
- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …

Design Thinking vs Critical Thinking: Unraveling the Key Differences

Design thinking and critical thinking are two approaches that individuals and organizations use to solve problems and make decisions. Design thinking, a non-linear, iterative process, involves understanding users, challenging assumptions, redefining problems, and creating innovative solutions through prototyping and testing. Whereas critical thinking involves analysis, evaluation, and logical reasoning to reach well-founded conclusions based on evidence and context.
However, these two approaches are not mutually exclusive. They can complement and strengthen each other in various fields and applications. Design thinking can offer educators creative new approaches to engage students in critical thinking, while critical thinking can be integrated into product design and development methods. Both approaches emphasize different aspects of problem-solving and decision-making, ultimately contributing to more effective and innovative solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Design thinking and critical thinking are distinct approaches to problem-solving, but can be combined effectively.
- Both methods can be applied in various fields, from education to product development.
- Empathy, feedback, and cultural context play significant roles in the successful integration of design thinking and critical thinking.
Understanding Design and Critical Thinking
In this section, we will explore the concepts of design thinking and critical thinking, their definitions, and how they relate to each other.
Definition of Design Thinking
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that focuses on understanding the user’s experience and needs. It is characterized by empathy, collaboration, and experimentation to develop innovative solutions for design challenges. This methodology encourages designers to take risks and iterate on their ideas until they find a solution that addresses users’ needs and desires effectively. Design thinking often involves creative thinking and abductive reasoning , as designers generate multiple alternative solutions and refine them based on feedback and iterations.
Definition of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a process of evaluating information, identifying assumptions, and making reasoned decisions based on evidence. It encompasses reflective thinking, deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, and abductive reasoning. Reflective thinking involves assessing one’s assumptions and beliefs, while deductive reasoning uses general principles to make specific conclusions. Inductive reasoning, on the other hand, draws general conclusions from specific observations and examples.
When problem-solving, both design thinking and critical thinking are essential components that contribute to effective decision-making. By incorporating elements of both creative thinking and reflective thinking, individuals can better grasp the nuances of a problem, identify potential solutions, and evaluate their efficacy. This balanced approach, drawing on the strengths of the critical thinking process and the design thinking mindset, can promote more successful outcomes in both product design and development.
Ultimately, understanding the relationship between design thinking and critical thinking is essential for designers, researchers, and problem solvers as they tackle complex problems and work together to create innovative solutions.
Differentiating Critical and Design Thinking
Process of design thinking.
Design thinking is a collaborative, creative methodology that focuses on defining and solving complex problems through empathy and experimentation. It involves understanding the users’ needs, brainstorming solutions, and rapidly prototyping to test and refine ideas. Design thinking includes techniques and tools for problem-solving and emphasizing human-centered design that enables businesses to create innovative solutions for their customers.
The design thinking process typically includes the following steps:
- Empathize : Understand the users’ needs, motivations, and constraints by putting oneself in their shoes and actively seeking feedback.
- Define : Identify users’ needs and pain points by observing and analyzing patterns and refining the problem statement.
- Ideate : Generate various solutions to the identified problems using brainstorming and other creative techniques, with an emphasis on divergent thinking.
- Prototype : Create low-fidelity representations of the proposed solution(s) for the purpose of testing with users.
- Test : Evaluate the prototypes with users, gather feedback, and iterate on the design to improve it further.
Process of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is an intellectual process that involves evaluating and analyzing information, concepts, and data. It is a method for evaluating situations from different perspectives to arrive at an unbiased, optimum solution. Critical thinking encompasses a range of cognitive skills and methods, such as logic, reasoning, and skepticism, for gathering and assessing evidence, making connections, and developing well-informed conclusions.
The critical thinking process can typically be broken down into the following steps:
- Identify : Determine the problem or issue faced and establish the context in which it exists.
- Gather : Collect relevant information and data from various sources to understand the issue better.
- Analyze : Break down the collected information into smaller components, identify patterns, relationships, and other essential factors.
- Evaluate : Assess the reliability, credibility, and relevance of the information found during the analysis phase.
- Synthesize : Integrate the analyzed information and insights to arrive at a well-informed conclusion or decision about the issue in question.
While both critical and design thinking involve problem-solving and analysis, they differ in their approach, focus, and methodology. Design thinking is more focused on empathy and creativity, creating innovative solutions to meet users’ needs. In contrast, critical thinking centers on logic, reasoning, and evidence-based evaluation to make well-informed decisions or judgments. The combination of both modes of thinking can enhance the problem-solving process and lead to more efficient and innovative outcomes for businesses and individuals.
Applications in Various Fields
Design thinking and critical thinking are essential skills that drive growth and innovation across various fields. This section explores their applications in product creation and decision making.
Design Thinking in Product Creation
Design thinking plays a crucial role in product creation as it enables organizations to develop innovative and user-centered solutions. By focusing on empathy, creativity, and iterative prototyping, design thinking fosters an environment where products are tailored to meet users’ needs.
For instance, through observing and interacting with potential customers, businesses can better understand their audience and identify their pain points. This process helps them formulate problems that need to be addressed, leading to more targeted product development strategies.
The iterative nature of design thinking encourages businesses to create multiple prototypes, test them, gather feedback, and refine their designs until the desired user experience is achieved. This flexibility often results in more innovative products that solve real-life problems while staying within the bounds of business models .
Critical Thinking in Decision Making
Critical thinking is an essential component of decision making across various fields, including business, science, and politics. Unlike design thinking, critical thinking revolves around the analysis and evaluation of information. It helps individuals and organizations to:
- Define clear objectives and criteria for decision making, enabling them to prioritize goals and assess the feasibility of different solutions.
- Analyze information to identify the underlying patterns, trends, and relationships that might influence a given situation.
- Evaluate the credibility of sources, data, and arguments to make well-informed decisions.
In the context of organizations, critical thinking can be applied to improve internal processes, optimize resource allocation, and identify potential risks. Furthermore, developing a culture of critical thinking can empower employees to make better decisions independently, leading to increased efficiency and more robust business models.
Both design thinking and critical thinking contribute significantly to the development of innovative products, enhanced user experiences, and improved decision-making processes. By leveraging these complementary skill sets, organizations can unleash their full potential and thrive in various fields.
The Role of Empathy and Feedback
Empathy plays a crucial role in design thinking as it helps designers understand and connect with their users’ emotions, perspectives, and concerns. By developing a strong sense of empathy, designers can tailor their designs to better meet users’ needs and expectations. Empathy allows designers to create more user-centric products and experiences, ultimately leading to higher levels of user satisfaction and engagement source .
Feedback, on the other hand, serves as a valuable tool for improving and refining designs. It enables designers to receive insights from users and stakeholders, helping them identify areas of improvement or new opportunities to explore. By actively seeking feedback, designers can ensure that their designs are aligned with users’ expectations while also addressing any potential issues or concerns. The feedback process also promotes collaboration and encourages critical thinking, essential components for any successful design project source .
Incorporating empathy and feedback into the design process can often yield innovative solutions to complex problems. By understanding users’ needs and expectations, designers can develop more targeted and effective designs. Open communication and a willingness to embrace feedback lead to continuous improvement and adaptation, resulting in better project outcomes.
When comparing design thinking and critical thinking, both empathy and feedback serve as key differentiators. While critical thinking focuses on objective analysis, design thinking prioritizes empathy and the emotional connection with users. Furthermore, feedback serves as a bridge between design and critical thinking, enabling designers to adapt their designs based on input from users and stakeholders.
Ultimately, the role of empathy and feedback in design thinking is critical for creating meaningful and impactful designs. By incorporating these elements into the process, designers can develop products and experiences that delight users and meet their needs, expectations, and preferences.
The Cultural Impact
Creating an innovative culture.
Design thinking and critical thinking play a vital role in shaping the culture of organizations and teams. Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that emphasizes empathy, experimentation, and iteration. It is often used in the fields of technology, services, and sustainability. Companies like IDEO and various businesses have integrated design thinking into their strategies to enhance innovation and user-centricity.
An innovative culture can be nurtured by embracing design thinking principles. The purpose is to promote collaboration and open-mindedness, allowing teams to approach problems from various perspectives. This also encourages a behavior of continuous learning, as individuals are urged to challenge their preconceptions and be more adaptable.
Integrating design thinking can lead to valuable advancements in technology and services, creating a sustainable business strategy. By fostering an environment that supports experimentation and growth, organizations can stay ahead in their respective industries.
Nurturing a Culture of Critical Examination
On the other hand, critical thinking focuses on systematic analysis, evaluation, and judgment. It aims to improve decision-making by helping individuals control their cognitive biases and maintain a neutral stance. This thought process adds value to problem-solving by promoting rationality and thorough examination.
A culture that nurtures critical thinking encourages individuals to question their assumptions and assess the validity of their beliefs. Implementation of this thinking process instills a sense of responsibility and accountability, thus contributing to a more effective problem-solving.
A blend of critical thinking and design thinking can lead to comprehensive problem-solving approaches, as it combines empathy, creativity, and in-depth analysis. By incorporating both methodologies into their organizational culture, businesses can foster an environment that continually drives growth, adaptability, and sustainable success.
Practical Approaches and Techniques
Design iteration process.
The design iteration process is a crucial aspect of design thinking, which is an approach for practical and creative problem-solving primarily focused on human-centered design ( source ). Tim Brown, an expert in design thinking, emphasizes the importance of empathizing with users to devise innovative problem-solving solutions. This human-centered approach can be applied to various fields such as interaction design, product design, and even urban planning.
In the design iteration process, teams go through multiple stages that involve empathizing, defining problems, ideating, prototyping, and testing. These stages are continuously repeated to improve and refine the final solution. Iterating is an essential part of this process as it allows designers to address any shortcomings in earlier stages and adjust their prototypes accordingly.
Critical Thinking and Decision Making Process
Critical thinking is a vital component in making well-informed decisions that account for authentic and accurate information ( source ). This process encompasses various aspects, including synthesizing information, evaluating evidence, reflecting on data, and reconstructing arguments. Critical thinking is essential in fields like product design, business, and engineering, as it enables professionals to analyze and validate various aspects of their work.
The decision-making process is intertwined with critical thinking as it relies on the accurate and logical evaluation of information. In this process, individuals apply critical thinking skills to weigh the pros and cons of different alternatives and choose the best course of action, considering both short-term and long-term consequences. It is also essential to revisit decisions regularly, as this allows for adjustments and improvements based on new evidence and insights.
By integrating both design thinking and critical thinking into their processes, individuals and teams can not only solve problems more creatively but also make decisions that are grounded in evidence and sound reasoning. Both approaches, when used effectively, can lead to better outcomes in a wide range of disciplines, including design, urban planning, and business.
Design thinking and critical thinking are two distinct approaches to problem-solving and decision-making. Design thinking emphasizes empathy, collaboration, and creative exploration to find innovative solutions to complex issues source . On the other hand, critical thinking focuses on evaluating and analyzing information to make well-informed decisions source .
While both of these methodologies have their unique advantages, they can also complement one another. By integrating design thinking practices into critical thinking, practitioners can enhance their ability to address problems and generate effective solutions. This happens through the potential for design thinking methods to augment traditional critical thinking practices source .
In the professional world, design thinking has become a valuable skill that can lead to career advancements and increased salaries, especially among marketing managers source . In tandem, critical thinking remains a widely accepted educational goal, making it an essential skill for nearly any profession source .
Ultimately, understanding both design thinking and critical thinking empowers individuals to tackle complex problems with comprehensive and flexible frameworks. By leveraging the strengths of each approach, professionals from various sectors can effectively navigate challenges and produce solutions that benefit their organizations and communities.
You may also like

Thinking Critically About New Information
We are constantly inundated with new information all of the time, even if it’s just sensory input from what we smell, hear, […]

The Connection between Associative Thinking and Entrepreneurship: Exploring the Link
Associative thinking is a cognitive process that involves connecting seemingly unrelated concepts to generate new ideas. This type of thinking is essential […]

How to Evaluate Sources Using Critical Thinking: A Concise Guide to Informed Research
In today’s world, the internet provides us with a wealth of information, but not all of it is trustworthy. Knowing how to […]

Critical thinking jokes
Critical thinking can make life smoother and smarter, solving all kinds of academic, professional and everyday problems. But it’s not something you […]
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Design Thinking (DT)
What is design thinking (dt).
Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test. It is most useful to tackle ill-defined or unknown problems and involves five phases: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test.
- Transcript loading…
Why Is Design Thinking so Important?
“Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that draws from the designer's toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success.”
— Tim Brown, CEO of IDEO
Design thinking fosters innovation . Companies must innovate to survive and remain competitive in a rapidly changing environment. In design thinking, cross-functional teams work together to understand user needs and create solutions that address those needs. Moreover, the design thinking process helps unearth creative solutions.
Design teams use design thinking to tackle ill-defined/unknown problems (aka wicked problems ). Alan Dix, Professor of Human-Computer Interaction, explains what wicked problems are in this video.
Wicked problems demand teams to think outside the box, take action immediately, and constantly iterate—all hallmarks of design thinking.
Don Norman, a pioneer of user experience design, explains why the designer’s way of thinking is so powerful when it comes to such complex problems.
Design thinking offers practical methods and tools that major companies like Google, Apple and Airbnb use to drive innovation. From architecture and engineering to technology and services, companies across industries have embraced the methodology to drive innovation and address complex problems.
The End Goal of Design Thinking: Be Desirable, Feasible and Viable
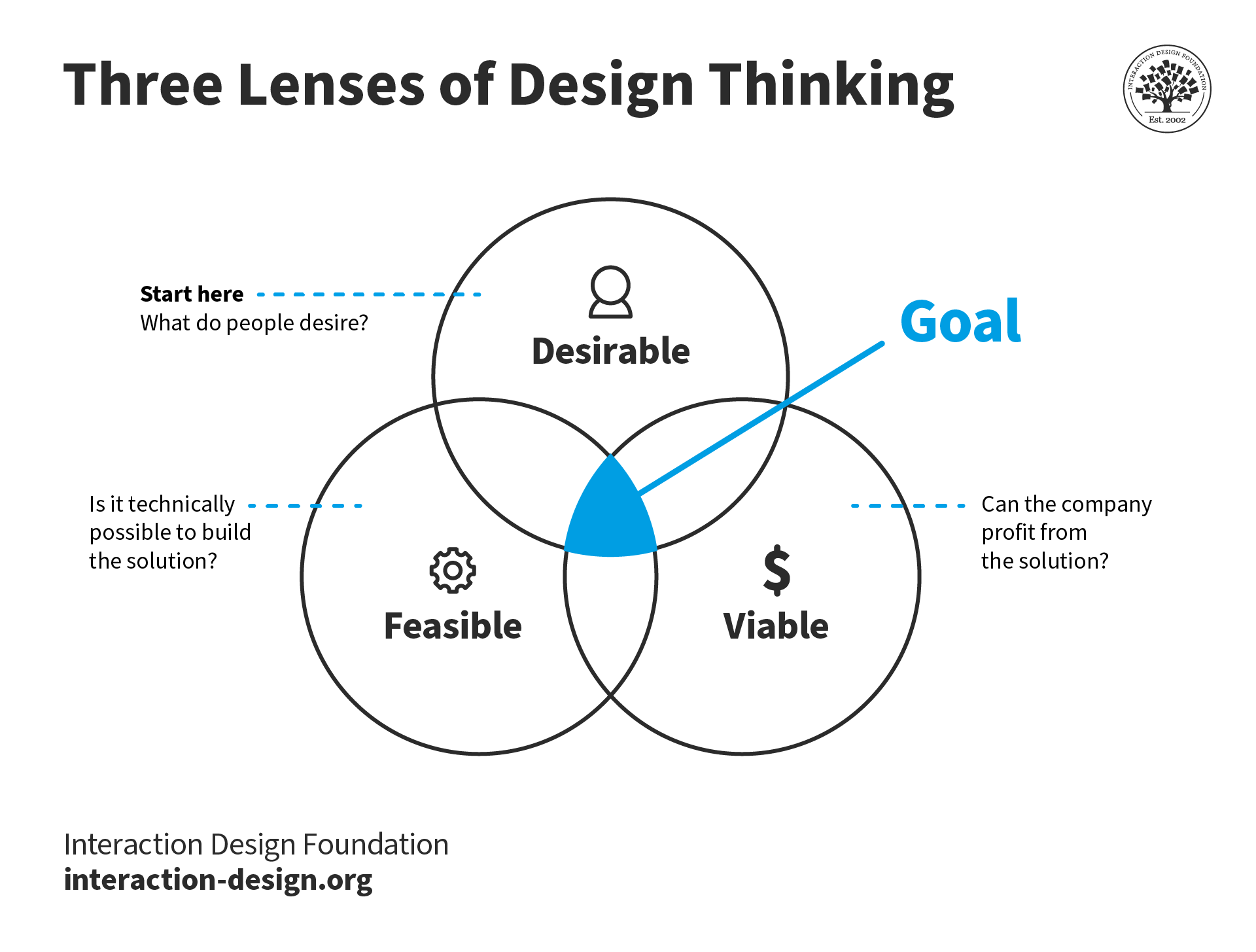
The design thinking process aims to satisfy three criteria: desirability (what do people desire?), feasibility (is it technically possible to build the solution?) and viability (can the company profit from the solution?). Teams begin with desirability and then bring in the other two lenses.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Desirability: Meet People’s Needs
The design thinking process starts by looking at the needs, dreams and behaviors of people—the end users. The team listens with empathy to understand what people want, not what the organization thinks they want or need. The team then thinks about solutions to satisfy these needs from the end user’s point of view.
Feasibility: Be Technologically Possible
Once the team identifies one or more solutions, they determine whether the organization can implement them. In theory, any solution is feasible if the organization has infinite resources and time to develop the solution. However, given the team’s current (or future resources), the team evaluates if the solution is worth pursuing. The team may iterate on the solution to make it more feasible or plan to increase its resources (say, hire more people or acquire specialized machinery).
At the beginning of the design thinking process, teams should not get too caught up in the technical implementation. If teams begin with technical constraints, they might restrict innovation.
Viability: Generate Profits
A desirable and technically feasible product isn’t enough. The organization must be able to generate revenues and profits from the solution. The viability lens is essential not only for commercial organizations but also for non-profits.
Traditionally, companies begin with feasibility or viability and then try to find a problem to fit the solution and push it to the market. Design thinking reverses this process and advocates that teams begin with desirability and bring in the other two lenses later.
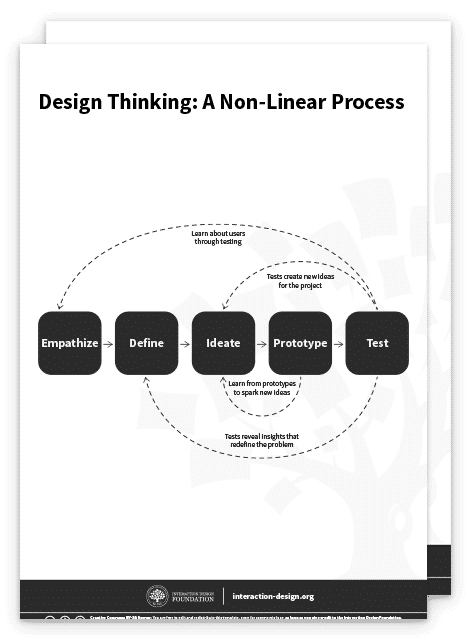
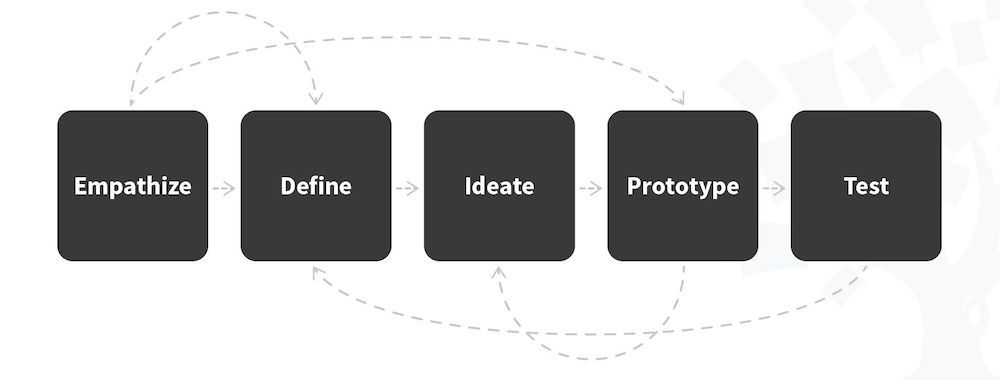
The Five Stages of Design Thinking
Stanford University’s Hasso Plattner Institute of Design, commonly known as the d.school, is renowned for its pioneering approach to design thinking. Their design process has five phases: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. These stages are not always sequential. Teams often run them in parallel, out of order, and repeat them as needed.
Stage 1: Empathize —Research Users' Needs
The team aims to understand the problem, typically through user research. Empathy is crucial to design thinking because it allows designers to set aside your assumptions about the world and gain insight into users and their needs.
Stage 2: Define—State Users' Needs and Problems
Once the team accumulates the information, they analyze the observations and synthesize them to define the core problems. These definitions are called problem statements . The team may create personas to help keep efforts human-centered.
Stage 3: Ideate—Challenge Assumptions and Create Ideas
With the foundation ready, teams gear up to “think outside the box.” They brainstorm alternative ways to view the problem and identify innovative solutions to the problem statement.
Stage 4: Prototype—Start to Create Solutions
This is an experimental phase. The aim is to identify the best possible solution for each problem. The team produces inexpensive, scaled-down versions of the product (or specific features found within the product) to investigate the ideas. This may be as simple as paper prototypes .
Stage 5: Test—Try the Solutions Out
The team tests these prototypes with real users to evaluate if they solve the problem. The test might throw up new insights, based on which the team might refine the prototype or even go back to the Define stage to revisit the problem.
These stages are different modes that contribute to the entire design project rather than sequential steps. The goal is to gain a deep understanding of the users and their ideal solution/product.
Design Thinking Frameworks
There is no single definition or process for design thinking. The five-stage design thinking methodology described above is just one of several frameworks.
Hasso-Platner Institute Panorama
Ludwig Wilhelm Wall, CC BY-SA 3.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
Innovation doesn’t follow a linear path or have a clear-cut formula. Global design leaders and consultants have interpreted the abstract design process in different ways and have proposed other frameworks of design thinking.
Head, Heart and Hand by the American Institution of Graphic Arts (AIGA)
The Head, Heart, and Hand approach by AIGA (American Institute of Graphic Arts) is a holistic perspective on design. It integrates the intellectual, emotional, and practical aspects of the creative process.

More than a process, the Head, Heart and Hand framework outlines the different roles that designers must perform to create great results.
© American Institute of Graphic Arts, Fair Use
“ Head ” symbolizes the intellectual component. The team focuses on strategic thinking, problem-solving and the cognitive aspects of design. It involves research and analytical thinking to ensure that design decisions are purposeful.
“ Heart ” represents the emotional dimension. It emphasizes empathy, passion, and human-centeredness. This aspect is crucial in understanding the users’ needs, desires, and experiences to ensure that designs resonate on a deeper, more personal level.
“ Hand ” signifies the practical execution of ideas, the craftsmanship, and the skills necessary to turn concepts into tangible solutions. This includes the mastery of tools, techniques, and materials, as well as the ability to implement and execute design ideas effectively.
Inspire, Ideate, Implement by IDEO
IDEO is a leading design consultancy and has developed its own version of the design thinking framework.

IDEO’s design thinking process is a cyclical three-step process that involves Inspiration, Ideation and Implementation.
© IDEO, Public License
In the “ Inspire ” phase, the team focuses on understanding users’ needs, behaviors, and motivations. The team empathizes with people through observation and user interviews to gather deep insights.
In the “ Ideate ” phase, the team synthesizes the insights gained to brainstorm a wide array of creative solutions. This stage encourages divergent thinking, where teams focus on quantity and variety of ideas over immediate practicality. The goal is to explore as many possibilities as possible without constraints.
In the “ Implement ” phase, the team brings these ideas to life through prototypes. The team tests, iterates and refines these ideas based on user feedback. This stage is crucial for translating abstract concepts into tangible, viable products, services, or experiences.
The methodology emphasizes collaboration and a multidisciplinary approach throughout each phase to ensure solutions are innovative and deeply rooted in real human needs and contexts.
The Double Diamond by the Design Council
In the book Designing Social Systems in a Changing World , Béla Heinrich Bánáthy, Professor at San Jose State University and UC Berkeley, created a “divergence-convergence model” diagram. The British Design Council interpreted this diagram to create the Double Diamond design process model.

As the name suggests, the double diamond model consists of two diamonds—one for the problem space and the other for the solution space. The model uses diamonds to represent the alternating diverging and converging activities.
© Design Council, CC BY 4.0
In the diverging “ Discover ” phase, designers gather insights and empathize with users’ needs. The team then converges in the “ Define ” phase to identify the problem.
The second, solution-related diamond, begins with “ Develop ,” where the team brainstorms ideas. The final stage is “ Deliver ,” where the team tests the concepts and implements the most viable solution.
This model balances expansive thinking with focused execution to ensure that design solutions are both creative and practical. It underscores the importance of understanding the problem thoroughly and carefully crafting the solution, making it a staple in many design and innovation processes.
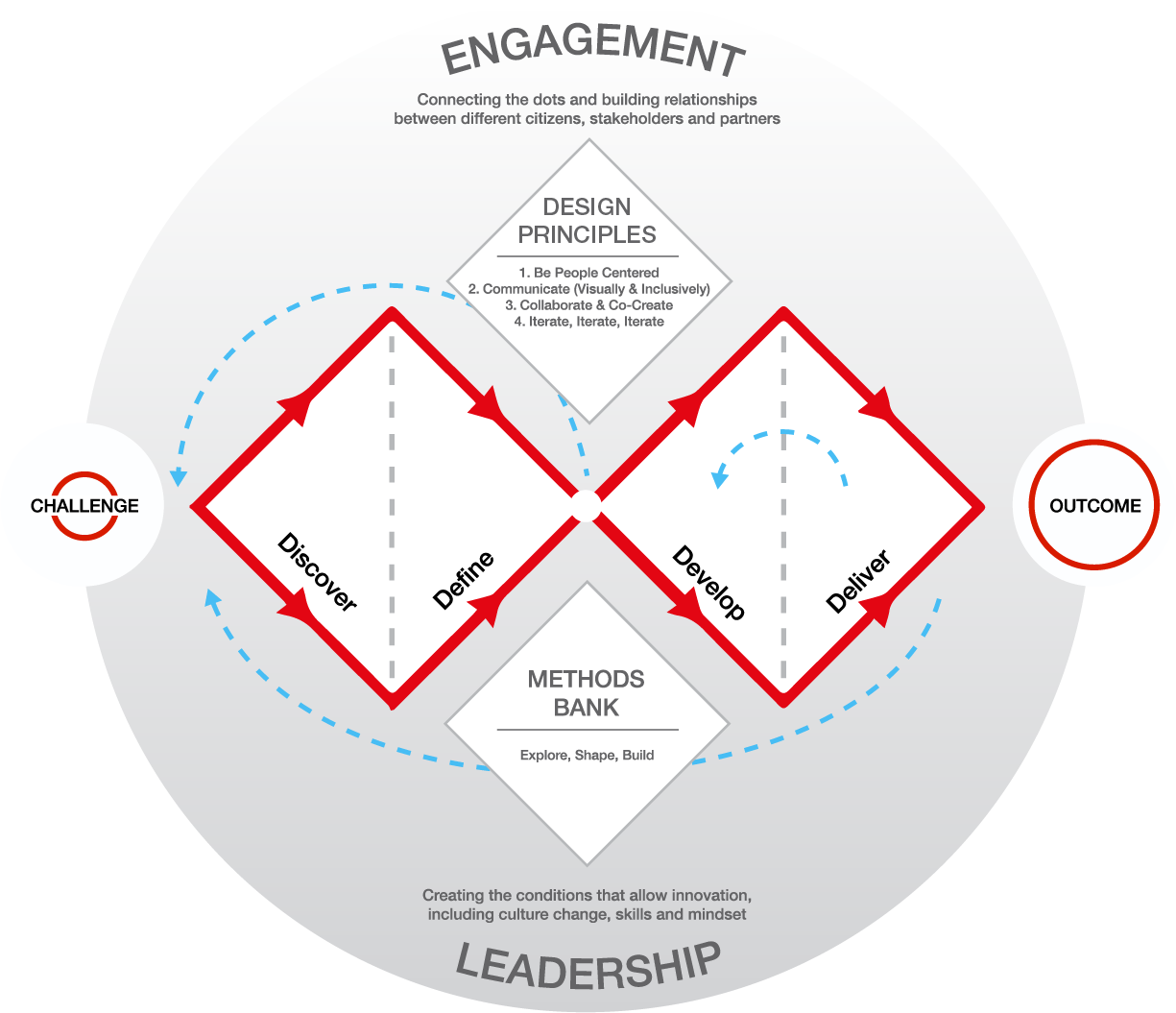
With the widespread adoption of the double diamond framework, Design Council’s simple visual evolved.
In this expanded and annotated version, the framework emphasizes four design principles:
Be people-centered.
Communicate (visually and inclusively).
Collaborate and co-create.
Iterate, iterate, iterate!
The updated version also highlights the importance of leadership (to create an environment that allows innovation) and engagement (to connect with different stakeholders and involve them in the design process).
Common Elements of Design Thinking Frameworks
On the surface, design thinking frameworks look very different—they use alternative names and have different numbers of steps. However, at a fundamental level, they share several common traits.
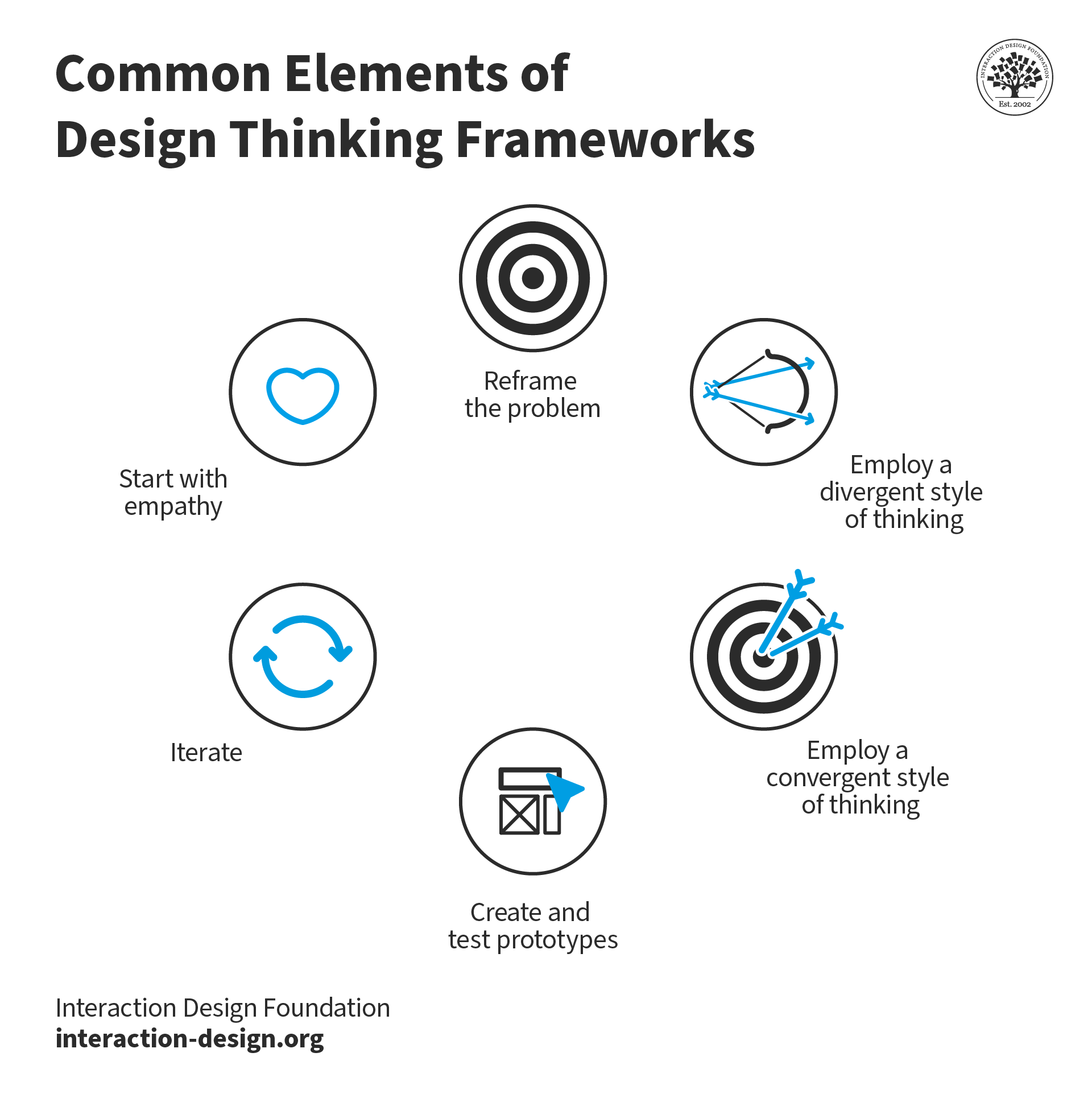
Start with empathy . Focus on the people to come up with solutions that work best for individuals, business, and society.
Reframe the problem or challenge at hand . Don’t rush into a solution. Explore the problem space and look at the issue through multiple perspectives to gain a more holistic, nuanced understanding.
Initially, employ a divergent style of thinking (analyze) . In the problem space, gather as many insights as possible. In the solution space, encourage team members to generate and explore as many solutions as possible in an open, judgment-free ideation space.
Later, employ a convergent style of thinking (synthesize) . In the problem space, synthesize all data points to define the problem. In the solution space, whittle down all the ideas—isolate, combine and refine potential solutions to create more mature ideas.
Create and test prototypes . Solutions that make it through the previous stages get tested further to remove potential issues.
Iterate . As the team progresses through the various stages, they revisit different stages and may redefine the challenge based on new insights.
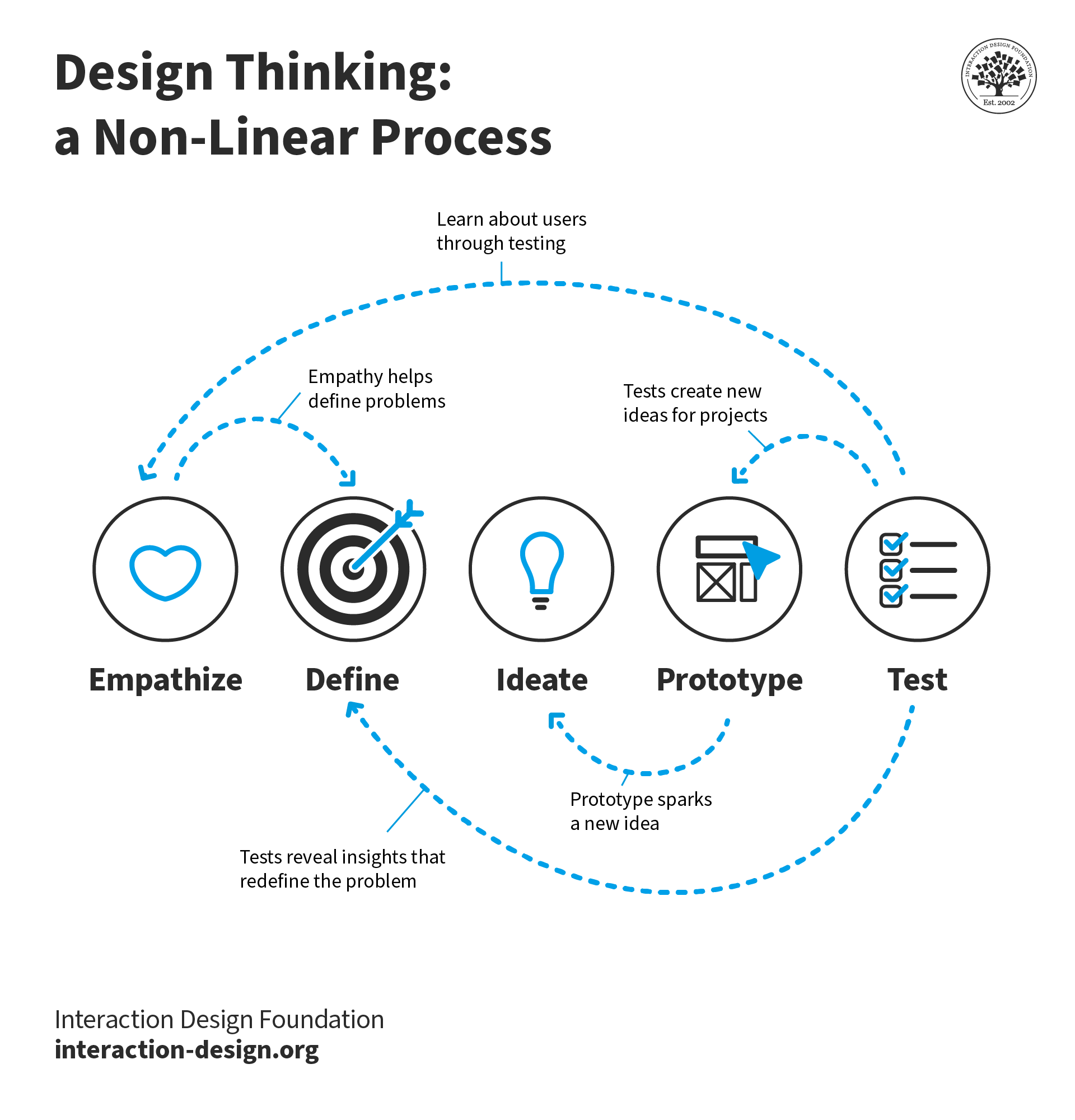
Design thinking is a non-linear process. For example, teams may jump from the test stage to the define stage if the tests reveal insights that redefine the problem. Or, a prototype might spark a new idea, prompting the team to step back into the ideate stage. Tests may also create new ideas for projects or reveal insights about users.
Design Thinking Mindsets: More than a Process

A mindset is a characteristic mental attitude that determines how one interprets and responds to situations . Design thinking mindsets are how individuals think , feel and express themselves during design thinking activities. It includes people’s expectations and orientations during a design project.
Without the right mindset, it can be very challenging to change how we work and think.
The key mindsets that ensure a team can successfully implement design thinking are.
Be empathetic: Empathy is the ability to place yourself, your thinking and feelings in another person’s shoes. Design thinking begins from a deep understanding of the needs and motivations of people—the parents, neighbors, children, colleagues, and strangers who make up a community.
Be collaborative: No one person is responsible for the outcome when you work in a team. Several great minds are always stronger than just one. Design thinking benefits from the views of multiple perspectives and lets others’ creativity bolster your own.
Be optimistic: Be confident about achieving favorable outcomes. Design thinking is the fundamental belief that we can all create change—no matter how big a problem, how little time, or how small a budget. Designing can be a powerful process no matter what constraints exist around you.
Embrace ambiguity: Get comfortable with ambiguous and complex situations. If you expect perfection, it is difficult to take risks, which limits your ability to create radical change. Design thinking is all about experimenting and learning by doing. It gives you the confidence to believe that new, better things are possible and that you can help make them a reality.
Be curious: Be open to different ideas. Recognize that you are not the user.
Reframe: Challenge and reframe assumptions associated with a given situation or problem. Don’t take problems at face value. Humans are primed to look for patterns. The unfortunate side effect of these patterns is that we form (often false and sometimes dangerous) stereotypes and assumptions. Design thinking aims to help you break through any preconceived notions and biases and reframe challenges.
Embrace diversity: Work with and engage people with different cultural backgrounds, experiences, and ways of thinking and working. Everyone brings a unique perspective to the team. When you include diverse voices in a team, you learn from each other’s experiences, further helping you break through your assumptions.
Make tangible: When you make ideas tangible, it is faster and easier for everyone on the team to be on the same page. For example, sketching an idea or enacting a scenario is far more convenient and easy to interpret than an elaborate presentation or document.
Take action: Run experiments and learn from them.
Design Thinking vs Agile Methodology
Teams often use design thinking and agile methodologies in project management, product development, and software development. These methodologies have distinct approaches but share some common principles.
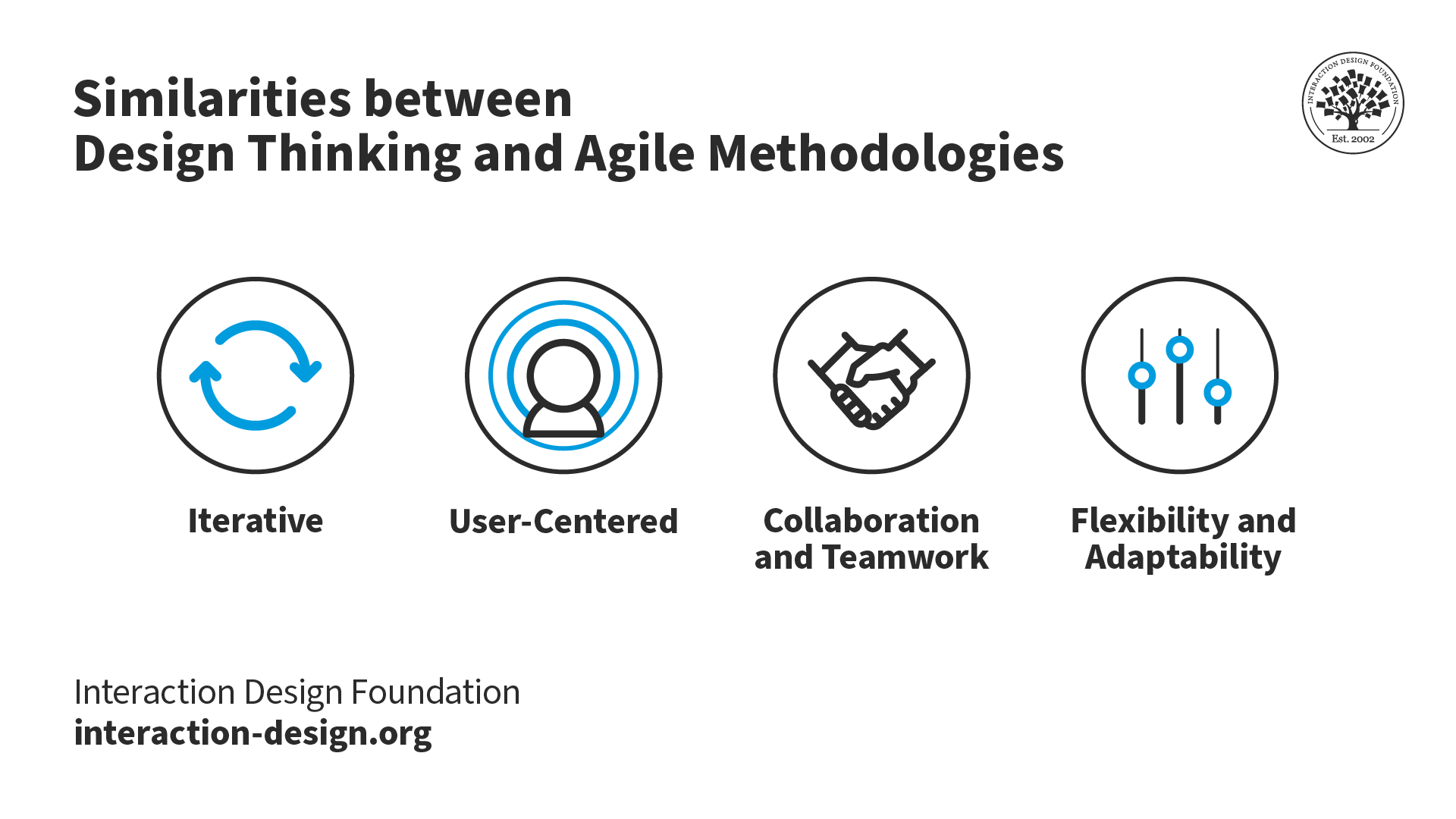
Similarities between Design Thinking and Agile
Iterative process.
Both methodologies emphasize iterative development. In design thinking, teams may jump from one phase to another, not necessarily in a set cyclical or linear order. For example, on testing a prototype, teams may discover something new about their users and realize that they must redefine the problem. Agile teams iterate through development sprints.
User-Centered
The agile and design thinking methodologies focus on the end user. All design thinking activities—from empathizing to prototyping and testing—keep the end users front and center. Agile teams continually integrate user feedback into development cycles.
Collaboration and Teamwork
Both methodologies rely heavily on collaboration among cross-functional teams and encourage diverse perspectives and expertise.
Flexibility and Adaptability
With its focus on user research, prototyping and testing, design thinking ensures teams remain in touch with users and get continuous feedback. Similarly, agile teams monitor user feedback and refine the product in a reasonably quick time.
In this video, Laura Klein, author of Build Better Products , describes a typical challenge designers face on agile teams. She encourages designers to get comfortable with the idea of a design not being perfect. Notice the many parallels between Laura’s advice for designers on agile teams and the mindsets of design thinking.
Differences between Design Thinking and Agile
While design thinking and agile teams share principles like iteration, user focus, and collaboration, they are neither interchangeable nor mutually exclusive. A team can apply both methodologies without any conflict.
From a user experience design perspective, design thinking applies to the more abstract elements of strategy and scope. At the same time, agile is more relevant to the more concrete elements of UX: structure, skeleton and surface. For quick reference, here’s an overview of the five elements of user experience.
Design thinking is more about exploring and defining the right problem and solution, whereas agile is about efficiently executing and delivering a product.
Here are the key differences between design thinking and agile.
Design Sprint: A Condensed Version of Design Thinking
A design sprint is a 5-day intensive workshop where cross-functional teams aim to develop innovative solutions.
The design sprint is a very structured version of design thinking that fits into the timeline of a sprint (a sprint is a short timeframe in which agile teams work to produce deliverables). Developed by Google Ventures, the design sprint seeks to fast-track innovation.
In this video, user researcher Ditte Hvas Mortensen explains the design sprint in detail.
Learn More about Design Thinking
Design consultancy IDEO’s designkit is an excellent repository of design thinking tools and case studies.
To keep up with recent developments in design thinking, read IDEO CEO Tim Brown’s blog .
Enroll in our course Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide —an excellent guide to get you started on your design thinking projects.
Questions related to Design Thinking
You don’t need any certification to practice design thinking. However, learning about the nuances of the methodology can help you:
Pick the appropriate methods and tailor the process to suit the unique needs of your project.
Avoid common pitfalls when you apply the methods.
Better lead a team and facilitate workshops.
Increase the chances of coming up with innovative solutions.
IxDF has a comprehensive course to help you gain the most from the methodology: Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide .
Anyone can apply design thinking to solve problems. Despite what the name suggests, non-designers can use the methodology in non-design-related scenarios. The methodology helps you think about problems from the end user’s perspective. Some areas where you can apply this process:
Develop new products with greater chances of success.
Address community-related issues (such as education, healthcare and environment) to improve society and living standards.
Innovate/enhance existing products to gain an advantage over the competition.
Achieve greater efficiencies in operations and reduce costs.
Use the Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide course to apply design thinking to your context today.
A framework is the basic structure underlying a system, concept, or text. There are several design thinking frameworks with slight differences. However, all the frameworks share some traits. Each framework:
Begins with empathy.
Reframes the problem or challenge at hand.
Initially employs divergent styles of thinking to generate ideas.
Later, it employs convergent styles of thinking to narrow down the best ideas,
Creates and tests prototypes.
Iterates based on the tests.
Some of the design thinking frameworks are:
5-stage design process by d.school
7-step early traditional design process by Herbert Simon
The 5-Stage DeepDive™ by IDEO
The “Double Diamond” Design Process Model by the Design Council
Collective Action Toolkit (CAT) by Frog Design
The LUMA System of Innovation by LUMA Institute
For details about each of these frameworks, see 10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview .
IDEO’s 3-Stage Design Thinking Process consists of inspiration, ideation and implementation:
Inspire : The problem or opportunity inspires and motivates the search for a solution.
Ideate : A process of synthesis distills insights which can lead to solutions or opportunities for change.
Implement : The best ideas are turned into a concrete, fully conceived action plan.
IDEO is a leader in applying design thinking and has developed many frameworks. Find out more in 10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview .
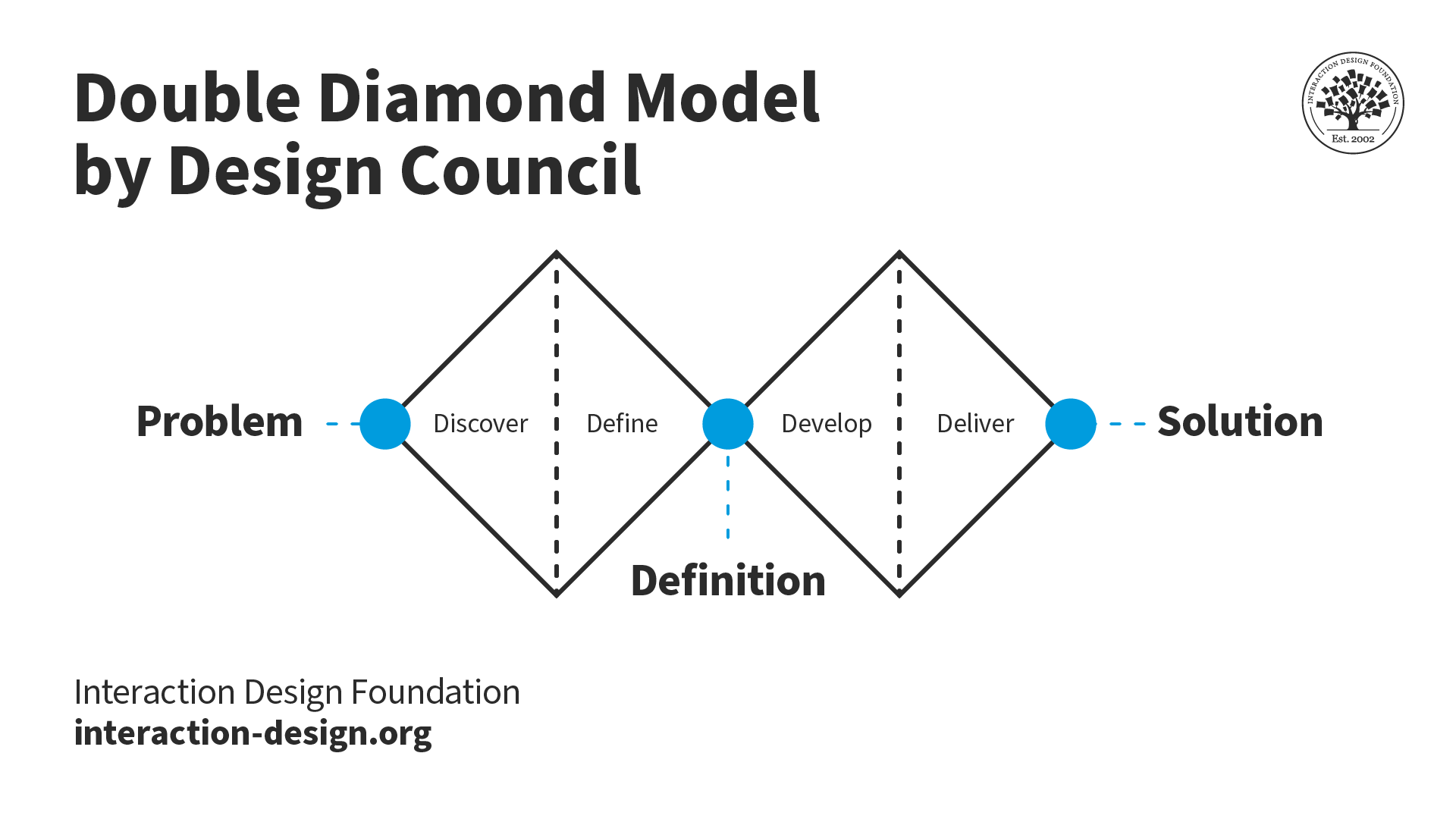
Design Council's Double Diamond diagram depicts the divergent and convergent stages of the design process.
Béla H. Bánáthy, founder of the White Stag Leadership Development Program, created the “divergence-convergence” model in 1996. In the mid-2000s, the British Design Council made this famous as the Double Diamond model.
The Double Diamond diagram graphically represents a design thinking process. It highlights the divergent and convergent styles of thinking in the design process. It has four distinct phases:
Discover: Initial idea or inspiration based on user needs.
Define: Interpret user needs and align them with business objectives.
Develop: Develop, iterate and test design-led solutions.
Deliver: Finalize and launch the end product into the market.
Double Diamond is one of several design thinking frameworks. Find out more in 10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview .
There are several design thinking methods that you can choose from, depending on what stage of the process you’re in. Here are a few common design thinking methods:
User Interviews: to understand user needs, pain points, attitudes and behaviors.
5 Whys Method: to dig deeper into problems to diagnose the root cause.
User Observations: to understand how users behave in real life (as opposed to what they say they do).
Affinity Diagramming: to organize research findings.
Empathy Mapping: to empathize with users based on research insights.
Journey Mapping: to visualize a user’s experience as they solve a problem.
6 Thinking Hats: to encourage a group to think about a problem or solution from multiple perspectives.
Brainstorming: to generate ideas.
Prototyping: to make abstract ideas more tangible and test them.
Dot Voting: to select ideas.
Start applying these methods to your work today with the Design Thinking template bundle .

For most of the design thinking process, you will need basic office stationery:
Pen and paper
Sticky notes
Whiteboard and markers
Print-outs of templates and canvases as needed (such as empathy maps, journey maps, feedback capture grid etc.) You can also draw these out manually.
Prototyping materials such as UI stencils, string, clay, Lego bricks, sticky tapes, scissors and glue.
A space to work in.
You can conduct design thinking workshops remotely by:
Using collaborative software to simulate the whiteboard and sticky notes.
Using digital templates instead of printed canvases.
Download print-ready templates you can share with your team to practice design thinking today.
Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that helps teams better identify, understand, and solve business and customer problems.
When businesses prioritize and empathize with customers, they can create solutions catering to their needs. Happier customers are more likely to be loyal and organically advocate for the product.
Design thinking helps businesses develop innovative solutions that give them a competitive advantage.
Gain a competitive advantage in your business with Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide .
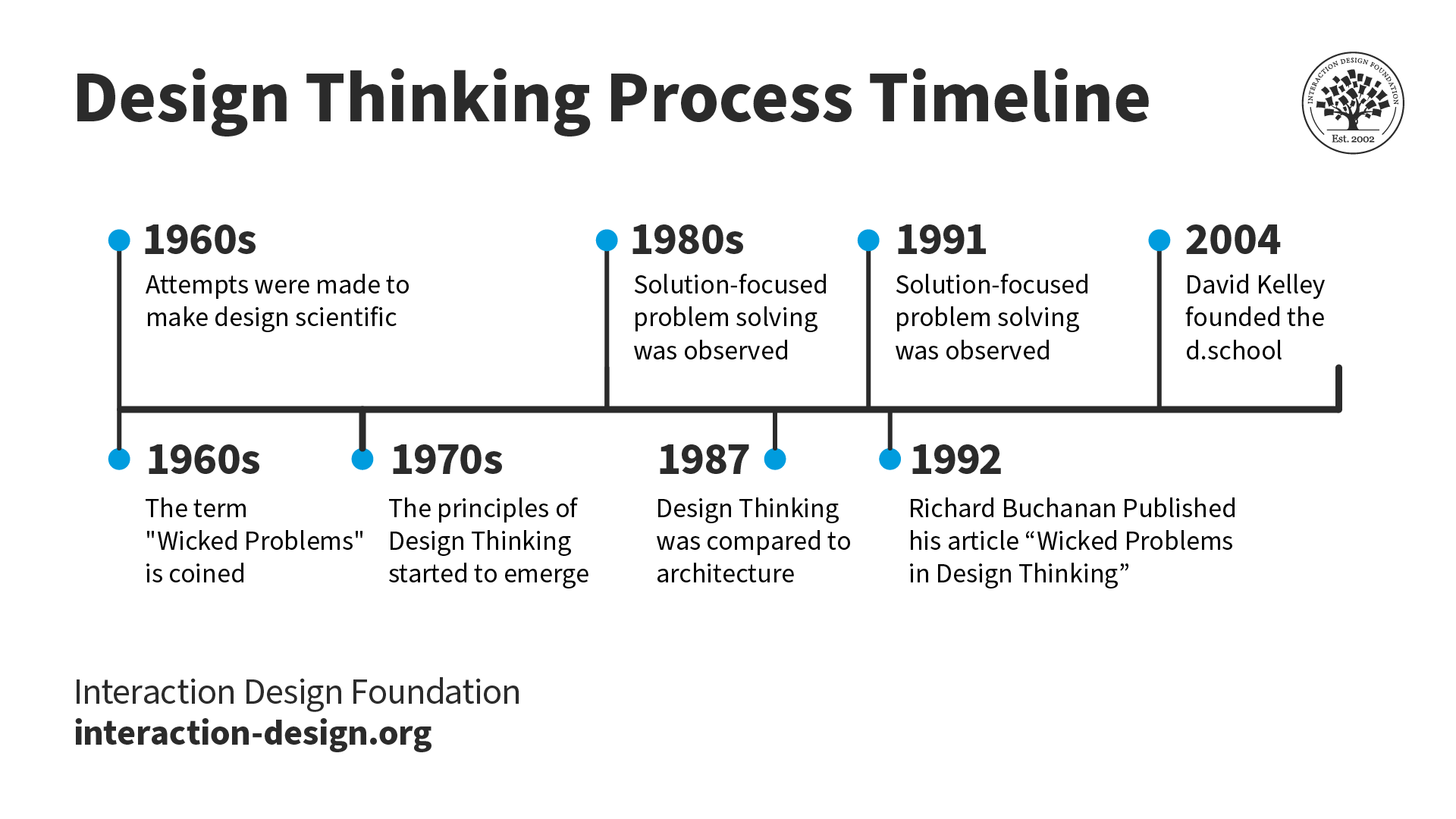
The evolution of Design Thinking can be summarised in 8 key events from the 1960s to 2004.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0.
Herbert Simon’s 1969 book, "The Sciences of the Artificial," has one of the earliest references to design thinking. David Kelley, founder of the design consultancy IDEO, coined the term “design thinking” and helped make it popular.
For a more comprehensive discussion on the origins of design thinking, see The History of Design Thinking .
Some organizations that have employed design thinking successfully are:
Airbnb: Airbnb used design thinking to create a platform for people to rent out their homes to travelers. The company focused on the needs of both hosts and guests . The result was a user-friendly platform to help people find and book accommodations.
PillPack: PillPack is a prescription home-delivery system. The company focused on the needs of people who take multiple medications and created a system that organizes pills by date and time. Amazon bought PillPack in 2018 for $1 billion .
Google Creative Lab: Google Creative Lab collaborated with IDEO to discover how kids physically play and learn. The team used design thinking to create Project Bloks . The project helps children develop foundational problem-solving skills "through coding experiences that are playful, tactile and collaborative.”
See more examples of design thinking and learn practical methods in Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide .
Innovation essentially means a new idea. Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that helps teams develop new ideas. In other words, design thinking can lead to innovation.
Human-Centered Design is a newer term for User-Centered Design
“Human-centred design is an approach to interactive systems development that aims to make systems usable and useful by focusing on the users, their needs and requirements, and by applying human factors/ergonomics, and usability knowledge and techniques. This approach enhances effectiveness and efficiency, improves human well-being, user satisfaction, accessibility and sustainability; and counteracts possible adverse effects of use on human health, safety and performance.”
— ISO 9241-210:2019(en), ISO (the International Organization for Standardization)
User experience expert Don Norman describes human-centered design (HCD) as a more evolved form of user-centered design (UCD). The word "users" removes their importance and treats them more like objects than people. By replacing “user” with “human,” designers can empathize better with the people for whom they are designing. Don Norman takes HCD a step further and prefers the term People-Centered Design.
Design thinking has a broader scope and takes HCD beyond the design discipline to drive innovation.
People sometimes use design thinking and human-centered design to mean the same thing. However, they are not the same. HCD is a formal discipline with a specific process used only by designers and usability engineers to design products. Design thinking borrows the design methods and applies them to problems in general.
Design Sprint condenses design thinking into a 1-week structured workshop
Google Ventures condensed the design thinking framework into a time-constrained 5-day workshop format called the Design Sprint. The sprint follows one step per day of the week:
Monday: Unpack
Tuesday: Sketch
Wednesday: Decide
Thursday: Prototype
Friday: Test
Learn more about the design sprint in Make Your UX Design Process Agile Using Google’s Methodology .
Systems Thinking is a distinct discipline with a broader approach to problem-solving
“Systems thinking is a way of exploring and developing effective action by looking at connected wholes rather than separate parts.”
— Introduction to Systems thinking, Report of GSE and GORS seminar, Civil Service Live
Both HCD and Systems Thinking are formal disciplines. Designers and usability engineers primarily use HCD. Systems thinking has applications in various fields, such as medical, environmental, political, economic, human resources, and educational systems.
HCD has a much narrower focus and aims to create and improve products. Systems thinking looks at the larger picture and aims to change entire systems.
Don Norman encourages designers to incorporate systems thinking in their work. Instead of looking at people and problems in isolation, designers must look at them from a systems point of view.
In summary, UCD and HCD refer to the same field, with the latter being a preferred phrase.
Design thinking is a broader framework that borrows methods from human-centered design to approach problems beyond the design discipline. It encourages people with different backgrounds and expertise to work together and apply the designer’s way of thinking to generate innovative solutions to problems.
Systems thinking is another approach to problem-solving that looks at the big picture instead of specific problems in isolation.
The design sprint is Google Ventures’ version of the design thinking process, structured to fit the design process in 1 week.
There are multiple design thinking frameworks, each with a different number of steps and phase names. One of the most popular frameworks is the Stanford d.School 5-stage process.
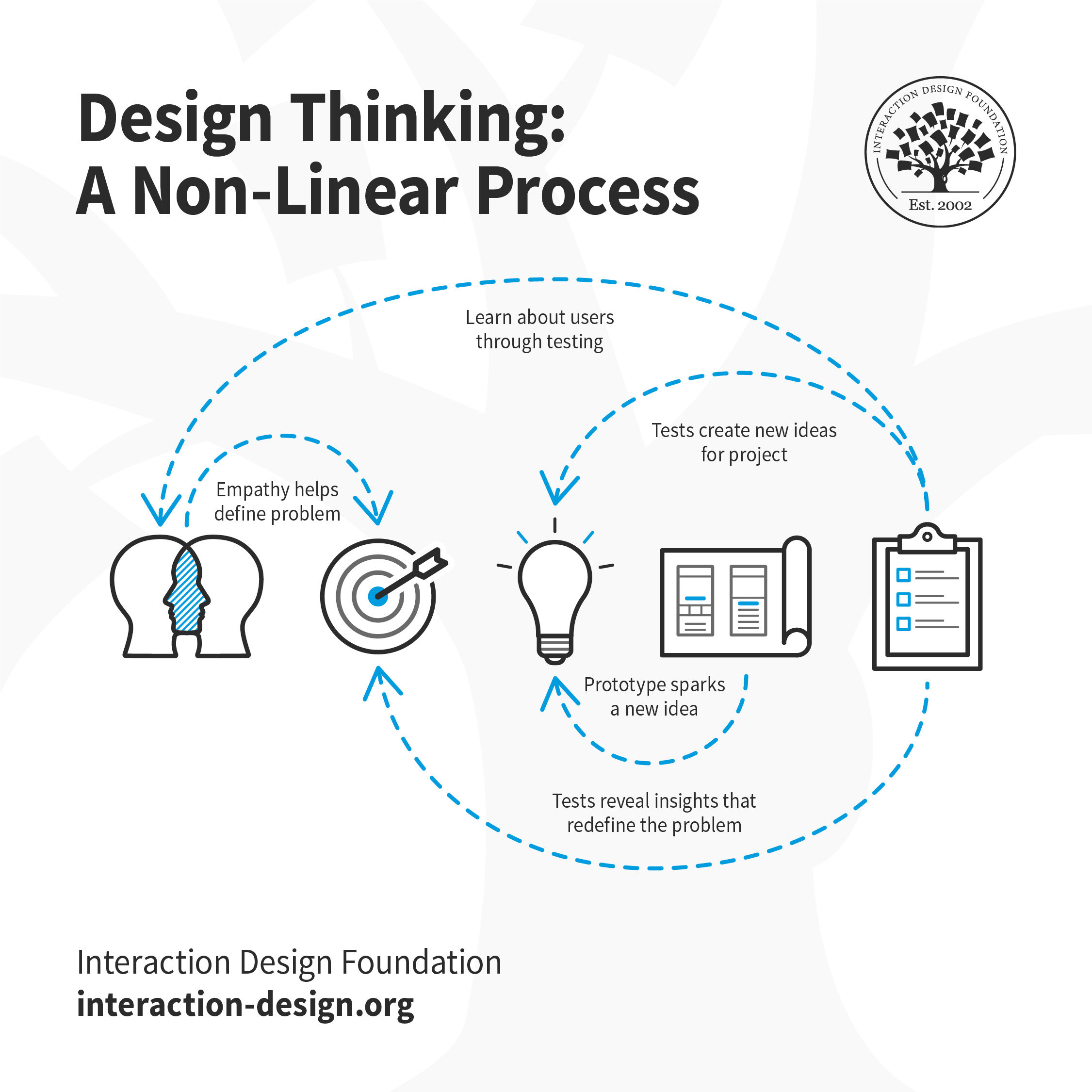
Design thinking is an iterative and non-linear process. It contains five phases: 1. Empathize, 2. Define, 3. Ideate, 4. Prototype and 5. Test. It is important to note the five stages of design thinking are not always sequential. They do not have to follow a specific order, and they can often occur in parallel or be repeated iteratively. The stages should be understood as different modes which contribute to the entire design project, rather than sequential steps.
For more details, see The 5 Stages in the Design Thinking Process .
IDEO is a leading design consultancy and has developed its own version of the design thinking framework and adds the dimension of implementation in the process.
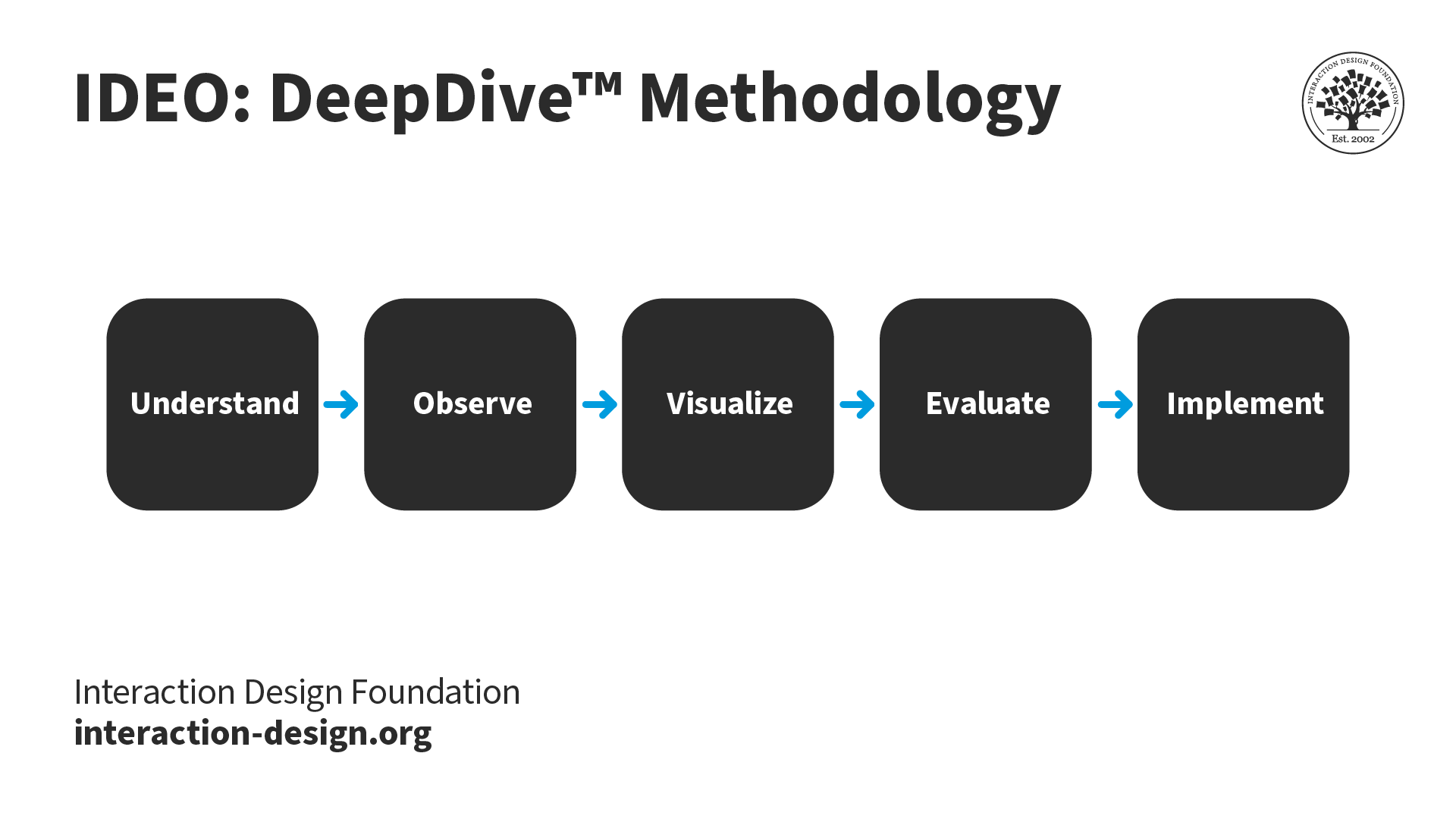
IDEO’s framework uses slightly different terms than d.school’s design thinking process and adds an extra dimension of implementation. The steps in the DeepDive™ Methodology are: Understand, Observe, Visualize, Evaluate and Implement.
IDEO’s DeepDive™ Methodology includes the following steps:
Understand: Conduct research and identify what the client needs and the market landscape
Observe: Similar to the Empathize step, teams observe people in live scenarios and conduct user research to identify their needs and pain points.
Visualize: In this step, the team visualizes new concepts. Similar to the Ideate phase, teams focus on creative, out-of-the-box and novel ideas.
Evaluate: The team prototypes ideas and evaluates them. After refining the prototypes, the team picks the most suitable one.
Implement: The team then sets about to develop the new concept for commercial use.
IDEO’s DeepDive™ is one of several design thinking frameworks. Find out more in 10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview .
Literature on Design Thinking (DT)
Here’s the entire UX literature on Design Thinking (DT) by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Design Thinking (DT)
Take a deep dive into Design Thinking (DT) with our course Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide .
Some of the world’s leading brands, such as Apple, Google, Samsung, and General Electric, have rapidly adopted the design thinking approach, and design thinking is being taught at leading universities around the world, including Stanford d.school, Harvard, and MIT. What is design thinking, and why is it so popular and effective?
Design Thinking is not exclusive to designers —all great innovators in literature, art, music, science, engineering and business have practiced it. So, why call it Design Thinking? Well, that’s because design work processes help us systematically extract, teach, learn and apply human-centered techniques to solve problems in a creative and innovative way—in our designs, businesses, countries and lives. And that’s what makes it so special.
The overall goal of this design thinking course is to help you design better products, services, processes, strategies, spaces, architecture, and experiences. Design thinking helps you and your team develop practical and innovative solutions for your problems. It is a human-focused , prototype-driven , innovative design process . Through this course, you will develop a solid understanding of the fundamental phases and methods in design thinking, and you will learn how to implement your newfound knowledge in your professional work life. We will give you lots of examples; we will go into case studies, videos, and other useful material, all of which will help you dive further into design thinking. In fact, this course also includes exclusive video content that we've produced in partnership with design leaders like Alan Dix, William Hudson and Frank Spillers!
This course contains a series of practical exercises that build on one another to create a complete design thinking project. The exercises are optional, but you’ll get invaluable hands-on experience with the methods you encounter in this course if you complete them, because they will teach you to take your first steps as a design thinking practitioner. What’s equally important is you can use your work as a case study for your portfolio to showcase your abilities to future employers! A portfolio is essential if you want to step into or move ahead in a career in the world of human-centered design.
Design thinking methods and strategies belong at every level of the design process . However, design thinking is not an exclusive property of designers—all great innovators in literature, art, music, science, engineering, and business have practiced it. What’s special about design thinking is that designers and designers’ work processes can help us systematically extract, teach, learn, and apply these human-centered techniques in solving problems in a creative and innovative way—in our designs, in our businesses, in our countries, and in our lives.
That means that design thinking is not only for designers but also for creative employees , freelancers , and business leaders . It’s for anyone who seeks to infuse an approach to innovation that is powerful, effective and broadly accessible, one that can be integrated into every level of an organization, product, or service so as to drive new alternatives for businesses and society.
You earn a verifiable and industry-trusted Course Certificate once you complete the course. You can highlight them on your resume, CV, LinkedIn profile or your website .
All open-source articles on Design Thinking (DT)
What is design thinking and why is it so popular.
- 1.6k shares
Personas – A Simple Introduction

- 1.5k shares
Stage 2 in the Design Thinking Process: Define the Problem and Interpret the Results

- 1.3k shares
What is Ideation – and How to Prepare for Ideation Sessions
- 1.2k shares
Stage 3 in the Design Thinking Process: Ideate

- 4 years ago
Stage 4 in the Design Thinking Process: Prototype

- 3 years ago
Affinity Diagrams: How to Cluster Your Ideas and Reveal Insights

Stage 1 in the Design Thinking Process: Empathise with Your Users
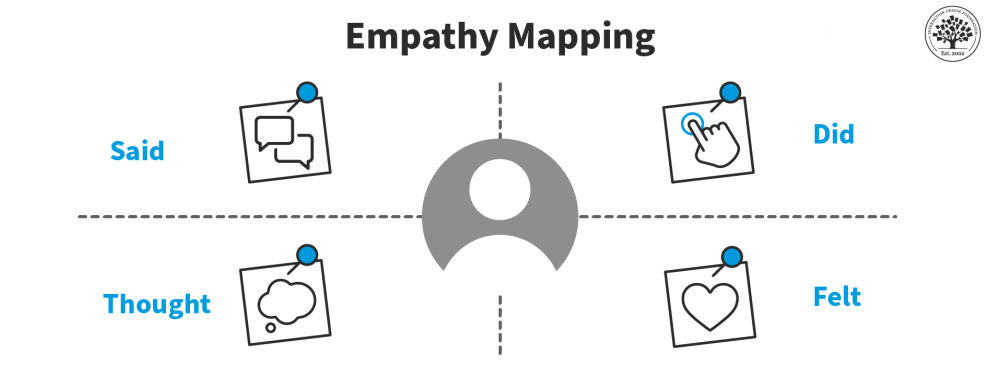
Empathy Map – Why and How to Use It
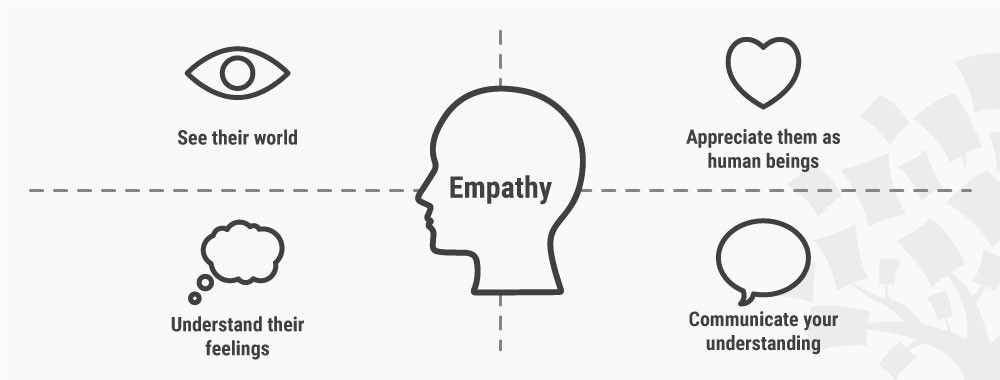
What Is Empathy and Why Is It So Important in Design Thinking?
10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview
Define and Frame Your Design Challenge by Creating Your Point Of View and Ask “How Might We”

- 1.1k shares
Design Thinking: Get Started with Prototyping

5 Common Low-Fidelity Prototypes and Their Best Practices

Design Thinking: New Innovative Thinking for New Problems

Test Your Prototypes: How to Gather Feedback and Maximize Learning

The History of Design Thinking
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding UX Roles and Which One You Should Go For
Stage 5 in the Design Thinking Process: Test

What Are Wicked Problems and How Might We Solve Them?
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share the knowledge!
Share this content on:
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
- Get in touch
- Enterprise & IT
- Banking & Financial Services
- News media & Entertainment
- Healthcare & Lifesciences
- Networks and Smart Devices
- Education & EdTech
- Service Design
- UI UX Design
- Data Visualization & Design
- User & Design Research
- In the News
- Our Network
- Voice Experiences
- Golden grid
Critical Thinking
- Enterprise UX
- 20 Product performance metrics
- Types of Dashboards
- Interconnectivity and iOT
- Healthcare and Lifesciences
- Airtel XStream
- Case studies
Data Design
- UCD vs. Design Thinking
User & Design Research
Critical thinking is a method of analyzing ideas, concepts or data collected to evaluate the situation from different perspectives and arrive at an unbiased optimum solution. A critical thinker can anticipate the consequences of certain actions in advance. A researcher with the competency to critically think can reflect, think independently, stay objective, problem solve to deduce a solution. Therefore, critical thinking requires self-actuated discipline and correction to get one step closer to the solution iteratively.
Quick details: Critical Thinking
Structure: Unstructured
Preparation: Information needed to analyze
Deliverables: Inferences, Insights
More about Critical Thinking
Most research methods require experienced or trained researchers to define the design specifications for a project. The researcher employs different methods to collect data, analyze it and arrive at the solution that addresses user needs and expectations. One of the most important competencies that a researcher must have in order to arrive at an optimum solution is the ability to critically think and analyze.
Critical Thinking can also help identify gaps in reasoning and assumptions. Although, design researchers are expected to have this competency independently, critical thinking promotes group ideation and task execution as well. Though, it shouldn’t be seen as an opportunity to criticize someone else’s ideas or work. In that sense, the objective of critical thinking is to strengthen a theory, process, product or service and not to find unnecessary faults to ensure that the ideas or processes collapse. A mature critical thinker can define project goals, define timelines, set expectations, manage expectations, handle conflicts and work collaboratively with a team to accomplish the project goals. It is more and more evident that critical thinking, even though not given its due importance in organizations, is a critical competency that cannot be undermined.
Critical Thinking vs. Design Thinking
It is also important to discuss the difference between Design Thinking and Critical Thinking. Design Thinking is a process that involves stages of observation/interaction, empathy, problem formulation, solution deduction, testing, alteration and reiteration. Here, Critical Thinking is a part of every stage of the Design Thinking process. Essentially, effective Design Thinking cannot take place in the absence of critical or creative thinking. There is also a common misconception that critical and creative thinking are distinct from each other.
However, critical thinking requires some form as well as level of creativity. Critical and creative thinking go hand-in-hand and cannot be separated or distinguished using any formal criteria.
Advantages of Critical Thinking
1. design thinking.
Critical thinking is an important component that comes into play at every stage of the design thinking process .
2. Creative Problem Solving
Critical Thinking is not just rational and based on a set of logical rules. There is plenty of room for solid creativity to play a significant role in the critical thinking process .
3. Reflection
Critical thinking promotes independent and reflective thinking in the researcher to question and evaluate the solutions they have devised and reiterate for an optimum solution .
4. Objectivity
Effective use of this method ensures objectivity and therefore doesn’t leave much scope for biases .
5. Applications
Critical thinking is a competency and method that is applicable in all projects irrespective of the type of solution expected .
Disadvantages of Critical Thinking
1. researcher can introduce unnecessary complexity.
Too much thinking can also be detrimental to a project. Some researchers can complicate an otherwise simple project by overthinking critical and pose questions when not required .
2. Expensive researcher
A mature Critical thinking researcher can be very expensive for a low budget project. However, Critical thinking is not a competency that is extremely difficult to master .
Think Design's recommendation
It is difficult to separate reasoning from thinking and hence, this is the best context to introduce the three reasoning types: Deductive, Inductive and Abductive.
Deductive reasoning
Deductive reasoning starts with the assertion of a general rule and ends up in a guaranteed specific conclusion.
Inductive reasoning
Inductive reasoning begins with observations that are specific and ends up with a conclusion that is likely but not certain.
Abductive reasoning
Abductive reasoning starts with an incomplete set of observations and ends up with a most likely explanation.
It is believed that Design, in general is an activity that can complement abductive reasoning; that it is not very essential in the process of Design to come up with deductive or inductive reasoning. However, we wouldn’t want to generalize this at this moment but would suggest that proceeding with abductive reasoning saves a lot of time and effort if that is the objective.
Critical Thinking, when coupled with the types of reasoning above, can generate magical results. It is therefore advised to employ Critical thinking in situations where we may need abductive reasoning skills… There are chances we over-complicate things if we indulge in Critical thinking when we have clear conclusions or clear observations (Deductive and Inductive).
Was this Page helpful?
Related methods.
- Audio/ Video Analysis
- Document Research
- Heatmap Analysis
- Social Network Mapping
- Time Lapse Video
- Trend Analysis
- Usage Analytics
UI UX DESIGN
Service design.
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue we'll assume that you accept this. Learn more
Recent Tweets
Sign up for our newsletter.
Subscribe to our newsletter to stay updated with the latest insights in UX, CX, Data and Research.
Get in Touch
Thank you for subscribing.
You will be receive all future issues of our newsletter.
Thank you for Downloading.
One moment….
While the report downloads, could you tell us…
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
Accelerated research about generative AI
Disciplined entrepreneurship: 6 questions for startup success
Startup tactics: How and when to hire technical talent
Credit: Mimi Phan
Ideas Made to Matter
Design thinking, explained
Rebecca Linke
Sep 14, 2017
What is design thinking?
Design thinking is an innovative problem-solving process rooted in a set of skills.The approach has been around for decades, but it only started gaining traction outside of the design community after the 2008 Harvard Business Review article [subscription required] titled “Design Thinking” by Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO.
Since then, the design thinking process has been applied to developing new products and services, and to a whole range of problems, from creating a business model for selling solar panels in Africa to the operation of Airbnb .
At a high level, the steps involved in the design thinking process are simple: first, fully understand the problem; second, explore a wide range of possible solutions; third, iterate extensively through prototyping and testing; and finally, implement through the customary deployment mechanisms.
The skills associated with these steps help people apply creativity to effectively solve real-world problems better than they otherwise would. They can be readily learned, but take effort. For instance, when trying to understand a problem, setting aside your own preconceptions is vital, but it’s hard.
Creative brainstorming is necessary for developing possible solutions, but many people don’t do it particularly well. And throughout the process it is critical to engage in modeling, analysis, prototyping, and testing, and to really learn from these many iterations.
Once you master the skills central to the design thinking approach, they can be applied to solve problems in daily life and any industry.
Here’s what you need to know to get started.

Understand the problem
The first step in design thinking is to understand the problem you are trying to solve before searching for solutions. Sometimes, the problem you need to address is not the one you originally set out to tackle.
“Most people don’t make much of an effort to explore the problem space before exploring the solution space,” said MIT Sloan professor Steve Eppinger. The mistake they make is to try and empathize, connecting the stated problem only to their own experiences. This falsely leads to the belief that you completely understand the situation. But the actual problem is always broader, more nuanced, or different than people originally assume.
Take the example of a meal delivery service in Holstebro, Denmark. When a team first began looking at the problem of poor nutrition and malnourishment among the elderly in the city, many of whom received meals from the service, it thought that simply updating the menu options would be a sufficient solution. But after closer observation, the team realized the scope of the problem was much larger , and that they would need to redesign the entire experience, not only for those receiving the meals, but for those preparing the meals as well. While the company changed almost everything about itself, including rebranding as The Good Kitchen, the most important change the company made when rethinking its business model was shifting how employees viewed themselves and their work. That, in turn, helped them create better meals (which were also drastically changed), yielding happier, better nourished customers.
Involve users
Imagine you are designing a new walker for rehabilitation patients and the elderly, but you have never used one. Could you fully understand what customers need? Certainly not, if you haven’t extensively observed and spoken with real customers. There is a reason that design thinking is often referred to as human-centered design.
“You have to immerse yourself in the problem,” Eppinger said.
How do you start to understand how to build a better walker? When a team from MIT’s Integrated Design and Management program together with the design firm Altitude took on that task, they met with walker users to interview them, observe them, and understand their experiences.
“We center the design process on human beings by understanding their needs at the beginning, and then include them throughout the development and testing process,” Eppinger said.
Central to the design thinking process is prototyping and testing (more on that later) which allows designers to try, to fail, and to learn what works. Testing also involves customers, and that continued involvement provides essential user feedback on potential designs and use cases. If the MIT-Altitude team studying walkers had ended user involvement after its initial interviews, it would likely have ended up with a walker that didn’t work very well for customers.
It is also important to interview and understand other stakeholders, like people selling the product, or those who are supporting the users throughout the product life cycle.
The second phase of design thinking is developing solutions to the problem (which you now fully understand). This begins with what most people know as brainstorming.
Hold nothing back during brainstorming sessions — except criticism. Infeasible ideas can generate useful solutions, but you’d never get there if you shoot down every impractical idea from the start.
“One of the key principles of brainstorming is to suspend judgment,” Eppinger said. “When we're exploring the solution space, we first broaden the search and generate lots of possibilities, including the wild and crazy ideas. Of course, the only way we're going to build on the wild and crazy ideas is if we consider them in the first place.”
That doesn’t mean you never judge the ideas, Eppinger said. That part comes later, in downselection. “But if we want 100 ideas to choose from, we can’t be very critical.”
In the case of The Good Kitchen, the kitchen employees were given new uniforms. Why? Uniforms don’t directly affect the competence of the cooks or the taste of the food.
But during interviews conducted with kitchen employees, designers realized that morale was low, in part because employees were bored preparing the same dishes over and over again, in part because they felt that others had a poor perception of them. The new, chef-style uniforms gave the cooks a greater sense of pride. It was only part of the solution, but if the idea had been rejected outright, or perhaps not even suggested, the company would have missed an important aspect of the solution.
Prototype and test. Repeat.
You’ve defined the problem. You’ve spoken to customers. You’ve brainstormed, come up with all sorts of ideas, and worked with your team to boil those ideas down to the ones you think may actually solve the problem you’ve defined.
“We don’t develop a good solution just by thinking about a list of ideas, bullet points and rough sketches,” Eppinger said. “We explore potential solutions through modeling and prototyping. We design, we build, we test, and repeat — this design iteration process is absolutely critical to effective design thinking.”
Repeating this loop of prototyping, testing, and gathering user feedback is crucial for making sure the design is right — that is, it works for customers, you can build it, and you can support it.
“After several iterations, we might get something that works, we validate it with real customers, and we often find that what we thought was a great solution is actually only just OK. But then we can make it a lot better through even just a few more iterations,” Eppinger said.
Implementation
The goal of all the steps that come before this is to have the best possible solution before you move into implementing the design. Your team will spend most of its time, its money, and its energy on this stage.
“Implementation involves detailed design, training, tooling, and ramping up. It is a huge amount of effort, so get it right before you expend that effort,” said Eppinger.
Design thinking isn’t just for “things.” If you are only applying the approach to physical products, you aren’t getting the most out of it. Design thinking can be applied to any problem that needs a creative solution. When Eppinger ran into a primary school educator who told him design thinking was big in his school, Eppinger thought he meant that they were teaching students the tenets of design thinking.
“It turns out they meant they were using design thinking in running their operations and improving the school programs. It’s being applied everywhere these days,” Eppinger said.
In another example from the education field, Peruvian entrepreneur Carlos Rodriguez-Pastor hired design consulting firm IDEO to redesign every aspect of the learning experience in a network of schools in Peru. The ultimate goal? To elevate Peru’s middle class.
As you’d expect, many large corporations have also adopted design thinking. IBM has adopted it at a company-wide level, training many of its nearly 400,000 employees in design thinking principles .
What can design thinking do for your business?
The impact of all the buzz around design thinking today is that people are realizing that “anybody who has a challenge that needs creative problem solving could benefit from this approach,” Eppinger said. That means that managers can use it, not only to design a new product or service, “but anytime they’ve got a challenge, a problem to solve.”
Applying design thinking techniques to business problems can help executives across industries rethink their product offerings, grow their markets, offer greater value to customers, or innovate and stay relevant. “I don’t know industries that can’t use design thinking,” said Eppinger.
Ready to go deeper?
Read “ The Designful Company ” by Marty Neumeier, a book that focuses on how businesses can benefit from design thinking, and “ Product Design and Development ,” co-authored by Eppinger, to better understand the detailed methods.
Register for an MIT Sloan Executive Education course:
Systematic Innovation of Products, Processes, and Services , a five-day course taught by Eppinger and other MIT professors.
- Leadership by Design: Innovation Process and Culture , a two-day course taught by MIT Integrated Design and Management director Matthew Kressy.
- Managing Complex Technical Projects , a two-day course taught by Eppinger.
- Apply for M astering Design Thinking , a 3-month online certificate course taught by Eppinger and MIT Sloan senior lecturers Renée Richardson Gosline and David Robertson.
Steve Eppinger is a professor of management science and innovation at MIT Sloan. He holds the General Motors Leaders for Global Operations Chair and has a PhD from MIT in engineering. He is the faculty co-director of MIT's System Design and Management program and Integrated Design and Management program, both master’s degrees joint between the MIT Sloan and Engineering schools. His research focuses on product development and technical project management, and has been applied to improving complex engineering processes in many industries.
Read next: 10 agile ideas worth sharing
Related Articles

- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Design Thinking & Why Is It Important?

- 18 Jan 2022
In an age when innovation is key to business success and growth, you’ve likely come across the term “design thinking.” Perhaps you’ve heard it mentioned by a senior leader as something that needs to be utilized more, or maybe you’ve seen it on a prospective employee's resume.
While design thinking is an ideology based on designers’ workflows for mapping out stages of design, its purpose is to provide all professionals with a standardized innovation process to develop creative solutions to problems—design-related or not.
Why is design thinking needed? Innovation is defined as a product, process, service, or business model featuring two critical characteristics: novel and useful. Yet, there’s no use in creating something new and novel if people won’t use it. Design thinking offers innovation the upgrade it needs to inspire meaningful and impactful solutions.
But what is design thinking, and how does it benefit working professionals?
What Is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is a mindset and approach to problem-solving and innovation anchored around human-centered design . While it can be traced back centuries—and perhaps even longer—it gained traction in the modern business world after Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO, published an article about it in the Harvard Business Review .
Design thinking is different from other innovation and ideation processes in that it’s solution-based and user-centric rather than problem-based. This means it focuses on the solution to a problem instead of the problem itself.
For example, if a team is struggling with transitioning to remote work, the design thinking methodology encourages them to consider how to increase employee engagement rather than focus on the problem (decreasing productivity).

The essence of design thinking is human-centric and user-specific. It’s about the person behind the problem and solution, and requires asking questions such as “Who will be using this product?” and “How will this solution impact the user?”
The first, and arguably most important, step of design thinking is building empathy with users. By understanding the person affected by a problem, you can find a more impactful solution. On top of empathy, design thinking is centered on observing product interaction, drawing conclusions based on research, and ensuring the user remains the focus of the final implementation.
The Four Phases of Innovation
So, what does design thinking entail? There are many models of design thinking that range from three to seven steps.
In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar leverages a four-phase innovation framework. The phases venture from concrete to abstract thinking and back again as the process loops, reverses, and repeats. This is an important balance because abstract thinking increases the likelihood that an idea will be novel. It’s essential, however, to anchor abstract ideas in concrete thinking to ensure the solution is valid and useful.
Here are the four phases for effective innovation and, by extension, design thinking.

The first phase is about narrowing down the focus of the design thinking process. It involves identifying the problem statement to come up with the best outcome. This is done through observation and taking the time to determine the problem and the roadblocks that prevented a solution in the past.
Various tools and frameworks are available—and often needed—to make concrete observations about users and facts gathered through research. Regardless of which tools are implemented, the key is to observe without assumptions or biased expectations.
Once findings from your observations are collected, the next step is to shape insights by framing those observations. This is where you can venture into the abstract by reframing the problem in the form of a statement or question.
Once the problem statement or question has been solidified—not finalized—the next step is ideation. You can use a tool such as systematic inventive thinking (SIT) in this stage, which is useful for creating an innovative process that can be replicated in the future.
The goal is to ultimately overcome cognitive fixedness and devise new and innovative ideas that solve the problems you identified. Continue to actively avoid assumptions and keep the user at the forefront of your mind during ideation sessions.
The third phase involves developing concepts by critiquing a range of possible solutions. This includes multiple rounds of prototyping, testing, and experimenting to answer critical questions about a concept’s viability.
Remember: This step isn’t about perfection, but rather, experimenting with different ideas and seeing which parts work and which don’t.
4. Implement
The fourth and final phase, implementation, is when the entire process comes together. As an extension of the develop phase, implementation starts with testing, reflecting on results, reiterating, and testing again. This may require going back to a prior phase to iterate and refine until you find a successful solution. Such an approach is recommended because design thinking is often a nonlinear, iterative process.
In this phase, don’t forget to share results with stakeholders and reflect on the innovation management strategies implemented during the design thinking process. Learning from experience is an innovation process and design thinking project all its own.
Check out the video about the design thinking process below, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more explainer content!
Why Design Thinking Skills Matter
The main value of design thinking is that it offers a defined process for innovation. While trial and error is a good way to test and experiment what works and what doesn’t, it’s often time-consuming, expensive, and ultimately ineffective. On the other hand, following the concrete steps of design thinking is an efficient way to develop new, innovative solutions.
On top of a clear, defined process that enables strategic innovation, design thinking can have immensely positive outcomes for your career—in terms of both advancement and salary.

As of December 2021, the most common occupations requiring design thinking skills were:
- Marketing managers
- Industrial engineers
- Graphic designers
- Software developers
- General and operations managers
- Management analysts
- Personal service managers
- Architectural and engineering managers
- Computer and information systems managers
In addition, jobs that require design thinking statistically have higher salaries. Take a marketing manager position, for example. The median annual salary is $107,900. Marketing manager job postings that require design thinking skills, however, have a median annual salary of $133,900—a 24 percent increase.

Overall, businesses are looking for talent with design thinking skills. As of November 2021, there were 29,648 job postings in the United States advertising design thinking as a necessary skill—a 153 percent increase from November 2020, and a 637 percent increase from November 2017.
As businesses continue to recognize the need for design thinking and innovation, they’ll likely create more demand for employees with those skills.
Learning Design Thinking
Design thinking is an extension of innovation that allows you to design solutions for end users with a single problem statement in mind. It not only imparts valuable skills but can help advance your career.
It’s also a collaborative endeavor that can only be mastered through practice with peers. As Datar says in the introduction to Design Thinking and Innovation : “Just as with learning how to swim, the best way to practice is to jump in and try.”
If you want to learn design thinking, take an active role in your education. Start polls, problem-solving exercises, and debates with peers to get a taste of the process. It’s also important to seek out diverse viewpoints to prepare yourself for the business world.
In addition, if you’re considering adding design thinking to your skill set, think about your goals and why you want to learn about it. What else might you need to be successful?
You might consider developing your communication, innovation, leadership, research, and management skills, as those are often listed alongside design thinking in job postings and professional profiles.

You may also notice skills like agile methodology, user experience, and prototyping in job postings, along with non-design skills, such as product management, strategic planning, and new product development.

Is Design Thinking Right for You?
There are many ways to approach problem-solving and innovation. Design thinking is just one of them. While it’s beneficial to learn how others have approached problems and evaluate if you have the same tools at your disposal, it can be more important to chart your own course to deliver what users and customers truly need.
You can also pursue an online course or workshop that dives deeper into design thinking methodology. This can be a practical path if you want to improve your design thinking skills or require a more collaborative environment.
Are you ready to develop your design thinking skills? Explore our online course Design Thinking and Innovation to discover how to leverage fundamental design thinking principles and innovative problem-solving tools to address business challenges.

About the Author

Designorate
Design thinking, innovation, user experience and healthcare design
Guide for Critical Thinking for Designers
In every single day in our life, we are faced with a number of choices to make, problems to solve, and ideas to evaluate or analyze. However, these activities are affected by both internal and external factors such as biases, incomplete information, distortion, and prejudices. All these factors affect the process of choosing the right decision or find the proper solution for problems, which may lead to misleading solutions or choices. In order to escape this idea trap, critical thinking can provide a way to alter our mindset in order to improve the way we think of problem or situations which subsequently reflect positively on our decisions.
Critical thinking is a thinking method that aims to achieve objective evaluation and analysis of problems, ideas, or different situations in order to build a clear unbiased understanding about it over the course of reaching the optimal solution. The critical thinking is a self-disciplined, self-directed, self-monitored, and self-corrective way of thinking to improve how we communicate ideas and solve problems.
Critical thinking is a handy method to address any situation before jumping directly to the analysis phase in order to evaluate or find a solution for it. This type of thinking is commonly used in different fields of science and art in order to build a clear objective perception about different situations that face designers, engineers and researchers.
Related articles:
- 6 Steps for Effective Critical Thinking
- The Six Hats of Critical Thinking and How to Use Them
Principles of Critical Thinking
In order to achieve the target behind the critical thinking approach, the below principles were introduced by Professor Larry Larson, Ohio University, in his paper published in the Journal of Biological Education 1990. These principles provides guidelines for critical thinking before moving to the thinking steps:
- Collect all the necessary information about the situation in hand
- Understand and clearly, define all terms associated with the situation
- Question the methods used to collect the information and the current conclusions
- Understand the hidden assumptions and biases including your own biases and values
- Question the source of facts
- Don’t expect all the answers
- Look at the big picture of the situation rather than the parts
- Examine the multiples cause and effect
- Watch for thought stoppers
The above principles aim to free our mind from biases and ensure that the situation is clearly defined. Also, it aims to ensure that the source of the data collected, the methods used to collect the data are also free from mistakes, biases, and inaccuracy. This can help us to focus on the problem without any external factors.
Wait, Join my Newsletters!
As always, I try to come to you with design ideas, tips, and tools for design and creative thinking. Subscribe to my newsletters to receive new updated design tools and tips!
Stages of Critical Thinking
Based on the above principles, the critical thinking process should have three main stages; Observe, Question, and Answer . In order to clearly understand the three stages, we will use a design example: how people with wheelchair use the stairs to move from one level to another. Many places are still not accessible for people with physical disabilities due to the hard usage of stairs as they always seek support from others or search fo electric elevators. Based on this situation, we would like to explore how to address this problem with the critical thinking, we can use the stages as below:

Stage 1: Observe
In this stage, we observe the whole situation thoroughly in terms of how people with disabilities use the stairs, the problems they face, and how they currently deal with it. At this stage, we collect all the necessary information about the current situation and how other people tried to solve it and the methods they used to achieve this target. At this stage, no questions are asked as we only observe and record our observation for the next stages.
While collecting information and observing the situation, we should take notes of our findings with a clear definition of the problem in order to ensure that we are addressing the problem properly. Also, we need to understand the biases that may affect our decision and the biases that may affect other designers who tried to solve the problem. This can help us to put the biases or the assumption aside and focus on the situation.
In the example we have, designers should observe how people with wheelchairs use the stairs and exactly define the problem they face and how they are trying to solve it. Also, we need to explore the previous researchers or attempt that tried to solve the problem and their fingers.
Stage 2: Question
Based on the observation, we start to ask questions about the situation and the current solution. For example, what is the wrong with the current stars? why people find it hard to use? These questions help clearly define the right problem to address and subsequently finding the solution that can directly build a holistic solution that considers all the facts regarding the user experience, surrounded environment, and other users in the place.
Asking the right questions contribute reaching a clear definition for the current situation and subsequently analyzing it properly. The questions may take different forms. One of the methods that can help exploring the situation from different aspects is the Starbursting method that allows you to cover the topic using five main types of questions; Why, Who, What, How, Where, and When. In this example, the questions can be organized as below:
- Who: Who is using the target user of the stairs?
- What: What is the current problem of using the stairs? What are the different approaches to solving the problem?
- How: How can we solve the problem? How can we make the stairs using experience easier for disabled people?
- Where: Where will the new idea be applied?
- When: When do disabled people use the stairs the most?
- Why: Why do we need to change the current stars design? Why disabled people suffer much from using the current stairs?
Another method to ask the right questions is to use the Elements of Thought, which reflect how we think about situations. The Elements of Thoughts include purpose, questions, information, concussions, concepts, assumptions, implications, and points of view.
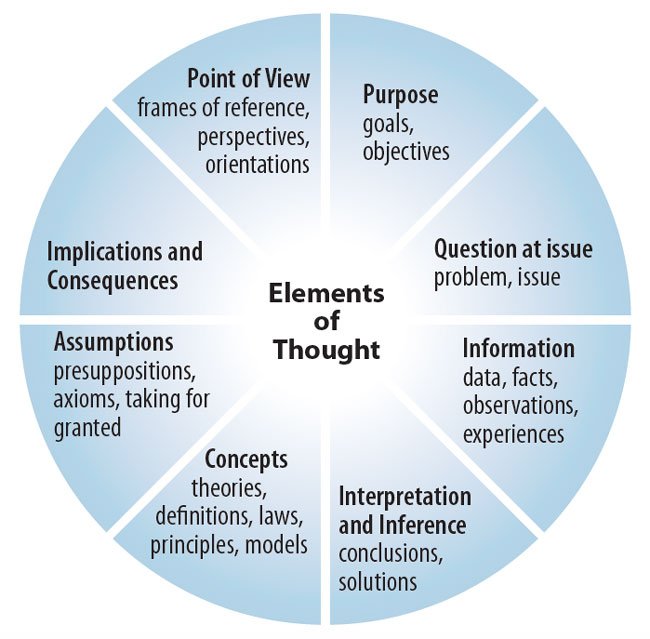
These elements can form the way we think in situations. These elements can be used to form the right questions as following:
- Purpose: What are we trying to solve?
- Questions: What are the questions?
- Information: What is the information needed to understand the problem?
- Conclusions: How do other reached different solutions?
- Concepts: What is the main concept behind the current ideas?
- Assumptions: What is the assumption we have this problem?
- Implications: How can we implicate the new ideas?
- The point of View: What are the different point of views related to the problem?
The third step in the critical thinking is to answer all the raised questions without any biases, prejudices, or assumptions. At this stage, we build a deep understanding of the problem where we can move forward with the steps required to the find the solution for the problem. In the above example, the solution can include placing the elevator next to the stairs so disabled people can easily find it, or using sliding area next to the stairs so they can easily use their wheelchairs.

Designers are faced with daily challenges to explore problems, observe current situations, or find solutions to improve products and services. Critical thinking provides a method to explore different situations with eliminating any chances for biases, prejudice, or misleading information. The critical thinking is a great method to understand the situation in order to analyze it to define the problems and prototype solutions.
Dr Rafiq Elmansy
As an academic and author, I've had the privilege of shaping the design landscape. I teach design at the University of Leeds and am the Programme Leader for the MA Design, focusing on design thinking, design for health, and behavioural design. I've developed and taught several innovative programmes at Wrexham Glyndwr University, Northumbria University, and The American University in Cairo. I'm also a published book author and the proud founder of Designorate.com, a platform that has been instrumental in fostering design innovation. My expertise in design has been recognised by prestigious organizations. I'm a fellow of the Higher Education Academy (HEA), the Design Research Society (FDRS), and an Adobe Education Leader. Over the course of 20 years, I've had the privilege of working with esteemed clients such as the UN, World Bank, Adobe, and Schneider, contributing to their design strategies. For more than 12 years, I collaborated closely with the Adobe team, playing a key role in the development of many Adobe applications.
You May Also Like

Creative Thinking: Inspired Lessons from Leonardo Da Vinci’s

How to Conduct Online Brainstorming

How to Use Lego Serious Play in the Design Thinking Process?

13 Online Design Thinking Tools for Mind Mapping

What is the Failure Mode and Effects (FMEA)?

10 Success Factors for the Experience Design Process
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Sign me up for the newsletter!
The 5 Design Thinking Steps

Table of contents
Navigating the process: key design thinking steps for success.
Design Thinking has become a cornerstone methodology in the design world, revered for its human-centric approach. Whether you're a seasoned professional or new to the game, understanding the design thinking steps will undoubtedly elevate your problem-solving skills. This article delves into these critical steps and offers tips for effectively running design thinking workshops.
Understanding Design Thinking
Design Thinking is a holistic, solution-focused approach to problem-solving that prioritizes empathy and experimentation. Rooted in understanding the user's needs, it leverages creative and critical thinking to deliver innovative solutions. By embracing this process, designers and design management professionals can create user-friendly products that align with both user needs and business goals.
The five fey steps of Design Thinking
The Design Thinking process comprises five key steps—empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. It's crucial to remember this is a non-linear process, and designers may oscillate between stages as insights emerge.
This first step is a deep dive into understanding the users' needs, context, and challenges. This empathy-building phase lays the groundwork for the entire Design Thinking process.
Empathy helps you step outside of your own perspectives, assumptions, and biases, providing a genuine understanding of your users. Techniques such as direct observations, interviews, or immersion can be employed, as well as building an empathy map .
When facilitating a workshop, encourage participants to truly listen and keep an open mind. Role-playing can be an effective technique to foster empathy and understand the user's experience.
At this stage, your accumulated observations are synthesized into a clear and actionable problem statement—what Design Thinking refers to as the "Point Of View." This statement should be user-focused and broad enough to allow for creative freedom yet narrow enough to make it manageable.
In a workshop setting, help participants to avoid rushing this phase. Use affinity diagrams to group and categorize findings and then craft problem statements. Keep refining until you have a statement everyone agrees resonates with the user insights.
Ideation is all about creativity and expansion. The goal here is to generate a wide range of ideas that might answer the defined problem statement. Encourage wild ideas, defer judgment, and aim for quantity over quality at this stage.
Facilitating ideation in a workshop can be both exciting and challenging. Diverse teams tend to generate diverse ideas, so be prepared to effectively manage and harness this diversity. Techniques like brainstorming, mind mapping , or "worst possible idea" can stimulate creativity.
Prototyping is all about bringing ideas to life. It's a stage of experimentation where solutions are created based on the ideas generated. These prototypes are preliminary models of the final product and can range from simple paper sketches to interactive digital models.
In a workshop, emphasize that the prototype doesn't have to be perfect; it's a tool for learning. Provide a range of materials for physical prototyping, and guide teams on using prototyping software for digital products.
Testing is where the rubber meets the road. Here, the prototypes are presented to the users, and their interactions and feedback are observed. This feedback is then used to refine the solution and may even unearth insights that lead you back to previous steps.
In a workshop, role-play can be a great way to test prototypes. Ensure that participants understand the value of constructive feedback and are ready to embrace changes to their prototypes based on the insights gathered.
Implementation of Design Thinking steps
Design Thinking is less about the steps and more about the mindset: curiosity, empathy, embracing ambiguity, and accepting failure
as a path to success. Here are some tips to ensure a smooth process:
Embrace Diversity: A mix of perspectives can provide a broader understanding of the user and stimulate more varied ideas.
Foster a Safe Space: Encourage openness and ensure all ideas are welcomed without judgment.
Encourage Active Listening: Whether interviewing users or receiving feedback from team members, active listening is key to gaining deeper insights.
Iterate, Iterate, Iterate: Don't be afraid to revisit previous steps. Iteration is at the heart of Design Thinking—it's all about learning and improving.
Design Thinking in different industries
Design Thinking isn't exclusive to design-centric fields. Its applicability spans various sectors, from healthcare to education and even government bodies. For instance, Airbnb used Design Thinking to redesign its user experience, leading to a significant increase in bookings. Meanwhile, the UK government used it to restructure its digital services, making them more user-friendly and accessible.
Common misconceptions and challenges in Design Thinking
One common misconception is that Design Thinking is a linear process. Remember, it's not unusual or wrong to circle back to previous steps. Also, don't be disheartened if your first solution isn't the winning one—it's part of the iterative process.
Another challenge is ensuring genuine empathy. Avoid making assumptions and stay true to the user insights you've gathered.
Finally, don't be pressured to race through the steps. The goal of Design Thinking isn't speed—it's finding the right solution.
The transformative power of Design Thinking lies not just in understanding the steps, but in adopting the underlying mindset. It's a methodology that helps us design products, services, processes, and strategies with a human-centric lens. As you navigate your way through empathizing, defining, ideating, prototyping, and testing, remember to stay open, curious, and flexible. And above all, keep your users at the heart of your decision-making.
Embrace Design Thinking—it's more than a process; it's a way to a better, more empathetic, and innovative world.
Read more about design
What is collaborative design?
Read article
The basics of the product design process
Wireframe vs. UI design
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Design Thinking: A Guide to Creative Problem-Solving (2024)
Updated: Jan 02, 2024 By: Dessign Team

Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that focuses on human needs. It is a human-centered approach to innovation that aims to create innovative solutions to complex problems. The process begins with empathy, where designers seek to understand the needs, behaviors, and pain points of the users.
This is followed by defining the problem, ideating, prototyping, and testing. The iterative process allows designers to refine their ideas and create solutions that are not only innovative but also meet the needs of the users.
Design thinking is a methodology that can be applied to a wide range of problems. It is used by designers, businesses, and organizations to develop new products, services, and processes. The methodology is based on the idea that the best solutions are created when designers work collaboratively with users and stakeholders.
By involving users in the design process, designers can create solutions that are more effective and meet the needs of the users. Design thinking can also be used to identify new opportunities for growth and innovation.
Key Takeaways
- Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that focuses on the needs of the users.
- The process involves empathy, defining the problem, ideating, prototyping, and testing.
- Design thinking can be applied to a wide range of problems and is used by designers, businesses, and organizations to develop new products, services, and processes.
Fundamentals of Design Thinking
Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that involves building innovative solutions by understanding human needs and constraints. It is a collaborative and iterative process that can help designers and developers create products and services that are both user-centric and profitable.
Understanding the Process
The design thinking process is a non-linear process that involves five stages: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. The process starts with empathizing with the user and understanding their needs. The next stage is defining the problem statement and organizing the observations. Then, ideation techniques are used to brainstorm solutions, followed by the experimental phase of prototyping. The final stage is testing and iterating on the prototype until the solution meets the user's needs and constraints.
Role of Empathy
Empathy is a critical component of design thinking. It involves putting oneself in the user's shoes and understanding their pain points, emotional needs, and visions. Through empathy, designers can gain insights into the user's behavior and develop innovative solutions that meet their needs.
Importance of Ideation
Ideation is the process of generating creative solutions to the problem statement. Designers use ideation techniques such as the worst possible idea and scampering to come up with innovative solutions. Ideation is an essential stage in the design thinking process because it helps designers generate a range of ideas and select the best solution.
Prototype Development
Prototyping is the process of building a physical or digital representation of the solution. Prototyping allows designers to test the solution and get feedback from users. It is an iterative process that involves building, testing, and refining the prototype until it meets the user's needs and constraints.
Testing and Iteration
Testing is the process of evaluating the prototype and getting feedback from users. It involves observing how users interact with the prototype and collecting data on their behavior. Based on the feedback, designers can iterate on the prototype and refine the solution until it meets the user's needs and constraints.
Design thinking is a powerful methodology that can help designers and developers create innovative solutions to complex problems. By focusing on human needs and constraints, designers can create products and services that provide value to customers and give organizations a competitive advantage.
Applications of Design Thinking
Design thinking has proven to be a valuable methodology for solving complex problems and creating innovative solutions. Its human-centered approach to problem-solving has made it a popular choice in various industries, including business, product development, service design, and organizational culture.
In Business and Strategy
Design thinking is becoming increasingly popular in the business world as it helps organizations to develop innovative solutions that meet the needs of their customers. By using design thinking, businesses can define their problem statement, understand their audience, and create solutions that have a competitive advantage.
Design thinking can also be used in strategy development. It helps businesses to identify and prioritize opportunities, create a vision for growth, and develop a plan to achieve their goals. By using design thinking, businesses can create a strategy that is grounded in human needs and insights.
In Product Development
Design thinking is a valuable methodology for product development as it helps designers to understand the needs of their users and develop products that meet those needs. The process involves empathizing with users, defining the problem, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing.
By using design thinking, designers can create products that provide value to their users and differentiate themselves from their competitors. It also helps them to iterate and improve their products based on feedback from their users.
In Service Design
Design thinking is widely used in service design as it helps designers to create services that are user-centric and meet the needs of their users. The process involves empathizing with users, defining the problem, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing.
By using design thinking, designers can create services that provide value to their users and differentiate themselves from their competitors. It also helps them to iterate and improve their services based on feedback from their users.
In Organizational Culture
Design thinking is not just a methodology for problem-solving but also a way of thinking that can transform organizational culture. By using design thinking, organizations can create a culture that is focused on human needs, collaboration, and innovation.
Design thinking can also be used to develop skills in employees, such as empathy, problem-solving, and collaboration. It helps organizations to create a culture of innovation and change that can drive growth and success.
In conclusion, design thinking is a powerful methodology that can be applied in various industries to create innovative solutions that meet the needs of their users. It is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that can transform organizational culture and drive growth and success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 stages of design thinking.
Design thinking involves five stages: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. Each stage is essential to the process and helps to ensure that the final product meets the needs of the user.
What are the key skills required for design thinking?
Design thinking requires a wide range of skills, including empathy, creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication. These skills are necessary to effectively understand the needs of the user and create a product that meets those needs.
What are the steps involved in design thinking?
The steps involved in design thinking include understanding the problem, researching the user, brainstorming ideas, prototyping, and testing. These steps are iterative and require constant feedback to ensure that the final product meets the needs of the user.
How can design thinking benefit individuals and organizations?
Design thinking can benefit individuals and organizations in many ways. By focusing on the needs of the user, design thinking can lead to more effective and innovative solutions. It can also help to improve communication and collaboration within teams and organizations.
What are some examples of design thinking frameworks?
Some examples of design thinking frameworks include the Stanford d.school Design Thinking Process, the IDEO Design Thinking Process, and the Hasso Plattner Institute of Design Thinking at Stanford. Each framework has its own unique approach, but all share a focus on the needs of the user.
Who can benefit from using design thinking?
Design thinking can benefit anyone who is involved in the creation of products or services, from designers and engineers to business leaders and entrepreneurs. By focusing on the needs of the user, design thinking can help to create more effective and innovative solutions.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How to Install a WordPress Theme: Beginners Guide 2023

Novel AI Review: Everything You Need to Know (2024)

10 Best Free WooCommerce WordPress Themes (Most Popular 2024)

20+ Best Bootstrap Website Examples for Inspiration (2024)

Join Our Weekly Newsletter
10,000+ Community Members
Best Resources for Designers, Developers & Digital Marketers
Best hand-picked and fully curated resources and tools...
What is the Design Thinking? Definition, Importance, Examples, and Process
By Paul VanZandt
Published on: April 19, 2024

What is the Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is defined as a human-centered approach to innovation and problem-solving that prioritizes understanding the needs of users, generating creative solutions, and iterating through rapid prototyping and testing. It originated in the field of design but has since been adopted by various industries and disciplines as a powerful methodology for addressing complex challenges and driving innovation.
Key principles of Design Thinking include:
- Empathy: Design Thinking begins with gaining a deep understanding of the needs, motivations, and behaviors of users or stakeholders through empathy. This involves observing, engaging with, and listening to users to uncover insights that inform the design process.
- Define: Once user needs and insights are gathered, the problem or challenge is defined in a human-centered way. This involves framing the problem statement based on the needs and aspirations of users, rather than predefined assumptions or constraints.
- Ideate: In the ideation phase, diverse ideas and solutions are generated through brainstorming and creative thinking techniques. The focus is on quantity and variety, encouraging wild ideas and lateral thinking to explore a wide range of possibilities.
- Prototype: Prototyping involves creating low-fidelity representations of potential solutions to quickly and cheaply test ideas and gather feedback. Prototypes can take various forms, such as sketches, wireframes, mock-ups, or physical models, depending on the context.
- Test: Prototypes are tested with users to gather feedback, validate assumptions, and refine ideas. Testing involves observing how users interact with prototypes, collecting feedback, and iterating based on insights gained from user testing.
- Iterate: Design Thinking is an iterative process, with multiple cycles of prototyping, testing, and refining. Each iteration builds on the insights gained from previous iterations, leading to continuous improvement and refinement of solutions.
Design Thinking is characterized by its collaborative and iterative nature, emphasizing creativity, empathy, and experimentation. It encourages a bias towards action and a willingness to embrace ambiguity and failure as part of the innovation process. By focusing on understanding user needs and rapidly iterating through prototyping and testing, Design Thinking enables teams to develop solutions that are more effective, user-centered, and impactful.
Design Thinking Importance
Design Thinking is important for several reasons:
- User-Centered Solutions: Design Thinking emphasizes understanding the needs, motivations, and behaviors of users. By focusing on empathy and human-centered design, it ensures that solutions are tailored to meet the real needs of users, resulting in products, services, and experiences that are more intuitive, relevant, and satisfying.
- Innovation and Creativity: Design Thinking fosters a culture of creativity and innovation by encouraging divergent thinking, experimentation, and risk-taking. It provides a structured framework for generating and exploring new ideas, leading to breakthrough innovations and novel solutions to complex problems.
- Problem-Solving Approach: Design Thinking offers a systematic approach to problem-solving that can be applied to a wide range of challenges, from product design to organizational change. It helps teams break down complex problems, frame them in a human-centered way, and develop practical and effective solutions through iterative prototyping and testing.
- Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: Design Thinking brings together diverse perspectives and expertise from multiple disciplines, including design, engineering, business, and psychology. By fostering collaboration and interdisciplinary teamwork, it enables teams to leverage the strengths and insights of different disciplines to tackle complex challenges more effectively.
- Adaptability and Agility: Design Thinking is inherently flexible and adaptable, making it well-suited for dynamic and uncertain environments. Its iterative approach allows teams to quickly test and iterate on ideas, respond to feedback, and adapt to changing circumstances, enabling organizations to stay agile and responsive in the face of evolving challenges.
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: By focusing on understanding and addressing user needs, Design Thinking helps organizations deliver products and services that resonate with customers, leading to higher levels of satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy. Customer-centric design can also drive competitive advantage and differentiation in the marketplace.
- Continuous Improvement: Design Thinking promotes a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging reflection, learning, and iteration. Its iterative nature allows teams to learn from failures and successes, refine their approach over time, and continuously enhance the quality and effectiveness of their solutions.
Overall, Design Thinking is important because it enables organizations to create innovative, user-centered solutions that address real needs, drive customer satisfaction, and foster a culture of creativity, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
Top 6 Design Thinking Examples
Here are some examples of Design Thinking in action across various industries:
- Apple’s iPhone:
Apple’s iPhone is a classic example of Design Thinking in product development. The iPhone revolutionized the smartphone industry by focusing on user experience, simplicity, and intuitive design. Apple’s design team used empathetic research to understand user needs and behaviors, resulting in a device that seamlessly integrates hardware and software to provide a delightful user experience.
Airbnb, the online marketplace for lodging and vacation rentals, is built on principles of Design Thinking. The founders of Airbnb used empathy to understand the needs of both hosts and guests, leading to the creation of a platform that facilitates meaningful connections and personalized experiences. Airbnb’s innovative business model and user-centric design have disrupted the hospitality industry.
- IDEO’s Shopping Cart Redesign:
IDEO, a global design consultancy, used Design Thinking to redesign the traditional shopping cart for a leading retailer. IDEO’s designers observed shoppers in stores, interviewed them about their experiences, and prototyped new cart designs based on their feedback. The result was a redesigned shopping cart that improved usability, efficiency, and convenience for shoppers.
- Stanford d.school’s Design Thinking for Social Impact:
Stanford University’s d.school (Hasso Plattner Institute of Design) applies Design Thinking principles to address social and environmental challenges. Projects include designing affordable healthcare solutions for underserved communities, creating sustainable transportation systems, and developing educational programs for children in low-income areas. These initiatives demonstrate how Design Thinking can be used to tackle complex social issues and drive positive change.
- IBM Design Thinking for Enterprise Solutions:
IBM has integrated Design Thinking into its approach to developing enterprise software and solutions. IBM Design Thinking emphasizes collaboration, rapid prototyping, and user feedback to create innovative solutions that address the needs of businesses and users. By applying Design Thinking principles, IBM has transformed its approach to software development and created more user-centric products and services.
- Toyota’s Production System:
Toyota’s Production System (TPS) is often cited as an example of Design Thinking applied to manufacturing. TPS emphasizes continuous improvement, waste reduction, and employee empowerment to create efficient and flexible production processes. By involving employees in problem-solving and encouraging experimentation, TPS has enabled Toyota to innovate and adapt to changing market demands.
These examples illustrate how Design Thinking can be applied across a wide range of industries and contexts to create innovative products, services, and solutions that address user needs, and drive business success. This also makes a positive impact on society.
Design Thinking Process
The Design Thinking process typically consists of several iterative stages, each focusing on a different aspect of problem-solving and innovation. While the specific steps and terminology may vary slightly depending on the source or context, the core principles remain consistent. Here’s a generalized overview of the Design Thinking process:
- Empathize: The first stage involves understanding the needs, motivations, and behaviors of the people who will use the product, service, or solution. This may include conducting interviews, observations, surveys, and other research methods to gain empathy and insights into users’ experiences.
- Define: In this stage, the insights gathered from the empathy phase are synthesized and reframed into a problem statement or challenge that guides the rest of the design process. The problem statement should be framed in a human-centered way, focusing on addressing the needs and aspirations of users.
- Ideate: The ideation stage involves generating a wide range of ideas and potential solutions to address the problem defined in the previous stage. This is a brainstorming phase where creativity is encouraged, and no idea is considered off-limits. Techniques such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and sketching are often used to stimulate ideation.
- Prototype: In the prototyping stage, rough, low-fidelity representations of potential solutions are created to quickly and cheaply explore ideas and concepts. Prototypes can take various forms, such as sketches, wireframes, mock-ups, or physical models, depending on the nature of the problem and the desired level of fidelity.
- Test: The testing stage involves gathering feedback and insights from users by presenting them with prototypes of the proposed solutions. Testing allows designers to evaluate the effectiveness, usability, and desirability of the solutions and identify areas for improvement. Iterative testing and refinement are key components of the Design Thinking process.
- Iterate: Based on the feedback received during testing, designers iterate on the prototypes, refining and improving the solutions iteratively. This may involve making adjustments to the design, adding new features, or exploring alternative approaches based on user feedback and insights gained from testing.
- Implement: Once a satisfactory solution has been identified through testing and iteration, it is implemented and brought to market or deployed in the real world. Implementation may involve further refinement, scaling up production, and integrating the solution into existing systems or processes.
- Learn: The learning stage involves reflecting on the design process, capturing lessons learned, and identifying opportunities for future improvement. Designers analyze the successes and challenges encountered during the project and apply these insights to inform future projects and iterations.
Throughout the Design Thinking process, teams often cycle back and forth between stages, iterating on ideas, gathering additional insights, and refining solutions based on feedback from users and stakeholders. This iterative approach enables designers to continuously improve and innovate, ultimately leading to more effective, user-centered solutions.
Igniting Innovation
Powerful innovation starts as an idea. Launch your IdeaScale community today
Ignite Innovation With Your IdeaScale Community!
IdeaScale is an innovation management solution that inspires people to take action on their ideas. Your community’s ideas can change lives, your business and the world. Connect to the ideas that matter and start co-creating the future.
Copyright © 2024 IdeaScale
Privacy Overview
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Right Way to Lead Design Thinking
- Christian Bason
- Robert D. Austin

The authors studied almost two dozen major design-thinking projects within large private- and public-sector organizations in five countries and found that effective leadership is critical to their success. They focused not on how individual design teams did their work but on how the senior executives who commissioned the work interacted with and enabled it. To employees accustomed to being told to be rational and objective, design-thinking methods can seem uncomfortably emotive. Being asked not to quickly converge on an answer can be difficult for people accustomed to valuing a clear direction, cost savings, and finishing sooner rather than later. Iterative prototyping and testing call on employees to repeatedly experience something they’ve historically tried to avoid: failure. Consequently, those who are unfamiliar with design thinking need guidance and support from leaders to navigate the landscape and productively channel their reactions to the approach. The authors have identified practices that executives can use to stay on top of such innovation projects and lead them to success.
How to help project teams overcome the inevitable inefficiencies, uncertainties, and emotional flare-ups
Idea in Brief
The challenge.
Design-thinking methods—such as empathizing with users and conducting experiments knowing many will fail—often seem subjective and personal to employees accustomed to being told to be rational and objective.
The Fallout
Employees can be shocked and dismayed by findings, feel like they are spinning their wheels, or find it difficult to shed preconceptions about the product or service they’ve been providing. Their anxieties may derail the project.
Leaders—without being heavy-handed—need to help teams make the space and time for new ideas to emerge and maintain an overall sense of direction and purpose.
Anne Lind, the head of the national agency in Denmark that evaluates the insurance claims of injured workers and decides on their compensation, had a crisis on her hands. Oddly, it emerged from a project that had seemed to be on a path to success. The project employed design thinking in an effort to improve the services delivered by her organization. The members of her project team immersed themselves in the experiences of clients, establishing rapport and empathizing with them in a bid to see the world through their eyes. The team interviewed and unobtrusively video-recorded clients as they described their situations and their experiences with the agency’s case management. The approach led to a surprising revelation: The agency’s processes were designed largely to serve its own wants and needs (to be efficient and to make claims assessment easy for the staff) rather than those of clients, who typically had gone through a traumatic event and were trying to return to a productive normal life.
- Christian Bason (@christianbason) was for eight years head of MindLab , a cross-governmental innovation unit in Denmark that involves citizens and businesses in developing new solutions for the public sector. Since November 2014 he has been chief executive of the Danish Design Centre .
- Robert D. Austin is a professor of information systems and the faculty director of the Learning Innovation Initiative at Ivey Business School. He is also a coauthor of The Adventures of an IT Leader (Harvard Business Review Press, 2016).
Partner Center
Mapping the Relationship Between Critical Thinking and Design Thinking
- Published: 02 February 2021
- Volume 13 , pages 406–429, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
- Jonathan D. Ericson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9076-0596 1
2439 Accesses
12 Citations
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Critical thinking has been a longstanding goal of education, while design thinking has gradually emerged as a popular method for supporting entrepreneurship, innovation, and problem solving in modern business. While some scholars have posited that design thinking may support critical thinking, empirical research examining the relationship between these two modes of thinking is lacking because their shared conceptual structure has not been articulated in detail and because they have remained siloed in practice. This essay maps eleven essential components of critical thinking to a variety of methods drawn from three popular design thinking frameworks. The mapping reveals that these seemingly unrelated modes of thinking share common features but also differ in important respects. A detailed comparison of the two modes of thinking suggests that design thinking methods have the potential to support and augment traditional critical thinking practices, and that design thinking frameworks could be modified to more explicitly incorporate critical thinking. The article concludes with a discussion of implications for the knowledge economy, and a research agenda for researchers, educators, and practitioners.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Social Constructivism—Jerome Bruner

Designing conceptual articles: four approaches
Elina Jaakkola
Research design: the methodology for interdisciplinary research framework
Hilde Tobi & Jarl K. Kampen
Aranda, M. L., Lie, R., & Guzey, S. (2019). Productive thinking in middle school science students’ design conversations in a design-based engineering challenge. International Journal of Technology and Design Education , (January). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-019-09498-5 .
Association for Computing Machinery. (2018). ACM Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct . Retrieved from https://www.acm.org/code-of-ethics .
Bailin, S. (1987). Critical and creative thinking. Informal Logic, 9 (1), 23–30.
Article Google Scholar
Bailin, S. (1988). Achieving extraordinary ends: An essay on creativity . Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Book Google Scholar
Banfield, R., Lombardo, C. T., & Wax, T. (2015). Design sprint: A practical guidebook for building great digital products . Sebastopol, CA: O’Reilly Media Inc.
Google Scholar
Benson, J., & Dresdow, S. (2014). Design thinking: A fresh approach for transformative assessment practice. Journal of Management Education, 38 (3), 436–461. https://doi.org/10.1177/1052562913507571 .
Bloom, B.S. (Ed.), Engelhart, M.D., Furst, E.J., Hill, W.H., & Krathwohl, D.R. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals. Handbook 1: Cognitive domain. New York: David McKay.
Wilner, S., & Micheli, P. (2015). Reconciling the tension between consistency and relevance: design thinking as a mechanism for brand ambidexterity. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43 (5), 589–609.
Bonwell, C., & Eison, J. (1991). Active Learning: Creating excitement in the classroom (ASHEERIC Higher Education Report No. 1) . Washington, DC: George Washington University.
Brown, A. (2015). Developing career adaptability and innovative capabilities through learning and working in Norway and the United Kingdom. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 6 (2), 402–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-014-0215-6 .
Brown, J. S., Collins, A., Duguid, P., & Seely, J. (2007). Situated cognition and the culture of learning. Educational Researcher, 18 (1), 32–42. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X018001032 .
Brown, T. (2021). Design thinking. Accessed 4 January 2021. http://www.ideou.com/pages/design-thinking
Callaway, M. R., & Esser, J. K. (1984). Groupthink: Effects of cohesiveness and problemsolving on group decision making. Social Behavior and Personality, 12, 157–164.
Carayannis, E. G., & Rakhmatullin, R. (2014). The quadruple/quintuple innovation helixes and smart specialisation strategies for sustainable and inclusive growth in Europe and beyond. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 5 (2), 212–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-014-0185-8 .
Churchman, C. W. (1967). Guest editorial: Wicked problems. Management Science, 14 (4), B141–B214.
Colzato, L. S., Szapora, A., Lippelt, D., & Hommel, B. (2017). Prior meditation practice modulates performance and strategy use in convergent- and divergent-thinking problems. Mindfulness, 8 (1), 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-014-0352-9 .
Cropley, A. (2006). In praise of convergent thinking. Creativity Research Journal, 18 (3), 391–404. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326934crj1803_13 .
Cross, N, Dorst, K. & Roozenburg, N. (Ed.). (1992). Research in design thinking . Delft: Delft University Press.
Cross, N. (1993). A history of design methodology. In M. J. de Vries, N. Cross, & D. Grant (Eds.), Design methodology and relationships with science (pp. 15–27). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-8220-9_2 .
Crossan, M. M. (1998). Improvisation in action. Organization Science, 9 (5), 593–599. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.9.5.593 .
Davies, M. (2015). A model of critical thinking in higher education. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12835-1_2 .
Davis, C. M. (1990). What is empathy, and can empathy be taught. Physical Therapy, 70 (11), 707–711. https://doi.org/10.2519/jospt.2011.3225 .
Dewey, J. (1910). How we think . Boston, MA: D.C. Health.
Dewey, J. (1933). How we think: A restatement of the relation of reflective thinking to the educative process . Lexington, MA: D.C. Health.
Dorst, K. (2011). The core of “design thinking” and its application. Design Studies, 32 (6), 521–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.destud.2011.07.006 .
Dym, C., Agogino, A., Erics, O., Frey, D., & Leifer, L. (2005). Engineering design thinking, teaching, and learning. Journal of Engineering Education, 94 (1), 103–120.
Ennis, R. H. (1962). A concept of critical thinking. Harvard Educational Review, 32 (1), 81–111.
Ennis, R. H. (1987a). A taxonomy of critical thinking dispositions and abilities. In Teaching Thinking Skills: Theory and practice . New York, NY: W. H. Freeman.
Ennis, R. H. (1987b). Critical thinking and the curriculum. Slomianko: In M. Heiman & J.(Eds.), Thinking skills instruction: Concepts and techniques. Building Students’ Thinking Skills Series. (pp. 40–48). National Education Association. https://doi.org/10.1177/019263658807250830 .
Ennis, R. H. (1991). Critical thinking: a streamlined conception. Teaching Philosophy, 14 (1), 5–24. https://doi.org/10.5840/teachphil19911412 .
Eyler, J., & Giles, D. (1999). Where’s the learning in service-learning . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Facione, P. A. (1990). Critical thinking : A statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction executive summary “ The Delphi Report. American Philosophical Association Delphi Research Report . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2009.07.002 .
Fisher, A., & Scriven, M. (1997). Critical thinking: Its definition and assessment . Norwich: Centre for Research in Critical Thinking, University of East Anglia.
Gibbons, S. (2018). Empathy Mapping: The first step in design thinking. Retrieved from https://www.nngroup.com/articles/empathy-mapping/ .
Glaser, E. M. (1941). An experiment in the development of critical thinking . New York: Columbia University Teacher’s College.
Gokhale, A. A. (1995). Collaborative learning enhances critical thinking. Journal of Technology Education , 7 (1), 22–30. https://doi.org/10.21061/jte.v7i1.a.2 .
Halonen, J. S. (1995). Demystifying critical thinking. Teaching of Psychology, 22 (1), 75–81. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15328023top2201_23 .
Halpern, D. F. (1998). Teaching critical thinking for transfer across domains. American Psychologist, 53 (4), 449–455. https://doi.org/10.1037//0003-066X.53.4.449 .
Haupt, G. (2015). Learning from experts: fostering extended thinking in the early phases of the design process. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 25 (4), 483–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-014-9295-7 .
Harley, A. (2018). UX Expert Reviews. https://www.nngroup.com/articles/ux-expert-reviews/
Haupt, G. (2018). Hierarchical thinking: a cognitive tool for guiding coherent decision making in design problem solving. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 28 (1), 207–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-016-9381-0 .
Hitchcock, D. (2018). Critical thinking. In E. Zalta (Ed.), Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2018). Retrieved from https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2018/entries/critical-thinking/ .
Hogland-Smith. (2017). Critical thinking skills are now in top demand in sales, business. Chicago Tribune . Retrieved from https://www.chicagotribune.com/suburbs/post-tribune/opinion/ct-ptb-hoagland-smith-problem-st-0723-20170723-story.html .
Hu, Y., Du, X., Bryan-Kinns, N., & Guo, Y. (2018). Identifying divergent design thinking through the observable behavior of service design novices. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 1, 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-018-9479-7 .
Hutchins, E. (1996). Cognition in the Wild . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Hutchins, E. (2010). Cognitive ecology. Topics in Cognitive . Science, 2 (4), 705–715. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-8765.2010.01089.x .
IDEO. (2015). The field guide to human-centered design (1st ed.). Canada: IDEO.org / DesignKit.
ITEA (2007). Standards for technological literacy: Content for the study of technology. (2007). In Phi Delta Kappan (3rd ed.). International Technology Education Association (ITEA). https://doi.org/10.1177/003172170108200707 .
Janis, I. L. (1971). Groupthink. Psychology Today, 5 (6), 43–46.
Janis, I. (1982). Groupthink: Psychological studies of policy decisions and fiascoes (2nd ed.). Boston, MA: Houghton-Mifflin.
Janis, I. L. (2008). Groupthink. IEEE Engineering Management Review, 36 (1), 36.
Johansson-Sköldberg, U., & Woodilla, J. (2013). Design thinking: past, present and possible futures. Creativity and Innovation Management, 22 (2), 121–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/caim.12023 .
Joyce, A., & Paquin, R. L. (2016). The triple layered business model canvas: A tool to design more sustainable business models. Journal of Cleaner Production , 135 (November 2017), 1474–1486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.067 .
Kelley, T. R., & Sung, E. (2017). Sketching by design: Teaching sketching to young learners. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 27 (3), 363–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-016-9354-3 .
Kolb, A. Y., & Kolb, D. A. (2016). Learning styles and learning spaces: Enhancing experiential learning in higher education. Academy of Management Learning & Education, 4 (2), 193–212. https://doi.org/10.5465/AMLE.2005.17268566 .
Kolko, J. (2018). The Divisiveness of Design Thinking. Interactions, 25 (3), 28–34. https://doi.org/10.1145/3194313 .
Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy: An overview. Theory Into Practice, 41(4), 212–218. https://www.jstor.org/stable/1477405
Kuiper, R. (2002). Enhancing metacognition through the reflective use of self-regulated learning strategies. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing, 33 (2), 78–87. https://doi.org/10.3928/0022-0124-20020301-11 .
Lancione, M., & Clegg, S. R. (2015). The lightness of management learning. Management Learning, 46 (3), 280–298. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350507614526533 .
Levin, J. S. (2018, May). Sharpen your critical thinking skills with these 14 leadership practices. Forbes . Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbescoachescouncil/2018/05/31/sharpen-your-critical-thinking-skills-with-these-14-leadership-practices/ .
Lloyd, P. (2013). Embedded creativity: Teaching design thinking via distance education. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 23 (3), 749–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-012-9214-8 .
Luchs, M. (2016). A brief introduction to design thinking. In M. Luchs, K. Swan & A. Griffin (eds.), Design thinking: new product development essentials from the PDMA (pp. 1–12). Hoboken: (NJ): Wiley.
Lukovics, M., Udvari, B., Nádas, N., & Fisher, E. (2019). Raising awareness of researchers-in-the-making toward responsible research and innovation. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 10 (4), 1558–1577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-019-00624-1 .
LUMA. (2012). Innovating for People: Handbook of Human-Centered Design Methods (1st ed.). Pittsburg, PA: LUMA Institute LLC.
Mason, T. H., Pollard, C. R., Chimalakonda, D., Guerrero, A. M., Kerr-Smith, C., Milheiras, S. A., & Bunnefeld, N. (2018). Wicked conflict: Using wicked problem thinking for holistic management of conservation conflict. Conservation letters, 11 (6), e12460.
McPeck (1981/2017). Critical thinking and education . New York: Routledge.
Montini, L. (2014, October). The trouble with hiring for “critical thinking” skills. Inc. Retrieved from https://www.inc.com/laura-montini/are-you-sure-you-want-to-hire-a-critical-thinker.html .
Moshavi, D. (2001). “Yes and...”: Introducing improvisational theatre techniques to the management classroom. Journal of Management Education , 25 (4), 437–449.
Nodder, C. (2013). Evil by design: Interaction design to lead us into temptation. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0703993104 .
Norris, P. E., O’Rourke, M., Mayer, A. S., & Halvorsen, K. E. (2016). Managing the wicked problem of transdisciplinary team formation in socioecological systems. Landscape and Urban Planning, 154, 115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2016.01.008 .
Osterwalder, A., & Pigneur, Y. (2010). Business model generation: A handbook for visionaries, game changers, and challengers. In Booksgooglecom (Vol. 30). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Owen, R., Macnaghten, P., & Stilgoe, J. (2012). Responsible research and innovation: from science in society to science for society, with society. Science and Public Policy, 39 (6), 751–760.
Park, W. W. (1990). A review of research on groupthink. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 3, 229–245.
Pithers, R. T., & Soden, R. (2000). Critical thinking in education: A review. Educational Research, 42 (3), 237–249. https://doi.org/10.1080/001318800440579 .
Price, R. (2016). March) . Business Insider: Microsoft is deleting its AI chatbot’s incredibly racist tweets.
Prince, M. (2004). Does active learning work ? A review of the research. Journal of Engineering Education, 93 (3), 223–231.
Quitadamo, I. J., Brahler, C. J., & Crouch, G. J. (2009). Peer-led team learning: A prospective method for increasing critical thinking in undergraduate science courses. Science Educator, 18 (1), 29–39.
Razzouk, R., & Shute, V. (2012). What is design thinking and why is it important? Review of Educational Research, 82 (3), 330–348.
Reed, L. (2018, January). Building critical thinking skills to solve problems at work. Business.Com . Retrieved from https://www.business.com/articles/building-critical-thinking-skills-at-work/ .
van Reine, P. P. (2017). The culture of design thinking for innovation. Journal of Innovation Management, 5 (2), 56–80.
Rittel, H. W., & Webber, M. M. (1973). Dilemmas in a general theory of planning. Policy Sciences, 4 (2), 155–169.
Rosenberger, C. (2000). Beyond empathy: Developing critical consciousness through service learning. In Integrating service learning and multicultural education in colleges and universities (pp. 23–43). https://doi.org/10.4324/9781410606051-9 .
Rowe (1987). Design thinking . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Runco, M. A. (1991). Divergent thinking (creativity research) . Norwood, NJ: Ablex Publishing Corporation.
Runco, M. A., & Acar, S. (2012). Divergent thinking as an indicator of creative potential. Creativity Research Journal, 24 (1), 66–75. https://doi.org/10.1080/10400419.2012.652929 .
Scheer, A., Noweski, C., & Meinel, C. (2012). Transforming constructivist learning into action: Design thinking in education. Design and Technology Education: An International Journal, 17 (3), 8–19.
Schleicher, D., Jones, P., & Kachur, O. (2010). Bodystorming as embodied designing. Interactions, 17 (6), 47. https://doi.org/10.1145/1865245.1865256 .
Scriven, M., & Paul, R. (1987). Critical thinking. 8th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking and Education Reform [Web page]. Retrieved from http://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/defining-critical-thinking/766
Spiro, H. M. (1992). What is empathy and can it be taught? Annals of Internal Medicine, 116 (10), 843–846. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-116-10-843 .
Somerson, R. (2013). The art of Critical Making: An introduction. In E. Somerson, M. Hermano, & J. Maeda (Eds.), The Art of Critical Making: Rhode Island School of Design on Creative Practice (pp. 19–31). John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Stempfle, J., & Badke-Schaub, P. (2002). Thinking in design teams - An analysis of team communication. Design Studies, 23 (5), 473–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-694X(02)00004-2 .
Suchman, L. (1987). Plans and situated actions . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Sun, J., Chen, Q., Zhang, Q., Li, Y., Li, H., Wei, D., & Qiu, J. (2016). Training your brain to be more creative: Brain functional and structural changes induced by divergent thinking training. Human Brain Mapping, 37 (10), 3375–3387. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23246 .
Totten, S., Sills, T., Digby, A., & Russ, P. (1991). Cooperative learning: A guide to research . New York, NY: Garland.
Varela, F., Thompson, E., & Rosch, E. (1991). The embodied mind . Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
Waddock, S. (2013). The wicked problems of global sustainability need wicked (good) leaders and wicked (good) collaborative solutions. Journal of Management for Global Sustainability , 1 (1), 91–111. https://doi.org/10.13185/JM2013.01106 .
Wells, A. (2013). The importance of design thinking for technological literacy: A phenomenological perspective. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 23 (3), 623–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-012-9207-7 .
Wilson, M. (2002). Six views of embodied cognition. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 9 (4), 625–636. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03196322 .
Yildirim, B., & Özkahraman, Ş. (2011). Critical thinking in nursing process and education. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 1 (13), 257–262.
Zidulka, A., & Mitchell, I. K. (2018). Creativity or cooptation? thinking beyond instrumentalism when teaching design thinking. Journal of Management Education, 42 (6), 749–760. https://doi.org/10.1177/1052562918799797 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Information Design & Corporate Communication, Bentley University, 175 Forest Street, Waltham, MA, 02452, USA
Jonathan D. Ericson
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jonathan D. Ericson .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Design Thinking: Challenges and Opportunities
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ericson, J.D. Mapping the Relationship Between Critical Thinking and Design Thinking. J Knowl Econ 13 , 406–429 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-021-00733-w
Download citation
Received : 20 July 2020
Accepted : 19 January 2021
Published : 02 February 2021
Issue Date : March 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-021-00733-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Critical thinking
- Design thinking
- Entrepreneurship
- Knowledge economy
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a widely accepted educational goal. Its definition is contested, but the competing definitions can be understood as differing conceptions of the same basic concept: careful thinking directed to a goal. Conceptions differ with respect to the scope of such thinking, the type of goal, the criteria and norms for thinking carefully, and the thinking components on which they focus. Its adoption as an educational goal has been recommended on the basis of respect for students’ autonomy and preparing students for success in life and for democratic citizenship. “Critical thinkers” have the dispositions and abilities that lead them to think critically when appropriate. The abilities can be identified directly; the dispositions indirectly, by considering what factors contribute to or impede exercise of the abilities. Standardized tests have been developed to assess the degree to which a person possesses such dispositions and abilities. Educational intervention has been shown experimentally to improve them, particularly when it includes dialogue, anchored instruction, and mentoring. Controversies have arisen over the generalizability of critical thinking across domains, over alleged bias in critical thinking theories and instruction, and over the relationship of critical thinking to other types of thinking.
2.1 Dewey’s Three Main Examples
2.2 dewey’s other examples, 2.3 further examples, 2.4 non-examples, 3. the definition of critical thinking, 4. its value, 5. the process of thinking critically, 6. components of the process, 7. contributory dispositions and abilities, 8.1 initiating dispositions, 8.2 internal dispositions, 9. critical thinking abilities, 10. required knowledge, 11. educational methods, 12.1 the generalizability of critical thinking, 12.2 bias in critical thinking theory and pedagogy, 12.3 relationship of critical thinking to other types of thinking, other internet resources, related entries.
Use of the term ‘critical thinking’ to describe an educational goal goes back to the American philosopher John Dewey (1910), who more commonly called it ‘reflective thinking’. He defined it as
active, persistent and careful consideration of any belief or supposed form of knowledge in the light of the grounds that support it, and the further conclusions to which it tends. (Dewey 1910: 6; 1933: 9)
and identified a habit of such consideration with a scientific attitude of mind. His lengthy quotations of Francis Bacon, John Locke, and John Stuart Mill indicate that he was not the first person to propose development of a scientific attitude of mind as an educational goal.
In the 1930s, many of the schools that participated in the Eight-Year Study of the Progressive Education Association (Aikin 1942) adopted critical thinking as an educational goal, for whose achievement the study’s Evaluation Staff developed tests (Smith, Tyler, & Evaluation Staff 1942). Glaser (1941) showed experimentally that it was possible to improve the critical thinking of high school students. Bloom’s influential taxonomy of cognitive educational objectives (Bloom et al. 1956) incorporated critical thinking abilities. Ennis (1962) proposed 12 aspects of critical thinking as a basis for research on the teaching and evaluation of critical thinking ability.
Since 1980, an annual international conference in California on critical thinking and educational reform has attracted tens of thousands of educators from all levels of education and from many parts of the world. Also since 1980, the state university system in California has required all undergraduate students to take a critical thinking course. Since 1983, the Association for Informal Logic and Critical Thinking has sponsored sessions in conjunction with the divisional meetings of the American Philosophical Association (APA). In 1987, the APA’s Committee on Pre-College Philosophy commissioned a consensus statement on critical thinking for purposes of educational assessment and instruction (Facione 1990a). Researchers have developed standardized tests of critical thinking abilities and dispositions; for details, see the Supplement on Assessment . Educational jurisdictions around the world now include critical thinking in guidelines for curriculum and assessment.
For details on this history, see the Supplement on History .
2. Examples and Non-Examples
Before considering the definition of critical thinking, it will be helpful to have in mind some examples of critical thinking, as well as some examples of kinds of thinking that would apparently not count as critical thinking.
Dewey (1910: 68–71; 1933: 91–94) takes as paradigms of reflective thinking three class papers of students in which they describe their thinking. The examples range from the everyday to the scientific.
Transit : “The other day, when I was down town on 16th Street, a clock caught my eye. I saw that the hands pointed to 12:20. This suggested that I had an engagement at 124th Street, at one o’clock. I reasoned that as it had taken me an hour to come down on a surface car, I should probably be twenty minutes late if I returned the same way. I might save twenty minutes by a subway express. But was there a station near? If not, I might lose more than twenty minutes in looking for one. Then I thought of the elevated, and I saw there was such a line within two blocks. But where was the station? If it were several blocks above or below the street I was on, I should lose time instead of gaining it. My mind went back to the subway express as quicker than the elevated; furthermore, I remembered that it went nearer than the elevated to the part of 124th Street I wished to reach, so that time would be saved at the end of the journey. I concluded in favor of the subway, and reached my destination by one o’clock.” (Dewey 1910: 68–69; 1933: 91–92)
Ferryboat : “Projecting nearly horizontally from the upper deck of the ferryboat on which I daily cross the river is a long white pole, having a gilded ball at its tip. It suggested a flagpole when I first saw it; its color, shape, and gilded ball agreed with this idea, and these reasons seemed to justify me in this belief. But soon difficulties presented themselves. The pole was nearly horizontal, an unusual position for a flagpole; in the next place, there was no pulley, ring, or cord by which to attach a flag; finally, there were elsewhere on the boat two vertical staffs from which flags were occasionally flown. It seemed probable that the pole was not there for flag-flying.
“I then tried to imagine all possible purposes of the pole, and to consider for which of these it was best suited: (a) Possibly it was an ornament. But as all the ferryboats and even the tugboats carried poles, this hypothesis was rejected. (b) Possibly it was the terminal of a wireless telegraph. But the same considerations made this improbable. Besides, the more natural place for such a terminal would be the highest part of the boat, on top of the pilot house. (c) Its purpose might be to point out the direction in which the boat is moving.
“In support of this conclusion, I discovered that the pole was lower than the pilot house, so that the steersman could easily see it. Moreover, the tip was enough higher than the base, so that, from the pilot’s position, it must appear to project far out in front of the boat. Moreover, the pilot being near the front of the boat, he would need some such guide as to its direction. Tugboats would also need poles for such a purpose. This hypothesis was so much more probable than the others that I accepted it. I formed the conclusion that the pole was set up for the purpose of showing the pilot the direction in which the boat pointed, to enable him to steer correctly.” (Dewey 1910: 69–70; 1933: 92–93)
Bubbles : “In washing tumblers in hot soapsuds and placing them mouth downward on a plate, bubbles appeared on the outside of the mouth of the tumblers and then went inside. Why? The presence of bubbles suggests air, which I note must come from inside the tumbler. I see that the soapy water on the plate prevents escape of the air save as it may be caught in bubbles. But why should air leave the tumbler? There was no substance entering to force it out. It must have expanded. It expands by increase of heat, or by decrease of pressure, or both. Could the air have become heated after the tumbler was taken from the hot suds? Clearly not the air that was already entangled in the water. If heated air was the cause, cold air must have entered in transferring the tumblers from the suds to the plate. I test to see if this supposition is true by taking several more tumblers out. Some I shake so as to make sure of entrapping cold air in them. Some I take out holding mouth downward in order to prevent cold air from entering. Bubbles appear on the outside of every one of the former and on none of the latter. I must be right in my inference. Air from the outside must have been expanded by the heat of the tumbler, which explains the appearance of the bubbles on the outside. But why do they then go inside? Cold contracts. The tumbler cooled and also the air inside it. Tension was removed, and hence bubbles appeared inside. To be sure of this, I test by placing a cup of ice on the tumbler while the bubbles are still forming outside. They soon reverse” (Dewey 1910: 70–71; 1933: 93–94).
Dewey (1910, 1933) sprinkles his book with other examples of critical thinking. We will refer to the following.
Weather : A man on a walk notices that it has suddenly become cool, thinks that it is probably going to rain, looks up and sees a dark cloud obscuring the sun, and quickens his steps (1910: 6–10; 1933: 9–13).
Disorder : A man finds his rooms on his return to them in disorder with his belongings thrown about, thinks at first of burglary as an explanation, then thinks of mischievous children as being an alternative explanation, then looks to see whether valuables are missing, and discovers that they are (1910: 82–83; 1933: 166–168).
Typhoid : A physician diagnosing a patient whose conspicuous symptoms suggest typhoid avoids drawing a conclusion until more data are gathered by questioning the patient and by making tests (1910: 85–86; 1933: 170).
Blur : A moving blur catches our eye in the distance, we ask ourselves whether it is a cloud of whirling dust or a tree moving its branches or a man signaling to us, we think of other traits that should be found on each of those possibilities, and we look and see if those traits are found (1910: 102, 108; 1933: 121, 133).
Suction pump : In thinking about the suction pump, the scientist first notes that it will draw water only to a maximum height of 33 feet at sea level and to a lesser maximum height at higher elevations, selects for attention the differing atmospheric pressure at these elevations, sets up experiments in which the air is removed from a vessel containing water (when suction no longer works) and in which the weight of air at various levels is calculated, compares the results of reasoning about the height to which a given weight of air will allow a suction pump to raise water with the observed maximum height at different elevations, and finally assimilates the suction pump to such apparently different phenomena as the siphon and the rising of a balloon (1910: 150–153; 1933: 195–198).
Diamond : A passenger in a car driving in a diamond lane reserved for vehicles with at least one passenger notices that the diamond marks on the pavement are far apart in some places and close together in others. Why? The driver suggests that the reason may be that the diamond marks are not needed where there is a solid double line separating the diamond lane from the adjoining lane, but are needed when there is a dotted single line permitting crossing into the diamond lane. Further observation confirms that the diamonds are close together when a dotted line separates the diamond lane from its neighbour, but otherwise far apart.
Rash : A woman suddenly develops a very itchy red rash on her throat and upper chest. She recently noticed a mark on the back of her right hand, but was not sure whether the mark was a rash or a scrape. She lies down in bed and thinks about what might be causing the rash and what to do about it. About two weeks before, she began taking blood pressure medication that contained a sulfa drug, and the pharmacist had warned her, in view of a previous allergic reaction to a medication containing a sulfa drug, to be on the alert for an allergic reaction; however, she had been taking the medication for two weeks with no such effect. The day before, she began using a new cream on her neck and upper chest; against the new cream as the cause was mark on the back of her hand, which had not been exposed to the cream. She began taking probiotics about a month before. She also recently started new eye drops, but she supposed that manufacturers of eye drops would be careful not to include allergy-causing components in the medication. The rash might be a heat rash, since she recently was sweating profusely from her upper body. Since she is about to go away on a short vacation, where she would not have access to her usual physician, she decides to keep taking the probiotics and using the new eye drops but to discontinue the blood pressure medication and to switch back to the old cream for her neck and upper chest. She forms a plan to consult her regular physician on her return about the blood pressure medication.
Candidate : Although Dewey included no examples of thinking directed at appraising the arguments of others, such thinking has come to be considered a kind of critical thinking. We find an example of such thinking in the performance task on the Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA+), which its sponsoring organization describes as
a performance-based assessment that provides a measure of an institution’s contribution to the development of critical-thinking and written communication skills of its students. (Council for Aid to Education 2017)
A sample task posted on its website requires the test-taker to write a report for public distribution evaluating a fictional candidate’s policy proposals and their supporting arguments, using supplied background documents, with a recommendation on whether to endorse the candidate.
Immediate acceptance of an idea that suggests itself as a solution to a problem (e.g., a possible explanation of an event or phenomenon, an action that seems likely to produce a desired result) is “uncritical thinking, the minimum of reflection” (Dewey 1910: 13). On-going suspension of judgment in the light of doubt about a possible solution is not critical thinking (Dewey 1910: 108). Critique driven by a dogmatically held political or religious ideology is not critical thinking; thus Paulo Freire (1968 [1970]) is using the term (e.g., at 1970: 71, 81, 100, 146) in a more politically freighted sense that includes not only reflection but also revolutionary action against oppression. Derivation of a conclusion from given data using an algorithm is not critical thinking.
What is critical thinking? There are many definitions. Ennis (2016) lists 14 philosophically oriented scholarly definitions and three dictionary definitions. Following Rawls (1971), who distinguished his conception of justice from a utilitarian conception but regarded them as rival conceptions of the same concept, Ennis maintains that the 17 definitions are different conceptions of the same concept. Rawls articulated the shared concept of justice as
a characteristic set of principles for assigning basic rights and duties and for determining… the proper distribution of the benefits and burdens of social cooperation. (Rawls 1971: 5)
Bailin et al. (1999b) claim that, if one considers what sorts of thinking an educator would take not to be critical thinking and what sorts to be critical thinking, one can conclude that educators typically understand critical thinking to have at least three features.
- It is done for the purpose of making up one’s mind about what to believe or do.
- The person engaging in the thinking is trying to fulfill standards of adequacy and accuracy appropriate to the thinking.
- The thinking fulfills the relevant standards to some threshold level.
One could sum up the core concept that involves these three features by saying that critical thinking is careful goal-directed thinking. This core concept seems to apply to all the examples of critical thinking described in the previous section. As for the non-examples, their exclusion depends on construing careful thinking as excluding jumping immediately to conclusions, suspending judgment no matter how strong the evidence, reasoning from an unquestioned ideological or religious perspective, and routinely using an algorithm to answer a question.
If the core of critical thinking is careful goal-directed thinking, conceptions of it can vary according to its presumed scope, its presumed goal, one’s criteria and threshold for being careful, and the thinking component on which one focuses. As to its scope, some conceptions (e.g., Dewey 1910, 1933) restrict it to constructive thinking on the basis of one’s own observations and experiments, others (e.g., Ennis 1962; Fisher & Scriven 1997; Johnson 1992) to appraisal of the products of such thinking. Ennis (1991) and Bailin et al. (1999b) take it to cover both construction and appraisal. As to its goal, some conceptions restrict it to forming a judgment (Dewey 1910, 1933; Lipman 1987; Facione 1990a). Others allow for actions as well as beliefs as the end point of a process of critical thinking (Ennis 1991; Bailin et al. 1999b). As to the criteria and threshold for being careful, definitions vary in the term used to indicate that critical thinking satisfies certain norms: “intellectually disciplined” (Scriven & Paul 1987), “reasonable” (Ennis 1991), “skillful” (Lipman 1987), “skilled” (Fisher & Scriven 1997), “careful” (Bailin & Battersby 2009). Some definitions specify these norms, referring variously to “consideration of any belief or supposed form of knowledge in the light of the grounds that support it and the further conclusions to which it tends” (Dewey 1910, 1933); “the methods of logical inquiry and reasoning” (Glaser 1941); “conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication” (Scriven & Paul 1987); the requirement that “it is sensitive to context, relies on criteria, and is self-correcting” (Lipman 1987); “evidential, conceptual, methodological, criteriological, or contextual considerations” (Facione 1990a); and “plus-minus considerations of the product in terms of appropriate standards (or criteria)” (Johnson 1992). Stanovich and Stanovich (2010) propose to ground the concept of critical thinking in the concept of rationality, which they understand as combining epistemic rationality (fitting one’s beliefs to the world) and instrumental rationality (optimizing goal fulfillment); a critical thinker, in their view, is someone with “a propensity to override suboptimal responses from the autonomous mind” (2010: 227). These variant specifications of norms for critical thinking are not necessarily incompatible with one another, and in any case presuppose the core notion of thinking carefully. As to the thinking component singled out, some definitions focus on suspension of judgment during the thinking (Dewey 1910; McPeck 1981), others on inquiry while judgment is suspended (Bailin & Battersby 2009, 2021), others on the resulting judgment (Facione 1990a), and still others on responsiveness to reasons (Siegel 1988). Kuhn (2019) takes critical thinking to be more a dialogic practice of advancing and responding to arguments than an individual ability.
In educational contexts, a definition of critical thinking is a “programmatic definition” (Scheffler 1960: 19). It expresses a practical program for achieving an educational goal. For this purpose, a one-sentence formulaic definition is much less useful than articulation of a critical thinking process, with criteria and standards for the kinds of thinking that the process may involve. The real educational goal is recognition, adoption and implementation by students of those criteria and standards. That adoption and implementation in turn consists in acquiring the knowledge, abilities and dispositions of a critical thinker.
Conceptions of critical thinking generally do not include moral integrity as part of the concept. Dewey, for example, took critical thinking to be the ultimate intellectual goal of education, but distinguished it from the development of social cooperation among school children, which he took to be the central moral goal. Ennis (1996, 2011) added to his previous list of critical thinking dispositions a group of dispositions to care about the dignity and worth of every person, which he described as a “correlative” (1996) disposition without which critical thinking would be less valuable and perhaps harmful. An educational program that aimed at developing critical thinking but not the correlative disposition to care about the dignity and worth of every person, he asserted, “would be deficient and perhaps dangerous” (Ennis 1996: 172).
Dewey thought that education for reflective thinking would be of value to both the individual and society; recognition in educational practice of the kinship to the scientific attitude of children’s native curiosity, fertile imagination and love of experimental inquiry “would make for individual happiness and the reduction of social waste” (Dewey 1910: iii). Schools participating in the Eight-Year Study took development of the habit of reflective thinking and skill in solving problems as a means to leading young people to understand, appreciate and live the democratic way of life characteristic of the United States (Aikin 1942: 17–18, 81). Harvey Siegel (1988: 55–61) has offered four considerations in support of adopting critical thinking as an educational ideal. (1) Respect for persons requires that schools and teachers honour students’ demands for reasons and explanations, deal with students honestly, and recognize the need to confront students’ independent judgment; these requirements concern the manner in which teachers treat students. (2) Education has the task of preparing children to be successful adults, a task that requires development of their self-sufficiency. (3) Education should initiate children into the rational traditions in such fields as history, science and mathematics. (4) Education should prepare children to become democratic citizens, which requires reasoned procedures and critical talents and attitudes. To supplement these considerations, Siegel (1988: 62–90) responds to two objections: the ideology objection that adoption of any educational ideal requires a prior ideological commitment and the indoctrination objection that cultivation of critical thinking cannot escape being a form of indoctrination.
Despite the diversity of our 11 examples, one can recognize a common pattern. Dewey analyzed it as consisting of five phases:
- suggestions , in which the mind leaps forward to a possible solution;
- an intellectualization of the difficulty or perplexity into a problem to be solved, a question for which the answer must be sought;
- the use of one suggestion after another as a leading idea, or hypothesis , to initiate and guide observation and other operations in collection of factual material;
- the mental elaboration of the idea or supposition as an idea or supposition ( reasoning , in the sense on which reasoning is a part, not the whole, of inference); and
- testing the hypothesis by overt or imaginative action. (Dewey 1933: 106–107; italics in original)
The process of reflective thinking consisting of these phases would be preceded by a perplexed, troubled or confused situation and followed by a cleared-up, unified, resolved situation (Dewey 1933: 106). The term ‘phases’ replaced the term ‘steps’ (Dewey 1910: 72), thus removing the earlier suggestion of an invariant sequence. Variants of the above analysis appeared in (Dewey 1916: 177) and (Dewey 1938: 101–119).
The variant formulations indicate the difficulty of giving a single logical analysis of such a varied process. The process of critical thinking may have a spiral pattern, with the problem being redefined in the light of obstacles to solving it as originally formulated. For example, the person in Transit might have concluded that getting to the appointment at the scheduled time was impossible and have reformulated the problem as that of rescheduling the appointment for a mutually convenient time. Further, defining a problem does not always follow after or lead immediately to an idea of a suggested solution. Nor should it do so, as Dewey himself recognized in describing the physician in Typhoid as avoiding any strong preference for this or that conclusion before getting further information (Dewey 1910: 85; 1933: 170). People with a hypothesis in mind, even one to which they have a very weak commitment, have a so-called “confirmation bias” (Nickerson 1998): they are likely to pay attention to evidence that confirms the hypothesis and to ignore evidence that counts against it or for some competing hypothesis. Detectives, intelligence agencies, and investigators of airplane accidents are well advised to gather relevant evidence systematically and to postpone even tentative adoption of an explanatory hypothesis until the collected evidence rules out with the appropriate degree of certainty all but one explanation. Dewey’s analysis of the critical thinking process can be faulted as well for requiring acceptance or rejection of a possible solution to a defined problem, with no allowance for deciding in the light of the available evidence to suspend judgment. Further, given the great variety of kinds of problems for which reflection is appropriate, there is likely to be variation in its component events. Perhaps the best way to conceptualize the critical thinking process is as a checklist whose component events can occur in a variety of orders, selectively, and more than once. These component events might include (1) noticing a difficulty, (2) defining the problem, (3) dividing the problem into manageable sub-problems, (4) formulating a variety of possible solutions to the problem or sub-problem, (5) determining what evidence is relevant to deciding among possible solutions to the problem or sub-problem, (6) devising a plan of systematic observation or experiment that will uncover the relevant evidence, (7) carrying out the plan of systematic observation or experimentation, (8) noting the results of the systematic observation or experiment, (9) gathering relevant testimony and information from others, (10) judging the credibility of testimony and information gathered from others, (11) drawing conclusions from gathered evidence and accepted testimony, and (12) accepting a solution that the evidence adequately supports (cf. Hitchcock 2017: 485).
Checklist conceptions of the process of critical thinking are open to the objection that they are too mechanical and procedural to fit the multi-dimensional and emotionally charged issues for which critical thinking is urgently needed (Paul 1984). For such issues, a more dialectical process is advocated, in which competing relevant world views are identified, their implications explored, and some sort of creative synthesis attempted.
If one considers the critical thinking process illustrated by the 11 examples, one can identify distinct kinds of mental acts and mental states that form part of it. To distinguish, label and briefly characterize these components is a useful preliminary to identifying abilities, skills, dispositions, attitudes, habits and the like that contribute causally to thinking critically. Identifying such abilities and habits is in turn a useful preliminary to setting educational goals. Setting the goals is in its turn a useful preliminary to designing strategies for helping learners to achieve the goals and to designing ways of measuring the extent to which learners have done so. Such measures provide both feedback to learners on their achievement and a basis for experimental research on the effectiveness of various strategies for educating people to think critically. Let us begin, then, by distinguishing the kinds of mental acts and mental events that can occur in a critical thinking process.
- Observing : One notices something in one’s immediate environment (sudden cooling of temperature in Weather , bubbles forming outside a glass and then going inside in Bubbles , a moving blur in the distance in Blur , a rash in Rash ). Or one notes the results of an experiment or systematic observation (valuables missing in Disorder , no suction without air pressure in Suction pump )
- Feeling : One feels puzzled or uncertain about something (how to get to an appointment on time in Transit , why the diamonds vary in spacing in Diamond ). One wants to resolve this perplexity. One feels satisfaction once one has worked out an answer (to take the subway express in Transit , diamonds closer when needed as a warning in Diamond ).
- Wondering : One formulates a question to be addressed (why bubbles form outside a tumbler taken from hot water in Bubbles , how suction pumps work in Suction pump , what caused the rash in Rash ).
- Imagining : One thinks of possible answers (bus or subway or elevated in Transit , flagpole or ornament or wireless communication aid or direction indicator in Ferryboat , allergic reaction or heat rash in Rash ).
- Inferring : One works out what would be the case if a possible answer were assumed (valuables missing if there has been a burglary in Disorder , earlier start to the rash if it is an allergic reaction to a sulfa drug in Rash ). Or one draws a conclusion once sufficient relevant evidence is gathered (take the subway in Transit , burglary in Disorder , discontinue blood pressure medication and new cream in Rash ).
- Knowledge : One uses stored knowledge of the subject-matter to generate possible answers or to infer what would be expected on the assumption of a particular answer (knowledge of a city’s public transit system in Transit , of the requirements for a flagpole in Ferryboat , of Boyle’s law in Bubbles , of allergic reactions in Rash ).
- Experimenting : One designs and carries out an experiment or a systematic observation to find out whether the results deduced from a possible answer will occur (looking at the location of the flagpole in relation to the pilot’s position in Ferryboat , putting an ice cube on top of a tumbler taken from hot water in Bubbles , measuring the height to which a suction pump will draw water at different elevations in Suction pump , noticing the spacing of diamonds when movement to or from a diamond lane is allowed in Diamond ).
- Consulting : One finds a source of information, gets the information from the source, and makes a judgment on whether to accept it. None of our 11 examples include searching for sources of information. In this respect they are unrepresentative, since most people nowadays have almost instant access to information relevant to answering any question, including many of those illustrated by the examples. However, Candidate includes the activities of extracting information from sources and evaluating its credibility.
- Identifying and analyzing arguments : One notices an argument and works out its structure and content as a preliminary to evaluating its strength. This activity is central to Candidate . It is an important part of a critical thinking process in which one surveys arguments for various positions on an issue.
- Judging : One makes a judgment on the basis of accumulated evidence and reasoning, such as the judgment in Ferryboat that the purpose of the pole is to provide direction to the pilot.
- Deciding : One makes a decision on what to do or on what policy to adopt, as in the decision in Transit to take the subway.
By definition, a person who does something voluntarily is both willing and able to do that thing at that time. Both the willingness and the ability contribute causally to the person’s action, in the sense that the voluntary action would not occur if either (or both) of these were lacking. For example, suppose that one is standing with one’s arms at one’s sides and one voluntarily lifts one’s right arm to an extended horizontal position. One would not do so if one were unable to lift one’s arm, if for example one’s right side was paralyzed as the result of a stroke. Nor would one do so if one were unwilling to lift one’s arm, if for example one were participating in a street demonstration at which a white supremacist was urging the crowd to lift their right arm in a Nazi salute and one were unwilling to express support in this way for the racist Nazi ideology. The same analysis applies to a voluntary mental process of thinking critically. It requires both willingness and ability to think critically, including willingness and ability to perform each of the mental acts that compose the process and to coordinate those acts in a sequence that is directed at resolving the initiating perplexity.
Consider willingness first. We can identify causal contributors to willingness to think critically by considering factors that would cause a person who was able to think critically about an issue nevertheless not to do so (Hamby 2014). For each factor, the opposite condition thus contributes causally to willingness to think critically on a particular occasion. For example, people who habitually jump to conclusions without considering alternatives will not think critically about issues that arise, even if they have the required abilities. The contrary condition of willingness to suspend judgment is thus a causal contributor to thinking critically.
Now consider ability. In contrast to the ability to move one’s arm, which can be completely absent because a stroke has left the arm paralyzed, the ability to think critically is a developed ability, whose absence is not a complete absence of ability to think but absence of ability to think well. We can identify the ability to think well directly, in terms of the norms and standards for good thinking. In general, to be able do well the thinking activities that can be components of a critical thinking process, one needs to know the concepts and principles that characterize their good performance, to recognize in particular cases that the concepts and principles apply, and to apply them. The knowledge, recognition and application may be procedural rather than declarative. It may be domain-specific rather than widely applicable, and in either case may need subject-matter knowledge, sometimes of a deep kind.
Reflections of the sort illustrated by the previous two paragraphs have led scholars to identify the knowledge, abilities and dispositions of a “critical thinker”, i.e., someone who thinks critically whenever it is appropriate to do so. We turn now to these three types of causal contributors to thinking critically. We start with dispositions, since arguably these are the most powerful contributors to being a critical thinker, can be fostered at an early stage of a child’s development, and are susceptible to general improvement (Glaser 1941: 175)
8. Critical Thinking Dispositions
Educational researchers use the term ‘dispositions’ broadly for the habits of mind and attitudes that contribute causally to being a critical thinker. Some writers (e.g., Paul & Elder 2006; Hamby 2014; Bailin & Battersby 2016a) propose to use the term ‘virtues’ for this dimension of a critical thinker. The virtues in question, although they are virtues of character, concern the person’s ways of thinking rather than the person’s ways of behaving towards others. They are not moral virtues but intellectual virtues, of the sort articulated by Zagzebski (1996) and discussed by Turri, Alfano, and Greco (2017).
On a realistic conception, thinking dispositions or intellectual virtues are real properties of thinkers. They are general tendencies, propensities, or inclinations to think in particular ways in particular circumstances, and can be genuinely explanatory (Siegel 1999). Sceptics argue that there is no evidence for a specific mental basis for the habits of mind that contribute to thinking critically, and that it is pedagogically misleading to posit such a basis (Bailin et al. 1999a). Whatever their status, critical thinking dispositions need motivation for their initial formation in a child—motivation that may be external or internal. As children develop, the force of habit will gradually become important in sustaining the disposition (Nieto & Valenzuela 2012). Mere force of habit, however, is unlikely to sustain critical thinking dispositions. Critical thinkers must value and enjoy using their knowledge and abilities to think things through for themselves. They must be committed to, and lovers of, inquiry.
A person may have a critical thinking disposition with respect to only some kinds of issues. For example, one could be open-minded about scientific issues but not about religious issues. Similarly, one could be confident in one’s ability to reason about the theological implications of the existence of evil in the world but not in one’s ability to reason about the best design for a guided ballistic missile.
Facione (1990a: 25) divides “affective dispositions” of critical thinking into approaches to life and living in general and approaches to specific issues, questions or problems. Adapting this distinction, one can usefully divide critical thinking dispositions into initiating dispositions (those that contribute causally to starting to think critically about an issue) and internal dispositions (those that contribute causally to doing a good job of thinking critically once one has started). The two categories are not mutually exclusive. For example, open-mindedness, in the sense of willingness to consider alternative points of view to one’s own, is both an initiating and an internal disposition.
Using the strategy of considering factors that would block people with the ability to think critically from doing so, we can identify as initiating dispositions for thinking critically attentiveness, a habit of inquiry, self-confidence, courage, open-mindedness, willingness to suspend judgment, trust in reason, wanting evidence for one’s beliefs, and seeking the truth. We consider briefly what each of these dispositions amounts to, in each case citing sources that acknowledge them.
- Attentiveness : One will not think critically if one fails to recognize an issue that needs to be thought through. For example, the pedestrian in Weather would not have looked up if he had not noticed that the air was suddenly cooler. To be a critical thinker, then, one needs to be habitually attentive to one’s surroundings, noticing not only what one senses but also sources of perplexity in messages received and in one’s own beliefs and attitudes (Facione 1990a: 25; Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001).
- Habit of inquiry : Inquiry is effortful, and one needs an internal push to engage in it. For example, the student in Bubbles could easily have stopped at idle wondering about the cause of the bubbles rather than reasoning to a hypothesis, then designing and executing an experiment to test it. Thus willingness to think critically needs mental energy and initiative. What can supply that energy? Love of inquiry, or perhaps just a habit of inquiry. Hamby (2015) has argued that willingness to inquire is the central critical thinking virtue, one that encompasses all the others. It is recognized as a critical thinking disposition by Dewey (1910: 29; 1933: 35), Glaser (1941: 5), Ennis (1987: 12; 1991: 8), Facione (1990a: 25), Bailin et al. (1999b: 294), Halpern (1998: 452), and Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo (2001).
- Self-confidence : Lack of confidence in one’s abilities can block critical thinking. For example, if the woman in Rash lacked confidence in her ability to figure things out for herself, she might just have assumed that the rash on her chest was the allergic reaction to her medication against which the pharmacist had warned her. Thus willingness to think critically requires confidence in one’s ability to inquire (Facione 1990a: 25; Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001).
- Courage : Fear of thinking for oneself can stop one from doing it. Thus willingness to think critically requires intellectual courage (Paul & Elder 2006: 16).
- Open-mindedness : A dogmatic attitude will impede thinking critically. For example, a person who adheres rigidly to a “pro-choice” position on the issue of the legal status of induced abortion is likely to be unwilling to consider seriously the issue of when in its development an unborn child acquires a moral right to life. Thus willingness to think critically requires open-mindedness, in the sense of a willingness to examine questions to which one already accepts an answer but which further evidence or reasoning might cause one to answer differently (Dewey 1933; Facione 1990a; Ennis 1991; Bailin et al. 1999b; Halpern 1998, Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001). Paul (1981) emphasizes open-mindedness about alternative world-views, and recommends a dialectical approach to integrating such views as central to what he calls “strong sense” critical thinking. In three studies, Haran, Ritov, & Mellers (2013) found that actively open-minded thinking, including “the tendency to weigh new evidence against a favored belief, to spend sufficient time on a problem before giving up, and to consider carefully the opinions of others in forming one’s own”, led study participants to acquire information and thus to make accurate estimations.
- Willingness to suspend judgment : Premature closure on an initial solution will block critical thinking. Thus willingness to think critically requires a willingness to suspend judgment while alternatives are explored (Facione 1990a; Ennis 1991; Halpern 1998).
- Trust in reason : Since distrust in the processes of reasoned inquiry will dissuade one from engaging in it, trust in them is an initiating critical thinking disposition (Facione 1990a, 25; Bailin et al. 1999b: 294; Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001; Paul & Elder 2006). In reaction to an allegedly exclusive emphasis on reason in critical thinking theory and pedagogy, Thayer-Bacon (2000) argues that intuition, imagination, and emotion have important roles to play in an adequate conception of critical thinking that she calls “constructive thinking”. From her point of view, critical thinking requires trust not only in reason but also in intuition, imagination, and emotion.
- Seeking the truth : If one does not care about the truth but is content to stick with one’s initial bias on an issue, then one will not think critically about it. Seeking the truth is thus an initiating critical thinking disposition (Bailin et al. 1999b: 294; Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001). A disposition to seek the truth is implicit in more specific critical thinking dispositions, such as trying to be well-informed, considering seriously points of view other than one’s own, looking for alternatives, suspending judgment when the evidence is insufficient, and adopting a position when the evidence supporting it is sufficient.
Some of the initiating dispositions, such as open-mindedness and willingness to suspend judgment, are also internal critical thinking dispositions, in the sense of mental habits or attitudes that contribute causally to doing a good job of critical thinking once one starts the process. But there are many other internal critical thinking dispositions. Some of them are parasitic on one’s conception of good thinking. For example, it is constitutive of good thinking about an issue to formulate the issue clearly and to maintain focus on it. For this purpose, one needs not only the corresponding ability but also the corresponding disposition. Ennis (1991: 8) describes it as the disposition “to determine and maintain focus on the conclusion or question”, Facione (1990a: 25) as “clarity in stating the question or concern”. Other internal dispositions are motivators to continue or adjust the critical thinking process, such as willingness to persist in a complex task and willingness to abandon nonproductive strategies in an attempt to self-correct (Halpern 1998: 452). For a list of identified internal critical thinking dispositions, see the Supplement on Internal Critical Thinking Dispositions .
Some theorists postulate skills, i.e., acquired abilities, as operative in critical thinking. It is not obvious, however, that a good mental act is the exercise of a generic acquired skill. Inferring an expected time of arrival, as in Transit , has some generic components but also uses non-generic subject-matter knowledge. Bailin et al. (1999a) argue against viewing critical thinking skills as generic and discrete, on the ground that skilled performance at a critical thinking task cannot be separated from knowledge of concepts and from domain-specific principles of good thinking. Talk of skills, they concede, is unproblematic if it means merely that a person with critical thinking skills is capable of intelligent performance.
Despite such scepticism, theorists of critical thinking have listed as general contributors to critical thinking what they variously call abilities (Glaser 1941; Ennis 1962, 1991), skills (Facione 1990a; Halpern 1998) or competencies (Fisher & Scriven 1997). Amalgamating these lists would produce a confusing and chaotic cornucopia of more than 50 possible educational objectives, with only partial overlap among them. It makes sense instead to try to understand the reasons for the multiplicity and diversity, and to make a selection according to one’s own reasons for singling out abilities to be developed in a critical thinking curriculum. Two reasons for diversity among lists of critical thinking abilities are the underlying conception of critical thinking and the envisaged educational level. Appraisal-only conceptions, for example, involve a different suite of abilities than constructive-only conceptions. Some lists, such as those in (Glaser 1941), are put forward as educational objectives for secondary school students, whereas others are proposed as objectives for college students (e.g., Facione 1990a).
The abilities described in the remaining paragraphs of this section emerge from reflection on the general abilities needed to do well the thinking activities identified in section 6 as components of the critical thinking process described in section 5 . The derivation of each collection of abilities is accompanied by citation of sources that list such abilities and of standardized tests that claim to test them.
Observational abilities : Careful and accurate observation sometimes requires specialist expertise and practice, as in the case of observing birds and observing accident scenes. However, there are general abilities of noticing what one’s senses are picking up from one’s environment and of being able to articulate clearly and accurately to oneself and others what one has observed. It helps in exercising them to be able to recognize and take into account factors that make one’s observation less trustworthy, such as prior framing of the situation, inadequate time, deficient senses, poor observation conditions, and the like. It helps as well to be skilled at taking steps to make one’s observation more trustworthy, such as moving closer to get a better look, measuring something three times and taking the average, and checking what one thinks one is observing with someone else who is in a good position to observe it. It also helps to be skilled at recognizing respects in which one’s report of one’s observation involves inference rather than direct observation, so that one can then consider whether the inference is justified. These abilities come into play as well when one thinks about whether and with what degree of confidence to accept an observation report, for example in the study of history or in a criminal investigation or in assessing news reports. Observational abilities show up in some lists of critical thinking abilities (Ennis 1962: 90; Facione 1990a: 16; Ennis 1991: 9). There are items testing a person’s ability to judge the credibility of observation reports in the Cornell Critical Thinking Tests, Levels X and Z (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005). Norris and King (1983, 1985, 1990a, 1990b) is a test of ability to appraise observation reports.
Emotional abilities : The emotions that drive a critical thinking process are perplexity or puzzlement, a wish to resolve it, and satisfaction at achieving the desired resolution. Children experience these emotions at an early age, without being trained to do so. Education that takes critical thinking as a goal needs only to channel these emotions and to make sure not to stifle them. Collaborative critical thinking benefits from ability to recognize one’s own and others’ emotional commitments and reactions.
Questioning abilities : A critical thinking process needs transformation of an inchoate sense of perplexity into a clear question. Formulating a question well requires not building in questionable assumptions, not prejudging the issue, and using language that in context is unambiguous and precise enough (Ennis 1962: 97; 1991: 9).
Imaginative abilities : Thinking directed at finding the correct causal explanation of a general phenomenon or particular event requires an ability to imagine possible explanations. Thinking about what policy or plan of action to adopt requires generation of options and consideration of possible consequences of each option. Domain knowledge is required for such creative activity, but a general ability to imagine alternatives is helpful and can be nurtured so as to become easier, quicker, more extensive, and deeper (Dewey 1910: 34–39; 1933: 40–47). Facione (1990a) and Halpern (1998) include the ability to imagine alternatives as a critical thinking ability.
Inferential abilities : The ability to draw conclusions from given information, and to recognize with what degree of certainty one’s own or others’ conclusions follow, is universally recognized as a general critical thinking ability. All 11 examples in section 2 of this article include inferences, some from hypotheses or options (as in Transit , Ferryboat and Disorder ), others from something observed (as in Weather and Rash ). None of these inferences is formally valid. Rather, they are licensed by general, sometimes qualified substantive rules of inference (Toulmin 1958) that rest on domain knowledge—that a bus trip takes about the same time in each direction, that the terminal of a wireless telegraph would be located on the highest possible place, that sudden cooling is often followed by rain, that an allergic reaction to a sulfa drug generally shows up soon after one starts taking it. It is a matter of controversy to what extent the specialized ability to deduce conclusions from premisses using formal rules of inference is needed for critical thinking. Dewey (1933) locates logical forms in setting out the products of reflection rather than in the process of reflection. Ennis (1981a), on the other hand, maintains that a liberally-educated person should have the following abilities: to translate natural-language statements into statements using the standard logical operators, to use appropriately the language of necessary and sufficient conditions, to deal with argument forms and arguments containing symbols, to determine whether in virtue of an argument’s form its conclusion follows necessarily from its premisses, to reason with logically complex propositions, and to apply the rules and procedures of deductive logic. Inferential abilities are recognized as critical thinking abilities by Glaser (1941: 6), Facione (1990a: 9), Ennis (1991: 9), Fisher & Scriven (1997: 99, 111), and Halpern (1998: 452). Items testing inferential abilities constitute two of the five subtests of the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (Watson & Glaser 1980a, 1980b, 1994), two of the four sections in the Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level X (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005), three of the seven sections in the Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level Z (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005), 11 of the 34 items on Forms A and B of the California Critical Thinking Skills Test (Facione 1990b, 1992), and a high but variable proportion of the 25 selected-response questions in the Collegiate Learning Assessment (Council for Aid to Education 2017).
Experimenting abilities : Knowing how to design and execute an experiment is important not just in scientific research but also in everyday life, as in Rash . Dewey devoted a whole chapter of his How We Think (1910: 145–156; 1933: 190–202) to the superiority of experimentation over observation in advancing knowledge. Experimenting abilities come into play at one remove in appraising reports of scientific studies. Skill in designing and executing experiments includes the acknowledged abilities to appraise evidence (Glaser 1941: 6), to carry out experiments and to apply appropriate statistical inference techniques (Facione 1990a: 9), to judge inductions to an explanatory hypothesis (Ennis 1991: 9), and to recognize the need for an adequately large sample size (Halpern 1998). The Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level Z (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005) includes four items (out of 52) on experimental design. The Collegiate Learning Assessment (Council for Aid to Education 2017) makes room for appraisal of study design in both its performance task and its selected-response questions.
Consulting abilities : Skill at consulting sources of information comes into play when one seeks information to help resolve a problem, as in Candidate . Ability to find and appraise information includes ability to gather and marshal pertinent information (Glaser 1941: 6), to judge whether a statement made by an alleged authority is acceptable (Ennis 1962: 84), to plan a search for desired information (Facione 1990a: 9), and to judge the credibility of a source (Ennis 1991: 9). Ability to judge the credibility of statements is tested by 24 items (out of 76) in the Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level X (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005) and by four items (out of 52) in the Cornell Critical Thinking Test Level Z (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985, 2005). The College Learning Assessment’s performance task requires evaluation of whether information in documents is credible or unreliable (Council for Aid to Education 2017).
Argument analysis abilities : The ability to identify and analyze arguments contributes to the process of surveying arguments on an issue in order to form one’s own reasoned judgment, as in Candidate . The ability to detect and analyze arguments is recognized as a critical thinking skill by Facione (1990a: 7–8), Ennis (1991: 9) and Halpern (1998). Five items (out of 34) on the California Critical Thinking Skills Test (Facione 1990b, 1992) test skill at argument analysis. The College Learning Assessment (Council for Aid to Education 2017) incorporates argument analysis in its selected-response tests of critical reading and evaluation and of critiquing an argument.
Judging skills and deciding skills : Skill at judging and deciding is skill at recognizing what judgment or decision the available evidence and argument supports, and with what degree of confidence. It is thus a component of the inferential skills already discussed.
Lists and tests of critical thinking abilities often include two more abilities: identifying assumptions and constructing and evaluating definitions.
In addition to dispositions and abilities, critical thinking needs knowledge: of critical thinking concepts, of critical thinking principles, and of the subject-matter of the thinking.
We can derive a short list of concepts whose understanding contributes to critical thinking from the critical thinking abilities described in the preceding section. Observational abilities require an understanding of the difference between observation and inference. Questioning abilities require an understanding of the concepts of ambiguity and vagueness. Inferential abilities require an understanding of the difference between conclusive and defeasible inference (traditionally, between deduction and induction), as well as of the difference between necessary and sufficient conditions. Experimenting abilities require an understanding of the concepts of hypothesis, null hypothesis, assumption and prediction, as well as of the concept of statistical significance and of its difference from importance. They also require an understanding of the difference between an experiment and an observational study, and in particular of the difference between a randomized controlled trial, a prospective correlational study and a retrospective (case-control) study. Argument analysis abilities require an understanding of the concepts of argument, premiss, assumption, conclusion and counter-consideration. Additional critical thinking concepts are proposed by Bailin et al. (1999b: 293), Fisher & Scriven (1997: 105–106), Black (2012), and Blair (2021).
According to Glaser (1941: 25), ability to think critically requires knowledge of the methods of logical inquiry and reasoning. If we review the list of abilities in the preceding section, however, we can see that some of them can be acquired and exercised merely through practice, possibly guided in an educational setting, followed by feedback. Searching intelligently for a causal explanation of some phenomenon or event requires that one consider a full range of possible causal contributors, but it seems more important that one implements this principle in one’s practice than that one is able to articulate it. What is important is “operational knowledge” of the standards and principles of good thinking (Bailin et al. 1999b: 291–293). But the development of such critical thinking abilities as designing an experiment or constructing an operational definition can benefit from learning their underlying theory. Further, explicit knowledge of quirks of human thinking seems useful as a cautionary guide. Human memory is not just fallible about details, as people learn from their own experiences of misremembering, but is so malleable that a detailed, clear and vivid recollection of an event can be a total fabrication (Loftus 2017). People seek or interpret evidence in ways that are partial to their existing beliefs and expectations, often unconscious of their “confirmation bias” (Nickerson 1998). Not only are people subject to this and other cognitive biases (Kahneman 2011), of which they are typically unaware, but it may be counter-productive for one to make oneself aware of them and try consciously to counteract them or to counteract social biases such as racial or sexual stereotypes (Kenyon & Beaulac 2014). It is helpful to be aware of these facts and of the superior effectiveness of blocking the operation of biases—for example, by making an immediate record of one’s observations, refraining from forming a preliminary explanatory hypothesis, blind refereeing, double-blind randomized trials, and blind grading of students’ work. It is also helpful to be aware of the prevalence of “noise” (unwanted unsystematic variability of judgments), of how to detect noise (through a noise audit), and of how to reduce noise: make accuracy the goal, think statistically, break a process of arriving at a judgment into independent tasks, resist premature intuitions, in a group get independent judgments first, favour comparative judgments and scales (Kahneman, Sibony, & Sunstein 2021). It is helpful as well to be aware of the concept of “bounded rationality” in decision-making and of the related distinction between “satisficing” and optimizing (Simon 1956; Gigerenzer 2001).
Critical thinking about an issue requires substantive knowledge of the domain to which the issue belongs. Critical thinking abilities are not a magic elixir that can be applied to any issue whatever by somebody who has no knowledge of the facts relevant to exploring that issue. For example, the student in Bubbles needed to know that gases do not penetrate solid objects like a glass, that air expands when heated, that the volume of an enclosed gas varies directly with its temperature and inversely with its pressure, and that hot objects will spontaneously cool down to the ambient temperature of their surroundings unless kept hot by insulation or a source of heat. Critical thinkers thus need a rich fund of subject-matter knowledge relevant to the variety of situations they encounter. This fact is recognized in the inclusion among critical thinking dispositions of a concern to become and remain generally well informed.
Experimental educational interventions, with control groups, have shown that education can improve critical thinking skills and dispositions, as measured by standardized tests. For information about these tests, see the Supplement on Assessment .
What educational methods are most effective at developing the dispositions, abilities and knowledge of a critical thinker? In a comprehensive meta-analysis of experimental and quasi-experimental studies of strategies for teaching students to think critically, Abrami et al. (2015) found that dialogue, anchored instruction, and mentoring each increased the effectiveness of the educational intervention, and that they were most effective when combined. They also found that in these studies a combination of separate instruction in critical thinking with subject-matter instruction in which students are encouraged to think critically was more effective than either by itself. However, the difference was not statistically significant; that is, it might have arisen by chance.
Most of these studies lack the longitudinal follow-up required to determine whether the observed differential improvements in critical thinking abilities or dispositions continue over time, for example until high school or college graduation. For details on studies of methods of developing critical thinking skills and dispositions, see the Supplement on Educational Methods .
12. Controversies
Scholars have denied the generalizability of critical thinking abilities across subject domains, have alleged bias in critical thinking theory and pedagogy, and have investigated the relationship of critical thinking to other kinds of thinking.
McPeck (1981) attacked the thinking skills movement of the 1970s, including the critical thinking movement. He argued that there are no general thinking skills, since thinking is always thinking about some subject-matter. It is futile, he claimed, for schools and colleges to teach thinking as if it were a separate subject. Rather, teachers should lead their pupils to become autonomous thinkers by teaching school subjects in a way that brings out their cognitive structure and that encourages and rewards discussion and argument. As some of his critics (e.g., Paul 1985; Siegel 1985) pointed out, McPeck’s central argument needs elaboration, since it has obvious counter-examples in writing and speaking, for which (up to a certain level of complexity) there are teachable general abilities even though they are always about some subject-matter. To make his argument convincing, McPeck needs to explain how thinking differs from writing and speaking in a way that does not permit useful abstraction of its components from the subject-matters with which it deals. He has not done so. Nevertheless, his position that the dispositions and abilities of a critical thinker are best developed in the context of subject-matter instruction is shared by many theorists of critical thinking, including Dewey (1910, 1933), Glaser (1941), Passmore (1980), Weinstein (1990), Bailin et al. (1999b), and Willingham (2019).
McPeck’s challenge prompted reflection on the extent to which critical thinking is subject-specific. McPeck argued for a strong subject-specificity thesis, according to which it is a conceptual truth that all critical thinking abilities are specific to a subject. (He did not however extend his subject-specificity thesis to critical thinking dispositions. In particular, he took the disposition to suspend judgment in situations of cognitive dissonance to be a general disposition.) Conceptual subject-specificity is subject to obvious counter-examples, such as the general ability to recognize confusion of necessary and sufficient conditions. A more modest thesis, also endorsed by McPeck, is epistemological subject-specificity, according to which the norms of good thinking vary from one field to another. Epistemological subject-specificity clearly holds to a certain extent; for example, the principles in accordance with which one solves a differential equation are quite different from the principles in accordance with which one determines whether a painting is a genuine Picasso. But the thesis suffers, as Ennis (1989) points out, from vagueness of the concept of a field or subject and from the obvious existence of inter-field principles, however broadly the concept of a field is construed. For example, the principles of hypothetico-deductive reasoning hold for all the varied fields in which such reasoning occurs. A third kind of subject-specificity is empirical subject-specificity, according to which as a matter of empirically observable fact a person with the abilities and dispositions of a critical thinker in one area of investigation will not necessarily have them in another area of investigation.
The thesis of empirical subject-specificity raises the general problem of transfer. If critical thinking abilities and dispositions have to be developed independently in each school subject, how are they of any use in dealing with the problems of everyday life and the political and social issues of contemporary society, most of which do not fit into the framework of a traditional school subject? Proponents of empirical subject-specificity tend to argue that transfer is more likely to occur if there is critical thinking instruction in a variety of domains, with explicit attention to dispositions and abilities that cut across domains. But evidence for this claim is scanty. There is a need for well-designed empirical studies that investigate the conditions that make transfer more likely.
It is common ground in debates about the generality or subject-specificity of critical thinking dispositions and abilities that critical thinking about any topic requires background knowledge about the topic. For example, the most sophisticated understanding of the principles of hypothetico-deductive reasoning is of no help unless accompanied by some knowledge of what might be plausible explanations of some phenomenon under investigation.
Critics have objected to bias in the theory, pedagogy and practice of critical thinking. Commentators (e.g., Alston 1995; Ennis 1998) have noted that anyone who takes a position has a bias in the neutral sense of being inclined in one direction rather than others. The critics, however, are objecting to bias in the pejorative sense of an unjustified favoring of certain ways of knowing over others, frequently alleging that the unjustly favoured ways are those of a dominant sex or culture (Bailin 1995). These ways favour:
- reinforcement of egocentric and sociocentric biases over dialectical engagement with opposing world-views (Paul 1981, 1984; Warren 1998)
- distancing from the object of inquiry over closeness to it (Martin 1992; Thayer-Bacon 1992)
- indifference to the situation of others over care for them (Martin 1992)
- orientation to thought over orientation to action (Martin 1992)
- being reasonable over caring to understand people’s ideas (Thayer-Bacon 1993)
- being neutral and objective over being embodied and situated (Thayer-Bacon 1995a)
- doubting over believing (Thayer-Bacon 1995b)
- reason over emotion, imagination and intuition (Thayer-Bacon 2000)
- solitary thinking over collaborative thinking (Thayer-Bacon 2000)
- written and spoken assignments over other forms of expression (Alston 2001)
- attention to written and spoken communications over attention to human problems (Alston 2001)
- winning debates in the public sphere over making and understanding meaning (Alston 2001)
A common thread in this smorgasbord of accusations is dissatisfaction with focusing on the logical analysis and evaluation of reasoning and arguments. While these authors acknowledge that such analysis and evaluation is part of critical thinking and should be part of its conceptualization and pedagogy, they insist that it is only a part. Paul (1981), for example, bemoans the tendency of atomistic teaching of methods of analyzing and evaluating arguments to turn students into more able sophists, adept at finding fault with positions and arguments with which they disagree but even more entrenched in the egocentric and sociocentric biases with which they began. Martin (1992) and Thayer-Bacon (1992) cite with approval the self-reported intimacy with their subject-matter of leading researchers in biology and medicine, an intimacy that conflicts with the distancing allegedly recommended in standard conceptions and pedagogy of critical thinking. Thayer-Bacon (2000) contrasts the embodied and socially embedded learning of her elementary school students in a Montessori school, who used their imagination, intuition and emotions as well as their reason, with conceptions of critical thinking as
thinking that is used to critique arguments, offer justifications, and make judgments about what are the good reasons, or the right answers. (Thayer-Bacon 2000: 127–128)
Alston (2001) reports that her students in a women’s studies class were able to see the flaws in the Cinderella myth that pervades much romantic fiction but in their own romantic relationships still acted as if all failures were the woman’s fault and still accepted the notions of love at first sight and living happily ever after. Students, she writes, should
be able to connect their intellectual critique to a more affective, somatic, and ethical account of making risky choices that have sexist, racist, classist, familial, sexual, or other consequences for themselves and those both near and far… critical thinking that reads arguments, texts, or practices merely on the surface without connections to feeling/desiring/doing or action lacks an ethical depth that should infuse the difference between mere cognitive activity and something we want to call critical thinking. (Alston 2001: 34)
Some critics portray such biases as unfair to women. Thayer-Bacon (1992), for example, has charged modern critical thinking theory with being sexist, on the ground that it separates the self from the object and causes one to lose touch with one’s inner voice, and thus stigmatizes women, who (she asserts) link self to object and listen to their inner voice. Her charge does not imply that women as a group are on average less able than men to analyze and evaluate arguments. Facione (1990c) found no difference by sex in performance on his California Critical Thinking Skills Test. Kuhn (1991: 280–281) found no difference by sex in either the disposition or the competence to engage in argumentative thinking.
The critics propose a variety of remedies for the biases that they allege. In general, they do not propose to eliminate or downplay critical thinking as an educational goal. Rather, they propose to conceptualize critical thinking differently and to change its pedagogy accordingly. Their pedagogical proposals arise logically from their objections. They can be summarized as follows:
- Focus on argument networks with dialectical exchanges reflecting contesting points of view rather than on atomic arguments, so as to develop “strong sense” critical thinking that transcends egocentric and sociocentric biases (Paul 1981, 1984).
- Foster closeness to the subject-matter and feeling connected to others in order to inform a humane democracy (Martin 1992).
- Develop “constructive thinking” as a social activity in a community of physically embodied and socially embedded inquirers with personal voices who value not only reason but also imagination, intuition and emotion (Thayer-Bacon 2000).
- In developing critical thinking in school subjects, treat as important neither skills nor dispositions but opening worlds of meaning (Alston 2001).
- Attend to the development of critical thinking dispositions as well as skills, and adopt the “critical pedagogy” practised and advocated by Freire (1968 [1970]) and hooks (1994) (Dalgleish, Girard, & Davies 2017).
A common thread in these proposals is treatment of critical thinking as a social, interactive, personally engaged activity like that of a quilting bee or a barn-raising (Thayer-Bacon 2000) rather than as an individual, solitary, distanced activity symbolized by Rodin’s The Thinker . One can get a vivid description of education with the former type of goal from the writings of bell hooks (1994, 2010). Critical thinking for her is open-minded dialectical exchange across opposing standpoints and from multiple perspectives, a conception similar to Paul’s “strong sense” critical thinking (Paul 1981). She abandons the structure of domination in the traditional classroom. In an introductory course on black women writers, for example, she assigns students to write an autobiographical paragraph about an early racial memory, then to read it aloud as the others listen, thus affirming the uniqueness and value of each voice and creating a communal awareness of the diversity of the group’s experiences (hooks 1994: 84). Her “engaged pedagogy” is thus similar to the “freedom under guidance” implemented in John Dewey’s Laboratory School of Chicago in the late 1890s and early 1900s. It incorporates the dialogue, anchored instruction, and mentoring that Abrami (2015) found to be most effective in improving critical thinking skills and dispositions.
What is the relationship of critical thinking to problem solving, decision-making, higher-order thinking, creative thinking, and other recognized types of thinking? One’s answer to this question obviously depends on how one defines the terms used in the question. If critical thinking is conceived broadly to cover any careful thinking about any topic for any purpose, then problem solving and decision making will be kinds of critical thinking, if they are done carefully. Historically, ‘critical thinking’ and ‘problem solving’ were two names for the same thing. If critical thinking is conceived more narrowly as consisting solely of appraisal of intellectual products, then it will be disjoint with problem solving and decision making, which are constructive.
Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives used the phrase “intellectual abilities and skills” for what had been labeled “critical thinking” by some, “reflective thinking” by Dewey and others, and “problem solving” by still others (Bloom et al. 1956: 38). Thus, the so-called “higher-order thinking skills” at the taxonomy’s top levels of analysis, synthesis and evaluation are just critical thinking skills, although they do not come with general criteria for their assessment (Ennis 1981b). The revised version of Bloom’s taxonomy (Anderson et al. 2001) likewise treats critical thinking as cutting across those types of cognitive process that involve more than remembering (Anderson et al. 2001: 269–270). For details, see the Supplement on History .
As to creative thinking, it overlaps with critical thinking (Bailin 1987, 1988). Thinking about the explanation of some phenomenon or event, as in Ferryboat , requires creative imagination in constructing plausible explanatory hypotheses. Likewise, thinking about a policy question, as in Candidate , requires creativity in coming up with options. Conversely, creativity in any field needs to be balanced by critical appraisal of the draft painting or novel or mathematical theory.
- Abrami, Philip C., Robert M. Bernard, Eugene Borokhovski, David I. Waddington, C. Anne Wade, and Tonje Person, 2015, “Strategies for Teaching Students to Think Critically: A Meta-analysis”, Review of Educational Research , 85(2): 275–314. doi:10.3102/0034654314551063
- Aikin, Wilford M., 1942, The Story of the Eight-year Study, with Conclusions and Recommendations , Volume I of Adventure in American Education , New York and London: Harper & Brothers. [ Aikin 1942 available online ]
- Alston, Kal, 1995, “Begging the Question: Is Critical Thinking Biased?”, Educational Theory , 45(2): 225–233. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5446.1995.00225.x
- –––, 2001, “Re/Thinking Critical Thinking: The Seductions of Everyday Life”, Studies in Philosophy and Education , 20(1): 27–40. doi:10.1023/A:1005247128053
- American Educational Research Association, 2014, Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing / American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, National Council on Measurement in Education , Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association.
- Anderson, Lorin W., David R. Krathwohl, Peter W. Airiasian, Kathleen A. Cruikshank, Richard E. Mayer, Paul R. Pintrich, James Raths, and Merlin C. Wittrock, 2001, A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives , New York: Longman, complete edition.
- Bailin, Sharon, 1987, “Critical and Creative Thinking”, Informal Logic , 9(1): 23–30. [ Bailin 1987 available online ]
- –––, 1988, Achieving Extraordinary Ends: An Essay on Creativity , Dordrecht: Kluwer. doi:10.1007/978-94-009-2780-3
- –––, 1995, “Is Critical Thinking Biased? Clarifications and Implications”, Educational Theory , 45(2): 191–197. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5446.1995.00191.x
- Bailin, Sharon and Mark Battersby, 2009, “Inquiry: A Dialectical Approach to Teaching Critical Thinking”, in Juho Ritola (ed.), Argument Cultures: Proceedings of OSSA 09 , CD-ROM (pp. 1–10), Windsor, ON: OSSA. [ Bailin & Battersby 2009 available online ]
- –––, 2016a, “Fostering the Virtues of Inquiry”, Topoi , 35(2): 367–374. doi:10.1007/s11245-015-9307-6
- –––, 2016b, Reason in the Balance: An Inquiry Approach to Critical Thinking , Indianapolis: Hackett, 2nd edition.
- –––, 2021, “Inquiry: Teaching for Reasoned Judgment”, in Daniel Fasko, Jr. and Frank Fair (eds.), Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Theory, Development, Instruction, and Assessment , Leiden: Brill, pp. 31–46. doi: 10.1163/9789004444591_003
- Bailin, Sharon, Roland Case, Jerrold R. Coombs, and Leroi B. Daniels, 1999a, “Common Misconceptions of Critical Thinking”, Journal of Curriculum Studies , 31(3): 269–283. doi:10.1080/002202799183124
- –––, 1999b, “Conceptualizing Critical Thinking”, Journal of Curriculum Studies , 31(3): 285–302. doi:10.1080/002202799183133
- Blair, J. Anthony, 2021, Studies in Critical Thinking , Windsor, ON: Windsor Studies in Argumentation, 2nd edition. [Available online at https://windsor.scholarsportal.info/omp/index.php/wsia/catalog/book/106]
- Berman, Alan M., Seth J. Schwartz, William M. Kurtines, and Steven L. Berman, 2001, “The Process of Exploration in Identity Formation: The Role of Style and Competence”, Journal of Adolescence , 24(4): 513–528. doi:10.1006/jado.2001.0386
- Black, Beth (ed.), 2012, An A to Z of Critical Thinking , London: Continuum International Publishing Group.
- Bloom, Benjamin Samuel, Max D. Engelhart, Edward J. Furst, Walter H. Hill, and David R. Krathwohl, 1956, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. Handbook I: Cognitive Domain , New York: David McKay.
- Boardman, Frank, Nancy M. Cavender, and Howard Kahane, 2018, Logic and Contemporary Rhetoric: The Use of Reason in Everyday Life , Boston: Cengage, 13th edition.
- Browne, M. Neil and Stuart M. Keeley, 2018, Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking , Hoboken, NJ: Pearson, 12th edition.
- Center for Assessment & Improvement of Learning, 2017, Critical Thinking Assessment Test , Cookeville, TN: Tennessee Technological University.
- Cleghorn, Paul. 2021. “Critical Thinking in the Elementary School: Practical Guidance for Building a Culture of Thinking”, in Daniel Fasko, Jr. and Frank Fair (eds.), Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Theory, Development, Instruction, and Assessmen t, Leiden: Brill, pp. 150–167. doi: 10.1163/9789004444591_010
- Cohen, Jacob, 1988, Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences , Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2nd edition.
- College Board, 1983, Academic Preparation for College. What Students Need to Know and Be Able to Do , New York: College Entrance Examination Board, ERIC document ED232517.
- Commission on the Relation of School and College of the Progressive Education Association, 1943, Thirty Schools Tell Their Story , Volume V of Adventure in American Education , New York and London: Harper & Brothers.
- Council for Aid to Education, 2017, CLA+ Student Guide . Available at http://cae.org/images/uploads/pdf/CLA_Student_Guide_Institution.pdf ; last accessed 2022 07 16.
- Dalgleish, Adam, Patrick Girard, and Maree Davies, 2017, “Critical Thinking, Bias and Feminist Philosophy: Building a Better Framework through Collaboration”, Informal Logic , 37(4): 351–369. [ Dalgleish et al. available online ]
- Dewey, John, 1910, How We Think , Boston: D.C. Heath. [ Dewey 1910 available online ]
- –––, 1916, Democracy and Education: An Introduction to the Philosophy of Education , New York: Macmillan.
- –––, 1933, How We Think: A Restatement of the Relation of Reflective Thinking to the Educative Process , Lexington, MA: D.C. Heath.
- –––, 1936, “The Theory of the Chicago Experiment”, Appendix II of Mayhew & Edwards 1936: 463–477.
- –––, 1938, Logic: The Theory of Inquiry , New York: Henry Holt and Company.
- Dominguez, Caroline (coord.), 2018a, A European Collection of the Critical Thinking Skills and Dispositions Needed in Different Professional Fields for the 21st Century , Vila Real, Portugal: UTAD. Available at http://bit.ly/CRITHINKEDUO1 ; last accessed 2022 07 16.
- ––– (coord.), 2018b, A European Review on Critical Thinking Educational Practices in Higher Education Institutions , Vila Real: UTAD. Available at http://bit.ly/CRITHINKEDUO2 ; last accessed 2022 07 16.
- ––– (coord.), 2018c, The CRITHINKEDU European Course on Critical Thinking Education for University Teachers: From Conception to Delivery , Vila Real: UTAD. Available at http:/bit.ly/CRITHINKEDU03; last accessed 2022 07 16.
- Dominguez Caroline and Rita Payan-Carreira (eds.), 2019, Promoting Critical Thinking in European Higher Education Institutions: Towards an Educational Protocol , Vila Real: UTAD. Available at http:/bit.ly/CRITHINKEDU04; last accessed 2022 07 16.
- Ennis, Robert H., 1958, “An Appraisal of the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal”, The Journal of Educational Research , 52(4): 155–158. doi:10.1080/00220671.1958.10882558
- –––, 1962, “A Concept of Critical Thinking: A Proposed Basis for Research on the Teaching and Evaluation of Critical Thinking Ability”, Harvard Educational Review , 32(1): 81–111.
- –––, 1981a, “A Conception of Deductive Logical Competence”, Teaching Philosophy , 4(3/4): 337–385. doi:10.5840/teachphil198143/429
- –––, 1981b, “Eight Fallacies in Bloom’s Taxonomy”, in C. J. B. Macmillan (ed.), Philosophy of Education 1980: Proceedings of the Thirty-seventh Annual Meeting of the Philosophy of Education Society , Bloomington, IL: Philosophy of Education Society, pp. 269–273.
- –––, 1984, “Problems in Testing Informal Logic, Critical Thinking, Reasoning Ability”, Informal Logic , 6(1): 3–9. [ Ennis 1984 available online ]
- –––, 1987, “A Taxonomy of Critical Thinking Dispositions and Abilities”, in Joan Boykoff Baron and Robert J. Sternberg (eds.), Teaching Thinking Skills: Theory and Practice , New York: W. H. Freeman, pp. 9–26.
- –––, 1989, “Critical Thinking and Subject Specificity: Clarification and Needed Research”, Educational Researcher , 18(3): 4–10. doi:10.3102/0013189X018003004
- –––, 1991, “Critical Thinking: A Streamlined Conception”, Teaching Philosophy , 14(1): 5–24. doi:10.5840/teachphil19911412
- –––, 1996, “Critical Thinking Dispositions: Their Nature and Assessability”, Informal Logic , 18(2–3): 165–182. [ Ennis 1996 available online ]
- –––, 1998, “Is Critical Thinking Culturally Biased?”, Teaching Philosophy , 21(1): 15–33. doi:10.5840/teachphil19982113
- –––, 2011, “Critical Thinking: Reflection and Perspective Part I”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking across the Disciplines , 26(1): 4–18. doi:10.5840/inquiryctnews20112613
- –––, 2013, “Critical Thinking across the Curriculum: The Wisdom CTAC Program”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking across the Disciplines , 28(2): 25–45. doi:10.5840/inquiryct20132828
- –––, 2016, “Definition: A Three-Dimensional Analysis with Bearing on Key Concepts”, in Patrick Bondy and Laura Benacquista (eds.), Argumentation, Objectivity, and Bias: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference of the Ontario Society for the Study of Argumentation (OSSA), 18–21 May 2016 , Windsor, ON: OSSA, pp. 1–19. Available at http://scholar.uwindsor.ca/ossaarchive/OSSA11/papersandcommentaries/105 ; last accessed 2022 07 16.
- –––, 2018, “Critical Thinking Across the Curriculum: A Vision”, Topoi , 37(1): 165–184. doi:10.1007/s11245-016-9401-4
- Ennis, Robert H., and Jason Millman, 1971, Manual for Cornell Critical Thinking Test, Level X, and Cornell Critical Thinking Test, Level Z , Urbana, IL: Critical Thinking Project, University of Illinois.
- Ennis, Robert H., Jason Millman, and Thomas Norbert Tomko, 1985, Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Level X & Level Z: Manual , Pacific Grove, CA: Midwest Publication, 3rd edition.
- –––, 2005, Cornell Critical Thinking Tests Level X & Level Z: Manual , Seaside, CA: Critical Thinking Company, 5th edition.
- Ennis, Robert H. and Eric Weir, 1985, The Ennis-Weir Critical Thinking Essay Test: Test, Manual, Criteria, Scoring Sheet: An Instrument for Teaching and Testing , Pacific Grove, CA: Midwest Publications.
- Facione, Peter A., 1990a, Critical Thinking: A Statement of Expert Consensus for Purposes of Educational Assessment and Instruction , Research Findings and Recommendations Prepared for the Committee on Pre-College Philosophy of the American Philosophical Association, ERIC Document ED315423.
- –––, 1990b, California Critical Thinking Skills Test, CCTST – Form A , Millbrae, CA: The California Academic Press.
- –––, 1990c, The California Critical Thinking Skills Test--College Level. Technical Report #3. Gender, Ethnicity, Major, CT Self-Esteem, and the CCTST , ERIC Document ED326584.
- –––, 1992, California Critical Thinking Skills Test: CCTST – Form B, Millbrae, CA: The California Academic Press.
- –––, 2000, “The Disposition Toward Critical Thinking: Its Character, Measurement, and Relationship to Critical Thinking Skill”, Informal Logic , 20(1): 61–84. [ Facione 2000 available online ]
- Facione, Peter A. and Noreen C. Facione, 1992, CCTDI: A Disposition Inventory , Millbrae, CA: The California Academic Press.
- Facione, Peter A., Noreen C. Facione, and Carol Ann F. Giancarlo, 2001, California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory: CCTDI: Inventory Manual , Millbrae, CA: The California Academic Press.
- Facione, Peter A., Carol A. Sánchez, and Noreen C. Facione, 1994, Are College Students Disposed to Think? , Millbrae, CA: The California Academic Press. ERIC Document ED368311.
- Fisher, Alec, and Michael Scriven, 1997, Critical Thinking: Its Definition and Assessment , Norwich: Centre for Research in Critical Thinking, University of East Anglia.
- Freire, Paulo, 1968 [1970], Pedagogia do Oprimido . Translated as Pedagogy of the Oppressed , Myra Bergman Ramos (trans.), New York: Continuum, 1970.
- Gigerenzer, Gerd, 2001, “The Adaptive Toolbox”, in Gerd Gigerenzer and Reinhard Selten (eds.), Bounded Rationality: The Adaptive Toolbox , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, pp. 37–50.
- Glaser, Edward Maynard, 1941, An Experiment in the Development of Critical Thinking , New York: Bureau of Publications, Teachers College, Columbia University.
- Groarke, Leo A. and Christopher W. Tindale, 2012, Good Reasoning Matters! A Constructive Approach to Critical Thinking , Don Mills, ON: Oxford University Press, 5th edition.
- Halpern, Diane F., 1998, “Teaching Critical Thinking for Transfer Across Domains: Disposition, Skills, Structure Training, and Metacognitive Monitoring”, American Psychologist , 53(4): 449–455. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.53.4.449
- –––, 2016, Manual: Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment , Mödling, Austria: Schuhfried. Available at https://pdfcoffee.com/hcta-test-manual-pdf-free.html; last accessed 2022 07 16.
- Hamby, Benjamin, 2014, The Virtues of Critical Thinkers , Doctoral dissertation, Philosophy, McMaster University. [ Hamby 2014 available online ]
- –––, 2015, “Willingness to Inquire: The Cardinal Critical Thinking Virtue”, in Martin Davies and Ronald Barnett (eds.), The Palgrave Handbook of Critical Thinking in Higher Education , New York: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 77–87.
- Haran, Uriel, Ilana Ritov, and Barbara A. Mellers, 2013, “The Role of Actively Open-minded Thinking in Information Acquisition, Accuracy, and Calibration”, Judgment and Decision Making , 8(3): 188–201.
- Hatcher, Donald and Kevin Possin, 2021, “Commentary: Thinking Critically about Critical Thinking Assessment”, in Daniel Fasko, Jr. and Frank Fair (eds.), Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Theory, Development, Instruction, and Assessment , Leiden: Brill, pp. 298–322. doi: 10.1163/9789004444591_017
- Haynes, Ada, Elizabeth Lisic, Kevin Harris, Katie Leming, Kyle Shanks, and Barry Stein, 2015, “Using the Critical Thinking Assessment Test (CAT) as a Model for Designing Within-Course Assessments: Changing How Faculty Assess Student Learning”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking Across the Disciplines , 30(3): 38–48. doi:10.5840/inquiryct201530316
- Haynes, Ada and Barry Stein, 2021, “Observations from a Long-Term Effort to Assess and Improve Critical Thinking”, in Daniel Fasko, Jr. and Frank Fair (eds.), Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Theory, Development, Instruction, and Assessment , Leiden: Brill, pp. 231–254. doi: 10.1163/9789004444591_014
- Hiner, Amanda L. 2021. “Equipping Students for Success in College and Beyond: Placing Critical Thinking Instruction at the Heart of a General Education Program”, in Daniel Fasko, Jr. and Frank Fair (eds.), Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Theory, Development, Instruction, and Assessment , Leiden: Brill, pp. 188–208. doi: 10.1163/9789004444591_012
- Hitchcock, David, 2017, “Critical Thinking as an Educational Ideal”, in his On Reasoning and Argument: Essays in Informal Logic and on Critical Thinking , Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 477–497. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-53562-3_30
- –––, 2021, “Seven Philosophical Implications of Critical Thinking: Themes, Variations, Implications”, in Daniel Fasko, Jr. and Frank Fair (eds.), Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Theory, Development, Instruction, and Assessment , Leiden: Brill, pp. 9–30. doi: 10.1163/9789004444591_002
- hooks, bell, 1994, Teaching to Transgress: Education as the Practice of Freedom , New York and London: Routledge.
- –––, 2010, Teaching Critical Thinking: Practical Wisdom , New York and London: Routledge.
- Johnson, Ralph H., 1992, “The Problem of Defining Critical Thinking”, in Stephen P, Norris (ed.), The Generalizability of Critical Thinking , New York: Teachers College Press, pp. 38–53.
- Kahane, Howard, 1971, Logic and Contemporary Rhetoric: The Use of Reason in Everyday Life , Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
- Kahneman, Daniel, 2011, Thinking, Fast and Slow , New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
- Kahneman, Daniel, Olivier Sibony, & Cass R. Sunstein, 2021, Noise: A Flaw in Human Judgment , New York: Little, Brown Spark.
- Kenyon, Tim, and Guillaume Beaulac, 2014, “Critical Thinking Education and Debasing”, Informal Logic , 34(4): 341–363. [ Kenyon & Beaulac 2014 available online ]
- Krathwohl, David R., Benjamin S. Bloom, and Bertram B. Masia, 1964, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, Handbook II: Affective Domain , New York: David McKay.
- Kuhn, Deanna, 1991, The Skills of Argument , New York: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511571350
- –––, 2019, “Critical Thinking as Discourse”, Human Development, 62 (3): 146–164. doi:10.1159/000500171
- Lipman, Matthew, 1987, “Critical Thinking–What Can It Be?”, Analytic Teaching , 8(1): 5–12. [ Lipman 1987 available online ]
- –––, 2003, Thinking in Education , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2nd edition.
- Loftus, Elizabeth F., 2017, “Eavesdropping on Memory”, Annual Review of Psychology , 68: 1–18. doi:10.1146/annurev-psych-010416-044138
- Makaiau, Amber Strong, 2021, “The Good Thinker’s Tool Kit: How to Engage Critical Thinking and Reasoning in Secondary Education”, in Daniel Fasko, Jr. and Frank Fair (eds.), Critical Thinking and Reasoning: Theory, Development, Instruction, and Assessment , Leiden: Brill, pp. 168–187. doi: 10.1163/9789004444591_011
- Martin, Jane Roland, 1992, “Critical Thinking for a Humane World”, in Stephen P. Norris (ed.), The Generalizability of Critical Thinking , New York: Teachers College Press, pp. 163–180.
- Mayhew, Katherine Camp, and Anna Camp Edwards, 1936, The Dewey School: The Laboratory School of the University of Chicago, 1896–1903 , New York: Appleton-Century. [ Mayhew & Edwards 1936 available online ]
- McPeck, John E., 1981, Critical Thinking and Education , New York: St. Martin’s Press.
- Moore, Brooke Noel and Richard Parker, 2020, Critical Thinking , New York: McGraw-Hill, 13th edition.
- Nickerson, Raymond S., 1998, “Confirmation Bias: A Ubiquitous Phenomenon in Many Guises”, Review of General Psychology , 2(2): 175–220. doi:10.1037/1089-2680.2.2.175
- Nieto, Ana Maria, and Jorge Valenzuela, 2012, “A Study of the Internal Structure of Critical Thinking Dispositions”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking across the Disciplines , 27(1): 31–38. doi:10.5840/inquiryct20122713
- Norris, Stephen P., 1985, “Controlling for Background Beliefs When Developing Multiple-choice Critical Thinking Tests”, Educational Measurement: Issues and Practice , 7(3): 5–11. doi:10.1111/j.1745-3992.1988.tb00437.x
- Norris, Stephen P. and Robert H. Ennis, 1989, Evaluating Critical Thinking (The Practitioners’ Guide to Teaching Thinking Series), Pacific Grove, CA: Midwest Publications.
- Norris, Stephen P. and Ruth Elizabeth King, 1983, Test on Appraising Observations , St. John’s, NL: Institute for Educational Research and Development, Memorial University of Newfoundland.
- –––, 1984, The Design of a Critical Thinking Test on Appraising Observations , St. John’s, NL: Institute for Educational Research and Development, Memorial University of Newfoundland. ERIC Document ED260083.
- –––, 1985, Test on Appraising Observations: Manual , St. John’s, NL: Institute for Educational Research and Development, Memorial University of Newfoundland.
- –––, 1990a, Test on Appraising Observations , St. John’s, NL: Institute for Educational Research and Development, Memorial University of Newfoundland, 2nd edition.
- –––, 1990b, Test on Appraising Observations: Manual , St. John’s, NL: Institute for Educational Research and Development, Memorial University of Newfoundland, 2nd edition.
- OCR [Oxford, Cambridge and RSA Examinations], 2011, AS/A Level GCE: Critical Thinking – H052, H452 , Cambridge: OCR. Past papers available at https://pastpapers.co/ocr/?dir=A-Level/Critical-Thinking-H052-H452; last accessed 2022 07 16.
- Ontario Ministry of Education, 2013, The Ontario Curriculum Grades 9 to 12: Social Sciences and Humanities . Available at http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/curriculum/secondary/ssciences9to122013.pdf ; last accessed 2022 07 16.
- Passmore, John Arthur, 1980, The Philosophy of Teaching , London: Duckworth.
- Paul, Richard W., 1981, “Teaching Critical Thinking in the ‘Strong’ Sense: A Focus on Self-Deception, World Views, and a Dialectical Mode of Analysis”, Informal Logic , 4(2): 2–7. [ Paul 1981 available online ]
- –––, 1984, “Critical Thinking: Fundamental to Education for a Free Society”, Educational Leadership , 42(1): 4–14.
- –––, 1985, “McPeck’s Mistakes”, Informal Logic , 7(1): 35–43. [ Paul 1985 available online ]
- Paul, Richard W. and Linda Elder, 2006, The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking: Concepts and Tools , Dillon Beach, CA: Foundation for Critical Thinking, 4th edition.
- Payette, Patricia, and Edna Ross, 2016, “Making a Campus-Wide Commitment to Critical Thinking: Insights and Promising Practices Utilizing the Paul-Elder Approach at the University of Louisville”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking Across the Disciplines , 31(1): 98–110. doi:10.5840/inquiryct20163118
- Possin, Kevin, 2008, “A Field Guide to Critical-Thinking Assessment”, Teaching Philosophy , 31(3): 201–228. doi:10.5840/teachphil200831324
- –––, 2013a, “Some Problems with the Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment (HCTA) Test”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking across the Disciplines , 28(3): 4–12. doi:10.5840/inquiryct201328313
- –––, 2013b, “A Serious Flaw in the Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA) Test”, Informal Logic , 33(3): 390–405. [ Possin 2013b available online ]
- –––, 2013c, “A Fatal Flaw in the Collegiate Learning Assessment Test”, Assessment Update , 25 (1): 8–12.
- –––, 2014, “Critique of the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal Test: The More You Know, the Lower Your Score”, Informal Logic , 34(4): 393–416. [ Possin 2014 available online ]
- –––, 2020, “CAT Scan: A Critical Review of the Critical-Thinking Assessment Test”, Informal Logic , 40 (3): 489–508. [Available online at https://informallogic.ca/index.php/informal_logic/article/view/6243]
- Rawls, John, 1971, A Theory of Justice , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Rear, David, 2019, “One Size Fits All? The Limitations of Standardised Assessment in Critical Thinking”, Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 44(5): 664–675. doi: 10.1080/02602938.2018.1526255
- Rousseau, Jean-Jacques, 1762, Émile , Amsterdam: Jean Néaulme.
- Scheffler, Israel, 1960, The Language of Education , Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas.
- Scriven, Michael, and Richard W. Paul, 1987, Defining Critical Thinking , Draft statement written for the National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking Instruction. Available at http://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/defining-critical-thinking/766 ; last accessed 2022 07 16.
- Sheffield, Clarence Burton Jr., 2018, “Promoting Critical Thinking in Higher Education: My Experiences as the Inaugural Eugene H. Fram Chair in Applied Critical Thinking at Rochester Institute of Technology”, Topoi , 37(1): 155–163. doi:10.1007/s11245-016-9392-1
- Siegel, Harvey, 1985, “McPeck, Informal Logic and the Nature of Critical Thinking”, in David Nyberg (ed.), Philosophy of Education 1985: Proceedings of the Forty-First Annual Meeting of the Philosophy of Education Society , Normal, IL: Philosophy of Education Society, pp. 61–72.
- –––, 1988, Educating Reason: Rationality, Critical Thinking, and Education , New York: Routledge.
- –––, 1999, “What (Good) Are Thinking Dispositions?”, Educational Theory , 49(2): 207–221. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5446.1999.00207.x
- Simon, Herbert A., 1956, “Rational Choice and the Structure of the Environment”, Psychological Review , 63(2): 129–138. doi: 10.1037/h0042769
- Simpson, Elizabeth, 1966–67, “The Classification of Educational Objectives: Psychomotor Domain”, Illinois Teacher of Home Economics , 10(4): 110–144, ERIC document ED0103613. [ Simpson 1966–67 available online ]
- Skolverket, 2018, Curriculum for the Compulsory School, Preschool Class and School-age Educare , Stockholm: Skolverket, revised 2018. Available at https://www.skolverket.se/download/18.31c292d516e7445866a218f/1576654682907/pdf3984.pdf; last accessed 2022 07 15.
- Smith, B. Othanel, 1953, “The Improvement of Critical Thinking”, Progressive Education , 30(5): 129–134.
- Smith, Eugene Randolph, Ralph Winfred Tyler, and the Evaluation Staff, 1942, Appraising and Recording Student Progress , Volume III of Adventure in American Education , New York and London: Harper & Brothers.
- Splitter, Laurance J., 1987, “Educational Reform through Philosophy for Children”, Thinking: The Journal of Philosophy for Children , 7(2): 32–39. doi:10.5840/thinking1987729
- Stanovich Keith E., and Paula J. Stanovich, 2010, “A Framework for Critical Thinking, Rational Thinking, and Intelligence”, in David D. Preiss and Robert J. Sternberg (eds), Innovations in Educational Psychology: Perspectives on Learning, Teaching and Human Development , New York: Springer Publishing, pp 195–237.
- Stanovich Keith E., Richard F. West, and Maggie E. Toplak, 2011, “Intelligence and Rationality”, in Robert J. Sternberg and Scott Barry Kaufman (eds.), Cambridge Handbook of Intelligence , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 3rd edition, pp. 784–826. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511977244.040
- Tankersley, Karen, 2005, Literacy Strategies for Grades 4–12: Reinforcing the Threads of Reading , Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.
- Thayer-Bacon, Barbara J., 1992, “Is Modern Critical Thinking Theory Sexist?”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking Across the Disciplines , 10(1): 3–7. doi:10.5840/inquiryctnews199210123
- –––, 1993, “Caring and Its Relationship to Critical Thinking”, Educational Theory , 43(3): 323–340. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5446.1993.00323.x
- –––, 1995a, “Constructive Thinking: Personal Voice”, Journal of Thought , 30(1): 55–70.
- –––, 1995b, “Doubting and Believing: Both are Important for Critical Thinking”, Inquiry: Critical Thinking across the Disciplines , 15(2): 59–66. doi:10.5840/inquiryctnews199515226
- –––, 2000, Transforming Critical Thinking: Thinking Constructively , New York: Teachers College Press.
- Toulmin, Stephen Edelston, 1958, The Uses of Argument , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Turri, John, Mark Alfano, and John Greco, 2017, “Virtue Epistemology”, in Edward N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2017 Edition). URL = < https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2017/entries/epistemology-virtue/ >
- Vincent-Lancrin, Stéphan, Carlos González-Sancho, Mathias Bouckaert, Federico de Luca, Meritxell Fernández-Barrerra, Gwénaël Jacotin, Joaquin Urgel, and Quentin Vidal, 2019, Fostering Students’ Creativity and Critical Thinking: What It Means in School. Educational Research and Innovation , Paris: OECD Publishing.
- Warren, Karen J. 1988. “Critical Thinking and Feminism”, Informal Logic , 10(1): 31–44. [ Warren 1988 available online ]
- Watson, Goodwin, and Edward M. Glaser, 1980a, Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal, Form A , San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
- –––, 1980b, Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal: Forms A and B; Manual , San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation,
- –––, 1994, Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal, Form B , San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
- Weinstein, Mark, 1990, “Towards a Research Agenda for Informal Logic and Critical Thinking”, Informal Logic , 12(3): 121–143. [ Weinstein 1990 available online ]
- –––, 2013, Logic, Truth and Inquiry , London: College Publications.
- Willingham, Daniel T., 2019, “How to Teach Critical Thinking”, Education: Future Frontiers , 1: 1–17. [Available online at https://prod65.education.nsw.gov.au/content/dam/main-education/teaching-and-learning/education-for-a-changing-world/media/documents/How-to-teach-critical-thinking-Willingham.pdf.]
- Zagzebski, Linda Trinkaus, 1996, Virtues of the Mind: An Inquiry into the Nature of Virtue and the Ethical Foundations of Knowledge , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139174763
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Association for Informal Logic and Critical Thinking (AILACT)
- Critical Thinking Across the European Higher Education Curricula (CRITHINKEDU)
- Critical Thinking Definition, Instruction, and Assessment: A Rigorous Approach
- Critical Thinking Research (RAIL)
- Foundation for Critical Thinking
- Insight Assessment
- Partnership for 21st Century Learning (P21)
- The Critical Thinking Consortium
- The Nature of Critical Thinking: An Outline of Critical Thinking Dispositions and Abilities , by Robert H. Ennis
abilities | bias, implicit | children, philosophy for | civic education | decision-making capacity | Dewey, John | dispositions | education, philosophy of | epistemology: virtue | logic: informal
Copyright © 2022 by David Hitchcock < hitchckd @ mcmaster . ca >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2024 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
Design Thinking and Innovation
Design Thinking and Innovation from Harvard Business School (HBS) Online will teach you how to leverage fundamental design thinking principles and innovative problem-solving tools to address business challenges.

Associated Schools

Harvard Business School
What you'll learn.
Break cognitive fixedness and approach problems with a new mindset that integrates creative problem-solving and management
Develop an innovation toolkit, and determine when to apply design thinking frameworks, tools, and exercises to your own strategic initiatives
Practice empathy and apply human-centered design through techniques such as ideation, prototyping, user journey mapping, and analyzing mental models
Assess group dynamics and maximize your team’s potential for developing and iterating prototypes and managing the implementation of new designs
Understand how leaders can create the optimal environment and team dynamics to guide innovation and collaboration
Put design thinking into action by collaborating with peers from a wide range of professional experiences and backgrounds
Course description
Design Thinking and Innovation, through Harvard Business School (HBS) Online, equips current and aspiring innovation managers with the design thinking principles and innovative problem-solving tools to solve business challenges and guide their organization’s strategy. The course features five weeks of course content and two weeks of cohort project work, enabling the opportunity to put learning into practice. Leaders interviewed include Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel, Royal Philips CEO Frans van Houten, and T-Mobile CEO Mike Sievert, among others. Participants will walk away with an innovation toolkit of frameworks and exercises for identifying business opportunities and generating possible solutions for their organization’s initiatives.
Instructors

Srikant Datar
You may also like.

Negotiating Salary
Learn salary negotiation techniques with this free, 15-minute Harvard Business School (HBS) Online lesson taught by Mike Wheeler of Negotiation Mastery.

Presenting With Confidence (In-Person Course)
Learn the unbreakable laws of communication that will make your next presentation engaging, attractive, and actionable.

Resilient Leadership
Develop the skills to lead with courage and conviction through challenging times with this free, 35-minute Harvard Business School (HBS) Online lesson.
- Accounting & Finance
- Communication
- Critical Thinking
- Marketing & Strategy
- Starting a Business
- Team Management
- Corporate Philosophy
- Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion
- Kokorozashi
- Sustainable Business
- AI Ventures
- Machine Learning
- Alumni Voices
- Yoshito Hori Blog
- Unlimited Insights
- Career Skills
Design Thinking Critique: Perils and Pitfalls of “The Crit”

Influencer Marketing
Expand your reach and engage with your target audience using this trending technique that blends celebrity endorsements with social media marketing .
Leading High Performing Remote Teams
How can leaders ensure that performance remains high in remote or hybrid-work environments?
Design Thinking
Learn the 5 phases of this problem-solving methodology and switch from technology-centered to user-centered thinking.
Reciprocity
Learn what reciprocity is and how it can motivate people and boost sales.
Gantt Chart
Invented in the early 20th century, the Gantt Chart is one of the building blocks of modern project management. In this online course, you'll learn how this tool can be used effectively to monitor progress and achieve your team's goals.
Navigating Change Successfully
The working landscape is continually shifting and being disrupted, so how to employees maintain a sense of stability? Listen to CEO and president of Carl ZEISS Japan Stefan Sacre share his expertise on dealing with change in organizations and entire industries.
Halo Effect
The halo effect is often leveraged for marketing and promotion. But as a type of cognitive bias, it can also have a subconscious impact on decision-making in the workplace. Learn why and (how to overcome it) in this online course.
Anchoring and Framing
Want to increase your confidence during negotiations? Master the principles of anchoring and framing to take your negotiation skills to the next level.
ZOPA and BATNA
Understanding ZOPA and BATNA will help you become a better negotiator, create more value, and feel more confident at the table.
Content Marketing
In this course, you’ll learn how compelling blogs, videos, podcasts, and other media can reach customers and drive sales. You’ll also learn steps for creating an effective content marketing plan, and some important ways to measure its impact and success.
Content marketing is a essential digital marketing strategy for companies looking to provide relevant and useful information to support your community and attract new customers.
Get started on your content marketing journey today.
Sustainable Innovation in Times of Disruption: Choices for a Better Society
There are opportunities for progress all around us. The key is to innovate on these opportunities sustainably.
To help identify most effective path forward, you'll need to gain a global perspective to these challenges in an open discussion. How can Japan and the world take action to create a more sustainable, innovative world? Where do you fit in?
It's time to find out.
Social Media & Digital Communications: Impact on Global Public Opinion
Social and digital media have dominated the communications industry for decades. But it's no secret that social media has the power to sway public opinion, and the way in which many companies use these platforms could be seen as manipulative.
What do companies need to be aware of when utilizing social and digital media? How can these mediums be used to better communicate strategically with the world? Discover what top media and communications experts have to say.
Blockchain is one of the most captivating technologies out there. Learn what it is and how to make use of its opportunities in this short online course.
Mehrabian’s Rule
The 7-38-55 Rule, developed by Albert Mehrabian, suggests that effective communication relies less on the words we choose than on our tone of our voice, appearance, and body language. Learn how to put this theory to use for better communication in business.
Pareto Principle
Your time and resources are limited. Efficiency means learning to prioritize. The Pareto principle (also called the 80-20 rule) can help you identify the best way to use your time for maximum results.
Country Analysis Framework
Overseas expansion requires careful planning. The Country Analysis Framework can help you look beyond an industry-level analysis and reframe your view based on performance, strategy, and context. Try this short course to learn how it works.
The SECI model illustrates how knowledge is created and shared. Learn how to put it to use for best practices, and how the Japanese concept of “ba” fits in to broaden your perspective.
Johari Window Model
The Johari Window Model is a self-awareness framework that helps you better understand . . . you. Learn how its four quadrants can help you identify gaps between how you see yourself, and how others see you.
Wondering if you should continue an investment or look for something new? Sunk costs can have a powerful psychological impact on decision-making. Learn how to recognize them to ensure rational decisions.
CAGE Distance Framework
Want to expand overseas? The CAGE distance framework can help ensure you're constructing a solid global strategy in four areas: cultural, administrative, economic, and geographic. Learn how to leverage useful differences between countries, identify potential obstacles, and achieve global business success.
Groupthink refers to group pressure and the perception of consensus which together lead to ill-formed decisions—or even unnecessary risks. Learn to identify the warning signs of groupthink and apply countermeasures in this online course.
Deductive and Inductive Reasoning
Solving problems with the best results means using two types of thinking: deductive and inductive reasoning. In this online course, learn to form a broad premise, make observations, and form conclusions from different perspectives.
Critical Thinking: Hypothesis-Driven Thinking
Anyone can come up with a good idea. The real challenge is putting that idea into action. In this online course, explore how to form compelling, testable hypotheses and bring ideas to life in your own organization.
Critical Thinking: Structured Reasoning
Even a few simple techniques for logical decision making and persuasion can vastly improve your skills as a leader. Explore how critical thinking can help you evaluate complex business problems, reduce bias, and devise effective solutions.
Critical Thinking: Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is a central business skill, and yet it's the one many people struggle with most. This course will show you how to apply critical thinking techniques to common business examples, avoid misunderstandings, and get at the root of any problem.
How to Dream
Join globally renowned author and Columbia Business School professor Dr. Sheena Iyengar as she explains how to approach your dreams with a new perspective. Learn to reflect on what you long to accomplish and what stands in your way.
Logical Thinking
Logical thinking is at the heart of confident, persuasive decisions. This course will equip you with a five-point approach to more becoming a more logical thinker. Learn to classify ideas and distinguish fact from opinion.
Investing & Diversity: The Changing Faces of Venture Capitalists
Is the venture capital industry embracing diversity in investors? Watch global venture capitalists from around the world discuss the state of things and what needs to be done for a more inclusive future.
Servant Leadership
There's more to leadership than driving a team to profit. In fact, there's a word for looking beyond self-interest to prioritize individual growth: servant leadership. Try this course for a quick breakdown of what that is, how it works, and how it can lead to organizational success.
Organizational Behavior and Leadership
Ever wonder what makes a great leader? Whether your role requires leadership or not, understanding organizational behavior is useful for your career. This course from GLOBIS Unlimited can set you on your way.
Leadership vs. Management
Leadership and management are different skills, but today’s leaders must have both. Try out this course from GLOBIS Unlimited to understand the difference, as well as when and why each skill is necessary for motivation, communication, and value.
Strategy: Creating Value Inside Your Company
Have you ever wondered why certain companies are more successful than others? The answer is strategy: internal processes that control costs, allocate resources, and create value. This course from GLOBIS Unlimited can give you the tools you need for that strategic edge.
Strategy: Understanding the External Environment
To plan strategy on any level, you need to understand your company's external environment. In fact, your level of understanding can impact hiring, budgeting, marketing, or nearly any other part of the business world. Want to learn how to do all that? This course from GLOBIS Unlimited is the perfect first step!
Using Japanese Values to Thrive in Global Business
Japanese companies have unique cultural, communication, and operational challenges. But they also have values that have led to remarkable longevity. Check out this seminar to hear how these values help earn trust from overseas head offices and develop employees.
Turnaround Leadership: The Differences Between Japan and the West
What's the best way for leaders to communicate a shift in corporate strategy? How do you even know when it's time for such a change? This course explains how Japan might have one answer, Western companies another.
Conflict Management
Conflicts in the workplace are inevitable. But they can lead to positive outcomes if they’re managed well. Check out this online course for a two-step process that can help you manage conflict successfully.
Evernote Founder: How Tech Startups Can Break through in Japan
Can startup models from Hollywood and Silicon Valley succeed anywhere? Phil Libin, cofounder and CEO of startup incubator All Turtles, explains how AI can solve everyday problems to bring products to market.
Women Empowerment: Lessons from Cartier
How can women overcome gender inequality and reach their leadership goals? Cartier Japan CEO June Miyachi shares her secret in this special course from GLOBIS Unlimited.
Marketing: Reaching Your Target
Every company works hard to get its products into the hands of customers. Are you doing everything you can to compete? In this course, you’ll find a winning formula to turn a product idea into real sales. Follow along through the fundamentals of the marketing mix and see how companies successfully bring products to market.
Marketing Mix
Seeing good products into the hands of customers is no easy task. The marketing mix can help. It's a collection of strategies and tactics companies utilize to get customers to purchase their products or services, and is an essential part of the overall marketing process.
The Principles of Negotiation
With the proper skills and attitude, anyone can become a successful negotiator. But first, you'll need to learn the basics to prepare for, assess, and respond to offers for the best results. GLOBIS Unlimited can help.
Negotiation: Creating Value
Want to create more shared value between yourself and your negotiation opponent? Discover how cognitive bias affects the judgment of others. Try this course from GLOBIS Unlimited to master the value of negotiation.
Finding Your Life Purpose with Ikigai
Ikigai can guide you in your quest for self-discovery. Listen to Japanese brain scientist Ken Mogi explain why and how.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Want to leverage Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs as a leader? Try this short course to see how the theory can be applied in practical work scenarios.
Confirmation Bias
We all subconsciously collect information that reinforces our preconceptions. It's natural . . . but it does lead to a kind of flawed decision-making called confirmation bias. To become more objective and impartial, check out this course from GLOBIS Unlimited!
An Investor's Lesson to Entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs have the power to transform societies for the better. But how do you attract investors to start or grow a business? Or to sell one? Check out this seminar for the answers to these and more, straight from a master venture capitalist!
Managerial Accounting
Managerial accounting is a powerful way to measure progress, identify problems, and meet your goals. Check out this course to learn how data-backed decisions can help you run your business.
Finance Basics: 1
For a healthy mix of quantitative planning, evaluation, and management, you need solid decision-making. And finance is the secret sauce! Get the essentials of finance in this two-part course from GLOBIS Unlimited.
Basic Accounting: Financial Analysis
Want to compare your performance vs. a competitor? Or evaluate a potential vendor? Then you'll need to conduct a financial analysis. This course will teach you how to use three financial statements and evaluate financial performance in terms of profitability, efficiency, soundness, growth, and overall strength.
Career Anchors
What drives you to be good at your job?
Career anchors are based on your values, desires, motivations, and abilities. They are the immovable parts of your professional self-image that guide you throughout your career journey.
Try this short GLOBIS Unlimited course to identify which of the eight career anchors is yours!
Digital Marketing Psychology to Transform Your Business
How does digital marketing really differ from traditional marketing? How is social media changing things really ? And what's going on in Asia?
Pyramid Structure
Having the pyramid structure in your communication toolkit can not only help you approach a problem, but convince others that your solution is valid. Break away from linear thinking and test your logical thinking with this course from GLOBIS Unlimited!
Leadership with Passion through Kokorozashi
The key ingredient to success? Passion.
Finding your kokorozashi will unify your passions and skills to create positive change in society. This GLOBIS Unlimited course will help you develop the values and lifelong goals you need to become a strong, passion-driven leader.
AI First Companies – Implementation and Impact
AI is changing the way companies operate. How do you structure teams to increase efficiency?
Technovate in the Era of Industry 4.0
Is Industry 4.0 is the next step of human evolution human civilization? Dr. Jorge Calvo seems to think so. Join him to learn how the past can help you set goals for an exciting future of digital innovation.
Technovate Thinking
Business leaders of tomorrow need to harness the power of technology and innovation. That means understanding algorithms and how they drive business results. Discover opportunities to make technology work for your competitive edge.
Product Life Cycle
Every product takes a natural course through the market—there's a how, when, and why customers adopt products at different stages. Check out this course from GLOBIS Unlimited to find out how a product you use every day is part of this cycle.
Logical thinking is the most valuable asset any business professional can have. That's why logic trees are such a valuable tool—they can help you identify a problem, break it down, and build it back up to a solution.
MECE Principle
Using the MECE principle can help ensure you categorize without gaps or overlaps. Check out this course from GLOBIS Unlimited for a practical demonstration of how it works!
You’ve no doubt heard about design thinking—a practical, step-by-step, user-centric method of solving problems. Though its roots reach back to the 1950s, design thinking was popularized by IDEO in the 1990s, and has since been adopted by leading global companies such as GE, Apple, IBM, and SAP.
Clearly the concept has been around for years, which begs the question: Why haven’t we moved on to the next fad? Is design thinking just that effective, or are we simply yet to master it?
My job as a creative consultant in international business development has given me opportunities to cross borders and deal with clients from various industries—automobile, food and beverage, IT, and so on. While working with these companies, I often hear about the importance of “the crit.” This, of course, refers to critique—an essential part of the design thinking process, and one of the main areas people falter in realizing design thinking’s potential.
Playing Fair
We all know getting critiques can be rough, but it’s surprisingly easy to forget that when giving a critique. Like brainstorming or discussion, feedback is important to help us gauge where we stand in order to improve ourselves. For the sake of effective communication, here are some key points to keep in mind when giving a crit:
1. Describe your thoughts and emotions.
How does the subject of your critique make you feel and why? Be thorough. Work to make your point clear in any way you can. Share your thought process. Invite back-and-forth discussion if something is unclear. As Dale Carnegie famously said, “When dealing with people, remember you are not dealing with creatures of logic, but creatures of emotion.”
2. Be constructive, not destructive.
Never critique just for the sake of saying something. If the project or proposal works as is, say so. If you do have something to critique, however, give suggestions for improvement and listen to the response . Your ears and heart should be open.
3. Avoid pointing fingers.
Fear of making mistakes… Everyone can empathize with that. During the crit, be careful not to blame others. Avoid stalling discussion by triggering emotions. Remember, design thinking calls for empathy. The ultimate purpose of the crit is to help , not call people out.
While the above may seem easy or obvious in theory, you may find some of these points to be more difficult than expected in practice.

Case in Point
When it comes to critiquing, there are 2 common pitfalls: giving overly harsh critique and holding back when we should speak up. For effective design thinking, striking a balance between these two extremes is crucial. Let’s explore this further with the example below:
Matthew is a manager who noticed cost leakage in his IT project. He called a meeting with his team to discuss why this was happening.
Anna, the delivery manager, immediately blamed Matthew for failing to meet deadlines. When Matthew tried to defend his team, he found himself facing harsh critique on his fundamental ability to manage. Angered by this attack, he walked out of the meeting.
Cody, a junior accountant in the team, has noticed that Marketing and Sales are focused on chasing revenue, leaving the IT staff to work doubly hard to meet high customer expectations. Cody wanted to share his thoughts, but struggled to think of how to phrase them. After witnessing the heated exchange between Anna and Matthew, Cody decided to keep quiet.
So…what went wrong at this meeting?
It’s easy for harsh critique to scale into a major problem. Bruised ego and discord among team members are just a few of the detriments to pointing fingers. Matthew and Anna will have a harder time moving forward now that their critique has gotten personal.
Looking at Cody, we find an entirely different problem. A common misconception is that we shouldn’t point something out if we can’t communicate the idea perfectly. Remember that your opinion is significant and always worth sharing. Reflect on how you usually communicate with people. If you’re not good at speaking, draw. If you’re bad at drawing, circle the problem and try to explain why you’re stuck. Use any means you can to articulate your point and get your message across. And remember what you did when you succeeded—you may be able to use that same method again in the future.
Better Communication = Better Crit
If you’re still wondering whether the crit is really that crucial to the design thinking process, imagine this scenario: An aircraft maintenance officer has noticed something off about an airplane’s engine for a few weeks, but he could not explain what it was. Since nothing has gone wrong, he’s decided it isn’t worth mentioning. Would you really want to fly on this airplane?
Like the danger posed in this analogy, missing information could potentially throw your entire project in the wrong direction. Team members who can’t effectively communicate can be detrimental—even deadly (to the project, anyway).
It’s natural for information to fall through the cracks when we have discussions, so remember that the design thinking process is flexible . You can always move back to the previous step or even start from scratch if need be. To do this, however, you’ll need to communicate. Sharing and critiquing information helps level the playing field and identify problem areas. If only one voice speaks out (for whatever reason), valuable input is inevitably lost.
“So if we just use design thinking, everything will be fine!” you might say. Well, not exactly. Design thinking is not a quick fix to magically enlighten us, solve our problems, or transform us into more efficient workers. Nor is it the only way to get more customers or design the best product. What it can do is provide a step-by-step approach to fine tune problem solving. The key to unlocking this approach: effective communication.
Related Articles
Need help prioritizing tasks try the eisenhower matrix.
One-to-one Marketing: The New Age of Parasocial Relationships
Nemawashi: Mastering Japanese Shadow Meetings
Get monthly Insights
Sign up for our newsletter! Privacy Policy
GLOBIS Insights
- Submission Guidelines
- Our Contributors
Accountability
- Privacy Policy
GLOBIS Group
- GLOBIS Corporation
- GLOBIS University
- GLOBIS Capital Partners
- GLOBIS Asia Pacific
- GLOBIS Asia Campus
- GLOBIS China
- GLOBIS Europe
- GLOBIS Thailand
- G1 Institute
- Ibaraki Robots Sports Entertainment
- KIBOW Foundation
© GLOBIS All Rights Reserved

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Design thinking and critical thinking are distinct approaches to problem-solving, but can be combined effectively. Both methods can be applied in various fields, from education to product development. Empathy, feedback, and cultural context play significant roles in the successful integration of design thinking and critical thinking.
Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test. It is most useful to tackle ill-defined or unknown problems and involves five phases: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test.
1. Design Thinking. Critical thinking is an important component that comes into play at every stage of the design thinking process. 2. Creative Problem Solving. Critical Thinking is not just rational and based on a set of logical rules. There is plenty of room for solid creativity to play a significant role in the critical thinking process. 3.
Design thinking is an innovative problem-solving process rooted in a set of skills.The approach has been around for decades, but it only started gaining traction outside of the design community after the 2008 Harvard Business Review article [subscription required] titled "Design Thinking" by Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO.
The first, and arguably most important, step of design thinking is building empathy with users. By understanding the person affected by a problem, you can find a more impactful solution. On top of empathy, design thinking is centered on observing product interaction, drawing conclusions based on research, and ensuring the user remains the focus ...
Critical thinking has been a longstanding goal of education, while design thinking has gradually emerged as a popular method for supporting entrepreneurship, innovation, and problem solving in modern business. While some scholars have posited that design thinking may support critical thinking, empirical research examining the relationship between these two modes of thinking is lacking because ...
The critical thinking is a self-disciplined, self-directed, self-monitored, and self-corrective way of thinking to improve how we communicate ideas and solve problems. Critical thinking is a handy method to address any situation before jumping directly to the analysis phase in order to evaluate or find a solution for it.
Understanding Design Thinking. Design Thinking is a holistic, solution-focused approach to problem-solving that prioritizes empathy and experimentation. Rooted in understanding the user's needs, it leverages creative and critical thinking to deliver innovative solutions.
Design thinking is often praised as a universal tool that can be utilized to address and resolve almost any design problem, even those that are the most complex. Judging by the recent criticism ...
The below principles were introduced to serve as guidelines for critical thinking before taking further steps: Collect all the necessary information about the design problem. Understand and define the terms for the design problem. Interrogate the methods used for collecting the information and the sources of facts.
The DeÞne mode is critical to the design process because it results in your point-of-view (POV): the explicit expression of the problem you are striving to address. More importantly, ... could by simply thinking about a problem. Another ideation technique is building Ð that is, prototyping itself can be an ideation technique. ...
Critical thinking has been a longstanding goal of education, while design thinking has gradually emerged as a popular method for supporting entrepreneurship, innovation, and problem solving in ...
Updated: Jan 02, 2024 By: Dessign Team. Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that focuses on human needs. It is a human-centered approach to innovation that aims to create innovative solutions to complex problems. The process begins with empathy, where designers seek to understand the needs, behaviors, and pain points of the users.
Critical thinking is the backbone of design thinking — a human-centered problem-solving approach emphasizing empathy, iteration, and creativity. By incorporating critical thinking within the design thinking framework, designers can enhance their ability to identify user needs, frame problems effectively, and develop innovative solutions.
Design Thinking is defined as a human-centered approach to innovation and problem-solving that prioritizes understanding the needs of users, generating creative solutions, and iterating through rapid prototyping and testing. Learn more about design thinking importance, examples and process.
The authors studied almost two dozen major design-thinking projects within large private- and public-sector organizations in five countries and found that effective leadership is critical to their ...
The present article clarifies the relationship between these two modes of thinking by mapping essential critical thinking components to specific design thinking methods. The mapping reveals that although the two modes of thinking share much in common, they also difer in several notable respects. The mapping also suggests that design thinking ...
Critical thinking is a widely accepted educational goal. Its definition is contested, but the competing definitions can be understood as differing conceptions of the same basic concept: careful thinking directed to a goal. ... ---, 1984, The Design of a Critical Thinking Test on Appraising Observations, St. John's, NL: Institute for ...
Abstract. Design thinking—understanding the human needs related to a problem, reframing the problem in human-centric ways, creating many ideas in brainstorming sessions, and adopting a hands-on approach to prototyping and testing—offers a complementary approach to the rational problem-solving methods typically emphasized in business schools.
Course description. Design Thinking and Innovation, through Harvard Business School (HBS) Online, equips current and aspiring innovation managers with the design thinking principles and innovative problem-solving tools to solve business challenges and guide their organization's strategy. The course features five weeks of course content and ...
Systems thinking, critical thinking, and design thinking are three different approaches to problem-solving, each with unique perspectives and methods. Each approach offers a different method that ...
The shortcut comes from the flawed reasoning that if most innovation seems to come from the "creation of something new" — in the sense of "the production of tangible artifacts" — therefore, creating new things is an innovation by itself.. The problem is that it is not a 1-1 causal relationship — all new things do not lead to significative changes — and reducing the outcomes ...
3. Avoid pointing fingers. Fear of making mistakes…. Everyone can empathize with that. During the crit, be careful not to blame others. Avoid stalling discussion by triggering emotions. Remember, design thinking calls for empathy. The ultimate purpose of the crit is to help, not call people out.
Turbulences, loss of senses and disillusion. Hi, Kevin here. D&CT is a community about building a shared understanding & collective knowledge at the intersection of different practices. We want to cross the boundaries of design, innovation, tech, change, management, ethics, (and more) to engage in discussions that bridge disciplines.
Roles of Design Processes Models as Didactic Materials. Conference Proceedings of the Academy for Design Innovation Management. 2. 10.33114/adim.2019.04.295. He described divergent thinking as the broadening of perspectives where a variety of ideas are explored and convergent thinking as the narrowing of perspectives to focus on a single problem.