languages, is equally trustworthy [ 148 ]; however, the only way to formally probe for the potential of such biases is to consider all languages in the initial search. The gray literature and a search of trials may also reveal important details about topics that would otherwise be missed [ 149 – 151 ]. Again, inclusiveness will allow review authors to investigate whether results differ in gray literature and trials [ 41 , 151 – 153 ].
Authors should make every attempt to complete their review within one year as that is the likely viable life of a search. (1) If that is not possible, the search should be updated close to the time of completion [ 154 ]. Different research topics may warrant less of a delay, for example, in rapidly changing fields (as in the case of the COVID-19 pandemic), even one month may radically change the available evidence.
Excluded studies
AMSTAR-2 requires authors to provide references for any studies excluded at the full text phase of study selection along with reasons for exclusion; this allows readers to feel confident that all relevant literature has been considered for inclusion and that exclusions are defensible.
Risk of bias assessment of included studies
The design of the studies included in a systematic review (eg, RCT, cohort, case series) should not be equated with appraisal of its RoB. To meet AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS standards, systematic review authors must examine RoB issues specific to the design of each primary study they include as evidence. It is unlikely that a single RoB appraisal tool will be suitable for all research designs. In addition to tools for randomized and non-randomized studies, specific tools are available for evaluation of RoB in case reports and case series [ 82 ] and single-case experimental designs [ 155 , 156 ]. Note the RoB tools selected must meet the standards of the appraisal tool used to judge the conduct of the review. For example, AMSTAR-2 identifies four sources of bias specific to RCTs and NRSI that must be addressed by the RoB tool(s) chosen by the review authors. The Cochrane RoB-2 [ 157 ] tool for RCTs and ROBINS-I [ 158 ] for NRSI for RoB assessment meet the AMSTAR-2 standards. Appraisers on the review team should not modify any RoB tool without complete transparency and acknowledgment that they have invalidated the interpretation of the tool as intended by its developers [ 159 ]. Conduct of RoB assessments is not addressed AMSTAR-2; to meet ROBIS standards, two independent reviewers should complete RoB assessments of included primary studies.
Implications of the RoB assessments must be explicitly discussed and considered in the conclusions of the review. Discussion of the overall RoB of included studies may consider the weight of the studies at high RoB, the importance of the sources of bias in the studies being summarized, and if their importance differs in relationship to the outcomes reported. If a meta-analysis is performed, serious concerns for RoB of individual studies should be accounted for in these results as well. If the results of the meta-analysis for a specific outcome change when studies at high RoB are excluded, readers will have a more accurate understanding of this body of evidence. However, while investigating the potential impact of specific biases is a useful exercise, it is important to avoid over-interpretation, especially when there are sparse data.
Synthesis methods for quantitative data
Syntheses of quantitative data reported by primary studies are broadly categorized as one of two types: meta-analysis, and synthesis without meta-analysis (Table 4.4 ). Before deciding on one of these methods, authors should seek methodological advice about whether reported data can be transformed or used in other ways to provide a consistent effect measure across studies [ 160 , 161 ].
Common methods for quantitative synthesis
CI confidence interval (or credible interval, if analysis is done in Bayesian framework)
a See text for descriptions of the types of data combined in each of these approaches
b See Additional File 4 for guidance on the structure and presentation of forest plots
c General approach is similar to aggregate data meta-analysis but there are substantial differences relating to data collection and checking and analysis [ 162 ]. This approach to syntheses is applicable to intervention, diagnostic, and prognostic systematic reviews [ 163 ]
d Examples include meta-regression, hierarchical and multivariate approaches [ 164 ]
e In-depth guidance and illustrations of these methods are provided in Chapter 12 of the Cochrane Handbook [ 160 ]
Meta-analysis
Systematic reviews that employ meta-analysis should not be referred to simply as “meta-analyses.” The term meta-analysis strictly refers to a specific statistical technique used when study effect estimates and their variances are available, yielding a quantitative summary of results. In general, methods for meta-analysis involve use of a weighted average of effect estimates from two or more studies. If considered carefully, meta-analysis increases the precision of the estimated magnitude of effect and can offer useful insights about heterogeneity and estimates of effects. We refer to standard references for a thorough introduction and formal training [ 165 – 167 ].
There are three common approaches to meta-analysis in current health care–related systematic reviews (Table 4.4 ). Aggregate meta-analyses is the most familiar to authors of evidence syntheses and their end users. This standard meta-analysis combines data on effect estimates reported by studies that investigate similar research questions involving direct comparisons of an intervention and comparator. Results of these analyses provide a single summary intervention effect estimate. If the included studies in a systematic review measure an outcome differently, their reported results may be transformed to make them comparable [ 161 ]. Forest plots visually present essential information about the individual studies and the overall pooled analysis (see Additional File 4 for details).
Less familiar and more challenging meta-analytical approaches used in secondary research include individual participant data (IPD) and network meta-analyses (NMA); PRISMA extensions provide reporting guidelines for both [ 117 , 118 ]. In IPD, the raw data on each participant from each eligible study are re-analyzed as opposed to the study-level data analyzed in aggregate data meta-analyses [ 168 ]. This may offer advantages, including the potential for limiting concerns about bias and allowing more robust analyses [ 163 ]. As suggested by the description in Table 4.4 , NMA is a complex statistical approach. It combines aggregate data [ 169 ] or IPD [ 170 ] for effect estimates from direct and indirect comparisons reported in two or more studies of three or more interventions. This makes it a potentially powerful statistical tool; while multiple interventions are typically available to treat a condition, few have been evaluated in head-to-head trials [ 171 ]. Both IPD and NMA facilitate a broader scope, and potentially provide more reliable and/or detailed results; however, compared with standard aggregate data meta-analyses, their methods are more complicated, time-consuming, and resource-intensive, and they have their own biases, so one needs sufficient funding, technical expertise, and preparation to employ them successfully [ 41 , 172 , 173 ].
Several items in AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS address meta-analysis; thus, understanding the strengths, weaknesses, assumptions, and limitations of methods for meta-analyses is important. According to the standards of both tools, plans for a meta-analysis must be addressed in the review protocol, including reasoning, description of the type of quantitative data to be synthesized, and the methods planned for combining the data. This should not consist of stock statements describing conventional meta-analysis techniques; rather, authors are expected to anticipate issues specific to their research questions. Concern for the lack of training in meta-analysis methods among systematic review authors cannot be overstated. For those with training, the use of popular software (eg, RevMan [ 174 ], MetaXL [ 175 ], JBI SUMARI [ 176 ]) may facilitate exploration of these methods; however, such programs cannot substitute for the accurate interpretation of the results of meta-analyses, especially for more complex meta-analytical approaches.
Synthesis without meta-analysis
There are varied reasons a meta-analysis may not be appropriate or desirable [ 160 , 161 ]. Syntheses that informally use statistical methods other than meta-analysis are variably referred to as descriptive, narrative, or qualitative syntheses or summaries; these terms are also applied to syntheses that make no attempt to statistically combine data from individual studies. However, use of such imprecise terminology is discouraged; in order to fully explore the results of any type of synthesis, some narration or description is needed to supplement the data visually presented in tabular or graphic forms [ 63 , 177 ]. In addition, the term “qualitative synthesis” is easily confused with a synthesis of qualitative data in a qualitative or mixed methods review. “Synthesis without meta-analysis” is currently the preferred description of other ways to combine quantitative data from two or more studies. Use of this specific terminology when referring to these types of syntheses also implies the application of formal methods (Table 4.4 ).
Methods for syntheses without meta-analysis involve structured presentations of the data in any tables and plots. In comparison to narrative descriptions of each study, these are designed to more effectively and transparently show patterns and convey detailed information about the data; they also allow informal exploration of heterogeneity [ 178 ]. In addition, acceptable quantitative statistical methods (Table 4.4 ) are formally applied; however, it is important to recognize these methods have significant limitations for the interpretation of the effectiveness of an intervention [ 160 ]. Nevertheless, when meta-analysis is not possible, the application of these methods is less prone to bias compared with an unstructured narrative description of included studies [ 178 , 179 ].
Vote counting is commonly used in systematic reviews and involves a tally of studies reporting results that meet some threshold of importance applied by review authors. Until recently, it has not typically been identified as a method for synthesis without meta-analysis. Guidance on an acceptable vote counting method based on direction of effect is currently available [ 160 ] and should be used instead of narrative descriptions of such results (eg, “more than half the studies showed improvement”; “only a few studies reported adverse effects”; “7 out of 10 studies favored the intervention”). Unacceptable methods include vote counting by statistical significance or magnitude of effect or some subjective rule applied by the authors.
AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS standards do not explicitly address conduct of syntheses without meta-analysis, although AMSTAR-2 items 13 and 14 might be considered relevant. Guidance for the complete reporting of syntheses without meta-analysis for systematic reviews of interventions is available in the Synthesis without Meta-analysis (SWiM) guideline [ 180 ] and methodological guidance is available in the Cochrane Handbook [ 160 , 181 ].
Familiarity with AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS makes sense for authors of systematic reviews as these appraisal tools will be used to judge their work; however, training is necessary for authors to truly appreciate and apply methodological rigor. Moreover, judgment of the potential contribution of a systematic review to the current knowledge base goes beyond meeting the standards of AMSTAR-2 and ROBIS. These tools do not explicitly address some crucial concepts involved in the development of a systematic review; this further emphasizes the need for author training.
We recommend that systematic review authors incorporate specific practices or exercises when formulating a research question at the protocol stage, These should be designed to raise the review team’s awareness of how to prevent research and resource waste [ 84 , 130 ] and to stimulate careful contemplation of the scope of the review [ 30 ]. Authors’ training should also focus on justifiably choosing a formal method for the synthesis of quantitative and/or qualitative data from primary research; both types of data require specific expertise. For typical reviews that involve syntheses of quantitative data, statistical expertise is necessary, initially for decisions about appropriate methods, [ 160 , 161 ] and then to inform any meta-analyses [ 167 ] or other statistical methods applied [ 160 ].
Part 5. Rating overall certainty of evidence
Report of an overall certainty of evidence assessment in a systematic review is an important new reporting standard of the updated PRISMA 2020 guidelines [ 93 ]. Systematic review authors are well acquainted with assessing RoB in individual primary studies, but much less familiar with assessment of overall certainty across an entire body of evidence. Yet a reliable way to evaluate this broader concept is now recognized as a vital part of interpreting the evidence.
Historical systems for rating evidence are based on study design and usually involve hierarchical levels or classes of evidence that use numbers and/or letters to designate the level/class. These systems were endorsed by various EBM-related organizations. Professional societies and regulatory groups then widely adopted them, often with modifications for application to the available primary research base in specific clinical areas. In 2002, a report issued by the AHRQ identified 40 systems to rate quality of a body of evidence [ 182 ]. A critical appraisal of systems used by prominent health care organizations published in 2004 revealed limitations in sensibility, reproducibility, applicability to different questions, and usability to different end users [ 183 ]. Persistent use of hierarchical rating schemes to describe overall quality continues to complicate the interpretation of evidence. This is indicated by recent reports of poor interpretability of systematic review results by readers [ 184 – 186 ] and misleading interpretations of the evidence related to the “spin” systematic review authors may put on their conclusions [ 50 , 187 ].
Recognition of the shortcomings of hierarchical rating systems raised concerns that misleading clinical recommendations could result even if based on a rigorous systematic review. In addition, the number and variability of these systems were considered obstacles to quick and accurate interpretations of the evidence by clinicians, patients, and policymakers [ 183 ]. These issues contributed to the development of the GRADE approach. An international working group, that continues to actively evaluate and refine it, first introduced GRADE in 2004 [ 188 ]. Currently more than 110 organizations from 19 countries around the world have endorsed or are using GRADE [ 189 ].
GRADE approach to rating overall certainty
GRADE offers a consistent and sensible approach for two separate processes: rating the overall certainty of a body of evidence and the strength of recommendations. The former is the expected conclusion of a systematic review, while the latter is pertinent to the development of CPGs. As such, GRADE provides a mechanism to bridge the gap from evidence synthesis to application of the evidence for informed clinical decision-making [ 27 , 190 ]. We briefly examine the GRADE approach but only as it applies to rating overall certainty of evidence in systematic reviews.
In GRADE, use of “certainty” of a body of evidence is preferred over the term “quality.” [ 191 ] Certainty refers to the level of confidence systematic review authors have that, for each outcome, an effect estimate represents the true effect. The GRADE approach to rating confidence in estimates begins with identifying the study type (RCT or NRSI) and then systematically considers criteria to rate the certainty of evidence up or down (Table 5.1 ).
GRADE criteria for rating certainty of evidence
a Applies to randomized studies
b Applies to non-randomized studies
This process results in assignment of one of the four GRADE certainty ratings to each outcome; these are clearly conveyed with the use of basic interpretation symbols (Table 5.2 ) [ 192 ]. Notably, when multiple outcomes are reported in a systematic review, each outcome is assigned a unique certainty rating; thus different levels of certainty may exist in the body of evidence being examined.
GRADE certainty ratings and their interpretation symbols a
a From the GRADE Handbook [ 192 ]
GRADE’s developers acknowledge some subjectivity is involved in this process [ 193 ]. In addition, they emphasize that both the criteria for rating evidence up and down (Table 5.1 ) as well as the four overall certainty ratings (Table 5.2 ) reflect a continuum as opposed to discrete categories [ 194 ]. Consequently, deciding whether a study falls above or below the threshold for rating up or down may not be straightforward, and preliminary overall certainty ratings may be intermediate (eg, between low and moderate). Thus, the proper application of GRADE requires systematic review authors to take an overall view of the body of evidence and explicitly describe the rationale for their final ratings.
Advantages of GRADE
Outcomes important to the individuals who experience the problem of interest maintain a prominent role throughout the GRADE process [ 191 ]. These outcomes must inform the research questions (eg, PICO [population, intervention, comparator, outcome]) that are specified a priori in a systematic review protocol. Evidence for these outcomes is then investigated and each critical or important outcome is ultimately assigned a certainty of evidence as the end point of the review. Notably, limitations of the included studies have an impact at the outcome level. Ultimately, the certainty ratings for each outcome reported in a systematic review are considered by guideline panels. They use a different process to formulate recommendations that involves assessment of the evidence across outcomes [ 201 ]. It is beyond our scope to describe the GRADE process for formulating recommendations; however, it is critical to understand how these two outcome-centric concepts of certainty of evidence in the GRADE framework are related and distinguished. An in-depth illustration using examples from recently published evidence syntheses and CPGs is provided in Additional File 5 A (Table AF5A-1).
The GRADE approach is applicable irrespective of whether the certainty of the primary research evidence is high or very low; in some circumstances, indirect evidence of higher certainty may be considered if direct evidence is unavailable or of low certainty [ 27 ]. In fact, most interventions and outcomes in medicine have low or very low certainty of evidence based on GRADE and there seems to be no major improvement over time [ 202 , 203 ]. This is still a very important (even if sobering) realization for calibrating our understanding of medical evidence. A major appeal of the GRADE approach is that it offers a common framework that enables authors of evidence syntheses to make complex judgments about evidence certainty and to convey these with unambiguous terminology. This prevents some common mistakes made by review authors, including overstating results (or under-reporting harms) [ 187 ] and making recommendations for treatment. This is illustrated in Table AF5A-2 (Additional File 5 A), which compares the concluding statements made about overall certainty in a systematic review with and without application of the GRADE approach.
Theoretically, application of GRADE should improve consistency of judgments about certainty of evidence, both between authors and across systematic reviews. In one empirical evaluation conducted by the GRADE Working Group, interrater reliability of two individual raters assessing certainty of the evidence for a specific outcome increased from ~ 0.3 without using GRADE to ~ 0.7 by using GRADE [ 204 ]. However, others report variable agreement among those experienced in GRADE assessments of evidence certainty [ 190 ]. Like any other tool, GRADE requires training in order to be properly applied. The intricacies of the GRADE approach and the necessary subjectivity involved suggest that improving agreement may require strict rules for its application; alternatively, use of general guidance and consensus among review authors may result in less consistency but provide important information for the end user [ 190 ].
GRADE caveats
Simply invoking “the GRADE approach” does not automatically ensure GRADE methods were employed by authors of a systematic review (or developers of a CPG). Table 5.3 lists the criteria the GRADE working group has established for this purpose. These criteria highlight the specific terminology and methods that apply to rating the certainty of evidence for outcomes reported in a systematic review [ 191 ], which is different from rating overall certainty across outcomes considered in the formulation of recommendations [ 205 ]. Modifications of standard GRADE methods and terminology are discouraged as these may detract from GRADE’s objectives to minimize conceptual confusion and maximize clear communication [ 206 ].
Criteria for using GRADE in a systematic review a
a Adapted from the GRADE working group [ 206 ]; this list does not contain the additional criteria that apply to the development of a clinical practice guideline
Nevertheless, GRADE is prone to misapplications [ 207 , 208 ], which can distort a systematic review’s conclusions about the certainty of evidence. Systematic review authors without proper GRADE training are likely to misinterpret the terms “quality” and “grade” and to misunderstand the constructs assessed by GRADE versus other appraisal tools. For example, review authors may reference the standard GRADE certainty ratings (Table 5.2 ) to describe evidence for their outcome(s) of interest. However, these ratings are invalidated if authors omit or inadequately perform RoB evaluations of each included primary study. Such deficiencies in RoB assessments are unacceptable but not uncommon, as reported in methodological studies of systematic reviews and overviews [ 104 , 186 , 209 , 210 ]. GRADE ratings are also invalidated if review authors do not formally address and report on the other criteria (Table 5.1 ) necessary for a GRADE certainty rating.
Other caveats pertain to application of a GRADE certainty of evidence rating in various types of evidence syntheses. Current adaptations of GRADE are described in Additional File 5 B and included on Table 6.3 , which is introduced in the next section.
Concise Guide to best practices for evidence syntheses, version 1.0 a
AMSTAR A MeaSurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews, CASP Critical Appraisal Skills Programme, CERQual Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative research, ConQual Establishing Confidence in the output of Qualitative research synthesis, COSMIN COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement Instruments, DTA diagnostic test accuracy, eMERGe meta-ethnography reporting guidance, ENTREQ enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research, GRADE Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation, MA meta-analysis, NRSI non-randomized studies of interventions, P protocol, PRIOR Preferred Reporting Items for Overviews of Reviews, PRISMA Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses, PROBAST Prediction model Risk Of Bias ASsessment Tool, QUADAS quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews, QUIPS Quality In Prognosis Studies, RCT randomized controlled trial, RoB risk of bias, ROBINS-I Risk Of Bias In Non-randomised Studies of Interventions, ROBIS Risk of Bias in Systematic Reviews, ScR scoping review, SWiM systematic review without meta-analysis
a Superscript numbers represent citations provided in the main reference list. Additional File 6 lists links to available online resources for the methods and tools included in the Concise Guide
b The MECIR manual [ 30 ] provides Cochrane’s specific standards for both reporting and conduct of intervention systematic reviews and protocols
c Editorial and peer reviewers can evaluate completeness of reporting in submitted manuscripts using these tools. Authors may be required to submit a self-reported checklist for the applicable tools
d The decision flowchart described by Flemming and colleagues [ 223 ] is recommended for guidance on how to choose the best approach to reporting for qualitative reviews
e SWiM was developed for intervention studies reporting quantitative data. However, if there is not a more directly relevant reporting guideline, SWiM may prompt reviewers to consider the important details to report. (Personal Communication via email, Mhairi Campbell, 14 Dec 2022)
f JBI recommends their own tools for the critical appraisal of various quantitative primary study designs included in systematic reviews of intervention effectiveness, prevalence and incidence, and etiology and risk as well as for the critical appraisal of systematic reviews included in umbrella reviews. However, except for the JBI Checklists for studies reporting prevalence data and qualitative research, the development, validity, and reliability of these tools are not well documented
g Studies that are not RCTs or NRSI require tools developed specifically to evaluate their design features. Examples include single case experimental design [ 155 , 156 ] and case reports and series [ 82 ]
h The evaluation of methodological quality of studies included in a synthesis of qualitative research is debatable [ 224 ]. Authors may select a tool appropriate for the type of qualitative synthesis methodology employed. The CASP Qualitative Checklist [ 218 ] is an example of a published, commonly used tool that focuses on assessment of the methodological strengths and limitations of qualitative studies. The JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Qualitative Research [ 219 ] is recommended for reviews using a meta-aggregative approach
i Consider including risk of bias assessment of included studies if this information is relevant to the research question; however, scoping reviews do not include an assessment of the overall certainty of a body of evidence
j Guidance available from the GRADE working group [ 225 , 226 ]; also recommend consultation with the Cochrane diagnostic methods group
k Guidance available from the GRADE working group [ 227 ]; also recommend consultation with Cochrane prognostic methods group
l Used for syntheses in reviews with a meta-aggregative approach [ 224 ]
m Chapter 5 in the JBI Manual offers guidance on how to adapt GRADE to prevalence and incidence reviews [ 69 ]
n Janiaud and colleagues suggest criteria for evaluating evidence certainty for meta-analyses of non-randomized studies evaluating risk factors [ 228 ]
o The COSMIN user manual provides details on how to apply GRADE in systematic reviews of measurement properties [ 229 ]
The expected culmination of a systematic review should be a rating of overall certainty of a body of evidence for each outcome reported. The GRADE approach is recommended for making these judgments for outcomes reported in systematic reviews of interventions and can be adapted for other types of reviews. This represents the initial step in the process of making recommendations based on evidence syntheses. Peer reviewers should ensure authors meet the minimal criteria for supporting the GRADE approach when reviewing any evidence synthesis that reports certainty ratings derived using GRADE. Authors and peer reviewers of evidence syntheses unfamiliar with GRADE are encouraged to seek formal training and take advantage of the resources available on the GRADE website [ 211 , 212 ].
Part 6. Concise Guide to best practices
Accumulating data in recent years suggest that many evidence syntheses (with or without meta-analysis) are not reliable. This relates in part to the fact that their authors, who are often clinicians, can be overwhelmed by the plethora of ways to evaluate evidence. They tend to resort to familiar but often inadequate, inappropriate, or obsolete methods and tools and, as a result, produce unreliable reviews. These manuscripts may not be recognized as such by peer reviewers and journal editors who may disregard current standards. When such a systematic review is published or included in a CPG, clinicians and stakeholders tend to believe that it is trustworthy. A vicious cycle in which inadequate methodology is rewarded and potentially misleading conclusions are accepted is thus supported. There is no quick or easy way to break this cycle; however, increasing awareness of best practices among all these stakeholder groups, who often have minimal (if any) training in methodology, may begin to mitigate it. This is the rationale for inclusion of Parts 2 through 5 in this guidance document. These sections present core concepts and important methodological developments that inform current standards and recommendations. We conclude by taking a direct and practical approach.
Inconsistent and imprecise terminology used in the context of development and evaluation of evidence syntheses is problematic for authors, peer reviewers and editors, and may lead to the application of inappropriate methods and tools. In response, we endorse use of the basic terms (Table 6.1 ) defined in the PRISMA 2020 statement [ 93 ]. In addition, we have identified several problematic expressions and nomenclature. In Table 6.2 , we compile suggestions for preferred terms less likely to be misinterpreted.
Terms relevant to the reporting of health care–related evidence syntheses a
a Reproduced from Page and colleagues [ 93 ]
Terminology suggestions for health care–related evidence syntheses
a For example, meta-aggregation, meta-ethnography, critical interpretative synthesis, realist synthesis
b This term may best apply to the synthesis in a mixed methods systematic review in which data from different types of evidence (eg, qualitative, quantitative, economic) are summarized [ 64 ]
We also propose a Concise Guide (Table 6.3 ) that summarizes the methods and tools recommended for the development and evaluation of nine types of evidence syntheses. Suggestions for specific tools are based on the rigor of their development as well as the availability of detailed guidance from their developers to ensure their proper application. The formatting of the Concise Guide addresses a well-known source of confusion by clearly distinguishing the underlying methodological constructs that these tools were designed to assess. Important clarifications and explanations follow in the guide’s footnotes; associated websites, if available, are listed in Additional File 6 .
To encourage uptake of best practices, journal editors may consider adopting or adapting the Concise Guide in their instructions to authors and peer reviewers of evidence syntheses. Given the evolving nature of evidence synthesis methodology, the suggested methods and tools are likely to require regular updates. Authors of evidence syntheses should monitor the literature to ensure they are employing current methods and tools. Some types of evidence syntheses (eg, rapid, economic, methodological) are not included in the Concise Guide; for these, authors are advised to obtain recommendations for acceptable methods by consulting with their target journal.
We encourage the appropriate and informed use of the methods and tools discussed throughout this commentary and summarized in the Concise Guide (Table 6.3 ). However, we caution against their application in a perfunctory or superficial fashion. This is a common pitfall among authors of evidence syntheses, especially as the standards of such tools become associated with acceptance of a manuscript by a journal. Consequently, published evidence syntheses may show improved adherence to the requirements of these tools without necessarily making genuine improvements in their performance.
In line with our main objective, the suggested tools in the Concise Guide address the reliability of evidence syntheses; however, we recognize that the utility of systematic reviews is an equally important concern. An unbiased and thoroughly reported evidence synthesis may still not be highly informative if the evidence itself that is summarized is sparse, weak and/or biased [ 24 ]. Many intervention systematic reviews, including those developed by Cochrane [ 203 ] and those applying GRADE [ 202 ], ultimately find no evidence, or find the evidence to be inconclusive (eg, “weak,” “mixed,” or of “low certainty”). This often reflects the primary research base; however, it is important to know what is known (or not known) about a topic when considering an intervention for patients and discussing treatment options with them.
Alternatively, the frequency of “empty” and inconclusive reviews published in the medical literature may relate to limitations of conventional methods that focus on hypothesis testing; these have emphasized the importance of statistical significance in primary research and effect sizes from aggregate meta-analyses [ 183 ]. It is becoming increasingly apparent that this approach may not be appropriate for all topics [ 130 ]. Development of the GRADE approach has facilitated a better understanding of significant factors (beyond effect size) that contribute to the overall certainty of evidence. Other notable responses include the development of integrative synthesis methods for the evaluation of complex interventions [ 230 , 231 ], the incorporation of crowdsourcing and machine learning into systematic review workflows (eg the Cochrane Evidence Pipeline) [ 2 ], the shift in paradigm to living systemic review and NMA platforms [ 232 , 233 ] and the proposal of a new evidence ecosystem that fosters bidirectional collaborations and interactions among a global network of evidence synthesis stakeholders [ 234 ]. These evolutions in data sources and methods may ultimately make evidence syntheses more streamlined, less duplicative, and more importantly, they may be more useful for timely policy and clinical decision-making; however, that will only be the case if they are rigorously reported and conducted.
We look forward to others’ ideas and proposals for the advancement of methods for evidence syntheses. For now, we encourage dissemination and uptake of the currently accepted best tools and practices for their development and evaluation; at the same time, we stress that uptake of appraisal tools, checklists, and software programs cannot substitute for proper education in the methodology of evidence syntheses and meta-analysis. Authors, peer reviewers, and editors must strive to make accurate and reliable contributions to the present evidence knowledge base; online alerts, upcoming technology, and accessible education may make this more feasible than ever before. Our intention is to improve the trustworthiness of evidence syntheses across disciplines, topics, and types of evidence syntheses. All of us must continue to study, teach, and act cooperatively for that to happen.
Acknowledgements
Michelle Oakman Hayes for her assistance with the graphics, Mike Clarke for his willingness to answer our seemingly arbitrary questions, and Bernard Dan for his encouragement of this project.
Authors’ contributions
All authors participated in the development of the ideas, writing, and review of this manuscript. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
The work of John Ioannidis has been supported by an unrestricted gift from Sue and Bob O’Donnell to Stanford University.
Declarations
The authors declare no competing interests.
This article has been published simultaneously in BMC Systematic Reviews, Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, BMC Infectious Diseases, British Journal of Pharmacology, JBI Evidence Synthesis, the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery Reviews , and the Journal of Pediatric Rehabilitation Medicine .
Publisher’ s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Search Menu
- Volume 8, Issue 2, 2024 (In Progress)
- Volume 8, Issue 1, 2024
- Volume 6, Issue Supplement_1, October 2022 (In Progress)
- Advance Articles
- Supplements
- Collections
- Current and future advances in practice series
- BSR Registers Papers
- General Instructions
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Trainee Publishing Program
- About Rheumatology Advances in Practice
- About British Society for Rheumatology
- Editorial Board
- Advertising & Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Lay summary, introduction, physical activity and exercise, mental health, supplementary material, data availability, authors’ contributions, acknowledgements.
- < Previous
Lifestyle interventions in the management of systemic sclerosis: a systematic review of the literature
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Ioannis Parodis, Alexander Tsoi, Alvaro Gomez, Jun Weng Chow, Charlotte Girard-Guyonvarc’h, Tanja Stamm, Carina Boström, Lifestyle interventions in the management of systemic sclerosis: a systematic review of the literature, Rheumatology Advances in Practice , Volume 8, Issue 2, 2024, rkae037, https://doi.org/10.1093/rap/rkae037
- Permissions Icon Permissions
We aimed to investigate the efficacy of lifestyle interventions for the management of SSc.
We searched the MEDLINE, Embase, Web of Science and CINAHL databases in June 2021. We included studies conducted on five or more patients with SSc published between 1 January 2000 and the search date evaluating lifestyle interventions, excluding systematic reviews without meta-analyses. Critical appraisal was conducted using critical appraisal tools from the Joanna Briggs Institute. Thirty-six studies were included for full-text evaluation.
A total of 17 studies evaluated the effect of physical exercise alone, whereas 14 studies evaluated educational interventions for mental health management, often with physical exercise as a central component. At an aggregated level, these studies support patient education and physical exercise for the improvement of physical function, in particular hand and mouth function. Studies on diet and nutrition were few ( n = 5) and pertained to gastrointestinal as well as anthropometric outcomes; these studies were insufficient to support any conclusions.
Physical exercise and patient education should be considered for improving physical function in patients with SSc. These interventions can be provided alongside pharmacotherapy, but there is no evidence supporting that they can be a substitute. Further research should aim at assessing the effects of reductions of harmful exposures, including tobacco smoking and alcohol, improving sleep and enhancing social relations, three hitherto underexplored facets of lifestyle in the context of SSc.
What does this mean for patients?
For individuals living with systemic sclerosis, a rare autoimmune disease affecting the skin and internal organs, managing symptoms and maintaining quality of life can be challenging. The present systematic review delves into lifestyle interventions, including exercise and dietary changes, aiming to improve patient outcomes. While exercise interventions showed promise in enhancing mobility and overall well-being, evidence regarding dietary modifications was limited. However, combining interventions targeting physical function with various aspects of self-management could further amplify their impact on quality of life. For patients, this research underscores the potential benefits of incorporating tailored lifestyle changes alongside drug treatments. It suggests that regular exercise could alleviate symptoms such as fatigue and pain, thereby improving daily functioning. Moreover, it hints at the importance of a holistic approach to self-care, with pharmacotherapy as just one, albeit irreplaceable, part of a whole. Ultimately, this highlights avenues for patients to actively participate in managing their condition, enhancing their overall well-being and quality of life. Further research is needed to explore the full scope of lifestyle interventions and their potential long-term benefits for patients with systemic sclerosis.
The efficacy of lifestyle interventions in systemic sclerosis is underexplored.
Patient education enhances outcomes and physical exercise improves physical function in systemic sclerosis.
Lifestyle interventions constitute a supplement, not a substitute, to pharmacotherapy.
SSc is a chronic connective tissue disease that primarily affects women, commonly in their fifth decade of life, and can manifest with limited cutaneous involvement, diffuse cutaneous involvement or with no cutaneous involvement [ 1 ]. The estimated prevalence ranges from <150–443 cases per million population, being higher in regions such as southern Europe, North America and Australia [ 1 ]. Areas commonly affected by skin fibrosis are the hands and face, which often results in impaired hand function [ 2 ] and microstomia [ 3 ]. Although advances in pharmacotherapy for rheumatic diseases have been achieved during the 21st century, the guidelines for non-pharmacological management in general, and lifestyle interventions in particular, are ill-defined.
Upon examination of the literature, the definition of a lifestyle intervention itself is not clearly characterized. The American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM) defines lifestyle medicine as ‘a medical specialty that uses therapeutic lifestyle interventions as a primary modality’ and lists six fundamental domains as targets of lifestyle medicine: nutrition, exercise, stress, substance abuse, sleep and relationships [ 4 ]. Analogously, the British Society of Lifestyle Medicine specifies six ‘pillars of lifestyle medicine’: healthy eating, physical activity, mental well-being, minimizing harmful substances, sleep and healthy relationships [ 5 ]. As such, a lifestyle intervention can be any intervention that covers any or all six domains, i.e. physical activity and exercise, diet and nutrition, mental health, harmful exposures, sleep and social relations.
The importance of lifestyle in the management of rheumatic diseases is gaining recognition. The EULAR recently published recommendations regarding lifestyle behaviours and work participation aimed at preventing disease progression in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases [ 6 ]. These 18 recommendations, accompanied by five overarching principles, were derived from systematic literature reviews geared toward six ‘lifestyle exposures’, i.e. exercise, diet, weight, alcohol, smoking and work participation [ 6 ]. Recently the EULAR also issued guidelines for the non-pharmacological management of SLE and SSc [ 7 ], following a thorough systematic literature review [ 8 ]. However, this review, while comprehensive, did not distinctly isolate lifestyle interventions from other approaches. Consequently, valuable insights into lifestyle interventions targeting modifiable health factors were obscured among the multitude of non-pharmacological management strategies examined. To bridge this gap in the literature, we herein conducted a systematic literature review to address the efficacy of lifestyle interventions in different aspects of the disease course in people living with SSc.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria for studies included a date of publication between 1 January 2000 and the search date, having a cohort of patients with SSc (as defined by classification criteria and/or International Classification of Diseases codes) as a population under investigation and evaluation of a lifestyle intervention. Studies were excluded if they had fewer than five participants, if they were systematic reviews without a meta-analysis, had no data on a distinct SSc patient population, were duplicates, were written in a language other than English, Spanish, or Swedish or if they did not assess an intervention that comprised one or more of the following: physical activity and exercise, diet and nutrition, mental health, harmful exposures, sleep and social relations.
Search strategy
On 22 June 2021, the MEDLINE, Embase, Web of Science and CINAHL databases were searched for studies concerning non-pharmacological management for SSc. Two investigators (A.G. and J.C.) screened the 11 089 initial hits under supervision of one senior investigator (I.P.). Conflicts were solved upon discussion with two investigators (I.P. and C.B.). The search and study selection was documented according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses statement ( Fig. 1 ) [ 9 ].

Flowchart of study selection
Data extraction
Data extraction was conducted by one researcher (J.C.) under the supervision of one senior investigator (I.P.). Data extracted included the number of participants for each study, interventions or management strategies given to both experimental and control groups, the characteristics of the comparator group, outcomes and the efficacy of the intervention. These data are provided in Supplementary Table S1 , available at Rheumatology Advances in Practice online.
Categorization
After data extraction and risk of bias (RoB) assessment, the studies were grouped by the category of lifestyle intervention they assessed. Studies combining exercise protocols with other educational interventions were separated from studies evaluating only physical exercise protocols, which in turn constituted their own group. Studies within the two above categories specifically evaluating the hand and mouth were further subgrouped into their own categories.
Quality assessment and evidence grading
RoB assessment for all included articles was conducted by one researcher (A.T.) using the Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal (CA) tools (checklists) [ 10 ]. Since all articles were already included before quality assessment for this review, the alternatives for overall appraisal ‘include’, ‘exclude’ and ‘seek further info’ were modified to ‘robust’, ‘weak’ and ‘intermediate’, respectively. The appropriate checklist for each study was selected based on the study design. A study was deemed weak if there were six or more checklist items it did not clearly fulfil, intermediate if there were three to five checklist items it did not clearly fulfil or robust if it clearly fulfilled all checklist items but two or fewer. After CA, studies were graded by level of evidence (LoE) according to the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine [ 11 ].
Study characteristics
Thirty-six studies were included. Of these, 17 evaluated physical activity and exercise alone rather than in combination with other interventions [ 12–28 ]. Fourteen studies evaluated the efficacy of mental health management [ 29–42 ] and five studies assessed diet and nutrition [ 43–47 ]. Fig. 1 presents a flowchart of the study selection. Studies and their characteristics, including the number of participants, interventions, characteristics of the comparator groups and outcomes are provided in Supplementary Table S1 , available at Rheumatology Advances in Practice online.
A randomized controlled trial (RCT) examining the effect of a tailored home-based exercise program (CA: intermediate; LoE: 2) found improvements in 6-min walking distance (6MWD) [ 48 ], the physical component score (PCS) of the 36-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) [ 49 ] and the HAQ Disability Index (HAQ-DI) [ 15 , 50 ]. Two RCTs evaluating the effect of exercise on microcirculation (CA: weak; LoE: 3) found no significant impact on cutaneous vascular conductance (CVC) after 12 weeks of high-intensity interval training alone [ 21 ]; however, this produced a significant effect when combined with endurance training [ 22 ]. An RCT evaluating tai chi (CA: weak; LoE: 3) found improvements in scores relating to balance (Berg Balance Scale [ 51 ]), sleep (Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index [ 52 ]) and fatigue (Fatigue Severity Scale [ 53 ]), but not trunk lateral endurance (trunk lateral endurance test [ 23 , 54 ]. Observational studies found that lower quadriceps strength associated with worse HAQ-DI scores (CA: robust; LoE: 3) [ 19 ] and that exercise habits associated with improved scores on the HAQ-DI and the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System [ 55 ] (PROMIS; CA: intermediate; LoE: 3) [ 20 ]. Aerobic exercise improved maximum oxygen consumption (VO 2 max) without exacerbation of skin induration, RP or digital ulcers at an 8-week follow-up (CA: intermediate; LoE: 3) [ 17 ].
An RCT by Rannou et al. [ 13 ] (CA: robust; LoE: 2) provided 4 weeks of personalized physical therapy to the experimental group and found an improvement in the HAQ-DI and hand function measured by the Cochin Hand Function Scale (CHFS) [ 56 ] after 4 weeks compared with patients receiving usual care. However, these improvements disappeared after 12 months. Stretching programs for hands improved scores in the Canadian Occupational Performance [ 57 ] after 3 months (CA: intermediate; LoE: 2) [ 12 ] but did not improve Hand Mobility in Scleroderma (HAMIS) test [ 2 ] scores at 9 or 18 weeks, regardless of adjunct treatment with paraffin baths (CA: intermediate; LoE: 2) [ 14 ]. Two RCTs evaluating functional impairment (CA: weak; LoE: 3) showed that app-delivered occupational therapy and stretching exercises administered through a telemedicine system were efficacious in improving hand function [ 25 ] as measured by a shortened version of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand questionnaire (QuickDASH) [ 58 ] and HAMIS [ 18 ]. A controlled quasi-experimental study (CA: intermediate; LoE: 3) found daily stretching exercises improved the range of motion in each finger in patients with SSc 1 month after baseline, and this improvement was maintained or further increased after 1 year from baseline [ 16 ].
The RCT by Rannou et al. [ 13 ] (CA: robust; LoE: 2) showed that 1 month of personalized physical therapy produced a sustained improvement in oral aperture up to 1 year from baseline. Another RCT (CA: weak; LoE: 3) found 12 weeks of an orofacial exercise protocol improved scores in the Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis index [ 3 ] up to 20 weeks from baseline [ 24 ]. An uncontrolled quasi-experimental study (CA: robust; LoE: 4) found daily mouth stretching exercises improved oral aperture 18 weeks after baseline.
An RCT evaluating the efficacy of a self-management website (CA: weak; LoE: 3) found no differences compared with issuing an educational patient-focused book when assessing PROMIS (primary outcome) scores at 16 weeks [ 35 ]. A controlled quasi-experimental study evaluating 3 weeks of patient education through occupational therapy (CA: robust; LoE: 3) found improvements in the HAQ-DI up to 24 weeks after baseline [ 34 ].
An RCT evaluating an educational program for self-management (CA: intermediate; LoE: 2) noted improvements in hand-related measures such as the HAMIS, Duruoz Hand Index [ 56 ], HAQ-DI and handgrip strength after 8 weeks [ 32 ]. A controlled quasi-experimental study (CA: intermediate; LoE: 3) found an educational self-management program for hands reduced the pain experienced by patients assessed using a visual analogue scale as well as improved CHFS scores after 24 weeks [ 36 ]. The protocol in this study was based on an uncontrolled study published the year before (CA: robust; LoE: 4), which also found amelioration of pain experienced by patients as well as improvements in CHFS scores after 8 weeks [ 42 ].
An RCT evaluating the effect of patient education with emphasis on orofacial exercises (CA: intermediate; LoE: 2) found that face-to-face training increased oral aperture more than educational material alone at 12 months after baseline in per-protocol analysis [ 30 ]. Another RCT (CA: intermediate; LoE: 2) found an increase in oral aperture after 1 month of orofacial exercise, regardless of whether they received oral hygiene advice before or after [ 31 ]. Two RCTs by Yuen et al. [ 29 , 33 ] examined the effects of oral health interventions, including instruction on dental product use and orofacial exercises. One of these studies [ 33 ] found an increase in oral aperture at 3 months, but not 6 months after baseline (CA: intermediate; LoE: 2), noting low adherence to the exercise program in particular, while the other study (CA: weak; LoE: 3) assessed gingival health and found significant improvements in the Löe–Silness gingival index [ 59 ] in both groups at 6 months after baseline, but a larger improvement in the intervention group compared with controls. Yet another multifaceted oral hygiene intervention was evaluated in an uncontrolled study by Poole et al. [ 39 ] (CA: intermediate; LoE: 4) and incorporated instruction of hand exercises on top of dental hygiene and orofacial exercise instruction. After a 6-month intervention, this study noted improvements in the Patient Hygiene Performance Index (PHP) [ 60 ] after 12 months from baseline, but no improvements in upper extremity measures such as the Keitel Function Test [ 61 ] or oral aperture [ 39 ].
Diet and nutrition
Five selected studies examined the effect of diet and nutrition (CA: four intermediate, one weak). Two RCTs on this topic examining the effects of probiotics found no significant changes in the University of California, Los Angeles Scleroderma Clinical Trial Consortium Gastrointestinal Tract Instrument (GIT-score) [ 62 ] compared with placebo after 60 days (CA: intermediate; LoE: 2) [ 43 ] and 8 weeks (CA: weak; LoE: 3) [ 44 ], respectively. However, the former study found an improvement in the GIT-score reflux component after 120 days [ 43 ] and the in latter study a decrease in Th17 cells after 8 weeks compared with placebo [ 44 ]. Conversely, one uncontrolled quasi-experimental study (CA: intermediate; LoE: 4) found that the use of probiotics associated with a significant reduction in total GIT-score as well as the reflux and bloating/distention component scores after 2 months [ 45 ].
Two quasi-experimental studies evaluated nutritional therapy. One found that nutritional support had no significant improvement in weight, body mass index (BMI) [ 63 ], energy intake or SF-36, with follow-up time points up to 12 months (CA: intermediate; LoE: 4) [ 46 ]. The other study found improvement in the abridged Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment [ 64 ] and a reduction in the number of patients classified as sarcopenic by DXA after 18 months (CA: intermediate; LoE: 4) [ 47 ]. The study did not find significant changes in caloric intake or macronutrient distribution in the enrolled patients [ 47 ].
This systematic review of the literature assessed the current evidence for lifestyle interventions as viable management strategies for people living with SSc. The main categories of intervention were physical activity and exercise, mental health and diet and nutrition. Physical exercise in general improved functional impairment and aerobic capacity, while stretching exercises of the hands and mouth efficaciously ameliorated hand impairment and microstomia. Stretching exercises of the hands and mouth were in turn often central components of educational interventions, which in principle focused on different facets of self-management. Studies on diet and nutrition showed sparse efficacy of probiotics in alleviating gastrointestinal symptoms and limited use of nutritional therapy for improving body composition. Overall, there was no rigorous investigation as to how lifestyle affects global disease activity in SSc. Furthermore, none of the included studies aimed to replace pharmacotherapy with lifestyle interventions.
These findings are largely in line with the comprehensive body of evidence compiled in the EULAR recommendations for lifestyle behaviours and work participation [ 6 ], which conclude that physical exercise can be a safe and beneficial way to improve functional impairment. However, factors such as comorbidities and disease severity warrant caution when recommending physical exercise as a part of disease management, which, as always, should be tailored to the patient. Furthermore, the findings in this review also agree that the evidence for recommending specific diets for the management of rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases is sparse [ 6 ]. Relating to the principal components of lifestyle medicine [ 4 , 5 ], there are gaps in knowledge regarding the effect of sleep, social relations and the use of harmful substances (such as nicotine, tobacco and alcohol) on SSc specifically. For these lifestyle domains, there exist EULAR recommendation sets [ 6 , 7 , 65 ] and other systematic reviews [ 8 , 66 ].
The categorization of interventions was not absolute, as many studies employed a combination of many different intervention categories. For example, studies on nutritional therapy [ 46 , 47 ] consisted of counselling and informative meetings, as in the studies on patient education. Similarly, educational interventions often had exercise programs as a central constituent [ 29–33 , 36 , 39 , 42 ]. The complexity of stratifying studies by category implies a tendency in current research toward examining multimodal approaches when evaluating lifestyle interventions. This may be based on mechanistic reasoning that certain lifestyle interventions should produce a larger effect size when made concurrently but complicates the assessment when trying to discern the efficacy of individual interventions in isolation.
A limitation that we encountered while compiling the evidence was the lack of a structured synthesis or meta-analysis. Moreover, the overall CA was derived from assessment by only one investigator, which potentially reduces the reliability of the RoB assessment. Despite this, there are strengths to this review in the form of a generous inclusion of studies spanning a period of >2 decades with varied study designs and a conservative approach in the CA of studies, treating unclearly fulfilled criteria as unfulfilled.
Considering that most of the studies included in this review were conducted in Europe (particularly Italy) and the USA, caution should be exercised when generalizing the findings to other regions, particularly those with different healthcare systems, demographics and environmental factors. While a focus on Western countries may provide valuable insights into lifestyle interventions in SSc, extrapolating these findings to populations worldwide should be approached with caution.
In conclusion, this systematic review found physical exercise and mental health management to be efficacious lifestyle interventions for improving functional impairment in patients with SSc, which we therefore advocate should be considered for patients suffering from hand or face involvement, reduced muscle function and reduced physical fitness. Importantly, it is worth mentioning that current evidence overall supports lifestyle interventions as a complement and not a substitute to pharmacotherapy. Future studies, preferably of RCT design, are needed for exploring other aspects of lifestyle interventions, namely concerning diet and nutrition, sleep, harmful exposures and social relations, and how these potentially impact the disease course and patient experience, particularly the degree of disease activity.
Supplementary material is available at Rheumatology Advances in Practice online.
The data underlying this article are available in the article and in its online supplementary material .
I.P. and C.B. were responsible for study conception and design, supervision of study selection and data extraction. I.P., C.G., T.S. and C.B. were responsible for the methodology. I.P., A.T., A.G. and J.C. were responsible for study selection and data extraction. A.T. was responsible for risk of bias assessment. I.P. and A.T. were responsible for drafting the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript and are responsible for its content.
I.P. has received grants from the Swedish Rheumatism Association (R-969696), King Gustaf V’s 80-year Foundation (FAI-2020–0741), Swedish Society of Medicine (SLS-974449), Nyckelfonden (OLL-974804), Professor Nanna Svartz Foundation (2021-00436), Ulla and Roland Gustafsson Foundation (2021-26), Region Stockholm (FoUI-955483) and Karolinska Institutet. C.B. has received grants from the Swedish Rheumatism Association and Norrbacka-Eugeniastiftelsen.
Disclosure statement : I.P. has received research funding and/or honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Aurinia, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Otsuka and Roche. The remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
The authors express gratitude to Emma-Lotta Säätelä, librarian at the KI Library, for her help with the search strategy.
Allanore Y , Simms R , Distler O et al. Systemic sclerosis . Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015 ; 1 : 15002 .
Google Scholar
Sandqvist G , Eklund M. Hand Mobility in Scleroderma (HAMIS) test: the reliability of a novel hand function test . Arthritis Care Res 2000 ; 13 : 369 – 74 .
Mouthon L , Rannou F , Bérezné A et al. Development and validation of a scale for mouth handicap in systemic sclerosis: the Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis scale . Ann Rheum Dis 2007 ; 66 : 1651 – 5 .
American College of Lifestyle Medicine . What is lifestyle medicine? 2022 . https://lifestylemedicine.org/ACLM/ACLM/About/What_is_Lifestyle_Medicine_/Lifestyle_Medicine.aspx?hkey=26f3eb6b-8294-4a63-83de-35d429c3bb88
British Society of Lifestyle Medicine . The pillars of lifestyle medicine. 2022 . https://bslm.org.uk/
Gwinnutt JM , Wieczorek M , Balanescu A et al. 2021 EULAR recommendations regarding lifestyle behaviours and work participation to prevent progression of rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases . Ann Rheum Dis 2022 ; 82 : 48 – 56 .
Parodis I , Girard-Guyonvarc’h C , Arnaud L et al. EULAR recommendations for the non-pharmacological management of systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis . Ann Rheum Dis 2023 ;doi:10.1136/ard-2023-224416.
Parodis I , Gomez A , Tsoi A et al. Systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the non-pharmacological management of systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis . RMD Open 2023 ; 9 : e003297 .
Moher D , Liberati A , Tetzlaff J , Altman DG , PRISMA Group . Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement . PLoS Med 2009 ; 6 : e1000097 .
Aromataris E , Munn Z , eds. JBI manual for evidence synthesis. 2020 . https://synthesismanual.jbi.global (1 April 2024, date last accessed).
Howick J , Chalmers I , Glasziou P et al. The Oxford levels of evidence 2. 2011 . https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/levels-of-evidence/ocebm-levels-of-evidence (1 April 2024, date last accessed).
Stefanantoni K , Sciarra I , Iannace N et al. Occupational therapy integrated with a self-administered stretching program on systemic sclerosis patients with hand involvement . Clin Exp Rheumatol 2016 ; 34(Suppl 100) : 157 – 61 .
Rannou F , Boutron I , Mouthon L et al. Personalized physical therapy versus usual care for patients with systemic sclerosis: a randomized controlled trial . Arthritis Care Res 2017 ; 69 : 1050 – 9 .
Gregory WJ , Wilkinson J , Herrick AL. A randomised controlled trial of wax baths as an additive therapy to hand exercises in patients with systemic sclerosis . Physiotherapy 2019 ; 105 : 370 – 7 .
Filippetti M , Cazzoletti L , Zamboni F et al. Effect of a tailored home-based exercise program in patients with systemic sclerosis: a randomized controlled trial . Scand J Med Sci Sports 2020 ; 30 : 1675 – 84 .
Mugii N , Hasegawa M , Matsushita T et al. The efficacy of self-administered stretching for finger joint motion in Japanese patients with systemic sclerosis . J Rheumatol 2006 ; 33 : 1586 – 92 .
Oliveira NC , dos Santos Sabbag LM , de Sá Pinto AL , Borges CL , Lima FR. Aerobic exercise is safe and effective in systemic sclerosis . Int J Sports Med 2009 ; 30 : 728 – 32 .
Piga M , Tradori I , Pani D et al. Telemedicine applied to kinesiotherapy for hand dysfunction in patients with systemic sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis: recovery of movement and telemonitoring technology . J Rheumatol 2014 ; 41 : 1324 – 33 .
Lima TR , Guimaraes FS , Carvalho MN et al. Lower limb muscle strength is associated with functional performance and quality of life in patients with systemic sclerosis . Braz J Phys Ther 2015 ; 19 : 129 – 36 .
Azar M , Rice DB , Kwakkenbos L et al. Exercise habits and factors associated with exercise in systemic sclerosis: a Scleroderma Patient-centered Intervention Network (SPIN) cohort study . Disabil Rehabil 2018 ; 40 : 1997 – 2003 .
Mitropoulos A , Gumber A , Crank H , Akil M , Klonizakis M. The effects of upper and lower limb exercise on the microvascular reactivity in limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis patients . Arthritis Res Ther 2018 ; 20 : 112 .
Mitropoulos A , Gumber A , Akil M , Klonizakis M. Exploring the microcirculatory effects of an exercise programme including aerobic and resistance training in people with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis . Microvasc Res 2019 ; 125 : 103887 .
Cetin SY , Calik BB , Ayan A. Investigation of the effectiveness of Tai Chi exercise program in patients with scleroderma: a randomized controlled study . Complement Ther Clin Pract 2020 ; 40 : 101181 .
Maddali Bongi S , Passalacqua M , Landi G et al. Rehabilitation of the face and temporomandibular joint in systemic sclerosis . Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 2021 ; 13 : 1759720X211020171 .
Murphy SL , Barber M , Huang S et al. Intensive and app-delivered occupational therapy to improve upper extremity function in early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: a pilot two-arm trial . Rheumatology (Oxford) 2021 ; 60 : 5002 – 11 .
Pizzo G , Scardina GA , Messina P. Effects of a nonsurgical exercise program on the decreased mouth opening in patients with systemic scleroderma . Clin Oral Invest 2003 ; 7 : 175 – 8 .
Pinto AL , Oliveira NC , Gualano B et al. Efficacy and safety of concurrent training in systemic sclerosis . J Strength Cond Res 2011 ; 25 : 1423 – 8 .
Defi IR , Gultom C , Chorman MJ , Jennie J. High-intensity interval training can improve hand grip strength, inspiratory muscle, and quality of life in systemic sclerosis subjects . Reumatologia 2021 ; 59 : 98 – 103 .
Yuen HK , Marlow NM , Reed SG et al. Effect of orofacial exercises on oral aperture in adults with systemic sclerosis . Disabil Rehabil 2012 ; 34 : 84 – 9 .
Uras C , Mastroeni S , Tabolli S et al. A comparison between two educational methods in the rehabilitation of the microstomia in systemic sclerosis: a randomized controlled trial . Clin Rehabil 2019 ; 33 : 1747 – 56 .
Cüzdan N , Türk İ , Çiftçi V et al. The effect of a home-based orofacial exercise program on oral aperture of patients with systemic sclerosis: a single-blind prospective randomized controlled trial . Arch Rheumatol 2021 ; 36 : 176 – 84 .
Gokcen N , Badak SO , Sarpel T , Sertdemir Y , Erken E. The efficacy of a home-based, self-administered hand exercise program for patients with systemic sclerosis: a randomized controlled, evaluator-blind, clinical trial . J Clin Rheumatol 2022 ; 28 : e422–9 .
Yuen HK , Weng Y , Bandyopadhyay D et al. Effect of a multi-faceted intervention on gingival health among adults with systemic sclerosis . Clin Exp Rheumatol 2011 ; 29 (2 Suppl 65): S26 – 32 .
Zanatta E , Rodeghiero F , Pigatto E et al. Long-term improvement in activities of daily living in women with systemic sclerosis attending occupational therapy . Br J Occup Ther 2017 ; 80 : 417 – 22 .
Khanna D , Serrano J , Berrocal VJ et al. Randomized controlled trial to evaluate an internet-based self-management program in systemic sclerosis . Arthritis Care Res 2019 ; 71 : 435 – 47 .
Landim S , Bertolo M , Del Rio A et al. Sustained efficacy of a concise self-management programme for hands in systemic sclerosis: a longitudinal case-control observational study . Rheumatology (Oxford) 2020 ; 59 : 3330 – 9 .
Samuelson UK , Ahlmen EM. Development and evaluation of a patient education program for persons with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) . Arthritis Care Res 2000 ; 13 : 141 – 8 .
Brown SJ , Somerset ME , McCabe CS , McHugh NJ. The impact of group education on participants’ management of their disease in lupus and scleroderma . Musculoskelet Care 2004 ; 2 : 207 – 17 .
Poole J , Conte C , Brewer C et al. Oral hygiene in scleroderma: the effectiveness of a multi-disciplinary intervention program . Disabil Rehabil 2010 ; 32 : 379 – 84 .
Poole JL , Skipper B , Mendelson C. Evaluation of a mail-delivered, print-format, self-management program for persons with systemic sclerosis . Clin Rheumatol 2013 ; 32 : 1393 – 8 .
Poole JL , Mendelson C , Skipper B , Khanna D. Taking charge of systemic sclerosis: a pilot study to assess the effectiveness of an internet self-management program . Arthritis Care Res 2014 ; 66 : 778 – 82 .
Landim SF , Bertolo MB , Marcatto de Abreu MF et al. The evaluation of a home-based program for hands in patients with systemic sclerosis . J Hand Ther 2019 ; 32 : 313 – 21 .
Low AHL , Teng GG , Pettersson S et al. A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial of probiotics in systemic sclerosis associated gastrointestinal disease . Semin Arthritis Rheum 2019 ; 49 : 411 – 9 .
Marighela TF , Arismendi MI , Marvulle V et al. Effect of probiotics on gastrointestinal symptoms and immune parameters in systemic sclerosis: a randomized placebo-controlled trial . Rheumatology (Oxford) 2019 ; 58 : 1985 – 90 .
Frech TM , Khanna D , Maranian P et al. Probiotics for the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated gastrointestinal bloating/distention . Clin Exp Rheumatol 2011 ; 29 (2 Suppl 65): S22 – 5 .
Ortiz-Santamaria V , Puig C , Soldevillla C et al. Nutritional support in patients with systemic sclerosis . Reumatol Clin 2014 ; 10 : 283 – 7 .
Doerfler B , Allen TS , Southwood C et al. Medical Nutrition Therapy for Patients With Advanced Systemic Sclerosis (MNT PASS): a pilot intervention study . J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2017 ; 41 : 678 – 84 .
Guyatt GH , Sullivan MJ , Thompson PJ et al. The 6-minute walk: a new measure of exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure . Can Med Assoc J 1985 ; 132 : 919 – 23 .
Ware JE Jr , Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection . Med Care 1992 ; 30 : 473 – 83 .
Fries JF , Spitz P , Kraines RG , Holman HR. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis . Arthritis Rheum 1980 ; 23 : 137 – 45 .
Berg KO , Wood-Dauphinee SL , Williams JI , Maki B. Measuring balance in the elderly: validation of an instrument . Can J Public Health 1992 ; 83(Suppl 2) : S7 – 11 .
Buysse DJ , Reynolds CF 3rd , Monk TH , Berman SR , Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research . Psychiatry Res 1989 ; 28 : 193 – 213 .
Krupp LB , LaRocca NG , Muir-Nash J , Steinberg AD. The Fatigue Severity Scale. Application to patients with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus . Arch Neurol 1989 ; 46 : 1121 – 3 .
McGill SM , Childs A , Liebenson C. Endurance times for low back stabilization exercises: clinical targets for testing and training from a normal database . Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1999 ; 80 : 941 – 4 .
Cella D , Yount S , Rothrock N et al. The Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS): progress of an NIH Roadmap Cooperative Group during its first two years . Med Care 2007 ; 45 (5 Suppl 1): S3 – 11 .
Duruöz MT , Poiraudeau S , Fermanian J et al. Development and validation of a rheumatoid hand functional disability scale that assesses functional handicap . J Rheumatol 1996 ; 23 : 1167 – 72 .
Law M , Baptiste S , McColl M et al. The Canadian occupational performance measure: an outcome measure for occupational therapy . Can J Occup Ther 1990 ; 57 : 82 – 7 .
Gummesson C , Ward MM , Atroshi I. The shortened disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand questionnaire (QuickDASH): validity and reliability based on responses within the full-length DASH . BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2006 ; 7 : 44 .
Löe H , Silness J. Periodontal disease in pregnancy. I. Prevalence and severity . Acta Odontol Scand 1963 ; 21 : 533 – 51 .
Podshadley AG , Haley JV. A method for evaluating oral hygiene performance . Public Health Rep 1968 ; 83 : 259 – 64 .
Keitel W , Hoffmann H , Weber G , Krieger U. [Evaluation of the percentage of functional decrease of the joints using a motor function test in rheumatology] . Dtsch Gesundheitsw 1971 ; 26 : 1901 – 3 .
Khanna D , Hays RD , Maranian P et al. Reliability and validity of the University of California, Los Angeles Scleroderma Clinical Trial Consortium Gastrointestinal Tract Instrument . Arthritis Rheum 2009 ; 61 : 1257 – 63 .
Keys A , Fidanza F , Karvonen MJ , Kimura N , Taylor HL. Indices of relative weight and obesity . J Chronic Dis 1972 ; 25 : 329 – 43 .
Vigano AL , di Tomasso J , Kilgour RD et al. The abridged patient-generated subjective global assessment is a useful tool for early detection and characterization of cancer cachexia . J Acad Nutr Diet 2014 ; 114 : 1088 – 98 .
Rausch Osthoff AK , Niedermann K , Braun J et al. 2018 EULAR recommendations for physical activity in people with inflammatory arthritis and osteoarthritis . Ann Rheum Dis 2018 ; 77 : 1251 – 60 .
Wieczorek M , Gwinnutt JM , Ransay-Colle M et al. Smoking, alcohol consumption and disease-specific outcomes in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs): systematic reviews informing the 2021 EULAR recommendations for lifestyle improvements in people with RMDs . RMD Open 2022 ; 8 : e002170 .
Supplementary data
Email alerts.
- Rheumatology Twitter
- BSR Twitter
- BSR Facebook
- Advertising and Corporate Services
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 2514-1775
- Copyright © 2024 British Society for Rheumatology
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Literature reviews establish the foundation of academic inquires. However, in the planning field, we lack rigorous systematic reviews. In this article, through a systematic search on the methodology of literature review, we categorize a typology of literature reviews, discuss steps in conducting a systematic literature review, and provide suggestions on how to enhance rigor in literature ...
It's common to confuse systematic and literature reviews because both are used to provide a summary of the existent literature or research on a specific topic. Regardless of this commonality, both types of review vary significantly. The following table provides a detailed explanation as well as the differences between systematic and ...
In general, scoping reviews are commonly used for 'reconnaissance' - to clarify working definitions and conceptual boundaries of a topic or field. Scoping reviews are useful for when a body of literature has not yet been comprehensively reviewed, or exhibits a complex or heterogeneous nature not amenable to a more precise systematic review of the evidence.
A systematic review is a type of review that uses repeatable methods to find, select, and synthesize all available evidence. It answers a clearly formulated research question and explicitly states the methods used to arrive at the answer. Example: Systematic review. In 2008, Dr. Robert Boyle and his colleagues published a systematic review in ...
However, in nursing, empty reviews are seemingly rare; a review of 293 systematic reviews published in nursing science journals found none that included no studies. 4. ... detailed preliminary checking of the literature may be more problematic. If researchers decide not to do a review because they already know there are no eligible studies ...
Systematic reviews and purposive (nonsystematic) reviews serve valuable and complementary roles in synthesizing the results of original research studies. ... All research projects begin with a clear question or purpose, and literature reviews are no exception. As acknowledged above, questions can differ widely, variously focusing on identifying ...
A systematic review collects all possible studies related to a given topic and design, and reviews and analyzes their results [ 1 ]. During the systematic review process, the quality of studies is evaluated, and a statistical meta-analysis of the study results is conducted on the basis of their quality. A meta-analysis is a valid, objective ...
Systematic literature reviews (SRs) are a way of synthesising scientific evidence to answer a particular research question in a way that is transparent and reproducible, while seeking to include all published evidence on the topic and appraising the quality of th is evidence. SRs have become a major methodology
Main. The aims of literature reviews range from providing a primer for the uninitiated to summarizing the evidence for decision making 1. Traditional approaches to literature reviews are ...
Abstract. Performing a literature review is a critical first step in research to understanding the state-of-the-art and identifying gaps and challenges in the field. A systematic literature review is a method which sets out a series of steps to methodically organize the review. In this paper, we present a guide designed for researchers and in ...
Systematic reviews: Structure, form and content. This article aims to provide an overview of the structure, form and content of systematic reviews. It focuses in particular on the literature searching component, and covers systematic database searching techniques, searching for grey literature and the importance of librarian involvement in the ...
2.1.1. Systematic literature review. What is it and when should we use it? Systematic reviews have foremost been developed within medical science as a way to synthesize research findings in a systematic, transparent, and reproducible way and have been referred to as the gold standard among reviews (Davis et al., 2014).Despite all the advantages of this method, its use has not been overly ...
The best reviews synthesize studies to draw broad theoretical conclusions about what a literature means, linking theory to evidence and evidence to theory. This guide describes how to plan, conduct, organize, and present a systematic review of quantitative (meta-analysis) or qualitative (narrative review, meta-synthesis) information.
Step 3: Search the Literature. The quality of literature review is highly dependent on the literature collected for the review—"Garbage-in, garbage-out.". The literature search finds materials for the review; therefore, a systematic review depends on a systematic search of literature. Channels for literature search.
Systematic literature reviews (SRs) are a way of synt hesising scientific evidence to answer a particular. research question in a way that is transparent and reproducible, while seeking to include ...
He is a regular writer for Salisbury Review magazine. In partnershipPurssell and McCrae have written several papers on research methodology and literature reviewing for healthcare journals. Both have extensive experience of teaching literature reviewing at all academic levels, and explaining complex concepts in a way that is accessible to all
This work integrates and summarizes the findings of 105 papers dealing with determinants of no-show in appointment schedul-ing. The average no-show rate across all studies was found to be 23.0%, and further analysis revealed that this rate was highest in the African continent (43.0%) and lowest in Oceania (13.2%).
Purpose: Nowadays, systematic literature reviews (SLRs) and meta-analyses are often placed at the top of the study hierarchy of evidence. The main objective of this paper is to evaluate the trends in SLRs of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) throughout the years. Methods: Medline database was searched, using a highly focused search strategy.
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research.1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis ...
In spite of the growing body of literature on this issue, no synthesis of the state-of-the-art is presently available and no systematic literature review (SLR) exists that encompasses all medical specialties. This paper provides a SLR of no-shows in appointment scheduling in which the characteristics of existing studies are analyzed, results ...
The aim of this systematic literature review is to identify and summarize the published evidence on the use and effectiveness of behavioural economic interventions to reduce no-shows for health ...
4.1 Review methodology. A systematic literature review approach (SLR) was used to answer the research questions. The aim of SLR is "to identify, evaluate, and interpret research relevant to a determined topic area, research question, or phenomenon of interest" (Kitchenham and Charters 2007; Muller et al. 2019, p. 398).
Method details Overview. A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is a research methodology to collect, identify, and critically analyze the available research studies (e.g., articles, conference proceedings, books, dissertations) through a systematic procedure [12].An SLR updates the reader with current literature about a subject [6].The goal is to review critical points of current knowledge on a ...
Receiving touch is of critical importance, as many studies have shown that touch promotes mental and physical well-being. We conducted a pre-registered (PROSPERO: CRD42022304281) systematic review ...
In this work, a systematic review of the literature on predicting patient no-shows is conducted aiming at establishing the current state-of-the-art. Based on a systematic review following the PRISMA methodology, 50 articles were found and analyzed. Of these articles, 82% were published in the last 10 years and the most used technique was ...
In this systematic literature review, 18 of 110 (16.4%) of the included studies discussed that outreach services or mobile clinics in primary care and rural hospital settings can improve access to PHC services in rural communities. Mobile outreach service is defined as healthcare services provided by a mobile team of trained providers, from a ...
Systematic reviews have historically focused on the benefits and harms of interventions; over time, various types of systematic reviews have emerged to address the diverse information needs of clinicians, patients, and policy makers Systematic reviews with traditional components have become defined by the different topics they assess (Table 2.1 ...
This systematic review of the literature assessed the current evidence for lifestyle interventions as viable management strategies for people living with SSc. The main categories of intervention were physical activity and exercise, mental health and diet and nutrition. Physical exercise in general improved functional impairment and aerobic ...
A systematic review was conducted of the literature published between 2010 and 2023 in the PsycINFO, ERIC, Education, and Psychology databases. An initial 1176 studies were reviewed by abstract, of which 485 were read in full text, leading to the selection and analysis of 22 studies.
A systematic review of the literature was conducted based on the selection and search of articles, available in English, Spanish, or Portuguese in the time frame of 1990-2022, of primary and secondary types in the PUBMED, Science Direct, SciELO, and LILACS databases through descriptors (MeSH) together with "AND": "CCR5"; "CCL5 ...