
- Table of Contents
- Course Home
- Assignments
- Peer Instruction (Instructor)
- Peer Instruction (Student)
- Change Course
- Instructor's Page
- Progress Page
- Edit Profile
- Change Password
- Scratch ActiveCode
- Scratch Activecode
- Instructors Guide
- About Runestone
- Report A Problem
- 1.1 Getting Started
- 1.1.1 Preface
- 1.1.2 About the AP CSA Exam
- 1.1.3 Transitioning from AP CSP to AP CSA
- 1.1.4 Java Development Environments
- 1.1.5 Growth Mindset and Pair Programming
- 1.1.6 Pretest for the AP CSA Exam
- 1.1.7 Survey
- 1.2 Why Programming? Why Java?
- 1.3 Variables and Data Types
- 1.4 Expressions and Assignment Statements
- 1.5 Compound Assignment Operators
- 1.6 Casting and Ranges of Values
- 1.7 Unit 1 Summary
- 1.8 Mixed Up Code Practice
- 1.9 Toggle Mixed Up or Write Code Practice
- 1.10 Coding Practice
- 1.11 Multiple Choice Exercises
- 1.3. Variables and Data Types" data-toggle="tooltip">
- 1.5. Compound Assignment Operators' data-toggle="tooltip" >
Time estimate: 90 min.

1.4. Expressions and Assignment Statements ¶
In this lesson, you will learn about assignment statements and expressions that contain math operators and variables.
1.4.1. Assignment Statements ¶
Assignment statements initialize or change the value stored in a variable using the assignment operator = . An assignment statement always has a single variable on the left hand side. The value of the expression (which can contain math operators and other variables) on the right of the = sign is stored in the variable on the left.
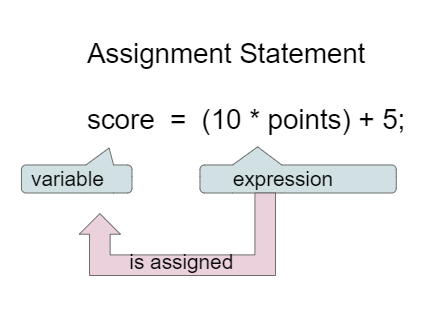
Figure 1: Assignment Statement (variable = expression;) ¶
Instead of saying equals for the = in an assignment statement, say “gets” or “is assigned” to remember that the variable gets or is assigned the value on the right. In the figure above score is assigned the value of the expression 10 times points (which is another variable) plus 5.
The following video by Dr. Colleen Lewis shows how variables can change values in memory using assignment statements.
As we saw in the video, we can set one variable’s value to a copy of the value of another variable like y = x; . This won’t change the value of the variable that you are copying from.
Let’s step through the following code in the Java visualizer to see the values in memory. Click on the Next button at the bottom of the code to see how the values of the variables change. You can run the visualizer on any Active Code in this e-book by just clicking on the Code Lens button at the top of each Active Code.
Activity: CodeLens 1.4.1.2 (asgn_viz1)

1-4-3: What are the values of x, y, and z after the following code executes? You can step through this code by clicking on this Java visualizer link.
- x = 0, y = 1, z = 2
- These are the initial values in the variable, but the values are changed.
- x = 1, y = 2, z = 3
- x changes to y's initial value, y's value is doubled, and z is set to 3
- x = 2, y = 2, z = 3
- Remember that the equal sign doesn't mean that the two sides are equal. It sets the value for the variable on the left to the value from evaluating the right side.
- x = 0, y = 0, z = 3
The following has the correct code to ‘swap’ the values in x and y (so that x ends up with y’s initial value and y ends up with x’s initial value), but the code is mixed up and contains one extra block which is not needed in a correct solution. Drag the needed blocks from the left into the correct order on the right. Check your solution by clicking on the Check button. You will be told if any of the blocks are in the wrong order or if you need to remove one or more blocks. After three incorrect attempts you will be able to use the Help Me button to make the problem easier.
1.4.2. Adding 1 to a Variable ¶
If you use a variable to keep score, you would probably increment it (add one to the current value) whenever score should go up. You can do this by setting the variable to the current value of the variable plus one ( score = score + 1 ) as shown below. The formula would look strange in math class, but it makes sense in coding because it is assigning a new value to the variable on the left that comes from evaluating the arithmetic expression on the right. So, the score variable is set to the previous value of score plus 1.
Try the code below to see how score is incremented by 1. Try substituting 2 instead of 1 to see what happens.
1.4.3. Input with Variables ¶
Variables are a powerful abstraction in programming because the same algorithm can be used with different input values saved in variables. The code below ( Java Scanner Input Repl using the Scanner class or Java Console Input Repl using the Console class) will say hello to anyone who types in their name for different name values. Click on run and then type in your name. Then, try run again and type in a friend’s name. The code works for any name: behold, the power of variables!
Although you will not be tested in the AP CSA exam on using the Java input or the Scanner or Console classes, learning how to do input in Java is very useful and fun. For more information on using the Scanner class, go to https://www.w3schools.com/java/java_user_input.asp , and for the newer Console class, https://howtodoinjava.com/java-examples/console-input-output/ .
1.4.4. Operators ¶
Java uses the standard mathematical operators for addition ( + ), subtraction ( - ), and division ( / ). The multiplication operator is written as * , as it is in most programming languages, since the character sets used until relatively recently didn’t have a character for a real multiplication sign, × , and keyboards still don’t have a key for it. Likewise no ÷ .
You may be used to using ^ for exponentiation, either from a graphing calculator or tools like Desmos. Confusingly ^ is an operator in Java, but it has a completely different meaning than exponentiation and isn’t even exactly an arithmetic operator. You will learn how to use the Math.pow method to do exponents in Unit 2.
Arithmetic expressions can be of type int or double . An arithmetic expression consisting only of int values will evaluate to an int value. An arithmetic expression that uses at least one double value will evaluate to a double value. (You may have noticed that + was also used to combine String and other values into new String s. More on this when we talk about String s more fully in Unit 2.)
Java uses the operator == to test if the value on the left is equal to the value on the right and != to test if two items are not equal. Don’t get one equal sign = confused with two equal signs == . They mean very different things in Java. One equal sign is used to assign a value to a variable. Two equal signs are used to test a variable to see if it is a certain value and that returns true or false as you’ll see below. Also note that using == and != with double values can produce surprising results. Because double values are only an approximation of the real numbers even things that should be mathematically equivalent might not be represented by the exactly same double value and thus will not be == . To see this for yourself, write a line of code below to print the value of the expression 0.3 == 0.1 + 0.2 ; it will be false !

Run the code below to see all the operators in action. Do all of those operators do what you expected? What about 2 / 3? Isn’t it surprising that it prints 0? See the note below.
When Java sees you doing integer division (or any operation with integers) it assumes you want an integer result so it throws away anything after the decimal point in the answer. This is called truncating division . If you need a double answer, you should make at least one of the values in the expression a double like 2.0.
With division, another thing to watch out for is dividing by 0. An attempt to divide an integer by zero will result in an ArithmeticException error message. Try it in one of the active code windows above.
Operators can be used to create compound expressions with more than one operator. You can either use a literal value which is a fixed value like 2, or variables in them. When compound expressions are evaluated, operator precedence rules are used, just like when we do math (remember PEMDAS?), so that * , / , and % are done before + and - . However, anything in parentheses is done first. It doesn’t hurt to put in extra parentheses if you are unsure as to what will be done first or just to make it more clear.
In the example below, try to guess what it will print out and then run it to see if you are right. Remember to consider operator precedence . How do the parentheses change the precedence?
1.4.5. The Remainder Operator ¶
The operator % in Java is the remainder operator. Like the other arithmetic operators is takes two operands. Mathematically it returns the remainder after dividing the first number by the second, using truncating integer division. For instance, 5 % 2 evaluates to 1 since 2 goes into 5 two times with a remainder of 1.
While you may not have heard of remainder as an operator, think back to elementary school math. Remember when you first learned long division, before they taught you about decimals, how when you did a long division that didn’t divide evenly, you gave the answer as the number of even divisions and the remainder. That remainder is what is returned by this operator. In the figures below, the remainders are the same values that would be returned by 2 % 3 and 5 % 2 .

Figure 1: Long division showing the integer result and the remainder ¶
Sometimes people—including Professor Lewis in the next video—will call % the modulo , or mod , operator. That is not actually correct though the difference between remainder and modulo, which uses Euclidean division instead of truncating integer division, only matters when negative operands are involved and the signs of the operands differ. With positive operands, remainder and mod give the same results. Java does have a method Math.floorMod in the Math class if you need to use modulo instead of remainder, but % is all you need in the AP exam.
Here’s the video .
In the example below, try to guess what it will print out and then run it to see if you are right.
The result of x % y when x is smaller than y is always x. The value y can’t go into x at all (goes in 0 times), since x is smaller than y, so the result is just x. So if you see 2 % 3 the result is 2.
1-4-10: What is the result of 158 % 10?
- This would be the result of 158 divided by 10. % gives you the remainder.
- % gives you the remainder after the division.
- When you divide 158 by 10 you get a remainder of 8.
1-4-11: What is the result of 3 % 8?
- 8 goes into 3 no times so the remainder is 3. The remainder of a smaller number divided by a larger number is always the smaller number!
- This would be the remainder if the question was 8 % 3 but here we are asking for the reminder after we divide 3 by 8.
- What is the remainder after you divide 3 by 8?
1.4.6. Programming Challenge : Dog Years ¶

In this programming challenge, you will calculate your age, and your pet’s age from your birthdates, and your pet’s age in dog years. In the code below, type in the current year, the year you were born, the year your dog or cat was born (if you don’t have one, make one up!) in the variables below. Then write formulas in assignment statements to calculate how old you are, how old your dog or cat is, and how old they are in dog years which is 7 times a human year. Finally, print it all out. If you are pair programming, switch drivers (who has control of the keyboard in pair programming) after every line of code.
Calculate your age and your pet’s age from the birthdates, and then your pet’s age in dog years.
Your teacher may suggest that you use a Java IDE like repl.it for this challenge so that you can use input to get these values using the Scanner class . Here is a repl template that you can use to get started if you want to try the challenge with input.
1.4.7. Summary ¶
Arithmetic expressions include expressions of type int and double .
The arithmetic operators consist of + , - , * , / , and % also known as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and remainder.
An arithmetic operation that uses two int values will evaluate to an int value. With integer division, any decimal part in the result will be thrown away.
An arithmetic operation that uses at least one double value will evaluate to a double value.
Operators can be used to construct compound expressions.
During evaluation, operands are associated with operators according to operator precedence to determine how they are grouped. ( * , / , % have precedence over + and - , unless parentheses are used to group those.)
An attempt to divide an integer by zero will result in an ArithmeticException .
The assignment operator ( = ) allows a program to initialize or change the value stored in a variable. The value of the expression on the right is stored in the variable on the left.
During execution, expressions are evaluated to produce a single value.
The value of an expression has a type based on the types of the values and operators used in the expression.
1.4.8. AP Practice ¶
The following is a 2019 AP CSA sample question.
1-4-13: Consider the following code segment.
What is printed when the code segment is executed?
- 0.666666666666667
- Don't forget that division and multiplication will be done first due to operator precedence.
- Yes, this is equivalent to (5 + ((a/b)*c) - 1).
- Don't forget that division and multiplication will be done first due to operator precedence, and that an int/int gives an int truncated result where everything to the right of the decimal point is dropped.
CS105: Introduction to Python
Variables and assignment statements.
Computers must be able to remember and store data. This can be accomplished by creating a variable to house a given value. The assignment operator = is used to associate a variable name with a given value. For example, type the command:
in the command line window. This command assigns the value 3.45 to the variable named a . Next, type the command:
in the command window and hit the enter key. You should see the value contained in the variable a echoed to the screen. This variable will remember the value 3.45 until it is assigned a different value. To see this, type these two commands:
You should see the new value contained in the variable a echoed to the screen. The new value has "overwritten" the old value. We must be careful since once an old value has been overwritten, it is no longer remembered. The new value is now what is being remembered.
Although we will not discuss arithmetic operations in detail until the next unit, you can at least be equipped with the syntax for basic operations: + (addition), - (subtraction), * (multiplication), / (division)
For example, entering these command sequentially into the command line window:
would result in 12.32 being echoed to the screen (just as you would expect from a calculator). The syntax for multiplication works similarly. For example:
would result in 35 being echoed to the screen because the variable b has been assigned the value a * 5 where, at the time of execution, the variable a contains a value of 7.
After you read, you should be able to execute simple assignment commands using integer and float values in the command window of the Repl.it IDE. Try typing some more of the examples from this web page to convince yourself that a variable has been assigned a specific value.
In programming, we associate names with values so that we can remember and use them later. Recall Example 1. The repeated computation in that algorithm relied on remembering the intermediate sum and the integer to be added to that sum to get the new sum. In expressing the algorithm, we used th e names current and sum .
In programming, a name that refers to a value in this fashion is called a variable . When we think of values as data stored somewhere i n the computer, we can have a mental image such as the one below for the value 10 stored in the computer and the variable x , which is the name we give to 10. What is most important is to see that there is a binding between x and 10.
The term variable comes from the fact that values that are bound to variables can change throughout computation. Bindings as shown above are created, and changed by assignment statements . An assignment statement associates the name to the left of the symbol = with the value denoted by the expression on the right of =. The binding in the picture is created using an assignment statemen t of the form x = 10 . We usually read such an assignment statement as "10 is assigned to x" or "x is set to 10".
If we want to change the value that x refers to, we can use another assignment statement to do that. Suppose we execute x = 25 in the state where x is bound to 10.Then our image becomes as follows:
Choosing variable names
Suppose that we u sed the variables x and y in place of the variables side and area in the examples above. Now, if we were to compute some other value for the square that depends on the length of the side , such as the perimeter or length of the diagonal, we would have to remember which of x and y , referred to the length of the side because x and y are not as descriptive as side and area . In choosing variable names, we have to keep in mind that programs are read and maintained by human beings, not only executed by machines.
Note about syntax
In Python, variable identifiers can contain uppercase and lowercase letters, digits (provided they don't start with a digit) and the special character _ (underscore). Although it is legal to use uppercase letters in variable identifiers, we typically do not use them by convention. Variable identifiers are also case-sensitive. For example, side and Side are two different variable identifiers.
There is a collection of words, called reserved words (also known as keywords), in Python that have built-in meanings and therefore cannot be used as variable names. For the list of Python's keywords See 2.3.1 of the Python Language Reference.
Syntax and Sema ntic Errors
Now that we know how to write arithmetic expressions and assignment statements in Python, we can pause and think about what Python does if we write something that the Python interpreter cannot interpret. Python informs us about such problems by giving an error message. Broadly speaking there are two categories for Python errors:
- Syntax errors: These occur when we write Python expressions or statements that are not well-formed according to Python's syntax. For example, if we attempt to write an assignment statement such as 13 = age , Python gives a syntax error. This is because Python syntax says that for an assignment statement to be well-formed it must contain a variable on the left hand side (LHS) of the assignment operator "=" and a well-formed expression on the right hand side (RHS), and 13 is not a variable.
- Semantic errors: These occur when the Python interpreter cannot evaluate expressions or execute statements because they cannot be associated with a "meaning" that the interpreter can use. For example, the expression age + 1 is well-formed but it has a meaning only when age is already bound to a value. If we attempt to evaluate this expression before age is bound to some value by a prior assignment then Python gives a semantic error.
Even though we have used numerical expressions in all of our examples so far, assignments are not confined to numerical types. They could involve expressions built from any defined type. Recall the table that summarizes the basic types in Python.
The following video shows execution of assignment statements involving strings. It also introduces some commonly used operators on strings. For more information see the online documentation. In the video below, you see the Python shell displaying "=> None" after the assignment statements. This is unique to the Python shell presented in the video. In most Python programming environments, nothing is displayed after an assignment statement. The difference in behavior stems from version differences between the programming environment used in the video and in the activities, and can be safely ignored.
Distinguishing Expressions and Assignments
So far in the module, we have been careful to keep the distinction between the terms expression and statement because there is a conceptual difference between them, which is sometimes overlooked. Expressions denote values; they are evaluated to yield a value. On the other hand, statements are commands (instructions) that change the state of the computer. You can think of state here as some representation of computer memory and the binding of variables and values in the memory. In a state where the variable side is bound to the integer 3, and the variable area is yet unbound, the value of the expression side + 2 is 5. The assignment statement side = side + 2 , changes the state so that value 5 is bound to side in the new state. Note that when you type an expression in the Python shell, Python evaluates the expression and you get a value in return. On the other hand, if you type an assignment statement nothing is returned. Assignment statements do not return a value. Try, for example, typing x = 100 + 50 . Python adds 100 to 50, gets the value 150, and binds x to 150. However, we only see the prompt >>> after Python does the assignment. We don't see the change in the state until we inspect the value of x , by invoking x .
What we have learned so far can be summarized as using the Python interpreter to manipulate values of some primitive data types such as integers, real numbers, and character strings by evaluating expressions that involve built-in operators on these types. Assignments statements let us name the values that appear in expressions. While what we have learned so far allows us to do some computations conveniently, they are limited in their generality and reusability. Next, we introduce functions as a means to make computations more general and reusable.

- Assignment Statement
An Assignment statement is a statement that is used to set a value to the variable name in a program .
Assignment statement allows a variable to hold different types of values during its program lifespan. Another way of understanding an assignment statement is, it stores a value in the memory location which is denoted by a variable name.

The symbol used in an assignment statement is called as an operator . The symbol is ‘=’ .
Note: The Assignment Operator should never be used for Equality purpose which is double equal sign ‘==’.
The Basic Syntax of Assignment Statement in a programming language is :
variable = expression ;
variable = variable name
expression = it could be either a direct value or a math expression/formula or a function call
Few programming languages such as Java, C, C++ require data type to be specified for the variable, so that it is easy to allocate memory space and store those values during program execution.
data_type variable_name = value ;
In the above-given examples, Variable ‘a’ is assigned a value in the same statement as per its defined data type. A data type is only declared for Variable ‘b’. In the 3 rd line of code, Variable ‘a’ is reassigned the value 25. The 4 th line of code assigns the value for Variable ‘b’.
Assignment Statement Forms
This is one of the most common forms of Assignment Statements. Here the Variable name is defined, initialized, and assigned a value in the same statement. This form is generally used when we want to use the Variable quite a few times and we do not want to change its value very frequently.

Tuple Assignment
Generally, we use this form when we want to define and assign values for more than 1 variable at the same time. This saves time and is an easy method. Note that here every individual variable has a different value assigned to it.
(Code In Python)
Sequence Assignment
(Code in Python)
Multiple-target Assignment or Chain Assignment
In this format, a single value is assigned to two or more variables.
Augmented Assignment
In this format, we use the combination of mathematical expressions and values for the Variable. Other augmented Assignment forms are: &=, -=, **=, etc.
Browse more Topics Under Data Types, Variables and Constants
- Concept of Data types
- Built-in Data Types
- Constants in Programing Language
- Access Modifier
- Variables of Built-in-Datatypes
- Declaration/Initialization of Variables
- Type Modifier
Few Rules for Assignment Statement
Few Rules to be followed while writing the Assignment Statements are:
- Variable names must begin with a letter, underscore, non-number character. Each language has its own conventions.
- The Data type defined and the variable value must match.
- A variable name once defined can only be used once in the program. You cannot define it again to store other types of value.
- If you assign a new value to an existing variable, it will overwrite the previous value and assign the new value.
FAQs on Assignment Statement
Q1. Which of the following shows the syntax of an assignment statement ?
- variablename = expression ;
- expression = variable ;
- datatype = variablename ;
- expression = datatype variable ;
Answer – Option A.
Q2. What is an expression ?
- Same as statement
- List of statements that make up a program
- Combination of literals, operators, variables, math formulas used to calculate a value
- Numbers expressed in digits
Answer – Option C.
Q3. What are the two steps that take place when an assignment statement is executed?
- Evaluate the expression, store the value in the variable
- Reserve memory, fill it with value
- Evaluate variable, store the result
- Store the value in the variable, evaluate the expression.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Data Types, Variables and Constants
- Variables in Programming Language
- Concept of Data Types
- Declaration of Variables
- Type Modifiers
- Access Modifiers
- Constants in Programming Language
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Variable declaration and assignment
A variable is introduced with the variable keyword.
A simple variable declaration looks like this:
As for constants, type inference is supported. Hence the above instruction is equivalent to:
A variable can be declared without assigning an initial value. In that case a value must be assigned subsequently:
After an object has been assigned to a variable, another object can be assigned to it subsequently:
The scope of a variable is limited to the block of instructions in which it is declared.
results matching " "
No results matching " ".
Computer Revolution (www.comrevo.com)
Search this website.
- Cloud Computing
- Web Designing
- Data Structures
- Multi-Threading
- Blogging Tips
- YouTube Tips
- Subscribe Youtube Channel
- Amazon Links
- Udemy Courses
Sunday 28 March 2021
Relational and boolean expressions | ppl | sebesta | expressions and assignment statements.
In this post, we will see Relational and Boolean Expressions | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | relational and boolean expressions, ppl, sebesta, expressions and assignment statements
4. Relational and Boolean Expressions
A relational operator is an operator that compares the values of its two operands. A relational expression has two operands and one relational operator.
The value of a relational expression is Boolean .
The syntax of the relational operators for equality and inequality differs among some programming languages. For example, for inequality, the C-based languages use != , Ada uses /= , Lua uses ~= , Fortran 95+ uses .NE. or <> , and ML and F# use <> .
JavaScript and PHP have two additional relational operators, === and !== . These are similar to their relatives, == and != , but prevent their operands from being coerced. For example, the expression
is true in JavaScript , because when a string and a number are the operands of a relational operator, the string is coerced to a number. However,
is false , because no coercion is done on the operands of this operator.
The relational operators always have lower precedence than the arithmetic operators , so that in expressions such as
a + 1 > 2 * b
the arithmetic expressions are evaluated first.
Boolean expressions consist of Boolean variables, Boolean constants, relational expressions, and Boolean operators. The operators usually include those for the AND, OR, and NOT operations, and sometimes for exclusive OR and equivalence. Boolean operators usually take only Boolean operands (Boolean variables, Boolean literals, or relational expressions) and produce Boolean values.
The precedence of the arithmetic, relational, and Boolean operators in the C-based languages is as follows:

Watch following video:
Watch on YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0eCfY9JgX1I
No comments:
Post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Assignment Statements | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | assignment statements, ppl, sebesta, expressions and assignment statements Ch...
6. Assignment Statements . Simple Assignments . i. Nearly all programming languages currently being used use the equal sign for the assignment operator. ii. ALGOL 60 and Ada makes use of := as the assignment operator. iii. In some languages, such as Fortran and Ada, an assignment can appear only as a stand-alone statement, and the destination ...
Short Circuit Evaluation | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | short circuit evaluation, ppl, sebesta, expressions and assignment stateme...
Mixed Mode Assignment | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | mixed mode assignment, ppl, sebesta, expressions and assignment statements Ch...
EXPRESSIONS AND STATEMENTS & CONTROL STRUCTURES 2.7 Expression: [Arithmetic, Relational and Boolean Expressions] 2.8 Short-Circuit Evaluation 2.9 Assignment Statements, Mixed-Mode Assignment [Referential Transparency & Functional Programming] 2.10 Control Structures [statement Level Control Structures, Compound statements]
In this lesson, you will learn about assignment statements and expressions that contain math operators and variables. 1.4.1. Assignment Statements ¶. Assignment statements initialize or change the value stored in a variable using the assignment operator =. An assignment statement always has a single variable on the left hand side.
The Beginnings of Data Abstraction: SIMULA 67. Orthogonal Design: ALGOL 68. Some Important Descendants of the ALGOLs. Programming Based on Logic: Prolog. History's Largest Design Effort: Ada. Object-Oriented Programming: Smalltalk. Combining Imperative and Object-Oriented Features: C++. Programming the World Wide Web: Java. 3.
The assignment operator = is used to associate a variable name with a given value. For example, type the command: a=3.45. in the command line window. This command assigns the value 3.45 to the variable named a. Next, type the command: a. in the command window and hit the enter key. You should see the value contained in the variable a echoed to ...
Assignment Statements CS516 4 Simple Assignment Statements • Simple Assignments - <target_variable> <assignment_operator> <exp> • The assignment operator symbol::= ALGOLs, Pascal, Modula-2, Ada = FORTRAN, BASIC, PL/I, C, C++, Java • = can be bad if it is overloaded for the relational operator for equality. CS516 5 Assignment Statements
In this post, we will see Overloaded Operators | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | overloaded operators, ppl, sebesta, expressions and assignment statements . 2. Overloaded Operators. e.g. + &-All these operators are used for multiple purpose. Watch following video:
Arithmetic Expressions | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | arithmetic expressions, ppl, sebesta, expressions and assignment statementsC...
1 Introduction!Expressions*are*the*fundamental*means*of* specifying*computationsin*a*PL "While*variables*are*the*means*for*specifying*storage Primary*use*of ...
The following table shows the built-in function names for operators that can be used in any type: Examples of expressions and operators: fb1 =v "foobar" and \. fb2 =v "foobar" and \. fb3 =v "foobar". In the following instruction 'to_string' is not executed, because 'find_first' returns null.
Assignment Statement. An Assignment statement is a statement that is used to set a value to the variable name in a program. Assignment statement allows a variable to hold different types of values during its program lifespan. Another way of understanding an assignment statement is, it stores a value in the memory location which is denoted.
In this post, we will see Mixed Mode Assignment | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | mixed mode assignment, ppl, sebesta, expressions and assignment statements . 7. Mixed mode Assignment. One of the design decisions concerning arithmetic expressions is whether an operator can have operands of different types.
Overloaded Operators | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | overloaded operators, ppl, sebesta, expressions and assignment statementsCheck...
Variable declaration and assignment. A variable is introduced with the variable keyword. A simple variable declaration looks like this: var counter zero_pos_32 = 0. As for constants, type inference is supported. Hence the above instruction is equivalent to: var counter = 0. A variable can be declared without assigning an initial value.
** stands for exponentiation operator. What are the operator associativity rules? When an expression contains two adjacent 2 occurrences of operators with the same level of precedence, the question of which operator is evaluated first is answered by the associativity rules of the language.. Associativity in common languages is left to right, except that the exponentiation operator (when ...
Assignment Statements • The general syntax <target_var> <assign_operator> <expression> • The assignment operator = Fortran, BASIC, the C-based languages:= Ada, Pascal = can be bad when it is overloaded for the relational operator for equality (that's why the C-based languages use == as the
Determines the order of operation between operators of the same precedence. In most cases, left to right. - y - z or x / y / z. b = 9; = 5; = b = c; 5 is assigned to both a and b because of the right-to-left associativity of the = operator. In Fortran, the exponentiation is right asssociative.
Type Conversions | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | type conversions, ppl, sebesta, expressions and assignment statementsCheck blog li...
Relational and Boolean Expressions | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | relational and boolean expressions, ppl, sebesta, expressions an...
In this post, we will see Relational and Boolean Expressions | PPL | Sebesta | Expressions and Assignment Statements | relational and boolean expressions, ppl, sebesta, expressions and assignment statements . 4. Relational and Boolean Expressions. A relational operator is an operator that compares the values of its two operands.