

Top 200+ Engaging Culture Research Topics: Ideas to Explore
Culture is all about the beliefs, traditions, art, and ways of living that make up different groups of people worldwide. Cultural studies open up interesting paths for learning. Researchers can explore how people express themselves, their identity, and their interactions.
Cultural research gives a view into our diverse world, whether studying traditions over time, how cultures mix, or the impacts of globalization. This blog lists the top 200+ engaging cultural research topics from varied topics and perspectives to excite researchers, students, and anyone interested in exploring questions that highlight human cultural diversity.
Studying culture covers art, stories, social rules, beliefs, and how communities shape their environments. By exploring cultural research, we gain insights into shared experiences, histories, and worldviews that unite people and cultural uniqueness.
Researchers untangle complex threads weaving a culture’s identity and meaning through expressions like religion, language, food, and art.
As our world interconnects, understanding cultural differences grows important. Digging into these areas builds cross-cultural understanding, appreciates diverse views, and works towards inclusive societies.
This blog explores potential research paths, encouraging scholars and students to take learning journeys highlighting the rich tapestry of human cultures.
How Does Culture Impact Various Aspects Of Society?
Table of Contents
Culture deeply affects nearly every part of society. It influences how we interact, build communities, govern, teach, create art, approach healthcare, and make economic choices. Understanding the role of culture is key to analyzing social issues and dynamics.
- Social Rules and Beliefs
Culture lays the foundation for the shared beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors that define what is considered okay or not okay within a society. It shapes gender roles, communication styles, concepts of privacy, rules of politeness, and moral principles.
- Family and Relatives
Cultural traditions largely decide family structures, parenting styles, marriage practices, and generational relationships. Rituals surrounding birth, becoming an adult, marriage, and death are deeply rooted in culture.
- Education Systems
Cultural contexts and education philosophies heavily influence the subjects taught, teaching methods, classroom setup, grading approaches, and even the idea of learning itself.
- Religious and Spiritual Beliefs
Culture and religion are closely linked, with faith and spiritual practices playing a profound role in an individual’s identity, worldview, ethics, and community connections.
- Art and Stories
Creative expression through art, music, dance, folklore, and literature reflects a culture’s collective identity, history, and artistic values passed down over generations.
- Food and Eating
Food is intimately tied to culture, with food traditions, ingredients, cooking methods, and dining customs reflecting agricultural practices, values, and social hierarchies.
- Health and Medicine
Cultural backgrounds shape attitudes towards physical and mental health, preferred treatment methods, views on the human body, and institutional structures around healthcare delivery.
By understanding how culture underpins so many areas of society, we gain critical insights into resolving conflicts, bridging gaps between communities, and creating policies and initiatives that resonate across all groups of people.
Topical Diversity in Culture Research
Cultural research covers various fascinating topics and angles that give us insight into human societies worldwide. Researchers explore everything from the arts and traditions to belief systems, languages, social structures, etc.
Exploring Various Sides of Culture
- Art and Creative Expression (music, dance, stories, visual arts, theater, etc.)
- Traditions and Customs (holidays, rituals, milestone celebrations, folk practices)
- Food and Eating Ways (ingredients, cooking methods, dining customs)
- Language and Communication Styles
- Clothing and Decorative Styles
- Social Rules and Value Systems
- Gender Roles and Family Structures
- Spiritual and Religious Beliefs
- Cultural Identity and Sense of Belonging
Different Ways to Study Culture
- On-the-Ground Research: Observing and documenting cultural practices and perspectives firsthand by living in the community
- Historical and Archaeological Study: Examining artifacts, records, and evidence to understand cultural evolution
- Comparing Cultures: Identifying similarities and differences across cultures.
- Sociological and Anthropological Views: Studying cultures through theoretical frameworks
- Mixed Methods: Combining insights from fields like psychology, linguistics, economics, and more
- Personal Stories and Oral Histories: Exploring culture through first-hand accounts and stories
- Digital Research: Researching cultures and communities online and in digital spaces
By considering the diverse topics and varied approaches, cultural researchers gain a multi-angle understanding of the rich tapestry of human experience worldwide.
Recommended Readings: “ Top 201+ Narrative Project Ideas To Spark Your Creativity! “.
Top 200+ Culture Research Topics For Students
Here is the list of the top 200+ culture research topics, provided in different categories; let’s look.
Arts and Literature
- Evolution of modern art movements.
- Impact of digital technology on literature.
- Representation of gender in classical literature.
- Role of art in social change movements.
- Cultural significance of traditional folk music.
- Influence of literature on societal norms.
- The intersection of art and politics.
- Comparative analysis of different art forms.
- Cultural implications of street art.
- Depiction of war in literature and art.
Media and Communication
- Effects of social media on cultural identity.
- The portrayal of race and ethnicity in mainstream media.
- The role of memes in contemporary culture.
- Influence of advertising on consumer behavior.
- Evolution of journalism in the digital age.
- Cultural impact of reality TV shows.
- Representation of the LGBTQ+ community in media.
- Cultural appropriation in fashion and media.
- Role of censorship in shaping cultural narratives.
- The rise of streaming services and cultural consumption.
Language and Linguistics
- Evolution of slang and its impact on language.
- Language revitalization efforts and their effectiveness.
- Influence of colonialism on indigenous languages.
- Sociolinguistic variations in different cultures.
- Language acquisition in multicultural societies.
- Impact of globalization on language diversity.
- Language and identity formation.
- Cultural implications of bilingualism.
- Role of language in preserving cultural heritage.
- Linguistic relativity and cultural cognition.
Religion and Belief Systems
- Rituals and ceremonies in different religions.
- The role of religion in shaping moral values.
- Impact of globalization on religious practices.
- Interfaith dialogue and cultural understanding.
- Evolution of religious art and architecture.
- Influence of religion on political ideologies.
- Religious syncretism and cultural fusion.
- Sacred texts and their interpretation across cultures.
- Secularization and its effects on cultural norms.
- Religion and cultural conflicts throughout history.
History and Heritage
- Cultural impact of colonialism and imperialism.
- Oral history and its role in preserving culture.
- Cultural significance of historical monuments.
- Impact of migration on cultural identity.
- Evolution of family structures over time.
- Cultural exchange along ancient trade routes.
- Archaeological discoveries and cultural insights.
- Cultural legacy of ancient civilizations.
- Historical trauma and its effects on culture.
- Preservation of intangible cultural heritage.
Sociology and Anthropology
- Cultural differences in concepts of beauty.
- Social hierarchies and cultural stratification.
- Cultural perceptions of mental health.
- Gender roles and expectations in different cultures.
- Cultural aspects of food and culinary traditions.
- Rituals surrounding birth, marriage, and death.
- Cultural expressions of love and intimacy.
- Impact of globalization on cultural homogenization.
- Cultural practices related to education.
- Cross-cultural communication and misunderstandings.
Politics and Governance
- Cultural factors influencing voting behavior.
- Nationalism and its impact on cultural identity.
- Cultural diplomacy and soft power.
- Role of culture in international relations.
- Cultural policies and government funding.
- Indigenous rights and cultural preservation.
- Cultural dimensions of conflict resolution.
- Impact of authoritarian regimes on culture.
- Cultural movements and political activism.
- Cultural implications of refugee crises.
Technology and Innovation
- Cultural attitudes towards emerging technologies.
- Digital divides and cultural disparities.
- Cultural appropriation in technology design.
- Impact of AI on cultural production.
- Virtual reality and cultural experiences.
- Ethical considerations in technological advancements.
- Technological innovations in cultural preservation.
- Cultural resistance to technological change.
- Cultural implications of genetic engineering.
- Technological determinism and cultural evolution.
Education and Learning
- Culturally relevant pedagogy in education.
- Indigenous knowledge systems in education.
- Role of cultural competence in teaching.
- Cultural factors influencing learning styles.
- Education and cultural reproduction.
- Multicultural education and curriculum development.
- Cultural barriers to access education.
- Language diversity in educational settings.
- Cultural perspectives on childhood and adolescence.
- Impact of globalization on educational systems.
Identity and Diversity
- Intersectionality and cultural identity.
- Cultural assimilation versus cultural preservation.
- Cultural hybridity and identity negotiation.
- Cultural stereotypes and their impact.
- Cultural identity and belonging in diaspora communities.
- Cultural representations of disability.
- LGBTQ+ rights and cultural acceptance.
- Cultural dimensions of age and aging.
- Cultural perceptions of beauty standards.
- Ethnocentrism and cultural relativism.
Environment and Sustainability
- Indigenous perspectives on environmental stewardship.
- Cultural attitudes towards climate change.
- Impact of consumer culture on the environment.
- Traditional ecological knowledge and conservation.
- Cultural practices promoting sustainability.
- Environmental justice and cultural disparities.
- Cultural dimensions of food security.
- Indigenous land rights and cultural survival.
- Cultural influences on consumption patterns.
- Eco-tourism and cultural exchange.
Health and Wellness
- Cultural variations in healthcare practices.
- Traditional medicine and cultural beliefs.
- The stigma surrounding mental health in different cultures.
- Cultural factors influencing diet and nutrition.
- Cultural representations of illness and disability.
- Cultural rituals related to healing and well-being.
- Access to healthcare in diverse cultural contexts.
- Cultural attitudes towards body image and health.
- End-of-life care and cultural practices.
- Cultural barriers to health education and promotion.
Migration and Transnationalism
- Cultural adaptation and acculturation processes.
- Transnational communities and cultural exchange.
- Impact of remittances on cultural dynamics.
- Diaspora identities and cultural preservation.
- Cultural challenges faced by immigrants.
- Cultural hybridization in multicultural societies.
- Cultural dimensions of refugee resettlement.
- Transnational media and its cultural effects.
- Cultural nostalgia and longing in migrant communities.
- Cultural integration policies and their effectiveness.
Economics and Globalization
- Cultural dimensions of economic development.
- Globalization and cultural homogenization.
- Cultural branding and marketing strategies.
- Cultural industries and creative economies.
- Cultural value chains and commodification.
- Cultural entrepreneurship and innovation.
- Cultural tourism and economic impact.
- Intellectual property rights and cultural heritage.
- Global supply chains and cultural production.
- Cultural implications of income inequality.
Leisure and Recreation
- Cultural significance of sports and games.
- Festivals and celebrations across cultures.
- Cultural norms surrounding leisure activities.
- Tourism and cultural authenticity.
- Cultural representations in entertainment media.
- Indigenous forms of entertainment and recreation.
- Cultural rituals of relaxation and rejuvenation.
- Impact of technology on leisure habits.
- Cultural perspectives on outdoor recreation.
- The role of leisure in community building.
Family and Kinship
- Cultural variations in family structures.
- Cultural expectations of parenthood.
- Intergenerational transmission of cultural values.
- Cultural rituals surrounding marriage and partnership.
- Cultural attitudes towards child-rearing.
- Kinship systems and cultural identity.
- Cultural perceptions of caregiving.
- Family dynamics in multicultural households.
- Cultural practices related to eldercare.
- Cultural representations of family in media.
Urbanization and Urban Culture
- Cultural diversity in urban environments.
- Urbanization and the erosion of traditional culture.
- Cultural gentrification and displacement.
- Street art and graffiti as cultural expressions.
- Cultural communities within urban spaces.
- Urban legends and folklore.
- Cultural aspects of urban planning.
- Impact of migration on urban culture.
- Cultural revitalization projects in cities.
- Subcultures and countercultures in urban settings.
Governance and Policy
- Cultural rights and human rights discourse.
- Multiculturalism policies and their effectiveness.
- Cultural diplomacy in international relations.
- Cultural heritage preservation laws.
- Indigenous land rights and sovereignty.
- Cultural dimensions of public policy.
- Cultural sensitivity training in government.
- Cultural impact assessments in policy-making.
- Cultural representation in political institutions.
- Cultural heritage protection in conflict zones.
Memory and Commemoration
- Cultural memory and collective trauma.
- Commemorative practices and cultural identity.
- Museums and cultural representation.
- Oral history projects and cultural preservation.
- Memorialization of historical events.
- Cultural heritage sites and tourism.
- Digital archives and cultural heritage.
- Cultural monuments and their meanings.
- Cultural responses to historical revisionism.
- Rituals of remembrance in different cultures.
Cultural Capital and Social Mobility
- Cultural capital and its role in social stratification.
- Cultural barriers to upward mobility.
- Cultural capital and educational attainment.
- Cultural capital and access to resources.
- Cultural capital and employment opportunities.
- Cultural dimensions of social capital.
- Cultural capital and political participation.
- Cultural mobility and globalization.
- Intergenerational transmission of cultural capital.
- Cultural capital and urban development.
- Cultural capital and well-being outcomes.
These topics cover various cultural aspects and can be a starting point for further research and exploration.
Tips For Choosing the Right Culture Research Topic
Picking a good topic is super important when researching culture. The topic you choose decides what your whole project will be about. If you pick the wrong topic, you might get bored or not learn anything useful.
But if you pick a cultural topic that interests you, your research will be more fun and valuable. With so many fascinating cultural issues, choosing just one to study can feel overwhelming. But by considering a few key points, you can find the perfect research topic that fits your interests, goals, and resources as a cultural researcher.
- Pick a topic you’re genuinely interested in and passionate about. Your enthusiasm will make the research process much more engaging.
- Consider cultural issues or phenomena that puzzle you, or you’ve personally experienced and want to understand better.
- Look for gaps in existing research on cultural topics. Identifying an understudied area can make your work more novel and valuable.
- Think about the practical applications of your research. Work that provides insights into reducing cultural misunderstandings or conflicts can greatly impact.
- Choose a topic that is narrow enough to explore in-depth within the scope of your project yet still broadly relevant.
- For a cross-cultural study, select cultures that provide an interesting contrast to compare and analyze.
- Ensure you have access to the necessary data sources, whether archival materials, interview subjects, survey populations, etc.
- Consider the ethical implications of your research, especially if studying vulnerable populations. Prioritize, not harm.
The right topic sparks your curiosity, fills a need, and is feasible to execute thoroughly and responsibly with your resources.
Trends To Come in Culture Research
Researchers are looking at lots of new and interesting cultural topics these days. Here are some of the latest areas scholars are studying when it comes to culture:
Culture and Technology Research Topics
- How social media is changing cultural values and norms
- Comparing how different cultures use and adopt new technologies
- Whether technology helps preserve cultural traditions or makes them disappear
- The rise of global digital cultures and subcultures online
- Cultural impacts of artificial intelligence and automation
Environmental Culture Research Topics
- What indigenous cultures know about living sustainably in the environment
- How climate change is affecting cultural practices and traditions
- Where environmental justice and cultural identity overlap
- The role culture plays in environmental-friendly (or unfriendly) behaviors
- Different cultural views on humanity’s relationship with nature
Contemporary Cultural Issues Research Topics
- Cultural experiences of immigrants, migrants, and refugees
- How popular culture (movies, TV, music, etc.) shapes cultural attitudes
- The cultural side of social movements like #MeToo, Black Lives Matter, LGBTQ+ rights
- Impacts of globalization on mixing and blending cultures
- How culture factors into political conflicts and clashing worldviews
These new and emerging cultural topics give researchers a chance to learn things that are very relevant to today’s world.
How can I choose the right culture research topic?
Consider your interests, societal relevance, and the availability of resources. Choose a topic that resonates with you and contributes to existing discourse.
Are there any ethical considerations in cultural research?
Researchers must respect cultural sensitivities, obtain informed consent, and avoid misrepresenting or exploiting cultural practices.
Can I conduct cross-cultural research as an undergraduate student?
Absolutely! Cross-cultural research offers valuable insights and can be conducted at various academic levels with proper guidance and supervision.
Similar Articles

How To Do Homework Fast – 11 Tips To Do Homework Fast
Homework is one of the most important parts that have to be done by students. It has been around for…

How to Write an Assignment Introduction – 6 Best Tips
In essence, the writing tasks in academic tenure students are an integral part of any curriculum. Whether in high school,…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Enjoy a completely custom, expertly-written dissertation. Choose from hundreds of writers, all of whom are career specialists in your subject.
List of Interesting Cultural Research Paper Topics

Cultural research paper topics allow students to explore people’s historical aspects, actions, ideas, and narratives that they have copied or altered over time. People express their cultures via various symbols and language. Additionally, different aspects of culture affect people’s mindsets.
When pursuing cultural students, students write research papers, essays, and articles on varied topics. However, most learners struggle to select the best titles for their papers. That’s because the topic that a student selects influences the path they take when completing this assignment. For this reason, we’ve come up with this guide with a list of interesting cultural research topics for learners to consider.
Discover a vast array of captivating cultural research paper topics with the expertise of our professional dissertation writers . Our dedicated team is ready to assist you in selecting compelling topics and crafting high-quality research papers that meet the highest academic standards.
How to Choose Cultural Research Topics
The internet is awash with cultural research ideas from which students can choose what to explore. However, not every topic you come across will be suitable for you. For that reason, consider the following aspects when choosing your cultural topic for research.
- Select a topic that meets your writing assignment requirements
- Settle on a topic you find interesting
- Pick a topic that meets the scope of your assignment
In addition to these criteria, check the available research to select a topic you will find sufficient information for before you start writing your paper. Also, brainstorm concepts and create a research question around the topic. Here are different categories of cultural research paper topics from which you can choose your favorite title.
Cultural Anthropology Research Topics
If you find cultural anthropology interesting, pick your topic from the following ideas.
- How traditional food can reflect a nation’s history
- Analysis of the refugees’ impact on the cultures of the European countries
- How Christian traditions differ from one culture to another
- How countries in the Soviet Union moved from communism
- Effects of liberalism on the education system
- Analysis of a communistic nation’s cultural values
- Causes of political division in the United States
- Why most people in the Netherlands love cycling
- How people view the death concept in Africa
- How the English language influences the American culture as the common language
Cultural Diversity Research Paper Topics
Perhaps, you’re interested in cultural diversity. In that case, consider these ideas for your research paper.
- Analysis of cultural diversity’s role in schools
- How cultural diversity influences modern society
- How significant is cultural diversity in this century?
- How multiculturalism and pluralism affect the American citizens’ lives
- Psychological counseling associations to cultural diversity
- How cultural diversity affects the medical industry
- How migration affects cultural diversity of the Asian land
- How cultural diversity affects people’s interactions
- Demonstrating critical thinking with special attention to diversity and multicultural issues
- Cultural diversity as a reason for not tolerating racism
Cross-Cultural Communication Research Topics
Cross-cultural communication is among fields with excellent topics for cultural research. Here are some of the best ideas in this field.
- Approaches to cross-cultural information exchange
- Practical cross-cultural dialogue strategies
- Intercultural dialogue and translation
- Teaching cross-cultural communication and culture
- Cross-cultural information exchange artifacts
- Factors enhancing cross-cultural dialogue competence
- Cultural and health-related issues between ethnic minorities and healthcare providers
- The adaptation of international students to American campuses
- Low-context cultures versus high-context cultures- Cross-cultural perspective
- Assessing cross-cultural effectiveness
Cultural Psychology Research Topics
If interested in cultural psychology research, consider these ideas for your papers and essays.
- How cultural psychology has evolved over the years
- How cultural psychology affects diversity
- Filial piety and personality among the British citizens
- Impacts of famous artists on the global culture
- Impacts of COVID-19 on the US political atmosphere
- Comparing women’s emotions and gender stereotypes as exhibited by men’s superior thinking
- Influences of cross-cultural psychology
- Social and self behavior among the United States’ Red Indians
- Analyzing the unemployed graduates’ experiences in the United Kingdom
- How parenting stress relates to the stigma of a mother with an autistic child
Cross-Cultural Research Topics
Cross-cultural research paper topics cover psychological behavior and processes across different cultures. Here are topic samples in this category.
- Communication styles among different cultures
- How attitudes towards conflicts differ among cultures
- How people from different cultures approach the same task differently
- How different cultures approach knowing
- Why humans should respect and work with people from different cultures
- The attitudes of different cultures towards disclosure
- How decision-making styles differ among cultures
- How non-verbal communication promotes a culture
- What determines business communication across cultures?
- How history and social organization affect modern society
Cultural Studies Research Paper Topics
When pursuing cultural studies, writing research papers is unavoidable. Here are cultural research paper topics to consider for your papers and essays.
- How stigma affects the efforts to prevent sexually transmitted diseases from spreading
- Challenges encountered by people with social disorders and anxiety
- How films influence the audiences’ cultures
- How songs promote feminism
- Coping mechanism for culturally different people
- How cultural studies facilitate the promotion of brands in global markets
- How people perceive the old and the youths in their cultures
- How cultural studies can help in promoting businesses internationally
- Cultural traits exhibition in exotic and indigenous animals
- Influence of associating with a particular language on a person’s culture
Cultural Geography Research Topics
Cultural geography focuses on cultural changes in various geographical settings. Here are topics to explore in this category.
- Explaining the cultural concept
- Analyzing a culture area and the culture itself
- Analysis of cultural landscapes
- Cultural ecology and culture history
- Focusing on the institutions
- Understanding cultural geography
- The history of cultural geography
- Understanding feminist geography
- Explain the evolution of urban geography
- Analysis of the geography of space and sexuality
Chinese Cultural Research Topics
Are you interested in studying Chinese culture? If yes, this list has the best cultural topics for research paper that you can explore.
- Evaluating Cultural Revolution in China
- The Chinese government and Tibet
- Culture-bound psychiatric syndromes in China
- The Chinese culture and silk road
- Cross-cultural competency in China
- How culture influences the Chinese politics
- Effects of Buddhism on the Chinese culture
- Chinese medicine and culture
- Childhood illness treatment in traditional China and religion
- The cultural perspective of the human stomach in China
Research Topics on Community-Centered Cultural Adaptation
Are you interested in community-centered cultural adaptation research? If yes, here are topics to consider for your papers.
- Stage-setting and professional consultations for cultural adaptation purposes
- Preliminary cultural content adaptation
- Iterative cultural content adaption with members of the community
- Cultural adaptation with meetings and community feedback
- Role of language during cultural adaptation
- The concept of cultural adaptation
- Factors that limit community-centered cultural adaptation
- How conflict of interest can hinder community-centered cultural adaptation
- How gender influences community-centered cultural adaptation
- How to enhance community-centered cultural adaptation
Cultural Analysis Topics for Research
Perhaps, you’re interested in analyzing a cultural aspect or phenomenon. In that case, consider these ideas for your research paper.
- Analysis of cultural phenomenon in your community
- Analyzing the influence of TikTok on local culture
- Analysis of “the dab” popularity
- Analyzing the effects of bandwagon on the culture
- Analysis of the normalization of the holocaust in some cultures
- Analyzing religious beliefs as a cultural phenomenon
- Analyzing the popularity of sitcoms
- Analyze the fan base of your favorite celebrity
- Analysis of social media as a cultural phenomena
- Analyzing cross-cultural fashion trends
Cultural Analysis Essay Topics
If interested in analyzing the culture, pick the idea to write about in this list.
- Analyzing drug use by sportspeople
- Analyzing homelessness in America
- Communication differences between males and females
- Analyzing obesity trends across age brackets
- How sports influence culture
- Analyzing multicultural identity
- Analysis of modeling and body size aspects of a culture
- Effects of multicultural families on the involved parties
- Analysis of gender role changes over time
- How being raised by a single parent affects a child- A cultural perspective
Unique Cultural Analysis Paper Topics
Are you looking for a unique topic for cultural research? If yes, this section has a good idea for you.
- Why are cultural studies essential?
- How society treats people based on their cultures
- How the minorities cope in a different culture
- How feminism affects the culture
- How isolated communities can conserve their cultures
- How religion influences culture- Use the Muslim community as a case study
- Describe the cultural commonalities among human beings
- Explain the correlation of sex and attitude as cultural tools
- The influence of associating with a particular language on a person’s culture
- How exotic and indigenous groups exhibit cultural differences
Pick your topics from this list and then take your time to develop them through research to come up with solid papers or essays that will earn you the top grades.
Frequently Asked Questions
Richard Ginger is a dissertation writer and freelance columnist with a wealth of knowledge and expertise in the writing industry. He handles every project he works on with precision while keeping attention to details and ensuring that every work he does is unique.

Succeed With A Perfect Dissertation

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
170 Engaging Cultural Research Topics for Students
Table of Contents
Would you have to submit a cultural research paper? If yes, then you must have a good topic to proceed with your research paper writing. In case, you have no idea what topic to choose for your cultural research paper, continue reading this blog post. Here, you will get 150+ interesting cultural research topics on various themes. Also, you will know how to pick a good topic and compose a detailed cultural research paper deserving of an A+ grade.
An Overview of Cultural Research
Performing in-depth research on topics related to culture is called cultural research. In general, culture is referred to as the behavioral pattern of a particular group of people determined by values, beliefs, and thoughts. Usually, the culture will be passed from one generation to the next through communication and imitation. In the wide world, people of each and every country, religion, and community follow a unique culture and traditional values according to the beliefs and thoughts passed by their ancestors.

As different types of cultures exist in this world, it is really exciting and challenging to conduct research on this broad subject. By conducting research on cultural topics, you can get to know about the various dimensions of culture that are a part of humanity. Conducting research on cultural areas is not easy because it requires more fieldwork and detailed information on the topic chosen.
Cultural Research Paper Topic Selection Tips
In order to write an impressive cultural research paper, you must have a perfect cultural research topic. When it comes to choosing the right cultural topic for research or dissertation, you may end up with a lot of confusion because of the wide range of topics and the subtopics the subject contains.
So, to wipe out all your confusion and help you in selecting the right topic, here we have shared a few tips on how to select a cultural research topic. Follow these tips while you are in the topic selection process.
- The topic you choose should match your interest, and it should also grab the attention of your readers.
- The topic should not be too broad.
- Pick a topic that is unique and convenient for you to conduct an in-depth study and complete the research paper on time.
- The topic should have relevant sources of references and supporting evidence.
How to Write an Engaging Cultural Research Paper?
Once you have selected a perfect cultural research topic, you need to undergo a few steps before writing the cultural research paper. Discussed below are the important strategies and tips you need to consider while writing a cultural research paper.
- First, consult a person who is native to the culture you have selected for study and then explore the tradition, habit, and style that is a part of that culture.
- To write an accurate research paper on a specific culture, it is mandatory to gather information from credible sources. Never rely on the information submitted on Wikipedia or other non-credible blog posts on the internet.
- Along with the information about the culture, collect the pieces of evidence supporting that information. The evidence can be in the form of text, images, charts, graphs, or tables.
- After you have gathered information about the selected culture, sketch an outline of your research paper. The outline will help you to organize your work and present the main points about the culture in a well-structured and coherent manner.
- When writing, put all the major points about the culture with relevant evidence in a simple and concise way that is understandable to your readers. Avoid sharing biased views about the culture you have selected.
- Finally, after writing the cultural research paper, do a complete revision. The final draft of your research that is ready for submission should not contain any grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors.
List of Captivating Cultural Research Topics
We know that finding a perfect cultural topic for research or dissertation is a tedious process. So, to save time and to make your topic selection process easier, here we have prepared a list of the top impressive cultural research topics.

Go through the cultural research topic ideas listed below and pick any topic of your choice.
Cultural Anthropology Research Topics
- The effects of cultural anthropology on the missionary.
- Exploration of the long-term impacts of physical labor on the physical appearance of humans.
- An evaluation of the cultural anthropology of our time
- The role of women in modern society as opposed to the traditional roles.
- How stigma affects efforts on stopping the spread of sexually transmitted diseases?
- What are the peculiarities of the Zulu community culture in Southern Africa?
- How is the concept of death viewed in Africa?
- The influence of English as a common language on American culture.
- What is the anthropological perspective on the development of the modern United States of America?
- Examination of various religious practices in the United States of America.
- Discuss the three branches of cultural anthropology
- Ethnocentrism and the strategies to minimize it
- Discuss the impact of the cultures of rituals and festivals on cultural identity, community development, and intercultural relationship
- Comparative assessment of the concept of social status in African and American communities
- Cultural similarities and differences. between Black/African and Colored Women in South Africa
- Feminism in the patriarchal societies
- Analysis of the Impact of culture on the global tourism
- Impact of patriarchy on African society
- Discuss the expansion of anthropology over the past decades
- Economic anthropological issues in the post-capitalist Societies
- Why medical anthropology is important?
- Lesbian Activism between 1985 and 2015
Cultural Psychology Research Paper Topics
- Cultural diversity and psychological counseling.
- Analyze the psychological aspects of the cultural phenomenon.
- American psychologists and their cultural competence needs.
- Factors that influence cross-cultural psychology .
- Native culture and human psychology.
- The implication of cultural psychology on diversity.
- Analyze the impact that famous artists have on world culture.
- Comparative analysis of gender stereotypes of superior thinking in men and emotions in women among students.
- Life experiences of unemployed graduates in the United Kingdom.
- The self and social behavior among Red Indians in the United States of America.
- The Difference in Skin Color: Current Situation of Black Americans
- Analyze the link between multinational businesses and cultural psychology
- Discuss the psychology of motherhood in different cultures
- Describe the cultural issues in psychology
- Intercultural dynamics and human development
- Exploration of the cross-cultural differences through cognition and perception analysis
- What is called cross-cultural psychology?
- Cultural psychology v/s cross-cultural psychology
- Cultural revolution in Asian countries
- Impact of social media on cultural psychology
- Discuss the current issues in cross-cultural psychology
Read more: Captivating Psychology Research Topics for Students
Cultural Diversity Research Topics
- Ethnic diversity and its advantages.
- The influence of cultural diversity in modern society.
- Analyze the role of cultural diversity in the schools.
- The impact of cultural diversity on the whole medical industry.
- The influence of cultural diversity on performance and communication process.
- The effects of migration on the cultural diversity of Asian land.
- The significance of preserving cultural diversity in the 21st century.
- Cultural diversity’s impact on the interaction process and performance.
- How pluralism and multiculturalism have impacted the lives of American citizens?
- Gender-based pay Structure
- Discussion on how to prevent diversity backlash
Cross-Cultural Research Paper Topics
- Compare and contrast the features of language and culture.
- Determinants of cross-cultural business communication.
- How does culture affect social and emotional development?
- The impacts of social organization and history in modern society.
- The role of non-verbal communication in promoting culture.
- The influence of environmental factors on the development and character of cultures.
- Members of any culture perceive their behavior as logical.
- The role of attitude toward accents and dialects in creating barriers in international business communication.
- Socio-linguistic as a tool for differentiating economic classes.
- Climate and topography affect transport and logistics, settlement, and territorial organization.
- Impact of Cross-Culture on Business Organizations and Society at Large

Best Cultural Research Topics
- The Olympic Games and its history.
- Elaborate on the key Renaissance artists.
- The Spread of Christianity across Europe.
- The impact of the 1848 revolution on art.
- Roman Empire and its heritage in the modern world.
- Ancient Britain and its architecture.
- Explore cross-cultural fashion trends.
- Thanksgiving celebration outside the United States.
- Spread of religious beliefs- Is it a cultural phenomenon?
- Do clothes identify the subculture of a person?
Unique Cultural Research Topics
- Elaborate on European fashion during a particular period.
- Athletic community and its relevance.
- Explain the reasons for social group development.
- The perception of death in different cultures.
- Time perception in tropical countries.
- How to mitigate cultural ignorance?
- How to avoid cultural narcissism?
- Discuss the social stigma of single mothers.
- Explore the conditions making a musician famous.
- Identify a song and explain the culture portrayed in its lyrics.
- How music, art, and drama influence culture
- International Cultural Interaction: Discussion
- Cultural development in the discourse of civilization between different races.
Interesting Cultural Research Topics
- Discuss the impact of social media on a person’s lifestyle.
- The Black Lives Matter movement and its impact on racism in the US.
- Isolated communities and conservation of culture.
- Mass media and pop culture.
- How does feminism affect the culture?
- Why are cultural studies essential?
- Analyze multicultural identity.
- Communication differences between males and females
- Analysis of modeling and body size aspects of a culture
- How do sports influence culture?
Impressive Cultural Research Topics
- Analysis of cultural landscapes
- The influence of TikTok on local culture
- Factors that limit community-centered cultural adaptation
- The effects of Buddhism on the Chinese culture
- Cultural ecology and culture history
- How do films influence the audiences’ cultures?
- How do decision-making styles differ among cultures?
- How do exotic and indigenous groups exhibit cultural differences?
- Why should humans respect and work with people from different cultures?
- How do cultural studies facilitate the promotion of brands in global markets?
- Social media and its ability to shape culture
Popular Cultural Research Paper Topics
- Discover the history and lifestyle of the Goths.
- Discuss the importance of the hairstyle for subcultures.
- What is the basis of slumber culture?
- Does traditional food reflect the history of a nation?
- Do Christian traditions vary from culture to culture?
- Analyze the cultural values of a communistic nation.
- How does architecture reflect a nation’s history?
- Explain the popularity of online shopping worldwide.
- How can one avoid cultural ignorance?
- Is transracial adoption becoming more common in the U.S.?
- Should the term “immigrant” be banned?
- Describe the culture shock experience of an international student.
- How did Brexit affect the British lifestyle?
- Manifestations of ethical egoism in modern society.
- Are the Americans guilty of ethnocentric
Read more: Top Synthesis Essay Topics and Ideas To Consider For Assignments
Trending Cultural Research Paper Topics
- Can art be misunderstood because of the socio-cultural context?
- Why was the Holocaust normalized in some nations?
- Does globalization put the national identity in danger?
- What are the most popular subcultures amongst Generation Z?
- The importance of developing cultural sensitivity.
- Impact of preventing the spread of the STD on the pertinent efforts.
- Discuss the impact of English as a common language in American culture.
- Talk about the uniqueness of the Zulu community culture in Southern America.
- sociolinguistics as a tool for identifying social classes
- Promotion of culture and the importance of nonverbal communication.
- the evolution of sexism’s types and prevalence over time.
- The Black Lives Matter movement’s effect on US racism.
- cultural diversity’s impact on contemporary society.
- Explain the notion of an alien civilization as it is presented in literature and film.
- Commonalities across cultures and their importance for all humans.
Art Culture Research Topics
- Cannibals, comedy, and movie legends were highlighted at the Venice Film Festival.
- Tips for executing an open kitchen design in your home.
- Flying Colors: A digital feather collection for Indian birds is getting off
- Interpretation of Bapu’s impressions through the arts
- Interested in becoming a digital nomad? Try before you purchase.
- The original Mickey Mouse copyright will soon be missed by Disney.
- Improve Home Interior with Stunning design ideas.
- A theatrical salute to India’s unsung heroes is presented by NSD.
- The link between Mental Health and Art Therapy.
- Anita Dongre talks about her Homage collection in an article in Firstpost’s Art and Culture section.
- An artist gets his due back home after making a mark in Manhattan.
- The protest was conducted at the Uffizi’s “Spring,” but the artwork was unharmed.
- Maharaja Serfoji II’s exquisite stolen picture from the 19th century has been found in a US museum.
- Italy prevents the Gentileschi painting from being sold illegally abroad.
- A new audio series emphasizes the cultural similarities between Pakistan and India.
- The reasons behind the debate about a picture in the Naumburg Cathedral.
- Drawings were discovered in an Amedeo Modigliani painting by an Israeli museum.
- Why is Picasso’s “Weeping Woman” regarded as a classic example of the Cubist movement?
- Reopening of the Black Parade Culture Museum in New Orleans.
- Milan Design Week features comfort, color, and craftsmanship.
Amazing Cultural Research Topics
- How have American Indians adapted their culture since colonization?
- What are the key elements of Southwest’s culture?
- Write about the business culture in America.
- What are the barriers to cultural competence?
- Write about cultural diversity issues in media presentations.
- Discuss the cultural rift in the UAE Construction industry.
- Analyze the culture of real-estate companies.
- Discuss the various intercultural conflict styles.
- Write about Sabbath in the Judaism Culture.
- Analyze the Indian culture portrayed in the ‘Pather Panchali’ Movie.
Final Words
Out of the different ideas recommended in this blog, pick any topic of your interest and write an impressive cultural research paper with proper evidence. In case, you are unsure what topic to select or if you struggle to compose an engaging cultural research paper, then get in touch with us immediately. We have numerous subject experts on our platform to offer you assignment help writing in accordance with your cultural research paper requirements. Moreover, by taking our cultural research paper help service online, you can also wind up your tasks prior to the submission date and boost your overall academic scores.

Related Post

220 Amazing Religious Research Paper Topics and Ideas

Read and Understand How to Write a Research Proposal

100+ Controversial Research Topics and Ideas to Focus On
About author.
Jacob Smith
I am an Academic Writer and have affection to share my knowledge through posts’. I do not feel tiredness while research and analyzing the things. Sometime, I write down hundred of research topics as per the students requirements. I want to share solution oriented content to the students.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Featured Posts
140 Unique Geology Research Topics to Focus On
200+ outstanding world history topics and ideas 2023, 190 excellent ap research topics and ideas, 150+ trending group discussion topics and ideas, 170 funny speech topics to blow the minds of audience, who invented exams learn the history of examination, how to focus on reading 15 effective tips for better concentration, what is a rhetorical analysis essay and how to write it, primary school teacher in australia- eligibility, job role, career options, and salary, 4 steps to build a flawless business letter format, get help instantly.
Raise Your Grades with Assignment Help Pro
Cultural Research Paper Topics: Exploring Heritage and Society
Culture is interconnected and ever-changing. It influences how we think, behave, and interact with everything around us. It is also a significant source of variation, as various cultures have varying values, beliefs, and practices.
Understanding different cultures is more important than ever in today’s globalized world. Cultural research can aid in creating a more inclusive and tolerant society by bridging cultural divisions.
Through a range of cultural research paper themes, such as pop culture essay topics , this article investigates the characteristics of human civilizations and diversity. These issues cover everything from the significance of culture in developing human identity to the influence of cultural variety on disagreements and partnerships.
How to Choose Research Paper Topics about Culture?
Culture is a vast and complex topic, so it can be difficult to choose a research paper topic that is both interesting and manageable.
Listed are a few tips for choosing research paper topics about culture:
- Consider your own interests
What aspects of culture are you most interested in? What do you know a lot about? Choosing a topic you are interested in will make the research process more enjoyable and rewarding.
- Consider your target audience.
Who is going to read your paper? What background in culture do they ask for? Choosing a topic that is intriguing and helpful to your readers will improve the quality of your paper.
- Conduct preliminary research .
Once you’ve developed a few concepts, perform some early research. This will assist you in selecting your topic and figuring out the sources you will use.
- Make it specific .
To what extent do you want the subject to go? A broader topic will allow you to examine more facets of culture, though it will also be more difficult to investigate.
- Consult with your lecturer.
Talk to your professor if you need help deciding on a cultural research topic. They can assist you in filtering your alternatives and selecting the best topic for you.
List of Interesting Culture Topics to Write About
Culture is a diverse and intriguing subject that may be approached from various perspectives. There are several interesting cultural research topics to write about, ranging from multiple civilizations’ history to culture’s influence on the arts and media.
This list is an excellent place to begin if you’re looking for fascinating cultural research topics to write about.
Cultural Anthropology Research Topics
The study of human societies and their traditions is known as cultural anthropology. Cultural anthropology research subjects might range from the study of distinct civilizations to the study of cross-cultural comparisons. These subjects in anthropological perspectives go into the cultural practices, rites, and norms of multiple cultures across all nations worldwide. They may include studies on kinship systems, gender roles, religious ceremonies, language development, and cultural adaptation.
Some examples of cultural research topics include;
- Cultural Adaptation and Assimilation of Immigrants in Modern Society
- The Impact of Globalization on Indigenous Cultures and Traditional Knowledge Systems
- Cultural Expressions and Identity Formation Among Marginalized Communities
- The Role of Rituals and Ceremonies in Shaping Cultural Beliefs and Practices
- Cross-Cultural Perspectives on Gender Roles and Sexuality
- Cultural Responses to Environmental Change and Sustainability
- The Influence of Technology on Cultural Performance and Communication Process
- Cultural Perspectives on Healthcare Practices and Healing Rituals
- Cultural Preservation and the Role of Museums in Safeguarding Intangible Heritage
- Comparative Study of Cultural Practices Related to Death and Mourning
Cultural Psychology Research Paper Topics
Cultural psychology research paper topics focus on the intersection between culture and human psychology. These subjects explore how cultural factors shape our thoughts, emotions, behaviors, and mental processes.
By examining these topics, researchers aim to unravel the complex interplay between cultural psychology, shedding light on the cultural influences that shape our individual and collective experiences.
At times, students get overwhelmed with the workload at hand and often ask – who can write my papers just how I want them? The answer is yes. There are professional writing services that provide this help.
Cultural research topics in this section are:
- Cultural Variations in Cognitive Processes and Perception
- The Influence of Culture on Personality Development and Individual Differences
- Cross-Cultural Perspectives on Emotion Expression and Regulation
- Cultural Factors in the Development and Treatment of Mental Disorders
- Cultural Influences on Parenting Styles and Child Development
- Cultural Variations in Moral Reasoning and Ethical Decision-Making
- The Role of Cultural Narcissism in Shaping Attitudes and Behaviors Towards Authority
- Cultural Differences in Motivation and Achievement
- The Impact of Acculturation and Bicultural Identity on Psychological Well-Being
- Cultural Factors in Intergroup Relations and Prejudice
Socio-Cultural Essay Topics
Socio-cultural topics explore a wide range of issues related to society and culture. The essays in the socio-cultural context examine the relationship between humanity and culture. Research topics in this field can range from the study of social institutions to the norms and values of cultural studies.
Among the possible cultural research topics are:
- The Societal Fabrication of Race and Its Consequences for Identity and Inequality
- Mass Media’s Involvement in Creating Cultural Norms and Values
- Perspectives on Economic Disparity and Hardship From a Socio-Cultural Perspective
- Social Media’s Influence on Interpersonal Relationships and Self-Esteem
- The Impact of Cultural Diversity on Academic Success in Schooling
- Socio-Cultural Variables Influence Health Inequalities and Access to Healthcare
- Religious Beliefs Influence Societal Attitudes and Behaviors
- Migration and Refugee Integration Have Socio-Cultural Elements
- Cultural Phenomena Influence Environmental Views and Sustainable Practices
- Race, Class, and Gender Intersectionality in Human Beings’ Socioeconomic Inequity
Cultural Diversity Research Topics
This area of study may investigate the impact of cultural diversity on healthcare inequalities, the role of cultural characteristics on psychological outcomes, or the efficacy of ethnically customized therapies in enhancing patient care and health results.
To get your cultural research papers crafted to your requirements, Edusson gets the hassle out of writing essays from start to end.
Being aware of various cultural aspects is essential for establishing inclusive and equitable healthcare systems that meet the specific requirements of varied groups.
The following are some cultural research topics to write on:
- The Effect of Cultural Diversity on Workplace Efficiency and Fulfillment
- The Impact of Ethnic Diversity on the Medical Industry and How Patients Respond
- Investigating the Importance of Cultural Phenomenon in Developing the Education System and Practices
- Cultural Diversity’s Impact on Team Dynamics and Collaboration in a Social Organization
- Cultural Diversity and Its Consequences for International Advertising Tactics
- The Link Between Cultural Diversity and Technological Innovation
- Understanding the Upsides and Challenges of Cultural Diversity in a Multicultural Society
- The Influence of Cultural Competence on Conflict Resolution and Peacebuilding Initiatives
- Multicultural Diversity’s Impact on National Identity and Social and Emotional Development
- Investigating and Preserving Native Culture Uniqueness
Cross-Cultural Research Paper Topics
Intercultural studies compare and analyze different cultures and their effects on many parts of society. Exploring disparities in healthcare beliefs and practices, investigating the efficacy of cross-cultural perspectives in hospital settings, or researching the influence of globalization on cultural practices and medical behaviors are all possible research subjects.
Cultural studies facilitate competence in healthcare and ensure culturally sensitive and effective care to individuals from a particular culture.
Writing a very good research paper is tedious, so you may need to find the best research paper topics to get ideas flowing.
Cultural research paper topics in this category include:
- A Comparative Analysis of Cross-Cultural Business Communication Across World Culture
- Cross-Cultural Communication Challenges and Strategies in International Business Negotiations
- The Impact of Cross-Cultural Interactions on Intercultural Competence Development
- Economic Classes in Parenting Styles and Their Effects on Child Development
- Cross-Cultural Perspectives on Sexually Transmitted Diseases Stigma and Its Implications for Non-verbal Communication
- Exploring Cross-Cultural Fashion Trends Variations and Experiences of Beauty and Body Image
- The Influence of Culture on Attitudes and Behaviors Related to Environmental Sustainability
- Cross-Cultural Perspectives on Aging and Elder Care Practices
- Understanding Cross-Cultural Psychology in Ethical Decision-Making Processes
- The Role of Western Culture History in Shaping Attitudes Towards Gender and Sexuality
Art Culture Research Topics for Assignments
The intersection of art and culture provides a rich landscape for research. Research in this field contributes to our understanding of art’s therapeutic and cultural significance and highlights its potential as a tool for healing, self-expression, and cultural values.
Potential cultural research paper topics are:
- The Influence of Ancient Art on Contemporary Artistic Expressions
- Exploring the Cultural Significance of Street Art and Graffiti in Urban Environments
- Female Culture in Art Throughout Ancient Britain
- Art as a Form of Cultural Resistance and Social Activism
- Analyzing How Traditional Food Reflects the Cultural Heritage
- Cultural Appropriation Versus Cultural Appreciation in Art and Its Ethical Implications
- The Intersection of Art and Technology: Exploring Digital Art and Its Cultural Implications
- The Importance of Museums in Maintaining and Displaying Various Works of Art and Cultural Artifacts
- The Study of How Art Reflects and Affects the Stories of Culture
- Therapeutic Art as a Technique for Boosting Mental Health and Well-Being Across Different Cultures
Good Essay Topics about Culture
Culture is an enthralling and varied part of human society. Cultural essay topics include customs, cultural interchange, cultural identity, cultural appropriation, and cultural preservation. Exploring these themes provides a more in-depth understanding of the values, religious practices, cultural clashes, and conventions that define different cultures.
The following are the best cultural studies selections in this category:
- Globalization’s Influence on Indigenous Cultural Practices
- A Critical Appraisal of Cultural Theft
- The Impact of Cultural Background on Individual Growth
- Language’s Impact on Cultural Norms and Values
- Issues and Benefits of Preserving Cultural Diversity in the Workplace
- A Systematic Examination of Gender Roles and Cultural Expectations
- Protection of Historic Resources in the Face of the Modern World
- Finding an Equilibrium Between Cultural Integration and Maintaining Culture
- Gender Stereotypes and Their Effects on Intercultural Relationships
- The Influence of Pop Culture on Societal Norms and Values
Topics on Globalization
The process of globalization has changed the global culture into an interlinked village. Globalization essay themes can cover a wide range of issues, including its influence on economics, politics, technology, interpersonal relationships, and cultural interaction in modern society.
Evaluating globalization’s good and bad consequences, investigating its place in influencing global politics, and debating the difficulties and possibilities it brings may provide significant insights into the complex dynamics of our increasingly linked world and mitigate cultural ignorance.
Among the more intriguing cultural research topics include:
- The Impact of Economic Globalisation on Developing Countries
- Viral Diseases Spread and Globalization
- Multinational Corporations’ Role in Globalization
- The Impact of Globalisation on Isolated Communities
- Cultural Diversity Versus Globalization in a Modern Society
- Environmental Sustainability and Globalization
- Globalization and Trends of Labor Migration
- Globalization’s Political Implications
- The Age of Technology and Its Impact on Globalization
- The Growth of Global Governing Institutions Is a Result of Globalization
American Culture Research Paper Topics
The richness and diversity of American culture make it an appealing subject for study. American culture research paper topics may include the global impact of American pop culture, the development, and history of American cuisine, the representation of American identity in movies and novels, the impact of immigration on modern United States society, or the part of Christian traditions in defining American and African culture.
Popular cultural research topics include:
- American Political Culture’s Development
- The Influence of Hollywood on American Culture
- The Role of Mass Media in Shaping American Societal Norms
- The Impact of Immigration on American Cultural Diversity
- American Exceptionalism: Myth or Reality?
- American Pop Culture and Its Consequences
- The History and Significance of Jazz Music in African Culture
- The Portrayal of Race and Ethnicity in American Pop Culture
- The Influence of American Literature on National Identity
- The American Dream: Its Changing Meaning and Societal Implications
Related posts:
- Poetry Analysis: Unboxing Topics and Outlines in a breeze
- Extensive List of 200+ Dissertation Topics for Strong Research
- Pop Culture Essay Topics: Find Out the Pulse of Modern Society
- Business Research Paper Topics: Management, Commerce, Entrepreneurship, etc
Improve your writing with our guides

Psychology Essay Topic: Theories Explaining Human growth and Development

200 Best Ideas for Research Paper Topics in 2023

Reflection Paper Topics: Art
Get 15% off your first order with edusson.
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.
100% privacy. No spam ever.

373 Culture Research Topics & Ideas for Essays and Papers
18 January 2024
last updated
Culture research topics include various human behaviors and beliefs, offering a deep dive into societal norms, values, traditions, and symbols that have shaped and continue to shape civilizations across time and space. Themes encompass many areas, such as linguistics, anthropology, sociology, psychology, history, and arts. Topics also may include investigating the effects of globalization on indigenous cultures, the role of pop culture in shaping societal values, impacts of cultural assimilation, or tracing the evolution of language in a particular region. Studies in this field illuminate the tapestry of human existence, providing rich insights into unique human histories. Thus, culture research topics are not only intrinsically fascinating but also have crucial implications for policy, education, and understanding of identity, community, and coexistence in an increasingly diverse and interconnected world.
Hot Cultural Topics
- Unearthing Indigenous Histories Through Technology
- Cryptocurrency’s Influence on Art and Culture
- Ethical Dilemmas in Genomic Data Sharing
- The Intersection of Environmentalism and Fashion Trends
- Debating Authenticity in Social Media Influencer Culture
- Exploring Minority Representation in Hollywood
- Augmented Reality as a Cultural Experience
- Redefining Gender Norms in Video Gaming
- Street Art as a Political Commentary
- Future of Libraries in the Digital Age
- Culinary Trends Sparked by Plant-Based Movements
- Cultural Shifts in Privacy Perception Post-Social Media
- Language Preservation in a Globalized World
- AI and the Transformation of Creative Industries
- Mental Health Narratives in Popular Music
- Eco-Cities: Blending Urbanism and Sustainability
- Cross-Cultural Understanding Through Travel During Pandemic
- Consumerism and Minimalism: Contrasting Cultural Phenomena
- Unconventional Family Structures in Contemporary Literature
- Futurism in Architectural Design and Cultural Identity

Easy Cultural Essay Topics
- Influence of Digital Art on Cultural Identity
- Food Traditions as Cultural Symbols
- Relationship Between Language and Cultural Heritage
- Rise of E-Sports and Its Cultural Significance
- Virtual Reality in the Realm of Cultural Preservation
- Social Media as a Tool for Cultural Exchange
- Influence of Climate Change on Cultural Practices
- Anime and Manga: Japanese Culture’s Global Reach
- Cultural Perception of Privacy in the Era of Big Data
- Reality TV’s Effect on Cultural Stereotypes
- Cultural Implications of Urban Green Spaces
- Nostalgia and Culture in Retro Fashion Trends
- Understanding Cultural Context in Classic Literature
- Cultural Diversity in Modern Cinema
- Significance of Cultural Festivals in Building Community
- Influence of Sci-Fi on Our Perception of Future Cultures
- Cultural Perspectives on Mental Health in Popular Literature
- Globalization’s Effect on Indigenous Cultures
- Street Food and Its Connection to Local Culture
Interesting Culture Topics to Research for Essays and Papers
- Maori Culture and Traditions
- Intricacies of Japanese Tea Ceremony
- Voodoo Practices in Haitian Culture
- Celtic Traditions and Mythology
- Arab Bedouin Traditions and Nomadic Lifestyle
- Native American Tribes and Their Cultural Diversity
- Balinese Rituals and Spiritual Practices
- The Complexity of Tibetan Buddhism
- Greek Orthodox Customs and Traditions
- Culture of the Sami People in Scandinavia
- Andean Cultures: Incas and Their Descendants
- Mayan Civilization: Ancient Practices and Beliefs
- Yoruba Religion and Cultural Traditions in West Africa
- Nomadic Culture of the Mongolian Steppes
- Diverse Cultural Practices of Australian Aboriginals
- Culture of the Maasai Tribes in East Africa
- Persian Poetry and Its Cultural Significance
- Dance Forms and Culture of Polynesian Islands
- Cultures of the Amazon Rainforest Tribes
- Korean Hanbok and Traditional Dress Culture
Cultural Anthropology Topics for a Research Paper
- Decoding Symbolism in Ancient Mayan Art
- Understanding Power Structures in Tribal Societies
- Exploring Ritualistic Practices of the Australian Aborigines
- Influence of Globalization on Indigenous Cultural Practices
- Rituals and Customs: A Comparative Study Between Maasai and Zulu Tribes
- Investigating Linguistic Diversity in the Amazon Rainforest
- Dynamics of Cultural Adaptation in Refugee Communities
- Indigenous Knowledge and Biodiversity Conservation
- Comparative Study of Death Rituals Across Cultures
- Cultural Contexts of Folklore and Mythology in Slavic Societies
- Digital Anthropology: Social Media and Cultural Practices
- Cultural Perspectives on Gender and Sexuality in Pacific Island Societies
- Transcultural Psychiatry: Mental Health Across Cultures
- Insights into Cultural Healing Practices of Native American Tribes
- Foodways and Culture: A Study of Mediterranean Societies
- Dynamics of Social Change in Post-Colonial Societies
- Material Culture: Analysis of Ancient Egyptian Artifacts
- Cultural Interpretations of Climate Change in Arctic Communities
- Cultural Factors in Public Health: A Case Study of Sub-Saharan Africa
- Sacred Spaces and Cultural Identity: An Exploration of Hindu Temples
Cultural Criticism Essay Topics
- Postmodernism and Cultural Representation in Media
- Interrogating Orientalism: Western Perception of Eastern Cultures
- Deconstructing the Beauty Standard in Pop Culture
- Eco-Criticism and Interpretation of Environmental Narratives
- Analyzing Power Structures in Classic Literature
- Cultural Bias in Artificial Intelligence Systems
- Culture and Censorship: Freedom of Expression in Various Societies
- Unpacking Gender Stereotypes in Advertising
- Culture of Fear: Media Representation of Terrorism
- Colonial Narratives and Indigenous Voices in History Textbooks
- Cyber Culture: The Dark Side of Online Communities
- Cultural Appropriation vs. Appreciation: A Thin Line
- Cultural Hegemony and Minority Representation in Film Industry
- Ethnocentrism in Anthropological Research: A Critique
- Understanding Whiteness: Critique of White Privilege
- Body Image and Self-Esteem: A Critique of the Fashion Industry
- Religion and Cultural Bias in Western Feminist Discourses
- Consumer Culture and Critique of Fast Fashion
- Mental Health Stigma: Cultural Perspectives and Criticisms
Cultural Diversity Topics for an Essay
- Navigating Cultural Diversity in Multinational Corporations
- Multilingualism and Cultural Identity in Diverse Societies
- Cultural Diversity in Urban Design and City Planning
- Influence of Cultural Diversity on Public Health Policies
- Diverse Cultures: Integration Challenges in Immigration Policies
- Cultural Diversity and Ethical Considerations in Clinical Trials
- Understanding Cultural Diversity in Early Childhood Education
- Cultural Diversity in Contemporary Literature: A Critical Analysis
- Representation of Cultural Diversity in the Animation Industry
- Multiculturalism and Its Influence on National Identity
- Promoting Cultural Diversity through Public Broadcasting
- Cultural Diversity and Inclusivity in Tech Industry
- Managing Cultural Diversity in International Space Missions
- Challenges of Cultural Diversity in Peacekeeping Missions
- Influence of Cultural Diversity on Artistic Expression
- Linguistic Diversity and Cultural Preservation
- Cultural Diversity in Global Climate Change Dialogues
- Cultural Diversity and Adaptation Strategies in Sports Teams
- Diversity in Cuisine: Culinary Traditions Across Cultures
- Cultural Diversity and Conflict Resolution in Global Diplomacy
Culture Heritage Research Topics
- Preservation of Indigenous Knowledge Systems
- Exploring Cultural Landscapes and Their Conservation
- Digital Archiving and Cultural Heritage Preservation
- Protection of Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Cultural Heritage Tourism: Balancing Preservation and Promotion
- Intersections of Cultural Heritage and Climate Change
- Restitution of Cultural Artifacts: Ethical Considerations
- Reconstructing Cultural Heritage in Post-War Regions
- Maritime Cultural Heritage: Underwater Archaeology Challenges
- Cultural Heritage and Memory: Significance of Oral Histories
- Revitalization of Endangered Languages: Strategies and Challenges
- Historic Urban Landscapes: Conserving Cultural Heritage in Cities
- World Heritage Sites and Their Sustainability Issues
- Conservation of Ancient Manuscripts and Rare Books
- Sacred Sites and Cultural Heritage: Managing Religious Tourism
- Cultural Heritage and Identity in Diaspora Communities
- Management of Archaeological Sites: Balancing Research and Preservation
- Investigating Looting and Illicit Trafficking of Cultural Property
- World Cuisine as an Element of Intangible Cultural Heritage
Cultural Phenomena Topics
- Unraveling the K-Pop Phenomenon: Cultural and Global Implications
- Cryptocurrency Culture: A New Financial Phenomenon
- Cross-Cultural Analysis of Conspiracy Theories
- Spread of Internet Memes: A Modern Cultural Phenomenon
- Cultural Aspects of the Global Wellness Movement
- Globalization and the Cultural Phenomenon of Fast Food
- Cyberculture and the Emergence of Virtual Communities
- Reality TV and Its Cultural Repercussions
- Influence of Celebrity Culture on Youth Values
- Pandemic Culture: Changes in Behavioral Patterns Due to COVID-19
- Examining the Cultural Phenomenon of Social Activism in Digital Spaces
- Coffee Culture: A Global Phenomenon With Local Variations
- Influence of Anime and Manga on Global Pop Culture
- Cultural Phenomena of Aging Societies in Developed Countries
- Nerd Culture and Its Influence on Entertainment Industry
- Fashion Trends as Reflections of Cultural Change
- Online Gaming Communities as Cultural Phenomena
- Cultural Shifts in Attitudes Toward Mental Health
- The Phenomenon of Remote Work and Cultural Implications
- Cultural Perception and Adoption of Renewable Energy Solutions
Cultural Psychology Research Topics in Culture Studies
- Cross-Cultural Perspectives on Emotional Expression
- Psychology of Superstitions in Various Cultures
- Analysis of Collectivist vs. Individualistic Cultural Psychologies
- Cultural Factors Influencing Child Development
- Cultural Psychology of Grief and Mourning Rituals
- Understanding Perception of Time in Different Cultures
- Body Language and Non-Verbal Communication Across Cultures
- Examining the Cultural Context of Dreams
- Cultural Influences on Human Memory
- Cultural Diversity and Its Effects on Learning Styles
- Cognitive Biases and Cultural Influences: A Comparative Study
- Cultural Influences on Risk Perception and Decision-Making
- Psychological Perspectives on Folklore and Mythology Across Cultures
- Understanding the Cultural Aspects of Empathy
- Interplay of Language and Thought in Cultural Psychology
- Cultural Differences in Coping Strategies for Stress
- Cultural Influences on Perception of Pain
- Influence of Culture on Self-Esteem and Self-Concept
- Psychological Analysis of Taboos Across Different Cultures
Environmentalism and Culture Research Topics
- Cultural Practices in Biodiversity Conservation
- Green Architecture: Cultural and Environmental Interactions
- Cultural Perceptions of Climate Change in Island Nations
- Understanding Indigenous Knowledge Systems in Environmental Stewardship
- Environmental Ethics in Native American Cultures
- Ecotourism and Its Influence on Local Culture
- Influence of Environmental Movements on Contemporary Art
- Cultural Factors Affecting Renewable Energy Adoption
- Influence of Traditional Farming Practices on Biodiversity
- Cultural Aspects of Waste Management Practices
- Sacred Natural Sites and Their Role in Conservation
- Cultural Landscapes and Strategies for Their Preservation
- Impact of Climate Migration on Cultural Identity
- Rituals and Myths Related to Nature Across Cultures
- Impact of Environmental Policies on Indigenous Cultures
- Understanding Cultural Dimensions of Urban Green Spaces
- Influence of Culture on Perceptions of Genetically Modified Organisms
- Culture and the Transition to a Circular Economy
- Perceptions of Water Scarcity in Different Cultures
- Cultural Responses to Deforestation in Rainforest Communities
Gender and Culture Research Topics
- Exploring the Cultural Construction of Masculinity
- Perception of Beauty Standards Across Different Cultures
- Cultural Interpretations of Transgender Identities
- Influence of Cultural Norms on Gender Equity in Education
- Understanding Gender Roles in Indigenous Cultures
- Implications of Matrilineal Societies for Gender Equality
- Cultural Factors Affecting Women’s Political Participation
- Gender Dynamics in Traditional Rituals and Festivals
- Intersectionality of Gender, Culture, and Religion
- Gender Representation in Global Advertising
- Investigating Gender Stereotypes in Children’s Literature
- Cultural Perception of Non-Binary Gender Identities
- Influence of Gender Roles on Career Choices Across Cultures
- Cultural Factors Influencing Maternal Health
- Gender Dynamics in Migration and Displacement
- Influence of Culture on Men’s Mental Health
- Gendered Spaces: A Cultural Perspective
- Culture and Gender Inequity in Access to Healthcare
- Cultural Perspectives on Domestic Roles and Responsibilities
Globalization and Culture Topics
- Understanding the Cultural Implications of Globalized Media
- Cultural Resistance to Globalization in Indigenous Communities
- Globalization and the Spread of English: Implications for Linguistic Diversity
- Influence of Globalization on Local Music Genres
- Exploring Cultural Homogenization in Global Cities
- Food Culture in the Age of Globalization: A Case Study
- Globalization and the Commodification of Indigenous Cultures
- Globalization and the Transformation of Traditional Art Forms
- Diaspora Communities: Navigating Globalization and Cultural Identity
- Transnational Cinema: Cross-Cultural Influences and Globalization
- Implications of Globalization for Indigenous Knowledge Systems
- Globalization and Changing Gender Norms: A Cross-Cultural Study
- Cultural Hybridity in Globalized Fashion Trends
- Internet Culture and Globalization: A Complex Relationship
- Globalization and Its Effect on Cultural Heritage Preservation
- Influence of Globalized Education on Cultural Diversity
- Cultural Adaptation in Global Marketing Strategies
- Globalization and Transformation of Religious Practices
- Impact of Global Migration on Cultural Diversity
- Understanding Globalization’s Effect on Cultural Autonomy
Intercultural Communication Topics
- Intercultural Communication in Multinational Corporations
- Exploring Communication Barriers in Intercultural Marriages
- Interpretation of Non-Verbal Cues Across Cultures
- Intercultural Communication in Virtual Teams
- Analysis of Humor in Intercultural Communication
- Influence of Cultural Stereotypes on Intercultural Communication
- Examining Intercultural Communication in Healthcare Settings
- Challenges of Intercultural Communication in Diplomacy
- Influence of Social Media on Intercultural Communication
- Impact of Language Proficiency on Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Communication in International Development Projects
- Implications of Cultural Taboos in Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Miscommunication: Case Studies and Analysis
- Influence of Cultural Dimensions on Communication Styles
- Intercultural Communication in Refugee and Immigrant Integration
- Strategies for Effective Intercultural Communication in Education
- Investigating the Role of Empathy in Intercultural Communication
- Impact of Intercultural Communication on Global Marketing Strategies
- Ethics in Intercultural Communication: A Critical Review
List of Culture Research Topics
- Cultural Perspectives on Death and Afterlife
- Influence of Pop Culture on Youth Identity Formation
- Understanding Culturally Specific Healing Practices
- Martial Arts as Cultural Phenomena: A Comparative Study
- Street Art and Its Cultural Significance
- Dynamics of Food Culture: Traditional vs. Modern
- Exploring the Cultural History of Tattoos
- Cultural Aspects of Aging: East vs. West
- Cultural Factors Influencing Childbirth Practices
- Language Revitalization in Endangered Cultures
- Cultural Significance of Traditional Dress Codes
- Examining Body Modification Practices Across Cultures
- Indigenous Knowledge and Sustainable Agriculture
- Analysis of Cultural Aspects in Cybersecurity
- Influence of Culture on Parenting Styles
- Representation of Culture in Animated Films
- Cultural Practices in Disaster Management and Preparedness
- Cultural Transformation in Post-Colonial Societies
- Cultural Understanding of Mental Health Disorders
- Decoding Cultural Symbolism in Mythology and Folklore
Multiculturalism and Diversity Research Topics
- Multiculturalism in Children’s Literature: A Content Analysis
- Exploring the Dynamics of Multicultural Teams in Organizations
- Multicultural Education and Student Achievement: An Empirical Study
- Influence of Multiculturalism on Urban Design and Architecture
- Multiculturalism and Its Effect on National Identity
- Implications of Multiculturalism for Social Justice Education
- Perceptions of Diversity in the Media Industry
- Understanding the Challenges of Multicultural Counselling
- Cultural Diversity and Innovation in Start-Up Ecosystems
- Effect of Multiculturalism on Interpersonal Relationships in Diverse Societies
- Diversity and Inclusion in the Tech Industry: Case Studies
- Cultural Diversity in the Judiciary: An International Comparison
- Multilingual Education in Multicultural Societies: Best Practices
- Multiculturalism and Its Influence on Public Health Policies
- Social Cohesion in Multicultural Neighborhoods: A Field Study
- Cultural Diversity in Political Representation: A Global Perspective
- Inclusion of Minority Cultures in National History Curriculum
- Multiculturalism and Its Influence on Contemporary Art Movements
- Challenges of Managing Diversity in Higher Education Institutions
- Multiculturalism and the Transformation of Urban Food Culture
Sociology of Culture Research Topics
- Sociological Perspectives on Cultural Taboos
- Culture and Social Class: Interplay and Implications
- Cultural Factors in the Sociology of Deviance
- Exploring Cultural Capital in Educational Achievement
- Sociological Analysis of Food Culture and Social Status
- Subcultures and Their Influence on Mainstream Society
- Sociology of Cultural Assimilation in Immigrant Communities
- Cultural Factors Affecting Social Mobility: An Empirical Study
- Sociological Dimensions of Popular Culture
- Understanding Cultural Factors in Health Disparities
- Sociology of Aging in Different Cultural Contexts
- Exploring the Sociology of Cultural Trauma
- Cultural Context of Social Movements
- Sociological Analysis of Celebrity Culture
- Cultural Dimensions of Urban Sociology
- Influence of Culture on Social Networks
- Sociological Perspectives on Cultural Appropriation
- Cultural Factors in Gender Inequality: A Sociological View
- Understanding the Cultural Aspects of Gentrification
- Sociology of Culture and Social Change: Case Studies
- Cultural Transformation and Its Sociological Implications
- Understanding Cultural Stigma in Mental Health
- Body Image Perceptions Across Different Cultures
- Cultural Influences on Societal Trust and Cohesion
- Sociology of Music: Exploring Cultural Genres
- Cultural Factors in Youth Gangs and Deviance
- Cultural Nuances in the Sociology of Emotions
- Exploring the Cultural Context of Aging Societies
- Cultural Perspectives on Social Stratification
- Sociological Implications of Intercultural Marriages
- Cultural Narratives in Gender Identity Construction
- Sociology of Art: Understanding Cultural Expressions
- Understanding Cultural Perspectives on Human Rights
- Cultural Factors in Environmental Sociology
- Cultural Interpretations of Religious Symbols
- Sociology of Language and Cultural Identity
- Cultural Influences on Children’s Socialization Processes
- Exploring the Cultural Dynamics of Social Protests
- Sociological Perspectives on Cultural Heritage and Identity
- Cultural Context of Intergenerational Relationships
Subculture Research Ideas
- Gothic Subculture: A Sociological Perspective
- Exploring the Culture of eSports Enthusiasts
- Punk Rock: An Ethnographic Study of Rebellion and Resistance
- Exploring the Vegan Subculture: Beliefs and Lifestyle
- Cosplay Subculture: Identity and Community
- Street Art: A Study of Subcultural Expression
- Influence of Hip-Hop Subculture on Urban Fashion
- In-Depth Study of the Online Gaming Subculture
- Psychedelic Subculture: Perception, Art, and Social Norms
- Understanding the Straight Edge Subculture: Music and Morality
- Subculture and Identity Formation in Adolescents
- Tattoo Subculture: Expressions of Individuality or Conformity?
- Exploring the Subculture of Comic Book Fandom
- Bodybuilding Subculture: Discipline, Lifestyle, and Body Image
- Subcultural Study of Skateboarders: Rebellion or Recreation?
- Hacker Subculture: Values, Beliefs, and Ethos
- Exploring the Subculture of Minimalist Lifestyle
- The Culture of Craft Beer Enthusiasts: A Subcultural Analysis
- Unveiling the Mysterious World of Secret Societies
Western Civilization Essay Topics in Culture Research
- Democracy and Its Origins in Ancient Greece
- Influence of Renaissance Art on Western Culture
- Exploring the Cultural Significance of the Magna Carta
- Western Civilization and the Emergence of Scientific Thinking
- Christianity’s Influence on Western Morality and Ethics
- Enlightenment Thought and Its Influence on Modern Western Society
- Fall of the Roman Empire: A Pivot Point in Western Civilization
- Imperialism and Western Civilization: A Historical Analysis
- Historiography of the French Revolution in Western Discourse
- Industrial Revolution: The Engine of Western Progress
- Influence of Western Civilization on Global Legal Systems
- The Age of Exploration: Western Civilization Expands
- Western Civilization: From Gutenberg’s Press to the Internet
- Interpretations of the American Revolution in Western Thought
- Historical and Cultural Analysis of Western Romanticism
- Contribution of Western Civilization to Modern Medicine
- Development and Influence of Western Classical Music
- The Influence of Western Philosophy on Modern Thought
- The Role of Western Civilization in Shaping Modern Economics
- Western Civilization and Its Influence on Modern Democracy
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles
509 capstone project topics & good ideas, 572 motivational speech topics & good ideas.
Thesis Helpers
Find the best tips and advice to improve your writing. Or, have a top expert write your paper.
50+ Out of the World Cultural Research Paper Topics

You have all needed to develop fast and quality articles, essays and research projects by examining and selecting your chosen topic. The writing ideas in this post were developed by experts and professionals in the cultural field, and thus we highly recommend the topics to all writers, including online writers.
With our back, you will waste none of your energy and time figuring out what and how to write about a given topic. Select your topic today as it makes time and energy cheap.
Let’s begin with defining what culture is:
Culture refers to the way of life of a particular group of people – the behaviours, values, beliefs, and symbols they accept, generally without thinking about them. They are passed on through communication and imitation from one generation to the next.
Below are some of the professionally tailored cultural research paper topics guaranteed to give you a first-class in your assignment. Be sure to use them as inspirations towards substantive writing prompts.
Cultural Research Paper Topics
- Investigating the benefits of cultural studies in promoting brands in international markets.
- Perception differences among youth and the old population of disabled people.
- Examination of different coping mechanisms of being culturally different in society.
- Impact of films, songs, and feminism on promoting women equality.
- Conservation of culture in isolated communities.
- Influence of religion on culture: A case study of the Muslim community
- Cultural commonalities for all human beings on earth.
- Correlation between attitude and sex as tools of culture.
- Exhibition of cultural traits in indigenous and exotic animals.
- How association to particular languages influences culture.
Cultural Anthropology Research Paper Topics
- An evaluation of the cultural anthropology of our time
The effects of cultural anthropology to the missionary.
- The role of women in modern society as opposed to the traditional roles.
- What are the peculiarities of the Zulu community culture in Southern Africa?
- Examination of various religious practices in the United States of America.
The influence of English as a common language on American culture.
- Exploration of the long-term impacts of physical labour on the physical appearance of humans.
- How stigma affects efforts on stopping the spread of sexually transmitted diseases.
- How is the concept of death viewed in Africa?
- What is the anthropological perspective on the development of the modern United States of America?

Cultural Diversity Research Paper Topics
- Evaluate the significance of preserving cultural diversity in the 21st century.
- What is the role of cultural diversity in modern society?
- How pluralism and multiculturalism have impacted the lives of American citizens.
- Associations of psychological counselling to cultural diversity.
- Demonstrate critical thinking about psychology with a special mention on multicultural issues and diversity.
- Effects of cultural diversity in the medical industry as a whole.
- Evaluate the role of cultural diversity in schools
- Impacts of migration on the cultural diversity of Asian land, especially on mental health.
- Cultural diversity’s impact on the interaction process and performance.
Cultural Psychology Research Paper Topics
- Personality and filial piety among British citizens.
- What are the cross-cultural perspectives on human developments in Central America?
- The self and social behaviour among Red Indians in the United States of America.
- Factors that influence cross-cultural psychology.
- Implication of cultural psychology on diversity.
- Life experiences of unemployed graduates in the United Kingdom.
- The relationship between parenting stress and stigma with parent-child interactions in mothers with autistic children.
- Comparative analysis of gender stereotypes of superior thinking in men and emotions in women among students
- How has Covid-19 affected the political atmosphere in the United States of America?
- Analyze the impact that famous artists have on world culture.
- Discuss the evolution of cultural psychology as a topic since the 17th century.
Cross-Cultural Research Paper Topics
- How does culture affect social and emotional development?
- Compare and contrast the features of language and culture.
- Impacts of social organization and history in modern society.
- Members of any culture perceive their behaviour as logical. Validate this statement.
- Determinants of cross-cultural business communication.
- The roles of attitudes toward accents and dialects in creating barriers in international business communication.
- Description of socio-linguistic as a tool of differentiating economic classes.
- Influence of environmental factors on the development and character of cultures.
- Climate and topography affect the transport and logistics, settlement, and territorial organization. Elucidate.
- Describe how Africa’s population size and its density and the availability of natural resources influence the continent toward export and domestic markets.
- Discuss ways in which conceptions of authority affects cross-cultural psychology, more so in India.
- The role of non-verbal communication in promoting culture.
Best Cultural Research Paper Topics
- The evolution of the amount and type of sexism over the years.
- Analysis of the impact of Michael Jackson on popular culture in the world.
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- Reasons for the emergence of female culture in closed communities.
- Influence of native culture on human psychology.
- Causes of assimilation of people in the foreign culture.
- How cultural studies in colleges and universities have helped demystify cultural myths and misconceptions.
- Why children need to stay with their grandparents at least once in a while
You might have considered this task a hard nut to crack, but with the comprehensive guide and topics above, I am sure that you can now navigate your way easily.
We hope that the content developed by our Writing help desk was useful to you, and thus, you have the foundation laid for you to kick off the write up. Save time as time is money and excellence awaits you. Let’s start it. We wish you all the best.

Make PhD experience your own
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Cultural Research Paper Topics
80 cultural research paper topics for students.
The term “culture” encompasses many aspects, such as language, beliefs, religion, symbols, traditions, cuisine, and others, that help to characterize a particular group of people and show their way of life. And it gives a lot of opportunities for writing research papers about culture.
How to Select the Best Cultural Research Paper Topic?
Students, who have such assignments, can choose from a wide variety of topics and focus on a particular group of people or explore one of the cultural aspects of different groups in society. But how to choose the best research paper topics about cultural studies? Let us help you with it.
Where to Find the Best Topic for Your Essay
There are a lot of sources that can help you to decide what to write about in a cultural research paper. Culture covers many aspects of our life, so sometimes all you need to find exciting topics is to look at people around you or your habits and traditions. However, here are some sources that also can help:
- Museums and galleries
- Journals of cultural studies
- Interviews and podcasts
- Study materials.
All you need to find a decent topic is to focus on what group of people or aspect of culture you’re interested in and spend time exploring all relevant current issues and hot topics.
However, if you’re not sure what you want to research, you can always rely on us! Our expert writer will create a perfect research paper topic about culture for you.
How to Formulate a Topic for a Cultural Research Paper?
The next step after choosing an area you want to research is to specify and formulate a topic. It will help you to outline the scope of your research and make it clear to readers what questions you investigate in your paper. Thus, it is necessary to take some time and think about how to formulate the topic of your research paper precisely. Here are some tips:
- Pay attention to the instructions provided by your professor.
- Indicate the scope of your research and set the limitations.
- Write down all questions related to the topic which you want to research.
- Think about how to indicate what you investigate in your paper accurately.
This way, you will understand the precise area of your research. But, if it seems complicated for you, don’t be afraid to ask for help from professionals. Place your request now on our website, and we will help you create a high-quality cultural research paper.
Great List of Cultural Research Paper Topics
If you’re out of ideas and need inspiration, these lists are for you! Here you can find diverse cultural topics that are great for writing a research paper. We are sure that our ideas will help you to decide what to write about.
- Diversity of Chinese Ethnic Groups and Their Culture
- Untranslatable Words of Different Languages
- The Impact of Heavy Metal Music on Different Cultures
- What famous paintings can tell us about the cultural background of artists
- Does global culture exist?
- The cultural domination of one country over another: Examples in History
- Religious beliefs’ effects on culture
- Does the Performance of Foreign Retailers Depend on the Host Country Culture?
- Does Popular Culture Promote Immoral Values?
- What Does the Term “ American Culture ” Mean?
- What Characteristics Define the Culture of South Asian countries?
- The legacy of the Roman Empire in the modern world
- The Key Elements of Spanish Culture and History
- Cultural Heritage of Egyptian Civilization
- The Impact of Cultural Background on Interpersonal Communication Models.
15 Cultural Anthropology Research Paper Topics
- Offensive Hand Gesture Around the World
- The Role of Social Status in South Korea
- The View of Marriage in Central Asian Countries
- Different Views of Death in Different Religions
- People’s Perception of Late Marriages in China
- The Importance of Literature for Spreading New Ideas
- Gender Roles in the Philippines Society
- Islamophobia: Main Causes and Public Opinion
- Homeless People in THE US: The Causes and Consequences
- Does a Person’s Subculture Show via Their Clothing?
- Feminism in Countries With Patriarchal Cultures.
- Examining How Different Nations Feel About the Monarchy.
- Ancestors and Their Role in Society
- Cultural Respect in Different Countries
- A Unique Cultural Relationship Between Children and Grandparents.
15 Cultural Psychology Research Paper Topics
- Cross-Cultural Psychology: How Culture Influence Our Behavior
- Cultural and Psychological Differences Between Western Europe and South-East Asia
- What Are the Cultural Conflicts ?
- The Psychological and Sociological Adaptation of Foreign Students
- Comparison of Future Goals of Teenagers in China and the UK
- Gender Stereotyping in Different Countries
- Stressful Parenting With Autistic Children
- Attitude to Mistakes in Asian Countries
- Importance of Marriage in Chinese Society
- Politeness and Respect in Different Cultures
- Types of Cultural Models
- How Cultural Psychology Affects Diversity
- Treatment Methods for Psychiatric Issues Across Cultures
- The Function of Self-Esteem Across Cultures
- The Development of Cultural Psychology.
15 Cultural Diversity Research Paper Topics
- The Link Between Migration and Cultural Diversity
- Cultural Diversity of India: Causes and Characteristics
- Family Traditions Across the World
- Significant Challenges of Intercultural Marriages
- Ethnic-Cultural Bullying in Chinese Schools
- Communication in the Multicultural Society
- How to Effectively Manage a Business With International Partners
- What Is Ethical Relativism ?
- Cultural Stress: How to Deal With It in a Foreign Country?
- The Impact of Multicultural Environment in the Workplace
- The Challenges of Studying Abroad
- The Impact of Westernization on Cultural Diversity
- Sex-Related Attitudes and How They Differ in Each Culture
- The Benefits of Ethnic Diversity
- the Importance of Cultural Competency for Clinical Nursing Practice.
10 Socio-Cultural Topics for Research Paper
- The Impact of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem among Adolescents.
- Exploring the Relationship between Cultural Diversity and Team Performance in the Workplace.
- Analyzing the Influence of Gender Stereotypes on Career Choices.
- Investigating the Role of Education in Promoting Social Equality and Social Mobility.
- Examining the Effects of Immigration on Cultural Identity and Integration.
- The Influence of Pop Culture on Youth Attitudes and Behaviors.
- Understanding the Societal Implications of Online Dating and Relationships.
- Exploring the Connection between Socioeconomic Status and Health Disparities.
- Analyzing the Impact of Mass Media on Public Opinion and Political Discourse.
- Investigating the Role of Cultural Heritage Preservation in Community Development.
10 Cultural Research Paper Ideas for Discussion
- The Nation’s Economy and the Residents’ Sense of Self-Worth: Is There a Connection?
- How Do Languages Affect Culture?
- The Impact of Culture on Fashion: Research on International Fashion Trends
- How Does Culture Influence Our Perception of Race and Body?
- The Role of Tattoos in Modern and Ancient Cultures.
- Sexism in Modern Society
- Accents and Dialects: How They Impact the Interpersonal Communication
- The Connection Between Culture and Shopping Habits
- The View of Self-Education in Different Countries
- How Does American Culture Impact Other Parts of the World?
If you find a subject complex or incomprehensible, you can request help from our experienced writers. We are competent in dozens of topics and disciplines and always are willing to handle your tricky assignments. Are you still wondering, “Could someone write my paper for me online?” Our experts are here to meet your deadlines and order instructions sticking to the academic standards. Your high results are closer than you believe!

I have always wanted to combine my passion for writing with a desire to help people. Now, I have a perfect job where I can express myself through my imagination and assist students with their assignments as well.
- All categories
- Essay Topics (39)
- Research Paper Guides (11)
- Research Paper Topics (39)
Biology Essay Topics
History essay topics, law essay topics.
- Write My Research Paper
- Research Paper for Sale
- Research Paper Help
- Buy Research Paper
- Cheap Research Papers
- College Paper Help
- Buy College Paper
- Write My Term Paper
- Paper Writing Service
- Pay for Paper
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Term Paper For Sale
- Custom Term Paper
- Term Paper Help
- Buy Term Paper
- Write My Philosophy Paper
- Term Paper Writer
- Pay for Research Papers
- Nursing Paper Writing Service
- Buy Nursing Paper
Using the Cultures Framework for Research
- Open Access
- First Online: 23 March 2023
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Janet Stephenson 2
4093 Accesses
This chapter is designed to guide academics and students who wish to undertake research using the cultures framework. It offers a structured approach to cultural research that can be used by researchers from diverse disciplinary backgrounds. The variables and dynamics depicted by the framework are able to be discovered, described and analysed using a wide variety of qualitative and quantitative methodologies. The framework can also be used as a meta-theoretical framing. It invites interdisciplinary endeavours and multi-method research approaches, and operates well as an integrating framework. Further research on culture and sustainability is needed to build up a better understanding of, amongst other things, universal cultural processes, transforming unsustainable meta-cultures, and the multiple roles that culture can play in sustainability transitions. The chapter concludes with suggesting further potential contributions to sustainability research from each of the nine perspectives of culture described in Chapter 2 .
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
- Sustainability
- Qualitative methodology
- Quantitative methodology
- Multi-method
- Meta-theoretical
- Interdisciplinary
- Integrative
- Cultural theory
Introduction
I cannot think of a single research topic relating to the human/sustainability nexus that does not have a cultural component. From globally influential paradigms and the practices of fossil fuel majors to the operations of small businesses and the daily lives of households, culture is involved. Yet as a research topic, culture is often remaindered—applied as a loose label for a collection of features of social existence that sit unexamined alongside other deeply analysed phenomena. Apart from the fraction of researchers trained in forms of cultural analysis, the slippery, qualitative features of culture can seem too hard to investigate by researchers interested in sustainability issues. The cultures framework addresses this difficulty by offering a structured way to approach cultural research that can be used by researchers from almost any disciplinary background. As described in earlier chapters, the framework has been sufficiently tested to have confidence that it can fruitfully guide research endeavours.
Over the 12 years since the framework was first introduced in the literature, it has been used with a broad range of research approaches. It has been used with qualitative methods, quantitative methods and mixed methods. It has been used to formulate research design, as an analytical frame for the interpretation of existing data sets, and as a conceptual framing for meta-reviews of data. It has been used by individual researchers from a single discipline as well as by interdisciplinary research teams. It has underpinned undergraduate studies, postgraduate dissertations and extensive research programmes. It has been used to design research-based interventions and as an evaluation framework. And as shown in earlier chapters, it has been applied to a wide variety of problems and fields of enquiry.
This chapter is designed to guide academics and students who wish to undertake research using the cultures framework. For most of the chapter, I discuss the use of the framework to explore the interplay between culture and sustainability. By providing a structure for research investigations, the framework can help reveal what cultural ensembles, consisting of what cultural features, have causal relationships with what outcomes, affected by what external influences. It can help determine who are the actors within the culture group under study, and which cultural ensembles are already more sustainable than others. By examining the internal dynamics of culture, we can see how this leads to the sustainability outcomes. By studying cultural ensembles in relation to external influences, we can gain insights into why cultures remain static or evolve. By investigating the scope of agency of cultural actors, we can better understand why it is difficult for them to change, and who comprise more powerful organisations or institutions. And by examining whether a culture is dynamically stable or has the potential to change, we can gain insights into whether transformation is possible. Of course, not all these questions will be relevant to a given study, and the choice of questions will be determined by the particular context of the research and the sustainability issues at stake, but this gives an indication of the types of questions for which the framework can be used.
Towards the end of the chapter, I discuss how the framework can also be used as a meta-theoretical framing. In this sense, it can be used as an overarching structuring device for multidisciplinary, multi-theoretical and multi-method research, as with the examples of the Energy Cultures research programmes discussed in Chapter 7 . As covered in Chapter 4 , it builds on mature social science and cultural theories, and the framework acts as a structuring device for reaching into these fields of knowledge to examine dynamics and causal mechanisms in greater depth. I finish by discussing how the diverse and currently fragmented cultural theories discussed in Chapter 2 can make a stronger contribution to sustainability research.
Core Concepts
On the assumption that some readers may skip directly to this chapter, I will first recap on some key concepts. First, what culture is not. Culture is not about how people operate as individuals, each with their unique personal history and psychology. It is not about demographics. It is not about features that all humans share as social beings. All of these may interplay with culture, but they are not its defining characteristics. Second, the cultures framework is not just about culture. Cultures do not exist in a vacuum, and the framework draws attention to important variables that shape culture and mediate its implications for sustainability outcomes.
Recapping on what I mean by culture in this context, I describe it in Chapter 4 as comprising distinctive patterns of motivators (norms, values, beliefs, knowledge and symbolism), activities (routines and actions) and materiality (products and acquisitions) that form dynamic ensembles which are shared by a group of people and learned through both cognitive and bodily processes . These cultural ensembles can be most simply described as similar ways of thinking, doing and having that are evident across a group of people. Depending on the focus of research, this could apply to the cultures of people in their everyday lives, or the cultures of organisations or businesses, or cultures at even broader scales of institutions and ideologies.
Rather than focusing on describing groups that we typically think of in cultural terms (e.g. ethnic cultures, youth cultures, American culture), the framework invites inquiries into actors and their cultural ensembles that have implications for sustainability. Relevant actors may be identified at any scale: individuals, households, communities, organisations and beyond. Culture can be investigated in relation to a sustainability problem in both a causal sense and in the way in which cultural dynamics can resist change. Culture can also be investigated as part of sustainability solutions in the sense that many existing cultures are exemplars of sustainability. Cultural change can be a creative and fast-moving force for sustainability transitions.
The range of concerns of sustainability is exemplified by the United Nations’ 17 Sustainable Development Goals (United Nations, 2015 ) but as discussed in Chapter 1 , the SDGs are only one perspective on sustainability. More critical perspectives suggest that sustainability will not be achieved without more radical change to established systems of production and expectations of consumption. The framework does not predetermine what is meant by sustainability outcomes—this is left to the researcher to determine for their particular context.
The cultures framework has evolved over time. All the research examples I included in previous chapters used earlier terminologies (‘energy cultures framework’ or ‘sustainability cultures framework’) but the core concepts have changed little over time apart from becoming more generic. Earlier versions have produced sound and fruitful findings, and there is no reason why researchers cannot continue to use it in its earlier and slightly simpler form, especially those wishing to take their first forays into this field, in which case the guidance in Stephenson ( 2018 , 2020 ) will be helpful. In this chapter, I continue to use examples from this prior research, but describe how researchers can undertake inquiries using the revised cultures framework which is presented in Chapter 4 . I encourage readers of this chapter to return to Chapter 4 for fuller descriptions of the language, elements and dynamics of the revised framework.
A Guide to Research with the Cultures Framework
The framework can be applied in many different ways to support research processes. One way is to simply use the diagram of the cultural ensemble (Fig. 8.2 ) as the basis for describing a culture—its distinctive elements and their dynamics. It can be surprisingly difficult to explain what culture is, and these concepts give a solid foundation for identifying cultural features in any given context. At my university, some lecturers ask students to undertake at-home research to describe their own cultural ensembles that relate to energy use or greenhouse gas emissions. The diagram showing the ensemble, agency barrier and external influences (Fig. 8.5 ) has been used as the basis for discussions about research culture in university departments, and by research organisations to analyse how their own culture may be holding them back from undertaking transformative research. In these instances, it can be a tool for self-reflection, enabling actors to understand and articulate elements of their culture and constraints on change.
But more commonly, the framework is used by researchers in its full form (Fig. 8.1 ) for sustainability-related investigations. Some studies primarily seek to describe the cultural characteristics of a particular population. Examples I have discussed in earlier chapters include cooking cultures in Zambia, energy cultures in rural households in Transylvania and mobility cultures in New Zealand. Studies have also used the framework to compare cultures within a population. These have generally sought to explore the contribution of cultural differences to sustainability outcomes. Examples discussed in previous chapters include identifying varied cultural ensembles across populations in relation to energy consumption, energy efficiency and water consumption. Others have explored aspects of culture as influences on people’s readiness to engage in new collective behaviours, their responses to efficiency retrofits and as a factor in nations’ willingness to decarbonise.
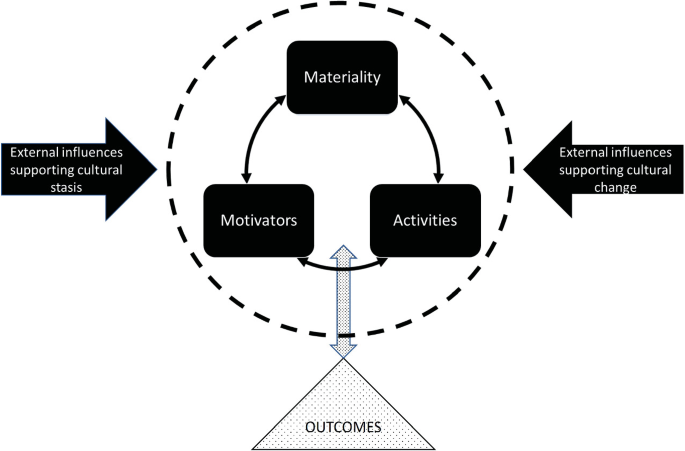
The cultures framework
The framework is also useful for exploring barriers to cultural change. Studies discussed in earlier chapters have identified cultural characteristics that help explain resistance to change in the US Navy, failures to achieve desired levels of change in social housing interventions and cultural barriers to change in academic air travel. Chapter 7 discusses at length how the framework can be used as a basis for policy development and to underpin the evaluation of interventions.
The following section describes how to use the revised cultures framework to underpin research. For easier reference, I repeat here (as Fig. 8.1) the complete cultures framework diagram (first appearing as Fig. 4.8 in Chapter 4 ). The section is ordered as a step-by-step process, although it should be noted that not all research will involve all stages, and some research may proceed in a different order or head in different directions. Following this, I describe the range of research methods that have so far been used with the framework, and its methodological inclusivity in general.
Research on culture is research with people. In exploring what is needed to achieve societal transitions towards sustainability, researchers might wish to learn from groups and organisations that have already grappled with what it takes to live sustainably. They may wish to explore unsustainable cultures that seem unlikely to change. They might seek to work with culture groups or organisations that wish to change but can’t, or with those that are already on change journeys. In any situation, the research process and its outcomes have the potential to destabilise established beliefs, ways of life and social processes. Social research is a serious business and must be undertaken ethically and with the consent of, and ideally in collaboration with, those with whose lives you may disrupt.
Determining the Sustainability Outcomes
The cultures framework theorises that cultural ensembles have a causal relationship with sustainability outcomes, a concept that is conveyed by the two-headed arrow in Fig. 8.1 . The starting point for research design could be at either end of the arrow. If the sustainability outcomes to be examined are predetermined (e.g. energy consumption, equity, waste reduction), the research might seek to characterise different cultural ensembles within the population that have a causal relationship with these outcomes. Alternatively, the outcomes may be uncertain at the outset, but will emerge from the study. For example, research on the cultural ensembles of elderly households may reveal multiple sustainability implications such as health outcomes, energy expenditure and carbon emissions.
As discussed earlier, the concept of sustainability outcomes can be as broad or as specific, and as conservative or as radical, as the researcher wishes to make it. To be useful for the purposes of the framework, outcomes ideally are measurable (i.e. empirical evidence is available as to whether that outcome is improving or degrading) or at least able to be qualitatively described and compared. Outcomes can be uni-dimensional (e.g. a measure of water quality) or might consist of multiple interconnected qualities (e.g. health, biodiversity, equity). Outcomes may be of widespread benefit (e.g. reducing greenhouse gas emissions) or directly beneficial to the households themselves (e.g. improved health).
The double-headed arrow between cultural ensembles and outcomes also reminds researchers that if outcomes change, this changed context can become a further external influence. For example, if a farmer introduces practices that result in cleaner rivers and streams, this may create positive reinforcement for further cultural change. The farmer may enjoy being able to catch fish again, or seeing their children swimming, or hear positive feedback from community members, and may be encouraged to do more. Research on this kind of feedback could help identify whether and how positive affirmation from more sustainable outcomes can lead to ongoing cultural transformation.
Determining the Cultural Elements and Their Interactions
At an early point in the research process, it will be necessary to determine both the scope of the cultural ensemble and the scope of the member actors. The cultural elements to be studied will ultimately be determined by the sustainability outcomes you are interested in and the actors you are focusing on. For example, if you are interested in carbon emissions from a business sector, the obvious cultural actors to focus on would be those businesses, and the elements to study would be the motivators, materiality and activities that have a direct relationship to carbon emissions. However, from identifying this first-order group of actors, it may become clear that other actors also play a role. It may prove more useful to focus on a sub-group within the business such as senior leadership, or shareholders, or alternatively it may prove important to examine cultural factors at broader scales, such as at the sector level, or within suppliers for these businesses. As a researcher, be open to which group/s of actors it might be most useful to focus on. Depending on the research aim, it might be more useful to gain a rich understanding of the cultural ensembles of a small number of actors, or alternatively to investigate a narrow range of cultural features across a much larger population.
You may find it is useful to examine cultures at multiple scales. Cultures are identifiable and discussable from a minute scale, such as the cultural ensemble of a particular actor or organisation, to massive scales, such as the distinctive and enduring features of Western civilisation. You may find it useful to study the ways in which culture can act as structure—a high-level ensemble of beliefs, symbolism, practices and institutions, which shape other cultures that have less power and reach. The framework is relevant to supporting research at any scale and scope.
The next step is to determine which cultural features are most relevant to your study. The core variables of the framework reflect concepts about culture that repeatedly appear in cultural theories (see Chapter 3 ). Materiality comprises items that are made, acquired, owned, accumulated, held or nurtured by cultural actors. Activities are frequent and infrequent actions undertaken by cultural actors. Motivators are shared aspects of cognition that include norms, values, beliefs, knowledge and meanings (Fig. 8.2 ). Which specific features comprise the ensemble for the purposes of your research will depend on the sustainability outcomes, the nature of the actors and of course your interests as a researcher.
I have described a cultural ensemble as a generally consistent pattern of materiality, motivators and activities displayed by an actor or group of actors, but all three may not have equal pertinence depending on the issue—for example, beliefs, meanings or understandings may be more relevant in a particular case than activities or materiality, and vice versa. Cultures will rarely be distinguishable by unique sets of cultural elements; there may be a great deal of overlap between the ensembles of culture groups. The ways in which they are differentiated will be determined by the research context.
When doing research with the cultures framework, how deeply to drill into each element will depend on the nature of the study. For example, in relation to ‘motivators’, many studies to date have focused on depicting norms, because this was the terminology of the original cultures framework. Other studies using the framework have explored morals, meanings, values, knowledge and beliefs, which is one of the reasons for replacing ‘norms’ with ‘motivators’ in the revised cultures framework. In terms of activities, some studies have focused on routines while others have been more interested in one-off or occasional actions. Some have centred on one type of material item, while others have been interested in material assemblages. The nature of the topic should shape the focus of the research, and the researcher should hold open the possibility that relevant but unsuspected cultural features may emerge in the course of the research.
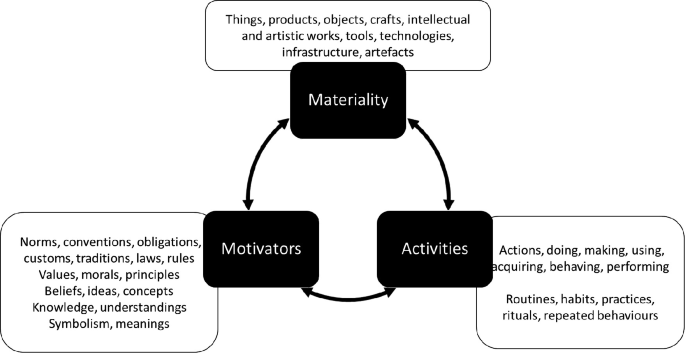
The cultural ensemble—the core elements and their dynamics
Although the research process will likely identify specific cultural features that can be directly causally related to the outcomes (e.g. the presence of particular technologies or practices), it is the cultural ensemble and dynamics between cultural features that make it ‘cultural’. Research should therefore seek to go beyond simply listing cultural features that bear a relationship to the outcomes of interest, to considering how they interact. Motivators, activities and materiality form the interconnected ‘system’ of culture, as indicated by the curved arrows in Fig. 8.2 . How people think influences what they acquire and how they act; people’s activities partly determine what they have and how they think; and the things that people have influence what they do and how they think. Exploring these interactions is critical to understanding how culture operates.
When considering the scope of cultural features to study, some may emerge as more significant than others depending on the sustainability outcomes you are interested in. For example, although sustainability research often focuses on routines or habits, it could be that in some instances, irregular or rare actions have the biggest impacts (noting that these can be equally culturally driven, such as the choice of a new house or whether to buy a car). In fields that you are familiar with, you may have a better chance of an ‘educated guess’ about which cultural features to start investigating, but you may be surprised. In research on household energy efficiency, we started by assuming that people’s values would strongly shape how efficient they were, but we found no consistent relationship between values and actions (Mirosa et al., 2011 ). So keep an open mind and, of course, explore literature in the field beforehand.
There will always be variability in the extent to which actors adopt cultural ensembles. Cultural uniformity is a myth—in reality, actors will have greater or lesser adherences to the ‘signature’ ensemble that is identified in research. This is not a problem, and indeed can provide useful insights into variability and opportunities for change. For example, if you are interested in sustainable transport, you might find that almost all actors own fossil fuelled cars, but some will use more fuel than others. Car owners will all have driving skills, but some may be more efficient drivers than others. All might drive their cars regularly, but some may drive more frequently than others. From a high-level perspective, they all share a similar mobility culture—one that is dependent on cars and fossil fuels—but if you drilled down you could identify variations in that culture. Where you choose to place your inclusion–exclusion delineation around this group, and whether you choose to segment it into sub-groups, will depend on the purpose of your research.
Ultimately, it doesn’t pay to agonise too much about exactly where to draw a line around the actors and cultural ensembles to study. What we’re interested in as researchers is finding patterns that reflect general similarities in cultural features which relate to sustainability outcomes. It is about sense-making through identifying fuzzy patterns of similarity and difference, which is more fruitful than assuming that everyone is identical.
Determining Cultural Vectors
If you are interested in how culture is transmitted, learned and adopted, you may also wish to examine the role of cultural vectors (Fig. 8.3 ). As discussed in Chapters 4 and 6 , vectors include such things as sensory encounters, forms of communication, bodily learning and semantic knowledge that are absorbed from sources such as social interactions, media, bodily experiences and formal learning. Through cultural vectors, people come to adopt similar activities to others, and/or acquire or make similar material items, and/or develop similar norms, aspirations, understandings and other motivators. Vectors are how people learn culture, how it is socially reinforced, and how new cultural concepts are passed from actor to actor.
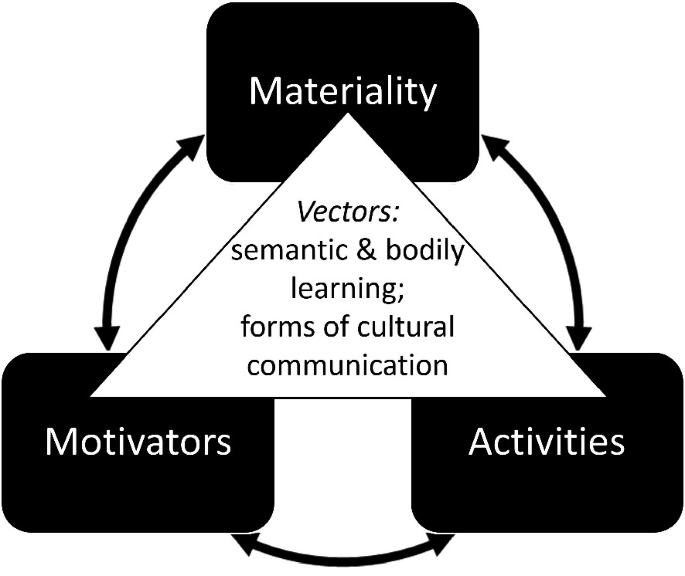
Cultural vectors—the means by which culture is learned and shared
Cultural vectors will not necessarily be important for all research, but they can help reveal processes of cultural continuity and cultural change. In New Zealand research, for example, we asked householders about alterations they had recently made to improve the heating in their homes, and found that family and friends were by far the biggest influence on their decision. Hearing others' stories of change and experiencing the warmth of others' homes were far more influential than information campaigns, online information or advisory services.
Determining the Agency Boundary
Culture is most often used to describe shared characteristics across a population, but the cultures framework asks researchers to identify a subset of cultural features: those that are both particular to their chosen actors and that could potentially be changed by those actors. This demarcation is indicated in the cultures framework by the agency boundary, shown as a dashed circle around the core elements of culture (Fig. 8.4 ). The boundary reflects the capacity of the actor to make choices regarding their cultural ensemble. It distinguishes between elements of culture that are particular to and/or controlled by the actor group under study and those that are particular to and/or controlled by others. The actors’ capacity may be constrained by many things, such as their financial circumstances, their age or gender, their education or their familiarity with bureaucratic systems.
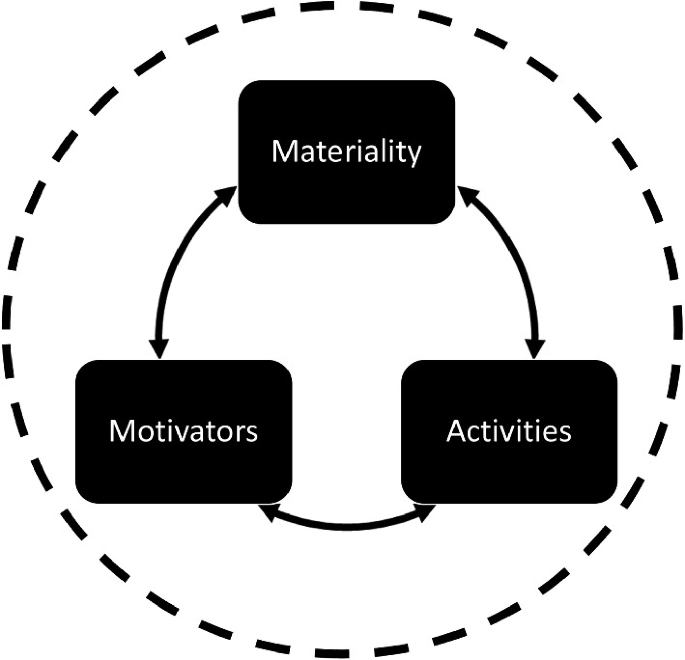
Depicting the agency boundary
In Chapters 4 – 6 , I describe several examples of how this agency distinction is made and used in research. One example is of people on low incomes living within rental housing; the outcomes of interest are energy consumption and wellbeing. Here, the house and chattels owned by the landlord are not considered part of the tenants’ energy culture because tenants have no control over them. The tenants’ cultural ensemble comprises the dynamic package of motivators, activities and materiality that they enact within those constraints. As well as being shaped by the landlord, their energy culture will be shaped by additional influences beyond the agency barrier, such as the cost of power, government policies and other external influences. Another example is personal mobility, where household actors’ cultural ensembles are strongly shaped and constrained by matters beyond their control, such as urban form, the availability of public transport, the safety of walking and cycling and government policies.
The agency boundary in the cultures framework thus invites researchers to differentiate between cultural features that are specific to the group they are studying (within the dashed circle), and other influences that shape (but are rarely influenced by) that culture. It also invites consideration of the factors that are limiting their agency, which may become highly relevant in studies where actors are unable to become more sustainable because of agency constraints. This invites the researcher to consider the implications of differentials in power, the relative responsibility for sustainability outcomes between actors within the agency boundary and those outside it, and their relative ability to act to alter these outcomes. Cultural features beyond actors’ agency belong in ‘external influences’ which may include more powerful cultures.
Determining the External Influences
External influences are exogenous factors that significantly shape the culture that is under study, and are conceptually located outside the agency boundary (Fig. 8.5 ). As discussed in prior chapters, external influences come in many forms, including qualities of the environment and infrastructure, purposeful policies and laws, pricing regimes, availability of technologies, and broadly accepted beliefs and conventions. For research purposes, it will be important to identify external influences that in some way affect the cultural ensembles under study, and thus ultimately affect the sustainability outcomes. They may, for example, reinforce existing cultural ensembles, erode the integrity of cultures that are already sustainable, force actors to become more unsustainable or support cultural change in a more sustainable direction. Depending on the research focus, some external influences may be apparent from the outset of the study, while others may be obscure and will need to be elicited through deep engagement with cultural actors. External factors that clearly have no influence on the culture under study can be ignored for the purposes of cultural analysis.

External influences on cultural ensembles
External influences can also be interpreted as broader cultures that influence the culture you are focusing on. For example, the mobility cultures of citizens are strongly shaped by cultural features of the municipality. A council that decides to invest its transport funding primarily in new motorways is not doing so arbitrarily. The decision will have emerged from a well-established system of beliefs, understandings, aspirations and organisational practices within the council—in other words, their culture. In researching external influences, it may therefore be important to look beyond their presenting qualities to understand the cultures within which they are embedded and replicated.
Another external influence to consider is your own impact on culture as a result of the research process. By asking questions of research participants, you are likely to be raising their own awareness of aspects of their culture that they may not have considered previously. In your interactions, even if it is not intended, you may make them more aware of the sustainability outcomes of their cultural ensembles, and/or aware of disjunctions between, say, their beliefs and practices, or between their aspirations and material possessions. Your interactions may also cause them to develop new understandings about the sustainability issue of interest, or open their eyes to external influences that they had not previously been aware were shaping their culture. The research process is never neutral, so be aware of how your work may influence your participants’ cultures, ensure that your work is carried out ethically and does no harm, and possibly build an evaluation of your impact as a researcher into your research.
Investigating Cultural Stability
Some cultures change very little over time, or at least in the features that give rise to sustainability outcomes. Some enduring cultural ensembles may be positive examples that research can learn much from, such as communities and organisations that have consciously set out to become more sustainable and have maintained that over time. Other cultural ensembles are deeply problematic from a sustainability perspective, and yet continue to endure. We can see this with highly consumptive lifestyles amongst many in the Western world, with beliefs in the value of consumption for its own sake, aspirations for material items goaded by the media (and today, by social influencers), practices of shopping valued in their own right and made more unsustainable through the proliferation of short-lived products, and wellbeing equated with more (or more wealth-signifying) possessions. The cultures framework offers a structure for exploring how and why many unsustainable cultural ensembles change little over time. It would be helpful to review the examples of research into cultural stability discussed in Chapter 5 .
Research into cultural stability might start by examining actors’ cultural ensembles, exploring relevant motivators, material assemblages and activities, and the extent to which these are aligned and mutually supportive. It may investigate cultural vectors in order to understand how cultural attributes are learned, reinforced and conveyed to new members. It would usefully identify what external influences (including structures, institutions and broader-scale cultures) are supporting the culture in its current form and enabling its continuance. It may be useful to look back in time and identify what has shaped the culture you see today. Unpacking these dynamic interactions can help explain how and why this culture is resistant to change.
Understanding these dynamics is particularly important if your research is seeking to understand why change interventions have failed to achieve their targets. Exploring culture as a dynamic system can reveal why change in one external influence or in a single cultural feature (e.g. new knowledge or a new technology) may make little or no difference to sustainability outcomes; for example because its impact is moderated by other cultural dynamics that tend to stabilise the cultural ensemble. Even if some aspects of culture (e.g. values, aspirations) are aligned with sustainable outcomes, other aspects (e.g. routines, agency limitations, external influences) may prevent or limit overall change. It is critical to gain a better understanding of the dynamics of cultural stability if we are to achieve widespread sustainability transitions.
Investigating Cultural Change
The cultures framework can also underpin research on how cultures change. From a sustainability perspective, your investigation might be into positive change, such as new cultural features being adopted with cascading impacts on the entire cultural ensemble. Of particular interest here might be how positive change processes are initiated, and the consequential effects on culture. An example that I described in Chapter 6 was how the replacement of kerosene lamps with solar lights in Vanuatu had a domino effect on many other aspects of culture including everyday practices, gender roles, beliefs, and aspirations for other solar and digital technologies. Your study could equally focus on negative cultural change, seeking to understand how sustainability-oriented cultural characteristics have been lost. For example, in Chapter 6 I described a Māori community where degradation of the inshore fisheries meant that community members could no longer gather traditional foods. The inability to undertake practices resulted in a loss of knowledge and skills that had previously sustained the fishery.
With the cultures framework as a structuring device, a researcher can explore what external influences might be tending to encourage change, as well as what changes are already occurring within that culture and whether these are leading to shifts in other cultural features. In the previous section, I discussed how cultural ensembles could become resistant to change due to strong alignments between motivators, activities and materiality. In contrast, systems where there are misalignments (e.g. aspirations are different to practices; material items don’t fit with beliefs) there is a greater potential for instability, innovation and change. Researchers interested in the potential for change might wish to examine the degree to which the relevant cultural elements are aligned.
Studying the processes of cultural change is critically important to sustainability transformations at all scales. The cultures framework can help to systematise analysis of where cultural change starts, whether it leads to consequential change to the cultural ensemble, the sustainability consequences of this change, and whether incipient changes are prevented by other factors. Cultural change is unlikely to occur all at once—it may involve incremental adjustments to the ensemble over time (e.g. a normative shift may precede a behavioural shift, or a new technology may precipitate new practices). Change also will not be uniform across a culture group, so the analysis may need to include identification of which actors have first made these changes, and through what vectors this has become more widely adopted. More research is needed to better understand the uneven, incremental processes of cultural change as well as the circumstances in which rapid transformation can occur.
People within a culture group rarely get to alter the more powerful external influences shaping their culture. But sometimes it happens, and this is possibly the most powerful driver of transformational change, as discussed towards the end of Chapter 6 . This is where cultural changes spread widely across less powerful actors, and membership of the new culture group grows to the extent that it starts to have influence beyond the agency barrier, reshaping the motivators, activities and/or materiality of more powerful actors. If researchers are interested in the potential for radical sustainability transformations, they should focus on the potential for outward as well as inwards flows through the agency barrier. The urgency of the sustainability crisis means that we need to know as much as possible about how to achieve rapid and widespread transformations of dominant unsustainable cultures.
Having an Impact
By now, your research will have produced an understanding of the various elements of the cultures framework and how they interact dynamically, and any external influences that are tending to prevent or enable change. You will understand the limits of actors’ agency, sub-cultures may have been identified and you may have also discovered cultural influences at other scales. You will have gathered evidence as to whether the cultural ensemble has positive or negative outcomes for the relevant measures of sustainability. You will know whether the culture is in the process of change or is resilient to change, and why this may be the case. If the ensemble has poor sustainability outcomes, your findings should indicate whether it has some latent potential for more sustainable change and possible ways in which change could be initiated or supported to achieve more sustainable consequences.
As a researcher, you might want to apply your findings further to actively help in the sustainability transition. Does it show a culture that already has great sustainability outcomes? If so, what can we learn from this and how can this success be supported and amplified? Does the research show a culture that is stuck in unsustainable patterns and unable to change? If so, where are the opportunities to support change? Does it show a culture that is gradually becoming more sustainable but has a way to go? If so, how can that journey be supported? Does is show a culture where attempts have been made towards greater sustainability but those attempts have been unsuccessful? If so, how can your findings help show why this might be the case?
As with many of the research projects using the cultures framework, you could develop recommendations for policy or practical actions. You might build on your work and develop a programme of action research that enables your insights to be trialled. You might assist an organisation or group of actors to interrogate their own culture and begin a process of change. You could collaborate with an already sustainable community over how to challenge the forces that are depleting it, or how to use cultural vectors to extend its reach. There are endless possibilities for making cultural research into a force for positive change.
Research Methodologies
Research with the cultures framework can be undertaken using a broad sweep of qualitative and quantitative methodologies. In this section, I outline the range of research methods that have been successfully used to date that I am aware of, and what functions these methods have played. This section is heavily referenced so that readers can go to the original papers for more detail on the specific methods of data elicitation and analysis.
Most studies to date using the cultures framework have used qualitative methods to examine cultural ensembles, either on their own or in combination with quantitative methods. Solely qualitative research often involves interviews followed by analysis to draw out evidence illustrating cultural elements (e.g. Bach et al., 2020 ; Lazowski et al., 2018 ; McKague et al., 2016 ; Scott & Lawson, 2018 ; Tesfamichael et al., 2020 ; Walton et al., 2014 ). Some projects have used a combination of qualitative methods such as workshops or focus groups together with interviews (e.g. Ambrosio-Albalá et al., 2019 ; Godbolt, 2015 ; Krietemeyer et al., 2021 ). A study of cultural change over an extensive period of time incorporated reviews of archaeological and historical evidence together with present-day interviews (Stovall, 2021 ). Researchers often apply thematic analyses to their qualitative material, but other analytical methods can be used. For example, a study on energy cultures of poverty analysed the interview texts using a computational social science methodology (Debnath et al., 2021 ).
Other researchers have used quantitative methods to characterise cultural ensembles. The elements of the framework have underpinned the design of surveys to elicit data from a larger population than is possible with face-to-face qualitative methods (e.g. Lawson & Williams, 2012 ) and as the basis of an ‘energy culture’ survey for businesses to determine the maturity of their energy efficiency efforts (Oksman et al., 2021 ). As well as using data produced from surveys specifically designed for this purpose, the cultures framework has been used retrospectively to underpin analysis of existing data sets to identify clusters of similar cultural characteristics aligned with different sustainability outcomes (e.g. Bardazzi & Pazienza, 2017 , 2018 , 2020 ; Walton et al., 2020 ). It has also been used as an integrating framework across multiple quantitative data sets (e.g. Manouseli et al., 2018 ). There will always be variations in the cultural ensembles of any group of actors, and sometimes it will be useful to explore this variability. Larger quantitative data sets have been used as a basis for segmenting populations into statistically distinctive groups using cluster analysis (e.g. Barton et al., 2013 ; Lawson & Williams, 2012 ).
In studies using mixed qualitative and quantitative methods, the cultures framework has underpinned both design and/or analysis, and has been used to facilitate the integration of findings (e.g. Bell et al., 2014 ; Muza & Thomas, 2022 ; Scott et al., 2016 ). Some studies have gathered both qualitative and quantitative data relating to cultural elements during face-to-face interviews and integrate these in the analysis (e.g. Khan et al., 2021 ). Research on indicators of national energy cultures used a combination of policy analysis and quantitative analysis of comparative data sets (Stephenson et al., 2021 ).
To explore external influences (including multi-level cultures), studies often ask interviewees within the culture group about their perceptions of what shapes their decision-making or constrains their ability to make more sustainable choices (e.g. Ambrosio-Albalá et al., 2019 ; Debnath et al., 2021 ; McKague et al., 2016 ). Some also seek the views of experts or key informants in particular fields (e.g. Stephenson et al., 2015 ) or review the impact of laws and policies (e.g. Barton et al., 2013 ). Some projects have also interviewed actors who represent aspects of external influences (e.g. Jürisoo et al., 2019 ; Nicholas, 2021 ).
Many different research approaches can be used to identify causal relationships between cultural ensembles and sustainability outcomes. Some studies have done this quantitatively, such as identifying relationships between householder age cohorts and energy consumption (Bardazzi & Pazienza, 2017 ) and between timber drying cultures and energy use (Bell et al., 2014 ). One study used regression analysis to relate householders' cultural features to their interest in being involved in a local energy management scheme (Krietemeyer et al., 2021 ). However, in most studies to date using the cultures framework causal relationships are not quantified but are assumed based on well-established understandings of sustainable practices or the impacts of different technologies (e.g. Dew et al., 2017 ; Hopkins, 2017 ). Often the focus of research has been on whether the cultural ensemble has features that are known to align with more sustainable outcomes (e.g. types of technology and practices that represent business energy efficiency [Oksman et al., 2021 ; Walton et al., 2020 ]) rather than setting out to prove the well-understood relationship between these and measurable outcomes.
The framework has also assisted with modelling. A design for agent-based modelling for smart grid development drew from the cultures framework to incorporate energy use behaviours into the models (Snape et al., 2011 ). A project using system dynamics modelling of the uptake of electric vehicles also used the elements of the cultures framework as foundational data for the model (Rees, 2015 ). Methods such as these align well with the original conceptual framing of culture as a system, and offer a dynamic structure to explore system-type interactions between components of the framework.
The framework lends itself to multi-scalar analysis, as with research on PV uptake in Switzerland, where the work described generalised cultural ensembles of adopters and non-adopters and also drew insights on cultural processes from individuals (Bach et al., 2020 ). By focusing on collectives, researchers can observe patterns of similar cultural features across a population and identify broadly similar influences on and outcomes of that culture. By focusing on individual actors, they can also explore in detail the dynamics within cultural ensembles.
The framework has also been used to structure reviews of literature. Examples include reviews of the adoption of energy-efficient technology innovations in buildings (Soorige et al., 2022 ), academic air travel cultures (Tseng et al., 2022 ) and adoption of natural gas (Binney & Grigg, 2020 ). In a study on barriers and drivers for industrial energy efficiency, the framework was refined to fit an industrial context and used as an organising framework for metadata from a literature review on the barriers and drivers of energy behaviour in firms. This approach enabled the researchers to consider many interdependent components of efficiency decision-making by industry, including attitudinal factors, behaviours and technologies (Rotzek et al., 2018 ).
Some studies have investigated the effectiveness of interventions intended to improve sustainability outcomes. In these instances, they have used the framework to guide collection of pre-intervention and post-intervention data on cultural ensembles and/or outcomes (e.g. Rau et al., 2020 ; Scott et al., 2016 ). Other work has used the framework to design evaluation tools (e.g. Ford et al., 2016 ; Karlin et al., 2015 ).
Within larger research programmes, the framework can be used as a structuring device for allocating research roles and methods across an interdisciplinary team. In the Energy Cultures 1 and 2 research programmes, for example, we identified the core elements of culture in relation to energy efficiency (material aspects, practices, norms, beliefs, etc.) through householder questionnaires, focus groups and interviews. To relate cultural ensembles to energy outcomes, we included questions about energy consumption in the surveys and in later work we used data from smart electricity meters. Interrelationships between elements of the framework were explored in various ways. We used a values ‘laddering’ approach (from consumer psychology) to look at the relationships between values and household energy efficiency actions (Mirosa et al., 2013 ) and used choice modelling (an economics tool) to examine the interactivity between people’s motivators and preferences for adoption of efficient technologies (Thorsnes et al., 2017 ). These were staged so that the values work helped in the design of the choice modelling. We explored interactions between norms, material culture and practices with community focus groups, and these groups also assisted in identifying external influence that were barriers to changing behaviour. Desktop studies were used to examine regulatory, market and policy influences on energy culture. We used social network analysis to identify the most common sources of external influence on householder choices to adopt more efficient technologies. All of these different sources of insight were linked though the framework, which supported an integrative approach across the team, learning from each other’s findings and contributing to a holistic understanding of household energy cultures in the New Zealand context (Barton et al., 2013 ; Stephenson et al., 2010 ).
The framework is thus helpful in underpinning the design of research as a single- or multi-method project by an individual researcher, or a multi-method multidisciplinary research programme by a team. It can be used proactively to design research and analyse the findings, or used retrospectively to help analyse existing data from single or multiple sources. It is fruitful when used as a theory in its own right, and also when used in combination with other theories.
Using the Cultures Framework as a Meta-Theoretical Framing
As these examples have shown, research using the cultures framework is not confined to particular methods, and neither is it confined to any particular theoretical or disciplinary perspective. In this sense, the framework offers a meta-theoretical set of universal elements, and leaves it to the researcher to determine which theories and methodologies are best used to examine them. Rau et al. ( 2020 ) describe the advantages of the framework thus:
The benefits of using the [cultures framework] to organise the empirical material and findings of this interdisciplinary energy research were considerable, especially given its focus on the multi-method investigation of a small number of households. Its relative simplicity, easy-to-understand terminology and focus on both social and material aspects of energy use made it an ideal tool for fusing insights from the social sciences, engineering and architecture. At the same time, [the framework] was capable of connecting a higher-order theoretical approach (energy cultures) to concrete empirical energy-related outcomes. (p. 10)
While many studies use the cultures framework as a framing theory in its own right, it is at the same time an organising framework that enables multiple methods, theories and disciplines to contribute to an understanding of culture in relation to sustainability. Studies using the cultures framework to date have drawn from complementary explanatory theories as diverse as sociological theories of agency, structure, institutions and practice, theories of power and gender, behavioural theories, socio-technical systems theories, consumer psychology, economic theories, the multi-level perspective and, of course, theories of culture. Generally, these are used to inform analysis of an aspect of the cultures framework.
This flexibility is well explained by Ambrosio-Albalá et al. ( 2019 ) in their conclusion to a paper on public perceptions on distributed energy storage in the United Kingdom:
… we find that the framework functions as a useful heuristic, allowing us to organise and reflect on a wide range of factors in a way that is more inclusive than a psychology-only perspective. The idea of there being multiple possible cultures in relation to energy use – and the observation of these at different scales – also helps to stimulate thinking on further research directions in terms of how different households, demographic segments, nationalities and entities may differ in terms of the nexus of norms, attitudes, behaviours or practices and material experiences. These cultures will likely need different types of communication, informational, institutional and contractual offers, given likely differing responses. A further value of the ECF [energy cultures framework] – regarding which we would concur with its originators – lies in its comprehensibility for non-social scientists. For more specialised and narrowly specified forms of analysis, we would defer to the psychological and sociological perspectives that the ECF draws upon. (p. 149)
There are many under-explored possibilities for the use of other theories and bodies of knowledge to help explore aspects of culture in relation to sustainability. For example, in relation to the theory of structuration, culture works both to replicate social life and as a creative force for change. The framework positions culture as constrained and shaped by structure, while simultaneously situating more powerful cultures as part of structure. Despite these constraints on their agency, cultural actors can and do make independent choices and can collectively reshape more powerful structures and cultures. This interplay (and the conceptual overlap of culture and structure) invites further exploration in both a theoretical and applied sense, particularly in the context of the implications for sustainability transitions.
Conceptual fields that underpinned the development of the cultures framework could be drawn from more extensively, including lifestyles literatures, socio-technical studies, actor network theory, systems approaches, and sociological and anthropological theories of culture. For example, social practice theory can help illuminate aspects of the inner elements of the framework, with a focus on habitual actions. Theories of power and justice can help elaborate on the reasons for limitations in agency and choice that are imposed by those outside the agency boundary. Socio-technical systems theories can assist in exploring the relationships between actors’ material items and their activities. Theories of gender can help explores difference in cultural meaning, gender equity and gender leadership in sustainability outcomes. In all of these ways and more, the framework can offer a meta-theoretical structure for deeper analysis depending on the inclinations and interests of the researcher.
Further Contributions From Cultural Theory
A further untapped potential lies in the application of cultural theories more generally to questions of sustainability. Cultural theory is a vast field that I could only sketch out lightly in Chapters 2 and 3 . There I discussed divergences and similarities across cultural theories and identified nine main clusters of perspectives on culture. I believe that each of these perspectives on culture can make an important contribution to research for a more sustainable future.
Culture-as-nature is the oldest of the nine perspectives. It is mostly overlooked by dominant ideologies, and yet its endurance offers the most hope. Culture-as-nature reflects many Indigenous perspectives that defy the intellectual separation of human society and natural systems. Culture-as-nature recognises our utter dependence on the natural world. The most powerful expressions of culture-as-nature continue to come from Indigenous peoples, although recent years have seen an increasingly strong voice from Western scholars (e.g. Haraway, 2016 ; Plumwood, 2005 ; Tsing et al., 2017 ). Culture-as-nature reinforces the indivisibility of human existence from nature and the responsibilities of human societies to maintain the integrity of natural systems. It also breaks down the barriers of cultural membership. Natural features are actors in culture: mountains and creatures are family members, trees communicate, rivers are people; they are all cultural members with agency. Many of the Indigenous societies of the world offer principles, values, practices, knowledges and worldviews that are crucial for a sustainable future (Artelle et al., 2018 ; Mazzocchi, 2020 ; Watene & Yap, 2015 ; Waldmüller et al., 2022 ; Yunkaporta, 2020 ).
Culture-as-nurture reflects the original meaning of culture in old English, referring to processes of husbandry—the careful tending of crops and animals. For the sustainability crisis, we are relearning the urgency of nurturing all life forms and regenerating natural systems. As well as reinforcing the importance of healthy natural systems and food production, culture-as-nurture can be further interpreted as the re-grounding of communities in caring for place, and reviving the spiritual roots of agriculture (Bisht & Rana, 2020 ; van den Berg et al., 2018 ). Urban agriculture or community gardens similarly reconnect people to the practices and rhythms of caring for nature, along with the sharing of food and strengthening a sense of community (Sumner et al., 2011 ). Culture-as-nurture reflects the ways in which we must re-learn practices of caring for nature, and how caring for nature aligns with caring for each other.
The original sense of culture-as-progress was the process of human development towards a so-called civilised state that reflected certain Western ideals of art and behaviours. Although it is now repellent and largely obsolete in this original sense, the idea of ‘progress’ can be reconfigured to refer to cultural journeys towards sustainability. Culture-as-progress in this sense can recognise the many cultural configurations that already have sustainable outcomes. It invites investigations of factors that underpin the relative sustainability of one culture compared to another (Buenstorf & Cordes, 2008 ; Minton et al., 2018 ) and the application of cultural evolution concepts to sustainability challenges (Brooks et al., 2018 ). A practical application of this in the world of business is the concept of energy culture ‘maturity’ and evaluation methods to assess such progress (Soorige et al., 2022 ). If the concept of progress is applied to outcomes rather than to cultural characteristics in themselves, this removes the suggestion that certain forms of cultural ensemble are better than others. Instead, a sustainable future requires a multitude of sustainable cultural ensembles specific to people and place, at a multitude of scales.
Culture is still commonly used to refer to works and practices of artistic and intellectual activity. In this sense, culture-as-product plays an important role as a cultural vector in transmitting ideas, values and possibilities. For the sustainability transition, creative works will play a critical role in challenging systems, institutions and practices that are destroying natural systems and demeaning humanity, as well as offering inspiration for alternate futures. Cultural products have the potential to convey different understandings, such as about the world’s ecological limits, actions for sustainability and new perspectives of the future (Curtis et al., 2014 ). This is already a strong theme in art and performance (Galafassi et al., 2018 ; Kagan, 2019 ) but could play an even stronger role in helping shape awareness and collective visioning for a sustainable future.
Culture-as-lifeways draws originally from anthropological studies of the distinctive way of life of a group of people. From a sustainability perspective, this concept can be redirected from studying the ways of life as a focus in their own right, to looking at the relationship between ways of life and the sustainability outcomes. From a research perspective, it encourages work that explores the variety of ways that people already live sustainably—for example, differences between ways of life in the global north and global south (Hayward & Roy, 2019 ), as well as how group or community ways of life can be re-oriented towards more sustainable consequences (Brightman & Lewis, 2017 ).
Culture-as-meaning focuses on the shared meanings and symbolisms of cultural objects such as text, discourse and possessions. For the sustainability challenge, culture-as-meaning can help reveal the ways in which symbolism can work for or against sustainable outcomes. Theories of cultural meaning could be applied to the analysis of how unsustainability is inherent in dominant rhetoric, text and discourse (e.g. Sturgeon, 2009 ), and the ways in which new meanings are being forged as part of cultural transformations (e.g. Hammond, 2019 ). Other examples of work using culture-as-meaning include a study of how the term ‘sustainable development’ is constructed in the disclosures of Finnish-listed companies (Laine, 2005 ), how the media interprets sustainability (Fischer et al., 2017 ) and the importance of symbolism in marketing for the sustainability transition (Kumar et al., 2012 ; Sheth & Parvatiyar, 2021 ).
Culture-as-structure is interested in the underlying rules by which social systems are reproduced—the cultural codes of social life. Culture-as-structure, as embedded in institutions and discourses, is intimately tied with questions of power and influence regardless of intent (Blythe et al., 2018 ). Drawing on this literature can help identify and challenge ideologies, assumptions and rules that replicate unsustainability. Relevant studies using culture-as-structure include how neoliberal ideology operates through sustainability discourses (Jacobsson, 2019 ) and the mental structures in which finance actors are embedded (Lagoarde-Segot & Paranque, 2018 ).
Culture-as-practice studies the bodily practices that produce and replicate social life, and the intimate linkages between routines, objects, meanings and competencies. This field of work can contribute to questions of how to alter practices, or develop new practices that support sustainability. Practice theory has already been widely applied to how to achieve less resource-intensive habits and routines, including how the reproduction of social practice can sustain inequality and injustice (Shove & Spurling, 2013 ) and to provide insights on collective action for social change (Welch & Yates, 2018 ).
Culture-as-purpose reflects bodies of work that focus on how to change the culture of organisations or groups of actors intentionally. Work in the field of organisational culture includes how to deliberately create more sustainable organisations (Galpin et al., 2015 ; Obal et al., 2020 ). Education for sustainability is another major field working on purposeful culture change, building on and extending educational theories (Huckle & Sterling, 1996 ) and education’s transformative potential (Filho et al., 2018 ). This includes using practices of dance and music to develop pro-social behaviours that align with sustainability goals (Bojner et al., 2022 ).
All nine conceptualisations of culture thus make important contributions to understanding the role of culture in sustainability. It is evident that at least some academics in each of these fields are applying relevant theories and methodologies to sustainability questions, but it appears to be occurring in a fragmented way with different bodies of knowledge scarcely acknowledging each other. Even if there is a ramping up of scholarly contributions on culture and sustainability, there is the risk that the slipperiness of culture as a concept will continue to handicap the use of research findings by practitioners and policymakers. If culture continues to be presented as if each part of the elephant is the full elephant, and the only true elephant, its ongoing indeterminacy will continue to confuse potential research users and dilute the effectiveness of scholarly contributions.
The cultures framework could help here by ‘locating’ these different approaches to culture and their contribution to sustainability challenges. Each of the nine clusters of meaning can offer insights for certain features or qualities of the framework. Using its meta framing, culture-as-purpose focuses on how to purposefully initiate cultural change and achieve better sustainability outcomes. Culture-as-practice focuses on routines as a subset of activities, emphasising how they cannot be understood in isolation from the objects, competencies and meanings associated with them. Culture-as-structure helps explore entrenched external influences or higher-order cultures that use their power to shape the cultural ensembles of less powerful actors. Culture-as-meaning focuses on the meanings and symbolism of activities and objects and can help illuminate the mechanisms of cultural vectors.
Culture-as-lifeways scholarship can help in studying how culture is learned, the dynamics of the core elements of culture, processes of replication or change, and the heterogeneity of cultural ensembles. In the arts, culture-as-product scholarship can help enhance the role of creative activities and products in building a more sustainable future. Academic fields that align with culture-as-progress focus more on the two-ended arrow that links cultural ensembles and outcomes and can help with studies on the many journeys involved in achieving cultures that touch lightly on the earth.
Culture-as-nurture scholarship contributes to the adoption of more nurturing food-production activities that also enhance social and environmental outcomes. Culture-as-nature opens the door to entirely different worldviews and knowledge systems regarding humans’ relationships with the natural world. Importantly, it extends cultural actors to include non-human life forms, spiritual beings and landscape features. In this way, it offers ways of understanding the sustainability transition as a process of restoring health and vitality to all living things and the natural systems that support them.
The cultures framework can thus work as an integrative heuristic, indicating how different interpretations of culture all contribute in important ways to a fuller understanding of the role of culture in sustainability. Used in this way, the framework can help reveal the complementary roles of these diverse approaches to practitioners and non-cultural academics. It can also indicate to researchers where it might be useful to reach back to the original bodies of cultural theory and bodies of knowledge to help illuminate particular aspects of the overall ‘elephant of culture’. In this way, cultural scholarship can be used more comprehensively and systematically to support sustainability transitions, and the slipperiness of culture is somewhat reduced.
As this chapter has demonstrated, there is no ‘right way’ to do research with the cultures framework. It is a set of highly generalised variables and their relationships, which can be explored using a wide range of research methods and theories. Researchers can choose which features within the general variables to focus on and can apply the framework at any scale and to any set of actors. The framework can be used as a framing theory in its own right, or alternatively (or simultaneously) can operate as an integrating frame for interdisciplinary, multi-method research, or as a meta-theoretical framing of the complex field of culture and sustainability. Either on its own or in combination with other frameworks and theories, the cultures framework thus offers ontological and epistemological inclusiveness for transdisciplinary research agendas.
There is an urgent need for a better understanding of the role of culture in the sustainability crisis and how to transform the unsustainable cultures that are inherent in most systems of production and consumption. Technologies alone will not achieve a net-zero world by 2050, or turn around our devastating losses of biodiversity, or enable equitable access to energy for families in developing countries. It will take more than simply changes in behaviour. It will require fundamental changes in the motivators, activities and materialities of people and organisations at every scale. We can learn much from cultures that are already sustainable or are on journeys of transition, but the biggest challenge is how to achieve transformational cultural change, at scale, and with unprecedented speed. To that end, research is desperately needed to improve our understanding of processes of cultural change, and particularly to understand how powerful meta-cultures can be destabilised and their unsustainable ideologies and institutions transformed.
Although the framework has already been used in a wide variety of fields, it has the potential to do much more to assist with journeys of transition. We need to know more about how sustainable cultures develop and endure, a better understanding of the dynamics of cultural change and the role of vectors in cultural learning, as well as processes of cultural expansion and collectivisation. More research is needed on the implications of actors having multiple cultural ensembles in different aspects of their life (e.g. the interplay between their food culture, mobility culture and household energy culture). Researchers could fruitfully explore how these overlapping cultures influence and shape each other, or divergences between cultural settings at home and at work. We need to better understand how cultural transformations can be enabled, and the roles that culture will need to play to achieve sustainability transitions. And while some research using the framework has explored issues of power and justice, there is much more to be done.
Cultural research can work at two levels in this quest for transformation. On the one hand, cultures are unique as to membership and cultural features. Researchers can draw conclusions regarding specific cultural ensembles and their sustainability outcomes, and can make recommendations for change initiatives. However, these will usually only be relevant to the case in question. On the other hand, as more studies are undertaken, we can start to build up generalisable understandings of cultural dynamics as they relate to sustainability. Across multiple studies, the research community can develop a better picture of universal cultural processes and effective change interventions.
Finally, although this chapter is about culture and sustainability, the research approach I describe in this chapter could be used in other fields of inquiry. It was developed for sustainability-related research and has mainly been used for that purpose, but it could equally be applied to investigations of culture for any other reason, and in relation to any other outcome. But my hope is that it will continue to be primarily used for research that helps achieve a just transition to a sustainable future.
Ambrosio-Albalá, P., Upham, P., & Bale, C. S. E. (2019). Purely ornamental? Public perceptions of distributed energy storage in the United Kingdom. Energy Research & Social Science, 48 , 139–150.
Article Google Scholar
Artelle, K. A., Stephenson, J., Bragg, C., Housty, J. A., Housty, W. G., Kawharu, M., & Turner, N. J. (2018). Values-led management: The guidance of place-based values in environmental relationships of the past, present, and future. Ecology and Society , 23 (3).
Google Scholar
Bach, L., Hopkins, D., & Stephenson, J. (2020). Solar electricity cultures: Household adoption dynamics and energy policy in Switzerland. Energy Research and Social Science , 63 , 101395.
Bardazzi, R., & Pazienza, M. G. (2017). Switch off the light, please! Energy use, aging population and consumption habits. Energy Economics, 65 , 161–171.
Bardazzi, R., & Pazienza, M. G. (2018). Ageing and private transport fuel expenditure: Do generations matter? Energy Policy, 117 , 396–405.
Bardazzi, R., & Pazienza, M. G. (2020). When I was your age: Generational effects on long-run residential energy consumption in Italy. Energy Research & Social Science, 70 , 101611.
Barton, B., Blackwell, S., Carrington, G., Ford, R., Lawson, R., Stephenson, J., Thorsnes, P., & Williams, J. (2013). Energy cultures: Implication for policymakers . Centre for Sustainability, University of Otago.
Bell, M., Carrington, G., Lawson, R., & Stephenson, J. (2014). Socio-technical barriers to the use of energy-efficient timber drying technology in New Zealand. Energy Policy, 67 , 747–755.
Binney, M., & Grigg, N. (2020). The energy cultures framework: Understanding material culture barriers to the uptake of natural gas. Journal of Asia Entrepreneurship and Sustainability, 16 (5), 105–139.
Bisht, I. S., & Rana, J. C. (2020). Reviving the spiritual roots of agriculture for sustainability in farming and food systems: Lessons learned from peasant farming of Uttarakhand hills in North-western India. American Journal of Food and Nutrition, 8 (1), 12–15.
Blythe, J., Silver, J., Evans, L., Armitage, D., Bennett, N. J., Moore, M., Morrison, T. H., & Brown, K. (2018). The dark side of transformation: Latent risks in contemporary sustainability discourse. Antipode , 50 (5), 1206–1223.
Bojner Horwitz, E., Korošec, K., & Theorell, T. (2022). Can dance and music make the transition to a sustainable society more feasible? Behavioral Sciences, 12 (11), 1–15.
Brightman, M., & Lewis, J. (Eds.). (2017). The anthropology of sustainability: Beyond development and progress . Palgrave Macmillan.
Brooks, J. S., Waring, T. M., Borgerhoff Mulder, M., & Richerson, P. J. (2018). Applying cultural evolution to sustainability challenges: An introduction to the special issue. Sustainability Science, 13 (1), 1–8.
Buenstorf, G., & Cordes, C. (2008). Can sustainable consumption be learned? A model of cultural evolution. Ecological Economics, 67 (4), 646–657.
Curtis, D. J., Reid, N., & Reeve, I. (2014). Towards ecological sustainability: Observations on the role of the arts. SAPIENS: Surveys and Perspectives Integrating Environment and Society , 7 (1), [online].
Debnath, R., Bardhan, R., Darby, S., Mohaddes, K., Sunikka-Blank, M., Coelho, A. C. V., & Isa, A. (2021). Words against injustices: A deep narrative analysis of energy cultures in poverty of Abuja, Mumbai and Rio de Janeiro. Energy Research & Social Science, 72 , 101892.
Dew, N., Aten, K., & Ferrer, G. (2017). How many admirals does it take to change a light bulb? Organizational innovation, energy efficiency, and the United States Navy’s battle over LED lighting. Energy Research & Social Science, 27 , 57–67.
Filho, W. L., Raath, S., Lazzarini, B., Vargas, V. R., Souza, L. De, Anholon, R., Quelhas, O. L. G., Haddad, R., Klavins, M., & Orlovic, V. L. (2018). The role of transformation in learning and education for sustainability. Journal of Cleaner Production , 199 , 286–295.
Fischer, D., Haucke, F., & Sundermann, A. (2017). What does the media mean by ‘sustainability’ or ‘sustainable development’? an empirical analysis of sustainability terminology in german newspapers over two decades. Sustainable Development , 25 (6), 610–624.
Ford, R., Karlin, B., & Frantz, C. (2016). Evaluating energy culture: Identifying and validating measures for behaviour-based energy interventions . Proceedings of the International Energy Policies & Programmes Evaluation Conference, 1–12.
Galafassi, D., Kagan, S., Milkoreit, M., Heras, M., Bilodeau, C., Bourke, S. J., Merrie, A., Guerrero, L., Pétursdóttir, G., & Tàbara, J. D. (2018). ‘Raising the temperature’: The arts in a warming planet. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability , 31 (2), 71–79.
Galpin, T., Whittington, J. L., & Bell, G. (2015). Is your sustainability strategy sustainable? Creating a culture of sustainability. Corporate Governance, 15 (1), 1–17.
Godbolt, Å. L. (2015). The ethos of energy efficiency: Framing consumer considerations in Norway. Energy Research & Social Science, 8 , 24–31.
Hammond, M. (2019). Sustainability as a cultural transformation: The role of deliberative democracy. Environmental Politics, 29 (1), 173–192.
Haraway, D. (2016). Staying with the trouble: Making kin in the Chthulucene . Duke University Press.
Hayward, B., & Roy, J. (2019). Sustainable living: Bridging the north-south divide in lifestyles and consumption debates. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 44 , 157–175.
Hopkins, D. (2017). Destabilising automobility? The emergent mobilities of generation Y. Ambio, 46 (3), 371–383.
Huckle, J., & Sterling, S. R. (Eds.). (1996). Education for sustainability . Earthscan.
Jacobsson, D. (2019). In the name of (Un)sustainability: A critical analysis of how neoliberal ideology operates through discourses about sustainable progress and equality. TripleC, 17 (1), 19–37.
Jürisoo, M., Serenje, N., Mwila, F., Lambe, F., & Osborne, M. (2019). Old habits die hard: Using the energy cultures framework to understand drivers of household-level energy transitions in urban Zambia. Energy Research and Social Science, 53 , 59–67.
Kagan, S. (2019). Culture and the arts in sustainable development. In T. Meireis & G. Rippl (Eds.), Cultural Sustainability: Perspectives from the humanities and social sciences (pp. 127–139). Routledge.
Karlin, B., Ford, R., & McPherson Frantz, C. (2015). Exploring deep savings: A toolkit for assessing behavior-based energy interventions. International Energy Program Evaluation Conference , 1–12.
Khan, I., Jack, M. W., & Stephenson, J. (2021). Dominant factors for targeted demand side management: An alternate approach for residential demand profiling in developing countries. Sustainable Cities and Society, 67 , 102693.
Krietemeyer, B., Dedrick, J., Sabaghian, E., & Rakha, T. (2021). Managing the duck curve: Energy culture and participation in local energy management programs in the United States. Energy Research & Social Science , 102055.
Kumar, V., Rahman, Z., Kazmi, A. A., & Goyal, P. (2012). Evolution of sustainability as marketing strategy: Beginning of new era. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences , 37 , 482–489.
Lagoarde-Segot, T., & Paranque, B. (2018). Finance and sustainability: From ideology to utopia. International Review of Financial Analysis, 55 , 80–92.
Laine, M. (2005). Meanings of the term “sustainable development” in Finnish corporate disclosures. Accounting Forum, 29 (4), 395–413.
Lawson, R., & Williams, J. (2012). Understanding energy cultures . Annual Conference of the Australia and New Zealand Academy of Marketing (ANZMAC). University of New South Wales, Adelaide.
Lazowski, B., Parker, P., & Rowlands, I. H. (2018). Towards a smart and sustainable residential energy culture: Assessing participant feedback from a long-term smart grid pilot project. Energy, Sustainability and Society, 8 (1), 1–21.
Manouseli, D., Anderson, B., & Nagarajan, M. (2018). Domestic water demand during droughts in temperate climates: Synthesising evidence for an integrated framework. Water Resources Management, 32 (2), 433–447.
Mazzocchi, F. (2020). A deeper meaning of sustainability: Insights from indigenous knowledge. Anthropocene Review, 7 (1), 77–93.
McKague, F., Lawson, R., Scott, M., & Wooliscroft, B. (2016). Understanding the energy consumption choices and coping mechanisms of fuel poor households in New Zealand. New Zealand Sociology, 31 (1), 106–126.
Minton, E. A., Spielmann, N., Kahle, L. R., & Kim, C. H. (2018). The subjective norms of sustainable consumption: A cross-cultural exploration. Journal of Business Research , 82 (December 2016), 400–408.
Mirosa, M., Gnoth, D., Lawson, R., & Stephenson, J. (2011). Rationalizing energy-related behavior in the home: Insights from a value laddering approach . (June), 2109–2119. European Council for an Energy Efficient Economy Summer Study.
Mirosa, M., Lawson, R., & Gnoth, D. (2013). Linking personal values to energy-efficient behaviors in the home. Environment and Behavior, 45 (4), 455–475.
Muza, O., & Thomas, V. M. (2022). Cultural norms to support gender equity in energy development: Grounding the productive use agenda in Rwanda. Energy Research & Social Science, 89 (February), 102543.
Nicholas, L. (2021). On common ground: How landlords & tenants shape thermal performance of private rental properties. University of Otago.
Obal, M., Morgan, T., & Joseph, G. (2020). Integrating sustainability into new product development: The role of organizational leadership and culture. Journal of Small Business Strategy, 30 (1), 43–57.
Oksman, V., Reda, F., Karjalainen, S., & Fatima, Z. (2021). Towards sustainable energy culture in the industrial sector: Introducing an interdisciplinary method for understanding energy culture in business industries. Energy, Sustainability and Society, 11 (1), 1–13.
Plumwood, V. (2005). Environmental culture: The ecological crisis of reason . Routledge.
Rau, H., Moran, P., Manton, R., & Goggins, J. (2020). Changing energy cultures? Household energy use before and after a building energy efficiency retrofit. Sustainable Cities and Society, 54 , 101983.
Rees, D. (2015). Modelling transport transitions in New Zealand: Reference guide for model version 1.0 . Centre for Sustainability, University of Otago.
Rotzek, J. N., Scope, C., & Günther, E. (2018). What energy management practice can learn from research on energy culture? Sustainability Accounting, Management and Policy Journal , 9 (515–551).
Scott, M. G., & Lawson, R. (2018). The road code: Encouraging more efficient driving practices in New Zealand. Energy Efficiency, 11 (7), 1617–1626.
Scott, M. G., McCarthy, A., Ford, R., Stephenson, J., & Gorrie, S. (2016). Evaluating the impact of energy interventions: Home audits vs. community events. Energy Efficiency , 9 (6), 1221–1240.
Sheth, J. N., & Parvatiyar, A. (2021). Sustainable marketing: Market-driving, not market-driven. Journal of Micromarketing, 41 (1), 150–165.
Shove, E., & Spurling, N. (Eds.). (2013). Sustainable practices: Social theory and climate change . Routledge.
Snape, J. R., Irvine, K. N., & Rynikiewicz, C. (2011). Understanding energy behaviours and transitions through the lens of a smart grid Agent Based Model . Proceedings of the European Council for an Energy Efficient Economy, Summer Study: Energy Efficiency First: The Foundation of a Low-Carbon Society.
Soorige, D., Karunasena, G., Kulatunga, U., Mahmood, M. N., & Silva, L. De. (2022). An energy culture maturity conceptual framework on adopting energy-efficient technology innovations in buildings. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity , 8 (60).
Stephenson, J. (2018). Sustainability cultures and energy research: An actor-centred interpretation of cultural theory. Energy Research & Social Science, 44 (May), 242–249.
Stephenson, J. (2020). Sustainability Cultures: Exploring the relationships between cultural attributes and sustainability outcomes. In K. Legun, J. Keller, M. Bell, & M. Carolan (Eds.), Cambridge handchapter of environmental sociology (pp. 236–248). Cambridge University Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
Stephenson, J., Hopkins, D., & Doering, A. (2015). Conceptualizing transport transitions: Energy cultures as an organizing framework. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Energy and Environment, 4 (4), 354–364.
Stephenson, J., Lawson, R., Carrington, G., Barton, B., Thorsnes, P., & Mirosa, M. (2010). The practice of interdisciplinarity. International Journal of Interdisciplinary Social Sciences, 5 (7), 271–282.
Stephenson, J. R., Sovacool, B. K., & Inderberg, T. H. J. (2021). Energy cultures and national decarbonisation pathways. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews , 137 (October).
Stovall, W. R. (2021). Faces of stone: Environmental history and cultures of Paha Sapa (The Black Hills) . University of Otago, New Zealand.
Sturgeon, N. L. (2009). Environmentalism in popular culture: Gender, race, sexuality, and the politics of the natural . University of Arizona Press.
Sumner, J., Mair, H., & Nelson, E. (2011). Putting the culture back into agriculture: Civic engagement, community and the celebration of local food. International Journal of Agricultural Sustainability, 8 (1–2), 54–61.
Tesfamichael, M., Bastille, C., & Leach, M. (2020). Eager to connect, cautious to consume: An integrated view of the drivers and motivations for electricity consumption among rural households in Kenya. Energy Research & Social Science, 63 , 101394.
Thorsnes, P., Lawson, R., & Stephenson, J. (2017). Heterogeneity in household preferences for energy-efficient heating systems. Economics Discussion Papers, 2293 (1713), 40.
Tseng, S. H. Y., Higham, J., & Lee, C. (2022). Academic air travel cultures: A framework for reducing academic flying. In K. Bjørkdahl, A. Santiago, & F. Duharte (Eds.), Academic flying and the means of communication (pp. 327–353). Palgrave Macmillan.
Tsing, A. L., Swanson, H. A., Gan, E., & Bubandt, N. (Eds.). (2017). Arts of living on a damaged planet: Ghosts and monsters of the anthropocene . University of Minnesota Press.
United Nations. (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 agenda for sustainable development .
van den Berg, L., Roep, D., Hebinck, P., & Teixeira, H. M. (2018). Reassembling nature and culture: Resourceful farming in Araponga, Brazil. Journal of Rural Studies, 61 , 314–322.
Waldmüller, J. M., Yap, M., & Watene, K. (2022). Remaking the sustainable development goals: relational Indigenous epistemologies. Policy and Society , 41 (4), 471–485.
Watene, K., & Yap, M. (2015). Culture and sustainable development: Indigenous contributions. Journal of Global Ethics, 11 (1), 51–55.
Walton, S., Doering, A., Gabriel, C.-A., & Ford, R. (2014). Energy transitions: Lighting in Vanuatu . Project report, Australian Aid.
Walton, S., Zhang, A., & O’Kane, C. (2020). Energy eco-innovations for sustainable development: Exploring organizational strategic capabilities through an energy cultures framework. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29 (3), 812–826.
Welch, D., & Yates, L. (2018). The practices of collective action: Practice theory, sustainability transitions and social change. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour, 48 (3), 288–305.
Yunkaporta, T. (2020). Sand talk: How indigenous thinking can save the world . HarperOne.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Sustainability, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand
Janet Stephenson
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Janet Stephenson .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Stephenson, J. (2023). Using the Cultures Framework for Research. In: Culture and Sustainability. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25515-1_8
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25515-1_8
Published : 23 March 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-25514-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-25515-1
eBook Packages : Earth and Environmental Science Earth and Environmental Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 113 great research paper topics.
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Lisa Fernandez Research Papers
This essay about Lisa Fernandez’s childhood explores the foundational years that shaped her into a softball legend. Born into a sports-loving family with Cuban and Puerto Rican heritage, Fernandez was introduced to athletics at a young age, fostering a passion and dedication for softball. Her early life was characterized by rigorous training, discipline, and the pursuit of excellence, with her family’s support playing a crucial role in her development. Despite facing the challenges of a then less-developed landscape for women’s softball, Fernandez’s resilience and commitment to improvement set the stage for her remarkable career. The essay highlights how her multicultural background influenced her team-oriented values and leadership qualities. Through Fernandez’s story, we see the impact of early mentorship, cultural pride, and unwavering determination in achieving greatness.
How it works
Lisa Fernandez, a name synonymous with excellence in softball, carved her path to greatness from an early age. Born on February 22, 1971, in Long Beach, California, Fernandez’s childhood was a melting pot of cultural heritage and sporting prowess. Her journey is not just a story of athletic achievement but a narrative of passion, determination, and the profound influence of family on personal and professional development.
From the outset, Fernandez was no stranger to the world of sports. Her Cuban immigrant father and Puerto Rican mother both shared a deep love for athletics, a trait they instilled in their daughter.
This familial sporting ethos was not merely about the games but was tethered to a broader understanding of discipline, hard work, and the pursuit of excellence. Fernandez’s mother, particularly, played a pivotal role in her early sporting life, serving not just as a supporter but as a mentor. She ensured that Lisa understood the importance of dedication, both on and off the field, a lesson that became the cornerstone of Fernandez’s approach to softball.
Fernandez’s childhood was marked by her involvement in various sports, but it was softball where her passion and talent truly shone. By the age of eight, she was already competing in local leagues, displaying a natural affinity for the game that was hard to overlook. Her early years in softball were characterized by an unwavering commitment to practice and improvement, attributes that would define her career. Despite the challenges of balancing academics, training, and competition, Fernandez remained dedicated to her sport, driven by an inner desire to excel and make her mark in softball history.
The landscape of women’s softball during Fernandez’s formative years was vastly different from today. Opportunities for female athletes were fewer, and the path to recognition and success was fraught with obstacles. However, Fernandez’s early exposure to competitive softball, coupled with her family’s support, provided her with a unique perspective on overcoming adversity. She learned to navigate the challenges of the sport, using each setback as a stepping stone towards her goals. This resilience, developed in the crucible of early competition, was instrumental in her ascent to softball stardom.
Beyond the field, Fernandez’s childhood was a blend of cultural experiences that enriched her understanding of identity and heritage. Growing up in a multicultural household, she was imbued with a strong sense of pride in her Cuban and Puerto Rican roots. This cultural background not only shaped her personal identity but also influenced her approach to teamwork and leadership. Fernandez often spoke of how her heritage taught her the value of unity, respect, and the collective effort towards a common goal—principles that she carried into her playing and coaching career.
Fernandez’s journey from a young girl with a dream to a legend in softball is a testament to the power of early dedication, the influence of supportive family, and the impact of cultural heritage on personal growth. Her childhood was not merely a precursor to her achievements but a fundamental chapter that molded her into the athlete and role model she is today. Through her story, we glean insights into the making of a champion, the importance of early mentorship, and the enduring legacy of cultural values in shaping one’s destiny.
In conclusion, Lisa Fernandez’s childhood is a rich narrative that offers more than just a glimpse into the making of a sports icon. It is a story of passion ignited early, of challenges transformed into stepping stones, and of the indelible impact of family and heritage on personal achievement. Fernandez’s early life reminds us that the journey to greatness begins with the first step, guided by determination, nurtured by support, and enriched by the diverse tapestry of our backgrounds. Her legacy, rooted in the fields of her youth, continues to inspire aspiring athletes, demonstrating that with dedication, resilience, and a strong support system, the dreams of childhood can indeed become the achievements of tomorrow.
Cite this page
Lisa Fernandez Research Papers. (2024, Apr 14). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/lisa-fernandez-research-papers/
"Lisa Fernandez Research Papers." PapersOwl.com , 14 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/lisa-fernandez-research-papers/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Lisa Fernandez Research Papers . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/lisa-fernandez-research-papers/ [Accessed: 15 Apr. 2024]
"Lisa Fernandez Research Papers." PapersOwl.com, Apr 14, 2024. Accessed April 15, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/lisa-fernandez-research-papers/
"Lisa Fernandez Research Papers," PapersOwl.com , 14-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/lisa-fernandez-research-papers/. [Accessed: 15-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Lisa Fernandez Research Papers . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/lisa-fernandez-research-papers/ [Accessed: 15-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
9 facts about americans and marijuana.

The use and possession of marijuana is illegal under U.S. federal law, but about three-quarters of states have legalized the drug for medical or recreational purposes. The changing legal landscape has coincided with a decades-long rise in public support for legalization, which a majority of Americans now favor.
Here are nine facts about Americans’ views of and experiences with marijuana, based on Pew Research Center surveys and other sources.
As more states legalize marijuana, Pew Research Center looked at Americans’ opinions on legalization and how these views have changed over time.
Data comes from surveys by the Center, Gallup , and the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health from the U.S. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Information about the jurisdictions where marijuana is legal at the state level comes from the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws .
More information about the Center surveys cited in the analysis, including the questions asked and their methodologies, can be found at the links in the text.
Around nine-in-ten Americans say marijuana should be legal for medical or recreational use, according to a January 2024 Pew Research Center survey . An overwhelming majority of U.S. adults (88%) say either that marijuana should be legal for medical use only (32%) or that it should be legal for medical and recreational use (57%). Just 11% say the drug should not be legal in any form. These views have held relatively steady over the past five years.
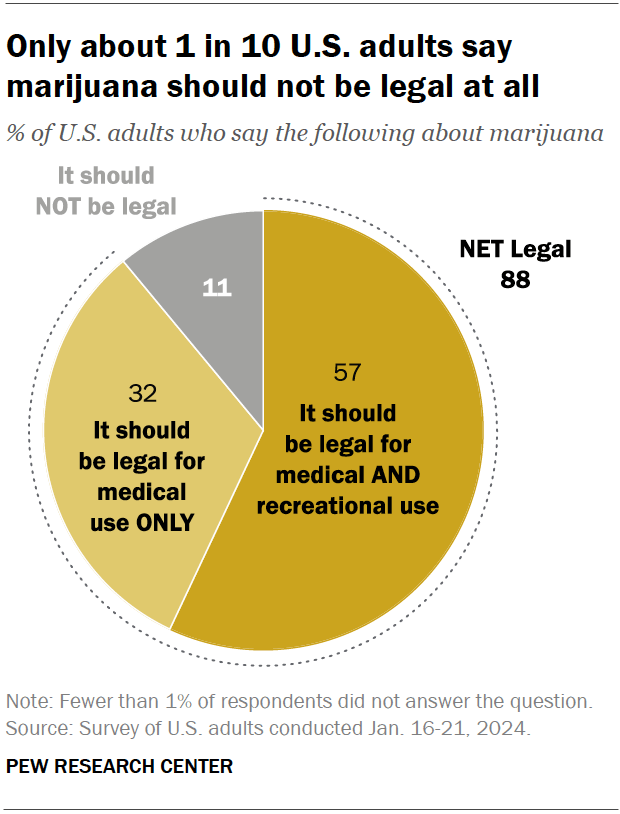
Views on marijuana legalization differ widely by age, political party, and race and ethnicity, the January survey shows.

While small shares across demographic groups say marijuana should not be legal at all, those least likely to favor it for both medical and recreational use include:
- Older adults: 31% of adults ages 75 and older support marijuana legalization for medical and recreational purposes, compared with half of those ages 65 to 74, the next youngest age category. By contrast, 71% of adults under 30 support legalization for both uses.
- Republicans and GOP-leaning independents: 42% of Republicans favor legalizing marijuana for both uses, compared with 72% of Democrats and Democratic leaners. Ideological differences exist as well: Within both parties, those who are more conservative are less likely to support legalization.
- Hispanic and Asian Americans: 45% in each group support legalizing the drug for medical and recreational use. Larger shares of Black (65%) and White (59%) adults hold this view.
Support for marijuana legalization has increased dramatically over the last two decades. In addition to asking specifically about medical and recreational use of the drug, both the Center and Gallup have asked Americans about legalizing marijuana use in a general way. Gallup asked this question most recently, in 2023. That year, 70% of adults expressed support for legalization, more than double the share who said they favored it in 2000.
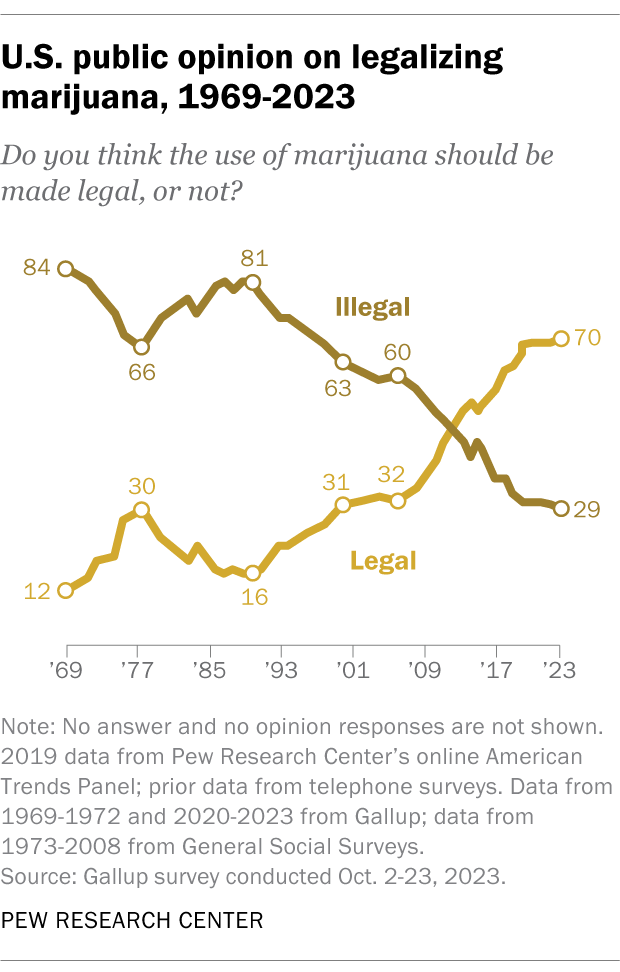
Half of U.S. adults (50.3%) say they have ever used marijuana, according to the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health . That is a smaller share than the 84.1% who say they have ever consumed alcohol and the 64.8% who have ever used tobacco products or vaped nicotine.
While many Americans say they have used marijuana in their lifetime, far fewer are current users, according to the same survey. In 2022, 23.0% of adults said they had used the drug in the past year, while 15.9% said they had used it in the past month.
While many Americans say legalizing recreational marijuana has economic and criminal justice benefits, views on these and other impacts vary, the Center’s January survey shows.
- Economic benefits: About half of adults (52%) say that legalizing recreational marijuana is good for local economies, while 17% say it is bad. Another 29% say it has no impact.
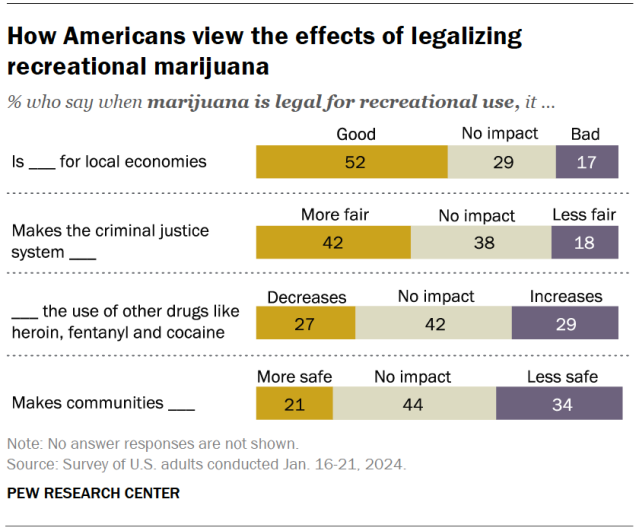
- Criminal justice system fairness: 42% of Americans say legalizing marijuana for recreational use makes the criminal justice system fairer, compared with 18% who say it makes the system less fair. About four-in-ten (38%) say it has no impact.
- Use of other drugs: 27% say this policy decreases the use of other drugs like heroin, fentanyl and cocaine, and 29% say it increases it. But the largest share (42%) say it has no effect on other drug use.
- Community safety: 21% say recreational legalization makes communities safer and 34% say it makes them less safe. Another 44% say it doesn’t impact safety.
Democrats and adults under 50 are more likely than Republicans and those in older age groups to say legalizing marijuana has positive impacts in each of these areas.
Most Americans support easing penalties for people with marijuana convictions, an October 2021 Center survey found . Two-thirds of adults say they favor releasing people from prison who are being held for marijuana-related offenses only, including 41% who strongly favor this. And 61% support removing or expunging marijuana-related offenses from people’s criminal records.
Younger adults, Democrats and Black Americans are especially likely to support these changes. For instance, 74% of Black adults favor releasing people from prison who are being held only for marijuana-related offenses, and just as many favor removing or expunging marijuana-related offenses from criminal records.
Twenty-four states and the District of Columbia have legalized small amounts of marijuana for both medical and recreational use as of March 2024, according to the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws (NORML), an advocacy group that tracks state-level legislation on the issue. Another 14 states have legalized the drug for medical use only.
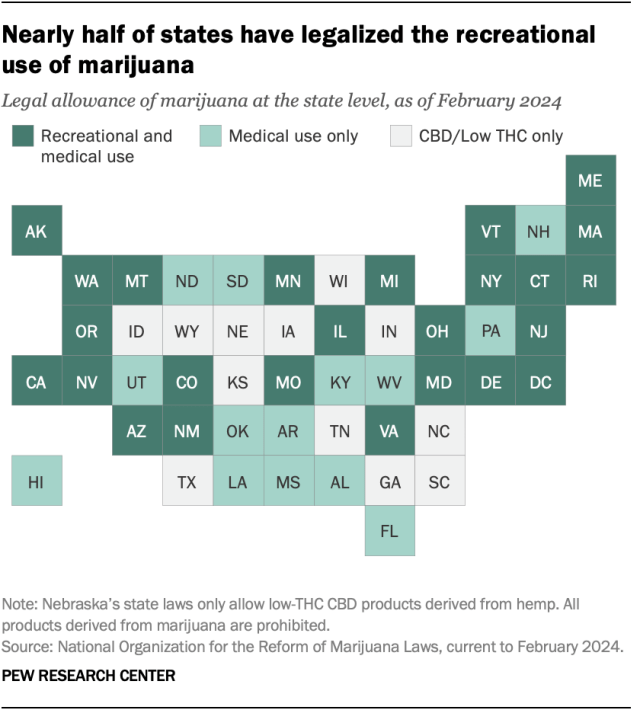
Of the remaining 12 states, all allow limited access to products such as CBD oil that contain little to no THC – the main psychoactive substance in cannabis. And 26 states overall have at least partially decriminalized recreational marijuana use , as has the District of Columbia.
In addition to 24 states and D.C., the U.S. Virgin Islands , Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands have legalized marijuana for medical and recreational use.
More than half of Americans (54%) live in a state where both recreational and medical marijuana are legal, and 74% live in a state where it’s legal either for both purposes or medical use only, according to a February Center analysis of data from the Census Bureau and other outside sources. This analysis looked at state-level legislation in all 50 states and the District of Columbia.
In 2012, Colorado and Washington became the first states to pass legislation legalizing recreational marijuana.
About eight-in-ten Americans (79%) live in a county with at least one cannabis dispensary, according to the February analysis. There are nearly 15,000 marijuana dispensaries nationwide, and 76% are in states (including D.C.) where recreational use is legal. Another 23% are in medical marijuana-only states, and 1% are in states that have made legal allowances for low-percentage THC or CBD-only products.
The states with the largest number of dispensaries include California, Oklahoma, Florida, Colorado and Michigan.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published April 26, 2021, and updated April 13, 2023.

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
Americans overwhelmingly say marijuana should be legal for medical or recreational use
Religious americans are less likely to endorse legal marijuana for recreational use, four-in-ten u.s. drug arrests in 2018 were for marijuana offenses – mostly possession, two-thirds of americans support marijuana legalization, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Cultural Studies Research Paper

Sample Cultural Studies Research Paper. Browse other research paper examples and check the list of research paper topics for more inspiration. iResearchNet offers academic assignment help for students all over the world: writing from scratch, editing, proofreading, problem solving, from essays to dissertations, from humanities to STEM. We offer full confidentiality, safe payment, originality, and money-back guarantee. Secure your academic success with our risk-free services.
This research paper attempts to describe that complex contemporary social formation: Cultural Studies (CS). A single thesis organizes the argument. Contemporary CS exists within competing fields of discourse. This discourse, as Carey (1997b) argues, is moving in several directions at the same time (see Frow and Morris 2000, Striphas 1998). This has the effect of simultaneously creating new spaces, new possibilities, and new formations for CS, while closing down others.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Thus, a process of containment is occurring, even as this interdisciplinary field expands globally (Public Culture 1988, Frow and Morris 2000, Alasuutari et al. 1998, Hartley 1998). There are those who would marginalize CS, equating it with Marxist thought, and chastising it for not paying adequate homage to Sociology’s founding fathers, including Weber and Durkheim (Long 1997). Others would seek a preferred, canonical, but flexible version of the project (see Grossberg 1997a, 1998). Within this framework (see Grossberg 1997a), there are attempts to establish a set of interpretive practices fitted to specific projects. For Grossberg (1997a, pp. 248-261) these practices, or interpretive principles involve a self-reflexive, inter-disciplinary project which always detours through theory. This version of CS maintains a commitment to political praxis and radical contextualization, including anti-reductionist, anti-essentialist ontologies. Still others would ironically equate CS with identity politics and critical readings of popular culture. Some would critique the formation from within, distinguishing semiotic, political economy, empiricist, and material approaches to the field’s subject matter (Fiske 1994). Still others challenge CS to take up the problems of feminism, gender, racism, colonialism, and nationality (Ferguson and Golding 1997).
1. The Origins And Definitions Of CS
Ferguson and Golding (1997) observe that ‘Few would dispute that CS’ ‘myths of origin’ were made in Britain, and that their ‘founding fathers’ were Raymond Williams, Richard Hoggart and E. P. Thompson, and subsequently Stuart Hall.’ The legacies of these figures is enduring, and includes a commitment to a Marxism without guarantees, a rejection of positivism and functional social theory, and a conception of culture that is political. But on beginnings and origins, Hall (1980) is quite firm, ‘there are no absolute beginnings and few unbroken continuities … What is important are the significant breaks.’
The culture in CS is not aesthetic, or literary, it is political, and located in the domain of the popular or the everyday (Storey 1996). The object of study is how culture, as a set of contested interpretive, representational practices, embraces and represents ‘a particular way of life, whether of a people, period or a group’ (Williams 1976). Popular, everyday cultural practices are treated as social texts. It is understood that nothing stands outside textual representation. Texts, however, involve material practices, structures, flows of power, money, and knowledge. Popular culture is conceptualized as a site of constant negotiation, consent, and resistance. Meaning is always contextual, structural, and anchored in historical processes (Hall 1996b). Cultural processes, in turn, embody class, gender, and racial divisions and relation-ships. These relationships involve the exercise of power.
1.1 The Circuits Of Culture
A complex interpretive process shapes the meanings things have for human beings. This process is anchored in the cultural world, in the ‘circuit of culture’ (du Gay et al. 1997) where meanings are defined by the mass media, including advertising, cinema, and television. This process is based on the articulation or inter-connection of several distinct and contingent processes (du Gay et al. 1997). In the circuits of cultural meaning five interconnected processes, representation, identification, production, consumption, and regulation, mutually influence one another (du Gay et al. 1997).
Objects and experiences are represented in terms of salient cultural categories. These categories are connected directly to social and personal identities. These identities are attached to representations of family, race, age, gender, nationality, and social class. These objects and identities are in turn located in an ongoing political economy. A political economy is a complex, interconnected system. It structures the production, distribution, and consumption of wealth in a society. It determines the Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How of wealth and power in everyday life; that is, who gets what income, at what time, in what places, for what labor, and why?
This economy regulates the production, distribution and consumption of cultural objects. It does so by repeatedly forging links between cultural objects (cars, clothing, food, houses), their material representations, and the personal identities of consumers as gendered human beings (see discussion below). To summarize, an understanding of these five processes leads re-searchers to examine how cultural objects are rep-resented in the media and in everyday popular culture. Scholars then move from this level of analysis to studies of those social identities that are attached to the cultural object, asking, at the same time, how is this object ‘produced and consumed, and what mechanisms regulate its distribution and use’ (du Gay et al. 1997). An instance is given in those moments when a cultural fad, a style of dress, or a hairstyle seemingly sweeps across an age or gender group. New and old identities are attached to the use of the object that is produced for consumption by a small number of manufacturers who regulate price and distribution.
2. The Narrative Turn
This concern for language and meaning has been called the narrative or discursive turn in CS. This turn implies greater interest in language, discourse, dis-cursive practices, and the argument that meaning is contextual (Hall 1996a). This narrative turn moves in two directions at the same time. First, CS scholars formulate and offer various narrative versions or stories about how the social world operates. This form of narrative is usually called a theory, for example, Freud’s theory of psychosexual development. Second, scholars study narratives and systems of discourse, arguing that these structures give coherence and meaning to the world. A system of discourse is a way of representing the world. A complex set of discourses is called a discursive formation (Hall 1996a). The traditional gender belief system in American culture, with its focus on patriarchy and a woman’s place in the home, is an instance of a discursive formation. Discursive formations are implemented through dis-cursive practices, for example, patriarchy and the traditional etiquette system.
Systems of discourse both summarize and produce knowledge about the world. These discursive systems are seldom just true or false. In the world of human affairs, truth and facts can be constructed in different ways. Consider this question, ‘Are those Palestinians who are fighting to regain a home on the West Bank of Israel freedom fighters or terrorists? (Hall 1996b). The very words that are used to describe these individuals prejudge and evaluate their activity. Freedom fighter or terrorist are not neutral terms. They are embedded in competing discourses. As such they are connected to struggles over power, that is who has the power to determine which term will be used? As Hall notes, ‘It is the outcome of this struggle which will define the ‘‘truth’’ of the situation.’ Often times it is power ‘rather than facts about reality, which makes things ‘‘true’’ ’ (Hall 1996b).
Power produces knowledge (Foucault 1980). Regimes of truth can be said to operate when discursive systems regulate relations of power and knowledge (Hall 1996b). The traditional gender belief system, which regulates the power relations between men and women in this culture is such a regime. In these ways discursive systems affect lives.
2.1 Experience And Its Representations
Of course it is not possible to study experience directly, so CS researchers examine representations of experience, interviews, stories, performances, myth, ritual, and drama. These representations, as systems of discourse, are social texts, narrative, discursive constructions. The meanings and forms of experience are always given in narrative representations. These representations are texts that are performed, stories told to others. Bruner (1986) is explicit on this point, representations must ‘be performed to be experienced.’ In these ways researchers deal with performed texts, rituals, stories told, songs sung, novels read, dramas performed. Paraphrasing Bruner (1986), experience is a performance.
2.2 Assessing Interpretations
The politics of representation is basic to the study of experience. How a thing is represented often involves a struggle over power and meaning. While scholars have traditionally privileged experience itself, it is now understood that no life, no experience can be lived outside of some system of representation (Hall 1996c). Indeed, ‘there is no escaping from the politics of representation’ (Hall 1996c).
This narrative turn suggests that researchers constantly are constructing interpretations about the world, giving shape and meaning to what they de-scribe. Still, all accounts, ‘however carefully tested and supported are, in the end ‘‘authored’’ ’ (Hall 1996a). CS explanations reflect the point of view of the author. They do not carry the guarantee of truth and objectivity.
The narrative turn leads scholars to be much more tentative in terms of the arguments and positions they put forward. It is now understood that there is no final or authorized version of the truth. Still, there are criteria of assessment that should be used. Researchers are ‘committed to providing systematic, rigorous, coherent, comprehensive, conceptually clear, well- evidenced accounts, which make their underlying theoretical structure and value assumptions clear to readers…(still) we cannot deny the ultimately interpretive character of the social science enterprise’ (Hall 1996a).
3. Diversity And Constraint
The open-ended nature of the CS project creates a perpetual resistance against attempts to impose a single, umbrella-like paradigm over the entire project. There are multiple CS projects, including: the articulation model of the Birmingham school, and the work of Stuart Hall, Paul Gilroy, Lawrence Grossberg, and their associates (du Gay et al. 1997, Grossberg 1997a, 1997b); Black British CS (Baker et al. 1996); the conjunctural, resistance perspective of Fiske (1994); feminist, ethnographic projects connected to the British and Frankfurt schools; American CS versions located in communication studies (Ferguson and Golding 1997), which work through pragmatism back to the arguments of McLuhan, Innis, Ong, and Dallas Smythe (Carey 1997a, 1997b, Denzin 1995); the African-American, prophetic, postmodern, neo-pragmatic marxism of West (1992); the empiricist, neo-functional American cultural sociology project which draws on the work of Bourdieu and Parsons (see Schudson 1997); a Chicana o, Latina o model that elaborates and then departs from the Birmingham approach (Chabram-Denersesian 1999); a critical, CS pedagogy (McCarthy 1998); Canadian and Australian CS models which focus on policy and public culture and attempt to de-Anglocize the British model (Blundell et al. 1993, Frow and Morris 1993); a Black feminist cultural criticism (Hooks 1990); an American-based, ethnographic, critical CS model centered on a resistance postmodernism; and more recently a trans-national CS focused on the critical, ethnographic study of public culture and the flow of cultural forms and cultural representations from one site to another (Public Culture 1988).
The generic focus of each version of CS involves an examination of how the history people live is produced by structures that have been handed down from the past. Within these traditions, culture is treated as a verb, a process, and a place, always in motion, where meaning and situated identities connected to race, class, and gender are created and performed (du Gay et al. 1997). A shared emphasis on international cultural and social processes unites these various programs. This shared focus moves in four directions: (a) the ‘detour through theory’ (Hall 1992, Grossberg 1997a), linked (b) to the politics of representation, the circuits of culture (Hall 1996a), and the textual analyses of the media, literary, and cultural forms, including their production, distribution, and consumption; (c) the ethnographic, qualitative study of these forms in everyday life and the analysis of the social and communication processes that they shape and define; (d) the investigation of new pedagogical practices that interactively engage critical cultural analysis in the classroom (Grossberg 1997a). Each of these versions of CS is joined by a threefold concern with cultural texts, lived experience, and the articulated relationship between texts, materiality, and everyday life. Within the cultural text tradition some scholars (Fiske 1994) examine the mass media and popular culture as sites of resistance where history, ideology, and subjective experiences come together. These scholars produce critical ethnographies of the active audience in relation to particular historical moments. Other scholars read texts as sites where hegemonic meanings are produced, distributed, and consumed. In the feminist ethnographic tradition, there is a postmodern concern for the social text and its production (see Denzin 1997).
These models see culture as a series of ongoing interactional practices, conversations, talk, ways of acting, and representing the meanings of experience. Any cultural practice is significant because it is an instance of a cultural practice that happened in a particular time and place. This practice cannot be generalized to other practices, its importance lies in the fact that it instantiates a cultural practice, a cultural performance (story telling), and a set of shifting, conflicting, cultural meanings (Fiske 1994).
The researcher strategically selects sites for interpretation that constitute the intersection of texts and interacting individuals. Interactional specimens are extracted from these sites, written off from the conversations and actions that occur within them. This model always work upward and outward from the concrete to the larger set of meanings that operate in a particular context. It offers glimpses of culture in practice, setting one set of practices and meanings off against others that may compete in the same situation (Fiske 1994). The concept of structure is critical. In interpretive CS structure is a set of generative (often hegemonic), interactional, and cultural practices that organize meanings at the local level. Critical emic inquiry guides this process, the researcher seeks to understand a subject (or class of subjects) within a given historical moment. Sartre’s (1963) progressive– regressive method is employed. A variant on the pragmatic emphasis on the consequences of acts, this method looks forward to the conclusion of a set of acts. It then works back to the conditions, interpretations, and situations that shape this decision. By moving forward and backward in time subjects and their projects are located within culture as a set of interpretive practices.
4. In Conclusion: The Calling Of CS
Frow and Morris (2000) observe that contemporary versions of CS have been shaped by encounters between diverse feminisms, ethnic and critical race studies, gay, lesbian, and queer studies, postcolonial and diasporic research, and with indigenous people’s scholarship. These interactions produce a sensitivity to culture in its multiple forms, including the aesthetic, political, anthropological, performative, historical, and the spatial. Thus, there are collections and essays in Australian-Asian CS, Asian-Pacific CS, Latin-American, Mexican, and Chicana o CS, as well as Black-British, Irish, British, Spanish, Italian, Nordic, and African CS.
At the same time, students of CS wrestle with the multiple meanings of such key terms as identity, place, globalization, the local, nationhood, and difference. These terms are debated constantly in the media, played out in arenas defined and shaped by the new information and communication technologies. CS scholars examine how meanings move between and within various media formations. This yields studies of Madonna, Elvis, the Gulf War, Anita Hill, the memory-work of museums, studies of tourism, shop-ping malls, and so on. In such work it becomes clear that culture is a contested, conflictual set of practices bound up with the meanings of identity and com-munity.
The disciplinary boundaries that define CS keep shifting, and there is no agreed standard genealogy of its emergence as a serious academic discipline. Nonetheless, there are certain prevailing tendencies including: feminist understandings of the politics of the everyday and the personal; disputes between proponents of textualism, ethnography, and autoethnography; continued debates surrounding the dreams of modern citizenship.
But of course CS is a discursive category, its meanings are established in and through rhetorical and material practices. Nonetheless, the sine qua non of CS is irrefutable. A core belief defines the project, the understanding that scholars have a commitment and a responsibility to record and analyze, and register the meanings of ‘the great events of our time for the benefit of future generations’ (Nelson and Gaonkar 1996). This is the calling of CS.
Bibliography:
- Alasuutari P, Gray A, Hermes J 1998 Editorial. European Journal of CS 1(1): 5–11
- Appadurai A 1996 Modernity at Large. University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, MN
- Baker H A Jr, Diawara M, Lindeborg R H (eds.) 1996 Black British Cultural Studies: A Reader. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
- Blundell V, Sheperd J, Taylor I (eds.) 1993 Relocating Cultural Studies: Developments in Theory and Research. Routledge, London
- Bruner E M 1986 Experience and its expressions. In: Turner V M, Bruner E M (eds.) The Anthropology of Experience. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, IL, pp. 3–30
- Carey J W 1997a Afterword: The culture in question. In: Munson E S, Warren C A (eds.) James Carey: A Critical Reader. University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, MN, pp. 308–39
- Carey J W 1997b Reflections on the Project of (American) Cultural Studies. In: Ferguson M, Golding P (eds.) Cultural Studies in Question. Sage, London, pp. 1–24
- Chabram-Denersesian A 1999 Introduction: Chicana/o Latina/o Cultural Studies: Transnational and transdisciplinary movements. Cultural Studies 13: 173–94
- Denzin N K 1995 Information technologies, communicative acts, and the audience: Couch’s legacy to communication research. Symbolic Interaction 18: 247–68
- Denzin N K 1997 Interpretive Ethnography. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA
- Ferguson M, Golding P 1997 Cultural Studies and changing times: An introduction. In: Ferguson M, Golding P (eds.) Cultutal Studies in Question. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA, pp. xiii–xxvii
- Fiske J 1994 Audiencing: Cultural practice and cultural studies. In: Denzin N K, Lincoln Y S (eds.) Handbook of Qualitative Research. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA, pp. 189–98
- Foucault M 1980 Power knowledge: Selected interviews and other writings 1972–1977. In: Gordon C (ed.) (Trans. Gordon C, Marshall L, Mepham J, Soper K). Pantheon, New York
- Frow J, Morris M (eds.) 1993 Australian Cultural Studies: A Reader. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, IL
- Frow J, Morris M 2000 CS. In: Denzin N K, Lincoln Y S (eds.) Handbook of Qualitative Research. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA
- du Gay P, Hall S, James L, Mackay H, Negus K 1997 Doing Cultural Studies: The Story of the Sony Walkman. Sage, London
- Grossberg L 1997a Bringing it all back Home: Essays in Cultural Studies. Duke University Press, Durham, NC
- Grossberg L 1997b Dancing in Spite of Myself: Essays on Popular Culture. Duke University Press, Durham, NC
- Grossberg L 1998 The cultural studies crossroads blues. European Journal of Cultural Studies 1: 65–82
- Hall S 1980 Cultural studies: two paradigms. Media, Culture and Society 2: 57–72
- Hall S 1992 Cultural Studies and its theoretical legacies. In: Grossberg L, Nelson C, Treichler P (eds.) Cultural Studies. Routledge, New York, pp. 277–94
- Hall S 1996a Introduction. In: Hall S, Held D, Hubert D, Thompson K (eds.) Modernity: An Introduction to Modern Societies. Blackwell, Cambridge, MA, pp. 3–18
- Hall S 1996b Gramsci’s relevance for the study of race and ethnicity. In: Morley D, Chen K-H (eds.) Stuart Hall: Critical Dialogues in Cultural Studies. Routledge, London, pp. 411–44
- Hall S 1996c What is this ‘black’ in black popular culture? In: Morley D, Chen K-H (eds.) Stuart Hall: Critical Dialogues in Cultural Studies. Routledge, London, pp. 465–75
- Hartley J 1998 Editoral (with goanna). International Journal of Cultural Studies 1(1): 5–10
- Hooks B 1990 Yearning: Race, Gender, and Cultural Politics. South End Press, Boston
- Long E 1997 Introduction: engaging sociology and cultural studies: disciplinarity and social change. In: Long E (ed.) From Sociology to Cultural Studies. Blackwell, Malden, MA, pp. 1–32
- McCarthy C 1998 The Uses of Culture. Routledge, New York
- Nelson C, Gaonkar D P 1996 Cultural studies and the politics of disciplinarity. In: Nelson C, Gaonkar D P (eds.) Disciplinarity and Dissent in Cultural Studies. Routledge, New York pp. 1–22
- 1988 Editor’s comments. Public Culture 1: 1–5
- Sartre J-P 1963 Search for a Method. Knopf, New York
- Schudson M 1997 Cultural politics and the social construction of ‘social construction’: Notes on teddy bear patriarchy. In: Long E (ed.) From Sociology to Cultural Studies. Blackwell, Malden, MA, pp. 379–98
- Striphas T 1998 Introduction: The long march: cultural studies and its institutionalization. Cultural Studies 12: 453–75
- Storey J 1996 CS: An introduction. In: Storey J (ed.) What Is Cultural Studies? A Reader. Arnold. London, pp. 1–13
- West C 1992 The postmodern crisis of the Black intellectuals. In: Grossberg L, Nelson C, Treichler P (eds.) Cultural Studies. Routledge, New York, pp. 689–716
- Williams R 1976 Keywords. Fontana, London
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Gender medicine ‘built on shaky foundations’, Cass review finds
Analysis finds most research underpinning clinical guidelines, hormone treatments and puberty blockers to be low quality
Review of gender services has major implications for mental health services
The head of the world’s largest review into children’s care has said that gender medicine is “built on shaky foundations”.
Dr Hilary Cass, the paediatrician commissioned to conduct a review of the services provided by the NHS to children and young people questioning their gender identity, said that while doctors tended to be cautious in implementing new findings in emerging areas of medicine, “quite the reverse happened in the field of gender care for children”.
Cass commissioned the University of York to conduct a series of analyses as part of her review.
Two papers examined the quality and development of current guidelines and recommendations for managing gender dysphoria in children and young people. Most of the 23 clinical guidelines reviewed were not independent or evidence based, the researchers found.
A third paper on puberty blockers found that of 50 studies, only one was of high quality.
Similarly, of 53 studies included in a fourth paper on the use of hormone treatment, only one was of sufficiently high quality, with little or only inconsistent evidence on key outcomes.
Here are the main findings of the reviews:
Clinical guidelines
Increasing numbers of children and young people experiencing gender dysphoria are being referred to specialist gender services. There are various guidelines outlining approaches to the clinical care of these children and adolescents.
In the first two papers, the York researchers examined the quality and development of published guidelines or clinical guidance containing recommendations for managing gender dysphoria in children and young people up to the age of 18.
They studied a total of 23 guidelines published in different countries between 1998 and 2022. All but two were published after 2010.

Most of them lacked “an independent and evidence-based approach and information about how recommendations were developed”, the researchers said.
Few guidelines were informed by a systematic review of empirical evidence and they lack transparency about how their recommendations were developed. Only two reported consulting directly with children and young people during their development, the York academics found.
“Healthcare services and professionals should take into account the poor quality and interrelated nature of published guidance to support the management of children and adolescents experiencing gender dysphoria/incongruence,” the researchers wrote.
Writing in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) , Cass said that while medicine was usually based on the pillars of integrating the best available research evidence with clinical expertise, and patient values and preferences, she “found that in gender medicine those pillars are built on shaky foundations”.
She said the World Professional Association of Transgender Healthcare (WPATH) had been “highly influential in directing international practice, although its guidelines were found by the University of York’s appraisal to lack developmental rigour and transparency”.
In the foreword to her report, Cass said while doctors tended to be cautious in implementing new findings “quite the reverse happened in the field of gender care for children”.
In one example, she said a single Dutch medical study, “suggesting puberty blockers may improve psychological wellbeing for a narrowly defined group of children with gender incongruence”, had formed the basis for their use to “spread at pace to other countries”. Subsequently, there was a “greater readiness to start masculinising/feminising hormones in mid-teens”.
She added: “Some practitioners abandoned normal clinical approaches to holistic assessment, which has meant that this group of young people have been exceptionalised compared to other young people with similarly complex presentations. They deserve very much better.”
Both papers repeatedly pointed to a key problem in this area of medicine: a dearth of good data.
She said: “Filling this knowledge gap would be of great help to the young people wanting to make informed choices about their treatment.”
Cass said the NHS should put in place a “full programme of research” looking at the characteristics, interventions and outcomes of every young person presenting to gender services, with consent routinely sought for enrolment in a research study that followed them into adulthood.
Gender medicine was “an area of remarkably weak evidence”, her review found, with study results also “exaggerated or misrepresented by people on all sides of the debate to support their viewpoint”.
Alongside a puberty blocker trial, which could be in place by December, there should be research into psychosocial interventions and the use of the masculinising and feminising hormones testosterone and oestrogen, the review found.
Hormone treatment
Many trans people who seek medical intervention in their transition opt to take hormones to masculinise or feminise their body, an approach that has been used in transgender adults for decades.
“It is a well-established practice that has transformed the lives of many transgender people,” the Cass review notes, adding that while these drugs are not without long-term problems and side-effects, for many they are dramatically outweighed by the benefits.
For birth-registered females, the approach means taking testosterone, which brings about changes including the growth of facial hair and a deepening of the voice, while for birth-registered males, it involves taking hormones including oestrogen to promote changes including the growth of breasts and an increase in body fat. Some of these changes may be irreversible.
However, in recent years a growing proportion of adolescents have begun taking these cross-sex, or gender-affirming, hormones, with the vast majority who are prescribed puberty blockers subsequently moving on to such medication.
This growing take-up among young people has led to questions over the impact of these hormones in areas ranging from mental health to sexual functioning and fertility.
Now researchers at the University of York have carried out a review of the evidence, comprising an analysis of 53 previously published studies, in an attempt to set out what is known – and what is not – about the risks, benefits and possible side-effects of such hormones on young people.
All but one study, which looked at side-effects, were rated of moderate or low quality, with the researchers finding limited evidence for the impact of such hormones on trans adolescents with respect to outcomes, including gender dysphoria and body satisfaction.
The researchers noted inconsistent findings around the impact of such hormones on growth, height, bone health and cardiometabolic effects, such as BMI and cholesterol markers. In addition, they found no study assessed fertility in birth-registered females, and only one looked at fertility in birth-registered males.
“These findings add to other systematic reviews in concluding there is insufficient and/or inconsistent evidence about the risks and benefits of hormone interventions in this population,” the authors write.
However, the review did find some evidence that masculinising or feminising hormones might help with psychological health in young trans people. An analysis of five studies in the area suggested hormone treatment may improve depression, anxiety and other aspects of mental health in adolescents after 12 months of treatment, with three of four studies reporting an improvement around suicidality and/or self-harm (one reported no change).
But unpicking the precise role of such hormones is difficult. “Most studies included adolescents who received puberty suppression, making it difficult to determine the effects of hormones alone,” the authors write, adding that robust research on psychological health with long-term follow-up was needed.
The Cass review has recommended NHS England should review the current policy on masculinising or feminising hormones, advising that while there should be the option to provide such drugs from age 16, extreme caution was recommended, and there should be a clear clinical rationale for not waiting until an individual reached 18.
Puberty blockers
Treatments to suppress puberty in adolescents became available through routine clinical practice in the UK a decade ago.
While the drugs have long been used to treat precocious puberty – when children start puberty at an extremely young age – they have only been used off-label in children with gender dysphoria or incongruence since the late 1990s. The rationale for giving puberty blockers, which originated in the Netherlands, was to buy thinking time for young people and improve their ability to smooth their transition in later life.
Data from gender clinics reported in the Cass review showed the vast majority of people who started puberty suppression went on to have masculinising or feminising hormones, suggesting that puberty blockers did not buy people time to think.
To understand the broader effects of puberty blockers, researchers at the University of York identified 50 papers that reported on the effects of the drugs in adolescents with gender dysphoria or incongruence. According to their systematic review, only one of these studies was high quality, with a further 25 papers regarded as moderate quality. The remaining 24 were deemed too weak to be included in the analysis.
Many of the reports looked at how well puberty was suppressed and the treatment’s side-effects, but fewer looked at whether the drugs had their intended benefits.
Of two studies that investigated gender dysphoria and body satisfaction, neither found a change after receiving puberty blockers. The York team found “very limited” evidence that puberty blockers improved mental health.
Overall, the researchers said “no conclusions” could be drawn about the impact on gender dysphoria, mental and psychosocial health or cognitive development, though there was some evidence bone health and height may be compromised during treatment.
Based on the York work, the Cass review finds that puberty blockers offer no obvious benefit in helping transgender males to help their transition in later life, particularly if the drugs do not lead to an increase in height in adult life. For transgender females, the benefits of stopping irreversible changes such as a deeper voice and facial hair have to be weighed up against the need for penile growth should the person opt for vaginoplasty, the creation of a vagina and vulva.
In March, NHS England announced that children with gender dysphoria would no longer receive puberty blockers as routine practice. Instead, their use will be confined to a trial that the Cass review says should form part of a broader research programme into the effects of masculinising and feminising hormones.
- Transgender
- Young people

Veteran trans campaigner: ‘Cass review has potential for positive change’

Cass review must be used as ‘watershed moment’ for NHS gender services, says Streeting

‘This isn’t how good scientific debate happens’: academics on culture of fear in gender medicine research

Five thousand children with gender-related distress awaiting NHS care in England

Ban on children’s puberty blockers to be enforced in private sector in England

What Cass review says about surge in children seeking gender services

Adult transgender clinics in England face inquiry into patient care

‘Children are being used as a football’: Hilary Cass on her review of gender identity services

Thousands of children unsure of gender identity ‘let down by NHS’, report finds

Most viewed

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cultural Anthropology Research Paper Topics. Here, you'll find a list of 10 ideas for research paper about culture that are concentrated on anthropological aspect: The Role of Rituals in Maintaining Social Order in Traditional Societies. Kinship and Social Structure: A Comparative Analysis of Matrilineal and Patrilineal Societies.
Here is the list of the top 200+ culture research topics, provided in different categories; let's look. Arts and Literature. Evolution of modern art movements. Impact of digital technology on literature. Representation of gender in classical literature. Role of art in social change movements.
2 List of Cultural Research Paper Topics. 2.1 Cultural Diversity Research Topics. 2.2 Anthropology Research Topics. 2.3 Subculture Study Ideas. 2.4 Heritage and Preservation Studies. 2.5 Identity Research Topics. 2.6 Socio-Cultural Essay Ideas. 2.7 Psychology Research Topics. 2.8 Western Civilization Essay Ideas.
Cultural Studies Research Paper Topics. When pursuing cultural studies, writing research papers is unavoidable. Here are cultural research paper topics to consider for your papers and essays. How stigma affects the efforts to prevent sexually transmitted diseases from spreading; Challenges encountered by people with social disorders and anxiety
Cultural Anthropology Research Topics. The effects of cultural anthropology on the missionary. Exploration of the long-term impacts of physical labor on the physical appearance of humans. An evaluation of the cultural anthropology of our time. The role of women in modern society as opposed to the traditional roles.
Socio-Cultural Essay Topics. Socio-cultural topics explore a wide range of issues related to society and culture. The essays in the socio-cultural context examine the relationship between humanity and culture. Research topics in this field can range from the study of social institutions to the norms and values of cultural studies.
Interesting Culture Topics to Research for Essays and Papers. Maori Culture and Traditions. Intricacies of Japanese Tea Ceremony. Voodoo Practices in Haitian Culture. Celtic Traditions and Mythology. Arab Bedouin Traditions and Nomadic Lifestyle. Native American Tribes and Their Cultural Diversity.
Cultural Research Paper Topics. Investigating the benefits of cultural studies in promoting brands in international markets. Perception differences among youth and the old population of disabled people. Examination of different coping mechanisms of being culturally different in society. Impact of films, songs, and feminism on promoting women ...
Cultural History Research Paper Topics. Exploring cultural history research paper topics opens the door to understanding humanity's diverse societal heritage. This comprehensive guide, presented by iResearchNet, is a valuable resource for students tasked with writing a research paper on this rich and wide-ranging subject.
15 Cultural Anthropology Research Paper Topics. Offensive Hand Gesture Around the World. The Role of Social Status in South Korea. The View of Marriage in Central Asian Countries. Different Views of Death in Different Religions. People's Perception of Late Marriages in China. The Importance of Literature for Spreading New Ideas.
International Journal of Cultural Studies is a fully peer-reviewed journal and a leading venue for scholarship committed to rethinking cultural practices, processes, texts and infrastructures beyond traditional national frameworks and regional biases. Established to revitalize cultural studies against the dangers of parochialism and intellectual ossification, the journal interrogates what ...
100 Cross-Cultural Psychology Research Paper Topics. Cross-cultural psychology stands as a pivotal discipline aimed at deciphering the intricate ways in which cultural factors sculpt human behavior and cognition. This field offers a profound understanding of the diversity and universality of psychological processes, providing valuable insights ...
Sociology of Culture Research Paper Topics. The sociology of culture and, the related, cultural sociology concerns the systematic analysis of culture, usually understood as the ensemble of symbolic codes used by a members of a society, as it is manifested in the society. Culture in the sociological field is analyzed as the ways of thinking and ...
Cultural Studies ↔ Critical Methodologies (CSCM) publishes open-peer reviewed research articles, critical analyses of contemporary media representations, autoethnography, poetry, and creative non-fiction.CSCM provides an explicit forum for the intersections of cultural studies, critical interpretive research methodologies, and cultural critique. . Average time from submission to first ...
Cross-Cultural Research (CCR) publishes peer-reviewed articles that describe cross-cultural and comparative studies in all human sciences. Each issue, published quarterly, examines topics that span societies, nations and cultures, providing … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).
The framework can be applied in many different ways to support research processes. One way is to simply use the diagram of the cultural ensemble (Fig. 8.2) as the basis for describing a culture—its distinctive elements and their dynamics.It can be surprisingly difficult to explain what culture is, and these concepts give a solid foundation for identifying cultural features in any given context.
The study of human culture in all its manifestations, across time and across cultures | Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on CULTURAL STUDIES.
Crane/Rossow/Becker Cultural Studies 02.06.2021 4/10 • The topic sentence states the arguments you are attempting to make in the paragraph.It should contain key words. • In the development you define, explain, analyse, or modify your argument and support or illustrate it with evidence/examples from secondary literature or your analysis of a primary source.
Cultural Studies welcomes empirically-rich, politically-engaged research that critically engages: Techniques, institutions, and systems of power. Formations of resistance, activism, and intervention. The history, politics, and philosophy of media/technology. Feminist, gender, and sexuality studies. Theories and practices of globalization.
113 Great Research Paper Topics. Posted by Christine Sarikas. General Education. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and ...
Cultural anthropology is the study of human patterns of thought and behavior, and how and why these patterns differ, in contemporary societies. Cultural anthropology is sometimes called social anthropology, sociocultural anthropology, or ethnology. Cultural anthropology also includes pursuits such as ethnography, ethnohistory, and cross ...
On cultural studies, again. Ien Ang. Institute for Culture and society, Western Sydney University, Australia. Abstract. This article reflects on the state of cultural studies today. It asks to ...
Essay Example: Lisa Fernandez, a name synonymous with excellence in softball, carved her path to greatness from an early age. Born on February 22, 1971, in Long Beach, California, Fernandez's childhood was a melting pot of cultural heritage and sporting prowess. Her journey is not just a story.
While many Americans say they have used marijuana in their lifetime, far fewer are current users, according to the same survey. In 2022, 23.0% of adults said they had used the drug in the past year, while 15.9% said they had used it in the past month. While many Americans say legalizing recreational marijuana has economic and criminal justice ...
Sample Cultural Studies Research Paper. Browse other research paper examples and check the list of research paper topics for more inspiration. iResearchNet offers academic assignment help for students all over the world: writing from scratch, editing, proofreading, problem solving, from essays to dissertations, from humanities to STEM.
Similarly, of 53 studies included in a fourth paper on the use of hormone treatment, only one was of sufficiently high quality, with little or only inconsistent evidence on key outcomes.. Here are ...