About . Click to expand section.
- Our History
- Team & Board
- Transparency and Accountability

What We Do . Click to expand section.
- Cycle of Poverty
- Climate & Environment
- Emergencies & Refugees
- Health & Nutrition
- Livelihoods
- Gender Equality
- Where We Work
Take Action . Click to expand section.
- Attend an Event
- Partner With Us
- Fundraise for Concern
- Work With Us
- Leadership Giving
- Humanitarian Training
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Donate . Click to expand section.
- Give Monthly
- Donate in Honor or Memory
- Leave a Legacy
- DAFs, IRAs, Trusts, & Stocks
- Employee Giving
How does education affect poverty?
For starters, it can help end it.
Aug 10, 2023

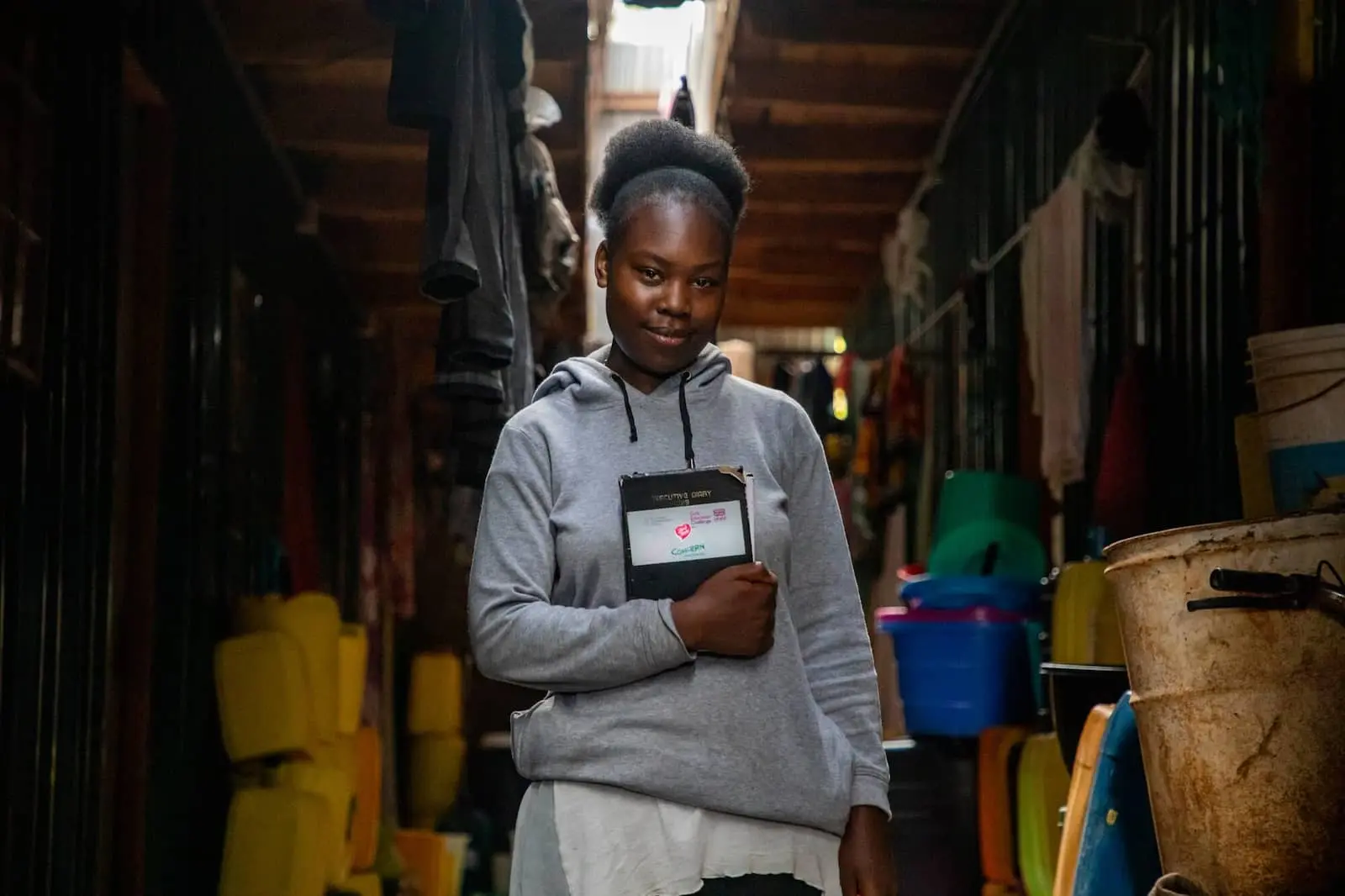
Access to high-quality primary education and supporting child well-being is a globally-recognized solution to the cycle of poverty. This is, in part, because it also addresses many of the other issues that keep communities vulnerable.
Education is often referred to as the great equalizer: It can open the door to jobs, resources, and skills that help a person not only survive, but thrive. In fact, according to UNESCO, if all students in low-income countries had just basic reading skills (nothing else), an estimated 171 million people could escape extreme poverty. If all adults completed secondary education, we could cut the global poverty rate by more than half.
At its core, a quality education supports a child’s developing social, emotional, cognitive, and communication skills. Children who attend school also gain knowledge and skills, often at a higher level than those who aren’t in the classroom. They can then use these skills to earn higher incomes and build successful lives.
Here’s more on seven of the key ways that education affects poverty.
Go to the head of the class
Get more information on Concern's education programs — and the other ways we're ending poverty — delivered to your inbox.
1. Education is linked to economic growth
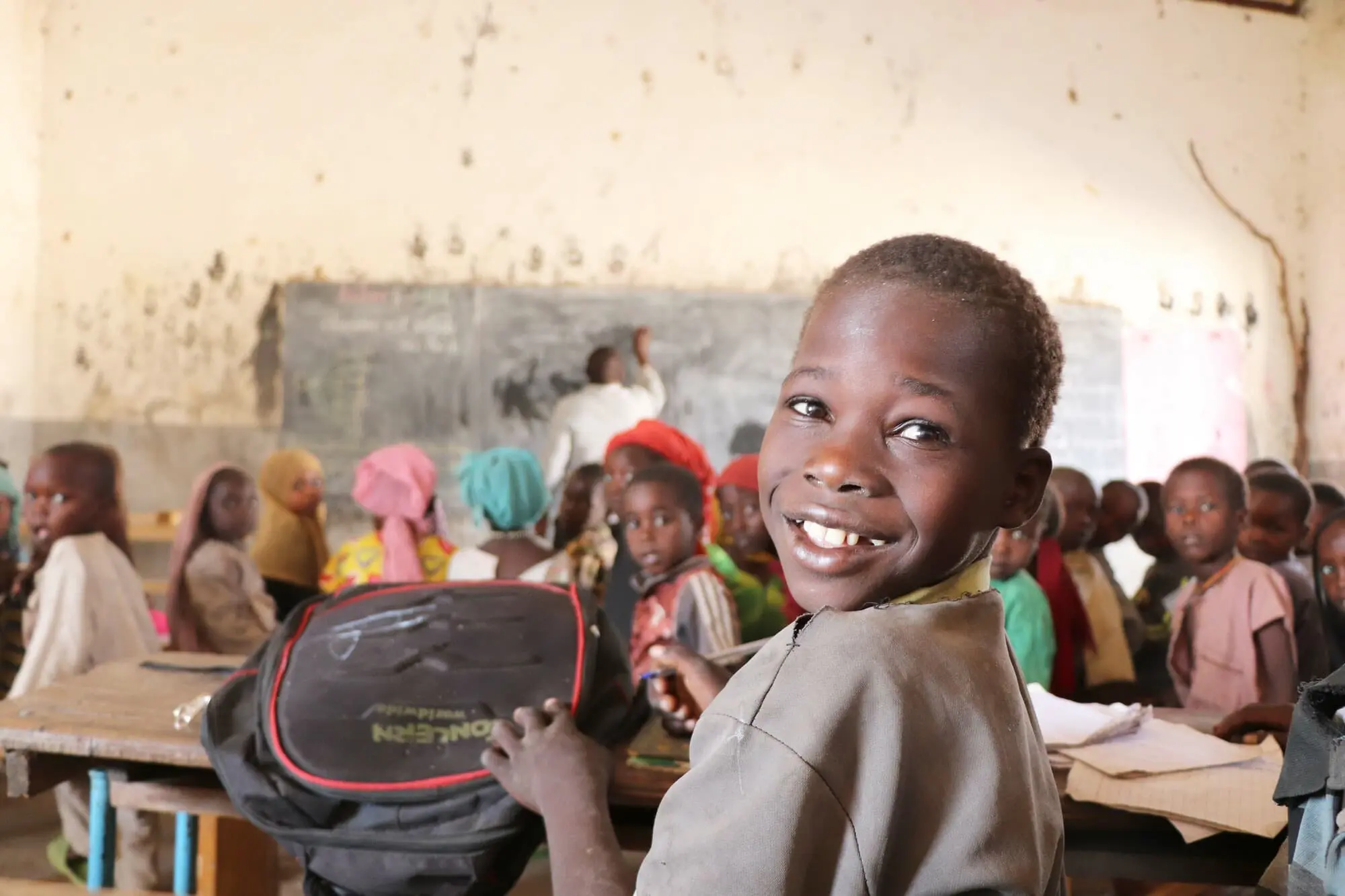

Education is the best way out of poverty in part because it is strongly linked to economic growth. A 2021 study co-published by Stanford University and Munich’s Ludwig Maximilian University shows us that, between 1960 and 2000, 75% of the growth in gross domestic product around the world was linked to increased math and science skills.
“The relationship between…the knowledge capital of a nation, and the long-run [economic] rowth rate is extraordinarily strong,” the study’s authors conclude. This is just one of the most recent studies linking education and economic growth that have been published since 1990.
“The relationship between…the knowledge capital of a nation, and the long-run [economic] growth rate is extraordinarily strong.” — Education and Economic Growth (2021 study by Stanford University and the University of Munich)
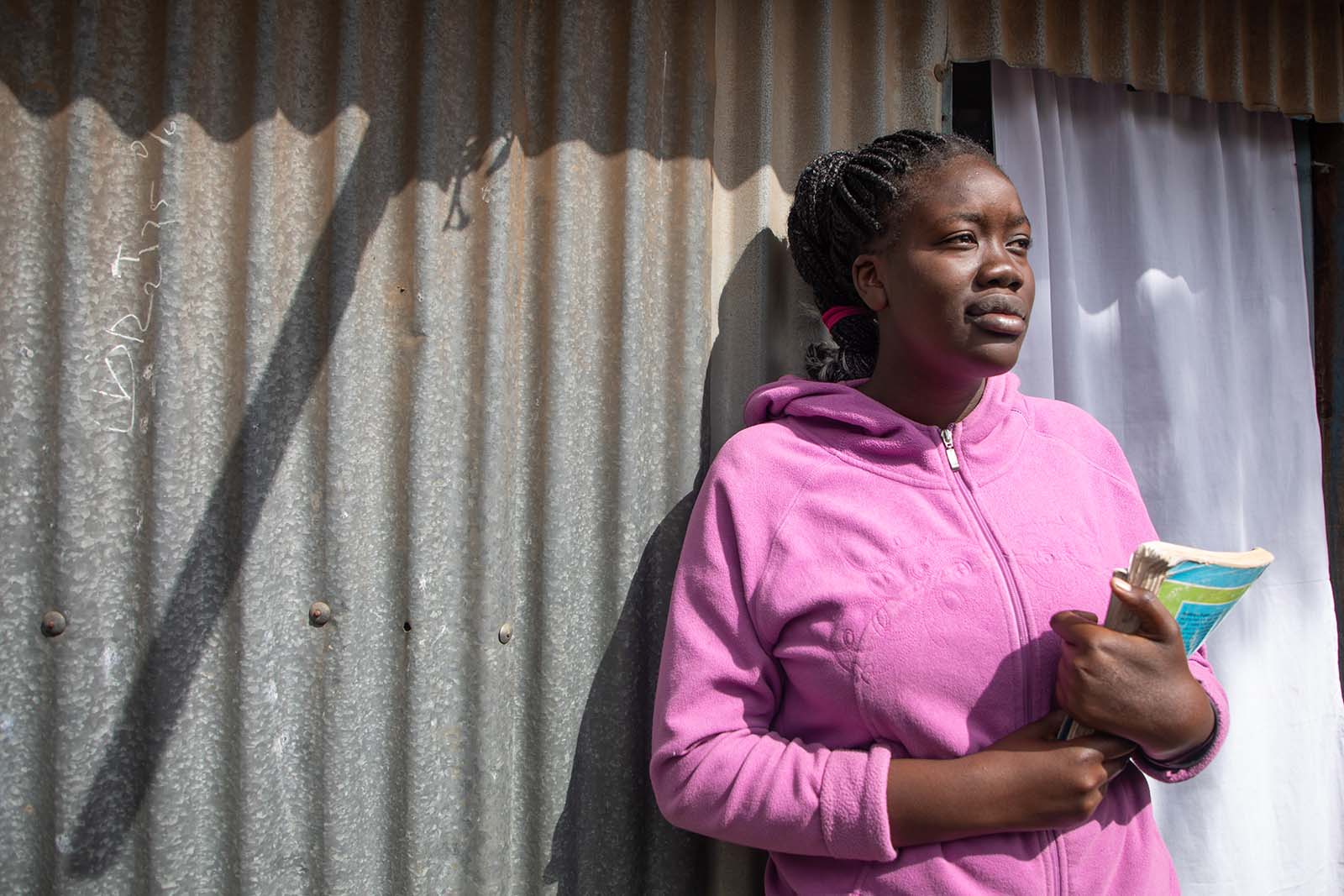
2. Universal education can fight inequality

A 2019 Oxfam report says it best: “Good-quality education can be liberating for individuals, and it can act as a leveler and equalizer within society.”
Poverty thrives in part on inequality. All types of systemic barriers (including physical ability, religion, race, and caste) serve as compound interest against a marginalization that already accrues most for those living in extreme poverty. Education is a basic human right for all, and — when tailored to the unique needs of marginalized communities — can be used as a lever against some of the systemic barriers that keep certain groups of people furthest behind.
For example, one of the biggest inequalities that fuels the cycle of poverty is gender. When gender inequality in the classroom is addressed, this has a ripple effect on the way women are treated in their communities. We saw this at work in Afghanistan , where Concern developed a Community-Based Education program that allowed students in rural areas to attend classes closer to home, which is especially helpful for girls.

Four ways that girls’ education can change the world
Gender discrimination is one of the many barriers to education around the world. That’s a situation we need to change.
3. Education is linked to lower maternal and infant mortality rates
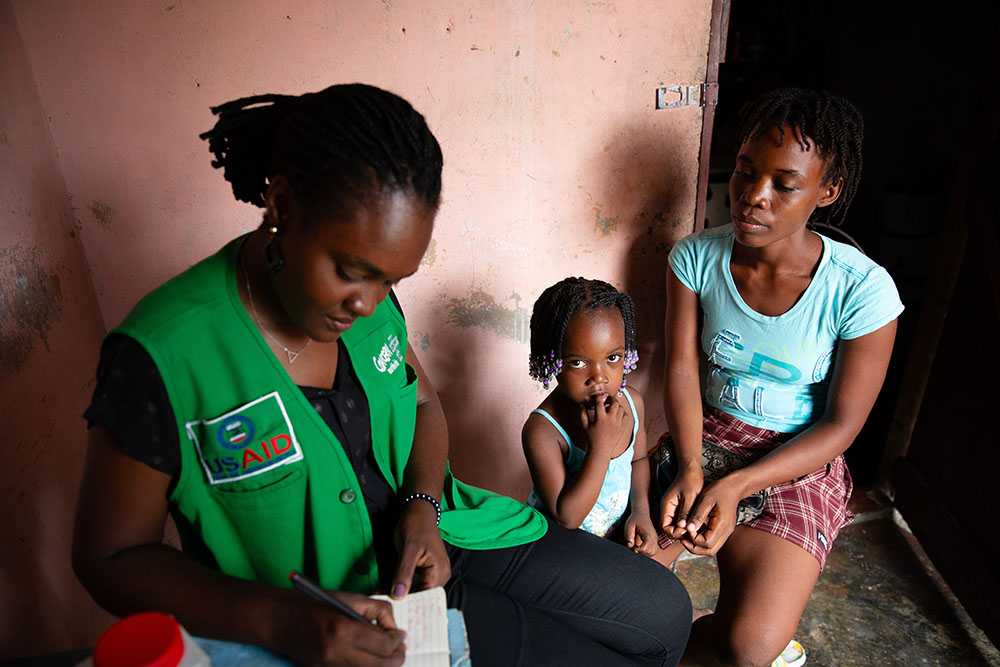
Speaking of women, education also means healthier mothers and children. Examining 15 countries in sub-Saharan Africa, researchers from the World Bank and International Center for Research on Women found that educated women tend to have fewer children and have them later in life. This generally leads to better outcomes for both the mother and her kids, with safer pregnancies and healthier newborns.
A 2017 report shows that the country’s maternal mortality rate had declined by more than 70% in the last 25 years, approximately the same amount of time that an amendment to compulsory schooling laws took place in 1993. Ensuring that girls had more education reduced the likelihood of maternal health complications, in some cases by as much as 29%.
4. Education also lowers stunting rates
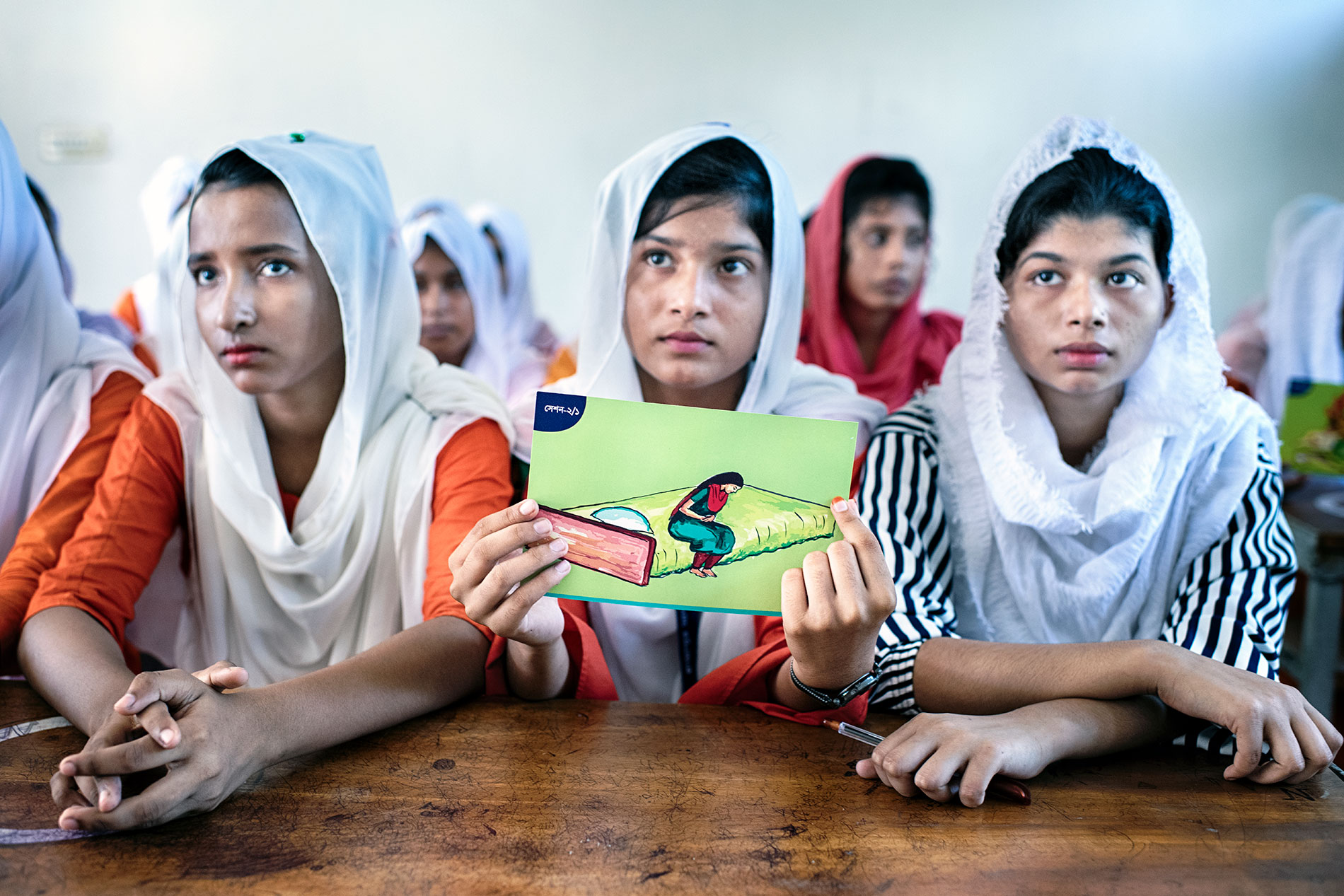

Children also benefit from more educated mothers. Several reports have linked education to lowered stunting , one of the side effects of malnutrition. Preventing stunting in childhood can limit the risks of many developmental issues for children whose height — and potential — are cut short by not having enough nutrients in their first few years.
In Bangladesh , one study showed a 50.7% prevalence for stunting among families. However, greater maternal education rates led to a 4.6% decrease in the odds of stunting; greater paternal education reduced those rates by 2.9%-5.4%. A similar study in Nairobi, Kenya confirmed this relationship: Children born to mothers with some secondary education are 29% less likely to be stunted.
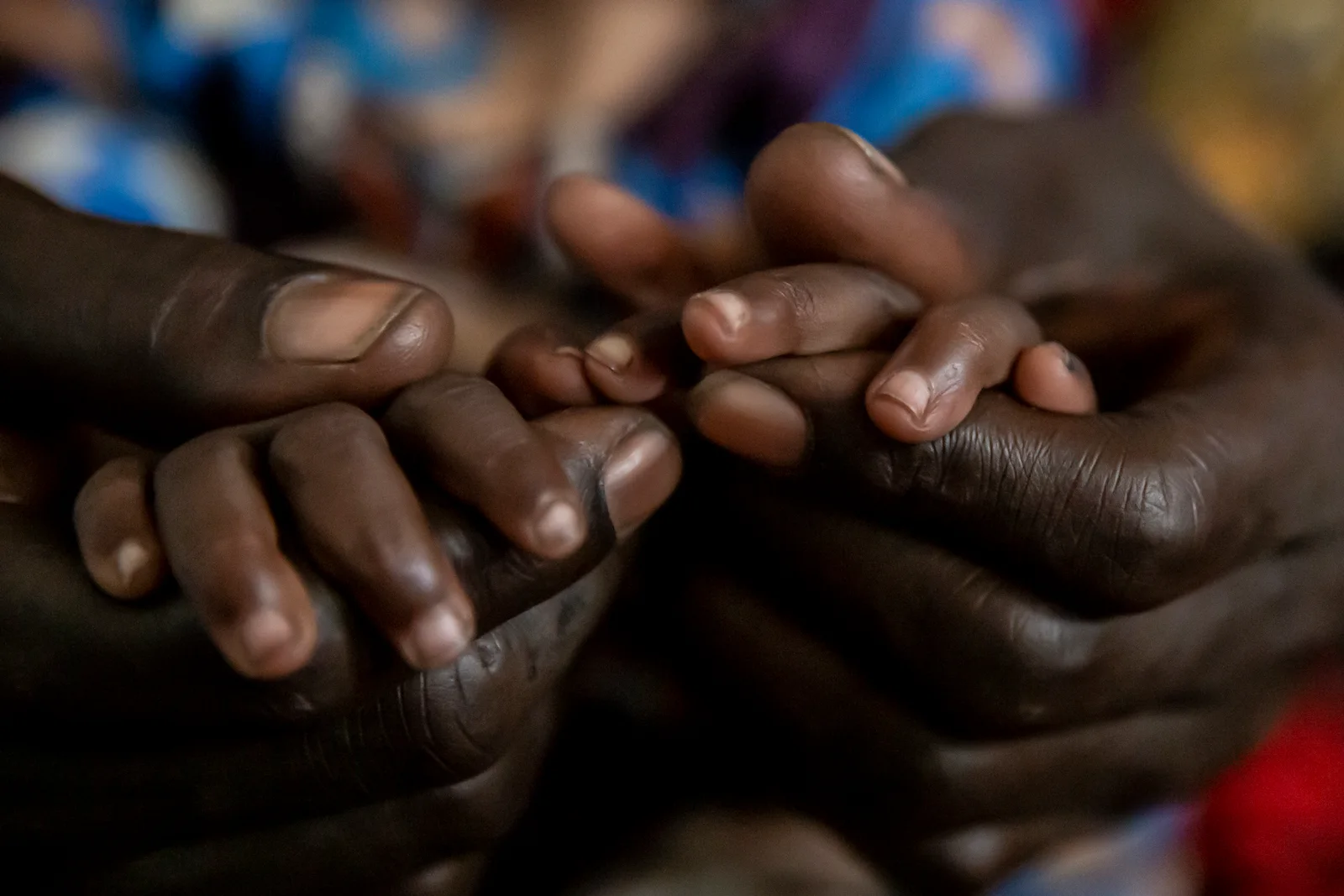

What is stunting?
Stunting is a form of impaired growth and development due to malnutrition that threatens almost 25% of children around the world.
5. Education reduces vulnerability to HIV and AIDS…

In 2008, researchers from Harvard University, Imperial College London, and the World Bank wrote : “There is a growing body of evidence that keeping girls in school reduces their risk of contracting HIV. The relationship between educational attainment and HIV has changed over time, with educational attainment now more likely to be associated with a lower risk of HIV infection than earlier in the epidemic.”
Since then, that correlation has only grown stronger. The right programs in schools not only reduce the likelihood of young people contracting HIV or AIDS, but also reduce the stigmas held against people living with HIV and AIDS.
6. …and vulnerability to natural disasters and climate change

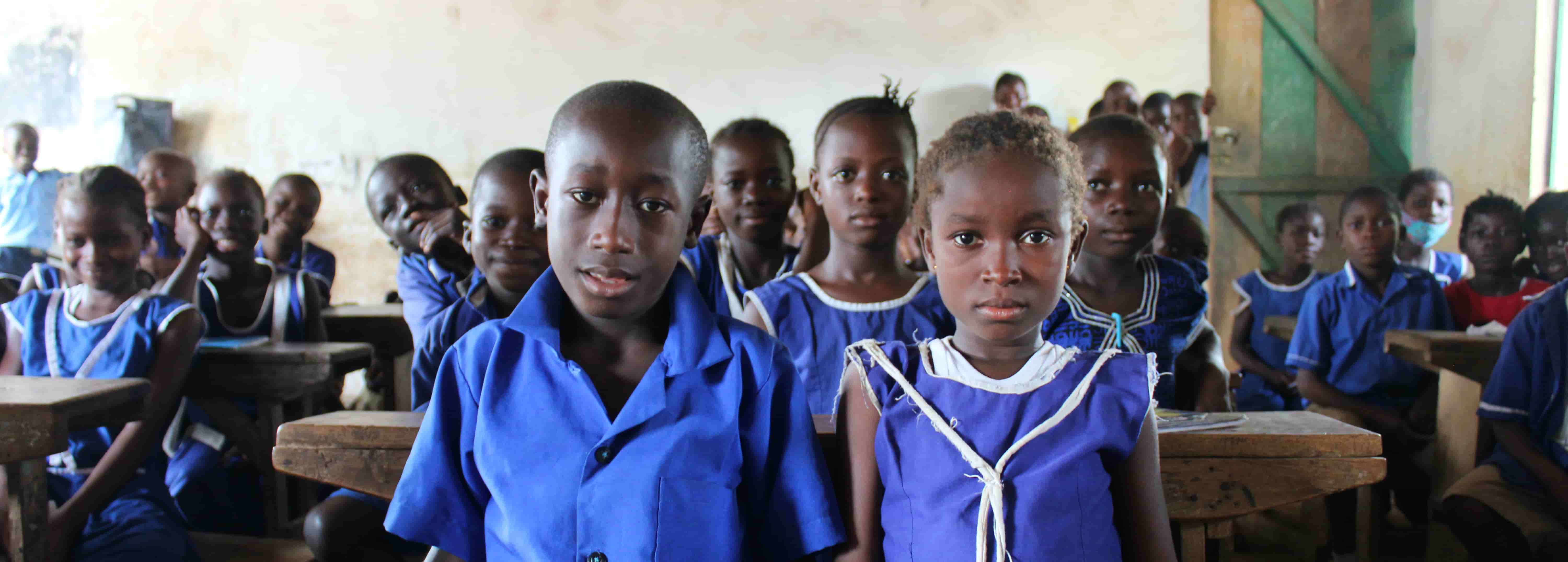
As the number of extreme weather events increases due to climate change, education plays a critical role in reducing vulnerability and risk to these events. A 2014 issue of the journal Ecology and Society states: “It is found that highly educated individuals are better aware of the earthquake risk … and are more likely to undertake disaster preparedness.… High risk awareness associated with education thus could contribute to vulnerability reduction behaviors.”
The authors of the article went on to add that educated people living through a natural disaster often have more of a financial safety net to offset losses, access to more sources of information to prepare for a disaster, and have a wider social network for mutual support.

Climate change is one of the biggest threats to education — and growing
Last August, UNICEF reported that half of the world’s 2.2 billion children are at “extremely high risk” for climate change, including its impact on education. Here’s why.
7. Education reduces violence at home and in communities

The same World Bank and ICRW report that showed the connection between education and maternal health also reveals that each additional year of secondary education reduced the chances of child marriage — defined as being married before the age of 18. Because educated women tend to marry later and have fewer children later in life, they’re also less likely to suffer gender-based violence , especially from their intimate partner.
Girls who receive a full education are also more likely to understand the harmful aspects of traditional practices like FGM , as well as their rights and how to stand up for them, at home and within their community.
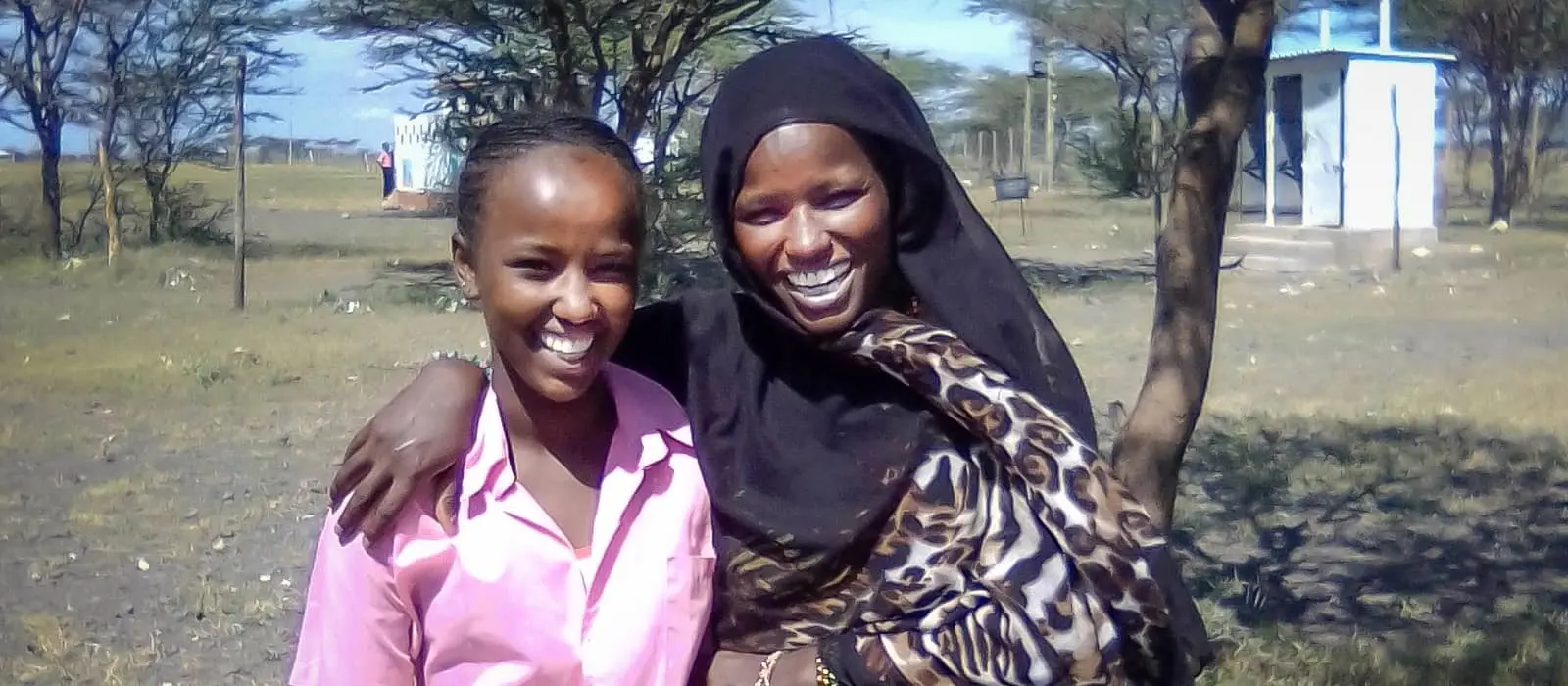

Fighting FGM in Kenya: A daughter's bravery and a mother's love
Marsabit is one of those areas of northern Kenya where FGM has been the rule rather than the exception. But 12-year-old student Boti Ali had other plans.
Education for all: Concern’s approach
Concern’s work is grounded in the belief that all children have a right to a quality education. Last year, our work to promote education for all reached over 676,000 children. Over half of those students were female.
We integrate our education programs into both our development and emergency work to give children living in extreme poverty more opportunities in life and supporting their overall well-being. Concern has brought quality education to villages that are off the grid, engaged local community leaders to find solutions to keep girls in school, and provided mentorship and training for teachers.
More on how education affects poverty
6 Benefits of literacy in the fight against poverty

Child marriage and education: The blackboard wins over the bridal altar

Project Profile
Right to Learn
Sign up for our newsletter.
Get emails with stories from around the world.
You can change your preferences at any time. By subscribing, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
- Get involved
The transformative power of education in the fight against poverty
October 16, 2023.

Zubair Junjunia, a Generation17 young leader and the Founder of ZNotes, presents at EdTechX.

Zubair Junjunia
Generation17 Young Leader and founder of ZNotes
Time and again, research has proven the incredible power of education to break poverty cycles and economically empower individuals from the most marginalized communities with dignified work and upward social mobility.
Research at UNESCO has shown that world poverty would be more than halved if all adults completed secondary school. And if all students in low-income countries had just basic reading skills, almost 171 million people could escape extreme poverty.
With such irrefutable evidence, how do we continue to see education underfunded globally? Funding for education as a share of national income has not changed significantly over the last decade for any developing country. And to exacerbate that, the COVID-19 shock pushed the level of learning poverty to an estimated 70 percent .
I have devoted the past decade of my life to fighting educational inequality, a journey that began during my school years. This commitment led to the creation of ZNotes , an educational platform developed for students, by students. ZNotes was born out of the problem I witnessed first-hand; the inequities in end-of-school examination, which significantly influence access to higher education and career opportunities. It is designed as a platform where students can share their notes and access top-quality educational materials without any limitations. ZNotes fosters collaborative learning through student-created content within a global community and levels the academic playing field with a student-empowered and technology-enabled approach to content creation and peer learning.
Although I started ZNotes as a solo project, today, it has touched the lives of over 4.5 million students worldwide, receiving an impressive 32 million hits from students across more than 190 countries, especially serving students from emerging economies. We’re proud to say that today, more than 90 percent of students find ZNotes resources useful and feel more confident entering exams , regardless of their socio-economic background. These globally recognized qualifications empower our learners to access tertiary education and enter the world of work.

Sixteen-year-old Zubair set up a blog to share the resources he created for his IGCSE exams. Through word of mouth, his revision notes were discovered by students all over the world and ZNotes was born.
In rapidly changing job market, young people must cultivate resilience and adaptability. World Economic Forum highlights the importance of future skills, encompassing technical, cognitive, and interpersonal abilities. Unfortunately, many educational systems, especially in under-resourced regions, fall short in equipping youth with these vital skills.
To address this challenge, I see innovative technology as a crucial tool both within and beyond traditional school systems. As the digital divide narrows and access to devices and internet connectivity becomes more affordable, delivering quality education and personalized support is increasingly achievable through technology. At ZNotes, we are reshaping the role of students, transforming them from passive consumers to active creators and proponents of education. Empowering youth through a community-driven approach, students engage in peer learning and generate quality resources on an online platform.
Participation in a global learning community enhances young people's communication and collaboration skills. ZNotes fosters a sense of global citizenship, enabling learners to communicate with a diverse range of individuals across race, gender, and religion. Such spaces also result in redistributing social capital as students share advice for future university, internship and career pathways.
“Studying for 14 IGCSE subjects wasn't easy, but ZNotes helped me provide excellent and relevant revision material for all of them. I ended up with 7 A* 7 A, and ZNotes played a huge role. I am off to Cornell University this fall now. A big thank you to the ZNotes team!"
Alongside ensuring our beneficiaries are equipped with the resources and support they need to be at a level playing field for such high stakes exams, we also consider the skills that will set them up for success in life beyond academics. Especially for the hundreds of young people who join our internship and contribution programs , they become part of a global social impact startup and develop both academic skills and also employability skills. After engaging with our internship programs, 77% of interns reported improved candidacy for new jobs and internships.
ZNotes addresses the uneven playing field of standardized testing with a student-empowered and technology-enabled approach for content creation and peer learning.
A few years ago, Jess joined our team as a Social Impact Analyst intern having just completed her university degree while she continued to search for a full-time role. She was able to apply her data analytics skills from a theoretical degree into a real-world scenario and was empowered to play an instrumental role in understanding and developing a Theory of Change model for ZNotes. In just 6 months, she had been able to develop the skills and gain experiences that strengthened her profile. At the end of internship, she was offered a full-time role at a major news and media agency that she is continuing to grow in!
Jess’s example applies to almost every one of our interns . As another one of them, Alexa, said “ZNotes offers the rare and wonderful opportunity to be at the center of meaningful change”.
Being part of an organization making a significant impact is profoundly inspiring and empowering for young people, and assuming high-responsibility roles within such organizations accelerates their skills development and sets them apart in the eyes of prospective employers.
On the International Day for the Eradication of Poverty, it is a critical moment to reflect and enact on the opportunity that we have to achieving two key SDGs, Goal 1 and 4, by effectively funding and enabling access to quality education globally.

Impact of Poverty on Education: Understanding the Effects and Seeking Solutions
Introduction.
Poverty has long been identified as a significant social issue that affects various aspects of individuals’ lives, including education. Many studies have shown that poverty and educational outcomes are strongly correlated, with children from low-income families experiencing significant academic achievement and educational attainment challenges. In this article, we will explore the impact of poverty on education, the barriers that prevent students from low-income families from accessing quality education, and some possible solutions to address this issue.
The Impact of Poverty on Education
Poverty affects education in multiple ways..
Firstly, financial constraints restrict access to educational resources, including books, technology, and other materials that can enhance learning. Children from low-income families are less likely to have access to quality preschool education, significantly impacting their readiness for kindergarten and subsequent academic success.
Secondly, poverty can lead to inadequate nutrition and healthcare, hindering cognitive development and negatively impacting academic performance. Children from low-income families often face food insecurity, which can lead to malnutrition, leading to health issues, and reduced attention and retention during learning.
Thirdly, poverty often leads to unstable home environments, including frequent moves, stress, and a lack of resources. These factors can lead to emotional and behavioral problems, making it challenging for children to focus on their studies and achieve their potential.
Barriers to Education for Low-Income Students
The impact of poverty on education is often exacerbated by systemic barriers that limit access to quality education for low-income students. For example, schools in low-income areas are often under-resourced, leading to overcrowded classrooms, outdated materials, and fewer opportunities for extracurricular activities. This can result in a lower quality of education and limited exposure to enrichment programs that may be beneficial.
Moreover, inadequate teacher training and support can lead to ineffective teaching and reduced student outcomes. Teachers may not have the necessary resources or expertise to address the unique needs of students from low-income families, such as language barriers, learning disabilities, and trauma.

Solutions to Address Poverty and Education Inequality
To address the impact of poverty on education, we need to implement systemic solutions that focus on reducing the disparities in access to quality education for low-income students. Some possible solutions include:
- Providing equitable funding for schools in low-income areas to improve resources and materials.
- Investing in high-quality preschool education to improve readiness for kindergarten and future academic success.
- Offering teacher training and support to address the unique needs of students from low-income families.
- Providing access to nutrition and healthcare services to support cognitive development and academic success.
- Engaging parents and communities in education to foster a culture of learning and support.
In conclusion, the impact of poverty on education is a significant issue that requires attention and action. By understanding the challenges and barriers that low-income students face, we can develop and implement practical solutions to address the issue.
“Join the Mission of Promoting Educational Equity with Reading Readiness School Franchise”
Reading Readiness School is committed to promoting educational equity and providing high-quality education to all children. As a Reading Readiness School franchisee, you will have access to resources and support that can help you make a meaningful difference in your community. Our franchise model is designed to help you establish and operate a successful school that provides a safe and nurturing environment for children to learn and grow. By becoming a Reading Readiness School franchisee, you can positively impact the lives of children and families in your community while also running a successful business. Visit readingreadiness.org to learn more about our franchise opportunities and how you can get involved in our mission to promote educational equity.
Click here to become a franchisee https://www.readingreadiness.org/become-a-franchisee/
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
What is Learning Poverty?
All children should be able to read by age 10. Reading is a gateway for learning as the child progresses through school—and conversely, an inability to read slams that gate shut. Beyond this, when children cannot read, it’s usually a clear indication that school systems aren’t well organized to help children learn in other areas such as math, science, and the humanities. And although it is possible to learn later in life with enough effort, children who don’t read by age 10—or at the latest, by the end of primary school—usually fail to master reading later in their schooling career.
In recent years, it has become clear that many children around the world are not learning to read proficiently. Even though most children are in school, a large proportion are not acquiring fundamental skills. Moreover, 260 million children are not even in school. This is the leading edge of a learning crisis that threatens c ountries’ efforts to build human capital and achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Without foundational learning, students often fail to thrive later in school or when they join the workforce. They don’t acquire the human capital they need to power their careers and economies once they leave school, or the skills that will help them become engaged citizens and nurture healthy, prosperous families. As a major contributor to human capital deficits, the learning crisis undermines sustainable growth and poverty reduction.
To spotlight this crisis, we are introducing the concept of Learning Poverty, drawing on new data developed in coordination with the UNESCO Institute for Statistics. Learning poverty means being unable to read and understand a simple text by age 10. This indicator brings together schooling and learning indicators: it begins with the share of children who haven’t achieved minimum reading proficiency (as measured in schools) and is adjusted by the proportion of children who are out of school (and are assumed not able to read proficiently).
Using a measure developed jointly by the World Bank and UNESCO’s Institute of Statistics , we have determined that 53 percent of children in low- and middle-income countries cannot read and understand a simple story by the end of primary school. In poor countries, the level is as high as 80 percent. Such high levels of illiteracy are an early warning sign that all global educational goals and other related sustainable development goals are in jeopardy.
Progress in reducing learning poverty is far too slow to meet the SDG aspirations: at the current rate of improvement, in 2030 about 43% of children will still be learning-poor. Even if countries reduce their learning poverty at the fastest rates we have seen so far in this century, the goal of ending it will not be attained by 2030.
There is an urgent need for a society-wide commitment to invest more and better in people. If children cannot read, all education SDGs are at risk. Eliminating learning poverty is as important as eliminating extreme monetary poverty, stunting, or hunger. To achieve it in the foreseeable future requires far more rapid progress at scale than we have yet seen.
The learning poverty indicator focuses on reading for three reasons:
- Reading proficiency is an easily understood learning measure
- Reading is a student’s gateway to learning in other areas
- Reading proficiency can serve as a proxy for foundational learning in other subjects
The learning poverty indicator allows us to illustrate progress toward SDG 4’s broader goal to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education for all. It particularly highlights progress towards SDG 4.1.1(b), which specifies that all children at the end of primary reach at least a minimum proficiency level in reading.
Methodology
The indicator combines the share of primary-aged children out-of-school who are schooling deprived (SD) , and the share of pupils below a minimum proficiency in reading, who are learning deprived (LD) . By combining schooling and learning, the indicator brings into focus both “more schooling”, which by itself serves a variety of critical functions, as well as “better learning” which is important to ensure that time spent in school translates into acquisition of skills and capabilities.
How Learning Poverty is defined
The learning poverty indicator is calculated as follows:
Lp = [ld x (1-sd)] + [1 x sd].
LP = Learning poverty
LD = Learning deprivation , defined as share of children at the end of primary who read at below the minimum proficiency level, as defined by the Global Alliance to Monitor Learning (GAML) in the context of the SDG 4.1.1 monitoring
SD = Schooling deprivation , defined as the share of primary aged children who are out-of-school. All out-of-school children are assumed to be below the minimum proficiency level in reading.
Learning poverty can be improved in two ways: (i) by reducing learning deprivation as countries raise proficiency levels for children below the minimum proficiency threshold, or (ii) by reducing schooling deprivation as countries expand coverage and bringing out-of-school population into the system.
While schooling deprivation can be directly observed depending on whether the child is enrolled or not enrolled in school, learning deprivation cannot be directly observed, and is measured through standardized assessments using SDG’s definition of minimum proficiency level, where reading proficiency is defined as:
Three complementary concepts: Learning poverty level, gap, and severity
The learning poverty level (or headcount ratio) shown above, that is the share of 10-year-olds who are not in school (schooling deprived) or are below the minimum proficiency level (learning deprived), has limitations. It does not capture the average learning shortfall among children under the minimum proficiency level. Hence, we include the learning poverty gap , that measures the average distance of a learning deprived child to the minimum proficiency level and indicates the average increase in learning required to eliminate learning poverty.
However, the gap measure cannot distinguish between an increase in the learning gap driven by students near the threshold and one driven by those at the very bottom of the learning distribution. Learning poverty severity captures the inequality of learning among the learning poor population and is the gap squared in relation to the minimum proficiency squared.
The concepts of learning poverty gap and learning poverty severity are important to fully understand children’s access to learning. It is possible that countries with the same learning poverty level have different learning poverty gaps, or countries with the same learning poverty gaps have different learning poverty severity, with implications for policies used to address learning poverty.
For example, where two countries have the same level of learning poverty, but one has a higher learning poverty gap , the latter would need greater effort to bring children above the minimum proficiency level. At the same time, where two countries have the same learning poverty gap , but one has higher learning poverty severity , the latter would need to adopt strategies that address the unequal distribution of learning among those below the minimum proficiency threshold. Furthermore, as we anticipate learning losses due to the pandemic, or the growing share of children who are learning poor, we can examine widening inequalities with the gap and severity calculations.
Calculation details
The implementation of this indicator and the production of the global estimates rely on:
- Reporting window of 9 years, a ±4 interval around a reference year. In the first release of the learning poverty, the reference year was set to 2015, implying data from 2011-2019 could be included. In practice, most recent data was from 2017.
- Learning assessments with a minimum proficiency threshold benchmarked by Global Alliance to Monitor Learning (GAML), which occurred within the reporting window. If a country has multiple eligible learning assessments, the following hierarchy is applied: PIRLS reading > TIMSS science > Regional assessments > National assessments. Between two rounds of the same assessments, the one closest to the reference year is preferred.
- School participation is derived from adjusted net enrollment rate (ANER) for primary schools and computed by the UIS using administrative records. Adjusted net enrollment is a measure of both “stock” and “flow” and accounts for both age- and grade-based distortions, as it is the percent of primary school age children enrolled either in primary or secondary education, as opposed to gross enrollment which is the share of children of any age that are enrolled in primary school, or net enrollment which is the share of primary school age children that are enrolled in primary school. We use the same year of school participation as the preferred learning assessment for each country.
- Aggregations for each region comprise the average learning poverty of countries with available data, weighted by their population ages 10–14 years old. To obtain a global estimate, we weight the regional aggregations by the 10–14-year-old population regardless of data availability. This is equivalent to imputing missing country data using regional values.
Note: While the reference age for Learning Poverty is age 10, learning assessments are sampled based on specific grades and not age. To incorporate assessments administered at different grades, we chose for each country the grade between 4 and 6 where relevant and reliable data were available.
You can download the Learning Poverty data directly from Development Data Hub . The database contains pooled and gender-disaggregated indicators for percent of children in learning poverty, percent of primary school-aged children who are out of school, and percent of children below minimum proficiency in reading at the end primary.
You may also access the learning poverty data directly through EdStats .
To load the Learning Poverty data directly in Stata you can use this code:
// Install the user-written command if you don't have itcapture which wbopendataif _rc == 111 ssc install wbopendata // Query Learning Poverty indicator from World Bank APIwbopendata, indicator(SE.LPV.PRIM) latest long clear
To load the Learning Poverty data directly in Python you can use this code:
# Load the packageimport wbgapi as wb # Query the most recent non-empty value (mrnev parameter)df = wb.data.DataFrame('SE.LPV.PRIM', db=12, mrnev=1, columns='time', numericTimeKeys=True)
Current findings
Learning poverty map.
The map below is a snapshot of Learning Poverty across the world. You can also view the indicator for females and males. You may edit this map directly in DataBank .
Learning Poverty Map
Figure 1 Learning Poverty around the World (hover to see country numbers)
How does learning poverty vary by gender?
Using all available cross-country assessments (as well as gender-disaggregated enrollment data from UIS), we have computed gender-specific learning poverty rates. Given data availability, we have only been able to compute this disaggregation for 92 countries. Access to microdata in some countries, particularly in South Asia, has been a significant challenge to compute gender-disaggregated outcomes.
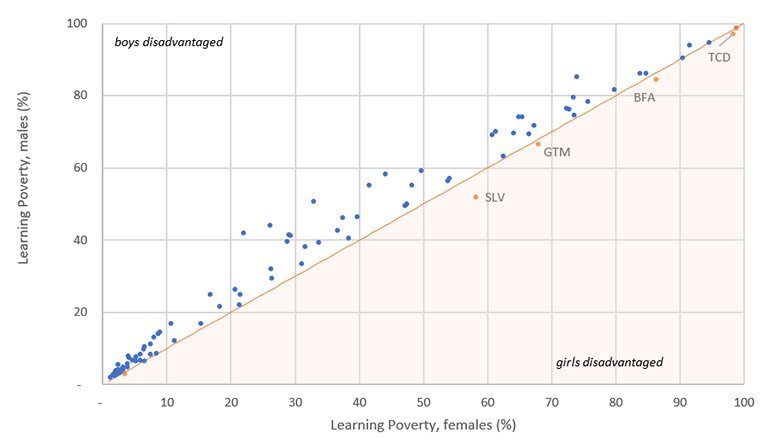
Learning Poverty gender gap, by country
Despite the barriers confronting girls in some areas of education, in virtually all countries for which we have data, girls have lower rates of learning poverty than boys do.
Replicate our results in GitHub
Our processes are documented on the LearningPoverty Github repository, which also includes instructions on how to replicate our numbers. You can find information about data source selection, calculations, aggregations here .
Forthcoming update
The recent release of new learning assessment results – TIMSS 2019, SEA-PLM 2019, and PASEC 2019 – calls for an update of the learning poverty indicator. A public update of the regional and global estimates is planned for September 2021 , to include the forthcoming LLECE 2019 results.
Significant changes are anticipated in some country estimates due to the replacement of national learning assessments by international ones. The initial learning poverty estimate was 52.7 percent in low- and middle-income countries, anchored in 2015. It used data from 62 countries, covering 80 percent of the target population. In September 2021, we plan to publish a corporate update of these global numbers. Using 2017 as the reference year implies accepting assessments from 2013 onwards, including the recently released TIMSS, SEA-PLM, PASEC from 2019 and the forthcoming LLECE 2019. With the new data, the coverage of the indicator will increase to 66 countries and 81 percent of the target population. The new update will also allow temporal comparisons in instances where countries have results from the same assessment in the last round.
Learning Poverty serves as an early-warning indicator for the Human Capital Project. For more information, visit website .
- "Literacy Makes Sense" campaign
- Ending Learning Poverty
- Country Learning Poverty Briefs
- Human Capital Project
- Education Homepage
- World Bank Human Capital Index
- Accelerator Program
- Learning Data Compact
- SDG Atlas - Quality Education: Learning Poverty
- Education Service Delivery Indicators
Brochure: What is Learning Poverty Overview
Reports using Learning Poverty Measures
The State of Global Learning Poverty: 2022 Update
Press Release: 70% of 10-Year-Olds now in Learning Poverty, Unable to Read and Understand a Simple Text
Ending Learning Poverty: What Will It Take?
Simulating the Potential Impacts of COVID-19 School Closures on Schooling and Learning Outcomes: A Set of Global Estimates
Learning Poverty: Measures and Simulations
Learning Poverty in the Time of COVID-19: A Crisis Within a Crisis
INFOGRAPHIC: A Policy Package to Promote Literacy for All Children
How could COVID-19 hinder progress with Learning Poverty? Some initial simulations
Learning for All: Within-country learning inequality
Learning for All: Beyond an Average Score
We should avoid flattening the curve in education – Possible scenarios for learning loss during the school lockdowns
Multiple exposures to learning assessments: A photo mosaic from Brazil
How to tackle Learning Poverty? Delivering education’s promise to children across the world Why focus on learning?
Communities working together to end learning poverty
Reducing learning poverty through a country-led approach
UIS Resources
Global Alliance to Monitor Learning (GAML)
Technical Cooperation Group on the Indicators for SDG 4 (TCG)
How the SDG 4.1.1 Framework and Learning Poverty Can Help Countries Focus Their Education Policy Response to COVID-19
Projections for Learning Proficiency Can Inform Post-COVID-19 Educational Strategies
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .

- Chronicle Conversations
- Article archives
- Issue archives
- Join our mailing list

Reducing Poverty Through Education - and How
About the author, idrissa b. mshoro.
There is no strict consensus on a standard definition of poverty that applies to all countries. Some define poverty through the inequality of income distribution, and some through the miserable human conditions associated with it. Irrespective of such differences, poverty is widespread and acute by all standards in sub-Saharan Africa, where gross domestic product (GDP) is below $1,500 per capita purchasing power parity, where more than 40 per cent of their people live on less than $1 a day, and poor health and schooling hold back productivity. According to the 2009 Human Development Report, sub-Saharan Africa's Human Development Index, which measures development by combining indicators of life expectancy, educational attainment, and income lies in the range of 0.45-0.55, compared to 0.7 and above in other regions of the world. Poverty in sub-Saharan Africa will continue to rise unless the benefits of economic development reach the people. Some sub-Saharan countries have therefore formulated development visions and strategies, identifying respective sources of growth.
Tanzania case study
The Tanzania Development Vision 2025, for example, aims at transforming a low productivity agricultural economy into a semi-industrialized one through medium-term frameworks, the latest being the National Strategy for Growth and Reduction of Poverty (NSGRP). A review of NSGRP implementation, documented in Tanzania's Poverty and Human Development Report 2009, attributed the falling GDP -- from 7.8 per cent in 2004 to 6.7 per cent in 2006 -- to the prolonged drought during 2005/06. A further fall to 5 per cent was projected by 2009 due to the global financial crisis. While the proportion of households living below the poverty line reduced slightly from 35.7 per cent in 2000 to 33.6 per cent in 2007, the actual number of poor Tanzanians is increasing because the population is growing at a faster rate. The 2009 HDR showed a similar trend whereby the Human Development Index in Tanzania shot up from 0.436 to 0.53 between 1990 and 2007, and in the same year the GDP reached $1,208 per capita purchasing power parity. Again, the improvements, though commendable, are still modest when compared with the goal of NSGRP and Millennium Development Goal 1 to reduce by 50 per cent the number of people whose income is less than $1 a day by 2010 and 2015.
More deliberate efforts are therefore required to redress the situation, with more emphasis placed particularly on education, as most poverty-reduction interventions depend on the availability of human capital for spearheading them. The envisaged economic growth depends on the quantity and quality of inputs, including land, natural resources, labour, and technology. Quality of inputs to a great extent relies on embodied knowledge and skills, which are the basis for innovation, technology development and transfer, and increased productivity and competitiveness.
A quick assessment in June 2010 of education statistics in Tanzania indicated that primary school enrolment increased by 5.8 per cent, from 7,959,884 pupils in 2006 to 8,419,305 in 2010. The Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) was 106.4 per cent. The transition rate from primary to secondary schools, however, decreased by 6.6 per cent from 49.3 per cent in 2005 to 43.9 per cent in 2009. On an annual average, out of 789,739 pupils who completed primary education, only 418,864 continued on to secondary education, notwithstanding the expansion of secondary school enrolment, from 675,672 students in 2006 to 1,638,699 in 2010, a GER increase from 14.8 to 34.0 percent. Moreover, the observed expansion in secondary school education mainly took place from grades one through four, where the number increased from 630,245 in 2006 to 1,566,685 students in 2010. As such, out of 141,527 students who on an annual average completed ordinary secondary education, only 36,014 proceeded to advanced secondary education. Some improvements have also been recorded at the tertiary level. While enrolment in universities was 37,667 students in 2004/05, there were 118,951 in 2009/10.
Adding to this number the students in non-university tertiary institutions totalled 50,173 in 2009/10 and the overall tertiary enrolment reached 169,124 students, providing a GER of 5.3 percent, which is very low.
The observed transition rates imply that, on average, 370,875 primary school children terminate their education journey every year at 13 to 14 years of age in Tanzania. The 17- to 19-year-old secondary school graduates, unable to obtain opportunities for further education, worsen the situation and the overall negative impact on economic growth is very apparent, unless there are other opportunities to develop and empower the secondary school graduates. Vocational education and training could be one such opportunity, but the total current enrolment in vocational education in Tanzania is about 117,000 trainees, which is still far from actual needs. A long-term strategy is therefore critical to expand the capacity for vocational education and training so as to increase the employability of the rising numbers of out-of-school youths. This fact was also apparent in the 2006 Tanzania Integrated Labour Force Survey, which indicated that youth between 15 and 24 years were more likely to be unemployed compared to other age groups because they were entering the labour market for the first time without any skills or work experience. The NSGRP target was to reduce unemployment from 12.9 per cent in 2000/01 to 6.9 per cent by 2010; hence the unemployment rate of 11 per cent in 2006 was disheartening.
One can easily notice that while enrolment in basic education is promising, the situation at other levels remains bleak in meeting poverty reduction targets. Moreover, apart from the noticeably low university enrolment in Tanzania, only 29 per cent of students are taking science and technology courses, probably due to the small catchment pool at lower levels. While this is so, sustainable and broad-based growth requires strengthening of the link between agriculture and industry. Agriculture needs to be modernized for increased productivity and profitability; small and medium enterprises, promoted, with particular emphasis on agro-processing, technology innovation, and upgrading the use of technologies for value addition; and all, with no or minimum negative impact on the environment. Increased investments in human and physical capital are also highly advocated, focusing on efficient and cost-effective provision of infrastructure for energy, information and communication technologies, and transport with special attention to opening up rural and other areas with economic potential. All these point to the promotion of education in science and technology. Special incentives for attracting investments towards accelerating growth are also emphasized. Experience from elsewhere indicates that foreign direct investment contributes effectively to economic growth when the country has a highly-educated workforce. Domestic firms also need to be supported and encouraged to pay attention to product development and innovation for ensuring quality and appropriate marketing strategies that make them competitive and capable of responding to global market conditions.
It is therefore very apparent from the Tanzania example that most of the required interventions for growth and the reduction of poverty require a critical mass of high-quality educated people at different levels to effectively respond to the sustainable development challenges of nations.
The UN Chronicle is not an official record. It is privileged to host senior United Nations officials as well as distinguished contributors from outside the United Nations system whose views are not necessarily those of the United Nations. Similarly, the boundaries and names shown, and the designations used, in maps or articles do not necessarily imply endorsement or acceptance by the United Nations.

Thirty Years On, Leaders Need to Recommit to the International Conference on Population and Development Agenda
With the gains from the Cairo conference now in peril, the population and development framework is more relevant than ever. At the end of April 2024, countries will convene to review the progress made on the ICPD agenda during the annual session of the Commission on Population and Development.

The LDC Future Forum: Accelerating the Attainment of the Sustainable Development Goals in the Least Developed Countries
The desired outcome of the LDC Future Forums is the dissemination of practical and evidence-based case studies, solutions and policy recommendations for achieving sustainable development.

From Local Moments to Global Movement: Reparation Mechanisms and a Development Framework
For two centuries, emancipated Black people have been calling for reparations for the crimes committed against them.

Documents and publications
- Yearbook of the United Nations
- Basic Facts About the United Nations
- Journal of the United Nations
- Meetings Coverage and Press Releases
- United Nations Official Document System (ODS)
- Africa Renewal
Libraries and Archives
- Dag Hammarskjöld Library
- UN Audiovisual Library
- UN Archives and Records Management
- Audiovisual Library of International Law
- UN iLibrary
News and media
- UN News Centre
- UN Chronicle on Twitter
- UN Chronicle on Facebook
The UN at Work
- 17 Goals to Transform Our World
- Official observances
- United Nations Academic Impact (UNAI)
- Protecting Human Rights
- Maintaining International Peace and Security
- The Office of the Secretary-General’s Envoy on Youth
- United Nations Careers
Education and Poverty in Education
This essay about the intricate relationship between education and poverty explores how each influences and perpetuates the other in a cyclic exchange. It discusses the barriers poverty creates for quality education and the transformative potential education holds in breaking the cycle of poverty. Highlighting disparities in access and efforts to address them, the essay emphasizes the importance of comprehensive solutions that go beyond traditional boundaries. Ultimately, it underscores the promise of education in shaping a brighter future for all, irrespective of their circumstances.
How it works
In the intricate fabric of societal challenges, the convergence of education and poverty unfolds a narrative both nuanced and profound, sculpting destinies with its myriad intricacies. Here, the interplay between education and poverty isn’t a straightforward path but rather a cyclic exchange, where each facet influences and perpetuates the other in a dance of mutual dependence. Within this elaborate dance lies the potential for profound metamorphosis, where education emerges as both a victim and a driving force, capable of shattering chains and nurturing hope amidst adversity.
At the nucleus of this intricate relationship lies an undeniable verity: poverty constructs formidable barriers to quality education, while education stands as a potent remedy to poverty’s clutches. In impoverished communities, these barriers manifest in myriad forms. Economic deprivation strips children of the essential prerequisites for learning—access to adequate nutrition, healthcare, and an environment conducive to education. For many, the stark decision between attending school and contributing to the family’s income isn’t a choice at all but a harsh reality dictated by uncontrollable circumstances.
The repercussions of this deprivation reverberate across generations. Children born into poverty often inherit a legacy of restricted opportunities and constrained possibilities. Without access to quality education, their potential remains untapped, perpetuating the cycle of poverty for yet another generation. Thus, poverty becomes not merely an economic condition but also a formidable barrier to social mobility and human flourishing.
Furthermore, disparities in educational access deepen the abyss, widening the chasm between the privileged and the marginalized. In schools deprived of resources, where outdated textbooks and overcrowded classrooms prevail, learning becomes an arduous task rather than a joyful exploration. Quality educators gravitate towards more affluent areas, leaving marginalized communities underserved and neglected. The resulting disparity in educational resources exacerbates socioeconomic inequalities, perpetuating a cycle where advantage begets advantage and disadvantage begets further disadvantage.
Yet, amidst the shadows, glimmers of hope emerge—testimonies to the transformative power of education. Across the globe, grassroots movements and innovative initiatives are challenging the status quo, dismantling barriers and fostering inclusivity. From community-driven literacy campaigns to initiatives leveraging technology for remote learning, imaginative solutions are reshaping the educational landscape in impoverished settings.
Moreover, the acknowledgment of education as a fundamental human right has spurred global action to ensure universal access. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) emphasize the pivotal role of education in poverty eradication, advocating for inclusive and equitable quality education for all. Initiatives such as UNESCO’s Education for All movement and the Malala Fund have mobilized resources and advocated for policy reforms to prioritize education in the fight against poverty.
Nevertheless, the journey towards educational equity is fraught with challenges. Deep-rooted systemic issues, from entrenched inequality to inadequate infrastructure, necessitate comprehensive solutions that transcend conventional boundaries. Effective policies must address not only access to education but also the quality and relevance of learning, equipping individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to thrive in a rapidly evolving world.
Furthermore, addressing poverty in education demands a multi-faceted approach that acknowledges the interconnectedness of social, economic, and cultural factors. Investments in healthcare, nutrition, and social protection are indispensable complements to educational initiatives, ensuring that children enter classrooms prepared to learn and succeed. Empowering communities and amplifying grassroots voices are vital steps towards fostering sustainable change from the ground up.
In this intricate interplay between education and poverty, each step forward signifies a triumph over adversity—a testament to the resilience of the human spirit. As we navigate the complexities of this relationship, let us remain unwavering in our commitment to unlocking the full potential of every individual, regardless of their circumstances. For within the pursuit of education lies the promise of a brighter future—not solely for a select few, but for all who dare to envision a world where poverty is not destiny but a challenge to be conquered.
Cite this page
Education And Poverty In Education. (2024, Apr 29). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/education-and-poverty-in-education/
"Education And Poverty In Education." PapersOwl.com , 29 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/education-and-poverty-in-education/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Education And Poverty In Education . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/education-and-poverty-in-education/ [Accessed: 16 May. 2024]
"Education And Poverty In Education." PapersOwl.com, Apr 29, 2024. Accessed May 16, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/education-and-poverty-in-education/
"Education And Poverty In Education," PapersOwl.com , 29-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/education-and-poverty-in-education/. [Accessed: 16-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Education And Poverty In Education . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/education-and-poverty-in-education/ [Accessed: 16-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
Perceived Impact of Poverty on Student Engagement, Motivation, and Academic Performance

2024, Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary Journal
This study, conducted in Pantar District, Lanao del Norte, during 2023-2024, explored how poverty affected student engagement and motivation. Using a descriptive-correlational design, 100 teachers observed poverty's impact on underprivileged students. Findings revealed that poverty moderately affected student engagement, particularly attendance and interconnected aspects like attention span, peer relationships, and class participation. Students consistently agreed on poverty's impact, emphasizing shared perceptions. On motivation, poverty had a moderate impact, influencing interest in learning, attitudes, and self-efficacy. Low standard deviation indicated agreement on poverty's motivational impact, urging tailored interventions. Academic performance was generally positive indicating "Satisfactory" standards and excelling Very Satisfactory. No students fell below expectations, highlighting overall positive academic trends. In analyzing factors influencing student motivation, attendance, attention span, and peer relationships did not predict motivation significantly. However, class participation emerged as a crucial positive predictor, underlining its role in fostering student motivation. Analyzing academic performance and student engagement or motivation did not yield significant results, emphasizing the complexity of factors influencing student achievement. In conclusion, poverty consistently impacted student engagement and motivation, urging targeted interventions. Despite challenges, positive academic trends highlighted students' resilience. Class participation was crucial for motivation, emphasizing the need for a holistic understanding of factors shaping academic success. Nonsignificant findings suggested a need for further exploration into the intricate relationship between student engagement, motivation, and achievement in the context of economic disparities.
Related Papers
Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary Journal
Psychology and Education
The goal of the study was to identify the difficulties and coping mechanisms faced by first-year students enrolled in online Master of Arts in Education courses at St. Peter's College in Iligan City during the first semester of the academic year 2022-2023. The survey provided information on the respondent profiles in terms of their age, sex, civil status, career, technology usage, and monthly family income. Also, the difficulties of taking lessons online, including isolation, instructor ability, motivation, and features. The respondents' coping strategies for the difficulties of taking online classes as well as for course, individual, technological, and environmental difficulties. Significant differences in the challenges and coping mechanisms for the challenges in the online classes of the respondents when grouped according to their socio-demographic profile and significant relationship between the respondents' challenges in online classes and their coping mechanisms. Family monthly income and age mediated the relationship between respondents' challenges and coping mechanisms were determined. The data gathered led to develop an action plan and made recommendations for this study. The study used the descriptive-correlational research method. It involved 149 students as respondents. The data used an adapted questionnaire that was validated through pilot testing. The result showed that most of the respondent's challenges in online classes were motivation, features of online classes, and isolation. The respondents' coping mechanisms for the challenges were in terms of environmental challenges; nevertheless, the other coping mechanisms-course challenges, technological challenges, and individual challenges-were also affirmed to have a better coping mechanism in their online class. The challenges faced by the respondents did significantly differed with the gadgets they used and their family's monthly income and coping mechanisms for online class challenges did significantly differed by their family's monthly income. The challenges in online classes were significantly correlated with their coping mechanisms. The challenges and coping mechanisms are not mediated by family monthly income and by age.
Psychology in the …
Mike Furlong
Research supports the connection between engagement, achievement, and school behavior across levels of economic and social advantage and disadvantage. Despite increasing interest and scientific findings, a number of interrelated conceptual and methodological issues ...
Psychology in the Schools
James Appleton
The California School …
Lawyer Akutei Emmanuel Akutei
GITIT KADAR-SATAT
This study aimed to determine the learners' academic performance and the learners' behavior. The respondents of the study were 49 grade 2 pupils and parents of Lanipao Elementary School. No sampling procedure was considered. Only 1 parent or guardian served as a respondent for every child or learner enrolled in school year 2021-2022. On the other hand, the grade 2 learners' academic performance in the second quarter was considered. The study sought to answer the parents' profile in terms of sex, age, parents' educational attainment, languages/dialects used/spoken at home, and parent's monthly income, the behavior of the learners in terms of learning behavior, management behavior, and emotional behavior, and the academic performance of the learners. The researcher utilized a researcher-made questionnaire in the data collection process. Contents of the 30-item questionnaire were under survey type. The gathered data were tabulated and analyzed using the following statistical tools, mean and percentage, Spearman rho, Chi-square, and Pearson-r Correlation Coefficient. The study entailed that the parents' demographic profile was not associated with the learners' academic performance. Thus, the null hypothesis of no significant relationship between the parents' profile and learners' academic performance was not rejected. Furthermore, the academic performance of the learners was unrelated to their learning behavior, management behavior, and emotional behavior. Thus, the null hypothesis of no significant relationship between the level of learners' behavior and their academic performance was not rejected. An action plan was drawn based on the findings of the study.
Journal of American Indian Education
Kristin Powers
The aim of this study was to determine the learners' level of excitement and problems as they returned to typical classroom settings after the pandemic at Lugait Central School, Lugait District, Division of Misamis Oriental for the academic year 2022-2023. One hundred thirteen (113) students participated in this descriptive-correlational study. The main aim was to investigate the relationship between the respondents' academic performance and the level of excitement and difficulties they were encountering as they returned to conventional educational settings after the pandemic. According to the results, the majority of the kids had demonstrated strong academic performance, with a significant portion of them exceeding expectations. It also indicated that, despite some implementation challenges after the epidemic, students were usually motivated to put in a good effort in class and learn the material. The results also showed that students' enthusiasm was a key factor in their academic achievement and that teachers should endeavor to provide a stimulating and engaging learning environment. This implied that learners' academic performance would rise as their level of excitement did. The findings also revealed a substantial inverse link between learners' academic achievement and their degree of difficulty. These results suggested that students who had greater difficulties could do worse in class. Teachers may hold a forum or workshop for the students on how to overcome the difficulties they faced in school after a pandemic, and they can use the appropriate intervention to assess the student's needs and current level of learning.
Handbook of Research on Student Engagement
David Shernoff
Youth & Society
Mark T Greenberg
RELATED PAPERS
ewing apriyan dananjaya
Microbiologica
P. Guglielmetti
Ana Reguillo
Ali Onuche John
Actes de l'Institut Agronomique et …
Mohammed Diouri
I Gde Sukadana
… españoles, Santander, 21 al 23 de septiembre de …
Paula Anael Cedillo De La Cruz
INTI Nusa Mandiri
Syarif Hidayatulloh
Science of The Total Environment
Sture Hobro
The Israel Medical Association journal : IMAJ
Antonio Fortunato
Proceedings Of International Conference On Communication Science
Deddy Irwandy
Metabolism-clinical and Experimental
Gideon Charach
Revista española de medicina nuclear e imagen molecular
Maria J Garcia-Velloso
Jaffna Medical Journal
Thirunavukarasu Kumanan
justin thomas
Journal of Governance and Accountability Studies
Mwesigwa David
Physical Review D
Gianni Penso
Ecology and Evolution
Line Nybakken
Asian Journal of Chemistry
Cordelia Dueke-Eze
Timothy HAMPTON
Applied Ocean Research
Mohammad Shalby
Ingeniería Investigación y Desarrollo
Javier Eduardo Becerra Becerra
Sustainability
Bashir ADELODUN
Methods in molecular biology
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage
Paolo Di Benedetto
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
The Hechinger Report
Covering Innovation & Inequality in Education
A decade of research on the rich-poor divide in education

Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
The Hechinger Report is a national nonprofit newsroom that reports on one topic: education. Sign up for our weekly newsletters to get stories like this delivered directly to your inbox. Consider supporting our stories and becoming a member today.
Get important education news and analysis delivered straight to your inbox
- Weekly Update
- Future of Learning
- Higher Education
- Early Childhood
- Proof Points
Americans like to believe that education can be a great equalizer, allowing even the poorest child who studies hard to enter the middle class. But when I looked at what academic researchers and federal data reports have said about the great educational divide between the rich and poor in our country, that belief turns out to be a myth. Basic education, from kindergarten through high school, only expands the disparities.
In 2015, during the Obama administration, the federal education department issued a report that showed how the funding gap between rich and poor schools grew 44 percent over a decade between 2001-2 and 2011-12. That meant that the richest 25 percent of school districts spent $1,500 more per student, on average, than the poorest 25 percent of school districts.
I wish I could have continued to track this data between rich and poor schools to see if school spending had grown more fair. But the Trump administration crunched the numbers differently. When it issued a report in 2018 , covering the 2014-15 school year, it found that the wealthiest 25 percent of districts spent $450 more per student than the poorest 25 percent.
That didn’t mean there was a giant 70 percent improvement from $1,500. The Trump administration added together all sources of funds, including federal funding, which amounts to 8 percent of total school spending, while the Obama administration excluded federal funds, counting only state and local dollars, which make up more than 90 percent of education funds. The Obama administration argued at the time that federal funds for poor students were intended to supplement local funds because it takes more resources to overcome childhood poverty, not to create a level playing field.
Rather than marking an improvement, there were signs in the Trump administration data that the funding gap between rich and poor had worsened during the Great Recession if you had compared the figures apples to apples, either including or excluding federal funds. In a follow-up report issued in 2019, the Trump administration documented that the funding gap between rich and poor schools had increased slightly to $473 per student between the 2014-15 and 2015-16 school years.
It’s not just a divide between rich and poor but also between the ultra rich and everyone else. In 2020, a Pennsylvania State University researcher documented how the wealthiest school districts in America — the top 1 percent — fund their schools at much higher levels than everyone else and are increasing their school spending at a faster rate. The school funding gap between a top 1 percent district (mostly white suburbs) and an average-spending school district at the 50th percentile widened by 32 percent between 2000 and 2015, the study calculated. Nassau County, just outside New York City on Long Island, has the highest concentration of students who attend the best funded public schools among all counties in the country. Almost 17 percent of all the top 1 percent students in the nation live in this one county.
Funding inequities are happening in a context of increased poverty in our schools. In 2013, I documented how the number of high poverty schools had increased by about 60 percent to one out of every five schools in 2011 from one out of every eight schools in 2000. To win this unwelcome designation, 75 percent or more of an elementary, middle or high school’s students lived in families poor enough to qualify for free or reduced-price lunch. It’s since gotten worse. In the most recent federal report , covering the 2016-17 school year, one out of every four schools in America was classified as high poverty.
It’s not just that poverty is becoming more concentrated in certain schools; more students in the school system are poor. In 2014, I documented a 40 percent jump in the number of school-aged children living in poverty between 2000 and 2012 from one out of every seven children to one out of every five students. In the most recent report, for the 2016-17 school year, the poverty rate declined from 21 percent in 2010 to 18 percent in 2017. About 13 million children under the age of 18 were in families living in poverty.
When you break the data down by race, there are other striking patterns. One third of all Black children under 18 were living in poverty in 2016-17, compared with a quarter of Hispanic children. White and Asian children have a similar poverty rate of 11 percent and 10 percent, respectively.
Sociologists like Sean Reardon at Stanford University and Ann Owens at the University of Southern California have built a body of evidence that school segregation by income is what’s really getting worse in America, not school segregation by race. But it’s a complicated argument because Black and Latino students are more likely to be poor and less likely to be rich. So the two things — race and poverty — are intertwined.
In 2019, Reardon studied achievement gaps in every school in America and found that the difference in poverty rates between predominantly Black and predominantly white schools explains the achievement gaps we see and why white schools tend to show higher test scores than Black schools. When white and Black schools have the same poverty rates, Reardon didn’t see a difference in academic achievement. The problem is that Black students are more often poor and attending schools with more poor students. And other than a handful of high-performing charter schools in a few cities, he couldn’t find examples of academic excellence among schools with a high-poverty student body.
“It doesn’t seem that we have any knowledge about how to create high-quality schools at scale under conditions of concentrated poverty,” said Reardon. “And if we can’t do that, then we have to do something about segregation. Otherwise we’re consigning Black and Hispanic and low-income students to schools that we don’t know how to make as good as other schools. The implication is that you have got to address segregation.”
Previous Proof Points columns cited in this column:
The number of high-poverty schools increases by about 60 percent
Poverty among school-age children increases by 40 percent since 2000
The gap between rich and poor schools grew 44 percent over a decade
Data show segregation by income (not race) is what’s getting worse in schools
In 6 states, school districts with the neediest students get less money than the wealthiest
An analysis of achievement gaps in every school in America shows that poverty is the biggest hurdle
Rich schools get richer: School spending analysis finds widening gap between top 1% and the rest of us
This story about education inequality in America written by Jill Barshay and produced by The Hechinger Report , a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for the Hechinger newsletter .
Related articles
The Hechinger Report provides in-depth, fact-based, unbiased reporting on education that is free to all readers. But that doesn't mean it's free to produce. Our work keeps educators and the public informed about pressing issues at schools and on campuses throughout the country. We tell the whole story, even when the details are inconvenient. Help us keep doing that.
Join us today.
Jill Barshay SENIOR REPORTER
(212)... More by Jill Barshay
Letters to the Editor
At The Hechinger Report, we publish thoughtful letters from readers that contribute to the ongoing discussion about the education topics we cover. Please read our guidelines for more information. We will not consider letters that do not contain a full name and valid email address. You may submit news tips or ideas here without a full name, but not letters.
By submitting your name, you grant us permission to publish it with your letter. We will never publish your email address. You must fill out all fields to submit a letter.
Thanks to Jill Barshay for the excellent column reminding us that there is much more to the rich/poor divide in our public schools than just the availability of digital devices and wi-fi. The real problem with equity in education is the lack of equity in school funding, which is an issue both of inequity in society and the ways in which public schools are funded (i.e., primarily local tax revenues).
Other barriers that kept the “school door blocked” for many low income students during this season of remote learning — and, presumably, next school year, as well — include: 1. Some with access to devices and wi-fi have had service disconnected at times due to unpaid (unpayable) bills. 2. Many have no private space in their homes from where to participate in synchronous learning/Zoom calls 3. With loss of family income and no child care, some have work or baby-sitting responsibilities that interfere with participation 4. Deadening effects of online learning cause many low-income students to disconnect and/or “drop out”. 5. In ability to access teacher supports and specialized instruction, esp. for English language learners and children with special needs. 6. Parent inability to assist students with computer routines, glitches, log-ins, etc
As districts address equity in the coming school year, we must also address the modes of learning that we consider both effective and valuable. If the top priority is engaging all students we need high engagement models based in trauma-informed practices, social and racial justice curricula, service learning, interdisciplinary project- and place-based learning, outdoor learning and other innovative ways to make education relevant to all students, regardless of their zip codes. Relax the standards. Cancel high stakes testing. Trust teachers to use their creativity to connect with every student and family. Otherwise, “remote” or “hybrid” learning, regardless of the availability of technology, will only be widening the gaps that structural racism has already created.
Why are we NOT reaching out to the teaching programs started by Marva Collins in Chicago and Ron Clark in Atlanta? Why are we NOT looking at a book called Schools That Work and viewing the achievements and strategies followed by successful programs. Let’s follow successful schools, successful environments in urban, rural, and suburban locations. As an eductor who started teaching in the Ocean-Hill Brownsville area of Brooklyn, N,Y. in 1971, there was a wildcat strike happening and this area was the where decentralization took place in N.Y.C. Rev. Al Sharpton’s church was down the block from I.S. 271. It took 2 years before a no nonsense, BLACK principal, took control over the choas and the movement of 125 teachers going and then coming to this “high poverty” intermediate school. There was stability of staff and the message was, you’re here to learn. I taught there for 7 incredible years and grew to understand what it was like being a minority teacher and human being. I then moved to Columbia, MD. where I lived in a planned community where diversity of color, homes, religions and belief in humanity living together as ONE took place. I taught in a white disadvantaged area for 2 years and observed the same behaviors students exhibited except there was no leadership at the top of this school. Now I teach in a suburban area for the last 31 years with limited diversity and succeeds because of innovative leadership, extraordinary teachers, and pretty high achieving students. Yes, I know every students must have access to technology as a MUST. Yes, I know urban education, rural education, and suburban education do education diffferently. Yes, I know poverty sucks, and I know distant learning may be around for a while. Change must come from the top. Let’s follow the successful educators, the successful programs, the dynamic elected officials who can shake up things so our students, our kids, our educational systems can be the change that can bring poverty to it’s knees.
I live on Long Island and know that whatever is written here about us is true. The Freeport Public School waste millions of taxpayers dollars throwing out teaching equipment, devices books that could be just given to the less fortunate schools next door-Queens, Brooklyn and the Bronx; where we see children suffering because of lack of proper learning tools. I am from the Caribbean where l taught for years. Oh l wish we were as privileged as these children. Maybe one day the disparity will end. Hopefully.
I enjoy reading this post. I am currently doing my thesis and the research question is: Do California K-12 public schools in lower-income communities offer the same level of academic curriculum as those in middle-income and wealthy communities? Do you have the reference page for those studies or even any peer reviewers where you got the information? I would like to review those studies and use them for my thesis. Thank you
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
Submit a letter
Poverty Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on poverty essay.
“Poverty is the worst form of violence”. – Mahatma Gandhi.

How Poverty is Measured?
For measuring poverty United nations have devised two measures of poverty – Absolute & relative poverty. Absolute poverty is used to measure poverty in developing countries like India. Relative poverty is used to measure poverty in developed countries like the USA. In absolute poverty, a line based on the minimum level of income has been created & is called a poverty line. If per day income of a family is below this level, then it is poor or below the poverty line. If per day income of a family is above this level, then it is non-poor or above the poverty line. In India, the new poverty line is Rs 32 in rural areas and Rs 47 in urban areas.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Causes of Poverty
According to the Noble prize winner South African leader, Nelson Mandela – “Poverty is not natural, it is manmade”. The above statement is true as the causes of poverty are generally man-made. There are various causes of poverty but the most important is population. Rising population is putting the burden on the resources & budget of countries. Governments are finding difficult to provide food, shelter & employment to the rising population.
The other causes are- lack of education, war, natural disaster, lack of employment, lack of infrastructure, political instability, etc. For instance- lack of employment opportunities makes a person jobless & he is not able to earn enough to fulfill the basic necessities of his family & becomes poor. Lack of education compels a person for less paying jobs & it makes him poorer. Lack of infrastructure means there are no industries, banks, etc. in a country resulting in lack of employment opportunities. Natural disasters like flood, earthquake also contribute to poverty.
In some countries, especially African countries like Somalia, a long period of civil war has made poverty widespread. This is because all the resources & money is being spent in war instead of public welfare. Countries like India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, etc. are prone to natural disasters like cyclone, etc. These disasters occur every year causing poverty to rise.
Ill Effects of Poverty
Poverty affects the life of a poor family. A poor person is not able to take proper food & nutrition &his capacity to work reduces. Reduced capacity to work further reduces his income, making him poorer. Children from poor family never get proper schooling & proper nutrition. They have to work to support their family & this destroys their childhood. Some of them may also involve in crimes like theft, murder, robbery, etc. A poor person remains uneducated & is forced to live under unhygienic conditions in slums. There are no proper sanitation & drinking water facility in slums & he falls ill often & his health deteriorates. A poor person generally dies an early death. So, all social evils are related to poverty.
Government Schemes to Remove Poverty
The government of India also took several measures to eradicate poverty from India. Some of them are – creating employment opportunities , controlling population, etc. In India, about 60% of the population is still dependent on agriculture for its livelihood. Government has taken certain measures to promote agriculture in India. The government constructed certain dams & canals in our country to provide easy availability of water for irrigation. Government has also taken steps for the cheap availability of seeds & farming equipment to promote agriculture. Government is also promoting farming of cash crops like cotton, instead of food crops. In cities, the government is promoting industrialization to create more jobs. Government has also opened ‘Ration shops’. Other measures include providing free & compulsory education for children up to 14 years of age, scholarship to deserving students from a poor background, providing subsidized houses to poor people, etc.
Poverty is a social evil, we can also contribute to control it. For example- we can simply donate old clothes to poor people, we can also sponsor the education of a poor child or we can utilize our free time by teaching poor students. Remember before wasting food, somebody is still sleeping hungry.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Poverty in education
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Education essays
- Reading time: 5 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 15 November 2018*
- File format: Text
- Words: 1,443 (approx)
- Number of pages: 6 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 1,443 words. Download the full version above.
Poverty in Education
Poverty remains to be the source of hardships financially, academically, and socially. The way that poverty levels affect the children of the world is a troubling concern. 43 percent of children are currently living in low-income homes while 21% of them are living below the financial poverty threshold set by the federal government (“NCCP | Child Poverty”, 2016). Families with no financial resources do not have access to educational supplies. Without educational resources, these families are constrained to their lives in poverty.
Concept of Poverty
Poverty is the result of not having proper resources to sustain effectively in the community (Sen,2009). This concept of poverty expands the notion that poverty is merely the lack of financial freedom. Although poverty does have direct correlations to finances, it is important to recognize the different facets of poverty and their effects. An aspect of financial income is educational output. Absolute poverty is the lack of financial necessities. This is more common in developing countries, however, it can be found often here in the United States. Absolute poverty will affect children and families as they are not able to provide themselves with materials to further their learning. These materials include a lack of books, pens/pencils or often times children will have no place to do their homework. Poor nutrition has also been found to prevent students from learning effectively. Relative poverty is pre-determined by where a family resides. Where you live typically determines the school your child will attend. Parents often choose their living arrangements based upon cost of living. Schools located in areas meant for these families typically receive little to no funding in comparison. These children will also lack the motivation to do well in school since the perception around them is that school is not important. Poverty lowers educational enrollment and restricts learning environments. To move poverty-stricken school districts in the right direction, they must develop personalized intervention strategies opposed to generalized conclusions.
Poverty in School Readiness
A child’s educational journey starts not from the first day they enter primary school, but from the moment they learn to observe their surroundings, form sentences, and make conclusions from the world around them. Their readiness for school is a clear demonstration of their likelihood to succeed emotionally, socially and academically in school. As determined by the National Education Goals Panel, a child deemed “school ready” is expected to be able to demonstrate five different dimensions of development/knowledge:
physical well-being/motor development
social/emotional development
language development
cognition knowledge
approaches to learning
Children living in poverty are less likely to have these school readiness skills at the same level as a child living in a middle or upper-class family. Research shows that children living in poverty-stricken environments are more likely to suffer from psychiatric disorders, physical health problems and less than average functioning both academically and socially. (Ferguson, 2007). Reversing the effects of children not being classified “school ready” as suggested by Ferguson, is to focus on early childhood intervention as this can help single out health problems, parenting issues, behavioral and social responsiveness.
Academic Achievement
Holistically, poverty is all about a lack of resources. As stated by Misty Lacour & Laura Tissington, these resources are financial, emotional, mental, spiritual, and physical. All of these resources combined lead to the issues faced by children in poverty inside of the classroom. Their studies have also shown that the factors that are a direct result of poverty can cause children to not perform at a high completion rate, academically. Higher incomes have been contributed to better student performance. These findings determined that children from low-income families suffered cognitively, reading/math scores, socially, and emotionally. Children from these households almost always scored below average in comparison to their wealthy peers.
Lacour & Tissington place emphasis on the lack of family systems/subsystems, emotional/mental support and role models as a contribution to low academic achievement. Race and gender were not found to be determining factors– only to show trends/data separated by race. These students in these communities are not receiving funding/experienced teachers to help bridge the gap.
To help boost academic achievement rates from an average of 19% (standardized test percentiles), there should be changes implemented in instructional techniques and strategies provided in the classroom. The three major areas of reform are school environment, home/community environment and policies of the district/state (Lacour & Tissington, 2011).
Change in Schools
Education at any level is a need in society today. The woes of poverty can place a large amount of burden on the shoulders of the educators that teach those students. Standardized testing has been put in place so that school administration can see the overall learning success and failure of their students. Due to this, it can be easy for teachers to place more emphasis on scores and remediation for better numbers. According to Theresa Capra (2009), the constant cycle of new teachers in minority areas negatively impacts the education that is being received. The lack of income obtained by students’ parents is highly associated with their lack of education. “History and evolution have shown that inequality is a reality. As the human race advances, however, it is plausible to think that civilization can prevent the decay of its social constructs through quality, accessible education. Embracing this perspective may help us to completely rethink education, leading to a more progressive system for our future” (Capra, 2009).
Through the research of the great scholars before me, I have realized that poverty is not a two nor three-dimensional issue. I was ignorant to this and now have a better understanding of what it means to be in poverty. Poverty is much more than the lack of financial means. Amartya Sen did a wonderful job of explaining the different aspects of poverty and how it affects the life of the families suffering. Poverty affects the families from functioning properly in their community — they have trouble paying their bills, yet can’t find a decent paying job without a good education. A good education costs money that they don’t have, therefore, the cycle continues. The absolute and relative view is extremely relevant to this detrimental cycle because they categorize the deficiencies caused by poverty.
Children that are from poverty-stricken areas are forced to go into schools that receive very little or no support from their communities. This is saddening — most times when parents request for students to go to a better school (provided they have reliable transportation of their own), they are denied due to the importance of scores. Districts place so much emphasis on scoring on standardized tests rather than the foundation of knowledge needed to succeed. This foundation starts with school readiness skills, which Ferguson & Mueller illustrated wonderfully. When students are not able to establish these skills effectively it sets them up for long-term failures not only academically but mentally and socially as well.
Scarce resources due to poverty such as family systems/subsystems, emotional/mental support, role models and monetary support directly correlate to the low academic achievement levels in students. I n The effects of poverty on academic achieve ment, the authors offered various solutions to close the academic gap such as assessing students through holistic assessments and using voluntary data. While this article provided a lot of important insight on the issues for students living in poverty, it did not give real solutions. In low-income households, children are often disassociated from the resources that middle or high-income students have. Changing the way these students are evaluated through assessments, does not change the education these students are receiving. It only helps them look better statistically.
In contrast, Captra touches on the importance of higher education and the difficulties students face in economically challenged schools.
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Poverty in education . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/education-essays/poverty-in-education/> [Accessed 15-05-24].
These Education essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
- 📑 Aspects to Cover in a Poverty Essay
Students who learn economics, politics, and social sciences are often required to write a poverty essay as part of their course. While everyone understands the importance of this topic, it can be hard to decide what to write about. Read this post to find out the aspects that you should cover in your essay on poverty.
🏆 Best Poverty Topics & Free Essay Examples
👍 powerful topics on poverty and inequality, 🎓 simple & easy topics related to poverty, 📌 interesting poverty essay examples, ⭐ strong poverty-related topics, 🥇 unique poverty topics for argumentative essay, ❓ research questions about poverty.
Topics related to poverty and inequality might seem too broad. There are so many facts, factors, and aspects you should take into consideration. However, we all know that narrowing down a topic is one of the crucial steps when working on an outline and thesis statement. You should be specific enough to select the right arguments for your argumentative essay or dissertation. Below, you will find some aspects to include in your poverty essay.
Poverty Statistics
First of all, it would be beneficial to include some background information on the issue. Statistics on poverty in your country or state can help you to paint a picture of the problem. Look for official reports on poverty and socioeconomic welfare, which can be found on government websites. While you are writing this section, consider the following:
- What is the overall level of poverty in your country or state?
- Has the prevalence of poverty changed over time? If yes, how and why?
- Are there any groups or communities where poverty is more prevalent than in the general population? What are they?
Causes of Poverty
If you look at poverty essay titles, the causes of poverty are a popular theme among students. While some people may think that poverty occurs because people are lazy and don’t want to work hard, the problem is much more important than that. Research books and scholarly journal articles on the subject with these questions in mind:
- Why do some groups of people experience poverty more often than others?
- What are the historical causes of poverty in your country?
- How is poverty related to other social issues, such as discrimination, immigration, and crime?
- How do businesses promote or reduce poverty in the community?
Consequences of Poverty
Many poverty essay examples also consider the consequences of poverty for individuals and communities. This theme is particularly important if you study social sciences or politics. Here are some questions that may give you ideas for this section:
- How is the psychological well-being of individuals affected by poverty?
- How is poverty connected to crime and substance abuse?
- How does poverty affect individuals’ access to high-quality medical care and education?
- What is the relationship between poverty and world hunger?
Government Policies
Governments of most countries have policies in place to reduce poverty and help those in need. In your essay, you may address the policies used in your state or country or compare several different governments in terms of their approaches to poverty. Here is what you should think about:
- What are some examples of legislation aimed at reducing poverty?
- Do laws on minimum wage help to prevent and decrease poverty? Why or why not?
- How do governments help people who are poor to achieve higher levels of social welfare?
- Should governments provide financial assistance to those in need? Why or why not?
Solutions to Poverty
Solutions to poverty are among the most popular poverty essay topics, and you will surely find many sample papers and articles on this subject. This is because poverty is a global issue that must be solved to facilitate social development. Considering these questions in your poverty essay conclusion or main body will help you in getting an A:
- What programs or policies proved to be effective in reducing poverty locally?
- Is there a global solution to poverty that would be equally effective in all countries?
- How can society facilitate the reduction of poverty?
- What solutions would you recommend to decrease and prevent poverty?
Covering a few of these aspects in your essay will help you demonstrate the in-depth understanding and analysis required to earn a high mark. Before you start writing, have a look around our website for more essay titles, tips, and interesting topics!
- Poverty Research Proposal To justify this, the recent and most current statistics from the Census Bureau shows that the level and rate of poverty in USA is increasing, with minority ethnic groups being the most disadvantaged.
- Wordsworth’s Vision of Childhood in His Poems “We Are Seven” and “Alice Fell or Poverty” Specifically, the joint publication he released in 1798 known as “Lyrical Ballads” are considered the most important publications in the rise of the Romantic literature in the UK and Europe.
- Poverty: A Sociological Imagination Perspective I was raised in a nuclear family, where my mum was a housewife, and my father worked in a local hog farm as the overall manager.
- “The Singer Solution to World Poverty” by Peter Singer The article “The Singer Solution to World Poverty” by author Peter Singer attempts to provide a workable solution to the world poverty problem.
- Poverty in the World In this paper, we will be looking at the situation of poverty in the world, its causes and the efforts of the international organizations to manage the same.
- The Philippines’ Unemployment, Inequality, Poverty However, despite the strong emphasis of the government on income equality and poverty reduction along with the growth of GDP, both poverty and economic and social inequality remain persistent in the Philippines.
- The End of Poverty Philippe Diaz’s documentary, The End of Poverty, is a piece that attempts to dissect the causes of the huge economic inequalities that exist between countries in the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere.
- Poverty in India and China India’s slow rate of poverty reduction compared to China is due to the differences in their approach to the economy. Improving the living conditions and general well being of the people is not only the […]
- Poverty in Africa These pictures have been published online to show the world the gravity of the poverty situation in the African continent. The pictures represent the suffering of majority of the African people as a result of […]
- Poverty Areas and Effects on Juvenile Delinquency The desire to live a better life contributes to the youths engaging in crimes, thus the increase in cases of juvenile delinquencies amid low-income families. The studies indicate that the fear of poverty is the […]
- Poverty Effects on Child Development and Schooling To help children from low-income families cope with poverty, interventions touching in the child’s development and educational outcomes are essential. Those programs campaign against the effects of poverty among children by providing basic nutritional, academic, […]
- Max Weber’s Thoughts on Poverty Weber has contributed to the exploration of the origins of poverty and the impact of religions on the attitude to it.
- Analysis of Theodore Dalrymple’s “What Is Poverty?” With ethical arguments from Burnor, it can be argued that Dalrymple’s statements are shallow and based on his values and not the experience of those he is judging.
- The Singer Solution to World Poverty: Arguments Against The article compares the lives of people in the developed world represented by America and that of developing world represented by Brazil; It is about a school teacher who sells a young boy for adoption […]
- What Causes Poverty in the World One of the major factors that have contributed to poverty in given areas of the world is overpopulation. Environmental degradation in many parts of the world has led to the increase of poverty in the […]
- Poverty and the Environment The human population affects the environment negatively due to poverty resulting to environmental degradation and a cycle of poverty. Poverty and the environment are interlinked as poverty leads to degradation of the environment.
- Community Work: Helping People in Poverty The first project would be water project since you find that in most villages water is a problem, hence $100 would go to establishing this project and it’s out of these water then the women […]
- Relationship Between Crime Rates and Poverty This shows that the strength of the relationship between the crime index and people living below the line of poverty is.427.
- Children Living in Poverty and Education The presence of real subjects like children is a benefit for the future of the nation and a free education option for poor families to learn something new and even use it if their children […]
- Is Poverty a Choice or a Generational Curse? The assumption that poverty is a choice persists in public attitudes and allows policy-makers to absolve themselves of any responsibility for ensuring the well-being of the lower socioeconomic stratum of society.
- Poverty and Global Food Crisis: Food and Agriculture Model Her innovative approach to the issue was to measure food shortages in calories as opposed to the traditional method of measuring in pounds and stones.
- Cause and Effect of Poverty For example, the disparities in income and wealth are considered as a sign of poverty since the state is related to issues of scarcity and allocation of resources and influence.
- The Problem of Poverty in Bob Marley’s “No Woman, No Cry” To see the situation from the perspective of its social significance, it is necessary to refer to Mills’ concept of sociological imagination and to the division of problems and issues into personal and social ones.
- Poverty Alleviation and Sustainable Development The research focuses on the causes of poverty and the benefits of poverty alleviation in achieving sustainable development. One of the causes of poverty is discrimination and social inequality.
- Poverty Simulation Reflection and Its Influence on Life Something that stood out to me during the process is probably the tremendous emotional and psychological impact of poverty on a person’s wellbeing.
- The Connection Between Poverty and Mental Health Problems The daily struggle to earn a daily bread takes a toll on an individual mental health and contributes to mental health problem.
- Third World Countries and the Barriers Stopping Them to Escape Poverty The phrase Third World was initially used in the Cold War period to represent those countries that were neither on the West NATO nations referred to as the first world countries, nor on the East-Communist […]
- Consumerism: Affecting Families Living in Poverty in the United States Hence, leading to the arising of consumerism protection acts and policies designed to protect consumers from dishonest sellers and producers, which indicates the high degree of consumer’s ignorance, and hence failure to make decisions of […]
- Global Poverty: Famine, Affluence, and Morality In the article Famine, Affluence, and Morality, Michael Slote contends that rich people have a moral obligation to contribute more to charities.
- Poverty in Bambara’s The Lesson and Danticat’s A Wall of Fire Rising It is important to note the fact that culture-based poverty due to discrimination of the past or political ineffectiveness of the nation can have a profound ramification in the lives of its victims.
- Environmental Degradation and Poverty It is however important to understand the causes of the environmental degradation and the ways to reduce them, which will promote the improvement of the environmental quality.
- Poverty in Urban Areas The main reason for escalation of the problem of poverty is urban areas is because the intricate problems of urban poverty are considered too small to attract big policies.
- Health, Poverty, and Social Equity: The Global Response to the Ebola Outbreak Canada and Australia, as well as several countries in the Middle East and Africa, were the most active proponents of this ban, halting the movements for both people and goods from states affected by the […]
- Poverty and Diseases A usual line of reasoning would be that low income is the main cause of health-related problems among vulnerable individuals. Such results that the relationship between mental health and poverty is, in fact, straightforward.
- “The End of Poverty” by Phillipe Diaz In the film End of Poverty, the filmmaker tries to unravel the mystery behind poverty in the world. The film is arranged in such a way that the author has persuasively argued his case that […]
- Social Issues of Families in Poverty With the tightened budget, parents of the families living in poverty struggle to make ends meet, and in the course of their struggles, they experience many stresses and depressions.
- We Can Stop Poverty in Ghana Today One of the main disadvantages of the document is that the problem of poverty is not considered separately, but only as a part of other economic and social problems.
- Poverty in Rural and Urban Areas My main focus is on articles explaining the sources of poverty in rural and urban areas and the key difference between the two.
- Reflective Analysis of Poverty It can be further classified into absolute poverty where the affected do not have the capability to make ends meet, and relative poverty which refer to the circumstances under which the afflicted do not have […]
- Poverty Through a Sociological Lens Poverty-stricken areas, such as slums, rural villages, and places hit by disasters, lack the required economic activities to improve the employment and wealth status of the people.
- Global Poverty: The Ethical Dilemma Unfortunately, a significant obstacle to such global reforms is that many economic systems are based on the concept of inequality and exploitation.
- Concept of Poverty The main difference between this definition and other definitions of poverty highlighted in this paper is the broad understanding of the concept.
- Social Issues; Crime and Poverty in Camden This has threatened the social security and peaceful coexistence of the people in the community. The larger the differences between the poor and the rich, the high are the chances of crime.
- The Myth of the Culture of Poverty Unfortunately, rather all of the stereotypes regarding poor people are widespread in many societies and this has served to further increase the problem of generational poverty. Poor people are regarded to be in the state […]
- Dependency Theory and “The End of Poverty?” It is also reflected in the film “The End of Poverty?” narrating the circumstances of poor countries and their precondition. It started at the end of the fifteenth century and marked the beginning of the […]
- Poverty, Government and Unequal Distribution of Wealth in Philippines The author of the book Poverty And The Critical Security Agenda, Eadie, added: Quantitative analyses of poverty have become more sophisticated over the years to be sure, yet remain problematic and in certain ways rooted […]
- Tourism Contribution to Poverty Reduction Managers usually make targeting errors such as poor delivery of tourism benefits to the poor and accruing tourism benefit to the rich in the society.
- Is Globalization Reducing Poverty and Inequality? & How to Judge Globalism The article Is Globalization Reducing Poverty and Inequality by Robert Hunter Wade explores the phenomenon of globalization and its influence on the poverty and inequality ratios all over the world.
- Analysis of a Social Problem: Poverty Furthermore, the World Bank predicts that both the number of people and the percentage of the population living in extreme poverty will increase in 2020 and 2021 due to the coronavirus outbreak.
- Poverty in Orwell’s “Down and Out in Paris and London” The fact that the structure of society is discussed is especially interesting, and it is suggested that opinions of people that live in poverty are not acknowledged most of the time.
- Poverty: $2.00 a Day in America When conversations about the poor occur in the city of Washington, they usually discuss the struggles of the working poor, forgetting about the issues that the non-working poor face day by day.
- Poverty as Capability Deprivation In this paper, the importance of social justice manifests through the understanding of social deprivation, as opposed to the understanding of income levels in the achievement of social justice.
- Poverty in the Bronx: Negative Effects of Poverty South Bronx is strictly the southwestern part of the borough of Bronx and Bronx is the only borough in New York city in the mainland.
- Social Work at Acacia Network: Poverty and Inequality Around the 1980s, the number of older adults was significantly increasing in society; the local government of New York established a home for the aged and was named Acacia Network. The supporting staff may bond […]
- Economic Growth vs. Development: Dreze and Sen’s Analysis The majority of the poor people in the slums and villages use small capital to run their businesses. Good institutions enforce the property rights of the majority in the society, create constraints for the elites, […]
- How Poverty Contributes to Poor Heath The results show that poverty is the main cause of poor health. The study was purposed to assess the effect of poverty in determining the health status of households.
- Global Poverty Project: A Beacon of Hope in the Fight Against Extreme Poverty The organization works with partners worldwide to increase awareness and understanding of global poverty and inspire people to take action to end it.
- The Causes of an Increase in Poverty in Atlanta, Georgia The key causes of the high poverty rise in the city include housing policies and instabilities, the lack of transit services and public transportation infrastructure in suburban areas, and childhood poverty.
- Thistle Farms: Help for Women Who Are Affected by Poverty As I said in the beginning, millions of women need help and assistance from the community to overcome poverty and heal emotional wounds caused by abuse. You can purchase a variety of its home and […]
- Median Household Incomes and Poverty Levels The patterns of poverty in the Denver urban area show that rates are higher in the inner suburb and the core city and lower in the outer suburb.
- Poverty: The American Challenge One of the main problems in the world is the problem of poverty, which means the inability to provide the simplest and most affordable living conditions for most people in a given country.
- The Poverty Issue From a Sociological Perspective The core of the perspective is the idea that poverty is a system in which multiple elements are intertwined and create outcomes linked to financial deficits.
- Saving the Planet by Solving Poverty The data is there to make the necessary links, which are needed when it comes to the economic variations and inadequate environmental impacts of climate change can be distinguished on a worldwide scale.
- Anti-Poverty Programs From the Federal Government The programs provide financial assistance to low-income individuals and families to cover basic needs like housing and food. The anti-poverty programs that have been most effective in reducing poverty rates in the United States are […]
- Rural Development, Economic Inequality and Poverty The percentage of the rural population is lower for developed countries, including the United States and the United Kingdom. Thus, the objective of the proposal is to determine how the inhabitants of the country in […]
- Global Poverty: Ways of Combating For example, one of such initiatives is social assistance and social protection programs, which ensure the safety and creation of various labor programs that will help increase the number of the working population.
- Poverty and Homelessness as a Global Social Problem What makes the task of defining poverty particularly difficult is the discrepancy in the distribution of social capital and, therefore, the resulting differences in the understanding of what constitutes poverty, particularly, where the line should […]
- Poverty: Aspects of Needs Assessment The target neighborhood and population for the following analysis are women of reproductive age, defined as 15 to 49 years, in Elmhurst and Corona, Queens. 2, and the percentage of births to women aged over […]
- What Is Poverty in the United States? Estimates of the amount of income required to meet necessities serve as the foundation for both the official and supplemental poverty measurements.
- The Caribbean Culture: Energy Security and Poverty Issues Globally, Latin American and the Caribbean also has the most expensive energy products and services because of fuel deprivation in the Caribbean and the Pacific regions.
- Poverty: The Main Causes and Factors Because of the constant process of societal development, the concept of poverty changes rapidly, adapting to the new standards of modern human life.
- How to Overcome Poverty and Discrimination As such, to give a chance to the “defeated” children and save their lives, as Alexie puts it, society itself must change the rules so that everyone can have access to this ticket to success. […]
- Poverty and Homelessness in American Society It is connected with social segregation, stigmatization, and the inability of the person to improve their conditions of life. The problem of affordable housing and poverty among older adults is another problem that leads to […]
- Private Sector’s Role in Poverty Alleviation in Asia The ambition of Asia to become the fastest-growing economic region worldwide has led to a rapid rise of enterprises in the private sector.
- Connection of Poverty and Education The economy of the United States has been improving due to the efforts that have been made to ensure that poverty will not prevent individuals and families from having access to decent education.
- The Opportunity for All Program: Poverty Reduction The limiting factors of the program may be the actions of the population itself, which will not participate in the employment program because of the realized benefits.
- Early Childhood Financial Support and Poverty The mentioned problem is a direct example of such a correlation: the general poverty level and the well-being of adults are connected with the early children’s material support.
- Discussion: Poverty and Healthcare One of the research questions necessary to evaluate this issue is “How do ethical theories apply to the issue?” Another critical research question worth exploring is “Which cultural values and norms influence the problem?” These […]
- Explosive Growth of Poverty in America The three richest Americans now own 250 billion USD, approximately the same amount of combined wealth as the bottom 50 percent of the country. Wealth inequality is a disturbing issue that needs to be at […]
- The Poverty and Education Quality Relationship Although the number of people living under the poverty threshold has decreased in the last 30 years, more than 800,000,000 people still have to live with insufficient money and a lack of food, water, and […]
- The Problems of Poverty and Hunger Subsequently, the cause in this case serves as a path to a solution – more social programs are needed, and wealthy citizens should be encouraged to become beneficiaries for the hungry.
- “Life on a Shoestring – American Kids Living in Poverty” by Claycomb Life on a Shoestring – American Kids Living in Poverty highlights the widening disparity between the poor and the wealthy in America and how the economic systems are set up to benefit the rich and […]
- Decreasing Poverty With College Enrollment Program In order to achieve that, it is necessary, first and foremost, to increase the high school students’ awareness of the financial aid programs, possibilities of dual enrollment, and the overall reality of higher education.
- Reducing Poverty in the North Miami Beach Community The proposed intervention program will focus on the students in the last semester of the 9th and 10th grades and the first semester of the 11th and 12th grades attending the client schools.
- Food Banks Board Members and Cycle of Poverty What this suggests is that a large portion of the leadership within these collectives aim to provide assistance and food but not to challenge the current system that fosters the related issues of poverty, unemployment, […]
- Poverty as a Social Problem in Burundi The rationale for studying poverty as a social problem in Burundi is that it will help to combat poverty through the advocacy plan at the end of this paper.
- Poverty: Subsidizing Programs Subsidizing programs are considered welfare and net initiatives that the government takes to aid low-income families and individuals affected by poverty.
- The Problem of Poverty in Chad Thus, the study of the causes of poverty in the Republic of Chad will help to form a complete understanding of the problem under study and find the most effective ways to solve it.
- “Poverty, Toxic Stress, and Education…” Study by Kelly & Li Kelly and Li are concerned with the lack of research about poverty and toxic stress affecting the neurodevelopment of preterm children.
- Poverty in “A Modest Proposal” by Swift The high number of children born to poor families presents significant problems for a country.”A Modest Proposal” is a satirical essay by Jonathan Swift that proposes a solution to the challenge facing the kingdom.
- Life Below the Poverty Line in the US The major problem with poverty in the US is that the number of people living below the poverty threshold is gradually increasing despite the economic growth of the country. SNAP is not considered to be […]
- The Relationship Between Single-Parent Households and Poverty The given literature review will primarily focus on the theoretical and empirical aspects of the relationship between single-parent households and poverty, as well as the implications of the latter on mental health issues, such as […]
- Aspects of Social Work and Poverty In terms of work principle, both the poor working and the welfare poor have it to varying degrees, but it does not help them much because the only employment available is low paying and leads […]
- Poverty and Its Effect on Adult Health Poverty in the UK is currently above the world average, as more than 18% of the population lives in poverty. In 2020, 7% of the UK population lived in extreme poverty and 11% lived in […]
- Child Poverty in the United States The causes of child poverty in the United States cannot be separated from the grounds of adult poverty. Thus, it is essential to take care of the well-being of children living in poverty.
- Poverty in New York City, and Its Reasons The poverty rate for seniors in New York is twice the poverty rate in the United States. New York City’s blacks and Hispanics have a much higher poverty rate than whites and Asians in the […]
- “The Hidden Reason for Poverty…” by Haugen It is also noteworthy that some groups of people are specifically vulnerable and join the arrays of those living in poverty.
- Juvenile Violent Crime and Children Below Poverty The effect of this trend is that the number of children below poverty will continue to be subjected to the juvenile and criminal justice systems.
- Poverty and Homelessness as Social Problem The qualifications will include a recommendation from the community to ensure that the person is open to help and willing to be involved in the neighborhood of Non-Return.
- Discussion of the Problem of the Poverty To help prevent homelessness for the woman in question and her children, I think it would be essential to provide mental support for her not to turn to alcohol and drugs as a coping mechanism.
- Poverty Effects and How They Are Handled Quality jobs will provide income to the younger people and women in the community. The focus on developing and facilitating small and medium-sized enterprises is a great strategy but more needs to be done in […]
- Feminization of Poverty and Governments’ Role in Solving the Problem However, women form the greatest percentage of the poor, and the problem continues to spread. Furthermore, the public supports available are inaccessible and inadequate to cater for women’s needs.
- Free-Trade Policies and Poverty Level in Bangladesh The purpose of this paper is to examine the way in which the end of the quota system and introduction of a free-trade system for the garment industry in Bangladesh has impacted on poverty in […]
- Poverty and Risks Associated With Poverty Adolescents that are at risk of being malnourished can be consulted about the existing programs that provide free food and meals to families in poverty.
- Poverty and Inequality Reduction Strategies Thus, comprehending the causes of poverty and inequalities, understanding the role of globalization, and learning various theoretical arguments can lead to the establishment of appropriate policy recommendations.
- International Aid – Poverty Inc This film, the research on the impact of aid on the states receiving it, and the economic outcomes of such actions suggest that aid is a part of the problem and not a solution to […]
- Poverty Effects on American Children and Adolescents The extent to which poor financial status influences the wellbeing of the young children and adolescents is alarming and needs immediate response from the community.
- Progress and Poverty Book by Henry George George wrote the book following his recognition that poverty is the central puzzle of the 20th century. Thus, George’s allegation is inconsistent with nature because the number of living organisms can increase to the extent […]
- Vicious Circle of Poverty in Brazil The vicious circle of poverty is “a circular constellation of forces that tend to act and react on each other in such a way that the country in poverty maintains its poor state”.
- Global Education as the Key Tool for Addressing the Third World Poverty Issue Global education leads to improvements in the state economy and finances. Global education helps resolve the unemployment problem.
- Poverty, Partner Abuse, and Women’s Mental Health In general, the study aimed at investigating the interaction between poverty and the severity of abuse in women. The research question being studied in this article is how income intersects with partner violence and impacts […]
- America’s Shame: How Can Education Eradicate Poverty The primary focus of the article was global poverty, the flaws in the educational system, as well as the U.S.government’s role in resolving the problem.
- Global Poverty and Ways to Overcome It These are some of the strategies, the subsequent application of which would significantly reduce the level of poverty around the world.
- Poverty and Sex Trafficking: Qualitative Systematic Review The proposed research question is to learn how the phenomenon of poverty is connected to sex trafficking. To investigate the relationship between the phenomenon of poverty and sex trafficking.
- Political Economy: Relationship Between Poverty, Inequality, and Nationalism The prevalence of nationalism leads to changes in the education system, as the government tries to justify the superiority of the country by altering the curriculum.
- End of Extreme Poverty Importantly, the ability to remain the owners of a substantial amount of accumulated wealth is the primary motivation for such individuals.
- Poverty and Inequality in the US Despite the progress of civilization and the establishment of democratic values, in the modern United States, such problems as poverty and inequality persist, which is a significant social gap.
- The Problem of Poverty in the United States The problem of increasing poverty is one of the major political issues in the United States, which became especially agile after the appearance of the COVID-19 pandemic due to the difficult economic situation all over […]
- Poverty and Unemployment Due to Increased Taxation The government on its side defended the move while trying to justify the new measures’ benefits, a move that would still not benefit the country.
- Poverty as a Global Social Problem For example, the research shows that Kibera is the largest slum in the country, and this is where many people move to settle after losing hope of getting employed in towns.
- Researching the Problem of Poverty However, the rich people and the rich countries reduce poverty to some extent by providing jobs and markets to the poor, but the help is too little compared to the benefits they get thus accelerating […]
- Poverty, Social Class, and Intersectionality I prefer the structural approach to the issue as I believe the created structures are responsible for the existence of diverse types of oppression.
- Wealth and Poverty: The Christian Teaching on Wealth and Poverty To illustrate the gap between the world’s richest and the world’s poorest, a recent UN publication reported that the wealth of the three richest persons in the world is greater than the combined wealth of […]
- Guns Do Not Kill, Poverty Does It is widely accepted that stricter gun control policies are instrumental in alleviating the problem, as they are supposed to reduce the rate of firearm-related deaths, limiting gun access to individuals at-risk of participating in […]
- Poverty’s Effects on Delinquency The economic status of people determines their social class and the manner in which they get their basic needs. Seeing these things and the kind of life rich people lead motivates the poor to commit […]
- The Criminalization of Poverty in Canada In this regard, with a special focus on Canada, the objective of this essay is to investigate how public policy has transformed alongside the public perception of social welfare reform.
- The Issue of Vicious Circle of Poverty in Brazil The persistence of poverty, regardless of the many shocks that every state receives in the normal course of its survival, raises the feeling that underdevelopment is a condition of equilibrium and that there are pressures […]
- Community Health Needs: Poverty Generally, the higher the level of poverty, the worse the diet, and hence the higher the chances of developing diabetes. Consequently, a considerable disparity in the prevalence of diabetes occurs between communities with high levels […]
- “Poverty, Race, and the Contexts of Achievement” by Maryah Stella Fram et al. The article “Poverty, race, and the contexts of achievement: examining the educational experience of children in the U.S. Multilevel models were then applied in the analyses of how children varied in their reading scores depending […]
- Couple Aims to Fight Poverty, One Village at a Time People are not afraid to risk their own financial savings, their investments, and even life’s safety to help the chosen community and improve the conditions this community has to live under.
- Microeconomic Perspective on Poverty Evolution in Pakistan The periodic spike in poverty levels, notwithstanding economic growth, implies incongruous policy functionality in relation to drivers of poverty and the subsequent failure to improve the indicators.
- The Impact of Poverty on Children Under the Age of 11 The strengths of the Marxist views on poverty are in the structural approach to the problem. Overall, the Marxist theory offers a radical solution to the problem of child poverty.
- Poverty Policy Recommendations Different leaders have considered several policies and initiatives in the past to tackle the problem of poverty and empower more people to lead better lives.
- Poverty Reduction and Natural Assets Therefore, the most efficient way to increase the efficiency of agriculture and reduce its environmental impacts is ensuring the overall economic growth in the relevant region.
- Corporate Social Responsibility & Poverty Alleviation Researchers state that “preventing and managing the negative impacts of the core business on the poor” are essential indicators of the social responsibility of the company.
- Children in Poverty in Kampong Ayer, Brunei Part of the reason is likely malnutrition that results from the eating or consumption patterns of the families and also dependency on the children to help out with the family or house chores.
- Health, Poverty, and Social Equity: Indigenous Peoples of Canada Another problem that much of northern Canada’s Indigenous Peoples face is the availability of healthcare services and people’s inability to access medical help.
- The Problem of Childhood Poverty Unequal income distribution, adult poverty, government policies that exclude children and premature pregnancy are some of the items from the long list of childhood poverty causes. Before discussing the causes and effects of childhood poverty, […]
- Individualistic Concepts and Structural Views on Poverty in American Society The concepts presented in the book Poverty and power help to better understand the content of the article and the reasons for such a different attitude of people to the same problem.
- Poor Kids: The Impact of Poverty on Youth Nevertheless, the environment of constant limitations shapes the minds of children, their dreams and the paths they pursue in life, and, most importantly, what they make of themselves.
- Poverty: Causes and Effects on the Population and Country Thesis: There are a great number of factors and issues that lead a certain part of the population to live in poverty and the input that such great numbers of people could provide, would be […]
- The Internet and Poverty in Society The information that can be found on the web is a very useful resource but at the same time it is important to consider several things with the treatment and examination of the presented information.
- Poverty in Africa: Impact of the Economy Growth Rate Thus, a conclusion can be made that economic growth in Africa will result in the social stability of the local population.
- Poverty and Disrespect in “Coming of Age in Mississippi” by Anne Moody Life was not fair to a little Anne the chapters about her childhood are alike to a chain of unfortunate events that happened to her and her relatives.
- Vietnam’s Economic Growth and Poverty & Inequality A significant part of the population was active in employment, and this means that the numerous income-generating activities improved the economy of this country.
- Poverty and Disasters in the United States Focusing on the precaution measures and the drilling techniques that will help survive in case of a natural disaster is one of the most common tools for securing the population.
- Intro to Sociology: Poverty It is challenging to pinpoint the actual and not mythological reasons for the presence of poverty in America. The former can be summed up as a “culture of poverty”, which suggests that the poor see […]
- The Notion of “Poverty” Is a Key Word of a Modern Society As far as the countries of the Third World are deprived of these possibilities, their development is hampered and the problem of poverty has become a chronic disease of the society.
- The Problem of Poverty in Africa The major aim of the study is to identify the causes of poverty and propose best strategies that can help Africans come out of poverty.
- Poverty Sustainability in Sub-Saharan Countries: The Role of NGOs The position of research and statistics in undertaking social-counting work is not queried. It is after the research method is used in other tribulations of the charity that gaps emerge between management and research.
- The Effects of Poverty Within Criminal Justice The approach used in this study is deductive since the reasoning in the study proceeds from the general principle regarding the fact that poverty has a role to play in the administering of fairness in […]
- The Poverty Rates in the USA Poverty in the U. Officially the rate of poverty was at14.3%.
- Poverty in America: A Paradox Many people especially the young people living in other countries and more so in developed countries wish to immigrate to America instead of working hard to achieve the dream of better opportunities.
- Values and Ethics: Poverty in Canada The case study1 has indicated for instance, that the number of people living in poverty in 2003 is at 4. A group of individuals would therefore be granted the mandate to lead the others in […]
- War and Poverty Connection in Developing Countries The scholars claim that conflict and war in most nations have been found to exacerbate the rate of poverty in the affected nations.
- Poverty in United States. Facts and Causes Schwartz carried out a research which showed that in the United States, about 13-17|% of the individuals live below the federal poverty line at any one single time and poverty is one of the main […]
- Cultures and Prejudice: Poverty Factors For instance, if the two cultures had in the past interacted in a negative way, the poor culture directs all the blame to the well up culture.
- Poverty and Criminal Behavoiur Relation The level of accuracy that the data collected holds cannot be 100%; there is a level of error that affects the reliability of the data collected.
- Urban Relationship Between Poverty and Crime The areas with high poverty level in the US urban areas have the highest cases of crime but this is inadequate to justify that poverty is the cause of crime.
- The End of Poverty Possibility He presents the difficulty as in inability of each poor country to get to the base rung of the ranking of economic progress if the rank is achieved; a country can drag itself up towards […]
- Poverty, Suburban Public School Violence and Solution
- Social and Economic Policy Program: Globalization, Growth, and Poverty
- Is Poverty From Developing Countries Imagined?
- How Gender and Race Structure Poverty and Inequality Connected?
- Poverty by Anarchism and Marxism Approaches
- Colonial Economy of America: Poverty, Slavery and Rich Plantations
- Poverty as a Great Social Problem and Its Causes
- Environmental Deterioration and Poverty in Kenya
- Management Issues: The Poverty Business
- Marginalization and Poverty of Rural Women
- Pockets of Poverty Mar the Great Promise of Canada
- Poverty. “How the Other Half Lives” by Jacob Riis
- The Underclass Poverty and Associated Social Problems
- Child Poverty in Toronto, Ontario
- Children’s Brain Function Affected by Poverty
- Poverty Issue in America Review
- Microeconomics. Poverty in America
- Poverty and Inequality in Modern World
- Poverty and Its Effects on Females
- Poverty and Its Effects on Women
- Poverty of America: Economic Assumptions
- Poverty as a General Problem
- Feminization of Poverty – A Grave Social Concern
- Global Poverty Dimensions and Alleviating Approaches
- Poverty Level in any Country
- Theories of Fertility. Economics Aspect and Poverty.
- The Cultural Construction of Poverty
- Poverty in the US: Causes and Measures
- Poverty Rates Issue in Alberta Analysis
- “Old Age Poverty” Study by Kwan & Walsh
- Phenomena of Poverty Review
- Development Economics: Poverty Traps in Africa
- Healthcare Development. Poverty in the 1800s
- Social Problem of Poverty in the United States
- Poverty and Hip-Hop: Notorious B.I.G.’s “Juicy”
- Globalization Issues and Impact on Poverty and Free Trade
- Anthropology: Culture of Poverty
- Poverty, Stratification and Gender Discrimination
- Teen Pregnancy Can Lead to Suicide and Poverty
- Poverty Around the World
- Poverty in Los Angeles
- “Rethinking the Sociological Measurement of Poverty” by Brady
- Poverty in the US: Essentials of Sociology
- Econometrics: Poverty, Unemployment, Household Income
- Religious Quotes on Poverty and Their Interpretations
- Poverty and Inequality in “Rich and Poor” by Peter Singer
- The Relation Between Poverty and Justice
- Canada and the Imposition of Poverty
- Poverty and Politics in “The Bottom Billion” by Collier
- The Impact of Poverty in African American Communities
- “Poverty and Joy: The Franciscan Tradition” by Short
- International Financial Institutions’ Poverty Reduction Strategy
- Social Study: Mamelodi Residents Living in Poverty
- Video Volunteers’ Interventions Against Poverty
- Poverty in American Single-Parent Families
- Single-Mother Poverty and Policies in the United States
- Poverty and Its Aspects in Historical Documents
- Poverty and Its Relative Definitions
- Poverty in America: An Ethical Dilemma
- Child Poverty and Academic Achievement Association
- Poverty as a Factor of Terrorist Recruitment
- Poverty Solution as a Political Issue in Australia
- Poverty: An Echo of Capitalism
- Poverty, Inequality and Social Policy Understanding
- Breastfeeding Impact on Canadian Poverty Gaps
- Urban and Suburban Poverty in the United States
- Inequality and Poverty Relationship
- Poverty and Child Health in the US and the UK
- Poverty Impact on Life Perception
- Energy Poverty Elimination in Developing Countries
- Why Nations Fail: The Origins of Power, Prosperity and Poverty
- Vietnamese Poverty and Productivity Increase
- Global Health Governance and Poverty
- Poverty Rates Among Whites and Blacks Americans
- Culture of Poverty in the “Park Avenue” Documentary
- Poverty in the US
- Poor Economics and Global Poverty
- Poverty as a Cause of the Sudanese Civil War
- “Halving Global Poverty” by Besley and Burges
- Do Poverty Traps Exist? Assessing the Evidence
- Poverty Reasons in Ancient Times and Nowadays
- American War on Poverty Throughout US History
- Poverty and Challenges in Finding Solutions
- Children and Poverty in “Born into Brothels” Documentary
- Poverty and Social Welfare in the United States
- Poverty in “A Theology of Liberation” by Gutierrez
- Poverty Reduction Among American Single Mothers
- The Relationship Between Poverty and Education
- Divorce Outcomes: Poverty and Instability
- African Poverty at the Millennium: Causes and Challenges
- Poverty Effect on Children
- Poverty and Education: School Funding Reinforces Inequality
- Global Poverty and the Endeavors of Addressing It
- Global Poverty Reduction: Economic Policy Recommendation
- Global Conflict and Poverty Crisis
- Poverty in the Novel “Snow” by Orhan Pamuk
- The Rise of Poverty in the US
- Profit From Organizing Tours to Poverty Areas
- Detroit Poverty and “Focus Hope” Organization
- Poverty Controversy in the USA
- Poverty as the Deprivation of Capabilities
- Suburbanisation of Poverty in the USA
- The Solution to World Poverty by Peter Singer
- The Poverty Across the US Culture
- How Racial Segregation Contributes to Minority’s Poverty?
- Catholic Dealing With Poverty and Homelessness
- Human Capital and Poverty in Scottsdale
- Global Poverty Studies and Their Importance
- The World Bank and the Poverty of Reform
- Challenges of Social Integration: Poverty
- Globalization and the Issue of Poverty: Making the World a Better Place
- The Economic Effect of Issuing Food Stamps to Those in Poverty
- Business and Pollution Inequality in Poor States
- “Facing Poverty With a Rich Girl’s Habits” by Suki Kim
- What Should You Do? Poverty Issue
- Causes of Poverty Traps in an Economy, Its Results and Ways of Avoiding Them
- Millennium Development Goals – Energy and Poverty Solutions
- Sociological Indicators of Energy Poverty
- Energy and Poverty Solutions – Non-Traditional Cookstoves
- Energy and Poverty Solutions – World Bank
- How do Migration and Urbanization Bring About Urban Poverty in Developing Countries?
- Poverty and Domestic Violence
- The Rise of Extremist Groups, Disparity and Poverty
- Measuring Poverty and Social Exclusion in Australia
- Does Poverty Lead to Terrorism?
- “Urban and Rural Estimates of Poverty: Recent Advances in Spatial Microsimulation in Australia” by Tanton, R, Harding, A, and McNamara, J
- Importance of Foreign Aid in Poverty Reducing
- Hispanic Childhood Poverty in the United States
- How Poverty Affects Children Development?
- Why Is Poverty Important in Contemporary Security Studies?
- Millennium Development Goals in Kenya, Ivory Coast, Haiti, and Chad
- Development Is No Longer the Solution to Poverty
- Issues Underlying Global Poverty and Provision of Aid
- Films Comparison: “The Fields” by Roland Joffe and “Hotel Rwanda” by Terry George
- Poverty Prevalence in the United States
- Terrorism, Poverty and Financial Instability
- Global Poverty and Education
- Critical Analyses of the Climate of Fear Report From Southern Poverty Law Center
- How World Vision International Contributes to Poverty Reduction
- Global Poverty, Social Poverty and Education
- Global Poverty, Social Policy, and Education
- Poverty Reduction in Africa, Central America and Asia
- Does Parental Involvement and Poverty Affect Children’s Education and Their Overall Performance?
- African Poverty: To Aid, or Not to Aid
- Poverty Fighting in Saudi Arabia and in USA
- Technological Development in Trade and Its Impacts on Poverty
- Poverty and Development Into the 21st Century
- Social Dynamics: The Southern Poverty Law Centre
- Property, Urban Poverty and Spatial Marginalization
- Rural Poverty in Indonesia
- Is Poverty of Poor Countries in Anyway Due to Wealth of the Rich?
- Poverty and Gender Violence in Congo
- Correlation Between Poverty and Obesity
- Fight Poverty, Fight Illiteracy in Mississippi Initiative
- Civil War and Poverty: “The Bottom Billion” by Paul Collier
- Analytical Research: Poverty in Thailand: Peculiarities and Perspectives
- Poverty Indicators in Developing Countries
- Poverty, Homelessness and Discrimination in Australia: The Case of the Aboriginal
- Social Business Scope in Alleviating Poverty
- Africa’s Poverty: The Influence of Western States
- Susceptibility of Women and Aboriginal People to Poverty in Canada
- MDG Poverty Goals May Be Achieved, but Child Mortality Is Not Improving
- Microcredit: A Tool for Poverty Alleviation
- Impacts of Global Poverty Resistance
- Reducing Poverty: Unilever and Oxfam
- Poverty in the United States
- The Mothers Who Are Not Single: Striving to Avoid Poverty in Single-Parent Families
- Effect of Poverty on Children Cognitive and Learning Ability
- Sweatshops and Third World Poverty
- War on Poverty: Poverty Problem in US
- Freedom from Poverty as a Human Right and the UN Declaration of Human Rights
- War on Poverty in US
- The Causes of Poverty Concentration in the Modern World
- Poverty in Saudi Arabia
- Poverty as a Peculiarity of the Economical Development
- Capitalism and Poverty
- The Problems of Poverty in the Modern World
- Poverty Among Women and Aboriginals
- On (Not) Getting by in America: Economic Order and Poverty in the U.S.
- The Singer Solution to World Poverty
- Poverty and Inequality in Jacksonian America
- Poverty in America Rural and Urban Difference (Education)
- What Is the Relationship Between Race, Poverty and Prison?
- Poverty and Its Effects on Childhood Education
- Poverty in Russia During the Late Nineteenth Century
- Banker to the Poor: Micro-Lending and the Battle Against World Poverty: Advantages of Microcredit
- Social Welfare Policy That Facilitates Reduction of Poverty and Inequality in the US
- Immigrant Status and Poverty: How Are They Linked?
- Effects of Poverty on Immigrant Children
- Poverty in Brazil
- The Problem of Immigrants Poverty in the US
- Why Poverty Rates are Higher Among Single Black Mothers
- Poverty and Its Impact on Global Health: Research Methodologies
- Poverty Concerns in Today’s Society
- Literature Study on the Modern Poverty Concerns
- Poverty and Wealth in “The Lesson” by Toni Cade Bambara
- Peter Singer on Resolving the World Poverty
- Aspects of Global Poverty
- Concepts of Prenatal Drug Exposure vs. Poverty on Infants
- UN Summit in New York: Ending Global Poverty
- Why Has Poverty Increased in Zimbabwe?
- Should Private Donations Help Eliminate Child Poverty?
- Why Was Poverty Re-Discovered in Britain in the Late 1950s and Early 1960?
- Why Does Child Labour Persist With Declining Poverty?
- Why Are Child Poverty Rates Higher in Britain Than in Germany?
- What Are the Principles and Practices for Measuring Child Poverty in Rich Countries?
- Why Did Poverty Drop for the Elderly?
- What Is the Relationship Between Income Distribution and Poverty Reduction in the UK?
- What Are the Pros and Cons of Poverty in Latin America?
- Should Poverty Researchers Worry About Inequality?
- What Helps Households With Children in Leaving Poverty?
- What Is the Connection Between Poverty and Crime?
- Why Have Some Indian States Done Better Than Others at Reducing Rural Poverty?
- What Is the Relationship Between Lack of Education and Poverty?
- Why Are Child Poverty Rates So Persistently High in Spain?
- Trade Liberalisation and Poverty: What Are the Links?
- What Are Academic Programs Available for Youth in Poverty?
- What Are the Main Factors Contributing to the Rise in Poverty in Canada?
- Single-Mother Poverty: How Much Do Educational Differences in Single Motherhood Matter?
- What Are the Causes and Effects of Poverty in the United?
- Why Are Some Countries Poor?
- What Is the Link Between Globalization and Poverty?
- What Are the Factors That Influence Poverty Sociology?
- What Causes Poverty Within the United States Economy?
- What Is the Relationship Between Poverty and Obesity?
- Why Were Poverty Rates So High in the 1980s?
- With Exhaustible Resources, Can a Developing Country Escape From the Poverty Trap?
- Why Does Poverty Persist in Rural Ethiopia?
- Who Became Poor, Who Escaped Poverty, and Why?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/poverty-essay-examples/
"390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/poverty-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/poverty-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/poverty-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "390 Poverty Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/poverty-essay-examples/.
- Social Norms Essay Ideas
- Drug Abuse Research Topics
- Juvenile Delinquency Essay Titles
- Segregation Research Topics
- Alcohol Abuse Paper Topics
- Challenges Essay Topics
- Community Service Questions
- Discrimination Essay Titles
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Why Submit?
- About Public Opinion Quarterly
- About the American Association for Public Opinion Research
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Anti-semitic attitudes of the mass public: estimates and explanations based on a survey of the moscow oblast.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
JAMES L. GIBSON, RAYMOND M. DUCH, ANTI-SEMITIC ATTITUDES OF THE MASS PUBLIC: ESTIMATES AND EXPLANATIONS BASED ON A SURVEY OF THE MOSCOW OBLAST, Public Opinion Quarterly , Volume 56, Issue 1, SPRING 1992, Pages 1–28, https://doi.org/10.1086/269293
- Permissions Icon Permissions
In this article we examine anti-Semitism as expressed by a sample of residents of the Moscow Oblast (Soviet Union). Based on a survey conducted in 1920, we begin by describing anti-Jewish prejudice and support for official discrimination against Jews. We discover a surprisingly low level of expressed anti-Semitism among these Soviet respondents and virtually no support for state policies that discriminate against Jews. At the same time, many of the conventional hypotheses predicting anti-Semitism are supported in the Soviet case. Anti-Semitism is concentrated among those with lower levels of education, those whose personal financial condition is deteriorating, and those who oppose further democratization of the Soviet Union. We do not take these findings as evidence that anti-Semitism is a trivial problem in the Soviet Union but, rather, suggest that efforts to combat anti-Jewish movements would likely receive considerable support from ordinary Soviet people.
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1537-5331
- Copyright © 2024 American Association for Public Opinion Research
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Served by the Norwegian Meteorological Institute and NRK
Elektrostal
Current conditions, weather forecast for the next 10 days, thursday 16 may, friday 17 may, saturday 18 may, sunday 19 may, monday 20 may, tuesday 21 may, wednesday 22 may, thursday 23 may, friday 24 may, saturday 25 may.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Education is the best way out of poverty in part because it is strongly linked to economic growth. A 2021 study co-published by Stanford University and Munich's Ludwig Maximilian University shows us that, between 1960 and 2000, 75% of the growth in gross domestic product around the world was linked to increased math and science skills.
Description of Poverty and the Role of Education. Poverty can best be described as a family of four or more whose average yearly. income falls below the federal poverty level of $22,050. In order for families to make. ends meet research shows that approximately twice the income of the federal poverty. level is needed.
Time and again, research has proven the incredible power of education to break poverty cycles and economically empower individuals from the most marginalized communities with dignified work and upward social mobility. Research at UNESCO has shown that world poverty would be more than halved if all adults completed secondary school. And if all ...
These goals represent a common vision for dramatically reducing poverty by 2015 and provide clear objectives for significant improvement in the quality of people's lives. Learning and education ...
The impact of poverty on education is often exacerbated by systemic barriers that limit access to quality education for low-income students. For example, schools in low-income areas are often under-resourced, leading to overcrowded classrooms, outdated materials, and fewer opportunities for extracurricular activities. ...
LP = [LD x (1-SD)] + [1 x SD] LP = Learning poverty. LD = Learning deprivation, defined as share of children at the end of primary who read at below the minimum proficiency level, as defined by the Global Alliance to Monitor Learning (GAML) in the context of the SDG 4.1.1 monitoring. SD = Schooling deprivation, defined as the share of primary ...
More than 5 million children in the United States live in deep poverty, including nearly 1 in 5 Black children under the age of 5. These numbers will no doubt grow, given the explosion of the health and economic crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Now, more than ever, school systems need a more robust, reliable, and valid measure of students experiencing deep poverty in order to align ...
PPT1. 1. Poverty among children is much higher among the Bangladeshi, Pakistani, Black and Chinese ethnic groups than it is among the Indian or. White ethnic groups, and has increased since the ...
The NSGRP target was to reduce unemployment from 12.9 per cent in 2000/01 to 6.9 per cent by 2010; hence the unemployment rate of 11 per cent in 2006 was disheartening. One can easily notice that ...
Education and Poverty: Confronting the Evidence . Helen F. Ladd . Working Papers Series . SAN11-01. November 4, 2011 . Abstract . Current U.S. policy initiatives to improve the U.S. education system, including No Child Left Behind, test-based evaluation of teachers and the promotion of competition, are
Here, the interplay between education and poverty isn't a straightforward path but rather a. Essay Example: In the intricate fabric of societal challenges, the convergence of education and poverty unfolds a narrative both nuanced and profound, sculpting destinies with its myriad intricacies. Here, the interplay between education and poverty isn ...
Evidence suggests that many of the effects of poverty on children are influenced by families' behavior. Low-income families often have limited education, reducing their ability to provide a responsive stimulating environment for their children. 30 They tend to limit their children's linguistic environment by using language that is dominated by commands and simple structure, rather than by ...
The reasons for focusing on the number of poor people are: (1) there is a strong relationship between the number of poor people and a low level of education [21]; (2) both poverty and a low level ...
Related Papers. Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary Journal . ... In the Philippines, poverty remains one of the significant problems that affect the quality of education. Poverty has an enormous impact on students' academic performance, engagement, and motivation, leading to negative outcomes. According to data from the Philippine ...
An analysis of achievement gaps in every school in America shows that poverty is the biggest hurdle. Rich schools get richer: School spending analysis finds widening gap between top 1% and the rest of us. This story about education inequality in America written by Jill Barshay and produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news ...
500+ Words Essay on Poverty Essay. "Poverty is the worst form of violence". - Mahatma Gandhi. We can define poverty as the condition where the basic needs of a family, like food, shelter, clothing, and education are not fulfilled. It can lead to other problems like poor literacy, unemployment, malnutrition, etc.
This page of the essay has 1,443 words. Download the full version above. Poverty has become an important factor in whether or not they are successful in their studies. As our economy grows, education is having an impact on salaries earned. Poverty is often referred to as having low wages. As indicated by Amartya Sen in Inequality Reexamined ...
English Essay Writing Topic - Impact of Poverty on Education. It is terrible that education systems all over the world are being held to captivity due to poverty, both at the governmental and family levels, despite the fact that education is claimed to be so important for human progress and the revitalization of global economies.
Essay on How Does Poverty Affect Education. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Our country is in dire need of a wake-up call to the sheer number of children falling victim to poverty and how their futures are consequently affected by ...
Poverty in "A Modest Proposal" by Swift. The high number of children born to poor families presents significant problems for a country."A Modest Proposal" is a satirical essay by Jonathan Swift that proposes a solution to the challenge facing the kingdom. Life Below the Poverty Line in the US.
Navbar Search Filter ... Mobile Microsite Search Term Search
0 mm. 3 m/s. Open hourly forecast. Updated 08:28. How often is the weather forecast updated? Forecast as PDF Forecast as SVG. Weather forecast for Elektrostal for the next 10 days.
Elektrostal. Elektrostal ( Russian: Электроста́ль) is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It is 58 kilometers (36 mi) east of Moscow. As of 2010, 155,196 people lived there.
What links here; Upload file; Special pages; Printable version; Page information