We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.

Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
Brought to you by:

H&M in China
By: Andrew Inkpen, Jonas Gamso
In March 2021, the Chinese government blocked access to H&M on leading e-commerce, ride-hailing, daily-deals, and map sites. The online blocking and calls for customer boycotts were in response to…
- Length: 9 page(s)
- Publication Date: Aug 31, 2021
- Discipline: Business Ethics
- Product #: TB0642-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Teaching Note
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
In March 2021, the Chinese government blocked access to H&M on leading e-commerce, ride-hailing, daily-deals, and map sites. The online blocking and calls for customer boycotts were in response to H&M's September 2020 statement that it would no longer source cotton from Xinjiang because of concerns about forced labor. At the time, H&M operated more than 500 stores in China, and it was the company's fourth largest country market. How will the boycott impact the H&M brand in China? How will H&M's decision impact its brand in other markets, such as the U.S., Germany, and the UK? Should H&M change its sourcing stance in China? Which stakeholders should H&M target in its messaging? Should H&M issue new supply chain statements?
Learning Objectives
In examining H&M in the Chinese market, students will learn about:
The challenges of balancing corporate CSR policies with national market strategies
The risks of CSR decisions on brand reputation
The balance between the benefits of outsourcing and its strategic risks
The relevant stakeholders impacted by CSR decisions
How to respond to local market brand and reputation problems with an action plan
Aug 31, 2021
Discipline:
Business Ethics
Geographies:
Industries:
Retail and consumer goods
Thunderbird School of Global Management
TB0642-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
H&M in China
In March 2021, the Chinese government blocked access to H&M on leading e-commerce, ride-hailing, daily-deals, and map sites. The online blocking and calls for customer boycotts were in response to H&M’s September 2020 statement that it would no longer source cotton from Xinjiang because of concerns about forced labor. At the time, H&M operated more than 500 stores in China, and it was the company’s fourth largest country market. How will the boycott impact the H&M brand in China? How will H&M’s decision impact its brand in other markets, such as the U.S., Germany, and the UK? Should H&M change its sourcing stance in China? Which stakeholders should H&M target in its messaging? Should H&M issue new supply chain statements?

Andrew Inkpen

Jonas Gamso

Product details

Geographical setting
Featured company.

- Share full article
Advertisement
H&M responds to a firestorm in China over Xinjiang cotton.

By Elizabeth Paton
- March 31, 2021
More than a week after the Swedish retailer H&M came under fire in China for a months-old statement expressing concern over reports of Uyghur forced labor in the region of Xinjiang, a major source of cotton, the company published a statement saying it hoped to regain the trust of customers in China.
In recent days, H&M and other Western clothing brands including Nike and Burberry that expressed concerns over reports coming out of Xinjiang have faced an outcry on Chinese social media, including calls for a boycott endorsed by President Xi Jinping’s government. The brands’ local celebrity partners have terminated their contracts, Chinese landlords have shuttered stores and their products have been removed from major e-commerce platforms.
Caught between calls for patriotism among Chinese consumers and campaigns for conscientious sourcing of cotton in the West, some other companies, including Inditex, the owner of the fast-fashion giant Zara, quietly removed statements on forced labor from their websites.
On Wednesday, H&M, the world’s second-largest fashion retailer by sales after Inditex, published a response to the controversy as part of its first quarter 2021 earnings report.
Not that it said much. There were no explicit references to cotton, Xinjiang or forced labor. However, the statement said that H&M wanted to be “a responsible buyer, in China and elsewhere” and was “actively working on next steps with regards to material sourcing.”
“We are dedicated to regaining the trust and confidence of our customers, colleagues, and business partners in China,” it said.
During the earnings conference call, the chief executive, Helena Helmersson, noted the company’s “long-term commitment to the country” and how Chinese suppliers, which were “at the forefront of innovation and technology,” would continue to “play an important role in further developing the entire industry.”
“We are working together with our colleagues in China to do everything we can to manage the current challenges and find a way forward,” she said.
Executives on the call did not comment on the impact of the controversy on sales, except to state that around 20 stores in China were currently closed.
H&M’s earnings report, which covered a period before the recent outcry in China, reflected diminished profit for a retailer still dealing with pandemic lockdowns. Net sales in the three months through February fell 21 percent compared with the same quarter a year ago, with more than 1,800 stores temporarily closed.
Elizabeth Paton is a reporter for the Styles section, covering the fashion and luxury sectors in Europe. Before joining The Times in 2015, she was a reporter at the Financial Times both in London and New York. More about Elizabeth Paton
Explore Our Business Coverage
Dive deeper into the people, issues and trends shaping the world of business..
Ghost Kitchens Are Disappearing: Delivery-only operations boomed during the pandemic. Now Wendy’s, Kroger’s and mom-and-pop food businesses are rethinking their operations.
Axios Shifts Its Strategy: Jim VandeHei, the chief executive of Axios, is becoming one of the first news executives to adjust their company’s strategy because of A.I.
The Worst Part of a Wall Street Career: A.I. tools can replace much of Wall Street’s entry-level white-collar work , raising tough questions about the future of finance.
Combining Business and Leisure Travel: As employees increasingly add leisure time to their business trips , companies are trying to figure out where their duty of care obligations begin and end.
Inside Executive Protection Jobs: Here’s how three women trained to work in jobs protecting prominent families and ultra-high-net-worth individuals.
Gen X-ers Inch Toward Retirement: The oldest members of Generation X are several years from stopping work , but some are already seeking homes that will suit their later years.
Statement on H&M in China
News article.
We are working together with our colleagues in China to do everything we can to manage the current challenges and find a way forward.
China is a very important market to us and our long-term commitment to the country remains strong. Having been present there for more than thirty years, we have witnessed remarkable progress within the Chinese textile industry. Being at the forefront of innovation and technology, China will clearly continue to play an important role in further developing the entire industry. We are proud our suppliers are being part of that development and we want to continue contributing to driving progress together with our partners and stakeholders in the country. We want to be a responsible buyer, in China and elsewhere, and are now building forward-looking strategies and actively working on next steps with regards to material sourcing. Together with all relevant stakeholders, we want to collaborate to be part of the solution and jointly build a more sustainable fashion industry.
As a global company, we comply with local laws and regulatory frameworks in all the markets where we operate. Our company values are built on trust, respect, integrity, and dialogue. We wish to focus on our core business and on what we do best – bringing fashion and design to our customers all around the world.
We are dedicated to regaining the trust and confidence of our customers, colleagues, and business partners in China. By working together with stakeholders and partners, we believe we can take steps in our joint efforts to develop the fashion industry, as well as serve our customers and act in a respectful way.

Global Business

H&M in China

H&M in China ^ TB0642
Want to buy more than 1 copy? Contact: [email protected]
Product Description
Publication Date: August 31, 2021
In March 2021, the Chinese government blocked access to H&M on leading e-commerce, ride-hailing, daily-deals, and map sites. The online blocking and calls for customer boycotts were in response to H&M's September 2020 statement that it would no longer source cotton from Xinjiang because of concerns about forced labor. At the time, H&M operated more than 500 stores in China, and it was the company's fourth largest country market. How will the boycott impact the H&M brand in China? How will H&M's decision impact its brand in other markets, such as the U.S., Germany, and the UK? Should H&M change its sourcing stance in China? Which stakeholders should H&M target in its messaging? Should H&M issue new supply chain statements?

This Product Also Appears In
Buy together, related products.

How Organizations Can Support Employees with Chronic Health Conditions
China's new development bank is a wake-up call for washington.

How to Talk to an Employee Who Isn't Meeting Their Goals
Copyright permissions.
If you'd like to share this PDF, you can purchase copyright permissions by increasing the quantity.
Order for your team and save!

You have no items in your shopping cart.

- Accounting & Control
- Business & Government
- Case Method
- Decision Analysis
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Leadership & Organizational Behavior
- Management Communications
- Operations Management
- Darden Course Pack
- Forio Simulation
- Multimedia Case
- Technical Note
- Video Playlist
Share This Product
H&m, china, and cotton: sourcing a solution, product overview.
In December 2021, Hennes & Mauritz AB (H&M), the Swedish fast-fashion clothing retailer, found itself in a difficult position regarding its business in China, one of the retailer’s important markets. H&M was a member of the sustainability organization, Better Cotton Initiative (BCI), which in March 2020 had suspended activities with licensed farmers in the Xinjiang province of China because of allegations of forced labor and human rights abuses against the Uyghur Muslim minority in that region. H&M’s statement of support for BCI’s actions, released in September 2020, had generated a fierce backlash from China. H&M’s business in that country, both online and in stores, virtually disappeared. Complicating the situation, the option of negotiating peace over Xinjiang cotton had now been taken out of the company’s hands by the passage of the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (HR 1115), signed into law by US president Joe Biden on December 23, 2021, which prohibited “imports made by forced labor into the United States of products made in Xinjiang.” The law would be implemented six months later on June 21, 2022. The European Union (EU), which in October 2021 had promised a ban on imports from the Xinjiang region, was also expected to act on that promise soon. H&M needed to decide how to navigate the tricky and delicate impasse with China. What could the company do about the allegations of human rights abuses in the supply chain when there was no way thus far to irrefutably confirm or deny their existence at the source? And how could it appease China without sacrificing its values and commitment to sustainably sourced cotton? There were few supply options outside China. Additionally, China was a major market. Yet H&M had joined and was committed to the move toward sustainable operations. How could it reconcile the conflicting pressures?
- Add to Cart
- Save to Library
- Learning Objectives
Customers Also Bought
- Sakara Life Weiss, Elliott N.; Goldberg, Rebecca Case
- Devils Backbone Brewing, LLC: An Idea Brews Fairchild, Gregory B.; Floyd, Casey Case
- Darden Capital Management: The Cavalier Fund Schill, Michael J. Case
H&M vows to rebuild trust in China after Xinjiang backlash
- Medium Text
Reporting by Anna Ringstrom and Helena Soderpalm. Additional reporting by Johan Ahlander anf Victoria Waldersee. Editing by Keith Weir, Mark Potter and Jonathan Oatis
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron
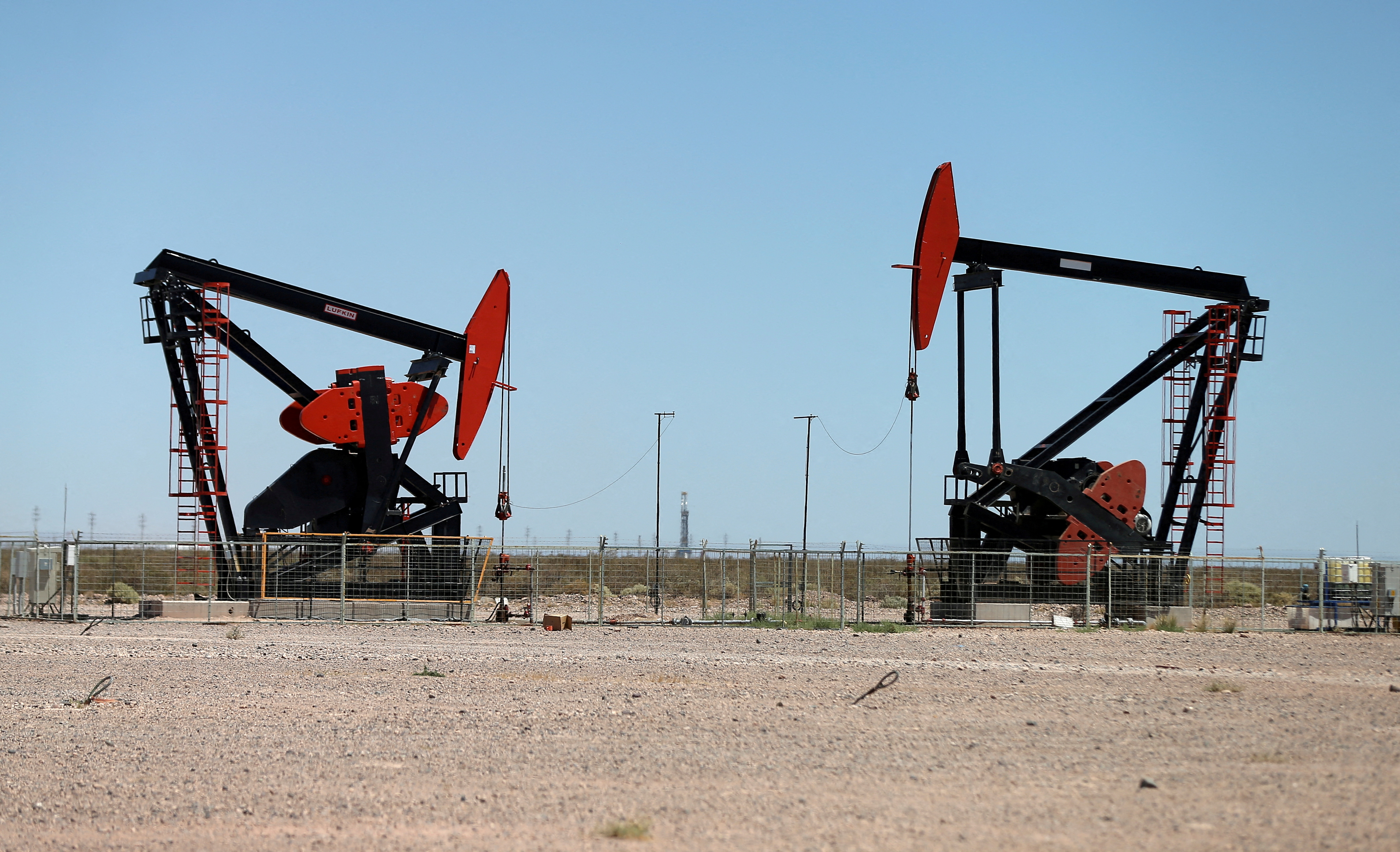

Oil prices steady after rallying on US stock decline, business data
Oil prices steadied above $88 a barrel on Wednesday after rallying in the previous session on a surprise fall in U.S. crude stocks and a drop in business activity in the world's largest oil consumer.

- The Inventory
Support Quartz
Fund next-gen business journalism with $10 a month
Free Newsletters
A year-old H&M statement about Xinjiang cotton is getting fierce blowback in China

H&M is facing a harsh backlash in China over a year-old statement it made expressing concerns about forced labor in Xinjiang.
On Weibo, a large Chinese social media platform, users have called for a boycott of the Swedish fast-fashion chain. It also appears to be blocked on China’s biggest e-commerce sites. On Alibaba’s Tmall platform, H&M’s official store is no longer accessible , and searches for its products on Taobao, Pinduoduo, and JD.com return no results, multiple sources have reported.
Actor Huang Xuan and singer Victoria Song, whom H&M had previously signed as brand ambassadors in the country, both emphasized they were no longer working with H&M. In a statement, Huang said he opposes behavior that “spreads rumor about China and human rights.”
State media has also gone on the attack against H&M. Broadcaster CCTV criticized the company for “eating China’s rice while smashing its pot,” France 24 reports . The Beijing-backed Global Times spotlighted comments from angry social media users calling for H&M to leave China, where H&M had more than 500 stores (pdf) and generated just over $1.1 billion in sales last year.
The uproar appears to have started after the Communist Youth League, once a powerful organization for grooming Chinese officials , lashed out at H&M on Weibo, according to fashion trade outlet WWD (paywall). “Spreading rumors to boycott Xinjiang cotton, while also wanting to make money in China? Wishful thinking!” it said. It included H&M’s statement in reply to the decision by Better Cotton Initiative, an organization focused on improving cotton’s environmental and social sustainability, to stop working in Xinjiang last year.
Western companies risk angering Beijing
The company has addressed its ties to Xinjiang in the past year as Western researchers and authorities allege China is pressing Uyghurs and other predominately Muslim ethnic minorities into forced labor and internment camps. Xinjiang is a major source of products such as cotton and tomatoes believed to be produced with forced labor and that make their way into the supply chains of international corporations. H&M has said (pdf) it is “deeply concerned” by the allegations and that it does not source products from Xinjiang. It declined to comment on the anger it is now contending with in the country.
It’s unclear why a year-old statement has become the center of the outrage online, but it comes as tensions escalate between China and western nations. This week, the US, European Union, and Canada imposed coordinated sanctions on Chinese officials they accused of human rights abuses in Xinjiang. China, which has routinely denied the claims, immediately struck back with sanctions on European officials and organizations.
The situation puts multinational corporations in a sensitive position. Many companies in clothing, footwear, and other industries are trying to distance themselves from ties to Xinjiang. But in doing so, they risk angering Beijing, which has a history of mobilizing citizens to punish foreign companies that take positions opposing its own. The costs can be high. The National Basketball Association lost hundreds of millions over a spat with Beijing after a team’s general manager voiced his support for pro-democracy protesters in Hong Kong.
Companies have refrained from condemning China’s actions in Xinjiang. But plenty have made statements against forced labor and insist they don’t source from the region, including big names such as Nike , Uniqlo , and Inditex , owner of Zara.
Chinese companies may take a different course. Vice News reports that Anta, China’s homegrown sports giant, has released a statement on Weibo saying it has always used Chinese cotton, including from Xinjiang.
📬 Sign up for the Daily Brief
Our free, fast, and fun briefing on the global economy, delivered every weekday morning.

Head of NASA claims China is conducting military experiments in space
If you buy through a BGR link, we may earn an affiliate commission, helping support our expert product labs.
NASA’s administrator, Bill Nelson, is once again making some pretty big claims about China’s ongoing space missions. While it is no secret that China’s secret space plane is doing things we don’t fully understand, Nelson claims that the country’s entire space program is actually just a cover-up for China’s ongoing military space experiments.
That said, China’s advancements in space exploration have improved drastically in the last several years, and Nelson seems to think that’s all because of China’s military space experiments. Of course, these claims are also being thrown around at the same time that Nelson and NASA as a whole are asking for more money, requesting roughly $25.384 billion for funding in 2025.

This isn’t all that surprising, especially considering the problems that NASA’s Mars Sample Return mission are facing right now in regards to budget. The interesting thing is, though, that Nelson doesn’t seem to have any actual data to back up these claims, at least not that he’s openly sharing. Instead, he just continues to make remarks about how China is advancing in the last decade.
Tech. Entertainment. Science. Your inbox.
Sign up for the most interesting tech & entertainment news out there.
By signing up, I agree to the Terms of Use and have reviewed the Privacy Notice.
Sure, that might be troublesome, and who knows, perhaps China is pouring money into its military space experiments. But so far, the country has given no indication publicly that it plans to hoard resources if it gets to the Moon first , or that the Chinese space station is anything more than a traditional research facility just like NASA’s International Space Station. In fact, China has even rebutted such claims that it plans to “steal the Moon.”
Obviously, I cannot speak to the validity of the statements about China’s military space experiments. But I can say that accusations without substantial data to back them up can only enflame tensions even more, and possibly lead to issues with other allies in our space exploration endeavors.
This article talks about:
Josh Hawkins has been writing for over a decade, covering science, gaming, and tech culture. He also is a top-rated product reviewer with experience in extensively researched product comparisons, headphones, and gaming devices.
Whenever he isn’t busy writing about tech or gadgets, he can usually be found enjoying a new world in a video game, or tinkering with something on his computer.
- Former NASA engineer claims he invented a ground-breaking thruster that doesn't need fuel
- NASA's Voyager 1 probe is finally making sense again
More Science

Scientists watched a once-in-a-lifetime evolutionary event happen right before their eyes

Groundbreaking hydrogel can remove microplastics from water

This is your last chance to see the ‘devil comet’ until 2095

Uranus is even more mysterious than we thought
Latest news.

Not enough people are watching this sweet British comedy on Apple TV+

This new fantasy RPG looks perfect for old-school Elder Scrolls fans

The Spider-Man easter egg in the Deadpool 3 trailer is killing us

Meta’s update to its AI-powered Ray-Bans make the case for Apple to make smart glasses
Sign up for the most interesting tech & entertainment news out there.
Study on deformation and failure mechanism of low-dip red bed slope with soft-hard interbedded structure: a case study of Chishui, China
- Original Paper
- Published: 23 April 2024
Cite this article

- Qin Yigen 1 , 2 ,
- Yang Genlan 1 , 2 ,
- Liu Bangyu 3 &
- Xu Jinxing 4
Taking the Chishui Wanglong slope as a case study, the actual deformation characteristics of the slope were obtained through geological field surveys. Using the base contact friction experiment and PFC discrete element numerical simulation, the deformation and failure mechanism of the low-dip red bed soft-hard interbedded slope were investigated. The results indicate that the Wanglong slope is a typical low-dip red bed slope with a soft-hard interbedded structure, characterized by falling and toppling failure as the primary deformation modes. The deformation and failure of the slope are primarily controlled by the depth of the concave cavity formed by differential weathering. Comprehensive analysis reveals that the slope's deformation and failure evolution process can be described as unloading cracks expansion stage, differential weathering stage, and slope deformation and failure stage. The findings of this study can be applied to develop a theoretical framework for determining the prevention and control measures of this type of engineering slope in the Chishui red bed area, which is crucial for reducing the potential risk of geological disasters.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data availability
Due to the nature of this research, participants of this study did not agree for their data to be shared publicly, so supporting data is not available.
Bolton MD, Nakata Y, Cheng YP (2008) Micro- and macro-mechanical behaviour of DEM crushable materials. Géotechnique 58(6):471–480. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.2008.58.6.471
Article Google Scholar
Castro-Filgueira U, Alejano LR, Arzúa J, Ivars DM (2017) Sensitivity analysis of the micro-parameters used in a PFC analysis towards the mechanical properties of rocks. Proc Eng 191:488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.05.208
Chang W, Wang P, Wang H, Chai S, Yu Y, Xu S (2021) Simulation of the Q2 loess slope with seepage fissure failure and seismic response via discrete element method. Bull Eng Geol Env 80(4):3495–3511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02139-z
Cheng Q, Zhou Y, Huang S (2004) Distortion and failure character of excavation slope in approximate level red beds. Rock Soil Mech-Wuhan 25:1311–1314
Google Scholar
Cundall PA, Hart RD (1992) Numerical modelling of discontinua. Eng Comput 9(2):101–113. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb023851
Dong S, Feng W, Feng W, Yin Y, Hu R, Dai H (2019) Examination of rainfall-induced landslide failure mechanisms via a centrifuge physical simulation test. Open J Geol 09(13):1004–1021. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2019.913102
Fan X-M, Xu Q, Zhang Z-Y, Meng D-S, Tang R (2009) The genetic mechanism of a translational landslide. Bull Eng Geol Env 68(2):231–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-009-0194-1
Feng W, Shi Y, Chai H (2004) Study of mechanism of deformation failure of a low-angle bedded high slope with physical simulation method. China J Highw Transp 17(2):32–36
Hai-bo M, Kun-long Y, Gong-hui W (2016) Dynamic mechanism of intermittent reactivation of deep-seated reservoir ancient landslide. Rock Soil Mech 37(9):2645–2653
He H, Dong X, Du S, Guo H, Yan Y, Chen G (2024) Study on the stability of cut slopes caused by rural housing construction in red bed areas: a case study of Wanyuan City, China. Sustainability 16:1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16031344
Huang R, Zhao S, Song X (2008) Formation and mechanical analysis of Tiantai landslide of Xuanhan county, Sichuan province
Huang R (2012) Mechanisms of large-scale landslides in China. Bull Eng Geol Env 71(1):161–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-011-0403-6
Jian W, Wang Z, Yin K (2009) Mechanism of the Anlesi landslide in the three gorges reservoir, China. Eng Geol 108(1–2):86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.06.017
Krasnovskii AA, Mirenkov VE (2009) Determination of boundary conditions in rocks under compression[J]. J Min Sci 45(04):315–323
Li WC, Li HJ, Dai FC, Lee LM (2012) Discrete element modeling of a rainfall-induced flowslide. Eng Geol 149–150:22–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.08.006
Liang Y, Li D, Lu X, Yang X, Pan X, Mu H et al (2010) Soil erosion changes over the past five decades in the red soil region of Southern China. J Mt Sci 7(1):92–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-010-1052-0
Article CAS Google Scholar
Liu J, Wang P, Liu J (2015) Macro- and micro-mechanical characteristics of crushed rock aggregate subjected to direct shearing. Transp Geotech 2:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2014.07.007
Luo Y, Xia B, Li J, Zhang Z (2010) Quantitative evaluation for danger level of geologic hazards in the region of three parallel rivers. Environ Sci Technol 09
Ma S, Wei J, Xu C, Shao X, Xu S, Chai S et al (2020) UAV survey and numerical modeling of loess landslides: an example from Zaoling, southern Shanxi Province, China. Nat Hazards 104(1):1125–1140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04207-1
Marat AR, Tămaş T, Samşudean C, Gheorghiu R (2022) Physico-mechanical and mineralogical investigations of red bed slopes (Cluj-Napoca, Romania). Bull Eng Geol Environ 81:78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02542-6
Potyondy DO, Cundall PA (2004) A bonded-particle model for rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(8):1329–1364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.011
Shangde X, Huiming T, Ruixuan T, Huagang Q (2016) Study on deformation and failure modes of red layer slope in Enshi Basin. J Eng Geol 24(6):1080–1087
Shi C, Li D, Chen K, Zhou J (2016) Failure mechanism and stability analysis of the Zhenggang landslide in Yunnan Province of China using 3D particle flow code simulation. J Mt Sci 13(5):891–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3399-0
Tang C, Hu J, Lin M, Angelier J, Lu C, Chan Y et al (2009) The Tsaoling landslide triggered by the Chi-Chi earthquake, Taiwan: Insights from a discrete element simulation. Eng Geol 106(1–2):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.02.011
Tang H, Yong R, Ez Eldin MAM (2017) Stability analysis of stratified rock slopes with spatially variable strength parameters: the case of Qianjiangping landslide. Bull Eng Geol Env 76(3):839–853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0876-4
Wu Q, Zhang B, Tang H et al (2023) Theoretical study on stability evolution of soft and hard interbedded bedding reservoir slopes. J Mt Sci 20:2744–2755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-023-8073-y
Wu LZ, Zhang LM, Zhou Y, Xu Q, Yu B, Liu GG et al (2018) Theoretical analysis and model test for rainfall-induced shallow landslides in the red-bed area of Sichuan. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77(4):1343–1353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1126-0
Wu Y, Zhang M, Yang L, Liu T, Zhang T, Sun Q et al (2021) Failure mechanisms and dynamics of the Shanzao rockslide in Yongjia County, China on 10 August 2019. Landslides 18(7):2565–2574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01673-x
Xie J, Yang G, Qin Y, Xu X (2020) Deformation failure mechanism and motion laws of near-horizontal thick-layer with thin-layer columnar dangerous rock mass in the chishui red bed area. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science. IOP Publishing, p 022045 2
Xu Q, Liu H, Ran J, Li W, Sun X (2016) Field monitoring of groundwater responses to heavy rainfalls and the early warning of the Kualiangzi landslide in Sichuan Basin, southwestern China. Landslides 13(6):1555–1570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0717-3
Yan Q, Li X, Tang X, Wu Y, He S (2021) Investigation of the strength recovery characteristics of a red-bed landslide soil by SHS and ultrasonic experiments. Bull Eng Geol Env 80(7):5271–5278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02263-w
Yin Y, Cheng Y, Liang J, Wang W (2016) Heavy-rainfall-induced catastrophic rockslide-debris flow at Sanxicun, Dujiangyan, after the Wenchuan Ms 8.0 earthquake. Landslides 13(1):9–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0554-9
Zhang M, Yin Y, Huang B (2015) Mechanisms of rainfall-induced landslides in gently inclined red beds in the eastern Sichuan Basin. SW China Landslides 12(5):973–983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0611-4
Zheng D, Frost JD, Huang RQ, Liu FZ (2015) Failure process and modes of rockfall induced by underground mining: a case study of Kaiyang Phosphorite Mine rockfalls. Eng Geol 197:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.08.011
Zhong Y, Su H, Pan H (2017) Deformation characteristics and mechanism of an excavation slope in red bed area of Chengren highway. Coal Geol Explor 45(2):96–100. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.02.017
Download references
This study was supported by the Basic Research Program of Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Foundation (ZK [2021] Basic 200).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Resource and Environment Engineering, Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025, China
Qin Yigen & Yang Genlan
Key Laboratory of Karst Georesources and Environment, Ministry of Education, Guizhou University, Guiyang, 500025, China
Natural Resources Bureau of Yinjiang Autonomous County, Guizhou Province, Tongren, 555299, China
Sichuan Xingshu Engineering Survey and Design Group Co., Ltd., Chengdu, 610072, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, GY and YQ; methodology, GY and YQ; software, YQ; validation, YQ and BL; formal analysis, GY and BL; investigation, YQ, BL and JX; resources, GY; data curation, BL and JX; writing—original draft preparation, YQ; writing—review and editing, GY; visualization, YQ; supervision, YQ; project administration, GY; funding acquisition, GY All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yang Genlan .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yigen, Q., Genlan, Y., Bangyu, L. et al. Study on deformation and failure mechanism of low-dip red bed slope with soft-hard interbedded structure: a case study of Chishui, China. Nat Hazards (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06617-x
Download citation
Received : 30 March 2023
Accepted : 04 April 2024
Published : 23 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06617-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Soft and hard
- Base contact friction experiment
- Discrete element
- Differential weathering
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
The rectangular tile classification model based on Sentinel integrated images enhances grassland mapping accuracy: A case study in Ordos, China
Affiliations.
- 1 School of Surveying and Land Information Engineering, Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo, Henan, China.
- 2 Research Centre of Arable Land Protection and Urban-Rural High-Quality Development of Yellow River Basin, Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo, China.
- 3 School of Geological Engineering and Geomatics, Chang'an University, Xi'an, China.
- PMID: 38626150
- PMCID: PMC11020762
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301444
Arid zone grassland is a crucial component of terrestrial ecosystems and plays a significant role in ecosystem protection and soil erosion prevention. However, accurately mapping grassland spatial information in arid zones presents a great challenge. The accuracy of remote sensing grassland mapping in arid zones is affected by spectral variability caused by the highly diverse landscapes. In this study, we explored the potential of a rectangular tile classification model, constructed using the random forest algorithm and integrated images from Sentinel-1A (synthetic aperture radar imagery) and Sentinel-2 (optical imagery), to enhance the accuracy of grassland mapping in the semiarid to arid regions of Ordos, China. Monthly Sentinel-1A median value images were synthesised, and four MODIS vegetation index mean value curves (NDVI, MSAVI, NDWI and NDBI) were used to determine the optimal synthesis time window for Sentinel-2 images. Seven experimental groups, including 14 experimental schemes based on the rectangular tile classification model and the traditional global classification model, were designed. By applying the rectangular tile classification model and Sentinel-integrated images, we successfully identified and extracted grasslands. The results showed the integration of vegetation index features and texture features improved the accuracy of grassland mapping. The overall accuracy of the Sentinel-integrated images from EXP7-2 was 88.23%, which was higher than the accuracy of the single sensor Sentinel-1A (53.52%) in EXP2-2 and Sentinel-2 (86.53%) in EXP5-2. In all seven experimental groups, the rectangular tile classification model was found to improve overall accuracy (OA) by 1.20% to 13.99% compared to the traditional global classification model. This paper presents novel perspectives and guidance for improving the accuracy of remote sensing mapping for land cover classification in arid zones with highly diverse landscapes. The study presents a flexible and scalable model within the Google Earth Engine framework, which can be readily customized and implemented in various geographical locations and time periods.
Copyright: © 2024 Guo et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
- Remote Sensing Technology / methods
- Satellite Imagery* / methods
Grants and funding
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
This article is part of the research topic.
Destination Advertising in the Digital Age
A Study on the Construction of Destination Image for China's County-Level Integrated Media Centers: A Case Study of Four Counties in Fuzhou Provisionally Accepted

- 1 Communication University of China, China
- 2 South China University of Technology, China
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
Today, as social media plays an increasingly important role in disseminating destination images, short videos have emerged as the primary channel through which tourists obtain information about their desired destinations. In comparison to traditional methods of using text and pictures, the new media accounts of local government agencies offer a means to convey more comprehensive local news and shape destination images that are more accurate and diverse, leveraging the potential of the short video platform. This study utilizes a combination of manual analysis (subject terms classification) and computer-assisted techniques (key-frame extraction and text mining) to examine the short videos posted on the TikTok (Douyin) platform by the integrated media centers of Minhou County, Yongtai County, Minqing County, and Lianjiang County in Fuzhou City, China. The objective is to explore the shared characteristics and variations in the dimensional aspects of destination images. The findings reveal that the short video contents released by the governmental new media accounts in these four locations primarily highlight three dimensions: stakeholders, urban infrastructures, and regional landscapes. These dimensions are evident in both descriptive texts and visual symbols.However, in terms of the presented destination image, a notable degree of homogeneity is observed, and there is a lack of emphasis on uncovering and presenting the cultural dimensions, thus failing to fully reflect the distinctive local characteristics.Consequently, it is essential for local integrated media centers to thoroughly explore the cultural uniqueness of their respective regions and enhance the development of thematic dimensions in creating short video content. This approach will effectively strengthen tourists' association with and perception of destination images.
Keywords: Short videos, Destination images, TikTok Platform, Governmental New Media, visual symbol
Received: 29 Nov 2023; Accepted: 23 Apr 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Lin, Wen and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Mx. Hanzheng Lin, Communication University of China, Beijing, China
People also looked at

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
H&M's decision to stop using cotton from China's contentious Xinjiang region provoked a furious social-media reaction in early 2021. But the brand—famous around the world for its extensive ...
Bestseller. H&M in China. By: Andrew Inkpen, Jonas Gamso. In March 2021, the Chinese government blocked access to H&M on leading e-commerce, ride-hailing, daily-deals, and map sites. The online blocking and calls for customer boycotts were in response to…. Length: 9 page (s) Publication Date: Aug 31, 2021. Discipline: Business Ethics.
An H&M store in Shanghai, a Zara in Hong Kong, a Burberry store in Shanghai and a Nike store at a shopping area in Beijing. ... This is a perfect case study of what happens when market imperatives ...
Compared to many competitors H&M entered the Chinese market relatively late. In comparison, the Danish retailer Besteller entered the market in the 1970s and the sports brand Nike in the 1980s. However, Inditex, which is H&M's strongest competitor, entered China with its largest brand Zara in 2006, thus, only one year prior to H&M.
H&M entered China in 2007 with the opening of that three-storey flagship store and rapidly expanded. It had more than 500 stores in mainland China early last year but its website currently only ...
H&M's statement of support for BCI's actions, released in September 2020, had generated a fierce backlash from China. H&M's business in that country, both online and in stores, virtually disappeared. ... Darden Case Collection. Subscribe to this free journal for more curated articles on this topic FOLLOWERS. 10,604. PAPERS. 4,558. This Journal ...
In March 2021, the Chinese government blocked access to H&M on leading e-commerce, ride-hailing, daily-deals, and map sites. The online blocking and calls for customer boycotts were in response to H&M's September 2020 statement that it would no longer source cotton from Xinjiang because of concerns about forced labor. At the time, H&M operated more than 500 stores in China, and it was the ...
In H&M's case, the timing of the furor seemed dictated not by anything the retailer did, but by sanctions imposed on Chinese officials last week by the United States, the European Union, Britain ...
July 1 - H&M reports a 28% year-on-year drop, or 23% measured in local currencies, in sales in China in the three months through May to 1.6 billion crowns ($189 million). The H&M brand remains off ...
Abstract. In March 2021, the Chinese government blocked access to H&M on leading e-Commerce, ride-hailing, daily-deals, and map sites. The online blocking and calls for customer boycotts were in response to H&M's September 2020 statement that it would no longer source cotton from Xinjiang because of concerns about forced labor.
March 31, 2021. More than a week after the Swedish retailer H&M came under fire in China for a months-old statement expressing concern over reports of Uyghur forced labor in the region of Xinjiang ...
How does H&M manage its ethical supply chains in China? Learn from this case study on the challenges and opportunities of sustainability in the fashion industry.
Statement on H&M in China. 31 March, 2021. We are working together with our colleagues in China to do everything we can to manage the current challenges and find a way forward. China is a very important market to us and our long-term commitment to the country remains strong. Having been present there for more than thirty years, we have ...
Publication Date: August 31, 2021. In March 2021, the Chinese government blocked access to H&M on leading e-commerce, ride-hailing, daily-deals, and map sites. The online blocking and calls for customer boycotts were in response to H&M's September 2020 statement that it would no longer source cotton from Xinjiang because of concerns about ...
In December 2021, Hennes & Mauritz AB (H&M), the Swedish fast-fashion clothing retailer, found itself in a difficult position regarding its business in China, one of the retailer's important markets. H&M was a member of the sustainability organization, Better Cotton Initiative (BCI), which in March 2020 had suspended activities with licensed farmers in the Xinjiang province of China because ...
The chief executive of H&M said the fashion giant wants to be a "responsible buyer," standing by a human-rights position that triggered the brand's disappearance from China's internet.
STOCKHOLM (Reuters) -H&M vowed on Wednesday to win back trust in China amid growing signs its fashion empire is suffering from a backlash after it voiced concerns last year about alleged human ...
H&M's business model, what the opportunities and threats of H&M's future development in China, and how H&M's business model influences H&M's short-term development as well as long term development. 1.2. Purpose and Research question The main purpose of the study is to examine how H&M business model
Published March 24, 2021. H&M is facing a harsh backlash in China over a year-old statement it made expressing concerns about forced labor in Xinjiang. On Weibo, a large Chinese social media ...
As a part of the Post-Graduation Programme, IIDE's flagship course, 2 students - Shivani Verma & Ritu Bhoite, conducted their thesis project on creating a multi-channel marketing strategy for H&M. This case study is written on the basis of their primary research and hypothetical marketing solution. The case study on H&M will walk you ...
SALES AND DISTRIBUTION CASE STUDY study h&M. ... • Inditex took over H&M in China, as well, but only in China. 6. Products/ Items Overview 7. Apparel Industry • Total market size of the global textiles, apparel and luxury goods market was worth $3049.5 billion in 2011. • Annual compounding growth rate of 3.7% for the period of 2007 to ...
China and NASA are in a race to get to the Moon first. Image source: helen_f / Adobe This isn't all that surprising, especially considering the problems that NASA's Mars Sample Return mission ...
The coupling coordination development of rural revitalization and rural e-commerce is of great significance in promoting the economic growth of rural areas. Based on the observational data of 14 prefectural-level cities in Hunan Province from 2013 to 2021, this study analyzes the spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and driving factors of the coupling coordination development of rural ...
Study area and data. The study area is located at the north of Nanjing, the capital city of Jiangsu province, China, as shown in Fig. 1. The area is essentially featured as a petrochemical industry park, situated many large companies which rank top of their kind in China. Air quality in this area is generally similar to the whole city.
In China, private-owned cooperatives are becoming increasingly involved in agricultural production. In order to find the key characteristics of smallholders' social networks after the appearance of cooperatives and better organize different farmland operators, this study completed a field survey of 114 smallholders who adopted farmland trusteeship service of a private-owned cooperative in ...
Exploring the different characteristics of water status at different time scales is essential for the understanding of the complex hydrological processes in lakes connected to rivers. Taking Dongting Lake, a large-scale lake connected to the Yangtze River, as an example, this study employed wavelet analysis and multiple models to explore the temporal characteristics of water area, level, and ...
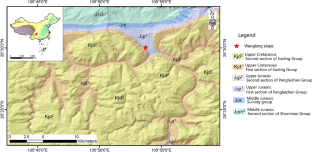
2.1 Engineering geological condition. The study area is situated in Xishui County, Chishui City, Guizhou Province, China. The Wanglong slope under investigation is located adjacent to the Wanglong Town toll station on the Renchi Expressway (Fig. 1), at coordinates 105°53′44′′ E and 28°30′ 03′′ N.It is a steep slope valley landform with an altitude ranging from 310 to 320 m and a ...
In this study, we explored the potential of a rectangular tile classification model, constructed using the random forest algorithm and integrated images from Sentinel-1A (synthetic aperture radar imagery) and Sentinel-2 (optical imagery), to enhance the accuracy of grassland mapping in the semiarid to arid regions of Ordos, China.
This study utilizes a combination of manual analysis (subject terms classification) and computer-assisted techniques (key-frame extraction and text mining) to examine the short videos posted on the TikTok (Douyin) platform by the integrated media centers of Minhou County, Yongtai County, Minqing County, and Lianjiang County in Fuzhou City, China.
Mountainous forests are pivotal in the global carbon cycle, serving as substantial reservoirs and sinks of carbon. However, generating a reliable estimate remains a considerable challenge, primarily due to the lack of representative in situ measurements and proper methods capable of addressing their complex spatial variation. Here, we proposed a deep learning-based method that combines ...