- Terms & Conditions
- Price Match Promise

- Kitchen Appliances
- Spare Parts
- Cooker Hood
- Cooker & Oven
- Fridge / Freezer
- Fridge Water Filters
- Kitchen (Small Appliances)
- Tumble Dryer
- Washing Machine
- Washer Dryer
- Accessories
- Shop By Brand
- Washers & Dryers
- Vacuum Bags
- Vacuum Cleaner
- Floor Polisher
- Steam Cleaner
- Window Vacuum
- Grass Trimmer
- Hedge Trimmer
- Pressure Washer
- DIY Power Tools
- Garden Tractor
- Our Range of Garden Accessories
- Garden Accessories
- Our Range of Garden Watering
- Garden Watering
- Spares & Accessories
- Desktop Computer
- Handheld, PDA, Pocket PC
- Printer & Fax
- Samsung Galaxy
- Tablet PC's
- Photography
- Universal Accessories
- Sound & Vision
- Remote Controls
- Audio & HiFi
- DVD, Video, Home Cinema
- Mobile / Phone
- MP3 & MP4
- TV & Projector
- Home and Garden Cleaning Essentials
- All Purpose Cleaning
- Fabric Care
- Appliance Cleaning
- Garden Essentials
- Energy Saving
- Personal Care
- Kitchen Accessories
- Office Accessories
- General Accessories
- Cables & Connectors
- Batteries & Chargers
- Lighting & Bulbs
- Electrical Accessories
- Household Safety
- Pest Control
- Smart Lighting
- Advice Centre
- Fridge & Freezer
- Vacuum/Steam Cleaners

- Currency ₤ GBP € EUR $ USD Delivery Country Ireland United Kingdom

Gtech Sweeper Repair Guide and Common Faults
You probably find that your Gtech sweeper comes in really handy for fast and efficient cleaning, even in awkward places. Due to its cordless and lightweight design it is the perfect choice for hard floors and many models can also be used as a handheld.
However, occasionally things can go wrong and faults develop. This guide to common Gtech sweeper problems is designed to help you tackle the most common sweeper repairs and maintenance.
For information on how to tackle and resolve faults and problems on a wide range of appliances see our other articles »

As part of your Gtech sweeper repair you may need to purchase a replacement part or consumable item. At BuySpares we sell a range of genuine Gtech vacuum cleaner spare parts for all models of sweeper and cordless vacuum cleaner, including the SW02, SW04 and SW10.
When shopping for sweeper spares you will need to know your model number, which can be found on the rating plate on the underside of the main cleaning unit.
My Gtech Cordless Sweeper No Longer Charges:
There are several reasons why the battery in your Gtech sweeper may not charge. Some of these are really straightforward to correct, while other solutions may require you to purchase a replacement Gtech part.
Firstly check that the on/off button is set to off before you attempt to charge the battery. The sweeper will not charge at all when the start button is 'on'.
Secondly, check that the Gtech charger is correctly connected to the sweeper. It sounds obvious but don't forget to check it is plugged in and switched on.
If these simple checks don't rectify the issue then there may be a fault with the battery or charger. One way to check is to plug the charger in and leave it for a few hours. If after this time period the charger is not warm to touch then it may be that the charger needs to be replaced.
The Battery Runs Down in My Gtech Sweeper Too Fast:
If your Gtech sweeper does not hold its charge then there are a few things you can check before you go out and purchase a replacement battery.
Like all batteries, Gtech sweeper batteries don't last forever and after many hours of constant use they can begin to lose their run time. The first thing to establish is that the battery is charging correctly and that it is fully charged before you use your sweeper.
You should also check for any obstructions, such as blockages and debris, which may be preventing the brush bar from turning freely and causing the sweeper to operate less efficiently. If after these checks the battery is still dying on a regular basis then it is advisable to replace the battery.
Dirt is Being Left Behind or the Sweeper has Lost Pick-Up Performance:
If you are vacuuming and notice that some dirt or debris is not being picked up then you should begin by checking and emptying the sweepers dust tray to ensure it is not overflowing.
If the dust tray is empty and the pick-up performance hasn't improved, turn the sweeper off and inspect it for any signs of damage. It is advisable to start by removing the brush roll and checking it for any damage. Lengths of hair or thread can easily become wrapped around the brush roll and stop the sweeper working effectively and efficiently.
It may be possible to clear the blockage, but failing this you can buy and fit a new Gtech sweeper brush roll and our guide to replacing the brush roll on a Gtech sweeper will help you carry out such a job.

Get the Part: View our range of Gtech Parts
* All information provided is a guide only . BuySpares accepts no liability for any problems occurred while attempting any advice shown. If in any doubt contact a qualified repair service.
Low Prices Guaranteed
We constantly check our prices so you get a good deal!
UK Next Working Day Delivery
Shop until 9pm and still get your order the next working day!
Over 1 Million Customers
We aim to provide exceptional customer service
Over 1.5 Million Products
We have the UK's largest range of Spare parts & Accessories
Sign up for Exclusive BuySpares Deals & Offers
By submitting your details you agree to our Terms and Conditions and understand our Privacy Policy
- Recruitment
- Become an affiliate
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Cookie Settings
- Finding My Model Number
- Delivery Information
- Order Tracking
- Returns Procedure
- Terms & Conditions
- Site Use Policy
- Safety Information
- Hotpoint Spares
- Dyson Spares
- Bosch Spares
- Samsung Spares
- Whirlpool Spares
- Cooker Spares
- Dishwasher Spares
- Fridge & Freezer Spares
- Washing Machine Spares
- Vacuum Cleaner Spares
- Cooker Knobs
- Cutlery Baskets
- Fridge Shelves
- Oven Elements

BuySpares - Buy genuine replacement spares, spare parts and accessories for all your Home and Garden Electrical Appliances
We value your privacy
We use small text files called cookies to give you the best experience on our website and help us show you relevant information. You can choose whether to manage these or allow them all. View Cookie Policy.
Manage your cookies
We use small text files called cookies to give you the best experience on our website and help us show you relevant information. You can choose whether to manage these or allow them all. See our cookies page for more information.

Why Is My Gtech Hedge Trimmer Not Working? (Solve the Problem Now)

Are you having trouble with your Gtech hedge trimmer ? Don’t worry, you’re not alone.
Many people struggle with this common issue.
In this article, we’ll provide step-by-step instructions on how to solve the problem.
We’ll cover what could be causing the issue, how to check the battery, motor, and blades, as well as troubleshooting tips and when to seek professional help.
So if your Gtech hedge trimmer isn’t working, read on to find out how to solve the problem!
Table of Contents
Short Answer
It could be a few things.
First, check the battery and make sure it is charged.
If the battery is charged and the trimmer still isn’t working, check the connection between the battery and the motor.
If everything looks good there, then it’s likely a problem with the motor itself, and you may need to take it in for repair.
What Could Be Causing the Issue?
If your Gtech hedge trimmer is not working properly, there could be a few different causes.
The most common ones are a faulty battery, an issue with the motor, or a blockage in the blade.
To determine the exact cause, you’ll need to troubleshoot the trimmer to check for any visible signs of damage.
If the issue is with the battery, make sure it is fully charged.
This can be done by plugging the battery into the charger and waiting for the indicator light to turn green.
If the battery is still not working, you may need to replace it.
If the issue is with the motor, you should check for any loose connections or wiring.
This can be done by opening up the trimmer and inspecting the connections.
If any of them appear loose, you may need to tighten them.
You should also check for any exposed wiring that could be causing the issue.
Finally, if the issue is with the blade, you should clean any debris or dirt from the blade and check for any obstructions.
This can be done by using a soft cloth and wiping down the blade.
You should also use a pair of tweezers or a small brush to inspect the blade for any obstructions.
If any are found, they should be removed.
Once the issue has been identified, you can then take the appropriate measures to fix it.
If the issue is with the battery, it may need to be replaced.
If the issue is with the motor, you may need to tighten the connections or replace any exposed wiring.
If the issue is with the blade, you may need to clean it or remove any obstructions.
It is important to remember that troubleshooting the trimmer is the first step in solving the issue.
Taking the time to identify the cause of the problem can save you time and money in the long run.
Checking the Battery

When it comes to troubleshooting a Gtech hedge trimmer, the first thing to check is the battery.
If the trimmer is not working, it could be due to a faulty battery or an issue with the motor.
To find out the exact cause, you should check the battery for any visible signs of damage.
If the battery appears to be in good condition, you should ensure it is fully charged.
To do this, connect the battery to the trimmer and plug it into a power source.
Depending on the model of trimmer you have, the charging time can vary.
Generally, it should take around 2-3 hours to charge a completely empty battery.
Once the battery is fully charged, check to see if the trimmer is working.
If it is, then the battery was likely the cause of the issue.
However, if the trimmer is still not working, then you should proceed to check the motor.
Checking the Motor
When it comes to troubleshooting a Gtech hedge trimmer that is not working, one of the first things you should check is the motor.
The motor is the heart of the trimmer and it is what powers the blade.
If the motor is not functioning properly, then the trimmer will not be able to cut through the hedges.
To check the motor, you should first inspect it for any visible signs of damage.
This includes looking for any cracks in the housing, any loose wires, or any other signs of wear and tear.
Next, you should check the wiring to ensure that it is securely connected and that there are no loose connections.
This is especially important if the trimmer has been in storage for a few months.
If you notice any damaged wiring, you should replace it before attempting to use the trimmer again.
Finally, if you have access to a multimeter, you can use it to check the voltage of the motor.
This will tell you if the motor is receiving enough power to function properly.
If the voltage is too low, then it could be due to a faulty battery or a faulty connection.
In this case, you should replace the battery or the connection before attempting to use the trimmer again.
Checking the Blades

When trying to diagnose why your Gtech hedge trimmer isn’t working, it’s important to check the blades for any obstructions.
If you notice any dirt, debris, or other obstructions stuck in the blade, you’ll need to clean it out before you can continue troubleshooting.
Start by removing any clippings or dirt that is stuck in the blade.
Then, take a look at the blades to make sure they are properly aligned and there are no obstructions.
You may also want to check for any signs of damage, such as bent or broken blades.
If the blades are not properly aligned, you can try to realign them yourself or take it to a professional to have it serviced.
Additionally, you should also check for any blockages in the blade guard or in the power cord.
If you determine that the blades are the source of the problem, you’ll need to replace the blades or take it to a professional for servicing.
Cleaning the Blades
One of the most common causes of a Gtech hedge trimmer not working is a blockage in the blade.
Fortunately, cleaning the blades of your trimmer is relatively easy and straightforward.
To begin, make sure the trimmer is unplugged and the battery is removed.
Then, carefully inspect the blades for any debris or dirt that may be stuck in them.
If you find any, use a small brush to gently remove it.
You can also use a can of compressed air to blow away any stubborn dirt or debris.
Make sure to clean the blades on both sides of the trimmer and to inspect for any obstructions.
If you find any, use a small pair of pliers to remove them.
Once youve finished cleaning the blades, use a light oil to lubricate them and then reassemble the trimmer.
With a few simple steps, youll have your Gtech hedge trimmer working again in no time.
Troubleshooting Tips

When your Gtech hedge trimmer stops working, it can be a frustrating experience. There are a few different things that could be causing the issue, and it is important to troubleshoot the trimmer to identify the exact cause. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you get your hedge trimmer up and running again:
1. Check the battery. If your Gtech hedge trimmer has a rechargeable battery, make sure it is fully charged. If the battery is not charged, plug the charger into an outlet and charge the battery. If the battery is still not working, it may need to be replaced.
2. Check the motor. If the motor is not working properly, it could be due to a loose connection or wiring. Carefully inspect the motor to see if any connections are loose or broken. If any are, make sure to tighten or repair them.
3. Clean the blade. If the blade is not working properly, it could be due to debris or dirt blocking the blade. Carefully inspect the blade and clean any debris or dirt from it. Make sure to also check for any obstructions that may be blocking the blade.
By following these troubleshooting tips, you can identify the exact cause of your Gtech hedge trimmer not working and take the necessary steps to fix it.
It is always a good idea to consult the user manual for your Gtech hedge trimmer to get more detailed instructions on how to troubleshoot and fix any issues.
Seeking Professional Help
If your Gtech hedge trimmer is still not working after completing the troubleshooting steps outlined above, it may be time to seek professional help.
Depending on the age and condition of your trimmer, it may be more cost-effective to contact a qualified technician to repair the device rather than purchasing a new one.
A qualified technician will be able to diagnose the issue and determine the best course of action.
They may be able to repair the trimmer or suggest a new or better model that meets your needs.
When seeking professional help, it is important to find a qualified and experienced technician who is knowledgeable about Gtech hedge trimmers .
You can find a technician by contacting Gtech directly or by checking local listings.
Alternatively, you can search online to find a technician in your area.
When speaking with a technician, make sure to provide as much information as possible about the issue, such as the model and serial number of your trimmer.
This will help the technician diagnose the problem quickly and accurately.
Additionally, make sure to ask about the cost of repair and any warranties that may be available on the repair.
By seeking professional help, you can ensure that your Gtech hedge trimmer is properly repaired and functioning as it should.
With the help of a qualified technician, you can get your trimmer back to working order in no time.
Final Thoughts
By troubleshooting your Gtech hedge trimmer, you can quickly and easily identify what is causing the issue.
With the right steps, you can easily diagnose and solve the problem yourself.
However, if you are unable to resolve the issue, it is best to contact a professional for help.
With the right information and advice, you can have your trimmer working again in no time!
James Lopez
James Lopez is a lifestyle journalist. In addition to working as a journalist, he also takes courses in landscape design. He is pretty focused on the outdoor space, especially the backyard.
Recent Posts
What to Do with Pine Cones Gardening: Creative Tips and Ideas
Pine cones can be a versatile and natural addition to your gardening routine. You can use them as a decorative element in flower beds or outdoor planters to add a rustic touch to your garden. Another...
How to Start Gardening From Scratch? Your Ultimate Beginner's Guide
To start gardening from scratch, begin by choosing a suitable location with adequate sunlight and access to water. Next, prepare the soil by removing any weeds and debris, then add compost or...
Log in or Sign up
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly. You should upgrade or use an alternative browser .
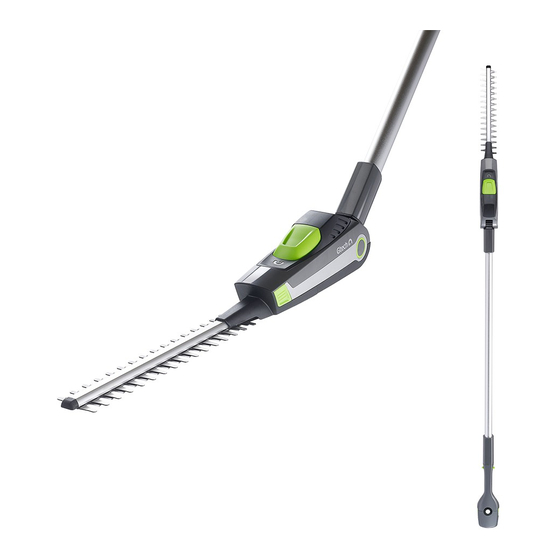
Gtech HT20 cordless hedge trimmer problem
Discussion in ' Landscaping and Outdoors ' started by Puffer , Jun 15, 2021 .
Puffer Member
My Gtech HT20 trimmer has given me more than one problem in its relatively short life. It now appears that one of the drive belts has broken, rendering the trimmer useless. Replacement belts are readily available (but not from Gtech) and people seem to have had no problem in fitting them. But, despite my skills with mechanical items (and all relevant tools), I cannot fully remove the casing on the head to access the belts! Gtech is useless when it comes to providing help with this, or similar problems. It does not 'advise' removal of the head cover and cannot or will not explain how to do so. It is of course willing to sell me a new head (quite unnecessary) for £60. Can anyone please explain how to remove the black casing from the head? I have it loose but I still cannot prise it away from the cast body.
Rich1 New Member
Puffer said: ↑ My Gtech HT20 trimmer has given me more than one problem in its relatively short life. It now appears that one of the drive belts has broken, rendering the trimmer useless. Replacement belts are readily available (but not from Gtech) and people seem to have had no problem in fitting them. But, despite my skills with mechanical items (and all relevant tools), I cannot fully remove the casing on the head to access the belts! Gtech is useless when it comes to providing help with this, or similar problems. It does not 'advise' removal of the head cover and cannot or will not explain how to do so. It is of course willing to sell me a new head (quite unnecessary) for £60. Can anyone please explain how to remove the black casing from the head? I have it loose but I still cannot prise it away from the cast body. Click to expand...
David Harper New Member
Hi- I’m struggling with this repair. Can’t seem to get the new belt on. Any tips? The rim around the cogs seems to prevent it from coming off but also from going on…..but there must be a way!
Attached Files:
03ba61dd-cf6d-476d-83d5-def95949251d.jpeg.
chesterw Well-Known Member
There will be some method of tensioning any drive belt, find that and loosen it off
Hi- turned out you can drop the large cog a few mm after prizing off a small retaining clip. Then there was enough space to get the belt in underneath. Small picture enclosed in case anyone else is searching the thread in future. It needed a small tap with a hummer to get it to move after the clip came off.
57606A00-B7EA-49F7-877D-675BC724927E.jpeg
Chrisparf New Member
David Harper said: ↑ Hi- I’m struggling with this repair. Can’t seem to get the new belt on. Any tips? The rim around the cogs seems to prevent it from coming off but also from going on…..but there must be a way! Click to expand...
Share This Page
- Log in with Facebook
- No, create an account now.
- Yes, my password is:
- Forgot your password?

- Search titles only
Separate names with a comma.
- Search this thread only
- Display results as threads
Useful Searches
- Recent Posts
- This site uses cookies to help personalise content, tailor your experience and to keep you logged in if you register. By continuing to use this site, you are consenting to our use of cookies. Accept Learn More... Dismiss Notice

- Gtech Manuals
- Operating manual
Gtech HT20 Operating Manual
- Operating manual (89 pages)
- page of 21 Go / 21
Table of Contents
- Troubleshooting
- Important Safeguards
- Personal Safety
- Electrical Safety
- Battery Safety
- Maintenance and Storage
- Intended Use
- Warning Label Descriptions
- What’s in the Box
- Rotating the Hedge Trimmer Blade
- Removing the Blade
- Using Your Hedge Trimmer
- Removing the Battery for Charging
- Checking Battery Charge Status
- Charging the Battery
- Reconnecting Battery to Hedge Trimmer
- Product Care
- Hedge Trimmer Technical Specification
- Environmental and Product Recycling
- Warranty – Terms and Conditions
- Ec Declaration of Conformity
Advertisement
Quick Links
- 1 Maintenance and Storage
- 3 Operation
- 4 Rotating the Hedge Trimmer Blade
- 5 Removing the Blade
- 6 Charging the Battery
- 7 Troubleshooting
- Download this manual
Related Manuals for Gtech HT20

Summary of Contents for Gtech HT20
- Page 1 Cordless Hedge Trimmer Model number: HT20 OPERATING MANUAL ORIGINAL INSTRUCTIONS 2016...
- Page 2 IMPORTANT SAFEGUARDS: IMPORTANT: READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USE. RETAIN INSTRUCTIONS FOR FUTURE REFERENCE. Do not use in rain or leave outdoors whilst raining. WARNING: Basic safety precautions should always be observed when using an electrical appliance to reduce the risk of fire, electrical shock or serious injury.
Page 3: Battery Safety
Page 4: maintenance and storage.
- Page 5 Warning Label Descriptions Measured sound power level: 90.47dB(A) Read instruction Guaranteed sound power level: 94dB(A) manual before use Note: Measured noise values determined according to 2000/14 EC (1.60m height, 1.0m distance away). Wear eye protection when using this product. Do not use in rain or leave outdoors whilst raining.
- Page 6 Your opinion is important to us. Please take the time to write a review of your new Hedge Trimmer at Trustpilot.co.uk. We will use your feedback to improve our products and services and let other people know what it’s like to be part of the Gtech family.” Nick Grey –...
- Page 7 Assembly Hedge trimmer head Hedge trimmer main body When inserting the body into the hedge trimmer head, ensure the body is the right way up. The shapes need to match or the handle will not fit. Fit the head to the main body With the blade cover still on, connect the hedge trimmer blade to the head.
- Page 8 Operation safety button (located both sides) safety button located both sides trigger Push and hold the safety button on either When you release the trigger the hedge side, then press the trigger to operate. trimmer will stop. Rotating the hedge trimmer blade Firmly grip the head of the trimmer and press and hold the green button.
- Page 9 Removing the blade Remove the battery and ensure the cover is Press the green buttons on either side of on the blade. the trimmer head. The blade will pivot away from the head.
- Page 10 Up high Firmly grip the base and lower end of the pole for reaching high hedge tops. Standard reach Firmly grip the base and middle section of the pole for reaching standard height hedge tops. Firmly grip the handle and lower end of the pole for trimming the bottom of hedges.
- Page 11 Using your hedge trimmer Hold the trimmer away from your body using both hands and stand on a solid and secure surface. The double edge blade allows you to cut with either a side to side or up and down motion: When cutting move slowly and steadily so that stems are fed directly into the blade.
- Page 12 Removing the battery for charging Press both buttons at the same time and pull to remove the battery. Checking battery charge status 100% - 60% - 30% -10% - 1% Figures are approximate. Press the button to check how much charge The number of lit LEDs shows the charge.
Page 13: Charging The Battery
- Page 14 To reduce risk of injury ensure that protective blade guard is fitted when the trimmer is not in use, being transported, handled or stored. To ensure that your HT20 gives you long and reliable service, carry out the following maintenance regularly: •...
Page 15: Troubleshooting
- Page 16 HEDGE TRIMMER TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Blade length 315mm Blade cutting width 15mm No load speed 1120min-1 Battery 18V DC 2000mAh Li-ion Charging period 4 hours Battery charger output 0.5A Battery charger input 100-240V~50/60Hz Battery charger type K135s270050B Measure sound power level, LpA,d 88.28dB(A) K:2.45dB(A) Guaranteed sound power level, LwA,d 96dB(A) Weight...
- Page 17 Environmental and Product Recycling symbol indicates that this product is covered by legislation for waste electrical and electronic products (EN2002/96/EC) When the product has reached the end of its life please do not dispose of it with general household waste. Consider the environment and take it to a recognised recycling facility. The product contains a Li-Ion battery which should not be disposed of with general household waste.
- Page 18 • Repairs or alterations carried out by parties other than Gtech or its authorised agents. • If you are in doubt as to what is covered by your warranty, please call the Gtech Customer Care Helpline on 01905 345 891.
Page 19: Ec Declaration Of Conformity
- Page 20 Grey Technology Limited Cupola Court, Spetchley, Worcestershire WR5 1RL email: [email protected] telephone: 01905 345891 www.gtech.co.uk...
Rename the bookmark
Delete bookmark, delete from my manuals, upload manual.
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
What Is Problem Solving? How Software Engineers Approach Complex Challenges

From debugging an existing system to designing an entirely new software application, a day in the life of a software engineer is filled with various challenges and complexities. The one skill that glues these disparate tasks together and makes them manageable? Problem solving .
Throughout this blog post, we’ll explore why problem-solving skills are so critical for software engineers, delve into the techniques they use to address complex challenges, and discuss how hiring managers can identify these skills during the hiring process.
What Is Problem Solving?
But what exactly is problem solving in the context of software engineering? How does it work, and why is it so important?
Problem solving, in the simplest terms, is the process of identifying a problem, analyzing it, and finding the most effective solution to overcome it. For software engineers, this process is deeply embedded in their daily workflow. It could be something as simple as figuring out why a piece of code isn’t working as expected, or something as complex as designing the architecture for a new software system.
In a world where technology is evolving at a blistering pace, the complexity and volume of problems that software engineers face are also growing. As such, the ability to tackle these issues head-on and find innovative solutions is not only a handy skill — it’s a necessity.
The Importance of Problem-Solving Skills for Software Engineers
Problem-solving isn’t just another ability that software engineers pull out of their toolkits when they encounter a bug or a system failure. It’s a constant, ongoing process that’s intrinsic to every aspect of their work. Let’s break down why this skill is so critical.
Driving Development Forward
Without problem solving, software development would hit a standstill. Every new feature, every optimization, and every bug fix is a problem that needs solving. Whether it’s a performance issue that needs diagnosing or a user interface that needs improving, the capacity to tackle and solve these problems is what keeps the wheels of development turning.
It’s estimated that 60% of software development lifecycle costs are related to maintenance tasks, including debugging and problem solving. This highlights how pivotal this skill is to the everyday functioning and advancement of software systems.
Innovation and Optimization
The importance of problem solving isn’t confined to reactive scenarios; it also plays a major role in proactive, innovative initiatives . Software engineers often need to think outside the box to come up with creative solutions, whether it’s optimizing an algorithm to run faster or designing a new feature to meet customer needs. These are all forms of problem solving.
Consider the development of the modern smartphone. It wasn’t born out of a pre-existing issue but was a solution to a problem people didn’t realize they had — a device that combined communication, entertainment, and productivity into one handheld tool.
Increasing Efficiency and Productivity
Good problem-solving skills can save a lot of time and resources. Effective problem-solvers are adept at dissecting an issue to understand its root cause, thus reducing the time spent on trial and error. This efficiency means projects move faster, releases happen sooner, and businesses stay ahead of their competition.
Improving Software Quality
Problem solving also plays a significant role in enhancing the quality of the end product. By tackling the root causes of bugs and system failures, software engineers can deliver reliable, high-performing software. This is critical because, according to the Consortium for Information and Software Quality, poor quality software in the U.S. in 2022 cost at least $2.41 trillion in operational issues, wasted developer time, and other related problems.
Problem-Solving Techniques in Software Engineering
So how do software engineers go about tackling these complex challenges? Let’s explore some of the key problem-solving techniques, theories, and processes they commonly use.
Decomposition
Breaking down a problem into smaller, manageable parts is one of the first steps in the problem-solving process. It’s like dealing with a complicated puzzle. You don’t try to solve it all at once. Instead, you separate the pieces, group them based on similarities, and then start working on the smaller sets. This method allows software engineers to handle complex issues without being overwhelmed and makes it easier to identify where things might be going wrong.
Abstraction
In the realm of software engineering, abstraction means focusing on the necessary information only and ignoring irrelevant details. It is a way of simplifying complex systems to make them easier to understand and manage. For instance, a software engineer might ignore the details of how a database works to focus on the information it holds and how to retrieve or modify that information.
Algorithmic Thinking
At its core, software engineering is about creating algorithms — step-by-step procedures to solve a problem or accomplish a goal. Algorithmic thinking involves conceiving and expressing these procedures clearly and accurately and viewing every problem through an algorithmic lens. A well-designed algorithm not only solves the problem at hand but also does so efficiently, saving computational resources.
Parallel Thinking
Parallel thinking is a structured process where team members think in the same direction at the same time, allowing for more organized discussion and collaboration. It’s an approach popularized by Edward de Bono with the “ Six Thinking Hats ” technique, where each “hat” represents a different style of thinking.
In the context of software engineering, parallel thinking can be highly effective for problem solving. For instance, when dealing with a complex issue, the team can use the “White Hat” to focus solely on the data and facts about the problem, then the “Black Hat” to consider potential problems with a proposed solution, and so on. This structured approach can lead to more comprehensive analysis and more effective solutions, and it ensures that everyone’s perspectives are considered.
This is the process of identifying and fixing errors in code . Debugging involves carefully reviewing the code, reproducing and analyzing the error, and then making necessary modifications to rectify the problem. It’s a key part of maintaining and improving software quality.
Testing and Validation
Testing is an essential part of problem solving in software engineering. Engineers use a variety of tests to verify that their code works as expected and to uncover any potential issues. These range from unit tests that check individual components of the code to integration tests that ensure the pieces work well together. Validation, on the other hand, ensures that the solution not only works but also fulfills the intended requirements and objectives.
Explore verified tech roles & skills.
The definitive directory of tech roles, backed by machine learning and skills intelligence.
Explore all roles
Evaluating Problem-Solving Skills
We’ve examined the importance of problem-solving in the work of a software engineer and explored various techniques software engineers employ to approach complex challenges. Now, let’s delve into how hiring teams can identify and evaluate problem-solving skills during the hiring process.
Recognizing Problem-Solving Skills in Candidates
How can you tell if a candidate is a good problem solver? Look for these indicators:
- Previous Experience: A history of dealing with complex, challenging projects is often a good sign. Ask the candidate to discuss a difficult problem they faced in a previous role and how they solved it.
- Problem-Solving Questions: During interviews, pose hypothetical scenarios or present real problems your company has faced. Ask candidates to explain how they would tackle these issues. You’re not just looking for a correct solution but the thought process that led them there.
- Technical Tests: Coding challenges and other technical tests can provide insight into a candidate’s problem-solving abilities. Consider leveraging a platform for assessing these skills in a realistic, job-related context.
Assessing Problem-Solving Skills
Once you’ve identified potential problem solvers, here are a few ways you can assess their skills:
- Solution Effectiveness: Did the candidate solve the problem? How efficient and effective is their solution?
- Approach and Process: Go beyond whether or not they solved the problem and examine how they arrived at their solution. Did they break the problem down into manageable parts? Did they consider different perspectives and possibilities?
- Communication: A good problem solver can explain their thought process clearly. Can the candidate effectively communicate how they arrived at their solution and why they chose it?
- Adaptability: Problem-solving often involves a degree of trial and error. How does the candidate handle roadblocks? Do they adapt their approach based on new information or feedback?
Hiring managers play a crucial role in identifying and fostering problem-solving skills within their teams. By focusing on these abilities during the hiring process, companies can build teams that are more capable, innovative, and resilient.
Key Takeaways
As you can see, problem solving plays a pivotal role in software engineering. Far from being an occasional requirement, it is the lifeblood that drives development forward, catalyzes innovation, and delivers of quality software.
By leveraging problem-solving techniques, software engineers employ a powerful suite of strategies to overcome complex challenges. But mastering these techniques isn’t simple feat. It requires a learning mindset, regular practice, collaboration, reflective thinking, resilience, and a commitment to staying updated with industry trends.
For hiring managers and team leads, recognizing these skills and fostering a culture that values and nurtures problem solving is key. It’s this emphasis on problem solving that can differentiate an average team from a high-performing one and an ordinary product from an industry-leading one.
At the end of the day, software engineering is fundamentally about solving problems — problems that matter to businesses, to users, and to the wider society. And it’s the proficient problem solvers who stand at the forefront of this dynamic field, turning challenges into opportunities, and ideas into reality.
This article was written with the help of AI. Can you tell which parts?
Get started with HackerRank
Over 2,500 companies and 40% of developers worldwide use HackerRank to hire tech talent and sharpen their skills.
Recommended topics
- Hire Developers
- Problem Solving
Does a College Degree Still Matter for Developers in 2024?

Gtech machines are built to the highest standards using the best quality components however nothing lasts forever.
Whatever the problem with your gtech, if it’s losing power or is no longer providing sufficient suction we can repair it. perhaps it cuts out intermittently or won’t switch on at all. with over 40 years’ experience and our extensive range of spare parts our highly trained staff will have your faulty gtech back to 100% performance in no time. so whatever the issue is with your vacuum cleaner, just give us a call..

Our experienced technicians can repair all faults with your Gtech vacuum cleaner, common problems we encounter on a regular basis are:
• burning smell from vacuum • worn brushes • vacuum cleaner overheats and cuts out • split or cracked pipe • power cord cut or split • vacuum not turning on • burning rubber smell • no suction • broken dust bin • very noisy during operation • blockages or clogged filters • low battery level • battery life is too short • weak suction power • brush bar not rotating .

The first step is to give us a call and speak to one of our engineers who can discuss the problem with your machine and give you an idea of the repair required. The engineer will give you a unique repair number to use in all future correspondence.

The next step is to obtain a suitable cardboard box and package up your Gtech machine remembering to include your name, address, contact details and most importantly your unique repair number .


Send your Gtech to us using a courier of your choice. A postal address label can be downloaded from our website or use the address at the bottom of this page. We recommend using a tracked courier service.

Upon delivery of you machine our engineers will perform a full diagnostic test to determine the cause of the problem. We will then contact you with a detailed quote for the repair including parts and labour.

If the quote is acceptable with the customer, we will then perform the necessary repairs to the machine using genuine Gtech parts where required. If the quote is unacceptable we will return the machine. (In this instance the customer pays the return postage)

Upon completion of the required repairs a member of our team will contact the customer to take secure payment using a debit or credit card. A copy of the payment details will be enclosed when we return the machine.

When payment has been made we will arrange free delivery of the machine to the customer and include a full receipt for the work carried out with a six month guarantee.

A&I Supplies
42 church road, monday 10.00am to 5.00pm, tuesday 10.00am to 5.00pm, wednesday 10.00am to 5.00pm, thursday 10.00am to 5.00pm, friday 10.00am to 5.00pm, saturday 10.00am to 5.00pm, sunday closed.
Gtechrepairs postal Gtech repair service covers the whole of the UK mainland including: Bath, Birmingham, Bradford, Brighton & Hove, Bristol, Cambridge, Canterbury, Carlisle, Chelmsford, Chester, Chichester, Coventry, Derby, Durham, Ely, Exeter, Gloucester, Hereford, Kingston upon Hull, Lancaster, Leeds, Leicester, Lichfield, Lincoln, Liverpool, London, Manchester, Newcastle upon Tyne, Norwich, Nottingham, Oxford, Peterborough, Plymouth, Portsmouth, Preston, Ripon, Salford, Salisbury, Sheffield, Southampton, St Albans, Stoke-on-Trent, Sunderland, Truro, Wakefield, Wells, Westminster, Winchester, Wolverhampton, Worcester, York Aberdeen, Dundee, Edinburgh, Glasgow, Inverness, Perth, Stirling, Bangor, Cardiff, Newport, St Davids, Swansea
© Copyright Gtechrepairs
Introduction to Problem Solving Skills
What is problem solving and why is it important.
The ability to solve problems is a basic life skill and is essential to our day-to-day lives, at home, at school, and at work. We solve problems every day without really thinking about how we solve them. For example: it’s raining and you need to go to the store. What do you do? There are lots of possible solutions. Take your umbrella and walk. If you don't want to get wet, you can drive, or take the bus. You might decide to call a friend for a ride, or you might decide to go to the store another day. There is no right way to solve this problem and different people will solve it differently.
Problem solving is the process of identifying a problem, developing possible solution paths, and taking the appropriate course of action.
Why is problem solving important? Good problem solving skills empower you not only in your personal life but are critical in your professional life. In the current fast-changing global economy, employers often identify everyday problem solving as crucial to the success of their organizations. For employees, problem solving can be used to develop practical and creative solutions, and to show independence and initiative to employers.
Throughout this case study you will be asked to jot down your thoughts in idea logs. These idea logs are used for reflection on concepts and for answering short questions. When you click on the "Next" button, your responses will be saved for that page. If you happen to close the webpage, you will lose your work on the page you were on, but previous pages will be saved. At the end of the case study, click on the "Finish and Export to PDF" button to acknowledge completion of the case study and receive a PDF document of your idea logs.
What Does Problem Solving Look Like?
The ability to solve problems is a skill, and just like any other skill, the more you practice, the better you get. So how exactly do you practice problem solving? Learning about different problem solving strategies and when to use them will give you a good start. Problem solving is a process. Most strategies provide steps that help you identify the problem and choose the best solution. There are two basic types of strategies: algorithmic and heuristic.
Algorithmic strategies are traditional step-by-step guides to solving problems. They are great for solving math problems (in algebra: multiply and divide, then add or subtract) or for helping us remember the correct order of things (a mnemonic such as “Spring Forward, Fall Back” to remember which way the clock changes for daylight saving time, or “Righty Tighty, Lefty Loosey” to remember what direction to turn bolts and screws). Algorithms are best when there is a single path to the correct solution.
But what do you do when there is no single solution for your problem? Heuristic methods are general guides used to identify possible solutions. A popular one that is easy to remember is IDEAL [ Bransford & Stein, 1993 ] :
- I dentify the problem
- D efine the context of the problem
- E xplore possible strategies
- A ct on best solution
IDEAL is just one problem solving strategy. Building a toolbox of problem solving strategies will improve your problem solving skills. With practice, you will be able to recognize and use multiple strategies to solve complex problems.
Watch the video
What is the best way to get a peanut out of a tube that cannot be moved? Watch a chimpanzee solve this problem in the video below [ Geert Stienissen, 2010 ].
[PDF transcript]
Describe the series of steps you think the chimpanzee used to solve this problem.
- [Page 2: What does Problem Solving Look Like?] Describe the series of steps you think the chimpanzee used to solve this problem.
Think of an everyday problem you've encountered recently and describe your steps for solving it.
- [Page 2: What does Problem Solving Look Like?] Think of an everyday problem you've encountered recently and describe your steps for solving it.
Developing Problem Solving Processes
Problem solving is a process that uses steps to solve problems. But what does that really mean? Let's break it down and start building our toolbox of problem solving strategies.
What is the first step of solving any problem? The first step is to recognize that there is a problem and identify the right cause of the problem. This may sound obvious, but similar problems can arise from different events, and the real issue may not always be apparent. To really solve the problem, it's important to find out what started it all. This is called identifying the root cause .
Example: You and your classmates have been working long hours on a project in the school's workshop. The next afternoon, you try to use your student ID card to access the workshop, but discover that your magnetic strip has been demagnetized. Since the card was a couple of years old, you chalk it up to wear and tear and get a new ID card. Later that same week you learn that several of your classmates had the same problem! After a little investigation, you discover that a strong magnet was stored underneath a workbench in the workshop. The magnet was the root cause of the demagnetized student ID cards.
The best way to identify the root cause of the problem is to ask questions and gather information. If you have a vague problem, investigating facts is more productive than guessing a solution. Ask yourself questions about the problem. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? When was the last time it worked correctly? What has changed since then? Can you diagram the process into separate steps? Where in the process is the problem occurring? Be curious, ask questions, gather facts, and make logical deductions rather than assumptions.
Watch Adam Savage from Mythbusters, describe his problem solving process [ ForaTv, 2010 ]. As you watch this section of the video, try to identify the questions he asks and the different strategies he uses.
Adam Savage shared many of his problem solving processes. List the ones you think are the five most important. Your list may be different from other people in your class—that's ok!
- [Page 3: Developing Problem Solving Processes] Adam Savage shared many of his problem solving processes. List the ones you think are the five most important.
“The ability to ask the right question is more than half the battle of finding the answer.” — Thomas J. Watson , founder of IBM
Voices From the Field: Solving Problems
In manufacturing facilities and machine shops, everyone on the floor is expected to know how to identify problems and find solutions. Today's employers look for the following skills in new employees: to analyze a problem logically, formulate a solution, and effectively communicate with others.
In this video, industry professionals share their own problem solving processes, the problem solving expectations of their employees, and an example of how a problem was solved.
Meet the Partners:
- Taconic High School in Pittsfield, Massachusetts, is a comprehensive, fully accredited high school with special programs in Health Technology, Manufacturing Technology, and Work-Based Learning.
- Berkshire Community College in Pittsfield, Massachusetts, prepares its students with applied manufacturing technical skills, providing hands-on experience at industrial laboratories and manufacturing facilities, and instructing them in current technologies.
- H.C. Starck in Newton, Massachusetts, specializes in processing and manufacturing technology metals, such as tungsten, niobium, and tantalum. In almost 100 years of experience, they hold over 900 patents, and continue to innovate and develop new products.
- Nypro Healthcare in Devens, Massachusetts, specializes in precision injection-molded healthcare products. They are committed to good manufacturing processes including lean manufacturing and process validation.
Making Decisions
Now that you have a couple problem solving strategies in your toolbox, let's practice. In this exercise, you are given a scenario and you will be asked to decide what steps you would take to identify and solve the problem.
Scenario: You are a new employee and have just finished your training. As your first project, you have been assigned the milling of several additional components for a regular customer. Together, you and your trainer, Bill, set up for the first run. Checking your paperwork, you gather the tools and materials on the list. As you are mounting the materials on the table, you notice that you didn't grab everything and hurriedly grab a few more items from one of the bins. Once the material is secured on the CNC table, you load tools into the tool carousel in the order listed on the tool list and set the fixture offsets.
Bill tells you that since this is a rerun of a job several weeks ago, the CAD/CAM model has already been converted to CNC G-code. Bill helps you download the code to the CNC machine. He gives you the go-ahead and leaves to check on another employee. You decide to start your first run.
What problems did you observe in the video?
- [Page 5: Making Decisions] What problems did you observe in the video?
- What do you do next?
- Try to fix it yourself.
- Ask your trainer for help.
As you are cleaning up, you think about what happened and wonder why it happened. You try to create a mental picture of what happened. You are not exactly sure what the end mill hit, but it looked like it might have hit the dowel pin. You wonder if you grabbed the correct dowel pins from the bins earlier.
You can think of two possible next steps. You can recheck the dowel pin length to make sure it is the correct length, or do a dry run using the CNC single step or single block function with the spindle empty to determine what actually happened.

- Check the dowel pins.
- Use the single step/single block function to determine what happened.
You notice that your trainer, Bill, is still on the floor and decide to ask him for help. You describe the problem to him. Bill asks if you know what the end mill ran into. You explain that you are not sure but you think it was the dowel pin. Bill reminds you that it is important to understand what happened so you can fix the correct problem. He suggests that you start all over again and begin with a dry run using the single step/single block function, with the spindle empty, to determine what it hit. Or, since it happened at the end, he mentions that you can also check the G-code to make sure the Z-axis is raised before returning to the home position.
- Run the single step/single block function.
- Edit the G-code to raise the Z-axis.
You finish cleaning up and check the CNC for any damage. Luckily, everything looks good. You check your paperwork and gather the components and materials again. You look at the dowel pins you used earlier, and discover that they are not the right length. As you go to grab the correct dowel pins, you have to search though several bins. For the first time, you are aware of the mess - it looks like the dowel pins and other items have not been put into the correctly labeled bins. You spend 30 minutes straightening up the bins and looking for the correct dowel pins.
Finally finding them, you finish setting up. You load tools into the tool carousel in the order listed on the tool list and set the fixture offsets. Just to make sure, you use the CNC single step/single block function, to do a dry run of the part. Everything looks good! You are ready to create your first part. The first component is done, and, as you admire your success, you notice that the part feels hotter than it should.
You wonder why? You go over the steps of the process to mentally figure out what could be causing the residual heat. You wonder if there is a problem with the CNC's coolant system or if the problem is in the G-code.
- Look at the G-code.
After thinking about the problem, you decide that maybe there's something wrong with the setup. First, you clean up the damaged materials and remove the broken tool. You check the CNC machine carefully for any damage. Luckily, everything looks good. It is time to start over again from the beginning.
You again check your paperwork and gather the tools and materials on the setup sheet. After securing the new materials, you use the CNC single step/single block function with the spindle empty, to do a dry run of the part. You watch carefully to see if you can figure out what happened. It looks to you like the spindle barely misses hitting the dowel pin. You determine that the end mill was broken when it hit the dowel pin while returning to the start position.
After conducting a dry run using the single step/single block function, you determine that the end mill was damaged when it hit the dowel pin on its return to the home position. You discuss your options with Bill. Together, you decide the best thing to do would be to edit the G-code and raise the Z-axis before returning to home. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code. Just to make sure, you use the CNC single step/single block function, to do another dry run of the part. You are ready to create your first part. It works. You first part is completed. Only four more to go.
As you are cleaning up, you notice that the components are hotter than you expect and the end mill looks more worn than it should be. It dawns on you that while you were milling the component, the coolant didn't turn on. You wonder if it is a software problem in the G-code or hardware problem with the CNC machine.
It's the end of the day and you decide to finish the rest of the components in the morning.
- You decide to look at the G-code in the morning.
- You leave a note on the machine, just in case.
You decide that the best thing to do would be to edit the G-code and raise the Z-axis of the spindle before it returns to home. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code.
While editing the G-code to raise the Z-axis, you notice that the coolant is turned off at the beginning of the code and at the end of the code. The coolant command error caught your attention because your coworker, Mark, mentioned having a similar issue during lunch. You change the coolant command to turn the mist on.
- You decide to talk with your supervisor.
- You discuss what happened with a coworker over lunch.
As you reflect on the residual heat problem, you think about the machining process and the factors that could have caused the issue. You try to think of anything and everything that could be causing the issue. Are you using the correct tool for the specified material? Are you using the specified material? Is it running at the correct speed? Is there enough coolant? Are there chips getting in the way?
Wait, was the coolant turned on? As you replay what happened in your mind, you wonder why the coolant wasn't turned on. You decide to look at the G-code to find out what is going on.
From the milling machine computer, you open the CNC G-code. You notice that there are no coolant commands. You add them in and on the next run, the coolant mist turns on and the residual heat issues is gone. Now, its on to creating the rest of the parts.
Have you ever used brainstorming to solve a problem? Chances are, you've probably have, even if you didn't realize it.
You notice that your trainer, Bill, is on the floor and decide to ask him for help. You describe the problem with the end mill breaking, and how you discovered that items are not being returned to the correctly labeled bins. You think this caused you to grab the incorrect length dowel pins on your first run. You have sorted the bins and hope that the mess problem is fixed. You then go on to tell Bill about the residual heat issue with the completed part.
Together, you go to the milling machine. Bill shows you how to check the oil and coolant levels. Everything looks good at the machine level. Next, on the CNC computer, you open the CNC G-code. While looking at the code, Bill points out that there are no coolant commands. Bill adds them in and when you rerun the program, it works.
Bill is glad you mentioned the problem to him. You are the third worker to mention G-code issues over the last week. You noticed the coolant problems in your G-code, John noticed a Z-axis issue in his G-code, and Sam had issues with both the Z-axis and the coolant. Chances are, there is a bigger problem and Bill will need to investigate the root cause .
Talking with Bill, you discuss the best way to fix the problem. Bill suggests editing the G-code to raise the Z-axis of the spindle before it returns to its home position. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code. Following the setup sheet, you re-setup the job and use the CNC single step/single block function, to do another dry run of the part. Everything looks good, so you run the job again and create the first part. It works. Since you need four of each component, you move on to creating the rest of them before cleaning up and leaving for the day.
It's a new day and you have new components to create. As you are setting up, you go in search of some short dowel pins. You discover that the bins are a mess and components have not been put away in the correctly labeled bins. You wonder if this was the cause of yesterday's problem. As you reorganize the bins and straighten up the mess, you decide to mention the mess issue to Bill in your afternoon meeting.
You describe the bin mess and using the incorrect length dowels to Bill. He is glad you mentioned the problem to him. You are not the first person to mention similar issues with tools and parts not being put away correctly. Chances are there is a bigger safety issue here that needs to be addressed in the next staff meeting.
In any workplace, following proper safety and cleanup procedures is always important. This is especially crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly and sometimes dangerous equipment. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost, and save money.
You now know that the end mill was damaged when it hit the dowel pin. It seems to you that the easiest thing to do would be to edit the G-code and raise the Z-axis position of the spindle before it returns to the home position. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code, raising the Z-axis. Starting over, you follow the setup sheet and re-setup the job. This time, you use the CNC single step/single block function, to do another dry run of the part. Everything looks good, so you run the job again and create the first part.
At the end of the day, you are reviewing your progress with your trainer, Bill. After you describe the day's events, he reminds you to always think about safety and the importance of following work procedures. He decides to bring the issue up in the next morning meeting as a reminder to everyone.
In any workplace, following proper procedures (especially those that involve safety) is always important. This is especially crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly, and sometimes dangerous equipment. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost, and save money. One tool to improve communication is the morning meeting or huddle.
The next morning, you check the G-code to determine what is wrong with the coolant. You notice that the coolant is turned off at the beginning of the code and also at the end of the code. This is strange. You change the G-code to turn the coolant on at the beginning of the run and off at the end. This works and you create the rest of the parts.
Throughout the day, you keep wondering what caused the G-code error. At lunch, you mention the G-code error to your coworker, John. John is not surprised. He said that he encountered a similar problem earlier this week. You decide to talk with your supervisor the next time you see him.
You are in luck. You see your supervisor by the door getting ready to leave. You hurry over to talk with him. You start off by telling him about how you asked Bill for help. Then you tell him there was a problem and the end mill was damaged. You describe the coolant problem in the G-code. Oh, and by the way, John has seen a similar problem before.
Your supervisor doesn't seem overly concerned, errors happen. He tells you "Good job, I am glad you were able to fix the issue." You are not sure whether your supervisor understood your explanation of what happened or that it had happened before.
The challenge of communicating in the workplace is learning how to share your ideas and concerns. If you need to tell your supervisor that something is not going well, it is important to remember that timing, preparation, and attitude are extremely important.
It is the end of your shift, but you want to let the next shift know that the coolant didn't turn on. You do not see your trainer or supervisor around. You decide to leave a note for the next shift so they are aware of the possible coolant problem. You write a sticky note and leave it on the monitor of the CNC control system.
How effective do you think this solution was? Did it address the problem?
In this scenario, you discovered several problems with the G-code that need to be addressed. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring and avoid injury to personnel. The challenge of communicating in the workplace is learning how and when to share your ideas and concerns. If you need to tell your co-workers or supervisor that there is a problem, it is important to remember that timing and the method of communication are extremely important.
You are able to fix the coolant problem in the G-code. While you are glad that the problem is fixed, you are worried about why it happened in the first place. It is important to remember that if a problem keeps reappearing, you may not be fixing the right problem. You may only be addressing the symptoms.
You decide to talk to your trainer. Bill is glad you mentioned the problem to him. You are the third worker to mention G-code issues over the last week. You noticed the coolant problems in your G-code, John noticed a Z-axis issue in his G-code, and Sam had issues with both the Z-axis and the coolant. Chances are, there is a bigger problem and Bill will need to investigate the root cause .
Over lunch, you ask your coworkers about the G-code problem and what may be causing the error. Several people mention having similar problems but do not know the cause.
You have now talked to three coworkers who have all experienced similar coolant G-code problems. You make a list of who had the problem, when they had the problem, and what each person told you.
When you see your supervisor later that afternoon, you are ready to talk with him. You describe the problem you had with your component and the damaged bit. You then go on to tell him about talking with Bill and discovering the G-code issue. You show him your notes on your coworkers' coolant issues, and explain that you think there might be a bigger problem.
You supervisor thanks you for your initiative in identifying this problem. It sounds like there is a bigger problem and he will need to investigate the root cause. He decides to call a team huddle to discuss the issue, gather more information, and talk with the team about the importance of communication.
Root Cause Analysis

Root cause analysis ( RCA ) is a method of problem solving that identifies the underlying causes of an issue. Root cause analysis helps people answer the question of why the problem occurred in the first place. RCA uses clear cut steps in its associated tools, like the "5 Whys Analysis" and the "Cause and Effect Diagram," to identify the origin of the problem, so that you can:
- Determine what happened.
- Determine why it happened.
- Fix the problem so it won’t happen again.
RCA works under the idea that systems and events are connected. An action in one area triggers an action in another, and another, and so on. By tracing back these actions, you can discover where the problem started and how it developed into the problem you're now facing. Root cause analysis can prevent problems from recurring, reduce injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost and save money. There are many different RCA techniques available to determine the root cause of a problem. These are just a few:
- Root Cause Analysis Tools
- 5 Whys Analysis
- Fishbone or Cause and Effect Diagram
- Pareto Analysis

How Huddles Work

Communication is a vital part of any setting where people work together. Effective communication helps employees and managers form efficient teams. It builds trusts between employees and management, and reduces unnecessary competition because each employee knows how their part fits in the larger goal.
One tool that management can use to promote communication in the workplace is the huddle . Just like football players on the field, a huddle is a short meeting where everyone is standing in a circle. A daily team huddle ensures that team members are aware of changes to the schedule, reiterated problems and safety issues, and how their work impacts one another. When done right, huddles create collaboration, communication, and accountability to results. Impromptu huddles can be used to gather information on a specific issue and get each team member's input.
The most important thing to remember about huddles is that they are short, lasting no more than 10 minutes, and their purpose is to communicate and identify. In essence, a huddle’s purpose is to identify priorities, communicate essential information, and discover roadblocks to productivity.
Who uses huddles? Many industries and companies use daily huddles. At first thought, most people probably think of hospitals and their daily patient update meetings, but lots of managers use daily meetings to engage their employees. Here are a few examples:
- Brian Scudamore, CEO of 1-800-Got-Junk? , uses the daily huddle as an operational tool to take the pulse of his employees and as a motivational tool. Watch a morning huddle meeting .
- Fusion OEM, an outsourced manufacturing and production company. What do employees take away from the daily huddle meeting .
- Biz-Group, a performance consulting group. Tips for a successful huddle .
Brainstorming
One tool that can be useful in problem solving is brainstorming . Brainstorming is a creativity technique designed to generate a large number of ideas for the solution to a problem. The method was first popularized in 1953 by Alex Faickney Osborn in the book Applied Imagination . The goal is to come up with as many ideas as you can in a fixed amount of time. Although brainstorming is best done in a group, it can be done individually. Like most problem solving techniques, brainstorming is a process.
- Define a clear objective.
- Have an agreed a time limit.
- During the brainstorming session, write down everything that comes to mind, even if the idea sounds crazy.
- If one idea leads to another, write down that idea too.
- Combine and refine ideas into categories of solutions.
- Assess and analyze each idea as a potential solution.
When used during problem solving, brainstorming can offer companies new ways of encouraging staff to think creatively and improve production. Brainstorming relies on team members' diverse experiences, adding to the richness of ideas explored. This means that you often find better solutions to the problems. Team members often welcome the opportunity to contribute ideas and can provide buy-in for the solution chosen—after all, they are more likely to be committed to an approach if they were involved in its development. What's more, because brainstorming is fun, it helps team members bond.
- Watch Peggy Morgan Collins, a marketing executive at Power Curve Communications discuss How to Stimulate Effective Brainstorming .
- Watch Kim Obbink, CEO of Filter Digital, a digital content company, and her team share their top five rules for How to Effectively Generate Ideas .
Importance of Good Communication and Problem Description

Communication is one of the most frequent activities we engage in on a day-to-day basis. At some point, we have all felt that we did not effectively communicate an idea as we would have liked. The key to effective communication is preparation. Rather than attempting to haphazardly improvise something, take a few minutes and think about what you want say and how you will say it. If necessary, write yourself a note with the key points or ideas in the order you want to discuss them. The notes can act as a reminder or guide when you talk to your supervisor.
Tips for clear communication of an issue:
- Provide a clear summary of your problem. Start at the beginning, give relevant facts, timelines, and examples.
- Avoid including your opinion or personal attacks in your explanation.
- Avoid using words like "always" or "never," which can give the impression that you are exaggerating the problem.
- If this is an ongoing problem and you have collected documentation, give it to your supervisor once you have finished describing the problem.
- Remember to listen to what's said in return; communication is a two-way process.
Not all communication is spoken. Body language is nonverbal communication that includes your posture, your hands and whether you make eye contact. These gestures can be subtle or overt, but most importantly they communicate meaning beyond what is said. When having a conversation, pay attention to how you stand. A stiff position with arms crossed over your chest may imply that you are being defensive even if your words state otherwise. Shoving your hands in your pockets when speaking could imply that you have something to hide. Be wary of using too many hand gestures because this could distract listeners from your message.
The challenge of communicating in the workplace is learning how and when to share your ideas or concerns. If you need to tell your supervisor or co-worker about something that is not going well, keep in mind that good timing and good attitude will go a long way toward helping your case.
Like all skills, effective communication needs to be practiced. Toastmasters International is perhaps the best known public speaking organization in the world. Toastmasters is open to anyone who wish to improve their speaking skills and is willing to put in the time and effort to do so. To learn more, visit Toastmasters International .
Methods of Communication
Communication of problems and issues in any workplace is important, particularly when safety is involved. It is therefore crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly, and sometimes dangerous equipment. As issues and problems arise, they need to be addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important skill because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost and save money.
There are many different ways to communicate: in person, by phone, via email, or written. There is no single method that fits all communication needs, each one has its time and place.
In person: In the workplace, face-to-face meetings should be utilized whenever possible. Being able to see the person you need to speak to face-to-face gives you instant feedback and helps you gauge their response through their body language. Be careful of getting sidetracked in conversation when you need to communicate a problem.
Email: Email has become the communication standard for most businesses. It can be accessed from almost anywhere and is great for things that don’t require an immediate response. Email is a great way to communicate non-urgent items to large amounts of people or just your team members. One thing to remember is that most people's inboxes are flooded with emails every day and unless they are hyper vigilant about checking everything, important items could be missed. For issues that are urgent, especially those around safety, email is not always be the best solution.
Phone: Phone calls are more personal and direct than email. They allow us to communicate in real time with another person, no matter where they are. Not only can talking prevent miscommunication, it promotes a two-way dialogue. You don’t have to worry about your words being altered or the message arriving on time. However, mobile phone use and the workplace don't always mix. In particular, using mobile phones in a manufacturing setting can lead to a variety of problems, cause distractions, and lead to serious injury.
Written: Written communication is appropriate when detailed instructions are required, when something needs to be documented, or when the person is too far away to easily speak with over the phone or in person.
There is no "right" way to communicate, but you should be aware of how and when to use the appropriate form of communication for your situation. When deciding the best way to communicate with a co-worker or manager, put yourself in their shoes, and think about how you would want to learn about the issue. Also, consider what information you would need to know to better understand the issue. Use your good judgment of the situation and be considerate of your listener's viewpoint.
Did you notice any other potential problems in the previous exercise?
- [Page 6:] Did you notice any other potential problems in the previous exercise?
Summary of Strategies
In this exercise, you were given a scenario in which there was a problem with a component you were creating on a CNC machine. You were then asked how you wanted to proceed. Depending on your path through this exercise, you might have found an easy solution and fixed it yourself, asked for help and worked with your trainer, or discovered an ongoing G-code problem that was bigger than you initially thought.
When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost, and save money. Although, each path in this exercise ended with a description of a problem solving tool for your toolbox, the first step is always to identify the problem and define the context in which it happened.
There are several strategies that can be used to identify the root cause of a problem. Root cause analysis (RCA) is a method of problem solving that helps people answer the question of why the problem occurred. RCA uses a specific set of steps, with associated tools like the “5 Why Analysis" or the “Cause and Effect Diagram,” to identify the origin of the problem, so that you can:
Once the underlying cause is identified and the scope of the issue defined, the next step is to explore possible strategies to fix the problem.
If you are not sure how to fix the problem, it is okay to ask for help. Problem solving is a process and a skill that is learned with practice. It is important to remember that everyone makes mistakes and that no one knows everything. Life is about learning. It is okay to ask for help when you don’t have the answer. When you collaborate to solve problems you improve workplace communication and accelerates finding solutions as similar problems arise.
One tool that can be useful for generating possible solutions is brainstorming . Brainstorming is a technique designed to generate a large number of ideas for the solution to a problem. The method was first popularized in 1953 by Alex Faickney Osborn in the book Applied Imagination. The goal is to come up with as many ideas as you can, in a fixed amount of time. Although brainstorming is best done in a group, it can be done individually.
Depending on your path through the exercise, you may have discovered that a couple of your coworkers had experienced similar problems. This should have been an indicator that there was a larger problem that needed to be addressed.
In any workplace, communication of problems and issues (especially those that involve safety) is always important. This is especially crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly, and sometimes dangerous equipment. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they be addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost and save money.
One strategy for improving communication is the huddle . Just like football players on the field, a huddle is a short meeting with everyone standing in a circle. A daily team huddle is a great way to ensure that team members are aware of changes to the schedule, any problems or safety issues are identified and that team members are aware of how their work impacts one another. When done right, huddles create collaboration, communication, and accountability to results. Impromptu huddles can be used to gather information on a specific issue and get each team member's input.
To learn more about different problem solving strategies, choose an option below. These strategies accompany the outcomes of different decision paths in the problem solving exercise.
- View Problem Solving Strategies Select a strategy below... Root Cause Analysis How Huddles Work Brainstorming Importance of Good Problem Description Methods of Communication
Communication is one of the most frequent activities we engage in on a day-to-day basis. At some point, we have all felt that we did not effectively communicate an idea as we would have liked. The key to effective communication is preparation. Rather than attempting to haphazardly improvise something, take a few minutes and think about what you want say and how you will say it. If necessary, write yourself a note with the key points or ideas in the order you want to discuss them. The notes can act as a reminder or guide during your meeting.
- Provide a clear summary of the problem. Start at the beginning, give relevant facts, timelines, and examples.
In person: In the workplace, face-to-face meetings should be utilized whenever possible. Being able to see the person you need to speak to face-to-face gives you instant feedback and helps you gauge their response in their body language. Be careful of getting sidetracked in conversation when you need to communicate a problem.
There is no "right" way to communicate, but you should be aware of how and when to use the appropriate form of communication for the situation. When deciding the best way to communicate with a co-worker or manager, put yourself in their shoes, and think about how you would want to learn about the issue. Also, consider what information you would need to know to better understand the issue. Use your good judgment of the situation and be considerate of your listener's viewpoint.
"Never try to solve all the problems at once — make them line up for you one-by-one.” — Richard Sloma
Problem Solving: An Important Job Skill
Problem solving improves efficiency and communication on the shop floor. It increases a company's efficiency and profitability, so it's one of the top skills employers look for when hiring new employees. Recent industry surveys show that employers consider soft skills, such as problem solving, as critical to their business’s success.
The 2011 survey, "Boiling Point? The skills gap in U.S. manufacturing ," polled over a thousand manufacturing executives who reported that the number one skill deficiency among their current employees is problem solving, which makes it difficult for their companies to adapt to the changing needs of the industry.
In this video, industry professionals discuss their expectations and present tips for new employees joining the manufacturing workforce.
Quick Summary
- [Quick Summary: Question1] What are two things you learned in this case study?
- What question(s) do you still have about the case study?
- [Quick Summary: Question2] What question(s) do you still have about the case study?
- Is there anything you would like to learn more about with respect to this case study?
- [Quick Summary: Question3] Is there anything you would like to learn more about with respect to this case study?
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Problem-Solving Strategies and Obstacles
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Sean is a fact-checker and researcher with experience in sociology, field research, and data analytics.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Sean-Blackburn-1000-a8b2229366944421bc4b2f2ba26a1003.jpg)
JGI / Jamie Grill / Getty Images
- Application
- Improvement
From deciding what to eat for dinner to considering whether it's the right time to buy a house, problem-solving is a large part of our daily lives. Learn some of the problem-solving strategies that exist and how to use them in real life, along with ways to overcome obstacles that are making it harder to resolve the issues you face.
What Is Problem-Solving?
In cognitive psychology , the term 'problem-solving' refers to the mental process that people go through to discover, analyze, and solve problems.
A problem exists when there is a goal that we want to achieve but the process by which we will achieve it is not obvious to us. Put another way, there is something that we want to occur in our life, yet we are not immediately certain how to make it happen.
Maybe you want a better relationship with your spouse or another family member but you're not sure how to improve it. Or you want to start a business but are unsure what steps to take. Problem-solving helps you figure out how to achieve these desires.
The problem-solving process involves:
- Discovery of the problem
- Deciding to tackle the issue
- Seeking to understand the problem more fully
- Researching available options or solutions
- Taking action to resolve the issue
Before problem-solving can occur, it is important to first understand the exact nature of the problem itself. If your understanding of the issue is faulty, your attempts to resolve it will also be incorrect or flawed.
Problem-Solving Mental Processes
Several mental processes are at work during problem-solving. Among them are:
- Perceptually recognizing the problem
- Representing the problem in memory
- Considering relevant information that applies to the problem
- Identifying different aspects of the problem
- Labeling and describing the problem
Problem-Solving Strategies
There are many ways to go about solving a problem. Some of these strategies might be used on their own, or you may decide to employ multiple approaches when working to figure out and fix a problem.
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that, by following certain "rules" produces a solution. Algorithms are commonly used in mathematics to solve division or multiplication problems. But they can be used in other fields as well.
In psychology, algorithms can be used to help identify individuals with a greater risk of mental health issues. For instance, research suggests that certain algorithms might help us recognize children with an elevated risk of suicide or self-harm.
One benefit of algorithms is that they guarantee an accurate answer. However, they aren't always the best approach to problem-solving, in part because detecting patterns can be incredibly time-consuming.
There are also concerns when machine learning is involved—also known as artificial intelligence (AI)—such as whether they can accurately predict human behaviors.
Heuristics are shortcut strategies that people can use to solve a problem at hand. These "rule of thumb" approaches allow you to simplify complex problems, reducing the total number of possible solutions to a more manageable set.
If you find yourself sitting in a traffic jam, for example, you may quickly consider other routes, taking one to get moving once again. When shopping for a new car, you might think back to a prior experience when negotiating got you a lower price, then employ the same tactics.
While heuristics may be helpful when facing smaller issues, major decisions shouldn't necessarily be made using a shortcut approach. Heuristics also don't guarantee an effective solution, such as when trying to drive around a traffic jam only to find yourself on an equally crowded route.
Trial and Error
A trial-and-error approach to problem-solving involves trying a number of potential solutions to a particular issue, then ruling out those that do not work. If you're not sure whether to buy a shirt in blue or green, for instance, you may try on each before deciding which one to purchase.
This can be a good strategy to use if you have a limited number of solutions available. But if there are many different choices available, narrowing down the possible options using another problem-solving technique can be helpful before attempting trial and error.
In some cases, the solution to a problem can appear as a sudden insight. You are facing an issue in a relationship or your career when, out of nowhere, the solution appears in your mind and you know exactly what to do.
Insight can occur when the problem in front of you is similar to an issue that you've dealt with in the past. Although, you may not recognize what is occurring since the underlying mental processes that lead to insight often happen outside of conscious awareness .
Research indicates that insight is most likely to occur during times when you are alone—such as when going on a walk by yourself, when you're in the shower, or when lying in bed after waking up.
How to Apply Problem-Solving Strategies in Real Life
If you're facing a problem, you can implement one or more of these strategies to find a potential solution. Here's how to use them in real life:
- Create a flow chart . If you have time, you can take advantage of the algorithm approach to problem-solving by sitting down and making a flow chart of each potential solution, its consequences, and what happens next.
- Recall your past experiences . When a problem needs to be solved fairly quickly, heuristics may be a better approach. Think back to when you faced a similar issue, then use your knowledge and experience to choose the best option possible.
- Start trying potential solutions . If your options are limited, start trying them one by one to see which solution is best for achieving your desired goal. If a particular solution doesn't work, move on to the next.
- Take some time alone . Since insight is often achieved when you're alone, carve out time to be by yourself for a while. The answer to your problem may come to you, seemingly out of the blue, if you spend some time away from others.
Obstacles to Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is not a flawless process as there are a number of obstacles that can interfere with our ability to solve a problem quickly and efficiently. These obstacles include:
- Assumptions: When dealing with a problem, people can make assumptions about the constraints and obstacles that prevent certain solutions. Thus, they may not even try some potential options.
- Functional fixedness : This term refers to the tendency to view problems only in their customary manner. Functional fixedness prevents people from fully seeing all of the different options that might be available to find a solution.
- Irrelevant or misleading information: When trying to solve a problem, it's important to distinguish between information that is relevant to the issue and irrelevant data that can lead to faulty solutions. The more complex the problem, the easier it is to focus on misleading or irrelevant information.
- Mental set: A mental set is a tendency to only use solutions that have worked in the past rather than looking for alternative ideas. A mental set can work as a heuristic, making it a useful problem-solving tool. However, mental sets can also lead to inflexibility, making it more difficult to find effective solutions.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
In the end, if your goal is to become a better problem-solver, it's helpful to remember that this is a process. Thus, if you want to improve your problem-solving skills, following these steps can help lead you to your solution:
- Recognize that a problem exists . If you are facing a problem, there are generally signs. For instance, if you have a mental illness , you may experience excessive fear or sadness, mood changes, and changes in sleeping or eating habits. Recognizing these signs can help you realize that an issue exists.
- Decide to solve the problem . Make a conscious decision to solve the issue at hand. Commit to yourself that you will go through the steps necessary to find a solution.
- Seek to fully understand the issue . Analyze the problem you face, looking at it from all sides. If your problem is relationship-related, for instance, ask yourself how the other person may be interpreting the issue. You might also consider how your actions might be contributing to the situation.
- Research potential options . Using the problem-solving strategies mentioned, research potential solutions. Make a list of options, then consider each one individually. What are some pros and cons of taking the available routes? What would you need to do to make them happen?
- Take action . Select the best solution possible and take action. Action is one of the steps required for change . So, go through the motions needed to resolve the issue.
- Try another option, if needed . If the solution you chose didn't work, don't give up. Either go through the problem-solving process again or simply try another option.
You can find a way to solve your problems as long as you keep working toward this goal—even if the best solution is simply to let go because no other good solution exists.
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
Dunbar K. Problem solving . A Companion to Cognitive Science . 2017. doi:10.1002/9781405164535.ch20
Stewart SL, Celebre A, Hirdes JP, Poss JW. Risk of suicide and self-harm in kids: The development of an algorithm to identify high-risk individuals within the children's mental health system . Child Psychiat Human Develop . 2020;51:913-924. doi:10.1007/s10578-020-00968-9
Rosenbusch H, Soldner F, Evans AM, Zeelenberg M. Supervised machine learning methods in psychology: A practical introduction with annotated R code . Soc Personal Psychol Compass . 2021;15(2):e12579. doi:10.1111/spc3.12579
Mishra S. Decision-making under risk: Integrating perspectives from biology, economics, and psychology . Personal Soc Psychol Rev . 2014;18(3):280-307. doi:10.1177/1088868314530517
Csikszentmihalyi M, Sawyer K. Creative insight: The social dimension of a solitary moment . In: The Systems Model of Creativity . 2015:73-98. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9085-7_7
Chrysikou EG, Motyka K, Nigro C, Yang SI, Thompson-Schill SL. Functional fixedness in creative thinking tasks depends on stimulus modality . Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts . 2016;10(4):425‐435. doi:10.1037/aca0000050
Huang F, Tang S, Hu Z. Unconditional perseveration of the short-term mental set in chunk decomposition . Front Psychol . 2018;9:2568. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02568
National Alliance on Mental Illness. Warning signs and symptoms .
Mayer RE. Thinking, problem solving, cognition, 2nd ed .
Schooler JW, Ohlsson S, Brooks K. Thoughts beyond words: When language overshadows insight. J Experiment Psychol: General . 1993;122:166-183. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.2.166
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Experts Predict More Digital Innovation by 2030 Aimed at Enhancing Democracy
- 5. Tech causes more problems than it solves
Table of Contents
- 1. The innovations these experts predict by 2030
- 2. Tech is (just) a tool
- 3. Power dynamics play a key role in problems and innovation
- 4. It’s all just history repeating itself
- 6. The net effects in 10 years will be negligible
- About this canvassing of experts
- Acknowledgments
A number of respondents to this canvassing about the likely future of social and civic innovation shared concerns. Some said that technology causes more problems than it solves. Some said it is likely that emerging worries over the impact of digital life will be at least somewhat mitigated as humans adapt. Some said it is possible that any remedies may create a new set of challenges. Others said humans’ uses and abuses of digital technologies are causing societal harms that are not likely to be overcome.
The following comments were selected from among all responses, regardless of an expert’s answer to this canvassing’s main question about the impact of people’s uses of technology. Some of these remarks of concern happen to also include comments about innovations that may emerge. Concerns are organized under four subthemes: Something is rotten in the state of technology; technology use often disconnects or hollows out a community; society needs to catch up and better address the threats and opportunities of tech; and despite current trends, there is reason to hope for better days.
The chapter begins with some overview insights:
Larry Masinter , internet pioneer, formerly with Adobe, AT&T Labs and Xerox PARC, who helped create internet and web standards with IETF and W3C, said, “Technology and social innovation intended to overcome the negatives of the digital age will likely cause additional negative consequences. Examples include: the decentralized web, end-to-end encryption, AI and machine learning, social media.”
James Mickens , associate professor of computer science at Harvard University, formerly with Microsoft, commented, “Technology will obviously result in ‘civic innovation.’ The real question is whether the ‘innovation’ will result in better societal outcomes. For example, the gig economy is enabled by technology; technology finds buyers for workers and their services. However, given the choice between an economy with many gig workers and an economy with an equivalent number of traditional middle-class jobs, I think that most people would prefer the latter.”
Michael Aisenberg , chair, ABA Information Security Committee, wrote, “Misappreciation of limits and genesis of, e.g., AI/machine learning will produce widely disparate results in deployment of tech innovations. Some will be dramatically beneficial; some may enable abuse of law enforcement, economic systems and other fundamental civic institutions and lead to exacerbation of gaps between tech controllers/users and underserved/under- or mis-skilled populations (‘digital divide’) in what may be a significant (embed limitations on career/economic advancement) or even life-threatening (de facto health care or health procedure rationing) manner.”
The problem is that we are becoming more and more dependent on machines and hence more susceptible to bugs and system failures. Yaakov J. Stein
Peter Lunenfeld , a professor of design, media arts and digital humanities at the University of California, Los Angeles, and author of “Tales of the Computer as Culture Machine,” predicted, “We will use technology to solve the problems the use of technology creates, but the new fixes will bring new issues. Every design solution creates a new design problem, and so it is with the ways we have built our global networks. Highly technological societies have to be iterative if they hope to compete, and I think that societies that have experienced democracy will move to curb the slide to authoritarianism that social media has accelerated. Those curbs will bring about their own unintended consequences, however, which will start the cycle anew.”
Yaakov J. Stein , chief technology officer of RAD Data Communications, based in Israel, responded, “The problem with AI and machine learning is not the sci-fi scenario of AI taking over the world and not needing inferior humans. The problem is that we are becoming more and more dependent on machines and hence more susceptible to bugs and system failures. This is hardly a new phenomenon – once a major part of schooling was devoted to, e.g., penmanship and mental arithmetic, which have been superseded by technical means. But with the tremendous growth in the amount of information, education is more focused on how to retrieve required information rather than remembering things, resulting not only in less actual storage but less depth of knowledge and the lack of ability to make connections between disparate bits of information, which is the basis of creativity. However, in the past humankind has always developed a more-advanced technology to overcome limitations of whatever technology was current, and there is no reason to believe that it will be different this time.”
A vice president for research and economic development wrote, “The problems we see now are caused by technology, and any new technological fixes we create will inevitably cause NEW social and political problems. Attempts to police the web will cause freedom of speech conflicts, for example.”
Something is rotten in the state of technology
A large share of these experts say among the leading concerns about today’s technology platforms are the ways in which they are exploited by bad actors who spread misinformation; and the privacy issues arising out of the business model behind the systems.
Misinformation – pervasive, potent, problematic
Numerous experts described misinformation and fake news as a serious issue in digital spaces. They expressed concern over how users will sort through fact and fiction in the coming decade.
Stephanie Fierman , partner, Futureproof Strategies, said, “I believe technology will meaningfully accelerate social and civic innovation. It’s cheap, fast and able to reach huge audiences. But as long as false information is enabled by very large websites, such social and civic innovators will be shadow boxing with people, governments, organizations purposely countering truthful content with lies.”
Sam Lehman-Wilzig , a professor of communications at Bar-Ilan University specializing in Israeli politics and the impact of technological evolution, wrote, “The biggest advance will be the use of artificial intelligence to fight disinformation, deepfakes and the like. There will be an AI ‘arms race’ between those spreading disinformation and those fighting/preventing it. Overall, I see the latter gaining the upper hand.”
Greg Shatan , a lawyer with Moses & Singer LLP and self-described “internet governance wonk,” predicted, “I see success, enabled by technology, as likely. I think it will take technology to make technology more useful and more meaningful. Many of us pride ourselves on having a ‘BS-meter,’ where we believe we can tell honestly delivered information from fake news and disinformation. The instinctual BS-meter is not enough. The next version of the ‘BS-meter’ will need to be technologically based. The tricks of misinformation have far outstripped the ability of people to reliably tell whether they are receiving BS or not – not to mention that it requires a constant state of vigilance that’s exhausting to maintain. I think that the ability and usefulness of the web to enable positive grassroots civic communication will be harnessed, moving beyond mailing lists and fairly static one-way websites. Could there be ‘Slack for Community Self-Governance?’ If not that platform, perhaps something new and aimed specifically at these tasks and needs.”
Oscar Gandy , a professor emeritus of communication at the University of Pennsylvania, said, “Corporate actors will make use of technology to weaken the possibility for improvements in social and civic relationships. I am particularly concerned about the use of technology in the communications realm in order to increase the power of strategic or manipulative communications to shape the engagement of members of the public with key actors within a variety of governance relationships.”
An expert in the ethics of autonomous systems based in Europe responded, “Fake news is more and more used to manipulate a person’s opinion. This war of information is becoming so important that it can influence democracy and the opinion of people before the vote in an election for instance. Some AI tools can be developed to automatically recognize fake news, but such tools can be used in turn in the same manner to enhance the belief in some false information.”
A research leader for a U.S. federal agency wrote, “At this point in time, I don’t know how we will reduce the spread of misinformation (unknowing/individual-level) and disinformation (nefarious/group-level), but I hope that we can.”
A retired information science professional commented, “Dream on, if you think that you can equate positive change with everybody yelling and those with the most clout (i.e., power and money) using their power to see their agendas succeed. Minority views will always be that, a minority. At present and in the near future the elites manipulate and control.”
A research scientist for a major technology company whose expertise is technology design said, “We have already begun to see increased protections around personal privacy. At present, it is less clear how we might avoid the deliberate misuse of news or news-like content to manipulate political opinions or outcomes, but this does not seem impossible. The trick will be avoiding government censorship and maintaining a rich, vigorous exchange of opinions.”
Privacy issues will continue to be a hot button topic
Multiple experts see a growing need for privacy to be addressed in online spaces.
Ayden Férdeline , technology policy fellow at the Mozilla Foundation, responded, “Imagine if everyone on our planet was naked, without any clear options for obtaining privacy technology (clothing). It would not make sense to ask people what they’d pay or trade to get this technology. This is a ‘build it and they will come’ kind of scenario. We’re now on the verge, as a society, of appropriately recognizing the need to respect privacy in our Web 2.0 world, and we are designing tools and rules accordingly. Back in 1992, had you asked people if they’d want a free and open internet, or a graphical browser with a walled garden of content, most would have said they prefer AOL. What society needed was not AOL but something different. We are in a similar situation now with privacy; we’re finally starting to grasp its necessity and importance.”
We’re now on the verge, as a society, of appropriately recognizing the need to respect privacy in our Web 2.0 world, and we are designing tools and rules accordingly. Ayden Férdeline
Graham Norris , a business psychologist with expertise in the future of work, said, “Privacy no longer exists, and yet the concept of privacy still dominates social-policy debates. The real issue is autonomy of the individual. I should own my digital identity, the online expression of myself, not the corporations and governments that collect my interactions in order to channel my behaviour. Approaches to questions of ownership of digital identity cannot shift until the realization occurs that autonomy is the central question, not privacy. Nothing currently visible suggests that shift will take place.”
Eduardo Villanueva-Mansilla , an associate professor of communications at Pontificia Universidad Catolica, Peru, and editor of the Journal of Community Informatics, wrote, “I’m trying to be optimistic, by leaving some room to innovative initiatives from civic society actors. However, I don’t see this as necessarily happening; the pressure from global firms will probably too much to deal with.”
An international policy adviser on the internet and development based in Africa commented, “Technology is creating and will continue to evolve and increase the impact of social and civic innovation. With technology we will see new accountability tools and platforms to raise voices to counter societal ills, be it in leadership, business and other faculties. We must however be careful so that these innovations themselves are not used to negatively impact end users, such issues like privacy and use of data must be taken on in a way that users are protected and not exposed to cybercrime and data breaches that so often occur now.”
Jamie Grady , a business leader, wrote, “As technology companies become more scrutinized by the media and government, changes – particularly in privacy rights – will change. People will learn of these changes through social media as they do now.”
Technology use often disconnects or hollows out community
Some respondents commented on rising problems with a loss of community and the need for more-organic, in-person, human-to-human connection and the impact of digital distancing.
Jonathan Grudin , principal researcher at Microsoft, commented, “Social and civic activity will continue to change in response to technology use, but will it change its trajectory? Realignments following the Industrial Revolution resulted from the formation of new face-to-face communities, including union chapters, community service groups such as Rotary Club and League of Women Voters, church groups, bridge clubs, bowling leagues and so on. Our species is designed to thrive in modest-sized collocated communities, where everyone plays a valued part. Most primates become vulnerable and anxious when not surrounded by their band or troop. Digital media are eroding a sense of community everywhere we look. Can our fundamental human need for close community be restored or will we become more isolated, anxious and susceptible to manipulation?”
Rebecca Theobald , an assistant research professor at the University of Colorado, Colorado Springs, said, “Technology seems to be driving people apart, which would lead to fewer connections in society.”
The program director of a university-based informatics institute said, “There is still a widening gap between rural and urban as well as digital ‘haves’ and ‘have nots.’ As well, the ability to interact in a forum in which all members of society have a voice is diminishing as those with technology move faster in the digital forums than the non-tech segment of the population that use non-digital discourse (interpersonal). The idea of social fabric in a neighborhood and neighborly interactions is diminishing. Most people want innovation – it is the speed of change that creates divisions.”
An infrastructure architect and internet pioneer wrote, “The kind of social innovation required to resolve the problems caused by our current technologies relies on a movement back toward individual responsibility and a specific willingness to engage in community. As both of these work against the aims of the corporate and political elite as they exist today, there is little likelihood these kinds of social innovations are going to take place. The family and church, for instance, which must be the core institutions in any rebuilding of a culture that can teach the kind of personal responsibility required, were both hollowed out in the last few decades. The remaining outward structures are being destroyed. There is little hope either families or churches will recover without a major societal event of some sort, and it will likely take at least one generation for them to rebuild. The church could take on the task of helping rebuild families, but it is too captured in attempts to grow ever larger, and consume or ape our strongly individualistic culture, rather than standing against it.”
A researcher based in North America predicted a reining in of the digital in favor of the personal: “Between email and phones, I think we’re close to peak screen time, a waste of time, and it’s ruining our eyes. Just as we have forsaken our landlines, stopped writing letters, don’t answer our cellphones, a concept of an average daily digital budget will develop, just as we have a concept of average daily caloric intake. We’ll have warning labels that rate content against recommended daily allowances of different types of content that have been tested to be good for our mental health and socialization, moderately good, bad, and awful – the bacon of digital media. And people who engage too much will be in rehab, denied child custody and unemployable. Communities, residences and vacation areas will promote digital-free, mindfulness zones – just as they have quiet cars on the train.”
Society needs to catch up and better address the threats and opportunities of tech
Some of these experts said that the accelerating technological change of the digital age is making it difficult for humans to keep up and respond to emerging challenges.
A chair of political science based in the American South commented, “Technology always creates two new problems for every one it solves. At some point, humans’ cognitive and cooperative capacities – largely hard-wired into their brains by millennia of evolution – can’t keep up. Human technology probably overran human coping mechanisms sometime in the later 19th century. The rest is history.”
There is a gap between the rate at which technology develops and the rate at which society develops. We need to take care not to fall into that gap. Louisa Heinrich
Larry Rosen , a professor emeritus of psychology at California State University, Dominguez Hills, known as an international expert on the psychology of technology, wrote, “I would like to believe that we, as citizens, will aid in innovation. Smart people are already working on many social issues, but the problem is that while society is slow to move, tech moves at lightning speed. I worry that solutions will come after the tech has either been integrated or rejected.”
Louisa Heinrich , a futurist and consultant expert in data and the Internet of Things, said, “There is a gap between the rate at which technology develops and the rate at which society develops. We need to take care not to fall into that gap. I hope we will see a shift in governance toward framework-based regulation, which will help mitigate the gap between the pace of change in technology and that in government. At the very least, we need to understand the ways in which technology can extend or undermine the rules and guidelines we set for our businesses, workplaces, public spaces and interactions. To name just one common example, recruitment professionals routinely turn to Facebook as a source of information on prospective employees. This arguably violates a number of regulations designed to protect people from being denied work based on personal details not relevant to that work. How do we unravel this conundrum, bearing in mind that there will always be another social network, another digital source to mine for information about people? Taken from another angle, there is a significant gap between what users understand about certain bits of technology and the risks they take using them. How can we educate people about these risks in a way that encourages participation and co-creation, rather than passivity? As the so-called Gen Z comes of age, we will see a whole generation of young adults who are politically engaged at a level not seen in several generations, who are also native users of technology tools. This could bring about a positive revolution in the way technology is used to facilitate civic engagement and mutually empower and assist citizens and government. Technology provides us with powerful tools that can help us advance socially and civically, but these tools need to be thoughtfully and carefully put to use – when we encode barriers and biases into the applications that people need to use in daily life, whether intentionally or no, we may exclude whole segments of society from experiencing positive outcomes. We are living through a time of rapid and radical change – as always, the early stages feel uncomfortable and chaotic. But we can already see the same tools that have been used to mislead citizens being used to educate, organise, motivate and empower them. What’s needed is a collective desire to prioritise and incentivise this. New Zealand is leading the way with the world’s first ‘well-being’ budget.”
Bulbul Gupta , founding adviser at Socos Labs, a think tank designing artificial intelligence to maximize human potential, responded, “Until government policies, regulators, can keep up with the speed of technology and AI, there is an inherent imbalance of power between technology’s potential to contribute to social and civic innovation and its execution in being used this way. If technology and AI can make decisions about people in milliseconds that can prevent their full social or civic engagement, the incentive structures to be used toward mitigating the problems of the digital age cannot then be solved by technology.”
Gene Policinski , a journalist and First Amendment law expert at the Freedom Forum Institute, observed, “We forget how new the ‘tech revolution’ really is. As we move forward in the next decade, the public’s awareness of the possibilities inherent in social and civic innovation, the creativity of the tech world working with the public sector and public acceptance of new methods of participation in democratic processes will begin to drown out and eventually will surpass the initial problems and missteps.”
Gabriel Kahn , former bureau chief for The Wall Street Journal, now a professor of journalism researching innovation economics in emerging media at the University of Southern California, wrote, “We are not facing a ‘Terminator’-like scenario. Nor are we facing a tech-driven social utopia. Humans are catching up and understanding the pernicious impact of technology and how to mitigate it.”
Kathee Brewer , director of content at CANN Media Group, predicted, “Much like society developed solutions to the challenges brought about by the Industrial Revolution, society will find solutions to the challenges of the Digital Revolution. Whether that will happen by 2030 is up for debate. Change occurs much more rapidly in the digital age than it did at the turn of the 20th century, and for society to solve its problems it must catch up to them first. AND people, including self-interested politicians, must be willing to change. Groups like the Mozilla Foundation already are working on solutions to invasions of privacy. That work will continue. The U.S. government probably won’t make any major changes to the digital elections framework until after the 2020 election, but changes will be made. Sadly, those changes probably will result from some nastiness that develops due to voters of all persuasions being unwilling to accept electoral results, whatever the results may be.”
Valerie Bock of VCB Consulting, former Technical Services Lead at Q2 Learning, responded, “I think our cultures are in the process of adapting to the power our technologies wield, and that we will have developed some communal wisdom around how to evaluate new ones. There are some challenges, but because ordinary citizens have become aware that images can be ‘photoshopped’ the awareness that video can be ‘deepfaked’ is more quickly spreading. Cultural norms as well as technologies will continue to evolve to help people to apply more informed critiques to the messages they are given.”
Bach Avezdjanov , a program officer with Columbia University’s Global Freedom of Expression project, said, “Technological development – being driven by the Silicon Valley theory of uncontrolled growth – will continue to outpace civic and social innovation. The latter needs to happen in tandem with technological innovation, but instead plays catch-up. This will not change in the future, unless political will to heavily regulate digital tools is introduced – an unlikely occurrence.”
A computing science professor emeritus from a top U.S. technological university commented, “Social/civic innovation will occur but most likely lag well behind technological innovation. For example, face-recognition technology will spread and be used by businesses at a faster pace than social and legal norms can develop to protect citizens from any negative effects of that technology. This technology will spread quickly, due to its various positives (increased efficiencies, conveniences and generation of profits in the marketplace) while its negatives will most likely not be countered effectively through thoughtful legislation. Past Supreme Court decisions (such as treating corporations as persons, WRT unlimited funding of political candidates, along with excessive privacy of PACs) have already undermined U.S. democracy. Current populist backlashes, against the corruption of the Trump government, may also undermine democracy, such as the proposed Elizabeth Warren tax, being not on profits, but upon passive wealth itself – a tax on non-revenue-producing illiquid assets (whose valuation is highly subjective), as in her statement to ‘tax the jewelry of the rich’ at 2% annually. Illiquid assets include great private libraries, great private collections of art, antiques, coins, etc. – constituting an assault on the private sector, that if successful, will weaken democracy by strengthening the confiscatory power of government. We could swing from current excesses of the right to future excesses of the left.”
Despite current trends, there is reason to hope for better days
Many of the experts in this canvassing see a complicated and difficult road ahead, but express hope for the future.
Cheryl B. Preston , an expert in internet law and professor at Brigham Young University Law School, said, “Innovation will bring risk. Change will bring pain. Learning will bring challenges. Potential profits will bring abuse. But, as was the decision of Eve in the Garden of Eden, we need to leave the comfortable to learn and improve. If we can, by more informed voting, reduce the corruption in governmental entities and control corporate abuse, we can overcome difficulties and advance as a society. These advances will ultimately bring improvement to individuals and families.”
John Carr , a leading global expert on young people’s use of digital technologies, a former vice president of MySpace, commented, “I know of no proof for the notion that more people simply knowing more stuff, even stuff that is certifiably factually accurate, will necessarily lead to better outcomes for societies. But I do harbour a hope that if, over time, we can establish the idea that there are places on the internet that are reliable sources of information, it will in the medium to longer term help enough people in enough countries to challenge local demagogues and liars, making it harder for the demagogues and liars to succeed, particularly in times of national crisis or in times when war might be on the visible horizon. I used to think that if the internet had been around another Hitler would be impossible. Recently I have had a wobble on that but my optimism ‘trumps’ that gloomy view.”
Mike Douglass , an independent developer, wrote, “There is a significant realization that a stampede to create connections between anonymous people and devices was a bad idea. It’s up to the technologists and – more importantly – those who want to make money out of technology – to come up with a more measured approach. There’s a reason why gentlemen obtained letter of introduction to other gentlemen – one shouldn’t trust some random individual turning up on your doorstep. We need the equivalent approach. I’ve no idea what new innovations might turn up. But if we don’t get the trust/privacy/security model right we’ll end up with more social media disasters.”
Hume Winzar , an associate professor and director of the business analytics undergraduate program at Macquarie University, Sydney, Australia, predicted, “With more hope than evidence, I’d like to think that reason will eventually overcome the extraordinary propaganda machines that are being built. When the educated upper-middle classes realise that the ‘system’ is no longer serving them, then legal and institutional changes will be necessary. That is, only when the managers who are driving the propaganda machine(s) start to feel that they, personally, are losing privacy, autonomy, money and their children’s future, then they will need to undermine the efforts of corporate owners and government bureaucrats and officials.”
Carolyn Heinrich , a professor of education and public policy at Vanderbilt University, said, “My hope (not belief) is that the ‘techlash’ will help to spur social and civic innovations that can combat the negative effects of our digitization of society. Oftentimes, I think the technology developers create their products with one ideal in mind of how they will be used, overlooking that technology can be adapted and used in unintended and harmful ways. We have found this in our study of educational technology in schools. The developers of digital tools envision them as being used in classrooms in ‘blended’ ways with live instructors who work with the students to help customize instruction to their needs. Unfortunately, more often than not, we have seen the digital tools used as substitutes for higher-quality, live instruction and have observed how that contributes to student disengagement from learning. We have also found some of the content lacking in cultural relevance and responsiveness. If left unchecked, this could be harmful for far larger numbers of students exposed to these digital instructional programs in all 50 states. But if we can spur vendors to improve the content, those improvements can also extend to large numbers of students. We have our work cut out for us!”
In the field I follow, artificial intelligence, the numbers of professionals who take seriously the problems that arise as a consequence of this technology are reassuring. Pamela McCorduck
Heywood Sloane , entrepreneur and banking and securities consultant, wrote, “I’m hopeful the it will be a positive contributor. It has the ability to alter the way we relate to our environment in ways that shrink the distances between people and help us exercise control over our personal and social spaces. We are making substantial progress, and 5G technology will accelerate that. On the flip side, we need to find mechanisms and processes to protect our data and ourselves. They need to be strong, economic and simple to deploy and use. That is going to be a challenge.”
Pamela McCorduck , writer, consultant and author of several books, including “Machines Who Think,” commented, “I am heartened by the number of organizations that have formed to enhance social and civic organization through technology. In the field I follow, artificial intelligence, the numbers of professionals who take seriously the problems that arise as a consequence of this technology are reassuring. Will they all succeed? Of course not. We will not get it right the first time. But eventually, I hope.”
Yoshihiko Nakamura , a professor of mechno-informatics at the University of Tokyo, observed, “The current information and communication technology loses diversity because it is still insufficient to enhance the affectivity or emotion side of societies. In this sense I can see the negative side of current technology to human society. However, I have a hope that we can invent uses of technology to enhance the weaker side and develop tomorrow’s technology. The focus should be on the education of society in the liberal arts.”
Ryan Sweeney , director of analytics at Ignite Social Media, commented, “In order to survive as a functioning society, we need social and civic innovation to match our use of technology. Jobs and job requirements are changing as a result of technology. Automation is increasing across a multitude of industries. Identifying how we protect citizens from these changes and help them adapt will be instrumental in building happiness and well-being.”
Miles Fidelman , founder, Center for Civic Networking and principal Protocol Technologies Group, responded, “We can see clear evidence that the internet is enabling new connections, across traditional boundaries – for the flow of information, culture and commerce. It is strengthening some traditional institutions (e.g., ties between geographically distributed family members) and weakening others (e.g., the press). Perhaps the most notable innovation is that of ad hoc, network-centric organizations – be they global project teams, or crisis response efforts. How much of this innovation will make things better, how much it will hurt us, remains an open question.”
A technology developer active in IETF said, “I hope mechanisms will evolve to exploit the advantages of new tech and mitigate the problems. I want to be optimistic, but I am far from confident.”
A renowned professor of sociology known for her research into online communications and digital literacies observed, “New groups expose the error of false equivalence and continue to challenge humans to evolve into our pre-frontal cortex. I guess I am optimistic because the downside is pretty terrible to imagine. It’s like E.O. Wilson said: ‘The real problem of humanity is the following: We have paleolithic emotions; medieval institutions; and god-like technology. And it is terrifically dangerous, and it is now approaching a point of crisis overall.’”
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Trust, Facts & Democracy
Most Popular
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Defense Technologies
- Digital Media
- Engineering
- K-12 Programs
- Manufacturing
- Mathematics
- Occupational Safety & Health
- Supply Chain & Logistics
- Graduate Certificates
- Professional Certificates
- Savannah Campus
- Workplace Learning & Professional Development
- Corporate Education
- Train at Your Location
- Georgia Tech Summer
- Military Programs
- ESL (English as a Second Language)
- Online Courses
- Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs)
- Global Learning Center
- Savannah Facilities
Craft of Problem Solving
- Course Content
- Requirements & Materials
COURSE ID: DEF 4522P
Contact for course-related questions
Instructors
This class builds on the core ideas in the Principles of Problem Solving class and introduces a rigorous problem-solving framework built around the notion of the modern problem solver — and encourages you to become one! The modern problem solver is a person who can build informative models (both qualitative and quantitative) of the problem at hand and use these models to gain insight to support decision making and further learning. This person also is someone who augments his or her domain knowledge with mathematical, statistical, and programming skills to create computational models that drive insight. Are you interested in honing your skills on how to create and apply simple models to aid in decision making? If so, you will find this class enormously beneficial.
WICKED PROBLEMS
- Review of wicked problems and opportunity driven problem solving
- Introduction to the modern problem solver
ELEMENTS OF EFFECTIVE THINKING
- Introduction to the five elements of effective thinking and learning
- Reintroduction to the scientific method
- Overview of statistical thinking and how it is related to problem solving
MODEL BASED PROBLEM SOLVING
- Introduction to systems engineering conceptual design and how it is a sound methodology for model-based problem solving
- Formal introduction to model-based problem solving
- Discussion on the differences between expert modelers and novice modelers
- Overview of the seven management and planning tools for building rigorous, qualitative models
MODELING FOR INSIGHT
- Introduction and application of the Modeling for Insight formal modeling process for creating quantitative models
- Introduction and application of Python and Jupyter Notebook as a means to lower the barrier to model building for those students that aren't “programming experts”
MODELING CASE STUDY
- Two case studies to reinforce the tools and techniques learned in the class
- DEF 4519P - Principles of Problem Solving
Recommended
- DEF 4501P - Fundamentals of Modern Systems Engineering
- Students must each bring a laptop with internet access and a modern web browser for the two case studies
- Notebook with lecture notes
- CD-ROM of reference materials and software
- Copies of “Modeling for Insight” and “The 5 Elements of Effective Thinking” for additional reading material outside of class
Session Details
Special Discounts: Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI) employees are eligible to receive a discount. If you are a GTRI employee, please go to the Organizational Development website and look for the coupon code under GT Professional Development . Review coupon instructions for more information.
Upcoming Sessions
Aug 27, 2024 - aug 29, 2024 register by aug 8, 2024 atlanta, ga $1,695, items to purchase, previous sessions, who should attend.
This class is designed for business analysts, scientists, and engineers who have not completed a Ph.D.

What You Will Learn
- The modern problem solver and the five elements of effective thinking
- Statistical thinking and how it is related to problem solving
- A formal introduction to systems engineering conceptual design and how it is a sound methodology for model-based problem solving
- An overview of the seven management and planning tools for building rigorous, qualitative models
- Tools and techniques learned in the class through two case studies

How You Will Benefit
- Improve how you assess and tackle complex, ill-defined problems.
- Gain a better understanding on how to improve your ability to learn new topics and explore wicked problems.
- Learn how to build simple qualitative and quantitative models of complex problems to gain insight.
- Apply tools and methods developed in the systems engineering field to add additional structure to model building and learning.
Taught by Experts in the Field
Grow your professional network.
The course schedule was well-structured with a mix of lectures, class discussions, and hands-on exercises led by knowledgeable and engaging instructors.
Related Programs

Access (ADA)
The Georgia Tech Global Learning Center and Georgia Tech-Savannah campus is compliant under the Americans with Disabilities Act. Any individual who requires accommodation for participation in any course offered by GTPE should contact us prior to the start of the course.
Courses that are part of certificate programs include a required assessment. Passing criteria is determined by the instructor and is provided to learners at the start of the course.
CEUs are awarded to participants who attend a minimum of 80% of the scheduled class time.
- Citizenship
Georgia Tech’s Office of Research Security and Compliance requires citizenship information be maintained for those participating in most GTPE courses. Citizenship information is obtained directly from the learner at the time of registration and is maintained in the Georgia Tech Student System.
Code of Conduct
Learners enrolled in any of Georgia Tech Professional Education's programs are considered members of the Georgia Tech community and are expected to comply with all policies and procedures put forth by the Institute, including the Student Code of Conduct and Academic Honor Code .
Course Changes and Cancellations
Please refer to our Terms and Conditions for complete details on the policies for course changes and cancellations.
Data Collection and Storage
Participants in GTPE courses are required to complete an online profile that meets the requirements of Georgia Tech Research Security. Information collected is maintained in the Georgia Tech Student System. The following data elements are considered directory information and are collected from each participant as part of the registration and profile setup process:
- Full legal name
- Email address
- Shipping address
- Company name
This data is not published in Georgia Tech’s online directory system and therefore is not currently available to the general public. Learner information is used only as described in our Privacy Policy . GTPE data is not sold or provided to external entities.
Sensitive Data The following data elements, if in the Georgia Tech Student Systems, are considered sensitive information and are only available to Georgia Tech employees with a business need-to-know:
- Georgia Tech ID
- Date of birth
- Religious preferences
- Social security numbers
- Registration information
- Class schedules
- Attendance records
- Academic history
At any time, you can remove your consent to marketing emails as well as request to delete your personal data. Visit our GTPE EU GDPR page for more information.
Inclement Weather
Classes and events being held at the Georgia Tech Global Learning Center in Atlanta or Georgia Tech-Savannah campus may be impacted by closures or delays due to inclement weather.
The Georgia Tech Global Learning Center will follow the guidelines of Georgia Tech main campus in Atlanta. Students, guests, and instructors should check the Georgia Tech homepage for information regarding university closings or delayed openings due to inclement weather. Please be advised that if campus is closed for any reasons, all classroom courses are also canceled.
Students, guests, and instructors attending classes and events at Georgia Tech-Savannah should check the Georgia Tech-Savannah homepage for information regarding closings or delayed openings due to inclement weather.
Program Completion
GTPE certificates of program completion consist of a prescribed number of required and elective courses offered and completed at Georgia Tech within a consecutive six-year period. Exceptions, such as requests for substitutions or credit for prior education, can be requested through the petition form . Exceptions cannot be guaranteed.
Please refer to our Terms and Conditions for complete details on the policy for refunds.
Smoking & Tobacco
Georgia Tech is a tobacco-free and smoke-free campus. The use of cigarettes, cigars, pipes, all forms of smokeless tobacco, and any other smoking devices that use tobacco are strictly prohibited. There are no designated smoking areas on campus.
Special Discounts
Courses that are eligible for special discounts will be noted accordingly on the course page. Only one coupon code can be entered during the checkout process and cannot be redeemed after checkout is complete. If you have already registered and forgot to use your coupon code, you can request an eligible refund . GTPE will cancel any transaction where a coupon was misused or ineligible. If you are unsure if you can use your coupon code, please check with the course administrator.
GTPE does not have a program for senior citizens. However, Georgia Tech offers a 62 or Older Program for Georgia residents who are 62 or older and are interested in taking for credit courses. This program does not pay for noncredit professional education courses. Visit the Georgia Tech Undergraduate Admissions page for more information on the undergraduate program and Georgia Tech Graduate Admissions page for more information on the graduate program.
Group Registrations
How do i register my group.
There is no special process or form to register your group. All interested learners must create and manage their own individual profiles, accounts, and registrations.
- Complete a GTPE profile .
- Shop for a course .
- Add the course(s) to the cart.*
- Apply a group discount code (if applicable).
- Provide an accepted payment method to complete the order (credit card, third party credit card holder, or one accepted payment document).
*Carts will remain active for 14 days, but seats are not held until the transaction is complete.
How do I apply for a group discount?
Courses that offer group discounts will display the discount code on the course page. Your employees will use the code during the registration process and cart totals will adjust accordingly. Group discounts can only be used if three or more employees from the company attend the same course and only one coupon code can be use per shopping cart.
If you have already registered and forgot to use your coupon code, you can request an eligible refund .
What are the accepted payment documents if I am unable to pay by credit card?
Accepted payment documents must be uploaded during the registration process. They include:
- A company purchase order (PO or SF182)
- A letter of authorization on company letterhead
- A corporate education application/voucher
What are the requirements for payment documents?
- Name of company and physical address
- Name of employee(s) approved for training
- Document number (SF-182 documents: Section C, Box 4)
- Billing address (SF-182 documents: Section C, Box 6)
- Course title and course dates
- Maximum disbursement amount (billing amount)
- Expiration date (if applicable)
- Authorized signature(s)
- Payment terms less than or equal to net 30
The employee can print of a copy of their shopping cart to submit if required for payment documents. The cart will remain active for 14 days, but the seat will not held until registration and payment is complete.
Registrations cannot be processed without payment. If your employee is concerned about losing a seat in a class because of internal company processes, we suggest that they go ahead and register and pay with a personal or corporate credit card and seek reimbursement.
Who can I contact for assistance?
If you need assistance with your group registration or have questions on how to start the process, please feel free to contact us at 404-385-3501 or [email protected] .
Individual Registrations
Where are your courses held.
Most GTPE classroom courses are held at the Georgia Tech Global Learning Center (GLC). Any courses that are held elsewhere will be clearly marked on the course page. Get information on parking, directions, and transportation to the GLC.
Do you provide overnight guest rooms?
We do not provide overnight rooms. However, accommodations can be made at the Georgia Tech Hotel and Conference Center, adjacent to us. Additional hotels can be found within walking distance. Get more information on accommodations .
What if I need to transfer to another course?
Learners may transfer to another course of equal or greater cost if notification is made at least 10 business days prior to the original course start date. The course to which one transfers must already be scheduled.
When should I register for a course?
We recommend you register for courses as early as possible. Session details will indicate when there is less than five reamining seats in a particular session.
How can I make updates to my contact information?
Updates to your company, address, email, phone, and passwords can be made directly on the GTPE website. Name changes and citizenship changes must be submitted to the GTPE Registrar’s Office.
How can I register for a course?
- Apply a special discount code (if applicable).
Do you accept walk-in registrations?
Walk-in registrations are accepted based on space availability but are not guaranteed for any courses.
Do you offer special discounts?
If available, discounts will display on the course page or will be automatically applied during the purchase process. Only one coupon code should be entered during the checkout process and will be validated by the system if applicable to items in your cart. If you have already registered and forgot to use your coupon code, you can request an eligible refund .
GTPE does not have a discount program for senior citizens. However, Georgia Tech offers a 62 or Older Program for Georgia residents who are 62 or older and are interested in taking for credit courses. This program does not pay for noncredit professional education courses. Visit the Georgia Tech Undergraduate Admissions page for more information on the undergraduate program and the Georgia Tech Graduate Admissions page for more information on the graduate program.
What professional education programs are eligible for veteran education benefits?
The following GTPE programs are eligible for veteran education benefits:
- Construction Safety and Health Certificate Program (Atlanta campus courses only)
- Project Management Certificate Program (Atlanta campus courses only)
- Safety and Health Management Certificate Program (Atlanta campus courses only)
View the GTPE veteran’s GI Bill benefits checklist for more information.
Do you have a program for senior citizens?
GTPE does not have a program for senior citizens. However, Georgia Tech offers a 62 or Older Program for Georgia residents who are 62 or older and are interested in taking for credit courses. This program does not pay for noncredit professional education courses. Visit the Georgia Tech Undergraduate Admissions page for more information on the undergraduate program and the Georgia Tech Graduate Admissions page for more information on the graduate program.
What happens if my course is cancelled?
In the event of a cancellation, we will provide you with a full refund or transfer to an equivalent course.
Do I need a student visa to take a course?
Short courses (1-5 days) and conferences do not require a student visa. A B-2 Tourist Visa, along with a copy of your registration confirmation email and a copy of your completed web registration order page, should suffice.
If participation in a course is employment related, with immediate departure from the U.S., then a B-1 Temporary Business Visa will be required.
We encourage you to contact your U.S. Consulate or Embassy to determine visa eligibility. Full refunds will be provided to participants who are unable to obtain an entry visa and contact our office prior to the start of the course.
English as a Second Language students should contact the Language Institute for admission and visa requirements.
Do you provide letters of invitations or immigration documents for student visas?
We do not issue letters of invitation and cannot provide immigration documents for the issuance of a student visa. Full refunds will be provided to participants who are unable to obtain an entry visa and contact our office prior to the start of the course.
What payment methods do you accept?
Full payment is due at time of registration. Accepted payment methods include:
- Credit cards
- Purchase orders (company and government)
- International wire payments *
- Georgia Tech Workday Number (for Georgia Tech employees only)
- Private loans *
- GI Bill benefits * (Eligible Atlanta campus courses only. Off-campus and online courses are not eligible for VA Benefits.)
- Company checks*
* Requires document upload or transaction verification during the checkout process.
What information is needed for a purchase order?
Purchase order documents must include the following:
- Name of company’s financial contact and/or ap (accounts payable) email address
Please do not include social security numbers on purchase order documents.
How do I pay with a company check?
- Make your check payable to “Georgia Institute of Technology” and include the order number and participant name on the face of the check.
- Choose “Company Purchase Order” as the payment method at checkout and upload a copy of your check to your order.
GTPE Accounting Georgia Institute of Technology Global Learning Center 84 5th St. NW Atlanta, GA 30308-1031
When is a payment due for a course?
Full payment is due at the time of registration.
How do I make a payment?
General Public Payment is due at the time of purchase. Invoice payments must adhere to the Board of Regent’s business terms of net 30.
Georgia Tech Employees PeopleSoft payments are processed at the time of registration. Georgia Tech employees cannot use PCards for GTPE registration charges.
Are there additional fees for books, supplies, or materials?
Additional fees vary by course. Be sure to review the Requirements & Materials tab on the course page for more information.
My company has offered to pay for this course. Can you invoice them directly?
Yes. Here are the steps to receive an invoice:
- Add the course(s) to the cart.
- Print your cart and submit to your employer as the cost estimate.
- Receive a copy of your company’s Purchase Order or payment approval document for GTPE to invoice against.
- Return to your cart, proceed through checkout and upload our company PO in the final payment step.
- The GTPE Business Office will generate an invoice 10 days prior to the start of the course at which point you are no longer eligible to withdraw with fund. Your company must:
- Abide by the Georgia Tech and Board of Regent’s business terms of net 30.
- Pay the full balance of a Georgia Tech invoice (there are no discounts for payments made early or on time).
- Pay the invoice if the employee fails to withdraw during the refund period and does not attend the course.
What is your policy for refunding a credit card payment?
Credit card refunds are processed to the original credit card. The credit card issuer is responsible for refund credit balances to the cardholder.
Do you offer payment plans?
We do not offer payment plans for any of our services, conferences, or courses. Payment must be made in full at time of purchase.
Will participants be issued a 1098-T tax form for courses taken at GTPE?
GTPE cannot issue 1098-T tax forms. If you have a payment history need for tax purposes, we are happy to provide you with receipts of payment. Please submit your requires to [email protected] . Be sure to include your full legal name and Georgia Tech ID which can be found within your GTPE profile .
Withdrawals, Substitutions, and Transfers
Course registration changes.
Please see our Terms and Conditions for complete details on our policies for course registration changes.
Transcripts, Certificates, and Credits
Are your ceus accredited.
GTPE’s use of CEU follows accepted criteria and guidelines established by the Georgia Board of Regents which follows international standards such as The International Association for Continuing Education and Training (IACET).
Do you provide transcripts or certificates for Professional Development Hours or Professional Development Units?
GTPE does not issue transcripts or certificates with Professional Develop Hours (PDH) or Professional Development Units (PDU), but the crosswalk here is provided for reference.
One CEU = 10 contact hours of instruction One PDH = 1 contact hour of instruction (one CEU = 10 PDH) One PDU = 1 contact hour of instruction (one CEU = 10 PDU)
Will I receive a course completion certificate?
Upon successful completion of most GTPE courses (80% minimum attendance and a passing grade in courses that require an assessment), you may receive a certificate indicating the number of CEUs earned. Certificate issuance exceptions include courses with outstanding credentialing entities (i.e. OSHA or PADI).
How do I request a transcript of my CEUs?
CEUs earned are recorded in the attendee’s name and will appear on a GTPE transcript. All transcripts must be requested by the attendee via the transcript request form . Requests are typically processed within three business days.
How do I petition for a program certificate audit?
For an audit of your transcript for progress toward completion of a certificate, please complete the transcript request form . GTPE courses do not provide academic or degree credit. Georgia Tech academic or degree credit is only available to matriculated students taking courses that meet degree requirements.
What requirements are required by my state and association?
For specific information on state licensing or credit requirements, please contact your state licensing board. If you are seeking certification through a professional association, please review the specific requirements with that association.
TRAIN AT YOUR LOCATION
We enable employers to provide specialized, on-location training on their own timetables. Our world-renowned experts can create unique content that meets your employees' specific needs. We also have the ability to deliver courses via web conferencing or on-demand online videos. For 15 or more students, it is more cost-effective for us to come to you.
Flexible Schedule
Group training, customize content, on-site training, earn a certificate, want to learn more about this course.
- Our Mission
How to Help Students Troubleshoot Technology Problems
Teaching students the basics of solving problems with tablets and laptops can empower them when things go wrong.

Technology has been the best thing and the worst thing when it comes to making remote learning work. It’s been a lifeline for connecting with our students during the pandemic, but it also can be a big headache when glitches pop up.
Sometimes, it feels like troubleshooting problems with technology is a job of its own. Students may ask for assistance when things go wrong, and it helps to have a process or steps to guide them. It’s also important that we empower our students to solve technology problems independently. One resource that I love to share with students and colleagues is this Edpuzzle troubleshooting article .
When I was in the classroom as a middle school teacher of Intro to Computer Science and Principles of Information Technology, I would begin the year with the Code.org Problem Solving Process lesson . I would tell my students that before we touched the computers or created programs, it was important that they understand how to solve or debug technology since they would be using it on a daily basis. We would go through a series of activities the first two weeks of school so that they would feel comfortable with the process, and then I would help them practice the process whenever issues arose throughout the year.
The problem-solving process has four steps: define, prepare, try, and reflect. As a digital learning coach, I have been using these steps in a similar way as I help students and my colleagues find solutions to their technology problems. The case study below will take you through how your students can use this process. It will also provide insight that may help in your own classroom.
Recently, I went through this process with a student who was having Chromebook issues. The student and I met through Google Meet. Clearly, her device was working, but she was unable to search for anything. I had never seen this problem. I was honest with the student that even though I didn’t have the answer, we would work to figure out something. We didn’t have a Chromebook to exchange out, so it was important to troubleshoot.
The first time we went through the cycle together, I asked the student to clear her cookies and restart the device. That didn’t resolve the issue. Then I got permission to go into her device remotely using Chrome Remote Desktop . I was able to take over the student’s device using this free software. Checking her settings and playing around with her search features didn’t solve anything. As we worked together, we took notes on what we were seeing.
Then I checked her Chrome extensions and discovered an extension that needed to be removed to solve the problem. The student said, “We spent all that time on one little extension.” I chuckled and said, “Yeah, but we got it.” Then the student said, “I learned a lot, though, and now I know what to do in the future.” I thanked her for her patience because I had learned right along with her. As educators, we may not have the answers to students’ questions about technology, but trying to solve them together will help our students learn how to do it, too.
The Problem-Solving Process
The first step is to define the problem. This will require many questions to be asked and answered about what’s occurring, especially if you seek help. When seeking help, the more details or visuals you can provide to the other person, the better. I have seen some teachers create videos using Screencastify , Loom , or Flipgrid to showcase what’s happening on their computers. This is a very good way to share information with someone who’s trying to help you.
The second step is to prepare, and the third step is to try to solve the problem. These steps require research and speaking to those you trust to help you troubleshoot. On my campus, I ask the teachers and students to always clear cookies and restart their devices as a habit. Clearing your cookies and restarting or updating your device will help avoid technology issues. Some Chrome extensions can create unexpected problems, so removing extensions that are not added by your technology department will help.
The last step is to reflect. It’s important to note what occurred should this happen again. Creating troubleshooting videos and/or guides to assist your school community is helpful. If someone on your campus is designated to do this, speak with them about how you can access these resources. Through my position, I encourage teachers to share the videos I create with their students and their students’ parents.
There will be times that you cycle through the process more than once until you find a solution, but it’s important you don’t give up. Asking for help is part of the prepare step. It’s important to reach out to colleagues and work together as everyone is learning how to troubleshoot technology together.
- Computer Vision
- Federated Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
- Natural Language Processing
- New Releases
- AI Dev Tools
- Advisory Board Members
- 🐝 Partnership and Promotion

Asif Razzaq
Asif Razzaq is the CEO of Marktechpost Media Inc.. As a visionary entrepreneur and engineer, Asif is committed to harnessing the potential of Artificial Intelligence for social good. His most recent endeavor is the launch of an Artificial Intelligence Media Platform, Marktechpost, which stands out for its in-depth coverage of machine learning and deep learning news that is both technically sound and easily understandable by a wide audience. The platform boasts of over 2 million monthly views, illustrating its popularity among audiences.
- Asif Razzaq https://www.marktechpost.com/author/6flvq/ Top Data Visualization Books to Read in 2024
- Asif Razzaq https://www.marktechpost.com/author/6flvq/ Google DeepMind Releases Penzai: A JAX Library for Building, Editing, and Visualizing Neural Networks
- Asif Razzaq https://www.marktechpost.com/author/6flvq/ Finally, the Wait is Over: Meta Unveils Llama 3, Pioneering a New Era in Open Source AI
- Asif Razzaq https://www.marktechpost.com/author/6flvq/ TrueFoundry Releases Cognita: An Open-Source RAG Framework for Building Modular and Production-Ready Applications
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Interpretable deep learning for biodiversity monitoring: introducing audioprotopnet, an overview of advancements in deep reinforcement learning (deep rl), kdk: a novel machine learning framework that protects vertical federated learning from all the known types of label inference attacks with very high performance, apple vision pro: use cases and special application in the biomedical sector, privacy-preserving training-as-a-service (ptaas): a novel service computing paradigm that provides privacy-friendly and customized machine learning model training for end devices, top 15 ai libraries/frameworks for automatically red-teaming your generative ai application, kdk: a novel machine learning framework that protects vertical federated learning from all the..., privacy-preserving training-as-a-service (ptaas): a novel service computing paradigm that provides privacy-friendly and customized machine..., this ai paper proposes a novel bayesian deep learning model with kernel dropout designed..., google ai proposes mathwriting: transforming handwritten mathematical expression recognition with extensive human-written and synthetic..., comparative analysis of llama 3 with ai models like gpt-4, claude, and gemini, nota ai researchers introduce ld-pruner: a novel performance-preserving structured pruning method for compressing latent....
- AI Magazine
- Privacy & TC
- Cookie Policy
🐝 FREE AI Courses on RAG + Deployment of an Healthcare AI App + LangChain Colab Notebook all included
Thank You 🙌
Privacy Overview
14 Major Tech Issues — and the Innovations That Will Resolve Them
Members of the Young Entrepreneur Council discuss some of the past year’s most pressing technology concerns and how we should address them.
The past year has seen unprecedented challenges to public-health systems and the global economy. Many facets of daily life and work have moved into the digital realm, and the shift has highlighted some underlying business technology issues that are getting in the way of productivity, communication and security.
As successful business leaders, the members of the Young Entrepreneur Council understand how important it is to have functional, up-to-date technology. That ’ s why we asked a panel of them to share what they view as the biggest business tech problem of the past year. Here are the issues they ’ re concerned about and the innovations they believe will help solve them.
Current Major Technology Issues
- Need For Strong Digital Conference Platforms
- Remote Internet Speed and Connections
- Phishing and Data Privacy Issues
- Deepfake Content
- Too Much Focus on Automation
- Data Mixups Due to AI Implementation
- Poor User Experience
1. Employee Productivity Measurement
As most companies switched to 100 percent remote almost overnight, many realized that they lacked an efficient way to measure employee productivity. Technology with “ user productivity reports ” has become invaluable. Without being able to “ see ” an employee in the workplace, companies must find technology that helps them to track and report how productive employees are at home. — Bill Mulholland , ARC Relocation
2. Digital Industry Conference Platforms
Nothing beats in-person communication when it comes to business development. In the past, industry conferences were king. Today, though, the move to remote conferences really leaves a lot to be desired and transforms the largely intangible value derived from attending into something that is purely informational. A new form or platform for industry conferences is sorely needed. — Nick Reese , Elder Guide
3. Remote Internet Speed and Equipment
With a sudden shift to most employees working remotely, corporations need to boost at-home internet speed and capacity for employees that didn ’ t previously have the requirements to produce work adequately. Companies need to invest in new technologies like 5G and ensure they are supported at home. — Matthew Podolsky , Florida Law Advisers, P.A.
4. Too Much Focus on Automation
Yes, automation and multi-platform management might be ideal for big-name brands and companies, but for small site owners and businesses, it ’ s just overkill. Way too many people are overcomplicating things. Stick to your business model and what works without trying to overload the process. — Zac Johnson , Blogger
5. Phishing Sites
There are many examples of phishing site victims. Last year, I realized the importance of good pop-up blockers for your laptop and mobile devices. It is so scary to be directed to a website that you don ’ t know or to even pay to get to sites that actually don ’t exist. Come up with better pop-up blockers if possible. — Daisy Jing , Banish
6. Data Privacy
I think data privacy is still one of the biggest business tech issues around. Blockchain technology can solve this problem. We need more and more businesses to understand that blockchains don’t just serve digital currencies, they also protect people’s privacy. We also need Amazon, Facebook, Google, etc. to understand that personal data belongs in the hands of the individual. — Amine Rahal , IronMonk Solutions
7. Mobile Security
Mobile security is a big issue because we rely so much on mobile internet access today. We need to be more aware of how these networks can be compromised and how to protect them. Whether it ’ s the IoT devices helping deliver data wirelessly to companies or people using apps on their smartphones, we need to become more aware of our mobile cybersecurity and how to protect our data. — Josh Kohlbach , Wholesale Suite
8. Deepfake Content
More and more people are embracing deepfake content, which is content created to look real but isn ’ t. Using AI, people can edit videos to look like someone did something they didn ’ t do and vice versa, which hurts authenticity and makes people question what ’ s real. Lawmakers need to take this issue seriously and create ways to stop people from doing this. — Jared Atchison , WPForms
9. Poor User Experience
I ’ ve noticed some brands struggling with building a seamless user experience. There are so many themes, plugins and changes people can make to their site that it can be overwhelming. As a result, the business owner eventually builds something they like, but sacrifices UX in the process. I suspect that we will see more businesses using customer feedback to make design changes. — John Brackett , Smash Balloon LLC
10. Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity threats are more prevalent than ever before with increased digital activities. This has drawn many hackers, who are becoming more sophisticated and are targeting many more businesses. Vital Information, such as trade secrets, price-sensitive information, HR records, and many others are more vulnerable. Strengthening cybersecurity laws can maintain equilibrium. — Vikas Agrawal , Infobrandz
11. Data Backup and Recovery
As a company, you ’ ll store and keep lots of data crucial to keeping business moving forward. A huge tech issue that businesses face is their backup recovery process when their system goes down. If anything happens, you need access to your information. Backing up your data is crucial to ensure your brand isn ’ t at a standstill. Your IT department should have a backup plan in case anything happens. — Stephanie Wells , Formidable Forms
12. Multiple Ad and Marketing Platforms
A major issue that marketers are dealing with is having to use multiple advertising and marketing platforms, with each one handling a different activity. It can overload a website and is quite expensive. We ’ re already seeing AdTech and MarTech coming together as MAdTech. Businesses need to keep an eye on this convergence of technologies and adopt new platforms that support it. — Syed Balkhi , WPBeginner
13. Location-Based Innovation
The concentration of tech companies in places like Seattle and San Francisco has led to a quick rise in living costs in these cities. Income isn ’ t catching up, and there ’ s stress on public infrastructure. Poor internet services in rural areas also exacerbate this issue. Innovation should be decentralized. — Samuel Thimothy , OneIMS
14. Artificial Intelligence Implementation
Businesses, especially those in the tech industry, are having trouble implementing AI. If you ’ ve used and improved upon your AI over the years, you ’ re likely having an easier time adjusting. But new online businesses test multiple AI programs at once and it ’ s causing communication and data mix-ups. As businesses settle with specific programs and learn what works for them, we will see improvements. — Chris Christoff , MonsterInsights
Recent Expert Contributors Articles

- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.
A.I.’s Original Sin
A times investigation found that tech giants altered their own rules to train their newest artificial intelligence systems..
This transcript was created using speech recognition software. While it has been reviewed by human transcribers, it may contain errors. Please review the episode audio before quoting from this transcript and email [email protected] with any questions.
From “The New York Times,” I’m Michael Barbaro. This is “The Daily.”
[MUSIC PLAYING]
Today, a “Times” investigation shows how as the country’s biggest technology companies race to build powerful new artificial intelligence systems, they bent and broke the rules from the start.
My colleague Cade Metz on what he uncovered.
It’s Tuesday, April 16th.
Cade, when we think about all the artificial intelligence products released over the past couple of years, including, of course, these chatbots we’ve talked a lot about on the show, we so frequently talk about their future their future capabilities, their influence on society, jobs, our lives. But you recently decided to go back in time to AI’s past, to its origins to understand the decisions that were made, basically, at the birth of this technology. So why did you decide to do that?
Because if you’re thinking about the future of these chatbots, that is defined by their past. The thing you have to realize is that these chatbots learn their skills by analyzing enormous amounts of digital data.
So what my colleagues and I wanted to do with our investigation was really focus on that effort to gather more data. We wanted to look at the type of data these companies were collecting, how they were gathering it, and how they were feeding it into their systems.
And when you all undertake this line of reporting, what do you end up finding?
We found that three major players in this race OpenAI, Google, and Meta as they were locked into this competition to develop better and better artificial intelligence, they were willing to do almost anything to get their hands on this data, including ignoring, and in some cases, violating corporate rules and wading into a legal gray area as they gathered this data.
Basically, cutting corners.
Cutting corners left and right.
OK, let’s start with OpenAI, the flashiest player of all.
The most interesting thing we’ve found, is that in late 2021, as OpenAI, the startup in San Francisco that built ChatGPT, as they were pulling together the fundamental technology that would power that chatbot, they ran out of data, essentially.
They had used just about all the respectable English language text on the internet to build this system. And just let that sink in for a bit.
I mean, I’m trying to let that sink in. They basically, like a Pac-Man on a old game, just consumed almost all the English words on the internet, which is kind of unfathomable.
Wikipedia articles by the thousands, news articles, Reddit threads, digital books by the millions. We’re talking about hundreds of billions, even trillions of words.
So by the end of 2021, OpenAI had no more English language texts that they could feed into these systems, but their ambitions are such that they wanted even more.
So here, we should remember that if you’re gathering up all the English language text on the internet, a large portion of that is going to be copyrighted.
So if you’re one of these companies gathering data at that scale, you are absolutely gathering copyrighted data, as well.
Which suggests that, from the very beginning, these companies, a company like OpenAI with ChatGPT, is starting to break, bend the rules.
Yes, they are determined to build this technology thus they are willing to venture into what is a legal gray area.
So given that, what does OpenAI do once it, as you had said, runs out of English language words to mop up and feed into this system?
So they get together, and they say, all right, so what are other options here? And they say, well, what about all the audio and video on the internet? We could transcribe all the audio and video, turn it into text, and feed that into their systems.
Interesting.
So a small team at OpenAI, which included its president and co-founder Greg Brockman, built a speech-recognition technology called Whisper, which could transcribe audio files into text with high accuracy.
And then they gathered up all sorts of audio files, from across the internet, including audio books, podcasts —
— and most importantly, YouTube videos.
Hmm, of which there’s a seemingly endless supply, right? Fair to say maybe tens of millions of videos.
According to my reporting, we’re talking about at least 1,000,000 hours of YouTube videos were scraped off of that video sharing site, fed into this speech recognition system in order to produce new text for training OpenAI’s chatbot. And YouTube’s terms of service do not allow a company like OpenAI to do this. YouTube, which is owned by Google, explicitly says you are not allowed to, in internet parlance, scrape videos en masse from across YouTube and use those videos to build a new application.
That is exactly what OpenAI did. According to my reporting, employees at the company knew that it broke YouTube terms of service, but they resolved to do it anyway.
So, Cade, this makes me want to understand what’s going on over at Google, which as we have talked about in the past on the show, is itself, thinking about and developing its own artificial intelligence model and product.
Well, as OpenAI scrapes up all these YouTube videos and starts to use them to build their chatbot, according to my reporting, some employees at Google, at the very least, are aware that this is happening.
Yes, now when we went to the company about this, a Google spokesman said it did not know that OpenAI was scraping YouTube content and said the company takes legal action over this kind of thing when there’s a clear reason to do so. But according to my reporting, at least some Google employees turned a blind eye to OpenAI’s activities because Google was also using YouTube content to train its AI.
So if they raise a stink about what OpenAI is doing, they end up shining a spotlight on themselves. And they don’t want to do that.
I guess I want to understand what Google’s relationship is to YouTube. Because of course, Google owns YouTube. So what is it allowed or not allowed to do when it comes to feeding YouTube data into Google’s AI models?
It’s an important distinction. Because Google owns YouTube, it defines what can be done with that data. And Google argues that it has a right to that data, that its terms of service allow it to use that data. However, because of that copyright issue, because the copyright to those videos belong to you and I, lawyers who I’ve spoken to say, people could take Google to court and try to determine whether or not those terms of service really allow Google to do this. There’s another legal gray area here where, although Google argues that it’s OK, others may argue it’s not.
Of course, what makes this all so interesting is, you essentially have one tech company Google, keeping another tech company OpenAI’s dirty little secret about basically stealing from YouTube because it doesn’t want people to know that it too is taking from YouTube. And so these companies are essentially enabling each other as they simultaneously seem to be bending or breaking the rules.
What this shows is that there is this belief, and it has been there for years within these companies, among their researchers, that they have a right to this data because they’re on a larger mission to build a technology that they believe will transform the world.
And if you really want to understand this attitude, you can look at our reporting from inside Meta.
And so what does Meta end up doing, according to your reporting?
Well, like Google and other companies, Meta had to scramble to build artificial intelligence that could compete with OpenAI. Mark Zuckerberg is calling engineers and executives at all hours pushing them to acquire this data that is needed to improve the chatbot.
And at one point, my colleagues and I got hold of recordings of these Meta executives and engineers discussing this problem. How they could get their hands on more data where they should try to find it? And they explored all sorts of options.
They talked about licensing books, one by one, at $10 a pop and feeding those into the model.
They even discussed acquiring the book publisher Simon & Schuster and feeding its entire library into their AI model. But ultimately, they decided all that was just too cumbersome, too time consuming, and on the recordings of these meetings, you can hear executives talk about how they were willing to run roughshod over copyright law and ignore the legal concerns and go ahead and scrape the internet and feed this stuff into their models.
They acknowledged that they might be sued over this. But they talked about how OpenAI had done this before them. That they, Meta were just following what they saw as a market precedent.
Interesting, so they go from having conversations like, should we buy a publisher that has tons of copyrighted material suggesting that they’re very conscious of the kind of legal terrain and what’s right and what’s wrong. And instead say, nah, let’s just follow the OpenAI model, that blueprint and just do what we want to do, do what we think we have a right to do, which is to kind of just gobble up all this material across the internet.
It’s a snapshot of that Silicon Valley attitude that we talked about. Because they believe they are building this transformative technology, because they are in this intensely competitive situation where money and power is at stake, they are willing to go there.
But what that means is that there is, at the birth of this technology, a kind of original sin that can’t really be erased.
It can’t be erased, and people are beginning to notice. And they are beginning to sue these companies over it. These companies have to have this copyrighted data to build their systems. It is fundamental to their creation. If a lawsuit bars them from using that copyrighted data, that could bring down this technology.
We’ll be right back.
So Cade, walk us through these lawsuits that are being filed against these AI companies based on the decisions they made early on to use technology as they did and the chances that it could result in these companies not being able to get the data they so desperately say they need.
These suits are coming from a wide range of places. They’re coming from computer programmers who are concerned that their computer programs have been fed into these systems. They’re coming from book authors who have seen their books being used. They’re coming from publishing companies. They’re coming from news corporations like, “The New York Times,” incidentally, which has filed a lawsuit against OpenAI and Microsoft.
News organizations that are concerned over their news articles being used to build these systems.
And here, I think it’s important to say as a matter of transparency, Cade, that your reporting is separate from that lawsuit. That lawsuit was filed by the business side of “The New York Times” by people who are not involved in your reporting or in this “Daily” episode, just to get that out of the way.
I’m assuming that you have spoken to many lawyers about this, and I wonder if there’s some insight that you can shed on the basic legal terrain? I mean, do the companies seem to have a strong case that they have a right to this information, or do companies like the “Times,” who are suing them, seem to have a pretty strong case that, no, that decision violates their copyrighted materials.
Like so many legal questions, this is incredibly complicated. It comes down to what’s called fair use, which is a part of copyright law that determines whether companies can use copyrighted data to build new things. And there are many factors that go into this. There are good arguments on the OpenAI side. There are good arguments on “The New York Times” side.
Copyright law says that can’t take my work and reproduce it and sell it to someone. That’s not allowed. But what’s called fair use does allow companies and individuals to use copyrighted works in part. They can take snippets of it. They can take the copyrighted works and transform it into something new. That is what OpenAI and others are arguing they’re doing.
But there are other things to consider. Does that transformative work compete with the individuals and companies that supplied the data that owned the copyrights?
And here, the suit between “The New York Times” company and OpenAI is illustrative. If “The New York Times” creates articles that are then used to build a chatbot, does that chatbot end up competing with “The New York Times?” Do people end up going to that chatbot for their information, rather than going to the “Times” website and actually reading the article? That is one of the questions that will end up deciding this case and cases like it.
So what would it mean for these AI companies for some, or even all of these lawsuits to succeed?
Well, if these tech companies are required to license the copyrighted data that goes into their systems, if they’re required to pay for it, that becomes a problem for these companies. We’re talking about digital data the size of the entire internet.
Licensing all that copyrighted data is not necessarily feasible. We quote the venture capital firm Andreessen Horowitz in our story where one of their lawyers says that it does not work for these companies to license that data. It’s too expensive. It’s on too large a scale.
Hmm, it would essentially make this technology economically impractical.
Exactly, so a jury or a judge or a law ruling against OpenAI, could fundamentally change the way this technology is built. The extreme case is these companies are no longer allowed to use copyrighted material in building these chatbots. And that means they have to start from scratch. They have to rebuild everything they’ve built. So this is something that, not only imperils what they have today, it imperils what they want to build in the future.
And conversely, what happens if the courts rule in favor of these companies and say, you know what, this is fair use. You were fine to have scraped this material and to keep borrowing this material into the future free of charge?
Well, one significant roadblock drops for these companies. And they can continue to gather up all that extra data, including images and sounds and videos and build increasingly powerful systems. But the thing is, even if they can access as much copyrighted material as they want, these companies may still run into a problem.
Pretty soon they’re going to run out of digital data on the internet.
That human-created data they rely on is going to dry up. They’re using up this data faster than humans create it. One research organization estimates that by 2026, these companies will run out of viable data on the internet.
Wow. Well, in that case, what would these tech companies do? I mean, where are they going to go if they’ve already scraped YouTube, if they’ve already scraped podcasts, if they’ve already gobbled up the internet and that altogether is not sufficient?
What many people inside these companies will tell you, including Sam Altman, the chief executive of OpenAI, they’ll tell you that what they will turn to is what’s called synthetic data.
And what is that?
That Is data generated by an AI model that is then used to build a better AI model. It’s AI helping to build better AI. That is the vision, ultimately, they have for the future that they won’t need all this human generated text. They’ll just have the AI build the text that will feed future versions of AI.
So they will feed the AI systems the material that the AI systems themselves create. But is that really a workable solid plan? Is that considered high-quality data? Is that good enough?
If you do this on a large scale, you quickly run into problems. As we all know, as we’ve discussed on this podcast, these systems make mistakes. They hallucinate . They make stuff up. They show biases that they’ve learned from internet data. And if you start using the data generated by the AI to build new AI, those mistakes start to reinforce themselves.
The systems start to get trapped in these cul-de-sacs where they end up not getting better but getting worse.
What you’re really saying is, these AI machines need the unique perfection of the human creative mind.
Well, as it stands today, that is absolutely the case. But these companies have grand visions for where this will go. And they feel, and they’re already starting to experiment with this, that if you have an AI system that is sufficiently powerful, if you make a copy of it, if you have two of these AI models, one can produce new data, and the other one can judge that data.
It can curate that data as a human would. It can provide the human judgment, So. To speak. So as one model produces the data, the other one can judge it, discard the bad data, and keep the good data. And that’s how they ultimately see these systems creating viable synthetic data. But that has not happened yet, and it’s unclear whether it will work.
It feels like the real lesson of your investigation is that if you have to allegedly steal data to feed your AI model and make it economically feasible, then maybe you have a pretty broken model. And that if you need to create fake data, as a result, which as you just said, kind of undermines AI’s goal of mimicking human thinking and language, then maybe you really have a broken model.
And so that makes me wonder if the folks you talk to, the companies that we’re focused on here, ever ask themselves the question, could we do this differently? Could we create an AI model that just needs a lot less data?
They have thought about other models for decades. The thing to realize here, is that is much easier said than done. We’re talking about creating systems that can mimic the human brain. That is an incredibly ambitious task. And after struggling with that for decades, these companies have finally stumbled on something that they feel works that is a path to that incredibly ambitious goal.
And they’re going to continue to push in that direction. Yes, they’re exploring other options, but those other options aren’t working.
What works is more data and more data and more data. And because they see a path there, they’re going to continue down that path. And if there are roadblocks there, and they think they can knock them down, they’re going to knock them down.
But what if the tech companies never get enough or make enough data to get where they think they want to go, even as they’re knocking down walls along the way? That does seem like a real possibility.
If these companies can’t get their hands on more data, then these technologies, as they’re built today, stop improving.
We will see their limitations. We will see how difficult it really is to build a system that can match, let alone surpass the human brain.
These companies will be forced to look for other options, technically. And we will see the limitations of these grandiose visions that they have for the future of artificial intelligence.
OK, thank you very much. We appreciate it.
Glad to be here.
Here’s what else you need to know today. Israeli leaders spent Monday debating whether and how to retaliate against Iran’s missile and drone attack over the weekend. Herzi Halevi, Israel’s Military Chief of Staff, declared that the attack will be responded to.
In Washington, a spokesman for the US State Department, Matthew Miller reiterated American calls for restraint —
^MATTHEW MILLER^ Of course, we continue to make clear to everyone that we talked to that we want to see de-escalation that we don’t want to see a wider regional war. That’s something that’s been —
— but emphasized that a final call about retaliation was up to Israel. ^MATTHEW MILLER^ Israel is a sovereign country. They have to make their own decisions about how best to defend themselves. What we always try to do —
And the first criminal trial of a former US President officially got underway on Monday in a Manhattan courtroom. Donald Trump, on trial for allegedly falsifying documents to cover up a sex scandal involving a porn star, watched as jury selection began.
The initial pool of 96 jurors quickly dwindled. More than half of them were dismissed after indicating that they did not believe that they could be impartial. The day ended without a single juror being chosen.
Today’s episode was produced by Stella Tan, Michael Simon Johnson, Muge Zaidi, and Rikki Novetsky. It was edited by Marc Georges and Liz O. Baylen, contains original music by Diane Wong, Dan Powell, and Pat McCusker, and was engineered by Chris Wood. Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly.
That’s it for “The Daily.” I’m Michael Barbaro. See you tomorrow.

- April 23, 2024 • 30:30 A Salacious Conspiracy or Just 34 Pieces of Paper?
- April 22, 2024 • 24:30 The Evolving Danger of the New Bird Flu
- April 19, 2024 • 30:42 The Supreme Court Takes Up Homelessness
- April 18, 2024 • 30:07 The Opening Days of Trump’s First Criminal Trial
- April 17, 2024 • 24:52 Are ‘Forever Chemicals’ a Forever Problem?
- April 16, 2024 • 29:29 A.I.’s Original Sin
- April 15, 2024 • 24:07 Iran’s Unprecedented Attack on Israel
- April 14, 2024 • 46:17 The Sunday Read: ‘What I Saw Working at The National Enquirer During Donald Trump’s Rise’
- April 12, 2024 • 34:23 How One Family Lost $900,000 in a Timeshare Scam
- April 11, 2024 • 28:39 The Staggering Success of Trump’s Trial Delay Tactics
- April 10, 2024 • 22:49 Trump’s Abortion Dilemma
- April 9, 2024 • 30:48 How Tesla Planted the Seeds for Its Own Potential Downfall
Hosted by Michael Barbaro
Featuring Cade Metz
Produced by Stella Tan , Michael Simon Johnson , Mooj Zadie and Rikki Novetsky
Edited by Marc Georges and Liz O. Baylen
Original music by Diane Wong , Dan Powell and Pat McCusker
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
A Times investigation shows how the country’s biggest technology companies, as they raced to build powerful new artificial intelligence systems, bent and broke the rules from the start.
Cade Metz, a technology reporter for The Times, explains what he uncovered.
On today’s episode

Cade Metz , a technology reporter for The New York Times.

Background reading
How tech giants cut corners to harvest data for A.I.
What to know about tech companies using A.I. to teach their own A.I.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Cade Metz writes about artificial intelligence, driverless cars, robotics, virtual reality and other emerging areas of technology. More about Cade Metz
Advertisement

COMMENTS
Our friendly Customer Service Agents are on-hand to help. Monday - Friday: 8am - 8pm Saturday - Sunday: 9am - 5:30pm. The Gtech Support and Customer Service website contains answers to all common queries about Gtech products including AirRam and Multi. It also allows you to download product manuals and quickly register any Gtech product ...
As part of your Gtech sweeper repair you may need to purchase a replacement part or consumable item. At BuySpares we sell a range of genuine Gtech vacuum cleaner spare parts for all models of sweeper and cordless vacuum cleaner, including the SW02, SW04 and SW10.. When shopping for sweeper spares you will need to know your model number, which can be found on the rating plate on the underside ...
1. Check the battery. If your Gtech hedge trimmer has a rechargeable battery, make sure it is fully charged. If the battery is not charged, plug the charger into an outlet and charge the battery. If the battery is still not working, it may need to be replaced. 2.
Rich1 New Member. My Gtech HT20 trimmer has given me more than one problem in its relatively short life. It now appears that one of the drive belts has broken, rendering the trimmer useless. Replacement belts are readily available (but not from Gtech) and people seem to have had no problem in fitting them. But, despite my skills with mechanical ...
Head to our support site for tailored help. If you want to purchase a new product, call our 24-hour order line on 08000 308 794 and select option 1. Make sure you've got your payment details ready and we'll do the rest. We know nobody wants to be on the line for longer than necessary, so we'll do our best to make it nice and speedy for you.
3. Charge battery. LEDs show solid red 1. The hedge trimmer has jammed. 2. Check blade and remove any debris. If this doesn't solve your problem don't worry, we will help. Go to www.gtech.co.uk or call 01905 345 891...
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions. With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so.
Problem solving, in the simplest terms, is the process of identifying a problem, analyzing it, and finding the most effective solution to overcome it. For software engineers, this process is deeply embedded in their daily workflow. It could be something as simple as figuring out why a piece of code isn't working as expected, or something as ...
OPERATING MANUAL Cordless Hedge Trimmer HT Series 4720_HT50 Manual Update 2020 aw2.indd 1 18/02/2021 10:35
Whatever the problem with your Gtech, if it's losing power or is no longer providing sufficient suction we can repair it. Perhaps it cuts out intermittently or won't switch on at all. With over 40 years' experience and our extensive range of spare parts our highly trained staff will have your faulty Gtech back to 100% performance in no time.
Problem solving is an activity, a context and a dominant pedagogical frame for Technology Education. It constitutes a central method and a critical skill through which school pupils learn about and become proficient in technology (Custer et al., 2001).Research has, among other things, been able to identify and investigate sets of intellectual and cognitive processes (Buckley et al., 2019 ...
Today's employers look for the following skills in new employees: to analyze a problem logically, formulate a solution, and effectively communicate with others. In this video, industry professionals share their own problem solving processes, the problem solving expectations of their employees, and an example of how a problem was solved.
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Nicholl, 2011). Problem solving, it seems, is a pervasive idea in technology education research and policy. Middleton (2009) notes that problem solving is found in almost all international technology education curricula. The pace, nature and complexity of contemporary societal challenges make it more
Problem-solving is a vital skill for coping with various challenges in life. This webpage explains the different strategies and obstacles that can affect how you solve problems, and offers tips on how to improve your problem-solving skills. Learn how to identify, analyze, and overcome problems with Verywell Mind.
4. It's all just history repeating itself. 5. Tech causes more problems than it solves. 6. The net effects in 10 years will be negligible. About this canvassing of experts. Acknowledgments. A number of respondents to this canvassing about the likely future of social and civic innovation shared concerns.
2. Brainstorming Techniques. Prompt: "Detail a structured brainstorming session for a (specific problem e.g., product design, team conflict). Incorporate diverse techniques and tools for idea generation." 3. Analytical Mindset Cultivation. Prompt: "Propose daily practices to enhance analytical thinking.
A formal introduction to systems engineering conceptual design and how it is a sound methodology for model-based problem solving. An overview of the seven management and planning tools for building rigorous, qualitative models. Tools and techniques learned in the class through two case studies.
The problem-solving process has four steps: define, prepare, try, and reflect. As a digital learning coach, I have been using these steps in a similar way as I help students and my colleagues find solutions to their technology problems. The case study below will take you through how your students can use this process.
The research team developed G-LLaVA, an MLLM that has been derived from the Geo170K dataset, which makes it highly proficient in solving geometric problems. As the name suggests, the LLAVA architecture has been used in the design of the model, and the model primarily consists of an LLM and a trained vision transformer (ViT).
Too Much Focus on Automation. Data Mixups Due to AI Implementation. Poor User Experience. 1. Employee Productivity Measurement. As most companies switched to 100 percent remote almost overnight, many realized that they lacked an efficient way to measure employee productivity. Technology with " user productivity reports " has become ...
The focus and procedure of teaching problem solving using technology should be flexible. This can be directed by how the teacher helps the student select a problem and frame the context of a problem. Students should examine situations (big and small, near and far, individual and societal) and use their creative problem solving abilities to try ...
A Times investigation found that tech giants altered their own rules to train their newest artificial intelligence systems. Hosted by Michael Barbaro. Featuring Cade Metz. Produced by Stella Tan ...