
Solving Problems that Include Fractions and Decimals
Introduction.
There are four important operations that you will encounter when solving problems in mathematics. The figures below indicate some of the actions in a problem that lead to different operations.
Addition and subtraction are related operations. Addition typically means to combine two or more numbers, and subtraction involves the difference , or removal, of one number from another.
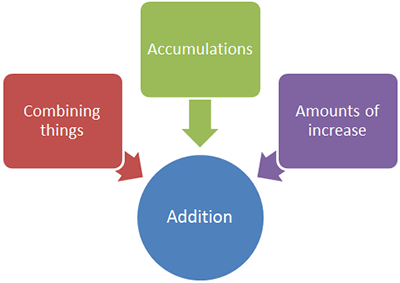
Multiplication and division are also related operations. Both operations involve grouping and rates.
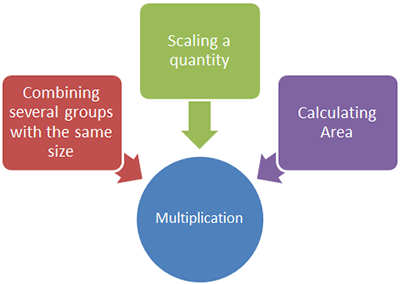
You have explored how to tell when to use which operation. Now, you will focus on identifying the operation from a word problem, and then use procedures to actually perform the operation and determine a solution to the problem.
Working with Signed Numbers
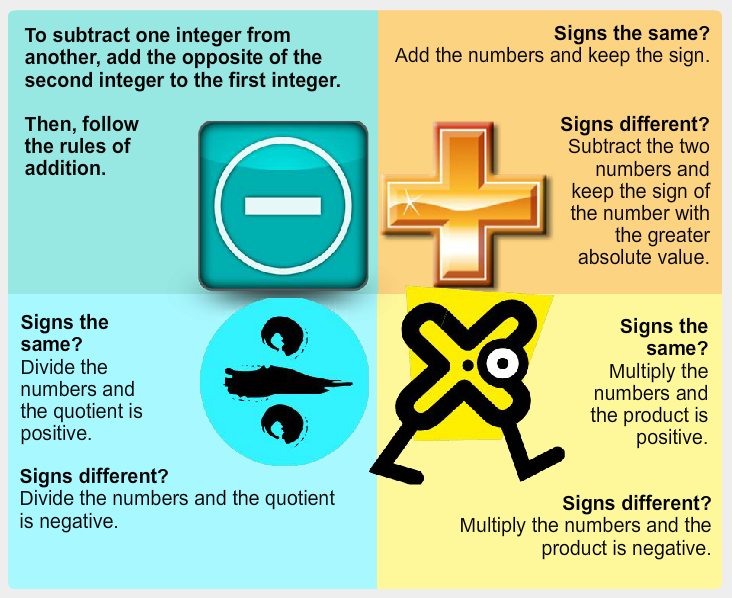
Signed numbers include integers and other rational numbers that have either a positive or a negative sign.

Source: Badwater Elevation Sign, Complex01 and Elevation Benchmark, Jeff Kramer, Wikimedia Commons
Use the diagram below to review standard procedures for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing integers.
Adding and Subtracting Decimals
You have applied the rules of integers to solve word problems. Now, you will review ways to add and subtract decimals, and then use what you learn to solve problems relating to addition and subtraction of positive and negative decimals.
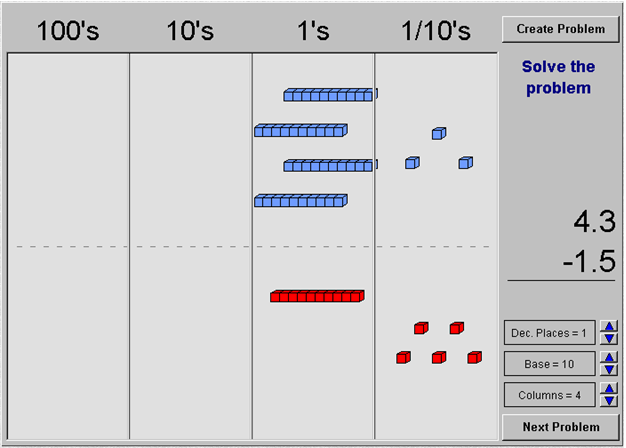
Click on the image below to open a base-ten model interactive in a new web browser tab or window. The interactive represents the two addends in an addition problem, or the minuend and subtrahend in a subtraction problem. Use the manipulative to work through at least 3 problems.
- Click on a block and drag it on top of its opposite block to remove zero pairs.
- Click on a block and drag it to the next column to regroup.
- Click “Next Problem” to move to the next problem when you are ready.
Need additional help for addition?
Need additional help for subtraction?
Use what you noticed in the interactive to answer the following questions.
In the original problem, 4.3 – 1.5, when you dragged a ones rod into the tenths column, it split into 10 tenths. How does that relate to the regrouping that was recorded symbolically in the image shown below?
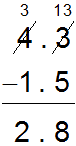
In an addition problem, such as 6.4 + 4.8, when you regroup 10 tenths into 1 one and drag the ones rod into the ones place, how did that action appear in the regrouping that was recorded symbolically such as the regrouping shown in the image below?
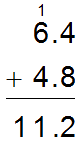
Pause and Reflect
1. Why is it important to line up the decimal point when adding or subtracting decimal numbers?
2. When regrouping 1 one and 3 tenths into 13 tenths, why do you cross out the original 3 in the tenths place and replace it with 13?
Adding and Subtracting Fractions
You have used models and algorithms to add and subtract decimals, paying special attention to the regrouping that was necessary to perform the computations. Now, you will extend the idea of regrouping to models and procedures used to add and subtract fractions, including mixed numbers.
Consider the following problem.

The example below shows how Marley used fraction strips to solve this problem.
Click the image below to view additional examples, including a video with a worked-out example for you to follow.
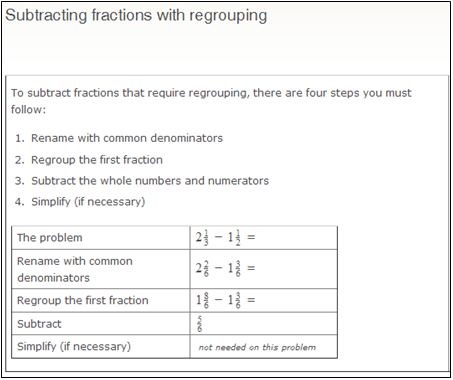
1. How is regrouping when subtracting mixed numbers similar to regrouping when subtracting decimals?
2. When adding decimals, you regroup when the sum of the two digits in a place value that is greater than 10. When would you need to regroup as you add mixed numbers?
Multiplying and Dividing Decimals
Now that you’ve investigated addition and subtraction with decimals and fractions, let’s take a closer look at multiplication and division. You will start in this section with decimals, and then use a similar model to multiply and divide fractions and mixed numbers in the next section.

- Write an expression that you can use to determine the amount of oil that Rachel started with.
- How would you represent 2.2 and 2.5 as improper fractions with denominators of 10?
The interactive below uses blocks to multiply decimals. When the blocks are combined, they will form a rectangle; the area of the rectangle is the product of the two decimals or the answer to Rachel’s problem.

- In the first activity, the first decimal is the length of the rectangle, and the second decimal is the width. Represent each decimal by dragging the appropriate blocks and moving them to the area for each decimal.
- In the second activity, use the information from the decimals and drag the blocks to the open area to create a rectangle. You will use the green blocks to fill in the missing pieces of the rectangle.
- Is the answer the same as what we found earlier in Anu's solution?
- Adjust the numerators to create and represent two more multiplication problems. Record those problems on a piece of paper.
Based on what you saw in the interactive, why do you think that the product has the same number of digits to the right of the decimal as the total number of digits to the right of the decimal in the two factors ?
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
In this section, you will look at models to represent multiplying and dividing fractions.
Multiplying Fractions

Use the interactive below to represent the problem and graphically illustrate the product. Use the Numerator and Denominator sliders to create each fraction or mixed number. You may also need to use the Zoom in/out sliders to see the entire model.
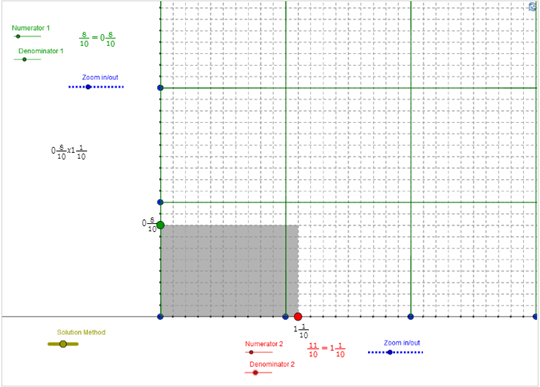
Need additional directions?
Use the interactive to answer the following questions:
- What are the dimensions of the shaded rectangle in the solution? Check Your Answer
- The solid lines represent the boundaries of a rectangle with an area of 1 square unit. The dashed lines represent the boundaries of a number of equal-sized regions within this area. What fraction of 1 does each smaller rectangle represent? Check Your Answer
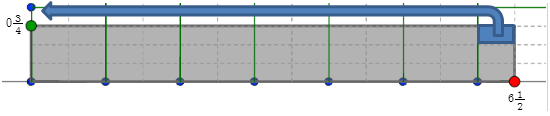
- What mixed number does this rearranged figure represent? How does this compare with the product of 3 4 and 6 1 2 ? Check Your Answer
Dividing Fractions
To solve this problem, Barbara used a fraction strip generator, which gave her the following diagram.
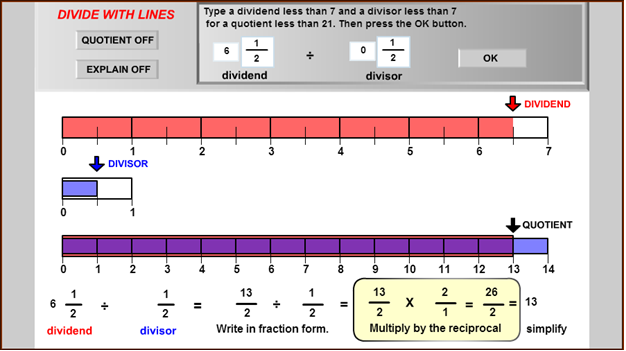
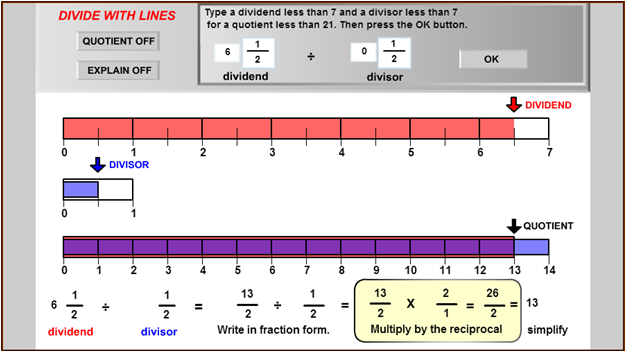
- Barbara knew this was a division problem, not a multiplication problem. How did she know that? Check Your Answer
- Use the diagram to explain why the quotient of 6 1 2 ÷ 1 2 is 13. Check Your Answer
Use the same fraction strip generator that Barbara used to solve the problem below.

Click the image below to open the fraction strip generator in a new web browser tab or window. Enter the key information from the problem, including the dividend and the divisor , and then use the results to answer the questions that follow.
In the fraction diagrams, both 5 3 4 and 3 8 are marked off into eighths. Why do you think that is the case? Check Your Answer
To divide 5 3 4 by 3 8 , the number sentence beneath the diagrams shows multiplication of 5 3 4 by 8 3 , which is the reciprocal of 3 8 . Multiplying by 8 3 is the same as multiplying by 8 , and then dividing by 3 . Why do you need to multiply 5 3 4 by 8 , which is the numerator of the reciprocal? Check Your Answer
The next step in the number sentence divides the product of 5 3 4 and 8 by 3 (multiplies 5 3 4 by the fraction 8 3 ) . Why do you need to divide by 3 at this point? Check Your Answer
See the completed fraction diagram for Patrice's ornament problem.
Completed fraction diagram
1. How does the multiplication algorithm connect to the area model that you used in the first interactive?
2. How does the division algorithm connect to the fraction strip model that you used in the interactive?
You studied models that represent operations on rational numbers (fractions and decimals). You also connected those models to the standard algorithms for performing the operations.
The graphic below summarizes procedures to add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals.
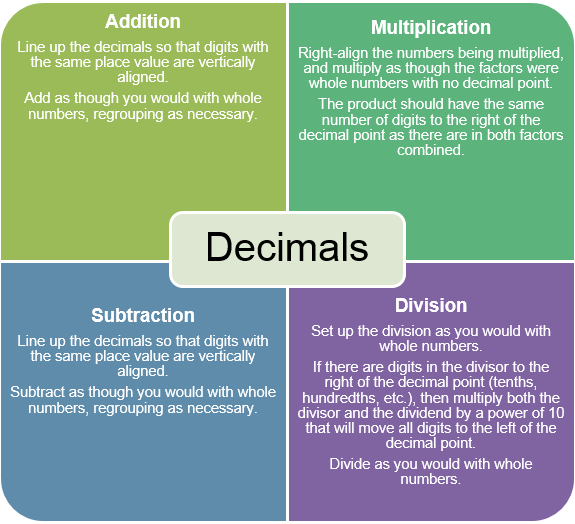
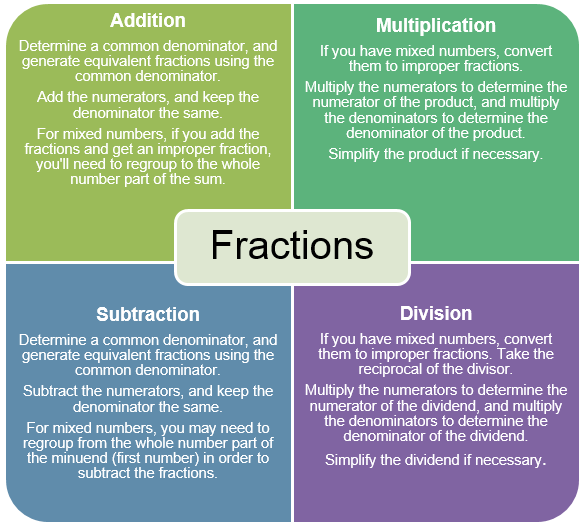
The graphic below summarizes procedures to add, subtract, multiply, or divide fractions, including mixed numbers.
Copy and paste the link code above.
Related Items
Decimal Fraction Worksheets
Addition :: Subtraction :: Multiplication :: Division :: Conversion
The following worksheets all use "Decimal Fractions", in other words tenths, hundredths, etc. This makes them a little easier to work with.
But remember to simplify your answer (example: 50 100 becomes 1 2 ).
Decimal Fractions - Addition
Decimal fractions - subtraction, decimal fractions - multiplication, decimal fractions - division, conversion to fractions.
We think you are located in South Africa . Is this correct?
- Yes, I reside in South Africa
- Change country/curriculum
We use this information to present the correct curriculum and to personalise content to better meet the needs of our users.
Open Textbooks
Download our open textbooks in different formats to use them in the way that suits you. Click on each book cover to see the available files to download, in English and Afrikaans. Better than just free, these books are also openly-licensed (except Information Technology and Computer Applications Technology)! Refer to the different open licences for each download and the explanations of the licenses at the bottom of the page.

- Read online
- 7A PDF (CC-BY-ND)
- 7B PDF (CC-BY-ND)

- 8A PDF (CC-BY-ND)
- 8B PDF (CC-BY-ND)

- 9A PDF (CC-BY-ND)
- 9B PDF (CC-BY-ND)

- PDF (CC-BY-ND)
- ePUB (CC-BY-ND)
- ePUB (CC-BY)

Information Technology

- ePUB (Closed copyright)
- Data files (Closed copyright)

Computer Applications Technology

Our book licensing
Better than just free, these books (except Information Technology and Computer Applications Technology) are also openly-licensed! The same content, but different versions (branded or not) have different licenses, as explained:
CC-BY-ND (branded versions)
You are allowed and encouraged to freely copy these versions. You can photocopy, print and distribute them as often as you like. You can download them onto your mobile phone, iPad, PC or flash drive. You can burn them to CD, email them around or upload them to your website. The only restriction is that you cannot adapt or change these versions of the textbooks, their content or covers in any way as they contain the relevant Siyavula brands, the sponsorship logos and are endorsed by the Department of Basic Education. For more information, visit Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported .
Find out more here about the sponsorships and partnerships with others that made the production of each of the open textbooks possible.
CC-BY (unbranded versions)
These unbranded versions of the same content are available for you to share, adapt, transform, modify or build upon in any way, with the only requirement being to give appropriate credit to Siyavula. For more information, visit Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported .
Information Technology and Computer Applications Technology
These books have been provided by MTN and are under a closed copyright license.

Decimal Fraction – Definition, Examples, Practice Problems
Definition of decimal fractions, examples of decimal fractions, solved examples on decimal fraction, practice problems on decimal fraction, frequently asked questions on decimal fraction.
The prerequisite for understanding decimal fractions is the understanding of normal fractions. You must know that a fraction comprises a numerator (top part) and a denominator (bottom part). The correct way of writing a fraction is –
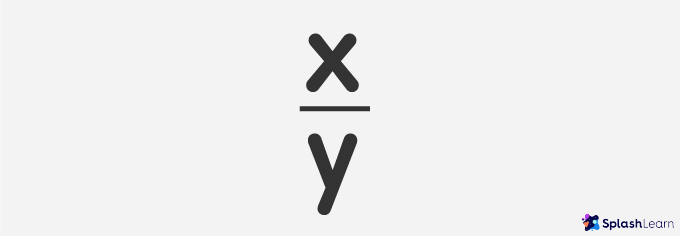
X is the numerator in this example, and y is the denominator. Decimal fractions are the fractions in which the denominator (y in the image) must be 10 or a multiple of 10 like 100, 1000, 10000, and so on. The numerator can be any integer (between -infinity and +infinity). These decimal fractions are usually expressed in decimal numbers (numbers with a decimal point).
In algebra , a decimal fraction is a number having 10 or the powers of 10 like 10¹, 10², 10³, and so on in the denominator.

- 7/10000 is a decimal fraction written in the decimal form as 0.0007.
- 19/10 is a decimal fraction written in the decimal form as 1.9.
- 39/1000 is a decimal fraction written as 0.039.
Non Examples of Decimal Fractions
Other fractions with non-ten numbers in the denominator are not decimal fractions. They are:
Reading Decimal Fractions
Let us consider a scenario where 1 is in the numerator. We will consider different denominators to understand how these terms are read with this numerator.
- 1/10 is read as one-tenth.
- 1/100 is read as one-hundredth.
- 1/1000 is read as one-thousandth.
When the value of the numerator is more than one, we add an ‘s’ to the name. So, for instance, 3/10 is read as three-tenths.
History of Decimal Fractions
The Chinese first developed and used decimal fractions at the end of the 4th century BC, which spread to the Middle East before reaching Europe.
Conversion to Decimal Fractions
1. Conversion from fractions to decimal fractions :
- Let us consider an example of a fraction, 3/2.
- The first step would be to consider the number that gives 10 or a multiple of 10 when multiplied by the denominator. In this case, 5 multiplied by 2 gives 10.
- Now multiply the numerator and denominator with the same number to get your decimal fraction. Here, 3 x 5/ 2 x 5 gives 15/10.
- Thus, the decimal fraction of 3/2 is 15/10.
2. Conversion from mixed numbers to decimal fractions :
- Convert the mixed fraction into a normal fraction.
- Follow the steps for converting fractions to decimal fractions.
3. Conversion from decimal numbers to decimal fractions :
- Write the original decimal number in the numerator and denominator form by placing 1 in the denominator: 4.3/1.
- For every space that you move the decimal point, add a zero next to the 1 in the denominator: 43/10 (As we can see one shift of decimal space, one 0 must be added to the denominator).
4.3/1
43.0/10
- Once the number in the numerator is non-decimal, you have got your decimal fraction: 4.3 = 43/10.
Real-Life Application of Decimal Fractions
Decimal fractions are used for understanding precise quantities instead of whole numbers. You will also use them for expressing percentages. For instance, 97% can be written as 97/100 for ease of calculation.
Here are some scenarios where you might encounter decimal fractions:
- Coins (They are a fraction of Rupees)
- Weighing products
- Measuring ingredients while cooking
Related Worksheets

Convert 2 ½ into a decimal fraction.
= 2 ½
= 5 x 5 / 2 x 5
Convert 5.4 into a decimal fraction.
Convert 8 ⅕ into a decimal fraction.
= 8 ⅕
= 41 x 2 / 5 x 2
Conclusion Decimal fractions encourage students to learn about precise quantities. This will help them understand weights like 3.2 kg and distances like 7.85 km. The first step towards a better understanding of decimal numbers is practicing decimal fraction problems every day. The idea of taking a pen and paper to solve sums is dull and uninteresting for students. They need entertaining ways to entice them towards practicing the sums.
SplashLearn makes the process of practicing decimal numbers fun and interactive for kids. With dozens of decimal fraction games, your child will never fall short of options to practice math. Instead, learning becomes engaging with interesting games that allure your kids towards solving sums.
Let’s do it!
Instead of teaching decimal fractions and handing out practice worksheets to your children, ask them to find and make decimal fractions of the decimals or fractions you say.
Decimal Fraction
Attend this Quiz & Test your knowledge.
Convert 6.34 into a decimal fraction.
Convert 4 ½ into a decimal fraction., convert 8/5 into a decimal fraction., convert 5/4 into a decimal fraction..
What is a decimal fraction example?
A decimal fraction is a fraction with a power of 10 (10^1, 10^2, etc.) in the denominator. These numbers are written in decimal form for the convenience of solving mathematical sums. For example, 4/1000 is a decimal fraction, written in decimals as 0.004.
How do you write a decimal fraction?
A decimal fraction is written as any number in the numerator with 10 and multiples of 10 in the denominator.
What is a decimal fraction in the simplest form?
The simplest form of a decimal fraction is the basic in-divisible fraction obtained by dividing the numerator by the denominator. For example, the simplest form of the decimal fraction 4/10 is 2/5.
Can all percentages be expressed as decimal fractions? Give an example.
Yes. All percentages can be expressed as decimal fractions. For instance, 80% is written as 80/100 in the decimal fraction form. This can be further divided to get the simplest form 4/5 of the decimal form.
Where are decimal fractions used?
Decimal fractions are used for expressing the weight of people and products. It can also be used to determine discounts on the price of products and measure the ingredients of a recipe.
RELATED POSTS
- Decompose Fractions
- Cube Numbers – Definition, Examples, Facts, Practice Problems
- What Is a Constant? Definition, Solved Examples, Facts
- Concurrent Lines – Definition, Formula, Examples, FAQs
- Order Of Operations – Definition, Steps, FAQs, Examples

Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Make study-time fun with 14,000+ games & activities, 450+ lesson plans, and more—free forever.
Parents, Try for Free Teachers, Use for Free

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
- The Number System and Place Value
- Calculations and Numerical Methods
- Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion
- Properties of Numbers
- Patterns, Sequences and Structure
- Algebraic expressions, equations and formulae
- Coordinates, Functions and Graphs
Geometry and measure
- Angles, Polygons, and Geometrical Proof
- 3D Geometry, Shape and Space
- Measuring and calculating with units
- Transformations and constructions
- Pythagoras and Trigonometry
- Vectors and Matrices
Probability and statistics
- Handling, Processing and Representing Data
- Probability
Working mathematically
- Thinking mathematically
- Mathematical mindsets
- Cross-curricular contexts
- Physical and digital manipulatives
For younger learners
- Early Years Foundation Stage
Advanced mathematics
- Decision Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Advanced Probability and Statistics
Published 2013 Revised 2019

Exploring Fractions
- The first group gives you some starting points to explore with your class, which are applicable to a wide range of ages. The tasks in this first group will build on children's current understanding of fractions and will help them get to grips with the concept of the part-whole relationship.
- The second group of tasks focuses on the progression of ideas associated with fractions, through a problem-solving lens. So, the tasks in this second group are curriculum-linked but crucially also offer opportunities for learners to develop their problem-solving and reasoning skills.
- are applicable to a range of ages;
- provide contexts in which to explore the part-whole relationship in depth;
- offer opportunities to develop conceptual understanding through talk.
- Math Article
- Decimals Word Problems
Word Problems on Decimal Fractions
A fraction represents a part of whole.
For example, it tells how many slices of a pizza left or eaten with respect to the whole pizza like, one-half, three-quarters.
Generally, a fraction has two parts i.e. the numerator and the denominator. A decimal fraction is a fraction where its denominator is a power of 10 i.e. 101,102, 103 etc.
For example 32/10,56/100,325/1000. It can be expressed as a decimal like 32/10=3.2,56/100=0.56.
We can perform all arithmetic operations on fractions by expressing them as a decimal. Let’s practice some word problems on decimal fractions by using various arithmetical operations.
Example 1: A barrel has 56.32 liters capacity. If Supriya used 21.19 liters how much water is left in the barrel.
Solution: Given,
Capacity of the barrel = 56.32 liters
Amount of water used= 21.19 liters
Amount of water left in the barrel = 56.32 – 21.19 = 35.13 liters
Example 2: Megha bought 12 bags of wheat flour each weighing 4563/100 kg. What will be the total weight?
Solution: Total no. of bags = 12
Weight of each bag = 4563/100 kg = 45.63 kg
Total weight =45.63 x 12=547.56 kg
Example 3: If circumference of a circle is 16.09 cm. What will be its diameter(π=3.14)?
Solution: Given, circumference = 16.09 cm
Circumference of a circle, C=2πr
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow 16.09 = 2 \pi r\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow 16.09 = 2 \times 3.14 \times r\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow r = \frac{16.09 \times 100}{6.28 \times 100}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow r = 2.56 \end{array} \) cm
Therefore Diameter = 2r = 2 x 2.56 = 5.12 cm.
Example 4: If the product of 38.46 and another number is 658.17, what is the other number?
One number = 38.46
Product of two numbers = 658.17
The other number = 658.17÷38.46
= \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{658.17}{100}\div \frac{38.46}{100}\end{array} \)
Example 5: Rakesh bought a new. He went on a road trip of 165.9 km on bike. After a week he went for another trip of 102.04 km. What will be the reading on meter reader of the bike?

Distance travelled on first trip = 165.9 km
Distance travelled on second trip = 102.04km
Total distance travelled = 165.9 + 102.04 = 267.94 km
To solve more problems on the topic, download Byju’s – The Learning App from Google Play Store and watch interactive videos. Also, take free tests to practice for exams. To study about other topics, visit www.byjus.com and browse among thousands of interesting articles.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Practice Questions
Click here for questions, click here for answers, gcse revision cards.

5-a-day Workbooks

Primary Study Cards

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Corbettmaths © 2012 – 2024
[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Fraction word prob.
Fraction word problems
Here you will learn about fraction word problems, including solving math word problems within a real-world context involving adding fractions, subtracting fractions, multiplying fractions, and dividing fractions.
Students will first learn about fraction word problems as part of number and operations—fractions in 4 th grade.
What are fraction word problems?
Fraction word problems are math word problems involving fractions that require students to use problem-solving skills within the context of a real-world situation.
To solve a fraction word problem, you must understand the context of the word problem, what the unknown information is, and what operation is needed to solve it. Fraction word problems may require addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division of fractions.
After determining what operation is needed to solve the problem, you can apply the rules of adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing fractions to find the solution.
For example,
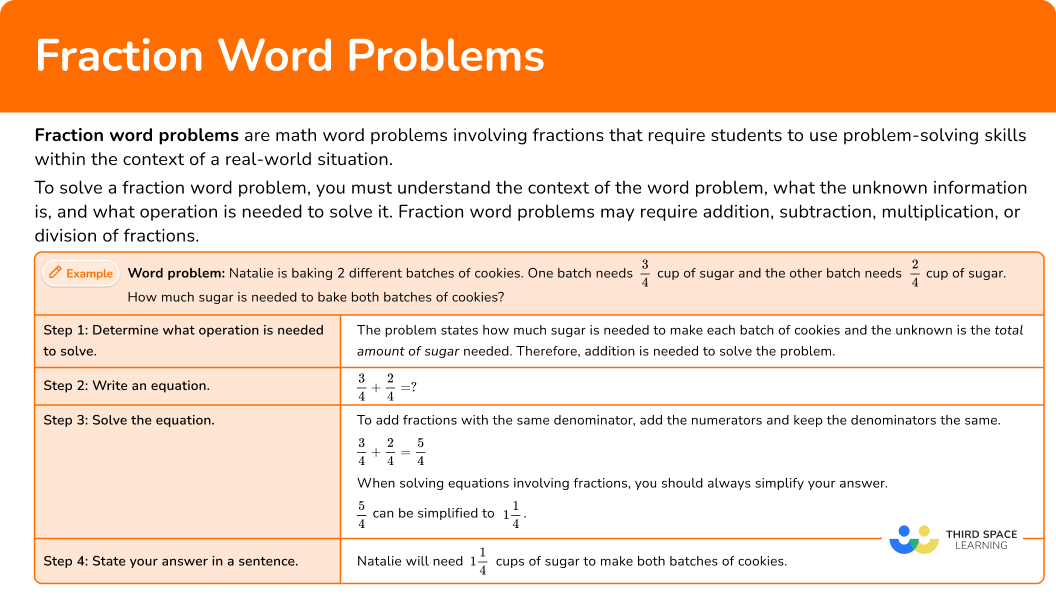
Natalie is baking 2 different batches of cookies. One batch needs \cfrac{3}{4} cup of sugar and the other batch needs \cfrac{2}{4} cup of sugar. How much sugar is needed to bake both batches of cookies?
You can follow these steps to solve the problem:
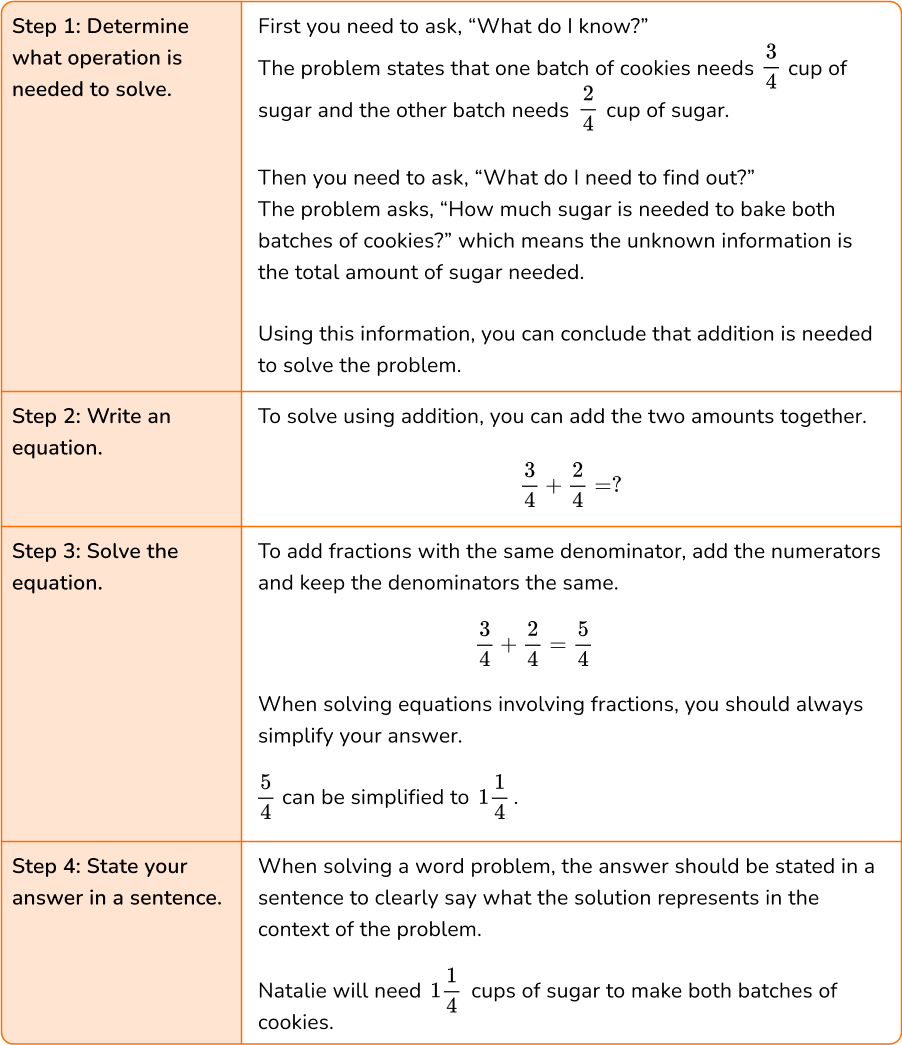
Step-by-step guide: Adding and subtracting fractions
Step-by-step guide: Adding fractions
Step-by-step guide: Subtracting fractions
Step-by-step guide: Multiplying and dividing fractions
Step-by-step guide: Multiplying fractions
Step-by-step guide: Dividing fractions
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 4 th grade math to 6 th grade math?
- Grade 4: Number and Operations—Fractions (4.NF.B.3d) Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions referring to the same whole and having like denominators, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem.
- Grade 4: Number and Operations—Fractions (4.NF.B.4c) Solve word problems involving multiplication of a fraction by a whole number, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, if each person at a party will eat \cfrac{3}{8} of a pound of roast beef, and there will be 5 people at the party, how many pounds of roast beef will be needed? Between what two whole numbers does your answer lie?
- Grade 5: Number and Operations—Fractions (5.NF.A.2) Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions referring to the same whole, including cases of unlike denominators, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. Use benchmark fractions and number sense of fractions to estimate mentally and assess the reasonableness of answers. For example, recognize an incorrect result \cfrac{2}{5}+\cfrac{1}{2}=\cfrac{3}{7} by observing that \cfrac{3}{7}<\cfrac{1}{2} .
- Grade 5: Number and Operations—Fractions (5.NF.B.6) Solve real world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem.
- Grade 5: Number and Operations—Fractions (5.NF.B.7c) Solve real world problems involving division of unit fractions by non-zero whole numbers and division of whole numbers by unit fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, how much chocolate will each person get if 3 people share \cfrac{1}{2} \: lb of chocolate equally? How many \cfrac{1}{3} cup servings are in 2 cups of raisins?
- Grade 6: The Number System (6.NS.A.1) Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, create a story context for \cfrac{2}{3} \div \cfrac{4}{5} and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient; use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that \cfrac{2}{3} \div \cfrac{4}{5}=\cfrac{8}{9} because \cfrac{3}{4} of \cfrac{8}{9} is \cfrac{2}{3}. (In general, \cfrac{a}{b} \div \cfrac{c}{d}=\cfrac{a d}{b c} \, ) How much chocolate will each person get if 3 people share \cfrac{1}{2} \: lb of chocolate equally? How many \cfrac{3}{4} cup servings are in \cfrac{2}{3} of a cup of yogurt? How wide is a rectangular strip of land with length \cfrac{3}{4} \: m and area \cfrac{1}{2} \: m^2?
![decimal fractions problem solving [FREE] Fraction Operations Worksheet (Grade 4 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Fraction-operations-check-for-understandin-quiz-listing-image-.png)
[FREE] Fraction Operations Worksheet (Grade 4 to 6)
Use this quiz to check your grade 4 to 6 students’ understanding of fraction operations. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 4th to 6th grade fraction operations topics to identify areas of strength and support!
How to solve fraction word problems
In order to solve fraction word problems:
Determine what operation is needed to solve.
Write an equation.
Solve the equation.
State your answer in a sentence.
Fraction word problem examples
Example 1: adding fractions (like denominators).
Julia ate \cfrac{3}{8} of a pizza and her brother ate \cfrac{2}{8} of the same pizza. How much of the pizza did they eat altogether?
The problem states how much pizza Julia ate and how much her brother ate. You need to find how much pizza Julia and her brother ate altogether , which means you need to add.
2 Write an equation.
3 Solve the equation.
To add fractions with like denominators, add the numerators and keep the denominators the same.
4 State your answer in a sentence.
The last step is to go back to the word problem and write a sentence to clearly say what the solution represents in the context of the problem.
Julia and her brother ate \cfrac{5}{8} of the pizza altogether.
Example 2: adding fractions (unlike denominators)
Tim ran \cfrac{5}{6} of a mile in the morning and \cfrac{1}{3} of a mile in the afternoon. How far did Tim run in total?
The problem states how far Tim ran in the morning and how far he ran in the afternoon. You need to find how far Tim ran in total , which means you need to add.
To add fractions with unlike denominators, first find a common denominator and then change the fractions accordingly before adding.
\cfrac{5}{6}+\cfrac{1}{3}= \, ?
The least common multiple of 6 and 3 is 6, so 6 can be the common denominator.
That means \cfrac{1}{3} will need to be changed so that its denominator is 6. To do this, multiply the numerator and the denominator by 2.
\cfrac{1 \times 2}{3 \times 2}=\cfrac{2}{6}
Now you can add the fractions and simplify the answer.
\cfrac{5}{6}+\cfrac{2}{6}=\cfrac{7}{6}=1 \cfrac{1}{6}
Tim ran a total of 1 \cfrac{1}{6} miles.
Example 3: subtracting fractions (like denominators)
Pia walked \cfrac{4}{7} of a mile to the park and \cfrac{3}{7} of a mile back home. How much farther did she walk to the park than back home?
The problem states how far Pia walked to the park and how far she walked home. Since you need to find the difference ( how much farther ) between the two distances, you need to subtract.
To subtract fractions with like denominators, subtract the numerators and keep the denominators the same.
\cfrac{4}{7}-\cfrac{3}{7}=\cfrac{1}{7}
Pia walked \cfrac{1}{7} of a mile farther to the park than back home.
Example 4: subtracting fractions (unlike denominators)
Henry bought \cfrac{7}{8} pound of beef from the grocery store. He used \cfrac{1}{3} of a pound of beef to make a hamburger. How much of the beef does he have left?
The problem states how much beef Henry started with and how much he used. Since you need to find how much he has left , you need to subtract.
To subtract fractions with unlike denominators, first find a common denominator and then change the fractions accordingly before subtracting.
\cfrac{7}{8}-\cfrac{1}{3}= \, ?
The least common multiple of 8 and 3 is 24, so 24 can be the common denominator.
That means both fractions will need to be changed so that their denominator is 24.
To do this, multiply the numerator and the denominator of each fraction by the same number so that it results in a denominator of 24. This will give you an equivalent fraction for each fraction in the problem.
\begin{aligned}&\cfrac{7 \times 3}{8 \times 3}=\cfrac{21}{24} \\\\ &\cfrac{1 \times 8}{3 \times 8}=\cfrac{8}{24} \end{aligned}
Now you can subtract the fractions.
\cfrac{21}{24}-\cfrac{8}{24}=\cfrac{13}{24}
Henry has \cfrac{13}{24} of a pound of beef left.
Example 5: multiplying fractions
Andre has \cfrac{3}{4} of a candy bar left. He gives \cfrac{1}{2} of the remaining bit of the candy bar to his sister. What fraction of the whole candy bar does Andre have left now?
It could be challenging to determine the operation needed for this problem; many students may automatically assume it is subtraction since you need to find how much of the candy bar is left.
However, since you know Andre started with a fraction of the candy bar and you need to find a fraction OF a fraction, you need to multiply.
The difference here is that Andre did NOT give his sister \cfrac{1}{2} of the candy bar, but he gave her \cfrac{1}{2} of \cfrac{3}{4} of a candy bar.
To solve the word problem, you can ask, “What is \cfrac{1}{2} of \cfrac{3}{4}? ” and set up the equation accordingly. Think of the multiplication sign as meaning “of.”
\cfrac{1}{2} \times \cfrac{3}{4}= \, ?
To multiply fractions, multiply the numerators and multiply the denominators.
\cfrac{1}{2} \times \cfrac{3}{4}=\cfrac{3}{8}
Andre gave \cfrac{1}{2} of \cfrac{3}{4} of a candy bar to his sister, which means he has \cfrac{1}{2} of \cfrac{3}{4} left. Therefore, Andre has \cfrac{3}{8} of the whole candy bar left.
Example 6: dividing fractions
Nia has \cfrac{7}{8} cup of trail mix. How many \cfrac{1}{4} cup servings can she make?
The problem states the total amount of trail mix Nia has and asks how many servings can be made from it.
To solve, you need to divide the total amount of trail mix (which is \cfrac{7}{8} cup) by the amount in each serving ( \cfrac{1}{4} cup) to find out how many servings she can make.
To divide fractions, multiply the dividend by the reciprocal of the divisor.
\begin{aligned}& \cfrac{7}{8} \div \cfrac{1}{4}= \, ? \\\\ & \downarrow \downarrow \downarrow \\\\ &\cfrac{7}{8} \times \cfrac{4}{1}=\cfrac{28}{8} \end{aligned}
You can simplify \cfrac{28}{8} to \cfrac{7}{2} and then 3 \cfrac{1}{2}.
Nia can make 3 \cfrac{1}{2} cup servings.
Teaching tips for fraction word problems
- Encourage students to look for key words to help determine the operation needed to solve the problem. For example, subtracting fractions word problems might ask students to find “how much is left” or “how much more” one fraction is than another.
- Provide students with an answer key to word problem worksheets to allow them to obtain immediate feedback on their solutions. Encourage students to attempt the problems independently first, then check their answers against the key to identify any mistakes and learn from them. This helps reinforce problem-solving skills and confidence.
- Be sure to incorporate real-world situations into your math lessons. Doing so allows students to better understand the relevance of fractions in everyday life.
- As students progress and build a strong foundational understanding of one-step fraction word problems, provide them with multi-step word problems that involve more than one operation to solve.
- Take note that students will not divide a fraction by a fraction as shown above until 6 th grade (middle school), but they will divide a unit fraction by a whole number and a whole number by a fraction in 5 th grade (elementary school), where the same mathematical rules apply to solving.
- There are many alternatives you can use in place of printable math worksheets to make practicing fraction word problems more engaging. Some examples are online math games and digital workbooks.
Easy mistakes to make
- Misinterpreting the problem Misreading or misunderstanding the word problem can lead to solving for the wrong quantity or using the wrong operation.
- Not finding common denominators When adding or subtracting fractions with unlike denominators, students may forget to find a common denominator, leading to an incorrect answer.
- Forgetting to simplify Unless a problem specifically says not to simplify, fractional answers should always be written in simplest form.
Related fractions operations lessons
- Fractions operations
- Multiplicative inverse
- Reciprocal math
- Fractions as divisions
Practice fraction word problem questions
1. Malia spent \cfrac{5}{6} of an hour studying for a math test. Then she spent \cfrac{1}{3} of an hour reading. How much longer did she spend studying for her math test than reading?
Malia spent \cfrac{1}{2} of an hour longer studying for her math test than reading.

Malia spent \cfrac{5}{18} of an hour longer studying for her math test than reading.

Malia spent \cfrac{1}{2} of an hour longer reading than studying for her math test.
Malia spent 1 \cfrac{1}{6} of an hour longer studying for her math test than reading.
To find the difference between the amount of time Malia spent studying for her math test than reading, you need to subtract. Since the fractions have unlike denominators, you need to find a common denominator first.
You can use 6 as the common denominator, so \cfrac{1}{3} becomes \cfrac{3}{6}. Then you can subtract.
\cfrac{3}{6} can then be simplified to \cfrac{1}{2}.
Finally, you need to choose the answer that correctly answers the question within the context of the situation. Therefore, the correct answer is “Malia spent \cfrac{1}{2} of an hour longer studying for her math test than reading.”
2. A square garden is \cfrac{3}{4} of a meter wide and \cfrac{8}{9} of a meter long. What is its area?
The area of the garden is 1\cfrac{23}{36} square meters.
The area of the garden is \cfrac{27}{32} square meters.
The area of the garden is \cfrac{2}{3} square meters.
The perimeter of the garden is \cfrac{2}{3} meters.
To find the area of a square, you multiply the length and width. So to solve, you multiply the fractional lengths by mulitplying the numerators and multiplying the denominators.
\cfrac{24}{36} can be simplified to \cfrac{2}{3}.
Therefore, the correct answer is “The area of the garden is \cfrac{2}{3} square meters.”
3. Zoe ate \cfrac{3}{8} of a small cake. Liam ate \cfrac{1}{8} of the same cake. How much more of the cake did Zoe eat than Liam?
Zoe ate \cfrac{3}{64} more of the cake than Liam.
Zoe ate \cfrac{1}{4} more of the cake than Liam.
Zoe ate \cfrac{1}{8} more of the cake than Liam.
Liam ate \cfrac{1}{4} more of the cake than Zoe.
To find how much more cake Zoe ate than Liam, you subtract. Since the fractions have the same denominator, you subtract the numerators and keep the denominator the same.
\cfrac{2}{8} can be simplified to \cfrac{1}{4}.
Therefore, the correct answer is “Zoe ate \cfrac{1}{4} more of the cake than Liam.”
4. Lila poured \cfrac{11}{12} cup of pineapple and \cfrac{2}{3} cup of mango juice in a bottle. How many cups of juice did she pour into the bottle altogether?
Lila poured 1 \cfrac{7}{12} cups of juice in the bottle altogether.
Lila poured \cfrac{1}{4} cups of juice in the bottle altogether.
Lila poured \cfrac{11}{18} cups of juice in the bottle altogether.
Lila poured 1 \cfrac{3}{8} cups of juice in the bottle altogether.
To find the total amount of juice that Lila poured into the bottle, you need to add. Since the fractions have unlike denominators, you need to find a common denominator first.
You can use 12 as the common denominator, so \cfrac{2}{3} becomes \cfrac{8}{12}. Then you can add.
\cfrac{19}{12} can be simplified to 1 \cfrac{7}{12}.
Therefore, the correct answer is “Lila poured 1 \cfrac{7}{12} cups of juice in the bottle altogether.”
5. Killian used \cfrac{9}{10} of a gallon of paint to paint his living room and \cfrac{7}{10} of a gallon to paint his bedroom. How much paint did Killian use in all?
Killian used \cfrac{2}{10} gallons of paint in all.
Killian used \cfrac{1}{5} gallons of paint in all.
Killian used \cfrac{63}{100} gallons of paint in all.
Killian used 1 \cfrac{3}{5} gallons of paint in all.
To find the total amount of paint Killian used, you add the amount he used for the living room and the amount he used for the kitchen. Since the fractions have the same denominator, you add the numerators and keep the denominators the same.
\cfrac{16}{10} can be simplified to 1 \cfrac{6}{10} and then further simplified to 1 \cfrac{3}{5}.
Therefore, the correct answer is “Killian used 1 \cfrac{3}{5} gallons of paint in all.”
6. Evan pours \cfrac{4}{5} of a liter of orange juice evenly among some cups.
He put \cfrac{1}{10} of a liter into each cup. How many cups did Evan fill?
Evan filled \cfrac{2}{25} cups.
Evan filled 8 cups.
Evan filled \cfrac{9}{10} cups.
Evan filled 7 cups.
To find the number of cups Evan filled, you need to divide the total amount of orange juice by the amount being poured into each cup. To divide fractions, you mulitply the first fraction (the dividend) by the reciprocal of the second fraction (the divisor).
\cfrac{40}{5} can be simplifed to 8.
Therefore, the correct answer is “Evan filled 8 cups.”
Fraction word problems FAQs
Fraction word problems are math word problems involving fractions that require students to use problem-solving skills within the context of a real-world situation. Fraction word problems may involve addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division of fractions.
To solve fraction word problems, first you need to determine the operation. Then you can write an equation and solve the equation based on the arithmetic rules for that operation.
Fraction word problems and decimal word problems are similar because they both involve solving math problems within real-world contexts. Both types of problems require understanding the problem, determining the operation needed to solve it (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division), and solving it based on the arithmetic rules for that operation.
The next lessons are
Still stuck.
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs .
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
Privacy Overview

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1: Whole Numbers, Fractions, Decimals, Percents and Problem Solving
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 45726
- 1.1: Introduction to Decimal Calculations
- 1.2: Place Value in Decimals
- 1.3: Adding and Subtracting Decimals
- 1.4: Multiplying and Dividing Decimals
- 1.5: Convert Between Decimals and Fractions
- 1.6: Introduction to Percent Calculations
- 1.7: Solving Problems Using Ratios
- 1.8: Writing Fractions and Decimals as Percents
- 1.9: Solving Problems Using Percents
- 1.10: Percent Increase and Decrease
- 1.11: Why It Matters- Whole Numbers, Fractions, Decimals, Percents, and Problem Solving
- 1.12: Putting It Together- Whole Numbers, Fractions, Decimals, Percents, and Problem Solving
- 1.13: Assignment- Whole Numbers, Fractions, Decimals, Percents, and Problem Solving
- 1.14: Introduction to Whole Number Calculations
- 1.15: Place Value in Whole Numbers
- 1.16: Rounding Whole Numbers
- 1.17: Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, and Dividing Whole Numbers
- 1.18: Introduction to Fraction Calculations
- 1.19: Convert Between Types of Fractions
- 1.20: Adding and Subtracting Fractions
- 1.21: Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Course: 7th grade > Unit 2
- Rewriting decimals as fractions: 2.75
Rewriting decimals as fractions challenge
- Worked example: Converting a fraction (7/8) to a decimal
- Fraction to decimal: 11/25
- Fraction to decimal with rounding
- Converting fractions to decimals
- Comparing rational numbers
- Order rational numbers
- Your answer should be
- a proper fraction, like 1 / 2 or 6 / 10

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Fraction to decimal with rounding . Video 2 minutes 17 seconds 2:17. Worked example: Converting a fraction (7/8) to a decimal . Video 1 minute 33 seconds 1:33. Fraction to decimal: 11/25 . Video 9 minutes 22 seconds 9:22. Rewriting tricky fractions to decimals . Report a problem.
The graphic below summarizes procedures to add, subtract, multiply, or divide fractions, including mixed numbers. Given problem situations, the student will use addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to solve problems involving positive and negative fractions and decimals.
The following worksheets all use "Decimal Fractions", in other words tenths, hundredths, etc. This makes them a little easier to work with. But remember to simplify your answer (example: 50100 becomes 12). Decimal Fractions - Addition. Worksheet. Example. Tenths, Single Digits. 310 + 810. Units and Tenths. 1 310 + 2 810.
Decimal fractions questions are offered here to help students comprehend the concept and achieve high results on their final exams. As each question comes with a detailed explanation, students can use these questions to improve their grades. We have also offered practice problems for pupils to help them develop their problem-solving skills.
The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on Decimals and Fractions. Previous: Decimal and Percentages Practice Questions
Fractions, Decimals and Percentages - Short Problems. This is part of our collection of Short Problems. You may also be interested in our longer problems on Fractions, Decimals and Percentages. Printable worksheets containing selections of these problems are available here.
You will see decimal numbers in calculations with different measurements. For example, when calculating the perimeter or area of a shape, the side measurements could be given in decimal notation. The side of this regular heptagon is \ (\text {9,1} \text { mm}\). To find its perimeter, you need to add all the sides or multiply the \ (\text {9,1 ...
Doughnut Percents. Age 7 to 14. Challenge Level. A task involving the equivalence between fractions, percentages and decimals which depends on members of the group noticing the needs of others and responding.
Example 1: If 58 out of 100 students in a school are boys, then write a decimal for the part of the school that consists of boys. Analysis: We can write a fraction and a decimal for the part of the school that consists of boys. fraction decimal 0.58 Answer: 0.58 Example 2: A computer processes information in nanoseconds. A nanosecond is one billionth of a second.
Decimal fractions are the fractions in which the denominator (y in the image) must be 10 or a multiple of 10 like 100, 1000, 10000, and so on. The numerator can be any integer (between -infinity and +infinity). These decimal fractions are usually expressed in decimal numbers (numbers with a decimal point). In algebra, a decimal fraction is a ...
Exploring Fractions. Introduction. At NRICH, our aim is to offer rich tasks which develop deep understanding of mathematical concepts. Of course, by their very nature, rich tasks will also provide opportunities for children to work like a mathematician and so help them develop their problem-solving skills alongside this conceptual understanding.
It can be expressed as a decimal like 32/10=3.2,56/100=0.56. We can perform all arithmetic operations on fractions by expressing them as a decimal. Let's practice some word problems on decimal fractions by using various arithmetical operations. Example 1: A barrel has 56.32 liters capacity. If Supriya used 21.19 liters how much water is left ...
Click here for Answers. equivalent. Practice Questions. Previous: Percentages and Fractions Practice Questions. Next: Ordering Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Practice Questions. The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on Fractions, Decimals and Percentages (FDP)
With denominator=100, take 56.0 and move the decimal two places to the left to get 0.56. Make the denominator 100 by multiplying the numerator and denominator by 4. With denominator=100, take 4.0 and move the decimal two places to the left to get 0.04. Find the decimal equivalent to the fraction. Example: 1/2 = .5.
Complexity=1. Convert the following decimals into fractions. Begin by taking out the whole number. In this case, the whole number is 7. We are left with 0.4 which goes out to the tenths place. Begin by taking out the whole number. In this case, the whole number is 2. We are left with 0.7 which goes out to the tenths place.
We'll also solve interesting word problems involving percentages (discounts, taxes, and tip calculations). ... Converting fractions to decimals Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Order rational numbers Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Quiz 1. Level up on the above skills and collect up to 320 Mastery points Start quiz.
Example Problem 1- Solve Word Problems by Converting Fractions into Decimals Jeremy worked 4 shifts at Little Andy's Ice Cream Shop last week. He had two shifts that were each 6 hours long.
Fraction word problems and decimal word problems are similar because they both involve solving math problems within real-world contexts. Both types of problems require understanding the problem, determining the operation needed to solve it (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division), and solving it based on the arithmetic rules for that ...
Step 1: Step 2: Answer: Rounded to the nearest tenth, the average speed of the car is 60.2 miles per hour. Summary: In this lesson we learned how to solve word problems involving decimals. We used the following skills to solve these problems: Estimating decimal products. Multiplying decimals by whole numbers.
1.5: Convert Between Decimals and Fractions; 1.6: Introduction to Percent Calculations; 1.7: Solving Problems Using Ratios; 1.8: Writing Fractions and Decimals as Percents; 1.9: Solving Problems Using Percents; 1.10: Percent Increase and Decrease; 1.11: Why It Matters- Whole Numbers, Fractions, Decimals, Percents, and Problem Solving
Course: 7th grade > Unit 2. Lesson 2: Converting fractions to decimals. Rewriting decimals as fractions: 2.75. Rewriting decimals as fractions challenge. Worked example: Converting a fraction (7/8) to a decimal. Fraction to decimal: 11/25. Fraction to decimal with rounding. Converting fractions to decimals.