- Hazardous Waste Disposal
- Non-Hazardous Waste Disposal
- Hazardous Waste Training
- Certified Product Disposal
- Hazmat Emergency Response
- Electronic Waste Disposal
- Facility Closures
- Industrial Cleaning Services
- Lab Pack Services
- Medical Waste Disposal
- Pharmaceutical Waste Disposal


How To Create A Hazardous Materials Business Plan
A Hazardous Materials Business Plan (HMBP) is an important document that contains information about hazardous materials used on site at a facility.
In California, some companies are required to create a hazardous materials business plan, depending on the amount or type of hazardous waste on the facility’s premises.
The purpose of this plan is to provide important information about hazardous materials on site to first responders when there is a threat to public health and the environment. It also satisfies federal and state Community Right-to-Know Act laws that require industries to report on the storage and use of hazardous materials.
If your company is required to create an HMBP based on how much hazardous waste that is generated in your facility, below are the steps you will need to take to meet federal, state and local laws.
Know Your County’s Specific Requirements

- 55 gallons in liquid form
- 500 pounds in solid form
- 200 cubic feet of compressed gas
Your facility must also create a HMBP if the materials being used are considered to be “extremely hazardous substances,” per Section 355.61 of Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations.
Additional state and federal requirements are outlined in this Governor’s Office of Emergency Services document . It’s important to note that some counties in California have stricter requirements such as the amount of a chemical that must be included in a facility’s plan. Facilities located in counties that do not have threshold amounts can refer to the California Health and Safety Code for guidance.
Compile And Submit The Plan
California’s Health and Safety Code establishes standards that must be included in a HMBP. Because local authorities may have additional requirements, it is important to check with your local government agency to determine any additional components that must be included in a plan.
In general, HMBPs include four elements:
- Business activities and owner identification
- Hazardous material inventory
- An emergency response plan and employee training
Business Activities And Owner Identification
This part of your HMBP should be pretty straight-forward and is a form found in the facility information section of the California Environmental Reporting System (CERS). This form includes business activities conducted at the facility, as well as information about the owner/operator.
Hazardous Material Inventory
This portion of your HMBP is a list of all the hazardous materials present at your facility that are subject to reporting. These inventory forms must be completed and submitted through CERS as well.
Your list must include all hazardous substances on site and stored in underground tanks. One way to recognize any inventory that is hazardous is by the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) that are provided by the manufacturer, as required by law. SDS documents contain:
- The substance’s chemical composition
- Fire and explosive potential
- Any health hazards
- Reactive characteristics
- Emergency procedures
- Special protection and precautions that should take place
Reported inventory also must include extremely hazardous substances that are in quantities equal to or greater than the “Threshold Planning Quantities,” which are established in the Federal Register or on the EPA website.
Facilities must develop a site map in the event that an emergency occurs and responding personnel must locate hazardous materials. This map, which must be submitted to Certified Unified Program Agencies (CUPA) through CERS, should include items such as:
- Loading areas
- Internal roads and adjacent streets
- Storm and sewer drains
- Access and exit points, including driveway entrances and parking lots
- Emergency shutoffs
- Evacuation staging areas
- Hazardous material handling and storage areas
- Fire hydrants and other connections
- Emergency response equipment, such as fire extinguishers and spill kits
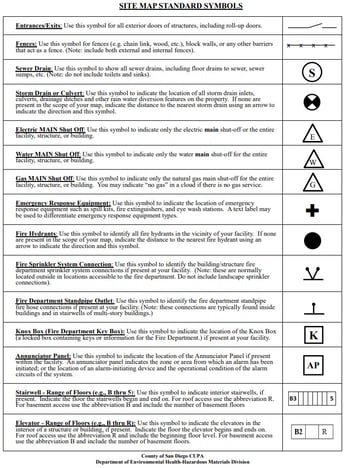
Indicate on the map the North direction, and be sure to label any adjacent properties, especially if they are schools, parks or residential areas.
Check with your local county for rules on using color versus black and white, and whether there are any requirements on whether maps must be drawn on a computer or by hand.
Emergency Response Plan And Employee Training
This portion of the HMBP outlines the facility’s emergency training program and a plan that should be put into action if an emergency occurs.
According to the Health and Safety Code, employees should be trained in disaster preparedness when they are first hired and should be given annual refresher training courses.
Training programs should ensure employees are familiar with the facility’s emergency response plan and should include notification procedures should an emergency occur. The facility’s emergency response plan should include procedures to mitigate harm to employees, the public and the environment.
Not having a proper plan in place can be costly and lead to major fines. Our article, No Hazardous Waste Contingency Plan Leads To Big Fine For Manufacturer , shows why it is important to adequately train staff and have an emergency plan in place.

Review Accuracy
Businesses change, and so may the amount of hazardous materials stored on site. After initially submitting a HMBP through CERS, companies should review the accuracy of their plan on an annual basis.
This is important because any change in hazardous material use or location could impact an emergency response.
Government hazardous materials divisions that inspect facilities will compare materials on site with what is outlined in the HMBP. If any parts do not align, a facility will need to update its HMBP within a certain time period or face fines.
A Critical Component
Facilities that generate hazardous waste and store hazardous materials on site are responsible for these substances from the moment they are generated to their final disposal . Called cradle to grave , this responsibility is critical to ensure the safety of the public and environment.
Creating a hazardous material business plan is a critical component of this requirement since it outlines information about each substance at the facility in the event an emergency occurs. Not having an HMBP can be costly - not only to your facility in the form of fines, but to the safety of employees and first responders as well.
If you need help, contact a hazardous waste disposal company. They can help you create a plan and review your processes to make sure you aren't in violation of any regulations.


CLICK HERE to sign up for LAFD Incident Alerts @ LAFD.org/Alerts

Hazardous Materials
Hazardous Materials Business Plan (HMBP) The Hazardous Materials Business Plan (HMBP) program was established to prevent or minimize the damage to public health and safety and the environment from a release or threatened release of hazardous materials. It also satisfies community right-to-know laws. The plan requires businesses that handle hazardous materials in quantities equal to or greater than 55 gallons of a liquid, 500 pounds of a solid, 200 cubic feet of compressed gas, or extremely hazardous substances above the threshold planning quantity (40 CFR, Part 355, Appendix A) to develop, implement and electronically submit a Hazardous Material Business Plan in the California Environmental Reporting System (CERS) . Please confirm if you meet the threshold reporting requirements HERE .
Components of a Hazardous Materials Business Plan A Hazardous Materials Business Plan consists of six (6) different sections that must be completed and electronically submitted in CERS. All business plans are required to be updated and resubmitted annually between January 1st and March 1st. Below is a brief description of each required section along with reference material to assist with gaining compliance.
This is a list of 12 YES or NO questions related your facility's operations that will determine which CUPA programs your facility will be subject to.
- Ensure that Business Owner information is entered as the LLC or corporation, if applicable. Do not use an individual's name if the business is owned by an LLC or corporation.
- Billing contact information is where the permit and invoice will be sent.
In this section, you will disclose an inventory of the chemicals you handle in quantities that exceed the reportable threshold. For specific information regarding each material you can reference the material's Safety Data Sheet.
Reportable thresholds for hazardous materials and defined in HSC 25507 . The thresholds are determined based on the physical state of the material (solid, liquid, or gas). Below are the basic thresholds for each physical state.
- Solids - 500 pounds
- Liquids - 55 gallons
- Gases - 200 cubic feet
All facilities storing reportable hazardous materials must prepare a site map. The intent is to provide emergency responders with vital information to mitigate hazards while conducting emergency operations. Detailed instructions have been developed to assist facilities in creating a compliant site map:
- Site Map Instructions - Single Building
- Site Map Instructions - Multi-Story Building
- Site Map Instructions - Multi-Building Facility
Regulated facilities are required to develop and implement an Emergency Response Plan and Procedures for immediate response to a reportable release or threatened release of a hazardous material. The state has developed a template to assist businesses to submit the required information linked below. Be aware that the state approved form is not required provided the emergency response plan meets all the requirements set forth in Title 19 CCR 4 § 2658 & HSC 6.95 25505 (a)(3).
- Emergency Response/Contingency Plan Form
- Emergency Response/Contingency Plan Instructions
HSC §25505(a)(4) requires that HMBP's include employee training in safe handling procedures and emergency response plans and procedures. Employees are required to be trained initially and annually thereafter. The Emergency Response/Contingency Plan Form linked above has an Employee Training section (section I) that satisfies your electronic reporting requirements, meaning if you complete this section of the form, you do not need to upload additional documents for employee training. However, you are required to maintain on-site training logs for a minimum of three (3) years.
Compliance Assistance The LAFD CUPA recognizes that regulatory compliance can be challenging. Below are some resources that you can use to achieve compliance, including a list of third-party contractors that can develop and submit a HMBP for your facility.
- Do I Need To Submit a HMBP?
- Instructional Videos
- CERS Contractor List
California Environmental Reporting System (CERS) The California Environmental Reporting System (CERS) is the statewide web-based system that supports the electronic exchange of required Unified Program information among businesses, local governments and the U.S. EPA. Assembly Bill 2286 requires all Unified Program regulated businesses and local regulating Unified Program Agencies (UPAs), to report and submit mandatory Unified Program information electronically, through CERS
- New CERS Account
- Existing CERS Account
- CalEPA CERS Business Portal Training
Reference California Health & Safety Code, Division 20, Chapter 6.95, Article 1 California Code of Regulations, Title 19, Sections 2620-2732 California Code of Regulations, Title 24, Part 9, Section 80.115 Los Angeles Municipal Code, Article 7 of Chapter V, Sections 120 and 120.1.4
Contact Information LAFD CUPA 200 N Main Street, Room 1780 Los Angeles, CA 90012 Phone: (213) 978-3680 Email: [email protected]
Hazardous Materials Business Plans are required to be submitted annually by March 1st . Please utilize the California Environmental Reporting System (CERS) to submit business plans.
CUPA QUICK LINKS
Email: [email protected]
Quick Links
LOCAL — Find Your Station — Fire Safety — Evacuation Info — Disaster Readiness — Volunteer — Smoking Violation — Fire Stat LA — Los Angeles Community Resource Guide for Immigrant Angelenos
STAY UP TO DATE — Alerts — News — Facebook — Twitter — Flickr — Instagram — Reddit — Red Flag No Parking
FIRE PREVENTION — Fire Code — Brush — View Parcel for Brush Clearance Status — Public Assemblage — Schools, Churches — Development — Commercial — CUPA — CalARP — Oil Wells
ABOUT — Central Bureau — South Bureau — Valley Bureau — West Bureau — Special Operations — About LAFD — Contact LAFD

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Hazardous Materials Business Plan (HMBP) aims to prevent or minimize harm to public health and safety and the environment from a release or threatened release of a hazardous material. This is accomplished by providing emergency responders with the necessary information to effectively protect the public.
The HMBP contains detailed information on the storage of hazardous materials at regulated facilities. The purpose of the HMBP is to prevent or minimize damage to public health, safety, and the environment, from a release or threatened release of a hazardous material. The HMBP also provides emergency response personnel with adequate information ...
A Hazardous Materials Business Plan (HMBP) contains basic information on the location, type, quantity, and health risks of hazardous materials stored, used, or disposed of by businesses operating in the state. Chapter 6.95 of the Health ... CONSOLIDATED EMERGENCY RESPONSE/ CONTINGENCY PLAN TEMPLATE CAN BE DOWNLOADED IN CERS. **
This optional template may be used to satisfy requirements that Hazardous Materials Business Plans (HMBP) contain emergency response plans, procedures, and employee training in the event of a reportable/threatened hazardous material release. HSC Section 6.95 Section 25505 (a) (3) 19 CCR Section 5030.9. Employee Training Program.
55 gallons in liquid form. 500 pounds in solid form. 200 cubic feet of compressed gas. Your facility must also create a HMBP if the materials being used are considered to be "extremely hazardous substances," per Section 355.61 of Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations. Additional state and federal requirements are outlined in this ...
Storage of any hazardous materials at or above State-defined thresholds makes a facility subject to the HMBP program. The general thresholds are 55 gallons of a liquid, 200 cubic feet of a gas, and 500 pounds of a solid. There are some exemptions to these thresholds. The Hazardous Materials Compliance Division (HMCD) is responsible for the HMBP ...
LOCAL REQUIREMENTS - If the business owner does not own the property, complete the Property Owner Identification form. ALAMEDA COUNTY DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH. 1131 Harbor Bay Parkway, Alameda, CA 94502-6577 Phone (510) 567-6700 Fax (510) 337-9335. BUSINESS OWNER/OPERATOR. IDENTIFICATION.
Hazardous Materials Release Response Plans and Inventories (Hazardous Materials Business Plan) Aboveground Petroleum Storage Act (APSA) California Fire Code; As a result of Assembly Bill 2286, effective January 1, 2013, the California Environmental Reporting System (CERS) is the only approved method for filing Hazardous Materials Business Plans.
Hazardous Material Business Plan (HMBP) is a document containing detailed information on the: Inventory of hazardous materials at a facility. Emergency response plans and procedures in the event of a reportable release or threatened release of a hazardous material. Training for all new employees and annual training, including refresher courses ...
Hazardous Materials Business Plan Program. ... HMBP Contingency Plan Template. 497.8 KB • pdf • January 25, 2022. get_app; HMBP Guidelines. 867.4 KB • pdf • November 30, 2021. get_app; HMBP Survey. 80.1 KB • pdf • November 30, 2021. get_app; Sample Site Map.
Reporting for the Hazardous Materials Business Plan Program Below Threshold Quantities If the governing body of a UPA has adopted a local law or ordinance requiring a business to report hazardous materials in quantities below those required by Health and Safety Code, Chapter 6.95, Section 25507, the UPA shall implement and enforce this ...
Hazardous Materials Business Plan. CalEPA oversees the statewide implementation of the Hazardous Materials Business. Plan (HMBP) program, which aims to prevent or minimize harm to public health and. safety and the environment from a release or threatened release of a hazardous material. Home.
Components of a Hazardous Materials Business Plan ... Response Plan and Procedures for immediate response to a reportable release or threatened release of a hazardous material. The state has developed a template to assist businesses to submit the required information linked below. Be aware that the state approved form is not required provided ...
The purpose of the Hazardous Materials Business Plan (HMBP) program is to prevent or minimize harm to public health and the environment from a release or threatened release of a hazardous material. By submitting an HMBP, emergency responders can effectively protect the public. The HMBP also satisfies the federal Emergency Planning and Community ...
What is a Hazardous Materials Business Plan (HMBP)? A HMBP is a plan that is used to protect public health and safety and the environment. A HMBP also meets the requirements of the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (EPCRA) that requires emergency planning and reporting on hazardous and toxic chemicals for federal, state, and local government, tribes, and industry.
Hazardous Material Business Plan (HMP) Forms. CUPA HMP Workshop Training Dates and Information. Call (916) 875-2377 or e-mail [email protected] to register to attend the free webinar. You MUST register at least 24 hours before the webinar.
HAZARDOUS MATERIALS BUSINESS PLAN Authority Cited: Ch. 6.95 HSC; Title 19, Div. 2, CCR; Title 22, Div. 4.5, CCR All facilities in Marin County that handle or store hazardous materials (defined as either virgin or waste materials) in a quantity ... Emergency Response/Contingency Plan (Sample forms and instructions attached)
SAMPLE FORMAT OF HAZARDOUS MATERIALS MANAGEMENT PLAN (HMMP) INSTRUCTIONS SECTION I-FACILITY DESCRIPTION 1.1 PartA 1. Fill out Items 1 through 11 and sign the declaration. 2. Only Part A of this section is required to be updated and submitted annually, or within 30 days of a change. 1.2 Part B-General Facility Description (Site Plan) 1.
HMMP (10/20) Page 4of 55. 1 Introduction. The purpose of the Hazardous Materials Management Plan (HMMP) is to describe the proper use, handling and storage practices and procedures to be followed by people working with hazardous materials anywhere on UCCS property to assist in protecting them from potential health and physical hazards presented ...
Adobe PDF and Microsoft Word template versions of this HMBP and a HMBP which includes the standard One-Chemical-Per-Page inventory format are available at www.unidocs.org. You may complete your HMBP on-line using the California Environmental Reporting System (CERS) at https://cers.calepa.ca.gov/cers/. If you wish to use forms other than those ...
A Business Emergency Response Plan and Inventory is required of any facility which handles hazardous materials in amounts equal to or greater than: 55 gallons for liquids. 500 pounds for solids. 200 cubic feet for compressed gases. Please note that if extremely hazardous materials or radiological materials are handled, the business may be ...
California Health and Safety Code §25507(a) and Title 19 California Code of Regulations §2651(a) require that a Hazardous Materials Business Plan (HMBP) facility implement its HMBP, including the training plan specified in HSC §25505(a)(4) and 19 CCR §2659(a)(4). Taking into account the position of each employee, training for new employees ...
CalEPA has issued an update to the regulated community subject to regulation under the Hazardous Materials Business Plan (HMBP) program regarding Assembly Bill (AB) 2059. View the CalEPA update on AB 2059. AB 2059 was approved on September 13, 2022, and is effective on January 1, 2023. This bill amends the California Health and Safety Code (HSC ...